Page 1

USER MANUAL
SPACEPC® 1232 SERIES
PC/104 SINGLE BOARD COMPUTER
(ALSO KNOWN AS THE CPU-1232)
5/18/2005
MNL-0501F-01
Page 2
ABOUT THIS MANUAL
This manual is meant for engineers and programmers who wish to use the Parvus SpaceP C®
1232. It contains technical specifications, and describes the connectors and how to properly use
and configure the product.
NOTICE
Although all the information contained herein has been carefully verified, Parvus
Corporation assumes no responsibility for errors that might appear in this document, or
for damage to property or persons resulting from an improper use of this manual and of
the related software. Parvus Corporation reserves the right to change the contents and
form of this document, as well as the features and specifications of its products at any
time, without notice.
Trademarks and registered trademarks appearing in this document are the property of their
respective owners.
CONVENTIONS
The following table lists conventions that are used throughout this guide.
Icon Notice Type Description
Information note
Important features or
instructions
Information to alert you to
Warning
potential damage to a
program, system or device
or potential personal injury
For a complete list of Parvus products and updated BIOS and drivers, please go to our Web site:
www.parvus.com
2
Page 3
Table of Contents
Table of Contents .......................................................................................................................... 3
Chapter 1 Product Overview .................................................................................................... 6
SpacePC 1232 Functional Block Diagram................................................................................... 7
Product Definition......................................................................................................................... 8
SpacePC 1232 PC/104 CPU Module.................................................................................... 8
AMD / NS Geode GX1 MMX Enhanced microprocessor...................................................... 8
Memory Configurations.........................................................................................................8
Solid State Disk..................................................................................................................... 8
DMA, Interrupts, Timers........................................................................................................ 8
Peripherals ............................................................................................................................ 9
BIOS...................................................................................................................................... 9
VGA interface........................................................................................................................ 9
LCD-TFT interface...............................................................................................................10
Chapter 2 Jumper Description............................................................................................... 11
Jumper Layout and Configuration.............................................................................................. 11
Chapter 3 Connectors Description........................................................................................ 13
Connectors Layout..................................................................................................................... 13
J1 and J2 for the ISA Bus.......................................................................................................... 15
The ISA BUS....................................................................................................................... 15
How to connect to the CPU other PC/104 & PC/104 devices: the stack assembly............ 15
J3 for Multifunction & J14 for Mouse.......................................................................................... 17
J3 Multifunction Connector.................................................................................................. 17
J14 Mouse Connector......................................................................................................... 19
Parvus Multifunction Adapter.............................................................................................. 20
J4 for PARALLEL or FDD..........................................................................................................22
HOW TO USE THE PARVUS FDD ADAPTER................................................................... 23
J5 and J6 Serial Port Interfaces................................................................................................. 24
J7 for 2 x USB, J8 for AUDIO-CODEC...................................................................................... 26
J7 for 2 x USB..................................................................................................................... 26
J8 for AC97 Audio port Section........................................................................................... 27
Parvus USB/AC97-AudioCODEC Adapter.......................................................................... 28
J9 IDE Connector, JP10 IDE LED Connector............................................................................ 29
J9 IDE Connector................................................................................................................29
JP10 IDE LED Connector.................................................................................................... 30
J10 VGA Connector................................................................................................................... 31
J11 Auxiliary Power Connector.................................................................................................. 32
J13 Fan power supply connector............................................................................................... 33
J18 for Ethernet.......................................................................................................................... 34
3
Page 4

J19 LCD-TFT Section ................................................................................................................ 36
Chapter 4 The Setup Program................................................................................................ 39
How to use the Setup program.................................................................................................. 40
The Setup pages........................................................................................................................ 41
General Page...................................................................................................................... 42
Devices Page ...................................................................................................................... 45
Communications Page........................................................................................................ 48
ATAPI Units Page ............................................................................................................... 51
Error Handling Page............................................................................................................ 54
Power Management............................................................................................................ 55
Chapter 5 How to update the BIOS. The SSD...................................................................... 57
How to update the BIOS: the BTOOL Program......................................................................... 58
OPTIONS EXPLANATION.................................................................................................. 59
The Integrated Solid State Disk.................................................................................................60
Chapter 6 Virtual Peripherals................................................................................................. 61
The “Virtual Peripherals” mode..................................................................................................61
Local and redirected peripherals................................................................................................62
“Virtual Peripherals” connection................................................................................................. 62
Important note............................................................................................................................ 65
Chapter 7 Watchdog Timer..................................................................................................... 66
Watchdog modalities.................................................................................................................. 67
BIOS INT 52h - functions 0Ch, 0Dh, 0Eh............................................................................ 67
Super I/O registers programming........................................................................................ 67
Watchdog time-out pin............................................................................................................... 69
Chapter 8 Troubleshooting..................................................................................................... 70
Common Problems and Solutions ............................................................................................. 71
Troubleshooting a PC/104 System............................................................................................ 72
Technical/Sales Assistance ....................................................................................................... 72
Returning For Service................................................................................................................ 73
Appendix ...................................................................................................................................... 74
A.1 Electrical and Environmental Specifications................................................................... 74
Operating Characteristics.................................................................................................... 74
Absolute Maximum Ratings................................................................................................. 75
MTBF................................................................................................................................... 75
Power Consumption............................................................................................................ 75
A.2 Mechanical Dimensions.................................................................................................. 76
CPU Dimensions................................................................................................................. 76
FDD Adapter Dimensions.................................................................................................... 77
USB Audio CODEC Dimensions......................................................................................... 78
Ethernet Adapter Dimensions ............................................................................................. 79
Multifunction Adapter Dimensions....................................................................................... 80
4
Page 5

5
A.3 Safety Summary.............................................................................................................. 81
Ground the Instrument ........................................................................................................ 81
Do Not Substitute Parts or Modify Equipment..................................................................... 82
Flammability........................................................................................................................ 82
EMI Caution......................................................................................................................... 82
CE Notice ............................................................................................................................ 82
Disclaimer of Warranty........................................................................................................ 82
Notice .................................................................................................................................. 82
Reliability............................................................................................................................. 83
Life Support Policy .............................................................................................................. 83
Acronyms and Abbreviations..................................................................................................... 85
5
Page 6
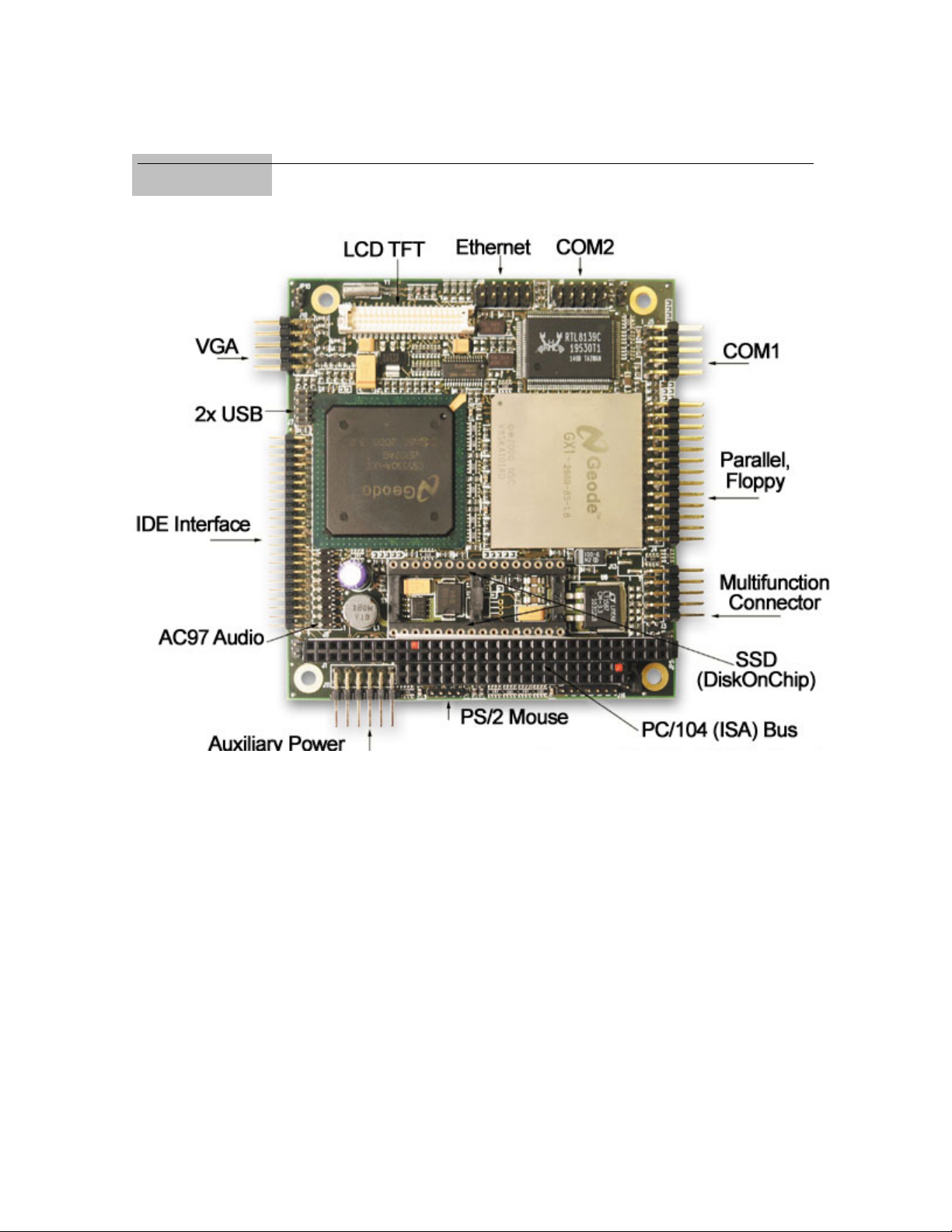
Chapter 1 Product Overview
The SpacePC 1232 is a highly integrated PC/104 CPU module, based on the AMD / National
Semiconductor Geode GX1 MMX Enhanced microprocessor. It is also kno wn a s the CPU-1232.
Related Products:
Development kit for SpacePC 1232 / multifunction adapter
Cable set for SpacePC 1232
AC97-CODEC and USB adapter
Parallel to Floppy adapter
Ethernet RJ45 adapter
For a complete list of our products please go to our web site: www.parvus.com
In the following paragraphs, you will find a brief description of the SpacePC 1232.
6
Page 7
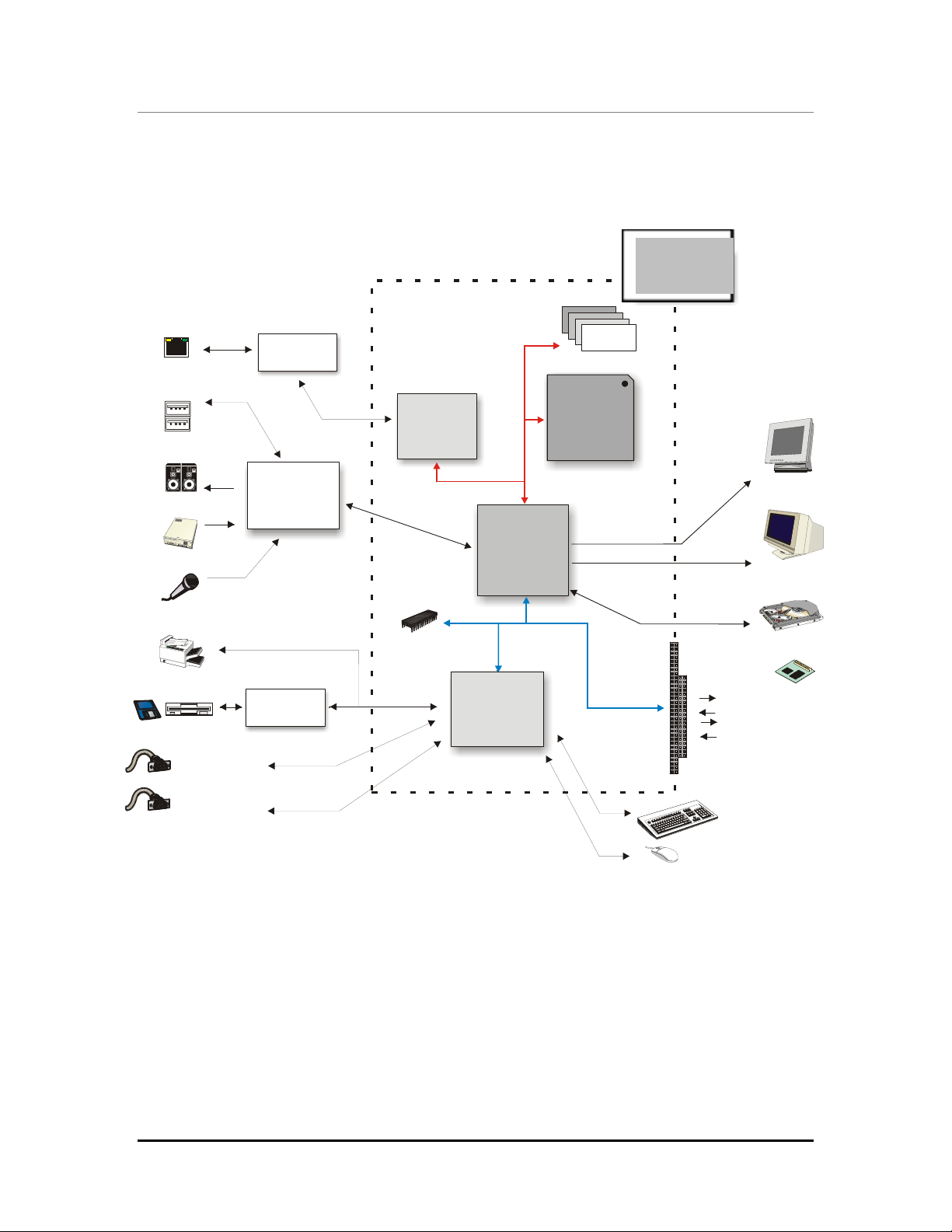
7
SpacePC 1232 Functional Block Diagram
The figure below shows the functional blocks diagram of the module.
Figure 1. Functional
block diagram of the
Ethernet 10/100
2 x USB
Speakers Line-out
CD-ROM Audio
Microphone
SpacePC 1232
Parallel / Floppy D D
Ethernet
Adapter
USB +
AC97 Codec
Adapter
FDD
Adapter
Ethernet
Controller
SSD
Fast
Super I/O
(SMC FD37B782)
Geode Gx1
PCI
3.3V Bus
NS Geode
CS5530A
I/O
Companion
ISA
Bus
SDRAM
NS
Processor
CPU-1232
CPU-1232
Module
LCD-TFT
VGA CRT
HDD/DOM
RS232
RS232/422/485
module
ISA BUS
Keyb
PS/2 Mouse
7
Page 8

Product Definition
SpacePC 1232 PC/104 CPU Module
¾ PC/AT compatible.
¾ PC/104 Form Factor: 3.550” x 3.775” (90 X 96 mm); height: 15 mm (0.6”)
¾ Low power consumption.
¾ High reliability.
¾ Operating systems supported: DOS (from 3.0 to 6.22), QNX, VxWorks, PSOS, Windows
3.11, Windows 95, Windows 98, Windows NT, Windows 2000, Linux.
AMD / NS Geode GX1 MMX Enhanced microprocessor
¾ 266MHz clock speed (300MHz version only available with a minimum quantity purchase)
¾ 1.8V core voltage processor supply
¾ 3.3V I/O interface voltage supply
¾ 16 KB unified L1 cache
¾ Six-stage pipelined integer unit
¾ Integrated Floating Point Unit (FPU)
¾ Supports a wide variety of Power Management standards:
APM (Advanced Power Management) for Legacy power management
ACPI (Advanced Configuration and Power Interface) for Windows power management
(Note: Geode processor family was acquired by AMD from National Semiconductor in 2003)
Memory Configurations
¾ 64 - 128 Mbytes surface mount SDRAM
¾ Integrated system memory and graphic frame memory (Unified Memory Architecture – UMA)
Solid State Disk
¾ A 640 KB of flash memory is available as re-programmable device (that is to say read-only
disk)
¾ One 32-pin socket for 32DIL Solid State Disk such as Disk On Chip (2000 and Millennium
series)
¾ The SpacePC 1232 supports all Flash IDE devices such as DOM, Compact Flash, ATA
Flash and 2.5” IDE-Flash disk
DMA, Interrupts, Timers
¾ Two cascaded 8237 DMA controllers (6 DMA channels)
8
Page 9

