SMC Networks SMCWBR14-N User Manual

USER GUIDE
SMCWBR14-N
Barricade™ N
2.4GHz Draft 11n
Wireless 4-port Broadband Router

LIMITED WARRANTY
Limited Warranty Statement: SMC Networks, Inc. (“SMC”) warrants its products to be free from
defects in workmanship and materials, under normal use and service, for the applicable warranty
term. All SMC products carry a standard 90-day limited warranty from the date of purchase from
SMC or its Authorized Reseller. SMC may, at its own discretion, repair or replace any product not
operating as warranted with a similar or functionally equivalent product, during the applicable
warranty term. SMC will endeavor to repair or replace any product returned under warranty within 30
days of receipt of the product. The standard limited warranty can be upgraded to a Limited Lifetime*
warranty by registering new products within 30 days of purchase from SMC or its Authorized
Reseller. Registration can be accomplished via the enclosed product registration card or online via
the SMC website. Failure to register will not affect the standard limited warranty. The Limited
Lifetime warranty covers a product during the Life of that Product, which is defined as the period of
time during which the product is an “Active” SMC product. A product is considered to be “Active”
while it is listed on the current SMC price list. As new technologies emerge, older technologies
become obsolete and SMC will, at its discretion, replace an older product in its product line with one
that incorporates these newer technologies. At that point, the obsolete product is discontinued and is
no longer an “Active” SMC product. A list of discontinued products with their respective dates of
discontinuance can be found at: http://www.smc.com/index.cfm?action=customer_service_warranty.
All products that are replaced become the property of SMC. Replacement products may be either
new or reconditioned. Any replaced or repaired product carries either a 30-day limited warranty or
the remainder of the initial warranty, whichever is longer. SMC is not responsible for any custom
software or firmware, configuration information, or memory data of Customer contained in, stored
on, or integrated with any products returned to SMC pursuant to any warranty. Products returned to
SMC should have any customer-installed accessory or add-on components, such as expansion
modules, removed prior to returning the product for replacement. SMC is not responsible for these
items if they are returned with the product. Customers must contact SMC for a Return Material
Authorization number prior to returning any product to SMC. Proof of purchase may be required.
Any product returned to SMC without a valid Return Material Authorization (RMA) number clearly
marked on the outside of the package will be returned to customer at customer’s expense. For
warranty claims within North America, please call our toll-free customer support number at (800)
762-4968. Customers are responsible for all shipping charges from their facility to SMC. SMC is
responsible for return shipping charges from SMC to customer.
WARRANTIES EXCLUSIVE: IF AN SMC PRODUCT DOES NOT OPERATE AS WARRANTED
ABOVE, CUSTOMER’S SOLE REMEDY SHALL BE REPAIR OR REPLACEMENT OF THE
PRODUCT IN QUESTION, AT SMC’S OPTION. THE FOREGOING WARRANTIES AND
REMEDIES ARE EXCLUSIVE AND ARE IN LIEU OF ALL OTHER WARRANTIES OR
CONDITIONS, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, EITHER IN FACT OR BY OPERATION OF LAW,
STATUTORY OR OTHERWISE, INCLUDING WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF
MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. SMC NEITHER ASSUMES
NOR AUTHORIZES ANY OTHER PERSON TO ASSUME FOR IT ANY OTHER LIABILITY IN
CONNECTION WITH THE SALE, INSTALLATION, MAINTENANCE OR USE OF ITS PRODUCTS.
SMC SHALL NOT BE LIABLE UNDER THIS WARRANTY IF ITS TESTING AND EXAMINATION
DISCLOSE THE ALLEGED DEFECT IN THE PRODUCT DOES NOT EXIST OR WAS CAUSED BY
CUSTOMER’S OR ANY THIRD PERSON’S MISUSE, NEGLECT, IMPROPER INSTALLATION OR
TESTING, UNAUTHORIZED ATTEMPTS TO REPAIR, OR ANY OTHER CAUSE BEYOND THE
RANGE OF THE INTENDED USE, OR BY ACCIDENT, FIRE, LIGHTNING, OR OTHER HAZARD.
LIMITATION OF LIABILITY: IN NO EVENT, WHETHER BASED IN CONTRACT OR TORT
(INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE), SHALL SMC BE LIABLE FOR INCIDENTAL, CONSEQUENTIAL,
INDIRECT, SPECIAL, OR PUNITIVE DAMAGES OF ANY KIND, OR FOR LOSS OF REVENUE,
i

