
/ GATEWAY USER MANUAL
For all Broadcom Chipset-based models including:
ADSL 3xx series
VDSL 5xx series
Release 3.5
June 2016

Table of Contents
Table of Contents 1
Disclaimer 3
Copyright and Trademarks 3
FCC Interference Statement 3
FCC Caution 3
Safety Warnings 4
Welcome! 5
Purpose & Scope 5
Intended Audience 5
Getting Assistance 5
GETTING FAMILIAR WITH YOUR GATEWAY 6
LED Status Indicators 6
Connections 6
External Buttons 8
Installing your SmartRG Gateway 9
Logging in to your SmartRG Gateway's UI 9
Device Info 11
Summary 11
WAN 12
Statistics 14
Statistics - WAN Page for SR515ac Gateway 16
References 21
Route 21
ARP 22
DHCP 23
ADVANCED SETUP 24
Layer2 Interface 24
WAN Service 30
Ethernet Config 44
MoCA 45
LAN 47
NAT 50
Security 55
Add a MAC Filtering Rule 59
Parental Control 60
Quality Of Service 62
Supported DSCP Values 64
Routing 73
DNS 77
DSL 81
DSL Bonding 84
UPnP 86
DNS Proxy 87
Interface Grouping 88
IP Tunnel 89
IPSec 92
Certificate 94
Multicast 98
WIRELESS 100
Basic 100
Security 103
MAC Filter 112
Wireless Bridge 113
Advanced 114
Station Info 118
DIAGNOSTICS 118
Diagnostics 118
Fault Management 119
Ethernet OAM 120
Ping 122
Trace Route to Host 122
Management 123
Settings 123
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016 1

System Log 127
Security Log 129
SNMP Agent 130
Management Server 131
Internet Time 136
Access Control 137
Add an Account 137
Modify or Delete an Account 138
Default Passwords 140
Update Software 144
Reboot 144
APPENDIX A: ADVANCED FEATURES 146
Connect-and-Surf (Automatic Broadband Connection Configuration) 146
Activation (Automatic ACS Connection Configuration) 146
TR-069 Remote Management: ACS Support 146
APPENDIX B: FEATURE COMPARISON MATRIX 148
Q&A 150
REVISION HISTORY 150
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016 2

Disclaimer
SmartRG does not assume any liability arising out of the application or use of any products, or software described herein. Neither does
it convey any license under its patent rights nor patent rights of others. SmartRG further reserves the right to make changes to any
products described herein without notice. This publication is subject to change without notice.
Any trademarks mentioned in this publication are used for identification purposes only and may be properties of their respective owners.
Copyright and Trademarks
Copyright © 2016 by SmartRG, Inc.
The contents of this publication may not be reproduced in any part or as a whole, transcribed, stored in a retrieval system, translated
into any language, or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, magnetic, optical, chemical, photocopying,
manual, or otherwise, without the prior written permission of SmartRG, Inc.
Published by SmartRG, Inc. All rights reserved.
FCC Interference Statement
This device complies with Part 15 of the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions:
l This device may not cause harmful interference.
l This device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the FCC Rules.
These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation.
If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment
off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
l Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
l Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
l Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is connected.
l Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
This Class B digital apparatus complies with Canadian ICES-003.
Cet appareil numrique de la classe B est conforme à la norme NMB-003 du Canada.
FCC Caution
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
3

Any changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for compliance could void the user's authority to operate
this equipment.
IMPORTANT NOTE: FCC Radiation Exposure Statement:
l This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure limits set forth for an uncontrolled environment.
l This equipment should be installed an operated with a minimum distance of 20cm between the radiator and your body.
l This transmitter must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any other antenna or transmitter.
Safety Warnings
For your safety, be sure to read and follow all warning notices and instructions.
l To reduce the risk of fire, use only No. 26 AWG (American Wire Gauge) or larger telecommunication line cord.
l Do NOT open the device or unit. Opening or removing covers can expose you to dangerous high voltage points or other risks.
ONLY qualified service personnel can service the device. Please contact your vendor for further information.
l Use ONLY the dedicated power supply for your device. Connect the power cord or power adapter to the correct supply voltage
(110V AC in North America or 230V AC in Europe).
l Do NOT use the device if the power supply is damaged as it might cause electrocution.
l If the power supply is damaged, remove it from the power outlet.
l Do NOT attempt to repair the power supply. Contact your local vendor to order a new power supply.
l Place connecting cables carefully so that no one will step on them or stumble over them. Do NOT allow anything to rest on the
power cord and do NOT locate the product where anyone can walk on the power cord.
l If you wall mount your device, make sure that no electrical, gas, or water pipes will be damaged.
l Do NOT install nor use your device during a thunderstorm. There may be a remote risk of electric shock from lightning.
l Do NOT expose your device to dampness, dust, or corrosive liquids.
l Do NOT use this product near water, for example, in a wet basement or near a swimming pool.
l Make sure to connect the cables to the correct ports.
l Do NOT obstruct the device ventilation slots, as insufficient airflow may harm your device.
l Do NOT store things on the device.
l Connect ONLY suitable accessories to the device.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
4

Welcome!
Thank you for purchasing this SmartRG product.
SmartRG proudly brings you the best, most innovative broadband gateways available. SmartRG enables service providers to monitor,
manage, and monetize the connected home through the design and production of reliable and highly interoperable hardware and software solutions.
As an early innovator in TR-069 remote management technology, SmartRG offers the finest in managed broadband and home networking solutions. Our products leverage various broadband access technologies and are outfitted with highly customizable software,
meeting diverse service provider requirements. Based in the USA, SmartRG provides local, proactive software development and customer support. In the rapidly evolving broadband market, SmartRG helps service providers keep their businesses on the cutting edge
through its laser-focused product line, leveraging the very latest in broadband access and home networking technologies. SmartRG solutions enable service providers to improve their bottom line by reducing service costs and increasing customer satisfaction.
Learn more at www.SmartRG.com.
Purpose & Scope
The purpose and scope of this document is to provide SmartRG customers with installation, configuration and monitoring information
for the SR300x and SR500x CPE platforms.
Intended Audience
The information in this document is intended for Network Architects, NOC Administrators, Field Service Technicians, and other networking professionals responsible for deploying and managing broadband access networks. Readers of this manual are assumed to have
a basic understanding of desktop computer operating systems, networking concepts and telecommunications.
Getting Assistance
Subscribers: If you require help with this product, please contact your service provider.
Service providers: if you require help with this product, please open a support request.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
5
GETTING FAMILIAR WITH YOUR GATEWAY
This section contains a quick description of the Gateway's lights, ports, and buttons. SmartRG produces several models that vary slightly
in capabilities (See Appendix B for details) but the basic scheme of lights, ports and buttons represented in this section exists on each
model.
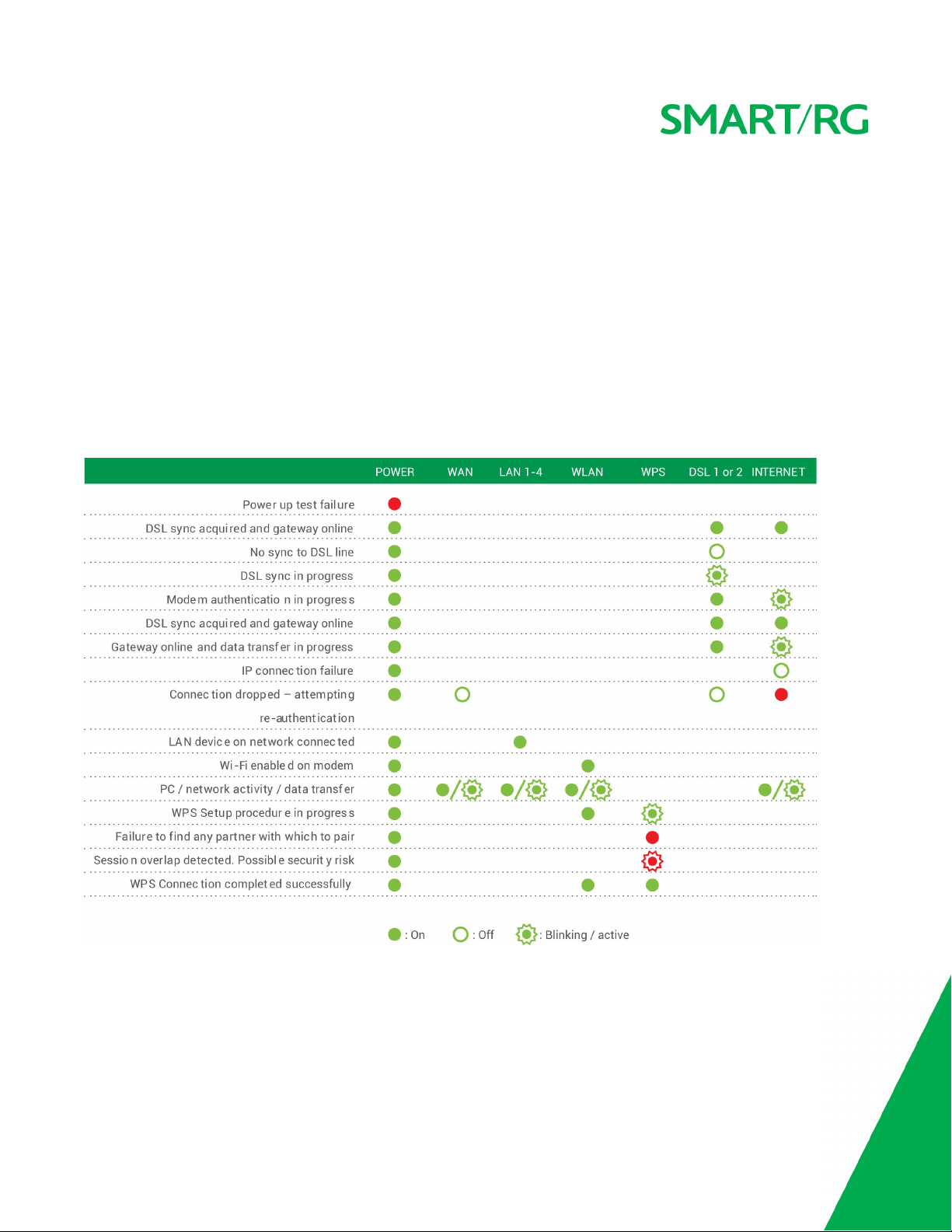
LED Status Indicators
Your SmartRG gateway has several indicator lights (LEDs) on its exterior. The number and type of ports vary from model to model. The
following table illustrates a comprehensive set of LEDs to cover the indicators available on all models.
Connections
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
6
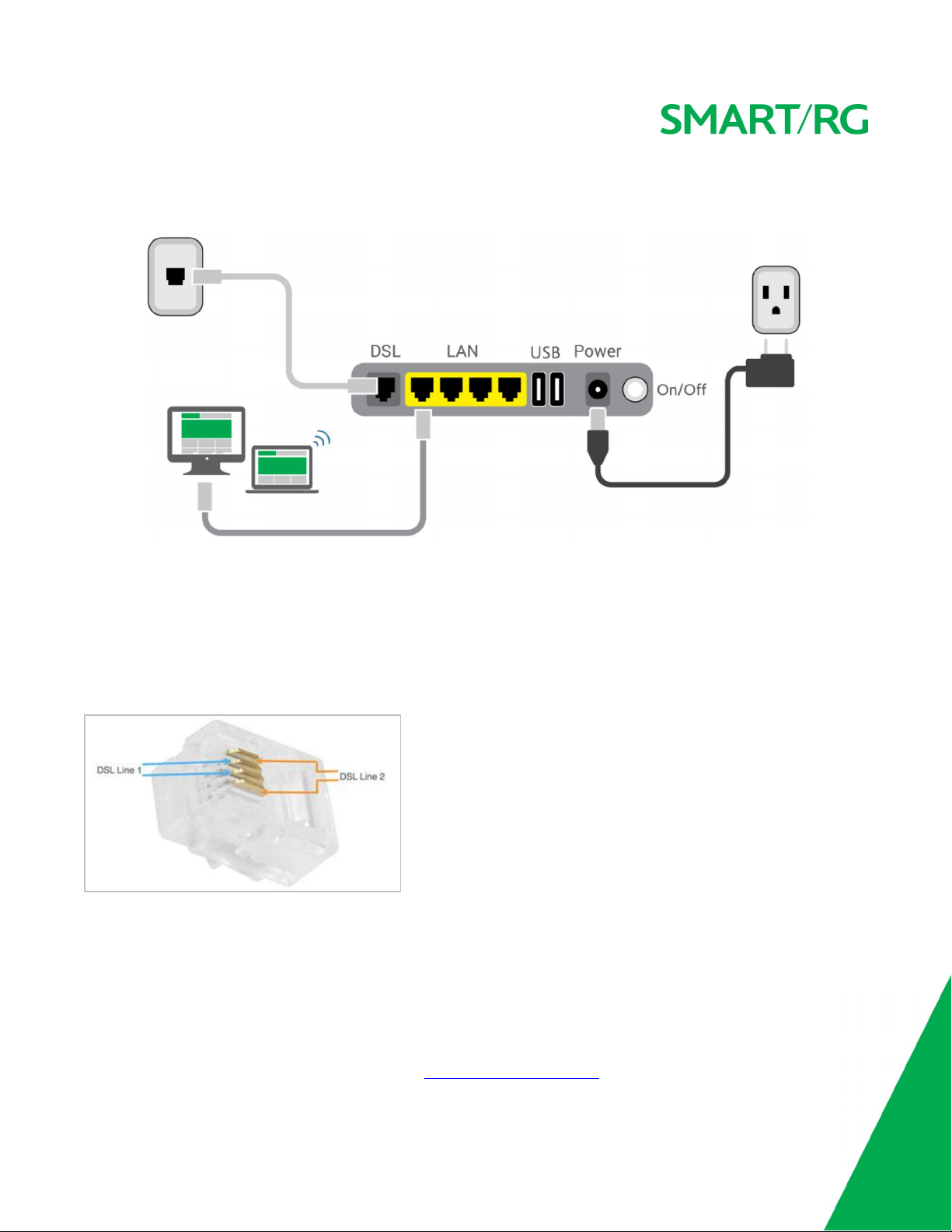
Below is a generic representation of a SmartRG gateway, Your specific model may have more or fewer ports and controls across the
back of the unit. Refer to the Quick Start Guide enclosed with your gateway for specifics regarding installation of your particular model.
The ports depicted in this example are described below.
DSL
The grey RJ12 port labeled DSL is specifically intended for connection to an internet provider via a DSL (Digital Subscriber Line) service.
The center pair carries the first DSL line. For models like the SR550n equipped with two DSL ports and bonded DSL capability, the outer
pair carries the second line.
WAN
A stand-alone RJ45 port labeled WAN enables your SmartRG gateway to be hard-wired to another network device with a RJ45/Ethernet
output such as a cable, fiber, or DSL modem.
For models with a stand-alone, RJ45, WAN port and a DSL port, the WAN port can be re-purposed to function as an additional LAN port
when your internet connection is via DSL.
For instructions to enable this SmartPortTMfeature, see the Ethernet Configuration section in this manual.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
7

