Page 1
QSG139: Bluetooth® SDK v2.x Quick Start
Guide
This document describes how to get started with Bluetooth
development using the Bluetooth software development kit (SDK)
and Simplicity Studio with a compatible wireless starter kit (WSTK).
If you have purchased a Blue Gecko Bluetooth Wireless Starter Kit
you can first experiment with precompiled demos and an Android
or iOS smartphone app before continuing with your own application
development.
KEY POINTS
• Introducing the Bluetooth development
environment.
• Using the Blue Gecko Wireless Starter K it
demos and Android or iOS smartphone
app to demonstrate Bluetooth features.
• Installing the Bluetooth SDK in Simplicity
Studio.
• Starting application development for Bluetooth dev ices with Simplicity Studio.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.7
Page 2
QSG139: Bluetooth® SDK v2.x Quick Start Guide
Introduction
1 Introduction
This document describes how to get started with Bluetooth development using Silicon Labs products. It introduces the features of the
Silicon Labs Bluetooth stack and the resources available to help with development. Application development is started using the Silicon
Labs development environment Simplicity Studio and the Bluetooth Software Development Kit (SDK). The SDK comes with a number of
example application that you can then modify to create your own applications. If you are developing with an EFR32BG device and have
purchased a Blue Gecko Bluetooth Wireless Starter Kit, you can use precompiled demos and an Android or iOS smartphone app to
demonstrate Bluetooth software features.
This document describes the following:
• Bluetooth Stack features and components (see section 2 About the Bluetooth Stack)
• Installing Simplicity Studio and the Bluetooth SDK (see section 3 Getting Started with Simplicity Studio and the Bluetooth SDK
• A description of the precompiled demos and example code available in the SDK (see section 4 About Demos and Examples)
• How to test prebuilt demo software with either an iOS or Android smartphone app (see section 5 Getting Started with Bluetooth Demo
Software)
• How to develop your own applications in Simplicity Studio (see section 6 Starting Application Development)
• A description of other section 7 Development Tools that are useful in the development process
1.1 Prerequisites
As well as Simplicity Studio v4, you should have the following before beginning application development:
• A basic understanding of Bluetooth technology and terminology. UG103.14: Bluetooth LE Fundamentals provides a good starting
point if you have not yet learned about Bluetooth.
• A compatible compiler:
• Simplicity Studio comes with a free GCC C-compiler.
• IAR Embedded Workbench for ARM (IAR-EWARM) can also be used as the compiler for all Silicon Labs protocols. See the
Bluetooth SDK’s release notes for the compatible IAR-EWARM version.
• A registered account at Silicon Labs is required in order to download the Silicon Labs Bluetooth SDK.
• You can register at https://siliconlabs.force.com/apex/SL_CommunitiesSelfReg?form=short
To get a 30-day evaluation license for IAR:
• Go to the Silicon Labs support portal at https://www.silabs.com/support
• Scroll down to the bottom of the page, and click Contact Support
• If you are not already signed in, sign in.
• Click the Software Releases tab. In the View list select Development Tools. Click Go. In the results is a link to the IAR-EWARM
version named in the release notes.
• Download the IAR package (takes approximately 1 hour).
• Install IAR.
• In the IAR License Wizard, click Register with IAR Systems to get an evaluation license.
• Complete the registration and IAR will provide a 30-day evaluation license.
• Once IAR-EWARM is installed, the next time Simplicity Studio starts it will automatically detect and configure the IDE to use IAR-
EWARM.
.
.
1.2 Support
You can access the Silicon Labs support portal at https://www.silabs.com/support
in section 3.7 Accessing Documentation and Other Resources. Use the support portal to contact Customer Support for any questions
you might have during the development process.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.7 | 2
through Simplicity Studio’s Resources tab, as described
Page 3
QSG139: Bluetooth® SDK v2.x Quick Start Guide
Introduction
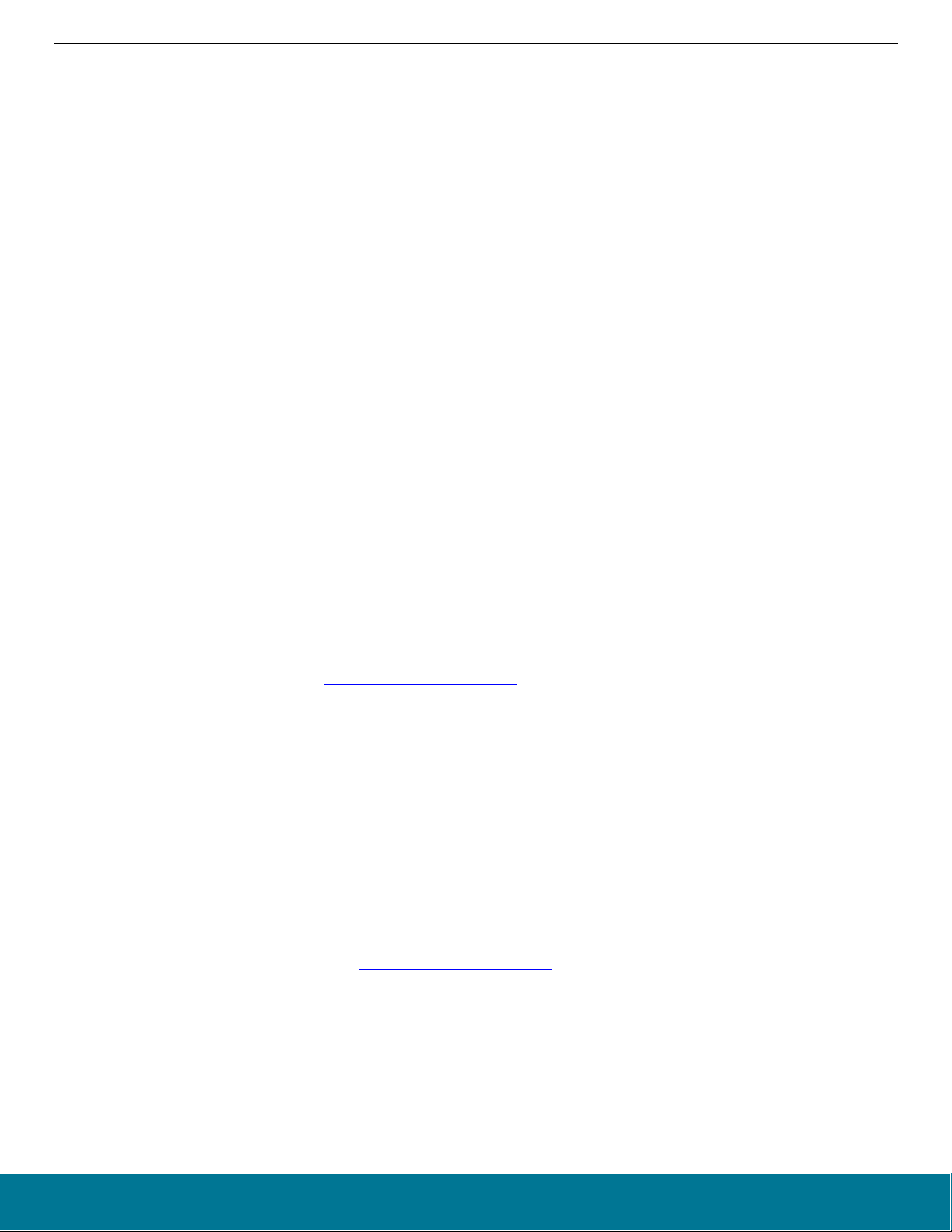
1.3 Documentation
Documentation for the Bluetooth SDK is summarized in the following figure.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.7 | 3
Page 4
QSG139: Bluetooth® SDK v2.x Quick Start Guide
Introduction
SDK documentation is accessed through Simplicity Studio, as described in section 3.7 Accessing Documentation and Other Resources.
Other resources available include Knowledge Base Articles (KBAs)
Simplicity Studio.
and Hardware documentation. All may be accessed through links in
Training materials are available on the Silicon Labs website at https://www.silabs.com/support/training/bluetooth and on
labs.com/bluetooth/latest/.
https://docs.si-
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.7 | 4
Page 5

