Page 1

TigerSwitch 1000
Gigabit Ethernet Switch
◆ 6 1000BASE-SX ports
Two slots for hot-swappable 1000BASE-X GBIC modules
◆
◆ 16 Gbps of aggregate switch bandwidth
◆ Support for redundant power unit
◆ Up to four port trunks per switch
◆ Port mirroring for non-intrusive analysis
◆ QoS support for two-level priority
◆ Full support for IEEE 802.1Q VLANs
◆ IGMP multicast filtering and snooping
◆ Manageable via console, Web, SNMP/RMON
Installation Guide
SMC8606SX
Page 2

Page 3

TigerSwitch 1000
Installation Guide
From SMC’s Tiger line of feature-rich workgroup LAN solutions
6 Hughes
Irvine, CA 92618
Phone: (949) 707-2400
October 2001
Pub. #150200001900A R01
Page 4

Information furnished by SMC Networks, Inc. (SMC) is believed to
be accurate and reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by
SMC for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights
of third parties which may result from its use. No license is granted
by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of
SMC. SMC reserves the right to change specifications at any time
without notice.
Copyright © 2001 by
SMC Networks, Inc.
6 Hughes
Irvine, CA 92618
All rights reserved. Printed in Taiwan
Trademarks:
SMC is a registered trademark; and EZ Switch, TigerStack and TigerSwitch are trademarks of
SMC Networks, Inc. Other product and company names are trademarks or registered
trademarks of their respective holders.
Page 5

L
IMITED WARRANTY
Limited Warranty
Limited Warranty Statement: SMC Networks, Inc. (“SMC”) warrants its products
to be free from defects in workmanship and materials, under normal use and
service, for the applicable warranty term. All SMC products carry a standard 90-day
limited warranty from the date of purchase from SMC or its Authorized Reseller.
SMC may, at its own discretion, repair or replace any product not operating as
warranted with a similar or functionally equivalent product, during the applicable
warranty term. SMC will endeavor to repair or replace any product returned under
warranty within 30 days of receipt of the product.
The standard limited warranty can be upgraded to a Limited Lifetime* warranty by
registering new products within 30 days of purchase from SMC or its Authorized
Reseller. Registration can be accomplished via the enclosed product registration
card or online via the SMC web site. Failure to register will not affect the standard
limited warranty. The Limited Lifetime warranty covers a product during the Life of
that Product, which is defined as the period of time during which the product is an
“Active” SMC product. A product is considered to be “Active” while it is listed on
the current SMC price list. As new technologies emerge, older technologies become
obsolete and SMC will, at its discretion, replace an older product in its product line
with one that incorporates these newer technologies. At that point, the obsolete
product is discontinued and is no longer an “Active” SMC product. A list of
discontinued products with their respective dates of discontinuance can be found at
http://www.smc.com/smc/pages_html/support.html.
All products that are replaced become the property of SMC. Replacement products
may be either new or reconditioned. Any replaced or repaired product carries
either a 30-day limited warranty or the remainder of the initial warranty, whichever
is longer. SMC is not responsible for any custom software or firmware,
configuration information, or memory data of Customer contained in, stored on, or
integrated with any products returned to SMC pursuant to any warranty. Products
returned to SMC should have any customer-installed accessory or add-on
components, such as expansion modules, removed prior to returning the product
for replacement. SMC is not responsible for these items if they are returned with the
product.
Customers must contact SMC for a Return Material Authorization number prior to
returning any product to SMC. Proof of purchase may be required. Any product
returned to SMC without a valid Return Material Authorization (RMA) number
clearly marked on the outside of the package will be returned to customers at
customer’s expense. For warranty claims within North America, please call our
toll-free customer support number at (800) 762-4968. Customers are responsible for
all shipping charges from their facility to SMC. SMC is responsible for return
shipping charges from SMC to customer.
WARRANTIES EXCLUSIVE: IF AN SMC PRODUCT DOES NOT OPERATE AS
WARRANTED ABOVE, CUSTOMER’S SOLE REMEDY SHALL BE REPAIR OR
REPLACEMENT OF THE PRODUCT IN QUESTION, AT SMC’S OPTION. THE
FOREGOING WARRANTIES AND REMEDIES ARE EXCLUSIVE AND ARE IN LIEU
OF ALL OTHER WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, EITHER
Page 6

L
IMITED WARRANTY
IN FACT OR BY OPERATION OF LAW, STATUTORY OR OTHERWISE, INCLUDING
WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A
PARTICULAR PURPOSE. SMC NEITHER ASSUMES NOR AUTHORIZES ANY OTHER
PERSON TO ASSUME FOR IT ANY OTHER LIABILITY IN CONNECTION WITH
THE SALE, INSTALLATION, MAINTENANCE OR USE OF ITS PRODUCTS. SMC
SHALL NOT BE LIABLE UNDER THIS WARRANTY IF ITS TESTING AND
EXAMINATION DISCLOSE THE ALLEGED DEFECT IN THE PRODUCT DOES NOT
EXIST OR WAS CAUSED BY CUSTOMER’S OR ANY THIRD PERSON’S MISUSE,
NEGLECT, IMPROPER INSTALLATION OR TESTING, UNAUTHORIZED ATTEMPTS
TO REPAIR, OR ANY OTHER CAUSE BEYOND THE RANGE OF THE INTENDED
USE, OR BY ACCIDENT, FIRE, LIGHTNING, OR OTHER HAZARD.
LIMITATION OF LIABILITY: IN NO EVENT, WHETHER BASED IN CONTRACT OR
TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE), SHALL SMC BE LIABLE FOR INCIDENTAL,
CONSEQUENTIAL, INDIRECT, SPECIAL, OR PUNITIVE DAMAGES OF ANY KIND,
OR FOR LOSS OF REVENUE, LOSS OF BUSINESS, OR OTHER FINANCIAL LOSS
ARISING OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SALE, INSTALLATION,
MAINTENANCE, USE, PERFORMANCE, FAILURE, OR INTERRUPTION OF ITS
PRODUCTS, EVEN IF SMC OR ITS AUTHORIZED RESELLER HAS BEEN ADVISED
OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
SOME STATES DO NOT ALLOW THE EXCLUSION OF IMPLIED WARRANTIES OR
THE LIMITATION OF INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES FOR
CONSUMER PRODUCTS, SO THE ABOVE LIMITATIONS AND EXCLUSIONS MAY
NOT APPLY TO YOU. THIS WARRANTY GIVES YOU SPECIFIC LEGAL RIGHTS,
WHICH MAY VARY FROM STATE TO STATE. NOTHING IN THIS WARRANTY
SHALL BE TAKEN TO AFFECT YOUR STATUTORY RIGHTS.
* SMC will provide warranty service for one year following discontinuance from the
active SMC price list. Under the limited lifetime warranty, internal and external
power supplies, fans, and cables are covered by a standard one-year warranty from
date of purchase.
SMC Networks, Inc.
6 Hughes
Irvine, CA 92618
Page 7

C
OMPLIANCES
FCC - Class A
This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio freq uency energy and, if not i nstalled
and used in accordance with the instruction manual, may cause interference to radio
communications. It has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A
computing device pursuant to Subpart B of Part 15 of FCC Rules, which are designed to
provide reasonable protection against such interference when operated in a commercial
environment. Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause
interference, in which case the user, at his own expense, will be required to take whatever
measures may be required to correct the interference. You are cautioned that changes or
modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for compliance could void
your authority to operate the equipment.
You may use Category 5 or 5e UTP or STP cable for RJ-45 connections. Use 62.5/125 or
50/125 micron multimode fiber cable, or 9/125 singlemode fiber cable for SC connections.
War ni ngs 1.
Wear an anti-static wrist strap or take other suitable measures to prevent
electrostatic discharge when handling this equipment.
2.
When connectin g this hub to a power outlet, connect the field ground lead on
the tri-pole power plug to a valid earth ground line to prevent electrical
hazards.
Industry Canada - Class A
This digital apparatus does not exceed the Class A limits for radio noise emissions from
digital apparatus as set out in the interference-causing equipment standard entitled “Digital
Apparatus,” ICES-003 of the Department of Communications.
Cet appareil numérique respecte les limites de bruits radioélectriques applicables aux
appareils numériques de Classe A prescrites dans la norme sur le matériel brouilleur:
“Appareils Numériques,” NMB-003 édictée par le ministère des Communications.
Japan VCCI Class A
i
Page 8