LAN
The four (yellow) RJ45 ports across the back of your gateway labeled LAN1, LAN2, LAN3, LAN4 are the means to connect client devices
such as computers and printers to your gateway.
On some models, one of these four ports may be labeled as WAN indicating SmartPortTMsupport. SmartPort allows a LAN port to be repurposed to function as an Ethernet WAN port (described above). When this port is serving as a LAN port, the corresponding LED on the
face of the unit is labeled "WAN"
For instructions to enable this SmartPortTMfeature, see the Ethernet Configuration section in this manual.
USB
USB ports on SmartRG products currently provide +5 DC volts.
POWER
Use only the power supply included with your gateway. Intended for indoor use only.
External Buttons
Smart RG gateways provide push-button controls on the exterior for critical features. These buttons provide a convenient way to trigger
WPS mode, toggle the WiFi radio on and off, or reset the gateway. Their presence and locations vary by model.
The following describes each of these controls.
WPS Button
The WPS button triggers WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup™) mode. WPS is a standard means for creating a secure connection between your
gateway and various wireless client devices. It is designed to simplify the pairing process between devices.
If you have client devices that support WPS, use this button to automatically configure wireless security for your network.
For specific instructions, refer to the Quick Start Guide included with your gateway. Also see the "Basic" section of this manual.
WPS configures one client device at a time. You can repeat the steps as necessary for each additional WPS-compliant device you wish
to connect.
The location of the WPS button varies by model:
l For SR360n models, the button is located on the top of the unit.
l For SR510n, SR550n, SR515ac, and SR552n models, the button is located on the left side of the unit.
For other models, an exterior button is not present. However, WPS is supported via the on-board software.
For specific instructions, refer to the Quick Start Guide included with your gateway.
WiFi or WLAN Button
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
8

The button labeled WiFi or WLAN (depending on model) toggles the WiFi radio on and off. The WLAN LED indicator on the gateway displays the current state of the WiFi radio.
The location of the WLAN button varies by model:
l For SR360n models, the button is located on the top of the unit.
l For SR510n, SR512nm, SR550n, and SR552n models, the button is located on the left side of the unit.
For other models, an exterior button is not present. However, WiFi is supported via the on-board software.
For specific instructions, refer to the Quick Start Guide included with your gateway.
To activate the WiFi radio, press and hold the WiFi (WLAN) button for 3-5 seconds and then release. Expect a 1-3 second delay before
the WiFi (WLAN) LED turns on. Repeat this step to deactivate the WiFi radio.
Reset Button
The Reset button is a small hole in the gateway's enclosure with the actual button mounted behind the surface. This style of push-button
prevents the gateway from being inadvertently reset during handling. Reset must be actuated with a paper clip or similar implement.
The location of the Reset button varies by model:
l For SR5xx and SR630n models, the button is located on the rear of the unit.
l For SR350n models, the button is located on the bottom of the unit.
l For SR360n models, the button is located on the left side of the unit.
This pin-hole sized reset button has three functions. The duration for which the button is held dictates which function is carried out.
Hold Duration Effect
Less than 6 seconds Performs a modem reset that is equivalent to the
6-20 seconds Performs the software equivalent to the
Restore Defaults
Reboot
function in the gateway software.
function in the gateway software.
20 or more seconds Changes the POWER LED to red and the gateway enters CFE mode which is a state associated with performing
firmware updates via Internet browser.
Installing your SmartRG Gateway
The following instructions explain all connection types offered for SmartRG gateways. For instructions specific to your gateway, follow
the instructions in the Quick Start Guide included in the box.
1. Attach your computer's RJ45 connection to any of the SmartRG gateway's LAN ports (1-4).
2. Configure your computer's IP interface to acquire an IP address using DHCP. (For instructions on logging in to a SmartRG gateway configured for "bridge mode"operation, see the Note below.)
Logging in to your SmartRG Gateway's UI
To manually configure the SmartRG Gateway, you can access the gateway's embedded web UI.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
9

1. Open a browser and enter the gateway's default address (usually http://192.168.1.1; may also be http://192.168.0.1) in the
address bar.
2. For some models, the Network status page appears. If so, click the Manage gateway (advanced) link (usually located in the
upper right corner). The Authentication Required dialog box appears.
3. For all models, enter the default username and password (usually: admin/admin) and click Login or OK to display the default
landing page. For many models, this is the Device Info page.
Note: The gateway's UI can be accessed via the WAN connection by entering the WAN IP address in your browser's address bar and
entering the default username and password: support/support. WAN HTTP access control MUST be enabled to access the gateway's UI
via the WAN connection. For more information, see the Management Access Control section.
If your SmartRG gateway is configured for "bridge mode" (modem) operation, your PC will NOT be able to acquire an address via CPE
DHCP. Instead, manually configure your PC's interface with an IP address on the default network (e.g., 192.168.1.100).
The remainder of this guide is dedicated to a sequential walk-through of the gateway user interface. Screen captures are provided along
with descriptions of the options available on the pictured page. Where applicable, valid values are provided.
For in-depth "how-to" information for specific scenarios, look at the knowledge base found on our support web site. Access to this site is
restricted to SmartRG customers and partners. Do not share links to this site with your subscribers.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
10

Device Info
There are several selections under Device Info in the left navigation bar. Each of them shows a different element of the gateway's
setup, status or nature of its connection with the provider and also with LAN devices. Device Info pages are read-only. You cannot interact with or change the settings in this section.
Summary
When you log into the gateway interface, the Device Info is the first page to appear. This page displays details about the hardware and
software associated with your gateway. In addition, the current status of the WAN connection (if present) is shown.
Note: The following variations exist:
l For the SR3xxn models, the Symmetric CPU Threads field and Aggregate Line Rate fields are not applicable.
l For the SR505n and SR510n models, the Aggregate Line Rate fields are not applicable. The B0 Traffic & B1 Traffic fields are
unique to these two models and are not shown below.
l For the SR515ac model, the Traffic Type and Aggregate Line Rate fields are not applicable.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
11

WAN
On this page, you can view information about the connection between your ISP and your gateway. The WAN interface can be DSL or Ethernet and supports a number of Layer 2 and above configuration options (explained later in this document). Some features are supported only on specific SmartRG models. Those exceptions are specified in this guide.
In the left navigation bar, click Device Info > WAN. The following page appears.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
12

The fields on this page are explained in the following table.
Field Name Description
Interface The connection interface (Layer 2 interface) through which the gateway handles the traffic.
Description The service description such ipoe_0_0_1, showing the type of WAN and its ID..
Type The service type. Options are PPPoE, IPoE, and Bridge.
VlanMuxId The VLAN ID. Options are Disabled or 0-4094.
IPv6 The state of IPv6. Options are Enabled and Disabled.
Igmp (Not available on SR515ac gateways) The state of IGMP. Options are Enabled and Disabled.
Igmp Pxy (
Igmp Src Enbl (
Applies to SR515ac gateways only
Applies to SR515ac gateways only
) The IGMP proxy.
) The IGMP source option is enabled for this connection.
MLD (Not available on SR515ac gateways) The state of MLD. Options are Enabled and Disabled.
MLD Pxy (
MLD Src Enbl (
Applies to SR515ac gateways only
Applies to SR515ac gateways only
) The MLD proxy.
) The MLD source option is enabled for this connection.
NAT The state of NAT. Options are Enabled and Disabled.
Firewall The state of the Firewall. Options are Enabled and Disabled.
Status The status of the WAN connection. Options are Disconnected, Unconfigured, Connecting, and
Connected.
IPv4 Address The obtained IPv4 address.
IPv6 Address The obtained IPv6 address.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
13

Statistics
The Statistic pages provide network interface information for LAN, WAN Service, xTM and xDSL. All data is updated in 15-minute intervals.
Notes:
l For SR512nm models, statistics are also provided for MoCA connections.
l For SR515ac models, statistics are also provided for the 2.4 Ghz and 5 Ghz wireless connections.
LAN
On this page, you can view the received and transmitted bytes, packets, errors and drops for each LAN interface configured on your gateway. All local LAN Ethernet ports, Ethernet WAN ports and w10 (Wireless Interface) are included.
In the left navigation bar, click Device Info > Statistics. The Statistics - LAN page appears where you can view detailed information
about the status of your LAN.
To reset the counters, click Reset Statistics near the bottom of the page.
Note: Only the SR360n and SR5xx models support the SmartPort feature where a LAN port can be re-purposed to function as a WAN
port (as shown in the Interface column).
The fields on this page are explained in the following table.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
14

Field Name Description
Interface
Available LAN interfaces. Options are
(Wireless LAN-side interface), and
Received&Transmitted
columns
LAN1-LAN4,WAN
2.4 Gh
z and
5 Ghz
(if configured on your device), and
(SR515ac only).
Wl0
Bytes Total number of packets in bytes.
Pkts Total number of packets.
Errs Total number of error packets.
Drops Total number of dropped packets.
WAN Service
On this page, you can view the received and transmitted bytes, packets, errors and drops for each WAN interface for your SmartRG
Gateway. All WAN interfaces configured for your gateway are included.
In the left navigation bar, click Device Info > Statistics > WAN Service. The Statistics - WAN page appears where you can view detailed
information about the status of your WAN.
To reset the counters, click Reset Statistics near the bottom of the page.
The fields on this page are explained in the following table.
Field Name Description
Interface Available WAN interfaces. Options are:
Description
Service description. Options are:
Received&Transmitted
columns
pppoe,ipoe
Bytes Total quantity of packets in bytes.
Pkts Total quantity of packets.
Errs
Drops
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
Total quantity of error packets.
Total quantity of dropped packets.
atm,ptm
, andb.
, and
eth
.
15
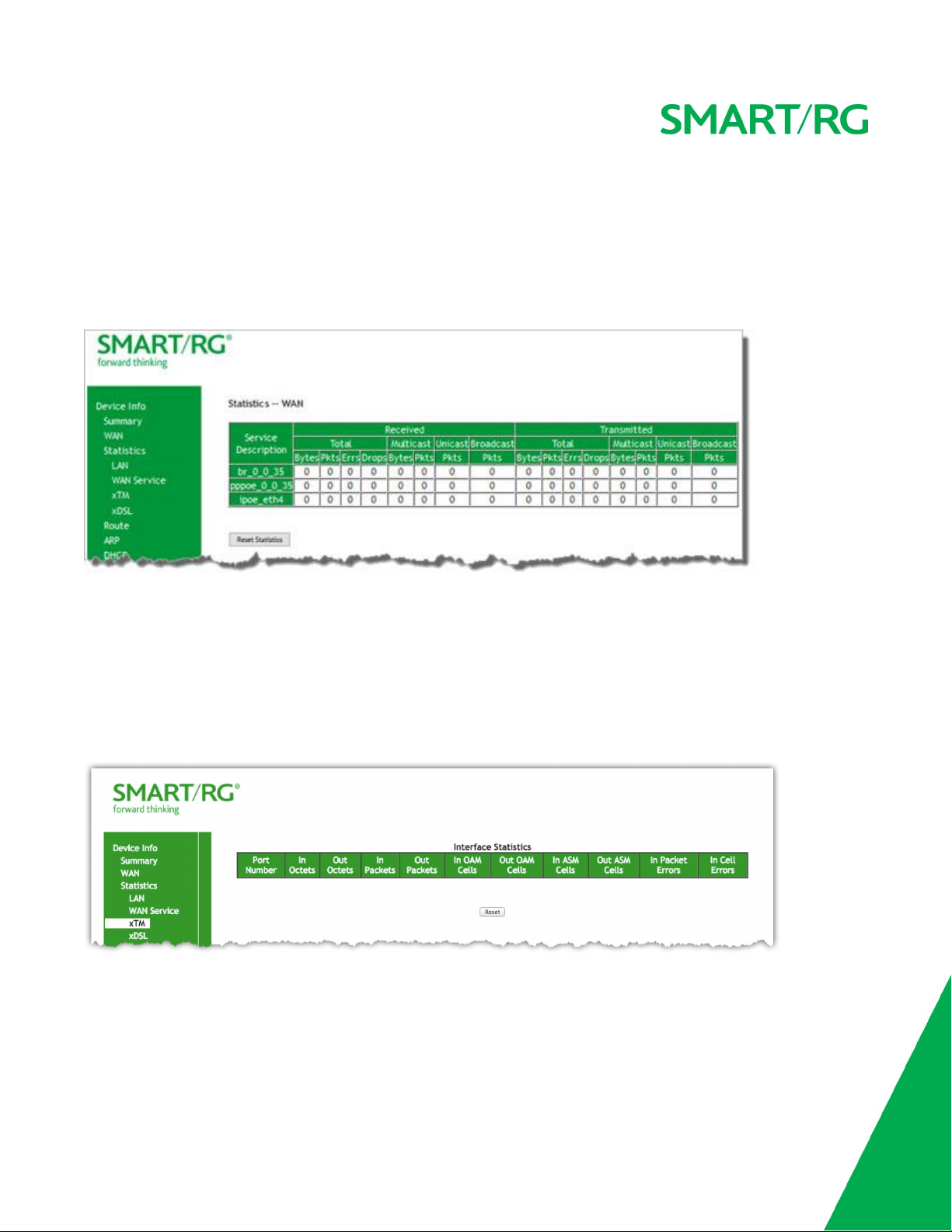
Statistics - WAN Page for SR515ac Gateway
The Statistics - WAN page for the SR515ac gateway is shown below. Statistics are provided for Multicast, Unicast, Broadcast, anf total
packets received and sent.
The columns labeled Interface and Description for the other gateway models are combined into the Service Description column on the
SR515ac page.
xTM
On this page, you can view the ATM/PTM statistics for your gateway. All WAN interfaces configured for your SmartRG gateway are
included.
In the left navigation bar, click Device Info > Statistics > xTM. The Interface Statistics page appears.
To reset these counters, click Reset Statistics near the bottom of the page.
The fields on this page are explained in the following table.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
16

