Page 1
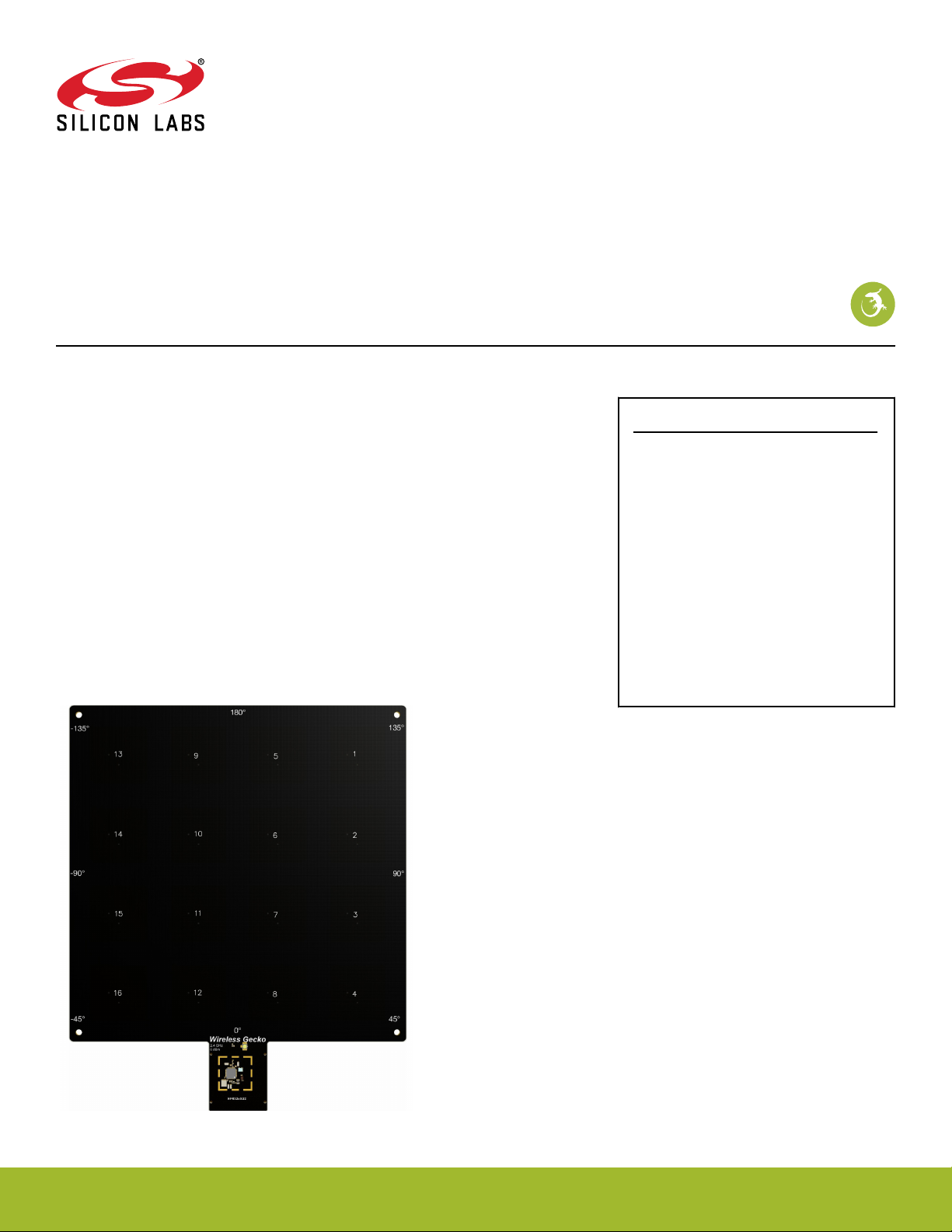
EFR32BG22 Direction Finding Radio
Board
BRD4185A Reference Manual
The BRD4185A Wireless Gecko Radio Board enables developers to develop RF-based
Real-Time Locationing Systems and applications, utilizing the protocol level support of
Angle of Arrival (AoA) and Angle of Departure (AoD) in Bluetooth 5. The board contains
a 2.4 GHz Wireless Gecko Wireless System-on-Chip, and an antenna array optimized
for accurate direction finding performance.
The BRD4185A Wireless Gecko Radio Board plugs into the Wireless Starter Kit Mainboard, which is included with the Wireless Gecko Starter Kit and gives access to debug
interface, Virtual COM port, packet trace, display, buttons, LEDs, and additional features
from expansion boards. With the supporting Simplicity Studio suite of tools, developers
can take advantage of graphical wireless application development and visual energy
profiling and optimization. The board also serves as an RF reference design for applications targeting Bluetooth 2.4 GHz AoA-based direction finding.
This document contains a brief introduction and description of the BRD4185A Radio
Board features, focusing on the RF sections and basic performance.
RADIO BOARD FEATURES
• Wireless SoC:
EFR32BG22C224F512IM40
•
CPU core: ARM® Cortex®-M33
• Flash memory: 512 kB
• RAM: 32 kB
• Operation frequency: 2.4 GHz
• Transmit power: 6 dBm
• Antenna array with PCB antennas
• UFL connector (optional)
• Crystals for LFXO and HFXO: 32.768 kHz
and 38.4 MHz
• 8 Mbit low-power serial flash for over-theair updates
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0
Page 2