9
¾ Two cascaded 8259 interrupt controllers (15 interrupt channels)
¾ Three 8254 counter/timers (There are no extra timers)
¾ Three extra timers
Peripherals
¾ Two serial ports UART 16550A-compatible: one selectable between RS232/422/485 and
one RS232 only
¾ One bidirectional parallel port: selectable between EPP, ECP, SPP
¾ One USB port compliant with the Open Host Controller Interface (OHCI)
¾ One AC97 port (CODEC board needed)
¾ One floppy disk interface available on the parallel port (J5) through an external adapter, or
on FPC (Flat Printed Circuit) connector (J15). They are mutually exclusive so only one FDD
can be used
¾ One PC/AT keyboard interface
¾ One PS/2 mouse connector
¾ One speaker port
¾ One standard EIDE HD interface
¾ One 10/100 Fast Ethernet Controller (RJ45 Ethernet Adapter needed)
¾ Software programmable watchdog from 1 second to 255 seconds or from 1 minute to 255
minutes
¾ Real time clock (external battery required for date and time backup)
BIOS
¾ The Parvus/Eurotech BIOS is stored into a reprogrammable on board device.
¾ Utilities for BIOS upgrade provided in the utility disk
¾ Setup parameters stored in Flash memory
¾ Virtual Peripheral (V.P.) operating mode: remote control of the CPU module through the
serial port.
¾ Boot selectable from floppy, SSD, HD, CD-ROM and V.P.
¾ Fast Boot selectable
¾ Embedded features implemented
VGA interface
¾ Backward compatibility to SVGA standards
¾ Full VGA and VESA mode support
¾ 2D graphics accelerator
¾ Display Compression Technology architecture
9
Page 10

¾ Display resolutions up to 1280x1024 8-bit per pixel
¾ UMA (Unified Memory Architecture)
LCD-TFT interface
¾ Also LCD-TFT flat panels can be connected to the SpacePC 1232
If LCD-TFT and CRT screens are used at the same time, the refresh frequency of the
CRT video will be modified according to the LCD-TFT setting. It may be possible to
view flickering on the CRT screen.
10
Page 11

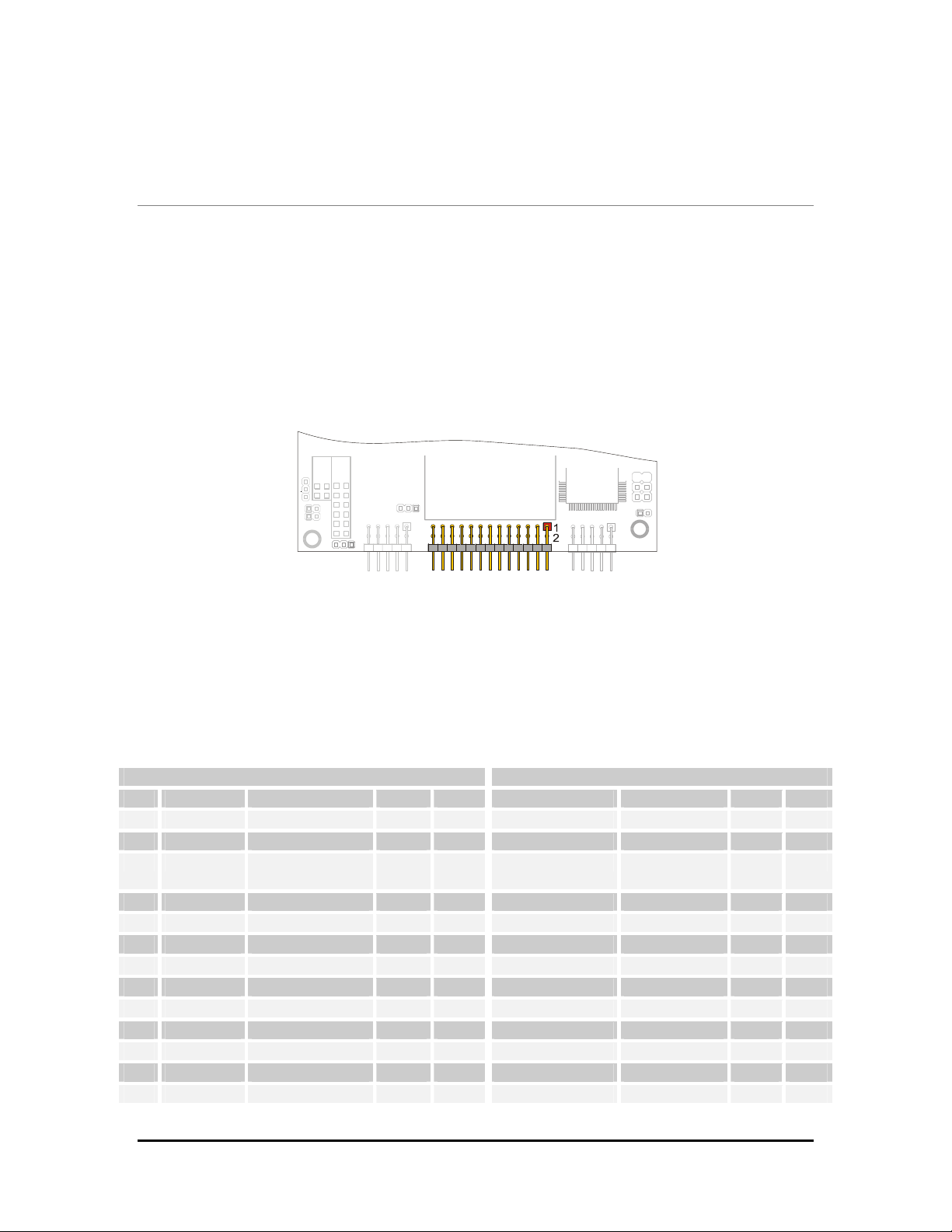
Chapter 2 Jumper Description
This chapter shows the jumpers layout and explains how to setup the jumpers.
Jumper Layout and Configuration
Figure below, shows the jumper layout of the SpacePC 1232 module.
In the below figure, the jumpers are indicated as JP followed by the jumper's number, while pin 1
of every jumper is indicated by a red square pad.
Figure 2. Jumpers and solder jumpers on the Spac ePC 1232 module
11
Page 12

The following jumpers are located on the module:
One 3-pin jumper (JP5) for which there are only two possibilities:
¾ Connecting pin 1 to pin 2 (which will be indicated as 1-2)
¾ Connecting pin 2 to pin 3 (which will be indicated as 2-3)
Three 2-pin jumpers (JP1, JP7, JP8), which can be set as follows:
¾ Pin 1 connected to pin 2 (which will be indicated as ‘Closed’)
¾ Pin 1 and pin 2 not connected (which will be indicated as ‘Open’)
The following table provides a quick cross-reference for the SpacePC 1232 module’s jumpers.
Table 1. Jumper Settings
PIN# Type Function Default
Write protection on Bios Flash
Closed: Write not allowed on Boot Block
Open: Boot Block can be written
1-2: Battery
2-3: VDD
Invalid Setup
Closed: Module starts with default settings
External BIOS
Closed: Module starts with External BIOS
Open
2-3
Open
Open
JP1
JP5
JP7
JP8
2 pin
jumper
2 pin
jumper
2 pin
jumper
2 pin
jumper
Power Supply Source Selection for SSD Socket
Open: Module starts with saved parameters
Open: Module starts with internal BIOS (inside Flash EPROM)
12
Page 13
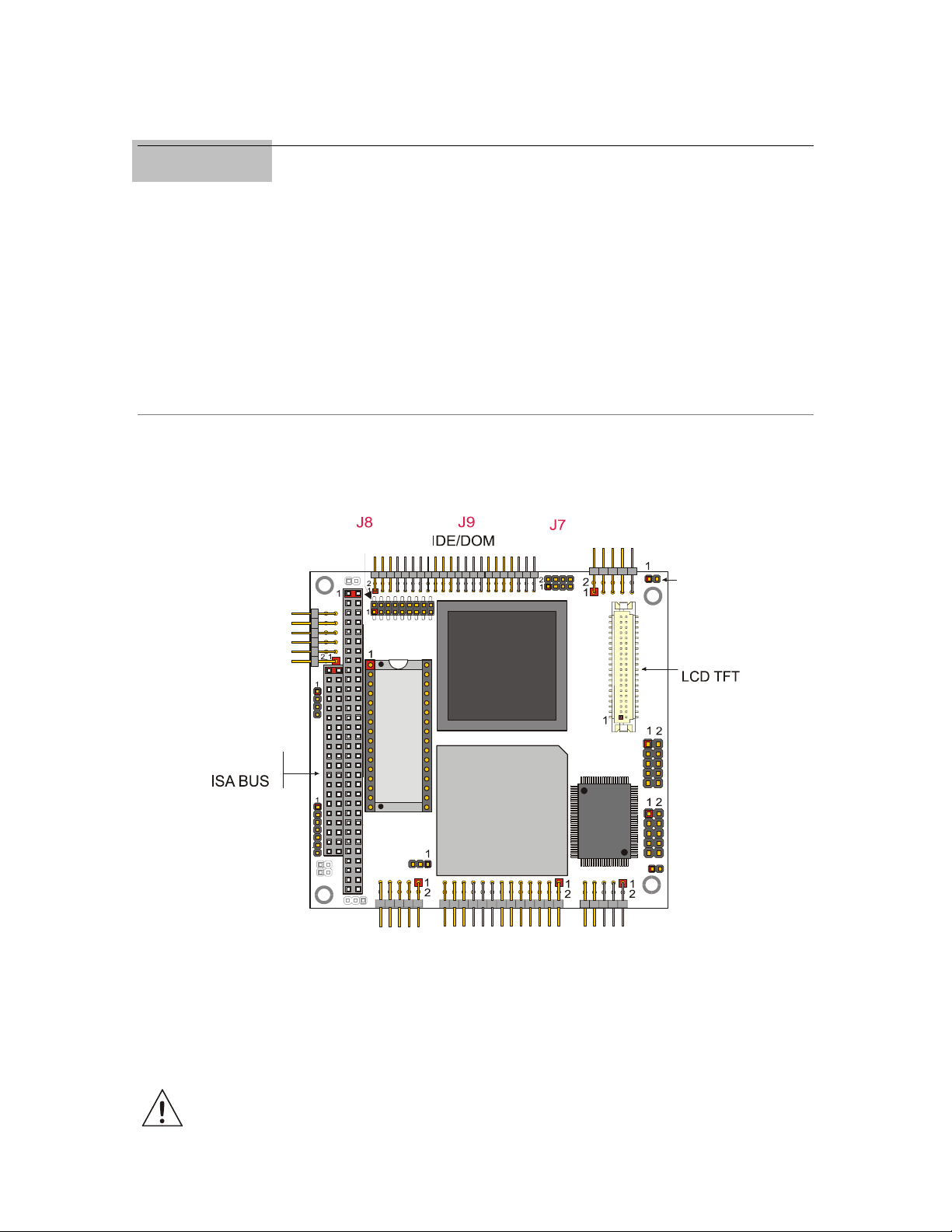
Chapter 3 Connectors Description
This chapter provides a brief description of the SpacePC 1232 module’s connectors, with their
positions and functions.
Connectors Layout
In the following figure are shown the connectors with their layout and function/s.
J10
AC97 Audio
2x USB
VGA
JP10
IDE Led
J11
Auxiliary
Power
NS Geode
CS5530A
J19
I/O
J14
PS/2 Mouse
J1
J2
SSD
J16
J13
J3
Multifunction
Connector
Companion
NS
Geode Gx1
U1
Processor
J4
Parallel
Port
J18
Ethernet
J6
Serial 2
J17
J5
Serial 1
Figure 3. Connectors layout
Note: in the previous figure, a red square pad indicates pin 1 of each connector.
13
Page 14