LOSS OF BUSINESS, OR OTHER FINANCIAL LOSS ARISING OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION
WITH THE SALE, INSTALLATION, MAINTENANCE, USE, PERFORMANCE, FAILURE, OR
INTERRUPTION OF ITS PRODUCTS, EVEN IF SMC OR ITS AUTHORIZED RESELLER HAS
BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES. SOME STATES DO NOT ALLOW
THE EXCLUSION OF IMPLIED WARRANTIES OR THE LIMITATION OF INCIDENTAL OR
CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES FOR CONSUMER PRODUCTS, SO THE ABOVE LIMITATIONS
AND EXCLUSIONS MAY NOT APPLY TO YOU. THIS WARRANTY GIVES YOU SPECIFIC LEGAL
RIGHTS, WHICH MAY VARY FROM STATE TO STATE. NOTHING IN THIS WARRANTY SHALL
BE TAKEN TO AFFECT YOUR STATUTORY RIGHTS.
* SMC will provide warranty service for one year following discontinuance from the active
SMC price list. Under the limited lifetime warranty, internal and external power supplies, fans,
and cables are covered by a standard one-year warranty from date of purchase.
SMC Networks, Inc.
38 Tesla
Irvine, CA 92618
ii

Compliances
Federal Communication Commission Interference Statement
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device,
pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection
against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses and can
radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions,
may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that
interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful
interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off
and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following
measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the distance between the equipment and receiver.
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is
connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
FCC Caution: To assure continued compliance, (example - use only shielded interface cables when
connecting to computer or peripheral devices) any changes or modifications not expressly approved
by the party responsible for compliance could void the user’s authority to operate this equipment.
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two
conditions: (1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any
interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
IMPORTANT NOTE
FCC Radiation Exposure Statement:
This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure limits set forth for an uncontrolled
environment. This transmitter must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any other
antenna or transmitter.
CE Mark Declaration of Conformance for EMI and Safety (EEC)
This device complies with the essential requirements of the R&TTE Directive 1999/5/EC.
The following references have been applied in order to prove presumption of compliance with the
R&TTE Directive 1999/5/EC:
• EN 300 328
• EN 301 489-1
• EN 301 489-17
• EN 60950-1
iii

Table of Contents
Getting Started with the SMCWBR14-N 3
Package Contents 4
Minimum System Requirements 4
Wireless LAN Networking 5
Introduction 9
Features 9
Hardware Overview 10
Rear Panel 10
LEDs 11
Installation Considerations 12
Getting Started 12
Using the Configuration Menu 13
Basic 14
Advanced 24
Tools 53
Status 70
Glossary 79
2

Getting Started with the SMCWBR14-N
Congratulations on purchasing the SMCWBR14-N. This manual provides information for setting
up and configuring the SMCWBR14-N. This manual is intended for both home users and
professionals.
The following conventions are used in this manual:
THE NOTE SYMBOL INDICATES ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ON THE
TOPIC A T HAND.
THE TIP SYMBOL INDICATES HELPFULL INFORMATION AND TIPS TO
IMPROVE YOUR NETWORK EXPERIENCE.
THE CAUTION SYMBOL ALERTS YOU T O SITUATIONS THAT MAY
DEGRADE YOUR NETWORKING EXPERIENCE OR COMPROMISE
LIKE NOTES AND TIPS, THE IMPORTANT SYMBOL INDICATES
INFORMA TION THAT CAN IMPROVE NETWORKING . THIS INFORMATION
SHOULD NOT BE OVERLOOKED.
3

Package Contents
z Barricade™ N Broadband Router (SMCWBR14-N)
z Yellow RJ-45 Ethernet Cable
z Power Adapter (5.0V, 2.5A)
z Documentation CD
z Quick Installation Guide
z Warranty registration card
Using a power supply with a different voltage than the one included with your
product will cause damage and void the warranty for this product.
Minimum System Requirements
z Broadband (Cable/xDSL) Internet service and Modem with Ethernet connection.
z 2.4GHz 802.11n draft wireless adapter or 2.4GHz 802.11b/g wireless adapter installed on
each PC. Alternatively an Ethernet adapter can be used.
z
Internet Explorer 5.5 or above, Netscape 4.7 or above, Mozilla Firefox 1.0 or above
4

Wireless LAN Networking
This section provides background information on wireless LAN networking technology. Consult
the Glossary for definitions of the terminology used in this section.
T
HE INFORMATION IN THIS SECTION IS FOR YOUR REFERENCE. CHANGING
NETWORK SETTINGS AND PARTICULARLY SECURITY SETTTINGS SHOULD ONLY
BE DONE BY AN AUTHORIZED ADMINISTRATOR.
Transmission Rate (Transfer Rate)
The SMCWBR14-N provides various transmission (data) rate options for you to select. In most
networking scenarios, the factory default Best (automatic) setting proves the most efficient. This
setting allows your SMCWBR14-N to operate at the maximum transmission (data) rate. When the
communication quality drops below a certain level, the SMCWBR14-N automatically switches to a
lower transmission (data) rate. Transmission at lower data speeds is usually more reliable.
However, when the communication quality improves again, the SMCWBR14-N gradually increases
the transmission (data) rate again until it reaches the highest available transmission rate.
Types of Wireless Networks
Wireless LAN networking works in either of the two modes: ad-hoc and infrastructure. In infrastructure mode, wireless devices communicate to a wired LAN via access points. Each access
point and its wireless devices are known as a Basic Service Set (BSS). An Extended Service Set
(ESS) is two or more BSSs in the same subnet. In ad hoc mode (also known as peer-to-peer
mode), wireless devices communicate with each other directly and do not use an access point.
This is an Independent BSS (IBSS).
To connect to a wired network within a coverage area using access points, set the operation mode
to Infrastructure (BSS). To set up an independent wireless workgroup without an access point, use
Ad-hoc (IBSS) mode.
A
D-HOC (IBSS) NETWORK
Ad-hoc mode does not require an access point or a wired network. Two or more wireless stations
communicate directly to each other. An ad-hoc network may sometimes be referred to as an
Independent Basic Service Set (IBSS).
To set up an ad-hoc network, configure all the stations in ad-hoc mode. Use the same SSID and
channel for each station.
5

