Silicon Labs BLUEGIGA BLUETOOTH LOW ENERGY SOFTWARE User Manual

BLUEGIGA BLUETOOTH LOW ENERGY
SOFTWARE
V.1.10 API DOCUMENTATION
Wednesday,
Version 4.1
2 December 2020

Table of Contents
1 Version History ________________________________________________________________________ 4
2 Introduction to Bluegiga Bluetooth Low Energy Software ________ ________________________________ 7
2.1 The Bluegiga Bluetooth Low Energy Stack ______________________________________________ 7
2.2 The Bluegiga Bluetooth Low Energy SDK _______________________________________________ 8
2.3 The BGAPI TM Protocol ______________________________________________________________ 9
2.4 The BGLIB TM Host Library __________________________________________________________ 10
2.5 The BGScript TM Scripting Language__________________________________________________ 11
2.6 The Profile Toolkit TM ______________________________________________________________ 12
3 API definition _________________________________________________________________________ 13
3.1 The BGAPI protocol definition ________________________________________________________ 13
3.1.1 Message types ____________________________________________________________ 13
3.1.2 Command Class IDs ________________________________________________________ 15
3.1.3 Packet Exchange __________________________________________________________ 15
3.2 The BGLIB functions definition _______________________________________________________ 19
3.3 The BGScript API definition _________________________________________________________ 20
3.4 Data Types ______________________________________________________________________ 21
4 API Reference ________________________________________________________________________ 22
4.1 Attribute Client ___________________________________________________________________ 23
4.1.1 Commands _______________________________________________________________ 23
4.1.2 Enumerations ______________________________________________________________ 46
4.1.3 Events ___________________________________________________________________ 47
4.2 Attribute Database ________________________________________________________________ 53
4.2.1 Commands ________________________________________________________________ 53
4.2.2 Enumerations ______________________________________________________________ 61
4.2.3 Events ___________________________________________________________________ 63
4.3 Connection ______________________________________________________________________ 66
4.3.1 Commands ________________________________________________________________ 66
4.3.2 Enumerations ______________________________________________________________ 76
4.3.3 Events ____________________________________________________________________ 77
4.4 Generic Access Profile _____________________________________________________________ 81
4.4.1 Commands ________________________________________________________________ 81
4.4.2 Enumerations _____________________________________________________________ 101
4.4.3 Events __________________________________________________________________ 110
4.5 Hardware ______________________________________________________________________ 111
4.5.1 Commands _______________________________________________________________ 111
4.5.2 Events ___________________________________________________________________ 142
4.6 Persistent Store _________________________________________________________________ 148
4.6.1 Commands ______________________________________________________________ 148
4.6.2 Events __________________________________________________________________ 157
4.7 Security Manager ________________________________________________________________ 158
4.7.1 Commands ______________________________________________________________ 158
4.7.2 Enumerations
4.7.3 Events
4.8 System ________________________________________________________________________ 176
4.8.1 Commands
4.8.2 Enumerations
4.8.3 Events
4.9 Testing ________________________________________________________________________ 202
4.9.1 Commands
4.10 Device Firmware Upgrade ________________________________________________________ 208
4.10.1 Commands _____________________________________________________________ 208
4.10.2 Events
4.11 Error Codes ___________________________________________________________________ 214
4.11.1 BGAPI Errors ____________________________________________________________ 214
4.11.2 Bluetooth Errors _________________________________________________________ 215
4.11.3 Security Manager Protocol Errors ____________________________________________ 217
4.11.4 Attribute Protocol Errors ___________________________________________________ 218
____________________________________________________________ 169
__________________________________________________________________ 172
_______________________________________________________________ 176
_____________________________________________________________ 194
__________________________________________________________________ 195
______________________________________________________________ 202
_________________________________________________________________ 213
Silicon Labs Page of 3 220
1
Version History
Version
1.3 API documentation for SW version v.1.0.3 (Build 43)
2.0 API documentation for v.1.1.0 beta (Build 46)
2.1 API documentation for v.1.1.0 beta (Build 55)
Note: API changes history is now included here (not separate)
Changed APIs:
* Attribute Database – User Read Response (function implemented for Beta 2)
* Connection – Connection Status Flags (fixed)
Doc improved for following APIs:
* Attribute Client – Attribute Value, Indicated, Procedure Completed, Group Found
* Attribute Database – User Read Request
* Generic Access Profile – Discover, Set Adv Parameters
* Hardware – I2c Read, I2c Write, Set Soft Timer, Set Txpower
* Security Manager – Delete Bonding, Get Bonds
* System – Whitelist Append
Other sections (outside API reference) has also been updated to improve the document
2.2 Added documentation how to use BGAPI protocol without UART flow control.
Section updated: BGAPI protocol definition
2.3 API documentation for v1.1.0 (Build 71+)
* Various typos and wording corrected.
3.0 Documentation updates for SW v1.2 compatibility
Changed APIs:
Channel quality testing commands added: Get Channel Map and Channel mode
Out of Bonds and Command Too Long error code added
Protocol error event added for indicating the invalid command or wrong length
GAP Discoverable Mode is updated to support the Enhanced Broadcasting.
Doc improved for following APIs/referenses:
Updated ADC internal reference to 1.24V (was 1.15V),
GAP - Set Scan Paremeters, Connect Selective, Connect Direct
3.1 Documentation updates for SW v1.2.2 compatibility
Added APIs:
Added API's for reading (Read Data), writing (Write Data), and erasing (Erase Page) the
user area data on the internal flash memory
Added API's for handling I/O port interrupts (Io Port Irq Enable) and setting the directions (Io
Port Irq Direction)
Added testing API's for sending and receiving data (Phy Tx, Phy Rx, Phy End)
Added API's for handling the comparator functionality under HW commands and events.
Silicon Labs Page of 4 220

Version
3.2 Documentation updates for SW v1.3.0 compatibility
Added APIs:
Added Set RXGain API for controlling RX Gain for lowering the sensitivity (Hardware
commands)
Added Usb Enable API for controlling whether USB interface is on or off (Hardware
commands)
Added AES API’s for using AES engine for de-/encryptions (System commands)
3.3 Documentation updates for SW v1.3.1 compatibility
Added APIs:
Added Send Attributes (attributes_send) command for controlling sending of notifications
and indications (Attributes commands)
Added Whitelist Bonds (sm_whitelist_bonds) command for adding all the bonded
devices to the whitelist (Security Manager commands).
3.4 Editorial changes and improvements and enhancements to command, response and event
descriptions.
3.5 Editorial changes and improvements and enhancements to command, response and event
descriptions.
3.6 Updates for the software v.1.4.0
New API added : Set Initiating Con Parameters
New API added : Slave Latency Disable
iOS9.1 pairing pairing instructions: Encrypt Start
3.7 New API added: Set Pairing Distribution Keys
3.8 New API added: Sleep Enable
3.9 New API added: Set Nonresolvable Address
Updated API: Set Privacy Flags
3.10 Updates for the software v.1.5.0
Corrected AFH Description in section.Connections and packet timings
New API added: and commands description.Channel Map Set Channel Map Get
Corrected and descriptions.Attribute Write Write Command
Added note about packet mode responses in BGAPI protocol definition
Refined descriptionPhy Tx
3.11 Updates for the software v.1.6.0
Corrected type, added Bluetooth 4.0 specification reference in
lolen
Set Initiating Con
section.Parameters
Added Bluetooth 4.0 specification reference in section.Set Scan Parameters--gap
Silicon Labs Page of 5 220
Version
3.12 Removed "Introduction to Bluetooth Smart Technology" paragraph
Updates for the software v.1.7.0
New BGAPI error code for BGScript stack overflow
I2C commands timeout documentation
New API added: Get Bootloader Crc
New API added: Delay Reset
New API added: Get Timestamp
New API added: USB Enumeration Status Get
New API event added: USB Enumerated
4.0 Updates for the software v.1.8.0
New API event added: Radio Error
4.1 Renamed "Bluetooth Smart" to "Bluetooth Low Energy" according to the official Bluetooth SIG
nomenclature.
