Page 1

NavStar
Operation Manual
Page 2
- 1 -
TABLE OF CONTENTS
NAVSTAR 10/12 Series
Welcome
6
NAVSTAR 10/12 Series
Introduction
Display Unit Inst al l at i on
8
HOW GPS WORKS 11
#Sonar - How it wor ks 13
Installation of GPS ANTENA
The installation of the GPS ANTENNA. 14
Installation of The Transduc er
Display Unit Location
15
Display Unit Inst al l at i on
15
Power Connection
16
Transducer Connection 16
Installing the T rans ducer Cable
18
Installing the P ower Cable 19
Installing a Thru-Hull Transducer 20
Positioning the Transom
-Mount Transducer
22
Mounting the Transom-Mount Transducer 23
Getting Started
1. The Keyboard 25
1.1. How to [PWR] use
2. Specification of the Connectors 27
3. Screen Overview 28
3.1. Chartplotter page
3.2. Sonar page
3.3. Navigation Data page
3.4. Highway page
3.5. Steering page
3.6. GPS Stat us page
4. Databar 34
4.1. Mode
4.2. Display
4.3. Position
5. Cursor 36
5.1. Calling the cursor
Page 3

- 2 -
5.2. Moving
5.3. Removing the cursor
5.4. Cursor information window
5.5 .Cursor information window shown/hidden
6. Page 38
6.1. Page mode
6.2. Modify
7. Active 41
8. Navigation Data 42
8.1. Type
8.2. Edit
9. MOB
44
9.1. Inputing
9.2. Exiting the alarm
9.3. Removing
10. Memory Card 45
11. Save Userdata
46
11.1. W P T
11.2. Route
11.3. Track
11.4. User Line
11.5. User Name
12. Load Userdata
48
12.1. W P T
12.2. Route
12.3. Track
12.4. User Line
12.5. User Name
Chartplotter ge tting started
1.
GOTO
51
1.1. Goto type1
1.2. Goto type2
2. WP T 52
2.1. List
2.2. Setting the WPT symbol
2.3. Setting WPT Color
2.4. Creating
2.5. Erasing
2.6. Erasing all o f WPT
2.7. Moving the WPT
2.8. Navigating
2.9. Move to vessel
2.10. Sorting
2.11. Editing
3. Route 60
3.1. List
Page 4
- 3 -
3.2. Route detail
3.3. Creating
3.4. Edit
3.5. Detail edit
3.6. Navigating
3.7. Erasing
4. Track
62
4.1. Track on/of f
4.2. Choosing the track
4.3. Setting the thickness
4.4. Track Color
4.5. Track type
5. Measuring the distance and bearing 68
6. User Line 69
7. User Name 70
Chartplotter operation
1. Map Orientation 71
1.1. True Motion
1.2. North Up/South Up/Eas t Up/West Up
1.3. Course Up
1.4. Head Up
2. Map setup 72
2.1. Map orientation
2.2. Userdata Display
2.3. Chart
2.4. C-Map (*Only for *C-MAP m ode. )
3. Vessel
75
3.1. Vessel Icon Size
3.2. Heading Line
3.3 Vessel style (Circle/Arrow/Vessel)
3.4. Orient. Resolution
4. Cursor Icon 76
5. Alarm 76
5.1. Navigation
5.2. Anchor
5.3. Interval
5.4. User Line
AIS getting started
1. What is A IS? 79
2. AIS syst em definitions 79
3. AIS information window 80
4. Quick INFO on A I S target 81
Page 5

- 4 -
AIS operation
1. AIS on/off 82
2. List 82
2.1. List
2.2. Detail
2.3. Goto
2.4. Sort
3. Display Radius 84
4. AIS target s i ze 84
5. Display vessels by Color 85
6. Display vessels by Type 85
7. Filter AIS types
85
8. Alarm 85
8.1. CPA Alarm
8.2. CPA Range
8.3. TCPA Alarm
8.4. TCPA Range
8.5. Radius Alarm
8.6. Radius
8.7. Ignore Vessel s if Speed Less
8.8. Speed less t han
9. Set up AIS out s etc
86
9.1. Mark vessels as lost after
9.2. Remove lost ves sels after
9.3. Vessel t arget
10. Others
86
10.1. Labels on vessels
10.2. Cursor Box info
10.3. Messages list
10.4. Test View
10.5. Fishing net
#Sonar getting s tarted
1. Choosing the frequency 89
2. Auto/Manual Gain 89
3. Gain/STC 89
4. Controlling Gain 89
5. Controlling STC 90
6. Mode 90
6.1. Normal
6.2. Bottom Zoom
6.3. Bottom Lock
7. VRM
9
2
Page 6
- 5 -
#Sonar operation
1. Menu 93
1.1. Userdata
1.2. Deep Depth Range
1.3. Shift
1.4. Mode
1.5. Bottom Zoom Range
1.6. Fish symbol
1.7. Fish size
1.8. Interference Rej ec tion
1.9. Noise Rejection
2. Advanced Menu 94
2.1. Display
2.2. Color
2.3. Pulse
2.4. Output Power
2.5. Alarm
2.6. W at er T emp
2.7. TD Setup
2.8. Speed Source
General operation
1. GPS
99
1.1. Coordinate System
1.2. Datum
1.3. LAT. Modific ation
1.4. LOT. Modification
1.5. POG filt ering
1.6. COG filtering
1.7. SOG filt ering
1.8. LAT/LON Unit
1.9. Receiving Port
2. Setup 100
2.1. Unit
2.2. Compass
2.3. Time & Dat e
2.4. Input/Output
2.5. Buzzer
2.6. Backlight t i me out
2.7. Customizing
2.8. TD Setup
3. Maintenance 105
3.1. Program Vers i on
3.2. OS Version
3.3. MAP Version
3.4. Simulator
3.5. Language
Page 7
- 6 -
3.6. Remote control set t i ng
3.7. Initialization
3.8. W i re LA N
4. Calendar 106
5. Others 106
5.1. Screen capture
5.2. Capture List
5.3. Save User Setti ng
Data layout
1. Display 107
2. EDIT 107
2.1. Move
2.2. GPS
2.3. Time&Date
2.4. Userdata Displ ay
2.5. Fishfi nder
2.6. Unspecified
NS-12 series
General specification
GPS Receiver specification
Chartplotter specif i cation
Sonar specific at i on
Standard equipment configuration Li st
NS-10 series
General specific at i on
GPS Receiver specification
Chartplotter specification
Sonar specification
Standard equipment c onfiguration List
Customizing items
Page 8

- 7 -
Pictorials
This manual uses the following symbols for easy understanding safety instructions. Always
follow these instructions carefully.
WARNING
Always follow this safety instruction to prevent death or
injury.
CAUTION
Follow this safety instruction to avoid possible injury or
damage to your property.
Symbol “△” is a CAUTION or WARNING label indicating
the safety instruction.
WARNING
This s y mbol is an Electrical Shock WARNING label.
Symbol is an instruction that you must not violate.
(This symbol instructs NOT to disassemble the system
components)
Symbol is an operation instruction that you must follow.
(This symbol shows the main power OFF instruction.)
Page 9

- 8 -
WARNING <For System Operators>
Always follow this instruction to prevent death or personal injury.
Turn power
off
During
abnormality.
If smoke or a small of burning occurs, a fire or an
electrical short circuit may result. Turn the power switch
OFF and shut down the power supply immediately. Never
try to repair the system yourself. Call for service.
Do not open
Cabinet.
High voltage exists in the instrument. Contact with voltage
may cause possible injury or death.
Do not touch
back
side of the
equipment.
Harmful line voltage is present on back side of the
equipment. Never try to touch back side while power is
turned on.
Avoid
excessive
shock
to display
unit.
The LCD display module contains a liquid. Do not apply
any mechanical shock to the display. If the display broken,
liquid may leak and injure your skin and eyes.
Do not use
with poor
ventilation.
If you cover this unit or use in an enclosed place, it may
malfunction or become damaged as a result of
overheating. Use only where there is sufficient ventilation.
Page 10
- 9 -
Installation Cautions <For service Personnel>
Follow installation instructions to avoid personal injury and system malfunction.
Installation in
rigid location.
Mount your NAVSTAR 10/12 on a rigid frame or base to prevent your
unit from working loose.
Use correct
Installation
materials.
Use the installation materials provided in the standard accessory pack
only. If you use hardware of insufficient strength, your system may
loosen causing damaged.
Keep away from
direct sunlight.
Keep your system out of direct sunlight as it may become damaged by
overheating.
Keep away from
water.
Take care not to get water on or in your unit as it may be damaged
and/or cause an electrical shock.
Keep away from
heat source.
Keep your system away from other heat source as it may malfunction,
be damaged, or burn.
Use correct
power source.
Operate your system within the specified power voltage. An incorrect
power supply may cause
Page 11
- 10 -
Maintenance Cautions<For Maintenanc e Personnel>
Use the following safety precaution internal inspection.
Discharge
capacitors.
High voltage may be retained in the capacitors if the high-tension
circuit several minutes after you have turned the power switch off.
Check that
power is OFF
To prevent an electrical injury due to erroneous power switching,
make sure that the main power supply and the system power switch
are both in the off position. Additionally, attach a safety label
showing that service is in progress.
Avoid EMI.
Take care not to damage the ESDs (Electrostat ic Sensit i ve Devices )
by static electricity from carpet and cloths.
Avoid dust.
Wear a safety mask so as not to breath in dust during inspection or
cleaning inside your system instruments.
Page 12

- 11 -
Operation Notes <For operators>
Observe the following operation notes, otherwise the system failure or deterioration can result. And
periodical inspection and maintenance are required for keeping the system in an optimum condition.
Backup important
data.
The waypoint and other registered data may become
unreadable by unexpec ted failure. We recommend
recording this data separate ly.
Use correct
transducer only.
If you use incorrect transducer, the transmitter circuit may
be damaged due to a matching error. Consult is for
system information.
Check transducer
Connection
before
power on
Do not turn the power switch ON if the transducer is
disconnected or if it is not inserted into the water. If done,
the transducer or transmitter circuit may be damaged.
Always clean the
transducer
Since transducer performan ce can drop due to
accumulated bottom growth, keep the transducer clean.
Never paint transducer surface.
Transducer must
be installed by
authorized
personnel.
Consult us for transducer installation by authorized
personnel.
WARNING
This product is designed to assist a navigation.
When you are sailing, use the certified chart from the
Government or IMO.
Page 13

- 12 -
NAVSTAR 10/12 Series
Welcome
The NAVSTAR 10/ 12 Series Color LCD Chartplott er & Fishfider Systems em pl oys the latest in proven
technology to provide accurate fish & bottom information. The Plotter functions of NAVSTAR 10/12
series are totally dependent upon the capability of the navigation source to provide accurate position
information. This device is only an aid to navigation. It should be used in conjunction with all other
navigation accuracy. For safety, always resolve any uncertaint y before conti nui ng navigation.
CAUTION
There is no direct relationship between the color of water areas and their depth. The navigator shall
always query the area for depth information and use the official paper chart.
CAUTION
The performance of LCD displays are degraded by continuous direct exposure to ultraviolet rays.
Locate your NAVSTAR 10/12 series Display away from direct sunlight. When not in use. Keep the
display covered.
DISPLAY BREAKAGE WARNING
The LCD display module contains a liquid. If the display is broken and the liquid contacts your skin,
wash it off immediately i n running water for 15 minutes. If the liquid contacts your eyes, immediatel y
flush your eyes with running water for 15 minutes. Contact a physician if any abnormal symptom is
experienced.
Page 14

- 13 -
INDICATION NOTI CE
*: It is important or warni ng notice on fr ont of article
[ ]: Keyboard.
Page 15