Table below lists the name of the connectors with their function and the reference page.
Table 2. Connector Functions
Connector Function Page
J1-J2 ISA BUS (PC/XT) 20
J3 Multifunction Connector 22
J4 Parallel Port / Floppy 26
J5 Serial Port 1 28
J6 Serial Port 2 28
J7 USB ports (A and B) 29
J8 AC97 Audio Interface Connector 30
J9 IDE/DOM 33
J10 VGA 34
J11 Auxiliary Power Supply 35
J13 Fan 36
J14 PS/2 Mouse 24
J16 Reserved J17 Reserved J18 Fast Ethernet 37
J19 LCD TFT 39
SSD Solid State Disk socket DIL 32
-
(Disk on Chip)
JP10 IDE Activity Led 33
14
Page 15
15
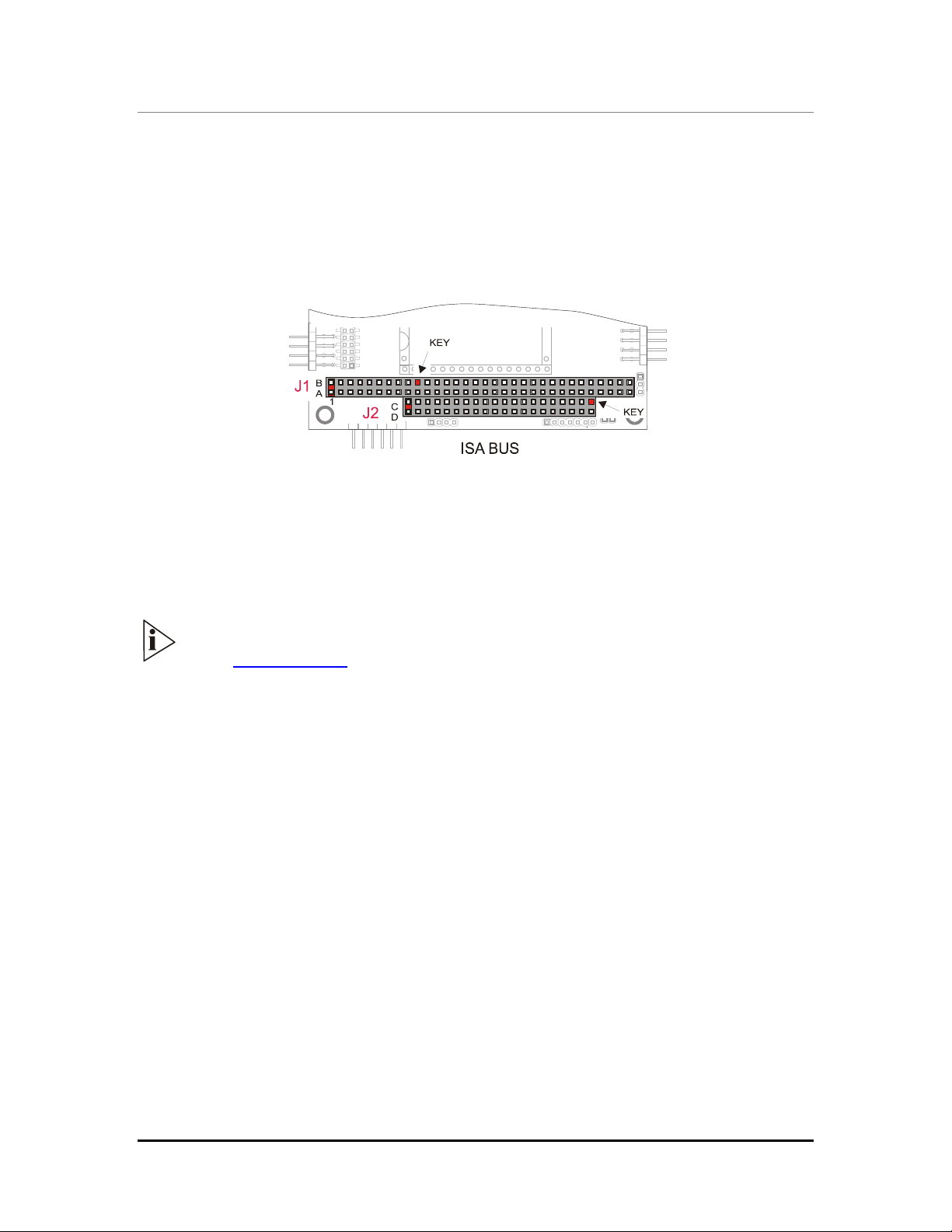
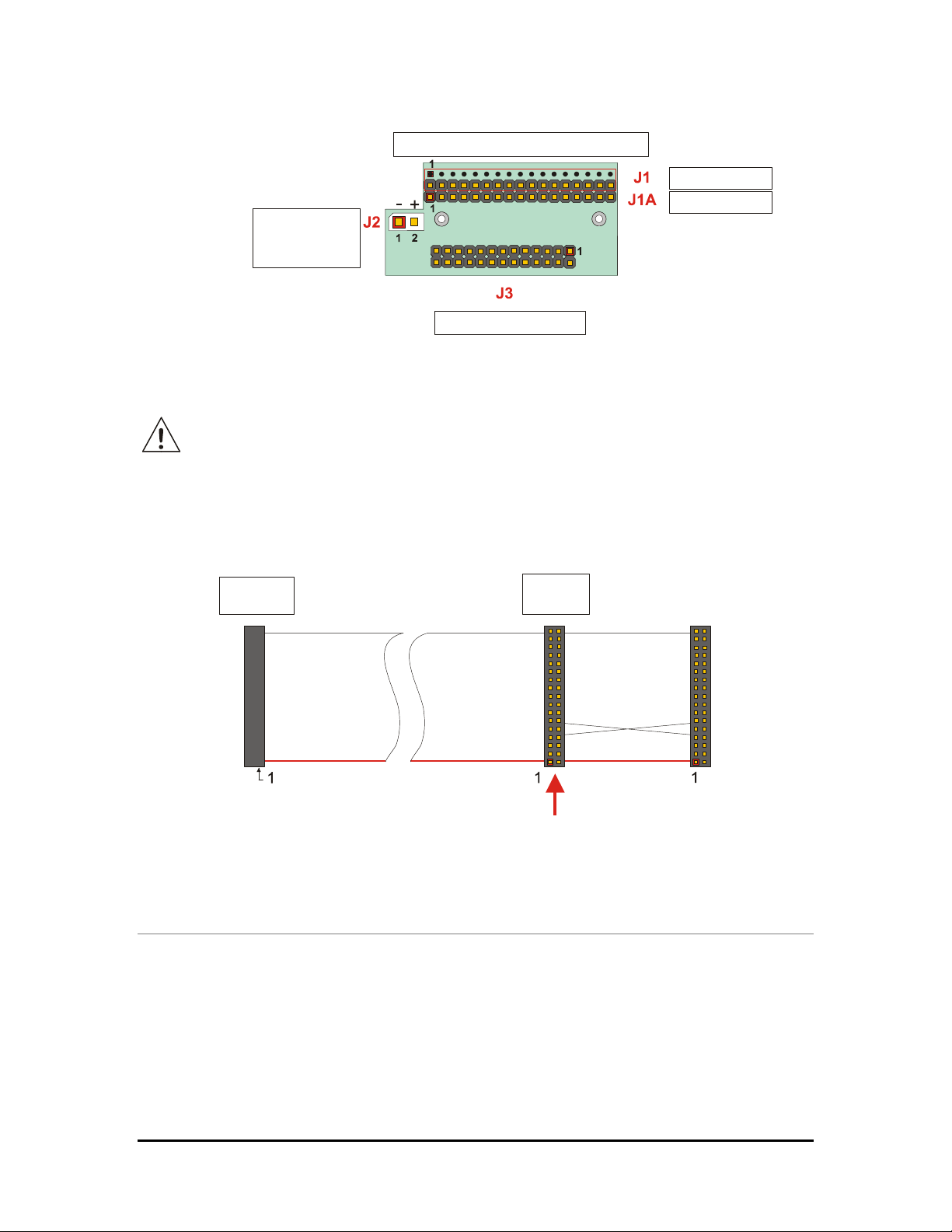
J1 and J2 for the ISA Bus
The ISA BUS
Connectors J1 and J2 carry the signals for the ISA Bus. These signals match definitions of the
IEEE P996 standard. Below is shown a picture of the ISA BUS
Figure 4. ISA BUS layout
According to PC/104 specifications, KEYs are filled holes in the upper side and missing pins in
the lower side of the bus connector. This is made to avoid the wrong insertion in/of another
module.
For further info about ISA (PC/104) bus, please refer to the PC/104 Consortium Web
site at www.pc104.org
.
How to connect to the CPU other PC/104 & PC/104 devices: the stack
assembly
The ISA Bus connectors of the module are designed to allow the connection onto a stack of other
PC/104 and/or PC/104Plus devices. We recommend you to follow the procedure below ensuring
that stacking of the modules does not damage connectors or electronics parts.
1. Turn off power to the PC/104 system or stack.
2. Select and install standoffs to properly position the module on the PC/104 stack.
3. Touch a grounded metal part of the rack to discharge any accumulation of static electricity.
4. Remove the module from its anti-static bag.
5. Check that keying pins in the bus connector are properly positioned.
6. Check the stacking order; make sure an XT bus card will not be placed between two AT bus
cards or it will interrupt the AT bus signals.
7. Hold the module by its edges and orient it so that the bus connector pins line up with the
matching connector on the stack.
15
Page 16
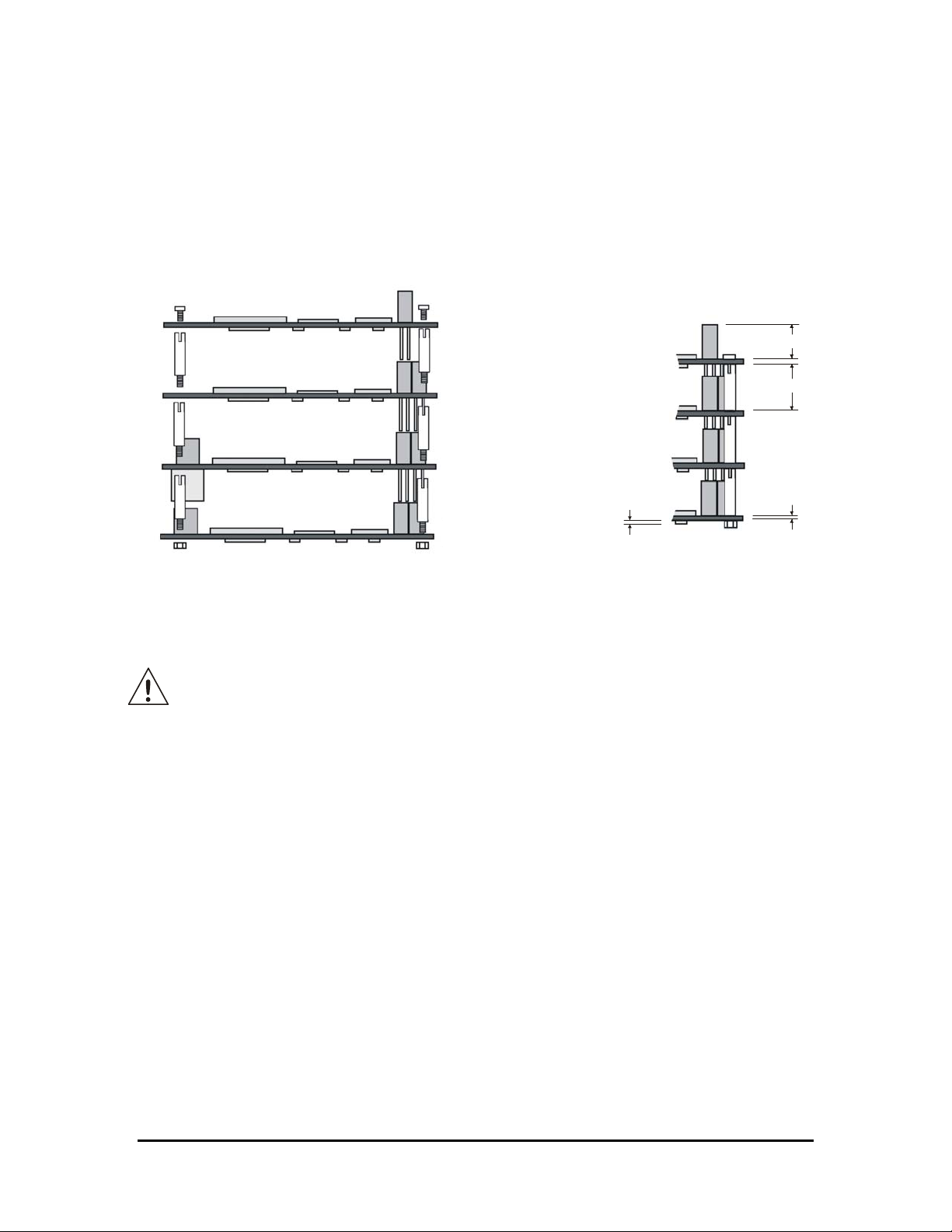
8. Press evenly the module onto the PC/104 stack.
The picture below shows a typical module stack with 2 PC/104 modules, 1 PC/104 16-BIT
module, and 1 PC/104 8-BIT module.
The maximum configuration for the PCI bus of PC/104 modules is 4 plus the Host Board.
If standard PC/104 modules are used in the stack, they must be the top module(s) because they
will normally not include the PCI bus.
Stackthrough
0.6 in. (15mm) Spacers (4 plcs.)
0.6 in. (15mm) Spacers (4 plcs.)
0.6 in. (15mm) Spacers (4 plcs.)
8-bit module
Stackthrough
16-bit module
Stackthrough
PC/104Plus module
0.100 in. (2.54 mm)
Non-Stackthrough
PC/104Plus module
0.435 in. (11 mm)
0.6 in. (15 mm)
0.062 in. (1.57 mm)
Figure 5. The Module Stack
Do not force the module onto the stack! Wiggling the module or applying too much
pressure may damage it. If the module does not readily press into place, remove it,
check for bent pins or out-of-place keying pins, and try again.
16
Page 17

17
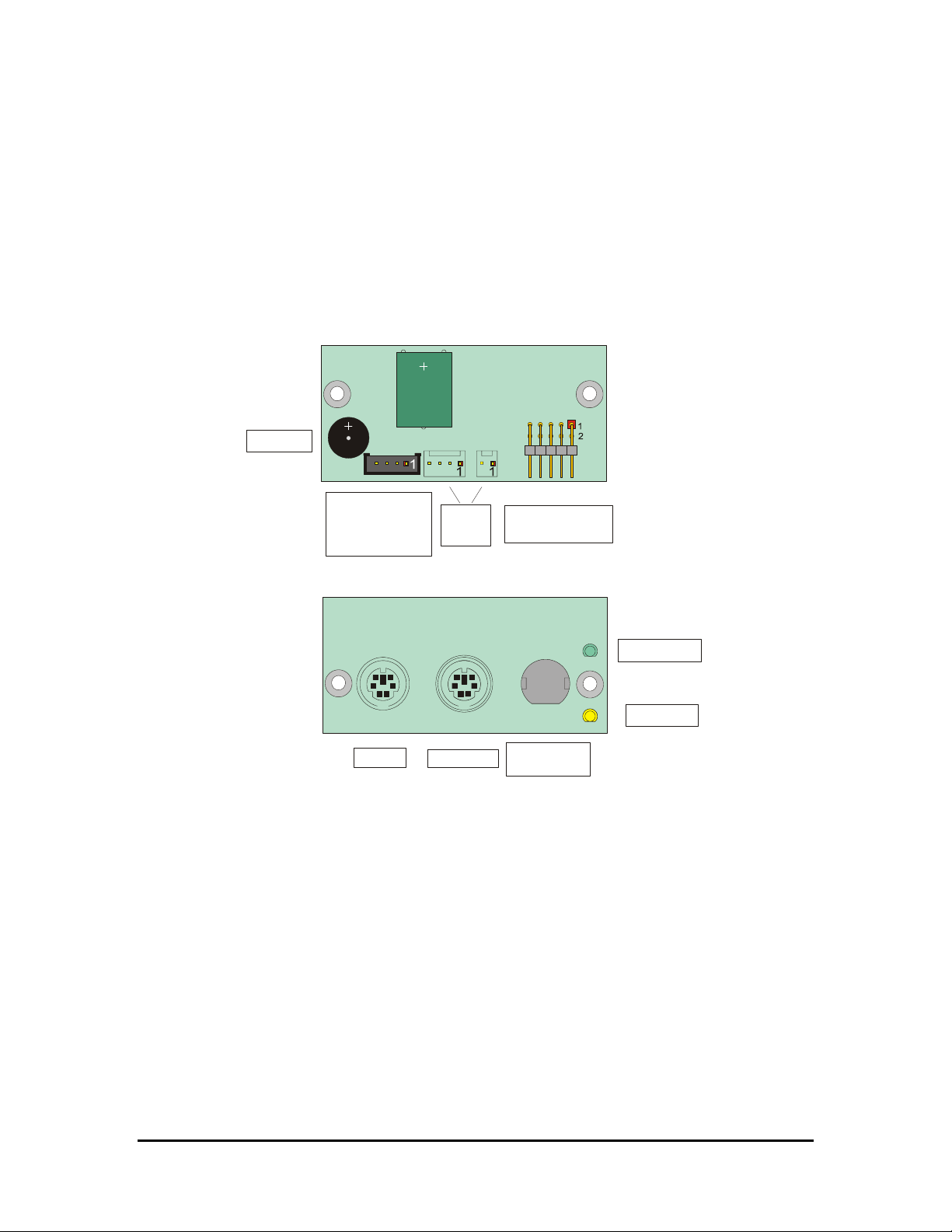
J3 for Multifunction & J14 for Mouse
J3 is a double row 5 x 2 pin with 2.54-mm step connector and allows the connection of a speaker,
a keyboard, and a battery to the SpacePC 1232 module.
J14 is a 4 pin with 2-mm step connector and allows the connection of a PS/2 compatible mouse.
Later on there is a brief description about the Parvus Multifunction Adapter and the VGA and the
Ethernet.
J3 Multifunction Connector
J3
Multifunction
Connector
Figure 6. J3 Connector layout
This connector implements the following functions:
¾ MULTIFUNCTION
AT Keyboard
System reset
External battery
Speaker
Power button
17
Page 18

Below is shown the connector pinout:
Table 3. Multifunction connector
Pin Signal Function
SPKR- Speaker output
1
SPKR+ Speaker output (+5V)
2
RESET External reset
3
WDTL Watch dog timeout latch
4
KBD Keyboard data
5
KBC Keyboard clock
6
GND Ground signal
7
KBP Keyboard power (+5V)
8
BAT External Battery input
9
P_B External Power Button
10
This section of the connector implements the following functions:
Keyboard
An AT compatible keyboard can be connected to the module through connector J3. The
following table lists the pin-out of connector J3.
System reset
Connecting the pin 3 of the multifunction connector to ground performs a hardware reset
of the module. It is possible to use an external push-button, normally open. J3 provides a
connection for an external normally-open pushbutton to manually reset the system.
Connect the other side of the switch to ground. The reset signal is “de-bounced” on the
board.
External Battery
Pin 9 of the multifunction connector allows the connection of an external backup battery
(typically from 3 to 3.9 V). This battery is used at power down to preserve the date-time in
the Real Time Clock.
The typical battery consumption with the module off is 7 uA.
Table 4. Keyboard connector
Pin Signal Function
5
6
7
8
KBD Keyboard data
KBC Keyboard clock
GND Ground signal
+5V Power supply
Speaker
A transistor to supply 0.1 watt of power to an external speaker controls these outputs. A
transistor amplifier buffers the speaker signal. Use a small general purpose 2 or 3-inch
permanent magnet speaker with an 8-ohm voice coil.
18
Page 19
19
The audio output is based on two signals: one come from the output of Timer 2, and the
other come from I/O port 61h compliant with the AT Standard.
Power button
If the soft power management is enabled, a low signal in the pin10 turns the system on or
off.
J14 Mouse Connector
A PS/2 compatible mouse can be connected to the J14 connector (4pins, 2-mm step).
The J14 pin out is given below.
Pin # Signal Function
J14
PS/2 Mouse
Figure 7. J14 Connector layout
Table 5. J14 for Mouse connector
1
2
3
4
+5V Power supply
MSCLK Mouse clock
GND Ground signal
MDAT Mouse data
19
Page 20
Parvus Multifunction Adapter
Parvus Multifunction Adapter simplifies the connection of mouse and keyboard with two PS/2
connectors, providing also a speaker, a battery and a reset pushbutton.
Battery
Speaker
J6
To J14 Conn.
of CPU Board
(Mouse sign.)
J3
Mouse
J1
J5
Not
used
J2 S1
Keyboard
J4
To Multif. Conn.
of CPU Board
Reset
Pushbutton
Power Led
Spkr Led
Figure 8. Multifunction Adapter (both sides)
20
Page 21