Silicon Labs Page of 6 220
2
The Bluegiga Low Energy Software enables developers to quickly and easily develop Low
Bluetooth Bluetooth
Energy applications without in-depth knowledge of the Low Energy technology. The Low
Bluetooth Bluetooth
Energy Software consists of two main parts:
The Low Energy Stack
Bluetooth
The Low Energy Software Development Kit (SDK)
Bluetooth
2.1
The Low Energy is meant for the Bluegiga Low Energy products such as BLE112, BLE113
Bluetooth Bluetooth
BLE121LR and BLED112.
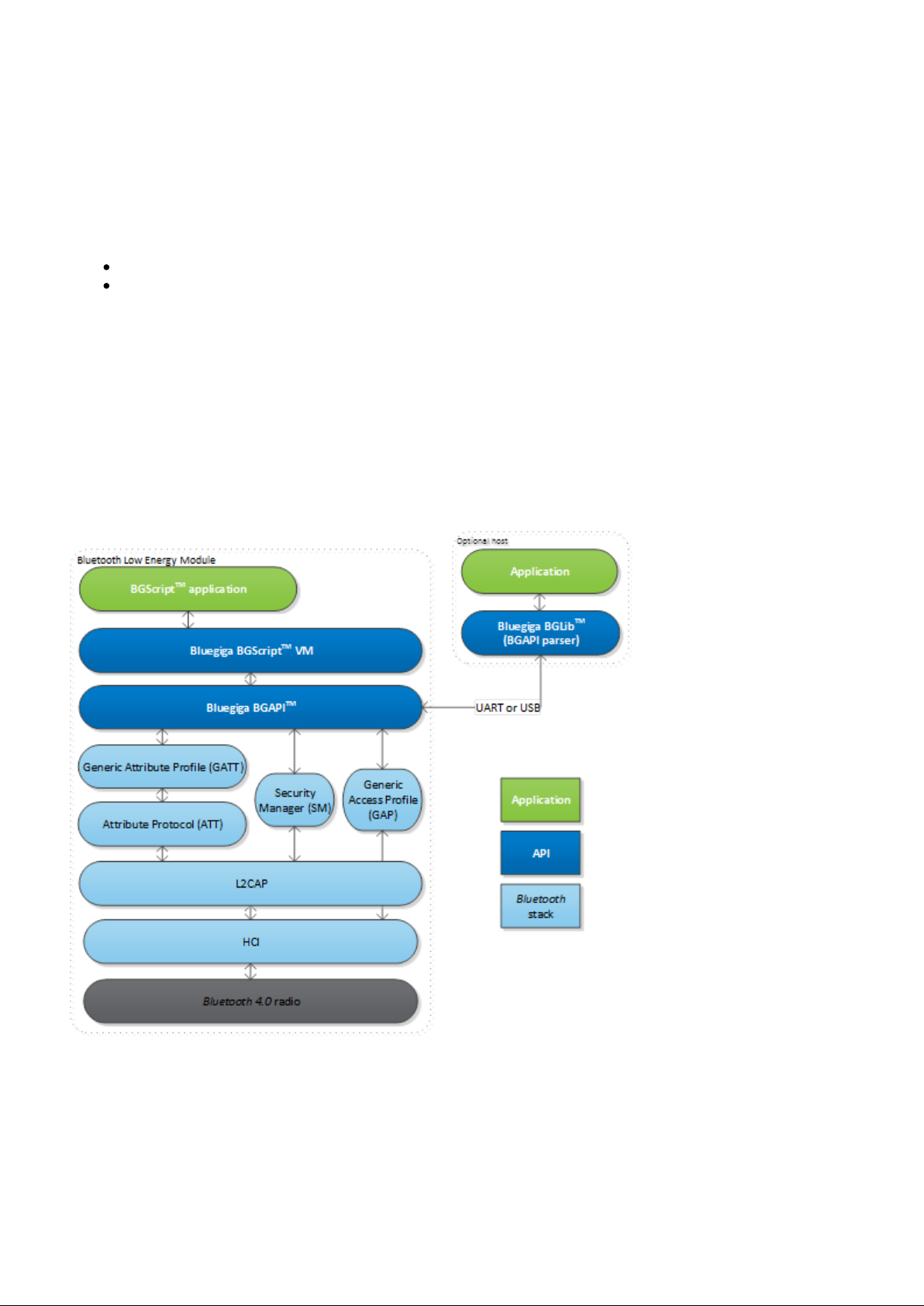
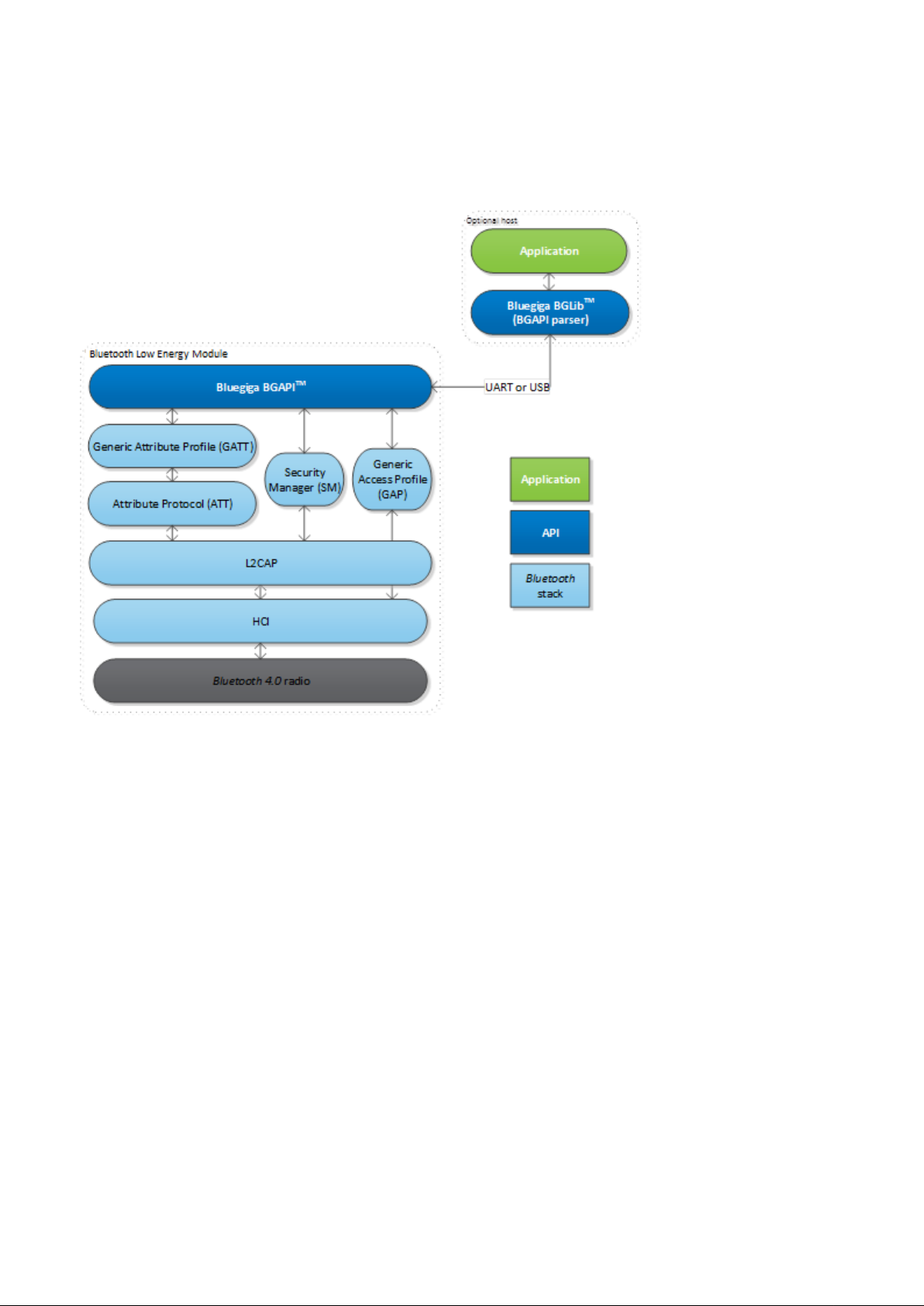
Figure: The Bluegiga Bluetooth Low Energy Stack
Introduction to Bluegiga Bluetooth Low Energy Software
The Bluegiga Bluetooth Low Energy Stack
The
Bluetooth Bluetooth
slave and master modes, all the protocol layers such as L2CAP, Attribute Protocol (ATT), Generic Attribute
Profile (GATT), Generic Access Profile (GAP) and Security Manager (SM). The Bluetooth Low Energy stack
also implements various other features such as interface APIs to SPI, UART, GPIO, ADC, flash etc. and other
features like the Device Firmware Update (DFU) API.