- 14 -
NAVSTAR 10/12 series Introduction
Fix Text Below, so that Words Do Not Separated Strangely at End of each Line.
For centuries, sailors have been searching for a reliable and precise method of travelli ng the world’s
waterways. From celestial navigating to the modern navigation techniques as Loran, Decc a navigator,
Omega or Transit Satnav, each system has had its problems with weather, range and reliability.
Without doubt, the “Global Positioning System”, or GPS for short, is the most significant advance i n
navigation: it provides the navigator a position 24 hours a day, 365 days a year in any weather
condition. GPS is a satellite based navigation system which provides suitabl y equi pped users with
accurate position, velocity and time data. Originally the GPS, developed by the U.S. Department of
Defense, was conceived for military purposes, but now it is used in a host of civilian applications.
GPS navigation uses satellite signals to determine your position in relation to a set of satellites orbit i ng
the earth. The GPS constellation of satellites continuously sends radio signals, containing the precis e
position for each satellite back to earth. By knowing the position of 3 or 4 satellites and calculating
various time differences between transmitted signals, the GPS receiver can determine its present
position anywhere on earth, and thanks to continuous updates, calculate speed and course
information.
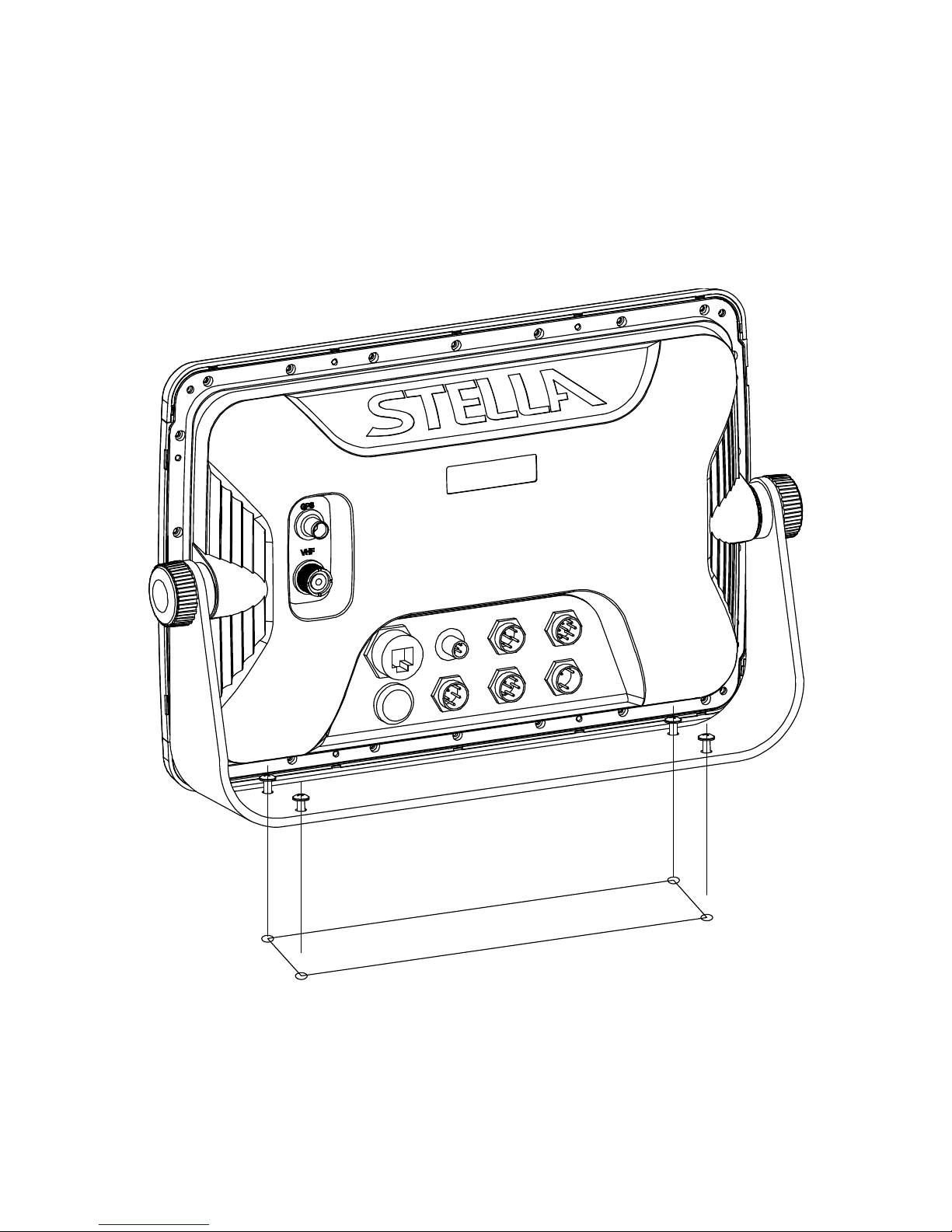
Display Unit Installation
Temporaril y i nst al l the mounting bracket on the Genesis display unit and place the unit at the selected
location.
CAUTION
The Smart4/5 series display unit is unstable when the mounting bracket is not secured. Hold the unit in
place at all times.
Check the suitability of the location and make any adjustments. When all is satisfactory, use the holes
in the mounting bracket as a guide and mark the holes locations on the mounting surface.
Drill a 1/4 in. diameter hole at each marked location. Mount the NavStar series display bracket using
Page 16
- 15 -
bolts through the mounting surface. Place large flat washers on the opposite side of the mounting
surface from the bracket and then install lock washers and nuts. Tighten securely.
Install the display unit into the mounting bracket. Check alignment and operation of the pivots and
security of the mounting. Make any adjustments necessary to prevent binding and assure even
meshing of the pivot locking washers. It is advised to remove the display unit and store it in a safe
place to prevent damage during the rest of the installation process.
[Mounting Bracket]
Page 17
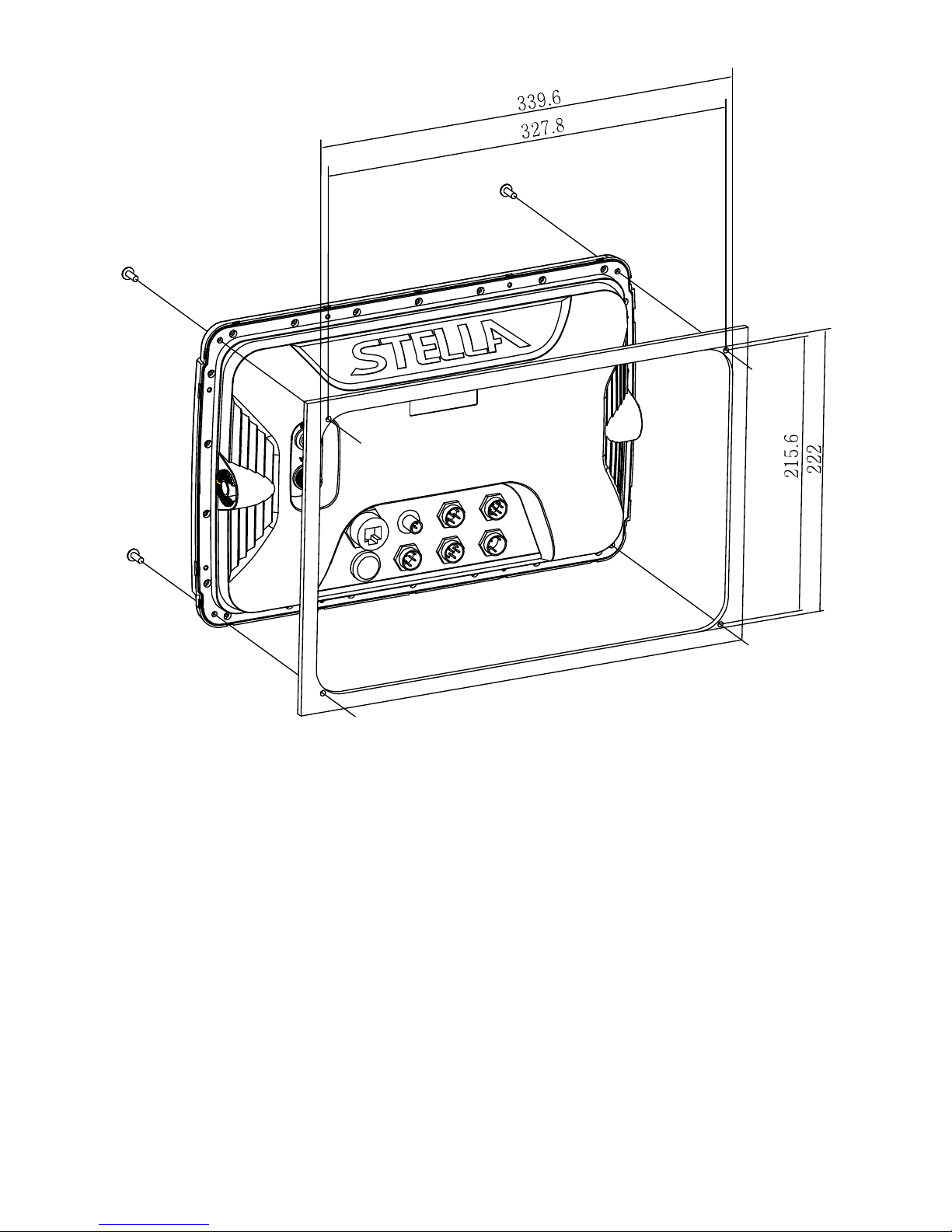
- 16 -
[Flush Mounting]
Page 18
- 17 -
NAVSTAR 10/12 series Introduction
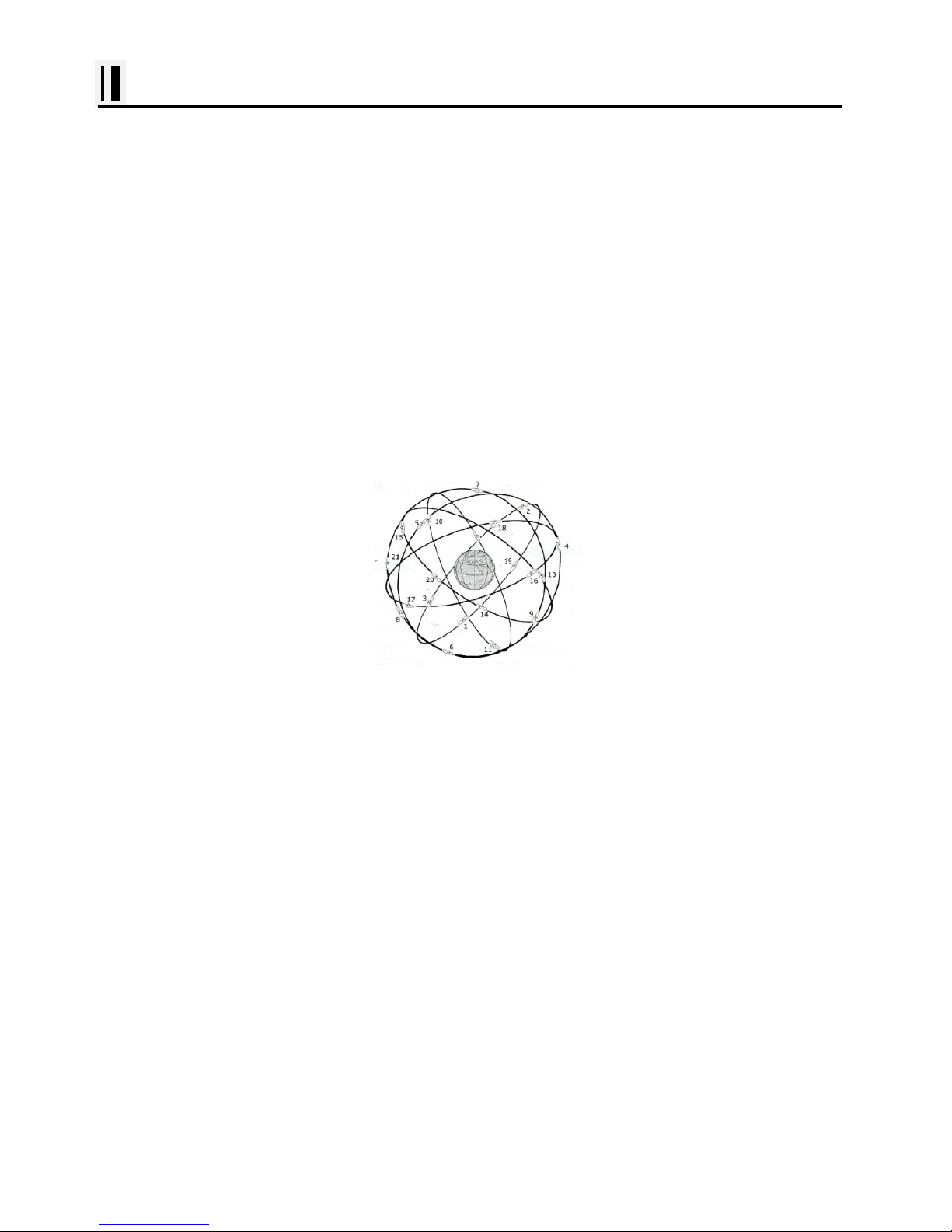
HOW GPS WORKS
Currently, the GPS constellation consists of 26 orbiting satellites (i ncluding 3 spares), but this num ber
will increase in the future.
The GPS receiver computes an accurate position by calculating the distance to the GPS satellites that
orbit the earth. Signals are required from 3 satellites for two dimensional (2D) position calculati on
whilst 4 satellites are required for three dimensional (3D) position calcul at i on.
As mentioned earlier, GPS satellites are not geostationary, but they are orbiting t he earth as illustrat ed
on the following figure:
[The GPS constellation]
Note that position is repeatedly fixed through the following three steps while any 3 satellites are in line
of sight.
The position calculation procedure is indicated in the following three st eps:
1. GPS satellites continuously transmit their own precise orbital data and the GPS receiver computes
