Page 1

C8051F320/1
Full Speed USB, 16k ISP FLASH MCU Family
ANALOG PERIPHERALS
- 10-Bit ADC
• Up to 200 ksps
• Up to 17 or 13 External Single-Ended or Differential
Inputs
• VREF from External Pin, Internal Reference, or VDD
• Built-in Temperature Sensor
• External Conversion Start Input
- Two Comparators
- Internal Voltage Reference
- POR/Brown-Out Detector
USB FUNCTION CONTROLLER
- USB Specification 2.0 Compliant
- Full Speed (12 Mbps) or Low Speed (1.5 Mbps)
Operation
- Integrated Clock Recovery; No External Crystal
Required for Full Speed or Low Speed
- Supports Eight Flexible Endpoints
- 1k Byte USB Buffer Memory
- Integrated Transceiver; No External Resistors Required
ON-CHIP DEBUG
- On-Chip Debug Circuitry Facilitates Full Speed,
Non-Intrusive In-System Debug (No Emulator
Required!)
- Provides Breakpoints, Single Stepping,
Inspect/Modify Memory and Registers
- Superior Performance to Emulation Systems Using
ICE-Chips, Target Pods, and Sockets
VOLTAGE REGULATOR INPUT: 4.0V TO 5.25V
HIGH SPEED 8051 µC Core
- Pipelined Instruction Architecture; Executes 70% of
Instructions in 1 or 2
System Clocks
- Up to 25 MIPS Throughput with 25 MHz Clock
- Expanded Interrupt Handler
MEMORY
- 2304 Bytes Internal RAM (1k + 256 + 1k USB FIFO)
- 16k Bytes FLASH; In-system programmable in 512-byte
Sectors
DIGITAL PERIPHERALS
- 25/21 Port I/O; All 5 V tolerant with High Sink Current
- Hardware Enhanced SPI™, Enhanced UART, and
SMBus™ Serial Ports
- Four General Purpose 16-Bit Counter/Timers
- 16-Bit Programmable Counter Array (PCA) with Five
Capture/Compare Modules
- Real Time Clock Mode using External Clock Source and
PCA or Timer
CLOCK SOURCES
- Internal Oscillator: 0.25% Accuracy with Clock
Recovery enabled. Supports all USB and UART Modes
- External Oscillator: Crystal, RC, C, or Clock (1 or 2 Pin
Modes)
- Can Switch Between Clock Sources on-the-fly; Useful in
Power Saving Strategies
PACKAGES
- 32-pin LQFP (C8051F320)
- 28-pin MLP (C8051F321)
TEMPERATURE RANGE: -40°C TO +85°C
ANALOG
PERIPHERALS
A
M
U
X
TEMP
SENSOR
10-bit
200ksps
ADC
PRECISION INTERNAL
OSCILLATOR
HIGH-SPEED CONTROLLER CORE
16KB
ISP FLASH
16
INTERRUPTS
+
-
+
-
VREGVREF
8051 CPU
(25MIPS)
DEBUG
CIRCUITRY
Timer 0
Timer 1
Timer 2
Timer 3
DIGITAL I/O
UART
SPI
SMBus
PCA
CROSSBAR
USB Controller /
Transceiver
2304 B
SRAM
POR
Port 0
Port 1
Port 2
Port 3
WDT
Preliminary Rev. 1.1 12/03 Copyright © 2003 by Silicon Laboratories C8051F320/1-DS11
This information applies to a product under development. Its characteristics and specifications are subject to change without notice.
Page 2

C8051F320/1
Notes
2 Rev. 1.1
Page 3

C8051F320/1
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. SYSTEM OVERVIEW .........................................................................................................17
1.1. CIP-51™ Microcontroller Core ......................................................................................20
1.1.1. Fully 8051 Compatible ..........................................................................................20
1.1.2. Improved Throughput ............................................................................................20
1.1.3. Additional Features................................................................................................21
1.2. On-Chip Memory ............................................................................................................22
1.3. Universal Serial Bus Controller.......................................................................................23
1.4. Voltage Regulator............................................................................................................23
1.5. On-Chip Debug Circuitry ................................................................................................24
1.6. Programmable Digital I/O and Crossbar .........................................................................25
1.7. Serial Ports.......................................................................................................................25
1.8. Programmable Counter Array .........................................................................................26
1.9. 10-Bit Analog to Digital Converter.................................................................................27
1.10.Comparators ....................................................................................................................28
2. ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS..................................................................................29
3. GLOBAL DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS ......................................................30
4. PINOUT AND PACKAGE DEFINITIONS........................................................................31
5. 10-BIT ADC (ADC0) .............................................................................................................39
5.1. Analog Multiplexer .........................................................................................................40
5.2. Temperature Sensor.........................................................................................................41
5.3. Modes of Operation.........................................................................................................42
5.3.1. Starting a Conversion.............................................................................................42
5.3.2. Tracking Modes .....................................................................................................43
5.3.3. Settling Time Requirements ..................................................................................44
5.4. Programmable Window Detector ....................................................................................50
5.4.1. Window Detector In Single-Ended Mode .............................................................52
5.4.2. Window Detector In Differential Mode.................................................................53
6. VOLTAGE REFERENCE....................................................................................................55
7. COMPARATORS ................................................................................................................57
8. VOLTAGE REGULATOR (REG0) ....................................................................................67
8.1. Regulator Mode Selection ...............................................................................................68
8.2. VBUS Detection..............................................................................................................69
9. CIP-51 MICROCONTROLLER .........................................................................................73
9.1. Instruction Set..................................................................................................................75
9.1.1. Instruction and CPU Timing..................................................................................75
9.1.2. MOVX Instruction and Program Memory.............................................................75
9.2. Memory Organization .....................................................................................................79
9.2.1. Program Memory...................................................................................................79
9.2.2. Data Memory .........................................................................................................80
9.2.3. General Purpose Registers .....................................................................................80
9.2.4. Bit Addressable Locations .....................................................................................80
9.2.5. Stack ...................................................................................................................80
9.2.6. Special Function Registers.....................................................................................81
Rev. 1.1 3
Page 4

C8051F320/1
9.2.7. Register Descriptions.............................................................................................84
9.3. Interrupt Handler .............................................................................................................87
9.3.1. MCU Interrupt Sources and Vectors .....................................................................87
9.3.2. External Interrupts .................................................................................................88
9.3.3. Interrupt Priorities..................................................................................................88
9.3.4. Interrupt Latency....................................................................................................88
9.3.5. Interrupt Register Descriptions..............................................................................90
9.4. Power Management Modes .............................................................................................96
9.4.1. Idle Mode...............................................................................................................96
9.4.2. Stop Mode..............................................................................................................96
10. RESET SOURCES ..............................................................................................................99
10.1.Power-On Reset.............................................................................................................100
10.2.Power-Fail Reset / VDD Monitor..................................................................................101
10.3.External Reset................................................................................................................102
10.4.Missing Clock Detector Reset .......................................................................................102
10.5.Comparator0 Reset ........................................................................................................102
10.6.PCA Watchdog Timer Reset .........................................................................................102
10.7.FLASH Error Reset .......................................................................................................102
10.8.Software Reset...............................................................................................................103
10.9.USB Reset .....................................................................................................................103
11. FLASH MEMORY ............................................................................................................107
11.1.Programming The FLASH Memory .............................................................................107
11.1.1. FLASH Lock and Key Functions ........................................................................107
11.1.2. FLASH Erase Procedure......................................................................................107
11.1.3. FLASH Write Procedure .....................................................................................108
11.2.Non-volatile Data Storage .............................................................................................109
11.3.Security Options ............................................................................................................109
12. EXTERNAL RAM .............................................................................................................113
12.1.Accessing User XRAM .................................................................................................113
12.2.Accessing USB FIFO Space..........................................................................................114
13. OSCILLATORS...................................................................................................................117
13.1.Programmable Internal Oscillator .................................................................................117
13.1.1. Programming the Internal Oscillator on C8051F320/1 Devices .........................118
13.1.2. Internal Oscillator Suspend Mode .......................................................................118
13.2.External Oscillator Drive Circuit...................................................................................120
13.2.1. Clocking Timers Directly Through the External Oscillator ................................120
13.2.2. External Crystal Example ....................................................................................120
13.2.3. External RC Example ..........................................................................................121
13.2.4. External Capacitor Example ................................................................................121
13.3.4x Clock Multiplier .......................................................................................................123
13.4.System and USB Clock Selection .................................................................................124
13.4.1. System Clock Selection .......................................................................................124
13.4.2. USB Clock Selection ...........................................................................................124
14. PORT INPUT/OUTPUT ...................................................................................................127
14.1.Priority Crossbar Decoder .............................................................................................129
4 Rev. 1.1
Page 5

C8051F320/1
14.2.Port I/O Initialization.....................................................................................................131
14.3.General Purpose Port I/O...............................................................................................134
15. UNIVERSAL SERIAL BUS CONTROLLER (USB0) ....................................................143
15.1.Endpoint Addressing .....................................................................................................144
15.2.USB Transceiver ...........................................................................................................144
15.3.USB Register Access.....................................................................................................146
15.4.USB Clock Configuration .............................................................................................150
15.5.FIFO Management.........................................................................................................151
15.5.1. FIFO Split Mode..................................................................................................151
15.5.2. FIFO Double Buffering .......................................................................................151
15.5.3. FIFO Access ........................................................................................................152
15.6.Function Addressing......................................................................................................153
15.7.Function Configuration and Control .............................................................................154
15.8.Interrupts .......................................................................................................................157
15.9.The Serial Interface Engine ...........................................................................................161
15.10.Endpoint0.....................................................................................................................161
15.10.1.Endpoint0 SETUP Transactions .........................................................................162
15.10.2.Endpoint0 IN Transactions .................................................................................162
15.10.3.Endpoint0 OUT Transactions .............................................................................163
15.11.Configuring Endpoints1-3 ...........................................................................................166
15.12.Controlling Endpoints1-3 IN .......................................................................................166
15.12.1.Endpoints1-3 IN Interrupt or Bulk Mode ...........................................................166
15.12.2.Endpoints1-3 IN Isochronous Mode...................................................................167
15.13.Controlling Endpoints1-3 OUT ...................................................................................170
15.13.1.Endpoints1-3 OUT Interrupt or Bulk Mode .......................................................170
15.13.2.Endpoints1-3 OUT Isochronous Mode...............................................................170
16. SMBUS..................................................................................................................................175
16.1.Supporting Documents ..................................................................................................176
16.2.SMBus Configuration....................................................................................................176
16.3.SMBus Operation ..........................................................................................................177
16.3.1. Arbitration............................................................................................................177
16.3.2. Clock Low Extension...........................................................................................178
16.3.3. SCL Low Timeout ...............................................................................................178
16.3.4. SCL High (SMBus Free) Timeout.......................................................................178
16.4.Using the SMBus...........................................................................................................179
16.4.1. SMBus Configuration Register............................................................................180
16.4.2. SMB0CN Control Register..................................................................................183
16.4.3. Data Register........................................................................................................186
16.5.SMBus Transfer Modes.................................................................................................187
16.5.1. Master Transmitter Mode ....................................................................................187
16.5.2. Master Receiver Mode.........................................................................................188
16.5.3. Slave Receiver Mode ...........................................................................................189
16.5.4. Slave Transmitter Mode.......................................................................................190
16.6.SMBus Status Decoding................................................................................................191
17. UART0 ..................................................................................................................................193
Rev. 1.1 5
Page 6

C8051F320/1
17.1.Enhanced Baud Rate Generation...................................................................................194
17.2.Operational Modes ........................................................................................................195
17.2.1. 8-Bit UART .........................................................................................................195
17.2.2. 9-Bit UART .........................................................................................................196
17.3.Multiprocessor Communications...................................................................................197
18. ENHANCED SERIAL PERIPHERAL INTERFACE (SPI0) .........................................203
18.1.Signal Descriptions........................................................................................................204
18.1.1. Master Out, Slave In (MOSI) ..............................................................................204
18.1.2. Master In, Slave Out (MISO) ..............................................................................204
18.1.3. Serial Clock (SCK) ..............................................................................................204
18.1.4. Slave Select (NSS)...............................................................................................204
18.2.SPI0 Master Mode Operation ........................................................................................205
18.3.SPI0 Slave Mode Operation ..........................................................................................207
18.4.SPI0 Interrupt Sources...................................................................................................207
18.5.Serial Clock Timing ......................................................................................................208
18.6.SPI Special Function Registers .....................................................................................210
19. TIMERS ...............................................................................................................................217
19.1.Timer 0 and Timer 1......................................................................................................217
19.1.1. Mode 0: 13-bit Counter/Timer.............................................................................217
19.1.2. Mode 1: 16-bit Counter/Timer.............................................................................218
19.1.3. Mode 2: 8-bit Counter/Timer with Auto-Reload.................................................219
19.1.4. Mode 3: Two 8-bit Counter/Timers (Timer 0 Only) ...........................................220
19.2.Timer 2 .......................................................................................................................225
19.2.1. 16-bit Timer with Auto-Reload ...........................................................................225
19.2.2. 8-bit Timers with Auto-Reload............................................................................226
19.2.3. USB Start-of-Frame Capture ...............................................................................227
19.3.Timer 3 .......................................................................................................................230
19.3.1. 16-bit Timer with Auto-Reload ...........................................................................230
19.3.2. 8-bit Timers with Auto-Reload............................................................................231
19.3.3. USB Start-of-Frame Capture ...............................................................................232
20. PROGRAMMABLE COUNTER ARRAY (PCA0) .........................................................235
20.1.PCA Counter/Timer.......................................................................................................236
20.2.Capture/Compare Modules............................................................................................237
20.2.1. Edge-triggered Capture Mode .............................................................................238
20.2.2. Software Timer (Compare) Mode........................................................................239
20.2.3. High Speed Output Mode ....................................................................................240
20.2.4. Frequency Output Mode ......................................................................................241
20.2.5. 8-Bit Pulse Width Modulator Mode ....................................................................242
20.2.6. 16-Bit Pulse Width Modulator Mode ..................................................................244
20.3.Watchdog Timer Mode..................................................................................................246
20.3.1. Watchdog Timer Operation .................................................................................246
20.3.2. Watchdog Timer Usage .......................................................................................247
20.4.Register Descriptions for PCA ......................................................................................248
21. C2 INTERFACE ..................................................................................................................253
21.1.C2 Interface Registers ...................................................................................................253
6 Rev. 1.1
Page 7

C8051F320/1
21.2.C2 Pin Sharing...............................................................................................................255
Rev. 1.1 7
Page 8

C8051F320/1
Notes
8 Rev. 1.1
Page 9

C8051F320/1
LIST OF FIGURES AND TABLES
1. SYSTEM OVERVIEW ........................................................................................................17
Table 1.1. Product Selection Guide......................................................................................17
Figure 1.1. C8051F320 Block Diagram.................................................................................18
Figure 1.2. C8051F321 Block Diagram.................................................................................19
Figure 1.3. Comparison of Peak MCU Execution Speeds.....................................................20
Figure 1.4. On-Chip Clock and Reset....................................................................................21
Figure 1.5. On-Board Memory Map ......................................................................................22
Figure 1.6. USB Controller Block Diagram ..........................................................................23
Figure 1.7. Development/In-System Debug Diagram ...........................................................24
Figure 1.8. Digital Crossbar Diagram....................................................................................25
Figure 1.9. PCA Block Diagram............................................................................................26
Figure 1.10. PCA Block Diagram............................................................................................26
Figure 1.11. 10-Bit ADC Block Diagram................................................................................27
Figure 1.12. Comparator0 Block Diagram ..............................................................................28
2. ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS .................................................................................29
Table 2.1. Absolute Maximum Ratings*..............................................................................29
3. GLOBAL DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS .....................................................30
Table 3.1. Global DC Electrical Characteristics...................................................................30
4. PINOUT AND PACKAGE DEFINITIONS .......................................................................31
Table 4.1. Pin Definitions for the C8051F320/1 ..................................................................31
Figure 4.1. LQFP-32 Pinout Diagram (Top View)................................................................33
Figure 4.2. LQFP-32 Package Diagram.................................................................................34
Table 4.2. LQFP-32 Package Dimensions............................................................................34
Figure 4.3. MLP-28 Pinout Diagram (Top View) .................................................................35
Figure 4.4. MLP-28 Package Drawing ..................................................................................36
Table 4.3. MLP-28 Package Dimensions .............................................................................36
Figure 4.5. Typical MLP-28 Landing Diagram .....................................................................37
Figure 4.6. Typical MLP-28 Solder Mask.............................................................................38
5. 10-BIT ADC (ADC0) ............................................................................................................39
Figure 5.1. ADC0 Functional Block Diagram.......................................................................39
Figure 5.2. Typical Temperature Sensor Transfer Function..................................................41
Figure 5.3. 10-Bit ADC Track and Conversion Example Timing.........................................43
Figure 5.4. ADC0 Equivalent Input Circuits .........................................................................44
Figure 5.5. AMX0P: AMUX0 Positive Channel Select Register..........................................45
Figure 5.6. AMX0N: AMUX0 Negative Channel Select Register........................................46
Figure 5.7. ADC0CF: ADC0 Configuration Register ...........................................................47
Figure 5.8. ADC0H: ADC0 Data Word MSB Register.........................................................47
Figure 5.9. ADC0L: ADC0 Data Word LSB Register ..........................................................48
Figure 5.10. ADC0CN: ADC0 Control Register.....................................................................49
Figure 5.11. ADC0GTH: ADC0 Greater-Than Data High Byte Register...............................50
Figure 5.12. ADC0GTL: ADC0 Greater-Than Data Low Byte Register................................50
Figure 5.13. ADC0LTH: ADC0 Less-Than Data High Byte Register....................................51
Figure 5.14. ADC0LTL: ADC0 Less-Than Data Low Byte Register .....................................51
Rev. 1.1 9
Page 10