Table 6. J4 To CPU Multifunction
Connector
PIN # SIGNAL
1
2-8
3
4-10
5
6
7
9
SPKR
+5V
RES_PB_IN
N.C.
KBDAT
KBCLK
GND
BATT_IN
Table 7. J6 To CPU J14 (Mouse
signals)
PIN # SIGNAL
1
2
3
4
+5V
MSCLK
GND
MSDAT
21
Page 22
J4 for PARALLEL or FDD
A parallel port is available on connector J4 of the SpacePC 1232 module. This connector is a
13x2 pin with 2.54-mm step.
Connector J4 has two operating modes:
Parallel port mode
Floppy disk interface mode
The selection between the two modes can be performed in the BIOS Setup (see Chapter 4).
J4
Parallel
Port
Figure 9. J4 Connector Layout
The following table gives the pin-out of connector J4 for both functions (parallel port and floppy).
Table 8. J4 Parallel/Floppy port connector
Parallel Function Floppy Function
Pin Signal Function in/out DB25 Signal Function In/out Pin
STB# (*) Strobe Data out 1 DSO# (*) Drive Select 0 In/out
1
AFD# (*) Autofeed out 14 DENSEL# (*) Out
2
PD0 LSB of printer
3
Data
ERR# (*) Printer error in 15 HDSEL# (*) Head Select Out
4
PD1 Printer Data 1 out 3 TRK0# (*) Track 0 In
5
Initialize printer out 16 DIR# (*) Step Direction Out
6
PD2 Printer Data 2 out 4 WP# (*) Write protect Out
7
SLIN# (*) Select printer out 17 STEP# (*) Step Pulse Out
8
PD3 Printer Data 3 out 5 RDATA# (*) Read Data In
9
GND Signal ground -- 18 GND Signal ground --
10
PD4 Printer Data 4 out 6 DSKCHG# (*) Disk Change In
11
GND Signal ground -- 19 GND Signal ground --
12
PD5 Printer Data 5 out 7 MEDIA-ID0# (*) In
13
out 2 INDEX# (*) Index Pulse
Inp
In
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
22
Page 23
23
GND Signal ground -- 20 GND Signal ground
14
PD6 Printer Data 6 out 8 MTR0# (*) Motor On 0 In/out
15
GND Signal ground -- 21 GND Signal ground --
16
PD7 MSB Printer
17
out 9 MEDIA-ID1# (*) In
14
15
16
17
Data
GND Signal ground -- 22 GND Signal ground --
18
ACK# (*) Character
19
in 10 DS1# Drive Select 1 Out
18
19
accepted
GND Signal ground -- 23 GND Signal ground --
20
BSY Busy in 11 MTR1# (*) Motor On 1 Out
21
GND Signal ground -- 24 GND Signal ground --
22
PE Paper End in 12 WDATA# (*) Write Disk
23
Out
20
21
22
23
Data
GND Signal ground -- 25 GND Signal ground --
24
SLCT Ready To
25
in 13 WGATE# (*) Write Gate Out
24
25
Receive
NC Reserved -- --- --- --- ---
26
26
(*) The “#” stands for: signal active low
Note. FDD shouldn’t be directly connected to the J4 connector. Before using a Floppy
Disk, an adapter must be inserted between the parallel port flat cable and the Floppy Disk
Drive.
HOW TO USE THE PARVUS FDD ADAPTER
There are two configurations available for the Parvus FDD Adapter:
1. - J1A :Male configuration (for plugging to the Floppy Disk Flat Cable)
2.- J1 :Female configuration (for direct plugging to the Floppy Disk Drive)
J2 :Power supply (5V) used to power the adapter.
(This connector can’t power the FDD that needs its normal power
supply).
J3 :Parallel Port Flat Cable Connector
A picture of this adapter is shown below.
23
Page 24
To the FDD Cable/Connector
Female Config.
Male Config.
Power Supply
GND PIN1
+5V PIN2
To the Parallel Port
Figure 10. Parvus Floppy Disk Drive Adapter
WARNING! TO AVOID MALFUNCTIONS, BE CAREFUL TO CONNECT THE FLOPPY
DRIVE CABLE IN THE FOLLOWING WAY:
The most diffuse Floppy Drive flat cable that is possible to find on the market is structured as
shown in the following schematic picture. With this type of cable only the second connector can
be connected to the Parvus Floppy Disk Drive Adapter. The “FDD connector” end of the cable is
connected to the rear connector of the Floppy Drive.
To FDD
connector
To FDD
adapter
X
Figure 11. Floppy Drive Cable
J5 and J6 Serial Port Interfaces
Two serial ports are available on connectors J5, J6 of the SpacePC 1232 module. These
connectors are 5x2 pin with 2.54-mm step.
24
Page 25
25
J5
Serial 1
J6
Serial 2
Figure 12. J5 and J6 Connectors layout
Both can be set as RS232 but only one (J5) can be set as RS422-485.
Refer to the following tables for the serial ports pinout assignment in RS232/422/485 modes.
Table 9. J5, J6 Serial Port Connectors in RS232 mode
Pin Signal Function DB25 DB9
1 DCD Data Carrier Detect 8 1
2 DSR Data Set Ready 6 6
3 RX Receive Data 3 2
4 RTS Request To Send 4 7
5 TX Transmit data 2 3
6 CTS Clear To Send 5 8
7 DTR Data Terminal
20 4
Ready
8 RI Ring Indicator 22 9
9,10 GND Signal Ground 7 5
Table 10. J5 Serial Port Connecto r in RS422-RS485 modes
RS422 RS485
Pin Signal Function In/out Signal Function In/out Pin
-TX Transmit data out -TX/-RX Transmit/Receive data out/in
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9,10
-- Not connected -- -- Not connected --
+TX Transmit Data out +TX/+RX Transmit/Receive data out/in
-- Not connected -- -- Not connected --
-RX Receive Data in -- Not connected --
-- Not connected -- -- Not connected --
+RX Receive Data in -- Not connected --
-- Not connected -- -- Not connected --
gnd Signal ground -- gnd Signal ground --
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9,10
Note. If the Serial port is used in RS485 mode, the bi-directional line must be controlled
via software, using the Data Terminal Ready (DTR) signal of the serial controller.
This signal is defined by bit 0 of the UART Modem Control Register (MCR) and the bi-
directional line is controlled as follows:
25
Page 26
- bit 0 of the MCR register = 0 means RS485 line receiving
- bit 0 of the MCR register = 1 means RS485 line transmitting
The I/O address of the MCR is "Serial port Base address"+4H.
See Chapter 4 for info about the Serial ports configuration.
J7 for 2 x USB, J8 for AUDIO-CODEC
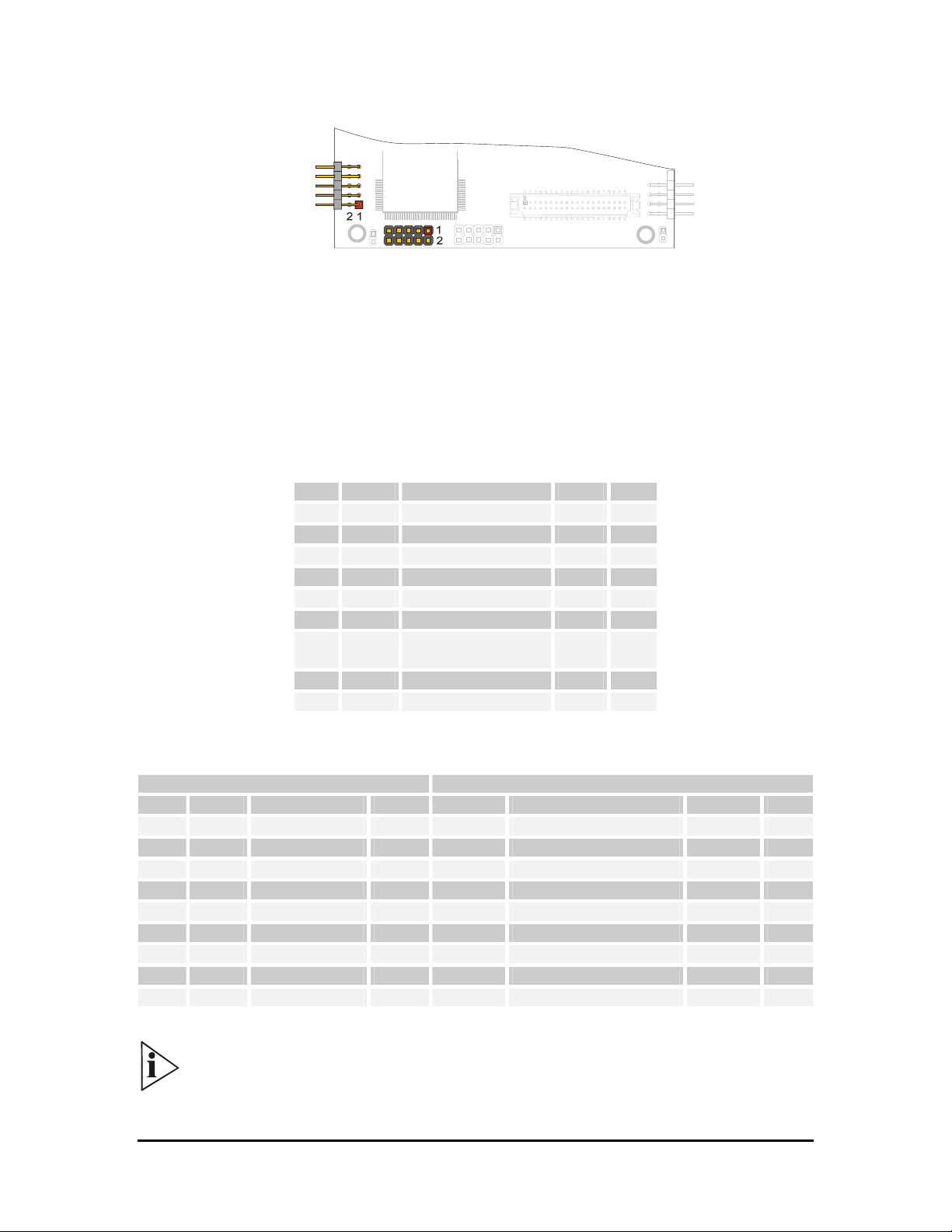
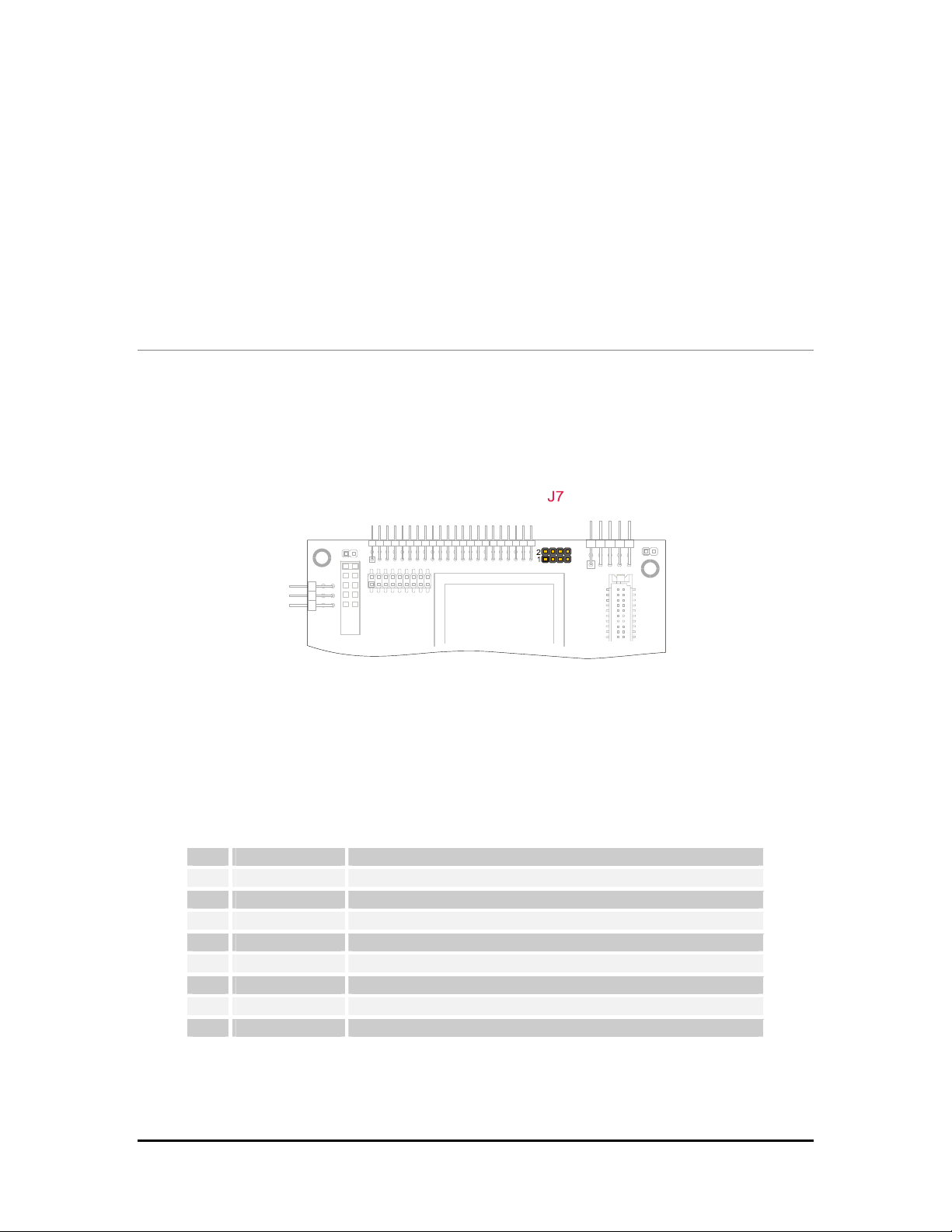
J7 for 2 x USB
J7 is a double row 4 x 2 pin with 2.00-mm step connector.
2 x USB
Figure 13. J7 Connector layout
Two USB ports are provided on the SpacePC 1232 module for the connection of USB devices.
Table 11. J7 2 x USB connector
Pin Signal Function
PE USB power enable
1
OC USB over current sense
2
USB1N USB port 1 differential line (minus line)
3
USB2N USB port 2 differential line (minus line)
4
USB1P USB port 1 differential line (plus line)
5
USB2P USB port 2 differential line (plus line)
6
GND Ground signal
7
GND Ground signal
8
All the timers have the same input clocks with a nominal frequency of 1MHz.
All the gate inputs are pulled high by a 4.7K resistor
26
Page 27
27
Note. USB devices shouldn’t be directly connected to the J4 connector. Parvus USB/Audio
CODEC Adapter can be used. In fact it provides for two USB standard connectors (but only
USB1 is useful for this CPU) and furthermore it provides for a better ESD (Electric Static
Discharge) and Over Current protection. Before using a different adapter please refer to
the Parvus Customer Support Service
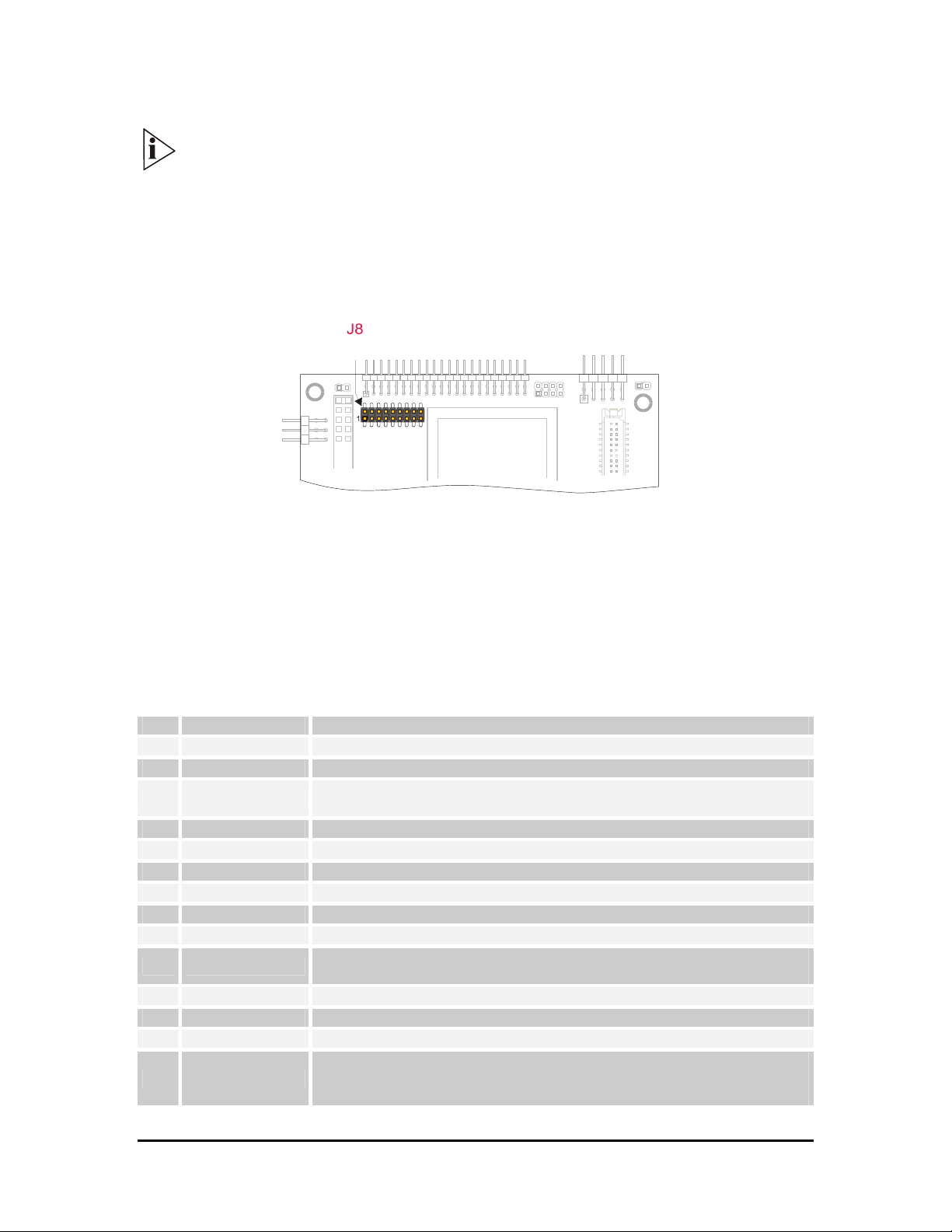
J8 for AC97 Audio port Section
J8 is a double row 9 x 2 pin with 2.00-mm step connector.
AC97 Audio
Figure 14. J8 Connector layout
The SpacePC 1232 module provides one AC97 (Specification Revision 1.3, 2.0, and 2.1) audio
interface adding audio capabilities to the PC/104 system. The Parvus Audio CODEC Adapter (but
also any AC97 CODEC which supports an independent input and output sample rate conversion
interface can be used) provides an AC97 and a CODEC for the SpacePC 1232 and should be
connected between the audio device and the J8 connector via a flat ribbon cable.
Table 12. J8 pinout connectors
Pin Signal Function
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
5V Power supply
5V Power supply
SDATA_OUT
This output transmit audio serial data to the codec
Serial DATA Out
GPIO0 General Purpose I/O
GND Ground Signal
GPIO1 General Purpose I/O
PC_BEEP Legacy PC/AT speaker output
GND Ground Signal
RESETDRV
BIT_CLK
The serial bit clock from the codec
Audio Bit Clock
GND Ground Signal
GND Ground Signal
GND Ground Signal
Serial Bus Synchronization
14
SYNC
This bit is asserted to synchronize the transfer of data between the
module and the AC97 codec
27
Page 28