their locations by receiving this data.
2. In this receiving process, the GPS receiver measures very accurate distances to the satellites, using
the "Spread Spectrum Modulation" method. Excellence in GPS's position-fi xing accuracy is mainly due
to this technology.
3. When the satellite locations and their distances are known, the GPS receiver fixes its own position
by triangulation:
Page 19
- 18 -
NAVSTAR 10/12 series Introduction
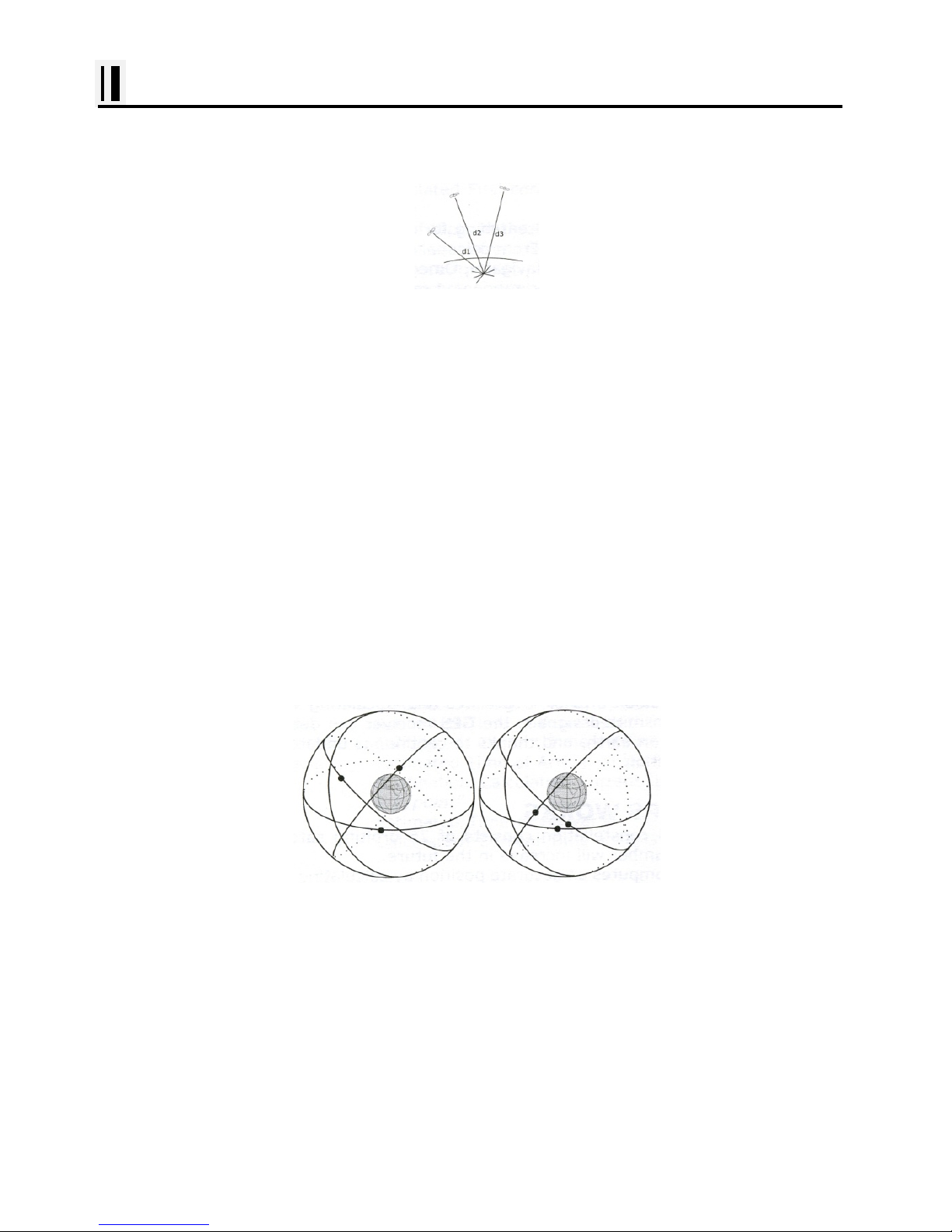
[The GPS position calculation]
As illustrated in the previous figure, the position is calculated as the meeting point of three
spheres, which are drawn around the three satellites with diameters d1, d2 and d3.
Position Fixing Accuracy: HDOP
The GPS fix accuracy is due to the locations of 3 satellites in the sky. High accuracy is obtainable
when the satellites are widely scattered in the sky; on the
contrary, accuracy is reduced when the satellites have gathered in a narrow space. In the following
figure, in both cases it is possible to obtain the GPS fix, but in the left case the accuracy will be higher
than the right:
[HDOP]
The index for position-fixing accuracy is called HDOP ("Horizontal Dilution Of Precision"). The smaller
the HDOP value, the more accurately the position can be fixed.
Page 20
- 19 -
NAVSTAR 10/12 series Introduction
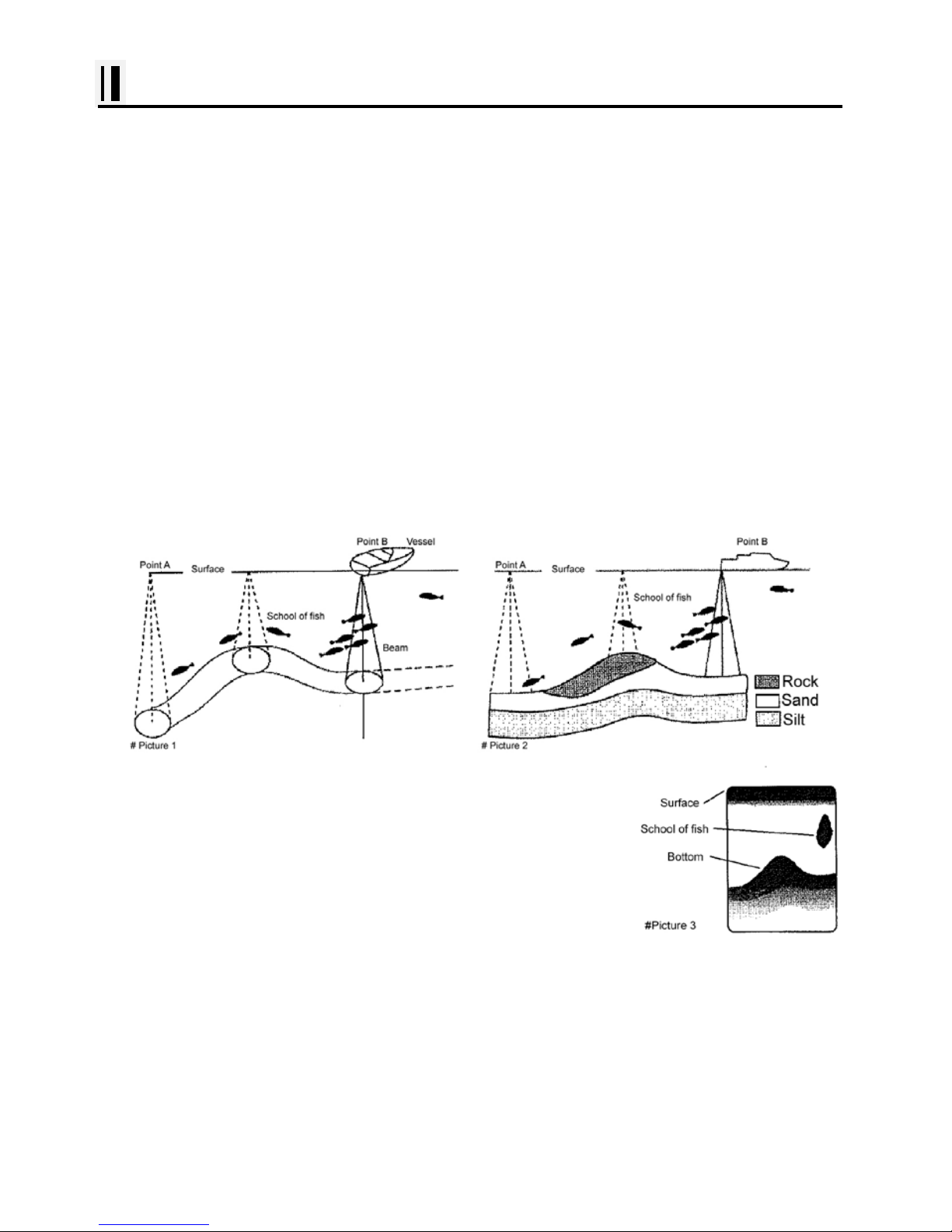
#Sonar - How it works-
The NAVSTAR 10/12CF sonar consists of a transceiver display unit and a dual frequency transducer.
An electronic signal pulse is generated in the transmitter section of the displ ay unit. When coupled to
the transducer, this signal is converted into an ultrasonic signal and is transmitted toward the bottom.
The signal travels through the water until it strikes an object or the bottom. It is reflected back , hits the
transducer surface, and is reconverted into an electronic signal by the transducer. Then it is amplified
in the receiver section, processed in the main logic section, and displayed, as an image on a LCD
screen. (Picture 3)
When your boat travels from point A to point B as shown in Picture 1, the beam of the transducer
installed on your boat shown a cross-sectional view in the water.
Picture 2 indicates a cutaway view under the water when your boat moves from A to point B.
The screen shows the latest scan data at its right position. After the next
scan, the previous data is moved to the left and the latest scan data is
shown at the right positi on. When your boat moves from point A to point
B, the screen shows the scan data as show n i n Pict ur e 3.
Page 21
- 20 -
Installation of GPS ANTENA
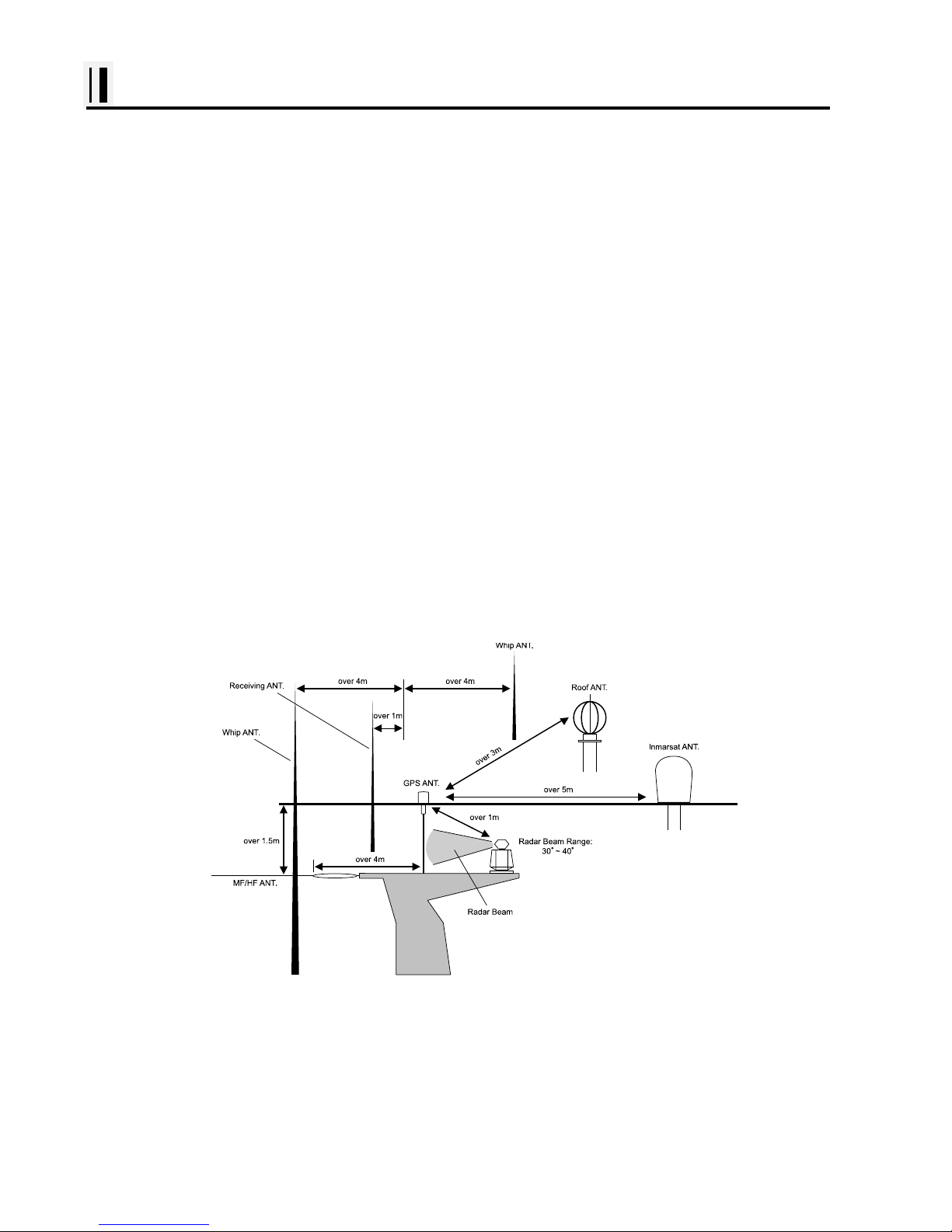
The installation of the GPS ANTENNA.
The GPS ANT must be installed at the highest area of the boat and the easiest place to receive the
signal from the satellites. If there are obs tac les around the GPS ANT, it isn't able to receive all s ignals.
The receiving time could be longer or the receiving power would be weaker . Please, follow the instruction
for your installation.
1. Keep from a metal.
2. Over 4m away from a MF/HF ANT, VHF or HF whip ANT.
3. Over 1.5m higher than MF/HF ANT.
4. Over 1m away from a receiving ANT.
5. Don't put the GPS ANT into the range of radar's beam. (Range: 30°~40°)
6. Over 1m away from the scanner of the radar.
7. Over 5m away from the ANT of the Inmarsat.
8. Over 3m away form the ANT of the roof.
9. Over 2m away from the engine.
10. Over 0.5m away from the metal surface.
※Warning: Not less than 0.5m away from the metal surface.
If the environment can't be satisfied from 1 to 10, have NO. 10 satisfied and consider the others.
Page 22