C
OMPLIANCES
EC Conformance Declaration - Class A
SMC contact for these products in Europe is:
SMC Networks Europe,
Edificio Conata II,
Calle Fructuós Gelabert 6-8, 2
08970 - Sant Joan Despí,
Barcelona, Spain.
This information technology equipment complies with the requirements of the
Council Directive 89/336/EEC on the Approximation of the laws of the Member
States relating to Electromagnetic Compatibility and 73/23/EEC for electrical
equipment used within certain voltage limits and the Amendment Directive 93/68/
EEC. For the evaluation of the compliance with these Directives, the following
standards were applied:
RFI Emission: • Limit class A according to EN 55022:1998
• Limit class A for harmonic current emission according to
EN 61000-3-2/1995
• Limitation of voltage fluctuation and flicker in low-voltage
supply system according to EN 61000-3-3/1995
Immunity: • Product family standard according to EN 55024:1998
• Electrostatic Discharge according to EN 61000-4-2:1995
(Contact Discharge: ±4 kV, Air Discharge: ±8 kV)
• Radio-frequency electromagnetic field according to
EN 61000-4-3:1996
(80 - 1000 MHz with 1 kHz AM 80% Modulation: 3 V/m)
• Electrical fast transient/burst according to EN 61000-4-4:1995
(AC/DC power supply: ±1 kV, Data/Signal lines: ±0.5 kV)
• Surge immunity test according to EN 61000-4-5:1995
(AC/DC Line to Line: ±1 kV, AC/DC Line to Earth: ±2 kV)
•Immunity to conducted disturbances, Induced by radio-frequency
fields: EN 61000-4-6:1996
(0.15 - 80 MHz with 1 kHz AM 80% Modulation: 3 V/m)
• Power frequency magnetic field immunity test according to
EN 61000-4-8:1993
(1 A/m at frequency 50 Hz)
• Voltage dips, short interruptions and voltage variations
immunity test according to EN 61000-4-11:1994
(>95% Reduction @10 ms, 30% Reduction @500 ms, >95%
Reduction @5000 ms)
LVD: • EN 60950 (A1/1992; A2/1993; A3/1993; A4/1995; A11/1997)
o
, 4a,
ii
Page 9

Taiwan BSMI Class A
Australia AS/NZS 3548 (1995) - Class A
SMC contact for products in Australia is:
SMC Communications Pty. Ltd.
Suite 18, 12 Tryon Road,
Lindfield NSW2070,
Phone: 61-2-94160437
Fax: 61-2-94160474
C
OMPLIANCES
iii
Page 10
C
OMPLIANCES
Safety Compliance
Warning: Fiber Optic Port Safety
When using a fiber optic port, never look at the transmit laser
while it is powered on. Also, never look directly at the fiber TX
port and fiber cable ends when they are powered on.
Avertissment: Ports pour fibres optiques - sécurité sur le plan
optique
Ne regardez jamais le laser tant qu'il est sous tension. Ne
regardez jamais directement le port TX (Transmission) à fibres
optiques et les embouts de câbles à fibres optiques tant qu'ils
sont sous tension.
Warnhinweis: Faseroptikanschlüsse - Optische Sicherheit
Niemals ein Übertragungslaser betrachten, während dieses
eingeschaltet ist. Niemals direkt auf den Faser-TX-Anschluß
und auf die Faserkabelenden schauen, während diese
eingeschaltet sind.
Underwriters Laboratories Compliance Statement
Important! Before making connections, make sure you have the correct cord set.
Check it (read the label on the cable) against the following:
Operating Voltage Cord Set Specifications
120 Volts UL Listed/CSA Certified Cord Set
Minimum 18 AWG
Type SVT or SJT three conductor cord
Maximum length of 15 feet
Parallel blade, grounding type attachment plug
rated 15A, 125V
240 Volts (Europe only) Cord Set with H05VV-F cord having three
conductors with minimum diameter of 0.75 mm
IEC-320 receptacle
Male plug rated 10A, 250V
2
The unit automatically matches the connected input voltage. Therefore, no additional
adjustments are necessary when connecting it to any input voltage within the range
marked on the rear panel.
iv
Page 11

C
OMPLIANCES
Wichtige Sicherheitshinweise (Germany)
1. Bitte lesen Sie diese Hinweise sorgfältig durch.
2. Heben Sie diese Anleitung für den späteren Gebrauch auf.
3. Vor jedem Reinigen ist das Gerät vom Stromnetz zu trennen. Verwenden Sie
keine Flüssigoder A erosolreiniger. Am besten eign et sich ein angefeuchtetes Tuch
zur Reinigung.
4. Die Netzanschlu ßsteckdose soll nahe dem Gerät angebracht und leicht
zugänglich sein.
5. Das Gerät ist vor Feuchtigkeit zu schützen.
6. Bei der Aufstellung des Gerätes ist auf sicheren Stand zu achten. Ein Kippen oder
Fallen könnte Beschädigungen hervorrufen.
7. Die Belüftungsöffnungen dienen der Luftzirkulation, die das Gerät vor
Überhitzung schützt. Sorgen Sie dafür, daß diese Öffnungen nicht abgedeckt
werden.
8. Beachten Sie beim Anschluß an das Stromnetz die Anschlußwerte.
9. Verlegen Sie die Netzanschlußleitung so, daß niemand darüber fallen kann. Es
sollte auch nichts auf der Leitung abgestellt werden.
10. Alle Hinweise und Warnungen, die sich am Gerät befinden, sind zu beachten.
11. Wird das Gerät über einen längeren Zeitraum nicht benutzt, sollten Sie es vom
Stromnetz trennen. Somit wird im Falle einer Überspannung eine Beschädigung
vermieden.
12. Durch die Lüftungsöffnungen dürfen niemals Gegenstände oder Flüssigkeiten in
das Gerät gelangen. Dies könnte einen Brand bzw. elektrischen Schlag auslösen.
13. Öffnen sie niemals das Gerät. Das Gerät darf aus Gründen der elektrischen
Sicherheit nur von authorisiertem Servicepersonal geöffnet werden.
14. Wenn folgende Situationen auftreten ist das Gerät vom Stromnetz zu trennen und
von einer qualifizierten Servicestelle zu überprüfen:
a. Netzkabel oder Netzstecker sind beschädigt.
b. Flüssigkeit ist in das Gerät eingedrungen.
c. Das Gerät war Feuchtigkeit ausgesetzt.
d. Wenn das Gerät nicht der B edienungsanleitung entsprechen d funktioniert oder
Sie mit Hilfe dieser Anleitung keine Verbesserung erzielen.
e. Das Gerät ist gefallen und/oder das Gehäuse ist beschädigt.
f. Wenn das Gerät deutliche Anzeichen eines Defektes aufweist.
15. Zum Netzanschluß dieses Gerätes ist eine geprüfte Leitung zu verwenden. Für
einen Nennstrom bis 6A und einem Gerätegewicht größer 3kg ist eine Leitung
nicht leichter als H05VV-F, 3G, 0.75mm
Der arbeitsplatzbezogene Schalldruckpegel nach DIN 45 635 Teil 1000 beträg t 70dB(A)
oder weniger.
2
einzusetzen.
v
Page 12

C
OMPLIANCES
vi
Page 13

T
ABLE OF
C
ONTENTS
1 About the TigerSwitch 1000 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-1
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-1
Description of Hardware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-2
1000BASE-SX Ports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-2
GBIC Slots . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-2
Status LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3
Network Management Agent . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-4
Optional Redundant Power Unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-6
Power Supply Receptacles . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-6
Features and Benefits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-7
Connectivity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-7
Performance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-7
Management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-8
2 Network Planning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-1
Introduction to Switching . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-1
Sample Applications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-2
Backbone Consolidation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-2
Making VLAN Connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-3
Connectivity Rules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-4
1000 Mbps Gigabit Ethernet Collision Domain . . . . . . . . 2-4
100 Mbps Fast Ethernet Collision Domain . . . . . . . . . . . 2-5
10 Mbps Ethernet Collision Domain . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-6
Application Notes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-6
3 Installing the Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-1
Selecting a Site . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-1
Equipment Checklist . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-2
Package Contents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-2
Optional Rack-Mounting Equipment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-2
Mounting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-3
Rack Mounting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-3
Desktop or Shelf Mounting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-5
Installing a GBIC Transceiver . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-6
Connecting to a Power Source . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-7
vii
Page 14