QSG139: Bluetooth® SDK v2.x Quick Start Guide
Introduction
1.4 Gecko Platform
The Gecko Platform is a set of drivers and other lower layer features that interact directly with Silicon Labs chips and modules. Gecko
Platform components include EMLIB, EMDRV, RAIL Library, NVM3, and mbedTLS. For more information about Gecko Platform, see
release notes that can be found in Simplicity Studio’s Launcher Perspective, under SDK Documentation > Bluetooth SDK n.n.n.n >
Release Notes.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.7 | 5
Page 6
QSG139: Bluetooth® SDK v2.x Quick Start Guide
About the Bluetooth Stack
2 About the Bluetooth Stack
The Silicon Labs Bluetooth stack is an advanced Bluetooth 5-compliant protocol stack implementing the Bluetooth low energy standard.
It supports multiple connections, concurrent central, peripheral, broadcaster, and observer roles. The Silicon Labs Bluetooth stack is
meant for Silicon Labs Wireless Gecko SoCs and modules.
The Silicon Labs Bluetooth stack provides multiple APIs for the developer to access the Bluetooth functionality. Two modes are supported:
1. Standalone mode, where both the Bluetooth stack and the application run in a Wireless Geckos SoC or module. The application can
be developed with C programming language.
2. Network Co-Processor (NCP) mode, where the Bluetooth stack runs in a Wireless Gecko and the application runs on a separate
host MCU. For this use case, the Bluetooth stack can be configured into NCP mode where the API is exposed over a serial interface such as UART.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.7 | 6
Page 7
QSG139: Bluetooth® SDK v2.x Quick Start Guide
EFR32[B|M]G21, EFR32[B|M]G22: NVM3
About the Bluetooth Stack
2.1 Bluetooth Stack Features
The features of the Silicon Labs Bluetooth stack are listed in the following table.
Feature Value and comments
Bluetooth version Bluetooth 5.2
Bluetooth 5.2 GATT caching
Bluetooth 5 2M PHY (EFR32[B|M]G12, EFR32[B|M]G13, EFR32[B|M]G21, and EFR32[B|M]G22)
Bluetooth 5 LE Long Range (EFR32[B|M]G13, EFR32[B|M]G21, and EFR32[B|M]G22)
Bluetooth 5 advertisement sets and scan event reporting
Bluetooth 5 extended advertisements (EFR32[B|M]G12, EFR32[B|M]G13, EFR32[B|M]G21, and
Bluetooth features
Simultaneous connections Up to 8 simultaneous connections regardless of role (master or slave)
EFR32[B|M]G22)
• Anonymous advertisement
• Periodic advertisement
• Extended advertisement packet size: up to 1650 B
Concurrent central, peripheral, broadcaster and observer modes LE secure connections
LE Privacy 1.2 (peripheral) LE packet length extensions LE dual topology
Whitelisting (central side only)
Maximum throughput
1300 kbps over 2M PHY
700 kbps over 1M PHY
Encryption AES-128
Pairing modes
Just works
Man-in-the-Middle with numeric comparison and passkey Out-Of-Band
Number of simultaneous
bondings
EFR32[B|M]G1, EFR32[B|M]G12 and EFR32[B|M]G13: Up to 13 when using PS, up to 32 with NVM3
EFR32[B|M]G21, EFR32[B|M]G22: Up to 32
Link Layer packet size Up to 251 B
ATT protocol packet size Up to 250 B
Supported Bluetooth profiles
and services
All GATT based profiles and services are supported
Apple HomeKit R15-compliant implementation (EFR32[B|M]12, EFR32[B|M]13, EFR32[B|M]21, and
Apple HomeKit
EFR32[B|M]G22)
Implements all Apple HomeKit profiles and services Available separately for Apple MFi licensees
Host (NCP) interfaces
4-wire UART with RTS/CTS control or 2-wire UART without RTS/CTS
GPIOs for sleep and wake-up management
Wi-Fi Coexistence Using Packet Trace Arbitration (PTA)
Secure Gecko Bootloader supporting authenticated and encrypted updates over OTA or UART and
Bootloaders
Secure Boot. The Gecko Bootloader also supports flash partitioning and both internal and external
(SPI) flash.
Non-volatile memory
* Example applications in the SDK that are generated for these platforms will use PS by default.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.7 | 7
EFR32[B|M]G1, EFR32[B|M]G12, EFR32[B|M]G13: NVM3 or Persistent Store (PS)*
Page 8
QSG139: Bluetooth® SDK v2.x Quick Start Guide
Link Layer (Bluetooth 5.2)
147971
About the Bluetooth Stack
2.2 Bluetooth Qualification
All products using Bluetooth technology must go through the Bluetooth SIG's Qualification Process, even if the product does not have the
Bluetooth logo or Bluetooth is not mentioned in the packaging and the documentation. In practice this means that, before you can sell a
Bluetooth-enabled product, the product must be qualified as an End Product through the Bluetooth SIG. The qualification listing has a
Declaration Fee. There are online resources to learn more about the Bluetooth Qualification Process as well as tutorials on the
Studio, which is the online tool used to complete the Bluetooth Qualification Process. If you need assistance to qualify your device you
can consider reaching out to your nearest Bluetooth Qualification Consultant.
When qualifying your end-product based on Silicon Labs’ Bluetooth stack you will integrate the pre-qualified components listed in the
table below, depending on which SDK version was used to build your application.
Bluetooth SDK version Component QDID
v2.10.x up to 2.13.x Link Layer (Bluetooth 5.1) 127618
Host stack (Bluetooth 5.1) [*] 126252
v2.13.x and above
v3.0.x and above
Host stack (Bluetooth 5.2) 146950
[*] Launch Studio: For end-product qualifications based on this component, you must check the items 21/19 and 34/15 and uncheck the
items 21/17 and 34/13 in the "Summary ICS" and upload the Erratum 11838 Test Evidences, which can be requested through the support
portal.
Launch
Note: According to Bluetooth SIG Qualification Program Reference Document (PRD)
, the Assessment Date of the tested Component
must be less than three years old at the time it is being imported into a Launch Studio project for a new End Product Listing (EPL). After
the expiration of a Component QDID (Qualified Design ID), a newer SDK version than the one used for the outdated QDID should be
used in order to qualify your product. There can be also newer QDIDs than the ones listed in the table above if there are newer Component
versions. You can browse our valid Qualified Components and their Assessment Date by inserting Silicon Laboratories in the search bar
of
Launch Studio. Contact technical support if there is a need to use an older SDK version.
The above software-based pre-qualified components are two out of the three components to integrate when proceeding with the
"Qualification Process with Required Testing
". Despite the “Required Testing", customers do not need to do any additional testing, given
that the test reports are embedded in the pre-qualified components for the SIG to review.
In addition to these two software components you must also have integrated a qualified RF-PHY component in your end-product listing.
If you are designing with one of Silicon Labs’ Bluetooth modules then refer to the module datasheet for the appropriate component QDID
to use. If you are designing with an SoC, then you may need to obtain your own RF-PHY qualification with the Bluetooth SIG, depending
on your hardware design. In the latter case, consult your nearest Bluetooth Qualification Consultant
, or Silicon Labs through the support
portal, to understand if an existing Silicon Labs RF-PHY pre-qualification could be used.
Silicon Labs does not provide prequalified profiles. Customers must provide these with their end applications that implement the functionality as per the SIG profile specification.
2.3 The Bluetooth Stack APIs
This section briefly describes the different software APIs available for the developer.
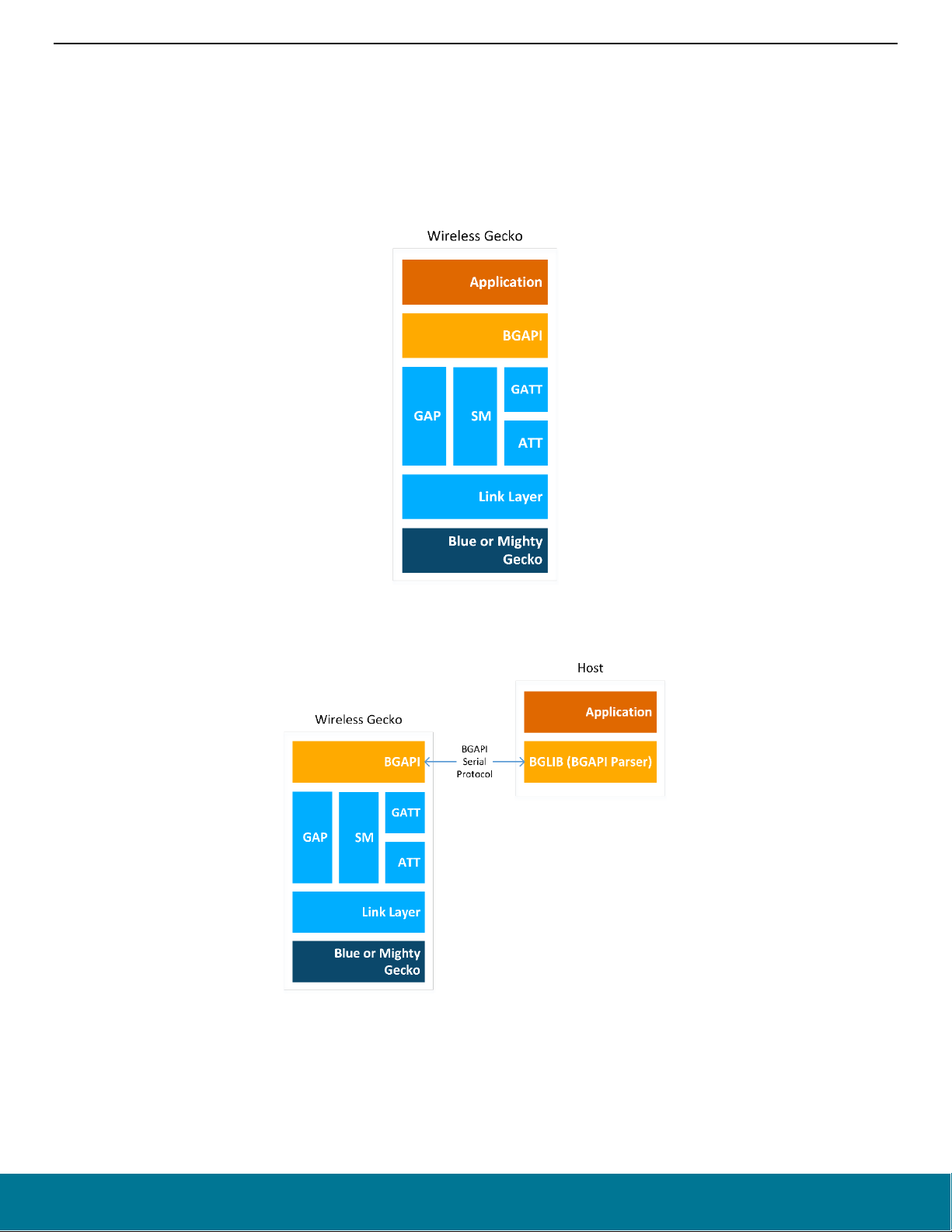
2.3.1 The BGAPI Bluetooth API
The BGAPI is the Bluetooth API provided by the Silicon Labs Bluetooth stack. It provides access to all the Bluetooth functionality implemented by the Bluetooth stack, such as: the Generic Access Profile (GAP), connection manager, the security manager (SM), and GATT
client and server.
In addition to the Bluetooth APIs, the BGAPI also provides access to a few other functions like the Direct Test Mode (DTM) API for RF
testing purposes, the Persistent Store (PS) API for reading and writing keys to and from the devices flash memory, the DFU (Device
Firmware Update) API for field firmware updates, and the System API for various system level functions.
2.3.2 CMSIS and emlib
The Cortex Microcontroller Software Interface Standard (CMSIS) is a common coding standard for all ARM Cortex devices. The CMSIS
library provided by Silicon Labs contains header files, defines (for peripherals, registers and bitfields), and startup files for all devices. In
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.7 | 8
Page 9
QSG139: Bluetooth® SDK v2.x Quick Start Guide
About the Bluetooth Stack
addition, CMSIS includes functions that are common to all Cortex devices, like interrupt handling, intrinsic functions, etc. Although it is
possible to write to registers using hard-coded address and data values, it is recommended to use the defines to ensure portability and
readability of the code.
To simplify programming Wireless Geckos, Silicon Labs developed and maintains a complete C function library called emlib that provides
efficient, clear, and robust access to and control of all peripherals and core functions in the device. This library resides within the em_xxx.c
(for example, em_dac.c) and em_xxx.h files in the SDK.
The emlib documentation is available on the Silicon Labs’ website
.
2.3.3 The BGAPI Serial Protocol and BGLIB Host API
When configured in NCP (network co-processor) mode, the Bluetooth stack also implements the BGAPI serial protocol. This allows the
Bluetooth stack to be controlled over a serial interface such as UART from a separate host like an EFM32 microcontroller. The BGAPI
serial protocol provides exactly the same Bluetooth APIs over UART as the BGAPI API when used in a standalone mode.
The BGAPI serial protocol is a lightweight, binary protocol that carries the BGAPI commands from the host to the Bluetooth stack and
responses and events from the Bluetooth stack back to the host.
The Bluetooth SDK delivers a ready-made BGAPI serial protocol parser implementation, called BGLIB. It implements the serial protocol
parser and C language function and events for all the APIs provided by the Bluetooth stack. The host code developed on top of BGLIB
can be written to be identical to the code for the Wireless Gecko, which allows easy porting of the application code from the Wireless
Gecko to a separate host or vice versa.
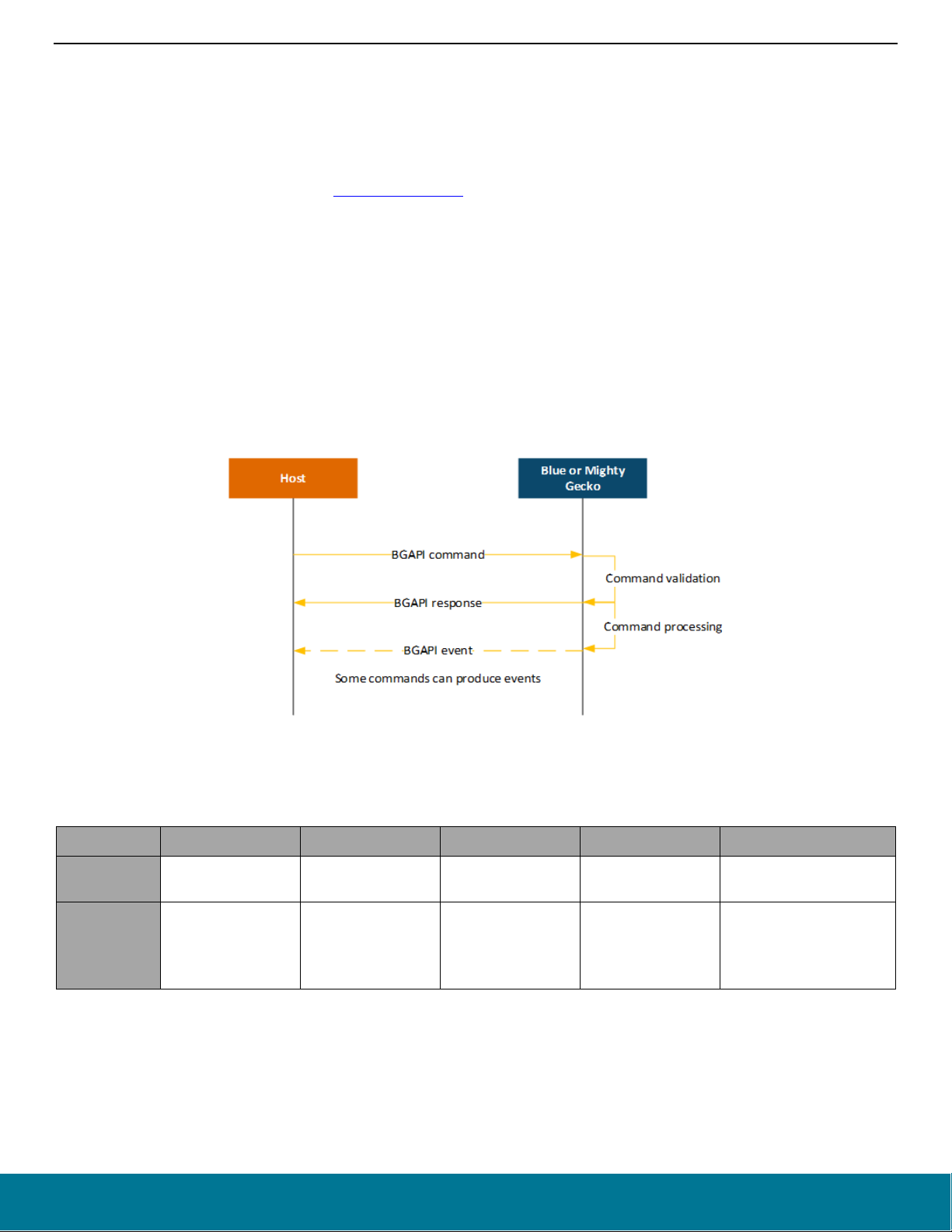
Figure 2-1. BGAPI Serial Protocol Message Exchange
The BGAPI serial protocol packet structure is described below.
Table 2-1. BGAPI Packet Structure
Byte Byte 0 Byte 1 Byte 2 Byte 3 Byte 4-255
Explanation Message type
0x20: command
Values
0x20: response
0xA0: event
Minimum payload
length
Message class Message ID Payload
0x00 - 0xFF 0x00 - 0xFF 0x00 - 0xFF
Specific to command,
response, or event
2.3.4 The Bluetooth Profile Toolkit GATT Builder
The Bluetooth Profile Toolkit is a simple XML-based API and description language used to describe the GATT-based service and characteristic easily without the need to write them in code. The XML files can be easily written by hand based on the information contained
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.7 | 9
Page 10