C8051F320/1
Figure 5.15. ADC Window Compare Example: Right-Justified Single-Ended Data..............52
Figure 5.16. ADC Window Compare Example: Left-Justified Single-Ended Data................52
Figure 5.17. ADC Window Compare Example: Right-Justified Differential Data.................53
Figure 5.18. ADC Window Compare Example: Left-Justified Differential Data ...................53
Table 5.1. ADC0 Electrical Characteristics..........................................................................54
6. VOLTAGE REFERENCE ...................................................................................................55
Figure 6.1. Voltage Reference Functional Block Diagram....................................................55
Figure 6.2. REF0CN: Reference Control Register ................................................................56
Table 6.1. Voltage Reference Electrical Characteristics ......................................................56
7. COMPARATORS ...............................................................................................................57
Figure 7.1. Comparator0 Functional Block Diagram ............................................................57
Figure 7.2. Comparator1 Functional Block Diagram ............................................................58
Figure 7.3. Comparator Hysteresis Plot.................................................................................59
Figure 7.4. CPT0CN: Comparator0 Control Register ...........................................................60
Figure 7.5. CPT0MX: Comparator0 MUX Selection Register..............................................61
Figure 7.6. CPT0MD: Comparator0 Mode Selection Register..............................................62
Figure 7.7. CPT1CN: Comparator1 Control Register ...........................................................63
Figure 7.8. CPT1MX: Comparator1 MUX Selection Register..............................................64
Figure 7.9. CPT1MD: Comparator1 Mode Selection Register..............................................65
Table 7.1. Comparator Electrical Characteristics.................................................................66
8. VOLTAGE REGULATOR (REG0) ...................................................................................67
Table 8.1. Voltage Regulator Electrical Specifications........................................................69
Figure 8.1. REG0 Configuration: USB Bus-Powered ...........................................................70
Figure 8.2. REG0 Configuration: USB Self-Powered...........................................................70
Figure 8.3. REG0 Configuration: USB Self-Powered, Regulator Disabled..........................71
Figure 8.4. REG0 Configuration: No USB Connection ........................................................71
Figure 8.5. REG0CN: Voltage Regulator Control.................................................................72
9. CIP-51 MICROCONTROLLER ........................................................................................73
Figure 9.1. CIP-51 Block Diagram ........................................................................................73
Table 9.1. CIP-51 Instruction Set Summary.........................................................................75
Figure 9.2. Memory Map .......................................................................................................79
Table 9.2. Special Function Register (SFR) Memory Map..................................................81
Table 9.3. Special Function Registers ..................................................................................81
Figure 9.3. DPL: Data Pointer Low Byte ..............................................................................84
Figure 9.4. DPH: Data Pointer High Byte .............................................................................84
Figure 9.5. SP: Stack Pointer .................................................................................................85
Figure 9.6. PSW: Program Status Word ................................................................................85
Figure 9.7. ACC: Accumulator..............................................................................................86
Figure 9.8. B: B Register .......................................................................................................86
Table 9.4. Interrupt Summary...............................................................................................89
Figure 9.9. IE: Interrupt Enable .............................................................................................90
Figure 9.10. IP: Interrupt Priority ............................................................................................91
Figure 9.11. EIE1: Extended Interrupt Enable 1 .....................................................................92
Figure 9.12. EIP1: Extended Interrupt Priority 1.....................................................................93
Figure 9.13. EIE2: Extended Interrupt Enable 2 .....................................................................94
10 Rev. 1.1
Page 11

C8051F320/1
Figure 9.14. EIP2: Extended Interrupt Priority 2.....................................................................94
Figure 9.15. IT01CF: INT0/INT1 Configuration Register ......................................................95
Figure 9.16. PCON: Power Control Register ..........................................................................97
10. RESET SOURCES .............................................................................................................99
Figure 10.1. Reset Sources ......................................................................................................99
Figure 10.2. Power-On and VDD Monitor Reset Timing .....................................................100
Figure 10.3. VDM0CN: VDD Monitor Control ....................................................................101
Figure 10.4. RSTSRC: Reset Source Register.......................................................................104
Table 10.1. Reset Electrical Characteristics .........................................................................105
11. FLASH MEMORY ...........................................................................................................107
Table 11.1. FLASH Electrical Characteristics .....................................................................108
Figure 11.1. FLASH Program Memory Map and Security Byte...........................................110
Figure 11.2. PSCTL: Program Store R/W Control................................................................110
Figure 11.3. FLKEY: FLASH Lock and Key Register .........................................................111
Figure 11.4. FLSCL: FLASH Scale Register ........................................................................111
12. EXTERNAL RAM ............................................................................................................113
Figure 12.1. External Ram Memory Map..............................................................................113
Figure 12.2. XRAM Memory Map Expanded View .............................................................114
Figure 12.3. EMI0CN: External Memory Interface Control .................................................115
13. OSCILLATORS ..................................................................................................................117
Figure 13.1. Oscillator Diagram ............................................................................................117
Figure 13.2. OSCICN: Internal Oscillator Control Register .................................................119
Figure 13.3. OSCICL: Internal Oscillator Calibration Register ............................................119
Figure 13.4. OSCXCN: External Oscillator Control Register...............................................122
Figure 13.5. CLKMUL: Clock Multiplier Control Register..................................................123
Table 13.1. Typical USB Full Speed Clock Settings ...........................................................124
Table 13.2. Typical USB Low Speed Clock Settings...........................................................124
Figure 13.6. CLKSEL: Clock Select Register .......................................................................125
Table 13.3. Internal Oscillator Electrical Characteristics.....................................................126
14. PORT INPUT/OUTPUT ..................................................................................................127
Figure 14.1. Port I/O Functional Block Diagram ..................................................................127
Figure 14.2. Port I/O Cell Block Diagram.............................................................................128
Figure 14.3. Crossbar Priority Decoder with No Pins Skipped .............................................129
Figure 14.4. Crossbar Priority Decoder with Crystal Pins Skipped ......................................130
Figure 14.5. XBR0: Port I/O Crossbar Register 0 .................................................................132
Figure 14.6. XBR1: Port I/O Crossbar Register 1 .................................................................133
Figure 14.7. P0: Port0 Register..............................................................................................135
Figure 14.8. P0MDIN: Port0 Input Mode Register ...............................................................135
Figure 14.9. P0MDOUT: Port0 Output Mode Register.........................................................136
Figure 14.10. P0SKIP: Port0 Skip Register...........................................................................136
Figure 14.11. P1: Port1 Register............................................................................................137
Figure 14.12. P1MDIN: Port1 Input Mode Register .............................................................137
Figure 14.13. P1MDOUT: Port1 Output Mode Register.......................................................138
Figure 14.14. P1SKIP: Port1 Skip Register...........................................................................138
Figure 14.15. P2: Port2 Register............................................................................................139
Rev. 1.1 11
Page 12

C8051F320/1
Figure 14.16. P2MDIN: Port2 Input Mode Register .............................................................139
Figure 14.17. P2MDOUT: Port2 Output Mode Register.......................................................140
Figure 14.18. P2SKIP: Port2 Skip Register...........................................................................140
Figure 14.19. P3: Port3 Register............................................................................................141
Figure 14.20. P3MDIN: Port3 Input Mode Register .............................................................141
Figure 14.21. P3MDOUT: Port3 Output Mode Register.......................................................142
Table 14.1. Port I/O DC Electrical Characteristics ..............................................................142
15. UNIVERSAL SERIAL BUS CONTROLLER (USB0) ...................................................143
Figure 15.1. USB0 Block Diagram........................................................................................143
Table 15.1. Endpoint Addressing Scheme............................................................................144
Figure 15.2. USB0XCN: USB0 Transceiver Control............................................................145
Figure 15.3. USB0 Register Access Scheme.........................................................................146
Figure 15.4. USB0ADR: USB0 Indirect Address Register ...................................................147
Figure 15.5. USB0DAT: USB0 Data Register ......................................................................148
Figure 15.6. INDEX: USB0 Endpoint Index (USB Register) ...............................................148
Table 15.2. USB0 Controller Registers................................................................................149
Figure 15.7. CLKREC: Clock Recovery Control (USB Register) ........................................150
Figure 15.8. USB FIFO Allocation........................................................................................151
Table 15.3. FIFO Configurations .........................................................................................152
Figure 15.9. FIFOn: USB0 Endpoint FIFO Access (USB Registers) ...................................152
Figure 15.10. FADDR: USB0 Function Address (USB Register) ........................................153
Figure 15.11. POWER: USB0 Power (USB Register) ..........................................................155
Figure 15.12. FRAMEL: USB0 Frame Number Low (USB Register) .................................156
Figure 15.13. FRAMEH: USB0 Frame Number High (USB Register) ................................156
Figure 15.14. IN1INT: USB0 IN Endpoint Interrupt (USB Register)...................................157
Figure 15.15. OUT1INT: USB0 Out Endpoint Interrupt (USB Register).............................158
Figure 15.16. CMINT: USB0 Common Interrupt (USB Register)........................................159
Figure 15.17. IN1IE: USB0 IN Endpoint Interrupt Enable (USB Register) .........................160
Figure 15.18. OUT1IE: USB0 Out Endpoint Interrupt Enable (USB Register)....................160
Figure 15.19. CMIE: USB0 Common Interrupt Enable (USB Register) ..............................161
Figure 15.20. E0CSR: USB0 Endpoint0 Control (USB Register) ........................................164
Figure 15.21. E0CNT: USB0 Endpoint 0 Data Count (USB Register).................................165
Figure 15.22. EINCSRL: USB0 IN Endpoint Control High Byte (USB Register) ...............168
Figure 15.23. EINCSRH: USB0 IN Endpoint Control Low Byte (USB Register) ...............169
Figure 15.24. EOUTCSRL: USB0 OUT Endpoint Control High Byte (USB Register) .......171
Figure 15.25. EOUTCSRH: USB0 OUT Endpoint Control Low Byte (USB Register) .......172
Figure 15.26. EOUTCNTL: USB0 OUT Endpoint Count Low (USB Register) ..................172
Figure 15.27. EOUTCNTH: USB0 OUT Endpoint Count High (USB Register) .................172
Table 15.4. USB Transceiver Electrical Characteristics ......................................................173
16. SMBUS .................................................................................................................................175
Figure 16.1. SMBus Block Diagram .....................................................................................175
Figure 16.2. Typical SMBus Configuration ..........................................................................176
Figure 16.3. SMBus Transaction ...........................................................................................177
Table 16.1. SMBus Clock Source Selection.........................................................................180
Figure 16.4. Typical SMBus SCL Generation.......................................................................181
12 Rev. 1.1
Page 13

C8051F320/1
Table 16.2. Minimum SDA Setup and Hold Times .............................................................181
Figure 16.5. SMB0CF: SMBus Clock/Configuration Register .............................................182
Figure 16.6. SMB0CN: SMBus Control Register .................................................................184
Table 16.3. Sources for Hardware Changes to SMB0CN ....................................................185
Figure 16.7. SMB0DAT: SMBus Data Register ...................................................................186
Figure 16.8. Typical Master Transmitter Sequence...............................................................187
Figure 16.9. Typical Master Receiver Sequence ...................................................................188
Figure 16.10. Typical Slave Receiver Sequence ...................................................................189
Figure 16.11. Typical Slave Transmitter Sequence...............................................................190
Table 16.4. SMBus Status Decoding....................................................................................191
17. UART0 .................................................................................................................................193
Figure 17.1. UART0 Block Diagram.....................................................................................193
Figure 17.2. UART0 Baud Rate Logic ..................................................................................194
Figure 17.3. UART Interconnect Diagram ............................................................................195
Figure 17.4. 8-Bit UART Timing Diagram ...........................................................................195
Figure 17.5. 9-Bit UART Timing Diagram ...........................................................................196
Figure 17.6. UART Multi-Processor Mode Interconnect Diagram .......................................197
Figure 17.7. SCON0: Serial Port 0 Control Register.............................................................198
Figure 17.8. SBUF0: Serial (UART0) Port Data Buffer Register .........................................199
Table 17.1. Timer Settings for Standard Baud Rates Using The Internal Oscillator ...........200
Table 17.2. Timer Settings for Standard Baud Rates Using an External Oscillator.............200
Table 17.3. Timer Settings for Standard Baud Rates Using an External Oscillator.............201
Table 17.4. Timer Settings for Standard Baud Rates Using an External Oscillator.............201
Table 17.5. Timer Settings for Standard Baud Rates Using an External Oscillator.............202
Table 17.6. Timer Settings for Standard Baud Rates Using an External Oscillator.............202
18. ENHANCED SERIAL PERIPHERAL INTERFACE (SPI0) ........................................203
Figure 18.1. SPI Block Diagram............................................................................................203
Figure 18.2. Multiple-Master Mode Connection Diagram ....................................................206
Figure 18.3. 3-Wire Single Master and 3-Wire Single Slave Mode Connection Diagram ...206
Figure 18.4. 4-Wire Single Master Mode and 4-Wire Slave Mode Connection Diagram ....206
Figure 18.5. Master Mode Data/Clock Timing......................................................................208
Figure 18.6. Slave Mode Data/Clock Timing (CKPHA = 0) ................................................209
Figure 18.7. Slave Mode Data/Clock Timing (CKPHA = 1) ................................................209
Figure 18.8. SPI0CFG: SPI0 Configuration Register............................................................210
Figure 18.9. SPI0CN: SPI0 Control Register ........................................................................211
Figure 18.10. SPI0CKR: SPI0 Clock Rate Register..............................................................212
Figure 18.11. SPI0DAT: SPI0 Data Register ........................................................................213
Figure 18.12. SPI Master Timing (CKPHA = 0)...................................................................214
Figure 18.13. SPI Master Timing (CKPHA = 1)...................................................................214
Figure 18.14. SPI Slave Timing (CKPHA = 0) .....................................................................215
Figure 18.15. SPI Slave Timing (CKPHA = 1) .....................................................................215
Table 18.1. SPI Slave Timing Parameters............................................................................216
19. TIMERS ..............................................................................................................................217
Figure 19.1. T0 Mode 0 Block Diagram................................................................................218
Figure 19.2. T0 Mode 2 Block Diagram................................................................................219
Rev. 1.1 13
Page 14

C8051F320/1
Figure 19.3. T0 Mode 3 Block Diagram................................................................................220
Figure 19.4. TCON: Timer Control Register.........................................................................221
Figure 19.5. TMOD: Timer Mode Register...........................................................................222
Figure 19.6. CKCON: Clock Control Register......................................................................223
Figure 19.7. TL0: Timer 0 Low Byte ....................................................................................224
Figure 19.8. TL1: Timer 1 Low Byte ....................................................................................224
Figure 19.9. TH0: Timer 0 High Byte ...................................................................................224
Figure 19.10. TH1: Timer 1 High Byte .................................................................................224
Figure 19.11. Timer 2 16-Bit Mode Block Diagram .............................................................225
Figure 19.12. Timer 2 8-Bit Mode Block Diagram ...............................................................226
Figure 19.13. Timer 2 SOF Capture Mode (T2SPLIT = ‘0’) ................................................227
Figure 19.14. Timer 2 SOF Capture Mode (T2SPLIT = ‘1’) ................................................227
Figure 19.15. TMR2CN: Timer 2 Control Register ..............................................................228
Figure 19.16. TMR2RLL: Timer 2 Reload Register Low Byte ............................................229
Figure 19.17. TMR2RLH: Timer 2 Reload Register High Byte ...........................................229
Figure 19.18. TMR2L: Timer 2 Low Byte ............................................................................229
Figure 19.19. TMR2H Timer 2 High Byte ............................................................................229
Figure 19.20. Timer 3 16-Bit Mode Block Diagram .............................................................230
Figure 19.21. Timer 3 8-Bit Mode Block Diagram ...............................................................231
Figure 19.22. Timer 3 SOF Capture Mode (T3SPLIT = ‘0’) ................................................232
Figure 19.23. Timer 3 SOF Capture Mode (T3SPLIT = ‘1’) ................................................232
Figure 19.24. TMR3CN: Timer 3 Control Register ..............................................................233
Figure 19.25. TMR3RLL: Timer 3 Reload Register Low Byte ............................................234
Figure 19.26. TMR3RLH: Timer 3 Reload Register High Byte ...........................................234
Figure 19.27. TMR3L: Timer 3 Low Byte ............................................................................234
Figure 19.28. TMR3H Timer 3 High Byte ............................................................................234
20. PROGRAMMABLE COUNTER ARRAY (PCA0) ........................................................235
Figure 20.1. PCA Block Diagram..........................................................................................235
Figure 20.2. PCA Counter/Timer Block Diagram.................................................................236
Table 20.1. PCA Timebase Input Options............................................................................236
Figure 20.3. PCA Interrupt Block Diagram...........................................................................237
Table 20.2. PCA0CPM Register Settings for PCA Capture/Compare Modules..................237
Figure 20.4. PCA Capture Mode Diagram ............................................................................238
Figure 20.5. PCA Software Timer Mode Diagram................................................................239
Figure 20.6. PCA High Speed Output Mode Diagram ..........................................................240
Figure 20.7. PCA Frequency Output Mode...........................................................................241
Figure 20.8. PCA 8-Bit PWM Mode Diagram ......................................................................243
Figure 20.9. PCA 16-Bit PWM Mode ...................................................................................244
Figure 20.10. PCA Module 4 with Watchdog Timer Enabled ..............................................246
Table 20.3. Watchdog Timer Timeout Intervals† ................................................................247
Figure 20.11. PCA0CN: PCA Control Register ....................................................................248
Figure 20.12. PCA0MD: PCA Mode Register ......................................................................249
Figure 20.13. PCA0CPMn: PCA Capture/Compare Mode Registers ...................................250
Figure 20.14. PCA0L: PCA Counter/Timer Low Byte .........................................................251
Figure 20.15. PCA0H: PCA Counter/Timer High Byte ........................................................251
14 Rev. 1.1
Page 15

C8051F320/1
Figure 20.16. PCA0CPLn: PCA Capture Module Low Byte ................................................252
Figure 20.17. PCA0CPHn: PCA Capture Module High Byte...............................................252
21. C2 INTERFACE .................................................................................................................253
Figure 21.1. C2ADD: C2 Address Register ..........................................................................253
Figure 21.2. DEVICEID: C2 Device ID Register .................................................................253
Figure 21.3. REVID: C2 Revision ID Register .....................................................................254
Figure 21.4. FPCTL: C2 FLASH Programming Control Register ........................................254
Figure 21.5. FPDAT: C2 FLASH Programming Data Register ............................................254
Figure 21.6. Typical C2 Pin Sharing .....................................................................................255
Rev. 1.1 15
Page 16