T
ABLE OF CONTENTS
4 Making Network Connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-1
Connecting Network Devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-1
Connecting to an SC-Type Fiber Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-2
A Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .A-1
Diagnosing Switch Indicators . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-1
Power and Cooling Problems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-1
Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-2
In-Band Access . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-2
B Cables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .B-1
Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . B-1
Console Port Pin Assignments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . B-2
DB-9 Port Pin Assignments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . B-2
Console Port to 9-Pin COM Port on PC . . . . . . . . . . . . . B-3
Console Port to 25-Pin DTE Port on PC . . . . . . . . . . . . B-3
C Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .B-1
Physical Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . B-1
Switch Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . B-2
Management Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . B-3
Standards . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . B-3
Compliances . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . B-4
Warranty . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . B-4
A Ordering Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . D-1
Glossary
Index
viii
Page 15

C
HAPTER
A
BOUT THE
T
IGERSWITCH
1000
Overview
The TigerSwitch 1000 is a high-performance Gigabit Ethernet
switch designed for the network core. It provides eight 1000 Mbps
ports that can significantly improve the performance of your
network’s backbone, and deliver the throughput needed to
support a broad range of advanced network applications.
With 16 Gigabits of aggregate bandwidth, the TigerSwitch 1000
can provide the quickest solution to meeting the growing demands
on your networkís limited resources. This switch has six
1000BASE-SX SC fiber ports and two GBIC slots. Each 1000 Mbps
port can support high-bandwidth connectivity within or between
workgroups, and increased capacity for server farms, giving your
users faster access to network-wide resources.
The TigerSwitch 1000 includes a built-in management agent that
allows you to configure or monitor the switch using the embedded
management program or SNMP/RMON applications. To manage
the switch, you can make a direct connection to the console port
on the switch’s front panel. You can also make a network
connection to manage the switch using Telnet, the on-board Web
agent, or any SNMP-based network management software.
1
1-1
Page 16

A
BOUT THE TIGERSWITCH
Figure 1-1. Front and Rear Panels
1000
Description of Hardware
1000BASE-SX Ports
These ports are SC-type fiber optic ports that operate at 1 Gbps full
and half duplex. The ports can be connected to other IEEE
802.3z-compliant devices up to 550 m (1805 ft.) away using fiber
optic cable. The switch is fitted with SC ports, but you can also
attach an ST plug to the switch using SMC’s optional SC-ST
Converter (Part Number: 99-012034-091).
GBIC Slots
The two slots on the switch front panel are for installing optional
5V GBIC transceivers. Note that GBIC transceivers are
hot-swappable. You do not need to power off the switch before
installing or removing a transceiver.
1-2
Page 17

A
BOUT THE TIGERSWITCH
Status LEDs
The LEDs, which are located on the front panel for easy viewing,
are shown below and described in the following table.
Figure 1-2. Port and System LEDs
Port and System Status LEDs
LED Condition Status
Power On Green Switch is receiving power.
Off Power off or failure.
RPU On Green Redundant power unit is attached and
is operating in a load-sharing mode.
Off Power off or failure.
1000
Diag. Flashing Green System self-diagnostic test in progress.
On Green System self-diagnostic test successfully
completed.
On Amber System self-diagnostic test has failed.
1-3
Page 18
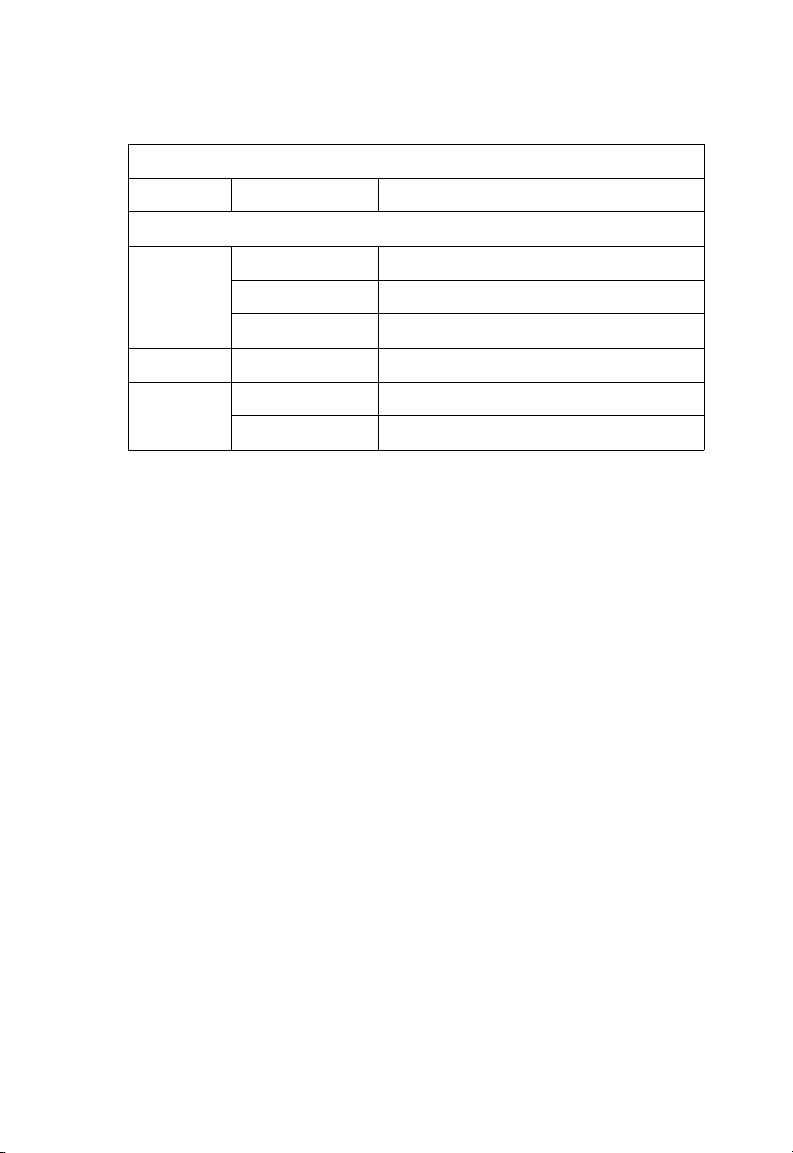
A
BOUT THE TIGERSWITCH
LED Condition Status
Ports
Link Flashing Green Port is operating at 1000 Mbps.
ACT On Green Traffic is passing through the port.
FDX On Green Port is operating at full duplex.
1000
Port and System Status LEDs
Flashing Amber Port has been manually disabled.
Off There is no valid link on the port.
On Amber Port is operating in half-duplex mode.
Network Management Agent
The TigerSwitch 1000 includes a built-in network management
agent. The agent offers a variety of management options, including
SNMP, RMON and a Web-based interface. The switch also provides
a serial port on the rear panel for out-of-band management. This is
an RS-232 serial port with a DB-9 connector. A PC may be
connected to this port for configuration and monitoring purposes
out-of band via a full-handshaking null-modem cable. (See
Appendix B for a description of wiring options.)
The network management agent provides a wide range of
advanced performance-enhancing features. Port-based and tagged
VLANs provide traffic security and efficient use of network
bandwidth. QoS priority queueing ensures the minimum delay for
moving real-time multi-media data across the network. Flow
control eliminates the loss of packets due to bottlenecks caused by
port saturation. And broadcast storm suppression prevents
broadcast traffic storms from engulfing the network. Some of the
management features are described below. For a detailed
description, refer to the Management Guide that is included with
the switch.
1-4
Page 19