QSG139: Bluetooth® SDK v2.x Quick Start Guide
About the Bluetooth Stack
in UG118: Blue Gecko Bluetooth® Profile Toolkit Developer Guide. Use the Profile Toolkit GATT Builder if you are developing outside of
Simplicity Studio.
Within Simplicity Studio, we provide the GATT Configurator, a tool that allows building the GATT in a visual way, without hand editing the
XML file. See section 7.1, The GATT Configurator for summary information, and UG365: GATT Configurator User’s Guide for details.
The GATT database developed with the Profile Toolkit is converted to a .c file and a .h file and included in the application project as a
pre-build step when the firmware is compiled. Then the GATT can be accessed with the Bluetooth stack GATT APIs or by a remote
Bluetooth device.
Figure 2-2. Example of a Generic Access Service
2.4 About the Bluetooth SDK
The Bluetooth SDK is a full software development kit that enables you to develop applications on top of the Bluetooth stack using C
programming language. The SDK also supports making standalone applications, where the Bluetooth stack and the application both run
in the Wireless Gecko, or the network co-processor (NCP) architecture, where the application runs on an external host and the Bluetooth
stack runs in the Wireless Gecko. SDK contents and folder structure are described in the following sections.
2.4.1 Libraries
The following libraries are delivered with the Bluetooth SDK and must be included in C application projects.
Library Explanation Mandatory
libbluetooth.a Bluetooth stack library Yes
librail_efr32xg1_gcc_release.a RAIL library for GCC Yes for GCC projects on EFR32xG1 platform
librail_efr32xg12_gcc_release.a RAIL library for GCC Yes for GCC projects on EFR32xG12 platform
librail_efr32xg13_gcc_release.a RAIL library for GCC Yes for GCC projects on EFR32xG13 platform
librail_efr32xg14_gcc_release.a RAIL library for GCC Yes for GCC projects on EFR32xG14 platform
librail_efr32xg21_gcc_release.a RAIL library for GCC Yes for GCC projects on EFR32xG21 platform
librail_efr32xg22_gcc_release.a RAIL library for GCC Yes for GCC projects on EFR32xG22 platform
librail_efr32xg1_iar_release.a RAIL library for IAR Yes for IAR projects on EFR32xG1 platform
librail_efr32xg12_iar_release.a RAIL library for IAR Yes for IAR projects on EFR32xG12 platform
librail_efr32xg13_iar_release.a RAIL library for IAR Yes for IAR projects on EFR32xG13 platform
librail_efr32xg14_iar_release.a RAIL library for IAR Yes for IAR projects on EFR32xG14 platform
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.7 | 10
Page 11
QSG139: Bluetooth® SDK v2.x Quick Start Guide
bootloader
Gecko Bootloader source code and project files.
common
Silicon Labs status codes
About the Bluetooth Stack
Library Explanation Mandatory
librail_efr32xg21_iar_release.a RAIL library for IAR Yes for IAR projects on EFR32xG21 platform
librail_efr32xg22_iar_release.a RAIL library for IAR Yes for IAR projects on EFR32xG22 platform
libmbedtls.a mbedtls library Yes
libpsstore.a PSStore library Yes, on series 1
binapploader.o Apploader for OTA updates No
libcoex.a Wi-Fi and Bluetooth coexistence No
libnvm3_CM33_gcc.a Yes, on series 2
2.4.2 Include Files
The following files are delivered with the Bluetooth SDK and must be included in C application projects.
Library Explanation When needed
Must be included in standalone C applications
where both Bluetooth stack and application run in
a Wireless Gecko.
Required when the Bluetooth stack is used
together with Micrium RTOS.
native_gecko.h
rtos_gecko.h
Bluetooth stack API for standalone applications
without Micrium RTOS
Bluetooth stack API for standalone applications
with Micrium RTOS
Must be included in NCP applications where the
ncp_gecko.h Bluetooth stack API for NCP applications
host controls the device via BGAPI protocol over
UART
gecko_configuration.h Bluetooth stack configuration Included automatically.
bg_errorcodes.h Error codes produced by the Bluetooth stack Included automatically.
bg_gattdb_def.h Bluetooth GATT database structure definition Included automatically.
bg_types.h Simple data type definitions and structures Included automatically.
gecko_bglib.h
An adaptation layer between host application and
BGAPI serial protocol
host_gecko.h Bluetooth API for host (NCP) applications
Must be included in C applications developed for
external hosts.
Must be included in C applications developed for
external hosts.
2.4.3 Platform Components
The following components are delivered with the Bluetooth SDK. The platform components are under the platform folder.
Folder Explanation
CMSIS
Device
Silicon Laboratories CMSIS-CORE device headers.
Documentation
EFR32BG and EFR32MG device files.
Documentation
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.7 | 11
Page 12