Low Energy stack is a fully
4.0 single mode compatible software stack implementing
Silicon Labs Page of 7 220
2.2 The Bluegiga Bluetooth Low Energy SDK
The Bluegiga Low Energy SDK is a software development kit, which enables the device and software
Bluetooth
vendors to develop products on top of the Bluegiga’s Low Energy hardware and software.
Bluetooth
The Low Energy SDK supports multiple development models and the software developers can decide
Bluetooth
whether the device’s application software runs on a separate host (for example a MCU) or whether they want to
make fully standalone devices and execute their application on-board the Bluegiga Low Energy
Bluetooth
modules.
The SDK also contains documentation, tools for compiling the firmware, installing it into the hardware and lot of
example application speeding up the development process.
The SDK contains the following components:
Bluetooth Low Energy
The BGAPI protocol
TM
is a binary based commend and response protocol that allows the Bluetooth
Low Energy stack to be controller form an external host and an application over for example UART or
USB interface.
The BGScript scripting language TMis a simple BASIC like scripting language that allows the software
developers to embed applications on-board the Bluegiga Low Energy modules. The BGScript
Bluetooth
applications are executed in the BGScript Virtual Machine (VM) and the benefit of this is that no external
host MCU is required.
The BGLIB host library
TM
is a lightweight parser for the BGAPI host protocol and it implements C
functions and callback handlers for all the BGAPI commands, responses and events. The benefit of the
BGLIB library is that speeds up the application development for the external host processors.
The Profile ToolkitTM is a simple XML based description language that enables quick and easy
development of GATT Bluetooth Low Energy services and characteristics on a device.
Each of these components are described in more detail in the following chapters.
Silicon Labs Page of 8 220
2.3
needed between the host and the Low Energy stack. The transport protocol is used to communicate
Bluetooth
with the stack as well to transmit and receive data packets. This protocol is called BGAPI and it's a
Bluetooth
lightweight binary based communication protocol designed specifically for ease of implementation within host
devices with limited resources.
The BGAPI protocol is a simple command, response and event based protocol and it can be used over UART
or USB physical interfaces.
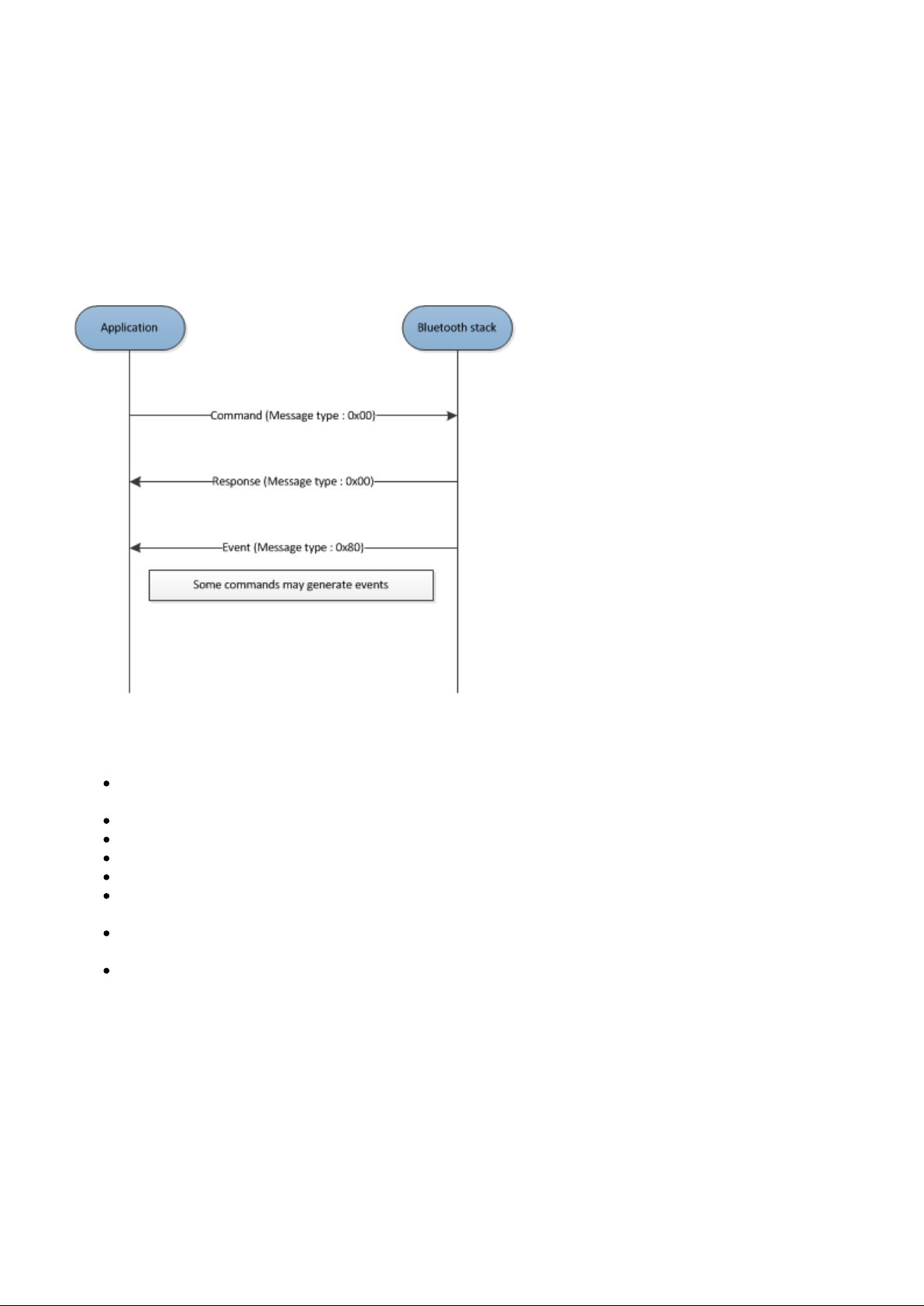
Figure: BGAPI message exchange
The BGAPI provides access for example to the following layers in the Low Energy Stack:
Bluetooth
The BGAPI TM Protocol
For applications where a separate host is used to implement the end user application, a transport protocol is
Generic
open connections
Security
Attribute Database - An class to access the local Attribute Database
Attribute
Connection - Provides an interface to manage
Hardware - An interface to access the various hardware layers such as timers, ADC and other hardware
interfaces
Persistent Store - User to access the parameters of the radio hardware and read/write data to non-
volatile memory
System
Access Profile
Manager -
Client - Provides
- Various system functions, such as querying the hardware status or reset it
- GAP allows the management of discoverability and connetability modes and
Provides access the
an interface
Bluetooth
discover, read
to
low energy security functions
write remote attributes
and
Bluetooth
low energy connections
Silicon Labs Page of 9 220
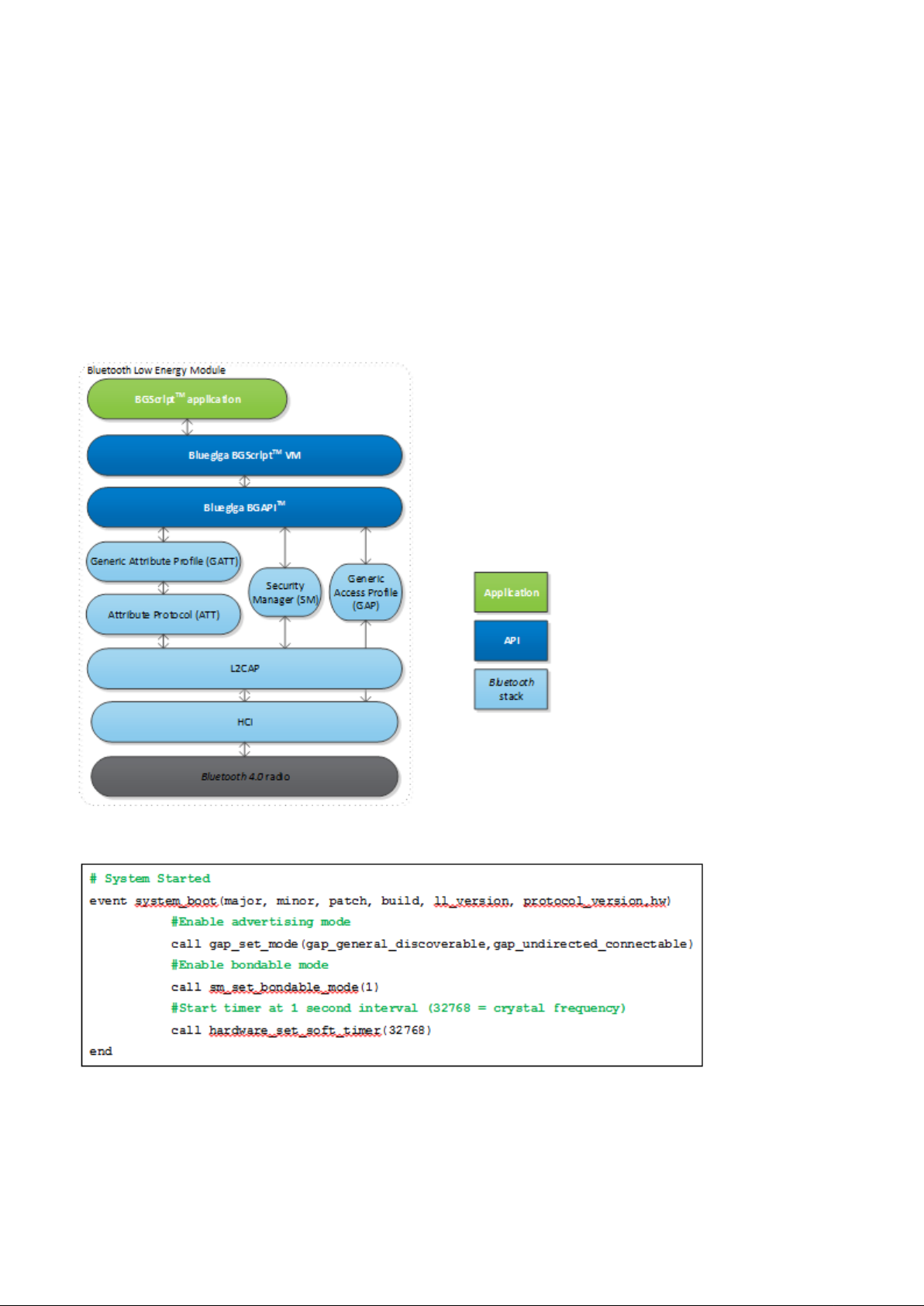
2.4
Figure: The BGLIB host library
The BGLIB TM Host Library
For easy implementation of BGAPI protocol an ANSI C host library is available. The library is easily portable
ANSI C code delivered within the Low Energy SDK. The purpose is to simplify the application
development to various host environments.
Bluetooth
Silicon Labs Page of 10 220
2.5
