
SR320n SR360n
User Manual
VER: 1.0

User Manual
Contents
1 Safety Instructions....................................................................................1
2 Overview..................................................................................................2
2.1 Application.............................................................................................2
2.2 Features ................................................................................................2
2.3 Standards Compatibility and Compliance..............................................3
3 Hardware Description and Installation .....................................................5
3.1 Hardware Description............................................................................5
3.1.1 Front Panel............................................................................5
3.1.2 Rear Panel and Side Panel...................................................6
3.2 Hardware Installation.............................................................................7
3.2.1 Choosing the Best Location for Wireless Operation .............7
3.2.2 Connecting the Device..........................................................8
4 PC Network Configuration and Login.....................................................10
4.1 PC Network Configuration...................................................................10
4.2 Logging In to the DSL Router..............................................................12
5 Web-Based Management ......................................................................13
5.1 Device Information...............................................................................13
5.1.1 Summary.............................................................................13
5.1.2 WAN....................................................................................14
5.1.3 Statistics..............................................................................15
5.1.4 LAN .....................................................................................15
5.1.5 WAN Service.......................................................................15
5.1.6 xTM .....................................................................................16
5.1.7 xDSL....................................................................................16
5.1.8 Route...................................................................................19
5.1.9 ARP.....................................................................................20
5.1.10 DHCP..................................................................................20
5.2 Advanced Setup..................................................................................20
5.2.1 Layer2 Interface ..................................................................22
5.2.2 WAN Service.......................................................................25
5.2.3 LAN Configuration...............................................................50
5.2.4 NAT.....................................................................................56
i

User Manual
5.2.5 Security ...............................................................................60
5.2.6 Parental Control ..................................................................63
5.2.7 Quality of Service................................................................ 65
5.2.8 Routing................................................................................68
5.2.9 DNS.....................................................................................72
5.2.10 DSL .....................................................................................73
5.2.11 UPnP...................................................................................74
5.2.12 DNS Proxy...........................................................................75
5.2.13 Print Server .........................................................................75
5.2.14 Packet Acceleration.............................................................76
5.2.15 Storage Service...................................................................76
5.2.16 Interface Grouping...............................................................77
5.2.17 IP Tunnel.............................................................................78
5.2.18 IPSec...................................................................................80
5.2.19 Certificate............................................................................82
5.2.20 Power Management............................................................86
5.2.21 Multicast.............................................................................. 87
5.3 Wireless...............................................................................................88
5.3.1 Basic Settings......................................................................89
5.3.2 Security ...............................................................................90
5.3.3 MAC Filter ...........................................................................98
5.3.4 Wireless Bridge................................................................... 99
5.3.5 Advanced Settings ............................................................100
5.3.6 Station Info........................................................................103
5.4 Diagnostics........................................................................................103
5.4.1 Diagnostics........................................................................103
5.5 Management......................................................................................104
5.5.1 Settings .............................................................................105
5.5.2 System Log .......................................................................106
5.5.3 SNMP Agent......................................................................107
5.5.4 TR-69 Client......................................................................108
5.5.5 Internet Time.....................................................................109
5.5.6 Access Control...................................................................111
5.5.7 Update Software................................................................ 112
ii

User Manual
5.5.8 Reboot............................................................................... 113
6 Q&A...................................................................................................... 114
iii

User Manual
1 Safety Instructions
Read the following information carefully before operating the device. Please follow
the following precaution items to protect the device from risks and damage caused
by fire and electric power:
Use volume labels to mark the type of power.
Use the power adapter that is packed within the device package.
Pay attention to the power load of the outlet or prolonged lines. An
overburden power outlet or damaged lines and plugs may cause electric
shock or fire accident. Check the power cords regularly. If you find any
damage, replace it at once.
Proper space left for heat dissipation is necessary to avoid any damage
caused by overheating to the device. The holes on the device are designed
for heat dissipation to ensure that the device works normally. Do not cover
these heat dissipation holes.
Do not put this device close to a place where a heat source exits or high
temperature occurs. Avoid the device from direct sunshine.
Do not put this device close to a place where is over damp or watery. Do not
spill any fluid on this device.
Do not connect this device to any PC or electronic product, unless our
customer engineer or your broadband provider instructs you to do this,
because any wrong connection may cause any power or fire risk.
Do not place this device on an unstable surface or support.
1

User Manual
2 Overview
The xDSL Router integrates wireless LAN, USB storage, and 3G WAN services
into one unit. It is designed to provide a simple and cost-effective xDSL Internet
connection for a private Ethernet and 802.11g/802.11b/802.11n wireless network.
The Router combines high-speed xDSL Internet connection, IP routing for the LAN
and wireless connectivity in one package. It is usually preferred to provide high
access performance applications for the individual users, the SOHOs, and the
small enterprises.
The Router is easy to install and use. The Router connects to an Ethernet LAN or
computers via standard Ethernet ports. The xDSL connection is made using
ordinary telephone line with standard connectors. The advanced security
enhancements, packet filtering and port redirection, can help protect your network
from potentially devastating intrusions by malicious agents from outside your
network.
Network and Router management is done through the web-based management
interface that can be accessed through the local Ethernet using any web browser.
Y ou may also enable remote management to enable configuration of the Router via
the WAN interface.
2.1 Application
Home gateway
3G Internet
Wireless LAN
SOHOs
Small enterprises
Higher data rate broadband sharing
Audio and video streaming and transfer
PC file and application sharing
Network and online gaming
USB storage
2.2 Features
2

User Manual
User-friendly GUI for web configuration
Several pre-configured popular games. Just enable the game and the port
settings are automatically configured.
Compatible with all standard Internet applications
Industry standard and interoperable xDSL interface
Simple web-based status page displays a snapshot of system configuration,
and links to the configuration pages
Downloadable flash software updates
Support for up to 8 permanent virtual circuits (PVC)
Support for up to 8 PPPoE sessions
Support RIP v1 & RIP v2
WLAN with high-speed data transfer rates, compatible with IEEE
802.11b/g/n
IP routing and bridging
Asynchronous transfer mode (ATM) and digital subscriber line (DSL) support
Point-to-point protocol (PPP)
Network/port address translation (NAT/PAT)
Quality of service (QoS)
Wireless LAN security: WPA, 802.1x, RADIUS client
Universal plug-and-play(UPnP)
Print server
Web filtering
Management and control
Web-based management (WBM)
Command line interface (CLI)
TR-069 WAN management protocol
Remote update
System statistics and monitoring
DSL router is targeted at the following platforms: DSL modems, wireless
access points and bridge.
2.3 Standards Compatibility and Compliance
Support application level gateway (ALG)
ITU G.992.1 (G.dmt)
ITU G.992.2 (G.lite)
3

User Manual
ITU G.994.1 (G.hs)
ITU G.992.3 (ADSL2)
ITU G.992.5 (ADSL2+)
3G (WCDMA, CDMA2000, TD-SCDMA)
ANSI T1.413 Issue 2
IEEE 802.3
IEEE 802.3u
IEEE 802.11b
IEEE 802.11g
IEEE 802.11n
4

User Manual
3 Hardware Description and Installation
Note:
The figures in this document are for reference only.
3.1 Hardware Description
3.1.1 Front Panel
Figure 1 Front panel
The following table describes the indicators on the front panel.
Indicator Color Status Description
On
Green
Power
Red
DSL Green
Internet
LAN
1/2/3/4
Green
Red On Authentication has failed.
Green
Blink The software is upgrading.
Off The device is powered off.
On The device is initiating.
Blink The software is upgrading.
On DSL link has established.
Blink The DSL line is training.
Off Device is powered off.
On
Blink Internet data is being transmitted.
Off Ethernet interface is disconnected.
On The Ethernet interface is connected.
Blink
Off The Ethernet interface is disconnected.
The device is powered on and the device operates
normally.
Internet is synchronized successfully in the route
mode.
Data is being transmitted through the Ethernet
interface.
5
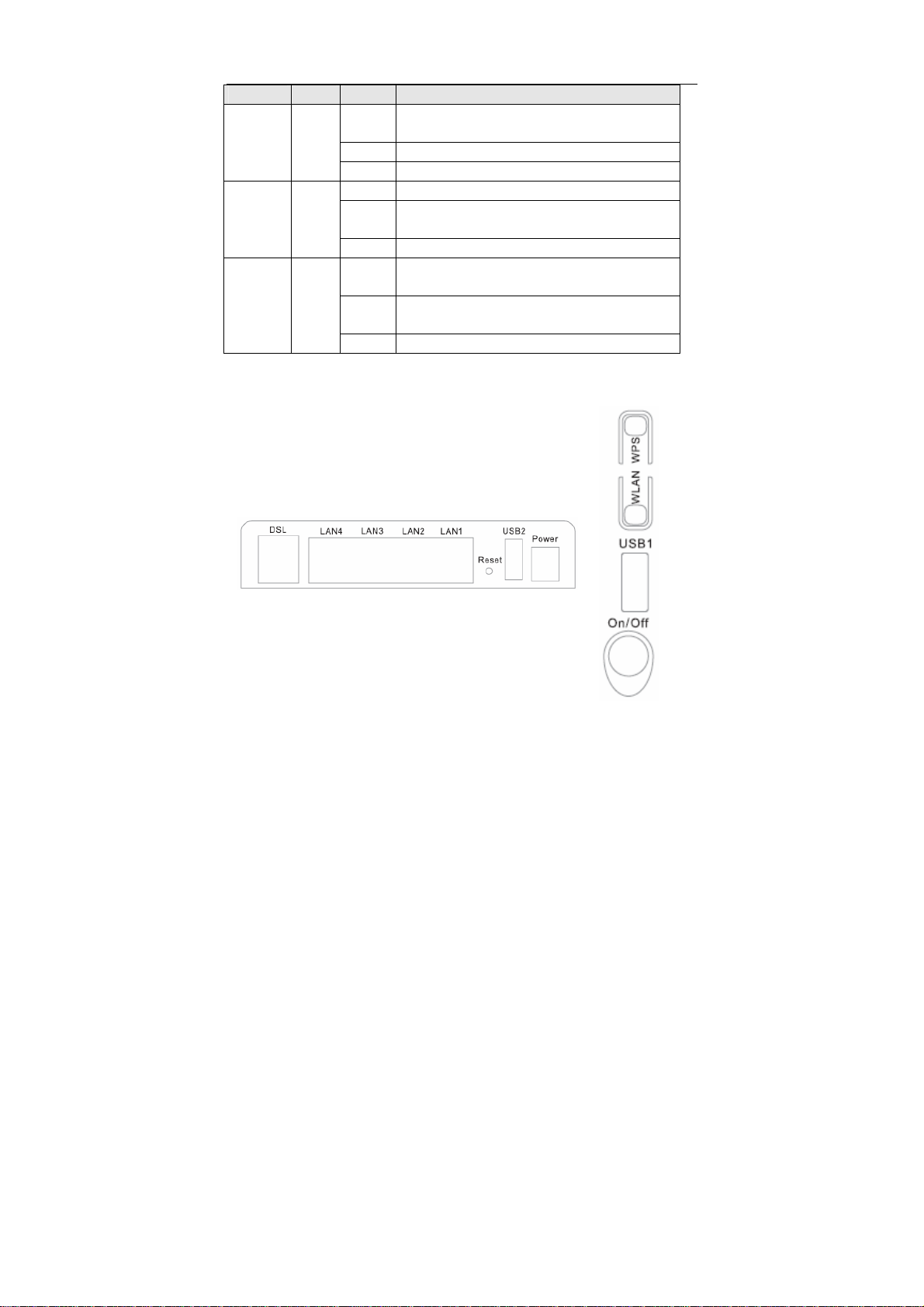
User Manual
Indicator Color Status Description
On
USB Green
WLAN Green
WPS Green
Blink Data is being transmitted.
Off No signal is detected.
On WLAN is enabled.
Blink
Off WLAN is disabled.
On
Blink
Off Wi-Fi Protected Setup is disabled.
The connection of 3G or USB flash disk has
established.
Data is being transmitted through the wireless
interface.
Connection succeeds under Wi-Fi Protected
Setup.
Negotiation is in progress under Wi-Fi Protected
Setup.
3.1.2 Rear Panel and Side Panel
6
User Manual
Figure 2 Rear panel
The following table describes the interfaces or the buttons.
Interface Description
DSL
LAN 4~1
Reset
USB
Power Power interface, for connecting the power adapter.
On/Off
WLAN WLAN switch, for enabling or disabling the WLAN function.
WPS
Warning:
Do not press the Reset button unless you want to clear the current settings. The
Reset button is in a small circular hole on the rear panel. If you want to restore the
default settings, please press the Reset button gently for 1 second with a fine needle
inserted into the hole and then release the button. The system reboots and returns to
the factory defaults.
RJ-11 port: Connect the router to DSL connector or splitter through
telephone cable.
RJ-45 port, for connecting the router to a PC or another network
device.
Press the button for at least 1 second and then release it. System
restores the factory default settings.
For connecting the 3G network adapter or other USB storage
devices.
Power switch.
This button is used for enabling WPS PBC mode. If WPS is enabled,
press this button, and then the wireless router starts to accept the
negotiation of PBC mode.
Figure 3 Side
panel
3.2 Hardware Installation
3.2.1 Choosing the Best Location for Wireless Operation
Many environmental factors may affect the effective wireless function of the DSL
Router. If this is the first time that you set up a wireless network device, read the
following information:
7