Table of Contents
1. Introduction ................................4
2. Radio Board Connector ...........................5
2.1 Introduction ...............................5
2.2 Radio Board Connector Pin Associations .....................5
3. Radio Board Block Summary .........................6
3.1 Introduction ...............................6
3.2 Radio Board Block Diagram .........................6
3.3 Radio Board Block Description ........................6
3.3.1 Wireless MCU.............................6
3.3.2 LF Crystal Oscillator (LFXO) ........................6
3.3.3 HF Crystal Oscillator (HFXO)........................6
3.3.4 Matching Network for 2.4 GHz .......................6
3.3.5 UFL Connector ............................7
3.3.6 Radio Board Connectors .........................7
3.3.7 2.4 GHz Antenna Array..........................7
3.3.8 Serial EEPROM ............................7
4. RF Section ................................8
4.1 Introduction ...............................8
4.2 Schematic of the RF Matching Network......................8
4.2.1 Description of the 2.4 GHz RF Matching ....................8
4.3 Bill of Materials for the 2.4 GHz Matching .....................8
4.4 Antenna Array ..............................8
5. Mechanical Details ............................ 10
6. EMC Compliance ..............................11
6.1 Introduction ...............................11
6.2 EMC Regulations for 2.4 GHz .........................11
6.2.1 ETSI EN 300-328 Emission Limits for the 2400-2483.5 MHz Band ...........11
6.2.2 FCC15.247 Emission Limits for the 2400-2483.5 MHz Band .............11
6.2.3 Applied Emission Limits for the 2.4 GHz Band ..................11
7. RF Performance ............................. 12
7.1 Conducted Power Measurements .......................12
7.1.1 Conducted Power Measurements with Unmodulated Carrier .............12
7.1.2 Conducted Power Measurements with Modulated Carrier ..............13
7.2 Radiated Power Measurements ........................14
7.2.1 Maximum Radiated Power Measurements ...................15
7.2.2 Antenna Pattern Measurements.......................15
8. EMC Compliance Recommendations ..................... 16
8.1 Recommendations for 2.4 GHz ETSI EN 300-328 Compliance ..............16
silabs.com
| Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 2
Page 3

8.2 Recommendations for 2.4 GHz FCC 15.247 Compliance ................16
9. Board Revision History .......................... 17
10. Errata................................. 18
11. Document Revision History ........................ 19
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 3
Page 4