Field Name Description
Port Number Statistics for Port 1, or both ports if Bonded.
In Octets Total quantity of received octets.
Out Octets Total quantity of transmitted octets.
In Packets Total quantity of received packets.
Out Packets Total quantity of transmitted packets.
In OAM Cells Total quantity of received OAM cells.
Out OAM Cells Total quantity of transmitted OAM cells.
In ASM Cells Total quantity of received ASM cells.
Out ASM Cells Total quantity of transmitted ASM cells.
In Packet Errors Total quantity of received packet errors.
In Cell Errors Total quantity of received cell errors.
xDSL
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
17

On this page, you can view the DSL statistics for your gateway. All xDSL (VDSL or ADSL) interfaces configured for your SmartRG gateway are included. The terms and their explanations are derived from the relevant ITU--T standards and referenced accordingly.
1. In the left navigation bar, click Device Info > Statistics > xDSL. The Statistics - xDSL page appears.
2. In the Bonding Line Selection field, select the line for which you want to view the statistics.
Note: For the SR350n, SR360n, and SR505n models, the Bonding Line Selection field does not appear.
3. To run an xDSL Bit Error Rate (BER) test which determines the quality of the xDSL connection:
a. Scroll to the bottom of the page and click xDSL BER Test. The ADSL BER Test dialog box appears.
b. In the Tested Time field, select the duration in seconds and click Start. Options range from 1 second to 360 seconds.
The test transfers idle cells containing a known pattern and compares the received data with this known pattern. Comparison errors are tabulated and displayed.
4. To reset the counters, click Reset Statistics at the bottom of the page.
The fields on this page are explained in the following table.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
18

Field Name Description
Mode xDSL mode that the modem has trained under, such as ADSL2+, G.DMT, etc.
Traffic Type Connection type. Options are:
ATM,PTM
Status Status of the connection. Options are:Up,
ETH
and
.
Disabled,NoSignal
, and
Initializing
.
Link Power State Current link power management state (e.g., L0, L2, L3).
Downstream
Line Coding (Trellis) State of theTrellis Coded Modulation. Options areOnand
and
Upstream
columns
Off
.
SNR Margin (0.1 db) The signal-to-noise ration margin (SNRM) is the maximum increase (in dB) of the
received noise power, such that the modem can still meet all of the target BERs over all
the frame bearers. [2]
Attenuation (0.1 db)
Output Power (0.1
The signal attenuation is defined as the difference in dB between the power received at
the near-end and that transmitted from the far-end. [2]
Transmit power from the gateway to the DSL loop relative to one Milliwat (dBm).
dBm)
Attainable Rate
(Kbps)
The typically obtainable sync rate, i.e., the attainable net data rate that the receive PMSTC and PMD functions are designed to support under the following conditions:
l Single frame bearer and single latency operation
l Signal-to-Noise Ratio Margin (SNRM) to be equal or above the SNR Target Mar-
gin
l BER not to exceed the highest BER configured for one (or more) latency paths
l Latency not to exceed the highest latency configured for one (or more) latency
paths
l Accounting for all coding gains available (e.g., trellis coding, RS FEC) with latency
bound
l Accounting for the loop characteristics at the instant of measurement [2]
PhyR Status (
G. inp Status (
Visible only for gateways connected via DSL
status. Options are
Inactive
and
Active
.
Visible only for gateways connected via DSL
buffer. Options are
Inactive
and
Active
.
) Physical Layer Retransmission feature
) The status of video data retrieval from the
Rate (Kbps) The current net data rate of the xDSL link. Net data rate is defined as the sum of all
frame bearer data rates over all latency paths. [2]
Downstream
B (# of bytes in Mux
Data Frame)
M (# of Mux Data
and
Upstream
columns for DSL-specific fields only
The nominal number of bytes from frame bearer #n per Mux Data Frame at Reference
Point A in the current latency path.
The number of Mux Data Frames per FEC Data Frame in the current latency path.
Frames in FEC Data
Frame
T (Mux Data Frames
over sync bytes)
R (# of check bytes in
FEC Data Frame)
The ratio of the number of Mux Data Frames to the number of sync bytes in the current
latency path.
The number of Reed Solomon redundancy bytes per codeword in the current latency
path. This is also the number of redundancy bytes per FEC Data Frame in the current
latency path.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
19

Field Name Description
S (ratio of FEC over
The ratio of FEC over PMD Data Frame length.
PMD Data Frame
length)
L (# of bits in PMD
The number of bits from the latency path included per PMD.
Data Frame)
D (interleaver depth) The interleaving depth in the current latency path.
Delay (msec) The PMS-TC delay in milliseconds of the current latency path (or the lowest latency path
when running dual-latency paths).
INP (DMT symbol) The input level for DMT-managed DSL environments.
OH Frames The number of xDSL OH Frames transmitted/received.
OH Frame Errors The number of xDSL OH Frames transmitted/received with errors.
(End of DSL-specific field group)
Super Frames The number of xDSL Super Frames transmitted/received.
Super Frame Errors The number of xDSL Super Frames transmitted/received with errors.
RS Words The number of Reed-Solomon-based Forward Error Correction (FEC) codewords trans-
mitted/received.
RS Correctable Errors The number of Reed-Solomon-based FEC codewords received with errors that have been
corrected.
RS Uncorrectable
Errors
RS Codewords
Received
RS Codewords Corrected
RS Codewords Uncorrected
The number of Reed-Solomon-based FEC codewords received with errors that were not
correctable.
Visible only for gateways connected via DSL
(
) Total number of Reed-Solomon Codewords
received.
Visible only for gateways connected via DSL
(
) Total number of Reed-Solomon Codewords
corrected.
Visible only for gateways connected via DSL
(
) Total number of Reed-Solomon Codewords
Uncorrected
HEC Errors A count of ATM HEC errors detected. As per ITU-T G.992.1 and G.992.3, a1-byte HEC is
generated for each ATM cell header. Error detection is implemented as defined in ITU-T
I.432.1 with the exception that any HEC error shall be considered as a multiple bit error,
and therefore, HEC Error Correction is not performed. [1],[2]
OCD Errors Total number of Out-of-Cell Delineation errors. ATM Cell delineation is the process which
allows identification of the cell boundaries. The HEC field is used to achieve cell delin-
eation. [4] An OCD Error is counted when the cell delineation process transitions from the
SYNC state to the HUNT state. [2]
LCD Errors Total number of Loss of Cell Delineation errors. An LCD Error is counted when at least
one OCD error is present in each of four consecutive overhead channel periods and SEF
(Severely Errored Frame) defect is present. [2]
Total Cells The total number of cells (OAM and Data cells) transmitted/received.
Data Cells The total number of data cells transmitted/received.
Bit Errors The total number of Idle Cell Bit Errors in the ATM Data Path. [3]
Total ES Total number of Errored Seconds. This parameter is a count of 1-second intervals with
one or more CRC-8 anomalies. [4]
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
20

Field Name Description
Total SES Total number of Severely Errored Seconds. An SES is declared if, during a 1-second inter-
val, there are 18 or more CRC-8 anomalies in one or more of the received bearer chan-
nels, or one or more LOS (Loss of Signal) defects, or one or more SEF (Severely Errored
Frame) defects, or one or more LPR (Loss of Power) defects. [4]
Total UAS
Total number of Unavailable Seconds. This parameter is a count of 1-second intervals for
which the xDSL line is unavailable. The xDSL line becomes unavailable at the onset of 10
contiguous SESs. These 10 SES’s shall be included in the unavailable time. Once unavail-
able, the xDSL line becomes available at the onset of 10 contiguous seconds with no
SESs. These 10 seconds with no SES’s shall be excluded from unavailable time. [4]
References
[1] ITU-T Recommendation G.992.1 (1999), Asymmetric digital subscriber line (ADSL) transceivers.
[2] ITU-T Recommendation G.992.3 (2005), Asymmetric digital subscriber line transceivers 2 (ADSL2).
[3] ITU-T Recommendation G.997.1 (2006), Physical layer management for digital subscriber line (DSL) transceivers.
[4] ITU-T Recommendation I.432.1 (1999), B-ISDN user-network interface – Physical layer specification: General characteristics.
Route
On this page, you can view the LAN and WAN route table information configured in your SmartRG Gateway for both IPv4 and IPv6
implementation.
In the left navigation bar, click Device Info > Route. The following page appears.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
21

The fields on this page are explained in the following table.
Field Name Description
Destination (Including IPv6 Route) Destination IP addresses.
Gateway Gateway IP address.
Subnet Mask Subnet Masks.
Flag (Including IPv6 Route) Status of the flags.
Metric (Including IPv6 Route) Number of hops required to reach the default gateway.
Service (Including IPv6 Route) Service type.
Interface (Including IPv6 Route) WAN/LAN interface.
Next Hop (IPv6 Route only) Next hop IP address.
ARP
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
22

On this page, you can view the host IP addresses and their hardware (MAC) addresses for each LAN Client connected to the gateway via
a LAN Ethernet port or wireless LAN.
In the left navigation bar, click Device Info > ARP. The following page appears.
The fields on this page are explained in the following table.
Field Name Description
IP address The IP address of the host.
Flags Each entry in the ARP cache will be marked with one of these flags. Options are: Complete, Permanent, and Published.
HW Address The hardware (MAC) address of the host.
Device The system level interface by which the host is connected. Options are: br(n), atm(n), eth(n), and atm(n).
DHCP
The DHCP page displays a list of locally connected LAN hosts and their DHCP lease status, which are directly connected to the SmartRG
Gateway via a LAN Ethernet port or Wireless LAN.
In the left navigation bar, select Device Info > DHCP. The following page appears.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
23