6

When a number of wireless stations are connected using a single access point, you have a Basic
Service Set (BSS).
In the ESS diagram below, communication is done through the access points, which relay data
packets to other wireless stations or devices connected to the wired network. Wireless stations
can then access resources, such as a printer, on the wired network.
7
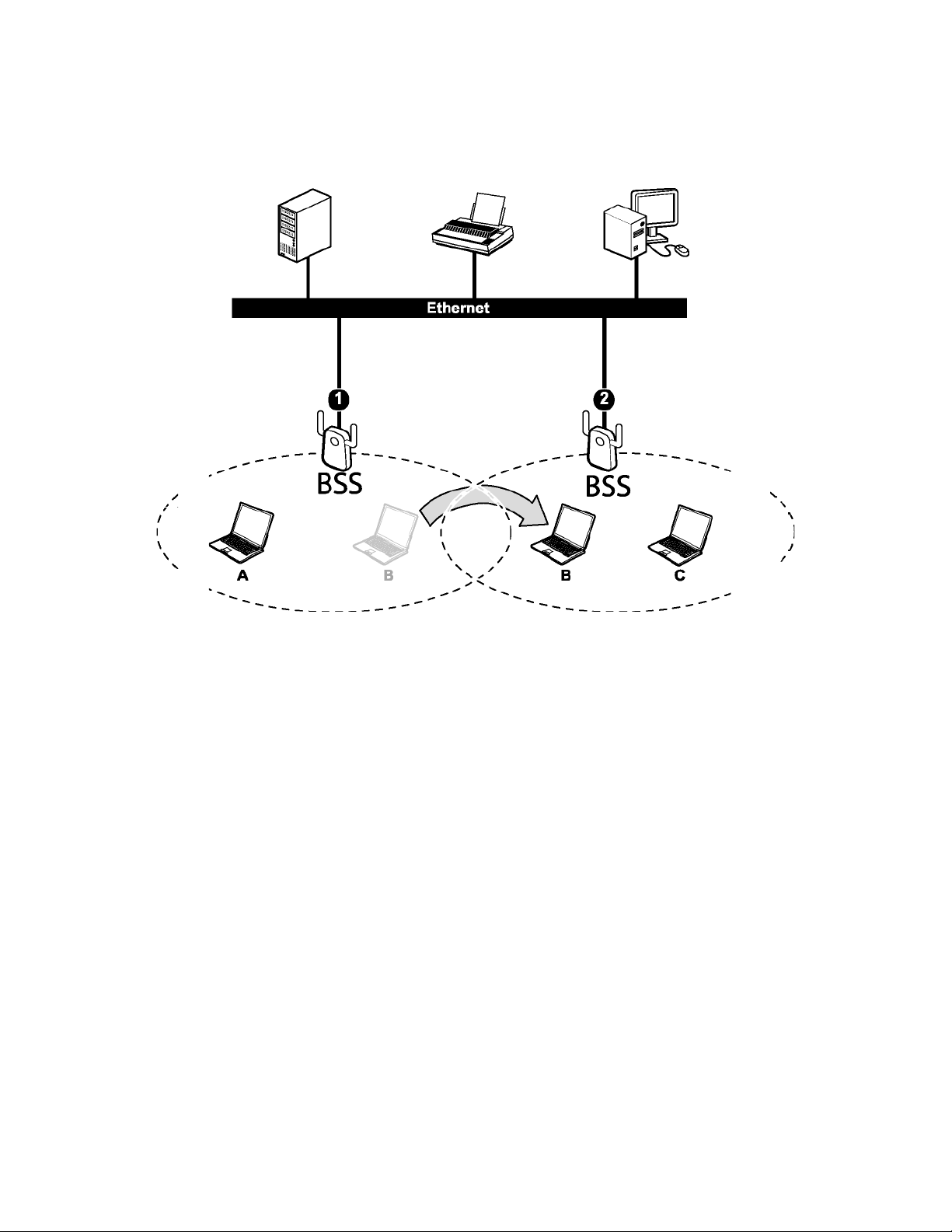
In an ESS environment, users are able to move from one access point to another without losing the
connection. In the diagram below, when the user moves from BSS (1) to BSS (2) the WLAN client
devices automatically switches to the channel used in BSS (2).
Roaming in an ESS network diagram
8