- 21 -
Installation of the Transducer
A careful installation will assure maximum performance from your new NAVSTAR
10/12 series.
Display Unit Location
Select a location for your Display unit that provides easy viewing from all likely operator’s positions.
The display unit is designed to be mounted on either a console or from an overhead surface. The
Display unit is also designed for flush mounting using six threaded holes on the rear panel. Locate the
display in an area with protection from the elements and avoid direct sunlight on the viewing window.
Also, consider access to the rear panel of the unit for connecting power and cables to the various
remote sensors. The mounting surface must be flat and solid to support the unit and prevent vibration.
There should be access to the inside of the surface to permit through bolt fastening for the mounting
bracket.
Display Unit Installation
Temporaril y i nst al l the mounting bracket on the NAVSTAR 10/12 series displ ay unit and pl ace the unit
at the selected location.
CAUTION
The Display unit is unstable when the mounting bracket is not secured. Hold the unit in place
at all times.
Check the suitability of the location and make any adjustments. When all is satisfactory, use the holes
in the mounting bracket as a guide and mark the holes locations on the mounting surface.
Page 23

- 22 -
Installation of the Transducer
Drill a 1/4 in. diameter hole at each marked location. Mount the Display unit bracket using bolts
through the mounting surface. Place large flat washers on the opposite side of the mounting surface
from the bracket and then install lock washers and nuts. Tighten securely.
Install the display unit into the mounting bracket. Check alignment and operation of the pivots and
security of the mounting. Make any adjustments necessary to prevent binding and assure even
meshing of the pivot locking washers. It is advised to remove the display unit and store it in a safe
place to prevent damage during the rest of the installation process.
Power Connection
Power is supplied to the Unit through a connector on the rear panel of the display unit.
Route the power cable from the Unit location to the ship’s power distribution panel.
Connect the black wire to a battery negative (-) terminal of the power panel.
Connect the white wire to a fused battery positive (+) terminal of the power panel ( 12 to 24 Vdc
nominal). If a fused terminal is not available, inst al l an in-li ne fuse holder.
Transducer Connection
There are many transducers available which may be used to expand the capabilities of the NAVSTAR
10/12 Sonar Unit. Connectors for these accessories are provided on the rear panel of the Sonar Unit.
See table on following page for list of optional transducers
Page 24
- 23 -
NAV S TAR 10/12 Transducer Options
Model # Beam Angles Type Hole Size
250/50/200ST-CX
45º @ 50kHz
11º @ 200kHz
Plastic transom mount w/
depth, spd, temp.
N/A
1700/50/200T-CX
45º @ 50kHz
11º @ 200kHz
Bronze thru hull depth &
temp.
7/8"
500/50/200ST-CX
45º @ 50kHz
11º @ 200kHz
Bronze thru hull depth,
speed, & temperature
2"
P319/50/200T-ES
45º @ 50kHz
12º @ 200kHz
Plastic thru-hull flush mount
with temp
2"
B-60-0 - CX
(for 0º to 7º hull dead
rise)
45º @ 50kHz
12º @ 200kHz
Bronze thru Hull, Tilted
Element Flush Mount, Depth
& Temperature Only
2.375"
B-60-12 - CX
(for 8º to 15º hull dead
rise)
45º @ 50kHz
12º @ 200kHz
Bronze thru Hull, Tilted
Element Flush Mount, Depth
& Temperature Only
2.375"
B-60-20 - CX
(for 16º to 24º hull dead
rise)
45º @ 50kHz
12º @ 200kHz
Bronze thru Hull, Tilted
Element Flush Mount, Depth
& Temperature Only
2.375"
810-15 15ft Transducer Extension Cable
810-30 30ft Transducer Extension Cable
Digital A Cable Adapter Cable for use with All Dual Freq. CVS-106 Versions
*All NavStar Transducers come with a Conxall (Model #CX-128) 8 pin Conn. On the end of the
transducer cable
Page 25

- 24 -
Installation of the Transducer
Installing the Transducer Cable-
Thru-Hull and tran som-Mount Installation
cable, with the connector attached, is supplied with the transducer. During the installation, do not cut
the transducer cable or remove the connector. Do not try shorten or splice the cable. The
transducer cable includes several wires, along with shielding and insulation. If the cable is cut, it
cannot be repaired. (Cutting the cable will also void the warranty.) During installation, if you need to
drill any holes for the cable, they must be large enough to accept the connector .(3/4" or 19mm)
This will allow you to complete the installation without cutting the wire.
1st) For a transom-mount installation - Route the cable up and over the top edge of transom. Secure
the cable using cable clamps. (These clamps are available from your local marine equipment supplier.)
If you do not want to expose the cable on the deck, you may drill a new hole (3/4" or 19mm) through
the transom for the cable. (Remember - this hole must be large enough to accept the cable with the
connector attached. Do not cut the cable!) To seal the opening, use a feed-thru cap where the cable
passes through the transom.
2nd) For either type of installation - Run the cable through the interior of the boat.
3rd) Be careful not to tear the cable jacket when passing it through bulkheads and other parts of
your boat. Secure the cable in place using Nylon Wire Ties. Coil the extra cable and tie it out of the
way.
4th) If transducer cable is not long enough, 15 & 30 foot extension cables are available from SI-TEX
When you attach the extension cable, be sure that the connections are tight and watertight. Use Dow
Corning DC-4 or an equivalent sealing compound to protect the connector assemblies.
Page 26

- 25 -
Installation of the Transducer
Installing the Power Cable-
1
st
) The 6-foot power cable supplied with the dis pl ay unit should reach the source of DC power.
Connect the power leads directly to the main battery isolation switch or breaker, or route the power
leads to the DC power distribution panel. At the power source, connect the red wire to the positive
terminal (+), and the black wire to the negative terminal (-). The negative terminal may also be called
"ground" or "earth." (The display unit is internally protected if you accidentally reverse t he polarit y of
the power wires.)
2
nd
) Attach the red or positive wire to a 5 amp circuit breaker. If the unit is connected directly to the
boat's battery, include a 2amp in-line fuse. (In-line fuses are available at most marine supply stores.)
3
rd
) To prevent any interference or electrical noise, separate the Sonar power wiring as much as
possible from other devices. See the section on "EMC Install ation Guideli nes."
4
th
) If you need to extend the power wiring by more than 10 feet, use a larger wire size. This will
allow the wires to deliver the correct voltage in spite of the longer wire distance. For runs of 20 to 35
feet, use #14 AWG wire. If you need to extend the power wiring, be sure all electrical connections
are solid and durable. Insulate all connections using heat-shrink tubing or electric al t ape. You may use
crimp connectors or a terminal strip, but be sure to use good-quality marine-grade parts.
5
th
) Plug in the power cable at the rear of the display unit.
6
th
) When you press the Power button, the display unit should turn on. If the unit will not turn on and
you suspect that you may have reversed the power connections, check the DC power lines all the way
back to the battery. If the polarity is not correct, reconnect the leads properly and try again.
(The display unit is internally protected if you accidentally reverse t he polarit y of the power wires.)
Page 27