A
BOUT THE TIGERSWITCH
Spanning Tree Protocol
The TigerSwitch 1000 supports ANSI/IEEE 802.1d Spanning Tree
Protocol. This protocol adds a level of fault tolerance by allowing
two or more redundant connections to be created between a pair
of LAN segments. When there are multiple physical paths between
segments, the protocol will choose a single path and disable all
others to ensure that only one route exists between any two
stations on the network. This prevents the creation of network
loops. However, if the chosen path should fail for any reason, an
alternate path will be activated to maintain the connection.
The default setting for the Spanning Tree Protocol is “enabled.”
This protocol may be configured (enabled or disabled)
out-of-band via the serial console port or in-band via the Web
interface, Telnet, or SNMP network management software.
VLANs
The TigerSwitch 1000 supports up to 256 VLANs. A Virtual LAN is
a collection of network nodes that share the same collision domain
regardless of their physical location or connection point in the
network. By segmenting your network into VLANs, you can:
1000
• Eliminate broadcast storms which severly degrade performance
in a flat network.
• Simplify network management for node changes/moves by
remotely configuring VLAN membership for the concerned
port, rather than having to manually change the node’s IP
address.
• Provide data security by restricting all traffic to the originating
VLAN, except where a connection has been configured
between separate VLANs using a router or Layer 3 switch.
1-5
Page 20
A
BOUT THE TIGERSWITCH
Multicast Switching
Specific multicast traffic can be assigned to its own VLAN to ensure
that it does not interfere with normal network traffic and to
guarantee real-time delivery by setting the required priority level
for the designated VLAN. The switch uses IGMP Snooping and
IGMP to manage multicast group registration.
Traffic Priority
This switch provides Quality of Service (QoS) by prioritizing each
packet based on the required level of service, using two distinct
categories with Weighted Fair Queuing. It uses IEEE 802.1Q and
802.1p tags to prioritize incomming traffic based on input from the
end-station application driver. These functions can be used, for
example, to provide independent priorities for real-time video,
real-time voice, guaranteed-delivery data, or best-effort data.
1000
Optional Redundant Power Unit
SMC provides an optional Redundant Power Unit (RPU),
SMCRPU150W, that can supply power to the switch in the event of
failure of the internal power supply.
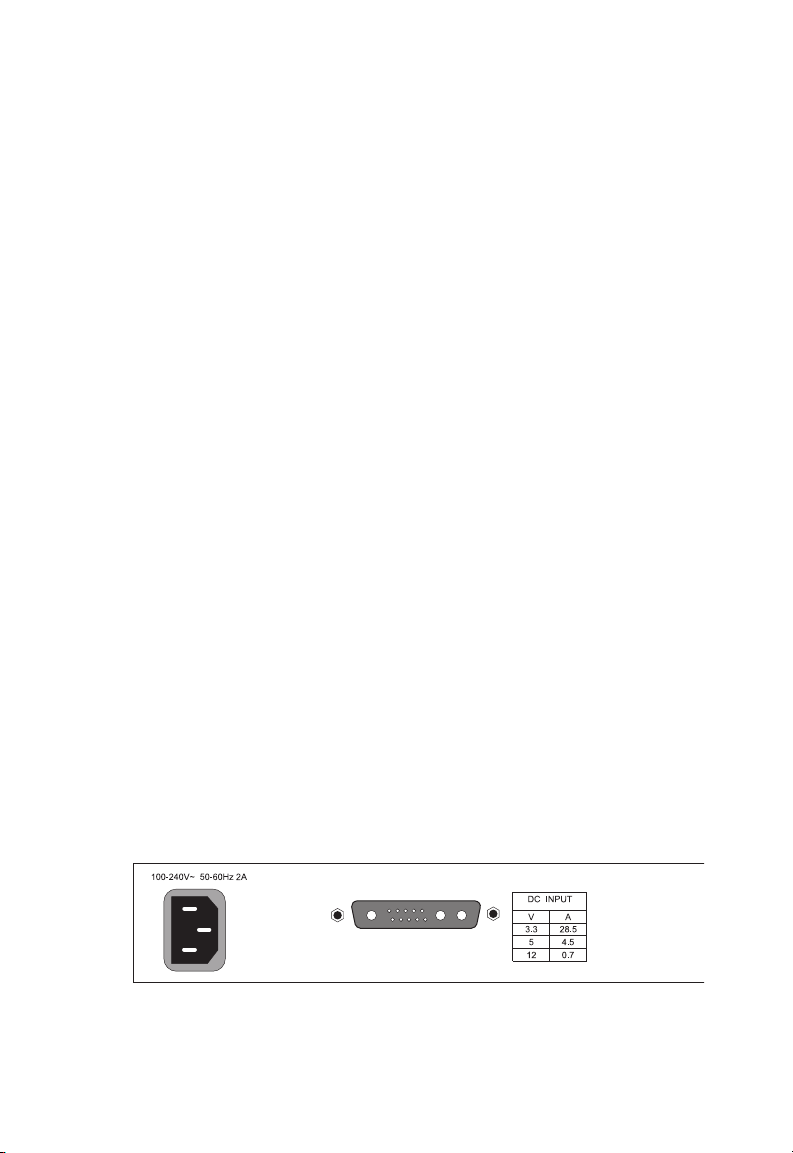
Power Supply Receptacles
There are two power receptacles on the rear panel of the switch.
The standard power receptacle is for the AC power cord. The
receptacle labeled “DC Input” is for the optional Redundant Power
Unit (RPU).
Figure 1-3. Power Supply Receptacles
1-6
Page 21

A
BOUT THE TIGERSWITCH
Features and Benefits
Connectivity
◆ 6 1000BASE-SX SC ports
◆ Two slots for optional GBIC modules
◆ Auto-negotiation of duplex mode and flow control
◆ IEEE 802.3z Gigabit Ethernet compliance ensures compatibility
with standards-based network cards and switches from any
vendor
Performance
◆ Transparent bridging
◆ Aggregate bandwidth of 16 Gbps
◆ Switching Table with 12K MAC address entries
◆ Provides Store-and-Forward switching
1000
◆ Filtering and forwarding at line speed
◆ Broadcast storm suppression
◆ Includes support for an optional Redundant Power Unit
◆ Desktop or rack-mountable
◆ Limited lifetime warranty
1-7
Page 22

A
BOUT THE TIGERSWITCH
1000
Management
◆ “At-a-glance” LEDs for easy troubleshooting
◆ Network management agent:
• Supports Telnet, SNMP/RMON and Web-based interface
• Spanning Tree Protocol for redundant network
connections
• VLAN support for 256 groups, port-based or with 802.1Q
VLAN tagging
• Quality of Service (QoS) supports two priority queues and
Weighted Fair Queueing
• Multicast Switching based on IGMP (Internet Group
Management Protocol) Snooping and Multicast Filtering
1-8
Page 23

C
HAPTER
N
ETWORK
P
LANNING
Introduction to Switching
A network switch allows simultaneous transmission of multiple
packets via non-crossbar switching. This means that it can partition
a network more efficiently than bridges or routers. The switch has,
therefore, been recognized as one of the most important building
blocks for today’s networking technology.
When performance bottlenecks are caused by congestion at the
network access point (such as the network card for a high-volume
file server), the device experiencing congestion (server, power
user or hub) can be attached directly to a switched port. And, by
using full-duplex mode, the bandwidth of the dedicated segment
can be doubled to maximize throughput.
When networks are based on repeater (hub) technology, the
maximum distance between end stations is limited. For Ethernet,
there may be up to four hubs between any pair of stations; for Fast
Ethernet, the maximum is two. This is known as the hop count.
However, a switch turns the hop count back to zero, so
subdividing the network into smaller and more manageable
segments, and linking them to the larger network by means of a
switch, removes this limitation.
2
A switch can be easily configured in any Ethernet or Fast Ethernet
network to significantly boost bandwidth while using conventional
cabling and network cards.
2-1
Page 24

N
ETWORK PLANNING
Sample Applications
The TigerSwtich 1000 is designed to consolidate your network
core providing high-bandwidth connections between workgroup
switches and server farms. Some typical applications are described
in this section.
Backbone Consolidation
The TigerSwtich 1000 can consolidate a switched network
backbone down into a single efficient bridged node, increasing
overall bandwidth and throughput.
In the figure below, the 1000BASE-SX ports on the TigerSwtich
1000 are providing 2 Gbps full-duplex connectivity to TigerSwitch
10/100 stacks and high-volume servers.
Figure 2-1. Backbone Consolidation
2-2
Page 25