The BGScript TM Scripting Language
without a separate host MCU and run all the application code on the Bluegiga Low Energy modules.
Bluetooth
The Low Energy modules can run simple applications along the Low Energy stack and this
Bluetooth Bluetooth
provides a benefit when one needs to minimize the end product’s size, cost and current consumption. For
developing standalone Low Energy applications the SDK includes a BGScript VM, compiler and other
Bluetooth
BGScript development tools. BGScript provides access to the same software and hardware interfaces as the
BGAPI protocol and the BGScript code can be developed and compiled with free-of-charge tools provided by
Bluegiga.
Typical BGScript applications are only few tens to hundreds lines of code, so they are really quick and easy to
develop and lots of readymade examples are provides with the SDK.
Figure: BGScript application model
Figure: BGScript code example
The
Bluetooth
Low Energy SDK Also allows the application developers to create fully standalone devices
Silicon Labs Page of 11 220

2.6
The Profile Toolkit TM
Figure: A profile toolkit example of GAP service
The
Bluetooth
Bluetooth
description language and templates, which can be used to describe the devices GATT database. The profile
toolkit also contains a compiler, which converts the XML to binary format and generates API to access the
characteristic values.
Low Energy profile toolkit is a simple set of tools, which can used to describe GATT based
Low Energy services and characteristics. The profile toolkit consists of a simple XML based
Silicon Labs Page of 12 220
3 API definition
The BGAPI host protocol API definition
TM
The BGLIB host library API description
TM
TM
Octet Octet bits Length Description Notes
Octet 0 7 1 bit
Message Type (MT) 0: Command/Response
Event1:
... 6:3 4 bits
Technology Type (TT) 0000:
... 2:0 3 bits
Length High (LH)
Payload length (high bits)
Octet 1 7:0 8 bits
Length Low (LL)
Payload length (low bits)
Octet 2 7:0 8 bits
Class ID (CID)
Command class ID
Octet 3 7:0 8 bits
Command ID (CMD)
Command ID
Octet 4-n - 0 - 2048 Bytes
Payload (PL)
Up to 2048 bytes of payload
With the Bluegiga
Bluetooth
3.1.1 Message types
The following message types exist in the BGAPI protocol.
Table: BGAPI message types
This section of the document contains the generic Bluetooth Low Energy Stack API
definition. The definition consist of three parts:
The BGScript scripting language API description
This section of the document only provides the generic definition and description of the API. The actual
commands, responses and events are described in detail in the section.API reference
3.1 The BGAPI protocol definition
The BGAPI protocol is a command, response and event protocol that can be used to communicate with the
Bluetooth
used to instruct the
Bluetooth Bluetooth
The BGAPI commands, responses and events use a binary format and the generic protocol format is described
in this section.
BGAPI Packet format
Low Energy stack over one of the physical interfaces like UART or USB. The BGAPI protocol can be
Bluetooth
devices or access the physical interfaces like SPI or I2C of the
Low Energy stack to do something like advertise, discover and connect other
Low Energy module.
The generic BGAPI protocol format is described in the table below. The BGAPI protocol uses a four (4) byte
header and data payload.
Packets in either direction use the following format.
Table: BGAPI packet format
bytes and
header so the maximum payload size is 60 bytes.
longer packet sizes cannot be used. Four (4) bytes will be used for the BGAPI protocol
Low Energy
products the maximum allowed BGAPI packet size is 64
Low EnergyBluetooth
: Wi-Fi0001
Silicon Labs Page of 13 220
Message type Message Type (MT)
Value
Description
Command 0x00 Command from host to the stack
Response 0x00 Response from stack to the host
Event 0x80 Event from stack to the host
Silicon Labs Page of 14 220
3.1.2 Command Class IDs
The following command classes exist.