Introduction
The SMCWBR14-N is a high-performance, wireless router that supports high-speed wireless
networking at home, at work or in public places.
Unlike most routers, the SMCWBR14-N provides data transfers at up to 300Mbps when using 11n
(Draft) connection. This router is also backwards compatible with 802.11g or 11b devices. This means
that you do not need to change your entire network to maintain connectivity. You may sacrifice some
of 11n’s (Draft) speed when you mix 11n (Draft) and 11b/g devices, but you will not lose the ability to
communicate when you incorporate the 11n (Draft) standard into your 11b/g network. You may
choose to slowly change your network by gradually replacing the 11b/g devices with 11n (Draft)
devices.
Features
¾ Wi-Fi Compliant with IEEE 802.11n (draft) and IEEEE 802.11b/g Standards
¾ 2.412 to 2.484GHz frequency band operation
¾ Compliant with IEEE 802.3 & 3u standards
¾ Support OFDM and CCK modulation
¾ High-Speed up to 300Mbps Data Rate using IEEE 802.11n (draft) connection
¾ Supports Cable/DSL Modems with Dynamic IP, Static IP, PPPoE, PPTP, L2TP or BigPond
Connection Types
¾ Firewall features Network Address Translation (NAT), and Stateful Packet Inspection (SPI)
protects against Dos attacks
¾ Traffic Control with Virtual Server (max 64 configurable servers) and DMZ
¾ UPnP (Universal Plug & Play) and ALGs Support for Internet applications such as Email, FTP,
Gaming, Remote Desktop, Net Meeting, Telnet, and more
¾ Provides Additional Security of Enable/Disable SSID, Internet Access Control (Services, URL and
MAC Filtering)
¾ Supports Multiple and Concurrent IPSec, L2TP and PPTP VPN Pass-Through Sessions
¾ Flash Memory for Firmware Upgrade, Save/Restore Settings
¾ Easy Management via Web Browser (HTTP) and Remote Management
¾ Supports 64/128-bit WEP, WPA/WPA2, and WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK
¾ Compliant with Windows 98/NT/2000/XP/2003 Server, Linux and Mac OS
¾ Support 4 x 10/100Mbps Auto-MDIX LAN Port and 1 x 10/100Mbps WAN Port (Internet)
¾ Built-in 3 External Antennas to support high speed performance and great coverage
9

Hardware Overview
Back Panel
POWER
The Power input connector is a single jack socket to supply power to the SMCWBR14-N.
Please use the Power Adapter provided in the SMCWBR14-N package.
RESET
Pressing the reset button restores the router to its original factory default settings.
WLAN ON/OFF
The WLAN ON/OFF slide switch can be used to turn the wireless AP function ON/OFF
WAN (Auto MDI/MDIX)
The WAN port is used to connect to an Ethernet Cable or xDSL modem
LAN1-4 (Auto MDI/MDIX)
The LAN ports are used for connecting networking devices such as PC’s, Printers & Switches. The
LAN ports automatically sense the cable type when connecting to Ethernet enabled computers.
10

Front Panel LED’s
POWER
A solid green LED indicates the SMCWBR14-N is receiving power – normal operation. If the LED is off
there is no power to device or failure.
LAN1-4
A solid green LED indicates the corresponding LAN port connection is established. The LED blinks
when data is transmitted. If the LED is off there is no link for corresponding LAN port.
WAN
A solid green LED indicates the WAN port connection is established. The LED blinks when data
is transmitted. If the LED is off there is no link for the WAN port.
WLAN
A solid green LED indicates the wireless AP is ready. The LED blinks when wireless data is
transmitted.
11

Installation Considerations
The SMCWBR14-N lets you access your network, using a wireless connection, from virtually
anywhere within its operating range. Keep in mind, however, that the number, thickness and location
of walls, ceilings, or other objects that the wireless signals must pass through, may limit the range.
Typical ranges vary depending on the types of materials and background RF (radio frequency) noise
in your home or business. The key to maximizing wireless range is to follow these basic guidelines:
1 Keep the number of walls and ceilings between the SMCWBR14-N and other network devices
to a minimum - each wall or ceiling can reduce your wireless product’s range from 3-90 feet
(1-30 meters.) Position your devices so that the number of walls or ceilings is minimized.
2 Be aware of the direct line between network devices. A wall that is 1.5 feet thick (.5 meters), at
a 45-degree angle appears to be almost 3 feet (1 meter) thick. At a 2-degree angle it looks
over 42 feet (14 meters) thick! Position devices so that the signal will travel straight through a
wall or ceiling (instead of at an angle) for better reception.
3 Building Materials can impede the wireless signal - a solid metal door or aluminum studs may
have a negative effect on range. Try to position wireless devices and computers with wireless
adapters so that the signal passes through drywall or open doorways and not other materials.
4 Keep your product away (at least 3-6 feet or 1-2 meters) from electrical devices or appliances
that generate extreme RF noise.
Getting Started
For a typical home setup, you will need a Broadband (Cable/xDSL) Internet service and Modem
with Ethernet connection. Consult with your Cable or xDSL provider for proper installation of the
modem. Please do the following:
1. Connect your Broadband modem (Cable/xDSL) to the blue WAN port on the Barricade™
2. Connect the network card of your PC to the yellow LAN port on the Barricade™ using the
yellow RJ-45 cable provided. Now connect the power adapter.
3. Reboot PC. Start web browser and enter address http://192.168.2.1. When prompted enter
password smcadmin then click [Log In]. Note: The User Name must be set to Admin
4. Click [BASIC], then [Setup Wizard], then [Launch Internet Connection Setup Wizard]. Follow
the on screen instructions to complete the set-up and reboot the Barricade™. You are now
ready to enjoy your Internet connection.
.
12