The fields on this page are explained in the following table.
Field Name Description
Hostname The host name of each connected LAN device.
MAC Address The MAC Address for each connected LAN device.
IP Address The IP Address for each connected LAN device.
Expires In The time until the DHCP lease expires for each LAN device.
ADVANCED SETUP
In this section, you can configure network interfaces, security, quality of service settings, and many other settings for your gateway and
network.
Layer2 Interface
In this section, you can configure interfaces for ATM, PTM and Ethernet interfaces. Generally you can accept the settings configured by
default. If your network is highly customized, you may need to modify some of the settings, such as Username and Password.
ATM Interface
On this page, you can configure Asynchronous Transfer Mode / Permanent Virtual Conduit (ATM/PVC) settings for your gateway. You
can customize latency options, link type, encapsulation mode and more.
Note: Devices (routers) on both ends of the connection must support ATM / PVC.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
24
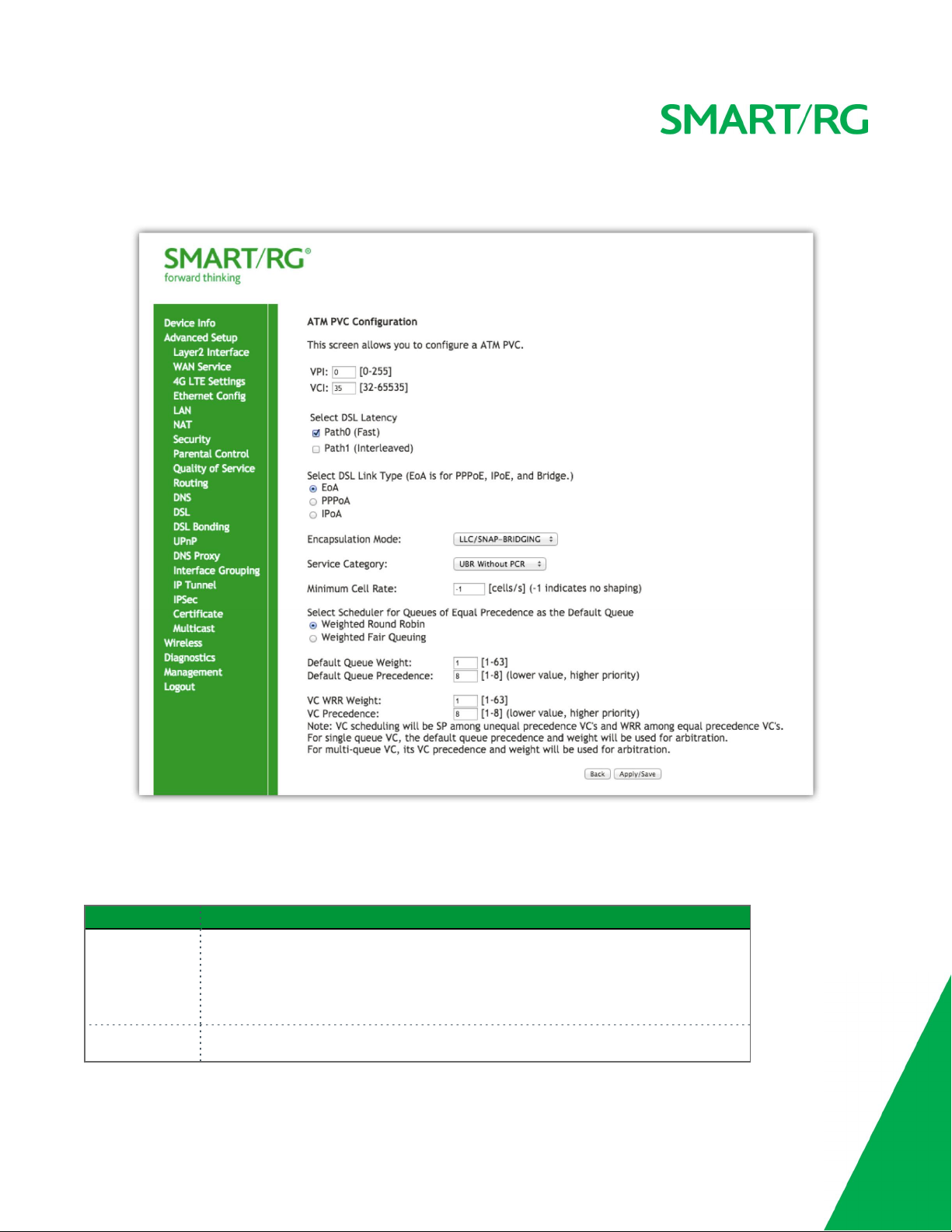
1. In the left navigation bar, click Advanced Setup > Layer2 Interface > ATM Interface and then click Add. The following page
appears.
2. Modify the settings as desired, using the information provided in the table below.
3. Click Apply/Save to commit your changes.
The fields on this page are explained in the following table.
Field Name Description
VPI Enter a Virtual Path Identifier. A VPI is an 8-bit identifier that uniquely identifies a network
path for ATM cell packets to reach its destination. A unique VPI number is required for each
ATM path. This setting works with the VCI. Each individual DSL circuit must have a unique
VPI/VCI combination. String limits are: 0-255.
VCI Enter a Virtual Channel Identifier.A VCI is a 16-bit identifier that has a unique channel.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
25

Field Name Description
Options are: 32-65535.
Select DSL Latency Select the level of DSL latency. Options are:
l Path0 Fast: No error correction and can provide lower latency on error free lines.
l Path1 Interleaved: Error checking that provides error free data which increases
latency.
l Path0&1 Both: Fast & Interleaved.
Select Link Type Select the linking protocol. EoA is the most popular with PPPoA a close second (used with
many legacy ISPs). Options are:
l EoA: Ethernet over ATM.
l PPPoA: Point-to-Point Protocol over ATM.
l IPoA: Internet Protocol over ATM.
Encapsulation
Mode
Select whether multiple protocols or only one protocl is carried per PVC (Permanent Virtual Circuit). Options are:
l LLC/SNAP-BRIDGING: Logical Link Control used to carry multiple protocols in a single
PVC.
l VC/MUX: Virtual Circuit Multiplexer creates a virtual connection used to carry one
protocol per PVC.
Service Category Select the bit rate protocol. Options are:
l UBR without PCR: Unspecified Bit Rate with no Peak Cell Rate, flow control or time
synchronization between the traffic source and destination. Commonly used with
applications that can tolerate data / packet loss.
l UBR with PCR: Same as above but with a Peak Cell Rate.
l CBR: Constant Bit Rate relies on timing synchronization to make the network traffic
predictable. Used commonly in Video and Audio traffic network applications.
l NON Realtime VBR: Non Realtime Variable Bit Rate used for connections that trans-
port traffic at a Variable Rate. This category requires a guaranteed bandwidth and
latency. It does not rely on timing synchronization between the destination and
source.
l Realtime VBR: Realtime Variable Bit Rate. Same as the above option but relies on
timing and synchronization between the destination and source. This category is commonly used in networks with compressed video traffic.
Minimum Cell
Rate
Scheduler for
Queues of Equal
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
Minimum allowable rate (cells per second) at which cells can be sent on a ATM network. For
no shaping, enter -1.
The algorithm used to schedule the queue behavior. VC scheduling is unique from Default
Queues. Options are:
26

Field Name Description
Precedence as the
Default Queue
l WRR: Weighted Round Robin packets are accessed in a round robin style and classes
can be given.
l WFQ: Weighted Fair Queuing packets are assigned in a specific queue.
l Default Queue Weight: The default weight of the specified queue. Options are: 1-63.
l Default Queue Precedence: The precedence of the specified group. Options are: 1-8
PTM Interface
The SmartRG gateway's VDSL2 standards support Packet Transfer Mode (PTM). An alternative to ATM mode, PTM transports packets
(IP, PPP, Ethernet, MPLS, and others) over DSL links. For more information, refer to the IEEE802.3ah standard for Ethernet in the First
Mile (EFM). Some 500 series gateways have a PTM interface configured by default.
On this page, you can configure a PTM interface for your gateway.
1. In the left navigation bar, click Advanced Setup > Layer2 Interface > PTM Interface and then click Add. The following page
appears.
2. Modify the settings as desired.
3. Click Apply/Save to commit your changes.
The fields on this page are explained in the following table.
Field Name Description
Weighted Round Robin Time slices are assigned to each process in equal portions and in circular order, hand-
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
27

Field Name Description
ling all processes without priority (also known as cyclic executive).
Weighted Fair Queuing A data packet scheduling technique allowing different scheduling priorities to be
assigned to statistically multiplexed data flows. Since each data flow has its own
queue, an ill-behaved flow (that sent larger packets or more packets per second than
the others since it became active) will only affect itself and not other sessions.
Default Queue Weight Enter a default weight of the specified queue. Options are: 1-63.
Default Queue Pre-
Enter a precedence for the specified queue. Options are: 1-8.
cedence
Default Queue Minimum Rate
Default Queue Shaping
Rate
Default Queue Shaping
Burst Rate
(Does not appear for SR350n models) The default minimum rate at which traffic can
pass through the queue. For no shaping, enter -1 (disabled). Options are: 1-0 Kbps.
(Does not appear for SR350n models) The shaping rate for the specified queue. For no
shaping, enter -1 (disabled). Options are: 1-0 Kbps.
(Does not appear for SR350n models) The maximum rate at which traffic can pass
through the queue. Options are 1600 or greater.
ETH Interface
If you are using a gateway that is Ethernet-specific (non-DSL), you may want to configure an ETH interface to manage communication.
Most models support Ethernet and can be configured for Ethernet and DSL at the same time. Your gateway has four LAN ports. One of
them can be re-purposed to become an RJ45 WAN port when needed.
On this page, you can configure an Ethernet interface for your gateway.
1. In the left navigation bar, click Advanced Setup > Layer2 Interface > ETH Interface. If no WAN port is configured, the following
page appears.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
28

2. Click Add.
3. If a WAN port is already configured or you clicked Add, the following page appears.
Note: If a WAN port it is already configured, you must remove it before you can define a new one. Before you can remove the
existing port, you must first modify or delete any WAN service that uses it. The Add button does not appear until the existing
port is removed. Click the Remove checkbox and then click the Remove button.
4. Select the LAN port you wish to act as a WAN port.
5. Click Apply/Save to commit your changes.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
29

WAN Service
In this section, you can configure WAN services for:
l "PPP over Ethernet"
l "IP over Ethernet"
A sample configuration scenario is provided for each variation.
PPP over Ethernet
There are several parts to configuring a PPP over Ethernet WAN service. You will progress through several pages to complete the configuration.
1. In the left navigation bar, click Advanced Setup > WAN Service and then click Add. The following page appears.
2. Select the Layer2 interface to use for the WAN service.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
30

3. Click Next. The following page appears.
4. Select the PPP over Ethernet (PPPoE) WAN service type.
5. Modify the other settings as needed.
The fields on this page are explained in the following table.
Field Name Description
Enter Service
Enter a name to describe this configuration.
Description
Network Protocol
Selection
(For SR515ac models, this field is named
applied to statistically multiplexed data flows. Since each data flow has its own queue, an ill-behaved flow
(which has sent larger packets or more packets per second than the others) will only punish itself and not
other sessions. Options are IPv4 Only, IPv4&IPv6 (Dual Stack), and IPv6 Only.
Note: When you select IPV4&IPV6 or IPV6, the subsequent options presented will change accordingly.
Enter 802.1P Priority
(Available for SR515ac models only) Options are 0 - 7. The default is 0.
For tagged service, enter values in this field and the 802.1Q VLAN ID field.
For untagged service, enter -1 (disabled) in this field and the 802.1Q VLAN ID field.
Enter 802.1Q
VLAN ID
(Available for SR515ac models only) Options are 0 - 4094. The default is -1 (disabled).
For tagged service, enter values in this field and the 802.1P Priority field.
Internet Protocol Selection
) Different scheduling priorities can be
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
31

Field Name Description
For untagged service, enter -1 (disabled) in this field and the 802.1P Priority field.
Select VLAN TPID (
Available for SR515ac models only
0x9100
.
) Select the TPID for this VLAN. Options are
0x8100,0x88A8
, and
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
32

6. Click Next. The following page appears where you will configure the PPP Username, Password and related information.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
33

7. Modify the fields as needed.
The fields on this page are explained in the following table.
Field Name Description
PPP Username Enter the username required for authentication to the PPP server.
PPP Password Enter the password required for authentication to the PPP server.
PPPoE Service Name (
Authentication Method
Optional
) Enter a description for this service.
Select a means for authentication. Options are:
l AUTO: Attempt to automatically detect handshake protocol (listed below)s.
l PAP: Password Authentication Protocol (plaintext passwords).
l CHAP: Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol. (MD5 hashing scheme on passwords).
l MSCHAP: Microsoft Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol. (Microsoft encrypted
password authentication protocol).
CP Keepalive Period The frequency with which the keepalive packet is sent by the gateway to the PPP server.
LCP Retry Threshold Enter the number of additional attempted packets that the gateway will send (in the event that the
PPP server does not respond to the Keepalive) before giving up and declaring the connection as
Failed.
Dial on Demand
Enables Inactivity Timeout (minutes). Enter the number of minutes before timeout kicks in. Options
are 0 - 4320. The default is zero (0) which equals not applicable.
Connection automatically starts when there is outbound traffic to the Internet. It automatically terminates if the connection is idle, based on the value in the Idle Timeout setting.
PPP IP Extension Select whether to forward all traffic to the advanced DMZ IP specified in the next field.
Advanced DMZ (Applies only when
PPP IP Extension
is selected) Specify the IP address to which PPPoE traffic is for-
warded.
Use Static IPv4 Address Specify the IPv4 Address to apply for this WAN service.
Retry PPP password on
authentication error
Enter the maximum number of PPP authentication retries on failure. Options are 1 - 65536. Entering
65536 sets the maximum to unlimited.
Enable PPP Debug Mode Select to have the system put more PPP connection information into the system log of the device.
This is for debugging errors and not for normal usage.
Bridge PPPoE Frames
Between WAN and Local
Select to enable PPPoE passthrough to relay PPPoE connections from behind the modem. Also known
as Half-Bridged mode.
Ports
Enable Firewall Select to enable functions in the Security sub-menu.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
34

Field Name Description
Enable NAT Select to enable sharing the WAN interface across multiple devices on the LAN. Additional NAT and
PPPoE NAT features appear.
Enable Fullcone NAT (Appears when
Enable SIP (Appears when
Enable NAT
Enable NAT
is selected) Click to enable what is known as one-to-one NAT.
is selected) Click to enable Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) pass-through
NAT. Used for Voice over IP (VOIP) applications.
Enable IGMP Multicast
Proxy
(Appears when
Enable NAT
is selected) Click to enable Internet Group Membership Protocol (IGMP)
multicast. Used by IPv4 hosts to report multicast group memberships to any neighboring multicast
routers.
No Multicast VLAN Filter
Enable IGMP Multicast
(Not available for SR515ac models) Disables multicast filtering between WAN and LAN (VlanMux)
network.
Available for SR515ac models onl
(
y) Select to enable this service to act as an IGMP multicast source.
Source
MTU sizes Enter the MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) size for SmartRG gateways supporting a gigabit-cap-
able WAN interface. Options are 1370 - 1492 bytes. The default is 1492 bytes.
This feature is supported by SmartRG models SR500n, SR505n, SR510n, SR550n and SR552n.
Firmware v2.5.0.7 or later is required.
Use Base MAC Address
on this WAN interface
Enable MACClone (
Use the SmartRG Devices Base (Primary) MAC address. When unchecked, a unique MAC is assigned
for each service.
Appears when
Use Base MAC Address
is deselected
) Enter the MAC address to be used as the close
adddress.
Additional options for
IPV6
Select options as needed. Options are:
l Enable IPv6 Unnumbered Model
l Enable IPv6 Unnumbered Model
l Launch Dhcp6c for Address Assignment (IANA)
l Launch Dhcp6c for Prefix Delegation (IAPD)
l Enable MLD Multicast Proxy
8. Click Next. The following page appears where you will select the interface used as a default gateway used for the PPP service
being created.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
35