QSG139: Bluetooth® SDK v2.x Quick Start Guide
Hwconf_data
Gather chip-specific hardware configuration
radio
Silicon Labs RAIL (Radio Abstraction Interface Layer) library
service
About the Bluetooth Stack
Folder Explanation
A set of function-specific high-performance drivers for EFR32 on-chip peripherals. Drivers are typically
emdrv
emlib
Halconfig Peripheral configuration
DMA based and are using all available low-energy features. For most drivers, the API offers both
synchronous and asynchronous functions.
Documentation
A low-level peripheral support library that provides a unified API for all EFM32, EZR32 and EFR32 MCUs
and SoCs from Silicon Laboratories.
Documentation
middleware
Display driver for WSTK development kits
Documentation
Sleeptimer driver and configuration file. Used by the BLE stack.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.7 | 12
Page 13

QSG139: Bluetooth® SDK v2.x Quick Start Guide
Getting Started with Simplicity Studio and the Bluetooth SDK
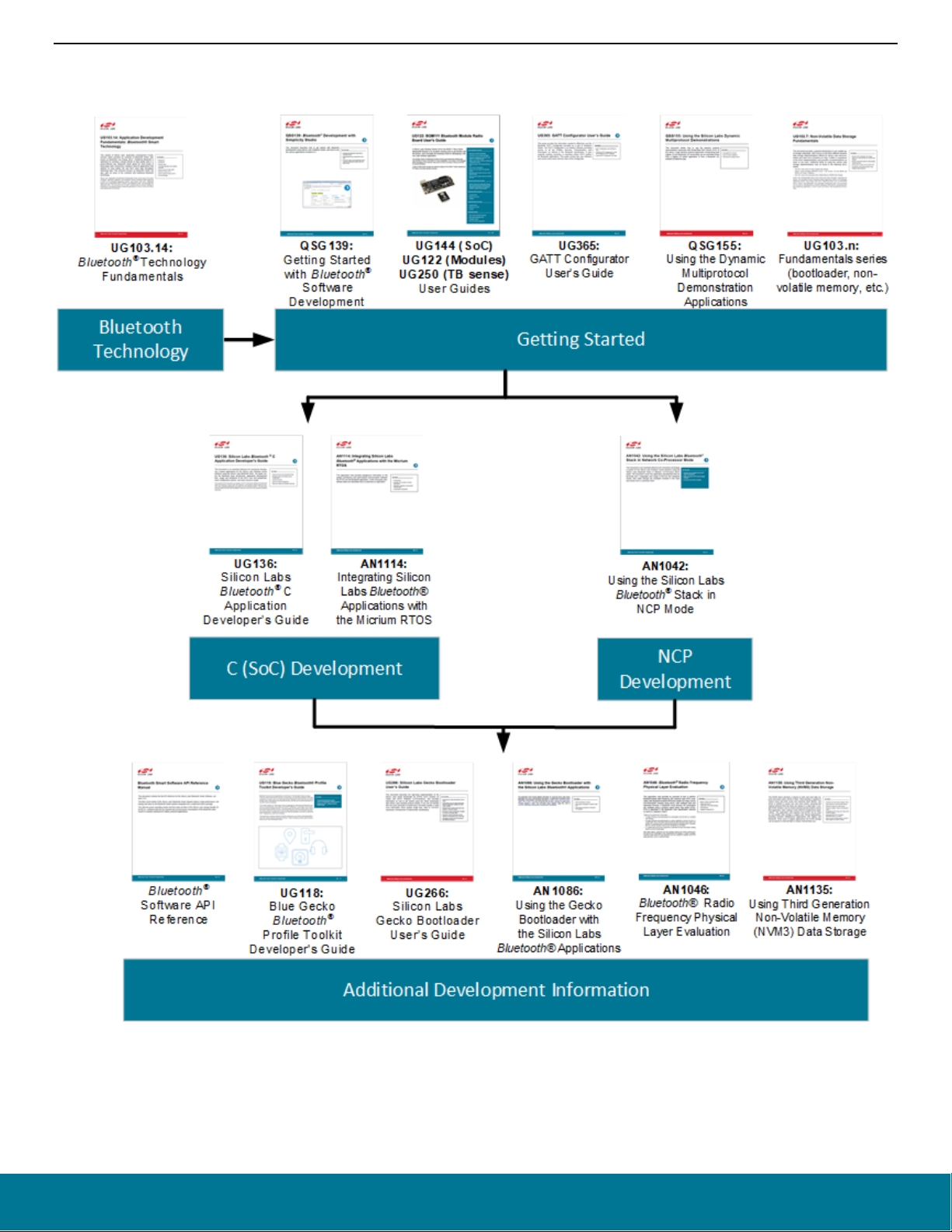
3 Getting Started with Simplicity Studio and the Bluetooth SDK
Simplicity Studio is a free Eclipse-based Integrated Development Environment (IDE) and a collection of value-add tools provided by
Silicon Labs. Developers can use Simplicity Studio to develop, debug and analyze their Bluetooth and other Silicon Labs SDK (Software
Development Kit) applications. Its main goal is to reduce development time so that you can focus on your application instead of researching the Bluetooth specification and hardware reference manuals. See section 3.3 Functionality in the Launcher Perspective for a review
of Simplicity Studio’s features.
If you have already installed Simplicity Studio with a different protocol stack, see section 3.4 Updating Software/New Elements for in-
structions on updating the installation with the Bluetooth stack.
3.1 Connect your Hardware
Connect your WSTK using a USB cable to the PC on which you will install Simplicity Studio. By having it connected when Simplicity
Studio installs, Simplicity Studio will automatically obtain the relevant additional resources it needs.
Note: For best performance in Simplicity Studio, be sure that the power switch on your WSTK is in the Advanced Energy Monitoring or
“AEM” position as shown in the following figure.
Figure 3-1. EFR32BG12 on a WSTK
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.7 | 13
Page 14

QSG139: Bluetooth® SDK v2.x Quick Start Guide
Getting Started with Simplicity Studio and the Bluetooth SDK
3.2 Installing Simplicity Studio and the Gecko Suite with the Bluetooth Stack
1. Run the Simplicity Studio installation application.
2. When Simplicity Studio first launches, it presents a License Agreement dialog. Accept the terms of the agreement and click Next.
3. Choose a destination location, click Next > and then click Install.
4. When the application launches, you are invited to log in. Log in using your support account username and password. Although you
can skip log in here, you must be logged in to access protected content.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.7 | 14
Page 15

QSG139: Bluetooth® SDK v2.x Quick Start Guide
Getting Started with Simplicity Studio and the Bluetooth SDK
5. After login, Simplicity Studio adds software information. Once initial software installation is complete, Simplicity Studio checks for
connected hardware. If you have the WSTK connected by USB cable, Simplicity Studio will detect the USB cable and prompt you to
download a Device Inspector. Click Yes.
6. After some additional items are installed, you are offered the option of installing by device (step 13) or installing by product group
(step 12). Install by Product Group will give you a more targeted set of installation options.
Throughout these procedures at any time you can click Home ( ) to return to this dialog.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.7 | 15
Page 16