Using the Configuration Menu
Whenever you want to configure your SMCWBR14-N, you can access the Configuration Menu
through your PC by opening the Web-browser and typing in the IP Address of the SMCWBR14-N. The
SMCWBR14-N default IP address is: http://192.168.2.1
¾ Open the Web browser.
¾ Type in the IP Address of the Router (http://192.168.2.1
).
If you have changed the default IP Address assigned to the SMCWBR14-N, make sure
you enter the correct IP Address.
¾ Select Admin in the User Name field.
¾ Enter Password: smcadmin (default).
¾ Click Log In.
If you have changed the default password assigned to the SMCWBR14-N, make sure you
enter the correct password.
13

Basic
The Basic tab provides the following configuration options: INTERNET, WIRELESS and NETWORK
SETTINGS.
Basic_Internet
Setup Wizard
If you are new to networking and have never configured a router before, click on Setup Wizard
and the router will guide you through a few simple steps to get your network up and running.
Manual Configure
If you consider yourself an advanced user and have configured a router before, click Manual
Configure to input all the settings manually.
14

Basic_Wireless
The wireless section is used to configure the wireless settings for your router. Note that changes made
in this section may also need to be duplicated on wireless clients that you want to connect to your
wireless network.
To protect your privacy, use the wireless security mode to configure the wireless security features.
This device supports three wireless security modes including: WEP, WPA-Personal, and
WPA-Enterprise. WEP is the original wireless encryption standard. WPA-Enterprise provides a higher
level of security. WPA-Personal does not require an authentication server. The WPA-Enterprise option
requires a RADIUS authentication server.
15

Enable Wireless
This option allows you to enable/disable the wireless AP function. The wireless can also be
turned ON/OFF by the slide switch on the back panel. When the wireless is enabled, the
following parameters are in effect.
Wireless Network Name
When you are browsing for available wireless networks, this is the name that will appear in the
list (unless Visibility Status is set to Invisible, see below). This name is also referred to as the
SSID. For security purposes, it is highly recommended to change from the pre-configured
network name.
Enable Auto Channel Scan
If you select this option, the router automatically finds the channel with least interference and
uses that channel for wireless networking. If you disable this option, the router uses the
channel that you specify with the following Wireless Channel option.
Wireless Channel
A wireless network uses specific channels in the wireless spectrum to handle communication
between clients. Some channels in your area may have interference from other electronic
devices. Choose the clearest channel to help optimize the performance and coverage of your
wireless network.
802.11 Mode
If all of the wireless devices you want to connect with this router can connect in the same
transmission mode, you can improve performance slightly by choosing the appropriate "Only"
mode. If you have some devices that use a different transmission mode, choose the
appropriate "Mixed" mode.
Channel Width
The "Auto 20/40 MHz" option is usually best. The other options are available for special
circumstances. Note that when 20/40MHz option is selected, an extended channel will be used
to extend the data rate.
Transmission Rate
By default the fastest possible transmission rate will be selected. You have the option of
selecting the speed if necessary.
Visibility Status
The Invisible option allows you to hide your wireless network. When this option is set to Visible,
your wireless network name is broadcast to anyone within the range of your signal. If you're not
using encryption then they could connect to your network. When Invisible mode is enabled,
you must enter the Wireless Network Name (SSID) on the client manually to connect to the
network.
Security Mode (NONE, WEP, WPA-Personal, WPA-Enterprise)
Unless one of these encryption modes is selected, wireless transmissions to and from your
wireless network can be easily intercepted and interpreted by unauthorized users.
WEP
A method of encrypting data for wireless communication intended to provide the same level of
privacy as a wired network. WEP is not as secure as WPA encryption. To gain access to a
16