- 26 -
Installation of the Transducer
Installing a Thru-Hull Transducer
Follow these instructions if you are installing the thru-hull transduc er.
1
st
) Once you have decided where to install the transducer, drill the hole for the part. B egi n by
drilling a small pilot hole (1/8" or 3mm) from the inside of the hull. (This small hole can be filled easily if
the mounting location is not suitable.) Before you drill the hole, be sure you will be able to reach the
large nut on the top of the transducer, once it has been mounted. Also be sure there will be enough
clearance for the cabl e. If there is a strake or other feature on the hull, drill from the outside of the hull
instead.
2
nd
) Drill a larger hole from the outside of the hull using the appropriate size hole saw or paddle bit
for the selected transducer.
3
rd
) Uncoil the transducer cable. Remove the large hex nut from the housing and slide it over the end
of the cable.
4
th
) Thread the cable through the hole to the inside of the hull. Never pull or carry the transducer in
place by pulling on the transducer cable.
5
th
) Apply a thin layer of sealant (1/8"" or 3mm) to the transducer between the upper flat surface of
the transducer and the faring block. Use a high quality marine sealant suitable for underwater use.
(Caution do not use 3M 5200) Also apply a thin layer up the side walls. this should cover all of the
threads where the part will touch the hull material, plus an additional 1/4""(6mm). This will seal the
threads for the large hex nut.
6
th
) Push the transducer housing (with the sealant applied) into the hole from the outside of the hull.
Twist the housing slightly to squeeze out any excess sealant and to get a good seal. Be sure that the
transducer is aligned so that the correct part of the unit is toward the bow of the vessel. Hold or prop
the transducer in place temporarily.
Page 28
- 27 -
Installation of the Transducer
7
th
) Go to the inside of the hull and slide the hex nut over the end of the cable. Fit the hex nut over
the end of the transducer and tighten it. (On a vessel with a wooden hull, do not tighten the nut
completely right away. Allow some time for the wood to swell after the vessel is put in the water. Be
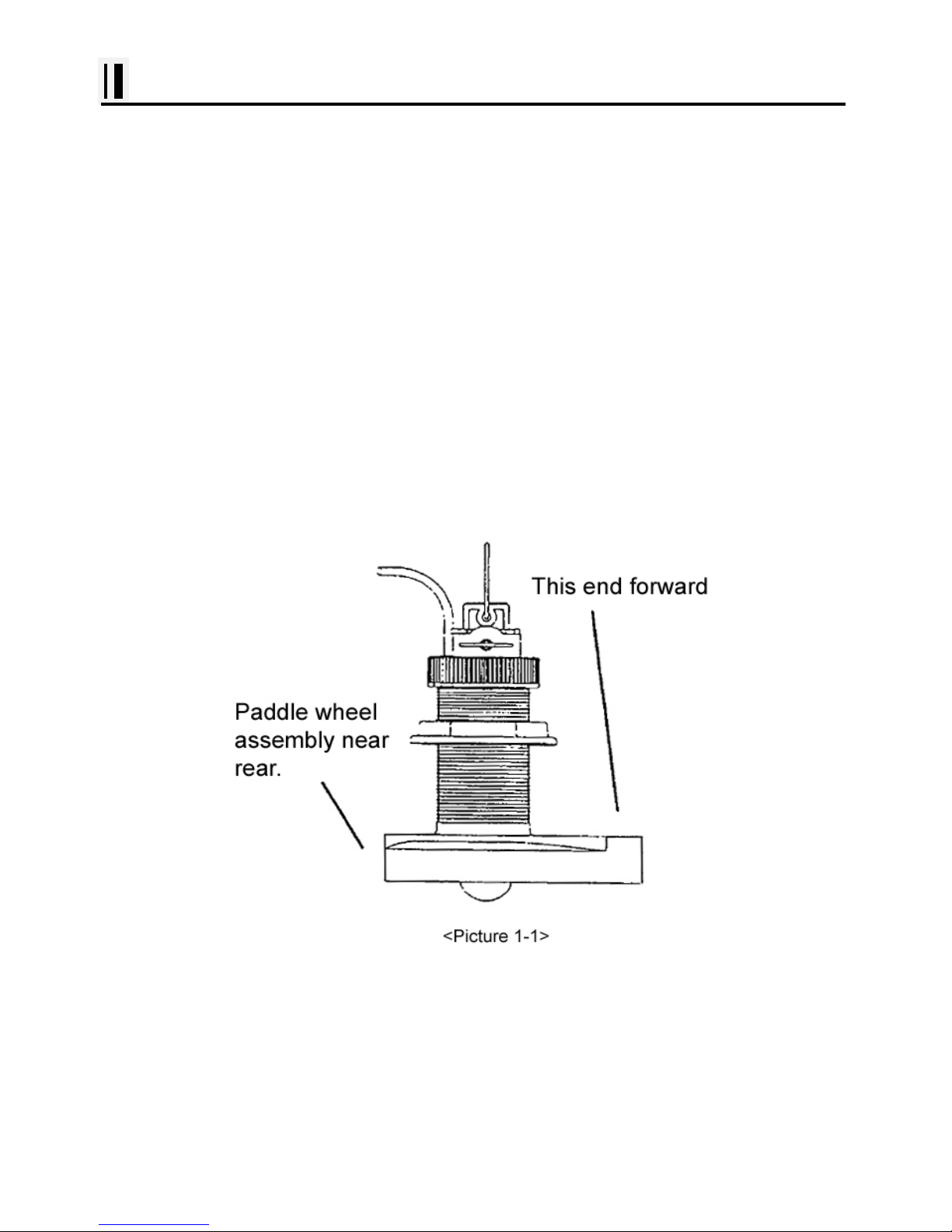
sure that the correct end of the transducer is pointing forward see Picture 1-1
8
th
) Remove any excess sealant from the outside of the unit to assure smooth water flow over the
face of the transducer.
9
th
) As soon as the boat is placed in the water, check for leaks. Check again within 3 to 5 hours.
(You may not be able to see a small leak right away.) If there are any leaks, you must repeat the
installation procedure.
Page 29
- 28 -
Installation of the Transducer
Positioning the Transom-Mount Transducer
Follow these instruction if you are installing the transom-mount transducer.
Begin by finding the best location for the mounting bracket. Here are the rules:
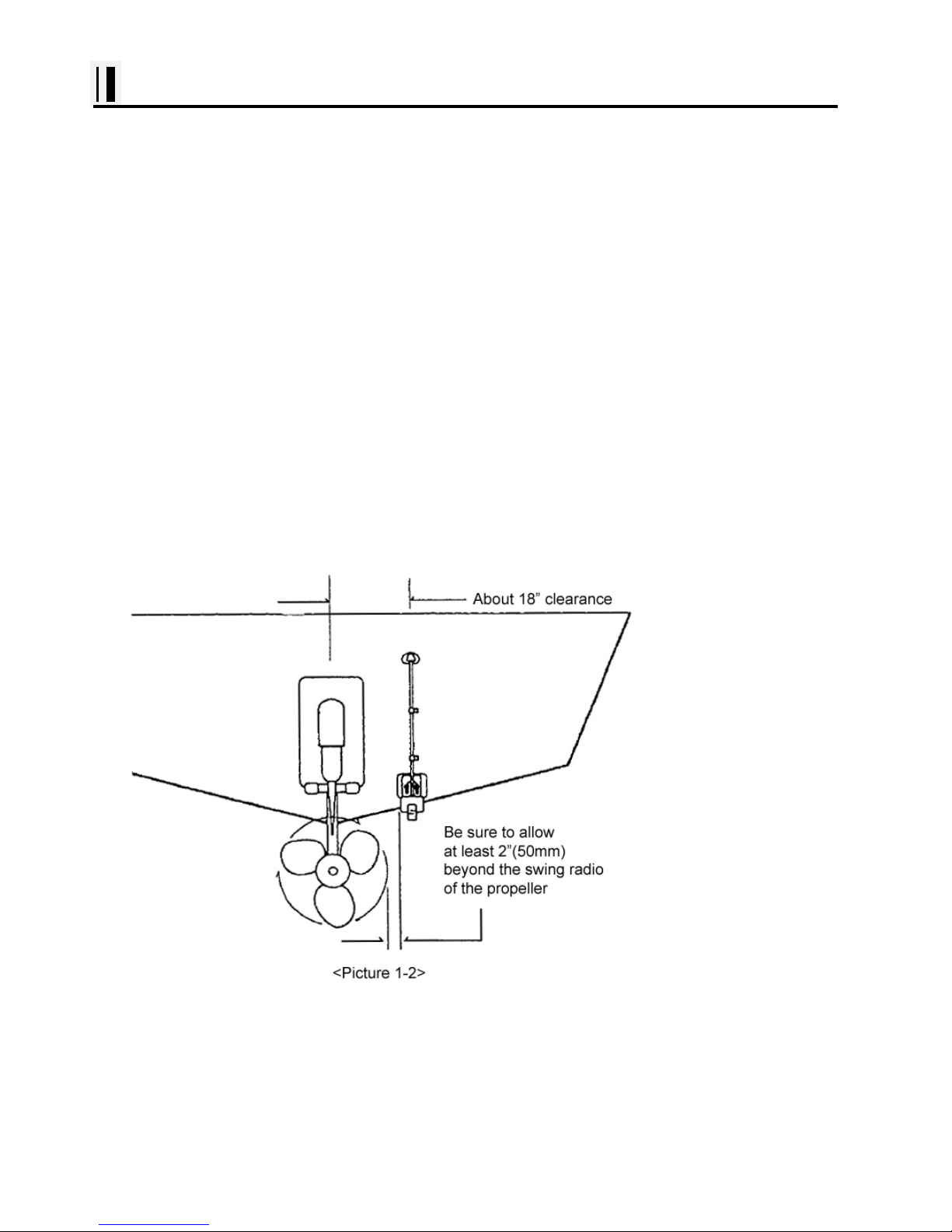
If your boat has one propeller (outboard or inboard-outboard), mount the transducer about
18"(455mm) to the side of the centerline of the boat. See Picture 1-2 Choose the side that is on the
down stroke of the propeller.(This is usually the starboard side of the boat.) This will reduce any
interference cause by air bubbles.
If your boat has twin propellers (outboard or inboard-outboard), place the transducer near t he
centerline of the boat.
If the propeller can be turned to steer the boat, allow at least 2"(50mm) beyond the swing radius of the
propeller. This will prevent the propeller from damaging the transducer when it is turned.
Do not mount the transducer behind any hull fittings, intakes, or other parts which extend from the hull.
These may cause turbulence or air bubbles.
If the boat will be carried
on a trailer, be sure the
transducer will not hit any
rollers, bunks or fittings
on the trailer.
Page 30

- 29 -
Installation of the Transducer
Mounting the Transom-Mount Transducer
Follow these instructions if you are installing the transom-mount transducer.
1
st
). On a boat with a fiberglass hull, the leading edge of the transducer should extend 1/8""(3.2mm) to
1/4""(6mm) below the bottom edge of the hull. See picture 1-3. On an aluminum hull, the transducer
should extend a bit more - 1/4"(6mm ) to 3/8"(9mm). If the boat will be operated at high speeds, t he
transducer may be mounted closer to the centerline of the hull.
2
nd
) The lower surface of the transducer should tilt down toward the rear at a slight angle(2° to 5°). The
mounting bracket includes a wedge. Depending on the angle of the transom on your boat, you may
need this wedge to get the correct angle for the bottom of the transducer.
3
rd
) Looking at the rear of the boat, be sure the bracket is vertical (perpendicular to the water line).
4
th
) Hold the bracket (and the wedge, if used) against the transom and trace the position of the screw
slots.
5
th
) Remove the bracket. The screws in the outer slots should be placed about 1/4"(6mm) up from
the bottom of each slot. The screw in the center slot should be placed 1/4" (6mm) down from the top.
(This will allow you to adjust the bracket up or down a bit.)
Drill pilot holes 3/4""(19mm) deep. Use a 9/64" (3.5mm) drill bit. To prevent drilling too deeply, wrap
masking tape around the drill bit about 7/8" (22mm ) from the tip. Drill in onl y as far as the tape marker.
If you are attaching the bracket to a fiberglass hull, you can minimize any surface cracking of the gel
coat. Before drilling each pilot hole, drill a shallow hole (chamfer) at each location about 1/16" (1.5mm)
deep. Use a 1/4"(6mm) drill bit.
6
th
) Attach the bracket to the hull using the pinhead screw with flat washers. Before you tighten the
screws, apply a good-quality marine sealant to the pilot hole. This will protect the hull from water
penetration. Do not tighten the screws completely yet.
Page 31

- 30 -
Installation of the Transducer
7
th
) Tilt the transducer in the brackets until it is positioned as illustrated in Picture 1-3
8
th
) Once the bracket is in the correct position, you can tighten the screws.
Page 32

- 31 -
Getting Started
1. The Keyboard
1.1. How to use
KEY Description
use this to select menu i tems, move the on-screen cursor and Choosing the
frequency
Rotary: use this to select menu items and Adjustment of gain & STC level
with turning.
Button: push the end of the everything to confirm a selection or entry
Change the chart of scale and Setting up the depth range
Open the menu
Select the Goto function
Select the configuration & modification you wish.
Choose your favorite function.
Press to place a waypoint and access the waypoint option.
Press and hold to place a MOB marker at your current position.
Start and stop AIS tracks & Vessel tracks .
Cancel the setting or exists from the menu
Power on/off, Restart, Control BRG, Day/Night, Lock touch screen, WiFi,
Bluetooth, Data layout, Browser.
Page 33

- 32 -
(Fig.1.1)
1.1.1. Turn on
Switch on.
1.1.2 Turn off
Choose “Power off” on (Fig. 1.1).
1.1.3 Restart
Choose Restart on (Fig. 1.1).
1.1.4. Adjust brightness
Choose “Brightness” on (Fig.1.1).
Control the brightness on (Fig.1.2).
1.1.5. Use day/night mode
Choose “night mode” on (Fig.1.1).
1.1.6. How to lock the tough screen
Keep pressing “Toughlock” on (Fig.1.1) and the color changes to orange and activate. In touchlock,
touch icons disappear on the screen and deactivate. For activate, keep pressing “ToughLock”.
(Fig.1.2)
Page 34

- 33 -
1.1.7. WiFi
Choose “WiFi” on (Fig.1.1).
1.1.8. Bluetooth
Choose “Bluetooth” on (Fig.1.1).
1.1.9. Data Layout
Choose “Data Layout” on (Fig.1.1).
(*For detailed information, PLS refer how to use data layout)
1.1.10. Sky Mat e
Choose “Sky Mat e ” on (Fig.1.1).
1.1.11. Web Browser
Choose “WWW” on (Fig.1.1).
2. Specification of the connectors
Page 35

- 34 -
3. Screen Overview
3.1. Chartplotter page
①
Vessel icon The present position.
②
Cursor Showing the cursor icon.
③
AIS target Showing the received AIS target.
④
Databar Showing various data on the top or bottom.
⑤
Cursor INFO The information of the cursor.
⑥
WPT INFO The information of WPT such as LAT/LOT, Range, etc.
④
③ ②
⑤
⑥
①
Page 36

- 35 -
3.2. Sonar page
.
①
Palette Showing the chosen colors.
②
Depth bar The current depth.
③
Low Frequency Showing 50KHz.
④
High Frequency Showing 200KHz.
⑤
LF INFO The information of Low Frequency, 50KHz.
⑥
HF INFO The information of High Frequency, 200KHz.
⑦
Databar Showing various data on the top or bottom
⑤
⑥
③
④
⑤
⑥
①
②
⑦
Page 37

- 36 -
3.3. Navigation Data page
3.3.1. Navigation Data Type1
3.3.2. Navigation Data Type2
Page 38