15
16
17
18
SDATA_IN
This input receives audio serial data from the codec
GND Ground Signal
GND Ground Signal
NC Reserved
Serial DATA In
Note. Audio devices (i.e. Speaker, Microphone, MIDI device, …) cannot be directly
connected to the J8 connector. The Parvus Audio CODEC Adapter board can be
connected between them.
Parvus USB/AC97-AudioCODEC Adapter
Before using a USB and/or an Audio Device, the Parvus USB/AC97-AudioCODEC Adapter can
be connected to the CPU board. The connection between the Parvus adapter and the CPU b oard
is established by a cable set provided with the adapter.
A picture of the adapter is given in the next page.
AUX IN
SpkPhone IN/OUT
Video IN
CD IN
Mic IN
Line IN
Line OUT
SPK OUT
Figure 15. USB/AC97-AudioCODEC Adapter
The table below shows the adapter connectors description.
Table 13. USB/AC97-AudioCODEC Connectors
Connector# Function
USB 2
To Multif.
CPU Board
Connector
USB 1
28
Page 29

29
J1 USB1
J2 USB2
J3 Microphone IN
J4 Line IN
J5 Speaker OUT
J6 Line OUT
J7 CD IN
J8 Aux IN
J9 Video IN
J10
J11
This adapter is composed of 2 functional sections:
¾ USB section, with 2 USB ports which are EMI protected and filtered, and can also supply
power to the peripheral device connected (5V, 500mA);
¾ Audio section, which is equipped with the LM4549 National, an AC97 compliant I.C.
The AC97 architecture separates the analog and digital functions of the PC audio system
allowing both for system design flexibility and increased performance.
The LM4549 is an Audio CODEC for PC systems, which is fully PC98
compliant and performs the analog intensive functions of the AC97 Rev2.1 architecture.
Using 18-bit Sigma-Delta A/D’s and D/A’s, the LM4549 provides 90dB of Dynamic Range.
This board, in its Audio Section, is
provided with 4 stereo inputs, 1 microphone input, 1 stereo line input, 1 stereo earphone
output (200mW) and 1 speakerphone Input/Output that can be connected to a
telephone/modem set.
Speakerphone
IN/OUT
To CPU Board
Connector (J4)
J9 IDE Connector, JP10 IDE LED Connector
The SpacePC 1232 module provides an interface for one or two Integrated Device Electronics
(IDE) devices.
J9 IDE Connector
J9 is a 22x2 pin connector with 2.0 mm step.
29
Page 30

JP10
IDE Led
Figure 16. J9 and JP10 Connectors layout
To install the hard disk, perform the following operations:
¾ Hardware installation. Connect the hard disk to the module using a data cable, and then
connect the hard disk to the power supply respecting the device’s specifications. Make sure
that pin 1 of connector J9 and pin 1 of the drive or drives are correctly connected. Pin 1 of the
interface cable is usually indicated by a stripe along the edge of the cable. If two hard disks
need to be connected, they must be configured for common operation (i.e. master/slave or
cable select connection).
¾ IDE BIOS Setup. The hard disk parameters can be configured using the Setup program. If
the hard disk is connected to the module without setup configuration or with a wrong setup
configuration, a time-out for a few minutes occurs, then the boot is performed from the floppy
disk.
¾ Software initialization for specific operating systems. Refer to the OS documentation.
JP10 IDE LED Connector
The IDE HDD activity LED output is implemented on connector JP10.
This is a 2-pin connector with 2-mm pitch header.
To this connector is possible to connect a led that display the IDE activity.
Check the pin out and pin functions on the following table:
Table 14. JP10 IDE LED Connector
Pin Signal Function
1
2
30
Ground IDE LED anode (-)
IDELED (+) IDE LED cathode (+)
Page 31

31
J10 VGA Connector
The J10 is a 5x2 pin connector with step =2.54 mm.
J10
VGA
Figure 17. J10 Connector layout
Refer to the following table for the VGA connector assignment.
Table 15. J10 VGA Connector
Pin Signal Function
VSYNC Vertical synchronization
1
HSYNC Horizontal synchronization
2
DDC0 Display Data Channel - Data
3
RED Analog RED
4
DDC1 Display Data Channel - Clock
5
GREEN Analog GREEN
6
NC
7
BLUE Analog BLUE
8
GND Analog ground
9
GND Analog Ground
10
The following table shows the supported CRT-VGA Display Modes
Table 16. Table CRT Display Modes
1
1
Resolution Simultaneous
Colors
Refresh Rate
(Hz)
640x480 8bpp 256 colors 60, 72, 75, 85
640x480 16bpp 64K colors 60, 72, 75, 85
800x600 8bpp 256 colors 60, 72, 75, 85
800x600 16bpp 64K colors 60, 72, 75, 85
1024x768 8bpp 256 colors 60, 70, 75, 85
1024x768 16bpp 64K colors 60, 70, 75, 85
1280x1024 8bpp 256 colors 60, 75, 85
1.- This list is not meant to be a complete list of all the possible supported CRT display modes
31
Page 32

J11 Auxiliary Power Connector
One auxiliary connector is available on the SpacePC 1232 module. J11 is a 6x2 pin connector
with 2.54-mm step used to power the module in alternative to the PC/104 bus.
J11
Auxiliary
Power
Figure 18. J11 Connector layout
Check pinout and functions on the following table.
Table 17. J11 Auxiliary Power Connector
Pin Signal Description
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
GND Ground
VDD (+5VDC) +5VDC signal
N.C. Not connected
+12VDC +12VDC signal
N.C. Not connected
-12VDC -12VDC signal
GND Ground
VDD (+5VDC) +5VDC signal
N.C. Not connected
N.C. Not connected
+5VSB Always high (ATX only)
ATX ON ATX Power on signal
The number and position of the pins that have to be connected depends on the Power Supply
model. Refer to the following topics in order to perform the right connections.
AT Power Supply
¾
Connect pin 1 and pin 7 to the ground signal of the AT Power Supply Unit.
¾ Connect pin 2 and pin 8 to the +5VDC source on the AT Power Supply Unit.
¾ Connect pin 4 to the +12VDC and pin 6 to the –12VDC sources on the AT Power Supply Unit
only if requested by other boards connected to the PC/104 ISA bus (see the following note).
32
Page 33

33
ATX Power Supply
¾
Connect pin 1 and pin 7 to the ground signal of the ATX Power Supply Unit.
¾ Connect pin 2 and pin 8 to the +5VDC source on the ATX Power Supply Unit.
¾ Connect pin 4 to the +12VDC and pin 6 to the –12VDC sources on the ATX Power Supply
Unit only if requested by other boards connected to the PC/104 ISA bus (see the following
note).
¾ Connect pin 11 to the +5VSB source on the ATX Power Supply Unit. This signal is always
high, even if the power supply is turned off.
¾ Connect pin 12 to the ATX ON signal of the ATX Power Supply Unit. This signal is used to
power on the Power Supply itself.
Power button
If the soft power management is enabled, a low signal in this pin turns the system on or off.
Note. The +12VDC and -12VDC voltages are neither used nor generated by the
SpacePC 1232 module: they are only conveyed on the PC/104 bus (connector J1)
and can be used by other devices or modules that are stacked onto the CPU module.
WARNING! IMPROPER CONNECTION OF THE POWER SUPPLY WILL RESULT IN
SERIOUS DAMAGE FOR THE MODULE.
J13 Fan power supply connector
It is possible to connect a fan to this connector (3pin, 2.54-mm step) according to these electrical
requirements: 5V, 500mA max.
J13
- +
Figure 19. J13 Connector layout
The connector pin out is shown below.
33
Page 34

Table 18. J13 Pin out Connector
PIN SIGNAL
1
2
3
+VDD
N.C.
GND
J18 for Ethernet
The SpacePC 1232 module features a single-chip Fast Ethernet controller that provides 32-bit
performance, 10/100Mbps auto-sensing, and full compliance with IEEE 802.3u 100Base-T
specifications and IEEE 802.3x Full Duplex Flow Control.
Ethernet connector J18 is a 5x2 pin with 2.54-mm step. Refer to the following table for the
Ethernet connector assignment.
J18
Ethernet
Figure 20. J18 Connector layout
Table 19. J18 Ethernet Connector
Pin#
Signal Function
1 5V Power Supply
2 LED0 On sending packets
3 RX+ 100/10Base-T receive data
4 RX- 100/10Base-T receive data
5 LED1 Link 10/100
6 GND Ground signal
7 LED2 On receiving packets
8 GND Ground signal
9 TX+ 100/10Base-T transmit data
10 TX- 100/10Base-T transmit data
Note: To establish a connection to the Ethernet, the Parvus Ethernet Adapter can be
plugged between the board (to the J18 connector) and the net cable.
34
Page 35

35
It is shown below.
To CPU Board
Ethernet
RJ45 Connector
Connector
Figure 21. Parvus Ethernet Adapter
The green led is fixed, and signals the correct connection of the module.
The yellow led blinks when there is activity (data IN/OUT) on the net connection.
With RJ45 connectors, only twisted pair cables can be used.
Important Note. Connection to a 100BASE-TX hub for 100 Mbps operation requires Cat. 5
Unshielded Twisted-Pair (UTP) cable or Cat. 5 Shielded Twisted-Pair (STP) cable. The
maximum length between the 100BASE-TX hub and the adapter is 100 meters.
Connection to a 10BASE-T hub for 10 Mbps operation requires a Cat. 3, 4, 5 UTP cable or
Cat. 5 STP cable. Preferred maximum cable length between SpacePC 1232 module and
Ethernet adapter is 10 cm (4”)
The SpacePC 1232 module features a single-chip Fast Ethernet controller that provides 32-bit
performance, 10/100Mbps auto-sensing, PCI bus master capability, and full compliance with
IEEE 802.3u 100Base-T specifications and IEEE 802.3x Full Duplex Flow Control.
Net drivers
The available drivers are supplied in a CD-ROM coming with the SpacePC 1232 module. There
are several OSs supported by the RTL8139 Ethernet controller. Check the Parvus web site in
order to get the latest information on driver availability for your operating system.
35
Page 36

J19 LCD-TFT Section
LCD-TFT flat panels can be connected to J19 that is a double row 20 x 2 pin with 1.25-mm step
connector.
J19
Figure 22. J19 Connector layout
Table 20. J19 TFT Digital Interface connector pinout
Pin Number Function Pin Number Function
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
18
20
22
24
26
28
30
32
34
36
38
40
Reserved
GND
NC
GND
GREEN5 (MSB)
GREEN4
GREEN3
GREEN2
GND
GREEN1
GREEN0 (LSB)
BLUE5 (MSB)
BLUE4
GND
BLUE3
BLUE2
BLUE1
BLUE0 (LSB)
GND
Dot Clock
1
3
5
7
9
11
13
15
17
19
21
23
25
27
29
31
33
35
37
39
The following table shows the supported LCD-TFT video resolutio n s
GND
GND
VDD
VDD
FP_HSYNC
GND
FP_VSYNC
VDD
VDD
Data Enable
GND
RED5 (MSB)
RED4
RED3
VDD Enable
BackLight Enable
RED2
RED1
RED0 (LSB)
GND
Table 21. LCD-TFT video resolutions (*)
Resolution
640x480
36
Simultaneous
Colours
8bpp 256 colors 60
Refresh Rate
(Hz)
Page 37

37
640x480
16bpp 64K colors 60
800x600 8bpp 256 colors 60
800x600 16bpp 64K colors 60
1024x768 8bpp 256 colors 60
1024x768 16bpp 64K colors 60
(*)- This list is not meant to be a complete list of all the possible supported TFT video
Refer to Chapter 4 to get info about how to set the flat panels.
For further information about other/new LCD-TFT flat panels supported or how to connect a flat
panel to the CPU module, please refer to Application Note An-0031 available on the Parvus Web
site or contact Parvus’ Technical Customer Support at tsupport@parvus.com.
37
Page 38

38
Page 39

Chapter 4 The Setup Program
This chapter explains how to use and modify the setup options. These options allow configuring
properly the CPU board.
Note. The Setup Program can be improved to match the technical requirements.
39
Page 40

How to use the Setup program
To enter in the Setup Program, reboot or switch-on your module and then press the “F2” key.
After waiting a few seconds the main menu will appear.
The Main menu of the setup program shows a list of options that are available.
A highlight shows which option is currently selected.
Use the cursor arrow keys to move the highlight to other options.
When an option (i.e.:
General) is highlighted, it is possible to execute it by pressing the “Enter”
key.
A table of items will be displayed on the right side of the screen.
Now it is possible to select among several items (i.e.:
arrow keys and the “
Enter” key.
When an item is highlighted, it is possible to change its value by pressing the “
PageDown” keys.
“
Time and Date items are set using the keys “PageUp” and “PageDown” and the keys from “0” to
“
9”; press “Enter” to confirm. To correct errors press the “BackSpace” key.
Time, Date, Floppy Disk 1,… ) using the
PageUp” and
40
Page 41

41
Press the “
ESC” key to return to the items of the Main menu.
Select “
Quit” to exit from the Setup program.
The follow screen will be displayed:
Select with the “
the EEPROM. Select
ENTER” key the first option Save data to EEPROM to store the parameters into
Discard changes to leave unaltered the previous stored parameters.
The Setup pages
The Setup Program is composed of several pages. They are listed below:
¾ General
¾ Devices
¾ Communications
¾ ATAPI Units
¾ Error Handling
¾ Power Management
41
Page 42

General Page
NOTE: The pictures below show the default configuration of the CPU Setup
Program. In case of bad/wrong setup configurations, returning to this one assure
the correct working.
(*) An asterisk in the following tables indicates the default configuration.
This page contain, as shown below, the setting for the following devices:
Time
Date (for the Real Time Clock)
Floppy Disk 1..4
Expansion Socket
DiskOnChip Map
Keyboard
Quick Boot
Boot Try Sequence
DRAM memory Speed
Time
The time is displayed in standard format: hh mm ss (hours - minutes - seconds); all the three
fields contain numerical values only.
42
Page 43

43
Date
The date is displayed in standard format: MMM DD YYYY (month - day - year); all the three fields
contain numerical values only.
Floppy disks 1..4
Each system incorporates a controller capable of driving up to four floppy disks, according to the
hardware mounted on-board. The floppy disks are numbered starting from
maps these drivers starting form the letter “A”
.
Note: during the floppy disk assignment it is a good practice filling the devices consecutively,
without any “hole” from one device to another.
Note: when the boot sequence starts from floppy disk number one (DOS letter “A”), any device
selected as
floppy disk 1 can be a bootable disk. Obviously this device must represent a real
bootable disk, with a proper boot sector and containing a valid O.S.
Note: In the SpacePC 1232 only one external FDD can be connected.
All the
floppy disks can be configured with the same options:
Option Description Note
None
360 KB
1.2 MB
720 KB
1.44 MB
Integrated SSD
The following one is the default configuration (as shown in the previous picture):
Floppy Disk 1: Integrated SSD
Floppy Disk 2: None
Floppy Disk 3: None
Floppy Disk 4: None
Note: with the previous default configuration, the Integrated SSD (that is a READ ONLY
MEMORY) is seen with the DOS letter “A”, and the system bootstraps from it. If you want
to use also a real Floppy Disk, you must set it as Floppy Disk 2. It will be seen with the
DOS letter “B”.
No floppy disk selected
Floppy disk 5 ¼ - size 360 Kbytes
Floppy disk 5 ¼ - size 1.2 Mbytes
Floppy disk 3 ½ - size 720 Kbytes
Floppy disk 3 ½ - size 1.44 Mbytes Common used size
On-board Flash EEPROM Always available on all boards
Note: the floppy controller use the same connector used by the parallel port. In this case when
the floppy controller is enabled, the parallel port is automatically disabled, even if it was already
enabled in the Setup. The parallel port can be used again after disabling the floppy disk
controller.
one and the BIOS
Expansion Socket
The Expansion Socket is available to mount different type of solid-state memory devices. If you
want to use a PEROM or a SRAM, you must also configure a “Floppy Disk 1..4” as Expansion
Socket. Anyway a Disk On Chip (DOC) is always seen as a hard disk, and it doesn’t need a
further setting in the “Floppy Disk 1..4” section. If the assigned floppy is
sequence
is FD1/HD1, the system starts bootstrapping from the memory mounted on the
expansion socket.
43
FD1 and the boot try
Page 44