9. Click the arrows to move your selection from left to right or from right to left.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
36

10. Click Next. The following page appears where you will select DNS Server settings.
11. Select the DNS Server Interface from available WAN interfaces.
12. Click the arrows to move your selection from left to right or from right to left.
13. Alternatively, you can enter static DNS IP addresses in the Use the following Static DNS IP address section.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
37

14. Click Next. The summary page appears indicating that your PPPoE WAN setup is complete.
15. Review the summary and either click Apply/Save to commit your changes or click Back to step through the pages in reverse
order to make any necessary alterations.
Note: For the SR515ac model, additional fields are listed for IGMP Multicast and MLD Multicast settings.
IP over Ethernet
There are several parts to configuring a IP over Ethernet WAN service. You will progress through several pages to complete the configuration.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
38

1. In the left navigation bar, click Advanced Setup > WAN Service and then click Add. The following page appears.
2. Select the Layer2 interface to use for the WAN service and click Next. The following page appears.
3. Select the IP over Ethernet WAN service type.
4. Modify the fields as needed.
The fields on this page are explained in the following table.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
39

Field Name Description
Enter Service
Description
Enter 802.1P Priority
Enter 802.1Q VLAN
ID
Network Protocol
Selection
(Optional) Enter a name to describe this configuration.
Options are 0 - 7. The default is 0.
For tagged service, enter values in this field and the 802.1Q VLAN ID field.
For untagged service, enter -1 (disabled) in this field and the 802.1Q VLAN ID
field.
Options are 0 - 4094. The default is -1 (disabled).
For tagged service, enter values in this field and the 802.1P Priority field.
For untagged service, enter -1 (disabled) in this field and the 802.1P Priority field.
This data packet scheduling technique allows different scheduling priorities to be
applied to statistically multiplexed data flows. Since each data flow has its own
queue, an ill-behaved flow (which has sent larger packets or more packets per
second than the others since it became active) will only punish itself and not other
sessions. Options are IPv4 Only, IPv4&IPv6 (Dual Stack), and IPv6 Only. The
default is IPv4 Only.
Note: When selecting IPV4&IPV6 or IPV6, the subsequent options presented will
change accordingly.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
40

5. Click Next. The following page appears.
6. Enter the relevant WAN IP Settings.
The fields on this page are explained in the following table.
Field Name Description
Obtain an IP address automatically When you wish the ISP to automatically assign the WAN IP to the gateway.
Option 60 Vendor ID (Optional) Broadcast a specific vendor ID for the DHCP server to accept the device.
Option 61 IAID (Optional) Interface Association Identifier (IAID). A unique identifier for an IA,
chosen by the client.
Option 61 DUID (Optional) DHCP Unique Identifier (DUID) is used by the client to get an IP address
from the DHCP server.
Use the following Static IP address Use this section to manually declare the static IP information provided by your ISP.
WAN IP Address If using a static IP address, enter the static WAN IPV4 Address.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
41

Field Name Description
WAN Subnet Mask If using a static IP address, enter the static Subnet Mask.
WAN gateway IP Address If using a static IP address, enter the static Gateway IP address.
Advanced DMZ (Optional) Select this option to enable Advanced DMZ on the WAN service. For
more information, see the knowledgebase on SmartRG Support site.
Non DMZ IP Address If using the Advanced DMZ feature, you can enter a specific vendor ID that will be
broadcast for the DHCP server to accept the device, y. e.g., 192.168.2.1.
Non DMZ Net Mask If using the Advanced DMZ feature, you can enter a secondary LAN IP address for
the gateway. The default is 255.255.255.0.
IPv6 settings
The following fields appear when either IPv6 Only or IPv4&IPv6 (Dual Stack) network protocols are selected on the WAN Ser-
vice Configuration page.
Obtain an IPv6 address automatically Enables the DHCPv6 Client on this WAN interface. Select this option when you want
the ISP to automatically assign the WAN IP to the gateway.
Dhcpv6 Address Assignment (IANA) Select this option for the CPE to receive WAN IP from ISP.
Dhcpv6 Prefix Delegation (IAPD) Select this option for the CPE to generate the WAN IP's prefix from the server's REST
by MAC address.
Use the following Static IPv6 address Select this option to manually declare the v6 Static IP information provided by your
ISP.
WAN IPv6 Address/Prefix Length If entering a static IP address, enter the IP address / prefix length. If you do not spe-
cify a prefix length, the default of /64 is used.
Specify the Next-Hop IPv6 address Enter the IP address of the next WAN in the group. This address can be either a local
link or a global unicast IPv6 address.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
42

7. Click Next. The NAT settings appears.
8. Modify the settings if desired. All settings are optional.
Network Address Translation (NAT) allows you to share one Wide Area Network (WAN) IP address for multiple computers on
your Local Area Network (LAN). If you do not want to enable NAT (atypical) and wish the user of this gateway to access the
Internet normally, you need to add a route on the uplink equipment. Failure to do so will cause access to the Internet to fail.
The fields on this page are explained in the following table.
FIELD NAME DESCRIPTION
Enable NAT Enable sharing the WAN interface across multiple devices on the LAN.
Also enables the functions in the NAT sub-menu and addition PPPoE NAT
features to select.
Enable Fullcone NAT (Appears when
Enable NAT
is selected) Enables what is known as one-to-
one NAT.
Enable SIP ALG (Appears when
Enable NAT is selected
) Enables Session Initiation Pro-
tocol (SIP) pass-through NAT. Used for Voice over IP (VOIP) applications.
Enable Firewall Enables functions in the Security sub-menu
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
43

FIELD NAME DESCRIPTION
Enable IGMP Multicast (Not available for SR515ac models) Enables Internet Group Membership
Protocol (IGMP) multicast. Used by IPv4 hosts to report multicast group
memberships to any neighboring multicast routers.
Enable IGMP Multicast
Proxy
Enable IGMP Multicast
Source
No Multicast VLAN Filter (Not available for SR515ac models) Disables multicast filtering between
Use Base MAC Address
on this WAN interface
Enable MACClone (
9. For the remaining WAN Service configuration pages, use the instructions provided in the default gateway step in the PPP over
Ethernet section.
Available for SR515ac models onl
(
bership Protocol (IGMP) multicast. Used by IPv4 hosts to report multicast
group memberships to any neighboring multicast routers.
Available for SR515ac models onl
(
an IGMP multicast source.
WAN and LAN (VlanMux) network.
Use SmartRG Devices Base (Primary) MAC address. When unchecked, a
unique MAC per service is assigned.
Appears when
address to be used as the close adddress.
Use Base MAC Address
y) Click to enable Internet Group Mem-
y) Select to enable this service to act as
is deselected
) Enter the MAC
Ethernet Config
On the Ethernet Port Configuration page, you can set the speed and duplex mode for each of the Ethernet ports.
1. In the left navigation bar, click Advanced Setup > Ethernet Config . The following page appears.
2.
In the Configure column, select an option (Auto, 100 Full, 100 Half, 10 Full or 10 Half) for each of the four Ethernet ports on
your gateway.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
44

These options represent 100 megabits or 10 megabits using half or full duplex transmission protocols. When you have a specific
device with a known limited transmission speed capability, select one of the latter four options. If you select Auto, your gateway will automatically select an appropriate setting based on Ethernet auto negotiation with the NIC of the LAN host.
Note: Always select Auto for 1000 BaseT connections.
The following are the variations for the 500 series of gateways:
l For the SR510 and SR552n models, the fourth port is shown on this page as eth3/LAN1 and the ports are listed in reverse
order.The eth4/WAN interface is also present on these models.
l SR505n v2.5.0.x and later has an additional option of 1000 Full for the LAN1/WAN port.
l SR552n v2.5.0.6 and later has an additional option of 1000 Full for all Ethernet interfaces.
3. Click Apply/Save to commit your changes.
MoCA
On this page, you can configure MoCA settings. The MoCA (Multimedia over Coax) protocol enables distribution of content over existing
in-home coaxial TV cabling at the same speed delivered by Ethernet networks.
Note: This feature is available only on the SR512nm model.
1. In the left navigation bar, click Advanced Setup > MoCA. The following page appears.
2. Update or complete the necessary fields.
3. Click Apply/Save to commit your changes.
The fields on this page are explained in the following table.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
45

Field Name Description
Auto Scan Allows your gateway to scan automatically for the best connection to your
provider. This option is enabled by default.
MoCA Band Select the operating band for this gateway. The default is
1625)
.
Band D (1125-
Last Operating Frequency Displays the most recent operating frequency in Megaherz.
Channel Bandwidth Select the bandwidth for your connection. Select
operability or select
100 MHz
for better performance.
50 MHz
for better inter-
MoCA Privacy To activate privacy mode, click the Enable checkbox.
Privacy Password (Appears when
for this gateway.
MoCA Privacy
is set to
Enabled
) Enter the MoCA password
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
46

LAN
On the Local Area Network (LAN) Setup page, you can configure the router’s local IP addresses, subnet mask, DHCP behavior and other
related LAN side settings for your gateway.
1. In the left navigation bar, click Advanced Setup > LAN. The following page appears.
2. Customize the fields as desired.
3. Click Apply/Save to commit your changes.
The fields on this page are explained in the following table.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
47

Field Name Description
Groupname (Available on SR515ac models only) Select an interface group from the list of available groups (defined on the Inter-
face Grouping page).
IP Address (Available on SR515ac models only) Enter the LAN IP address by which LAN devices will connect to this gateway.
Subnet Mask (Available on SR515ac models only) Enter the Subnet mask to be used by LAN devices connecting to this gateway.
Enable IGMP
Snooping
(Available on SR515ac models only) Enables your gateway to listen to IGMP network traffic between hosts and
routers. By listening to these conversations, the gateway maintains a map of which links need which IP multicast
streams.
Standard Mode Allows multicast traffic will flood to all bridge ports when there is no client subscribed to any multicast group.
Blocking Mode Blocks multicast data traffic, preventing it from flooding to all bridge ports when no client subscriptions to a mul-
ticast group are present.
Enable IGMP LAN
Available on SR515ac models only
(
) Allows multicast traffic between LANs. This option is enabled by default.
to LAN Multicast
Enable LAN Side
Enables the restriction of traffic between LAN hosts.
Firewall
Disable DHCP
Server
Enable / Disable
DHCP Server
Start IP Address (Becomes editable when
Prevents the DHCP functionality of your gateway from automatically assigning LAN IPaddresses to host devices
as they connect with the gateway.
Allows the DHCP functionality of your gateway to automatically assign LAN IP addresses to host devices as they
connect with the gateway. Fill in the next three fields to configure this action.
Enable DHCP Server
is selected) Enter the beginning of the class C, IP address range to
be assigned by the DHCP server.
End IP Address (Becomes editable when
Enable DHCP Server
is selected) Enter the end of the class C, IP address range to be
assigned by the DHCP server.
Leased Time
(hour)
(Becomes editable when
be leased.
Enable DHCP Server
is selected) Enter the number of hours for which an IP address will
Static IP Lease List Specify a literal, static, IP address to be associated with a specific MAC Address of one of your LAN host devices.
Click Add Entries. Enter the MACaddress and IP address and click Apply/Save. Repeat this step to create any addi-
tional entries that you need.
Automatically create static IP leases
For LAN hosts, IP addresses can be assigned manually or by using DHCP. Click Add OUI. Enter the OUI and click
Apply/Save. Repeat this setp to create any additional entries that you need.
from the following
OUIs
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
48

Field Name Description
Option 66 For some devices that also require access to a TFTP server (device configuration name filesare in .cnf file format),
which enables the device to communicate with other infrastructure, select this option to specify the name of the
TFTP server. Option 66 is an IEEE standard.
Option 150 A Cisco proprietary methodology for pointing to one or two TFTP servers.
Enable DHCP
Server Relay
DHCP Server IP
Address
Configure the
second IP address
and subnet mask
for LAN interface
(Not available on SR515ac models ) The DHCP relay agent operates as the interface between DHCP clients and the
server. It listens for client requests and adds vital configuration data, such as the client’s link information, which is
needed by the server to allocate the address for the client. When the DHCP server responds, the DHCP relay
agent forwards the reply back to the DHCP client.
(Not available on SR515ac models ) Set the IP address to which LAN clients must connect to receive DHCP services.
When you select this option, the IP Address and Subnet Mask fields appear where you can enter a second IP
address and Subnet mask to support a second, simultaneous LAN, i.e., the primary LAN might be defined as
192.168.0.1 and this secondary LAN defined as 192.168.2.1.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
49

NAT
In the NAT section you can configure the settings for Network Address Translation including setting up virtual servers, port triggering
and DMZ host. There is seldom need to customize these settings as the default settings manage the related features sufficiently for
most environments.
Virtual Servers
Virtual Servers (more commonly known as Port Forwards) is a technique used to facilitate communications by external hosts with services provided within a private local area network.
On this page, you can configure the virtual server settings for your gateway.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
50