C8051F320/1
Notes
16 Rev. 1.1
Page 17
C8051F320/1
1. SYSTEM OVERVIEW
C8051F320/1 devices are fully integrated mixed-signal System-on-a-Chip MCUs. Highlighted features are listed
below. Refer to
• High-speed pipelined 8051-compatible microcontroller core (up to 25 MIPS)
• In-system, full-speed, non-intrusive debug interface (on-chip)
• Universal Serial Bus (USB) Function Controller with eight flexible endpoint pipes, integrated transceiver, and
1k
FIFO RAM
• Supply Voltage Regulator (5V-to-3V)
• True 10-bit 200 ksps 17-channel single-ended/differential ADC with analog multiplexer
• On-chip Voltage Reference and Temperature Sensor
• On-chip Voltage Comparators (2)
• Precision programmable 12 MHz internal oscillator and 4x clock multiplier
• 16k bytes of on-chip FLASH memory
• 2304 total bytes of on-chip RAM (256 + 1k + 1k USB FIFO)
•SMBus/I2C, Enhanced UART, and Enhanced SPI serial interfaces implemented in hardware
• Four general-purpose 16-bit timers
• Programmable Counter/Timer Array (PCA) with five capture/compare modules and Watchdog Timer function
• On-chip Power-On Reset, VDD Monitor, and Missing Clock Detector
• 25/21 Port I/O (5V tolerant)
Tabl e 1.1 for specific product feature selection.
With on-chip Power-On Reset, VDD monitor, Voltage Regulator, Watchdog Timer, and clock oscillator,
C8051F320/1 devices are truly stand-alone System-on-a-Chip solutions. The FLASH memory can be reprogrammed
in-circuit, providing non-volatile data storage, and also allowing field upgrades of the 8051 firmware. User software
has complete control of all peripherals, and may individually shut down any or all peripherals for power savings.
The on-chip Silicon Labs 2-Wire (C2) Development Interface allows non-intrusive (uses no on-chip resources), full
speed, in-circuit debugging using the production MCU installed in the final application. This debug logic supports
inspection and modification of memory and registers, setting breakpoints, single stepping, run and halt commands.
All analog and digital peripherals are fully functional while debugging using C2. The two C2 interface pins can be
shared with user functions, allowing in-system debugging without occupying package pins.
Each device is specified for 2.7 V-t o- 3. 6 V operation over the industrial temperature range (-40°C to +85°C). (Note
that 3.0
to 5
V-t o- 3. 6 V is required for USB communication.) The Port I/O and /RST pins are tolerant of input signals up
V. C8051F320/1 are available in a 32-pin LQFP or a 28-pin MLP package.
Tab le 1.1. Product Selection Guide
C
2
MIPS (Peak)
FLASH Memory
C8051F320 25 16k 2304 3 3 3 3 3 3 4 3 25 3 3 3 2 LQFP-32
C8051F321 25 16k 2304 3 3 3 3 3 3 4 3 21 3 3 3 2 MLP-28
RAM
Calibrated Internal Oscillator
USB
Supply Voltage Regulator
SMBus/I
Enhanced SPI
UART
Timers (16-bit)
Programmable Counter Array
Digital Port I/Os
10-bit 200ksps ADC
Temperature Sensor
Voltage Reference
Rev. 1.1 17
Analog Comparators
Package
Page 18
C8051F320/1
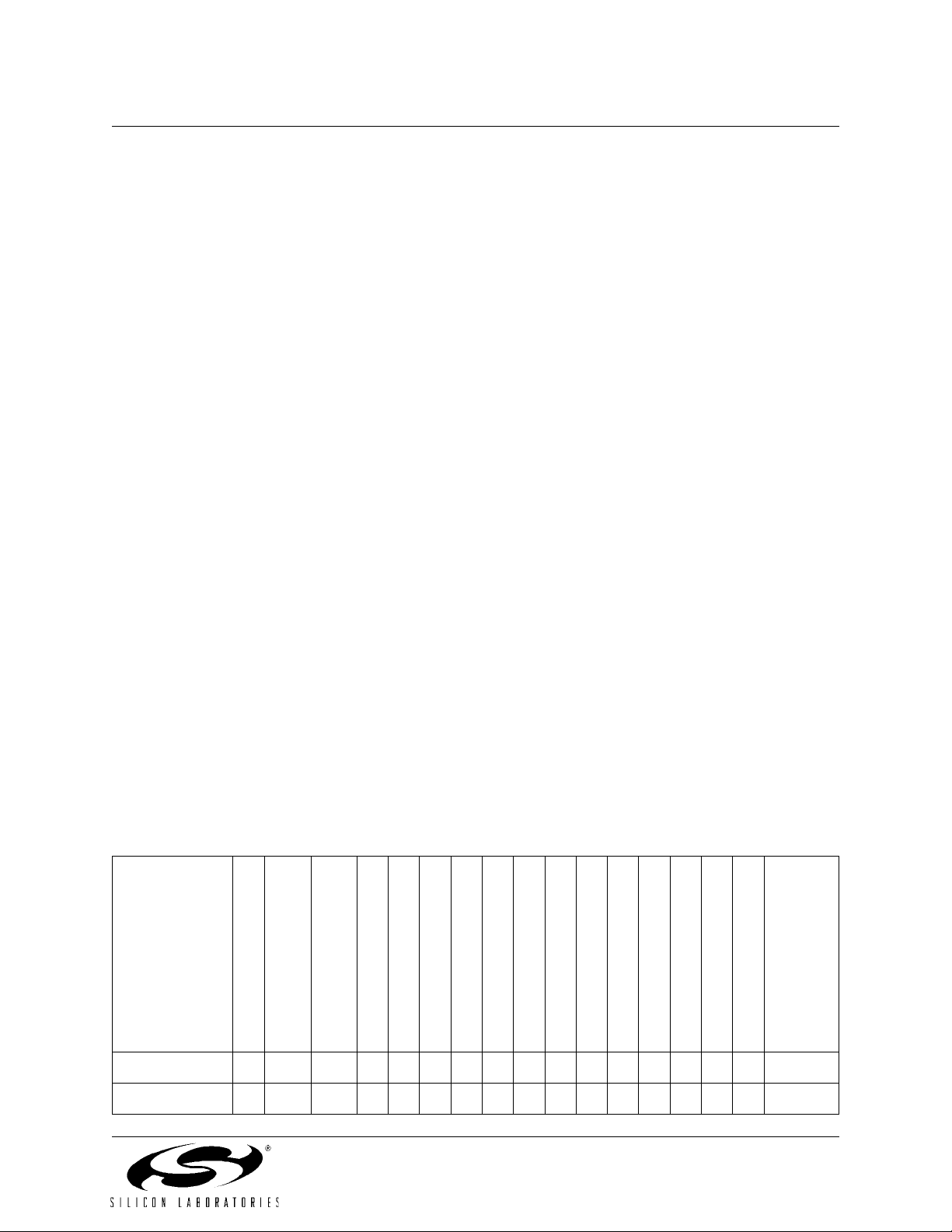
Figure 1.1. C8051F320 Block Diagram
REGIN
VDD
GND
/RST/C2CK
VBUS
D+
D-
Analog/Digital
C2D
XTAL1 XTAL2
External
Oscillator
Circuit
12MHz
Internal
Oscillator
Clock
Recovery
5.0V
Power
IN
Regulator
POR
Voltage
OUT
Debug HW
Brown-
Out
x4 2
2
1,2,3,4
USB
Transceiver
Enable
USB Clock
Controller
1K byte USB
System
USB
SRAM
Reset
Clock
8
0
5
1
C
o
SFR Bus
r
e
16kbyte
FLASH
256 byte
SRAM
1K byte
XRAM
VREF
VDD
Port 0
Latch
Port 1
Latch
UART
Timer
0,1,2,3 /
RTC
PCA/
WDT
SMBus
SPI
Port 2
Latch
Port 3
Latch
VREF
10-bit
200ksps
ADC
P
0
D
r
v
C
P
R
1
O
S
D
S
r
B
v
A
R
P
2
D
r
v
P
3
D
r
v
CP0
+
-
CP1
+
-
Temp
A
AIN0-AIN16
M
VDD
U
X
VREF
P0.0
P0.1
P0.2/XTAL1
P0.3/XTAL2
P0.4
P0.5
P0.6/CNVSTR
P0.7/VREF
P1.0
P1.1
P1.2
P1.3
P1.4
P1.5
P1.6
P1.7
P2.0
P2.1
P2.2
P2.3
P2.4
P2.5
P2.6
P2.7
P3.0/C2D
18 Rev. 1.1
Page 19
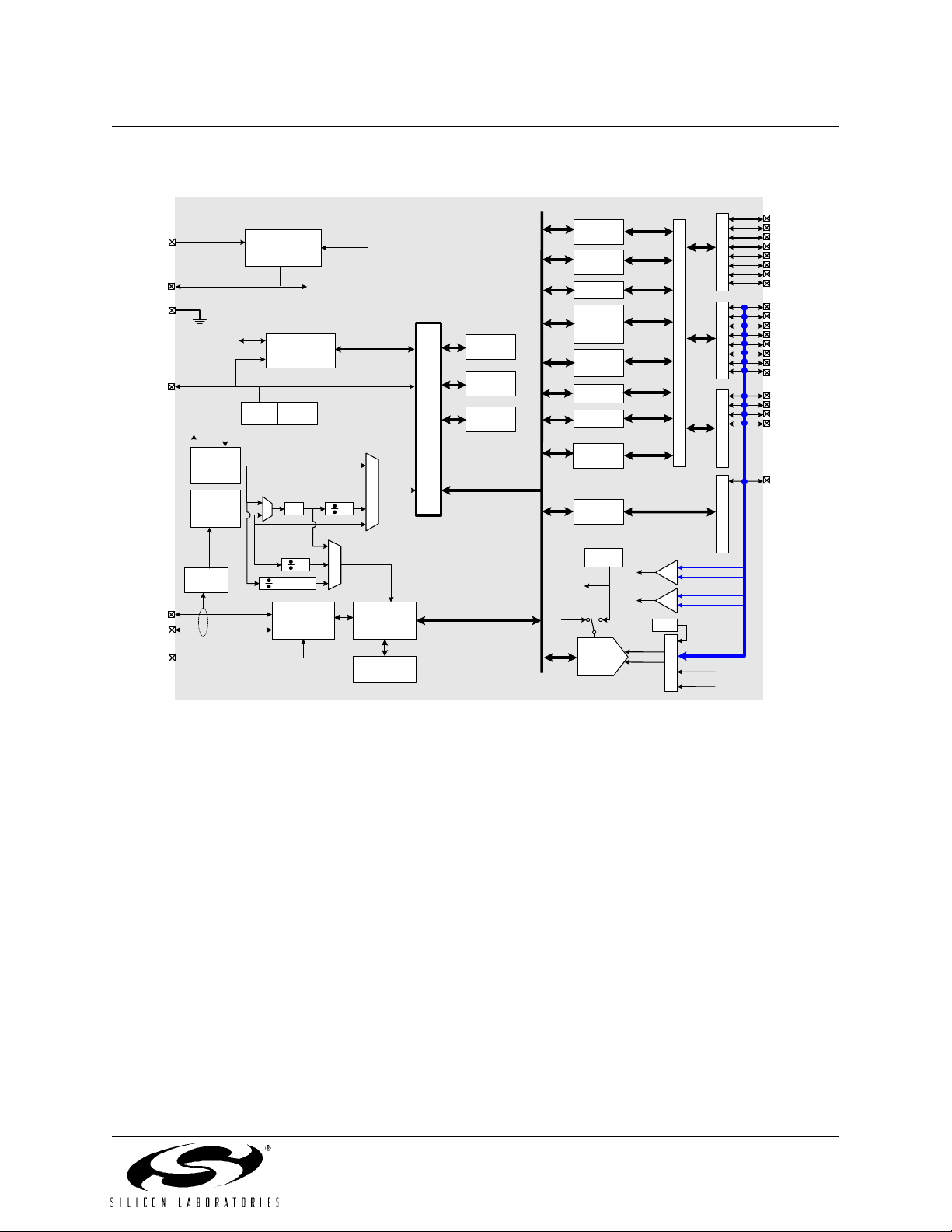
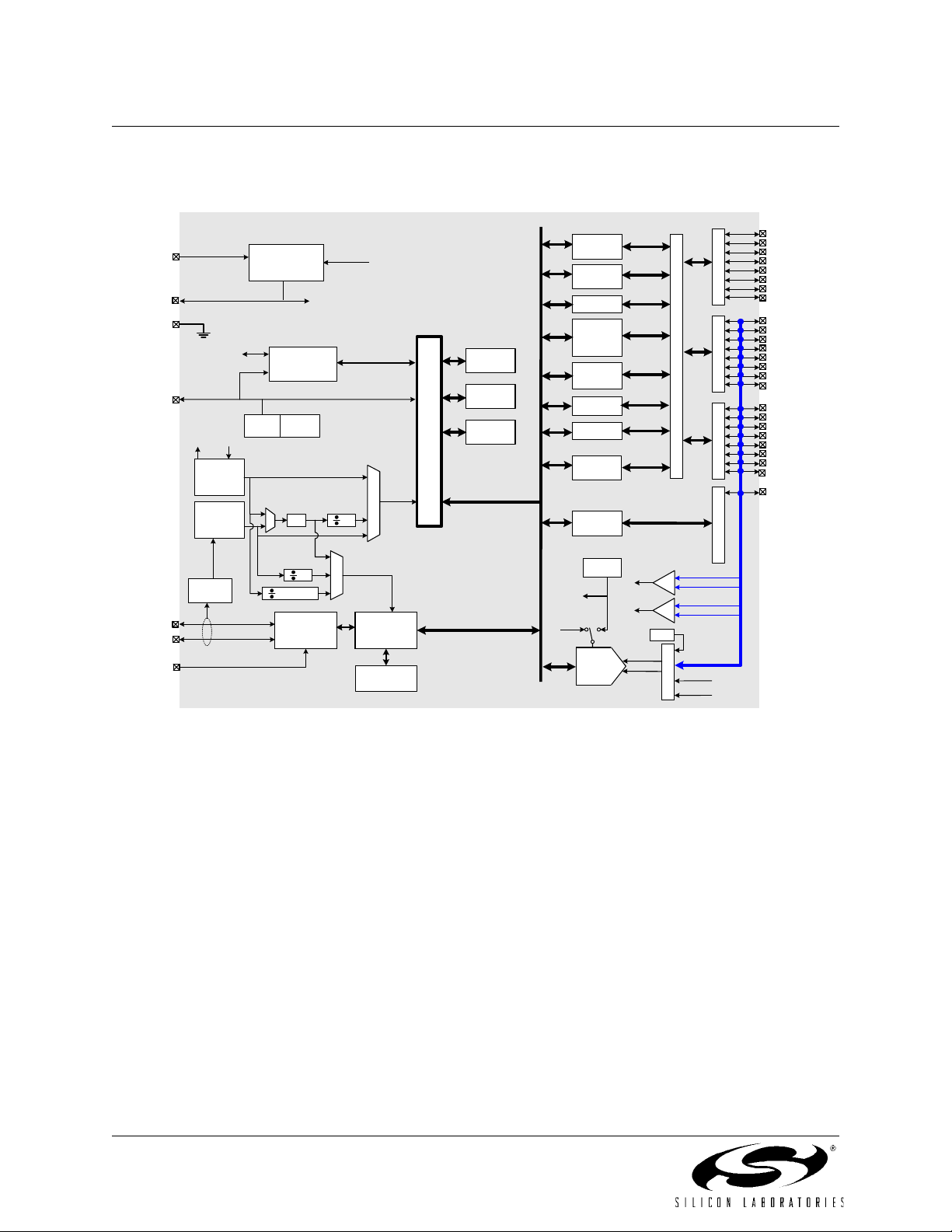
Figure 1.2. C8051F321 Block Diagram
C8051F320/1
REGIN
VDD
GND
/RST/C2CK
VBUS
D+
D-
Analog/Digital
C2D
XTAL1 XTAL2
External
Oscillator
Circuit
12MHz
Internal
Oscillator
Clock
Recovery
5.0V
Power
IN
Regulator
POR
Voltage
OUT
Debug HW
Brown-
Out
x4 2
2
1,2,3,4
USB
Transceiver
Enable
USB Clock
Controller
1K byte USB
System
USB
SRAM
Reset
Clock
8
0
5
1
C
o
SFR Bus
r
e
16kbyte
FLASH
256 byte
SRAM
1K byte
XRAM
VREF
VDD
Port 0
Latch
Port 1
Latch
UART
Timer
0,1,2,3 /
RTC
PCA/
WDT
SMBus
SPI
Port 2
Latch
Port 3
Latch
VREF
10-bit
200ksps
ADC
P
0
D
r
v
C
P
R
1
O
S
D
S
r
B
v
A
R
P
2
D
r
v
P
3
D
r
v
CP0
+
-
CP1
+
-
Temp
A
AIN0-AIN11
M
VDD
U
X
VREF
P0.0
P0.1
P0.2/XTAL1
P0.3/XTAL2
P0.4
P0.5
P0.6/CNVSTR
P0.7/VREF
P1.0
P1.1
P1.2
P1.3
P1.4
P1.5
P1.6
P1.7
P2.0
P2.1
P2.2
P2.3
P3.0/C2D
Rev. 1.1 19
Page 20
C8051F320/1
1.1. CIP-51™ Microcontroller Core
1.1.1. Fully 8051 Compatible
The C8051F320/1 family utilizes Silicon Labs' proprietary CIP-51 microcontroller core. The CIP-51 is fully compatible with the MCS-51™ instruction set; standard 803x/805x assemblers and compilers can be used to develop software. The CIP-51 core offers all the peripherals included with a standard 8052, including four 16-bit counter/timers,
a full-duplex UART with extended baud rate configuration, an enhanced SPI port, 2304
128
byte Special Function Register (SFR) address space, and 25/21 I/O pins.
1.1.2. Improved Throughput
The CIP-51 employs a pipelined architecture that greatly increases its instruction throughput over the standard 8051
architecture. In a standard 8051, all instructions except for MUL and DIV take 12 or 24 system clock cycles to exe
cute with a maximum system clock of 12-to-24 MHz. By contrast, the CIP-51 core executes 70% of its instructions in
one or two system clock cycles, with only four instructions taking more than four system clock cycles.
The CIP-51 has a total of 109 instructions. The table below shows the total number of instructions that require each
execution time.
Clocks to Execute 1 2 2/3 3 3/4 4 4/5 5 8
bytes of on-chip RAM,
-
Number of Instructions 26 50 5 14 7 3 1 2 1
With the CIP-51's maximum system clock at 25 MHz, it has a peak throughput of 25 MIPS. Figure 1.3 shows a comparison of peak throughputs for various 8-bit microcontroller cores with their maximum system clocks.
Figure 1.3. Comparison of Peak MCU Execution Speeds
25
20
15
MIPS
10
5
Silicon Labs
CIP-51
(25MHz clk)
20 Rev. 1.1
Microchip
PIC17C75x
(33MHz clk)
Philips
80C51
(33MHz clk)
ADuC812
8051
(16MHz clk)
Page 21
C8051F320/1
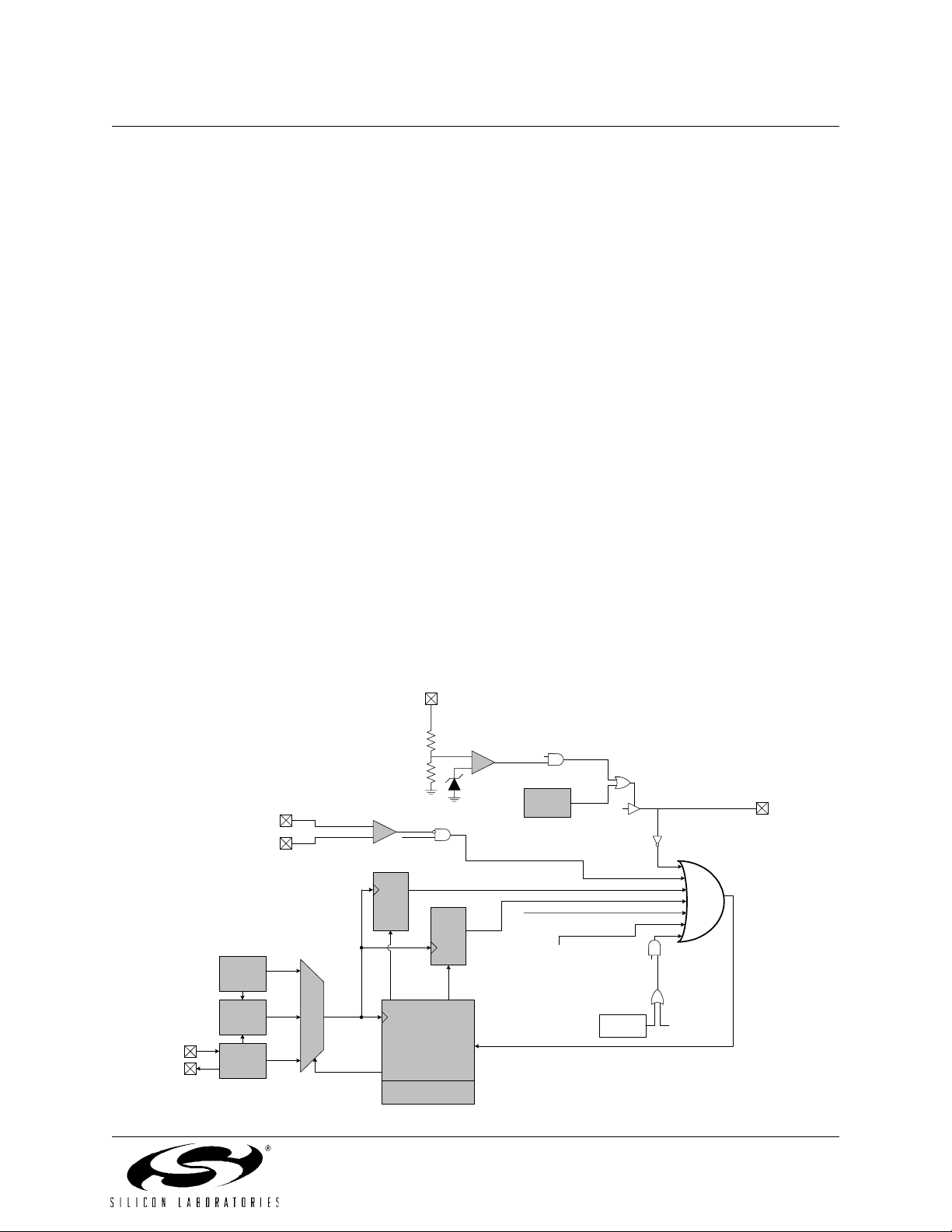
1.1.3. Additional Features
The C8051F320/1 SoC family includes several key enhancements to the CIP-51 core and peripherals to improve performance and ease of use in end applications.
The extended interrupt handler provides 16 interrupt sources into the CIP-51 (as opposed to 7 for the standard 8051),
allowing numerous analog and digital peripherals to interrupt the controller. An interrupt driven system requires less
intervention by the MCU, giving it more effective throughput. The extra interrupt sources are very useful when build
ing multi-tasking, real-time systems.
Nine reset sources are available: power-on reset circuitry (POR), an on-chip VDD monitor (forces reset when power
supply voltage drops below V
transition), a Watchdog Timer, a Missing Clock Detector, a voltage level detection from Comparator0, a forced software reset, an external reset pin, and an errant FLASH read/write protection circuit. Each reset source except for the
POR, Reset Input Pin, or FLASH error may be disabled by the user in software. The WDT may be permanently
enabled in software after a power-on reset during MCU initialization.
The internal oscillator is factory calibrated to 12 MHz ±1.5%, and the internal oscillator period may be user programmed in ~0.25% increments. A clock recovery mechanism allows the internal oscillator to be used with the 4x
Clock Multiplier as the USB clock source in Full Speed mode; the internal oscillator can also be used as the USB
clock source in Low Speed mode. External oscillators may also be used with the 4x Clock Multiplier. An external
oscillator drive circuit is also included, allowing an external crystal, ceramic resonator, capacitor, RC, or CMOS
clock source to generate the system clock. The system clock may be configured to use the internal oscillator, external
oscillator, or the Clock Multiplier output divided by 2. If desired, the system clock source may be switched on-the-fly
between oscillator sources. An external oscillator can be extremely useful in low power applications, allowing the
MCU to run from a slow (power saving) external clock source, while periodically switching to the internal oscillator
as needed.
as given in Table 10.1 on page 105), the USB controller (USB bus reset or a VBUS
RST
-
XTAL1
XTAL2
Internal
Oscillator
Clock
Multiplier
External
Oscillator
Drive
Px.x
Px.x
Figure 1.4. On-Chip Clock and Reset
VDD
Supply
Monitor
Enable
+
-
Power On
Reset
Software Reset (SW RSF)
Errant
FLASH
Operation
Controller
System
Clock
Clock Select
Comparator 0
+
-
Missing
Clock
Detector
(one-
shot)
EN
MCD
Enable
Microcontroller
Extended Interrupt
C0RSEF
CIP-51
Core
Handler
PCA
WDT
EN
WDT
Enable
System Reset
'0'
USB
(wired-OR)
Enable
Reset
Funnel
VBUS
Transition
/RST
Rev. 1.1 21
Page 22
C8051F320/1
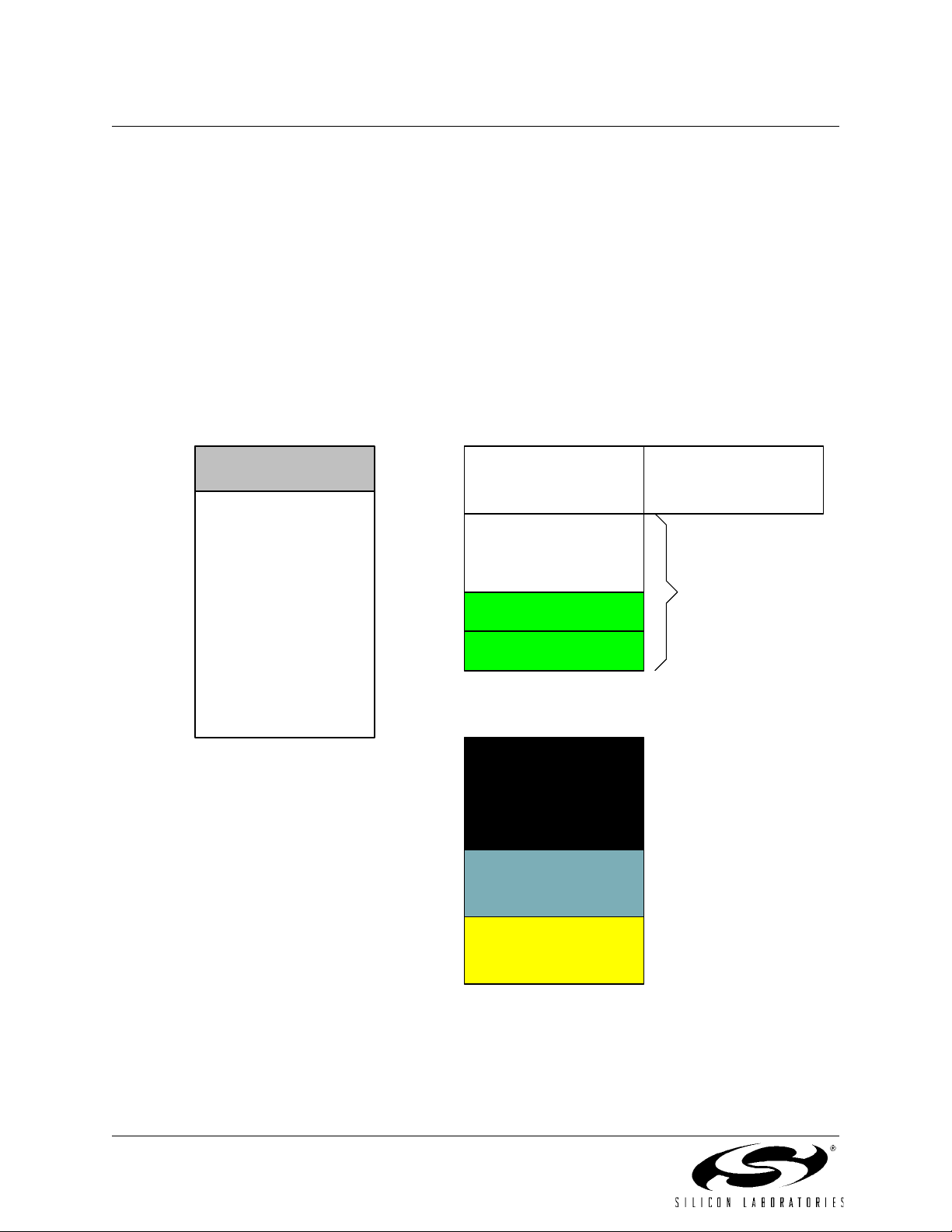
1.2. On-Chip Memory
The CIP-51 has a standard 8051 program and data address configuration. It includes 256 bytes of data RAM, with the
upper 128 bytes dual-mapped. Indirect addressing accesses the upper 128 bytes of general purpose RAM, and direct
addressing accesses the 128 byte SFR address space. The lower 128 bytes of RAM are accessible via direct and indi
rect addressing. The first 32 bytes are addressable as four banks of general purpose registers, and the next 16 bytes
can be byte addressable or bit addressable.
Program memory consists of 16k bytes of FLASH. This memory may be reprogrammed in-system in 512 byte sectors, and requires no special off-chip programming voltage. See Figure 1.5 for the MCU system memory map.
Figure 1.5. On-Board Memory Map
PROGRAM/DATA MEMORY
(FLASH)
0x3E00
0x3DFF
RESERVED
16K FLASH
(In-Syste m
Programmable in 512
Byte Sectors)
0xFF
0x80
0x7F
0x30
0x2F
0x20
0x1F
0x00
INTERNAL DATA ADDRESS SPACE
Upper 128 RAM
(Indirect Addressing
(Direct and Indirect
Bit Addressable
General Purpose
DATA MEMORY (RAM)
Only)
Addressing)
Registers
(Direct Addressing Only)
Special Fun c t ion
Register's
Lower 128 RAM
(Direct and Indirect
Addressing)
-
0x0000
0xFFFF
0x0800
0x07FF
0x0400
0x03FF
0x0000
EXTERNAL DATA ADDRESS SPACE
Same 2048 bytes as from
0x0000 to 0x07FF, wrapped
on 2K-byte boundaries
USB FIFOs
1024 Bytes
XRAM - 1024 Bytes
(accessable using MOVX
instruction)
22 Rev. 1.1
Page 23
C8051F320/1
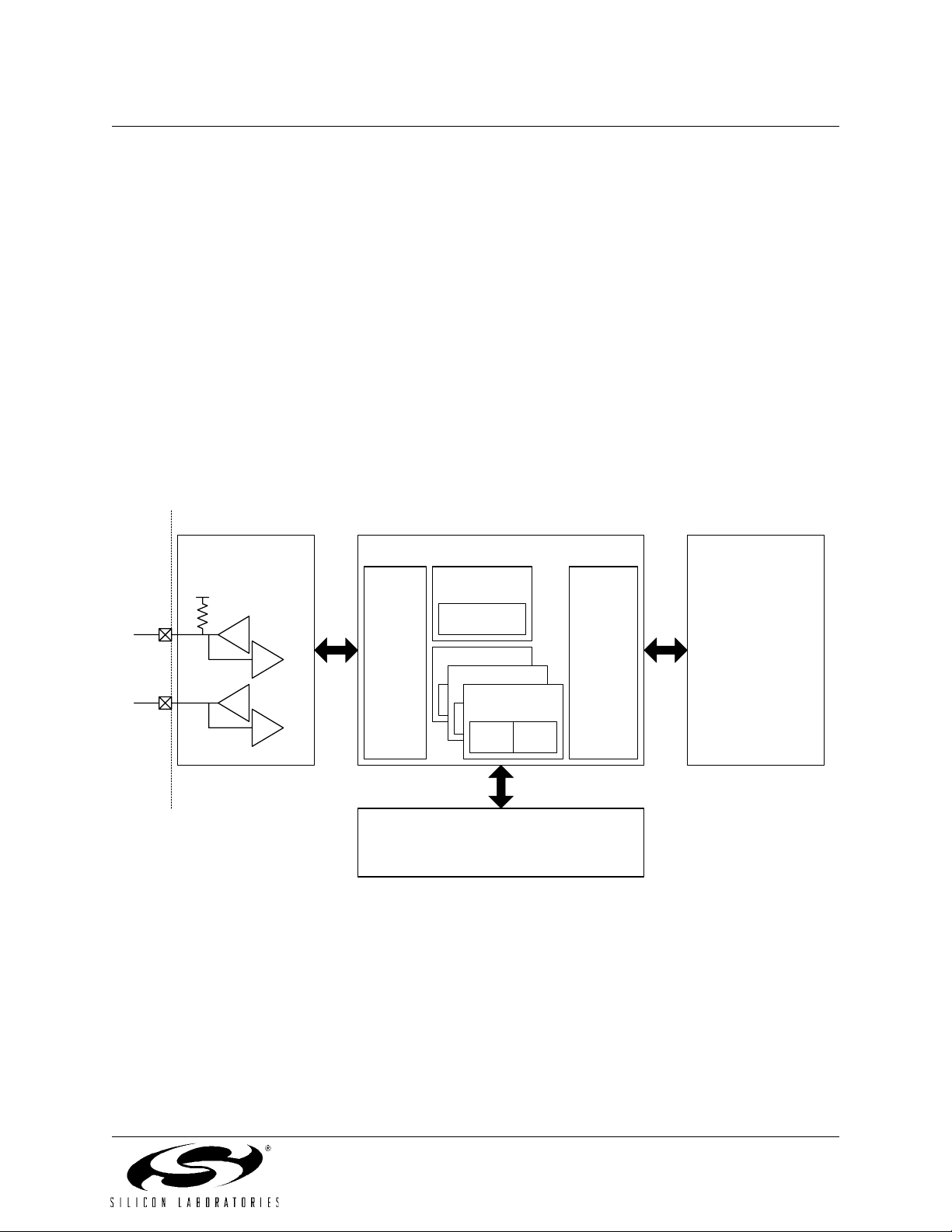
1.3. Universal Serial Bus Controller
The Universal Serial Bus Controller (USB0) is a USB 2.0 compliant Full or Low Speed function with integrated
transceiver and endpoint FIFO RAM. A total of eight endpoint pipes are available: a bi-directional control endpoint
(Endpoint0) and three pairs of IN/OUT endpoints (Endpoints1-3 IN/OUT).
A 1k block of XRAM is used as dedicated USB FIFO space. This FIFO space is distributed among Endpoints0-3;
Endpoint1-3 FIFO slots can be configured as IN, OUT, or both IN and OUT (split mode). The maximum FIFO size is
512 bytes (Endpoint3).
USB0 can be operated as a Full or Low Speed function. On-chip 4x Clock Multiplier and clock recovery circuitry
allow both Full and Low Speed options to be implemented with the on-chip precision oscillator as the USB clock
source. An external oscillator source can also be used with the 4x Clock Multiplier to generate the USB clock. The
CPU clock source is independent of the USB clock.
The USB Transceiver is USB 2.0 compliant, and includes on-chip matching and pull-up resistors. The pull-up resistors can be enabled/disabled in software, and will appear on the D+ or D- pin according to the software-selected
speed setting (Full or Low Speed).
Figure 1.6. USB Controller Block Diagram
Transceiver Serial Interface Engine (SIE)
VDD
D+
D-
1.4. Voltage Regulator
Data
Transfer
Control
Endpoint0
IN/OUT
Endpoint1
Endpoint2
Endpoint3
IN OUT
IN OUT
IN OUT
USB FIFOs
(1k RAM)
USB
Control,
Status, and
Interrupt
Registers
CIP-51 Core
C8051F320/1 devices include a 5 V- to -3 V voltage regulator (REG0). When enabled, the REG0 output appears on
the VDD pin and can be used to power external devices. REG0 can be enabled/disabled by software.
Rev. 1.1 23
Page 24
C8051F320/1
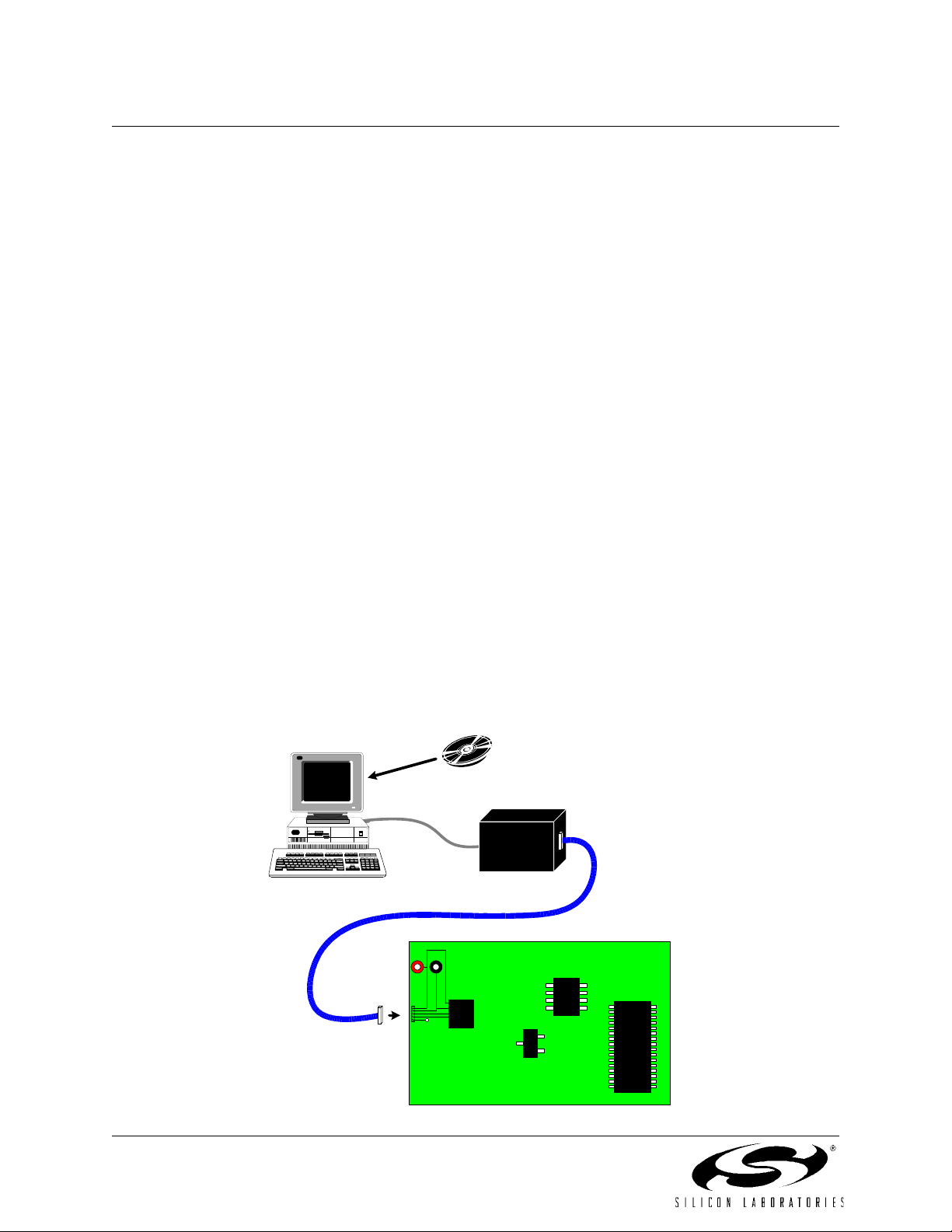
1.5. On-Chip Debug Circuitry
The C8051F320/1 devices include on-chip Silicon Labs 2-Wire (C2) debug circuitry that provides non-intrusive, full
speed, in-circuit debugging of the production part installed in the end application.
Silicon Labs' debugging system supports inspection and modification of memory and registers, breakpoints, and single stepping. No additional target RAM, program memory, timers, or communications channels are required. All the
digital and analog peripherals are functional and work correctly while debugging. All the peripherals (except for the
USB, ADC, and SMBus) are stalled when the MCU is halted, during single stepping, or at a breakpoint in order to
keep them synchronized.
The C8051F310DK development kit provides all the hardware and software necessary to develop application code
and perform in-circuit debugging with the C8051F320/1 MCUs. The kit includes software with a developer's studio
and debugger, an integrated 8051 assembler, and an RS-232 to C2 serial adapter. It also has a target application board
with the associated MCU installed and prototyping area, plus the RS-232 and C2 cables, and wall-mount power sup
ply. The Development Kit requires a Windows 95/98/NT/ME/2000 computer with one available RS-232 serial port.
As shown in
Serial Adapter to the user's application board, picking up the two C2 pins and VDD and GND. The Serial Adapter
takes its power from the application board. For applications where there is not sufficient power available from the tar
get board, the provided power supply can be connected directly to the Serial Adapter.
Figure 1.7, the PC is connected via RS-232 to the Serial Adapter. A six-inch ribbon cable connects the
-
-
The Silicon Labs IDE interface is a vastly superior developing and debugging configuration, compared to standard
MCU emulators that use on-board "ICE Chips" and require the MCU in the application board to be socketed. Silicon
Labs' debug paradigm increases ease of use and preserves the performance of the precision analog peripherals.
Figure 1.7. Development/In-System Debug Diagram
Silicon Labs Integrated
Development Environment
WINDOWS 95/ 9 8/NT/ME/2000
RS-232
Serial
Adapter
C2 (x2), VDD, GND
VDD GND
TARGET PCB
C8051F320
24 Rev. 1.1
Page 25
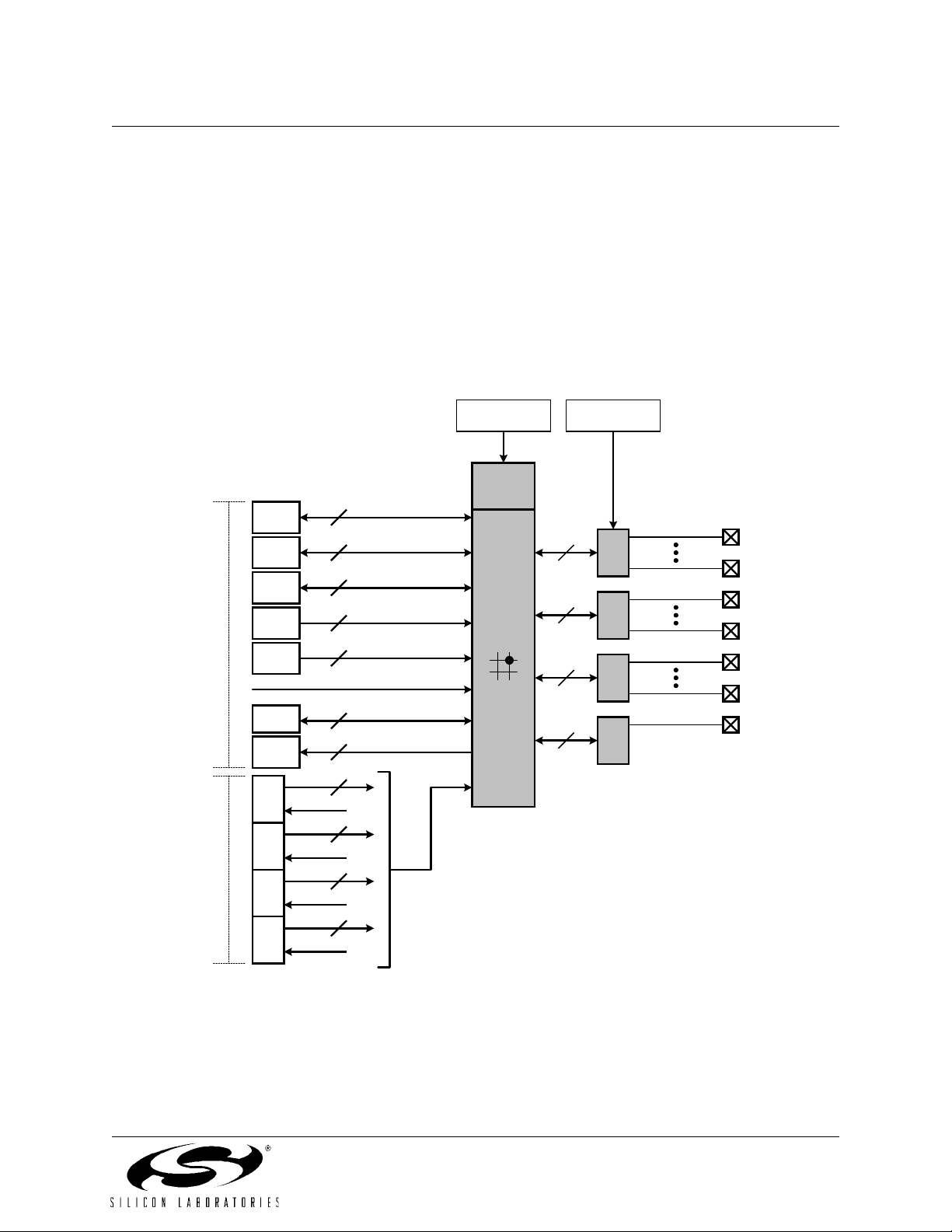
C8051F320/1
1.6. Programmable Digital I/O and Crossbar
C8051F320 devices include 25 I/O pins (three byte-wide Ports and one 1-bit-wide Port); C8051F321 devices include
21 I/O pins (two byte-wide Ports, one 4-bit-wide Port, and one 1-bit-wide Port). The C8051F320/1 Ports behave like
typical 8051 Ports with a few enhancements. Each Port pin may be configured as an analog input or a digital I/O pin.
Pins selected as digital I/Os may additionally be configured for push-pull or open-drain output. The “weak pull-ups”
that are fixed on typical 8051 devices may be globally disabled, providing power savings capabilities.
The Digital Crossbar allows mapping of internal digital system resources to Port I/O pins (See Figure 1.8). On-chip
counter/timers, serial buses, HW interrupts, comparator outputs, and other digital signals in the controller can be configured to appear on the Port I/O pins specified in the Crossbar Control registers. This allows the user to select the
exact mix of general purpose Port I/O and digital resources needed for the particular application.
Highest
Priority
Lowest
Priority
Figure 1.8. Digital Crossbar Diagram
XBR0, XBR1,
PnSKIP Registers
PnMDOUT,
PnMDIN Registers
Priority
Decoder
(P0.0-P0.7)
(P1.0-P1.7)
(P2.0-P2.7)
(P3.0)
2
P0
4
2
2
2
6
2
8
8
8
8
Digital
Crossbar
8
I/O
Cells
P1
8
I/O
Cells
P2
8
I/O
Cells
P3
1
I/O
Cells
Note: P2.4-P2.7 only available
on the C8051F320
P0.0
P0.7
P1.0
P1.7
P2.0
P2.7
P3.0
UART
SPI
SMBus
CP0
Outputs
CP1
Outputs
SYSCLK
(Internal Digital Signals)
PCA
T0, T1
P0
P1
P2
(Port Latches)
P3
1.7. Serial Ports
The C8051F320/1 Family includes an SMBus/I2C interface, a full-duplex UART with enhanced baud rate configuration, and an Enhanced SPI interface. Each of the serial buses is fully implemented in hardware and makes extensive
use of the CIP-51's interrupts, thus requiring very little CPU intervention.
Rev. 1.1 25
Page 26
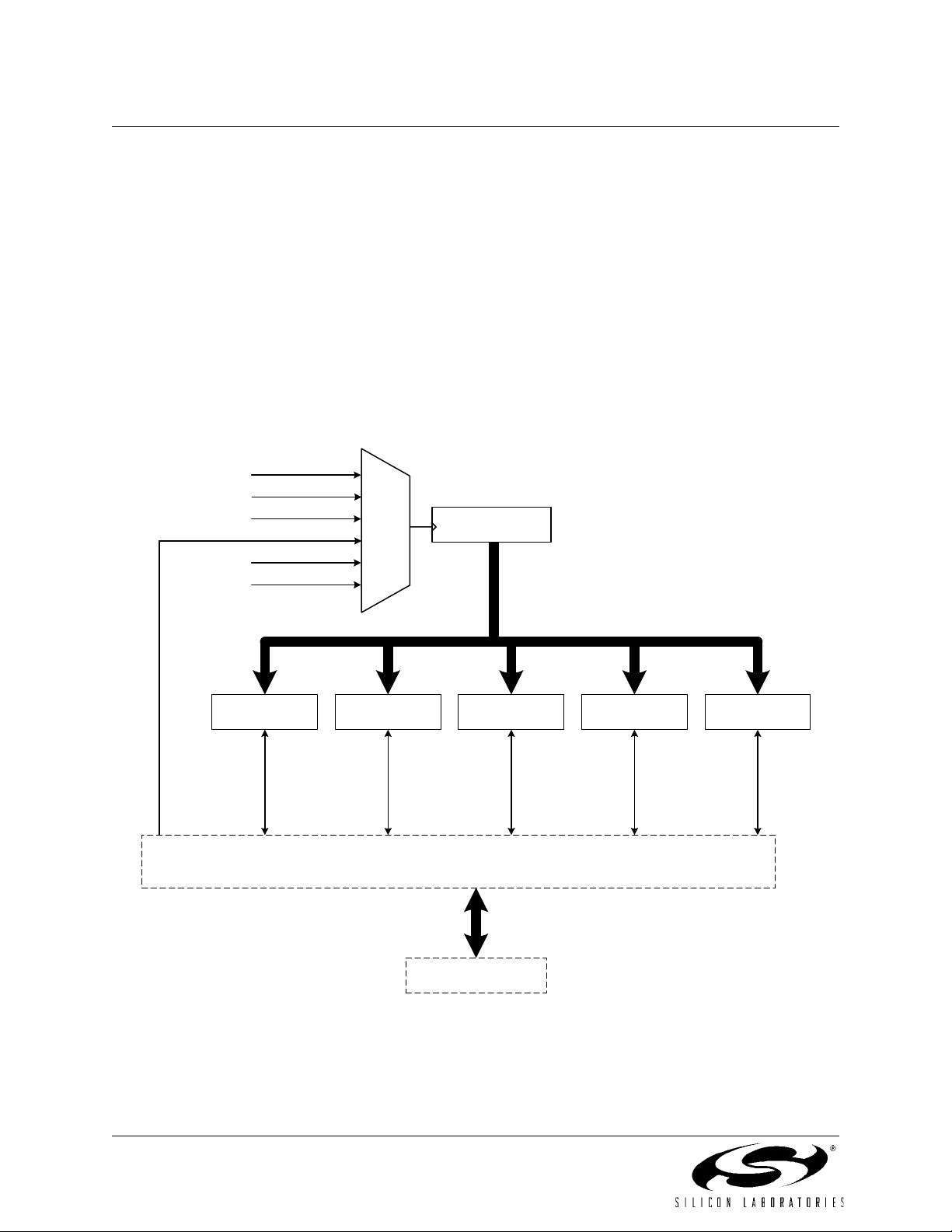
C8051F320/1
1.8. Programmable Counter Array
An on-chip Programmable Counter/Timer Array (PCA) is included in addition to the four 16-bit general purpose
counter/timers. The PCA consists of a dedicated 16-bit counter/timer time base with five programmable capture/com
pare modules. The PCA clock is derived from one of six sources: the system clock divided by 12, the system clock
divided by 4, Timer 0 overflows, an External Clock Input (ECI), the system clock, or the external oscillator clock
source divided by 8. The external clock source selection is useful for real-time clock functionality, where the PCA is
clocked by an external source while the internal oscillator drives the system clock.
Each capture/compare module can be configured to operate in one of six modes: Edge-Triggered Capture, Software
Timer, High Speed Output, 8- or 16-bit Pulse Width Modulator, or Frequency Output. Additionally, Capture/Compare
Module 4 offers watchdog timer (WDT) capabilities. Following a system reset, Module 4 is configured and enabled
in WDT mode. The PCA Capture/Compare Module I/O and External Clock Input may be routed to Port I/O via the
Digital Crossbar.
Figure 1.9. PCA Block Diagram
SYSCLK/12
SYSCLK/4
Timer 0 Overflow
ECI
SYSCLK
External Clock/8
PCA
CLOCK
MUX
16-Bit Counter/Timer
-
Capture/Compare
Module 0
ECI
CEX0
Capture/Compare
Module 1
CEX1
Capture/Compare
Module 2
CEX2
Capture/Compare
Module 3
CEX3
Capture/Compare
Module 4 / WDT
CEX4
Crossbar
Port I/O
26 Rev. 1.1
Page 27
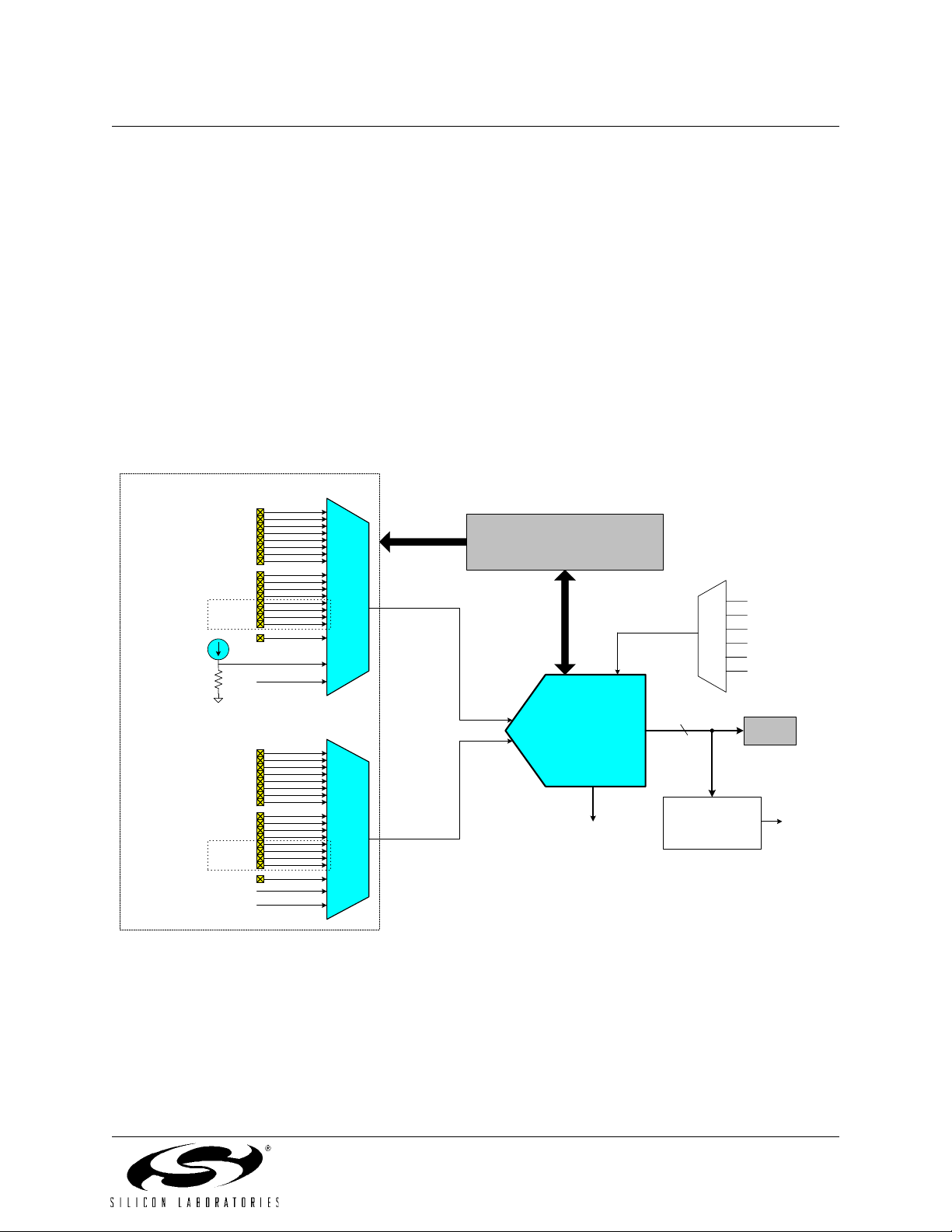
C8051F320/1
1.9. 10-Bit Analog to Digital Converter
The C8051F320/1 devices include an on-chip 10-bit SAR ADC with a 17-channel differential input multiplexer. With
a maximum throughput of 200
includes a configurable analog multiplexer that selects both positive and negative ADC inputs. Ports1-3 are available
as ADC inputs; additionally, the on-chip Temperature Sensor output and the power supply voltage (VDD) are avail
able as ADC inputs. User firmware may shut down the ADC to save power.
Conversions can be started in six ways: a software command, an overflow of Timer 0, 1, 2, or 3, or an external convert start signal. This flexibility allows the start of conversion to be triggered by software events, a periodic signal
(timer overflows), or external HW signals. Conversion completions are indicated by a status bit and an interrupt (if
enabled). The resulting 10-bit data word is latched into the ADC data SFRs upon completion of a conversion.
Window compare registers for the ADC data can be configured to interrupt the controller when ADC data is either
within or outside of a specified range. The ADC can monitor a key voltage continuously in background mode, but not
interrupt the controller unless the converted data is within/outside the specified range.
Analog Multiplexer
P1.0
ksps, the ADC offers true 10-bit linearity with an INL of ±1LSB. The ADC system
Figure 1.10. 10-Bit ADC Block Diagram
-
P2.4-2.7
available on
C8051F320
Temp
Sensor
P2.4-2.7
available on
C8051F320
P1.7
P2.0
P2.7
P3.0
VDD
P1.0
P1.7
P2.0
P2.7
P3.0
VREF
GND
19-to-1
AMUX
19-to-1
AMUX
Configuration, Control, and Data Registers
(+)
10-Bit
SAR
(-)
ADC
End of
Conversion
Interrupt
Start
Conversion
16
Window Compare
000 AD0BUSY (W)
Timer 0 Overflow
001
Timer 2 Overflow
010
011
Timer 1 Overflow
100
CNVSTR Input
Timer 3 Overflow
101
ADC Data
Registers
Window
Logic
Compare
Interrupt
Rev. 1.1 27
Page 28
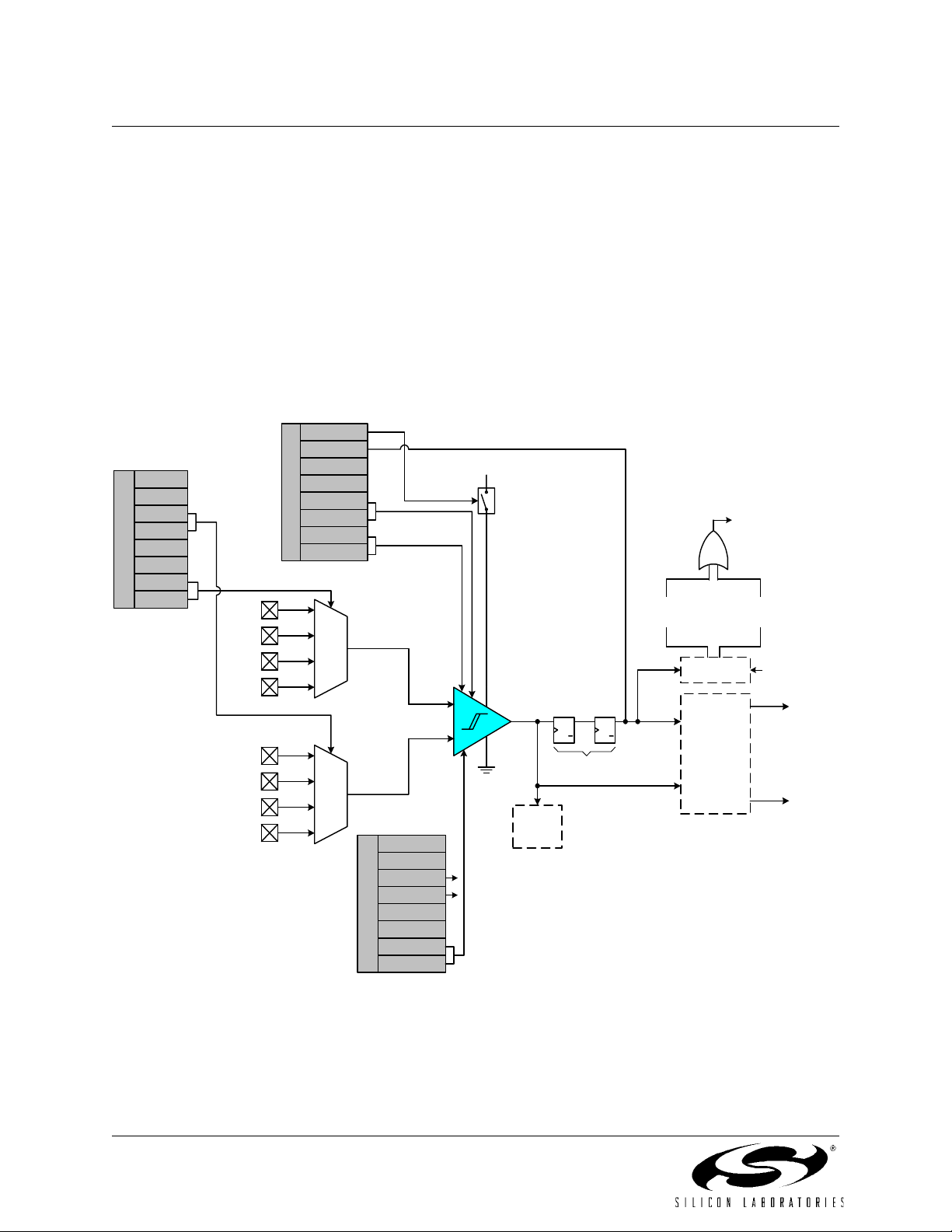
C8051F320/1
1.10. Comparators
C8051F320/1 devices include two on-chip voltage comparators that are enabled/disabled and configured via user
software. Port I/O pins may be configured as comparator inputs via a selection mux. Two comparator outputs may be
routed to a Port pin if desired: a latched output and/or an unlatched (asynchronous) output. Comparator response time
is programmable, allowing the user to select between high-speed and low-power modes. Positive and negative hyster
esis are also configurable.
Comparator interrupts may be generated on rising, falling, or both edges. When in IDLE mode, these interrupts may
be used as a “wake-up” source. Comparator0 may also be configured as a reset source.
Comparator0 block diagram.
Figure 1.11. Comparator0 Block Diagram
CP0EN
CP0OUT
CMX0N1
CMX0N0
CPT0MX
CMX0P1
CMX0P0
P1.0
P1.4
P2.0
P2.4
P1.1
P1.5
P2.1
P2.5
CP0RIF
CP0FIF
CP0HYP1
CPT0CN
CP0HYP0
CP0HYN1
CP0HYN0
CP0 +
CP0 -
VDD
Rising-edge
+
-
GND
Reset
Decision
Tree
SET
D
(SYNCHRONIZER)
SET
D
Q
Q
CLR
CLR
Q
Q
Figure 1.11 shows the
Interrupt
CP0
Falling-edge
Interrupt
Logic
Crossbar
CP0
CP0
CP0RIE
CP0FIE
CP0
CP0A
-
CP0RIE
Note: P2.4 and P2.5 available
only on C8051F320
CP0FIE
CPT0MD
CP0MD1
CP0MD0
28 Rev. 1.1
Page 29
2. ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
C8051F320/1
Tab le 2.1. Absolute Maximum Ratings
PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
Ambient temperature under bias -55 125 °C
Storage Temperature -65 150 °C
Voltage on any Port I/O Pin or /RST with respect
to GND
Voltage on VDD with respect to GND -0.3 4.2 V
Maximum Total current through VDD and GND 500 mA
Maximum output current sunk by /RST or any
Port pin
*
Note: stresses above those listed under “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device.
This is a stress rating only and functional operation of the devices at those or any other conditions above those indicated in the operation listings of this specification is not implied. Exposure to maximum rating conditions for
extended periods may affect device reliability.
*
-0.3 5.8 V
100 mA
Rev. 1.1 29
Page 30
C8051F320/1
3. GLOBAL DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Tab le 3.1. Global DC Electrical Characteristics
-40°C to +85°C, 25 MHz System Clock unless otherwise specified.
PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
Digital Supply Voltage (Note 1) 2.7 3.3 3.6 V
Digital Supply Current with CPU
active
Digital Supply Current with CPU
active and USB active (Full or Low
Speed)
Digital Supply Current with CPU
inactive (not accessing FLASH)
Digital Supply Current (suspend
mode or shutdown mode)
Digital Supply RAM Data Retention Voltage
SYSCLK (System Clock) (Note 2) 0 25 MHz
T
(SYSCLK High Time) 18 ns
SYSH
(SYSCLK Low Time) 18 ns
T
SYSL
Specified Operating Temperature
Range
VDD=3.3V, Clock=24MHz
VDD=3.3V, Clock=1MHz
VDD=3.3V, Clock=32kHz
VDD=3.3V, Clock=24MHz
VDD=3.3V, Clock=6MHz
VDD=3.3V, Clock=24MHz
VDD=3.3V, Clock=1MHz
VDD=3.3V, Clock=32kHz
Oscillator not running < 0.1 µA
-40 +85 °C
10
0.6
30
TBD
TBD
5
0.3
14
1.5 V
mA
mA
µA
mA
mA
mA
mA
µA
Note 1: USB Requires 3.0 V Minimum Supply Voltage.
Note 2: SYSCLK must be at least 32 kHz to enable debugging.
30 Rev. 1.1
Page 31