BRD4185A Reference Manual
Introduction
1. Introduction
The EFR32™ Wireless Gecko Radio Boards provide a development platform (together with the Wireless Starter Kit Mainboard) for the
Silicon Labs EFR32 Wireless Gecko Wireless System-on-Chips and serve as reference designs for the matching network of the RF
interface.
The BRD4185A Radio Board is designed to operate in the 2400-2483.5 MHz band with the RF matching network optimized for operating at 6 dBm output power, and the on-board antenna array optimized for accurate direction finding perfromance.
To develop and/or evaluate the EFR32 Wireless Gecko, the BRD4185A Radio Board can be connected to the Wireless Starter Kit Mainboard to get access to debug interface, Virtual COM port, packet trace, display, buttons, LEDs, and additional features from expansion
boards, and also to evaluate the performance of the RF interface and the direction finding accuracy.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 4
Page 5
GND
F9 / PA07 / VCOM_RTS
3v3
NC / P36
P200
Upper Row
NC / P38
NC / P40
DBG_TDO_SWO / PA03 / P42
NC / P44
DBG_TMS_SWDIO / PA02 / F0
VCOM_ENABLE / DISP_ENABLE / PB04 / F14
UIF_BUTTON0 / PB00 / F12
UIF_LED0 / PB02 / F10
VCOM_CTS / PA08 / F8
DBG_RESET / #RESET / F4
DBG_TDO_SWO / PA03 / F2
DISP_MOSI / PC00 / F16
VCOM_TX / PA05 / F6
PTI_DATA / PD02 / F20
DISP_EXTCOMIN / PA00 / F18
USB_VBUS
5V
Board ID SCL
GND
Board ID SDA
USB_VREG
F7 / PA06 / VCOM_RX
F5 / PB04 / VCOM_ENABLE / DISP_ENABLE
F3 / PA04 / DBG_TDI*
F1 / PA01 / DBG_TCK_SWCLK
P45 / NC
P43 / NC
P41 / PA04 / DBG_TDI*
P39 / NC
P37 / NC
F11 / PB03 / UIF_LED1
F13 / PB01 / UIF_BUTTON1
F15 / PC02 / DISP_SCLK
F17 / PC03 / DISP_SCS
F19 / PD03 / PTI_SYNC
F21 / NC
GND
VMCU_IN
VCOM_CTS / PA08 / P0
P201
Lower Row
VCOM_RTS / PA07 / P2
UIF_BUTTON0 / PB00 / P4
UIF_BUTTON1 / PB01 / P6
GND
VRF_IN
P35 / PC07
P7 / PC03 / DISP_SCS
P5 / PC02 / DISP_SCLK
P3 / PC01
P1 / PC00 / DISP_MOSI
P33 / PC06
P31 / PC05
P29 / PC04
P27 / PD03 / PTI_SYNC
P25 / PD02 / PTI_DATA
P23 / NC
P21 / NC
P19 / NC
P17 / NC
P15 / PB04 / VCOM_ENABLE / DISP_ENABLE
P13 / NC
P11 / PA06 / VCOM_RX
P9 / PA05 / VCOM_TX
NC / P34
NC / P32
NC / P30
NC / P28
NC / P26
NC / P24
DBG_TDI* / PA04 / P22
DBG_TDO_SWO / PA03 / P20
DBG_TMS_SWDIO / PA02 / P18
DBG_TCK_SWCLK / PA01 / P16
DISP_EXTCOMIN / PA00 / P14
NC / P12
UIF_LED1 / PB03 / P10
UIF_LED0 / PB02 / P8
*Optional 0R resistor should be mounted to enable this connection. (Mutually exclusive with FLASH_SCS.)
BRD4185A Reference Manual
Radio Board Connector
2. Radio Board Connector
2.1 Introduction
The board-to-board connector scheme allows access to all EFR32BG22 GPIO pins as well as the RESETn signal. For more information
on the functions of the available pins, see the EFR32BG22 data sheet.
2.2 Radio Board Connector Pin Associations
The figure below shows the mapping between the connector and the EFR32BG22 pins and their function on the Wireless Starter Kit
Mainboard.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 5
Figure 2.1. BRD4185A Radio Board Connector Pin Mapping
Page 6