- 37 -
3.4. Highway page
①
WPT name The current WPT name.
②
Direction of steer The best di rect i on of the steering.
③
WPT icon The remaining distance of the WPT.
④
Vessel The out of the range from the best.
⑤
XTE Range The range of the XTE alarm.
⑥
Navigation Data The information of the various data.
①
⑥
⑤
③
④
②
Page 39

- 38 -
3.5. Steering page
①
WPT name Name of the WPT.
②
Direction of steer The best di rect i on of the steering.
③
WPT icon Showing the WPT and the bearing
④
Navigation Data Information of the various data.
①
④
③
②
Page 40

- 39 -
3.6. GPS Status page
①
Receiver status The current GPS status.
②
Position of SAT. Position of the satellites.
③
SNB Graph Showing the WPT and the bearing.
④
Navigation Data Information of the various dat a.
* Colors of the GPS status
Black: Tracked, but no signal
Blue: Tracked, but not used, Satellite
Green: Used Satellite
Light Blue: SBAS Satellite
④
②
③
①
Page 41

- 40 -
4. Databar
Showing various data on the top or bottom.
4.1. Mode
▶[MENU]->Advance->Setup->Customizing->Databar->Mode
Databar has three meanings as below.
4.1.1. GPS
Showing the largest LAT/LOT.
4.1.2. HY
Showing the LAT/LOT, SOG, COG and userdata.
4.1.3. HY2
Showing LON/LAT, mark, track and time/date.
4.1.4.Customizing
Showing various data as what the user wants.
▶[MENU]->Advance->Setup->Customizing->Databar->Edit or keep pressing the databar on the
screen.
Page 42

- 41 -
(Fig.1.3.1)
The databar is coming as (Fig.1.3.1), and choose the frame with [◀][▶].
Four frames are available as (Fig 1.3.2).
(Fig.1.3.2)
When choosing the frame, setting up in each box as (Fig.1.3.3).
Page 43

- 42 -
(Fig.1.3.3)
When finishing the set up, press [CANCEL] to exit or touch “EXIT” on the screen..
(*Please, refer “Customizing” for further question.)
4.2. Display
▶[MENU]->Advance->Setup->Customizing->Databar->Display
Setting the databar, “Shown/Hidden”.
4.3. Positio n
▶[MENU]->Advance->Setup->Customizing->Databar->Position
Setting the databar position on the top or bottom.
5. Cursor
5.1. Calling the cursor
Press [◀][▶][▼][▲] on the chart, the cursor comes out.
5.2. Moving
Press [◀][▶][▼][▲], the cursor is moving to the direction.
Page 44

- 43 -
Press [◀][▼] together, the cursor is moving to “↙”.
Press [▶][▼] together, the cursor is moving to “↘”.
Press [◀][▲] together, the cursor is moving to “↖”.
Press [▶][▲] together, the cursor is moving to “↗”.
5.3. Removing the cursor
Press to remove the cursor.
5.4. Cursor information windo w
①
Latitude/Longitude LAT/LON of the cursor.
②
Range Distance between the cursor and the present position.
③
Bearing Bearing from the present position to the cursor.
5.5 . Cursor information window shown/hidden
▶MENU->Advance->Setup->Customizing->INFO window->Cursor
Cursor information window “Shown/Hidden”.
①
②
③
Page 45

- 44 -
6. Page
�[PAGE]
Choosing the various pages that set up pages or customized.
Move the red box to choose the page.
Rotate the knob or press [◀][▶][▼][▲] to move the red box on your page and Enter to finish.
(Fig.1.4)
6.1. Page mode
▶[MENU]->Advance->Setup->Customizing->Page mode
Two ways to choose the page.
6.1.1. Standard
With seeing the set up page, choosing the page or modifying.
6.1.2. Flip
Showing the set up pages in order.
(* In Flip mode, modifying the order is available.)
6.2. Modify
Move the red box on your page of (Fig1.4) and keep pressing [PAGE] or long press to move
(Fig.1.4.1).
Selected (red color)
Page 46

- 45 -
(Fig.1.4.1)
Choose your frame on (Fig.1.4.1).
Using key: use [▼][▲] and move the red box to choose the pages and press [▶]. When you finish,
press Enter.
1. Choose the pages with [▼][▲]
2. P ress [▶], choos e with [▼][▲]
Page 47

- 46 -
(Fig.1.4.2)
Long press: Choose the page and long press for drag the page into the frame..
(Fig.1.4.3)
When complete, press Enter to finish.
3. Enter
4. Keep choosing and Enter to finish
Page 48

- 47 -
7. Active
▶[ACTIVE]
When pressing [FUNC], the red box moves to to chartplotter or sonar.
(*All key functions change to chartplotter or sonar)
Selected (red color)
Page 49

- 48 -
8. Navigation Data
Navigation data is available in Navigation data page, Steering page, Highway page as (Fi g.1.5).
(Fig.1.5)
8.1. Type
▶[MENU]->Advance->Setup->Customizing->Navigation data->Type
Two types of Navigation data page.
8.1.1.Type1
Large LAT/LOT as (Fig.1.5.1).
(*Editing the LAT/LOT is unavailable)
8.1.2. Type2
Various data as (Fig.1.5.2).
(Fig.1.5.1) (Fig.1.5.2)
Page 50

- 49 -
8.2. Edit
(*If there is no navigation data on the page, editing the navigation data is unavailable)
▶[MENU]->Advance->Setup->Customizing->Navigation data->Edit
After finishing as (Fig.1.5.3), press [CANCEL] to exit.
(*Please, refer “Customizing” for further question)
(Fig.1.5.3)
Page 51

- 50 -
9.MOB
If a person or missing an object overboard and you need to get present position, use the MOB
function.
9.1. Inputin g
Keep pressing [WPT] until the window comes out as [Fig.1.6] and then “MOB” com es out with alarm.
9.2. Exiting the alarm
When alarming, press [CANCEL] and you may exit the alarm.
9.3. Removing
While MOB is sett i ng, press [WPT] again and you may remove the “MOB”.
(*MOB is not stored in the flash memory)
Page 52

- 51 -
10. Memory Card
Inserting the SD, micro SD & USB OTG as (Fig.1.7.1).
(Fig.1.7.1)
Page 53

- 52 -
11. Save Userdata
▶[MENU]->Userdata->Save Userdata
Userdata is stored in the external Micro SD. So if you want to save the userdata, a micro SD must be
inserted in the slot.
(*Userdata is in “..\HY\UserData\”)
11.1. WPT
WPT can be stored in a SD/Micro SD/USB.
When storing, give it a name and you will be able to store many WPT’ in the SD/Micro SD/USB.
11.2. Route
Route can be stored in a SD/Micro SD/USB.
When storing, give it a name and you will be able to store many routes in the SD/Micro SD/USB.
11.3. Track
11.3.1. Type1
Page 54

- 53 -
Track can be stored in a SD/Micro SD/USB.
When storing, give it a name and you will be able to store many tracks in the SD/Micro SD/USB.
11.3.2. Type2
Track can be stored in a SD/Micro SD/USB.
Index will be a standard in Type2. After choosing the index, stored i t.
11.4. User Line
User Line can be stored in a SD/Micro SD/USB.
When storing, give it a name and you will be able to store many user lines in the SD/Micro SD/U SB.
11.5. User Name
User Name can be stored in a SD/Micro SD/USB.
When storing, give it a name and you will be able to store many user names in the SD/M icr o SD /USB.
Page 55

- 54 -
12. Load Userdata
▶[MENU]->Userdata->Load Userdata
Userdata loads from the stored SD/MicroSD/USB. If you need to load the userdata, the stored
SD/MicroSD/USB must be inserted in the slot.
(*Userdata is in “..\HY\UserData\”)
12.1. WPT
WPT loads from the stored SD/MicroSD/USB.
All of WPT in the SD/MicroSD/USB show on the list. Choose one of them and it will show.
There are two ways to load WPT.
First, showing the stored WPT as well as the existing on the sceen. After loading the stored, you will
see the window and press [MENU].
Second, showing only stored WPT. After loading the stored, press [ENTER].
12.2. Route
Route loads from the stored SD/MicroSD/USB.
All of route in the SD/MicroSD/USB show on the list. Choose one of them and it will show.
Page 56

- 55 -
12.3.Track
12.3.1. Type1
Track loads from the stored SD/MicroSD/USB.
All of track in the SD/MicroSD/USB show on the list. Choose one of them and it will show.
12.3.2. Type2
Track loads from the stored SD/MicroSD/USB.
Index will be a standard in Type2. After choosing the index, stored i t.
12.4. User Line
User line loads from the stored SD/MicroSD/USB.
All of user line in the SD/MicroSD/USB show on the list. Choose one of them and it will show.
12.5. User Name
User name loads from the stored SD/MicroSD/USB.
All of user name in the SD/MicroSD/USB show on the list. Choose one of them and it will show.
Page 57

- 56 -
Page 58

- 57 -
Chartplotter get ting sta rt ed
1. GOTO
1.1. Goto type1
1.1.1. Setting
▶[MENU]->Navigation->Goto type->type1
Setting GOTO with creating a route at the same time.
Move the cursor to the position where you want to go and press [ENTER].
(*While navigating, WPT can be added in the route)
1.1.1.2. Exit/Store
If you want to exit, remove the cursor and press [GOTO]. The window to store or not shows up.
Choose one of them and you will exit.
(*If you have one WPT in the route, the WPT will be stored. If you have more than two, all of WPT and
the route will be stored together)
1.2. Goto type2
1.2.1. Setting
▶[MENU]->Navigation->Goto type->type2
Direct GOTO where you want to go. Only one destination is available.
1.2.2. Exit/Store
If you want to exit, remove the cursor and press [GOTO]. The window to store or not shows up.
Choose one of them and you will exit.
1.2.3. Changing
While navigating, you can change a new destination. Move the cursor and press [GOTO] for the new
destination.
Page 59

- 58 -
2. WPT
2.1. List
▶[MENU]->Userdata->WPT->List
Editing, creating, erasing and navigating are available on the WPT list.
①
List Showing all of the stored WPT.
②
Latitude/Longitude LAT/LOT of the WPT .
③
Name Name of the WPT.
④
Date & Time Date and time of the WPT when stored
⑤
Depth Depth of the WPT.
⑥
Bearing Bearing between the WPT and the present position.
⑦
Range Distance between the WPT and the present position.
⑧
Symbol Symbol of the WPT.
⑨
Color Color of the WPT.
①
Selected
②
③ ④
⑤ ⑥
⑦
⑧
⑨
Page 60

- 59 -
2.2. Setting the WPT symbol
▶[MENU]->WPT Symbol
Choose the symbol and press [ENTER].
The chosen symbol will show when inputting WPT.
2.3. Setting WPT Color
▶[MENU]->WPT Color
Selected(red color)
Selected(red color)
Page 61

- 60 -
Choose the color and press [ENTER].
The chosen color will show when inputting WPT.
2.4. Creating
2.4.1. Creating on the list
▶[MENU]->Userdata->WPT->List->[2.Add]
Adding WPT with pressing [2.Add].
(*When adding, LAT/LOT show the present position and current symbol/color show for the WPT)
2.4.1. Inputting on the chart
Call the cursor and move the position where you want, and press [WPT].
(*The current symbol/color show for the WPT)
2.5. Erasing
2.5.1. Erasing on the list
▶[MENU]->Userdata->WPT->List->[3.Erase]
Choose the WPT you want to erase and press [3.Erase] .
2.5.2. Erasing on the chart
Call the cursor and put it on the WPT, and press [ENTER].
Page 62

- 61 -
2.6 Erasing all of WPT
▶[MENU]->Userdata->WPT->List->[5.All Erase]
On the WPT list, press [5.All Erase].
1. Erase all: Choose “ALL” of symbol and color and “Erase” and Enter.
2. Erase by color and symbol: Choose the color and the symbol and “Erase” and Enter.
2.7. Moving the WPT
1. Call the cursor and move it on the WPT, and press [ENTER].
2. Choose “Move”.
(Fig.1.8.)
Selected
Page 63

- 62 -
3. Move the WPT to the position where you want to move, and press [ENTER].
2.8. Navigating
2.8.1. Navigating on the list
▶[MENU]->Userdata->WPT->List->[6.Goto]
Choose the WPT on the list and press [6.Goto].
2.8.2. Navigating on the chart
Call the cursor and move it on the WPT, and press [ENTER]. Choose “GOTO” to start.
2.8.2. Navigating on the chart
Call the cursor and move it on the WPT, and press [ENTER]. Choose “GOTO” to start.
Page 64