QSG139: Bluetooth® SDK v2.x Quick Start Guide
Getting Started with Simplicity Studio and the Bluetooth SDK
7. If you click Install by Product Group you are offered a list of product groups. Click the SDKs you want to install, or click Wireless &
RF to check all. If you plan to work on the RAIL/Bluetooth Dynamic Multiprotocol examples, select both Bluetooth and Proprietary
groups. Click Next and go to step 10.
8. If you click Install by Devices, an Install Device Support dialog appears. After a short delay, it shows your connected device. If the
connected device does not show, click Refresh. Select either a connected device, or search for a product and select it. When a
product is selected click >> to add it to the Selected Device pane. Simplicity Studio calculated available space required for installation.
You can also click a selected device and click << to remove it. Click Next to continue.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.7 | 16
Page 17
QSG139: Bluetooth® SDK v2.x Quick Start Guide
Getting Started with Simplicity Studio and the Bluetooth SDK
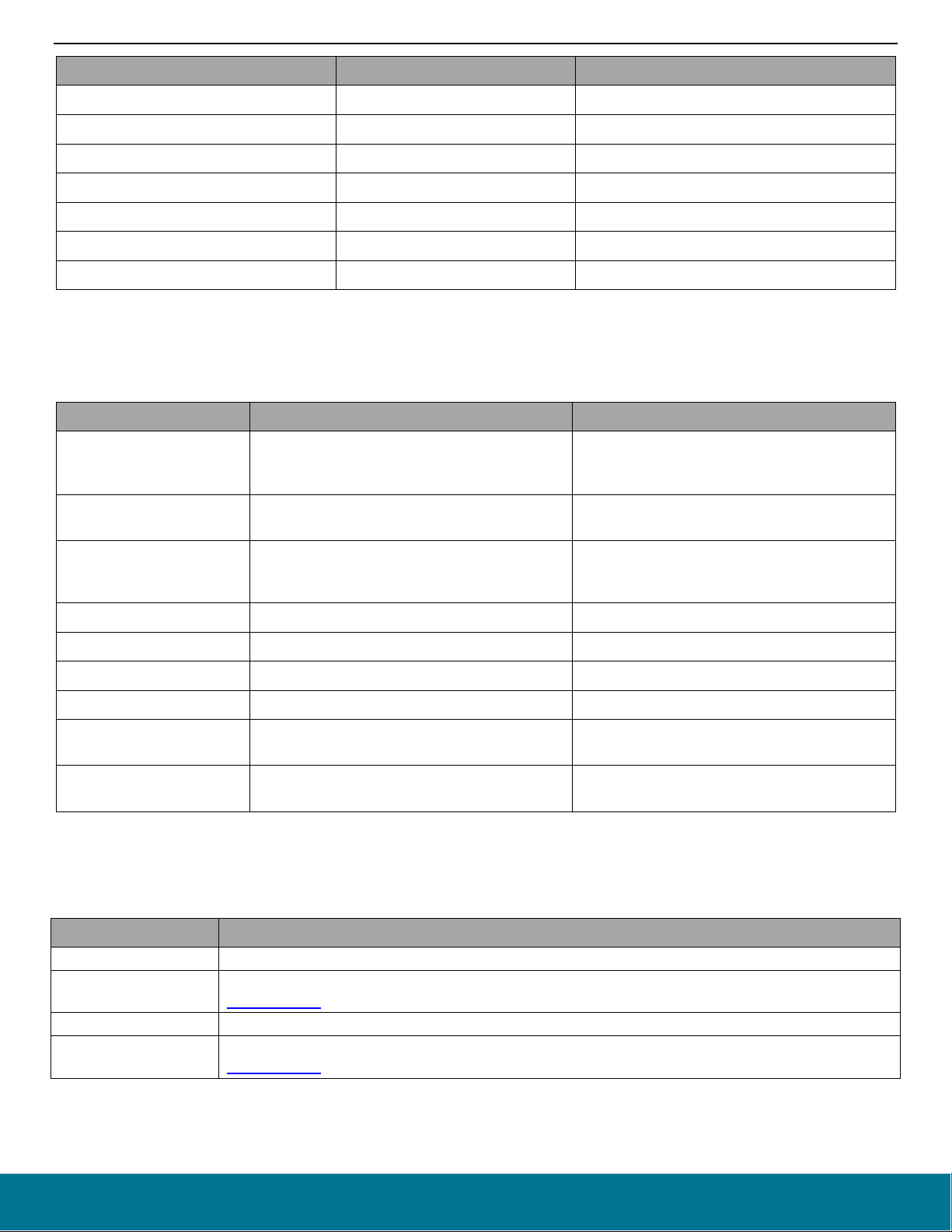
9. The next dialog varies depending on whether or not you have signed in. If you have not signed in, you have no access to restricted
content and must sign in first. Once you have signed in and see Bluetooth SDK on the list of available content, click Next.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.7 | 17
Page 18

QSG139: Bluetooth® SDK v2.x Quick Start Guide
Getting Started with Simplicity Studio and the Bluetooth SDK
10. The Installation Options dialog shows the tools and software packages that can be installed (your versions may be different). The
following shows Installation options after selecting the Bluetooth product group (a), and after selecting an EFR32MG device (b). In
both views you can uncheck anything you don’t want to install. If you have installed by Product Group, the selection is filtered more
specifically to your needs than if you have installed by device, and installing all checked options is recommended. If you have installed
by device, and are unchecking items:
• If you plan to use GCC, leave GNU ARM Toolchain checked.
• If you plan to work on the RAIL/Bluetooth Dynamic Multiprotocol examples, leave Micrium OS Kernel and the Flex SDK checked.
Click Next.
a) b)
Note: Previous stack versions are shown under Other Options.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.7 | 18
Page 19

QSG139: Bluetooth® SDK v2.x Quick Start Guide
Getting Started with Simplicity Studio and the Bluetooth SDK
11. Studio displays a Review Licenses dialog. Accept the licenses shown and click Finish. Note that this dialog will present again if in
the future you install a component with a separate license.
Installation takes several minutes. During installation, Simplicity Studio offers you viewing and reading options to learn more about
the environment.
12. After installation is complete, restart Simplicity Studio.
13. When Simplicity Studio restarts, you are invited to take a tour. To clear this option now or at any time during or after the tour, click
Exit tour.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.7 | 19
Page 20

QSG139: Bluetooth® SDK v2.x Quick Start Guide
Getting Started with Simplicity Studio and the Bluetooth SDK
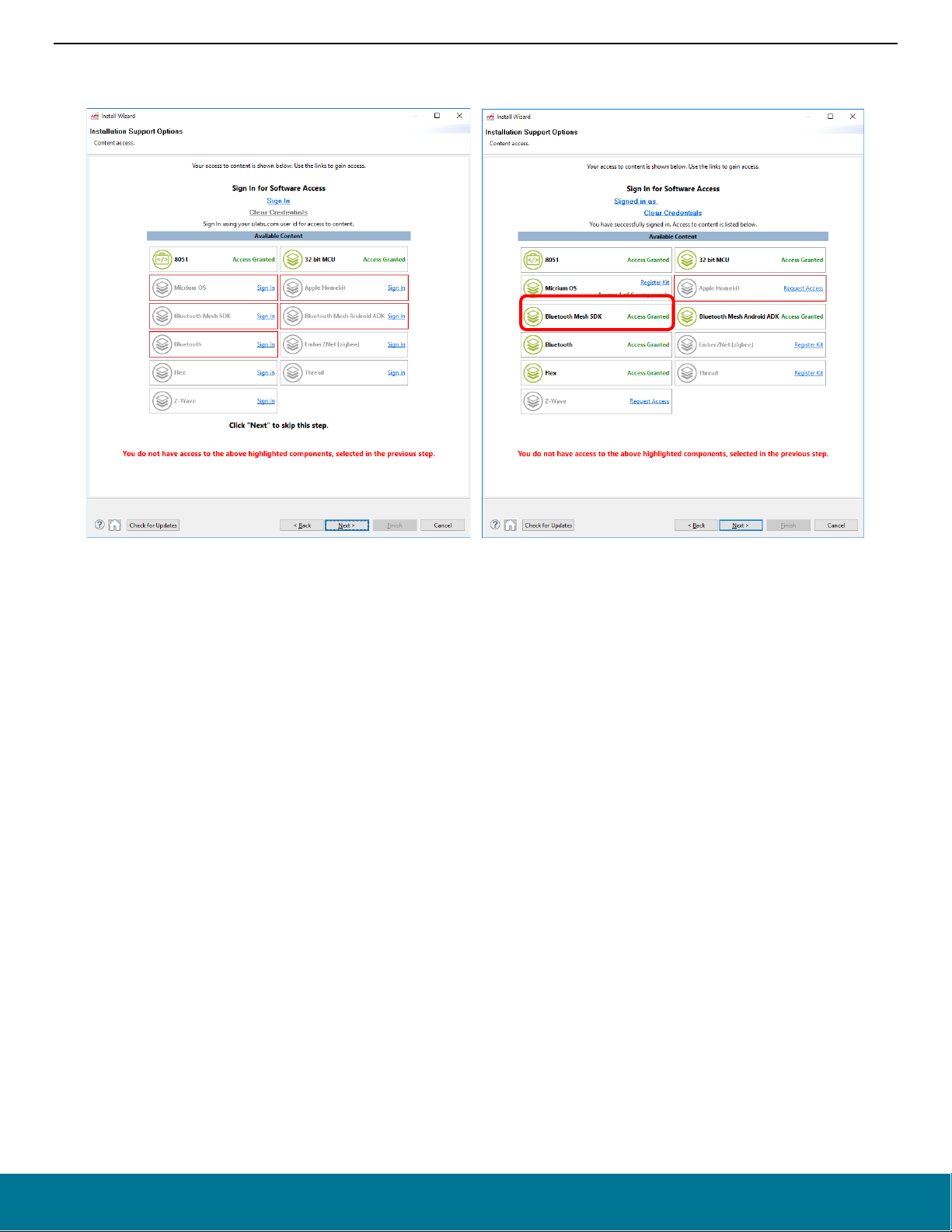
14. The Launcher perspective opens, but it is not yet fully populated. Click the connection entry in the devices tab or a part in the solutions
tab to populate it. Note that USB-connected WSTK devices are identified as J-Link devices as shown.
15. The Launcher perspective then is populated with the software components and functionality associated with your hardware and
installed SDKs. Before proceeding, if you have a device connected update your device firmware as described in section 3.6 Updating
Adapter Firmware.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.7 | 20
Page 21