3. Radio Board Block Summary
2.4 GHz RF
UFL
Connector
LF
Crystal
32.768k
HF
Crystal
38.4M
Radio
Board
Connectors
I2C
24AA024
Serial
EEPROM
Matching
Network &
Output
Selection
GPIO
UART
Debug
Packet Trace
AEM
I2C
SPI
2.4 GHz RF
EFR32
EFR32
Wireless SoC
8 Mbit
MX25R
Serial Flash
SPI
RF
Switches
GPIO
Antenna Array
2.4 GHz RF
2.4 GHz RF
3.1 Introduction
This section introduces the blocks of the BRD4185A Radio Board.
3.2 Radio Board Block Diagram
The block diagram of the BRD4185A Radio Board is shown in the figure below.
BRD4185A Reference Manual
Radio Board Block Summary
Figure 3.1. BRD4185A Block Diagram
3.3 Radio Board Block Description
3.3.1 Wireless MCU
The BRD4185A Wireless Gecko Radio Board incorporates an EFR32BG22C224F512IM40 Wireless System-on-Chip featuring 32-bit
Cortex®-M33 core, 512 kB of flash memory, 32 kB of RAM and a 2.4 GHz band transceiver with output power up to 6 dBm. For addi-
tional information on the EFR32BG22C224F512IM40, refer to the EFR32BG22 Data Sheet.
3.3.2 LF Crystal Oscillator (LFXO)
The BRD4185A Radio Board has a 32.768 kHz crystal mounted. For details regarding the crystal configuration, refer to application note
AN0016.2: Oscillator Design Considerations.
3.3.3 HF Crystal Oscillator (HFXO)
The BRD4185A Radio Board has a 38.4 MHz crystal mounted. For details regarding the crystal configuration, refer to application note
AN0016.2: Oscillator Design Considerations.
3.3.4 Matching Network for 2.4 GHz
The BRD4185A Radio Board incorporates a 2.4 GHz matching network which connects the 2.4 GHz RF input/output of the
EFR32BG22 to the one on-board printed Inverted-F antenna. The component values were optimized for the 2.4 GHz band RF performance and current consumption with 6 dBm output power.
For detailed description of the matching network, see section 4.2.1 Description of the 2.4 GHz RF Matching.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 6
Page 7

BRD4185A Reference Manual
Radio Board Block Summary
3.3.5 UFL Connector
To be able to perform conducted measurements, Silicon Labs added a UFL connector to the Radio Board. The connector allows an
external 50 Ohm cable or antenna to be connected during design verification or testing.
Note: By default, the output of the matching network is connected to the printed inverted-F antenna by a series 0 Ohm resistor. To
support conducted measurements, or the connection of an external antenna, there is option to connect the output to the UFL connector.
For this, the series 0 Ohm resistor to the antenna should be moved to the position of the series resistor to the UFL connector (see
section 4.2.1 Description of the 2.4 GHz RF Matching for further details). On the layout, the footprints of these two resistors have overlapping pads to prevent simultaneous connection of the antenna and the UFL connector.
3.3.6 Radio Board Connectors
Two dual-row, 0.05” pitch polarized connectors make up the BRD4185A Radio Board interface to the Wireless Starter Kit Mainboard.
For more information on the pin mapping between the EFR32BG22C224F512IM40 and the Radio Board Connector, refer to section
2.2 Radio Board Connector Pin Associations.
3.3.7 2.4 GHz Antenna Array
The BRD4185A Radio Board incorporates an antenna array, that is optimized for the accurate direction finding performance. For detailed description of the antenna matrix, see section 4.4 Antenna Array
3.3.8 Serial EEPROM
The BRD4185A Radio Board is equipped with a serial I2C EEPROM for board identification and to store additional board-related information.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 7
Page 8

4. RF Section
PAVDD
VDCDC
GND
GNDGND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
ANTO_Common
C2
L102
BLM18AG102SN1
1 2
CC1
P2
U.FL
3
2
1
X1
38.4 MHz
31
2
4
C1
L103
BLM18AG102SN1
1 2
C3
C105
120P
Ground
RF I/ORF Crystal
RF Analog Power
PA Power
U1B
EFR32BG22
RF2G4_IO
14
RFVDD
12
HFXTAL_I
9
HFXTAL_O
10
PAVDD
15
RFVSS
13
C106
100N
C102
100N
R1
0R
C101
120P
L1
R2
0R
NM
50R_P2
50R_CC1 50R_R1
2.4 GHz
Matching
Network
Path
Selection
Supply
Filtering
UFL
Connector
High
Frequency
Crystal
Output to the
Antenna Array
4.1 Introduction
This section gives a short introduction to the RF section of the BRD4185A Radio Board.
4.2 Schematic of the RF Matching Network
The schematic of the RF section of the BRD4185A Radio Board is shown in the following figure.
Figure 4.1. Schematic of the RF Section of the BRD4185A
BRD4185A Reference Manual
RF Section
4.2.1 Description of the 2.4 GHz RF Matching
The 2.4 GHz RF matching connects the RF2G4_IO pin to the on-board printed Inverted-F Antenna. The component values were optimized for the 2.4 GHz band RF performance and current consumption with the targeted 6 dBm output power.
The matching network consists of a three-element impedance matching and harmonic filter circuitry and a DC blocking capacitor.
For conducted measurements the output of the matching network can also be connected to the UFL connector by removing the series
R1 resistor between the antenna and the output of the matching and adding a 0 Ohm resistor to the R2 resistor position between the
output of the matching and the UFL connector.
4.3 Bill of Materials for the 2.4 GHz Matching
The Bill of Materials of the 2.4 GHz matching network of the BRD4185A Radio Board is shown in the following table.
Table 4.1. Bill of Materials for the BRD4185A 2.4GHz RF Matching Network
Component Name Value Manufacturer Part Number
L1 2.6 nH Murata LQP03HQ2N6B02
C1 1.2 pF Murata GRM0335C1H1R2WA01D
C2 1.3 pF Murata GRM0335C1H1R3BA01D
CC1 18 pF Murata GJM0335C1E180GB01D
C3 Not Mounted - -
4.4 Antenna Array
The BRD4185A Radio Board includes an on-board antenna array, which consists of 16 rectangular patch antennas in a 4x4 matrix. The
antennas are optimized for the 2.4 GHz band. The dimensions, the feeding structure (50 Ohm transmission lines, printed hybrid couplers), and the arrangement of the antennas, together with the PCB stackup, are carefully designed to occupy relatively small PCB
area, while achieving accurate direction finding performance.
For detailed description of the antenna array, and its direction finding performance, refer to application note AN1195: Antenna Array
Design Guidelines for Direction Finding.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 8
Page 9