User Manual
The access point can be placed on a shelf or desktop, ideally you should be able to
see the LED indicators in the front, as you may need to view them for troubleshooting.
Designed to go up to 100 meters indoors and up to 300 meters outdoors, wireless
LAN lets you access your network from anywhere you want. However, the numbers of
walls, ceilings, or other objects that the wireless signals must pass through limit sign al
range. Typical ranges vary depending on types of materials and background RF
noise in your home or business.
3.2.2 Connecting the Device
Step 1 Connect the DSL port of the router and the Modem port of the splitter
with a telephone cable; connect the phone to the phone port of the
splitter through a cable; and connect the incoming line to the Line port of
the splitter.
The spliiter has three ports:
Line: Connect to a wall phone jack (RJ-11 jack)
Modem: Connect to the Line interface of the router
Phone: Connect to a telephone set
Step 2 Connect the LAN port of the router to the network card of the PC through
an Ethernet cable.
Step 3 Plug the power adapter to the wall outlet and then connect the other end
of it to the Power port of the router.
Note:
If you use 3G WAN service, connect the 3G USB data card to the USB port of
the router.
The followig figure displays the connection of the DSL router, PC, and telephones.
8
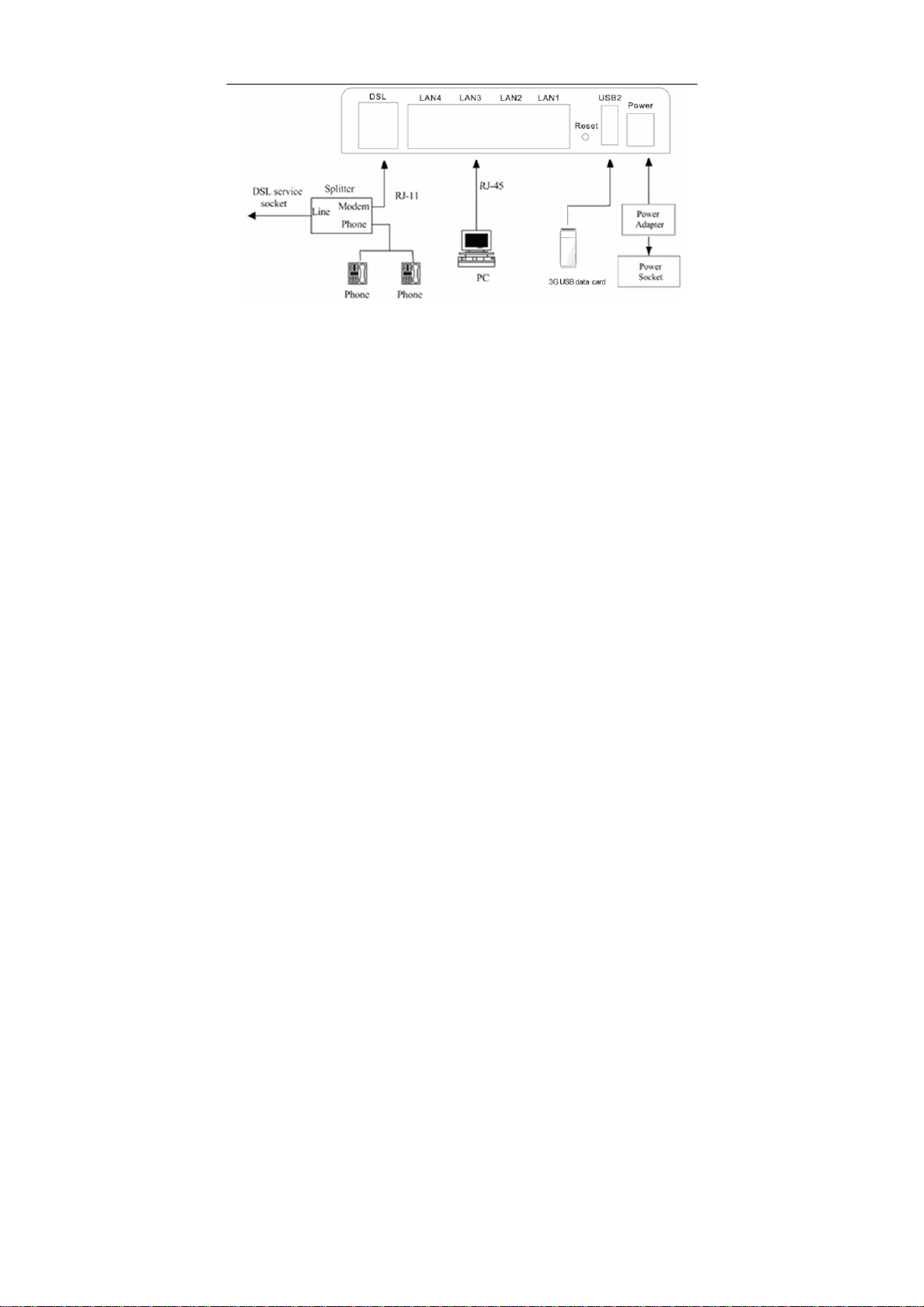
User Manual
Figure 4 Connecting the DSL router
9

User Manual
4 PC Network Configuration and Login
4.1 PC Network Configuration
Each network interface on the PC should either be configured with a statically defined
IP address and DNS address, or be instructed to automatically obtain an IP address
using the network DHCP server. DSL router provides a DHCP server on its LAN and
it is recommended to configure your LAN to automatically obtain its IP address and
DNS server IP address.
The configuration principle is identical but should be carried out differently on each
operating system.
The following displays the TCP/IP Properties dialog box on Windows XP.
10
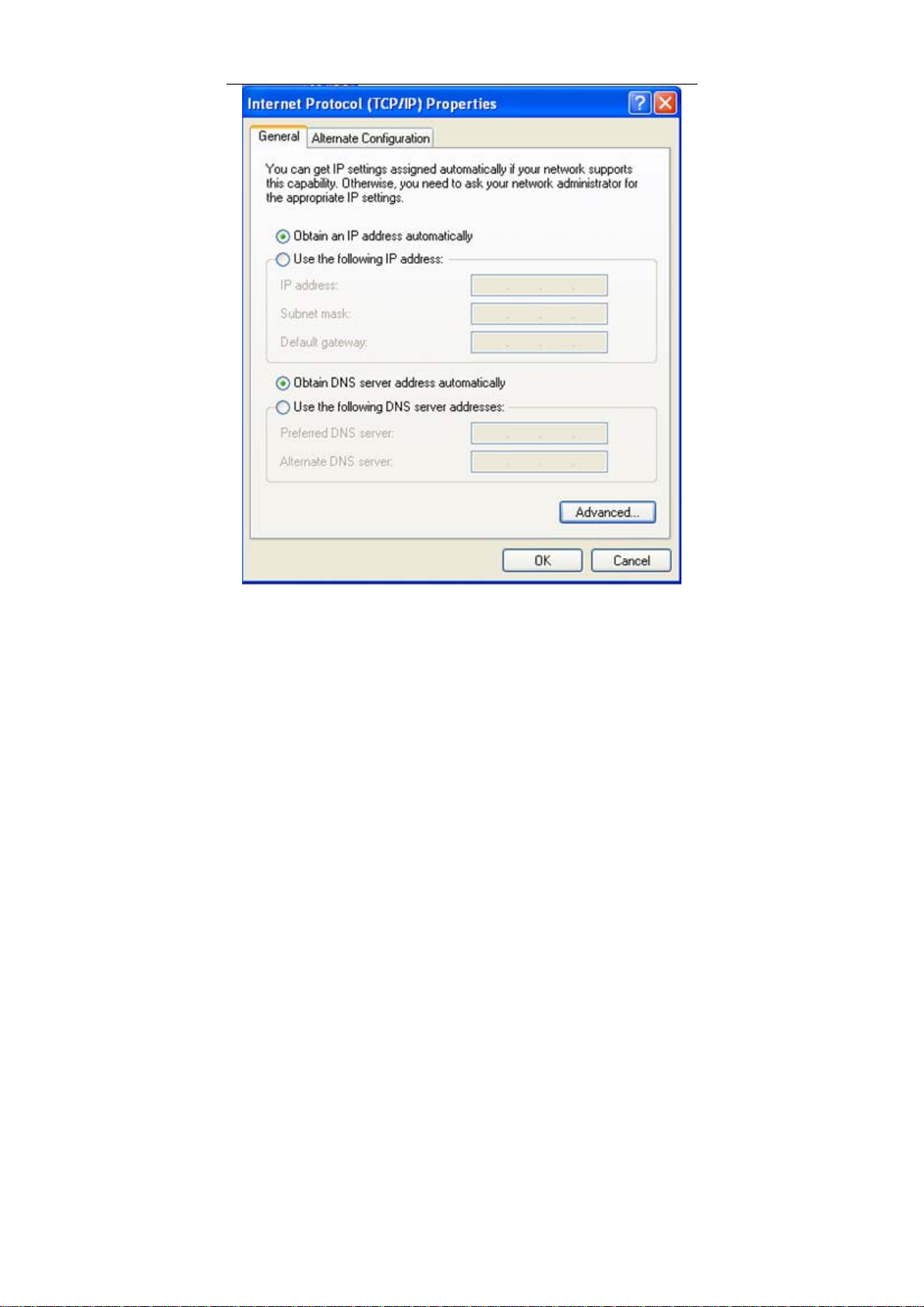
User Manual
Figure 5 IP and DNS configuration
TCP/IP configuration steps for Windows XP are as follows:
Choose Start > Control Panel > Network Connections.
Right-click the Ethernet connection icon and choose Properties.
On the General tab, select the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) component and click
Properties.
The Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties window appears.
11
User Manual
Select the Obtain an IP address automatically radio button.
Select the Obtain DNS server address automatically radio button.
Click OK to save the settings.
4.2 Logging In to the DSL Router
To log in to the DSL router, do as follows:
Open a Web browser on your computer.
Enter http://192.168.1.1 (the default IP address of the DSL router) in the address
bar. The login page appears.
Enter the user name and the password. The default username and password of the
super user are admin and admin. The username and password of the
common user are user and user. You need not enter the username and
the password again if you select the option Remember my password. It
is recommended to change these default values after logging in to the
DSL router for the first time.
Click OK to log in to the Web page. Otherwise, please click Cancel to exit the login
page.
Figure 6 Login page
12