QSG139: Bluetooth® SDK v2.x Quick Start Guide
1 2 3 4 5
6
Getting Started with Simplicity Studio and the Bluetooth SDK
3.3 Functionality in the Launcher Perspective
Perspectives are made up of a number of tiles or panes, called views, as well as the content in those views. You can perform a number
of functions in the Launcher Perspective, as shown in the following figure. Additional information on some of these is provided later in the
section. Note: Your installed version may be different than the version shown in the graphics in this section.
On the toolbar (1) you can:
• Sign in or out
• Open application settings ( )
• Update your software ( , see section 3.4 Updating Software/New Elements for more information)
• Open the Tools menu ( ) to access tools such as Simplicity Commander or Energy Profiler.
• Search for information including entries in the Community forums.
• Change perspectives (2). As you open the Simplicity IDE or other tools, buttons for their perspectives are displayed in the upper right.
Use those buttons to easily navigate back to the Launcher perspective or to other perspectives. You can change the layouts of various
perspectives by expanding or relocating views, or adding or removing views. To return to the default layout, right-click the perspective
button in the upper right and select Reset.
In the main view you can:
• Change your preferred SDK (3, see section 3.5 Changing the Preferred SDK for more information).
• Change debug mode (4) (displayed only if a device is connected).
• Update adapter firmware (5, displayed only if a device is connected, see section 3.6 Updating Adapter Firmware for more information).
• Create solutions of multiple parts (6). If you are developing for complex networks with a number of different parts involved, you can
add them all to the solution and then select the one you are working on from the list. You do not need to have the hardware connected
to your computer.
• Access demos, examples, documentation, and other resources from the Getting Started and other tabs (see section 3.7 Accessing
Documentation and Other Resources for more information).
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.7 | 21
Page 22

QSG139: Bluetooth® SDK v2.x Quick Start Guide
Getting Started with Simplicity Studio and the Bluetooth SDK
3.4 Updating Software/New Elements
The Update Software icon will be red if updates to installed components are available. If Simplicity Studio detects an available update,
and you are in another perspective, you will be notified that an update is available.
To download a new or updated component, click the Update Software icon. Click Package Manager. Note: If you are installing based on
a new device, or want to install a new product group, you can do so through this dialog as well. In subsequent dialogs, click Home ( )
to return to this dialog. Note that Studio does not show you options, such as the GNU ARM Toolchain, that have already been installed.
Simplicity Studio shows you available updates or SDKs in the Package Manager dialog. You can update all or select individual updates
for installation. Click the tabs in the Package Manager dialog to see other components available for installation. Use the filters to reduce
long lists.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.7 | 22
Page 23

QSG139: Bluetooth® SDK v2.x Quick Start Guide
Getting Started with Simplicity Studio and the Bluetooth SDK
3.5 Changing the Preferred SDK
Use this function if on startup Simplicity Studio defaults to Stackless applications. Otherwise, most Silicon Labs protocol stack users will
have one SDK available to them, the Gecko SDK Suite.
Within that suite you can have multiple protocols installed. The protocol used in any given instance is controlled either by the example
you select, or the stack you select if you go through the ‘New Project’ interface. In general, you should add or remove protocol stacks
through the Simplicity Studio update manager. If you need to install a stack or the Gecko SDK Suite outside of the normal installation
process, you will receive separate instructions.
3.6 Updating Adapter Firmware
Initially the Launcher perspective may display “No local adapter firmware available.” Click Download to download any updates.
If an update is available, click Install to install the firmware.
Once you have installed a current update, the version is displayed. Simplicity Studio will notify you if another firmware update is available.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.7 | 23
Page 24

QSG139: Bluetooth® SDK v2.x Quick Start Guide
Getting Started with Simplicity Studio and the Bluetooth SDK
3.7 Accessing Documentation and Other Resources
The Getting Started tab provides access to demos, example applications, and stack related documentation. To show/hide specific cat-
egories, click Customize ( ). Select or deselect categories, then click OK.
The Documentation tab lists documentation about the stack and about the hardware on the right, and documents you selected as
favorites on the left. Click the star icon on any document to show it in the My Favorite Documents list.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.7 | 24
Page 25
QSG139: Bluetooth® SDK v2.x Quick Start Guide
Getting Started with Simplicity Studio and the Bluetooth SDK
The Compatible Tools tab is an alternative way to access the tools available through the Tools dropdown.
The Resources tab provides access to support, marketing collateral, and the Silicon Labs community.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.7 | 25
Page 26

QSG139: Bluetooth® SDK v2.x Quick Start Guide
About Demos and Examples
4 About Demos and Examples
Because starting application development from scratch is difficult, the Bluetooth SDK comes with a number of built-in demos and examples covering the most frequent use cases, as shown in the following figure. Demos are pre-built application images that you can run
immediately. Software examples can be modified before building the application image. Demos with the same name as software examples
are built from their respective example.
Note: The demos and examples you see are determined by the part selected. If you are using a custom solution with more than one
part, click on the part you are working with to see only the items applicable to that part.
• To download and run a demo on your device, click the demo. In the Mode drop-down in the next dialog, select Run. Click Start. See
section 5 Getting Started with Bluetooth Demo Software for more information about testing the demos.
• To import software example code into your workspace as a new project using default project configurations, click the name of the
example to open the Simplicity Studio IDE. To build the example project click Debug ( ) in the upper left corner of the Simplicity
IDE perspective. The Debug perspective opens. Click Play ( ) to start running you project on the device. To create a project with
different configurations, click New Project (above the Demos column in the Launcher perspective), and proceed as described in
section 6 Starting Application Development.
If an example project closely matches your needs, you need only extend the code with your application code, and rewrite only what must
be customized for your needs. Otherwise you should start with the SOC-Empty application as described in section 6 Starting Application
Development. Note that the ‘SOC-Empty’ application is not blank, but rather provides a minimal project that only starts advertising.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.7 | 26
Page 27

QSG139: Bluetooth® SDK v2.x Quick Start Guide
About Demos and Examples
4.1 Demo/Example Descriptions
The following examples are provided. Examples with (*) in their names have a matching pre-built demo.
• Silicon Labs Gecko Bootloader examples (see UG266: Silicon Labs Gecko Bootloader User Guide and
Bootloader with Silicon Labs Bluetooth Applications)
• Bluetooth Examples
• Bluetooth (NCP)
• NCP – Host: NCP (Network co-processor) Host example that connects to an NCP target via USART. It demonstrates the
usage of BGLib with or without USART flow-control. This example does not have a Bluetooth function over the radio as it uses
the EFR32 only as a host device.
• NCP target – Empty(*): Network co-processor target application with a minimal GATT database. Use this as a starting point
to create an NCP firmware. An NCP device can be controlled from another (host) device or directly from your PC with BGTool.
This example together with BG Tool provides an easy way to get started and also debug your application by issuing commands
to the stack step-by-step.
• Bluetooth (SOC – Basic)
• SOC – Empty(*): A minimal project structure, used as a starting point for custom applications. The project has the basic
functionality enabling peripheral connectivity and contains a minimal GATT database that can be expanded to fit your application requirements.
• SOC – iBeacon(*): An iBeacon device implementation that sends non-connectible advertisements in iBeacon format. The
iBeacon Service gives Bluetooth accessories a simple and convenient way to send iBeacons to iOS devices. This example
demonstrates the power consumption at 0 dBm TX power.
• SOC – Thermometer – Client: Implements a Client that discovers and connects up to 4 BLE devices advertising themselves
as Thermometer Servers. It displays the discovery process and the temperature values received via UART.
• SOC – Thermometer(*): Implements the Thermometer (GATT Server) Role of the Health Thermometer Profile, which enables
a Collector device to connect and interact with a Thermometer.
AN1086: Using the Gecko
Note: Some radio boards will exhibit random pixels in in the display when this example is running because they have a shared
pin for sensor and display enable signals.
• Bluetooth (SOC – Advanced)
• SOC – DTM: Used to run Bluetooth DTM (direct test mode) tests for radio testing. See
AN1046: Bluetooth® Radio Frequency
Physical Layer Evaluation for more information.
• SOC – Thermometer - RTOS: The SOC - Thermometer example based on Micrium RTOS.
• Thunderboard
• SOC - Thunderboard React, - Thunderboard Sense, and - Thunderboard Sense 2(*): Examples used to show the appli-
cable Thunderboard features.
• SOC - Voice over Bluetooth Low Energy: Demonstrates how voice capture can be sent over a Bluetooth Low Energy Link.
• Dynamic Multiprotocol Examples (see
AN1134: Dynamic Multiprotocol Development with Bluetooth and Proprietary Protocols on
RAIL for more information)
• SOC - Empty - RAIL – DMP(*): A minimal project structure, used as a starting point for custom Dynamic Multiprotocol applications.
The project has the basic functionality enabling peripheral connectivity, without GATT services. It runs on top of Micrium OS RTOS
and multiprotocol RAIL.
• SOC - Light - RAIL – DMP(*): Implements the Light (GATT Server) Role, which enables a Switch device to connect to and interact
with it. The device acts as a connection Peripheral. This is a Dynamic Multiprotocol reference application, running on top of Micrium
OS RTOS and multiprotocol RAIL. To learn how to test this demo see
QSG155: Using the Silicon Labs Dynamic Multiprotocol
Demonstration Applications.
• SOC - Range Test - RAIL - DMP(*): Range Test with Bluetooth connectivity. It runs on top of Micrium OS RTOS and multiprotocol
RAIL.
• NCP Host Examples (located in C:\SiliconLabs\SimplicityStudio\v4\developer\sdks\gecko_sdk_suite\<version>\app\bluetooth\exam-
ples_ncp_host)
• Empty: Minimal host-side project structure, used as a starting point for NCP host applications.
• ota-dfu: Demonstrates how to perform an OTA DFU on a Silicon Labs Bluetooth Device. It requires a WSTK with a radio board
flashed with an NCP firmware to be used as the GATT client that performs the OTA.
• uart-dfu: Demonstrates how to perform a UART DFU on a Silicon Labs Bluetooth Device running NCP firmware.
• Voice over Bluetooth Low Energy: Client-side application that couples with the “SOC – Voice over Bluetooth Low Energy” for
the Thunderboard Sense and Thunderboard Sense 2 kits. It requires a WSTK with a radio board flashed with an NCP firmware.
For information on how to test this example see the Knowledge Base Article “
How to use Voice over Bluetooth Low Energy
example for Thunderboard Sense”.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.7 | 27
Page 28