WEP network, you must know the key. The key is a string of characters that you create. When
using WEP, you must determine the level of encryption. The type of encryption determines the
key length. 128-bit encryption requires a longer key than 64-bit encryption. Keys are defined by
entering in a string in HEX (hexadecimal - using characters 0-9, A-F) or ASCII (American
Standard Code for Information Interchange - alphanumeric characters) format. ASCII format is
provided so you can enter a string that is easier to remember. The ASCII string is converted to
HEX for use over the network. Four keys can be defined so that you can change keys easily. A
default key is selected for use on the network.
Example:
64-bit hexadecimal keys are exactly 10 characters in length. (12345678FA is a valid string
of 10 characters for 64-bit encryption.)
128-bit hexadecimal keys are exactly 26 characters in length.
(456FBCDF123400122225271730 is a valid string of 26 characters for 128-bit
encryption.)
64-bit ASCII keys are up to 5 characters in length (DMODE is a valid string of 5
characters for 64-bit encryption.)
128-bit ASCII keys are up to 13 characters in length (2002HALOSWIN1 is a valid string of
13 characters for 128-bit encryption.)
Note that, if you enter fewer characters in the WEP key than required, the remainder of the key
is automatically padded with zeros.
WPA-Personal and WPA-Enterprise
Both of these options select some variant of Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) -- security
standards published by the Wi-Fi Alliance. The WPA Mode further refines the variant that the
router should employ.
WPA Mode: WPA is the older standard; select this option if the clients that will be used with
the router only support the older standard. WPA2 is the newer implementation of the stronger
IEEE 802.11i security standard. With the "WPA or WPA2" option, the router tries WPA2 first,
but falls back to WPA if the client only supports WPA. The strongest cipher that the client
supports will be used. With the "WPA2 Only" option, the router associates only with clients that
also support WPA2 security. If the clients support the AES cipher, it will be used across the
wireless network to ensure best security.
Group Key Update Interval: The amount of time before the group key used for broadcast and
multicast data is changed.
WPA-Personal
This option uses Wi-Fi Protected Access with a Pre-Shared Key (PSK).
Pre-Shared Key: The key is entered as a pass-phrase of up to 63 alphanumeric characters in
ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange) format at both ends of the
wireless connection. It cannot be shorter than eight characters, although for proper security it
needs to be of ample length and should not be a commonly known phrase. This phrase is used
to generate session keys that are unique for each wireless client.
Example:
Wireless Networking technology enables ubiquitous communication
WPA-Enterprise
17

This option works with a RADIUS Server to authenticate wireless clients. Wireless clients
should have established the necessary credentials before attempting to authenticate to the
Server through this Gateway. Furthermore, it may be necessary to configure the RADIUS
Server to allow this Gateway to authenticate users.
Authentication Timeout: Amount of time before a client will be required to re-authenticate.
RADIUS Server IP Address: The IP address of the authentication server.
RADIUS Server Port: The port number used to connect to the authentication server.
RADIUS Server Shared Secret: A pass-phrase that must match with the authentication
server.
MAC Address Authentication: If this is selected, the user must connect from the same
computer whenever logging into the wireless network.
Advanced:
Optional Backup RADIUS Server
This option enables configuration of an optional second RADIUS server. A second
RADIUS server can be used as backup for the primary RADIUS server. The second
RADIUS server is consulted only when the primary server is not available or not
responding. The fields Second RADIUS Server IP Address, RADIUS Server Port,
Second RADIUS server Shared Secret, Second MAC Address Authentication provide
the corresponding parameters for the second RADIUS Server.
18

Basic_Network Settings
Use this section to configure the internal network settings of your router. The IP Address that is
configured here is the IP Address that you use to access the Web-based management interface. If
you change the IP Address here, you may need to adjust your PC’s network settings to access the
network again.
19

Router Settings
These are the settings of the LAN (Local Area Network) interface for the router. The router's
local network (LAN) settings are configured based on the IP Address and Subnet Mask
assigned in this section. The IP address is also used to access this Web-based management
interface. It is recommended that you use the default settings if you do not have an existing
network.
IP Address
The IP address of your router on the local area network. Your local area network settings
are based on the address assigned here. For example, 192.168.2.1.
Subnet Mask
The subnet mask of your router on the local area network.
Local Domain Name
This entry is optional. Enter a domain name for the local network. The router's DHCP
server will give this domain name to the computers on the wireless LAN. So, for example,
if you enter mynetwork.net here, and you have a wireless laptop with a name of chris,
that laptop will be known as chris.mynetwork.net. Note, however, if the router's settings
specify "DHCP (Dynamic)" Address, and the router's DHCP server assigns a domain
name to the AP, that domain name will override any name you enter here.
DNS Relay
When DNS Relay is enabled, the router plays the role of a DNS server. DNS requests
sent to the router are forwarded to the ISP's DNS server. This provides a constant DNS
address that LAN computers can use, even when the router obtains a different DNS
server address from the ISP upon re-establishing the WAN connection. You should
disable DNS relay if you implement a LAN-side DNS server as a virtual server.
RIP (Routing Information Protocol)
Used to broadcast routing information among routers.
Enable RIP
Enable RIP if required by the ISP, if the LAN has multiple routers, or if the LAN has
auto-IP devices.
RIP Operating mode
This router supports both version 2 and version 1 of the RIP specification.
V1. Use if none of the routers supports Version 2.
V2 Broadcast. Use if some routers are capable of Version 2, but some are only capable
of Version 1.
V2 Multicast. Use if this is the only router on the LAN or if all the routers support Version
2.
Router Metric
The additional cost of routing a packet through this router. The normal value for a simple
network is 1. This metric is added to routes learned from other routers; it is not added to
static or system routes.
Act as default router
20