User Manual
After logging in to the DSL router as a super user, you can query, configure, and
modify all the settings, and diagnose the system.
5 Web-Based Management
This chapter describes how to use Web-based management of the DSL router, which
allows you to configure and control all of DSL router features and system parameters
in a user-friendly GUI.
5.1 Device Information
Choose Device Info, and the submenus of Device Info are shown as below:
5.1.1 Summary
Choose Device Info > Summary, and the following page appears.
13

User Manual
This page displays the device information such as the board ID, software version, and
the information of your WAN connection such as the upstream rate and the LAN
address.
5.1.2 WAN
Choose Device Info > WAN and the following page appears.
14
User Manual
This page displays the information of the WAN interface, such as the connection
status, and the IP address.
5.1.3 Statistics
5.1.4 LAN
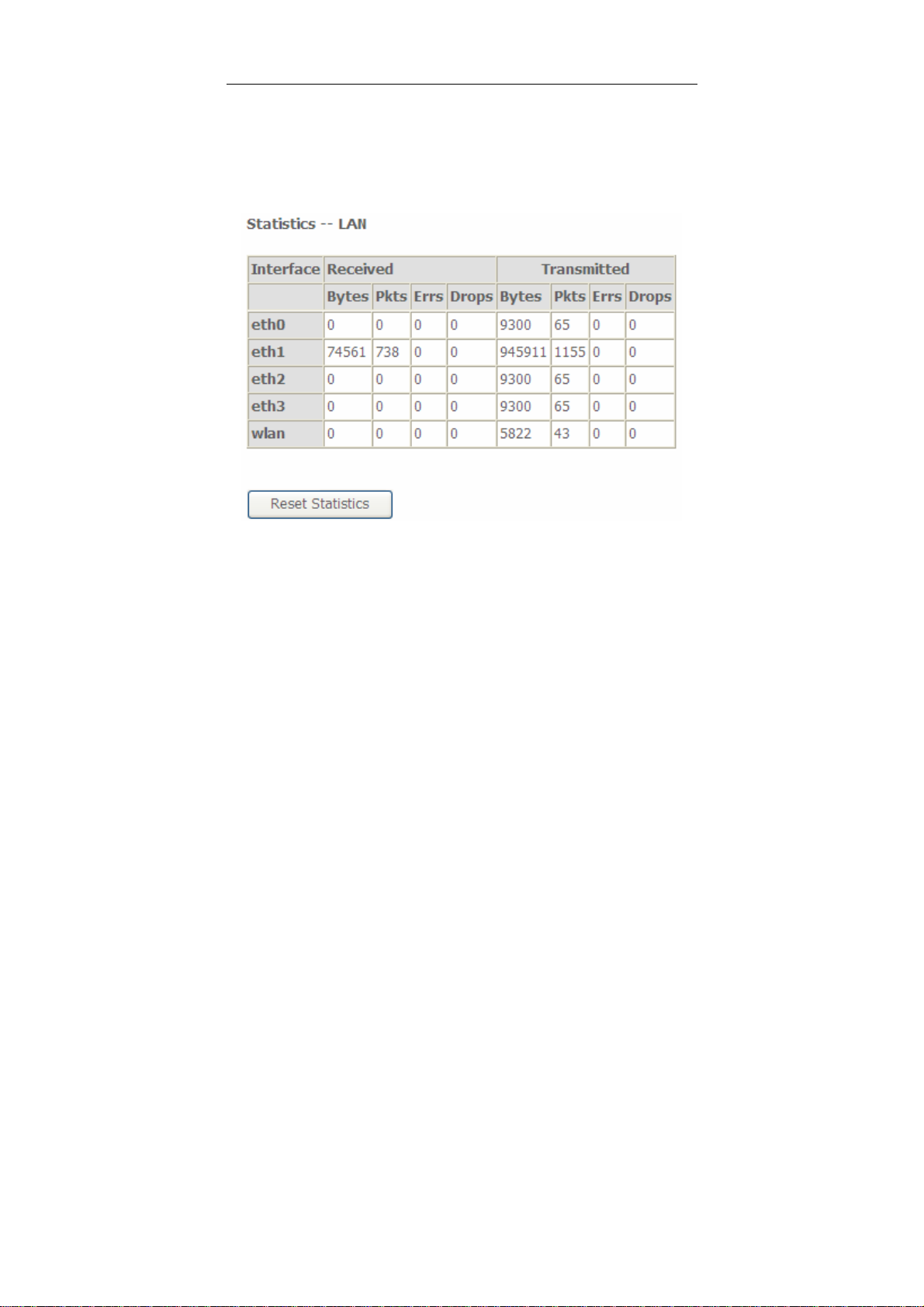
Choose Device Info > Statistics > LAN and the following page appears.
In this page, you can view the statistical information about the recevied and
transmitted data packets of the Ethernet and wireless interfaces.
Click Reset Statistics to restore the values to zero and recount them.
5.1.5 WAN Service
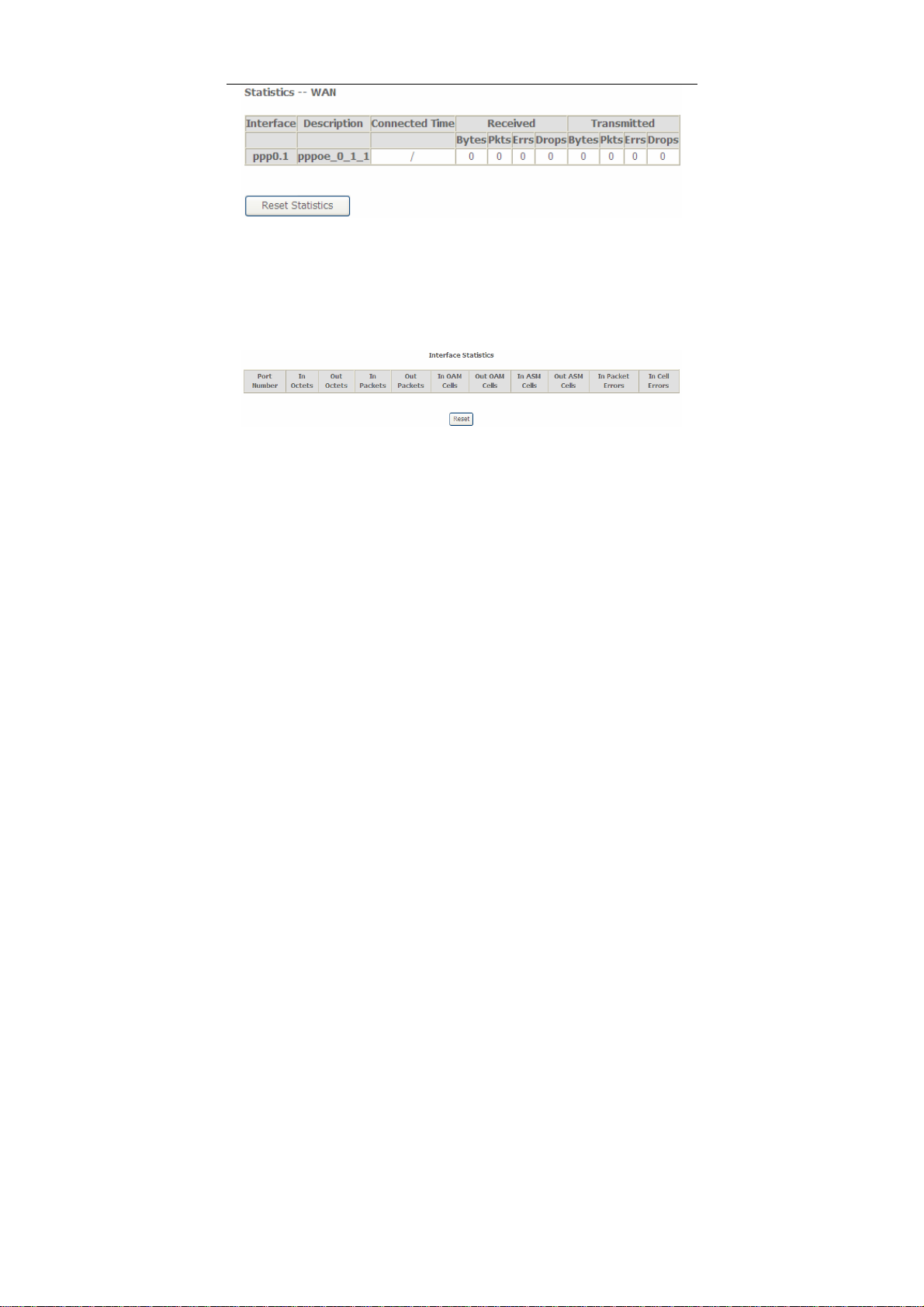
Choose Device Info > Statistics > WAN Service and the following page appears.
15
User Manual
In this page, you can view the statistical information about the recevied and
transmitted data packets of the WAN interface.
Click Reset Statistics to restore the values to zero and recount them.
5.1.6 xTM
Choose Device Info > Statistics > xTM and the following page appears.
In this page, you can view the statistical information about the recevied and