N
ETWORK PLANNING
Making VLAN Connections
VLANs can be based on port groups, or each data frame can be
explicitly tagged to identify the VLAN group it belongs to. When
using port-based VLANs, ports can either be assigned to one
specific group or to all groups. Port-based VLANs are suitable for
small networks. A single switch can be easily configured to
support several VLAN groups for various organizational entities
(such as Finance and Marketing).
When you expand port-based VLANs across several switches, you
need to make a separate connection for each VLAN group. This
approach is, however, inconsistent with the Spanning Tree
Protocol, which can easily segregate ports that belong to the same
VLAN. When VLANs cross separate switches, it is therefore better
to use VLAN tagging. This allows you assign multiple VLAN groups
to the trunk ports (that is, tagged ports) connecting different
switches.
Figure 2-2. Making VLAN Connections
Note: When connecting to a switch that does not support IEEE
802.1Q VLAN tags, use untagged ports.
2-3
Page 26

N
ETWORK PLANNING
Connectivity Rules
When adding hubs (repeaters) to your network, please follow the
connectivity rules listed below for Ethernet and Fast Ethernet.
However, note that because switches break up the path for
connected devices into separate collision domains, you should not
include the switch or connected cabling in your calculations for
cascade length involving other devices.
1000 Mbps Gigabit Ethernet Collision Domain
Maximum Fiber Optic Cable Distance for 1000BASE-SX
Fiber Size Fiber Bandwidth Maximum Cable Length
62.5/125 micron 160 MHz/km 2-220 m (7-722 ft)
200 MHz/km 2-275 m (7-902 ft)
50/125 micron 400 MHz/km 2-500 m (7-1641 ft)
500 MHz/km 2-550 m (7-1805 ft)
Maximum Fiber Optic Cable Distance for 1000BASE-LX
2-4
Fiber Size Fiber Bandwidth Maximum Cable Length
9/125 micron N/A 2 m - 5 km (7 - 16404 ft)
Page 27

N
ETWORK PLANNING
100 Mbps Fast Ethernet Collision Domain
SMC 3-2 Rule for Class II Repeaters
Between any two PCs or other stations in the same 100BASE-TX
collision domain, there may be:
• up to 3 link segments and
• up to 2 Class II repeaters (hubs)
SMC 2-1 Rule for Class I Repeaters
Between any two PCs or other stations in the same 100BASE-TX
collision domain, there may be:
• up to 2 link segments and
• up to 1 Class I repeater (hub)
Maximum 100BASE-TX Network Diameter Using Repeaters
Repeater Type
and Number
1 Class I 200 m (656 ft.)
1 Class II 200 m (656 ft.)
2 Class II 205 m (672.4 ft.)
Twisted Pair
100BASE-TX
Maximum Fast Ethernet Cable Distance
Cable Type Connecting Max. Distance
Twisted Pair Any two devices 100 m (328 ft.)
Fiber Switch to switch, server or PC
Half duplex 412 m (1,351.4 ft.)
Full duplex 2 km (1.24 mi.)
2-5
Page 28

N
ETWORK PLANNING
10 Mbps Ethernet Collision Domain
SMC 5-4-3 Rule
Between any two PCs or other stations in the same 10 Mbps collision
domain, there may be:
• up to 5 link segments in series,
• up to 4 repeaters (hubs),
• up to 3 populated cable segments, that is, segments attached to
two or more PCs (coax networks only).*
* The remaining two segments are unpopulated; these are known as
inter-repeater links or IRLs. This distinction between populated and
unpopulated segments is significant for coax networks only.
Maximum Cable Length
Cable Type Maximum Length
Twisted Pair, Categories 3, 4, 5 100 m (328 ft.)
Thin Coax 185 m (607 ft.)
External Transceiver Drop 50 m (165 ft.)
Application Notes
1. Full-duplex operation only applies to point-to-point access,
such as when a switch is attached to a workstation, server or
another switch.
2. For network applications that actually require routing, such as
when interconnecting dissimilar network types or distinct
VLANs, you may have to attach the TigerSwtich 1000 directly
to a router or Layer 3 switch.
2-6
Page 29

C
HAPTER
I
NSTALLING THE
S
Selecting a Site
TigerSwitch 1000 units can be mounted in a standard 19-inch
equipment rack or on a flat surface. Be sure to follow the
guidelines below when choosing a location.
◆ The site should:
• be at the center of all the devices you want to link and near
a power outlet.
• be able to maintain its temperature within 0° to 50° C and
its humidity within 5% to 95%, non-condensing
• provide adequate space (approximately two inches) on all
sides for proper air flow
• be accessible for installing, cabling and maintaining the
devices
3
WITCH
• allow the status LEDs to be clearly visible
◆ Make sure twisted-pair cable is always routed away from power
lines, fluorescent lighting fixtures and other sources of electrical
interference, such as radios, transmitters, etc.
◆ Make sure that a separate grounded power outlet that provides
100 to 240 VAC, 50 to 60 Hz, is within 8 feet (2.44 m) of each
device and is powered from an independent circuit breaker. As
with any equipment, using a filter or surge suppressor is
recommended.
3-1
Page 30

I
NSTALLING THE SWITCH
Equipment Checklist
After unpacking the TigerSwitch 1000, check the contents to be
sure you have received all the components. Then, before
beginning the installation, be sure you have all other necessary
installation equipment.
Package Contents
◆ TigerSwitch 1000 (SMC8606SX) unit
◆ Four adhesive foot pads
◆ Bracket Mounting Kit containing two brackets and four screws
for attaching the brackets to the switch
◆ Power Cord—either US, Continental Europe or UK
◆ This Installation Guide
◆ Management Guide
◆ SMC Warranty Registration Card—be sure to complete and
return to SMC
Optional Rack-Mounting Equipment
If you plan to rack-mount the switch, be sure to have the
following equipment available:
◆ Four mounting screws for each device you plan to install in a
rack—these are not included
◆ A screwdriver (Phillips or flathead, depending on the type of
screws used)
3-2
Page 31

I
NSTALLING THE SWITCH
Mounting
A TigerSwitch 1000 unit can be mounted in a standard 19-inch
equipment rack or on a desktop or shelf. Mounting instructions for
each type of site follow.
Rack Mounting
Before rack mounting the switch, pay particular attention to the
following factors:
◆ Temperature: Since the temperature within a rack assembly
may be higher than the ambient room temperature, check that
the rack-environment temperature is within the specified
operating temperature range. (See Appendix C)
◆ Mechanical Loading: Do not place any equipment on top of a
rack-mounted unit
◆ Circuit Overloading: Be sure that the supply circuit to the rack
assembly is not overloaded.
◆ Grounding: Rack-mounted equipment should be properly
grounded. Particular attention should be given to supply
connections other than direct connections to the mains.
To rack-mount devices:
1. Attach the brackets to the device using the screws provided in
the Bracket Mounting Kit.
3-3
Page 32

I
NSTALLING THE SWITCH
Figure 3-1. Attaching the Brackets
2. Mount the device in the rack, using four rack-mounting screws
(not provided).
Figure 3-2. Installing the Switch in a Rack
3. If installing a single switch only, turn to “Connecting to a
Power Source” at the end of this chapter.
3-4
Page 33

I
NSTALLING THE SWITCH
4. If installing multiple switches, mount them in the rack, one
below the other, in any order.
5. If also installing RPUs, mount them in the rack below the other
devices.
Desktop or Shelf Mounting
1. Attach the four adhesive feet to the bottom of the first switch.
Figure 3-3. Attaching the Adhesive Feet
2. Set the device on a flat surface near an AC power source,
making sure there are at least two inches of space on all sides
for proper air flow.
3. If installing a single switch only, go to “Connecting to a Power
Source” at the end of this chapter.
4. If installing multiple switches, attach four adhesive feet to each
one. Place each device squarely on top of the one below, in
any order.
5. If also installing RPUs, place them close to the stack.
3-5
Page 34