Table: BGAPI command classes
Class ID Description Explanation
0x00 System Provides access to system functions
0x01 Persistent Store Provides access the persistence store (parameters)
0x02
Provides access to local GATT database
0x03 Connection Provides access to connection management functions
0x04
Functions to access remote devices GATT database
0x05 Security Manager Bluetooth low energy security functions
0x06 Generic Access Profile GAP functions
0x07 Hardware Provides access to hardware such as timers and ADC
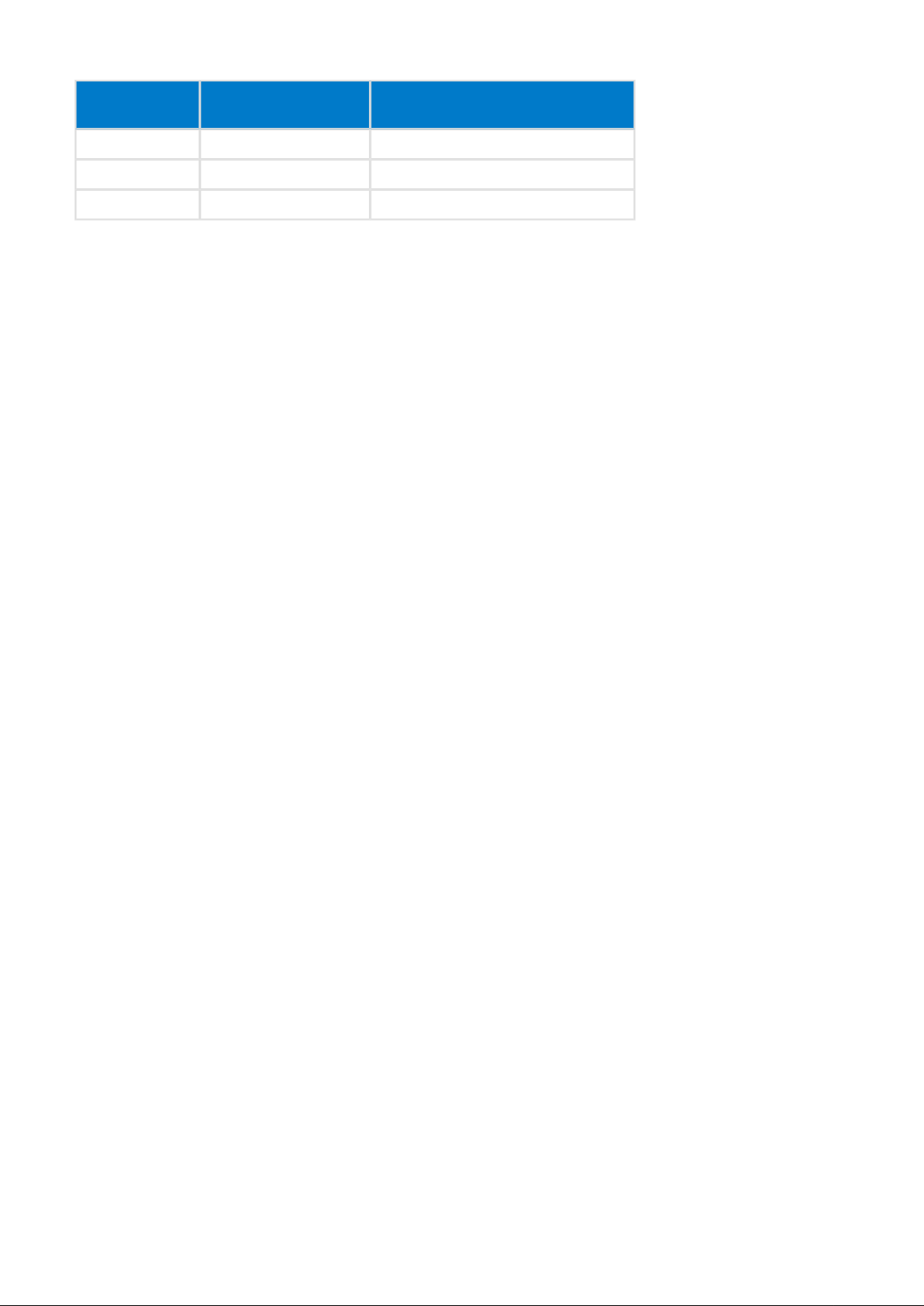
3.1.3 Packet Exchange
The BGAPI protocol is a simple command / response protocol and the BGAPI messages are exchanged as
show in the picture below.
The command messages are transmitted from the Application to the Stack and the Stack provides a response
to every successfully received command.
Some commands may generate events, which are transmitted from the Stack to the Application.
Attribute Database
Attribute Client
Silicon Labs Page of 15 220

The Application should always wait for the response to a command before issuing another command.
Silicon Labs Page of 16 220
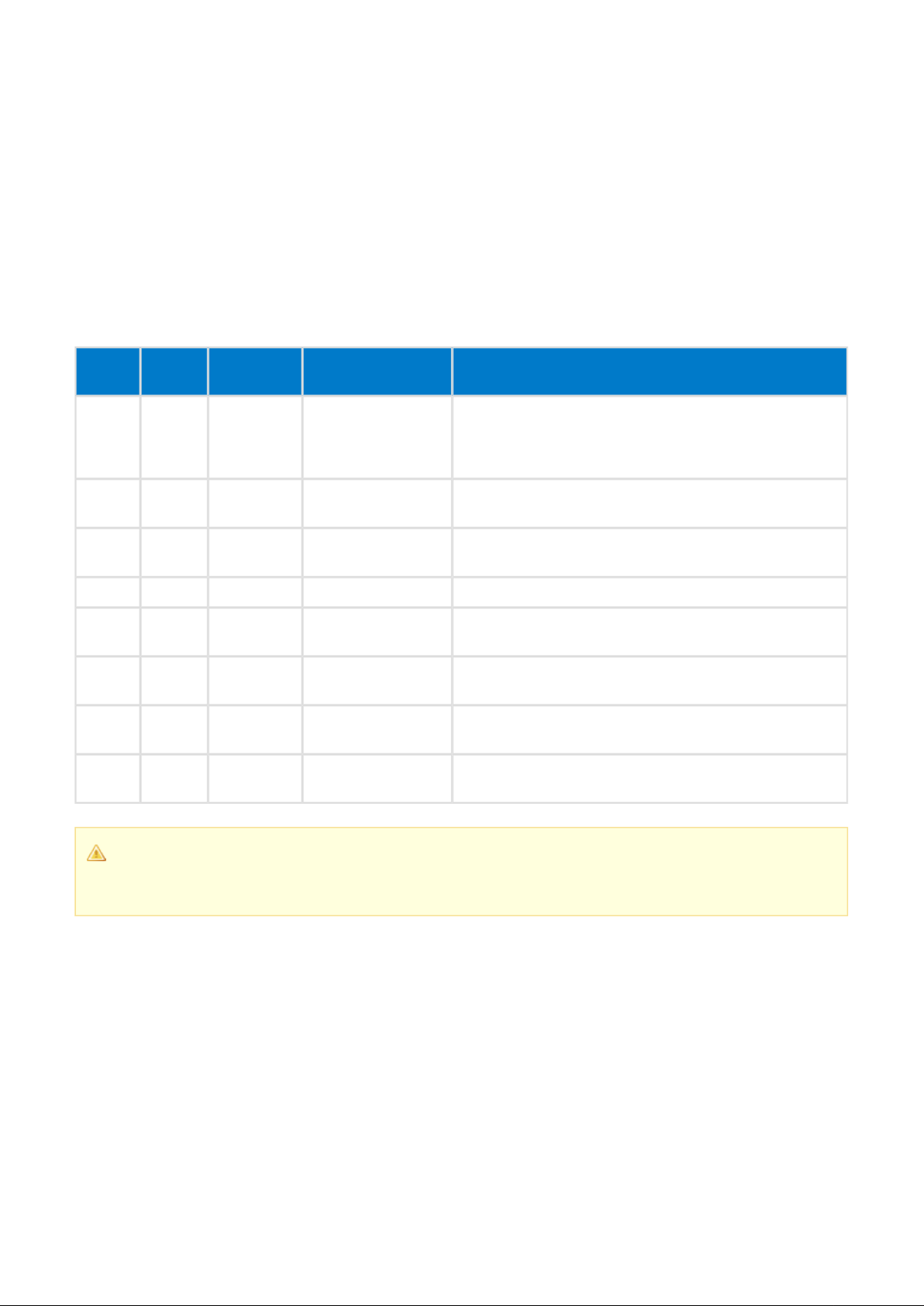
Using BGAPI protocol without UART flow control (Packet mode)
By default the BGAPI protocol assumes that UART flow control (RTS/CTS) is used to ensure reliable data
transmission and to prevent lost data because of buffer overflows. It is however possible to use the BGAPI
protocol without UART flow control.
When using the BGAPI protocol without UART flow control over a simple 2-wire (TX and RX) UART interface
and additional needs to be added to the BGAPI packets, which tells the total length of the BGAPI
length byte
packet excluding the itself. This is used by the BGAPI protocol parser to identify the length of
length byte
incoming commands and data and make sure they are fully received.