transmitted data packets at the xTM interfaces.
Click the Reset button to restore the values to zero and recount them.
5.1.7 xDSL
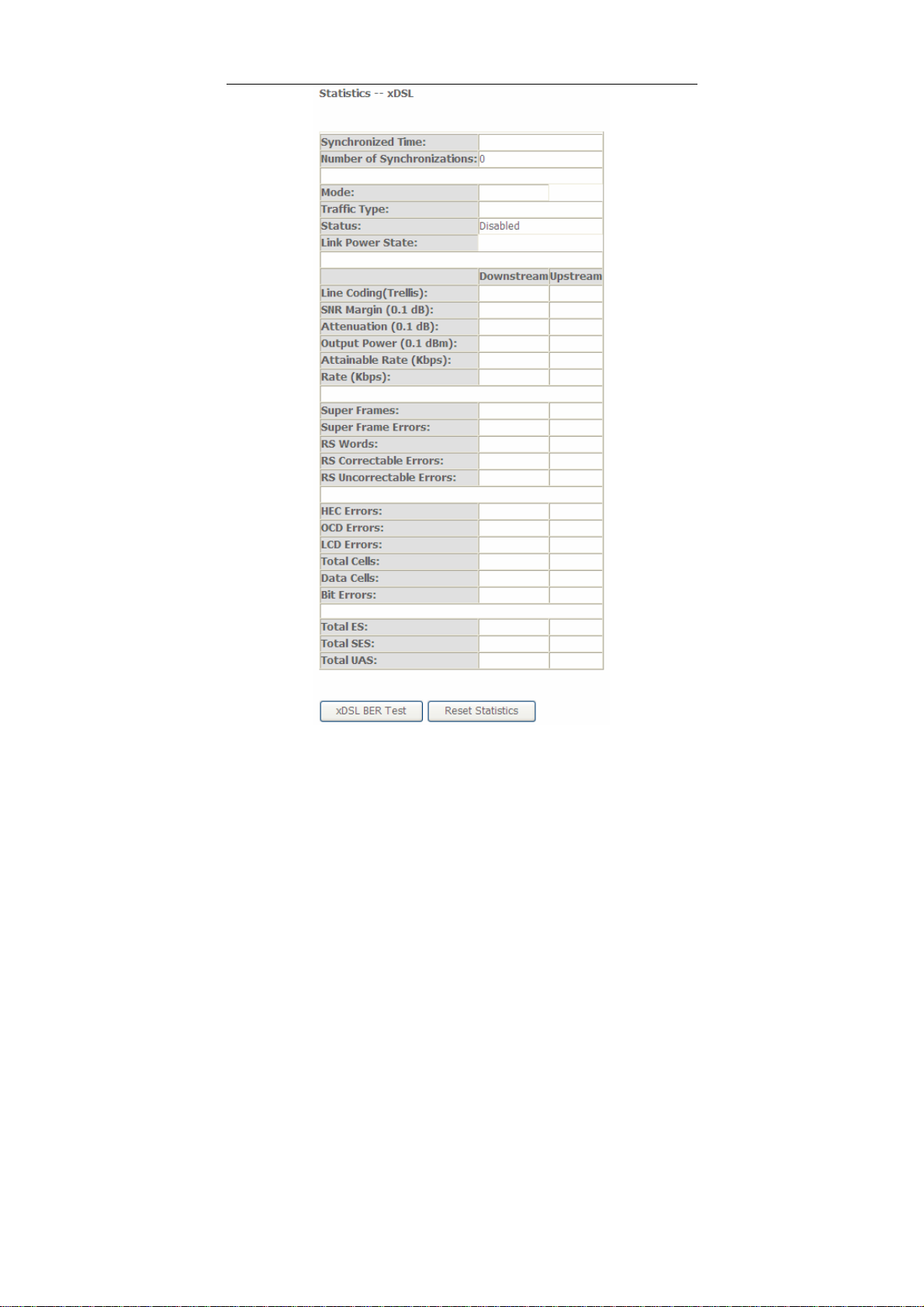
Choose Device Info > Statistics > xDSL and the following page appears.
16
User Manual
17
User Manual
In this page, you can view the statistical information about the recevied and
transmitted data packets of the xDSL interfaces.
Click xDSL BER Test to test the xDSL Bit Error Rate.
Click Reset Statistics to restore the values to zero and recount them.
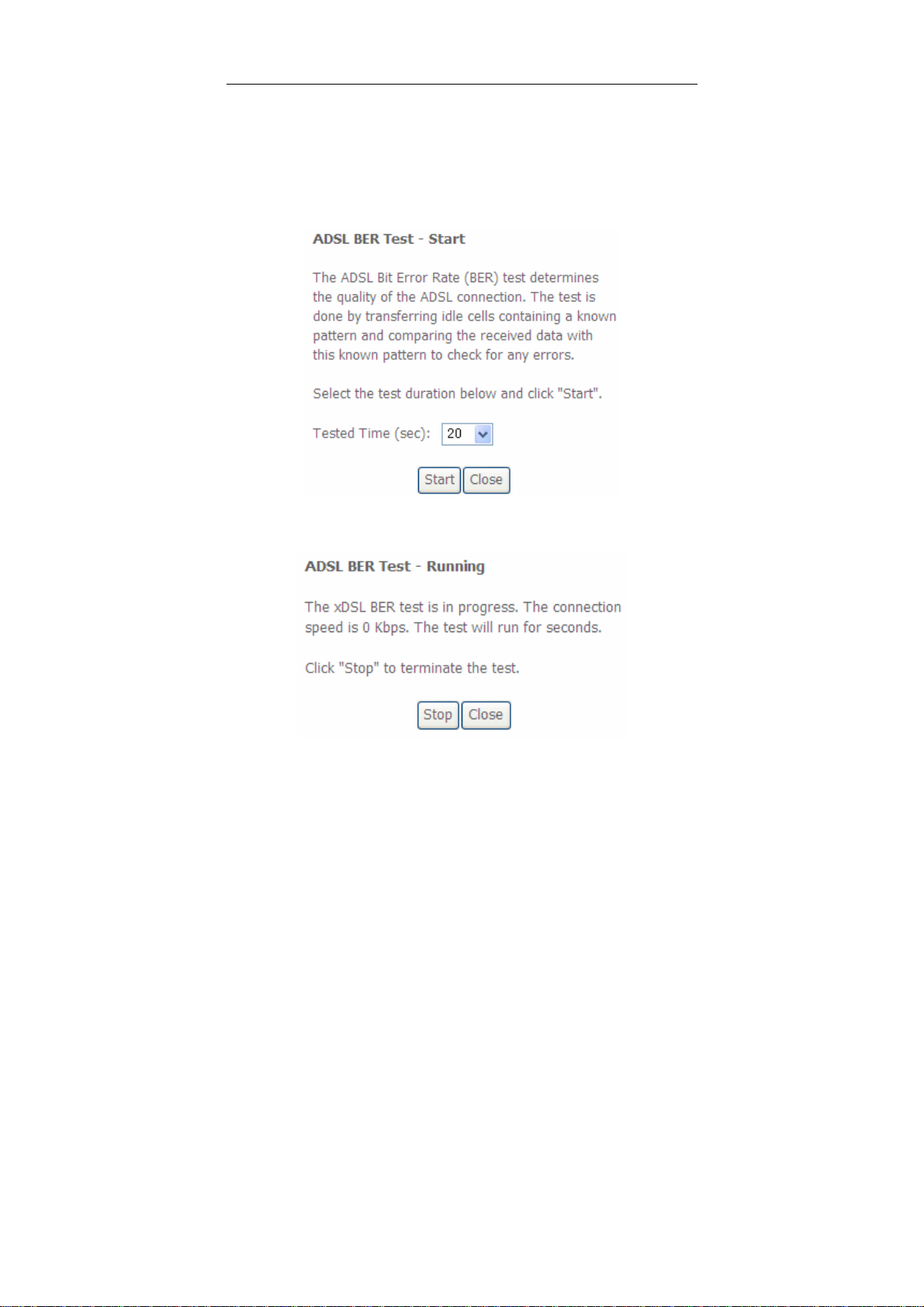
xDSL BER Test
Click xDSL BER Test to perform a bit error rate (BER) test on the DSL line. The test
page is as follows:
The Tested Time (sec) can be 1, 5, 10, 20, 60, 120, 180, 240, 300, or 360. Select a
time in the drop-down list and click Start. The following pages appear.
18
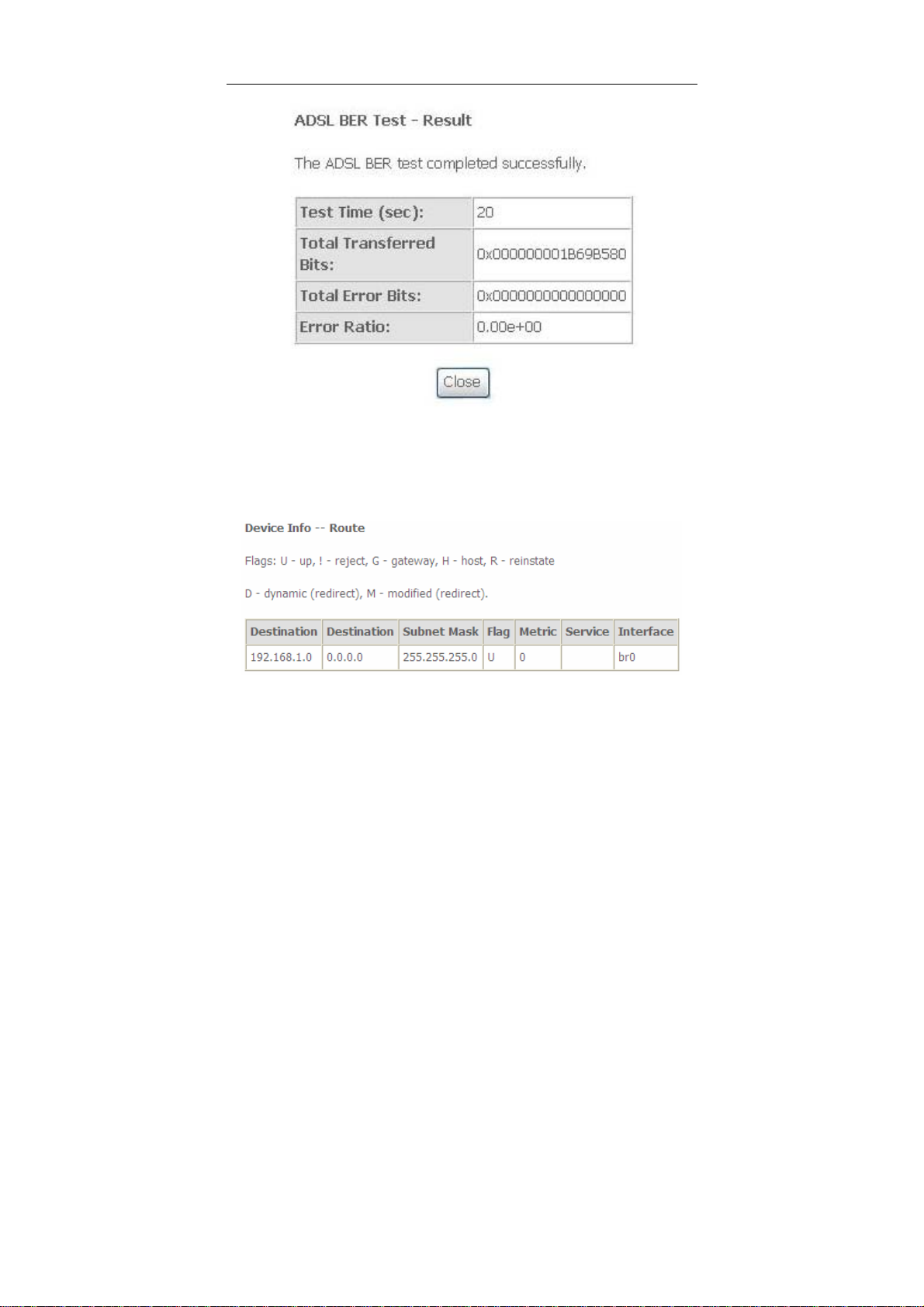
User Manual
When the ADSL BER test completes, the following page appears.
Note:
If the BER reaches e-5, you cannot access the Internet.
5.1.8 Route
Choose Device Info > Route and the following page appears.
In this page, you can view the route table information.
19
User Manual
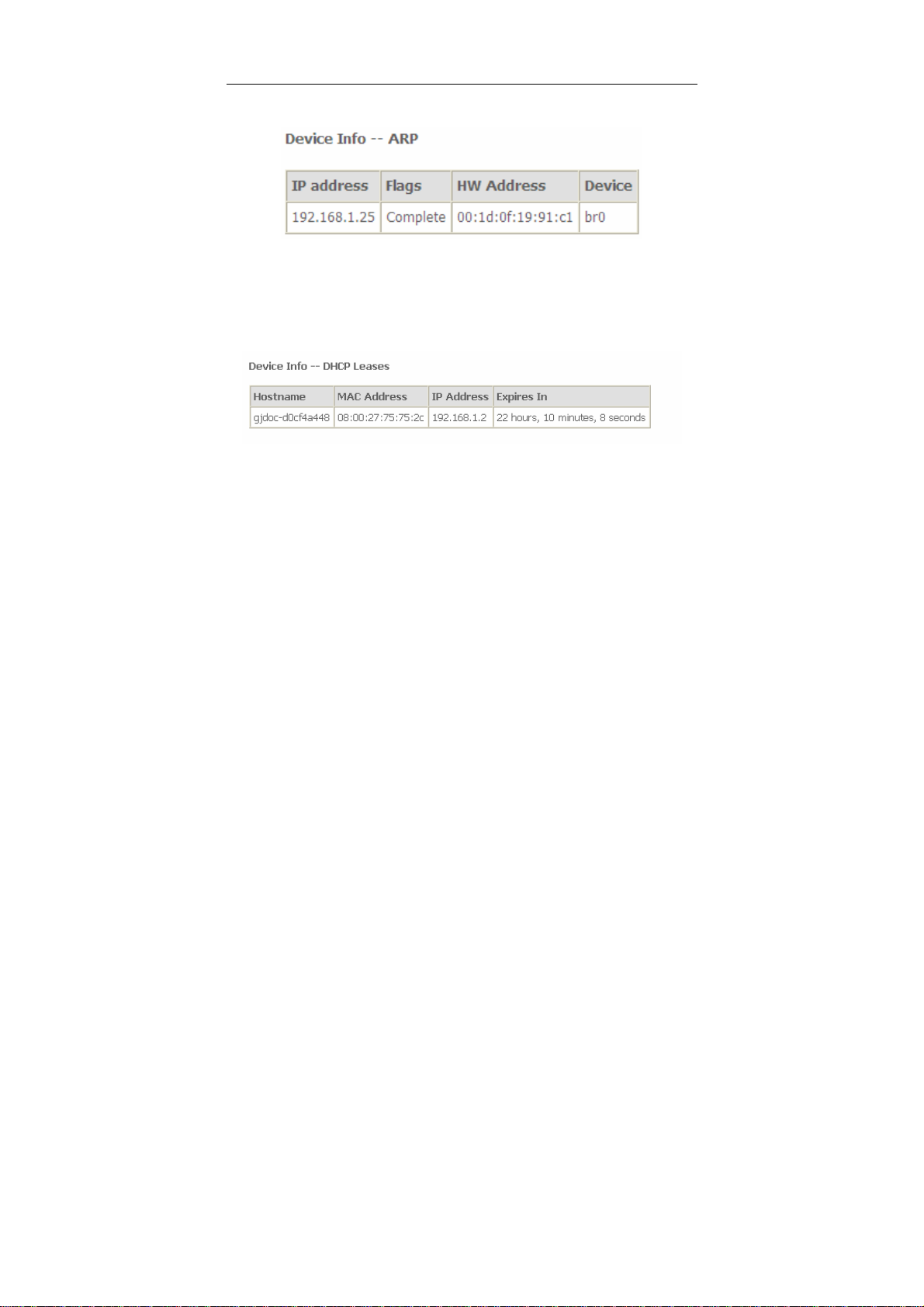
5.1.9 ARP
Choose Device Info > ARP and the following page appears.
In this page, you can view the MAC address and IP address information of the device
connected to the router.
5.1.10 DHCP
Choose Device Info > DHCP and the following page appears.
In this page, you can view the host name, the IP address assigned by the DHCP
server, the MAC address this is corresponding to the IP address, and the DHCP lease
time.
5.2 Advanced Setup
Choose Adva nced Setup and the submenus of Advanced Setup are shown as
below:
20
User Manual
21