Make this router the preferred destination for packets that are not otherwise destined.
Allow RIP updates from WAN
For security, disable this option unless required by the ISP.
RIP Password
RIP Version 2 supports the use of a password to limit access to routers through the RIP
protocol. If the ISP or other LAN router requires a RIP password, enter the password here.
DHCP Server Settings
DHCP stands for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol. The DHCP section is where you
configure the built-in DHCP Server to assign IP addresses to the computers and other devices
on your local area network (LAN).
Enable DHCP Server
Once your router is properly configured and this option is enabled, the DHCP Server will
manage the IP addresses and other network configuration information for computers and
other devices connected to your Local Area Network. There is no need for you to do this
yourself.
The computers (and other devices) connected to your LAN also need to have their TCP/IP
configuration set to "DHCP" or "Obtain an IP address automatically".
When you set Enable DHCP Server, the following options are displayed.
DHCP IP Address Range
These two IP values (from and to) define a range of IP addresses that the DHCP Server
uses when assigning addresses to computers and devices on your Local Area Network.
Any addresses that are outside of this range are not managed by the DHCP Server; these
could, therefore, be used for manually configured devices or devices that cannot use
DHCP to obtain network address details automatically.
It is possible for a computer or device that is manually configured to have an address that
does reside within this range. In this case the address should be reserved (see Static
DHCP Client below), so that the DHCP Server knows that this specific address can only
be used by a specific computer or device.
Your router, by default, has a static IP address of 192.168.2.1. This means that addresses
192.168.2.2 to 192.168.2.254 can be made available for allocation by the DHCP Server.
Example:
Your router uses 192.168.2.1 for the IP address. You've assigned a computer that you
want to designate as a Web server with a static IP address of 192.168.2.3. You've
assigned another computer that you want to designate as an FTP server with a static IP
address of 192.168.2.4. Therefore the starting IP address for your DHCP IP address
range needs to be 192.168.2.5 or greater.
Example:
Suppose you configure the DHCP Server to manage addresses From: 192.168.2.100
To: 192.168.2.199. This means that 192.168.2.3 to 192.168.2.99 and 192.168.2.200 to
192.168.2.254 are NOT managed by the DHCP Server. Computers or devices that use
addresses from these ranges are to be manually configured. Suppose you have a web
server computer that has a manually configured address of 192.168.2.100. Because
21

this falls within the "managed range" be sure to create a reservation for this address
and match it to the relevant computer (see Static DHCP Client below).
DHCP Lease Time
The amount of time that a computer may have an IP address before it is required to renew
the lease. The lease functions just as a lease on an apartment would. The initial lease
designates the amount of time before the lease expires. If the tenant wishes to retain the
address when the lease is expired then a new lease is established. If the lease expires
and the address is no longer needed than another tenant may use the address.
Always Broadcast
If all the computers on the LAN successfully obtain their IP addresses from the router's
DHCP server as expected, this option can remain disabled. However, if one of the
computers on the LAN fails to obtain an IP address from the router's DHCP server, it may
have an old DHCP client that incorrectly turns off the broadcast flag of DHCP packets.
Enabling this option will cause the router to always broadcast its responses to all clients,
thereby working around the problem, at the cost of increased broadcast traffic on the LAN.
Add/Edit DHCP Reservation
This option lets you reserve IP addresses, and assign the same IP address to the network
device with the specified MAC address any time it requests an IP address. This is almost the
same as when a device has a static IP address except that the device must still request an IP
address from the router. The router will provide the device the same IP address every time.
DHCP Reservations are helpful for server computers on the local network that are hosting
applications such as Web and FTP. Servers on your network should either use a static IP
address or use this option.
Computer Name
You can assign a name for each computer that is given a reserved IP address. This may
help you keep track of which computers are assigned this way. Example: Game Server.
IP Address:
The LAN address that you want to reserve.
MAC Address
To input the MAC address of your system, enter it in manually or connect to the router's
Web-Management interface from the system and click the Copy Your PC’s MAC
Address button.
A MAC address is usually located on a sticker on the bottom of a network device. The
MAC address is comprised of twelve digits. Each pair of hexadecimal digits are usually
separated by dashes or colons such as 00-0D-88-11-22-33 or 00:0D:88:11:22:33. If your
network device is a computer and the network card is already located inside the computer,
you can connect to the router from the computer and click the Copy Your PC’s MAC
Address button to enter the MAC address.
As an alternative, you can locate a MAC address in a specific operating system by
following the steps below:
22

Windows 98
Windows Me
Windows 2000
Windows XP
Mac OS X Go to the Apple Menu, select System Preferences, select Network, and
DHCP Reservations List
This shows clients that you have specified to have reserved DHCP addresses. An entry can be
changed by clicking the Edit icon, or deleted by clicking the Delete icon. When you click the
Edit icon, the item is highlighted, and the "Edit DHCP Reservation" section is activated for
editing.
Number of Dynamic DHCP Clients
In this section you can see what LAN devices are currently leasing IP addresses.
Go to the Start menu, select Run, type in winipcfg, and hit Enter. A
popup window will be displayed. Select the appropriate adapter from the
pull-down menu and you will see the Adapter Address. This is the MAC
address of the device.
Go to your Start menu, select Programs, select Accessories, and select
Command Prompt. At the command prompt type ipconfig /all and hit
Enter. The physical address displayed for the adapter connecting to the
router is the MAC address.
select the Ethernet Adapter connecting to the router. Select the Ethernet
button and the Ethernet ID will be listed. This is the same as the MAC
address.
Revoke
The Revoke option is available for the situation in which the lease table becomes full or
nearly full, you need to recover space in the table for new entries, and you know that
some of the currently allocated leases are no longer needed. Clicking Revoke cancels the
lease for a specific LAN device and frees an entry in the lease table. Do this only if the
device no longer needs the leased IP address, because, for example, it has been
removed from the network.
Reserve
The Reserve option converts this dynamic IP allocation into a DHCP Reservation and
adds the corresponding entry to the DHCP Reservations List.
23