4. PINOUT AND PACKAGE DEFINITIONS
Tab le 4.1. Pin Definitions for the C8051F320/1
Pin Numbers
Name
‘F320 ‘F321
Type Description
C8051F320/1
Power In
VDD 6 6
GND 3 3 Ground.
/RST/
9 9
C2CK
P3.0/
10 10
C2D
REGIN
VBUS 8 8 D In
D+ 4 4 D I/O USB D+.
D- 5 5 D I/O USB D-.
7 7
Power
Out
D I/O
D I/O
D I/O
D I/O
Power In 5 V Regulator Input. This pin is the input to the on-chip voltage
2.7-3.6 V Power Supply Voltage Input.
3.3 V Voltage Regulator Output. See Section 8.
Device Reset. Open-drain output of internal POR or VDD monitor. An external source can initiate a system reset by driving this
pin low for at least 15
Clock signal for the C2 Debug Interface.
Port 3.0. See Section 14 for a complete description.
Bi-directional data signal for the C2 Debug Interface.
regulator.
VBUS Sense Input. This pin should be connected to the VBUS
signal of a USB network. A 5
network connection.
µs. See Section 10.
V signal on this pin indicates a USB
P0.0 2 2 D I/O Port 0.0. See Section 14 for a complete description.
P0.1 1 1 D I/O Port 0.1. See Section 14 for a complete description.
P0.2/
32 28
XTAL1
P0.3/
31 27
XTAL2
P0.4 30 26 D I/O Port 0.4. See Section 14 for a complete description.
P0.5 29 25 D I/O Port 0.5. See Section 14 for a complete description.
D I/O
A In
D I/O
A I/O or
D In
Port 0.2. See Section 14 for a complete description.
External Clock Input. This pin is the external oscillator return for
a crystal or resonator. See
Port 0.3. See Section 14 for a complete description.
External Clock Output. This pin is the excitation driver for an
external crystal or resonator, or an external clock input for CMOS,
capacitor, or RC oscillator configurations. See
Rev. 1.1 31
Section 13.
Section 13.
Page 32