I
NSTALLING THE SWITCH
Installing a GBIC Transceiver
The two slots on the switch front panel are for installing optional
GBIC transceivers. The GBIC slots support the following
transceivers:
◆ 1000BASE-SX
◆ 1000BASE-LX
The 1000BASE-SX GBIC transceivers provide one short-wavelength
(850 nm) Gigabit port that can be used for a high-speed backbone or
server connection. This port can be connected to a site up to 550 m
(1805 ft) away with multimode fiber cable.
The 1000BASE-LX GBIC transceivers provide one RJ-45
twisted-pair Gigabit port that can be used for a high-speed
backbone or server connection. This port can be connected to a
site up to 5 km (16404 ft) away with single-mode fiber cable.
Caution: Install only 5 V GBIC transceivers into the GBIC slots.
You can install a GBIC transceiver as described below:
1. Insert the tranceiver with the media connector facing out
toward you. Note that the transceiver is keyed so that it can
only be installed in one orientation.
2. Press in on the transceiver’s side tabs, and gently slide it into the
GBIC interface slot until it clicks into place.
Note: GBIC transceivers are hot-swappable. You do not need to
power off the switch before installing or removing a
transceiver.
3-6
Page 35

I
NSTALLING THE SWITCH
Connecting to a Power Source
To connect a device to a power source:
1. Insert the power cable plug directly into the receptacle located at
the back of the device.
Figure 3-4. Power Receptacle
2. Plug the other end of the cable into a grounded, 3-pin socket.
Note: For International use, you may need to change the AC line
cord. You must use a line cord set that has been approved for
the receptacle type in your country.
3. Check the front-panel LEDs as the device is powered on to be
sure the Power LED is lit. If not, check that the power cable is
correctly plugged in.
4. If you have a purchased Redundant Power Unit, connect it to the
device and to an AC power source now, following the
instructions included with the package.
3-7
Page 36

I
NSTALLING THE SWITCH
3-8
Page 37

C
HAPTER
M
AKING
C
Connecting Network Devices
The TigerSwitch 1000 is designed to connect to IEEE 802.3z
compliant devices. For most applications, the TigerSwitch 1000
would be connected to other switches in the network backbone. It
may also be connected directly to Gigabit Ethernet network cards
in PCs and servers.
N
ETWORK
ONNECTIONS
4
4-1
Page 38

M
AKING NETWORK CONNECTIONS
Connecting to an SC-Type Fiber Port
When connecting fiber cable to a 1000BASE-SX or 1000BASE-LX
(GBIC) port on the switch, be sure you use an SC-type connector.
Follow the steps below.
Warning: This switch uses lasers to transmit signals over fiber optic
cable. The lasers are compliant with the requirements of a
Class 1 Laser Product and are inherently eye safe in normal
operation. However, you should never look directly at a
transmit port when it is powered on.
1. Remove and keep the SC port’s rubber cover. When not
connected to a fiber cable, the rubber cover should be replaced to
protect the optics.
2. Check that the fiber terminators are clean. You can clean the
cable plugs by wiping them gently with a clean tissue or cotton
ball moistened with a little ethanol. Dirty fiber terminators on
fiber optic cables will impair the quality of the light transmitted
through the cable and lead to degraded performance on the port.
3. Connect one end of the cable to the SC port on the switch and the
other end to the SC port on the other device. Since SC connectors
are keyed, the cable can be attached in only one orientation.
When inserting the cable, be sure the tab on the plug clicks into
position to ensure that it is properly seated.
All the SC-type ports operate at 1000 Mbps with support for
auto-negotiation of duplex mode (full/half) and flow control. Also
note the maximum length for 1000BASE-SX and 1000BASE-LX fiber
optic cable depends on the core size and the rating of the cable, as
shown in the following table.
4-2
Page 39

M
AKING NETWORK CONNECTIONS
Maximum 1000BASE-SX Gigabit Ethernet Cable Length
Fiber Size Fiber Bandwidth Maximum Cable Length
62.5/125 micron 160 MHz/km 2-220 m (7-722 ft)
200 MHz/km 2-275 m (7-902 ft)
50/125 micron 400 MHz/km 2-500 m (7-1641 ft)
500 MHz/km 2-550 m (7-1805 ft)
Maximum 1000BASE-LX Gigabit Ethernet Cable Length
Fiber Size Fiber Bandwidth Maximum Cable Length
9/125 micron N/A 2 m - 5 km (7 - 16404 ft)
4-3
Page 40

M
AKING NETWORK CONNECTIONS
4-4
Page 41

A
PPENDIX
T
ROUBLESHOOTING
A
Diagnosing Switch Indicators
Troubleshooting Chart
Symptom Action
Power LED is Off • Internal or redundant power supply has failed or
is disconnected.
• Check connections between the switch, the
power cord, the wall outlet, and the RPU if you
are using one.
• Contact SMC Technical Support.
Link LED is Off • Verify that the switch and attached device are
powered on.
• Be sure the cable is plugged into both the switch
and corresponding device.
• Verify that the proper cable type is used and its
length does not exceed specified limits.
• Check the adapter on the attached device and
cable connections for possible defects. Replace
the defective adapter or cable if necessary.
Power and Cooling Problems
If the power indicator does not turn on when the power cord is
plugged in, you may have a problem with the power outlet, power
cord, or internal power supply. However, if the unit powers off
after running for a while, check for loose power connections,
power losses or surges at the power outlet, and verify that the fans
A-1
Page 42

T
ROUBLESHOOTING
on the unit are unobstructed and running prior to shutdown. If
you still cannot isolate the problem, then the internal power
supply may be defective. In this case, contact SMC Technical
Support for assistance.
Installation
Verify that all system components have been properly installed. If
one or more components appear to be malfunctioning (such as the
power cord or network cabling), test them in an alternate
environment where you are sure that all the other components are
functioning properly.
In-Band Access
You can access the management agent in the switch from
anywhere within the attached network using Telnet, a Web
browser, or other network mangement software such as EliteView.
However, you must first configure the switch with a valid IP
address, subnet mask, and default gateway. If you have trouble
establishing a link to the management agent, check to see if you
have a valid network connection. Then verify that you entered the
correct IP address. Also, be sure the port through which you are
connecting to the switch has not been disabled. If it has not been
disabled, then check the network cabling that runs between your
remote location and the switch.
Note: You can configure the management agent to accept from
one to four simultaneous Telnet sessions. If the maximum
number of sessions already exists, an additional Telnet
connection will not be able to log into the system.
A-2
Page 43

A
PPENDIX
C
Specifications
Cable Types and Specifications
Cable Type Max. Length Connector
1000BASE-T Cat. 5, 5e 100-ohm UTP 100 m (328 ft) RJ-45
Maximum 1000BASE-SX Gigabit Ethernet Cable Length
Fiber Size Fiber Bandwidth Maximum Cable Length
62.5/125 micron 160 MHz/km 2-220 m (7-722 ft)
200 MHz/km 2-275 m (7-902 ft)
50/125 micron 400 MHz/km 2-500 m (7-1641 ft)
500 MHz/km 2-550 m (7-1805 ft)
Maximum 1000BASE-LX Gigabit Ethernet Cable Length
Fiber Size Fiber Bandwidth Maximum Cable Length
9/125 micron N/A 2 m - 5 km (7 - 16404 ft)
B
ABLES
B-1
Page 44

C
ABLES
Console Port Pin Assignments
The DB-9 se rial por t on the swi tch’s rear panel is used to connect to
the switch for out-of-band console configuration. The on-board
menu-driven configuration program can be accessed from a terminal
or a PC running a terminal emulation program. The pin assignments
used to connect to the serial port are provided in the following tables.
Figure B-1. DB-9 Console Port Pin Numbers
DB-9 Port Pin Assignments
EIA
Circuit
CF 109 DCD (Data Carrier Detected) 1 1 <-----BB 104 RxD (Received Data) 2 2 <-----BA 103 TxD (Transmitted Data) 3 3 ------>
CD 108.2 DTR (Data Terminal Ready) 4 4 ------>
AB 102 SG (Signal Ground) 5 5 ------CC 107 DSR (Data Set Ready) 6 6 <-----CA 105 RTS (Request-to-Send) 7 7 ------>
CB 106 CTS (Clear-to-Send) 8 8 <-----CE 125 RI (Ring Indicator) 9 9 <------
CCITT
Signal
Description Switch’s
DB9 DTE
Pin #
PC DB9
DTE
Pin #
Signal
Direction
DTE-DCE
B-2
Page 45