13
ANT9
ANT14 ANT10
ANT15 ANT11
ANT16 ANT12
ANT5 ANT1
ANT6 ANT2
ANT7 ANT3
ANT8 ANT4
ANT13
BRD4185A Reference Manual
RF Section
On the BRD4185A Radio Board the antennas are selected through five Single Pole Quad Through RF switches, that are controlled by
the GPIOs of the EFR32BG22 as shown in the figure below.
Antenna PC04 PC05 PC06 PC07
ANT1 L L L L
ANT2 H L L L
ANT3 L H L L
ANT4 H H L L
ANT5 L L H L
ANT6 H L H L
ANT7 L H H L
ANT8 H H H L
ANT9 L L L H
ANT10 H L L H
ANT11 L H L H
ANT12 H H L H
ANT13 L L H H
ANT14 H L H H
ANT15 L H H H
ANT16 H H H H
Figure 4.2. Antenna Selection
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 9
Page 10

5. Mechanical Details
2.4 GHz
Matching
Network
Frame
of the
Optional
Shielding
Can
EFR32xG22
LFXTAL
HFXTAL
PAVDD
Supply
Filtering
RFVDD
Supply
Filtering
RF Output
Selection
DCDC
Inductor
DCDC &
Supply
Filter
Caps.
OTA
Flash
UFL
Connector
170 mm
205 mm
170 mm
70 mm
30 mm
Patch Antenna Array
13
24 mm
5 mm
Interface
Connector
Interface
Connector
27.3 mm
28.6 mm
15 mm
Board
Identification
PAVDD
Supply
Selection
Antenna
Switches
PA04 to
DBG_TDI
Selection
Display
Enable
Selection
The BRD4185A Radio Board is illustrated in the figures below.
BRD4185A Reference Manual
Mechanical Details
Figure 5.1. BRD4185A Top View
Figure 5.2. BRD4185A Bottom View
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 10
Page 11