C8051F320/1
Pin Numbers
Name
‘F320 ‘F321
Table 4.1. Pin Definitions for the C8051F320/1
Type Description
P0.6/
28 24
CNVSTR
P0.7/
27 23
VREF
P1.0 26 22
P1.1 25 21
P1.2 24 20
P1.3 23 19
P1.4 22 18
P1.5 21 17
P1.6 20 16
D I/O
A I/O
D I/O or
A In
D I/O or
A In
D I/O or
A In
D I/O or
A In
D I/O or
A In
D I/O or
A In
D I/O or
A In
Port 0.6. See Section 14 for a complete description.
ADC0 External Convert Start Input. See Section 5.
Port 0.7. See Section 14 for a complete description.
External VREF input or output. See Section 6.
Port 1.0. See Section 14 for a complete description.
Port 1.1. See Section 14 for a complete description.
Port 1.2. See Section 14 for a complete description.
Port 1.3. See Section 14 for a complete description.
Port 1.4. See Section 14 for a complete description.
Port 1.5. See Section 14 for a complete description.
Port 1.6. See Section 14 for a complete description.
P1.7 19 15
P2.0 18 14
P2.1 17 13
P2.2 16 12
P2.3 15 11
P2.4 14
P2.5 13
P2.6 12
32 Rev. 1.1
D I/O or
A In
D I/O or
A In
D I/O or
A In
D I/O or
A In
D I/O or
A In
D I/O or
A In
D I/O or
A In
D I/O or
A In
Port 1.7. See Section 14 for a complete description.
Port 2.0. See Section 14 for a complete description.
Port 2.1. See Section 14 for a complete description.
Port 2.2. See Section 14 for a complete description.
Port 2.3. See Section 14 for a complete description.
Port 2.4. See Section 14 for a complete description.
Port 2.5. See Section 14 for a complete description.
Port 2.6. See Section 14 for a complete description.
Page 33