User Manual
5.2.1 Layer2 Interface
5.2.1.1 ATM Interface
Choose Adv a n c e d S e tup > La yer2 Interface > ATM Interface . In this page, you
can add or remove to configure DSL ATM Interfaces.
Click Add to add ATM Interface and the following page appears.
22
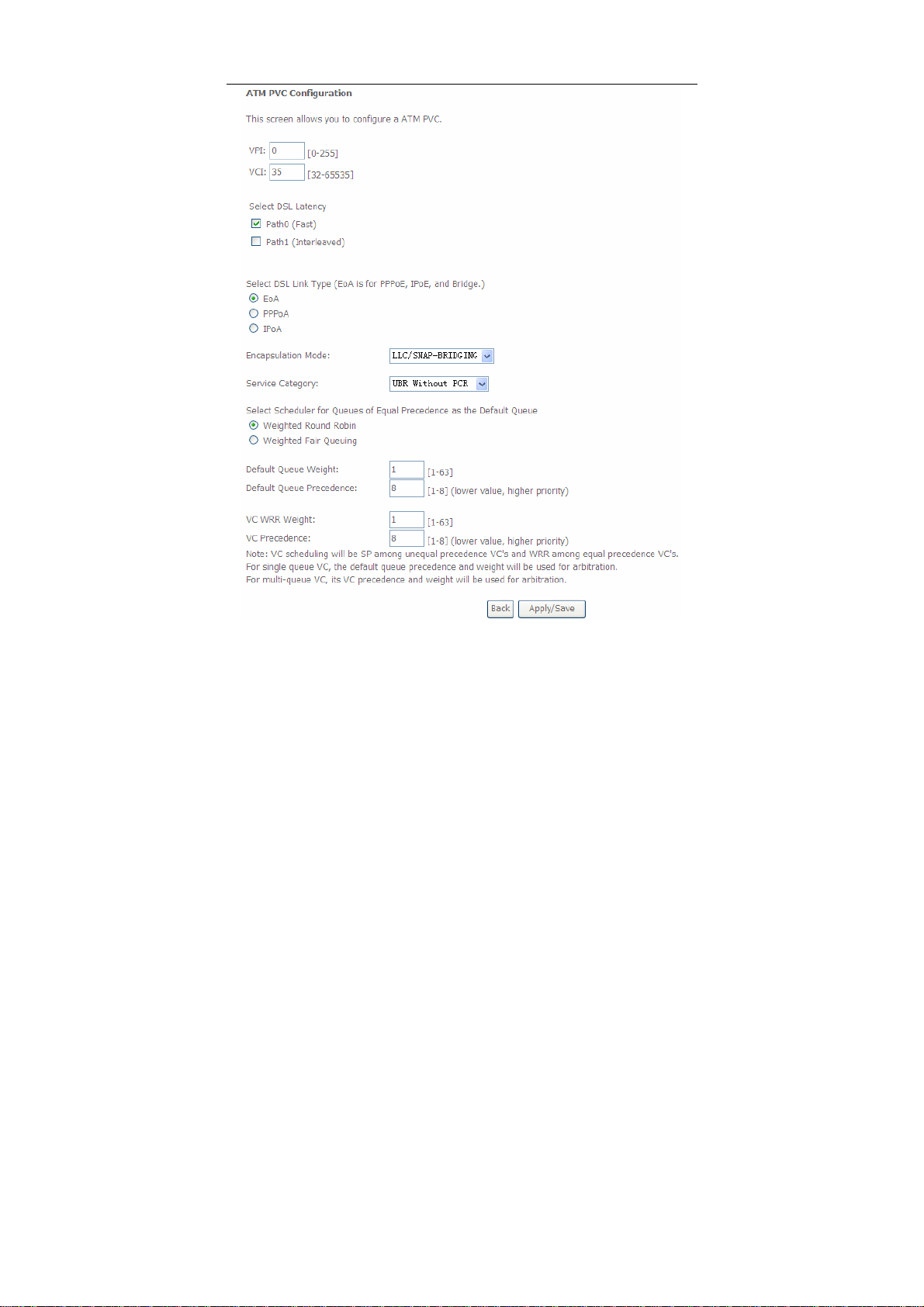
User Manual
In this page, you can enter this PVC (VPI and VCI) value, and select DSL link type
(EoA is for PPPoE, IPoE, and Bridge.), encapsulation mode, service category.
VPI (Virtual Path Identifier): The virtual path between two points in an ATM
network, and its valid value is from 0 to 255.
VCI (Virtual Channel Identifier): The virtual channel between two points in
an ATM network, ranging from 32 to 65535 (1 to 31 are reserved for known
protocols).
23
User Manual
DSL Link Type: EoA (it is for PPPoE, IPoE, and Bridge), PPPoA, or IPoA
Encapsulation Mode: LLC/SNAP-BRIDGING, or VC/MUX
Service Category: UBR Without PCR, UBR With PCR, CBR, Non Realtime
VBR, Realtime VBR.
Select Scheduler for Queues of Equal Precedence as the Default
Queue: Weighted Round Robin or Weighted Fair Queuing.
Click Apply/Save to save the configuration, and return the following page:
If you want to remove this Interface, please select the Remove check box and click
Remove.
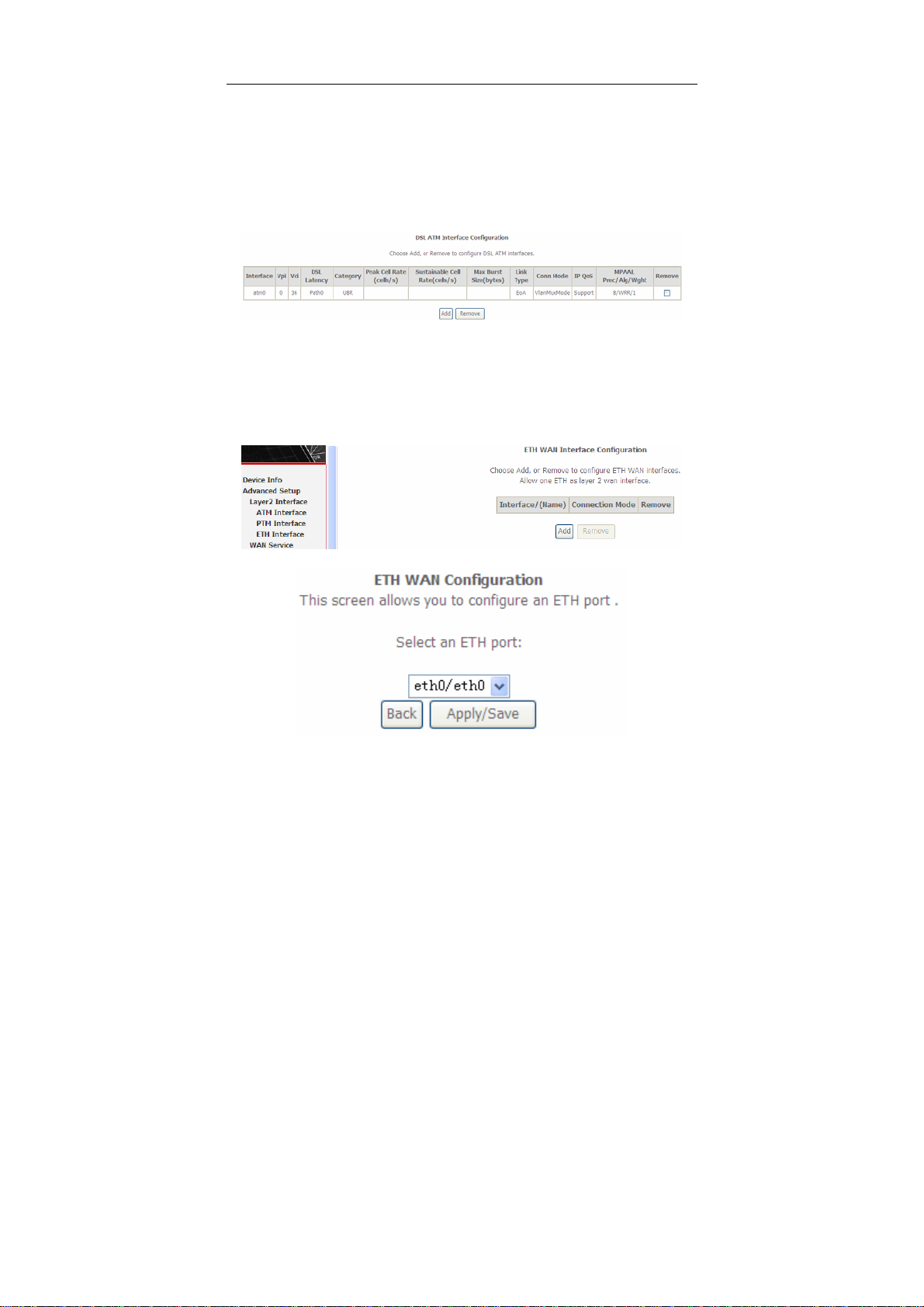
5.2.1.2 ETH Interface
Choose Ad va nc ed Se t up > Layer2 Interface > ETH Interface, and the following
page appears. In this page, you can add or remove to configure ETH WAN
Interfaces.
Click Add and the following page appears.
24