1. In the left navigation bar, select Advanced Setup > NAT. The following page appears.
2. Customize the fields to create your port forwarding entry.
3. Click Apply/Save to commit your changes.
The fields on this page are explained in the following table.
Field Name Description
Use Interface Select the WAN interface to which this NAT rule will apply.
Select a Service Select from a list of application that typically require port forwards configured. The port ranges
and protocol fields will be pre-populated.
Custom Service If your application does not appear in the Select a Service list, you can enter a unique name
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
51

Field Name Description
for the application in this field.
Server IP Address Enter the IP address of the LAN client where the service is hosted.
External Port Start Enter the first external port for this server.
External Port End Enter the last external port for this server.
Protocol Select the protocol to be used with this range of ports. Options are: TCP, UDP, or TCP/UDP.
Internal Port Start Enter the first internal port for this server.
Internal Port End Enter the last internal port for this server.
Port Triggering
Some applications require that specific ports in the gateway's firewall be opened for access by remote parties. The Port Trigger feature
dynamically opens up the open ports in the firewall when an application on the LAN initiates a TCP/UDP connection to a remote party
using the triggering ports. The gateway allows the remote party from the WAN side to establish new connections back to the application
on the LAN side using the Open Ports.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
52

1. In the left navigation bar, click Advanced Setup > NAT > Port Triggering and then click Add. The following page appears.
2. Customize the fields as needed for the firewall pinholes you wish to establish. A maximum 96 entries can be configured.
3. Click Apply/Save to commit your changes.
The fields on this page are explained in the following table.
Field Name Description
Use Interface Select the interface for which the port triggering rule will apply.
Select an Application Select the application which requires a port trigger entry.
Custom Application If the application you want does not appear in the selection list, enter a unique name
for the application for which you are creating a port trigger entry. This is a free-form
text field.
Trigger Port Start Enter the starting number of the range of available outgoing trigger ports. Options
are: 1 - 65535.
Trigger Port End Enter the end number of the range of available outgoing trigger ports. Options are: 1
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
53

Field Name Description
- 65535.
Trigger Protocol Select the protocol required by the application that will be using the ports in the spe-
cified range. Options are: TCP, UDP, and TCP/UDP.
Open Port Start Enter the starting number of the range of available incoming ports. Options are: 1 -
65535.
Open Port End Enter the end number of the range of available incoming ports. Options are: 1 -
65535.
Open Protocol Select the protocol for the open port. Options are: TCP, UDP, and TCP/UDP.
DMZ Host
The Broadband Router will forward IP packets from the WAN that do not belong to any of the applications configured in the Virtual Servers table to the DMZ host computer. If you want to route all internet traffic to a specific LAN device with no filtering or security, add the
IP address of that device to this page.
1. In the left navigation bar, click Advanced Setup > NAT > DMZ Host. The following page appears.
2. Enter the DMZ Host IP Address.
3. Click Apply/Save to commit the new or changed address.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
54

Security
In this section, you can configure filtering for IP and MAC.
IP Filtering - Incoming
On this page, you can add an incoming filter when refusal of data from the WAN to the LAN is desired.
Note: This option is not available in the SR515ac model.
1. In the left navigation bar, click Advanced Setup > Security > IP Filtering > Incoming and then click Add. The following page
appears.
2. Fill in the fields, using the information in the table below.
3. Click Apply/Save to commit your changes.
The fields on this page are explained in the following table.
Field Name Description
Filter Name A free-form text field. Enter a descriptive name for this filter.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
55

Field Name Description
IP Version Select the IP version for this filter. Options are IPv4 and IPv6. The default is
IPv4.
Protocol Select the protocol to be associated with this incoming filter. Options are:
TCP/UDP, TCP, UDP, or ICMP.
Source IP address [/prefix
Enter the source IP address for rule. For IPv6, enter the prefix as well.
length]
Source Port (port or port:-
Enter source port number or range (xxxxx:yyyyy).
port)
Destination IP address
Enter the destination IP address for rule. For IPv6, enter the prefix as well.
[/prefix length]
Destination Port (port or
Enter destination port number or range (xxxxx:yyyyy).
port:port)
Select All Click to apply this rule to all WAN interfaces or only certain types. Options are
Select All or the types defined for your network.
First WAN interface
Last WAN interface
Click the applicable options to apply this rule on specific WAN interfaces. The
WAN interfaces display that you configured for your network in Routing and
that have a firewall enabled.
First LAN interface
Click the applicable options to apply this rule on specific LAN interfaces.
Second LAN interface
Bridged Interface Click the applicable options to apply this rule on specific bridged interfaces.
IP Filtering - Outgoing
On this page, you can add an outgoing filter when refusal of data from the LAN to the WAN is desired.
1. In the left navigation bar, click Advanced Setup > Security > IP Filtering > Outgoing and then click Add. The following page
appears.
Note: For SR515ac models, click Advanced Setup > Security to access this page.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
56

2. Fill in the fields, using the information in the table below.
3. Click Apply/Save to commit the completed entry.
The fields on this page are explained in the following table.
Field Name Description
Filter Name Enter a descriptive name for this filter. This is a free-form text field.
IP Version For the filter to be configured and effective for IPV6 , the gateway must be installed on a net-
work that is either a pure IPV6 network (with that protocol enabled) or is both IPV4 and IPV6
dual protocol enabled/configured. Options are IPv4 and IPv6. The default is IPv4.
If you select IPV6, both the Source and Destination IP address must be specified in IPV6
format. The following is an IPV6-compliant, hexadecimal address:
2001:0DB8:AC10:FE01:0000:0000:0000:0001.
Protocol Select the protocol profile for the filter you are defining. TCP/UDP is most commonly used. The
options are TCP/UDP, TCP, UDP, and ICMP].
Source IP address
[/prefix length]
Enter the source IP address of a LAN side host for which you wish to filter/block outgoing traffic
for the specified protocol(s).
Note: The address specified here can be a particular address or a block of IP addresses on a
given network subnet. This is done by appending the associated routing "/prefix" length
decimal value (preceded with the slash) to the addresses. A valid decimal routing prefix is
required for defining the subnet mask per CIDR notation.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
57

Field Name Description
Source Port (port
or port:port)
Set the outgoing host port (or range of ports) for the above host (or range of hosts defined by
optional routing "/prefix"subnet mask) to define the ports profile for which egress traffic will
be filtered from reaching the specified destination(s).
Destination IP
address
Enter the destination IP address of a LAN side host for which you wish to filter/block outgoing
traffic for the specified protocol(s).
Note: The address specified here can be a particular address or a block of IP address on a given
network subnet. This is done through appending the address with the routing " /prefix " length
decimal value (preceded with the slash) associated. A valid decimal routing prefix is required
for defining the subnet mask per CIDR notation.
Destination Port
(port or port:port)
Set the destination host port (or range of ports) for the above host (or range of hosts) to define
the destination port profile for which the filtered host egress traffic will be filtered from reaching the otherwise intended destination(s), e.g., to block the traffic to those ports on, say, a computer external to the local network.
MAC Filtering
Your SmartRG gateway can block or forward packets based on the originating device. This MAC filtering feature is available only in
Bridge mode. For other modes, similar functionality is available via IP Filtering. On this page, you can manage MAC filtering for your
gateway.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
58

1. In the left navigation bar, click Advanced Setup > Security > MAC Filtering. The following page appears.
2. To modify policy settings:
a. Review the information on the page.
b. Once you understand the consequences of changing the policy, click the Change checkbox, and then click Change
Policy. The policy is switched to FORWARD or BLOCKED.
3. To add a rule, follow the instructions in "MAC Filtering".
4. To remove a rule, click the Remove checkbox next to the rule and click the Remove button.
5. When your changes are completed, click Apply/Save to commit your changes.
The fields on this page are explained in the following table.
Field Name Description
Interface The interface associated with an established policy rule.
Policy The current/active policy type that is in place. Options are FORWARD and BLOCKED.
Add a MAC Filtering Rule
You cannot edit rules but you can add new ones and then remove the obsolete ones.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
59

1. On the MAC Filtering page, click Add. The following page appears.
2. Fill in the fields, using the information provided in the following table..
3. Click Apply/Save to commit your changes.
The fields on this page are explained in the following table.
Field Name Description
Protocol Type Select the protocol associated with the device at the destination MAC address. Options are PPPoE, IPv4/IPv6,
AppleTalk, IPX, NetBEUI, and IGMP.
Destination MAC
Address
Source MAC
Address
Frame Direction Select the incoming/outgoing packet interface.
WAN Interfaces Applies the filter to the selected interface(s).
Enter the MAC address of the hardware you wish to associate with this filter.
Enter the MAC address of the device that is originating requests intended for the device associated with the
Destination MAC address.
Parental Control
In this section, you can configure the Parental Control features of your SmartRG gateway to restrict Internet access to certain hours and
to certain URLS.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
60

Time Restriction
On this page, you can restrict Internet access to particular days and specific times for each device that accesses your gateway.
1. In the left navigation bar, click Advanced Setup > Parental Control > Time Restriction and then click Add. The following page
appears.
2. Fill in the fields using the information in the table below.
3. Click Apply/Save.
The fields on this page are explained in the following table.
Field Name Description
User Name Enter a descriptive name for this restriction. This is a free-form text
field.
Browser's MAC Address The MAC address of the connected device. This option is selected by
default.
Other MAC Address Select this option to restrict access to another device. You can view a
list of the connected devices and MAC addresses on the Device Info >
ARP page.
Days of the week Select the days (Mon - Sun) for which the restrictions apply.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
61

Field Name Description
Start Time Blocking / End Time
Blocking
Enter the range of time that the devices listed above are restricted
from access to the Internet. Use 24-hour clock notation (00:00 24:00).
URL Filter
The other side of the Parental Controls coin is URL filtering. On this page, you can exclude and include URLs as desired. Each list can
include up to 100 addresses.
Note: Only one Exclude list and one Include list are supported for each gateway. Unique lists are not supported for connecting devices.
1. In the left navigation bar, click Advanced Setup > Parental Control > Url Filter.
2. To block a URL:
a. Select Exclude List.
b. Click Add. The following page appears.
c. Click Apply/Save to save your settings. You are returned to the Url Filter page.
3. To create a list of URLs to allow, select Include and repeat the above steps.
The fields on this page are explained in the following table.
Field Name Description
URL Address Enter the URL address to be included in the list.
Port Number (Optional) Enter the port number associated with the URL. The default is 80.
Quality Of Service
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
62

Quality of Service (QoS) enables prioritization of Internet content to help ensure the best possible performance. This is particularly useful for streaming video and audio content with minimized potential for drop-outs. QoS becomes significant when the sum of all traffic
(audio, vid"QoS Classification", data) exceeds the capacity of the line.
In this section, you can configure QoS settings including traffic queues, classifications (rules) and port shaping.
QoS Config
On this page, you can enable QoS and set the DSCP Mark classification.
The maximum number of queues that can be configured vary by mode, as shown below.
Mode Maximum # of queues
ATM 16
Ethernet 4 per interface
PTM 8
Note: Queues for Wireless (e.g., WMM Voice Priority for wl0 interface) are shown only when wireless is enabled. If the WMM Advert-
ise function on the Wireless Basic Setup page is disabled, assigning classifications to wireless traffic has no effect.
1. In the left navigation bar, click Advanced Setup > Quality Of Service > QoS Config. The following page appears.
2. Click Enable QoS.
The QoS Queue Management Configuration field appears where you can select the default Differentiated Services Code Point
(DSCP) Mark classification value to be used. For a list of supported values, see "Supported DSCP Values".
Note: If this option was already enabled and you clear the checkbox, QoS will be disabled for ALL interfaces.
3. Click Apply/Save to save your settings.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
63

Supported DSCP Values
The DSCP marking QoS Queue Management Configuration marking on ingress packets is based on the selection you make in the Select
Default DSCP Mark field. The selected default marking is applied automatically to all incoming packets without reference to a particular
classification.
Note: A default DSCP mark value of Default(000000) will mark all egress packets that do NOT match any classification.
The following values are supported. For more information about commonly used DSCP values, refer to RFC 2475.
No Change(-1) CS1(001000) AF32(011100)
Auto Marking(-2) AF23(010110) AF31(011010)
Default(000000) AF22(010100) CS3(011000)
AF13(001110) AF21(010010) AF43(100110)
AF12(001100) CS2(010000) AF42(100100)
AF11(001010) AF33(011110) AF41(100010)
CS4
(100000)
EF
(101110)
CS5
(101000)
CS6
(110000)
QoS Queue Config
On this page you can configure a queue and add it to a selected Layer2 interface.
1. In the left navigation bar, click Advanced Setup > Quality Of Service > QoS Queue Config and then click Add. The following
page appears.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
64

2. Fill in the fields, using the information in the table below.
3. Click Apply/Save to save your settings.
The fields on this page are explained in the following table.
Field Name Description
Name Enter a descriptive name for this configuration. This is a free-form text
field.
Enable
Select to enable or disable a given QoS queue configured on the selected
interface.
Note: Only one queue can be defined for any one interface/precedence
pair, resulting in a maximum of three queues per interface.
Interface Select the Layer 2 interface to be associated with the defined QoS queue,
e.g., eth0 or eth4.
Queue Precedence
(Appears when you select an interface) Select the priority value to be associated with QoS queue defined. Options include levels for SP and
SP|WRR|WFQ.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
65