BRD4185A Reference Manual
EMC Compliance
6. EMC Compliance
6.1 Introduction
Compliance of the fundamental and harmonic levels of the BRD4185A Radio Board is tested against the following standards:
• 2.4 GHz:
• ETSI EN 300-328
• FCC 15.247
6.2 EMC Regulations for 2.4 GHz
6.2.1 ETSI EN 300-328 Emission Limits for the 2400-2483.5 MHz Band
Based on ETSI EN 300-328, the allowed maximum fundamental power for the 2400-2483.5 MHz band is 20 dBm EIRP. For the unwanted emissions in the 1 GHz to 12.75 GHz domain, the specific limit is -30 dBm EIRP.
6.2.2 FCC15.247 Emission Limits for the 2400-2483.5 MHz Band
FCC 15.247 allows conducted output power up to 1 W (30 dBm) in the 2400-2483.5 MHz band. For spurious emissions, the limit is
-20 dBc based on either conducted or radiated measurement, if the emission is not in a restricted band. The restricted bands are specified in FCC 15.205. In these bands, the spurious emission levels must meet the levels set out in FCC 15.209. In the range from
960 MHz to the frequency of the 5th harmonic, it is defined as 0.5 mV/m at 3 m distance which equals to -41.2 dBm in EIRP.
If operating in the 2400-2483.5 MHz band, the 2nd, 3rd, and 5th harmonics can fall into restricted bands. As a result, for those harmonics the -41.2 dBm limit should be applied. For the 4th harmonic the -20 dBc limit should be applied.
6.2.3 Applied Emission Limits for the 2.4 GHz Band
The above ETSI limits are applied both for conducted and radiated measurements.
The FCC restricted band limits are radiated limits only. In addition, Silicon Labs applies the same restrictions to the conducted spectrum. By doing so, compliance with the radiated limits can be estimated based on the conducted measurement, by assuming the use of
an antenna with 0 dB gain at the fundamental and the harmonic frequencies.
The overall applied limits are shown in the table below. For the harmonics that fall into the FCC restricted bands, the FCC 15.209 limit is
applied. ETSI EN 300-328 limit is applied for the rest.
Table 6.1. Applied Limits for Spurious Emissions for the 2.4 GHz Band
Harmonic Frequency Limit
2nd 4800~4967 MHz -41.2 dBm
3rd 7200~7450.5 MHz -41.2 dBm
4th 9600~9934 MHz -30.0 dBm
5th 12000~12417.5 MHz -41.2 dBm
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 11
Page 12

BRD4185A Reference Manual
RF Performance
7. RF Performance
7.1 Conducted Power Measurements
During measurements, the BRD4185A Radio Board was attached to a Wireless Starter Kit Mainboard which was supplied by USB. The
voltage supply for the Radio Board was 3.3 V.
7.1.1 Conducted Power Measurements with Unmodulated Carrier
The transceiver was operated in unmodulated carrier transmission mode. The output power of the radio was set to 6 dBm. The typical
output spectrums are shown in the following figures.
Figure 7.1. Typical Output Spectrum of the BRD4185A; PAVDD = 3.3 V
As shown in the figure, the fundamental is close to 6 dBm and all of the unwanted emissions are under the -41.2 dBm limit.
Note: The conducted measurement is performed by connecting the on-board UFL connector to a Spectrum Analyzer through an SMA
Conversion Adapter (P/N: HRMJ-U.FLP(40)). This connection itself introduces approximately 0.3 dB insertion loss.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 12
Page 13

BRD4185A Reference Manual
RF Performance
7.1.2 Conducted Power Measurements with Modulated Carrier
Depending on the applied modulation scheme, and the Spectrum Analyzer settings specified by the relevant EMC regulations, the
measured power levels are usually lower compared to the results with unmodulated carrier. These differences will be measured and
used as relaxation factors on the results of the radiated measurement performed with unmodulated carrier. This way, the radiated compliance with modulated transmission can be evaluated.
In this case, both the ETSI EN 300-328 and the FCC 15.247 regulations define the following Spectrum Analyzer settings for measuring
the unwanted emissions above 1 GHz:
• Detector: Average
• RBW: 1 MHz
The table below shows the measured differences in case of the supported modulation schemes.
Table 7.1. Measured Relaxation Factors for the Supported Modulation Schemes
Applied Modulation
(Packet Length:
255 bytes)
BLE Coded PHY:
125 Kb/s (PRBS9) [dB]
BLE Coded PHY:
500 Kb/s (PRBS9) [dB]
BLE 1M PHY: 1 Mb/s
(PRBS9) [dB]
BLE 2M PHY: 2 Mb/s
(PRBS9) [dB]
2nd harmonic -2.7 -3.1 -3.3 -9.1
3rd harmonic -4.8 -5.2 -5.2 -10.7
4th harmonic -5.5 -6.5 -6.7 -11.9
5th harmonic -6.3 -6.5 -6.7 -11.4
As it can be observed, the BLE 125 Kb/s coded modulation scheme has the lowest relaxation factors. These values will be used as the
worst case relaxarion factors for the radiated measurements.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 13
Page 14