User Manual
In this page, you can select a ETH port. Click Apply/Save to save configuration.
Note:
If ETH Interface is selected, there are two WAN service types (PPPoE and
IPoE).
5.2.2 WAN Service
Choose Advanced Setup > WAN Service, and the following page appears.
In this page, you are allowed to add, remove, or edit a WAN service.
5.2.2.1 Adding a PPPoE WAN Service
This section describes the steps for adding the PPPoE WAN service.
Step1 In the Wide Area Network (WAN) Service Setup page, click the Add
button to display the following page. (At first, you must add a proper ATM
interface for this WAN service.)
25
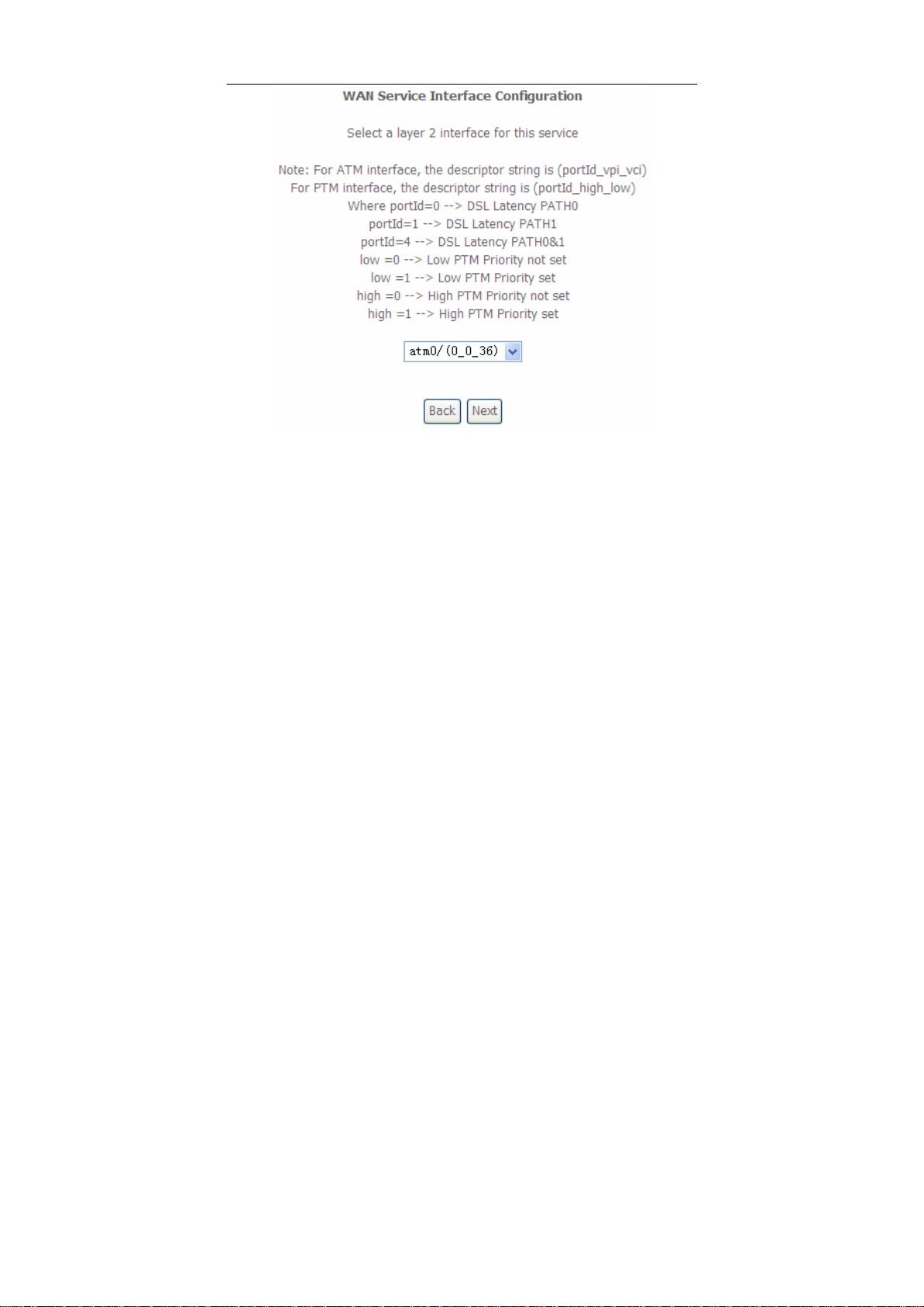
User Manual
Step2 In this page, you can select a ATM Interface for the WAN service. After
selecting the ATM interface, click Next to display the following page.
26

User Manual
Step3 In this page, select the WAN service type to be PPP over Ethernet
(PPPoE). Click Next to display the following page.
27

User Manual
Step4 In this page, you can modify the PPP username, PPP password, PPPoE
service name and authentication method.
PPP Username: The correct user name provided by your ISP.
PPP Password: The correct password provided by your ISP.
PPPoE Service Name: If your ISP provides it to you, please enter it. If not,
do not enter any information.
Authentication Method: The value can be AUTO, PAP, CHAP, or MSCHAP.
Usually, you can select AUTO.
Enable Fullcone NAT:. NAT is one where all requests from the same
internal IP address and port are mapped to the same external IP address
and port. Furthermore, any external host can send a packet to the internal
host, by sending a packet to the mapped external address.
28

User Manual
Dial on demand (with idle timeout timer): If this function is enabled, you
need to enter the idle timeout time. Within the preset minutes, if the modem
does not detect the flow of the user continuously, the modem automatically
stops the PPPoE connection. Once it detects the flow (like access to a
webpage), the modem restarts the PPPoE dialup. If this function is disabled,
the modem performs PPPoE dial-up all the time. The PPPoE connnection
does not stop, unless the modem is powered off and DSLAM or uplink
equipment is abnormal.
PPP IP extension: If you want to configure DMZ Host, you should enable it
first.
Use Static IPv4 Address: If this function is disabled, the modem obtains an
IP address assigned by an uplink equipment such as BAS, through PPPoE
dial-up. If this function is enabled, the modem uses this IP address as the
WAN IP address.
Enable PPP Debug Mode:Enable or disable this function.
Bridge PPPoE Frames Between WAN and Local Ports:Enable or disable
this function.
Enable IGMP Multicast Proxy:If you want PPPoE mode to support IPTV,
enable it.
Step5 After setting the parameters, click Next to display the following page.
29

User Manual
Step6 In this page, select a preferred WAN interface as the system default
gateway and then click Next to display the following page.
Step7 In this page, you can obtain the DNS server addresses from the selected
WAN interface. Click Next, and the following page appears.
30

User Manual
Step8 In this page, it displays the information about the PPPoE settngs. Click
Apply/Save to save and apply the settings.
5.2.2.2 Adding a MER (IPoE) WAN service
This section describes the steps for adding the MER WAN service.
Step1 In the Wide Area Network (WAN) Service Setup page, click the Add
button to display the following page. (At first, you must add a ATM
interface for this WAN service.)
Step2 Select an ATM Interface, and then click Next to display the following
page.
31

User Manual
Step3 In this page, select the WAN service type to be IP over Ethernet, enter
the service description for this service. After finishing setting, click Next to
display the following page.
32

User Manual
Step4 In this page, you may modify the WAN IP settings. You may select obtain
an IP address automatically or manually enter the IP address provided by
your ISP. Click Next and the following page appears.
Note:
If selecting Obtain an IP address automatically, DHCP will be enabled for PVC in
MER mode.
If selecting Use the following Static IP address, please enter the WAN IP address,
subnet mask and gateway IP address.
33

User Manual
Step5 In this page, you can set the network address translation settings,for
example, enabling NAT, enabling firewall, and enabling IGMP multicast.
After finishing setting, click Next and the following page appears.
Step6 In this page, select a preferred WAN interface as the system default
gateway and then click Next to display the following page.
34

User Manual
Step7 In this page, you can obtain the DNS server addresses from the selected
WAN interface. After finishing setting, click Next to display the following
page.
35

User Manual
Step8 In this page, it displays the information about the IPoE settngs.Click
Apply/Save to save and apply the settings.
5.2.2.3 Adding a PPPoA WAN service
This section describes the steps for adding the PPPoA WAN service.
Step1 Choose Advanced Setup > Layer2 Interface > ATM Interface to
dsipaly the DSL ATM I nterface Configuration page. In this page, you
need to add a PVC for PPPoA mode. Click the Add button in the DSL
ATM Interface Configuration page to display the following page.
36

User Manual
Step2 Select the DSL link type to be PPPoA, and select the encapsulation
mode to be VC/MUX (according to the uplink equipment). After finishing
setting, click the Apply/Save button to apply the setings.
Step3 Choose WAN Service and click Add to display the following page.
37

User Manual
Step4 Select the proper interface for the WAN service, and then click Next to
display the following page.
Step5 In this page, you may modify the service description. Click Next to
display the following page.
38

User Manual
PPP Username: The correct user name provided by your ISP.
PPP Password: The correct password provided by your ISP.
Authentication Method: The value can be AUTO, PAP, CHAP, or MSCHAP.
Usually, you can select AUTO.
Enable Fullcone NAT:. NAT is one where all requests from the same
internal IP address and port are mapped to the same external IP address
and port. Furthermore, any external host can send a packet to the internal
host, by sending a packet to the mapped external address.
Dial on demand (with idle timeout timer): If this function is enabled, you
need to enter the idle timeout time. Within the preset minutes, if the modem
does not detect the flow of the user continuously, the modem automatically
stops the PPPoA connection. Once it detects the flow (like access to a
webpage), the modem restarts the PPPoA dialup. If this function is disabled,
the modem performs PPPoA dial-up all the time. The PPPoA connnection
does not stop, unless the modem is powered off and DSLAM or uplink
equipment is abnormal.
PPP IP extension: If you want to configure DMZ Host, you should enable it
first.
Use Static IPv4 Address: If this function is disabled, the modem obtains an
IP address assigned by an uplink equipment such as BAS, through PPPoA
39

User Manual
dial-up. If this function is enabled, the modem uses this IP address as the
WAN IP address.
Enable PPP Debug Mode:Enable or disable this function.
Enable IGMP Multicast Proxy: If you want PPPoE mode to support IPTV,
enable it.
Step6 In this page, you can enter the PPP username and PPP password
provided by your ISP. Select the authentication method according to your
requirement. After finishing setting, click Next to display the following
page.
Step7 In this page, select a preferred WAN interface as the system default
gateway and then click Next to display the following page.
40

User Manual
Step8 In this page, you can obtain the DNS server addresses from the selected
WAN interface. After finishing setting, click Next to display the following
page.
41

User Manual
Step9 In this page, it displays the information about the PPPoA settngs.Click
Apply/Save to apply the settings. You can modify the settings by clicking
the Back button if necessary.
5.2.2.4 Adding an IPoA WAN service
This section describes the steps for adding the IPoA WAN service.
Step1 Choose Advanced Setup > Layer2 Interface > ATM Interface to
dsipaly the DSL ATM I nterface Configuration page. In this page, you
need to add a PVC for IPoA mode. Click the Add button in the DS L ATM
Interface Configuration page to display the following page.
42

User Manual
Step2 Select the DSL link type to be IPoA, and select the encapsulation mode
to be LLC/SNAP-ROUTING (according to the uplink equipment). After
finishing setting, click the Apply/Save button to save the settings.
Step3 Choose WAN Service and click Add to display the following page.
43

User Manual
Step4 Select the proper interface for the WAN service ,and then click Next to
display the following page.
Step5 In this page, you may modify the service description. Click Next to
display the following page.
44

User Manual
Step6 In this page, enter the WAN IP address, the WAN subnet mask, and
primary DNS server provided by your ISP and then click Next to display
the following page.
In this page, Network Address Translation (NAT) allows you to share one Wide
Area Network (WAN) IP address for multiple computers on your Local Area
Network (LAN).
If you do not want to enable NAT, and wish the user of modem to access the
Internet normally, you need to add a route on the uplink equipment. Otherwise, the
access to the Internet fails. Normally, please enable the NAT function.
45

User Manual
Step7 After finishing setting, click Next to display the following page.
Step8 In this page, select a preferred WAN interface as the system default
gateway and then click Next to display the following page.
46

User Manual
Step9 In this page, you can obtain the DNS server addresses from the selected
WAN interface. After finishing setting, click Next to display the following
page.
Step10 In this page, it displays the information about the IPoA settngs. Click
Apply/Save to save and appl y the settings. You can modify the settings
by clicking the Back button if necessary.
5.2.2.5 Addi ng a Bridge WAN service
This section describes the steps for adding the Bridge WAN service.
Step1 In the Wide Area Network (WAN) Service Setup page, click the Add
button to display the following page. (At first, you must add a proper ATM
interface for this WAN service.) Click the Add button to display the
following page.
47

User Manual
Step2 Select the proper ATM Interface and then click Next to display the
following page.
48

User Manual
Step3 In this page, you can select the WAN service type, and modify the service
description for this service. After finishing setting, click Next to display the
following page.
49