Advanced
The Advanced tab provides the following configuration options: Virtual Server, Special Applications,
Gaming, StreamEngine, Routing, Access Control, WEB Filter, MAC Address Filter, Firewall,
Inbound Filter, Advanced Wireless and Advanced Network.
Advanced_Virtual Server
The Virtual Server option gives Internet users access to services on your LAN. This feature is useful
for hosting online services such as FTP, Web, or game servers. For each Virtual Server, you define a
public port on your router for redirection to an internal LAN IP Address and LAN port.
Example:
You are hosting a Web Server on a PC that has LAN IP Address of 192.168.2.50 and your ISP
is blocking Port 80.
1. Name the Virtual Server (for example: Web Server)
24

2. Enter the IP Address of the machine on your LAN (for example: 192.168.2.50
3. Enter the Private Port as [80]
4. Enter the Public Port as [8888]
5. Select the Protocol (for example TCP).
6. Ensure the schedule is set to Always
7. Click Save to add the settings to the Virtual Servers List
8. Repeat these steps for each Virtual Server Rule you wish to add. After the list is
complete, click Save Settings at the top of the page.
With this Virtual Server entry, all Internet traffic on Port 8888 will be redirected to your internal
web server on port 80 at IP Address 192.168.2.50.
Virtual Server Parameters
Name
Assign a meaningful name to the virtual server, for example Web Server. Several
well-known types of virtual server are available from the "Application Name" drop-down
list. Selecting one of these entries fills some of the remaining parameters with standard
values for that type of server.
IP Address
The IP address of the system on your internal network that will provide the virtual service,
for example 192.168.2.50. You can select a computer from the list of DHCP clients in the
"Computer Name" drop-down menu, or you can manually enter the IP address of the
server computer.
Protocol
Select the protocol used by the service. The common choices -- UDP, TCP, and both UDP
and TCP -- can be selected from the drop-down menu. To specify any other protocol,
select "Other" from the list, then enter the corresponding protocol number ( as assigned
by the IANA) in the Protocol box.
Private Port
The port that will be used on your internal network.
Public Port
The port that will be accessed from the Internet.
Inbound Filter
Select a filter that controls access as needed for this virtual server. If you do not see the
filter you need in the list of filters, go to the Advanced → Inbound Filter screen and create
a new filter.
Schedule
Select a schedule for when the service will be enabled. If you do not see the schedule you
need in the list of schedules, go to the Tools → Schedules screen and create a new
schedule.
25

Add/Edit Virtual Server
In this section you can add an entry to the Virtual Servers List below or edit an existing entry.
Enable
Entries in the list can be either active (enabled) or inactive (disabled).
Save
Saves the new or edited virtual server entry in the following list. When finished updating
the virtual server entries, you must still click the Save Settings button at the top of the
page to make the changes effective and permanent.
Virtual Servers List
The section shows the currently defined virtual servers. A Virtual Server can be changed by
clicking the Edit icon, or deleted by clicking the Delete icon. When you click the Edit icon, the
item is highlighted, and the "Edit Virtual Server" section is activated for editing.
You might have trouble accessing a virtual server using its public identity (WAN-side
IP-address of the gateway or its dynamic DNS name) from a machine on the LAN. Your
requests may not be looped back or you may be redirected to the "Forbidden" page.
This will happen if you have an Access Control Rule configured for this LAN machine.
The requests from the LAN machine will not be looped back if Internet access is blocked at the time of
access. To work around this problem, access the LAN machine using its LAN-side identity.
Requests may be redirected to the "Forbidden" page if web access for the LAN machine is restricted
by an Access Control Rule. Add the WAN-side identity (WAN-side IP-address of the router or its
dynamic DNS name) on the Advanced → Web Filter screen to work around this problem.
26

Advanced_Special Applications
An application rule is used to open single or multiple ports on your router when the router senses data
sent to the Internet on a "trigger" port or port range. An application rule applies to all computers on
your internal network.
Parameters for an Application Rule
Example:
You need to configure your router to allow a software application running on any computer
on your network to connect to a web-based server or another user on the Internet.
Name
Enter a name for the Special Application Rule, for example Game App, which will help
you identify the rule in the future. Alternatively, you can select from the Application list of
common applications.
Application
Instead of entering a name for the Special Application rule, you can select from this list of
common applications, and the remaining configuration values will be filled in accordingly.
Trigger Port Range
27
 Loading...
Loading...