In this case the BGAPI protocol uses the following format:
Table: BGAPI packet format
Octet Octet
bits
Length Description Notes
Octet 07:0 8 bits
BGAPI command
length
Tells the length of the BGAPI command excluding the
length byte itself
Range of this octet is 4 - 62
Octet 17 1 bit
Message Type
(MT)
0: Command/Response
Event1:
... 6:3 4 bits
Technology Type
(TT)
0000: Bluetooth Low Energy
Wi-Fi0001:
... 2:0 3 bits
Length High (LH)
Payload length (high bits)
Octet 27:0 8 bits
Length Low (LL)
Payload length (low bits)
Octet 37:0 8 bits
Class ID (CID)
Command class ID
Octet 47:0 8 bits
Command ID
(CMD)
Command ID
Octet
5-n
- 0 - 2048
Bytes
Payload (PL)
Up to 64 bytes of payload
This operational mode needs to be especially enabled in devices hardware configuration file (typically
) and is not used by default. The default operational mode assumes a UART with flow hardware.xml
control is used.
Below is a simple example which shows how a command (Raw: 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x08) is sent System Get Info
using the BGAPI packet format.
Silicon Labs Page of 17 220
Packet mode responses
The extra length byte required in Packet Mode is only used in the traffic from host to the stack. When
the Bluetooth stack produces responses or events to the host the length byte is not included in them.
Silicon Labs Page of 18 220
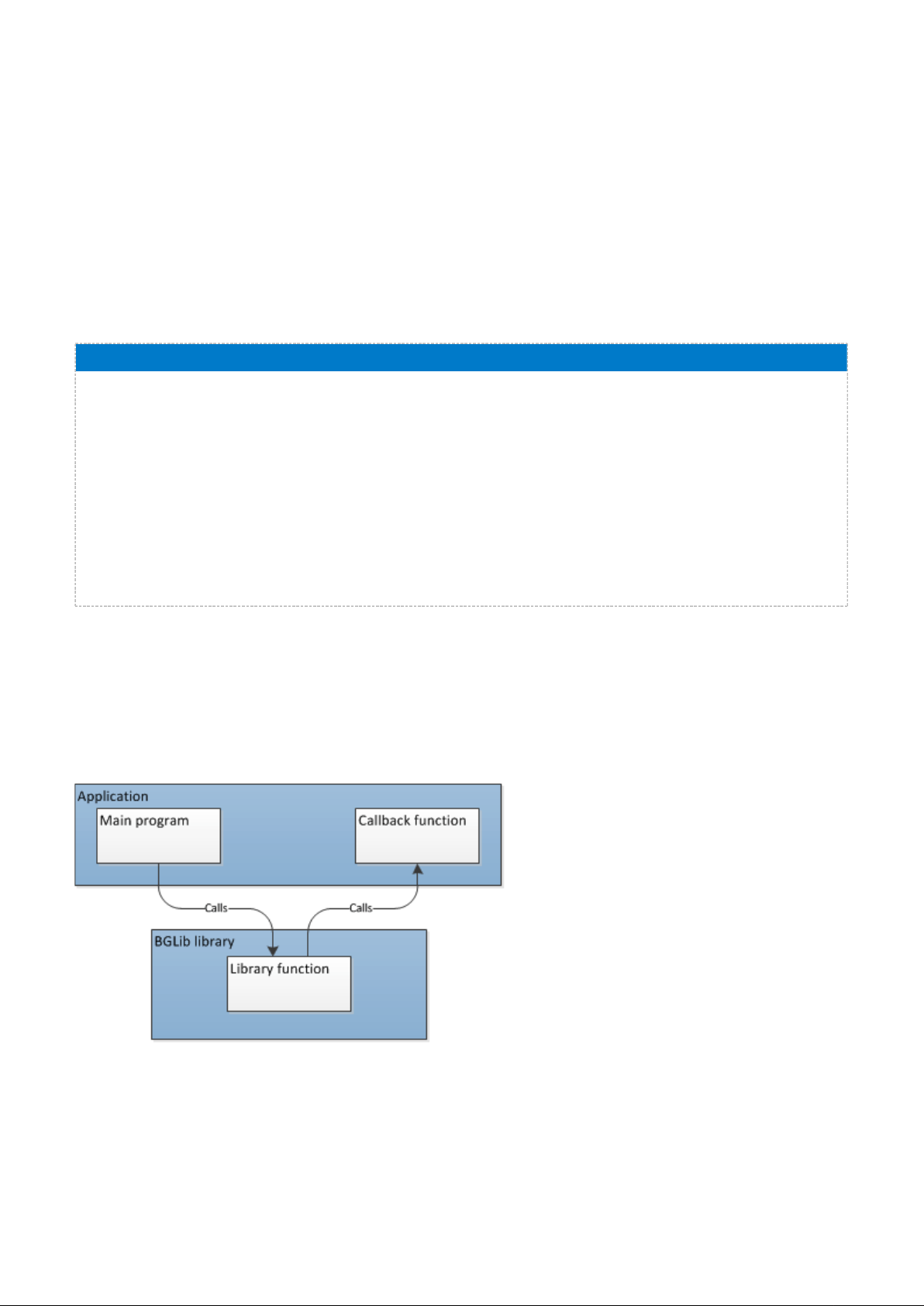
3.2 The BGLIB functions definition
Bluegiga provides a reference parser for the BGAPI protocol called the BGLIB. The BGLIB is an ANSI C
implementation of BGAPI packet parser and it's provided in source code format with the Bluegiga Bluetooth Low
Energy SDK. The purpose of the BGLIB is to simplify and speed up the development process and also to
provide higher level, easier to use C functions and callbacks so the developers do not need to fully learn the
raw BGAPI protocol.
In BGLIB all of the BGAPI commands are available as C functions and for the BGAPI responses and events
there are callback handlers.
The BGLIB functions and callbacks are documented as show below:
C Functions
/* Function */
void ble_cmd_gap_connect_direct(
bd_addr address ,
uint8 addr_type ,
uint16 conn_interval_min ,
uint16 conn_interval_max ,
uint16 timeout
);
/* Callback */
void ble_rsp_gap_connect_direct(
uint16 result ,
uint8 conn
);
The command parameters and return values are the same as used in the BGAPI protocol and they are not
documented separately in the API reference section.
Callback programming
Callback programming is a style of computer programming, which allows lower layer of software to call functions
defined on a higher layer. Callback is piece of code or a reference to a piece of code that is passed as an
argument. The figure below illustrates the callback architecture used with BGLIB.
Figure: Callback
are not familiar with callback programming a basic tutorial can for example be found
If you
architecture
from
http://www.codeguru.com/cpp/cpp/cpp_mfc/callbacks/article.php/c10557
here:
Silicon Labs Page of 19 220
3.3 The BGScript API definition
The BGScript functions are also documented in the API reference section. The format of the commands varies
slightly from the BGLIB functions and instead of using callbacks the BGScript functions take the return values
as parameters.
BGScript commands are documented as follows:
BGScript Functions
CALL gap_connect_direct(address ,addr_type ,conn_interval_min ,conn_interval_max ,timeout )(result
,conn )
The BGScript command parameters and return values are the same as used in the BGAPI binary protocol and
they are not documented separately.