X
Z
Y
BRD4185A Reference Manual
RF Performance
7.2 Radiated Power Measurements
During measurements, the BRD4185A Radio Board was attached to a Wireless Starter Kit Mainboard which was supplied by USB. The
voltage supply for the Radio Board was 3.3 V.
The Bluetooth stack uses ANT1 for transmission, therefore the radiated tests have also been performed by using that antenna.
The radiated power was measured in an antenna chamber by rotating the board 360 degrees with horizontal and vertical reference
antenna polarizations in the XY, XZ, and YZ cuts. The measurement planes are illustrated in the figure below.
Figure 7.2. Illustration of Reference Planes with a Radio Board Plugged into the Wireless Starter Kit Mainboard
Note: The radiated measurement results presented in this document were recorded in an unlicensed antenna chamber. Also, the radi-
ated power levels may change depending on the actual application (PCB size, used antenna, and so on). Therefore, the absolute levels
and margins of the final application are recommended to be verified in a licensed EMC testhouse.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 14
Page 15

0°
45°
90°
135°
180°
225°
270°
315°
-30
-25
-20
-15
-10-50
Normalized Radiation Pattern [dB], BRD4185A
ANT1 with WSTK, YZ cut
Horizontal
Vertical
0°= Z axis
0°
45°
90°
135°
180°
225°
270°
315°
-30
-25
-20
-15
-10-50
Normalized Radiation Pattern [dB], BRD4185A
ANT1 with WSTK, XZ cut
Horizontal
Vertical
0°= Z axis
0°
45°
90°
135°
180°
225°
270°
315°
-30
-25
-20
-15
-10-50
Normalized Radiation Pattern [dB], BRD4185A
ANT1 with WSTK, XY cut
Horizontal
Vertical
0°= X axis
BRD4185A Reference Manual
RF Performance
7.2.1 Maximum Radiated Power Measurements
For the transmitter antenna, the on-board printed inverted-F antenna of the BRD4185A Radio Board was used (the R1 resistor was
mounted). The supply for the RF section (RFVDD) and the 2.4 GHz power amplifier (PAVDD) was 1.8 V provided by the on-chip DC-DC
converter; for details, see the schematic of the BRD4185A. The transceiver was operated in unmodulated carrier transmission mode.
The output power of the radio was set to 6 dBm based on the conducted measurement.
The results are shown in the tables below. The correction factors are applied based on the BLE 125 Kb/s coded modulation, showed in
section 7.1.2 Conducted Power Measurements with Modulated Carrier. For the rest of the supported modulation schemes the correction factors are larger, thus the related calculated margins would be higher compared to the ones shown in the table below. Thus the
below margins can be considered as worst case margins.
Table 7.2. Maximums of the Measured Radiated Powers in EIRP [dBm] and the Calculated Modulated Margins in [dB] with the
Wireless Starter Kit Mainboard; PAVDD = 1.8 V
Frequency
(2450 MHz)
Measured Un-
modulated EIRP
[dBm]
Orientation
Correction Fac-
tor [dB]
Calculated
Modulated EIRP
[dBm]
Modulated Mar-
gin [dB]
Limit in EIRP
[dBm]
Fund 2.4 YZ/V NA (0 is used) 2.4 27.6 30.0
2nd -57.0 XZ/V -2.7 -59.7 18.5 -41.2
3rd -38.8 YZ/H -4.8 -43.6 2.4 -41.2
BLE 125 Kb/s Coded Modulation
4th
<-50
*
-/- -5.5 - >10 -30.0
5th -37.9 XZ/H -6.3 -44.2 3.0 -41.2
* Signal level is below the Spectrum Analyzer noise floor.
As it it is shown in the table above, with 6 dBm output power, the radiated power of the fundamental is lower than 6 dBm due to the low
antenna gain. The 3rd and 5th harmonics are above the limit in case of the unmodulated carrier transmission. But with the relaxation of
the supported modulation schemes, the margin is at least 2.4 dB and 3.0 dB, respectively.
7.2.2 Antenna Pattern Measurements
The measured normalized antenna patterns are shown in the following figures.
Figure 7.3. Normalized Antenna Pattern of the BRD4185A with the Wireless Starter Kit Mainboard
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 15
Page 16

BRD4185A Reference Manual
EMC Compliance Recommendations
8. EMC Compliance Recommendations
8.1 Recommendations for 2.4 GHz ETSI EN 300-328 Compliance
As shown in section , the power of the fundamental of the BRD4185A Wireless Gecko Radio Board with 6 dBm output is compliant with
the 20 dBm limit of the ETSI EN 300-328 regulation. With the supported modulation schemes, the harmonics are also compliant with
the relevant limits. Although the BRD4185A Radio Board has an option for mounting a shielding can, it is not required for the compliance.
8.2 Recommendations for 2.4 GHz FCC 15.247 Compliance
As shown in section , the power of the fundamental of the BRD4185A Wireless Gecko Radio Board with 6 dBm output is compliant with
the 30 dBm limit of the FCC 15.247 regulation. With the supported modulation schemes, the harmonics are also compliant with the
relevant limits. Although the BRD4185A Radio Board has an option for mounting a shielding can, it is not required for the compliance.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 16
Page 17