T
Option Description Note
Disabled (*)
Disk On Chip
PEROM 512 KB
SRAM 512 KB
No device selected
Solid-state memory device - size: 2 ... 144 MB
Programmable and Erasable ROM -size 512 KB
Static RAM - size 512 KB
(*) = Default setting
DiskOnChip Map
This option allows to chose the starting address of Disk On Chip (DOC) memory window
Option Description Note
0CC000h
0D0000h
0D4000h
0D8000h
0DC000h
0E0000h
0E4000h
0E8000h (*)
The starting address is 0CC000h
The starting address is 0D0000h
The starting address is 0D4000h
The starting address is 0D8000h
The starting address is 0DC000h
The starting address is 0E0000h
The starting address is 0E4000h
The starting address is 0E8000h
(*) = Default setting
IMPORTANT NOTE: With Win N
Keyboard
If the keyboard is not really necessary in the system, you can disable it. In this way the system
can bootstrap ignoring the keyboard.
Option Description Note
Not Present (*)
Present
Keyboard presence ignored Useful for embedded systems
(*) = Default setting
BIOS look for keyboard
Quick Boot
With quick boot enabled, the system takes less than 5 seconds for a bootstrapping. This
improvement is obtained to the disadvantage of BIOS tests (the setup must be correct and the
peripheral must be connected to the module and ready at the boot); in particular the following test
are skipped:
system memory pattern test
keyboard detection
floppy disk presence (seek test)
44
Page 45

45
RTC time test
Option Description Note
Disabled (*)
Enabled
Normal BIOS test are used
Reduce set of BIOS test are used
(*) = Default setting
Boot Try Sequence
The Boot Try Sequence allows exchanging the boot disk order among Floppy Disk 1 and Hard
Disk 1.
Option Description Note
FD1 / HD1 (*)
HD1 / FD1
Bootstrap starts from the FD1 then try with HD1
Bootstrap starts from the HD1 then try with FD1
(*) = Default setting
DRAM Memory Speed
The working speed of the DRAM memory can set as follows:
Option Description Note
Low (*)
High
Low speed whit minimal power consumption
High speed for maximum performance
(*) = Default setting
Devices Page
This page controls all the on-board system-devices; in particular:
Floppy Disk Controller
EIDE Ports
Video memory
Network Adapter
PS/2 Mouse
USB
Audio
MPU-401
45
Page 46

Floppy Controller
This option enables or disables the on-board floppy disk controller. For example, if an external
floppy disk controller needs to be used, the internal one must be disabled.
Option Description Note
Disabled (*)
Enabled
• Note: The floppy controller use the same connector used by the parallel port. In this case
when the floppy controller is enabled, the parallel port is automatically disabled, even if was
already enabled in the Setup. The parallel port can be used again after disabling the floppy
disk controller.
Disable the on-board floppy disk controller An external controller can be used
(*) = Default setting
Enable the on-board floppy disk controller
EIDE Port
This option enables or disables the on-board EIDE hard disk controller. For example, if an
external hard disk controller needs to be used, the internal one must be disabled.
Option Description Note
Disabled
Disable the on-board hard disk
An external controller can be used
controller
Enabled (*)
Enable the on-board hard disk
(*) = Default setting
controller
Video Memory
The video memory size can be adjusted according the user necessities: more space is reserved
for video, less space is available for the applicative programs and vice versa.
Option Description Note
46
Page 47

47
1 MB
2 MB
4 MB (*)
1 Megabyte reserved for Video Memory
2 Megabyte reserved for Video Memory
4 Megabyte reserved for Video Memory
(*) = Default setting
Network Adapter
The user can manually enables or disables the on-board network adapter.
Option Description Note
Disabled
Enabled (*)
• Note: if an external network controller is connected o n the ISA bus, be sure don’t use the
same address space or IRQ, to avoid possible conflicts.
Option Description Note
9 (*)
10
11
12
Disable the on-board network controller
Enable the on-board network controller
IRQ 9 for ISA network controller
IRQ 10 for ISA network controller
IRQ 11 for ISA network controller
IRQ 12 for ISA network controller
(*) = Default setting
(*) = Default setting
PS/2 Mouse
If not used, the PS/2 mouse can be disabled. In this way the interrupt IRQ 12, normally reserved
for mouse, is free for PCI bus or other devices.
• Note: the interrupt reserved for mouse is fixed (IRQ 12); it is displayed for information only.
Option Description Note
Disabled
Enabled (*)
Disable the on-board mouse controller
Enable the on-board mouse controller
(*) = Default setting
USB
This option allows enabling and disabling the USB Port.
Option Description Note
Disabled
Enabled (*)
Disable the on-board USB interface
Enable the on-board USB interface
(*) = Default setting
Audio
This option allows enabling and disabling the Audio emulator.
Option Description Note
Disabled (*)
0220h
0240h
0260h
Disable the Audio emulator
Audio emulator address selected at 220h
Audio emulator address selected at 240h
Audio emulator address selected at 260h
(*) = Default setting
47
Page 48

0280h
Audio IRQ number
Option Description Note
None (*)
5
7
10
8 bit DMA channel
Option Description Note
None (*)
0
1
3
16 bit DMA channel
Option Description Note
None (*)
5
6
7
Audio emulator address selected at 280h
No IRQ selected
IRQ 5 selected
IRQ 7 selected
IRQ 10 selected
No DMA channel selected
DMA 0 selected
DMA 1 selected
DMA 3 selected
No DMA channel selected
DMA 5 selected
DMA 6 selected
DMA 7 selected
(*) = Default setting
(*) = Default setting
(*) = Default setting
MPU-401
This option allows enabling and disabling the MIDI emulator.
Option Description Note
Disabled (*)
0300h
0330h
Enable the MIDI emulator
MIDI emulator address selected at 300h
MIDI emulator address selected at 330h
Communications Page
This page concerns all the on-board communication interfaces:
Serial Port1
Serial Port2
Parallel Port
(*) = Default setting
48
Page 49

49
Serial Ports 1 and 2
The number of serial ports is two. The Serial Port Mode is selectable (RS232, RS 422 and RS
485), like the IRQ number.
Serial Port1 (J5)
The user according the device connected to the interface can choose The Serial Port1 Mode. The
default mode is
Serial Port1 Modes
RS 232
RS 422 (*)
RS 485
Serial Port1 Addresses
Disabled
3F8h (*)
2F8h
3E8h
2E8h
Serial Port1 IRQ
None
3
4 (*)
5
7
9
10
11
12
RS232.
Option Description Note
RS 232 Mode selected “Standard” serial mode
RS 422 Mode selected
(*) = Default setting
RS 485 Mode selected
Option Description Note
Disable the serial port
Serial Port address selected at 3F8h
(*) = Default setting
Serial Port address selected at 2F8h
Serial Port address selected at 3E8h
Serial Port address selected at 3E8h
Option Description Note
No IRQ selected
IRQ 3 selected
IRQ 4 selected
(*) = Default setting
IRQ 5 selected
IRQ 7 selected
IRQ 9 selected
IRQ 10 selected
IRQ 11 selected
See Note(!) below
IRQ 12 selected
49
Page 50

• Note(!): IRQ 11 can’t be used by peripherals connected to the ISA BUS if the printed
circuit board code ends with the letter “S” (PC100112S). If the printed circuit board
code ends with the letter “A” (PC100112S), there aren’t any problems.
• Note: not all consecutive IRQ numbers from 3 to 15 can be used; to help the selection, the
Setup program displays legal IRQ numbers only.
• Note: if the IRQ is shared, all the ports using the same share number can use the same IRQ
number.
Serial Port2 (J6)
The Serial Port2 Mode is fixed: RS232
Serial Port2 Addresses
Option Description Note
Disabled
3F8h
2F8h (*)
3E8h
2E8h
Disable the serial port
Serial Port address selected at 3F8h
Serial Port address selected at 2F8h
Serial Port address selected at 3E8h
Serial Port address selected at 3E8h
(*) = Default setting
Serial Port2 IRQ
Option Description Note
None
3 (*)
4
5
7
9
10
11
12
No IRQ selected
IRQ 3 selected
IRQ 4 selected
IRQ 5 selected
IRQ 7 selected
IRQ 9 selected
IRQ 10 selected
IRQ 11 selected
IRQ 12 selected
(*) = Default setting
See Note(!) below
• Note(!): IRQ 11 can’t be used by peripherals connected to the ISA BUS if the printed
circuit board code ends with the letter “S” (PC100112S). If the printed circuit board
code ends with the letter “A” (PC100112A), there aren’t any problems.
Parallel Port
Parallel Port Address
Option Description Note
Disabled
0378h (*)
0278h
Parallel Port IRQ number
Option Description Note
50
Disable the serial port
Parallel Port address selected at 378h
Parallel Port address selected at 278h
(*) = Default setting
Page 51

51
None
3
4
5
7 (*)
No IRQ selected
IRQ 3 selected
IRQ 4 selected
IRQ 5 selected
IRQ 7 selected
(*) = Default setting
• Note: not all consecutive IRQ numbers from 3 to 15 can be used; to help the selection, the
Setup program displays legal IRQ numbers only.
Parallel DMA Channel
Option Description Note
None (*)
0
1
3
No DMA selected for the Parallel Port
DMA Channel 0 selected
DMA Channel 1 selected
DMA Channel 3 selected
(*) = Default setting
Parallel Port Mode
The user according the parallel device connected to the interface can choose The Parallel Port
Mode
. The default mode is Bidirectional.
Option Description Note
Printer (*)
Bidirectional
EPP-1.9 and SPP
EPP-1.7 and SPP
ECP
ECP and EPP-1.9
ECP and EPP-1.7
Standard mono-directional printer interface
Bidirectional printer interface
EPP and SPP mode
EPP and SPP mode
ECP mode
ECP and EPP mode
ECP and EPP mode
(*) = Default setting
ATAPI Units Page
This option concerns about mass storage devices using a standard
The CPU board has two EIDE controllers, so the
ATAPI Units can be separated in two parts:
ATAPI Primary and ATAPI Secondary. In any case the options are the same.
• Note: ATAPI (or EIDE) devices can be both hard disks and CD_ROM devices or, sometimes,
storage
tape-units.
• Note: each EIDE interface supports two peripherals, called master unit and slave unit.
Remember to select as
master unit a bootable disk (containing any valid O.S.).
51
EIDE interface.
Page 52

ATAPI unit type
Option Description Note
None (*)
No unit selected Default setting for both
ATAPI Units (Master1 &
Slave1)
(*) = Default setting
Auto
LBA
CHS
CD-ROM
Other
Unit auto-detection
LBA unit selected
CHS unit selected
CD-ROM unit selected
Other unit selected
• Note: when the Auto feature is selected, the BIOS ignores any other data (like Mode, Cyls,
Head, etc.). Use this option for the most of hard disks or other ATAPI devices.
• Note: LBA and CHS are two different types of ATAPI units addressing mode. The first one is
normally used with modern hard disk, from 512 Kbytes to above 8 Gbytes. For both modes
you have to know the
So, for an easy use of any kind of disk, the
physical hard-disk structure in terms of Cylinders, Heads and Sectors.
Auto option is preferable.
•
Note: to speed-up the bootstrap select the option None for unu sed ATAPI devices.
PIO Mode
PIO is a special data-transfer system between two or more EIDE devices, where all the data pass
through the processor. There are five transfer rates, called
PIO mode n (with n=0..4). If the Auto
(autodetect) option is disabled, the PIO mode must be specified.
Option Description Note
PIO-0
PIO-1
PIO-2
PIO-3
PIO-4 (*)
Transfer Rate of 3.3 MBps
Transfer Rate of 5.2 MBps
Transfer Rate of 8.3 MBps
Transfer Rate of 11.1 MBps
Transfer Rate of 16.6 MBps Default setting for both
ATAPI Units (Master1 &
Slave1)
(*) = Default setting
52
Page 53

53
Translation Mode
Modern hard-disks have more cylinders than maximum number of cylinders permitted by DOS,
so, theoretically, a DOS machine couldn’t use a modern big-sized hard disk. This problem is
solved using a special addressing mechanism. This “mechanism” is called
common translation methods are
LBA (Logical Block Addressing) and ECHS (Enhanced
translation. The most
Cylinders - Heads - Sectors).
Option Description Note
LBA (*)
LBA translation Default setting for both
ATAPI Units (Master1 &
Slave1)
(*) = Default setting
ECHS
Extended CHS translation
Cylinders
Number of hard-disk cylinders (normally written on the disk label). If the autodetection is used
(suggested method!), the cylinders value is ignored by the BIOS.
Option Description Note
0..65536
Number of cylinders 0 is the default setting for
both ATAPI Units (Master1
& Slave1)
Heads
Number of hard-disk heads (normally written on the disk label). If the autodetection is used
(suggested method!), the heads value is ignored by the BIOS.
Option Description Note
0..64
Number of heads 0 is the default setting for
both ATAPI Units (Master1
& Slave1)
Sect/Tr
Number of sectors per track (normally written on the disk label). If the autod etection is used, the
sectors value is ignored by the BIOS.
Option Description Note
0..255
Number of sectors per track 0 is the default setting for
both ATAPI Units (Master1
& Slave1)
Size (MB)
This is the hard-disk size, in Mbytes, calculated by the BIOS, using either the autodetect method
or the user hand-written values (for cylinders, heads and sectors).
• Note: the size cannot be changed directly by the user.
53
Page 54

Detect Now
Using the Detect Now option, the user can start manually the hard-disk autodetect procedure and
see immediately the result, as well as the size (in Mbytes), in terms of cylinders, head s and
sectors numbers.
Error Handling Page
Generally, in a normal desktop BIOS, when an error is encountered by the POST sequence, the
bootstrap stops and waits for a reboot. For example a simple keyboard ab sence represents an
irrecoverable error. This can be a serious problem in embedded systems. Using the
Handling page, the user can decide to ignore one or more of errors that could be encounte re d
during the boot.
Error
Error on Keyboard
The user can decide for himself if a keyboard error must stop the boot process or not.
Option Description Note
Ignore
Prompt User (*)
The keyboard error is ignored
When a keyboard error occurs, the system stops and waits for the
user
Error on Video
The user can decide for himself if a video error must stop the boot process or not.
Option Description Note
Ignore
Prompt User (*)
The video error is ignored
When a video error occurs, the system stops and waits for the user
Error on Floppy Disks
The user can decide for himself if a
floppy disks error must stop the boot process or not.
(*) = Default
setting
(*) = Default
setting
54
Page 55

55
Option Description Note
Ignore
Prompt User (*)
The floppy disks error is ignored
When a floppy disks error occurs, the system stops and waits for
the user
(*) = Default
setting
Error on Fixed Disks
The user can decide for himself if a floppy disks error must stop the boot process or not.
Option Description Note
Ignore
Prompt User (*)
The fixed disks error is ignored
When a fixed disks error occurs, the system stops and waits for the
user
(*) = Default
setting
Error on Real Time Clock
The user can decide for himself if a Real Time Clock (RTC) error must stop the boot process or
not.
Option Description Note
Ignore
Prompt User (*)
The RTC error is ignored
When a RTC error occurs, the system stops and waits for the user
(*) = Default
setting
Power Management
Not available at this moment.
This function is
DISABLED
55
Page 56

56
Page 57

Chapter 5 How to update the BIOS. The SSD
This chapter explains how to use the BTOOL Program and gives information about the Integrated
Solid State Disk.
Warning: The BTOOL Program can be different for each CPU and each BIOS version.
For the last versions visit the site: www.parvus.com.
57
Page 58