QSG139: Bluetooth® SDK v2.x Quick Start Guide
Getting Started with Bluetooth Demo Software
5 Getting Started with Bluetooth Demo Software
The Blue Gecko Bluetooth Wireless Starter Kit is meant to help you evaluate Silicon Labs’ Bluetooth modules and get you started with
your own software development. The kits come in different versions with different module radio boards. See
ucts/development-tools/wireless/bluetooth/bluegecko-bluetooth-low-energy-module-wireless-starter-kit for details on the current configu-
rations.
To get started with Bluetooth demo software, you should have downloaded Simplicity Studio and the Bluetooth SDK as described in
section 3 Getting Started with Simplicity Studio and the Bluetooth SDK. The Bluetooth SDK comes with some prebuilt demos that can be
flashed to your EFR32 device, and tested using a Smartphone. This section describes how to test three prebuilt demos on both Android
and iOS devices:
• SoC – Empty demo
• iBeacon demo
• Health Thermometer demo
5.1 Prepare the WSTK
1. Connect a Bluetooth Module Radio Board to the WSTK Main Board as shown in the following figure.
2. Connect the WSTK to a PC using the Main Board USB connector.
3. Turn the Power switch to "AEM" position.
Note: At this stage you might be prompted to install the drivers for the WSTK Main Board but you can skip this for now.
https://www.silabs.com/prod-
4. Check that the blue USB Connection Indicator LED turns on or starts blinking.
5. Check that the Main Board LCD display turns on and displays a Silicon Labs logo.
Before starting to test the demo application note the following parts on the WSTK Main Board
• Temperature & Humidity Sensor
• PB0 button
• LED0
5.2 Flash the Demo
• With your device connected as described above, open Simplicity Studio.
• Select your device in the Debug Adapters pane.
• Under the Demos column, open the Bluetooth (SoC) Basic group and select the desired demo.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.7 | 28
Page 29

QSG139: Bluetooth® SDK v2.x Quick Start Guide
Getting Started with Bluetooth Demo Software
• In the Mode drop-down in the next dialog, select Run. Click Start.
5.3 Test the Bluetooth Demos Using an Android Smartphone
5.3.1 Testing the SoC - Empty Demo
After flashing SoC - Empty demo to your device, the device automatically starts advertising itself as "Empty Example", and makes it
possible to connect to it by other Bluetooth devices.
Install the EFR Connect app from Google Play Store, and open it. To find your advertising device, tap the Develop tab, and tap Bluetooth
Browser. This shows all advertising devices nearby. Connect to your device by tapping Connect next to "Empty Example”. Its GATT
database is automatically discovered and displayed. Tap any service to list its characteristics and tap any characteristic to read its value.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.7 | 29
Page 30

QSG139: Bluetooth® SDK v2.x Quick Start Guide
Getting Started with Bluetooth Demo Software
5.3.2 Testing the iBeacon Demo
Bluetooth beacons are unconnectable advertisements that help you locate a device, determine your own position, or get minimal information about an asset the beaconing device is attached to.
After flashing the iBeacon demo to your device, you can find the beacon signal with the Bluetooth Browser in the EFR Connect app.
Start EFR Connect, tap the Develop tab, and tap Bluetooth Browser. To filter beacons, tap , and select the beacon types you
want to be displayed. The app provides you with basic information about the beacon, like RSSI - which can help determine the distance
of the beacon. Tap the beacon to get more information about the data it provides.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.7 | 30
Page 31

QSG139: Bluetooth® SDK v2.x Quick Start Guide
Getting Started with Bluetooth Demo Software
5.3.3 Testing the Health Thermometer Demo
While the SoC - Empty demo implements a minimal GATT database with basic static information like device name, the Health Thermometer demo extends this database with live temperature measurements.
After flashing the Health Thermometer demo to your device, start EFR Connect, tap the Demo tab, and tap Health Thermometer. Find
your device advertising as Thermometer Example in the device list, and tap it to connect. The smartphone app automatically finds the
Temperature measurement characteristic of the device, reads its value periodically, and displays the value on the screen of the phone.
Try touching the temperature sensor located on the WSTK (see section 5.1 Prepare the WSTK). You should be able to see the temperature changing.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.7 | 31
Page 32

QSG139: Bluetooth® SDK v2.x Quick Start Guide
Getting Started with Bluetooth Demo Software
5.4 Testing the Bluetooth Demos Using an iOS Smartphone
5.4.1 Testing the SoC - Empty Demo
After flashing SoC - Empty demo to your device, the device automatically starts advertising itself as "Empty Example", and makes it
possible to connect to it by other Bluetooth devices.
Install the EFR Connect app from the Apple App Store, and open it. To find your advertising device, tap the Develop tab, and tap
Bluetooth Browser. This shows all advertising devices nearby. Connect to your device by tapping Connect next to "Empty Example”.
Its GATT database is automatically discovered and displayed. Tap any service to list its characteristics and tap any characteristic to read
its value.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.7 | 32
Page 33

QSG139: Bluetooth® SDK v2.x Quick Start Guide
Getting Started with Bluetooth Demo Software
5.4.2 Testing the iBeacon Demo
Bluetooth beacons are unconnectable advertisements that help you locate a device, determine your own position, or get minimal information about an asset the beaconing device is attached to.
After flashing the iBeacon demo to your device, you can find the beacon signal with the Bluetooth Browser in the EFR Connect app.
Start EFR Connect, tap the Develop tab, and tap Bluetooth Browser. To filter beacons, tap , and select the beacon types you
want to be displayed. The app provides you with basic information about the beacon, like RSSI - which can help determine the distance
of the beacon. Tap the beacon to get more information about the data it provides.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.7 | 33
Page 34

QSG139: Bluetooth® SDK v2.x Quick Start Guide
Getting Started with Bluetooth Demo Software
5.4.3 Testing the Health Thermometer Demo
While the SoC - Empty demo implements a minimal GATT database with basic static information like device name, the Health Thermometer demo extends this database with live temperature measurements.
After flashing the Health Thermometer demo to your device, start EFR Connect, tap the Demo tab, and tap Health Thermometer. Find
your device advertising as Thermometer Example in the device list, and tap it to connect. The smartphone app automatically finds the
Temperature measurement characteristic of the device, reads its value periodically, and displays the value on the screen of the phone.
Try touching the temperature sensor located on the WSTK (see section 5.1 Prepare the WSTK). You should be able to see the temperature changing.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.7 | 34
Page 35

QSG139: Bluetooth® SDK v2.x Quick Start Guide
Starting Application Development
6 Starting Application Development
Developing a Bluetooth application consists of two main steps: defining the GATT database structure, and defining the event handlers
for events such as
The most common starting point for application development is the SOC – Empty example. This project contains a simple GATT database
(including the Generic Access service, Device Information service, and OTA service) and a while loop that handles some events raised
by the stack. You can extend both the GATT database and the event handlers of this example according to your needs.
Note: Beginning with Bluetooth SDK version 2.7.0.0, all devices must be loaded with the Gecko Bootloader as well as the application.
While you are getting started, the easiest way to do this is to load any of the precompiled demo images, which come with the
bootloader configured as part of the image. When you flash your application it overwrites the demo application, but the bootloader
remains. Subsequently you may wish to build your own bootloader, as described in UG266: Silicon Labs Gecko Bootloader User
Guide. The first bootloader loaded on a clean device should always be the combined bootloader.
To start developing your application, follow these steps (illustrated in the following figure). Note: Your SDK version may be later than the
version shown in the procedure illustrations. :
1. Click New Project in the Launcher perspective.
2. Select Bluetooth SDK and click Next.
3. Select SoC – Empty and click Next.
4. Name your project and click Next.
5. Verify that your selected part is shown, and select your preferred toolchain. Note: You should only select one toolchain. If you are
using GCC, you must uncheck IAR. Otherwise the system will revert to IAR when you generate your files. Click Finish.
connection_opened, connection_closed, and so on.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.7 | 35
Page 36