Silicon Labs Page of 20 220
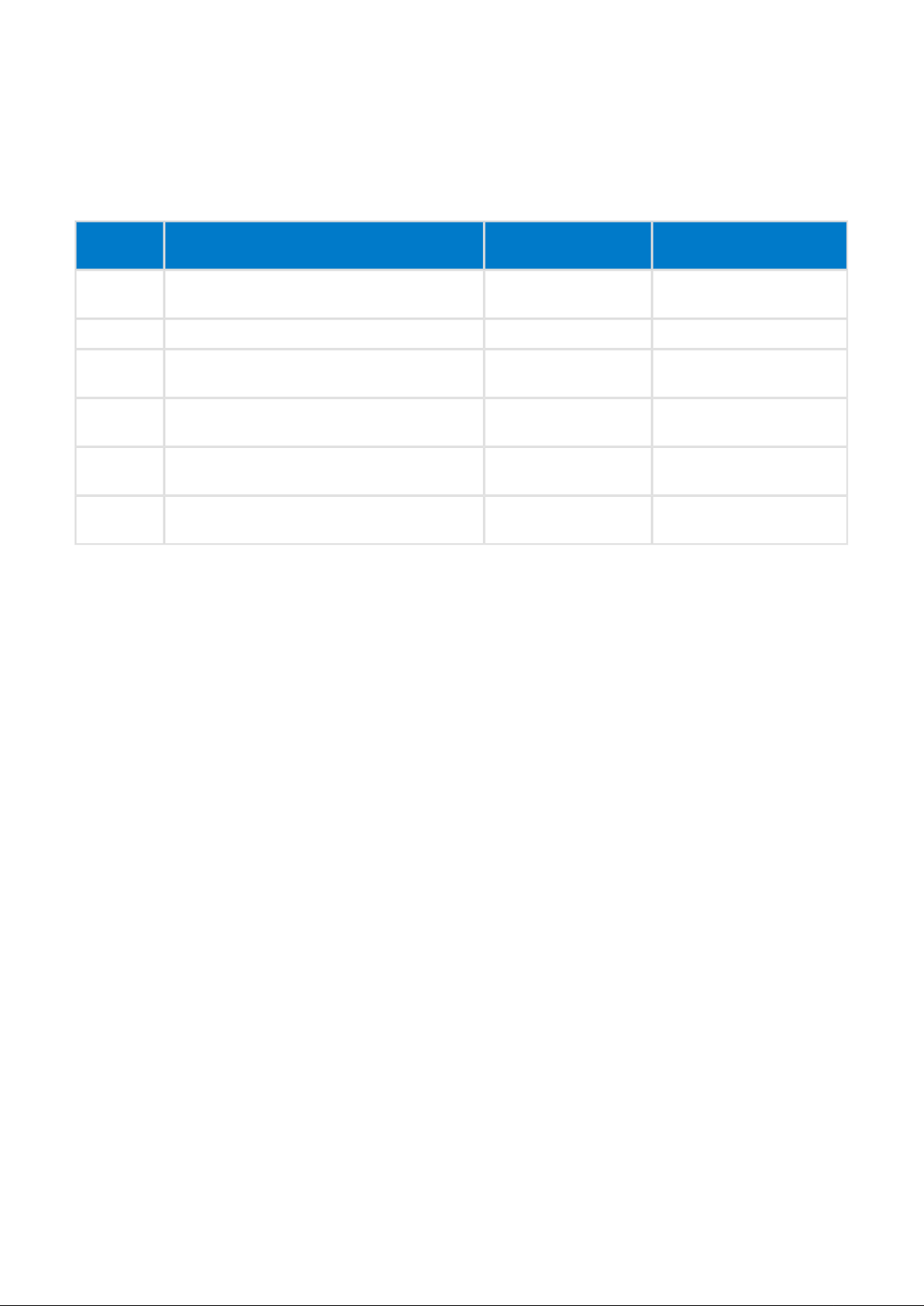
3.4
Data Types
Type Description Example: Human
readable
Example Packet data in
hex
int8
signed integer stored in 1 byte twos
complement form
-42 0xd6
uint8
unsigned integer stored in 1 byte 42 0x2a
uint16
unsigned integer stored in 2 bytes little
endian format
1701 0xa5 0x06
uint32
unsigned integer stored in 4 bytes little
endian format
1000000 0x40 0x42 0x0f 0x00
uint8array
byte array, first byte is array size "Hello" 0x05 0x68 0x65 0x6c
0x6c 0x6f
bd_addr
Bluetooth address in little endian format 00:07:80:c0:ff:ee 0xee 0xff 0xc0 0x80 0x07
0x00
The following data types are used in this documentation.
Table: Used data types
Silicon Labs Page of 21 220
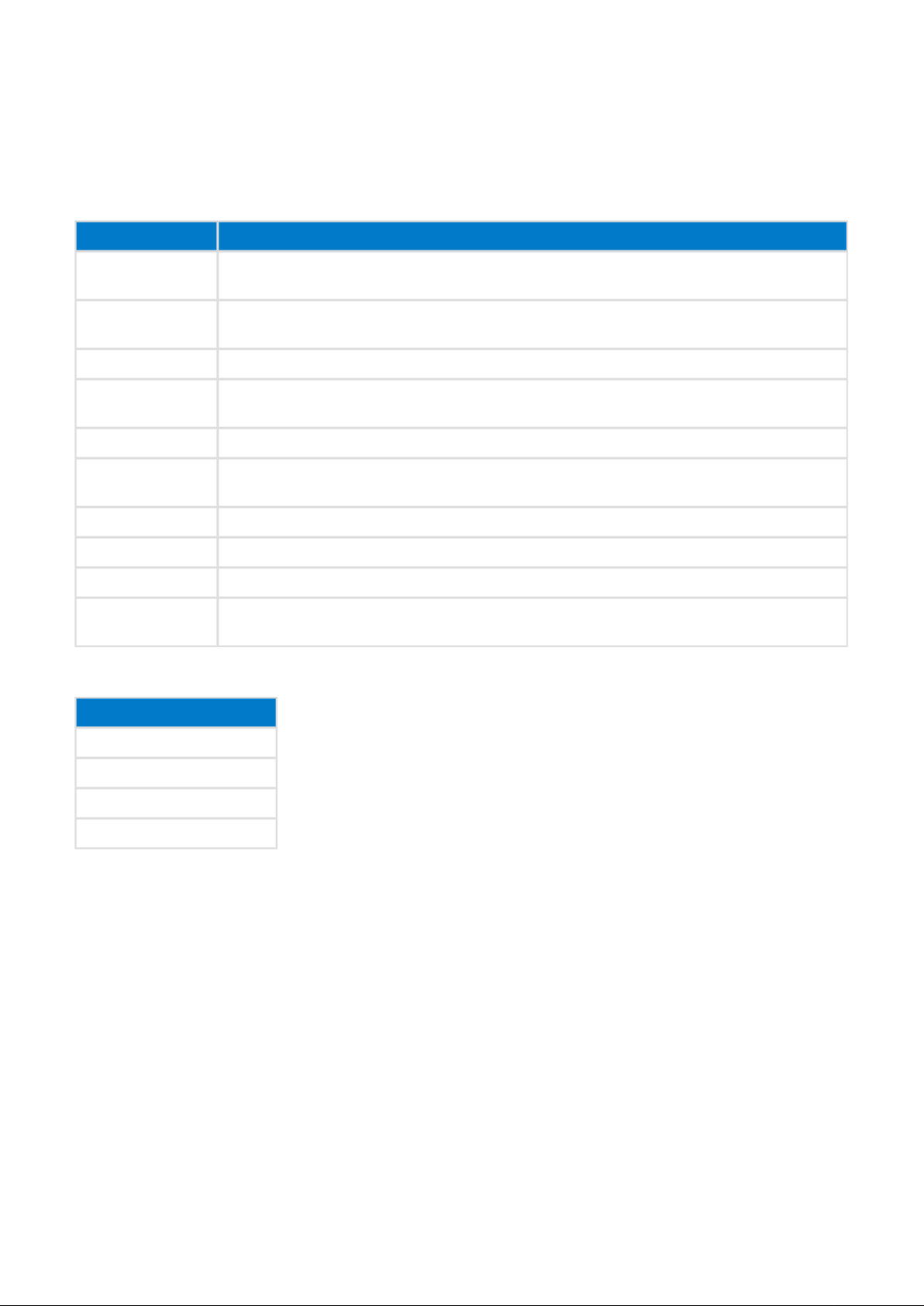
4 API Reference
This section of the document contains the actual API description, so the description of commands, responses,
events and enumerations and their possible parameters and values. The high level categorization is made
based on the command classes, which are:
Description Explanation
Provides access to local GATT database and allows data to be written there for remote
devices to access it.
Provides access to ATT protocol operationsa and allows a remote devices data to be
accessed.
Connection Provides access to connection and status management
Bluetooth
Generic Access
Profile
Provides access to GAP functions which allows one to control the local
Bluetooth
devices discoverability and connectability
Hardware Provides access to hardware interfaces such as SPI, I2C, timers and ADC
Persistent Store Provides access to the local persistence store, which allows data to be written and read
to the devices flash.