Name
C8051F320/1
Table 4.1. Pin Definitions for the C8051F320/1
Pin Numbers
Type Description
‘F320 ‘F321
P2.7 11
P0.1
P0.0
GND
VDD
D-
1
2
3
4
5
6
D I/O or
A In
Port 2.7. See Section 14 for a complete description.
Figure 4.1. LQFP-32 Pinout Diagram (Top View)
P1.1
P1.0
P0.7
P0.6
P0.5
P0.4
P0.3
P0.2
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
C8051F320
Top View
24
23
22
21
20
19
P1.2
P1.3
P1.4
P1.5D+
P1.6
P1.7
REGIN
VBUS
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
P2.6
/RST / C2CK
P2.7
P3.0 / C2D
P2.5
P2.4
P2.3
P2.2
Rev. 1.1 33
18
17
P2.0
P2.1
Page 34

C8051F320/1
32
PIN 1
IDENTIFIER
A2
1
Figure 4.2. LQFP-32 Package Diagram
D
D1
E1
E
Package Dimensions
A- -1.60
A1 0.05 - 0.15
A2 1.35 1.40 1.45
b 0.30 0.37 0.45
D-9.00-
D1 - 7.00 -
e-0.80-
E-9.00-
E1 - 7.00 -
Table 4.2. LQFP-32
MM
MIN TYP MAX
A1
eb
A
34 Rev. 1.1
Page 35

Figure 4.3. MLP-28 Pinout Diagram (Top View)
C8051F320/1
GND
P0.1
P0.0
GND
D+
D-
VDD
REGIN
P0.2
28
1
2
3
P0.3
27
P0.4
26
P0.5
25
P0.6
24
P0.7
23
P1.0
22
21
20
19
P1.1
P1.2
P1.3
C8051F321
4
18
P1.4
Top View
5
6
GND
7
17
16
15
P1.5
P1.6
P1.7
8
VBUS
9
/RST / C2CK
10
P3.0 / C2D
11
P2.3
Rev. 1.1 35
12
P2.2
13
P2.1
14
P2.0
Page 36

C8051F320/1
Figure 4.4. MLP-28 Package Drawing
Bottom View
8
9
L
7
6
b
5
4
e
3
2
1
DETAIL 1
28
D2
2
27
10
26
D2
6 x e
D
11
25
E2
12
24
13
14
15
16
17
E2
2
23
18
R
19
20
21
22
Side View
Table 4.2. MLP-28 Package
Dimensions
MM
MIN TYP MAX
A 0.80 0.90 1.00
A1 0 0.02 0.05
A2 0 0.65 1.00
A3 - 0.25 -
b 0.18 0.23 0.30
E
6 x e
D-5.00-
D2 2.90 3.15 3.35
E-5.00-
E2 2.90 3.15 3.35
e-0.5-
L 0.45 0.55 0.65
N-28-
ND - 7 -
NE - 7 -
R0.09 - -
AA - 0.435 -
BB - 0.435 -
CC - 0.18 -
DD - 0.18 -
A2
e
A3
DETAIL 1
AA
BB
CC
DD
36 Rev. 1.1
A
A1
Page 37

Figure 4.5. Typical MLP-28 Landing Diagram
Top View
0.50 mm
0.20 mm
C8051F320/1
0.85 mm
0.30 mm
0.20 mm
0.50 mm
0.20 mm
Optional
GND
Connection
0.20 mm
0.30 mm
0.50 mm
0.10 mm
0.35 mm
b
D2
L
E2
e
D
0.50 mm
0.85 mm
0.35 mm
0.10 mm
E
Rev. 1.1 37
Page 38

C8051F320/1
0.50 mm
Figure 4.6. Typical MLP-28 Solder Mask
Top View
0.20 mm
0.20 mm
0.85 mm
0.30 mm
0.50 mm
0.20 mm
0.20 mm
0.30 mm
0.50 mm
0.10 mm
0.60 mm
0.60 mm
0.70 mm
b
L
e
E2
0.30 mm
0.20 mm
0.40 mm
0.35 mm
D2
D
0.50 mm
0.85 mm
0.35 mm
0.10 mm
38 Rev. 1.1
E
Page 39

C8051F320/1
5. 10-BIT ADC (ADC0)
The ADC0 subsystem for the C8051F320/1 consists of two analog multiplexers (referred to collectively as AMUX0)
with 17 total input selections, and a 200
and-hold and programmable window detector. The AMUX0, data conversion modes, and window detector are all
configurable under software control via the Special Function Registers shown in
Single-ended and Differential modes, and may be configured to measure P1.0-P3.0, the Temperature Sensor output,
or VDD with respect to P1.0-P3.0, VREF, or GND. The ADC0 subsystem is enabled only when the AD0EN bit in the
ADC0 Control register (ADC0CN) is set to logic
logic
0.
ksps, 10-bit successive-approximation-register ADC with integrated track-
Figure 5.1. ADC0 operates in both
1. The ADC0 subsystem is in low power shutdown when this bit is
Figure 5.1. ADC0 Functional Block Diagram
P2.4-2.7
available on
C8051F320
Sensor
P2.4-2.7
available on
C8051F320
Temp
P1.0
P1.7
P2.0
P2.7
P3.0
VDD
P1.0
P1.7
P2.0
P2.7
P3.0
VREF
GND
19-to-1
AMUX
19-to-1
AMUX
AMX0P
AMX0P4
AMX0N
AMX0N4
ADC0CN
AD0EN
AD0TM
AMX0P3
AMX0P2
AMX0P1
AMX0P0
VDD
(+)
10-Bit
AD0INT
AD0BUSY
AD0CM1
AD0CM2
AD0WINT
Start
Conversion
AD0CM0
000 AD0BUSY (W)
Timer 0 Overflow
001
Timer 2 Overflow
010
Timer 1 Overflow
011
CNVSTR Input
100
101 Timer 3 Overflow
ADC0L
SAR
(-)
AD0SC2
AD0SC3
AMX0N3
AMX0N2
AMX0N1
AD0SC4
AMX0N0
ADC0CF
AD0SC1
AD0SC0
AD0LJST
ADC
ADC0LTH
ADC0GTH ADC0GTL
SYSCLK
REF
ADC0LTL
ADC0H
AD0WINT
Window
Compare
32
Logic
Rev. 1.1 39
Page 40