Field Name Description
Note: Lower value = higher priority.
Scheduler Algorithm
The following options appear only when the Queue Precedence field is set to SP|WRR|WFQ and the Scheduler
Algorithm field is set to Strict Priority. These options are do not appear in the SR3xxn models.
Minimum Rate
Shaping Rate Enter the shaping rate for packets in QoS queues. Options are 1 - 100000
(Appears when you select SP|WRR|WFQ in the
Select an algorithm for data priority in queues. Options are:
Strict Priority: Allows shaping of rate and burst size for packets in queue.
Weighted Round Robin: Applies a fair round robin scheme weighting that
is effective for networks with fixed packet sizes, e.g., ATM networks.
Weighted Fair Queuing: Applies a fair queuing weighting scheme via allowing different sessions to have different service shares for improved data
packets flow in networks with variable packet size, e.g., PTM/IP networks.
Enter the minimum shaping rate for packets in QoS queues. Options are 1 100000 Kbps.
To specify no minimum shaping, enter -1 .
Kbps.
To specify no minimum shaping, enter -1 .
Queue Precedence
field)
Shaping Burst Size Enter the shaping burst size to be applied to packets in the defined queue.
Options are 1600 bytes or greater.
Minimum Rate (Appears when you select either
uler Algorithm
in QoS queues. Options are: 1 - 100000 kbps.
To specify no minimum shaping, enter -1 .
Shaping Rate (Appears when you select either
uler Algorithm
Options are: 1 - 100000 Kbps.
To specify no minimum shaping, enter -1 .
Queue Weight (
Appears for the SR515ac model when you select either of the
algorithm options in the
oritizing this queue. Options are 1 - 63.
field) Enter the minimum shaping rate defined for packets
field) Enter the shaping rate for packets in QoS queues.
Weighted
Weighted
algorithm option in the
algorithm option in the
Scheduler Algorithm
field
) Enter a weight for pri-
WLAN Queue
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
Sched-
Sched-
Weighted
66

Note: This options is available for the SR515ac gateway only.
On this page, you can view the wireless queues and classifications.
Note: The WMM Advertise option must be enabled before these classifications will function. This option is enabled by default. If you
have disabled it, go to the Wireless > Basic page and clear the Disable WMM Advertise checkbox.
In the left navigation bar, click Advanced Setup > Quality Of Service > QoS Queue Config > Wlan Queue. The following page appears.
QoS Classification
On this page, you can create traffic class rules for classifying the ingress traffic into a priority queue. You can also mark the DSCP or Ethernet priority of the packet.
1. In the left navigation bar, click Advanced Setup > Quality Of Service > QoS Classification and then click Add. The following
page appears. A maximum of 32 entries can be configured.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
67

2. Fill in the fields, using the information in the table below.
3. Click Apply/Save to commit your changes.
The fields on this page are explained in the following table.
Field Name Description
Traffic Class Name Enter a descriptive name for this rule. This is a free-form text field.
Rule Order Select whether this rule is processed next or last in the list of classification rules.
Options are:
l Last: Sets this rule as the very last classification rule to be processed.
l Null: Sets this rule as the next classification rule to be processed.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
68

Field Name Description
Rule Status Select whether this rule is active or inactive. Options are: Enable and Disable.
Specify Classification Criteria section
Class Interface (Not applicable for SR515ac models ) Select an interface. Options are: local, eth0 -
eth4, and wl0.
Ingress Interface (
Available for SR515ac models only
) Select an interface. Options are
LAN,WAN
and any interface already configured for your gateway.
Ether Type Select the Ethernet interface type for this classification. Options include: IP, ARP,
and IPV6 for most models, and additional options for the SR515ac model.
Source MAC Address
Enter the source MAC Address and Source MAC Mask for this classification.
Source MAC Mask
Destination MAC
Address
Enter the destination MAC Address and destination MAC Mask for this classification.
Destination MAC Mask
Source IP Address/Mask Enter the source IP Address and Source IP Mask for this classification.
Protocol (Optional) Enter the Protocol specified for this classification.
UDP/TCP Source Port (Optional) Enter the Source Port applicable for this classification. You can enter a
range (port:port) or a single port.
UDP/TCP Destination
Port
(Optional) Enter the destination port applicable for this classification. You can
enter a range (port:port) or a single port.
Specify Class Queue (Not applicable for SR515ac models ) Select from the available queues.
Note: Make sure to select a queue that is configured for the interface that you
selected. If you select a queue that is not configured for the selected interface, any
packets classified into that queue are processed by the default queue for the interface.
Specify Classification Results
Egress Interface (
Available for SR515ac models only
section (
Available for SR515ac models only
Options are the interfaces already configured.
Egress Queue Available for SR515ac models only
are the queues already configured.
Mark Applied Dif-
Select the desired DSCP code.
ferentiated Service Code
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
)
) Select the egress interface for this rule.
) Select the egress queue for this rule. Options
69

Field Name Description
Point
802.1P priority This value is inserted into the Ethernet frame and used to differentiate traffic.
Lower values assign higher priorities. Options are: 1 - 7.
Rate Limit (Kbps) Enter the data traffic rate limit applied for this classification.
For SR515ac models, this field is labeled Set Rate Limit.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
70

QoS Port Shaping
QoS Port Shaping facilitates setting a fixed rate (Kbps) for each of the Ethernet ports.
Note: This feature is not available for the SR3xxn model.
1. In the left navigation bar, click Advanced Setup > Quality Of Service > QoS Port Shaping. The following page appears.
2. Fill in the fields, using the information in the table below.
3. Click Apply/Save to commit your changes.
The fields on this page are explained in the following table.
Field Name Description
Interface Each entry in this column represents one of the Ethernet LAN ports on the gateway.
Type Each entry in this column identifies the function for which each physical port is con-
figured on the gateway.
Shaping Rate (Kbps) (Not applicable for SR515ac models ) Enter the data rate for packets on the specified
Interface. Options are: 1 - 1,000,000 Kbps. The default is -1 (no shaping).
Burst Size (bytes) (Not applicable for SR515ac models ) Enter the burst size to be applied to packets in the
defined queue. Options are 1600 bytes or greater.
If you enter a value of -1 (disabled) in the Shaping Rate field, the value in this field is
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
71

Field Name Description
ignored.
Egress Shaping Rate
(Kbps)
Egress Burst Size
(bytes
Ingress Policing Rate
(Kbps)
Available for SR515ac models only
(
Interface. Options are:1-
) Enter the data rate for packets on the specified
1,000,000
Kbps. The default is-1(no shaping).
(Available for SR515ac models only) Enter the burst size to be applied to packets in the
defined queue. Options are 1600 bytes or greater. The default is 0 (no size limit).
If you enter a value of -1 (disabled) in the Egress Shaping Rate field, the value in this
field is ignored.
Available for SR515ac models only
(
) Enter data rate for policing incoming packets in the
defined queue. The default is-1(no policing).
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
72

Routing
In this section, you can configure default gateways, static routing, policy routing and RIP settings.
Default Gateway
On this page, you can configure the default gateway interface list to establish access priority, that is, iInterfaces are accessed in the
order listed in the Selected Default Gateway Interfaces column.
1. In the left navigation bar, select Advanced Setup > Routing > Default Gateway. The following page appears.
2. Select the interfaces that you want used as default gateway interfaces. Click the arrows to move your selection between the
columns. Move the highest priority interface first, followed by the next highest priority interface, and so on.
3. (Optional) In the Selected WAN Interface field, select an IPv6 interface. You must configure the IPv6 interface before it
appears in this field. The default is NO CONFIGURED INTERFACE.
4. Click Apply/Save to commit your changes.
Static Route
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
73

On this page, you can configure static routes for your network. A static route is a manually configured, fixed route for IP data. You can
enter a maximum of 32 entries.
1. In the left navigation bar, click Advanced Setup > Routing > Static Route and then click Add. The following page appears.
2. Fill in the fields, using the information in the table below.
3. Click Apply/Save to commit your changes.
The fields on this page are explained in the following table.
Field Name Description
IP Version Select the IP version associated with the static route you wish to create.
Options are: IPv4 and IPv6.
Destination IP address/-
Enter the destination network address / subnet mask for route.
prefix length
Interface Select the WAN Interface for this route. This list filtered by the selected IP ver-
sion.
Gateway IP Address Enter the destination IP address for this route. If needed, include the /prefix
length.
Metric (Optional) Establishes traffic priority/weighting. Must be equal to or greater
than zero (> 0).
Policy Routing
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
74

Policy routing makes somewhat automated routing choices based on policies defined by a network administrator. For example, a network administrator might want to deviate from standard routing based on destination markers in the packet and, instead, forward a
packet based on the source address.
On this page, you can configure similar policies.
1. In the left navigation bar, click Advanced Setup > Routing > Policy Routing and then click Add. The following page appears.
2. Fill in the fields, using the information in the table below.
3. Click Apply/Save to commit your changes.
The fields on this page are explained in the following table.
Field Name Description
Policy Name Enter a descriptive name for this entry to the policy routing table. This is a free-form text field.
Physical LAN Port Select a physical LAN interface for the policy route.
Source IP Enter the IP address for the source of this policy route.
Use Interface Select the WAN Interface for this policy route
Default Gateway IP Enter the IP address of the default gateway.
RIP (Routing Information Protocol)
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
75

RIP is a type of distance-vector routing protocol, which leverages hop count as a metric for routing. RIP puts a limit on the number of
hops (maximum of 15) allowed in order to prevent routing loops. This can sometimes limit the size of networks where RIP can be successfully employed.
On this page, you can configure the RIP settings.
1. In the left navigation bar, click Advanced Setup > Routing > RIP, and then click Add. The following page appears.
2. Fill in the fields, using the information in the table below.
3. Click Apply/Save to commit your changes.
The fields on this page are explained in the following table.
Field Name Description
Interface Displays a list of available WAN interfaces. Complete the line item(s) associated with the inter-
face where you wish to employ RIP.
Version Select the version of Routing Interface Protocol you desire. Reference RFC 1058 and RFC 1453
for detailed information on RIP versions. Options are: 1, 2, and Both.
Operation Select the operation mode. Options are:
l Active: This mode listens and advertises routes.
l Passive: This mode listens only. It does not advertise routes.
Enabled Select to employ RIP on the displayed interface.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
76

DNS
In this section, you can configure a DNS server, dynamic DNS and static DNS.
DNS Server
On this page, you can input the Domain Name Server (DNS) information supplied by your service provider.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
77

1. In the left navigation bar, click Advanced Setup > DNS > DNS Server. The following page appears.
2. Enter your desired settings. Click Apply/Save to commit changes.
The fields on this page are explained in the following table.
Field Name Description
Selected DNS Server Interfaces WAN service(s) selected to be your primary DNS server.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
78

Field Name Description
Available Wan Interfaces WAN services available to be selected for the DNS server.
Primary DNS Server Enter the IP address of the primary DNS server.
Secondary DNS Server Enter the IP address of the secondary DNS server.
WAN Interface Selected Alter this field only for IPv6 environments.
Primary IPv6 DNS Server Enter the IP address of the primary IPv6 primary DNS.
Secondary IPv6 DNS Server Enter the IP address of the primary IPv6 primary DNS.
Dynamic DNS
Dynamic DNS (DDNS) automatically updates a name server in the DNS with the active DNS configuration of its configured hostnames,
addresses or other data. Often this update occurs in real time. On this page, you can configure the settings for this feature.
1. In the left navigation bar, click Advanced Setup > DNS > Dynamic DNS and then click Add. The following page appears.
2. Enter your desired settings.
3. Click Apply/Save to commit your changes.
The fields on this page are explained in the following table.
Field Name Description
D-DNS provider Select a dynamic Domain Name Server provider.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
79

Field Name Description
Hostname Enter the hostname of the dynamic DNS server.
Interface Select the gateway WAN interface whose traffic will be pointed at the specified Dynamic DNS provider.
Username Enter the username for the dynamic DNS server .
Password Enter the password for the dynamic DNS server.
Static DNS
The Static DNS service allows you to resolve DNS queries on the Broadband Router by adding a static host name to the IP Address mappings. On this page, you can configure up to 10 static DNS entries.
1. In the left navigation bar, click Advanced Setup > DNS > Static DNS and then click Add. The following page appears.
2. Enter your desired settings.
3. Click Apply/Save to commit your changes.
The fields on this page are explained in the following table.
Field Name Description
Hostname Enter the hostname of the client computer.
Interface Enter the IP address of the DNS server client uses to assist in resolving domain names.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
80

DSL
On this page, you can configure settings for the DSL interface.
Caution: Altering these settings unnecessarily can result in the gateway being unable to attain DSL synchronization.
1. In the left navigation bar, click Advanced Setup -> DSL. The following page appears.
2. Enter your desired settings.
3. To configure advanced settings, see "Advanced settings".
4. Click Apply/Save to commit your changes.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
81

Note: For the SR3xxn models, the following fields are not available: VDSL2 modulation, profile options, and US0 checkbox.
The fields on this page are explained in the following table.
Modulation Data Transmission Rate Max Downstream
(Mbps)
G.Dmt ITU-T G.992.1 standard.
G.lite ITU-T G.991.2 standard.
T1.413 ANSI T1.413 Issue 2 standard.
ADSL2 ITU-T G.992.3 standard.
12 1.3
4 0.5
8 1.0
12 1.0
AnnexL Annex L of ITU-T G.992.3 standard which supports longer loops but with reduced
transmission rates.
ADSL2+ ITU-T G.992.5 standard.
AnnexM Annex L of ITU-T G.992.5 standard which supports extended upstream band-
28 1.0
24 3
width.
VDSL2 ITU-T G.993.2 standard.
100 60
The following table explains the maximum transaction power for each profile supported for SRG gateways.
Max
Upstream
(Mbps)
Parameter 8a 8b 8c 8d 12a 12b 17a
Max DS Tx Power (dBm) +17.5 +20.5 +11.5 +14.5
Max US Tx Power (dBm) +14.5
Min bidirectional net data rate 50Mbps 68Mbps 100Mbps
Other Settings
Field Name Description
Inner Pair/Outer
Pair
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
The RJ11 connector has four contacts. The center pair of pins is DSL1. The outer pair pins are the contacts for DSL2.
Select which pair should be used.
82