User Manual
Step4 In this page, it displays the information about the bridge settngs. Click
Apply/Save to save and apply the settings. You can modify the settings
by clicking the Back button if necessary.
5.2.3 LAN Configuration
Choose Advanced Setup > LAN, and the following page appears.
50

User Manual
In this page, you can configure an IP address for the DSL router, enable IGMP
snooping, enable or disable the DHCP server, edit the DHCP option, configure the
DHCP advanced setup and set the binding between a MAC address and an IP
address.
Configuring the Private IP Address for the DSL Router
In this page, you can modify the IP address of the device. The preset IP address is
192.168.1.1.
Enabling IGMP Snooping
IGMP snooping enables the router to forward multicast traffic intelligently, instead of
flooding all ports in the VLAN. With IGMP snooping, the router listens to IGMP
membership reports, queries and leave messages to identify the switch ports that are
members of multicast groups. Multicast traffic will only be forwarded to ports identified
as members of the specific multicast group or groups.
Enabling the LAN Side Firewall
Firewall can prevent unexpected traffic on the Internet from your host in the LAN.
In this page, you can enable or disable the LAN side firewall.
51

Configuring the DHCP Server
User Manual
If you enable the DHCP sever, the clients will automatically acquire the IP address
from the DHCP server. If the DHCP server is disabled, you need to manually set the
start IP address, end IP address and the lease time for the clients in the LAN.
Editing the DHCP Option60
Click the Edit DHCP Option60 button in the Local Area Network (LAN) Setup page
to display the DHCP Option60 Setup page.
In this page, you can add, edit or delete the DHCP60 options.
Editing the DHCP Option
Click the Edit DHCP Option button in the Local Area Network (LAN) Setup page to
display the DHCP Option Setup page.
In this page, you can add, edit or delete the DHCP options, and these options will be
sent to the DHCP client.
52

User Manual
DHCP Advanced Setup
Click the DHCP Advance Setup button in the Local Area Network (LAN) Setup
page to display the following page. In this page, you can enable or disable DHCP for
every LAN interface.
Configuring the DHCP Static IP Lease List
The lease list of static IP address can reserve the static IP addresses for the hosts
with the specific MAC addresses. When a host whose MAC address is in the lease
list of static IP address requests the DHCP server for an IP address, the DHCP server
assigns the reserved IP address to the host.
Click the Add En tries button in the Local Area Netw ork (LAN) Setup page to
display the DHCP Static IP Lease page.
53

User Manual
In this page, enter the MAC address of the LAN host and the static IP address that
is reserved for the host, and then click the Apply/Save button to apply the settings.
Configuring the Second IP Address and Subnet Mask for a LAN
Interface
In the Local Area Network (LAN) Setup page, you are allowed to set the second I P
address and the subnet mask for a LAN interface.
After enabling Configure the second IP Address and Subnet Mask for LAN
interface, enter an IP address and a subnet mask for the LAN interface.
After finishing setting, click the Apply/Save button to apply the settings.
5.2.3.1 IPv6 Auto-configuration
Click Advanced Setup > LAN >IPv6 Autoconfig, and the following page appears.
54

User Manual
In this page, you can set an IP address for the DSL IPv6 router, enable the
DHCPv6 server, enable RADVD and enable the MLD snooping function.
Enable DHCPv6 Server:
WIDE-DHCPv6 is an open-source implementation
of dynamic host configuration protocol for IPv6 (DHCPv6) originally
developed by the KAME project. The implementation mainly complies with
the following standards: RFC3315, RFC3319, RFC3633, RFC3646,
RFC4075, RFC 4272 etc.
55

User Manual
Enable RADVD: The router advertisement daemon (RADVD) is run by Linux
or BSD systems acting as IPv6 routers. It sends router advertisement
messages, specified by RFC2461, to a local Ethernet LAN periodically and
when requested by a node sending a router solicitation message. These
messages are required for IPv6 stateless auto-configuration.
Enable MLD Snooping: Multicast Listener Discovery Snooping (MLD
Snooping) is an IPv6 multicast constraining mechanism that runs on Layer 2
devices to manage and control IPv6 multicast groups. By analyzing received
MLD messages, a Layer 2 device running MLD Snooping establishes
mappings between ports and multicast MAC addresses and forwards IPv6
multicast data based on these mappings.
After finishing setting, click the Save/Apply button to apply the settings.
5.2.4 NAT
5.2.4.1 Virtual Servers
Firewall can prevent unexpected traffic on the Internet from your host on the LAN.
The virtual server can create a channel that can pass through the firewall. In that
case, the host on the Internet can communicate with a host on your LAN within
certain port range.
Choose Advanced Setup > NAT > Virtual Servers, and the following page
appears.
In this page, you are allowed to add or remove a virtual server entry.
To add a virtual server, do as follows:
Step 1 Click the Add button to display the following page.
56

User Manual
Use interface: Select an interface that you want to configure.
Select a Service: Select a proper service in the drop-down list.
Custom Server: Enter a new service name to establish a user service type.
Server IP Address: Assign an IP address to virtual server.
External Port Start: When selecting a service, the port number will
automatically be displayed. You can modify it if necessary.
External Port End: When selecting a service, the port number will
automatically be displayed. You can modify it if necessary.
Protocol: You may select TCP/UDP, TCP, or UDP in the drop-down list.
Internal Port Start: When selecting a service, the port number will
automatically be displayed. You can modify it if necessary.
57

User Manual
Internal Port End: When selecting a service, the port number will
automatically be displayed. You can modify it if necessary.
Step 2 After finishing setting, click Save/Apply to save and apply the settings.
5.2.4.2 Port Triggering
Some applications need some ports to be opened in the firewall for the remote
access. When an application initializes a TCP/UDP to connect to a remote user,
port triggering dynamically opens the open ports of the firewall.
Choose Advanced Settings > NAT > Port Triggering, and the following page
appears.
In this page, you may add or remove an entry of port triggering.
Click the Add button to display the following page.
58

User Manual
Use interface: Select an interface that you want to configure.
Select an application: Select a proper application in the drop-down list.
Custom application: Manually define an application.
Trigger port Start: The start port number that LAN uses to trigger the open
port.
Trigger port End: The end port number that LAN uses to trigger the open
port.
Trigger Protocol: Select the application protocol. You may select TCP/UDP,
TCP, or UDP.
Open Port Start: The start port number that is opened to WAN.
Open Port End: The end port number that is opened to WAN.
Open Protocol: Select the proper protocol that is opened to WAN. You may
select TCP/UDP, TCP, or UDP.
After finishing setting, click Save/Apply to apply the settings.
Note:
59

User Manual
Y ou can us e a si ngle port n umber, several port numbers separated by commas,
port blocks consisting of two port numbers separated by a dash, or any
combination of these, for example 80, 90-140, 180.
5.2.4.3 DMZ Host
DMZ allows all the ports of a PC on your LAN to be exposed to the Internet. Set the
IP address of the PC to be DMZ host, so that the DMZ host will not be blocked by
firewall.
Choose Advanced Setup > NAT > DMZ host to display the following page.
In this page, enter the IP address of the DMZ host.
After finishing the settings, click the Apply/Save button to apply the settings.
If you want to clear the DMZ function of the host, please delete the IP address of
the host in the field of DMZ Host IP Address, and then click the Apply/Save
button.
5.2.5 Security
Firewall
Choose Security > Firewall and the following page appears.
Click Modif y Firewall or Remove Firewall to modify or remove the firewall. And
click Modify Rule or Remove Rule to modify or remove the rule.
60

User Manual
Click Add Firewall, and the following page appears.
name: The name of firewall.
interface: You can select LAN or WAN from the drop-down list.
type: You can select IN or OUT from the drop-down list.
defaultaction: You can select Permit or Drop from the drop-down list.
MAC Filtering Setup
In some cases, you may want to manage Layer2 MAC address to block or permit a
computer within the home network. When you enable MAC filter rules, the DSL
router serves as a firewall that works at layer 2.
Note:
MAC filtering is only effective on ATM PVCs configured in bridge mode.
Choose Security > MAC Filtering and the following page appears.
61

User Manual
In this page, you can add or remove the MAC filtering rule. You may change the MAC
filtering policy from FORWARDED to BLOCKED by clicking the Change Policy
button.
Click the Add button to display the following page.
62

User Manual
Protocol Type: Select the proper protocol type.
Destination MAC Address: Enter the destination MAC address.
Source MAC Address: Enter the source MAC address.
Frame Direction: The direction of transmission frame.
WAN Interface (Configured in bridge mode only): Select the proper WAN
interface in the drop-down list.
After finishing setting, click Apply/Save to save and apply the filtering rule.
5.2.6 Parental Control
Time Restriction
Choose Advanced Setup > Parental Control > Time Restriction, and the
following page appears.
Click the Add button to display the following page.
This page is used to control the time restriction to a special LAN device that
connects to the DSL router. In this page, se the user name and configure the time
settings.
After finishing setting, click the Apply/Save button to save and apply the settings.
63

User Manual
Url Filter
Click Advanced Setup > Parental Control > Url Filter, and the following page
appears.
Thisp age is used to prevent the LAN users from accessing some Websites in the
WAN.
In this page, you may select the Exclude URL list type or the Include URL list ty pe.
If you select the Exclude URL list type, it means that the URLs in the list are not
accessible. If you select the select the Include URL list type, you are allowed to
access the the URLs in the list.
Click the Add button to display the following page.
In this page, enter the URL address and its corresponding port number. For
example, enter the URL address http://www.google.com and the port number 80,
and then click the Apply/Save button. See the following figure:
64

User Manual
5.2.7 Quality of Service
Enabling QoS
Choose Advance Setup > Quality of Service and the following page appears.
Select Enable QoS to enable QoS and configure the default DSCP mark.
In this page, enable the QoS function and select the default DSCP mark.
After finishing setting, click Apply/Save to save and apply the settings.
Note:
65

User Manual
If the Enable Qos checkbox is not selected, all QoS will be disabled for all
interfaces. The default DSCP mark is used to mark all egress packets that do
not match any classification rules.
Queue Configuration
Choose Ad va nc ed S et up > Qualit y of Service > QoS Queue, and the following
page appears.
In this page, you can enable, add or remove a QoS rule.
Note:
The lower integer value f or precedence indicates the higher priority.
Click the Add button to display the following page.
66

User Manual
Name: Enter the name of QoS queue.
Enable: Enable or disable the QoS queue.
Interface: Select the proper interface for the QoS queue.
After finishing setting, click Apply/Save to save and apply the settings.
QoS Classification
Choose Adva nced Set up > Quality of Service > Qos Classification and the
following page appears.
In this page, you can enable, add or remove a QoS classification rule.
Click the Add button to display the following page.
67

User Manual
5.2.8 Routing
Default Gateway
Choose Ad va nc ed Set up > Routing > Default Gateway, and the following page
appears.
68

User Manual
In this page, you can modify the default gateway settings.
Select a proper WAN interface in the drop-down list of Selected WAN Interface as
the system default gateway.
After finishing setting, click Apply/Save to save and apply the settings.
Static Route
Choose Advanced Setup > Routing > Static Route and the following page
appears.
In this page, you can add or remove a static routing rule.
Click the Add button to display the following page.
69

User Manual
IP Version: Select the IP version.
Destination IP address/prefix length: Enter the destination IP address.
Interface: select the proper interface for the rule.
Gateway IP Address: The next-hop IP address.
Metric: The metric value of routing.
After finishing setting, click Apply/Save to save and apply the settings.
Policy Routing
Choose Ad vance d Setup > Routing > Policy Routing and the following page
appears.
In this page, you can add or remove a static policy rule.
Click the Add button to display the following page.
70

User Manual
In this page, enter the policy name, source IP and default gateway, and select the
physical LAN port and interface.
After finishing setting, click Apply/Save to save and apply the settings.
RIP
Choose Advanced Setup > Routing > RIP and the following page appears.
In this page, if you want to configure an individual interface, select the desired RIP
version and operation, and then select the Enabled checkbox for the interface.
After finishing setting, click Apply/Save to save and apply the settings.
71