C8051F320/1
5.1. Analog Multiplexer
AMUX0 selects the positive and negative inputs to the ADC. Any of the following may be selected as the positive
input: P1.0-P3.0, the on-chip temperature sensor, or the positive power supply (VDD). Any of the following may be
selected as the negative input: P1.0-P3.0, VREF, or GND. When GND is selected as the negative input, ADC0
operates in Single-ended Mode; all other times, ADC0 operates in Differential Mode. The ADC0 input channels
are selected in the AMX0P and AMX0N registers as described in
The conversion code format differs between Single-ended and Differential modes. The registers ADC0H and ADC0L
contain the high and low bytes of the output conversion code from the ADC at the completion of each conversion.
Data can be right-justified or left-justified, depending on the setting of the AD0LJST bit (ADC0CN.0). When in Sin
gle-ended Mode, conversion codes are represented as 10-bit unsigned integers. Inputs are measured from ‘0’ to
VREF * 1023/1024. Example codes are shown below for both right-justified and left-justified data. Unused bits in the
ADC0H and ADC0L registers are set to ‘0’.
Figure 5.5 and Figure 5.6.
-
Input Voltage
(Single-Ended)
VREF * 1023/1024 0x03FF 0xFFC0
VREF * 512/1024 0x0200 0x8000
VREF * 256/1024 0x0100 0x4000
0 0x0000 0x0000
When in Differential Mode, conversion codes are represented as 10-bit signed 2’s complement numbers. Inputs are
measured from -VREF to VREF * 511/512. Example codes are shown below for both right-justified and left-justified
data. For right-justified data, the unused MSBs of ADC0H are a sign-extension of the data word. For left-justified
data, the unused LSBs in the ADC0L register are set to ‘0’.
Input Voltage
(Differential)
VREF * 511/512 0x01FF 0x7FC0
VREF * 256/512 0x0100 0x4000
0 0x0000 0x0000
-VREF * 256/512 0xFF00 0xC000
- VREF 0xFE00 0x8000
Important Note About ADC0 Input Configuration: Port pins selected as ADC0 inputs should be configured as
analog inputs, and should be skipped by the Digital Crossbar. To configure a Port pin for analog input, set to ‘0’ the
corresponding bit in register PnMDIN (for n = 0,1,2,3). To force the Crossbar to skip a Port pin, set to ‘1’ the corre
sponding bit in register PnSKIP (for n = 0,1,2). See Section “14. Port Input/Output” on page 127 for more Port I/O
configuration details.
Right-Justified ADC0H:ADC0L
(AD0LJST = 0)
Right-Justified ADC0H:ADC0L
(AD0LJST = 0)
Left-Justified ADC0H:ADC0L
(AD0LJST = 1)
Left-Justified ADC0H:ADC0L
(AD0LJST = 1)
-
40 Rev. 1.1
Page 41

5.2. Temperature Sensor
C8051F320/1
The typical temperature sensor transfer function is shown in Figure 5.2. The output voltage (V
) is the positive
TEMP
ADC input when the temperature sensor is selected by bits AMX0P4-0 in register AMX0P.
Figure 5.2. Typical Temperature Sensor Transfer Function
(mV)
1000
900
800
V
= 2.86(TEMPC) + 776 mV
700
600
500
0-50 50 100
Note that parameters which affect ADC measurement, in particular the voltage reference value, will also affect
temperature measurement.
TEMP
(Celsius)
Rev. 1.1 41
Page 42

C8051F320/1
5.3. Modes of Operation
ADC0 has a maximum conversion speed of 200 ksps. The ADC0 conversion clock is a divided version of the system
clock, determined by the AD0SC bits in the ADC0CF register (system clock divided by (AD0SC + 1) for
0
≤ AD0SC ≤ 31).
5.3.1. Starting a Conversion
A conversion can be initiated in one of five ways, depending on the programmed states of the ADC0 Start of Conversion Mode bits (AD0CM2-0) in register ADC0CN. Conversions may be initiated by one of the following:
1. Writing a ‘1’ to the AD0BUSY bit of register ADC0CN
2. A Timer 0 overflow (i.e., timed continuous conversions)
3. A Timer 2 overflow
4. A Timer 1 overflow
5. A rising edge on the CNVSTR input signal (pin P0.6)
6. A Timer 3 overflow
Writing a ‘1’ to AD0BUSY provides software control of ADC0 whereby conversions are performed "on-demand".
During conversion, the AD0BUSY bit is set to logic 1 and reset to logic 0 when the conversion is complete. The fall
ing edge of AD0BUSY triggers an interrupt (when enabled) and sets the ADC0 interrupt flag (AD0INT). Note: When
polling for ADC conversion completions, the ADC0 interrupt flag (AD0INT) should be used. Converted data is avail
able in the ADC0 data registers, ADC0H:ADC0L, when bit AD0INT is logic 1. Note that when Timer 2 or Timer 3
overflows are used as the conversion source, Low Byte overflows are used if Timer 2/3 is in 8-bit mode; High byte
overflows are used if Timer 2/3 is in 16-bit mode. See
Section “19. Timers” on page 217 for timer configuration.
-
-
Important Note About Using CNVSTR: The CNVSTR input pin also functions as Port pin P0.6. When the
CNVSTR input is used as the ADC0 conversion source, Port pin P0.6 should be skipped by the Digital Crossbar. To
configure the Crossbar to skip P0.6, set to ‘1’ Bit6 in register P0SKIP. See
page 127 for details on Port I/O configuration.
Section “14. Port Input/Output” on
42 Rev. 1.1
Page 43

C8051F320/1
5.3.2. Tracking Modes
The AD0TM bit in register ADC0CN controls the ADC0 track-and-hold mode. In its default state, the ADC0 input is
continuously tracked, except when a conversion is in progress. When the AD0TM bit is logic 1, ADC0 operates in
low-power track-and-hold mode. In this mode, each conversion is preceded by a tracking period of 3 SAR clocks
(after the start-of-conversion signal). When the CNVSTR signal is used to initiate conversions in low-power tracking
mode, ADC0 tracks only when CNVSTR is low; conversion begins on the rising edge of CNVSTR (see
Tracking can also be disabled (shutdown) when the device is in low power standby or sleep modes. Low-power trackand-hold mode is also useful when AMUX settings are frequently changed, due to the settling time requirements
described in
Section “5.3.3. Settling Time Requirements” on page 44.
Figure 5.3. 10-Bit ADC Track and Conversion Example Timing
A. ADC0 Timing for External Trigger Source
CNVSTR
(AD0CM[2:0]=100)
Figure 5.3).
SAR Clocks
AD0TM=1
Write '1' to AD0BUSY,
Timer 0, Timer 2,
Timer 1, Timer 3 Overflow
(AD0CM[2:0]=000, 001,010
011, 101)
SAR Clocks
AD0TM=1
SAR Clocks
AD0TM=0
Low Power
or Convert
Track or Convert Convert TrackAD0TM=0
123456789
Track Convert
10 11
Low Po we r
B. ADC0 Timing for Internal Trigger Source
Low Po we r
or Convert
Track or
Convert
123456789101112
Track Convert Low Power Mode
123456789
Convert Track
10
13 14
11
Mode
Rev. 1.1 43
Page 44

C8051F320/1
5.3.3. Settling Time Requirements
When the ADC0 input configuration is changed (i.e., a different AMUX0 selection is made), a minimum tracking
time is required before an accurate conversion can be performed. This tracking time is determined by the AMUX0
resistance, the ADC0 sampling capacitance, any external source resistance, and the accuracy required for the conver
sion. Note that in low-power tracking mode, three SAR clocks are used for tracking at the start of every conversion.
For most applications, these three SAR clocks will meet the minimum tracking time requirements.
Figure 5.4 shows the equivalent ADC0 input circuits for both Differential and Single-ended modes. Notice that the
equivalent time constant for both input circuits is the same. The required ADC0 settling time for a given settling
accuracy (SA) may be approximated by
respect to GND, R
TOTAL
reduces to R
Equation 5.1. ADC0 Settling Time Requirements
Where:
SA is the settling accuracy, given as a fraction of an LSB (for example, 0.25 to settle within 1/4 LSB)
t is the required settling time in seconds
R
is the sum of the AMUX0 resistance and any external source resistance.
TOTAL
n is the ADC resolution in bits (10).
Equation 5.1. When measuring the Temperature Sensor output or VDD with
. See Tabl e 5.1 for ADC0 minimum settling time requirements.
MUX
n
2
t
-------
×ln=
SA
R
TOTALCSAMPLE
-
Px.x
Px.x
Figure 5.4. ADC0 Equivalent Input Circuits
Differential Mode
MUX
Select
R
= 5k
MUX
RC
= R
* C
Input
MUX
SAMPLE
R
= 5k
MUX
MUX Select
C
C
SAMPL E
SAMPL E
= 5pF
= 5pF
Single-Ended Mode
MUX Select
Px.x
RC
Input
= R
MUX
R
* C
MUX
= 5k
SAMPLE
C
SAMPLE
= 5pF
44 Rev. 1.1
Page 45

C8051F320/1
Figure 5.5. AMX0P: AMUX0 Positive Channel Select Register
R R R R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W Reset Value
- - - AMX0P4 AMX0P3 AMX0P2 AMX0P1 AMX0P0 00000000
Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0 SFR Address:
Bits7-5: UNUSED. Read = 000b; Write = don’t care.
Bits4-0: AMX0P4-0: AMUX0 Positive Input Selection
AMX0P4-0 ADC0 Positive Input
00000 P1.0
00001 P1.1
00010 P1.2
00011 P1.3
00100 P1.4
00101 P1.5
00110 P1.6
00111 P1.7
01000 P2.0
01001 P2.1
01010 P2.2
01011 P2.3
01100† P2.4†
01101† P2.5†
01110† P2.6†
01111† P2.7†
10000 P3.0
10001 - 11101 RESERVED
11110 Temp Sensor
11111 VDD
0xBB
†Only applies to C8051F320; selection RESERVED on C8051F321 devices.
Rev. 1.1 45
Page 46

C8051F320/1
Figure 5.6. AMX0N: AMUX0 Negative Channel Select Register
R R R R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W Reset Value
- - - AMX0N4 AMX0N3 AMX0N2 AMX0N1 AMX0N0 00000000
Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0 SFR Address:
Bits7-5: UNUSED. Read = 000b; Write = don’t care.
Bits4-0: AMX0N4-0: AMUX0 Negative Input Selection.
Note that when GND is selected as the Negative Input, ADC0 operates in Single-ended mode. For all
other Negative Input selections, ADC0 operates in Differential mode.
AMX0N4-0 ADC0 Negative Input
00000 P1.0
00001 P1.1
00010 P1.2
00011 P1.3
00100 P1.4
00101 P1.5
00110 P1.6
00111 P1.7
01000 P2.0
01001 P2.1
01010 P2.2
01011 P2.3
01100† P2.4†
01101† P2.5†
01110† P2.6†
01111† P2.7†
10000 P3.0
10001 - 11101 RESERVED
11110 VREF
11111 GND (ADC in Single-Ended Mode)
0xBA
†Only applies to C8051F320; selection RESERVED on C8051F321 devices.
46 Rev. 1.1
Page 47

C8051F320/1
Figure 5.7. ADC0CF: ADC0 Configuration Register
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W Reset Value
AD0SC4 AD0SC3 AD0SC2 AD0SC1 AD0SC0 AD0LJST - - 11111000
Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0 SFR Address:
0xBC
Bits7-3: AD0SC4-0: ADC0 SAR Conversion Clock Period Bits.
SAR Conversion clock is derived from system clock by the following equation, where AD0SC refers
to the 5-bit value held in bits AD0SC4-0. SAR Conversion clock requirements are given in Table 5.1.
AD0SC
Bit2: AD0LJST: ADC0 Left Justify Select.
0: Data in ADC0H:ADC0L registers are right-justified.
1: Data in ADC0H:ADC0L registers are left-justified.
Bits1-0: UNUSED. Read = 00b; Write = don’t care.
SYSCLK
----------------------1–=
CLK
SAR
Figure 5.8. ADC0H: ADC0 Data Word MSB Register
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W Reset Value
Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0 SFR Address:
Bits7-0: ADC0 Data Word High-Order Bits.
For AD0LJST = 0: Bits 7-2 are the sign extension of Bit1. Bits 1-0 are the upper 2 bits of the 10-bit
ADC0 Data Word.
For AD0LJST = 1: Bits 7-0 are the most-significant bits of the 10-bit ADC0 Data Word.
00000000
0xBE
Rev. 1.1 47
Page 48

C8051F320/1
Figure 5.9. ADC0L: ADC0 Data Word LSB Register
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W Reset Value
Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0 SFR Address:
Bits7-0: ADC0 Data Word Low-Order Bits.
For AD0LJST = 0: Bits 7-0 are the lower 8 bits of the 10-bit Data Word.
For AD0LJST = 1: Bits 7-6 are the lower 2 bits of the 10-bit Data Word. Bits 5-0 will always read ‘0’.
00000000
0xBD
48 Rev. 1.1
Page 49

C8051F320/1
Figure 5.10. ADC0CN: ADC0 Control Register
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W Reset Value
AD0EN AD0TM AD0INT AD0BUSY AD0WINT AD0CM2 AD0CM1 AD0CM0 00000000
Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0 SFR Address:
(bit addressable)
Bit7: AD0EN: ADC0 Enable Bit.
0: ADC0 Disabled. ADC0 is in low-power shutdown.
1: ADC0 Enabled. ADC0 is active and ready for data conversions.
Bit6: AD0TM: ADC0 Track Mode Bit.
0: Normal Track Mode: When ADC0 is enabled, tracking is continuous unless a conversion is in
progress.
1: Low-power Track Mode: Tracking Defined by AD0CM2-0 bits (see below).
Bit5: AD0INT: ADC0 Conversion Complete Interrupt Flag.
0: ADC0 has not completed a data conversion since the last time AD0INT was cleared.
1: ADC0 has completed a data conversion.
Bit4: AD0BUSY: ADC0 Busy Bit.
Read:
0: ADC0 conversion is complete or a conversion is not currently in progress. AD0INT is set to
logic 1 on the falling edge of AD0BUSY.
1: ADC0 conversion is in progress.
Write:
0: No Effect.
1: Initiates ADC0 Conversion if AD0CM2-0 = 000b
Bit3: AD0WINT: ADC0 Window Compare Interrupt Flag.
0: ADC0 Window Comparison Data match has not occurred since this flag was last cleared.
1: ADC0 Window Comparison Data match has occurred.
Bits2-0: AD0CM2-0: ADC0 Start of Conversion Mode Select.
When AD0TM = 0:
000: ADC0 conversion initiated on every write of ‘1’ to AD0BUSY.
001: ADC0 conversion initiated on overflow of Timer 0.
010: ADC0 conversion initiated on overflow of Timer 2.
011: ADC0 conversion initiated on overflow of Timer 1.
100: ADC0 conversion initiated on rising edge of external CNVSTR.
101: ADC0 conversion initiated on overflow of Timer 3.
11x: Reserved.
When AD0TM = 1:
000: Tracking initiated on write of ‘1’ to AD0BUSY and lasts 3 SAR clocks, followed by conversion.
001: Tracking initiated on overflow of Timer 0 and lasts 3 SAR clocks, followed by conversion.
010: Tracking initiated on overflow of Timer 2 and lasts 3 SAR clocks, followed by conversion.
011: Tracking initiated on overflow of Timer 1 and lasts 3 SAR clocks, followed by conversion.
100: ADC0 tracks only when CNVSTR input is logic low; conversion starts on rising CNVSTR
edge.
101: Tracking initiated on overflow of Timer 3 and lasts 3 SAR clocks, followed by conversion.
11x: Reserved.
0xE8
Rev. 1.1 49
Page 50

C8051F320/1
5.4. Programmable Window Detector
The ADC Programmable Window Detector continuously compares the ADC0 conversion results to user-programmed
limits, and notifies the system when a desired condition is detected. This is especially effective in an interrupt-driven
system, saving code space and CPU bandwidth while delivering faster system response times. The window detector
interrupt flag (AD0WINT in register ADC0CN) can also be used in polled mode. The ADC0 Greater-Than
(ADC0GTH, ADC0GTL) and Less-Than (ADC0LTH, ADC0LTL) registers hold the comparison values. The window
detector flag can be programmed to indicate when measured data is inside or outside of the user-programmed limits,
depending on the contents of the ADC0 Less-Than and ADC0 Greater-Than registers.
The Window Detector registers must be written with the same format (left/right justified, signed/unsigned) as that of
the current ADC configuration (left/right justified, single-ended/differential).
Figure 5.11. ADC0GTH: ADC0 Greater-Than Data High Byte Register
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W Reset Value
Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0 SFR Address:
Bits7-0: High byte of ADC0 Greater-Than Data Word.
11111111
0xC4
Figure 5.12. ADC0GTL: ADC0 Greater-Than Data Low Byte Register
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W Reset Value
Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0 SFR Address:
Bits7-0: Low byte of ADC0 Greater-Than Data Word.
11111111
0xC3
50 Rev. 1.1
Page 51

C8051F320/1
Figure 5.13. ADC0LTH: ADC0 Less-Than Data High Byte Register
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W Reset Value
Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0 SFR Address:
Bits7-0: High byte of ADC0 Less-Than Data Word.
Figure 5.14. ADC0LTL: ADC0 Less-Than Data Low Byte Register
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W Reset Value
Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0 SFR Address:
00000000
0xC6
00000000
0xC5
Bits7-0: Low byte of ADC0 Less-Than Data Word.
Rev. 1.1 51
Page 52