Console Port to 9-Pin COM Port on PC
Switch’s 9-Pin
Serial Port
1 DCD ----------- DCD ------------ 1
2 RXD <--------- TXD ------------ 3
3 TXD ----------- RXD ----------> 2
4 DTR ----------- DSR ----------> 6
5 SGND ----------- SGND ---------- 5
6 DSR ----------- DTR ------------ 4
7 RTS ----------- CTS -----------> 8
8 CTS <--------- RTS ------------- 7
9 RI ----------- RI --------------- 9
CCITT Signal PC’s 9-Pin
Console Port to 25-Pin DTE Port on PC
COM Port
C
ABLES
Switch’s 9-Pin
Serial Port
1 DCD 8 DCD
2 RXD 3 TXD
3 TXD 2 RXD
4 DTR 20 DTR
5 SGND 7 SGND
6 DSR 6 DSR
7 RTS 4 RTS
8 CTS 5 CTS
9 RI 22 RI
Null Modem PC’s 25-Pin
DTE Port
11
23
32
48
520
67
74
95
20 6
B-3
Page 46

C
ABLES
B-4
Page 47

A
PPENDIX
S
PECIFICATIONS
Physical Characteristics
Ports
6 1000BASE-SX ports
2 GBIC slots
Network Interface
SC connector, multimode fiber cable; 62.5/125 or 50/125 microns
Buffer Architecture
2 Mbytes per port
Aggregate Bandwidth
16 Gbps
Switching Database
12K MAC address entries
C
LEDs
System: Power, RPU, Diag
Port: Link, ACT, FDX
Weight
10.14 lbs (4.6 kg)
Size
17.37 x 11.22 x 1.699 in (44.0 x 28.5 x 4.3 cm)
Temperature
Operating: 32 to 122
Storage: -40 to 158°F (-40 to 70°C)
°F (0 to 50°C)
C-1
Page 48

S
PECIFICATIONS
Humidity
Operating: 5% to 95%
Power Supply
Internal, auto-ranging transformer: 100 to 240 VAC, 50 to 60 Hz
Redundant DC input
Power Consumption
70 Watts maximum
Heat Dissipation
239 BTU/hr maximum
Maximum Current
0.5A @ 110VAC
0.7A @ 240VAC
Switch Features
Spanning Tree Protocol
Broadcast Storm Suppression
Forwarding Mode
Store-and-forward
Flow Control
IEEE 802.3x
VLAN Support
Up to 256 groups; port-based or with IEEE 802.1Q VLAN tagging
Quality of Service
Supports two priority queues with Weighted Fair Queueing
C-2
Page 49

Management Features
In-Band Management
Telnet, Web-based HTTP, or SNMP manager
Out-of-Band Management
RS-232 DB-9 console port
Software Loading
TFTP in-band or XModem out-of-band
MIB Support
MIB II (RFC 1213), Bridge MIB (RFC 1493), Ethernet-Like MIB (RFC
1643), RMON MIB (RFC 1757), SMC’s private MIB
RMON Support
Groups 1, 2, 3, 9 (Statistics, History, Alarm, Event)
Additional Features
Port Mirroring
Port Trunking
IGMP Snooping and Multicast Filtering
S
PECIFICATIONS
Standards
IEEE 802.3z Gigabit Ethernet
IEEE 802.3ab Gigabit Ethernet
IEEE 802.1D Spanning Tree Protocol
IEEE 802.1p priority tags
IEEE 802.1Q VLANs
IEEE 802.3ac VLAN tagging
IEEE 802.3x full-duplex flow control
ISO/IEC 8802-3
SNMP (RFC 1157), RMON (RFC 1757), ARP (RFC 826), IGMP (RFC
1112), MIB II (RFC 1213), Ethernet-Like MIB (RFC 1643), Bridge
MIB (RFC 1493)
C-3
Page 50

S
PECIFICATIONS
Compliances
CE Mark
Emissions
FCC Class A
Industry Canada Class A
EN55022 (CISPR 22) Class A
VCCI Class A
EN 61000-3-2/3
C-Tick - AS/NZS 3548 (1995) Class A
Immunity
EN 61000-4-2/3/4/6/8/10/11
Safety
CSA/NRTL (UL1950, CSA 22.2.950)
TUV/GS(EN60950)
Warranty
Limited lifetime
C-4
Page 51

A
PPENDIX
O
RDERING INFORMATION
TigerSwitch 1000 Products and Accessories
Product Number Description
SMC8606SX 6-port Gigabit Ethernet switch with two
SMCRPU150W* Redundant Power Unit with cables,
* Also available in models for Continental Europe and the UK.
GBIC slots
supports one device
A
A-1
Page 52

O
RDERING INFORMATION
A-2
Page 53

G
LOSSARY
10BASE-T
IEEE 802.3 specification for 10 Mbps Ethernet over two pairs of
Category 3, 4, or 5 UTP cable..
100BASE-TX
IEEE 802.3u specification for 100 Mbps Fast Ethernet over two
pairs of Category 5 UTP cable.
1000BASE-T
IEEE 802.3ab specification for Gigabit Ethernet over two pairs of
Category 5, 5e 100-ohm UTP cable.
Auto-Negotiation
Signalling method allowing each node to select its optimum
operational mode (e.g., 10 Mbps or 100 Mbps and half or full
duplex) based on the capabilities of the node to which it is
connected.
Bandwidth
The difference between the highest and lowest frequencies
available for network signals. Also synonymous with wire speed,
the actual speed of the data transmission along the cable.
Glossary-1
Page 54

G
LOSSARY
Class I Repeater
Fast Ethernet repeater that is principally used to connect different
physical signaling systems (e.g., 100BASE-TX, 100BASE-FX) and
that has an internal delay such that only one repeater of this type
can reside within a single collision domain when maximum cable
lengths are used.
Class II Repeater
Fast Ethernet repeater that typically supports a single physical
signaling system (e.g., 100BASE-TX, or 100BASE-FX) and that has a
smaller internal delay so that two such repeaters can reside within
a single collision domain when maximum cable lengths are used.
Collision
A condition in which packets transmitted over the cable interfere
with each other. Their interference makes both signals
unintelligible.
Collision Domain
Single CSMA/CD LAN segment.
CSMA/CD
Carrier Sense Multiple Access/Collision Detect is the
communication method employed by Ethernet and Fast Ethernet.
Crossover Port
Twisted-pair port with a built-in wiring crossover.
End Station
A workstation, server, or other device that does not act as a
network interconnection.
Glossary-2
Page 55

Ethernet
A network communication system developed and standardized by
DEC, Intel, and Xerox, using baseband transmission, CSMA/CD
access, logical bus topology, and coaxial cable. The successor IEEE
802.3 standard provides for integration into the OSI model and
extends the physical layer and media with repeaters and
implementations that operate on fiber, thin coax and twisted-pair
cable.
Fast Ethernet
A 100 Mbps network communication system based on Ethernet
and the CSMA/CD access method.
Fast Ethernet Switch
Device that provides a full 100 Mbps bandwidth (or either 10 or
100 Mbps bandwidth with auto-negotiation) to each port
(LAN segment).
Full Duplex
Transmission method that allows switch and network card to
transmit and receive concurrently, effectively doubling the
bandwidth of that link.
G
LOSSARY
Gigabit Ethernet
A 1000 Mbps network communication system based on Ethernet
and the CSMA/CD access method.
IEEE 802.3
Defines carrier sense multiple access with collision detection
(CSMA/CD) access method and physical layer specifications.
IEEE 802.3ac
Defines frame extensions for VLAN tagging.
Glossary-3
Page 56

G
LOSSARY
IEEE 802.3u
Defines CSMA/CD access method and physical layer specifications
for 100BASE-TX Fast Ethernet.
IEEE 802.3x
Defines Ethernet frame start/stop requests and timers used for
flow control on full-duplex links.
IEEE 802.3z
Defines CSMA/CD access method and physical layer specifications
for 1000BASE Gigabit Ethernet.
IGMP Snooping
Listening to IGMP Query and IGMP Report packets transferred
between IP Multicast Routers and IP Multicast host groups to
indentify IP Multicast group members.
LAN Segment
Separate LAN or collision domain.
Layer 3
Network layer in the ISO 7-Layer Data Communications Protocol.
This layer handles the routing functions for data moving from one
open system to another.
LED
Light emitting diode used for monitoring a device or network
condition.
Link Segment
Length of twisted-pair or fiber cable joining a pair of repeaters or a
repeater and a PC.
Glossary-4
Page 57