How to update the BIOS: the BTOOL Program
The BTOOL program is a utility used to program the BIOS (that is stored in the Flash EPROM) in
the following cases:
¾ BIOS upgrade;
¾ Installation of a MiniDOS compatible program into the Flash (Integrated SSD);
¾ Installation of a BIOS Extension into the Flash.
PLEASE NOTE:
BTOOL program must be run under MS-DOS environment, not DOS WINDOW, (so, if it
is necessary, create a bootable floppy disk, with the command FORMAT/S. The diskette
must be formatted as a 1.44 MB disk.).
Power supply must be assured during all the program execution.
Please run AUTOEXEC.BAT and CONFIG.SYS without any parameters!
Please don’t run any memory manager. If HIMEM.SYS or EMM386 are running, the
BTOOL program doesn’t work!
It will be useful if the BTOOL program is stored in a Floppy Disk (for example in the bootable disk)
The program must be run using the
The on line help, with the available options will be displayed, as follow:
BTOOL (or BTOOL.EXE) command line at the DOS prompt.
58
Page 59

59
OPTIONS EXPLANATION
BTOOL /S This option runs the Setup program without the necessity of rebooting
the system and then pressing “F2”
BTOO L/L This option locks the setup. In this way the access to the Setup
Program is denied.
BTOOL /U This option unlocks the setup. In this way the access to the Setup
Program is re-established.
BTOOL /G FILENAME (*) This option gets the Setup Data from the system and save it in a file
with the name “FILENAME.BIN”.
BTOOL /P FILENAME (*) This option reads the Setup Data from the file named
“FILENAME.BIN” and put it in the system
BTOOL /B FILENAME (*) This option updates the entire BIOS firmware with the version stored
in the file named “FILENAME.BIN”; for example BIOS.BIN, stored on
a floppy.
BTOOL /V FILENAME (*) This option updates only the video BIOS firmware with the new
version stored in the file named “FILENAME.BIN”
BTOOL /U FILENAME (*) This option updates the Emergency BIOS Firmware with the new
version stored in the file: “FILENAME.BIN” (this option is not used in
the SpacePC 1232)
BTOOL /DA This option creates the image of the Floppy “A:” in the Integrated SSD
BTOOL /DB This option creates the image of the Floppy “B:” in the Integrated SSD
(*): all these files are in binary (.BIN) format
The BTOOL program always ends with a module’s hardware reset (pressing
CTRL+ALT+DEL is not enough). It is necessary to switch off and then switch on the
CPU in order that the changes take effect.
EXAMPLE: Update the BIOS
For the BIOS files and for upgrades, visit www.parvus.com. It is very useful to store
the new BIOS version in a floppy disk.
¾
Before proceeding, you have to be running DOS (or ROM-DOS) environment without any
memory manager
¾ Type the following command at the DOS prompt and press “ENTER”:
A:\>BTOOL /B BIOS.BIN (*) (*) The file name can be different according to technical
needs.
59
Page 60

¾ The program will store the new BIOS version.
¾ Follow all the instructions the BTOOL gives you
¾ BTOOL will inform you about the results of the operation,
¾ Power off and then power on the CPU module.
The Integrated Solid State Disk
A portion of the Flash EPROM can be used as an Integrated SSD. This Integrated SSD is like a
write-protected floppy disk for storing files.
In the SpacePC 1232, the portion is 768 KB, and before enabling it needs to be written-to using
the
BTOOL program.
Then it is possible to copy data from a real floppy disk.
EXAMPLE: Create an image of a floppy disk into the Integrated SSD
¾ The internal Solid State Disk can be either enabled or disabled in the Setup (Floppy Disk
1..4).
¾ Before proceeding, you have to format a new floppy disk, with the command FORMAT/U (or
FORMAT/S if you want to create a bootable floppy).
¾ Create the “image disk” copying into the diskette all the files and the directories you need.
During this copying process
create empty sectors that will be mirror-like stored into the SSD, wasting space.
don’t delete any file/data on the floppy, because this will
Restart over again with the format procedure if you have any troubles or mistakes occur.
Data stored on floppy mustn’t go above 640 KB (which is the effective Flash size
dedicated to be used as Solid State Disk).
¾ Type the following command at the DOS prompt:
A:\>BTOOL /D A (BTOOL /D B)
¾
The program will ask you to insert the “image disk” in drive A (or B).
¾ Follow all the instructions the BTOOL gives you: the program will proceed by erasing the
Flash device blocks and then wr iting and verifying them with the data present on the “image
disk”.
¾ BTOOL will inform you about the results of the operation. If everything is ok and if you have
already enabled the SSD please reset the system with CTRL+ALT+DEL. If you haven’t
enabled the SSD before, you can use the Setup Program to enable the Solid State Disk; quit
the Setup Program saving data to EEPROM (in this case, rebooting the system with
CTRL+ALT+DEL is not necessary).
60
Page 61

Chapter 6 Virtual Peripherals
This chapter describes how to control the SpacePC 1232 module directly from a Laptop or a
standard PC compatible computer:
Use this mode when the PC/104 system doesn’t have I/O devices connected to it.
The “Virtual Peripherals” mode
The SpacePC 1232 module is designed to be used in industrial environments as a stand-alone
module, independent from specific peripherals. Nevertheless, it might become necessary, for
operation or maintenance, to interface the module with I/O devices: keyboard, monitor, and floppy
disk.
The SpacePC 1232 module can operate in a specific modality, called “Virtual Peripheral” mode.
Thanks to this modality the CPU can use the peripherals of another PC compatible computer
(called Host computer), which are not directly connected to the module’s PC/104 bus.
To enable this modality, the SpacePC 1232 module must be connected to the Host computer
through a serial port or a parallel port, and the VP program must run on the Host computer. In
“Virtual Peripheral” mode, the operator runs with the SpacePC 1232 module using the I/O devices
of the PC or AT compatible computer. The PC’s I/O are redirected on a serial (or parallel) line.
61
Page 62

Local and redirected peripherals
In “Virtual Peripherals” mode, two types of peripherals are used:
¾ The peripheral directly connected to the module (keyboard, video interface, SSD and floppy)
named “local peripherals”
¾ The Host computer’s peripherals used for the remote control of the module (keyboard, video
interface and Floppy) named “remote or redirected peripheral”.
You can select which remote peripherals are redirected in your VP connection: all the Host
computer’s peripherals or only some of them.
“Virtual Peripherals” connection
To perform the “Virtual Peripheral” connection, you need the following items:
¾ The CPU module with power supply and one free serial/parallel port;
¾ The Utility Disk (CD-ROM) provided with the SpacePC 1232 module;
¾ A PC or AT compatible computer (the Host computer) with a serial port working at 115Kbaud,
or a parallel bi-directional port and
Win95/98/2000!);
¾ A VP cable (parallel or serial cable). Parvus doesn’t supply any VP cable. You must make
it according to the tables on the following pages. If you are using a serial cable, you must
make a VP adjustment (as described in the following figure) in it.
provided between the RTS and CTS (or DTR and RI) signals on the end facing the
Multifunction cable;
The Virtual Peripherals connection can be performed as follows:
¾ Connect the Host computer to the SpacePC 1232 module through the parallel port or
through the serial port using the multifunction cable and the VP cable. Turn on the Host
computer
¾ Run the VP2000.EXE program on the Host computer
¾ Turn on the CPU
the possibility to boot in ROM-DOS OS (Not in NT or
A short circuit must be
62
Page 63

63
CPU HOST COMPUTER
Short ( ) for using VP mode with SERIAL1
RTS1 CTS1
Short ( ) for using VP mode with SERIAL2
VP mode with Parallel DOESN’T NEED ANY SHORTs
with or with
RTS2 CTS2
with or with
DTR1 RI1
DTR2 RI2
PARALLEL PORT
SERIAL PORT 1
SERIAL PORT 2
VP adjustment
(this end only)
RTS
CTS
or
DTR
RI
= short circuit
Parallel VP cable (*)
Serial VP cable (*)
(*) This VP cables must be made observing the
connections explained in the following tables
Figure 23. Completing the VP connection
Table 22. Serial1 and 2 VP cable connection s
PC/104 serial interface HOST PC serial interface
J5 SERIAL1
PIN Nr.
DB25
PIN Nr.
DB9
PIN Nr.
Signal Function Signal
DB25
PIN Nr.
3 3 2 RX Receive Data TX 2 3
5 2 3 TX Transmit data RX 3 2
9, 10 7 5 GND Signal Ground GND 7 5
For VP mode connect RTS1 with CTS1, or DTR1 with RI1.
Pins not included in the table above are not connected
DB9
PIN Nr.
Table 23. Parallel VP cable connections
From PC/104
Parallel connector
J5 PARALLEL
PIN Nr.
DB25
PIN Nr.
VP2000 Cable
Signal Signal
DB25
PIN Nr.
To Host
Computer
Parallel
port
1 1 STB#* ACK#* 10
2 14 AFD# BSY 11
3,5,7,9,11,13,15,17 2..9 PD#* PD#* 2..9
6 16 INIT#* PE 12
8 17 SLIN#* SLCT 13
19 10 ACK#* STB#* 1
21 11 BSY AFD# 14
23 12 PE INIT#* 16
25 13 SLCT SLIN#* 17
63
Page 64

10,12,14,16,
18,20,22,24
18..25 GND GND 18..25
(*) The “#” stands for: signal active low
Pins not included in the table above are not connected
IMPORTANT NOTE: The VP2000 functionality performed via the parallel cable may
not work with some host computers.
It is important to set the host computer parallel port to "bi-directional".
Start the
tech support area) on the
VP2000.EXE program (you will find it in the CPU utility CD-ROM or in www.parvus.com
Host computer. Select the following options based on the Host
computer serial or parallel port used.
EXAMPLE: A:\VP2000 /COM=1 /A
A:\VP2000 [/COM=n] [/V] [/K] [/D [/C] [/A]
/COM=1 - Use Serial Port at 3F8H (IRQ=4)
/COM=2 - Use Serial Port at 2F8H (IRQ=3)
/COM=3 - Use Serial Port at 3E8H (IRQ=4)
/COM=4 - Use Serial Port at 2E8H (IRQ=3)
/LPT=1 - Use Parallel Port at 378h
/LPT=2 - Use Parallel Port at 278h
7LPT=3 - Use Parallel Port at 3BCh
The COM ports listed above, refer to the serial port on the Host
computer.
/V - Redirect Video
/K - Redirect Keyboard
/D - Redirect Diskette A:
/C - Redirect Console (Video + Keyboard)
/A - Redirect All (Video + Keyboard + Diskette A:)
At the end of this procedure this message will appear:
Connection on serial port at 3F8H. (=COM1)
Use PrintScreen KEY to EXIT VP2000…
Now turn on the SpacePC 1232 module.
If you select the [/A] parameter, the VP connection will be performed according to the following
rules:
¾ All the remote peripherals are redirected in VP connection.
¾ The local keyboard, video interface and floppy disk are disabled.
¾ The Boot is performed from the remote floppy.
64
Page 65

65
If you select the [/V] [/K] [/D] [/C] parameters, the VP connection will be performed according to
the following rules:
¾ Only the selected remote peripherals are redirected in VP connection.
¾ The local peripherals connected are used according to the setup.
¾ If the floppy disks are redirected, it is not possible to use the local Host computer floppy for
PC operations.
¾ The Boot is performed from the selected peripheral.
From now on, the host computer's peripherals selected are at the disposal of the SpacePC 1232
module. It is now possible to boot from the host computer's floppy disk/CD-ROM, or to debug a
program and edit files using the host computer's peripherals.
Pressing the “printscreen” key will terminate the VP2000 program returning the CPU
module to DOS.
To re-connect the SpacePC 1232 module to the host computer, run the VP2000.EXE program
again.
This message will appear:
Connection on serial port at 3F8H. (=COM1)
Use PrintScreen KEY to EXIT VP2000…
Important note
¾ While the VP2000 program is running, the CTRL+ALT+DEL key combination on the host
computer causes the restart in the host computer and
¾
The Virtual Peripheral mode doesn’t support the “Format” command.
¾ Virtual peripheral handles the BIOS services of the redirected devices. It is therefore
not possible to use programs performing direct accesses to video memory, keyboard,
floppy disk or hard disk.
NOT in the SpacePC 1232 module!
65
Page 66

Chapter 7 Watchdog Timer
This chapter describes the configuration of the Watchdog Timer with some examples.
The watch dog is a part of the on–board SUPER I/O device SMSC FDC 37B782
The Super I/0 watchdog allows managing time-outs in order to seconds or minutes (depending on
the Super I/O programming).
66
Page 67

67
Watchdog modalities
The watchdog function resets the board at the end of the countdown.
There are two ways to program the watchdog:
• Using BIOS INT 52h
Using direct Super I/O registers programming
•
BIOS INT 52h - functions 0Ch, 0Dh, 0Eh
This method can be used under DOS or under Operating Systems using the board BIOS (i.e. not
under Linux which erases the BIOS after the boot and autonomously manage the module
hardware).
The functions implemented from the BIOS are:
INT 52h, function 0Ch: watchdog enabling with a fixed time of 2 seconds. This function programs
and starts immediately the watchdog counter.
INT 52h, function 0Dh: watchdog erasing. Counting is interrupted and watchdog disabled.
INT 52h, function 0Eh: watchdog refresh. Every call to this function restarts the counting from the
initial value.
When the watchdog is activated, the countdown starts immediately. If no refresh occurs, when
the default timeout expires, the board reset is executed. So the watchdog must be enabled and
continuously refreshed, avoiding in this way the board reset.
Example:
...
MOV AH, 0Ch
INT 52h ; Enable the watchdog (fixed timeout = 2 seconds)
...
Super I/O registers programming
This method must be used when the OS doesn’t manage the BIOS (i.e. Linux) or when a
personalized watchdog programming is required.
The following example shows how to change the Super I/O (SPIO)
registers:
; SPIO: enter in configuration mode ...
MOV DX, 03F0h ; SPIO Index Port
67
FDC 37B782 watchdog
Page 68

MOV AL, 55h ; SPIO Configuration Mode Enable Key
OUT DX, AL ; Enter in configuration mode
; Select Logical Device 8 (watch dog) ...
MOV DX, 3F0h ; SPIO Index Port
MOV AL, 07h ; Logical Device selector is the register 7
OUT DX, AL ; Point to Logical Device selector
INC DX ; SPIO Data Port
MOV AL, 08h ; Logical Device number 8
OUT DX, AL ; Select the Logical Device 8
; Select the time base (seconds or minutes) ...
MOV DX, 3F0h ; SPIO Index Port
MOV AL, F1h ; Watchdog timer units register (WDT_UNITS)
OUT DX, AL ; Point to register WDT_UNITS
INC DX ; SPIO Data Port
IN AL, DX ; Read WDT_UNITS
OR AL, 01h ; Mask reserved bits and set time in seconds
; AND AL, FEh ; Mask reserved bits and set time in minutes
MOV BL, AL ; Save new WDT_UNITS value
MOV DX, 3F0h ; SPIO Index Port
MOV AL, F1h ; Watchdog timer units register (WDT_UNITS)
OUT DX, AL ; Point to register WDT_UNITS
INC DX ; SPIO Data Port
MOV AL, BL ; WDT_UNITS value
OUT DX, AL ; Write the new WDT_UNITS value
; Select the watchdog timer timeout value ...
MOV DX, 3F0h ; SPIO Index Port
MOV AL, F2h ; Watchdog timeout value (WDT_VAL)
OUT DX, AL ; Point to register WDT_ VAL
INC DX ; SPIO Data Port
MOV AX, 37 ; New WDT_ VAL value (from 0 to 255 - seconds in this
case)
OUT DX, AL ; Write the new WDT_ VAL value
; SPIO: exit from configuration mode ...
MOV DX, 3F0h ; SPIO Index Port
MOV AL, 0AAh ; SPIO Configuration Mode Disable Key
OUT DX, AL ; Exit from configuration mode
• Note: for further information about the watchdog programming, refer to “FDC 37B78x
Advance Information”
manual from SMSC.
68
Page 69

69
Watchdog time-out pin
For external control purposes, the status of the watchdog time-out event is provided to connector
J11 pin 9. This signal goes high when the watchdog resets the system. The software can reset
this signal by setting and resetting bit 2 of the I/O port 110h. This signal is also initialized by
hardware at power-on.
The following example shows how to reset the watchdog time-out pin:
MOV DX, 110h ; Control Port
IN AL, DX ; Read actual value
OR AL, 04h ; Mask reserved bits and set bit 2
OUT DX, AL ; Write new value
AND AL, FBh ;
OUT DX, AL ; Write new value
Mask reserved bits and reset bit 2
69
Page 70

Chapter 8 Troubleshooting
Many problems that you may encounter with operation of your SpacePC 1232 module are due to
common errors like bad connections or wrong settings in the Setup Progra m.
This chapter will help you for getting your system operating properly.
It contains:
¾ • Common problems and solutions
¾ • Troubleshooting a PC/104 system
¾ • How to obtain technical support
¾ • How to return a product
70
Page 71