User Manual
5.2.9 DNS
DNS Server
Choose Advanced Setup > DNS > DNS Server and the following page appears.
In this page, you can select a DNS server interface from the available interfaces,
manually enter the DNS server addresses, or obtain the DNS address from a WAN
interface.
After finishing setting, click Apply/Save to save and apply the settings.
Dynamic DNS
Choose Advanced Setup > DNS > Dynamic DNS and the following page
appears.
72

User Manual
In this page, you are allowed to modify the DDNS settings.
Click the Add button to display the following page.
D-DNS provider: Select a proper DDNS server in the drop-down list.
Hostname: It is the domain name and it can be modified.
Interface: The interface that the packets pass through on the DSL router.
Username: Enter the username for accessing the DDNS management
interface.
Password: Enter the password for accessing the DDNS management
interface.
After finishing setting, click Apply/Save to save and apply the settings.
5.2.10 DSL
Choose Advanced Setup > DSL and the following page appears. In this page, you
can view the DSL settings. Usually, you can kee p this factory default setting. The
modem negotiates the modulation mode with the DSLAM.
73

User Manual
In this page, you can set the DSL settings. Usually, you do not need to modify the
factory default settings.
After finishing setting, click Apply/Save to save and apply the settings.
5.2.11 UPnP
Choose Advanced Setup > UPnP and the following page appears.
In this page, you can enable or disable the UPnP function.
74

User Manual
After finishing setting, click Apply/Save to save and apply the settings.
5.2.12 DNS Proxy
Choose Advanced Setup > DNS Proxy and the following page appears.
In this page, you can enable or disable the DNS proxy function.
After enabling the DNS proxy function, enter the host name of the broadband
router and the domain name of the LAN network, and then click Apply/Save to
save and apply the settings.
5.2.13 Print Server
Choose Advanced Setup > Printer Server and the following page appears.
75

User Manual
In this page, you can enable or disable the printer server.
After finishing setting, click Apply/Save to save and apply the settings.
5.2.14 Packet Acceleration
Choose Advanced Setup > Packet Acceleration and the following page appears.
In this page, you can enable packet flow accelerator.
5.2.15 Storage Service
Storage Device Info
Choose Advanced Setup > Storage Service > Storage Device Info and the
following page appears.
76

User Manual
This page is used to display the information of the storage device that connects to
the DSL router.
5.2.16 Interface Grouping
Choose Advanced Setup > Interface Grouping and the following page appears.
Interface grouping supports multiple ports to PVC and bridging groups. Each group
will perform as an independent network. To support this feature, you must create
mapping groups with the appropriate LAN and WAN interfaces using the Add
button. The Remove button will remove the grouping and add the ungrouped
interfaces to the default group. Only the default group has IP interface.
Click the Add button to display the following page.
77

User Manual
In this page, please follow the on-screen configuration steps to configure the
parameters of the interface grouping.
After finishing setting, click Apply/Save to save and apply the settings.
5.2.17 IP Tunnel
5.2.17.1 IPv6 in IPv4
Choose Advanced Setup > IP Tunnel > IPv6inIPv4 and the following page
appears. The default value is IPv6 in IPv4 information.
78

User Manual
Click Add and the following page appears. In this page, you can add a new tunnel.
5.2.17.2 IPv4 in IPv6
Choose Advanced Setup > IP Tunnel > IPv4inIPv6 and the following page
appears.
Click Add and th e following page appears. In this page, you can add a new tunnel
of IPv4 in IPv6.
79

User Manual
5.2.18 IPSec
Choose Advanced Setup > IPSec and the following page appears.
In this page, you can add or remove the IPSec tunnel connections.
Click the Add button to display the following page.
80

User Manual
In this page, set the parameters such as the IPSec connection name, tunnel mode,
and remote IPSec gateway address.
If you need to configure the advanced settings of this IPSec tunnel connection,
please click the Show Advanced Settings button to display the other parameters.
After finishing setting, click Apply/Save to save and apply the settings.
81

User Manual
5.2.19 Certificate
Local
Choose Advanced Setup > Certificate > local and the following page appears.
In this page, you can acquire the local certificate by creating a certificate request or
importing a certificate. You may also create or remove a certificate.
Creating a New Certificate Request
Click the Create Certificate Request button to display the following page.
In this page, please set the following parameters.
Certificate name: Set the certificate name.
Common Name: The common name is the "fully qualified domain name,"
(or FQDN) used for DNS lookups of your server (for example,
www.mydomain.com). Browsers use this information to identify your Web
site. Some browsers will refuse to establish a secure connection with your
site if the server name does not match the common name in the certificate.
Please do not include the protocol symbol "http://" or any port numbers or
82

User Manual
pathnames in the common name. Do not use wildcard characters such as *
or ?, and do not use an IP address.
Organization Name: The name of the organization to which the entity
belongs (such as the name of a company).
State/Province Name: This is the name of the state or province where your
organization's head office is located. Please enter the full name of the state
or province.
Country/Region Name:
country (for example, GB for the United Kingdom).
After finishing setting, click the Apply button to apply the settings.
This is the two-letter ISO abbreviation for your
The certificate request needs to be submitted to a certificate authority, which will
sign the request. Then the signed certificate needs to be loaded to the DSL router.
Click Load Signed Certificate in this page, and the following page appears.
83

User Manual
In this page, paste the signed certificate, and then click the Apply button. A new
certificate is created.
Importing an Existing Local Certificate
To import an existing certificate, click the Import Certificate button to display the
following page.
84

User Manual
In this page, paste the certificate and the private key. Finally, click the Apply button
to import the certificate.
Trusted CA
Choose Advanced Setup > Certificate > Trusted CA and the following page
appears.
85

User Manual
In this page, you may import or remove a CA certificate.
Click the Import Certificate button to display the following page.
In this page, enter the certificate name and paste the certificate content. Finally,
click the Apply button to import the certificate.
5.2.20 Power Management
Choose Advanced Setup > Power Management and the following page appears.
This page allows control of Hardware modules to evaluate power consumption.
Use the control buttons to select the desired option.
86

User Manual
After proper configurations, click Apply to take the configurations effect.
5.2.21 Multicast
Choose Advanced Setup > Multicast and the following page appears.
87

User Manual
In this page, you can configure the multicast parameters.
After finishing setting, click Apply/Save to save and apply the settings.
5.3 Wireless
Choose Wireless and the submenus of Wireless are shown as below:
88

User Manual
5.3.1 Basic Settings
Choose Wireless > Basic to display the following page. In this page, the figure in
the right area is 2-dimensional code. It includes the wireless SSID and password.
You can obtain the wireless SSID and password through scanning this figure.
89

User Manual
This page allows you to configure the basic features of the wireless LAN interface.
Enable Wireless: Enable or disable the wireless function.
Hide Access Point: if you want to hide any access point for your router,
select this option, and then a station cannot obtain the SSID through the
passive scanning.
Clients Isolation: When many clients connect to the same access point,
they can access each other. If you want to disable the access between the
clients that connect to the same access point, you can select this option.
Disable WMM Advertise: After enabling this option, the transmission
performance multimedia of the voice and video data can be improved.
Enable Wireless Multicast Forwarding (WMF): After enabling this option,
the transmission quality of video service such as IPTV can be improved.
SSID: For the security reason, you should change the default SSID to a
unique name.
BSSID: Display the MAC address of the wireless interface.
Country: The name of the country with which your gateway is configured.
This parameter further specifies your wireless connection. For example, The
channel will adjust according to nations to adapt to each nation's frequency
provision.
Max Clients: Specify the maximum wireless client stations to be enabled to
link with AP. Once the clients exceed the max vlaue, all other clients are
refused. The value of maximum clients is 16.
Wireless - Guest/Virtual Access Points: If you want to make Guest/Virtual
network function be available, you have to check those boxes in the table
below. In the current software version, three virtual access points can be
configured.
After finishing setting, click Apply/Save to save the basic wireless settings and
make the settings take effect.
5.3.2 Security
Choose Wireless > Security to display the following page.
90

User Manual
This page allows you to configure the security features of the wireless LAN
interface. In this page, you can configure the network security settings by the Wi-Fi
Protected Setup (WPS) method or setting the network authentication mode.
WPS Setup
91

User Manual
There are 2 primary methods used in the Wi-Fi Protected Setup:
PIN entry, a mandatory method of setup for all WPS certified devices.
– Enter STA PIN: If you select it, you need to enter the station PIN from
client.
– Use AP PIN: The PIN is generated by AP.
Push button configuration (PBC), an actual push button on the hardware or
through a simulated push button in the software. (This is an optional method
on wireless client).
If you are using the PIN method, you will need a Registrar (access point/wireless
router) to initiate the registration between a new device and an active access
point/wireless router. (Note: The PBC method may also need a Registrar when
used in a special case where the PIN is all zeros)
In order to use the push-button for WPS authentication, you must ensure that the
network card support the function. if it supports, you need not to do any
configuration. You can press the WPS button directly to enable the WPS function.
Manual Setup AP
This page provides 9 types of network authentication modes, including Open,
Shared, 802.1X, WPA, WPA-PSK, WPA2, WPA2-PSK, Mixed WPA2/WPA, and
Mixed WPA2/WPA-PSK.
92

User Manual
- Open Mode
Select SSID: Select a SSID for configuring the security settings.
Network Authentication: Select the Open mode.
WEP Encryption: Enable or disable WEP encryption. After enabling this
function, you can set the encryption strength, current network key, and
network keys.
Encryption Strength: You can set 64-bit or 128-bit key.
Current Network Key: The current key that you use.
Network Key1/2/3/4: Set the network key. If it is 128-bit key, you need to
enter 13 ASCII characters or 26 hexadecimal digits. For the 64-bit key, you
need to enter 5 ASCII characters or 10 hexadecimal digits.
93

- Shared Mode
User Manual
The parameters’ description of shared mode, please refer to the Open Mode.
- 802.1x
Select SSID: Select a SSID for configuring the security settings.
Network Authentication: Select the 802.1X in the drop-down list.
94

User Manual
RADIUS Server IP Address: Enter the IP address of the RADIUS server.
RADIUS server is used to authenticate the hosts on the wireless network.
RADIUS Port: The port number that the RADIUS server uses. The default
port number is 1812. You may change it according to the server setting.
RADIUS Key: Set the RADIUS key for accessing the RADIUS server.
WEP Encryption: You can only select Enabled.
Encryption Strength: You can set 64-bit or 128-bit key.
Current Network Key: The current key that you use.
Network Key1/2/3/4: Set the network key. If it is 128-bit key, you need to
enter 13 ASCII characters or 26 hexadecimal digits. For the 64-bit key, you
need to enter 5 ASCII characters or 10 hexadecimal digits.
- WPA Mode
Select SSID: Select a SSID for configuring the security settings.
Network Authentication: Select the WPA-PSK mode.
WPA Group Rekey Interval: Setting the interval for renewing key.
RADIUS Server IP Address: Enter the IP address of the RADIUS server.
RADIUS server is used to authenticate the hosts on the wireless network.
RADIUS Port: The port number that the RADIUS server uses. The default
port number is 1812. You may change it according to the server setting.
RADIUS Key: Set the RADIUS key for accessing the RADIUS server.
WPA/WAPI Encryption: You may select AES, or TKIP+AES.
95

- WPA-PSK Mode
User Manual
Select SSID: Select a SSID for configuring the security settings.
Network Authentication: Select the WPA-PSK mode.
WPA/WAPI passphrase: The key for WPA encryption. Click the Click here
to display button to display the current key. The default key is 87654321.
WPA Group Rekey Interval: Setting the interval for renewing key.
WPA/WAPI Encryption: You may select AES, or TKIP+AES.
- WPA2 Mode
Select SSID: Select a SSID for configuring the security settings.
Network Authentication: Select the WPA2 mode.
96
 Loading...
Loading...