Local Area Network (LAN)
A group of interconnected computer and support devices.
Media Access Control (MAC)
A portion of the networking protocol that governs access to the
transmission medium, facilitating the exchange of data between
network nodes.
MIB
An acronym for Management Information Base. It is a set of
database objects that contains information about the device.
MII
Media Independent Interface, the standard interface for Fast
Ethernet—similar to the AUI interface for traditional Ethernet.
Network Diameter
Wire distance between two end stations in the same collision
domain.
G
LOSSARY
RJ-45 Connector
A connector for twisted-pair wiring.
Redundant Power Supply (RPS)
A backup power supply that automatically takes over in case the
primary power supply should fail.
Remote Monitoring (RMON)
RMON provides comprehensive network monitoring capabilities. It
eliminates the polling required in standard SNMP, and can set
alarms on a variety of traffic conditions, including specific errors
types.
Glossary-5
Page 58

G
LOSSARY
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
An application protocol offering network management services in
the Internet suite of protocols.
Spanning Tree Algorithm (STA)
A technology that checks your network for any loops. A loop can
often occur in complicated network systems or systems with
redundant links. Spanning-tree detects and directs data along the
shortest path, maximizing the performance and efficiency of the
network.
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
See Spanning Tree Algorithm.
Straight-through Port
An RJ-45 port which does not cross the receive and transmit
signals internally so it can be connected with straight-through
twisted-pair cable to any device having a crossover port. Also
referred to as a “Daisy-Chain” port.
Switched Ports
Ports that are on separate collision domains or LAN segments.
Telnet
Defines a remote communication facility for interfacing to a
terminal device over TCP/IP.
Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)
Protocol suite that includes TCP as the primary transport protocol,
and IP as the network layer protocol.
UTP
Unshielded twisted-pair cable.
Glossary-6
Page 59

Virtual LAN (VLAN)
A Virtual LAN is a collection of network nodes that share the same
collision domain regardless of their physical location or connection
point in the network. A VLAN serves as a logical workgroup with
no physical barriers, allowing users to share information and
resources as though located on the same LAN.
G
LOSSARY
Glossary-7
Page 60

G
LOSSARY
Glossary-8
Page 61

I
NDEX
Numerics
10 Mbps connectivity rules 2-6
100 Mbps connectivity rules 2-5
1000BASE-LX
fiber cable lengths 2-4
1000BASE-SX
fiber cable lengths 2-4
1000BASE-SX connections 4-2
1000BASE-SX ports 1-2
A
accessories, ordering D-1
address table size B-1
adhesive feet, attaching 3-5
air flow requirements 3-1
applications
backbone consolidation 2-2
VLAN connections 2-3
B
brackets, attaching 3-4
broadcast storm control 1-4
buffer size B-1
contents of package 3-2
cooling problems A-1
cord sets, international 3-7
D
DC input 1-6
desktop mounting 3-5
device connections 4-1
E
E1-2
EC conformance i
electrical interference, avoiding 3-1
EMC/safety compliance i
equipment checklist 3-2
Ethernet connectivity rules 2-6
, ii
F
Fast Ethernet connectivity rules 2-5
fault tolerance, Spanning Tree 1-5
FCC compliance i
features of switch 1-7
front panel of switch 1-2
full-duplex connectivity 2-1
C
cable
lengths 2-4
CE Mark i
compliances i
connectivity rules
10 Mbps 2-6
100 Mbps 2-5
1000 Mbps 2-4
console port 1-4
console port pin assignments B-2
, ii
G
Gigabit Ethernet cable lengths 2-4
grounding for racks 3-3
I
IEEE 802.3z devices, conecting to 4-1
IEEE 802.3z Gigabit Ethernet 1-7
indicators, LED 1-3
installation
Index-1
Page 62

I
NDEX
desktop or shelf mounting 3-5
port connections 4-2
power requirements 3-1
problems A-2
rack mounting 3-3
RPUs in racks 3-5
site requirements 3-1
L
laser safety iv, 4-2
LED indicators
ACT 1-4
Power 1-3
problems A-1
limited warranty B-4
location requirements 3-1
M
management
features 1-8
out-of-band 1-4
SNMP 1-4
Telnet 1-5
Web-based 1-4
managment agent 1-4
MIB support B-3
mounting the switch
in a rack 3-3
on a desktop or shelf 3-5
multicast switching
IGMP 1-6
IGMP Snooping 1-6
, B-3
N
network connections 4-2
network examples 2-2
null-modem cable 1-4
O
ordering information D-1
out-of-band management 1-4
P
package contents 3-2
pin assignments, console port B-2
port saturation 1-4
port-based VLANs 2-3
ports, connecting to 4-2
power, connecting to 3-7
priority queues 1-6
problems, troubleshooting A-1
Q
QoS 1-4
R
rack mounting 3-3
rear panel of switch 1-2
rear panel receptacles 1-6
redundant power unit (RPU) 1-6
regulatory compliance
BSMI compliance iii
RMON 1-4
routing applications 2-6
RPUs
connecting 3-7
installing in a rack 3-5
installing on a desktop 3-5
RS-232 serial port 1-4
rubber foot pads, attaching 3-5
S
safety compliance iv
Index-2
Page 63

I
NDEX
sample applications 2-2
screws for rack mounting 3-2
serial port 1-4
site selelction 3-1
SNMP agent 1-4
Spanning Tree Protocol 1-5
specifications
compliances B-4
environmental B-1
physical B-1
power B-2
standards compliance i
standards, IEEE B-3
status LEDs 1-3
surge suppressor, using 3-1
switching, introduction to 2-1
, 2-3
, B-4
T
tagging, VLAN 2-3
tags, priority 1-6
Telnet 1-5, A-2
temperature within a rack 3-3
traffic priority 1-6
troubleshooting
in-band access A-2
power and cooling problems A-1
switch indicators A-1
W
warranty B-4
Web-based management 1-4
Weighted Fair Queuing 1-6
U
UL compliance iv
V
VCCI compliance i
VLAN tagging 2-3
VLANs 1-4
, 1-5, 2-3
Index-3
Page 64

I
NDEX
Index-4
Page 65

Page 66

FOR TECHNICAL SUPPORT, CALL:
From U.S.A. and Canada (24 hours, 7 days a week)
(800) SMC-4-YOU; (949) 707-2400; (949) 707-2460 (Fax)
From Europe (8:00 AM - 5:30 PM UK Greenwich Mean Time)
44 (0) 1188 748740; 44 (0) 1189 748741 (Fax)
INTERNET
E-mail addresses:
techsupport@smc.com
european.techsupport@smc-europe.com
Driver updates:
http://www.smc.com/support.html
World Wide Web:
http://www.smc.com/
FOR LITERATURE OR ADVERTISING RESPONSE, CALL:
U.S.A. and Canada: (800) SMC-4-YOU; Fax (949) 707-2460
Spain: 34-93-477-4920; Fax 34-93-477-3774
UK: 44 (0) 1188 748700; Fax 44 (0) 1189 748701
Southern Europe: 33 (1) 41.38.32.32; Fax 33 (1) 41.38.01.58
Central/Eastern Europe: 49 (0) 89 92861-200; Fax 49 (0) 89 92861-230
Nordic: 46 (8) 564 33145; Fax 46 (8) 87 62 62
Middle East: 971-48818410; Fax 971-48817993
South Africa: 27 (0) 11-3936491; Fax 27 (0) 11-3936491
PRC: 86-10-6235-4958; Fax 86-10-6235-4962
Taiwan: 886-2-2659-9669; Fax 886-2-2659-9666
Asia Pacific: (65) 238 6556; Fax (65) 238 6466
Korea: 82-2-553-0860; Fax 82-2-553-7202
Japan: 81-45-224-2332; Fax 81-45-224-2331
Australia: 61-2-9416-0437; Fax 61-2-9416-0474
India: 91-22-8204437; Fax 91-22-8204443
6 Hughes
Irvine, CA 92618
Phone: (949) 707-2400
Model Number: SMC8606SX
Publication Number: 150200001900A E102001-R01
 Loading...
Loading...