QSG139: Bluetooth® SDK v2.x Quick Start Guide
Starting Application Development
A visual GATT Configurator automatically appears after creating the project, to help you create your own GATT database with a few
clicks. Note that a Simplicity IDE perspective button is now included in the upper right of the screen.
You can create your own database at this point, or return to it later by clicking the .isc file in the Project Explorer pane on the left. For
more information, see section 7.1 The GATT Configurator.
A reference for each characteristic is generated and defined in gatt_db.h. You can use this references in your code to read / write the
values of the characteristics in the GATT database with gecko_cmd_gatt_server_read_attribute_value() /
gecko_cmd_gatt_server_write_attribute_value() commands.
You will find the event handlers in the main loop in app.c. You can extend this list with further event handlers. The full list of events – and
stack commands – can be found in the Bluetooth Software API Reference Manual.
To build and debug your project click Debug ( ) in the upper left corner of the Simplicity IDE perspective. It will build and download
your project, and open up the Debug perspective. Click Play ( ) to start running you project on the device.
6.1 Enabling Field Updates
Deploying new firmware for devices in the field can be done by UART DFU (Device Firmware Update) or, for SoC applications, OTA
DFU. For more information on each of these methods refer to
Applications.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.7 | 36
AN1086: Using the Gecko Bootloader with the Silicon Labs Bluetooth
Page 37

QSG139: Bluetooth® SDK v2.x Quick Start Guide
Development Tools
7 Development Tools
7.1 The GATT Configurator
Every Bluetooth connection has a GATT client and a GATT server. The server holds a GATT database: a collection of Characteristics
that can be read and written by the client. The Characteristics are grouped into Services, and the group of Services determines a Bluetooth
Profile.
If you are implementing a GATT server (typically on the peripheral device), you have to define a GATT database structure. This structure
cannot be modified during runtime, so it has to be designed in advance. Clients (typically the central device) can also have a GATT
database, even if no device will query it, so you can keep the default database structure in your code.
The GATT Configurator is a simple-to-use tool to help you build your own GATT database. A list of predefined Profiles/Services/Characteristics/Descriptors is shown in a pane in the upper left and your current GATT database structure is shown in a pane in the upper right.
An options menu is provided to the right of the Database pane.
Click an item in the Database pane to see and modify its settings in a pane in the lower right. To add a Profile/Service/Characteristic/Descriptor to your database, simply drag and drop it from the list to your database.
To get more information about a Profile/Service/Characteristic/Descriptor, click it either in the list or in your database. The description is
displayed in the lower-left pane. You can find a detailed description of any Profile/Service/Characteristic/Descriptor on
tooth.com/specifications/gatt.
Characteristics are generally complex structures of fields. The GATT Configurator currently does not list the fields within a characteristic.
If you want to know what fields a characteristic has, visit https://www.bluetooth.com/specifications/gatt/characteristics
More information about the GATT Configurator can be found in UG365: GATT Configurator User’s Guide.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.7 | 37
https://www.blue-
.
Page 38

QSG139: Bluetooth® SDK v2.x Quick Start Guide
Development Tools
7.2 Multi-Node Energy Profiler
Multi-Node Energy profiler is an add-on tool, with which you can easily measure the energy consumption of your device in runtime. You
can easily find peak and average consumption, and check for sleep mode current.
Note: The SDK sample apps for EFR32BG22 enable EM2 debug (see init_mcu.c), which adds current consumption overhead compared
to the datasheet values.
To profile the current project, drop down the Profile as menu ( ) in the Simplicity IDE perspective and select Profile as / Simplicity
Energy Profiler target. This automatically builds your project, uploads it to the device, and starts Energy Profiler. A new Energy Profiler
perspective appears, shown in the following figure.
See UG343: Multi-Node Energy Profiler User’s Guide for details on how to use this tool. You can switch easily between Simplicity IDE
and Energy Profiler perspectives using the Perspective buttons in the upper right corner of your current perspective.
You can see peaks in the energy consumption diagram. Pause profiling by clicking Play , click one of the peaks, and zoom in with
time axis (y-axis) zoom until you see three distinguishable peaks. These represent the three advertisement packets sent on the three
advertisement channels. You can also see the three corresponding Tx events in the Rx/Tx bar below, provided that you enabled Rx/Tx
view in the upper right corner. Note that the maximum consumption may now be greater than it appeared on the diagram before you
zoomed in. This is because in zoomed-out mode, the displayed values are averaged. If you need exact values, always zoom in.
To measure average consumption, simply click and drag your mouse over a time interval. A new window appears in the upper right corner
showing consumption information for the given interval. Bluetooth communication typically has a periodicity: the advertisement or the
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.7 | 38
Page 39

QSG139: Bluetooth® SDK v2.x Quick Start Guide
Development Tools
connection interval. It is recommended to measure average over an advertisement or connection interval to obtain a proper average
consumption. Overall average is measured as well, but this is influenced by transient events.
Multi-node Energy Profiler is also able to simultaneously measure the consumption of multiple devices. To start measuring a new device
click the Quick Access menu (upper left corner) and select Start Energy Capture. To stop measuring, click the Quick Access menu, and
select End/Save session.
To learn more about how to use this tool, see UG343: Multi-Node Energy Profiler User’s Guide.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.7 | 39
Page 40

QSG139: Bluetooth® SDK v2.x Quick Start Guide
Development Tools
7.3 Network Analyzer
Silicon Labs Network Analyzer is a free-of-charge packet capture and debugging tool that can be used to debug Bluetooth connectivity
between Wireless Geckos and other Bluetooth devices. It significantly accelerates the network and application development process with
graphical views of network traffic, activity, and duration.
The Packet Trace application captures the packets directly from the Packet Trace Interface (PTI) available on the Wireless Gecko SoCs
and modules. It therefore provides a more accurate capture of the packets compared to air-based capture.
Figure 7-1. Bluetooth Traffic Capture with Packet Trace
7.4 Simplicity Commander
Simplicity Commander is a simple flashing tool, which can be used to flash firmware images, erase flash, lock and unlock debug access,
and write-protect flash pages via the J-Link interface. Both GUI and CLI (Command Line Interface) are available. See UG162: Simplicity
Commander Reference Guide for more information.
Figure 7-2. Simplicity Commander
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.7 | 40
Page 41

QSG139: Bluetooth® SDK v2.x Quick Start Guide
Development Tools
7.5 BGTool Application
The BGTool application can be used to test and evaluate the Bluetooth SoCs and modules, and it can be used to control the Bluetooth
hardware using the BGAPI Serial Protocol (NCP) over a Serial/UART interface.
Figure 7-3. BGTool Application
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.7 | 41
Page 42

QSG139: Bluetooth® SDK v2.x Quick Start Guide
Development Tools
7.6 IAR Embedded Workbench
IAR’s Embedded Workbench can also be used as an IDE for developing and debugging Bluetooth applications. You must use the version
of IAR that is compatible with the SDK version. See the SDK's release notes for compatible version information.
Figure 7-4. IAR Embedded Workbench
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.7 | 42
Page 43

Simplicity Studio
One-click access to MCU and wireless
tools, documentation, software, source
code libraries & more. Available for
Windows, Mac and Linux!
IoT Portfolio
www.silabs.com/IoT
Disclaimer
Silicon Labs intends to provide customers with the la test, accurate, and in- depth document ation of all peripherals and modules available for system and software
implementers using or intending to use the Silicon Labs products. Charac terization data, available modules and peripherals, memory sizes and memor y addresses refer to
of use of the information supplied in this document. This document does not imply or expressly grant any license to design or fabricate any integrated circui ts. The
products are not designed or authorized to be used within any FDA C lass III devices, applications for which FDA premarket approval is required, or Life Support Systems
products shall under no circumstances be used in weapons of mass destruction including (but not limited to) nuclear, biological or chemical weapons, or missiles c apable
of delivering such weapons. Silicon Labs disclaims all express and implie d warranties and shall not be responsible or liable for any injur ies or damages related to use of a
Silicon Labs product in such unauthor ized applica tions.
Trademark Information
Silicon Laboratories Inc.®, Silicon Laboratories®, Silicon Labs®, Si
EFM32®, EF R, Ember®, Energy Micro, Energy Micro logo and combinations thereof, “the world ’s most energ y friendly microcontrollers”, Ember®, EZLink®, EZRadio®,
EZRadioPRO®, Gecko®, Gecko OS , Gecko OS Studio, ISOmodem®, Precision32®, ProSLIC®, Simplicit y Studio®, SiPHY®, Telegesis , the Telegesis Logo®, USBXpress®, Zentri,
the Zentri logo and Zentri DMS, Z-Wave®, and ot hers are trademarks
regis tered trademarks of ARM Holding s. Keil is a regis tered trademark of ARM Limited. W i-Fi is a registered trademark of the Wi -Fi Alliance. All other product s or brand
names mentioned herein are trademarks of their resp ective holder s.
Silicon Laboratories Inc.
400 West Cesar Chavez
Austin, T X 78701
USA
http: //www.silabs.com
www.silabs.com/simplicit y
SW/HW
Labs® and the Silicon Labs logo®, Bluegiga®, Bluegiga Logo®, ClockBuilder®, CMEMS®, DSPLL®, EFM®,
or registered trademark s of Silicon Labs. A RM, CORTEX, Cor tex-M3 and THUMB are trademarks or
Quality
www.silabs.com/quality
Support & Community
www.silabs.com/community
 Loading...
Loading...