Security Manager
Provides
to security functions
Bluetooth
System Provides access to various system functions
Testing Functions needed for conformance testing
Bluetooth
Device Firmware
Upgrade
Provides access to functions required for field firmware upgrades
Final section of the API reference contains description of the error codes categorized as follows:
Description
BGAPI errors
Bluetooth errors
Attribute protocols errors
Attribute Database
Attribute Client
Security Manager errors
Silicon Labs Page of 22 220
4.1
Attribute Client
This command should be used for writing data to characteristic with property write="true".
The data payload for the Attribute Write command can be up to 20 bytes.
Table: COMMAND
Byte Type Name Description
0 0x00 hilen Message type: command
1 0x04 lolen Minimum payload length
2 0x04 class Message class: Attribute Client
3 0x05 method Message ID
4
uint8 connection
Connection handle
5 - 6
uint16 atthandle
Attribute handle to write to
7
uint8array data
Attribute value
Table: RESPONSE
Byte Type Name Description
0 0x00 hilen Message type: response
1 0x03 lolen Minimum payload length
2 0x04 class Message class: Attribute Client
3 0x05 method Message ID
4
uint8 connection
Connection handle
5 - 6
uint16 result 0 : write was successful
Otherwise error occurred
Table: EVENTS
The Attribute Client class implements the
to the ATT protocol methods. The Attribute Client class can be used to discover services and characteristics
from the ATT server, read and write values and manage indications and notifications.
Bluetooth
Low Energy Attribute Protocol (ATT) and provides access
4.1.1 Commands
Attribute Client commands
Attribute Write
This command can be used to write an attributes value on a remote device. In order to write the value of an
attribute a
A successful attribute write will be acknowledged by the remote device and this will generate an event
the Bluetooth connection will be dropped.
Bluetooth
connection must exists and you need to know the handle of the attribute you want to write.
. The acknowledgement should happen within a 30 second window or otherwise attclient_procedure_completed
Silicon Labs Page of 23 220

Event Description
attclient
procedure_completed
This event is generated when the write operation has been acknowledged by
remote device.
C Functions
/* Function */
void ble_cmd_attclient_attribute_write(
uint8 connection,
uint16 atthandle,
uint8 data_len,
const uint8* data_data
);
/* Callback */
struct ble_msg_attclient_attribute_write_rsp_t{
uint8 connection,
uint16 result
}
void ble_rsp_attclient_attribute_write(
const struct ble_msg_attclient_attribute_write_rsp_t * msg
)
BGScript Functions
call attclient_attribute_write(connection, atthandle, data_len, data_data)(connection, result)
Silicon Labs Page of 24 220

Execute Write
command on a remote prepare_write
Byte Type Name Description
0 0x00 hilen Message type: command
1 0x02 lolen Minimum payload length
2 0x04 class Message class: Attribute Client
3 0x0A method Message ID
4
uint8 connection
Connection Handle
5
uint8 commit 1: commits queued writes
0: cancels queued writes
Table: RESPONSE
Byte Type Name Description
0 0x00 hilen Message type: command
1 0x03 lolen Minimum payload length
2 0x04 class Message class: Attribute Client
3 0x0A method Message ID
4
uint8 connection
Connection Handle
5 - 6
uint16 result
Command result
Table: EVENTS
Event Description
attclient procedure_completed Write operation has been acknowledged by remote end
C Functions
/* Function */
void ble_cmd_attclient_execute_write(
uint8 connection,
uint8 commit
);
/* Callback */
struct ble_msg_attclient_execute_write_rsp_t{
uint8 connection,
uint16 result
}
void ble_rsp_attclient_execute_write(
const struct ble_msg_attclient_execute_write_rsp_t * msg
)
BGScript Functions
call attclient_execute_write(connection, commit)(connection, result)
This command can be used to execute or cancel a previously queued
device.
Table: COMMAND
Silicon Labs Page of 25 220

Silicon Labs Page of 26 220

Find By Type Value
Byte Type Name Description
0 0x00 hilen Message type: command
1 0x08 lolen Minimum payload length
2 0x04 class Message class: Attribute Client
3 0x00 method Message ID
4
uint8 connection
Connection handle
5 - 6
uint16 start
First requested handle number
7 - 8
uint16 end
Last requested handle number
9 - 10
uint16 uuid
2 octet UUID to find
11
uint8array value
Attribute value to find
Table: RESPONSE
Byte Type Name Description
0 0x00 hilen Message type: response
1 0x03 lolen Minimum payload length
2 0x04 class Message class: Attribute Client
3 0x00 method Message ID
4
uint8 connection
Connection handle
5 - 6
uint16 result 0 : the operation was successful
Otherwise error occurred
Table: EVENTS
Event Description
attclient group_found Attributes found
attclient
procedure_completed
Procedure has completed and new procedure can be started on GATT server
C Functions
/* Function */
void ble_cmd_attclient_find_by_type_value(
uint8 connection,
uint16 start,
uint16 end,
uint16 uuid,
uint8 value_len,
const uint8* value_data
This command can be used to find specific attributes on a remote device based on their 16-bit UUID value and
value. The search can be limited by a starting and ending handle values.
The command returns the handles of all attributes matching the type (UUID) and value.
Table: COMMAND
Silicon Labs Page of 27 220
);
/* Callback */
struct ble_msg_attclient_find_by_type_value_rsp_t{
uint8 connection,
uint16 result
}
void ble_rsp_attclient_find_by_type_value(
const struct ble_msg_attclient_find_by_type_value_rsp_t * msg
)
BGScript Functions
call attclient_find_by_type_value(connection, start, end, uuid, value_len, value_data)(connection,
result)
Silicon Labs Page of 28 220
Find Information
Byte Type Name Description
0 0x00 hilen Message type: command
1 0x05 lolen Minimum payload length
2 0x04 class Message class: Attribute Client
3 0x03 method Message ID
4
uint8 connection
Connection handle
5 - 6
uint16 start
First attribute handle
7 - 8
uint16 end
Last attribute handle
Table: RESPONSE
Byte Type Name Description
0 0x00 hilen Message type: response
1 0x03 lolen Minimum payload length
2 0x04 class Message class: Attribute Client
3 0x03 method Message ID
4
uint8 connection
Connection handle
5 - 6
uint16 result 0: if the command was successful
Otherwise error occurred
Table: EVENTS
Event Description
attclient find_information_found Handle, type - mapping found
attclient procedure_completed Find information procedure has completed
C Functions
/* Function */
void ble_cmd_attclient_find_information(
uint8 connection,
uint16 start,
uint16 end
);
/* Callback */
struct ble_msg_attclient_find_information_rsp_t{
uint8 connection,
uint16 result
}
void ble_rsp_attclient_find_information(
const struct ble_msg_attclient_find_information_rsp_t * msg
)
This command is used to discover attribute handles and their types (UUIDs) in a given handle range.
Table: COMMAND
Silicon Labs Page of 29 220

BGScript Functions
call attclient_find_information(connection, start, end)(connection, result)
Silicon Labs Page of 30 220
Indicate Confirm
In order to use this feature the manual indication acknowledgements must be enabled to the
application configuration file (config.xml).
Table: COMMAND
Byte Type Name Description
0 0x00 hilen Message type: command
1 0x01 lolen Minimum payload length
2 0x04 class Message class: Attribute Client
3 0x07 method Message ID
4
uint8 connection
Connection Handle
Table: RESPONSE
Byte Type Name Description
0 0x00 hilen Message type: command
1 0x02 lolen Minimum payload length
2 0x04 class Message class: Attribute Client
3 0x07 method Message ID
4 - 5
uint16 result
Command result
C Functions
/* Function */
void ble_cmd_attclient_indicate_confirm(
uint8 connection
);
/* Callback */
struct ble_msg_attclient_indicate_confirm_rsp_t{
uint16 result
}
void ble_rsp_attclient_indicate_confirm(
const struct ble_msg_attclient_indicate_confirm_rsp_t * msg
)
BGScript Functions
call attclient_indicate_confirm(connection)(result)
This command can be used to send a acknowledge a received indication from a remote device. This function
allows the application to manually confirm the indicated values instead of the
automatically doing it. The benefit of this is extra reliability since the application can for example store the
received value on the flash memory before confirming the indication to the remote device.
Bluetooth
Low Energy
stack
Silicon Labs Page of 31 220
 Loading...
Loading...