Page 1

silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 1 | Page
RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming
Reference Manual
Version 2.1
February 10, 2021
Page 2

RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 2 | Page
Table of Contents
1 Overview ................................................................................................................................................................. 4
2 Bootloader .............................................................................................................................................................. 7
3 Host Interfaces ..................................................................................................................................................... 19
3.1 UART Interface ............................................................................................................................................. 19
4 Classic Command Mode Selection ..................................................................................................................... 21
5 Classic Command Format ................................................................................................................................... 22
6 BT Classic Commands......................................................................................................................................... 33
6.1 Generic Commands ...................................................................................................................................... 33
6.1.1 Set Operating Mode ................................................................ ......................................................................... 33
6.1.2 Set Local Name ............................................................................................................................................... 38
6.1.3 Query Local Name ........................................................................................................................................... 38
6.1.4 Set Local COD ................................................................................................................................................. 39
6.1.5 Query Local COD ............................................................................................................................................. 39
6.1.6 Query RSSI...................................................................................................................................................... 39
6.1.7 Query Link Quality............................................................................................................................................ 40
6.1.8 Query Local BD Address .................................................................................................................................. 40
6.1.9 Query BT Stack Version ................................................................................................................................... 41
6.1.10 Initialize BT Module .......................................................................................................................................... 41
6.1.11 Deinitialize BT Module...................................................................................................................................... 41
6.1.12 BT Antenna Select ........................................................................................................................................... 42
6.1.13 Set Feature Bitmap ................................................................................................ .......................................... 42
6.1.14 Set Antenna Tx power level .............................................................................................................................. 42
6.2 PER Commands ........................................................................................................................................... 43
6.2.1 BR-EDR PER Transmit .................................................................................................................................... 43
6.2.2 BR-EDR PER Receive ..................................................................................................................................... 44
6.2.3 Per Stats ................................................................ .......................................................................................... 44
6.3 Core Commands ........................................................................................................................................... 48
6.3.1 Set Profile Mode .............................................................................................................................................. 48
6.3.2 Get Device Discovery Mode ............................................................................................................................. 49
6.3.3 Set Connectability Mode .................................................................................................................................. 49
6.3.4 Get Connectablility Mode ................................................................................................................................. 50
6.3.5 Remote Name Request .................................................................................................................................... 50
6.3.6 Remote Name Request Cancel ........................................................................................................................ 50
6.3.7 Inquiry .............................................................................................................................................................. 51
6.3.8 Inquiry Cancel .................................................................................................................................................. 51
6.3.9 Extended Inquiry Response Data ..................................................................................................................... 51
6.3.10 Bond or Create Connection .............................................................................................................................. 52
6.3.11 Bond Cancel or Create Connection Cancel ....................................................................................................... 52
6.3.12 UnBond Or Disconnect ..................................................................................................................................... 52
6.3.13 Set Pin Type ................................................................................................ .................................................... 53
6.3.14 Get Pin Type .................................................................................................................................................... 53
6.3.15 User Confirmation ............................................................................................................................................ 54
6.3.16 Pass Key Request Reply .................................................................................................................................. 54
6.3.17 Pincode Request Reply .................................................................................................................................... 54
6.3.18 Get Local Device Role...................................................................................................................................... 55
6.3.19 Set Local Device Role Or Switch The Role ....................................................................................................... 55
6.3.20 Get Service List................................................................................................................................................ 55
6.3.21 Search Service................................................................................................................................................. 56
6.3.22 Linkkey Reply .................................................................................................................................................. 56
6.3.23 Set SSP Mode ................................................................................................................................................. 57
6.3.24 Sniff Mode ....................................................................................................................................................... 57
6.3.25 Sniff Exit .......................................................................................................................................................... 58
6.3.26 Sniff Subrating ................................................................................................................................................. 58
6.3.27 Add Device ID .................................................................................................................................................. 58
6.4 SPP commands ............................................................................................................................................ 59
6.4.1 SPP Connect ................................................................................................................................................... 59
6.4.2 SPP Disconnect ............................................................................................................................................... 59
6.4.3 SPP Transfer ................................................................................................................................................... 59
6.5 Core Events .................................................................................................................................................. 60
6.5.1 User Linkkey Save ........................................................................................................................................... 60
6.5.2 Auth Complete ................................................................................................................................................. 60
6.5.3 Mode Change .................................................................................................................................................. 60
6.5.4 Disconnected ................................................................ ................................................................................... 61
7 BT Classic Error Codes ....................................................................................................................................... 62
8 BT Power Save Operation .................................................................................................................................... 69
9 BT AT CMD Configuration Changes/Enhancements ......................................................................................... 72
10 Revision History ................................................................................................................................................... 73
11 Appendix A: Sample Flows ................................................................................................................................. 75
Page 3
RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 3 | Page
About this Document
This document describes the Bluetooth (BT) Classic commands, including parameters used in commands, valid
values for each command, and expected responses from the modules. This document is also used to write software
for host (to control and operate the module).
Note:
This document should be used with WiSeConnect version 2.3.0.
Page 4
RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 4 | Page
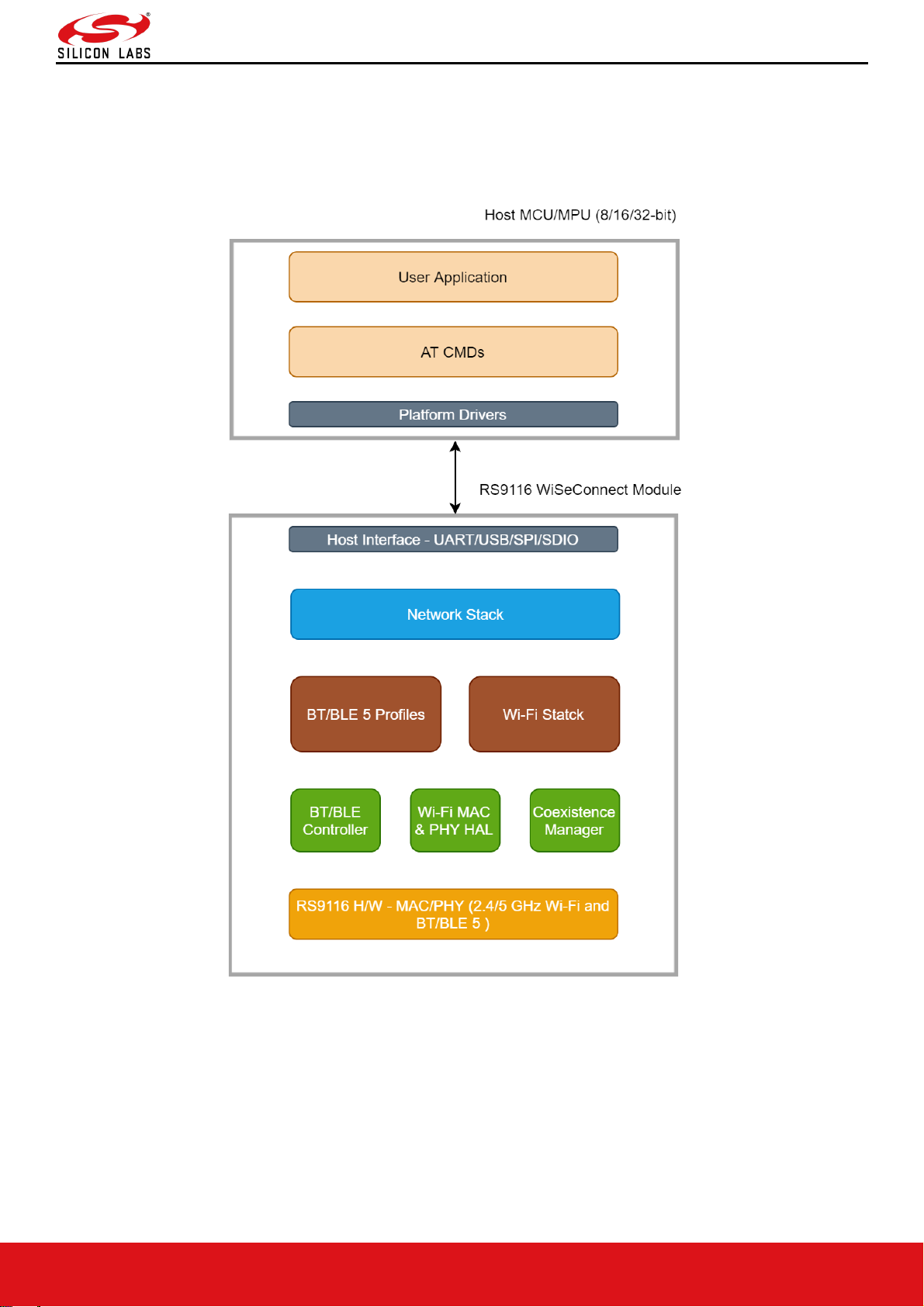
1 Overview
Architecture
The following figure depicts the software architecture of the RS9116-WiSeConnect:
Figure 1: Architecture Overview for RS9116 WiSeConnect
Page 5

RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 5 | Page
Bluetooth Classic Architecture
Figure 2: Bluetooth Software Architecture
Application
The application layer launches the Bluetooth stack and uses commands to access various profiles on remote
Bluetooth devices over the network.
Profiles
There are number of Bluetooth profiles defined in the Bluetooth specification. This design currently supports profiles
including Serial Port Profile (SPP), provided framework to develop new profiles very easily. We will continue to add
new profiles.
Bluetooth Core
The Bluetooth core contains the following higher layers of the stack.
• RFCOMM
• SDP
• L2CAP
• HCI Generic Driver
• HCI BUS Driver
RFCOMM is a transport protocol based on L2CAP. It emulates RS-232 serial ports. The RFCOMM protocol supports
up to 60 simultaneous connections between two BT devices. RFCOMM provides data stream interface for higher level
applications and profiles.
SDP (Service Discovery Protocol) provides a means for applications to discover which services are available and to
determine the characteristics of those available services. SDP uses an existing L2CAP connection. Further
connection to Bluetooth devices can be established using information obtained via SDP.
L2CAP (Logical Link Control and Adaptation Protocol) provides connection-oriented and connection-less data
services to upper layer protocols with data packet size up to 64 KB in length. L2CAP performs the segmentation and
reassemble of I/O packets from the base-band controller.
HCI Generic Driver – This driver implements HCI Interface standardized by Bluetooth SIG. It establishes the
communication between Stack and HCI firmware in the Bluetooth hardware. It communicates with the Bluetooth
controller hardware via the HCI Bus driver.
HCI Transport Layer Driver – The Bluetooth controllers are connected to the host using interface like UART, USB,
SDIO, SPI, USB-CDC etc. The HCI Transport Layer Driver provides hardware abstraction to the rest of the Bluetooth
stack software. This driver makes it possible to use Bluetooth stack with different hardware interfaces.
Bluetooth Profiles are additional protocols that build upon the basic Bluetooth standard to more clearly define what
kind of data a Bluetooth module is transmitting. While Bluetooth specifications define how the technology works,
profiles define how it's used.
Page 6

RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 6 | Page
The profile(s) a Bluetooth device supports determine(s) what application it's geared towards. A hands-free Bluetooth
headset, for example, would use headset profile (HSP), while a Nintendo Wii Controller would implement the human
interface device (HID) profile. For two Bluetooth devices to be compatible, they must support the same profiles.
OS Abstraction Layer
This layer abstracts RTOS services (semaphores, mutexes and critical sections) that are used by the whole stack and
the applications. The stack, which is designed in an RTOS-independent manner, can be used with any RTOS by
porting this layer. It is also possible to use the Bluetooth stack standalone without RTOS.
Page 7

RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 7 | Page
2 Bootloader
This section briefs about features that are supported by Network and Security Processor (NWP) bootloader. It is
applicable for RS9116 WiSeConnect.
Basic Features
• Load default firmware
• Load selected firmware
• Upgrade firmware from host
• Selecting default images
• Enable / Disable host interaction bypass
• Support for multiple host interfaces (SDIO / SPI / UART / USB / USB-CDC)
• Firmware integrity check
• Upgrading Keys
• JTAG selection
The RS9116W module supports two boot loading modes:
1. Host Interaction (Non-bypass) Mode:
In this mode host interacts with the bootloader and gives boot up options (commands) to configure different boot
up operations. The host tells the module what operations it has to perform based on the selections made by the
user.
2. Bypass Mode:
In this mode bootloader interactions are completely bypassed and uses stored bootup configurations (which are
selected in host interaction mode) & loads default firmware image in the module. This mode is recommended for
final production software to minimize the boot up time.
Host Interaction Mode
In This mode host interaction varies based on host interface. Host interaction in SPI / USB and UART / USB-CDC are
different. In UART & USB-CDC boot up options are menu based and in SPI / USB using command exchanges. The
details are explained below.
Host Interaction Mode in UART / USB-CDC
This section explains the host interaction mode in UART / USB CDC mode.
Startup Operation
After powering up, host is required to carry out ABRD (Auto baud rate detection) operation. After successful ABRD,
the module displays the menu of bootup options to host. The host needs to select the appropriate option.
Note:
On powerup, bootloader checks the integrity of the bootup options. If the integrity fails, it computes the integrity
from backup. If integrity passes, it copies the backup to the actual location. If the integrity of the backup options
also fails, the bootup options are reset/cleared. In either of the cases, bootloader bypass is disabled or
corresponding error messages are given to host. In case of integrity failure and when the backup integrity check
passes, "LAST CONFIGURATION NOT SAVED" message is displayed. When backup integrity also fails,
“BOOTUP OPTIONS CHECKSUM FAILED" is displayed before displaying the bootup options.
Hyper Terminal Configuration
RS9116W uses the following UART interface configuration for communication:
Baud Rate: The following baud rates are supported by the module: 9600 bps, 19200 bps, 38400 bps, 57600 bps,
115200 bps, 230400 bps, 460800 bps, 921600 bps.
Data bits: 8
Parity: None
Stop bits: 1
Flow control: None
Page 8
RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 8 | Page
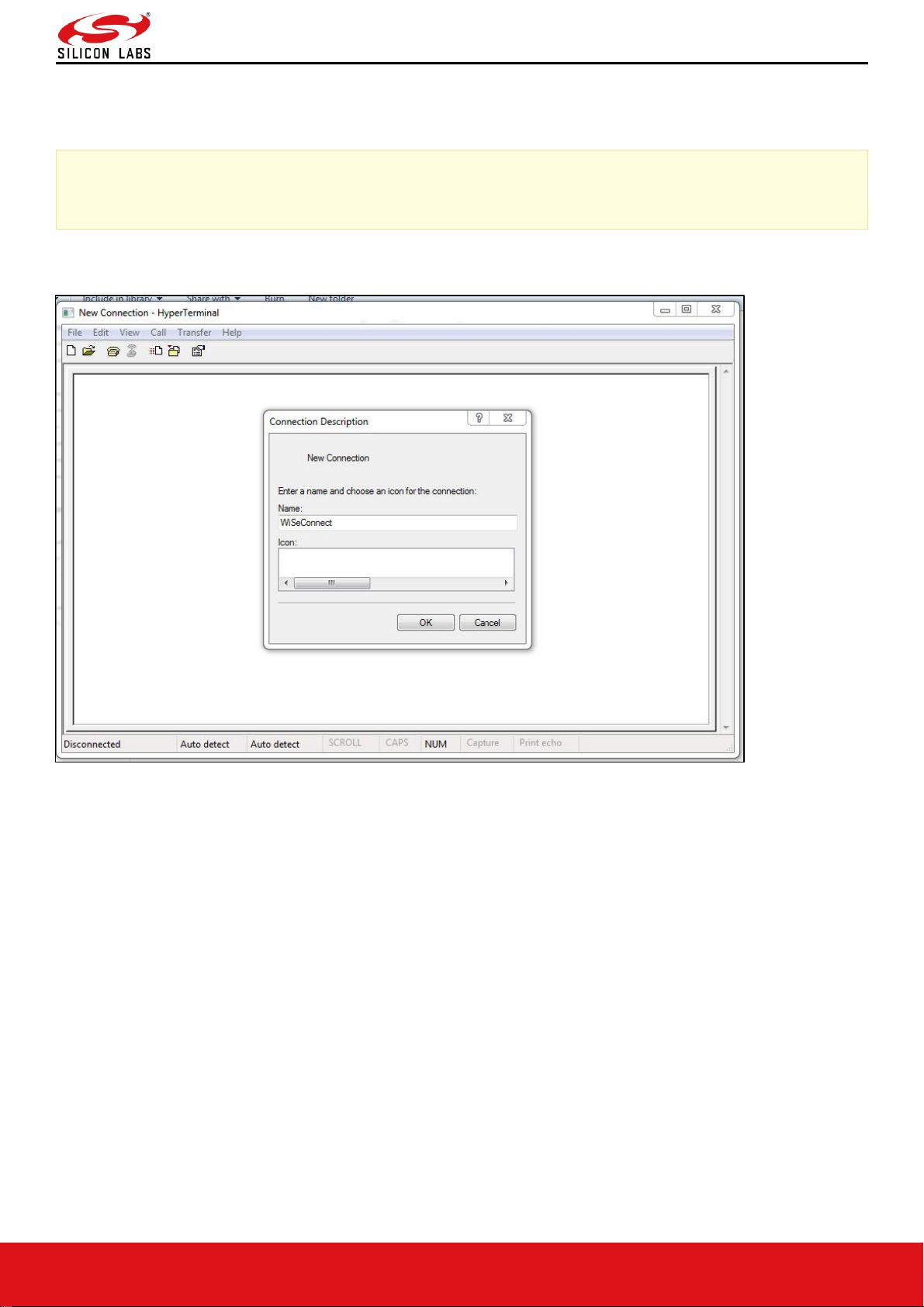
Follow sequence of steps as given below:
• Open Hyper terminal and enter any name in the "Name" field. After this, click "OK" button.
Here, "WiSeConnect" is entered as shown in the figure below.
Note:
Default baud rate of the module is 115200.
Figure 3: HyperTerminal Name field Configuration
• After clicking "OK", the following dialog box is displayed as shown in the figure below.
Page 9
RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 9 | Page
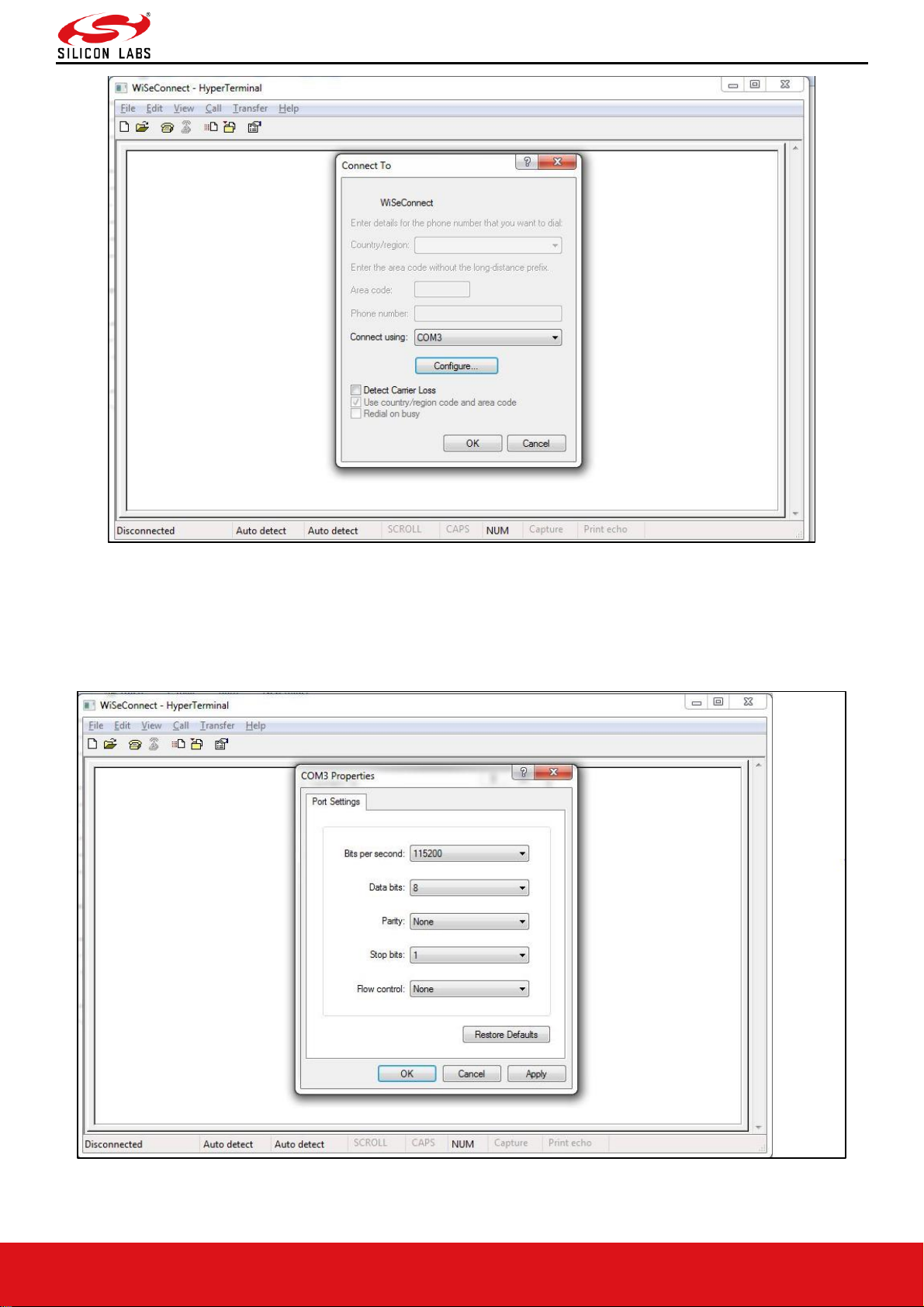
Figure 4: HyperTerminal COM Port Field Configuration
• In the "Connect using" field, select appropriate com port. In the figure above COM3 is selected.
Click "OK" button.
• After clicking the "OK" button the following dialog box is displayed as shown in the figure below
Figure 5: HyperTerminal Baud Rate Field Configuration
Page 10
RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 10 | Page
Set the following values for the fields shown in the Figure 6.
• Set baud rate to 115200 in "Bits per second" field.
• Set Data bits to 8 in "Data bits" field.
• Set Parity to none in "Parity" field.
• Set stop bits to 1 in "Stop bits" field.
• Set flow control to none in "Flow control" field.
• Click "OK" button after entering the data in all the fields.
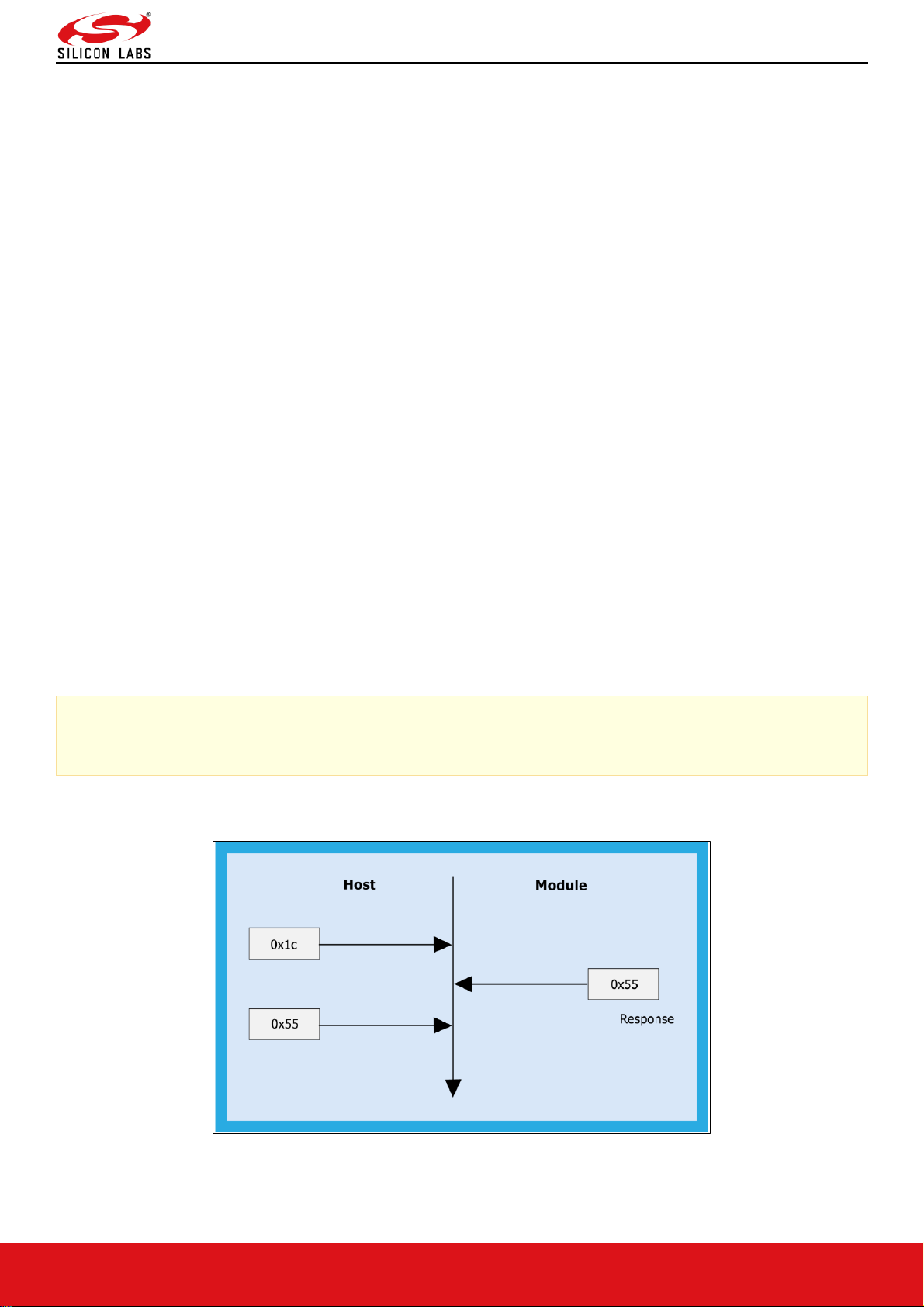
Auto Baud Rate Detection (ABRD)
The RS9116W automatically detects the baud rate of the Host's UART interface by exchanging some bytes. The Host
should configure the UART interface for the following parameters for ABRD detection.
RS9116W uses the following UART interface configuration for communication:
Baud Rate: The following baud rates are supported: 9600 bps, 19200 bps, 38400 bps, 57600 bps, 115200 bps,
230400 bps, 460800 bps, 921600 bps.
Data bits: 8
Stop bits: 1
Parity: None
Flow control: None
To perform ABRD on the RS9116W, the host must follow the procedure outlined below.
1. Configure the UART interface of the Host at desired baud rate.
2. Power on the RS9116W.
3. The Host, after releasing the module from reset, should wait for 20 ms for initial boot-up of the module to complete
and then transmit 0x1C at the baud rate to which its UART interface is configured. After transmitting '0x1C' to the
module, the Host should wait for the module to transmit 0x55 at the same baud rate.
4. If the '0x55' response is not received from the module, the host has to re-transmit 0x1C, after a delay of 200ms.
5. After finally receiving '0x55', the host should transmit '0x55' to the module. The module is now configured with the
intended baud rate.
Note:
Performing ABRD in host interaction mode is must for USB CDC mode.
Figure 6: ABRD Exchange Between Host And Module
Page 11
RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 11 | Page
Below are the boot-up options, Firmware upgrade and Firmware loading procedures for WiSeConnect Product.
Start Up Messages on Power-Up
After powering up the module and performing ABRD you will see a welcome message on host, followed by boot up
options:
Note:
Windows Hyper Terminal is used to demonstrate boot up /up-gradation procedure.
Figure 7: RS9116-WiSeConnect Module UART/USB-CDC Welcome Message
Loading the default wireless firmware in the module
To load the default firmware flashed onto the module, choose Option 1: "Load Default Wireless Firmware ".
Load Default Wireless Firmware
• After welcome message is displayed as shown in the above figure, select option 1 "Load Default Wireless
Firmware " for loading Image.
Page 12
RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 12 | Page
Figure 8: RS9116-WiSeConnect Module UART / USB-CDC Default Firmware Loaded
Note:
By default, the module will be configured in AT mode. If mode switch from AT plus command mode to binary
mode is required, then user must give 'H' in the boot-loader options.
The module lasts in the binary mode unless it changed to AT plus command mode and vice-versa.
To change from binary mode to AT mode, then user must give 'U' in the boot-loader options.
Loading selected Wireless Firmware in the Module
To load the selected firmware (from flash) onto the module, choose Option A: "Load Wireless Firmware (Image No: 0-
f)".
Load Wireless Firmware
• After welcome message is displayed as shown in the above figure, select option A "Load Wireless Firmware
(Image No: 0-f)" for loading Image.
• In response to the option A, Module ask to Enter Image No.
• Select the image number to be loaded from flash.
• After successfully loading the default firmware, "Loading Done" message is displayed.
• After firmware loading is completed, module is ready to accept commands
Note:
1. In order to use host bypass mode, the user has to select one of the images as default image by selecting
option 5 (Select Default Wireless Firmware).
2. In Host interaction mode, if no option is selected after bootup menu for 20 seconds then the bootloader will
load selected Wireless default image.
3. If the valid firmware is not present, then a message prompts "Valid firmware not present".
Page 13
RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 13 | Page
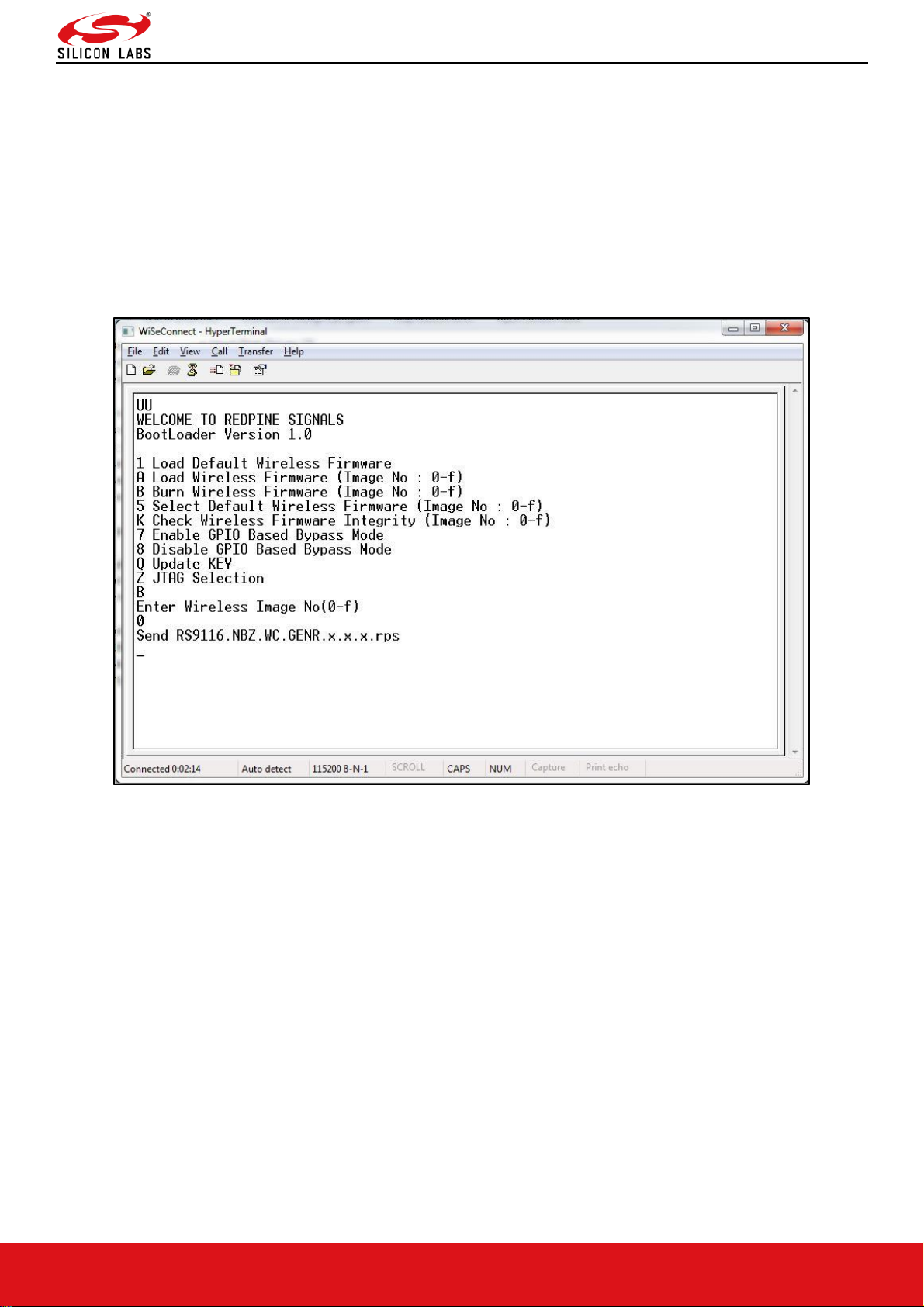
Firmware Upgradation
After powering up the module, a welcome message is displayed.
Upgrade NWP firmware Image
• After the welcome message is displayed, select option B "Burn Wireless Firmware (Image No: 0-f)" to upgrade
Wireless Image.
• The message "Enter Wireless Image No (0-f)" is displayed.
• Then select the Image no to be upgraded.
• The message "Send RS9116.NBZ.WC.GENR.x.x.x.rps" should appear as shown in the figure below.
Figure 9: RS9116-WiSeConnect Module Firmware Upgrade File Prompt Message
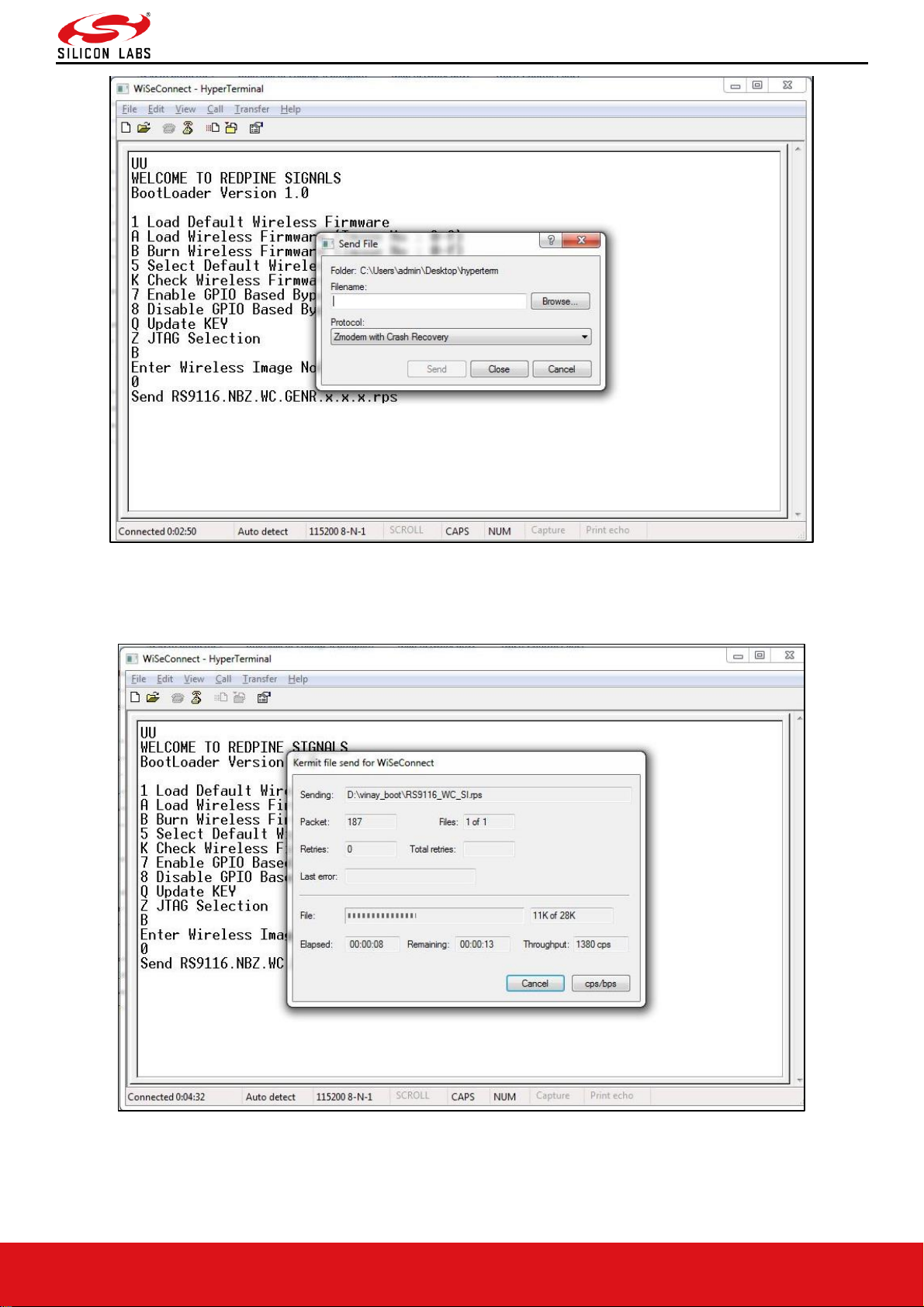
• In the "File" menu of HyperTerminal, select the "send file" option. A dialog box will appear as shown in the figure
below. Browse to the path where "RS9116.NBZ.WC.GENR.X.X.X.rps" is located and select Kermit as the protocol
option. After this, click the "Send" button to transfer the file.
• If the valid firmware is not present, then a message prompts "Valid firmware not present".
Page 14
RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 14 | Page
Figure 10: RS9116-WiSeConnect Module Firmware Upgrade File Selection Message
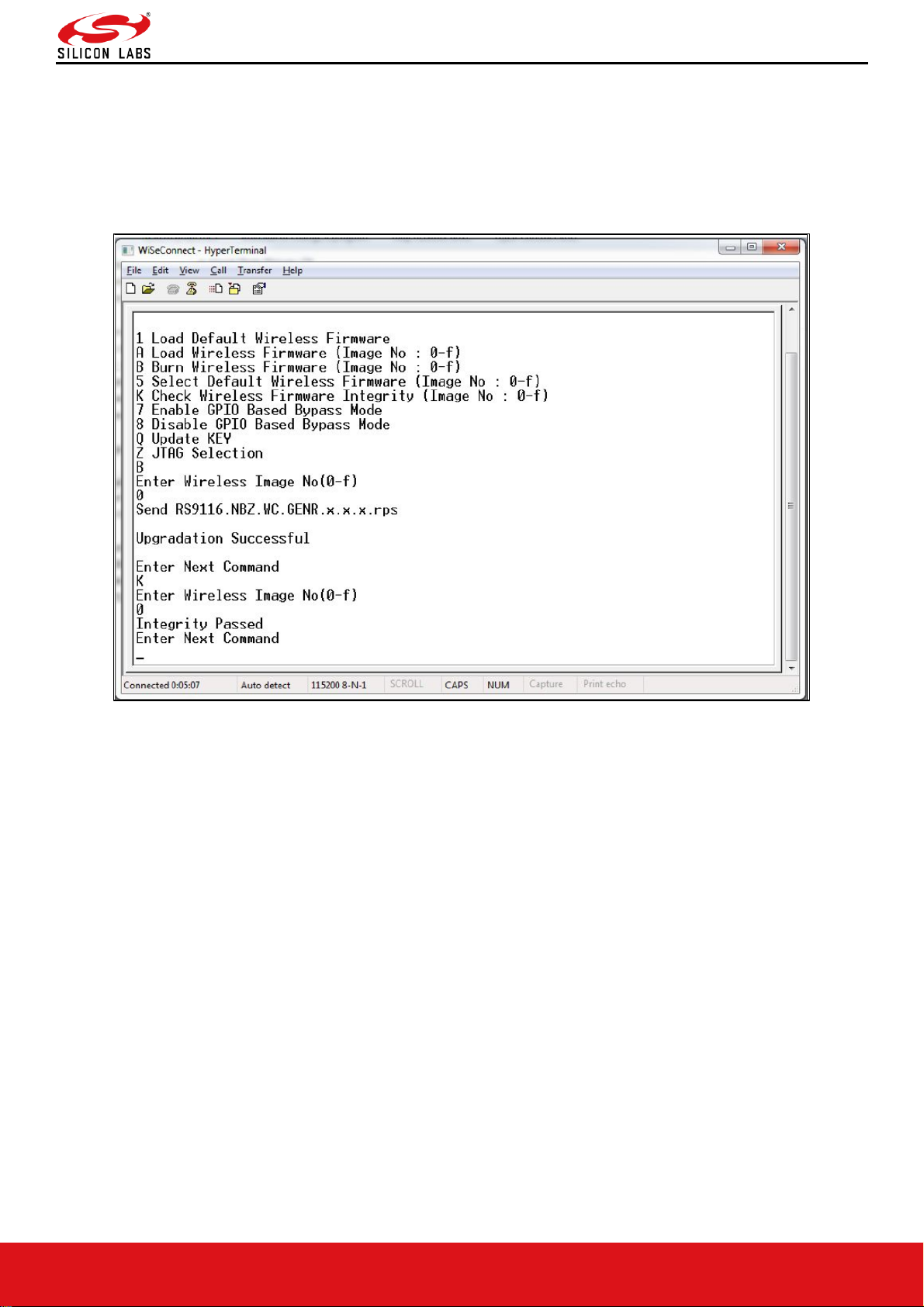
The dialog box message is displayed while file transfer is in progress as shown in the figure below.
Figure 11: RS9116-WiSeConnect Module Firmware Upgrade File Transfer Message
Page 15
RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 15 | Page
• After successfully completing the file transfer, module computes the integrity of the image and displays
"Upgradation Failed, re-burn the image" in the case of failure and "Upgradation Failed and default image invalid,
Bypass disabled" in the case of both failure and corruption of the default image.
• In the case of success, module checks if bootloader bypass is enabled and computes the integrity of the default
image selected. If the integrity fails, it sends "Upgradation successful, Default image invalid, gpio bypass
disabled." If integrity passes or gpio bypass not enabled, it sends "Upgradation Successful" message on terminal
as shown in the figure below.
Figure 12: RS9116-WiSeConnect Module Firmware Upgrade Completion Message
• At this point, the upgraded firmware Image is successfully flashed to the module.
• User can again cross check the integrity of the Image by selecting the Option K " Check Wireless Firmware
Integrity (Image No : 0-f)" for Wireless Image.
• Follow the steps mentioned in Loading the Default Wireless Firmware in the Module to load the firmware from
flash, select Option 1 from the above the Figure.
• The module is ready to accept commands from the Host.
Bypass Mode in UART / USB-CDC
Making Default Wireless Firmware Selection
With this option, the host can select the default firmware image to be loaded.
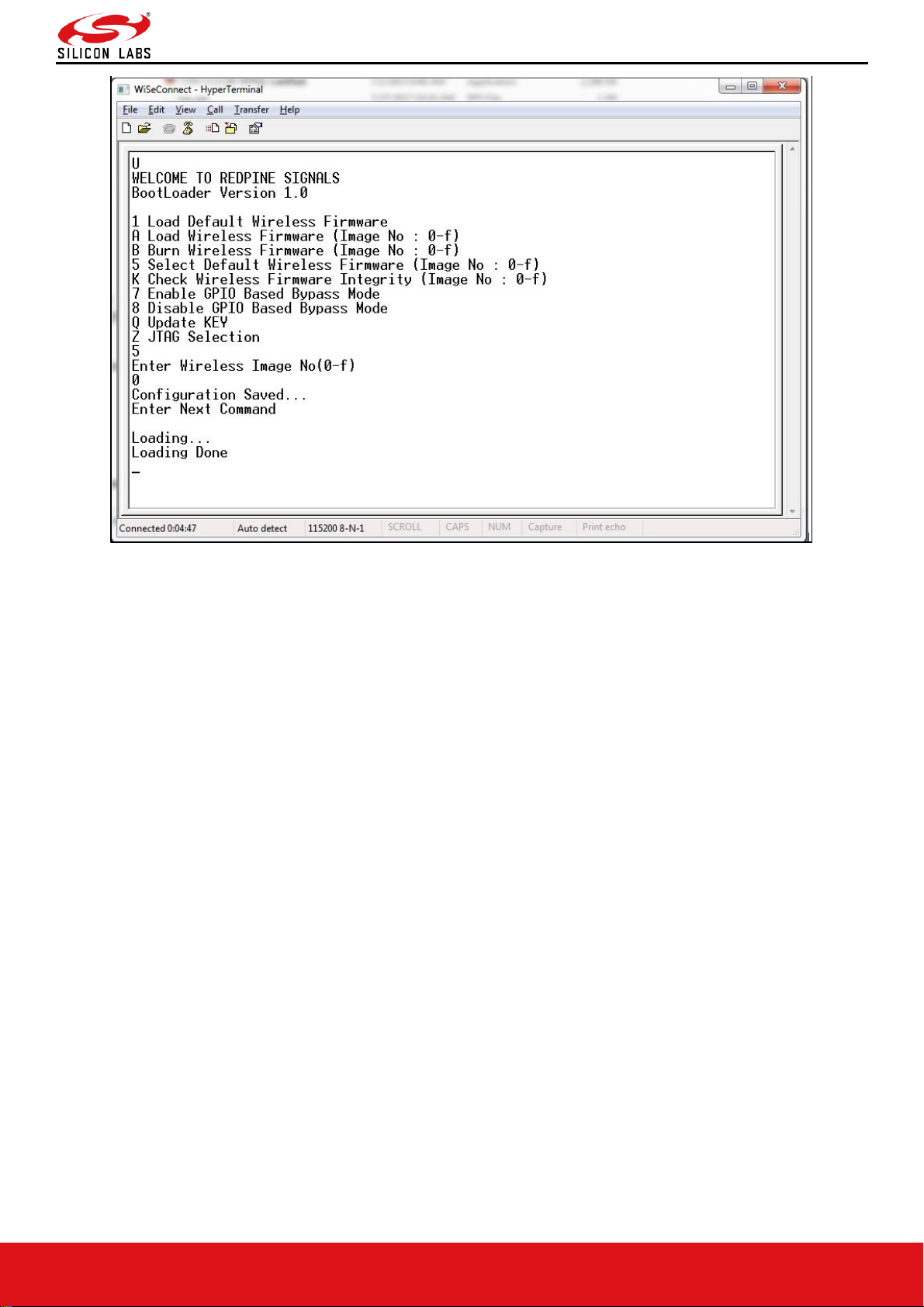
Selecting a valid Image as the Default Image
• After the welcome message is displayed, user can select option 5 "Select Default Wireless Firmware ( Image No:
0-f )".
• The message "Enter Wireless Image No. ( 0-f )" is displayed.
• Then select the Image number
• It is better to check the Integrity of Image before selecting it as Default Image.
• When default image is selected, module checks for the validity of the image selected and displays "Configuration
saved".
Page 16
RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 16 | Page
Figure 13: Making Image no - 0 as Default Image
Enable/Disable GPIO Based Bypass Option
This option is for enabling or disabling the GPIO bootloader bypass mode.
Enabling the GPIO Based Bypass Mode
If user select option 7, GPIO based Bootloader bypass gets enabled. When this option is selected, module checks for
the validity of the image selected and displays "Configuration saved" if valid and "Default image invalid" if valid default
image is not present. Once enabled, from next bootup, Bootloader will latch the value of UULP_GPIO_2. If asserted, it
will bypass the whole boot loading process and will load the default firmware image selected.
• After the welcome message is displayed, user can select option 5 "Select Default Wireless Firmware (Image No:
0-f)".
• The message "Enter Wireless Image No. (0-f)" is displayed.
• Then select the Image no.
• It is better to check the Integrity of Image before selecting it as Default Image.
• When default image is selected, module checks for the validity of the image selected and displays "Configuration
saved".
• Then select option 7 to "Enable GPIO Based Bypass Mode"
• Module responds to select the host interface in Bypass mode (0 - UART, 1 - SDIO, 2 - SPI, 4 - USB, 5 - USB-
CDC)
• Select the required interface.
• If the default image is valid, then it enables GPIO Bypass mode, otherwise it will not enable the GPIO Bypass
mode.
Page 17

RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 17 | Page
Figure 14: Enabling the GPIO-based Bypass Mode a) Valid Default Firmware b) Invalid Firmware
Disabling the GPIO Based Bypass Mode
• If host selects option 8, GPIO based bypass gets disabled.
Note:
LP_WAKEUP needs to be de-asserted on power up to move to host interaction mode, to select bootup options
like disable Bypass mode or to change default image.
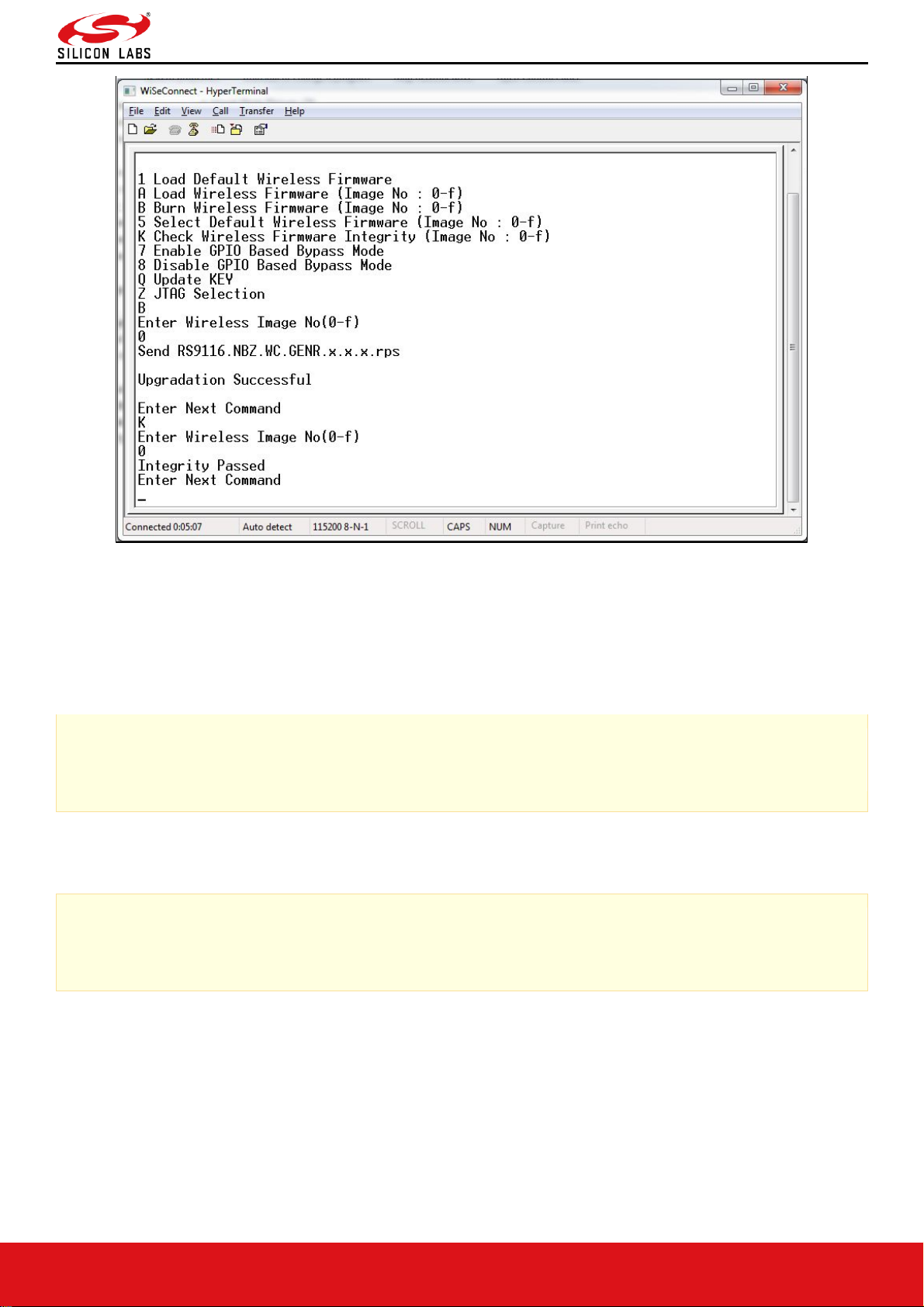
Check Integrity of the Selected Image
This option enables the user to check whether the given image is valid or not. When this command is given,
bootloader asks for the image for which integrity has to be verified as shown in the figure below.
Page 18
RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 18 | Page
Figure 15: Integrity Check Passed
Other Operations
This section contains additional, less frequently used boot-loader options.
Update KEY
Note:
This feature is not enabled in current release.
JTAG Selection
Note:
This feature is not enabled in current release.
Page 19

RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 19 | Page
3 Host Interfaces
RS9116 WiSeConnect Module supports SPI, USB, UART and SDIO for interfacing to host. This section describes
UART interface in detail including the supported features, protocols and commands.
Only UART and USB-CDC interfaces are supported in AT mode.
Note:
USB and SDIO interfaces are currently not supported.
3.1 UART Interface
This section describes RS9116-WiSeConnect UART interface, including the commands and processes to operate the
module via UART.
UART on the RS9116-WiSeConnect is used as a host interface to configure the module to send data and to receive
data.
Features
• Supports hardware (RTS/CTS) flow control.
• Supports following list of baud rates,
o 9600 bps
o 19200 bps
o 38400 bps
o 57600 bps
o 115200 bps
o 230400 bps
o 460800 bps
o 921600 bps
Note:
For baud rates greater than 115200, it is mandatory to enable UART hardware flow control.
Hardware Interface
RS9916W uses TTL serial UART at an operating voltage of 3.3V.
Host UART device must be configured with the following settings:
• Data bits - 8
• Stop bits - 1
• Parity - None
• Flow control - None
Software Protocol
AT+ command mode
This section explains the procedure that the host needs to follow in order to send Wi-Fi commands frames to the
module and to receive responses from the module in AT+ command mode.
TX Operation
The Host uses TX operations:
1. To send management commands to the module from the Host.
Page 20
RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 20 | Page
2. To send actual data to the module which is to be transmitted onto the air.
3. If the host receives error code indicating packet dropped, the host has to wait for a while and send the next
command /data.
4. The host should send next data packet only if it receives "OK<number of bytes sent>" response for the previous
one.
Rx Operation
The RS9116W responds with either an 'OK' or 'ERROR' string, for Management or Data frames along with a result or
error code.
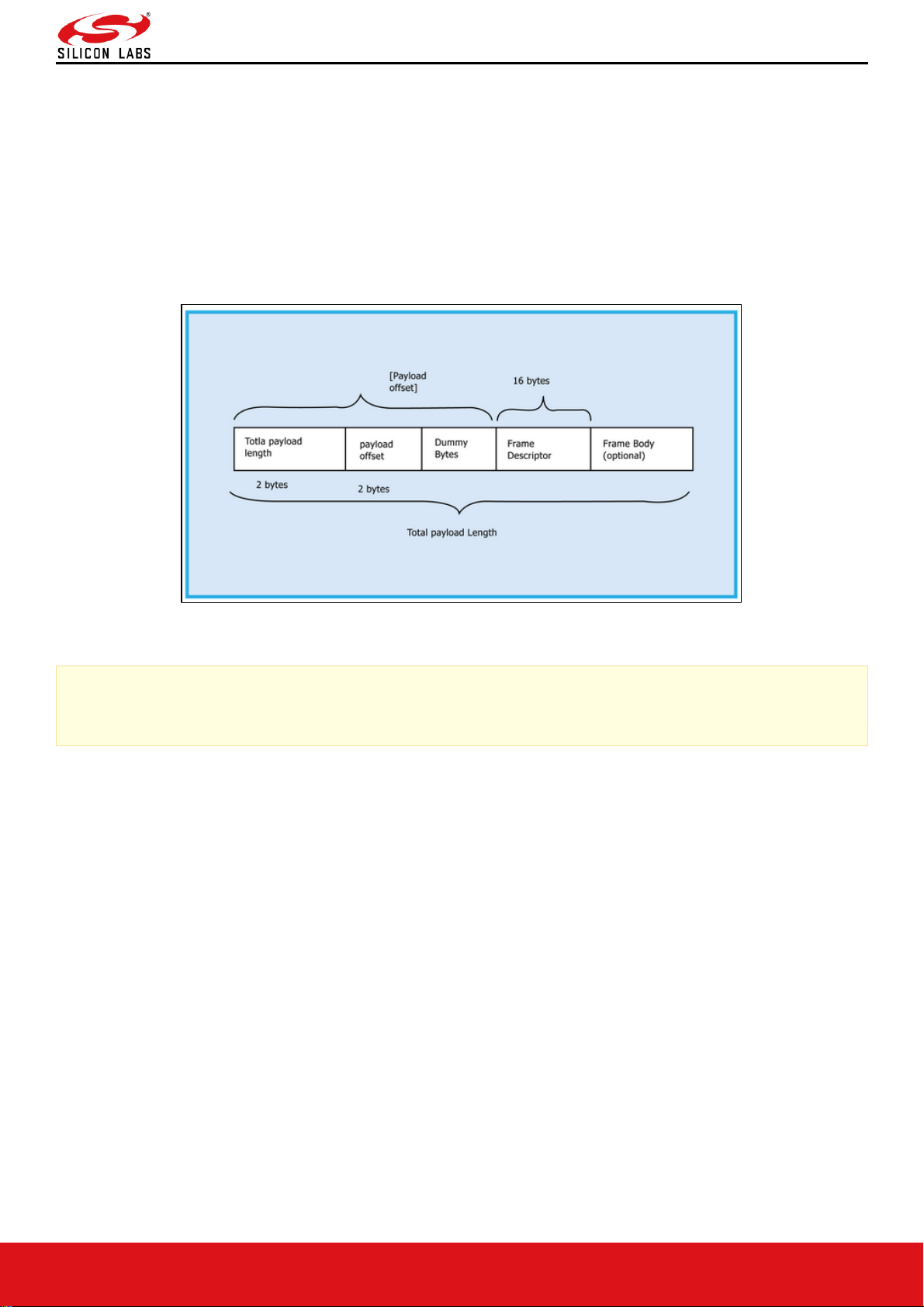
The module sends the response/received data to Host in a format as shown below:
Figure 16: RX Frame Format
Note:
If Payload offset is 'x', 'x-4' dummy bytes will be added before Frame Descriptor.
The host needs follow the steps below to read the frame from the Module:
Read 4 bytes using Frame read.
1. Decode Total payload length and payload offset.
2. Read remaining payload by sending Frame to read with (total payload length – 4 bytes), discard Dummy bytes
and then decode Frame descriptor and Frame Body.
Page 21

RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 21 | Page
4 Classic Command Mode Selection
This section describes AT command mode or Binary mode selection in UART and USB-CDC. It is applicable for
RS9116 WiSeConnect.
After boot-loader interaction, module gives "Loading Done" string in ASCII format to host.
After receiving "Loading Done", based on first command received from host, the module selects command mode.
The module reads first 4 bytes, if it matches with "AT+R", select AT command mode, otherwise select Binary mode.
Once mode is selected, it will remain in same mode until it is reset or power cycle.
There is an option in bootloader to select AT mode or binary mode.
Note:
"AT+R" is not case sensitive.
Page 22
RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 22 | Page
5 Classic Command Format
This section explains the general command format. The commands should be sent to the Module in the specified
format. It is applicable for RS9116 WiSeConnect. Commands are sent to the module and responses are read from the
module using frame write/frame read (as mentioned in the preceding sections). These commands are called as
command frames.
The format of the command frames is divided into two parts:
1. Frame descriptor
2. Frame Body (Frame body is often called as Payload)
Frame Descriptor (16 bytes)
Frame Body (multiples of 4 bytes)
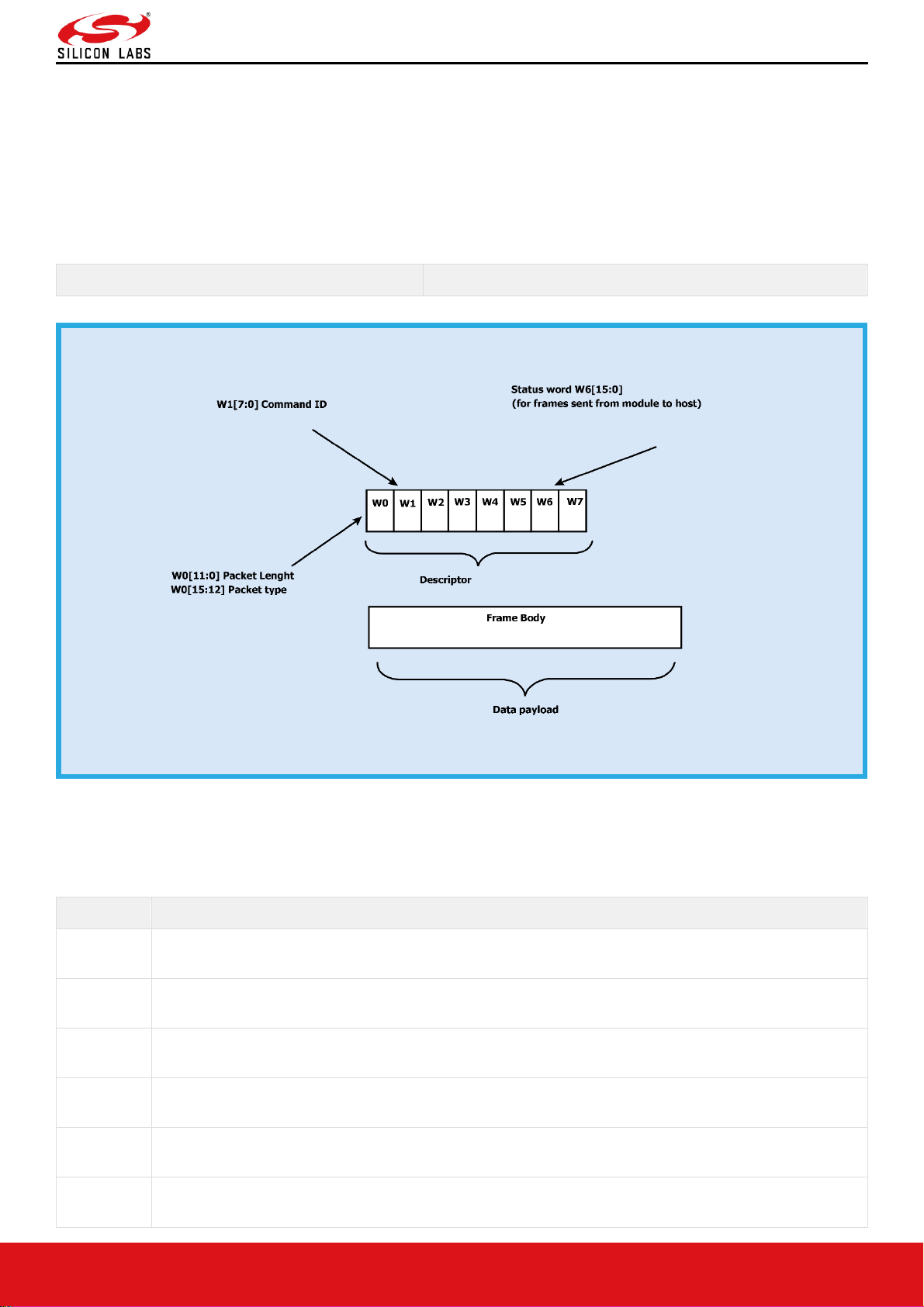
Command frame format is shown below. This description is for a Little-Endian System
Figure 17: Command Frame Format
The following table provides the general description of the frame descriptor.
Table 1: Frame Descriptor
Word
Frame Descriptor
Word0
W0[15:0]
Bits [11:0] – Length of the frame
Bits [15:12] – 2(indicates Bluetooth packet).
Word1
W1[15:0]
Bits [15:0] - Packet type
Word2
W2[15:0]
Reserved
Word3
W3[15:0]
Reserved
Word4
W4[15:0]
Reserved
Word5
W5 [15:0]
Reserved
Page 23

RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 23 | Page
Word
Frame Descriptor
Word6
W6 [15:0]
1. (0x0000) when sent from host to module.
2. When sent from module to host (as response frame), it contains the status.
Word7
W7 [15:0]
Reserved
Three types of frames will get exchanged between the module and host.
1. Request/Command frames
o These are sent from Host to Module. Each Request/ Command has an associated response with it.
2. Response frames
o These are sent from Module to Host. These are given in response to the previous Request/Command
from the Host. Each command has a single response.
3. Event frames
o These are sent from Module to Host. These are given when there are multiple responses for a particular
Request/ Command frame. This is Asynchronous message to be sent to host.
The following are the types of frame requests and responses and the corresponding codes. The commands are
different for both Classic and LE modes. The below table lists the Command, Response and Event frames in Classic
mode.
In both the modes, the corresponding code is to be filled in W1 [15:0] mentioned in the table above.
Table 2: Command IDs in BT Classic mode
Command
Command ID
Set Local Name
0x0001
Query Local Name
0x0002
Set Local COD
0x0003
Query Local COD
0x0004
Query RSSI
0x0005
Query Link Quality
0x0006
Query Local BD Address
0x0007
Set Profile Mode
0x0008
Set Device Discover Mode
0x0009
Get Device Discover Mode
0x000A
Set Connection Mode
0x000B
Get Connection Mode
0x000C
Set Pair Mode
0x000D
Get Pair Mode
0x000E
Remote Name Request
0x000F
Remote Name Request Cancel
0x0010
Inquiry
0x0011
Inquiry Cancel
0x0012
Bond or Create Connection
0x0013
Page 24

RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 24 | Page
Command
Command ID
Bond Cancel or Create Connection Cancel
0x0014
Unbond or Disconnect
0x0015
Set Pin Type
0x0016
Get Pin Type
0x0017
User Confirmation
0x0018
Passkey Reply
0x0019
Pincode Reply
0x001A
Get Local Device Role
0x001B
Set Local Device Role
0x001C
Get Service List
0X001D
Search Service
0X001E
SPP connect
0X001F
SPP Disconnect
0X0020
SPP Transfer
0X0021
Initialize BT Module
0x008D
Deinitialize BT Module
0x008E
Antenna Select
0x008F
Linkkey Reply
0x0091
PER Transmit
0x0098
PER Receive
0x0099
PER Stats
0x009A
PER CW mode
0x009B
Sniff Mode
0x009D
Sniff Exit
0x009E
Sniff Subrating
0x009F
Feature Bit map
0x00A6
Set Antenna Tx Power Level
0x00A7
AFH channel Classification
0x00D2
Set SSP mode
0x00A0
Set EIR data
0X00A9
A2DP Connect
0x0022
A2DP Disconnect
0x0023
A2DP Start
0x00CE
A2DP Suspend
0x00CF
A2DP PCM Data
0x00D0
Page 25

RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 25 | Page
Command
Command ID
A2DP SBC Data
0x00D1
AVRCP Connect
0X0024
AVRCP Disconnect
0X0025
AVRCP Play
0X0026
AVRCP Pause
0X0027
AVRCP Stop
0X0028
AVRCP Next
0X0029
AVRCP Previous
0X002A
HFP Connect
0x002D
HFP Disconnect
0x002E
HFP Phone operator
0x002F
HFP Call accept
0x0030
HFP Call reject
0x0031
HFP Dial number
0x0032
HFP Dial member
0x0033
HFP Redial
0x0034
HFP Voice Recognition Active
0x0035
HFP Voice Recognition Deactive
0x0036
HFP Speak Gain
0x0037
HFP Mic Gain
0x0038
HFP Get Calls
0x0039
HFP Audio
0x003A
PBAP Connect
0x003B
PBAP Disconnect
0x003C
PBAP Contacts
0x003D
Set AFH Channel Classification
0x00D2
AVRCP Get Capabilities
0x00D3
AVRCP Get Attributes List
0x00D4
AVRCP Get Attributes Values List
0x00D5
AVRCP Get Current Attribute Value
0x00D6
AVRCP Set Current Attribute Value
0x00D7
AVRCP Get Element Attributes
0x00D8
AVRCP Get Play Status
0x00D9
AVRCP Get Register Notification
0x00DA
AVRCP Get Version
0x00DB
Page 26

RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 26 | Page
Command
Command ID
AVRCP Get Attribute Tex
0x00DC
AVRCP Get Attribute Value Text
0x00DD
AVRCP Get Battery Status
0x00DE
AVRCP Get Character Sets
0x00DF
AVRCP Capabilities Response
0x00E0
AVRCP Attributes List Response
0x00E1
AVRCP Attributes Values List Response
0x00E2
AVRCP Get Current Attributes Values List Response
0x00E3
AVRCP Set Current Attributes Values List Response
0x00E4
AVRCP Get Element Attributes Response
0x00E5
AVRCP Get Play Status Response
0x00E6
AVRCP Get Register Notification Response
0x00E7
AVRCP Get Attribute Text Response
0x00E8
AVRCP Get Attribute Value Text Response
0x00E9
AVRCP Get Battery Status Response
0x00EA
AVRCP Get Character Sets Response
0x00EB
AVRCP Notification
0x00EC
AVRCP CMD Reject
0x00ED
Add Device ID
0x00EE
A2DP Get Config
0x00FE
A2DP Set Config
0x00FF
Note: A2DP, AVRCP and HFP command IDs are currently not supported.
Table 3: Response IDs in BT Classic Mode
Response
Response ID
Set Local Name
0x0001
Query Local Name
0x0002
Set Local COD
0x0003
Query Local COD
0x0004
Query RSSI
0x0005
Query Link Quality
0x0006
Query Local BD Address
0x0007
Set Profile Mode
0x0008
Set Device Discover Mode
0x0009
Get Device Discover Mode
0x000A
Page 27

RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 27 | Page
Response
Response ID
Set Connection Mode
0x000B
Get Connection Mode
0x000C
Set Pair Mode
0x000D
Get Pair Mode
0x000E
Remote Name Request
0x000F
Remote Name Request Cancel
0x0010
Inquiry
0x0011
Inquiry Cancel
0x0012
Bond or Create Connection
0x0013
Bond Cancel or Create Connection Cancel
0x0014
Unbond or Disconnect
0x0015
Set Pin Type
0x0016
Get Pin Type
0x0017
User Confirmation
0x0018
Passkey Reply
0x0019
Pincode Reply
0x001A
Get Local Device Role
0x001B
Set Local Device Role
0x001C
Get Service List
0X001D
Search Service
0X001E
SPP connect
0X001F
SPP Disconnect
0X0020
SPP Transfer
0X0021
Initialize BT Module
0x008D
Deinitialize BT Module
0x008E
Antenna Select
0x008F
Linkkey Reply
0x0091
PER Transmit
0x0098
PER Receive
0x0099
PER Stats
0x009A
PER CW mode
0x009B
Sniff Mode
0x009D
Sniff Exit
0x009E
Sniff Subrating
0x009F
Feature Bit map
0x00A6
Page 28

RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 28 | Page
Response
Response ID
Set Antenna Tx Power Level
0x00A7
AFH channel Classification
0x00D2
Set SSP mode
0x00A0
Set EIR data
0X00A9
A2DP Connect
0x0022
A2DP Disconnect
0x0023
A2DP Start
0x00CE
A2DP Suspend
0x00CF
A2DP PCM Data
0x00D0
A2DP SBC Data
0x00D1
AVRCP Connect
0X0024
AVRCP Disconnect
0X0025
AVRCP Play
0X0026
AVRCP Pause
0X0027
AVRCP Stop
0X0028
AVRCP Next
0X0029
AVRCP Previous
0X002A
HFP Connect
0x002D
HFP Disconnect
0x002E
HFP Phone operator
0x002F
HFP Call accept
0x0030
HFP Call reject
0x0031
HFP Dial number
0x0032
HFP Dial member
0x0033
HFP Redial
0x0034
HFP Voice Recognition Active
0x0035
HFP Voice Recognition Deactive
0x0036
HFP Speak Gain
0x0037
HFP Mic Gain
0x0038
HFP Get Calls
0x0039
HFP Audio
0x003A
PBAP Connect
0x003B
PBAP Disconnect
0x003C
PBAP Contacts
0x003D
Set AFH Channel Classification
0x00D2
Page 29

RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 29 | Page
Response
Response ID
AVRCP Get Capabilities
0x00D3
AVRCP Get Attributes List
0x00D4
AVRCP Get Attributes Values List
0x00D5
AVRCP Get Current Attribute Value
0x00D6
AVRCP Set Current Attribute Value
0x00D7
AVRCP Get Element Attributes
0x00D8
AVRCP Get Play Status
0x00D9
AVRCP Get Register Notification
0x00DA
AVRCP Get Version
0x00DB
AVRCP Get Attribute Text
0x00DC
AVRCP Get Attribute Value Text
0x00DD
AVRCP Get Battery Status
0x00DE
AVRCP Get Character Sets
0x00DF
AVRCP Capabilities Response
0x00E0
AVRCP Attributes List Response
0x00E1
AVRCP Attributes Values List Response
0x00E2
AVRCP Get Current Attributes Values List Response
0x00E3
AVRCP Set Current Attributes Values List Response
0x00E4
AVRCP Get Element Attributes Response
0x00E5
AVRCP Get Play Status Response
0x00E6
AVRCP Get Register Notification Response
0x00E7
AVRCP Get Attribute Text Response
0x00E8
AVRCP Get Attribute Value Text Response
0x00E9
AVRCP Get Battery Status Response
0x00EA
AVRCP Get Character Sets Response
0x00EB
AVRCP Notification
0x00EC
AVRCP CMD Reject
0x00ED
Add Device ID
0x00EE
A2DP Get Config
0x00FE
A2DP Set Config
0x00FF
Note: A2DP, AVRCP and HFP response IDs are not supported in the v2.1 version of the document
Table 4: Event IDs in BT Classic Mode
Event
Event ID
Role Change Status
0x1000
Page 30

RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 30 | Page
Event
Event ID
Unbond or Disconnect
0x1001
Bond Response
0x1002
Inquiry response
0x1003
Remote Device Name
0x1004
Remote Name Request cancelled
0x1005
Disconnected
0x1006
User Confirmation Request
0x1007
User Passkey Display
0x1008
User Pincode Request
0x1009
User Passkey Request
0x100A
Inquiry Complete
0x100B
Authentication Complete
0x100C
User Linkkey Request
0x100D
User Linkkey Save
0x100E
SSP Complete
0x100F
BT Mode Changed
0x1010
BT Sniff Subrating Changed
0x1011
BT User Passkey Notify
0x1012
SPP Receive Data
0x1100
SPP Connected
0x1101
SPP Disconnected
0x1102
A2DP Connected
0x1200
A2DP Disconnected
0x1201
A2DP Configured
0x1202
A2DP Open
0x1203
A2DP Start
0x1204
A2DP Suspend
0x1205
A2DP Abort
0x1206
A2DP Close
0x1207
A2DP Encoded data
0x1208
A2DP PCM data
0x1209
A2DP More data request
0x120A
A2DP Codec Config
0x120B
AVRCP Connected
0x1300
AVRCP Disconnected
0x1301
Page 31

RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 31 | Page
Event
Event ID
AVRCP Play
0x1302
AVRCP Pause
0x1303
AVRCP Next
0x1304
AVRCP Previous
0x1305
AVRCP Stop
0x1306
AVRCP Notify
0x1310
AVRCP Capabilities Request
0x1311
AVRCP Attributes List Request
0x1312
AVRCP Values List Request
0x1313
AVRCP Current Attribute Value Request
0x1314
AVRCP Set Attribute Value Request
0x1315
AVRCP Attribute Text Request
0x1316
AVRCP Value Text Request
0x1317
AVRCP Character Set Request
0x1318
AVRCP Battery Status Request
0x1319
AVRCP Element Attribute Request
0x131A
AVRCP Player Status Request
0x131B
AVRCP Register Notification
0x131C
HFP Connected
0x1400
HFP Disconnected
0x1401
HFP Ring
0x1402
HFP Call caller id
0x1403
HFP Audio Connected
0x1404
HFP Audio Disconnected
0x1405
HFP Dial complete
0x1406
HFP answer complete
0x1407
HFP Hang up complete
0x1408
HFP Send DTMF Complete
0x1409
HFP Call wait
0x140A
HFP Voice recognition deactivated
0x140B
HFP Voice recognition activated
0x140C
HFP Service not found
0x140D
HFP Call status
0x140E
HFP Signal strength
0x140F
HFP Battery level
0x1410
Page 32

RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 32 | Page
Event
Event ID
HFP Phone service
0x1411
HFP Roaming status
0x1412
HFP Call setup
0x1413
HFP Call held status
0x1414
PBAP Connected
0x1450
PBAP Disconnected
0x1451
PBAP Data
0x1452
Note: A2DP, AVRCP and HFP Event IDs are not supported in the v2.1 version of the document
Page 33

RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 33 | Page
6 BT Classic Commands
This section explains various Bluetooth Classic commands, their structures, parameters and their responses. For API
prototypes of these commands, please refer to the API Library Section.
Note:
A command should not be issued by the host before receiving the response of a previously issued command
from the module.
6.1 Generic Commands
6.1.1 Set Operating Mode
Description:
This is the first command that needs to be sent from the Host after receiving card ready frame from module. This
command configures the module in different functional modes.
Note:
Opermode must be the first command to be issued as per the system design. Other BT commands should be
only issued after receiving a SUCCESS response for opermode command.
Command Format:
AT Mode:
at+rsi_opermode=
<oper_mode>,<feature_bit_map>,<tcp_ip_feature_bit_map>,<custom_feature_bit_map>,<ext_custom_feature_bit_m
ap>,<bt_feature_bit_map>,<ext_tcp_ip_feature_bit_map>,<ble_feature_bit_map>,<ble_custom_ext_feature_bit_map
>,<config_feature_bit_map>\r\n
Note:
If BIT(31) is set to ‘1’ in custom_feature_bitmap
at+rsi_opermode=<oper_mode>,<feature_bit_map>,<tcp_ip_feature_bit_map>,<custom_feature_bitmap><ext_
custom_feature_bit_map>\r\n
if BIT(31) is set to ‘1’ in tcp_ip_feature_bit_map
at+rsi_opermode=<oper_mode>,<feature_bit_map>,<tcp_ip_feature_bit_map>,<custom_feature_bitmap><ext_
tcp_ip_feature_bit_map>\r\n
if BIT(31) is set to ‘1’ in both custom_feature and ext_custom_feature bit maps
at+rsi_opermode=<oper_mode>,<feature_bit_map>,<tcp_ip_feature_
bit_map>,<custom_feature_bitmap><ext_custom_feature_bit_map> <bt_feature_bit_map>\r\n
if BIT(31) is set to 1 in bt_feature_bit_map
at+rsi_opermode=<oper_mode>,<feature_bit_map>,<tcp_ip_feature_
bit_map>,<custom_feature_bitmap><ext_custom_feature_bit_map><bt_feature_bit_map><ext_tcp_ip_feature_
bit_map><ble_feature_bit_map>\r\n
If BIT(31) is set to 1 in ble_custom_feature_bit_map
at+rsi_opermode=<oper_mode>,<feature_bit_map>,<tcp_ip_feature_
bit_map>,<custom_feature_bitmap><ext_custom_feature_bit_map><bt_custom_feature_bit_map><ext_tcp_ip_
feature_bit_map><ble_custom_feature_bit_map>,<ble_custom_ext_feature_bit_map>\r\n
Page 34
RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 34 | Page
If BIT(31) is set to '1' in both tcp_ip_feature_bit_map and ext_tcp_ip_feature_bit_map
at+rsi_opermode=<oper_mode>,<feature_bit_map>,<tcp_ip_feature_bit_map>,<custom_feature_bitmap>
<ext_custom_feature_bit_map><bt_custom_feature_bit_map><ext_tcp_ip_feature_bit_map><ble_custom_feat
ure_bit_map>,<ble_custom_ext_feature_bit_map>,<config_feature_bit_map>\r\n
Command Parameters:
Oper_mode:
Sets the mode of operation. oper_mode contains two parts <wifi_oper_mode, coex_mode>. Lower two bytes
represent wifi_oper_mode and higher two bytes represent coex_modes.
oper_mode = ((wifi_oper_mode) | (coex_mode << 16))
Note:
Please refer to RS9116W Wi-Fi AT Command Programming Reference Manual.pdf at
https://docs.silabs.com/rs9116 for more details on WLAN and co-existence of other protocols with WLAN.
In BTLE mode, BT mode also needs to be enabled.
Following table represents BT coex modes supported:
Coex_mode
Description
4
Bluetooth
8
Dual Mode (Bluetooth and BLE)
Table 12: Coex Modes of BT Supported
Note:
1. If coex mode is enabled in opermode command, then BT / BLE protocol get starts and gives corresponding
card ready in parallel with opermode command response (which will be handled by corresponding
application).
2. BT card ready frame is described in RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference
Manual.pdf (available at https://docs.silabs.com/rs9116), BLE card ready frame is described in RS9116W
BLE AT Command Programming Reference Manual.pdf (available at https://docs.silabs.com/rs9116).
3. Feature selection utility is provided in the package. WiSeConnect device supports the selected features
combination only if it is feasible as per the RSXXXXX_TCPIP_Feature_Selection_vX.xlsx
custom_feature_bit_map:
This bitmap is used to enable following BT/BLE custom features:
BIT[11]: To Enable Packet Pending Indication(wake on wireless) in UART mode
1 - Enable
0 – Disable
BIT[29]: To Enable IAP support in BT mode
1 - Enable
0 – Disable
BIT[31]: This bit is used to validate extended custom feature bitmap.
1 – Extended feature bitmap valid
0 – Extended feature bitmap is invalid
BIT[0:1],BIT[3:4],BIT[7],BIT[21], BIT[30]: Reserved, should be set to all '0'.
Page 35

RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 35 | Page
Note:
For UART / USB-CDC in AT mode:
Parameters- feature_bit_map, tcp_ip_feature_bit_map and custom_feature_bit_map are optional in opermode
command in UART mode for AT mode. If user does not give these parameters, then default configuration gets
selected as explained above based on the operating mode configured.
ext_custom_feature_bit_map:
This feature bitmap is an extension of custom feature bitmap and is valid only if BIT[31] of custom feature bitmap is
set. This enables the following feature.
BIT[0]: To enable antenna diversity feature.
1 – Enable antenna diversity feature
0 – Disable antenna diversity feature
BIT[1]:This bit is used to enable 4096 bit RSA key support
1 – Enable 4096 bit RSA key support
0 – Disable 4096 bit RSA key support
Note:
If this bit is enable then connected clients which are in power save may observe packet miss.
BIT[5]: This bit is used to enable Pre authentication Support.
1 – Enable Pre authentication Support
0 – Disable Pre authentication Support
BIT[6]: This bit is used to enable 40MHZ Support
1 – Enable 40MHZ Support
0 – Disable 40MHZ Support
(BIT[20] | BIT[21]) - This bit is used to configure 384k mode.
Note:
It is mandatory to configure 384k mode for any use-case.
1- enable
0-disable
BIT[31]: This bit is used to validate bt and ble feature bitmap.
1 – bt & ble feature bitmap valid
0 – bt & ble feature bitmap is invalid
bt_feature_bit_map:
This bitmap is valid only if BIT[31] of extended custom feature bit map is set.
BIT[0:7] – reserved
BIT[8] – BT_EDR_3MBPS_DISABLE
1- Disable BT EDR 3Mbps Feature
0- Enable BT EDR 3Mbps Feature
BIT[9] – BT_EDR_2MBPS_DISABLE
1- Disable BT EDR 2Mbps Feature
0- Enable BT EDR 2Mbps Feature
BIT[10] – BT_5_SLOT_PACKETS_DISABLE
Page 36

RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 36 | Page
1- Disable BT 5 Slot Packet Feature
0- Enable BT 5 Slot Packet Feature
BIT[11] – BT_3_SLOT_PACKETS_DISABLE
1- Disable BT 3 Slot Packet Feature
0- Enable BT 3 Slot Packet Feature
BIT[12] – Noise Figure Feature
1 - Enable Noise Figure
0 - Disable Noise Figure
BIT[13] – SNIFF Feature Disable
1- Disable SNIFF Feature
0- Enable SNIFF Feature
BIT[14] – reserved
BIT[15] – HFP profile bit enable
1- enable the HFP profile
0- disable the HFP profile
BIT[16:19] – reserved for future use
BIT[20:22] – number of slaves supported by BT
Maximum no of bt slaves: 2
BIT [23] – A2DP profile bit enable
1- enable the A2DP profile
0- disable the A2DP profile
BIT [24] – A2DP profile role selection
1- A2DP source
0- A2DP sink
BIT [25] – A2DP accelerated mode selection
1- enable accelerated mode
0- disable accelerated mode
BIT [26] – A2DP i2s mode selection
1- enable i2s mode
0- disable i2s mode
BIT [27:29] – reserved
BIT[30] – RF Type selection
1 - Internal Rf Type selection
0 - External Rf Type selection
BIT[31] - Validate ble feature bit map. For classic opermode this can be ignored.
1 - valid ble feature bit map
0 - Ignore ble feature bit map
Note:
A2DP, AVRCP and HFP Profiles are not supported currently.
config_feature_bit_map:
This bitmap is valid only if BIT[31] of ext_tcp_ip_feature_bit_map is set.
Config Feature bitmap
Functionality
Bit set
to 0
bit Set
to 1
Note and Info
config_feature_bit_map[0]
To select wakeup indication to host.
Disable
Enable
Page 37

RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 37 | Page
Config Feature bitmap
Functionality
Bit set
to 0
bit Set
to 1
Note and Info
If it is disabled UULP_GPIO_3 is
used as a wakeup indication to
host.
If it is enabled UULP_GPIO_0 is
used as a wakeup indication to
host.
config_feature_bi_map[1:15]
Reserved
config_feature_bi_map[16]
Active high or low interrupt mode
selection for wake on wireless
operation
If it is disabled active low interrupt is
used in wake on wireless operation.
If it is enabled active high interrupt
is used in wake on wireless
operation.
Disable
Enable
config_feature_bi_map[17:23]
Reserved
config_feature_bit_map[24:25]
Configurability options for 40MHz
XTAL good time in μs
BIT(25)
BIT(24)
Good
time
0 0 1000
0 1 2000
1 0 3000
1 1 600
These bits are used to select
XTAL good time.
These changes are available
from Release 2.3.0 onwards.
Releases prior to 2.3.0 these
config_feature_bitmap[31:17]
are reserved.
Its only applicable for customers
using chip and not the module.
Please contact support for more
details.
Default value is 1000 μs.
config_feature_bit_map[31:26]
Reserved for LMAC
Note:
32KHz external clock connection and power save pins
As per Silicon Labs datasheet updated in May 2019, 32KHz external clock and the power save pins
connections have changed. To keep SW compatibility between initial design (i.e. first EVKs developed by
Silicon Labs) and new designs, there are currently 2 options for connecting 32KHz external clock and the power
save pins:
Option 1:
External 32KHz clock connection pins : XTAL_32KHZ_P & XTAL_32KHZ_N
Power Save connection pins : HOST_BYP_ULP_WAKEUP & UULP_VBAT_GPIO_3
Option 2:
External 32KHz clock connection pin : UULP_VBAT_GPIO_3
Power Save connection pins : HOST_BYP_ULP_WAKEUP & UULP_VBAT_GPIO_0
Note:
Page 38

RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 38 | Page
As per Silicon Labs datasheet updated in May'2019, Option 2 must be used for External 32KHz clock and
Power save connections in new designs.
Response:
Result Code
Description
OK
Successful execution of the command
ERROR<Error code>
Failure
Example:
AT Mode:
at+rsi_opermode=327680,0,1,2147483648,2150629376,1073741824\r\n
Response:
OK\r\n
bt_loaded\r\n
6.1.2 Set Local Name
Description: This is used to set name to the local device.
AT command format:
at+rsibt_setlocalname=<NameLength>,<Name>\r\n
Parameters:
NameLength – Length of the name of local device.
Name (50 bytes) – Name of the local device.
AT command Ex:
at+rsibt_setlocalname=6,silabs\r\n
Response:
OK\r\n
6.1.3 Query Local Name
Description:
This is used to query the name of the local device.
AT command format:
at+rsibt_getlocalname?\r\n
Response:
Result Code
Description
OK <name_length>,<local_device_name>
Command Success.
ERROR <Error_code>
Command Fail.
Response Parameters:
name_length - Length of the name
local_device_name (50 bytes)- Name of the local device
AT command Ex:
at+rsibt_getlocalname?\r\n
Response:
Page 39

RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 39 | Page
OK 8,silabs\r\n
6.1.4 Set Local COD
Description:
This is used to indicate the capabilities of local device to other devices. It is a parameter received during the device
discovery procedure on the BR/EDR physical transport, indicating the type of device. The Class of Device parameter
is only used on BR/EDR and BR/EDR/LE devices using BR/EDR physical transport.
AT command format:
at+rsibt_setlocalcod=<local_device_class>\r\n
Parameters:
Local COD – Class of the Device of local device
AT command Ex:
at+rsibt_setlocalcod=7A020C\r\n
Response:
OK\r\n
6.1.5 Query Local COD
Description:
This is used to query Class of Device of the local device.
AT command format:
at+rsibt_getlocalcod?\r\n
Response:
Result Code
Description
OK <local_device_class>
Command Success.
ERROR <Error_code>
Command Fail.
Response Parameters:
LocalCOD – Class of the Device of the local device
AT command Ex:
at+rsibt_getlocalcod?\r\n
Response:
OK 7A020C\r\n
6.1.6 Query RSSI
Description:
This is used to query RSSI of the connected remote BT Device.
AT command format:
at+rsibt_getrssi=<BDAddress>?\r\n
Parameters:
BDAddress (6 bytes) – BD Address of the connected remote device.
Response:
Result Code
Description
OK <rssi value>
Command Success.
ERROR <Error_code>
Command Fail.
Page 40
RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 40 | Page
Response parameters:
RSSI – RSSI value of the connected remote device.
AT command Ex:
at+rsibt_getrssi=AA-BB-CC-DD-EE-FF?\r\n
Response:
OK 127\r\n
Note:
The rssi value should be within the range of -128 to +127
6.1.7 Query Link Quality
Note:
This command is not currently supported
Description:
This is used to query the link quality between local device and connected remote device.
AT command format:
at+rsibt_getlinkqlty=<BDAddress>?\r\n
Parameters:
BDAddress(6 bytes) – BD Address of the connected remote device
Response:
Result Code
Description
OK <link_quality>
Command Success with valid response.
ERROR <Error_code>
Command Fail.
Response parameters:
LinkQuality – Link quality value.
AT command Ex:
at+rsibt_getlinkqlty=AA-BB-CC-DD-EE-FF?\r\n
Response:
OK 123\r\n
6.1.8 Query Local BD Address
Description:
This is used to query BD address of the local device.
AT command format:
at+rsibt_getlocalbdaddr?\r\n
Response:
Result Code
Description
OK <bd_addr>
Command Success with valid response.
Page 41

RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 41 | Page
Result Code
Description
ERROR <Error_code>
Command Fail.
Response Parameters:
BDAddress (6 bytes) - BD Address of the local device
AT command Ex:
at+rsibt_getlocalbdaddr?\r\n
Response:
OK AA-BB-CC-DD-EE-FF\r\n
6.1.9 Query BT Stack Version
Description:
This is used to query Current BT Stack Version.
AT command format:
at+rsibt_getbtstackversion?\r\n
Response:
Result Code
Description
OK <stack version>
Command Success with valid response.
ERROR <Error_code>
Command Fail.
Response Parameters:
stackVersion (1 byte) - Stack version
AT command Ex:
at+rsibt_getbtstackversion?\r\n
Response:
OK 2.0
6.1.10 Initialize BT Module
Description:
This is used to initialize the BT module.
AT command format:
at+rsibt_btinit\r\n
AT command Ex:
at+rsibt_btinit\r\n
Response:
OK\r\n
6.1.11 Deinitialize BT Module
Description:
This is used to de-initialize the BT module. To again initialize the module 'Initialize BT module' command can be used.
AT command format:
at+rsibt_btdeinit\r\n
AT command Ex:
at+rsibt_btdeinit\r\n
Response:
Page 42

RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 42 | Page
OK\r\n
6.1.12 BT Antenna Select
Description:
This is used to select internal or external antenna of the BT module.
AT command format:
at+rsibt_btantennaselect=<antenna_val>\r\n
Parameters:
AntennaVal(1 byte) – To select the internal or external antenna
0 – Internal Antenna.
1 – External Antenna.
AT command Ex:
at+rsibt_btantennaselect=1\r\n
Response:
OK\r\n
6.1.13 Set Feature Bitmap
Description:
This is used to enable/disable the features.
AT command format:
at+rsibt_setfeaturebitmap=<featurebitmap>\r\n
Parameters:
featurebitmap (2 bytes)
1 – Enable BT security
0 – Disable BT security
ATcommandEx:
at+rsibt_setfeaturebitmap =1\r\
Response:
OK\r\n
6.1.14 Set Antenna Tx power level
Description:
This is used to set the Bluetooth antenna transmit power level. This command serves for selecting the maximum
power to be used for the device.
AT command format:
at+rsibt_setantennatxpowerlevel=<protocol_mode>,<power_level>\r\n
Parameters:
protocol_mode (1 byte)
1 –BT Classic
Power_level (1 byte)- range of the power levels used in terms of dBm
Minimum value – 1
Maximum value - 14
ATcommandEx:
at+rsibt_setantennatxpowerlevel =1,10\r\n
Response:
OK\r\n
Page 43

RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 43 | Page
6.2 PER Commands
6.2.1 BR-EDR PER Transmit
Description:
This command can be given to start br -edr transmission.
AT Command format:
at+rsibt_bredrtransmit=<enable/disable>,<device_address>,<pkt_len>,<pkt_type>,<BR/EDR_mode>,<rx_channel_nu
m>,<tx_channel_num>,<link_type>,<scrambler_seed>,<hopping_type>,<antenna_sel>,<pll_mode>,<rf_type>,<rf_cha
in>,<payload_type>,<tx_power_index>,<tx_mode>,<inter_packet_gap>,<num_of_packets>\r\n
Parameters:
enable: 1
dev_addr (6 bytes): It is a 48-bit address in hexadecimal format, e.g.,0023A7010203
pkt_type (1 byte): Type of the packet to be transmitted as per the Bluetooth standard.
pkt_length (1 byte): Length of the packet in bytes to be transmitted.
br_edr_mode (1 byte): basic rate - 1, enhanced_rate - 2 or 3
rx_channel_index (1 byte): Receive channel index as per the Bluetooth standard. i.e., 0 to 78
tx_channel_index (1 byte): Transmit channel index as per the Bluetooth standard. i.e., 0 to 78
link_type : sco - 0, acl - 1, esco - 2
scrambler_seed (1 byte): Initial seed to be used for whitening. It should be set to ‘0’ in order to disable whitening.
no_of_packets (1 byte): Number of packets to be transmitted. It is valid only when the <tx_mode> is set to Burst mode
payload_type (1 byte): Type of payload to be transmitted. ‘0’ – Payload consists of all zeros
‘1’ – Payload consists of all 0xFF’s
‘2’ – Payload consists of all 0x55’s
‘3’ – Payload consists of all 0xF0’s
‘4’ – Payload consists of PN9 sequence.
tx_power(1 byte): Transmit power value should be between 0 and 18
tx_mode(1 byte): Burst mode - 0, Continuous mode - 1
hopping type(1 byte) : no hopping -0, fixed hopping - 1, random hopping - 2
ant_sel(1 byte) : on-chip antenna - 2, u.fl - 3
inter_pkt_gap: Number of slots to be skipped between two packets Each slot will be 625usec (At Always will happen
at Tx slot).
pll_mode: PLL_MODE0 – 0, PLL_MODE1 – 1, PLL_MODE2 – 2
rf_type: External RF – 0, Internal RF – 1
rf_chain: WLAN_HP_CHAIN 0, WLAN_LP_CHAIN 1, BT_HP_CHAIN 2, BT_LP_CHAIN 3
AT command Ex:
at+rsibt_bredrtransmit=1,11-11-11-11-11-11,339,15,3,10,10,1,0,0,3,0,1,3,1,31,0,0,0\r\n(enable/start)
Response:
OK\r\n
1. After the transmission starts, the following command can be given to stop the transmission.
at+rsibt_bredrtransmit=0\r\n
2. Stop the Transmission first before starting of Transmission.
Page 44

RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 44 | Page
3. dev_addr need not be module's BD address, it can be any 48bit BD address. But it should be same for
transmit and receive command.
6.2.2 BR-EDR PER Receive
Description:
This command can be given to start the br -edr transmission.
AT Command format:
at+rsibt_bredrreceive=<enable/disable>,<device_address>,<pkt_len>,<pkt_type>,<BR/EDR_mode>,<rx_channel_nu
m>,<tx_channel_num>,<link_type>,<scrambler_seed>,<hopping_type>,<antenna_sel>,<pll_mode>,<rf_type>,<rf_cha
in>,<loop_back_mode>\r\n
Parameters:
enable: 1
dev_addr(6 byte): It is a 48-bit address in hexadecimal format, e.g.,000012345678
link_type(1 byte) : sco - 0, acl - 1, esco - 2
pkt_type(1 byte): Type of the packet to be transmitted, as per the Bluetooth standard.
pkt_length(1 byte): Length of the packet in bytes to be transmitted.
scrambler_seed(1 byte): Initial seed to be used for whitening. It should be set to ‘0’ in order to disable whitening.
br_edr_mode(1 byte) : basic rate - 1, enhanced_rate - 2
rx_channel_index(1 byte) : Receive channel index as per the Bluetooth standard .i.e., 0 to 78
tx_channel_index(1 byte): Transmit channel index as per the Bluetooth standard. i.e., 0 to 78
hopping type: no hopping -0, fixed hopping - 1, random hopping - 2
ant_sel(1 byte): onchip antenna - 2, u.fl - 3
loop_back_mode: Disable - 0, Enable - 1
pll_mode : PLL_MODE0 – 0, PLL_MODE1 – 1, PLL_MODE2 – 2
rf_type : External RF - 0, Internal RF – 1
rf_chain: WLAN_HP_CHAIN 0, WLAN_LP_CHAIN 1, BT_HP_CHAIN 2, BT_LP_CHAIN 3
AT command Ex:
at+rsibt_bredrreceive=1,11-11-11-11-11-11,339,15,3,10,10,1,0,0,3,0,1,3,0\r\n(enable/start)
Response:
OK\r\n
6.2.3 Per Stats
Description:
The following statistics are returned.
Command:
at+rsibt_perstats
Parameters:
Crc_pass_count (2 bytes): The number of packets received which are passed CRC check.
Crc_fail_count(2 bytes): The number of packets received which failed CRC check.
RSSI(2 bytes): The RSSI value of the last received packet. .
AT command Ex:
at+rsibt_perstats
Response:
Page 45

RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 45 | Page
Appendix
Frequencies and channel numbers used for Bluetooth Classic Mode:
Band (GHz)
Bandwidth (MHz)
Channel Number
Centre Freq (MHz)
2.4 1 0
2402
2.4 1 1
2403
2.4 1 2
2404
2.4 1 3
2405
2.4 1 4
2406
2.4 1 5
2407
2.4 1 6
2408
2.4 1 7
2409
2.4 1 8
2410
2.4 1 9
2411
2.4 1 10
2412
2.4 1 11
2413
2.4 1 12
2414
2.4 1 13
2415
2.4 1 14
2416
2.4 1 15
2417
2.4 1 16
2418
2.4 1 17
2419
2.4 1 18
2420
2.4 1 19
2421
2.4 1 20
2422
2.4 1 21
2423
2.4 1 22
2424
2.4 1 23
2425
2.4 1 24
2426
2.4 1 25
2427
2.4 1 26
2428
2.4 1 27
2429
2.4 1 28
2430
2.4 1 29
2431
2.4 1 30
2432
2.4 1 31
2433
2.4 1 32
2434
Page 46

RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 46 | Page
Band (GHz)
Bandwidth (MHz)
Channel Number
Centre Freq (MHz)
2.4 1 33
2435
2.4 1 34
2436
2.4 1 35
2437
2.4 1 36
2438
2.4 1 37
2439
2.4 1 38
2440
2.4 1 39
2441
2.4 1 40
2442
2.4 1 41
2443
2.4 1 42
2444
2.4 1 43
2445
2.4 1 44
2446
2.4 1 45
2447
2.4 1 46
2448
2.4 1 47
2449
2.4 1 48
2450
2.4 1 49
2451
2.4 1 50
2452
2.4 1 51
2453
2.4 1 52
2454
2.4 1 53
2455
2.4 1 54
2456
2.4 1 55
2457
2.4 1 56
2458
2.4 1 57
2459
2.4 1 58
2460
2.4 1 59
2461
2.4 1 60
2462
2.4 1 61
2463
2.4 1 62
2464
2.4 1 63
2465
2.4 1 64
2466
2.4 1 65
2467
2.4 1 66
2468
2.4 1 67
2469
Page 47
RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 47 | Page
Band (GHz)
Bandwidth (MHz)
Channel Number
Centre Freq (MHz)
2.4 1 68
2470
2.4 1 69
2471
2.4 1 70
2472
2.4 1 71
2473
2.4 1 72
2474
2.4 1 73
2475
2.4 1 74
2476
2.4 1 75
2477
2.4 1 76
2478
2.4 1 77
2479
2.4 1 78
2480
Packet Summary:
Packet
Type
br edr mode
Packet length
Link Type
DM1 3 1
0-17
1
DH1 4 1
0-27
1
DH3
11 1 0-183
1
DM3
10 1 0-121
1
DH5
15 1 0-339
1
DM5
14 1 0-224
1
2-DH1 4 2
0-54
1
2-DH3
10 2 0-367
1
2-DH5
14 2 0-679
1
3-DH1 8 3
0-83
1
3-DH3
11 3 0-552
1
3-DH5
15 3 0-1021
1
HV1 5 1
10
0
HV2 6 1
20
0
HV3 7 1
30
0
DV 8 1
10+(0-9)D
0
EV3 7 1
1-30
2
EV4
12 1 1-120 *
2
EV5
13 1 1-180 *
2
2-EV3 6 2
1-60
2
2-EV5
12 2 1-360 *
2
Page 48
RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 48 | Page
Packet
Type
br edr mode
Packet length
Link Type
3-EV3 7 3
1-90
2
3-EV5
13 3 1-540 *
2
'*' In eSCO (link type = 3), having capability of maximum 90 bytes (Packet Length) only.
at+rsibt_rmtnamereqcancel= AA-BB-CC-DD-EE-FF \r\n
6.3 Core Commands
6.3.1 Set Profile Mode
Note:
Currently only SPP, HID profiles are supported.
Description:
This is used to initialize the particular profiles in Bluetooth embedded host stack.
AT command format:
at+rsibt_setprofilemode=<ProfileMode>\r\n
Parameters:
Profile Mode (1 byte) – Set specific bits to enable the profiles.
Bit No
Description
0
SPP Profile
1
A2DP Profile
2
AVRCP Profile
3
HFP Profile
4
PBAP Profile
5
IAP Profile
6
HID Profile
Response Parameters:
ProfileMode(1 byte) : Value is represented in HEX format for respective profile bits
1 - SPP Profile
40 - HID Profile
AT command Ex:
at+rsibt_setprofilemode=1\r\n
Response:
OK\r\n
Note:
According to profile requirements, need to give bit numbers. For example if required spp profile + A2DP profile then
value 3 should be given.
Set Device Discovery Mode
Description:
This is used to set the BT module in any of the three Discovery modes. Time out can be used for only limited
discovering.
Page 49

RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 49 | Page
AT command format:
at+rsibt_setdiscvmode=<mode>,<timeout>\r\n
Parameters:
Mode(1 byte) – To enable/disable discovering
0 – disable discovering
1 – enable discovering
2 – limited discovering
TimeOut(4 bytes) – time out value in milli seconds.
Note:
Better to use below 1 hour(i.e.. >3600000ms)
AT command Ex:
at+rsibt_setdiscvmode=2,10000\r\n
Response:
OK\r\n
6.3.2 Get Device Discovery Mode
Description:
This is used to get the discovery mode of the BT module, currently the BT module was set.
AT command format:
at+rsibt_getdiscvmode?\r\n
Response:
Result Code
Description
OK <mode>
Command Success with valid response.
ERROR <Error_code>
Command Fail.
Response Parameters:
DiscoveryMode(1 byte) – enabled/disabled discovering
0 – Disabled device discover
1 – Enabled device discover
AT command Ex:
at+rsibt_getdiscvmode?\r\n
Response:
OK 1\r\n
6.3.3 Set Connectability Mode
Description:
This is used to set the BT module in one of the two Connectability modes.
AT command format:
at+rsibt_setconnmode=<ConnMode>\r\n
Parameters:
ConnMode(1 byte) – To enable/disable connectability
0 – disable connection mode
1 – enable connection mode
AT command Ex:
at+rsibt_setconnmode=1\r\n
Response:
Page 50
RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 50 | Page
OK\r\n
6.3.4 Get Connectablility Mode
Description:
This is used to get the connectable mode, currently the BT module was set.
AT command format:
at+rsibt_getconnmode?\r\n
Response:
Result Code
Description
OK <mode>
Command Success with valid response.
ERROR <Error_code>
Command Fail.
Response Parameters:
ConnMode(1 byte) – enabled/disabled connection mode
0 – Disabled connection mode
1 – Enabled connection mode
AT command Ex:
at+rsibt_getconnmode?\r\n
Response:
OK 1\r\n
6.3.5 Remote Name Request
Description:
This is used to know the name of the remote BT device, using its BD address. The response to this command
containing the remote BT device name will be sent to the host through "RMTDEVNAME" event.
AT command format:
at+rsibt_rmtnamereq=<BDAddress>\r\n
Parameters:
BDAddress(6 bytes) – remote device BD Address
AT command Ex:
at+rsibt_rmtnamereq= AA-BB-CC-DD-EE-FF\r\n
Response:
OK\r\n
6.3.6 Remote Name Request Cancel
Description:
This will cancel the request served by "Remote Name Request" command. The cancellation is confirmed through
"Remote Name Request Cancelled" event.
AT command format:
at+rsibt_rmtnamereqcancel=<BDAddress>\r\n
Parameters:
BDAddress(6 bytes) – remote device BD Address
AT command Ex:
Response:
OK\r\n
Page 51

RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 51 | Page
6.3.7 Inquiry
Description:
This performs an inquiry scan to find any BT devices in the vicinity. The response is sent using "INQRESP" event.
AT command format:
at+rsibt_inquiry=<InquiryType>,<Duration>,<MaxNbrdev>\r\n
Parameters:
InquiryType (1 byte)–
0 -Standard Inquiry
1 - Inquiry with RSSI
2 - Extended Inquiry
Duration (4 bytes)– Extended Time in milliseconds (up to 10000ms)
MaxNbrdev(1 byte) – maximum number of devices to scan (from 1 to 10)
AT command Ex:
at+rsibt_inquiry=1,10000,10\r\n
Response:
OK\r\n
6.3.8 Inquiry Cancel
Description:
This will cancel the inquiry scan, which was already in the process, served by "Inquiry" command.
AT command format:
at+rsibt_inquirycancel\r\n
AT command Ex:
at+rsibt_inquirycancel\r\n
Response:
OK\r\n
6.3.9 Extended Inquiry Response Data
Description:
This command is used to set the Extended Inquiry Response data.
AT Command format:
at+rsibt_seteir=<DataLen>,<Data>\r\n
Parameters:
Length(1 byte) – data length. Max EIR data length is 200 Bytes.
Data (200 bytes)– Actual data
Note:
Data should be in hex format
AT command Ex:
at+rsibt_seteir=8,2,1,0,4,9,72,72,72\r\n
Response:
OK\r\n
Page 52

RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 52 | Page
Figure 18: Extended Inquiry Response
6.3.10 Bond or Create Connection
Description:
This will create bonding (connection) between the BT module and the remote BT device based on BD address along
with security.
AT command format:
at+rsibt_bond=<BDAddress>\r\n
Parameters:
BDAddress(6 bytes) – remote device BD Address.
AT command Ex:
at+rsibt_bond= AA-BB-CC-DD-EE-FF\r\n
Response:
OK\r\n
6.3.11 Bond Cancel or Create Connection Cancel
Description:
This will disconnect the connection between the BT module and the remote BT device only while the bonding is in
progress.
AT command format:
at+rsibt_bondcancel=<BDAddress>\r\n
Parameters:
BDAddress(6 bytes) – remote device BD Address
AT command Ex:
at+rsibt_bondcancel = AA-BB-CC-DD-EE-FF\r\n
Response:
OK\r\n
6.3.12 UnBond Or Disconnect
Description:
This command is used to un-bond the device which was already bonded based on BD address of the remote BT
device.
AT command format:
at+rsibt_unbond=<BDAddress>\r\n
Parameters:
BDAddress(6 bytes) – remote device BD Address
Page 53

RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 53 | Page
AT command Ex
at+rsibt_unbond= AA-BB-CC-DD-EE-FF\r\n
Response:
OK\r\n
6.3.13 Set Pin Type
Note:
This command is not currently supported
Description:
This is used to set the PIN code or pass key of the local BT module.
AT command format:
at+rsibt_setpintype=<PINType>\r\n
Parameters:
PINType(1 byte)
0 – variable pin
1 – fixed pin
AT command Ex:
at+rsibt_setpintype=1\r\n
Response:
OK\r\n
6.3.14 Get Pin Type
Note:
This command is not currently supported.
Description:
This is used to get the PIN code or pass key of the local BT module.
AT command format:
at+rsibt_getpintype?\r\n
Response:
Result Code
Description
OK <pintype>
Command Success.
ERROR <Error_code>
Command Fail.
Response Parameters:
PINType(1 byte) –
0 – variable pin
1 – fixed pin
AT command Ex:
at+rsibt_getpintype?\r\n
Response:
OK 1\r\n
Page 54

RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 54 | Page
6.3.15 User Confirmation
Description:
This gives the confirmation for the values sent by remote BT devices at the time of bonding.
AT command format:
at+rsibt_usrconfirmation=<BDAddress>,<Confirmation>\r\n
Parameters:
BDAddress(6 bytes): BD address of the remote BT device which sends connection request.
confirmation ( 1 byte):
0- NO. If both remote and local values are not same.
1- YES. If both remote and local values are same.
AT command Ex:
at+rsibt_usrconfirmation= AA-BB-CC-DD-EE-FF,1\r\n
Response:
OK\r\n
6.3.16 Pass Key Request Reply
Description:
The user passkey entry is used to respond on a user passkey entry request (UPER).
AT command format:
at+rsibt_usrpasskey=<BDAddress>,<ReplyType>,<Passkey>\r\n
Parameters:
BDAddress(6 bytes) – Remote BD Address.
ReplyType (1 byte)–
0 – negative reply
1 – positive reply
Passkey(4 bytes) – Entered Passkey number in decimal (range from 0 to 999999).
AT command Ex:
at+rsibt_usrpasskey = AA-BB-CC-DD-EE-FF,1,123456\r\n
Response:
OK\r\n
6.3.17 Pincode Request Reply
Description:
The user pincode entry is used to respond on a user pin code entry request (UPER). To make connection with remote
device then need to respond with positive reply.else send negative reply.
AT command format:
at+rsibt_usrpincode=<BDAddress>,<ReplyType>,<Pincode>\r\n
Parameters:
BDAddress(6 bytes) – Remote BD Address.
ReplyType(1 byte) –
0 – negative reply
1 – positive reply
Reserved - Padding
Pincode(16 bytes) – Entered Pincode number(must be in string format max string length is 16 bytes).
Response:
Page 55

RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 55 | Page
Result Code
Description
OK <role>
Command Success with valid response.
ERROR <Error_code>
Command Fail
AT command Ex:
at+rsibt_usrpincode= AA-BB-CC-DD-EE-FF,1,1234\r\n
Response:
OK\r\n
6.3.18 Get Local Device Role
Description:
This gets the role of the local BT module when connected with a particular remote BT device, based on BD address of
the remote BT device.
AT command format:
at+rsibt_getmasterslaverole=<BDAddress>?\r\n
Parameters:
BDAddress (6 bytes)– Remote BD Address
Response:
Result Code
Description
OK <role>
Command Success with valid response.
ERROR <Error_code>
Command Fail.
Response Parameters:
Role(1 byte) –
0 – Master role
1 – slave role
AT command Ex:
at+rsibt_getmasterslaverole= AA-BB-CC-DD-EE-FF?\r\n
Response:
OK 1\r\n
6.3.19 Set Local Device Role Or Switch The Role
Description:
This is used to change the current role of the local BT module with respect to the remote BT device.
AT command format:
at+rsibt_setmasterslaverole=<BDAddress>,<Role>\r\n
Parameters:
BDAddress (6 bytes)– Remote BD Address
Role(1 byte) - 0 – Master role
1 – Slave role
AT command Ex:
at+rsibt _setmasterslaverole=AA-BB-CC-DD-EE-FF,1\r\n
Response:
OK\r\n
6.3.20 Get Service List
Description:
Page 56

RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 56 | Page
This is used to search for the services supported by the remote BT device.
AT command format:
at+rsibt_getsrvs=<BDAddress>\r\n
Parameters:
BDAddress(1 byte) – Remote BD Address
Response:
AT Mode:
Result Code
Description
OK <bd_addr>,<nbr_srvs_found>,<srv_uuid_1>,<srv_uuid_2>,…….
Command Success with valid response.
ERROR <Error_code>
Command Fail.
Parameters:
NumberOfServices (1 byte)– Number of services in the list
ServiceUUIDs (4 bytes)– list of service UUID's
Note:
It will display only 32-bit UUID's
AT command Ex:
at+rsibt_getsrvs= AA-BB-CC-DD-EE-FF \r\n
Response:
OK\r\n
6.3.21 Search Service
Description:
This is used to find whether a particular service is supported by the remote BT device.
AT command format:
at+rsibt_searchsrv=<BDAddress>,<ServiceUUID>\r\n
Parameters:
BDAddress (6 bytes)– Remote BD Address
ServiceUUID – 16-bit or 32-bit UUID.
Response:
AT Mode:
Result Code
Description
OK <search_result>
Command Success with valid response.
ERROR <Error_code>
Command Fail.
Response parameters:
Search status(1 byte): 1-Yes, 0-No
AT command Ex:
at+rsibt_searchsrv= AA-BB-CC-DD-EE-FF,1105\r\n
Response:
OK 1\r\n
6.3.22 Linkkey Reply
Description:
Page 57

RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 57 | Page
The link key reply is used to respond on a link key request event. If previous link key of connecting device available
then need to respond with positive reply, else send negative reply.
AT command format:
at+rsibt_usrlinkkey=<BDAddress>,<ReplyType>,<LinkKey>\r\n
Parameters:
BDAddress (6 bytes)– Remote BD Address.
ReplyType(1 byte) –
0 – negitive reply
1 – positive reply
LinkKey(16 bytes) – Link key saved for the remote BD address in host.
AT command Ex:
at+rsibt_usrlinkkey=AA-BB-CC-DD-EE-FF,1,3C,A5,50,25,DC,D0,B0,AB,B7,C3,4F,4D,9,79,2C,5C\r\n
Response:
OK\r\n
6.3.23 Set SSP Mode
Description:
Set SSP mode is used to enable Simple Secure Pair mode and also used to select the IO Capability for SSP mode.
AT command format:
at+rsibt_setsspmode=<PairMode>,<IOCapability>\r\n
Parameters:
PairMode(1 byte)–
0 – Disable
1 - Enable
IOCapability(1 byte) –
0x00 - DisplayOnly
0x01 - DisplayYesNo
0x02 - KeyboardOnly
0x03 - NoInputNoOutput
AT command Ex:
at+rsibt_setsspmode=1,1\r\n
Response:
OK\r\n
6.3.24 Sniff Mode
Description:
Enables the Host to support a low-power policy and allows the devices to enter Inquiry Scan, Page Scan, and a
number of other possible actions.
The local device will return the actual sniff interval in the Interval parameter of the Mode Change event, if the
command is successful.
AT command format:
at+rsibt_sniffmode=<BDAddress>,<SniffMaxIntr>,<SniffMinIntr>,<SniffAttempt>,<sniffTimeout>\r\n
Parameters:
bd_addr(6 bytes)- Remote BD Address.
SniffMaxIntr(2 bytes) & SniffMinIntrv (2 bytes)- The Sniff_Max_Interval and Sniff_Min_Interval command parameters
are used to specify the requested acceptable maximum and minimum periods in the Sniff Mode.
SniffAttempt(2 bytes)- Master shall poll the slave at least once in the sniff attempt transmit slots starting at each sniff
anchor point.
SniffTimeout(2 bytes)- Timeout after which device enter sniff subrating mode.
AT command Ex:
at+rsibt_sniffmode= AA-BB-CC-DD-EE-FF,192,160,4,2\r\n
Page 58

RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 58 | Page
Response:
OK\r\n
6.3.25 Sniff Exit
Description:
To end the Sniff mode.
AT command format:
at+rsibt_sniffexit=<BDAddress>\r\n
Parameters:
BDAddress(6 bytes)- Remote BD Address.
AT command Ex:
at+rsibt_sniffexit= AA-BB-CC-DD-EE-FF \r\n
Response:
OK\r\n
6.3.26 Sniff Subrating
Note:
Currently, the sniff subrating command is not supported.
Description:
When the sniff mode timeout has expired a device shall enter sniff subrating mode. Sniff subrating mode allows a
device to use a reduced number of sniff anchor points.
AT command format:
at+rsibt_sniffsubrating=< BDAddress >,< MaxLatency>,<MinRemoteTimeout >,< MinLocalTimeout >\r\n
Parameters:
BDAddress(6 bytes)- Remote BD Address.
maximum_latency(2 bytes)- Maximum allowed sniff subrate of the remote device.
minimum_remote_timeout(2 bytes)- Minimum base sniff subrate timeout that the remote device may use
minimum_local_timeout(2 bytes)- Minimum base sniff subrate timeout that the local device may use.
AT command Ex:
at+rsibt_sniffsubrating= AA-BB-CC-DD-EE-FF , 192,1000,1000\r\n
Response:
OK\r\n
6.3.27 Add Device ID
Description:
Add device Identification in SDP protocol.
AT command format:
at+rsibt_adddeviceid=<SpecificationID>,<VendorID>,<ProductID>,<Version>,<PrimaryRecord>,<VendorIDSource>\r\
n
Parameters:
SpecificationID(2 bytes) - the version number of the Bluetooth Device ID Profile specification supported by the device.
VendorID (2 bytes)- uniquely identify vendor of the device.
ProductID(2 bytes) - to distinguish between different products made by the vendor
Version(2 bytes) - A numeric expression identifying the device release number in Binary-Coded Decimal
Page 59

RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 59 | Page
PrimaryRecord(INT BOOL) - Set to TRUE in the case single Device ID Service Record exists in the device.
If multiple Device ID Service Records exist, and no primary record has been defined, set to FALSE.
VendorIDSource(2 bytes) - This attribute designates which organization assigned the VendorID attribute, 0x201.
AT command Ex:
at+rsibt_adddeviceid=512,513,514,515,1,2 \r\n
Response:
OK\r\n
6.4 SPP commands
Note:
SPP profile will not connect without pair process or authentication.
6.4.1 SPP Connect
Description:
This is used to establish SPP connection with the remote BT device specified by the BD address.
AT command format:
at+rsibt_sppconn=<BDAddress>\r\n
Parameters:
BDAddress(6 bytes) – Remote BD address.
AT command Ex:
at+rsibt_sppconn= AA-BB-CC-DD-EE-FF\r\n
Response:
OK\r\n
6.4.2 SPP Disconnect
Description:
This is used to disconnect the SPP connection with the remote BT device.
AT command format:
at+rsibt_sppdisconn=<BDAddress>\r\n
Parameters:
BDAddress(6 bytes) – Remote BD address
AT command Ex:
at+rsibt_sppdisconn= AA-BB-CC-DD-EE-FF \r\n
Response:
OK\r\n
6.4.3 SPP Transfer
Description:
This is used to send data to the remote BT device using SPP profile. This command contains a data length field which
tells the BT module about the length of data in bytes user wants to send from the application.
AT command format:
at+rsibt_spptx=<DataLength>,<Data>\r\n
Parameters:
DataLength(1 byte) – SPP data length (range of Data length is 1 to 200 Bytes).
Data(200 bytes) – SPP data.
Page 60

RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 60 | Page
AT command Ex:
at+rsibt_spptx=5,iiiii\r\n
Response:
OK\r\n
6.5 Core Events
6.5.1 User Linkkey Save
Description:
This event is raised when a device is paired and linkkey for remote BT Device is given to host.
AT Event Format:
AT+RSIBT_USRLNKKEYSAVE < BDAddress ><LinkKey>\r\n
Parameters:
BDAddress – BD Address of the remote BT device.
LinkKey – Link key for the remote BT device.
AT event Ex:
AT+RSIBT_USRLINKKEYSAVE AA-BB-CC-DD-EE-FF,3C,A5,50,25,DC,D0,B0,AB,B7,C3,4F,4D,9,79,2C,5C\r\n
6.5.2 Auth Complete
Description:
This event tells about the status of authentication process.
AT Event Format:
AT+RSIBT_AUTHENTICATION_STATUS < BDAddress >, <STATUS>, <ERROR>\r\n
Parameters:
BDAddress – BD Address of the remote device.
6.5.3 Mode Change
Description:
This event occurs when sniff mode is enable by either remote device or local device and it is raised to indicate
whenever the device changes between Active mode and Sniff mode.
AT Event Format:
AT+RSIBT_MODECHANGED < BDAddress >,<current mode>,< ModeInterval >\r\n
Parameters:
BDAddress – BD Address of the remote BT device.
CurrentMode - State the connection is currently in.
0 - Active mode
1 - Hold mode (currently Not supported)
2 - Sniff mode
Mode Interval - Specify a time amount specific to each state. Time Range: 2-65534
AT event Ex:
AT+RSIBT_MODECHANGED AA-BB-CC-DD-EE-FF,1,192\r\n
Page 61

RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 61 | Page
6.5.4 Disconnected
Description:
This event is raised when disconnection happens between the local BT device and the remote device.
AT Event Format:
AT+RSIBT_DISCONNECTED < BDAddress>,<reason>\r\n
Parameters:
BDAddress – BD address of the remote BT device.
AT event Ex:
AT+RSIBT_CLASSIC_DISCONNECTED AA-BB-CC-DD-EE-FF,0\r\n
Page 62

RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 62 | Page
7 BT Classic Error Codes
Generic Error Codes
Table 5: Generic Error Codes
Error Code
Description
0x4C01
BT_A2DP_ERR_PKT_ALLOC_FAILED
0x4C02
BT_A2DP_ERR_DMA_BUSY
0x4C03
BT_A2DP_ERR_INVALIED_M4_BUF
0x4C04
BT_A2DP_ERR_PKT_ADDED_QUEUE_FULL
0x4C05
BT_A2DP_ERR_QUEUE_PKT_NULL
0x4E01
Unknown HCI command
0x4E02
Unknown Connection Identifier
0x4E03
Hardware failure
0x4E04
Page timeout
0x4E05
Authentication failure
0x4E06
Pin missing
0x4E07
Memory capacity exceeded
0x4E08
Connection timeout
0x4E09
Connection limit exceeded
0x4E0A
SCO limit exceeded
0x4E0B
ACL Connection already exists
0x4E0C
Command disallowed
0x4E0D
Connection rejected due to limited resources
0x4E0E
Connection rejected due to security reasons
0x4E0F
Connection rejected for BD address
0x4E10
Connection accept timeout
0x4E11
Unsupported feature or parameter
0x4E12
Invalid HCI command parameter
0x4E13
Remote user terminated connection
0x4E14
Remote device terminated connection due to low resources
0x4E15
Remote device terminated connection due to power off
0x4E16
Local device terminated connection
0x4E17
Repeated attempts
0x4E18
Pairing not allowed
0x4E19
Unknown LMP PDU
0x4E1A
Unsupported remote feature
0x4E1B
SCO offset rejected
Page 63

RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 63 | Page
Error Code
Description
0x4E1C
SCO interval rejected
0x4E1D
SCO Air mode rejected
0x4E1E
Invalid LMP parameters
0x4E1F
Unspecified
0x4E20
Unsupported LMP Parameter
0x4E21
Role change not allowed
0x4E22
LMP response timeout
0x4E23
LMP transaction collision
0x4E24
LMP PDU not allowed
0x4E25
Encryption mode not acceptable
0x4E26
Link key cannot change
0x4E27
Requested QOS not supported
0x4E28
Instant passed
0x4E29
Pairing with unit key not supported
0x4E2A
Different transaction collision
0x4E2B
Reserved 1
0x4E2C
QOS parameter not acceptable
0x4E2D
QOS rejected
0x4E2E
Channel classification not supported
0x4E2F
Insufficient security
0x4E30
Parameter out of mandatory range
0x4E31
Reserved 2
0x4E32
Role switch pending
0x4E33
Reserved 3
0x4E34
Reserved slot violation
0x4E35
Role switch failed
0x4E36
Extended Inquiry Response too large
0x4E37
Extended SSP not supported
0X4E38
Host busy pairing
0x4E39
Wrong BD Address
0x4e3C
ADVERTISING TIMEOUT
0x4E3E
Connection Failed to be Established
0x4FF8
BT Invalid Command
Page 64

RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 64 | Page
Core Error Codes
Table 6: Core Error Codes
Error Code
Description
0x4040
IO Fail
0x4041
Unknown
0x4042
HW Busy
0x4043
Max Sock
0x4044
Short Buf
0x4045
Max Name Size
0x4046
Invalid Args
0x4047
Sock open fail
0x4048
Timeout
0x4049
Socket state invalid
0x404A
Bad bd address
0x404B
Acl packet error
0x404C
Pool alloc fail
0x404D
Tx fail
0x404E
Connection refused
0x404F
Confirmation result
0x4050
Remote user disconnected
0x4051
Remote device not responding
0x4052
Invalid command
0x4053
Unsupported feature param value
0x4054
Thread create fail
0x4055
Sem wait fail
0x4056
Pool full
0x4057
Hw buffer overflow
0x4058
Tx buffer empty
0x4059
HCI connection fail
0x405A
Operation incomplete
0x405B
Operation cancel
0x405C
BSP error
0x4060
Sco connection fail
0x4061
No HCI connection
0x4062
Socket disconnected
0x4063
Socket timeout
Page 65

RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 65 | Page
Error Code
Description
0x4064
HCI connection encrypt fail
0x4065
Max acl packet buffer length
0x4066
Max nbr acl packets
0x4067
Invalid state
0x4069
Remote name fail
0x406A
Invalid response
0x4071
Invalid psm
0x4072
Psm in use
0x4073
Invalid hci connection handle
0x4074
Invalid cid
0x4075
Invalid pkt
0x4080
Scn is in use
0x4081
Max acl connections
0x4082
Sock already exists
0x4100
Invalid pdu
0x4101
Invalid pdu data element
0x4102
Sdp service not found
0x4103
Sdp attribute not found
0x4104
Sdp max service attribute
0x4200
Max RF communication channels
0x4201
RF communication disconnected
0x4202
RF communication channel not found
0x4203
RF communication invalid packet
0x4204
RF communication remote credits zero
0x4205
RF communication invalid state
0x4206
RF communication fcoff
0x4207
RF communication no service connection
0x4300
HCI connection already exists
0x4301
Max hci connection
0x4302
SCO invalid state
0x0102
Unknown
0x0103
Firmware Timeout
0x0104
Memory alloc fail
0x0106
Io fail
0x0108
Unsupported
Page 66

RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 66 | Page
Error Code
Description
0x0109
Short buf
0x010A
Buf overflow
0x010B
Too large buf
0x010C
Io abort
0x010D
File open fail
0x1010
Os task invalid prio
0x1011
Os task prio exists
0x1012
Os task not stopped
0x1020
Os sem max value
0x1021
Os sem not available
0x1022
Os sem reset
0x1030
Os mutex not owner
0x1031
Os mutex not locked
0x1032
Os mutex lock failed
0x1033
Os mutex try lock failed
0x1040
Os msg queue full
0x1041
Os message queue empty
0x1050
Pipe empty
0x1051
Pipe full
0x1052
Invalid len
0x1053
Pipe read in use
0x1054
Pipe write in use
0x1060
Os timer expired
0x1061
Os timer state running
0x1070
Os can not wait
0x1080
Os mem pool empty
0x1081
Os mem pool size short
0x4500
SPP not connected
0x4501
SPP not initialized
0x4FF9
Inquiry cancel command is given when device is not in Inquiry State
0x4604
SPP Tx FAIL
Page 67

RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 67 | Page
Queue Error Codes
Table 7: Queue Error Codes
Error Code
Description
0x1090
OS Event queue full
0x1091
OS Event not available
0x1092
OS Event not created
0x1093
OS Event prio not created
0x1094
OS Event no event created
IAP Error Codes
Table 8: IAP Error Codes
Error Code
Description
0x8000
ERR_IAP1_SUCCESS
0x8001
ERR_IAP1_UNKNOWN_DATABASE
0x8002
ERR_IAP1_COMMAND_FAILED
0x8003
ERR_IAP1_DEVICE_OUTOF_RESOURCE
0x8004
ERR_IAP1_BAD_PARAM
0x8005
ERR_IAP1_UNKNOWN_ID
0x8006
ERR_IAP1_COMMAND_PENDING
0x8007
ERR_IAP1_NOT_AUTHENTICATED
0x8008
ERR_IAP1_BAD_AUTHENTICATION_VERSION
0x8009
ERR_IAP1_ACCESSORY_PWR_REQ_FAILED
0x800A
ERR_IAP1_CERTIFICATE_INVALID
0x800B
ERR_IAP1_CERTIFICATE_PERMISSION_FAILED
0x800C
ERR_IAP1_FILE_IN_USE
0x800D
ERR_IAP1_INVALID_FILE_HANDLE
0x800E
ERR_IAP1_DIRECTORY_NOT_EMPTY
0x800F
ERR_IAP1_OPERATION_TIMED_OUT
0x8010
ERR_IAP1_COMMAND_UNAVAILABLE
0x8011
ERR_IAP1_ACC_DETECT_NOT_GROUNDED
0x8012
ERR_IAP1_SELECTION_NOT_GENIUS
0x8013
ERR_IAP1_MULTISECTION_DATA_RECV_SUCCESS
0x8014
ERR_IAP1_LINGO_BUSY
0x8015
ERR_IAP1_MAX_ACCESSORY_CONN_REACHED
0x8016
ERR_IAP1_HID_DESC_INDEX_INUSE
0x8017
ERR_IAP1_DROPPED_DATA
Page 68

RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 68 | Page
Error Code
Description
0x8018
ERR_IAP1_UNSUPPORTED_IPODOUT_VIDEO_SETTINGS
0x8100
ERR_IAP1_IDPS_SUCCESS
0x8101
ERR_IAP1_IDPS_TKN_FIELDS_REJECTED
0x8102
ERR_IAP1_IDPS_TKN_FIELDS_MISSING
0x8103
ERR_IAP1_IDPS_TKN_FIELDS_INCORRECT_RESEND
0x8104
ERR_IAP1_IDPS_ACCESSORY_MAY_RETRY
0x8105
ERR_IAP1_IDPS_TIMEOUT
0x8106
ERR_IAP1_IDPS_NOT_SUPPORTED
0x8107
ERR_IAP1_IDPS_INVALID_TKN_FIELDS
0x8300
ERR_IAP_CP_SUCCESS
0x8301
ERR_IAP_CP_INVALID_READ_REGISTER
0x8302
ERR_IAP_CP_INVALID_WRITE_REGISTER
0x8303
ERR_IAP_CP_INVALID_SIGNATURE_LEN
0x8304
ERR_IAP_CP_INVALID_CHALLENGE_LEN
0x8305
ERR_IAP_CP_INVALID_CERTIFICATE_LEN
0x8306
ERR_IAP_CP_SIGNATURE_GENERATION
0x8307
ERR_IAP_CP_CHALLENGE_GENERATION
0x8308
ERR_IAP_CP_SIGNATURE_VERIFICATION
0x8309
ERR_IAP_CP_CERITIFICATE_VERIFICATION
0x830A
ERR_IAP_CP_INVALID_PROCESS_CTRL
0x830B
ERR_IAP_CP_PROCESS_CTRL_OUTOF_SEQUENCE
0x83F0
ERR_IAP_CP_I2C_WRITE_FAILED
Page 69

RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 69 | Page
8 BT Power Save Operation
Description:
This feature explains the configuration of Power Save modes of the module. These modes can be issued at any time
after Opermode command. By default, Power Save is in disable state.
There are five different modes of Power Save.
1. Power Save mode 0
2. Power Save mode 2
3. Power Save mode 3
4. Power Save mode 8
5. Power Save mode 9
Power Save Operations
The behavior of the module differs according to the power save mode configured.
The following terminology can be used in below section in order to describe the functionality.
Protocol
Non-Connected State
Connected State
BT Classic
This mode is significant when module is
in Idle (standby) state.
This mode is significant when
module is in Connected
mode, connected sniff mode, Discoverable mode
(ISCAN) and Connectable
mode (PSCAN)
In BT classic, Power Save mode 2 and 3 can be used during PAGE SCAN (Connectable mode) /INQUIRY
SCAN(Discoverable mode) /Connected state. Operational behavior is as below depending on the state.
• Inquiry Scan State: In this state, the module is awake during Inquiry scan window duration and sleeps till the
next Inquiry scan interval
• Page Scan State: In this state, the module is awake during page scan window duration and sleeps till the next
page scan interval
• Connected state: In this state, the module wakes up randomly based on the data transfer. Sleep duration is
random in this state.
• Connected Sniff state: In this state, the module wakes up for every sniff anchor point and wake up until the sniff
timeout. Sleep duration depends on the sniff anchor point interval in this state.
Power Save Mode 0
In this mode the module is in active state and power save is disabled. It can be configured at any time while power
save is enable with Power Save mode 2 and 3 or Power Save mode 8 and 9.
Power Save Mode 2 (GPIO based mode)
Once the module is configured to power save mode 2, it can be woken up either by the host or periodically during its
sleep-wake up cycle based upon the connected state intervals.
Power mode 2 is GPIO based. In ULP mode, feature_bit_map[4]has to be set in opermode command. In this mode,
whenever host wants to send data to module, it gives wakeup indication by setting UULP GPIO #2. After wakeup, if
the module is ready for data transfer, it sends wakeup indication to host by setting UULP GPIO #3. Host is required to
wait until module gives wakeup indication before sending any data to the module.
After the completion of data transfer, host can give sleep permission to module by resetting UULP GPIO #2. After
recognizing sleep permission from host, module gives confirmation to host by resetting UULP GPIO #3 and again gets
back to its sleep-wake up cycle.
Module can send received packets or responses to host at any instant of time. No handshake is required on Rx path.
Page 70
RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 70 | Page
Power Save Mode 3 (Message-based Mode)
Power Mode 3 is message-based power save, both radio and SOC of the module are in power save mode.
Module wakes up periodically upon every deep sleep duration and gives wakeup message ("WKP") to host. Module
cannot be woken up asynchronously. Every time module intends to go to sleep it sends a sleep request message
("SLP") to the host and expects host to send the ack ("ACK") message. Host either sends ack ("ACK") or any other
pending message. But once ack ("ACK") is sent, Host should not send any other message unless next wakeup
message from module is received.
Module shall not go into complete power-save state if ack is not received from host for given sleep message. Module
can send received packets or responses to host at any instant of time. No handshake is required on Rx path.
AT mode
"WKP"
"SLP"
Message from Module in Power save Mode
AT mode
"ACK"
Message from host in Power save Mode
Note:
Power save disable command has to be given before changing the state from standby to the remaining states
and wise-versa.
Suppose if Power Save is enabled in standby state, in order to move to Scanning state, first Power Save
disable command needs to be issued before giving Scan command.
When the module is configured in a co-ex mode and WLAN is in INIT_DONE state, power save mode 2 & 3 are valid
after association in the WLAN. Whereas in BT & BLE alone modes, it will enter into power save mode (2 & 3) in all
states except in standby state.
Power Save Mode 8
This command has to be issued after the opermode command. Module should be in non-connected state before
giving this command. Please refer to the above table for the state description.
In Power Mode 8 both RF and SoC are in complete power save mode. This mode is significant when module is not
connected with any AP. Power mode 8 is GPIO based. In ULP mode, feature_bit_map[4]has to be set in opermode
command.
In case of LP (when ulp_mode_enable is '0') host can wakeup the module from power save by making ULP_GPIO_5
high.
In case of ULP (when ulp_mode_enable is '1' or '2') host can wakeup the module from power save by making
UULP_GPIO_2 high.
When ulp_mode_enable is set to '0' or '1', once the module gets wakeup it continues to be in wakeup state until it gets
power mode 8 commands from host.
When ulp_mode_enable is set to '2', after waking up from sleep module sends following message to host when RAM
retention is not enabled. After receiving this message host needs to start giving commands from beginning
(opermode) as module's state is not retained.
AT mode
"WKP FRM SLEEP"
Message from Module in ULP Mode 2
Page 71
RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 71 | Page
Power Save Mode 9
In Power Mode 9 both Radio and SoC are in complete power save mode. This command has to be issued after the
opermode command. Module should be in non-connected state before giving this command. Once power mode 9
command is given, the module goes to sleep immediately and wakes up after sleep duration configured by host. If
host does not set any default time, then the module wakes up in 1 sec by default. Upon wakeup module sends a
wakeup message to the host and expects host to give ACK before it goes into next sleep cycle. Host either sends
ACK or any other messages but once ACK is sent no other packet should be sent before receiving next wakeup
message.
When ulp_mode_enable is set to '2', after waking up from sleep, the module sends following message to host when
RAM retention is not enabled. After receiving this message, host needs to start giving commands from beginning
(opermode) as module's state is not retained.
AT mode
"WKP FRM SLEEP"
Message from Module in ULP Mode
Page 72
RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 72 | Page
9 BT AT CMD Configuration Changes/Enhancements
S.No
Configuration
Existing
Configuration
New/Modified
Configuration
Comments
1
384k mode is
mandatory from 2.X.X
release for any BT
use-case
256K mode was
supported
256K mode is no longer
supported. Only 384K
mode is supported from
2.X.X
Set BIT[20] and BIT[21] in
'ext_custom_feature_bit_map' parameter
in 'at+rsi_opermode' command.
Page 73

RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 73 | Page
10 Revision History
Revision
Number
Version
Number
Date
Changes
1
1.0
Nov 2017
Advance version
2
1.1
Feb 2018
Formatting changes
3
1.2
Apr 2018
Generalized for Wiseconnect and Wisemcu
4
1.3
Jun 2018
1. Old thread of figures was replaced with new ones,
2. Response codes are updated
3. Alignment issues are resolved
5
1.4
Jul 2018
1. Reviewed and updated Commands and event formats
2. Added command , command response and event id's
3. Structural changes are done
6
1.5
Sep 2018
1. Added ext_custom_feat_bitmap field and modified feature bitmap description
in opermode command
2. Added a2dp burst mode command and more data req event related
information
3. Added BT A2DP error commands
4. Added Device ID command
5. Segregation of features for different products
7
1.6
Mar 2019
Deleted the Zigbee section
8
1.7
May 2019
Added BT HID Device related commands
9
1.8
Jul 2019
Added BT HID Device related AT commands
10
1.9
Sep 2019
1. Updated BT feature bitmap for 3mbps, 2mpbs and Sniff mode configurations
2. Updated BT Feature bitmap for Sniff feature and Noise figure feature
configurations
11
1.10
Dec 2019
Added BLE CW mode support
12
1.11
Dec 2019
Added AT command to change the BLE MTU size
13
1.12
Feb 2020
Added a Note in EXT_TCP_IP_FEATURE_BITMAP in oper mode
Added configure_feature_bit_map in set operating mode
14
2.0
Sep 2020
1. Added AT mode based "HID conn process with SSP mode enabled".
2. Removed 'Related Resources' section.
3. Moved 'SPI Interface', 'UART Interface', 'USB Interface' sections to 'Host
Interfaces'.
4. Renamed document name from 'Embedded BT Classic Software
Programming Reference Manual (PRM)' to 'RS9116W BT Classic AT
Command Programming Reference Manual'.
5. Removed all Binary Commands.
6. Updated 384k mode.
7. Added note in BT Opermode command.
8. Added note in RSSI signal strength.
9. Removed SDIO, USB, SPI interfaces from Host Interfaces section.
Page 74

RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 74 | Page
Revision
Number
Version
Number
Date
Changes
10. Added 'Changes/Enhancements in BT AT Commands, Configurations and
Mechanisms' section.
11. Added length for each AT CMD (parameters and responses).
15
2.1
Feb 2021
1. Added BT Events/Commands for
USRLINKKEYSAVE, AUTHENTICATION_STATUS, MODECHANGED
and DISCONNECTED in Master BT Classic Commands.
2. Removed SPI and USB host interaction and Bypass Mode in SPI / USB
details from section 2 Bootloader.
3. Updated Section 5 BT Classic Command Format (A2DP, AVRCP and HFP
command/response/event IDs are not supported in this document version.)
4. Added description for config_feature_bitmap[25:24], refer to Section 6.1.1
Note: This document should be used with WiSeConnect version 2.3.0.
Page 75

RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 75 | Page
11 Appendix A: Sample Flows
1. Configure BT device in Master mode
Figure 19: Sample Flow in BT Master Mode while Link Key Reply is Negative
Page 76

RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 76 | Page
Figure 20: Sample Flow in BT Master Mode while Link Key Reply is Positive
Page 77

RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 77 | Page
2. Configure BT device in Slave mode
Figure 21: Sample Flow in BT Slave Mode
Page 78

RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 78 | Page
3. Configure BT device in Master Mode and do SPP Tx
Figure 22: Sample Flow in BT Master Mode and Do SPP Tx
Page 79

RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 79 | Page
4. Configure BT Device in Slave Mode and Do SPP Tx
Figure 23: Sample Flow in BT Slave Mode and Do SPP Tx
Page 80

RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 80 | Page
5. AT Command Sequence to Perform SPP Data Transfer in BT Master Mode
Figure 24: AT Command Flow in BT Master Mode
Page 81

RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 81 | Page
6. AT Command Sequence to Perform SPP Data Transfer in BT Slave Mode
Figure 25: AT Command Flow in BT Slave Mode
Page 82

RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 82 | Page
7. Configure Device in BT HID Device Mode to Perform HID Data Transfer
Figure 26: Sample Flow Configuring Device Mode and Perform HID Data Transfer
Page 83

RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 83 | Page
8. AT Command Sequence to Perform HID Data Transfer in BT HID Device Mode (without Secure Pairing
(SSP))
Figure 27: AT Command Flow in BT HID Device Mode (SSP Mode not Enabled)
Page 84

RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 84 | Page
9. AT Command Sequence to Perform HID Data Transfer in BT HID Device Mode (enabled Secure Pairing
(SSP))
Figure 28: AT Command Flow in BT HID Device Mode (SSP Mode Enabled)
Page 85

RS9116W BT Classic AT Command Programming Reference Manual
Version 2.1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. 85 | Page
http://www.silabs.com
 Loading...
Loading...