- 63 -
2.9. Move to vessel
Call the cursor and move the WPT and Enter. Choose “Move to vessel”.
2.10. Sorting
▶[MENU]->Userdata->WPT->List->[4.Sort]
Sorting the order of WPT on the list.
Page 65

- 64 -
Page 66

- 65 -
2.11. Editing
▶[MENU]->Userdata->WPT->List
Editing the WPT on the list.
1. Choose the WPT as the blue and press [ENTER].
2. Choose the item as the green and you may begin to edit.
3. After finishing, press [CANCEL] to exit.
Edit Selected
WPT Selected
Page 67

- 66 -
3. Route
3.1. List
▶[MENU]->Userdata->Route->List
①
List Showing the stored WPT
②
Name Name of the route
③
Number of WPT Number of WPT in the route
④
Total distance Total distance of the route
⑤
Display Shown/Hidden the route on the chart
⑥
Date & Time Date and time of the WPT when stored
⑦
Start WPT The beginning of the route
⑧
End WPT The end of the route
①
②
③
④
⑤
⑥
⑦ ⑧
Page 68

- 67 -
3.2. Route detail
▶[MENU]->Userdata->Route->List->[4.Detail]
①
List Showing the stored WPT
②
Latitude/Longitude LAT/LOT of the WPT
③
Name Name of the WPT
④
Date & Time Date and time of the WPT when stored
⑤
Depth Depth of the WPT
⑥
Bearing Bearing between the WPT and the present position
⑦
Range Distance between the WPT and the present position
⑧
Symbol Symbol of the WPT
⑨
Color Color of the WPT
①
②
③
④
⑤
⑥
⑦ ⑧
⑨
Page 69

- 68 -
3.3. Creating
Two ways to create route
The first uses “GOTO type1” and the second is “Creating new route” on the list.
3.3.1. Using “GOTO”
Use “GOTO type1” and create a route. Press [ENTER] to start.
Press [GOTO] to exit and choose “Store” if needed.
3.3.2. Creating new route on the list
▶MENU->Userdata->Route->List
Press [2.Add] on the list to create a route.
Selected
Page 70

- 69 -
3.4. Edit
▶MENU->Userdata->Route->List
Choose the route on the list to edit.
3.5. Detail edit
▶[MENU]->Userdata->Route->List->[4.Detail]
Choose the route on the list and press [4.Detail]. The window of Route detail shows.
3.5.1. Adding WPT
Two ways to add WPT
3.5.1.1. Adding the stored WPT
▶[MENU]->Userdata->Route->List->[PAGE]->[2.Saved WPT]
(Fig.2.1)
Page 71

- 70 -
Press [2.Saved WPT] on the Route detail and you may add the stored WPT as (Fig.2.1).
3.5.2.1. Adding new WPT
Press [3.New WPT] on Rout detail and you may add new WPT.
3.5.3. Erasing WPT
Choose the WPT and press [4.Erase].
3.6. Navigating
▶[MENU]->Userdata->Route->List->[6.Goto]
Choose the route on Route list and press [6.Goto].
3.7. Erasing
Choose the route and press [3.Erase] .
4. Track
The maximum point is 50,000.
Tw o ways to manage the track. The first is to manage the total 50,000 points by colors. The second is
to divide 50,000 points in five rooms, and you can store 10,000 points for the maximum in each room.
Tracking has two types, “by time and by distance”.
4.1. Track on/off
▶Press [TRACK]
4.2. Choosing the track
4.2.1. By time
▶[MENU]->Userdata->Track->Track Setup->Record Setup->Time
Tracking by the set time.
4.2.2. Setting the time interval
▶[MENU]->Userdata->Track->Track Setup->Time Interval
Setting the time interval.
4.2.3. By distance
▶[MENU]->Userdata->Track->Track Setup->Record Setup->Distance
Tracking by the set distance.
Page 72

- 71 -
4.2.4. Setting the distance interval
▶[MENU]->Userdata->Track->Track Setup->DIST Interval
Setting the distance interval.
4.3. Setting the thickness
▶[MENU]->Userdata->Track->Track Setup->Thickness
Setting the track thickness.
4.4. Track Color
▶[MENU]->Track Color
Choose the color and press [ENTER].
(* The number next the color shows the number point of the track color)
4.5. Track type
4.5.1. Erasing
▶[MENU]->Userdata->Track->Erase
Choose the color and press [ENTER].
(*The number next the color shows the number point of the track color.)
Selected(red color)
Page 73

- 72 -
4.5. 2. Erasing all of track
▶[MENU]->Userdata->Track->Erase
Press [1.All Erase].
4.5. 3. Erase with cursor
▶[MENU]->Userdata->Track->Erase->Partial Erase
Choose [2.Partial Erase].
Long press where you want to start erasing the track.
(*1 should show on the left top.)
Page 74

- 73 -
Choose the end of the track to erase.
Page 75

- 74 -
5. Measuring the distance and bearing
1. Measuring two points, “A” and “B”.
2. Call the cursor and move it on the point, “A”.
3. After Enter, c alcul ating the distance/BRG.
4. Move the cursor on the point, “B”.
5. The cursor windows provides the distance and bearing between A and B.
6. Press [CANCEL] to exit.
A point
B point
Range
Bearin
Page 76

- 75 -
6. User Line
Adding lines directly on the chart.
1. Call the cursor.
2. Press [ENTER] and “User Line” shows.
3. Move the cursor to the beginning point and press [ENTER].
4. Keep moving the cursor and press [ENTER] each time.
5. Press [CANCEL] to exit.
Start point
Page 77

- 76 -
7. User Name
Adding a place name directly on the chart.
1. Call the cursor and move it to the point.
2. Press [ENTER] and choose “User Name”.
4. Inputting letters with [◀][▶][▼][▲].
5. Press [CANCEL] to exit.
Page 78

- 77 -
Chartplotter operation
1. Map Orientation
▶[MENU]->Advance->Map Setup->Map Orientation
1.1. True Motion
▶[MENU]->Advance->Map Setup->Map Orientation->True motion
The True Motion is in the way the vessel position is presented. In True Motion mode, the vessel icon
moves over the map while the map remains stationary.
(* It is not available to operate on Course up and Head up.)
1.2. North Up/South Up/East Up/West Up
▶[MENU]->Advance->Map Setup->Map Orientation->Up mode
They setting the vessel present position remains fixed in the center of the Main Screen while the map
moves under it.
1.3. Course Up
▶[MENU]->Advance->Map Setup->Map Orientation->Up mode
The Course Up mode screen orientation is determined by whether or not navigation is in progress.
During navigation vessel present position is in the center of the Screen and the course line to the
destination is straight up. As your present position changes, the map moves under the stationary
vessel icon.
(*If navigation is stopped, the Main Screen appears as Head up.)
1.4. Head Up
▶[MENU]->Advance->Map Setup->Map Orientation->Up mode
For Head Up mode, vessel present position is fixed in the center of the Main Screen and vessel
heading is upward. As your present position changes, the map moves under the vessel icon.
Page 79

- 78 -
2. Map setup
▶[MENU]->Advance->Map Setup
2.1. Map orientation
2.1.1. True motion
You can select “True motion”
(☞ The default setting is OFF.)
2.1.2. Up mode
You can select “Map Orientation”
(☞ The default setting is North Up.)
2.2. UserData Display
You can set up shown/hide the user data on the display.
2.3. Chart
Select the chart among C-map and Navionics
(☞Navionics will be updated later.)
2.4. C-Map (*Only for *C-MAP mode.)
2.4.1. Chart Display Configuration
2.4.1.1. Land Setting
The Land Settings menu controls the display on the chart of the terrestrial features.
- Fresh Waters: turns On or Off canals, lake areas, rapids, rivers, waterfallsB.
- Cultural Features: turns On or Off any man-made topographic features (as built-up areas, airport
areas, tunnel entrances, rai l ways B).
- Natural Features: turns On or Off any topographic feature formed by the action of natural process (as
dunes, hills, vegetation areas B).
- Landmarks: turns On or Off any prominent object on land which can be used in determining a
location or a direction (as monuments, buildings, silos, chimneys B).
- Points Of Interest (POIs): turns On or Off Points Of Interest (attractions, emergencies,
entertainmentsB). When it is On, it is possible to see detailed information that includes facilit i es
and services in ports and surrounding areas.
Page 80

- 79 -
- Multimedia: turns On or Off Multimedia which allows assigning one or more image to any chart
object, such as high definition pictures of ports, piers, bridges diagram...
2.4.1.2. Marine Setting
The Marine Settings menu controls the display on the chart of the marine features.
- Tides & Currents: turns the Tides and Currents On or Off. When the GPS signal is available, Tidal
stream arrows are shown on the charts, indicating the direction and strength of the Tidal Current. Ports
& Services: turns On or Off the areas along the shore with facilities for mooring, loading and unloading
of ships, generally sheltered from waves and winds (as causeways, dams,landing places, rescue
stations, port areasB).
- Nature Of Seabed: turns On or Off the type, color and other characteristics of the seabed area.
- Areas & Limits: turns the Areas and Limits On or Off. It controls the display of areas in which special
attention by the mariner is required, due to some natural or man-made hazards or sailing regulations
and restrictions, by filling them with a special pattern. Moreover special s ym bols are placed insi de
these areas. When the area is small, it is identified only by its boundary. Examples are anchorage
areas, caution areas, free port areas B.
- Port Names: turns On or Off the Port names.
- Place Names: turns On or Off the local area names.
- Lat/Lon Grid: turns On or Off the Latitude and Longitude grid lines.
- Chart Boundaries: turns On, Off the displaying of the available boundaries of the charts.
- VAD Boundaries: turns On, Off or Auto the display of the Value-Added Data boundaries which
indicate areas where more VAD details are available.
2.4.1.3. Depth Setting
The Depth Settings menu controls the depth information on the chart display.
-Decimal Mode: turns On or Off the display of the decimal digits.
2.4.1.4. Nav Aids Setting
The Nav Aids Settings menu controls the display of the Navigational Aids.
- Light Sectors: turns On or Off the sectors of the lights.
2.4.2. Chart Presentation
Page 81

- 80 -
This feature has preprogrammed settings which allow to customize the look of the cartographic pages.
2.4.2.1. Presentation Setting
You can select and configure the chart symbology and palette.
- US: draws the chart using US symbology
- International: draws charts using International symbology
(☞ The default setting is US.)
2.4.2.2. Fonts & Symbols Size
You can set the size of all names and icons drawn on the charts.
2.4.2.2.1. Fonts Size
You can set the size of all names drawn on the charts.
(☞ The default setting is Normal.)
2.4.2.2.2. Symbols Size
You can set the size of icons drawn on the charts.
(☞ The default setting is Large.)
2.4.2.2.3. Pale t te
It is possible to the palette used to enhance the visibility of the screen depending on the surround light
condition.
(☞ The default setting is Normal.)
2.4.3. Raster Setting
The Chart Mode feature allows to select the mode to display the chart on the screen. See below the
available modes.
2.4.3.1. Raster Mode
Select where to overlay the overlay. You can choose between land and Water.
(*The raster mode is only active when the satellite images are overlay .)
(☞ The default setting is No Ras ter.)
2.4.3.2. Overlay
You can choose to overlay image of a satellite image and a Raster image.
2.4.3.3. Alpha Trans
Page 82

- 81 -
You can set the alpha value of the overlaid image..
2.4.4. 3D
2.4.4.1. 3D View
You can turn on/off the 3D view.
(☞ The default setting is off.)
2.4.4.2. Draw Mode
You can set the draw mode of the 3D view..
(☞ The default setting is Normal.)
2.4.4.3. Height Multiplier
You can set the strength of the 3D view.
(☞ The default setting is 3.)
2.4.5. Multi Language
Select language for name of the place, lighthouse or buoy.
2.4.6. Quick View
It is available to set up. Place the cursor on buoys or icons on the C-MAP, the information window is
shown up automatically.
(☞ The default setting is Shown.)
2.4.7. Touch
2.4.7.1. Pitch
You can set the Pitch to any value in the displayed range
(☞ The default setting is On.)
3. Vessel
3.1. Vessel Icon Size
The size of the present position is adjustable from 0 to 9. The biggest size is ‘0’.
(� The default setting is 9.)
3.2. Heading Line
The length of the heading line is adjustable from 50 until 300. The bigger number, the longer line. The
heading line is used in modes of the true motion and the north up.
Page 83