Other Settings
Field Name Description
Capability
Inventory Management
l Bitswap Enable: Enables adaptive handshaking functionality.
l SRA Enable: Enables Seamless Rate Adaptation.
l PhyR Enable: Enables Physical Layer Retransmission.
l ADSL PTM Mode Enable: Enables Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line in Packet Transfer Mode.
Select whether to use the gateway serial number as the EOC serial number in your inventory management database.
Advanced settings
1. To configure the test mode, click Advanced Settings on the Advanced > DSL page. The following page appears.
2. Click Apply to place the gateway in test mode.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
83

3. To view the ADSL tone settings, click Tone Selection. TADSL Tone Settings page appears.
Caution: Do not modify the tones selected unless under explicit instruction from a telecommunications professional.
4. Click Apply to commit your changes or Close to return to the previous page.
The fields on this page are explained in the following table.
Mode Description
Normal Puts the DSL PHY in test mode, sending only a Normal signal.
Reverb Puts the DSL PHY in test mode, sending only a REVERB signal.
Medley Puts the DSL PHY in test mode, sending only a MEDLEY signal.
No Retrain The DSL PHY attempts to establish a connection as in Normal mode, but once the connection is up, it
does not retrain even if the signal is lost.
L3 Puts the DSL modem in the L3 power state.
DSL Bonding
Note: This feature is supported only on the SR550n and SR552n models.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
84

Bonding enables two DSL lines to feed the same modem and leveraging the bandwidth of both lines. Once bonded, the lines behave as a
single, higher bandwidth connection.
1. In the left navigation bar, click Advanced Setup > DSL Bonding. The following page appears.
2. To enable bonding, click xDSL Bonding Capability.
3. Click Save/Reboot to commit your changes. Your gateway is rebooted.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
85

UPnP
On this page, you can enable UPnP when 3rd party devices on your LAN support this Universal Plug and Play standard. Common client
devices include gaming consoles, IP cameras, printers and others. This feature is enabled by default.
1. In the left navigation bar, select Advanced Setup > UPnP. The following page appears.
2. To disable this option, click Enable UPnP to clear the box.
3. Click Apply/Save to commit your changes.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
86

DNS Proxy
On this page, you can configure the DNS proxy settings. A DNS proxy improves domain look-up performance for clients by creating a
historical cache of look-ups.
1. In the left navigation bar, click Advanced Setup > DNS Proxy. The following page appears.
2. If not already selected, click Enable DNS Proxy.
The Host name and Domain Name fields appear.
3. Enter the host name of the broadband router and the domain name of the LAN network.
4. Click Apply/Save to commit your changes.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
87

Interface Grouping
You can create an interface group to map local interfaces to WAN interfaces. A typical application for this feature is assigning IPTV STBs
to a WAN interface.
1. In the left navigation bar, click Advanced Setup > Interface Grouping and then click Add (below the table). The following page
appears.
2. To create a new interface group, enter a unique Group Name, then proceed with either step 3 (dynamic) or step 4 (static)
below.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
88

3. If this new grouped interface is to share the WAN interface, click Shared WAN Interface. Not selecting this option this will
cause the WAN interface you select to be removed from any other interface groups.
Important: If a vendor ID is configured for a specific client device, make sure to reboot the client device attached to the gate-
way to allow it to obtain an appropriate IP address.
4. Map the ports for the WAN or LAN interface:
a. Select an interface from the applicable Available Interface list.
b. Add it to the Grouped Interface list by clicking the arrow to create the required mapping of the ports. Hold down the
Shift key to select multiple interfaces.
Note: Depending on the WAN interface configuration, these clients may obtain public IP addresses.
5. To automatically add LAN clients (such as set-top boxes) to a WAN Interface in the new group, enter the DHCP vendor ID
string. You can add up to 16 vendor IDs.
When you configure a DHCP vendor ID string, any DHCP client request that includes this vendor ID is denied an IP address from
the local DHCP server (DHCP option 60).
6. Click Apply/Save. Your changes take effect immediately.
7. To remove a grouping, select the grouping and click Remove. You can only remove groupings that you create.
IP Tunnel
IP Tunneling is typically used as a means to establish a path between two independent networks. Your SmartRG gateway supports connecting islands of IPv6 networks across the IPv4 internet or IPv4 in IPv6 as well.
On this page, you can configure IP tunnel settings.
Note: For IPv6inIPv4, only 6rd configuration is supported. For IPv4inIPv6, only DS-Lite configuration is supported.
IPv6inIPv4
On this page, you can configure the IPv6inIP4 settings.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
89

1. In the left navigation bar, click Advanced Setup > IP Tunnel > IPv6inIPv4 and then click Add. The following page appears.
2. Enter a Tunnel Name.
3. Select the WAN and LAN interfaces associated with the tunnel you wish to establish.
4. IPv4 Mask Length, 6rd Prefix with Prefix Length and Border Relay IPv4 Address can be configured automatically. To configure
these settings manually, select Manual under Associated LAN Interface and enter the appropriate values.
5. Click Apply/Save to commit your changes.
IPv4inIPv6
On this page, you can configure the IPv4inIP6 settings.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
90

1. In the left navigation bar, click Advanced Setup > IP Tunnel > IPv6inIPv4 and then click Add. The following page appears.
Note: Currently, only the DS-Lite Mechanism is supported. Consult RFC6333 for further information regarding DS-Lite.
2. Enter a Tunnel Name
3. Select the LAN and WAN interfaces associated with the tunnel you wish to establish.
4. AFTR (Address Family Transition Router) may be configured automatically. To configure AFTR manually, select Manual under
Associated LAN Interface and enter the appropriate values.
5. Click Apply/Save to commit your changes.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
91

IPSec
Internet Protocol Security is a protocol for securing communications by packet level encryption and authentication.
On this page, you can enable and remove connections, or edit existing connections.
1. In the left navigation bar, click Advanced Setup > IP Sec and then click Add New Connection. The following page appears.
2. Enter your connection details by completing the appropriate fields.
3. If desired, click Advanced IKE Settings to select Phase 1 and Phase 2 specific parameters. For detailed information about these
settings, see "Advanced IKE Settings".
4. Click Apply/Save to commit your changes.
The fields on this page are explained in the following table.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
92

Field Name Description
IPSec Connection Name A free form text field. Enter a descriptive name for this connection
IP Version Select the IP version environment associated with your infrastructure. Options are IPv4 and IPv6.
Tunnel Mode Select the encapsulation method to be used. Options are:
l AH: Use this mode to encapsulate a packet with AH and IP headers. For authentication, the entire
packet is signed.
l ESP: Use this mode to encapsulate a packet with ESP and IP headers. An ESP trailer is added to
the packet for authentication and integrity.
Local Gateway Interface Select the WAN connection to be associated with this tunnel.
Remote IPSec Gateway
Enter the WAN IP for this tunnel.
Address
Tunnel Access From Local IP
Addresses
Select IP information for site A and B. Options are:
l Subnet: Allows access to the entire LAN.
l Single Address: For single host, select this option.
IP Address for VPN Enter the IP address for local access.
Mask or Prefix Length Enter the subnet mask or prefix length for IP address entered for local access, e.g., 255.255.255.0.
Tunnel Access From
Remote IP Addresses
Select IP information for site A and B. Options are:
l Subnet: Allows access to the entire LAN.
l Single Address: For single host, select this option.
IP Address for VPN Enter the IP address for remote access.
Mask or Prefix Length Enter the subnet mask or prefix length for IP address entered for remote access, e.g., 255.255.255.0.
Key Exchange Method The key-exchange method to be used for IPSec. Options are:
l Auto(IKE): This method uses the negotiated key-exchange method for IPSec. This is the default
and recommended for best results.
l Manual: This nethod requires that you configure the details.
Authentication Method Select the method by which the remote end will authenticate.
l Pre-Shared Key: A key is distributed to authorized users for logging into the system. Enter the
key in the Pre-shared Key field.
l Certificate (x.509): A certificate is used for authentication. Select the certificate file in the Cer-
tificate field that appears.
Perfect forwarding Secrecy This setting determines whether a session key derived from a set of long-term keys is compromised if
one of the long-term keys in the set is compromised.
l Enable: Prevents long-term key from being compromised.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
93

Field Name Description
l Disable: Permits long-term keys to be compromised.
Advanced IKE Settings
You can configure advanced IKE settings if desired.
1. On the IPSec Settings page, click Show Advanced IKE Settings to display the Phase 1 and Phase 2 fields.
2. Fill in the fields, using the information in the table below.
Field Name Description
Mode Select a mode. Options are Main and Aggressive.
Encryption Algorithm Select the encryption algorithm. Options are 3DES , AES -
128, AES-192, and AES-256.
Integrity Algorithm Select the integrity algorithm. Options are MD5 and SHA1.
Select Diffie-Hellman Group for
Key Exchange
Key Life Time Enter the number of seconds that a key is valid. The default
3. Click Apply/Save to commit your changes.
Select the D-H group. Options are 768bit - 8192bit. The
default is 1024bit.
is 3600 seconds.
Certificate
On this page, you can configure certificates for the gateway. You can use Local and Trusted CA certificates on this gateway.
Local
Local certificates are used to identify the gateway to other users. On this page, you can create a new certificate request locally and have
it signed by a certificate authority, or you can import an existing certificate.
For additional info regarding Public Key Infrastructure (PKI), refer to ITU-T X.509.
1. In the left navigation bar, click Advanced Setup > Certificate > Local and then click Create Certificate Request. The following
page appears.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
94

2. Enter your connection details by completing the appropriate fields. For more information about certificates, refer to the ITU
X.509 standard.
3. Click Apply to complete the request.
The fields on this page are explained in the following table.
Field Name Description
Certificate Name A free-form text field used to describe the intended use of the certificate.
Common Name Enter the IPaddress (in dotted decimal notation), domain name or email address in
the field provided. The domain name or email address is for identification purposes
and is a free-form text field.
Organization Name A free form text field. Typically, this is the name of the company creating the
request.
Country/Region Select the country or region in which this certificate will be employed.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
95

4. To import a certificate and the corresponding private key, click Import Certificate. The following page appears.
5. In the Certificate Name field, type "cpecert".
6. Paste the Certificate details between the BEGIN and END markers.
7. Paste the Private Key information between the BEGIN and END markers.
8. Click Apply to implement this certificate.
Trusted CA
On this page you import and store up to four trusted certificates. Trusted Certificates are used to identity other gateways to your gateway as a trusted source.
1. In the left navigation bar, click Advanced Setup > Certificate > Trusted CA and then click Import Certificate. The following
page appears.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
96

2. In the Certificate Name field, type "acscert", and then paste the certificate details between the BEGIN and END markers.
3. Click Apply to commit this certificate.
After you add one certificate, a Remove button appears on the Trusted CA landing page. Click this button to remove the current cer-
tificate and replace it with a new one.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
97

Multicast
Multicast methodology is used for applications shipping information simultaneously to multiple destinations. The most common scenario is Internet television and other streaming media. In IP Multicast, the implementation occurs at the IP routing level, where routers
create the most efficient distribution paths for packets sent to a destination.
On this page, you can configure the multicast settings.
1. In the left navigation bar, select Advanced Setup > Multicast. The following page appears.
2. Update or complete the necessary fields. The same fields are provided for both IGMP and MLD configuration.
3. Click Apply/Save to commit your changes.
The fields on this page are explained in the following table.
Field Name Description
Multicast Precedence Select whether IGMP packets are given priority handling and at what level.
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
98

Field Name Description
Options are:
l Enable: IGMP packets are prioritized using the multicast precedence
value. The lower the multicast precedence value, the higher that IGMP
packets will be placed in the queue.
l Disable: IGMP packets are not prioritized.
Multicast Strict Grouping
Enforcement
Available for SR515ac models only
(
IGMP packets. Options are
Enable
) Select whether strict grouping is applied to
Disable
and
.
Default Version Enter the supported IGMP version. Options are: 1 - 3.
Query Interval The interval at which the multicast router sends a query messages to hosts,
expressed in seconds.
If you enter a number below 128, the value is used directly. If you enter a number
128, it is interpreted as an exponent and mantissa.
Query Response Interval Upon receiving a query packet, a host begins counting down seconds, from a ran-
dom number. When the timer expires, the host sends its report.
Enter the maximum number of seconds that a host can pick to count down from.
The value must be greater than the Query Interval. If using IGMP v1, this value is
fixed at 10 seconds.
Last Member Query Interval
Enter the maximum response time within which the host must respond to the Out
of Sequence query from the router. The default is 1000ms.
IGMP uses this value when the router receives an IGMPv2 Leave report indicating
at least one host wants to leave the group. Upon receiving the Leave report, the
router verifies whether the interface is configured for IGMP Immediate Leave. If
not, the router sends the out-of-sequence query.
Robustness Value Enter the value representing the complexity of the query. The greater the value,
the more robust the query. Options are: 2 - 7.
Maximum Multicast
Enter the maximum number of groups allowed.
Groups
Maximum Multicast Data
Enter the maximum number of data sources allowed. Options are: 1 - 24.
Sources (for IGMP v3)
Maximum Multicast
Group Members
Enter the maximum number of multicast groups that can be joined on a port or
group of ports.
Fast leave Select whether the IGMP proxy removes group members immediately without
SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016
99
 Loading...
Loading...