Board
Revision
PCB
Revision
BRD4185A Rev. A01
PCB4185A Rev. A01
123456789
BRD4185A Reference Manual
Board Revision History
9. Board Revision History
The board revision is laser engraved in the Board Info field on the bottom side of the PCB, as outlined in the figure below. The revision
printed on the silkscreen is the PCB revision.
Figure 9.1. Revision Info
Table 9.1. BRD4185A Radio Board Revision History
Board Revision Description
A01 Updated PCB prod. panel frame. No change on the board area.
A00 Initial production release.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 17
Page 18

10. Errata
There are no known errata at present.
BRD4185A Reference Manual
Errata
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 18
Page 19

11. Document Revision History
Revision 1.0
June, 2020
• Initial document release.
BRD4185A Reference Manual
Document Revision History
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 19
Page 20

Simplicity Studio
One-click access to MCU and
wireless tools, documentation,
software, source code libraries &
more. Available for Windows,
Mac and Linux!
IoT Portfolio
www.silabs.com/IoT
Disclaimer
Silicon Labs intends to provide customers with the latest, accurate, and in-depth documentation of all peripherals and modules available for system and software implementers using or
intending to use the Silicon Labs products. Characterization data, available modules and peripherals, memory sizes and memory addresses refer to each specific device, and "Typical"
parameters provided can and do vary in different applications. Application examples described herein are for illustrative purposes only. Silicon Labs reserves the right to make changes
without further notice to the product information, specifications, and descriptions herein, and does not give warranties as to the accuracy or completeness of the included information.
Without prior notification, Silicon Labs may update product firmware during the manufacturing process for security or reliability reasons. Such changes will not alter the specifications or the
performance of the product. Silicon Labs shall have no liability for the consequences of use of the information supplied in this document. This document does not imply or expressly grant
any license to design or fabricate any integrated circuits. The products are not designed or authorized to be used within any FDA Class III devices, applications for which FDA premarket
approval is required or Life Support Systems without the specific written consent of Silicon Labs. A "Life Support System" is any product or system intended to support or sustain life and/or
health, which, if it fails, can be reasonably expected to result in significant personal injury or death. Silicon Labs products are not designed or authorized for military applications. Silicon
Labs products shall under no circumstances be used in weapons of mass destruction including (but not limited to) nuclear, biological or chemical weapons, or missiles capable of delivering
such weapons. Silicon Labs disclaims all express and implied warranties and shall not be responsible or liable for any injuries or damages related to use of a Silicon Labs product in such
unauthorized applications.
Trademark Information
Silicon Laboratories Inc.® , Silicon Laboratories®, Silicon Labs®, SiLabs® and the Silicon Labs logo®, Bluegiga®, Bluegiga Logo®, ClockBuilder®, CMEMS®, DSPLL®, EFM®,
EFM32®, EFR, Ember®, Energy Micro, Energy Micro logo and combinations thereof, "the world’s most energy friendly microcontrollers", Ember®, EZLink®, EZRadio®, EZRadioPRO®,
Gecko®, Gecko OS, Gecko OS Studio, ISOmodem®, Precision32®, ProSLIC®, Simplicity Studio®, SiPHY®, Telegesis, the Telegesis Logo®, USBXpress® , Zentri, the Zentri logo and Zentri
DMS, Z-Wave®, and others are trademarks or registered trademarks of Silicon Labs. ARM, CORTEX, Cortex-M3 and THUMB are trademarks or registered trademarks of ARM Holdings.
Keil is a registered trademark of ARM Limited. Wi-Fi is a registered trademark of the Wi-Fi Alliance. All other products or brand names mentioned herein are trademarks of their respective
holders.
Silicon Laboratories Inc.
400 West Cesar Chavez
Austin, TX 78701
USA
SW/HW
www.silabs.com/simplicity
Quality
www.silabs.com/quality
Support and Community
community.silabs.com
http://www.silabs.com
 Loading...
Loading...