- 82 -
(� The default setting is 270.)
3.3. Vessel style (Circle/Arrow/Vessel)
Select the vessel symbol among Circle, Arrow and vessel.
(☞ The default setting is circle.)
3.4. Orient. Resolution
Sets you preferred Rolling Road Scale.
(� The default setting is 0.)
4. Cursor Icon
Select the cursor icon between Cross to Arrow.
(� The default setting is Cross.)
5. Alarm
5.1. Navigation
5.1. 1. Arrival Alar m:
When you approach into the waypoint range, it gives you a notice with alarm.
(� The default setting is OFF.)
5.1.2. Arrival Radius:
It is to adjust the range of arrival from your waypoint. If you have a route, it changes to the next
waypoint automatically.
(� The default setting is 0.05nm.)
5.1.3. XTE Alarm:
If you are out of the course, it gives you a notice with alarm.
(� The default setting is OFF. )
5.1.4. XTE Radius:
It is to adjust the range of the off course.
(� The default setting is 0.25nm.)
5.2. A nchor
5.2.1. Anchor Alarm:
It is necessary when your vessel anchors.
Page 84

- 83 -
(� The default setting is OFF.)
5.2.2. Anchor Radius:
If you vessel is out of the range of the anchor, it gives you notice with alarm.
(� The default setting is 0.05nm.)
5.3. Interval
5.3.1. Interval Alarm:
It alarms every time you set.
(� The default setting is OFF.)
5.3.2. Interval Time
The time is available from one minute until sixty minutes.
(� The default setting is 3 min.)
5.4 User Line
5.4.1. User Line Alarm
It alarms if it breaks into the setting area.
(� The default setting is OFF. )
5.4.2. User Line Radius
It sets the range of the course alarm.
(� The default setting is 0.05nm.)
Page 85

- 84 -
Page 86

- 85 -
AIS getti ng started
1. What is AIS?
AIS is an Automatic Identification System. It has been introduced to improve the safety of navigation
by assisting in the efficient operation of ship to ship, ship reporting and VTS applications. The system
should enable operators to obtain information from the ship automatically, requiring a minimum of
involvement of ship’s personnel, and should have a high level of availability.
Connecting to the chart pl otter an AIS receiver, vessels with AIS transponder within VHF range are
displayed on screen giving he skipper or navigator a visual interpretation of the data of nearby vessels.
This improves safety, and specifically for collision avoidance reasons.
2. AI S system definitions
CPA
Closest Point of Approach is the closest distance that will be achieved between
your vessel and the tracked target, based on your vessel’s speed and direction
and the target’s speed and direction.
TCPA
Time to Closest P oint of Approach is the time remaining until the CPA will occur.
Name
Name of ship, 20 characters.
MMSI
Maritime Mobile Service Identity.
MMSI number
A unique 9 digit number that is assigned to DSC radio station. It primarily
registers the boat information in the U.S. Coast Guard’s national distress
database for use in emergency situations.
Target
It is a vessel equipped with AIS. Information about the targets is being received
by AIS Receiver and displayed on the screen.
Active T arget
Target l ocat ed within t he Activation Range. Active target is represented by
oriented triangle with COG and Heading vectors. Rate of turn may also be
displayed.
Selected
Target
Target selected with cursor. Can view AIS information window.
Dangerous
Target det ected by CPA or TCPA Alarm. Dangerous target is Active Target by
definition. For better visibility Dangerous Target symbol is charged from basic
Page 87

- 86 -
Target
color to red color.
Sleeping
Target
Target l ocat ed outside the Activation Range. Sleeping target is represented by a
small oriented triangle.
Lost Target
When the AIS info is not received from that vessel. The presentation will be
marked X on the target.
3. AIS information window
Press [ENTER] key on Target which wants to see. It shows Information of “AIS INFO” window.
(Fig.3.1)
Page 88

- 87 -
4. Quick INFO on AIS target
Choose “AIS information window” on (Fig. 3.1) and AIS data shows under the AIS target.
(*Up to four kinds of data is available to choose in Quick INFO)
Page 89

- 88 -
AIS operation
▶[MENU]->AIS
1. AIS On/Off
Turns the display of AIS targets overlay on the screen On or Off.
(� The default setting is On.)
2. List
2.1. List
①
Name Name of the AIS target
②
MMSI MMSI of the AIS target
③
CPA Distance between AIS target and your position
④
COG BRG between AIS target and your position
⑤
SOG Speed between AIS target and your position
⑥
TCPA ETA from AIS target
⑦
NATION Nationality of AIS target
Selected(blue color)
① ② ③
④
⑤ ⑥
⑦
(Fig.3.2)
Page 90

- 89 -
2.2. Detail
Choose the AIS target and press [ENTER].
2.3. Goto
Choose the AIS target and press [4.Find].
Page 91

- 90 -
2.4. Sort
Press [3.Sort] to choose how to sort on (Fig.3.2).
3. Display radius
Displays range rings centered on your current position.
(☞ The default setting is OFF.)
4. AIS target size
Choose the size of AIS tartget.
(☞ The default setting is Large.)
Page 92

- 91 -
5. Display vessels by Color
Different types of AIS transmissions can be selected to display different colors of icons on the chart
display.
6. Display vessels by Type
Different types of AIS transmissions can be selected to display different types of icons on the chart
display.
7. Filter A IS types
This function allows you to turn on or off reception from different types of AIS transmissions, for
instance if you only wanted to view Class B vessels on the chart display then select Class B On and all
the others Off.
8. Alarm
8.1. CPA Alarm
The CPA alarm is the closest approach alarm, this allows you to set a distance when the alarm will
sound if a vessel comes within that distance .
(☞ The default setting is OFF.)
8.2. CP A Ra nge
The values allowed are from 0.1nm to 10nm.
(☞ The default setting is OFF.)
8.3. TCPA Alarm
The TCPA alarm is the time that a vessel will take to be in the same position as you currently are.
(☞ The default setting is OFF.)
8.4. TCPA Range
The values allowed are from 1 to 50 min.
(☞ The default setting is 1 min.)
8.5. Radius Alarm
When any AIS target breaks into the radius, alarming.
8.6. Radius
The values allowed are from 0.1nm to 10nm.
Page 93

- 92 -
(☞ The default setting is OFF.)
8.7. Ignore Vessels if Speed Less
If you want the alarms to ignore vessels that are travelling at less than a particular speed then switch
ON.
8.8. Speed less than
The values allowed are from 0.1kt to 9.9kt.
9. Set up AIS outs etc
9.1. Mark vessels as lost after
Setting the time of “Lost target”.
(☞ The default setting is 7min.)
9.2. Remove lost vessels after
If the updating AIS target is unavailable in the set time, erasing the AIS target on the screen..
(☞ The default setting is 10min.)
9.3. Vessel target
It is available to setup the own vessel’s AIS target display on the screen.
(� The default setting is On.)
10. Others
10.1. Labels on vessels
This menu controls what details are displayed alongside the vessels icons on the chart display.
10.2. Cursor Box info
When you move the cursor in chart mode over an AIS target a box appears showing details of that
vessel.
10.3. Messages List
This window displays lists of specific AIS messages, such as Safety Messages that the unit has
received. Scrolling down the list and highlighting a message allows you to see the contents by
pressing the [ENTER] key. Whilst in the main list pressing the [MENU] key when a message is
highlighted will erase that message, pressing the [►] [◄] keys will allow you to view any other pages
of messages.
Page 94

- 93 -
★ AIS SART Messages
If an AIS SART message is received it will immediately be displayed on whatever screen you are
viewing. If the “Status” shows “Test” then no further action is required as it is just a test transmission. If
the “ Status” shows “Active” it will also show the MMSI, Name and position, the SART icon should now
be displayed on your chart screen at that location. Monitor your VHF radio on Channel 16 and
establish whether any other station has received this SART message, if not take the appropriate
action.
10.4. Test View
Showing the text massage of SART Message.
(� The default setting is Off.)
10.5. Fishing net
10.5.1. Fishing net
Display the programmed Fishing net AIS target.
(☞ The default setting is Off.)
10.5.2. Select name
Program the name of Fishing Net
10.5.3. Alarm
The alarm goes off when no Fishing net AIS target is in setting range.
(☞ The default setting is Off.)
10.5.4. Alarm Radius
Setup the Fishing net alarm range.
(☞ The default setting is 0.05nm.)
10.6. Display Scale
It is possible to setup AIS Targets with Scale
(� The default setting is 60nm.)
10.7. Group Fishing
Showing chosen AIS targets only in group fishing list.
10.7.1. Group Fishing
Page 95

- 94 -
- Highlight : Showing the registered MMSI of AIS targets with the chosen color/symbol.
- Only : Showing the registered MMSI AIS t argets only.
10.7.2 List
Add/Erase MMSI of AIS targets for group fishing.
10.7.3. Vessel Symbol
Choose the symbol of MMSI of AIS targets for group fishing.
10.7.4. Vessel Color
Choose the color of MMSI of AIS targets for group fishing.
(☞ Standard is blue)
Page 96

- 95 -
Sonar getting started
1. Choosing the frequency
In dual frequency mode, choosing the frequency with [▲][▼].
(*The chosen frequency shows in red)
2. Auto/Manual Gain
Press [ENTER ] to choose” AUTO/Manual” of Gain.
3. Gain/STC
Choose “Gain” and “STC” with [◀][▶].
4. Controlling Gain
1. Choose the frequency.
2. Choose the gain.
3. Twisting the rotary key to control the gain.
Selected
Page 97

- 96 -
5. Controlling STC
1. Choose the frequency.
2. Choose the STC.
3. Twisting the rotary key to control the STC.
6. Mode
▶[MENU]->Mode
Three kinds in Sonar.
6.1. Normal
Normal mode (with Auto Range active) displays the sounder image with the surface at the top of the
screen and the sea bottom in the lower part of the screen. The depth scale indicates the depth range
appearing in the display. Bottom contours and fish echoes are displayed at the depths where they are
detected. If the depth Range is set manually to a value less than actual water depth, sea bottom
echoes are not displayed, but all other echoes within the Range setting are displayed.
6.2. Bottom Zoom
Bottom Zoom magnifies the sounder display from the sea bottom toward the surface for a short
Page 98

- 97 -
distance. The sea bottom contour is displayed and additional contour lines are added at intervals
above the sea bottom to aid in determining distances of echoes near the bottom. Use the Sounder
Menu to set the magnified Bottom Range from 2.5 to 20m (10 to 60ft.). Default setting is 10m (40ft.). If
the depth Range is set manually, the setting must place the sea bottom ec ho in the lower portion of the
screen for Bottom Zoom to be effective.
6.3. Bottom Lock
Bottom Lock divides the Sonar main screen image for the selected Sonar into two sections. The left
hand section displays a Normal Mode image. The right hand section of the screen displays the Sonar
image relative to the sea bottom. The sea bottom appears as a straight line with the Sonar image
magnified for a short distance toward the surface. A sc al e
appears on the right for estimating distances of echoes near the bottom. Use the Sonar Manu to set
the magnified Bottom range from 2.5 to 20m (10 to 60ft.). Default setting is 10m (40ft.). If the depth
Range is set manually, the setting must place the sea bottom echo in the
lower portion of the screen for Bottom Lock to be effective.
Sonar modes are selectable for single frequency or dual and some functions, for example bottom
Page 99

- 98 -
zoom or lock.
7. VRM
▶ [WPT]
The VRM (movable marker) shown by the green line can be moved up and down.
It is convenient to measure the depth by aligning with the target such as school of fish.
[Fig.2.1]
Page 100

- 99 -
Sonar operation
1.Menu
▶ [MENU]
1.1. Userdata
It is same as Chartplotter. PLS refer the Chartplotter operation manual.
1.2. Deep Depth Range
Smart4/5 selects the best condition for measuring the depth automatically in the environment of the
sea.
(� The default setting is Auto.)
1.3. Shift
A user selects this function to see more detailed bottom of the sea. When you turn up the shift, the
range of Fish finder shall go up from the shift range. For example, if you raise 5m of shift at 20m
range, the surface shall start 5m and the bottom range shall be 25m.
(� The default setting is 0m.)
1.4. Mode
Fish finder modes are selectable for single frequency or dual and some functions.
1.5. Bottom Zoom Range
Select the range of the bottom zoom or lock. It is necessary to modify the bottom.
(� The default setting is 10m.)
1.6. Fish symbol
Fish symbol with sizes and levels show for targets.
(*Fish symbol is only for reference. This could be different from the real.)
1.7. Fish size
Setup to display of the size of fish.
(� The default setting is Off.)
1.8. Interference Rejection
 Loading...
Loading...