71
Common Problems and Solutions
The following table lists some of the common problems that you may encounter while using your
SpacePC 1232 module, and suggests possible solutions. If you are having problems with your
SpacePC 1232 module, please review this table
Table 24. Common problems and solutions
SpacePC 1232 Module "will not boot"
No power or wrong polarity Check for correct power on PC/104 bus connectors
Incorrect Setup (video disabled,
Reboot and press “F2” key to run Setup
etc.)
Defective or mis-connected device
Check for misaligned bus connectors, remove other cards from stack
on bus
Cable connected backwards Verify all cables are connected correctly
SSD installed backwards Check for an SSD memory installed in socket backwards
before contacting technical support.
SpacePC 1232 Module will not boot from particular drive or device
Device not bootable Use sys command on drive or reformat the device using the “Format
/s” option
Device not formatted Format drive using “Format /s” option
Power not connected to boot drive Connect the power cable to floppy or ha rd drive
Floppy/HardDisk cable connected
Verify that all cables are properly connected
backwards (floppy drive light always
on)
SpacePC 1232 Module will not boot from DiskOnModule
DiskOnModule is not the only hard
Disable other hard drive(s) in system and set DOM as master
drive in system
Hard disk is not set as boot device Run Setup and set Hard Drive as boot device
SpacePC 1232 Module will not boot when video card is removed
Illegal calls to video controller Look for software trying to access non existent video controller for
video, sound, or beep commands
SpacePC 1232 Module erratic operation
Excessive bus loading Reduce number of PC/104 modules in stack, remove termination
components from bus signals
Power supply noise Examine power supply output with oscilloscope, glitches below
4.75Vdc will trigger a reset, add bypass caps
Power supply limiting Examine power supply output with oscilloscope, check for voltage drop
71
Page 72

below 4.75V when hard drive or floppy drive starts, add bypass caps
Temperature too high Add fan, processor heat sink, or other cooling device(s)
Memory address conflict Check for two hardware devices (e.g. Ethernet, SSD, PCMCIA) trying
to use the same memory address
Check for two software devices (e.g. EMM386, PCMCIA drivers, etc.)
trying to use the same memory addresses
Check for an address range shadowed while in use by another
hardware or software device
I/O address conflict Check for another module trying to use I/O addresses reserved for the
Module between 0E0h and 0EAh check for two modules (e.g. I/O
Modules, PCMCIA cards, Ethernet) trying to use the same I/O
addresses
Keyboard does not work
Keyboard interface damaged by
misconnection
Wrong keyboard type Verify keyboard is an 'AT' type or switch to 'AT' mode
Both drives configured as master Set one drive as master and the other as slave operation (consult drive
Check if LEDs on the keyboard (i.e.: Num lock) are working
Two hard drives will not work, but one does
documentation)
Date and time not saved when power is off
No backup battery Conne ct a ba ckup battery t o the multifunction connector
Troubleshooting a PC/104 System
If you have reviewed the preceding table and still cannot isolate the problem with your SpacePC
1232 module, please try the following troubleshooting steps. Even if the resulting information
does not help you find the problem, it will be very helpful if you contact technical support.
¾ Simplify the system. Remove items one at a time and see if one particular item seems to
cause the problem.
¾ Swap components. Try replacing items in the system one-at-a-time with similar items.
Technical/Sales Assistance
If you have a technical question, please call Parvus Customer Support Service at one of the
numbers below, or e-mail our technical support team at:
¾ Email: tsupport@parvus.com
72
Page 73

73
¾ Phone: 801-483-1533
¾ Fax: 801-483-1523
If you have a sales question, please contact your local Parvus Sales Representative or the
Regional Sales Office for your area.
Additional and latest information is available at Parvus website:
http://www.parvus.com
Returning For Service
Before returning any of Parvus' products, you must contact Parvus and obtain a Returned
Material Authorization (RMA) number.
Note. You must have the RMA number in order to return any product for any reason!
The following information is needed to expedite the shipment of a replacement to you:
¾ Your company name and address for invoice
¾ Shipping address and phone number
¾ Product I.D. number
¾ The name of a technically qualified individual at your company familiar with the mode of
failure on the board
¾ A detailed description of the problem and of the current configuration including OS and
software loaded.
If the unit is out of warranty, service is available at a predesignated service charge. Contact
Parvus for pricing and please supply a purchase order number for invoicing the repair. Pack the
board in anti-static material and ship in a sturdy cardboard box with enough packing material to
adequately cushion it.
Warning! Any product returned to Parvus improperly packed will immediately void the
warranty for that particular product!
73
Page 74

Appendix
A.1 Electrical and Environmental Specifications
The following section provides tables and illustrations showing the electrical, mechanical and
environmental specifications for the SpacePC 1232 module.
In the following tables you will find:
¾ Operating Characteristics
Electrical operating characteristics
Operating temperature Range
Battery backup characteristics
¾ Absolute maximum ratings
¾ MTBF
¾ Power Consumption
Operating Characteristics
Electrical Operating Characteristics
Table 25. DC Operating Characteristics
Supply Voltage Vcc=+5V+/-5% (4.75V to 5.25V).
Battery current draw
(board off, without any device on the SSD)
Note. This CPU module is not warranted against damage caused by overheating due to
improper or insufficient cooling or airflow.
7 uA.
Operating Temperature Range
For proper operation of the CPU module, the ambient air temperature must remain inside this range:
0°C to +60°C (+32°F to +140°F).
74
Page 75

75
Note. In order to ensure proper operation and good reliability up to +60°C of ambient air
temperature, the Geode GX1 chip and the Geode CS5530 I/O Companion are supplied with an
attached passive heat sink.
Battery Backup Characteristics
There is no configuration data saved by the BIOS into the CMOS Real Time Clock. Therefore, the
module does not need a battery except in the case of applications that need to hold the date and time
at power-off.
Note. Setup data is stored into the BIOS Flash EPROM; it is therefore impossible to lose the
setup data due to a lack of backup-battery supply.
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Table 26. Absolute Maximum Ratings
Supply Voltage: Vcc: 0.00 to 7.00V
Storage Temperature Range: -40°C to +85°C (-40°F to +185°F)
Non-Condensing Relative Humidity: <95% at 40°C (+104°F)
Operating Temperature Range: 0°C to +60°C (+32°F to +140°F)
A SpacePC 1232 CPU module with an extended Operating Temperature Range, –40°C to +85°C, is
also available.
Warning! Stressing the device beyond the “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause
permanent damage. These are stress ratings only. Operation beyond the “Operating
Conditions” is not recommended. Extended exposure beyond the “Operating
Conditions” may affect device reliability.
MTBF
Hours: 615,000 Standard: MIL-STD-217 ground benign Temperature: 25.0 °C
Power Consumption
Table 27. Power Consumption
Frequency 64MB 128 MB
266MHz 1030mA 1080mA
75
Page 76

A.2 Mechanical Dimensions
CPU Dimensions
The SpacePC 1232 module’s mechanical dimensions are shown in the following picture:
¾ Dimensions: 90 X 96 mm (3.6”X3.8”), height:15 mm (0.6”)
Dimensions are in millimeters
Figure 24. SpacePC 1232 Board dimensions
76
Page 77

77
Note: For further information about the mechanical dimensions of ISA and PCI buses
please refer to the pc104 consortium site (www.pc104.org
FDD Adapter Dimensions
In the following picture are shown the FDD Adapter mechanical dimensions:
)
4
.
2
5
.
6
3.0 12.7
Dimensions are in inches
43,6
1.4
41.5
6.3
1,5
7
.
4
0
.
3
1
77
Page 78

Dimensions are in millimeters
Figure 25. FDD Adapter Dimensions
USB Audio CODEC Dimensions
In the following picture are shown the USB Audio CODEC mechanical dimensions:
Dimensions are in inches
95.3
91.3
22.0
10.9
4.0
3
0
8
.
.
.
5
4
3
1
7
.
6
2
0
.
2
3.1
13.1 13.1
14.9
13.1
75.6
82.6
91.2
1.5
1
.
1
2
.
3
7
3
Dimensions are in millimeters
78
Page 79

79
USB Audio CODEC Dimensions
Figure 26. USB Audio CODEC Dimensions
Ethernet Adapter Dimensions
In the following picture are shown the Ethernet Adapter mechanical dimensions:
Dimensions are in inches
0
.
1
3
49.0
43.4
5
.
0
1
Dimensions are in millimeters
3.0
0
.
3
9
.
1
1
79
Page 80

Figure 27. Ethernet Adapter Dimensions
Figure 28.
Figure 29. Recommended Mounting Hole Locations for Ethernet Adapter Mod ule
Multifunction Adapter Dimensions
In the following picture are shown the Multifunction Adapter mechanical dimensions:
Dimensions are in inches
80
Page 81

81
Figure 30. Multifunction Adapter Dimensions
A.3 Safety Summary
The following general safety precautions must be observed during all phases of operation, service,
and repair of this equipment. Failure to comply with these precautions or with specific warnings
elsewhere in this manual violates safety standards of design, manufacture, and intended use of the
equipment. Parvus assumes no liability for the customer’s failure to comply with these requi rements.
The safety precautions listed below represent warnings of certain dangers of which Parvus is aware.
You, as the user of the product, should follow these warnings and all other safety precautions
necessary for the safe operation of the equipment in your operating environment.
Ground the Instrument
To minimize shock hazard, the equipment chassis and enclosure must be connected to an electrical
ground. The equipment is supplied with a three-conductor ac power cable; the power cable must be
plugged into an approved three-contact electrical outlet, with the grounding wire (green) firmly
connected to an electrical ground (safety ground) at the power outlet. The power jack and mating
plug of the power cable meet International Electro technical Commission QEC) safety standards.
81
Page 82

Do Not Substitute Parts or Modify Equipment
Because of the danger of introducing additional hazards, do not install substitute parts or perform any
unauthorized modification of the equipment. Contact Parvus technical staff or your local
representative for service and repair to ensure that safety features are maintained.
Flammability
All Parvus PWBs (printed wiring boards) are manufactured by UL-recognized manufacturers, with a
flammability rating of UL-V0.
EMI Caution
This equipment generates, uses and can radiate electromagnetic energy. It may cause or be
susceptible to electromagnetic interference (EMI) if not installed and used in a cabinet with adequate
EMI protection.
CE Notice
This product complies with the EMC Directive (89/336/EEC). Compliance with this directive implies
conformity to the following European Norms:
¾ EN55022 (CISPR 22) Radio Frequency Interference
¾ EN50082-1 (IEC801-2, IEC801-3, IEC801-4) Electromagnetic Immunity
The product also fulfills EN60950 (product safety), which is essentially the requirement for the Low
Voltage Directive (73/23/EEC). This product was tested in a representative system to show
compliance with the above-mentioned requirements. A proper installation in a CE-marked system will
maintain the required EMC/safety performance.
Disclaimer of Warranty
THIS MANUAL IS PROVIDED ’AS IS’ WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EITHER EXPRESS
OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF
MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. The laws of some states and
countries do not allow the disclaimer of express or implied warranties in certain transactions;
therefore, this statement may not apply to you. As such, the above warranty disclaimer shall only
apply to the extent permitted by law.
Notice
While reasonable efforts have been made to assure the accuracy of this document, Parvus assumes
no liability resulting from any omissions in this document, or from the use of the information contained
therein. It is not warranted that the contents of this publication or any accompanying source code
examples, whether individually or as one or more groups, will meet your requirements or that the
publication or the accompanying source code examples are error-free. This publication could include
technical inaccuracies or typographical errors.
Parvus reserves the right to revise this document and to change its contents at any time without
obligation to notify any person of such revision or changes.
82
Page 83

83
Any reference to a licensed program in this publication is not intended to state or imply that you can
use only that licensed program. You can use any functionally equivalent program instead.
No part of this material may be reproduced or copied in any tangible medium, or stored in a retrieval
system, or transmitted in any form or by any means, radio, electronic, mechanical, photocopying,
recording or facsimile, or otherwise, without the prior written permission of Parvus.
Reliability
Parvus has taken extra care of product design in order to ensure reliability. The two major ways in
which reliability is achieved are:
¾ The product is designed in top-down fashion, utilizing the latest in hardware and software
techniques, so unwanted side effects and unclean interactions between parts of the
system are eliminated.
¾ Parvus / Eurotech tests each board by exercising its functions, burns it in under power,
and retests it to ensure that the infant mortality phase is passed before the product is
shipped.
Life Support Policy
Parvus products are not authorized for use as critical components in life support devices or systems
without the express written approval of the president of Parvus.
83
Page 84

Page 85

Acronyms and Abbreviations
ACPI Advanced Configuration and
Power Interface
AGP Accelerated Graphic Port
APM Advanced Power Management
ATA AT Attachment
ATAPI ATA Packet Interface
BIOS Basic I/O System
CRT Cathode Ray Tube
DDC Display Data Channel
DDC2B DDC Standard, Version 2.0, Level
B
DMA Direct Memory Access
DSTN Double Supertwisted Nematic
ECC Error Correction Code
ECP Enhanced Capabilities Port
FAT File Allocation Table
FDC Floppy Disk Drive Controller
FDD Floppy Disk Drive
FDDI Fiber Distributed Data Interface
FIFO First In First Out
FM Frequency Modulation
fps frames per second
GSM Global System for Mobile
communications
HDC Hard Disk Drive controller
HDD Hard Disk Drive
IDE Integrated Device Electronics
IEEE Institute for Electrical and
Electronics Engineers, Inc.
I/O Input/Output
IP Internet Protocol
IRQ Interrupt Request
ISA Industry Standard Architecture
KB Kilobyte
Kbps Kilobits per Second
KHz Kilohertz
LAN Local Area Network
LBA Logical Block Addressing
LCD Liquid Crystal Display
LPT Line Printer
LVD Low Voltage Differential
MB Megabyte
Mbps Megabits per second
MHZ Megahertz
MIDI Musical Instrument Digital
Interface
MPEG Moving Picture Expert Group
NIDS Network Driver Interface
Specification
NMI Nonmaskable Interrupt
NTSC National Television System
Committee
OEM Original Equipment Manufacturer
PAL Phase Alternation Line
PCI Peripheral Component
Interconnect
PCMCIA Personal Computer Memory
Card International Association
PIC Programmable Interrupt
Controller
PIO Programmed I/O
POST Power-On Self Test
RAM Random Access Memory
RAMDAC RAM digital-to-analog converter
RGB Red-Green-Blue
SECAM SEquential Coleur A Memoire
SCSI Small Computer System
Interface
SMBus System Management Bus
TCP/IP Transmission Control
Provocol/Internet Protocol
UART Universal Asynchronous
Receiver/Transmitter
USB Universal Serial Bus
V Volts
VESA Video Electronics Standards
Association
VGA Video Graphics Array
WAN Wide Area Network
85
Page 86

For more information about this or other products in the Parvus line of embedded developm ent
tools and control systems call (801) 483-1533 from 8:00AM to 5:00PM Mountain Time, E-mail us
at parvus@parvus.com or visit our web-site at: http://www.parvus.com
LIMITED WARRANTY
Parvus Corporation warrants this product to be free of defects in materials and workmanship, and
that the product meets or exceeds the current specifications published by Parvus. This Warranty
is valid for a period of one (1) year from the date of purchase. Parvus reserves the right to repair
or replace any Warranted products at its sole discretion. Any product returned to Parvus for repair
or replacement under the provisions of this warranty must be accompanied by a valid Return
Material Authorization (RMA) number issued by the Parvus Customer Service Department.
Parvus Corporation makes no warranty not expressly set forth in this document. Parvus disclaims
and excludes all implied warranties of merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose. The
aggregate liability of Parvus arising from or relating to (regardless of the form of action or claim) is
limited to the total of all payments made to purchase the product. Parvus shall not in any case be
liable for any special, incidental, consequential, indirect or punitive damages, even if Parvus has
been advised of the possibility of such damages. Parvus is not responsible for lost profits or
revenue, loss of the use of software, loss of data, costs of recreating lost data, or the cost of any
substitute equipment or program.
This Warranty shall be governed by the laws of the United States of America and the State of
Utah, and any claim brought under this Warranty may only be brought in state or federal court
located in Salt Lake County, State of Utah, and purchaser hereby consents to personal
jurisdiction in such courts.
FEDERAL COMMUNICATIONS
COMMISSION RADIO FREQUENCY
INTERFERENCE STATEMENT
Warning: The equipment described herein has been designed to comply with the limits for a
Class B computing device, pursuant to Subpart J of Part 15 of FCC rules. Only peripherals
(computer input/output devices, terminals, printers, etc.) designed to comply with the Class B
limits may be attached to this computer.
INSTRUCTIONS TO USER: This equipment generates and uses radio frequency energy and if
not installed and used properly, i.e., in strict accordance with the operating instructions, reference
manuals, and the service manual, may cause interference to radio or TV reception. It has been
designed to comply with the limits for a Class B computing device pursuant to Subpart J of Part
15 of FCC rules, which are designed to provide reasonable protection against such interference
when operated in a residential installation.
86
Page 87

87
For further information contact:
Parvus® Corporation
3222 S. Washington St.
Salt Lake City, Utah, USA 84115
(801) 483-1533, FAX (801) 483-1523
Web-site: http://www.parvus.com
Email: parvus@parvus.com
87
 Loading...
Loading...