C8051F320/1
5.4.1. Window Detector In Single-Ended Mode
Figure 5.15 shows two example window comparisons for right-justified, single-ended data, with
ADC0LTH:ADC0LTL = 0x0080 (128d) and ADC0GTH:ADC0GTL = 0x0040 (64d). In single-ended mode, the input
voltage can range from ‘0’ to VREF * (1023/1024) with respect to GND, and is represented by a 10-bit unsigned inte
ger value. In the left example, an AD0WINT interrupt will be generated if the ADC0 conversion word
(ADC0H:ADC0L) is within the range defined by ADC0GTH:ADC0GTL and ADC0LTH:ADC0LTL
(if
0x0040 < ADC0H:ADC0L < 0x0080). In the right example, and AD0WINT interrupt will be generated if the
ADC0 conversion word is outside of the range defined by the ADC0GT and ADC0LT registers
(if
ADC0H:ADC0L < 0x0040 or ADC0H:ADC0L > 0x0080). Figure 5.16 shows an example using left-justified data
with equivalent ADC0GT and ADC0LT register settings..
Figure 5.15. ADC Window Compare Example: Right-Justified Single-Ended Data
ADC0H:ADC0L ADC0H:ADC0L
Input Voltage
(Px.x - GND)
VREF x (1023/1024)
0x03FF
Input Voltage
(Px.x - GND)
VREF x (1023/1024)
0x03FF
-
AD0WINT
not affected
VREF x (128/1024)
VREF x (64/1024)
0
0x0081
0x0080
0x007F
0x0041
0x0040
0x003F
0x0000
ADC0LTH:ADC0LTL
ADC0GTH:ADC0GT L
AD0WINT
not affected
VREF x (128/1024)
AD0WINT=1
VREF x (64/1024)
0
0x0081
0x0080
0x007F
0x0041
0x0040
0x003F
0x0000
ADC0GTH:ADC0GTL
AD0WINT
not affected
ADC0LTH:ADC0LTL
Figure 5.16. ADC Window Compare Example: Left-Justified Single-Ended Data
ADC0H:ADC0L ADC0H:ADC0L
Input Voltage
(Px.x - GND)
VREF x (1023/1024)
VREF x (128/1024)
VREF x (64/1024)
0xFFC0
0x2040
0x2000
0x1FC0
0x1040
0x1000
0x0FC0
AD0WINT
not affected
ADC0LTH:ADC0LTL
ADC0GTH:ADC0GTL
AD0WIN T=1
Input Voltage
(Px.x - GND)
VREF x (1023/1024)
VREF x (128/1024)
VREF x (64/1024)
0xFFC0
0x2040
0x2000
0x1FC0
0x1040
0x1000
0x0FC0
ADC0GTH:ADC0GTL
AD0WINT
not affected
ADC0LTH:ADC0LTL
AD0WINT= 1
AD0WINT= 1
AD0WINT=1
AD0WINT
not affected
0
0x0000
52 Rev. 1.1
AD0WINT=1
0
0x0000
Page 53

C8051F320/1
5.4.2. Window Detector In Differential Mode
Figure 5.17 shows two example window comparisons for right-justified, differential data, with
ADC0LTH:ADC0LTL = 0x0040 (+64d) and ADC0GTH:ADC0GTH = 0xFFFF (-1d). In differential mode, the measurable voltage between the input pins is between -VREF and VREF*(511/512). Output codes are represented as 10bit 2’s complement signed integers. In the left example, an AD0WINT interrupt will be generated if the ADC0 con
version word (ADC0H:ADC0L) is within the range defined by ADC0GTH:ADC0GTL and ADC0LTH:ADC0LTL
(if
0xFFFF (-1d) < ADC0H:ADC0L < 0x0040 (64d)). In the right example, an AD0WINT interrupt will be generated
if the ADC0 conversion word is outside of the range defined by the ADC0GT and ADC0LT registers
(if
ADC0H:ADC0L < 0xFFFF (-1d) or ADC0H:ADC0L > 0x0040 (+64d)). Figure 5.18 shows an example using
left-justified data with equivalent ADC0GT and ADC0LT register settings..
Figure 5.17. ADC Window Compare Example: Right-Justified Differential Data
ADC0H:ADC0LADC0H:ADC0L
Input Voltage
(Px.x - Px.x)
VREF x (511/512)
0x01FF
Input Voltage
(Px.x - Px.x)
VREF x (511/512)
0x01FF
-
AD0WINT
not affected
0x0041
0x0040
0x003F
0x0000
0xFFFF
0xFFFE
0x0200
ADC0GTH:ADC0GTL
AD0WINT
not affected
ADC0LTH:ADC0LTL
VREF x (64/512)
VREF x (-1/512)
-VREF
0x0041
0x0040
0x003F
0x0000
0xFFFF
0xFFFE
0x0200
ADC0LTH:ADC0LTL
ADC0GTH:ADC0GTL
AD0WINT
not affected
VREF x (64/512)
AD0WINT=1
VREF x (-1/512)
-VREF
Figure 5.18. ADC Window Compare Example: Left-Justified Differential Data
ADC0H:ADC0LADC0H:ADC0L
Input Voltage
(Px.x - Px.x)
VREF x (511/512)
VREF x (64/512)
VREF x (-1/512)
0x7FC0
0x1040
0x1000
0x0FC0
0x0000
0xFFC0
0xFF80
AD0WINT
not affected
ADC0LTH:ADC0LTL
ADC0GTH:ADC0GTL
AD0WINT=1
Input Voltage
(Px.x - Px.y)
VREF x (511/512)
VREF x (64/512)
VREF x (-1/512)
0x7FC0
0x1040
0x1000
0x0FC0
0x0000
0xFFC0
0xFF80
ADC0GTH:ADC0GTL
AD0WINT
not affected
ADC0LTH:ADC0LTL
AD0WINT= 1
AD0WINT= 1
AD0WINT= 1
-VREF
0x8000
AD0WINT
not affected
AD0WINT= 1
-VREF
0x8000
Rev. 1.1 53
Page 54

C8051F320/1
Tab le 5.1. ADC0 Electrical Characteristics
VDD = 3.0 V, VREF = 2.40 V, -40°C to +85°C unless otherwise specified
PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN TY P MAX UNITS
DC ACCURACY
Resolution 10 bits
Integral Nonlinearity ±0.5 ±1 LSB
Differential Nonlinearity Guaranteed Monotonic ±0.5 ±1 LSB
Offset Error 0 LSB
Full Scale Error -1 LSB
Offset Temperature Coefficient 10 ppm/°C
DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE (10 kHz sine-wave Single-ended input, 1 dB below Full Scale, 200 ksps)
Signal-to-Noise Plus Distortion 53 55.5 dB
Total Harmonic Distortion
Spurious-Free Dynamic Range 78 dB
CONVERSION RATE
SAR Conversion Clock 3 MHz
Conversion Time in SAR Clocks 10 clocks
Track/Hold Acquisition Time 300 ns
Throughput Rate 200 ksps
ANALOG INPUTS
ADC Input Voltage Range Single Ended (AIN+ - GND)
Absolute Pin Voltage with respect to
GND
Input Capacitance 5 pF
TEMPERATURE SENSOR
Linearity Note 1 ±0.1 °C
Gain Note 2 2.86 mV / °C
Offset Notes 1, 2 (Temp = 0 °C) 0.776
POWER SPECIFICATIONS
Power Supply Current (VDD supplied to ADC0)
Power Supply Rejection ±0.3 mV/V
Note 1: Includes ADC offset, gain, and linearity variations.
Note 2: Represents one standard deviation from the mean.
Up to the 5th harmonic
0
Differential (AIN+ - AIN-)
Single Ended or Differential 0 VDD V
Operating Mode, 200 ksps 400 900 µA
-VREF
-67 dB
VREF
VREF
mV
±8.5
V
V
54 Rev. 1.1
Page 55

C8051F320/1
6. VOLTAGE REFERENCE
The Voltage reference MUX on C8051F320/1 devices is configurable to use an externally connected voltage reference, the internal reference voltage generator, or the power supply voltage VDD (see Figure 6.1). The REFSL bit in
the Reference Control register (REF0CN) selects the reference source. For the internal reference or an external
source, REFSL should be set to ‘0’; For VDD as the reference source, REFSL should be set to ‘1’.
The BIASE bit enables the internal ADC bias generator, which is used by the ADC and Internal Oscillator. This
enable is forced to logic 1 when either of the aforementioned peripherals is enabled. The ADC bias generator may be
enabled manually by writing a ‘1’ to the BIASE bit in register REF0CN; see
The Reference bias generator (see Figure 6.1) is used by the Internal Voltage Reference, Temperature Sensor, and
Clock Multiplier. The Reference bias is automatically enabled when any of the aforementioned peripherals are
enabled. The electrical specifications for the voltage reference and bias circuits are given in
Important Note About the VREF Input: Port pin P0.7 is used as the external VREF input. When using an external
voltage reference, P0.7 should be configured as analog input and skipped by the Digital Crossbar. To configure P0.7
as analog input, set to ‘0’ Bit7 in register P0MDIN. To configure the Crossbar to skip P0.7, set to ‘1’ Bit7 in register
P0SKIP. Refer to
Section “14. Port Input/Output” on page 127 for complete Port I/O configuration details.
The temperature sensor connects to the ADC0 positive input multiplexer (see Section “5.1. Analog Multiplexer” on
page 40 for details). The TEMPE bit in register REF0CN enables/disables the temperature sensor. While disabled,
the temperature sensor defaults to a high impedance state and any ADC0 measurements performed on the sensor
result in meaningless data.
Figure 6.2 for REF0CN register details.
Tabl e 6.1.
VDD
GND
R1
Figure 6.1. Voltage Reference Functional Block Diagram
REF0CN
BIASE
REFSL
REFBE
TEMPE
AD0EN
EN
ADC Bias
IOSCEN
External
Voltage
Reference
Circuit
VREF
VDD
0
1
TEMPE
CLKMUL
Enable
REFBE
EN
Internal
Reference
EN
Temp Sensor
EN
Reference
Bias
To ADC,
Internal Oscillator
To Analog Mux
VREF
(to ADC)
To Clock Multiplier,
Temp Sensor
Rev. 1.1 55
Page 56

C8051F320/1
Figure 6.2. REF0CN: Reference Control Register
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W Reset Value
- - - - REFSL TEMPE BIASE REFBE 00000000
Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0 SFR Address:
Bits7-3: UNUSED. Read = 00000b; Write = don’t care.
Bit3: REFSL: Voltage Reference Select.
This bit selects the source for the internal voltage reference.
0: VREF pin used as voltage reference.
1: VDD used as voltage reference.
Bit2: TEMPE: Temperature Sensor Enable Bit.
0: Internal Temperature Sensor off.
1: Internal Temperature Sensor on.
Bit1: BIASE: Internal Analog Bias Generator Enable Bit.
0: Internal Bias Generator off.
1: Internal Bias Generator on.
Bit0: REFBE: Internal Reference Buffer Enable Bit.
0: Internal Reference Buffer disabled.
1: Internal Reference Buffer enabled. Internal voltage reference driven on the VREF pin.
0xD1
Tab le 6.1. Voltage Reference Electrical Characteristics
VDD = 3.0 V; -40°C TO +85°C UNLESS OTHERWISE SPECIFIED
PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN TY P MAX UNITS
INTERNAL REFERENCE (REFBE = 1)
Output Voltage 25°C ambient 2.38 2.44 2.50 V
VREF Short-Circuit Current 10 mA
VREF Temperature Coefficient 15 ppm/°C
Load Regulation Load = 0 to 200 µA to GND 1.5 ppm/µA
VREF Turn-on Time 1 4.7µF tantalum, 0.1µF ceramic bypass 2 ms
VREF Turn-on Time 2 0.1µF ceramic bypass 20 µs
VREF Turn-on Time 3 no bypass cap 10 µs
Power Supply Rejection 140 ppm/V
EXTERNAL REFERENCE (REFBE = 0)
Input Voltage Range 0 VDD V
Input Current Sample Rate = 200 ksps; VREF = 3.0 V 12 µA
BIAS GENERATORS
ADC Bias Generator BIASE = ‘1’ 100 µA
Reference Bias Generator 40 µA
56 Rev. 1.1
Page 57

C8051F320/1
7. COMPARATORS
C8051F320/1 devices include two on-chip programmable voltage Comparators: Comparator0 is shown in Figure 7.1;
Comparator1 is shown in Figure 7.2. The two Comparators operate identically with the following exceptions: (1)
Their input selections differ as shown in Figure 7.1 and Figure 7.2; (2) Comparator0 can be used as a reset source.
Each Comparator offers programmable response time and hysteresis, an analog input multiplexer, and two outputs
that are optionally available at the Port pins: a synchronous “latched” output (CP0, CP1), or an asynchronous “raw”
output (CP0A, CP1A). The asynchronous signal is available even when the system clock is not active. This allows the
Comparators to operate and generate an output with the device in STOP mode. When assigned to a Port pin, the Com
parator outputs may be configured as open drain or push-pull (see Section “14.2. Port I/O Initialization” on
page 131). Comparator0 may also be used as a reset source (see Section “10.5. Comparator0 Reset” on page 102).
The Comparator0 inputs are selected in the CPT0MX register (Figure 7.5). The CMX0P1-CMX0P0 bits select the
Comparator0 positive input; the CMX0N1-CMX0N0 bits select the Comparator0 negative input. The Comparator1
inputs are selected in the CPT1MX register (
tive input; the CMX1N1-CMX1N0 bits select the Comparator1 negative input.
Important Note About Comparator Inputs: The Port pins selected as Comparator inputs should be configured as
analog inputs in their associated Port configuration register, and configured to be skipped by the Crossbar (for details
on Port configuration, see
Section “14.3. General Purpose Port I/O” on page 134).
Figure 7.8). The CMX1P1-CMX1P0 bits select the Comparator1 posi-
-
CMX0N1
CMX0N0
CPT0MX
CMX0P1
CMX0P0
Note: P2.4 and P2.5 available
only on C8051F320
Figure 7.1. Comparator0 Functional Block Diagram
CP0EN
CP0OUT
P1.0
P1.4
P2.0
P2.4
P1.1
P1.5
P2.1
P2.5
CP0RIF
CP0FIF
CP0HYP1
CPT0CN
CP0HYP0
CP0HYN1
CP0HYN0
CP0 +
CP0 -
CP0RIE
CP0FIE
CPT0MD
CP0MD1
CP0MD0
VDD
Rising-edge
+
-
GND
Reset
Decision
Tree
SET
SET
D
D
Q
Q
CLR
CLR
(SYNCHRONIZER)
Q
Q
CP0
Interrupt
Logic
Crossbar
CP0
Interrupt
CP0
Falling-edge
CP0RIE
CP0FIE
CP0
CP0A
Rev. 1.1 57
Page 58

C8051F320/1
Comparator outputs can be polled in software, used as an interrupt source, and/or routed to a Port pin. When routed to
a Port pin, Comparator outputs are available asynchronous or synchronous to the system clock; the asynchronous out
put is available even in STOP mode (with no system clock active). When disabled, the Comparator output (if
assigned to a Port I/O pin via the Crossbar) defaults to the logic low state, and supply current falls to less than
100
nA. See Section “14.1. Priority Crossbar Decoder” on page 129 for details on configuring Comparator outputs
via the digital Crossbar. Comparator inputs can be externally driven from -0.25 V to (VDD) + 0.25 V without damage
or upset. The complete Comparator electrical specifications are given in
Comparator response time may be configured in software via the CPTnMD registers (see Figure 7.6 and Figure 7.9).
Selecting a longer response time reduces the Comparator supply current. See Table 7.1 for complete timing and supply current specifications.
Figure 7.2. Comparator1 Functional Block Diagram
CP1EN
CP1OUT
CMX1N1
CMX1N0
CPT1MX
CMX1P1
CMX1P0
P1.2
P1.6
P2.2
P2.6
P1.3
P1.7
P2.3
P2.7
CP1RIF
CP1FIF
CP1HYP1
CPT1CN
CP1HYP0
CP1HYN1
CP1HYN0
CP1 +
CP1 -
VDD
+
-
GND
Table 7.1.
SET
SET
Q
D
D
Q
CLR
CLR
(SYNCHRONIZER)
Q
Q
CP1
Rising-edge
Interrupt
Logic
Crossbar
CP1
Interrupt
CP1
Falling-edge
CP1RIE
CP1FIE
CP1
CP1A
-
CP1RIE
Note: P2.6 and P2.7 available
only on C8051F320
CP1FIE
CPT1MD
CP1MD1
CP1MD0
58 Rev. 1.1
Page 59

Figure 7.3. Comparator Hysteresis Plot
C8051F320/1
VIN+
VIN-
CP0+
CP0-
+
CP0
_
OUT
CIRCUIT CONFIGURATION
Posi tive Hy steresi s Volt age
(Programmed with CP0HYP Bits)
INPUTS
VIN-
VIN+
V
OH
Negative Hysteresis Vo ltage
(Programmed by CP0HYN Bits)
OUTPUT
V
OL
Posi tive Hy steresi s
Disabled
Maximum
Posi tive H ysteresi s
Negative Hysteresis
Disabled
Maximum
Negative Hysteresis
Comparator hysteresis is programmed using Bits3-0 in the Comparator Control Register CPTnCN (shown in
Figure 7.4 and Figure 7.7). The amount of negative hysteresis voltage is determined by the settings of the CPnHYN
bits. As shown in Figure 7.3, settings of 20, 10 or 5 mV of negative hysteresis can be programmed, or negative
hysteresis can be disabled. In a similar way, the amount of positive hysteresis is determined by the setting the
CPnHYP bits.
Comparator interrupts can be generated on both rising-edge and falling-edge output transitions. (For Interrupt enable
and priority control, see
Section “8.3. Interrupt Handler” on page 58.) The CPnFIF flag is set to ‘1’ upon a Com-
parator falling-edge, and the CPnRIF flag is set to ‘1’ upon the Comparator rising-edge. Once set, these bits remain
set until cleared by software. The output state of the Comparator can be obtained at any time by reading the CPnOUT
bit. The Comparator is enabled by setting the CPnEN bit to ‘1’, and is disabled by clearing this bit to ‘0’.
Rev. 1.1 59
Page 60

C8051F320/1
Figure 7.4. CPT0CN: Comparator0 Control Register
R/W R R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W Reset Value
CP0EN CP0OUT CP0RIF CP0FIF CP0HYP1 CP0HYP0 CP0HYN1 CP0HYN0 00000000
Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0 SFR Address:
Bit7: CP0EN: Comparator0 Enable Bit.
0: Comparator0 Disabled.
1: Comparator0 Enabled.
Bit6: CP0OUT: Comparator0 Output State Flag.
0: Voltage on CP0+ < CP0-.
1: Voltage on CP0+ > CP0-.
Bit5: CP0RIF: Comparator0 Rising-Edge Flag.
0: No Comparator0 Rising Edge has occurred since this flag was last cleared.
1: Comparator0 Rising Edge has occurred.
Bit4: CP0FIF: Comparator0 Falling-Edge Flag.
0: No Comparator0 Falling-Edge has occurred since this flag was last cleared.
1: Comparator0 Falling-Edge Interrupt has occurred.
Bits3-2: CP0HYP1-0: Comparator0 Positive Hysteresis Control Bits.
00: Positive Hysteresis Disabled.
01: Positive Hysteresis = 5 mV.
10: Positive Hysteresis = 10 mV.
11: Positive Hysteresis = 20 mV.
Bits1-0: CP0HYN1-0: Comparator0 Negative Hysteresis Control Bits.
00: Negative Hysteresis Disabled.
01: Negative Hysteresis = 5 mV.
10: Negative Hysteresis = 10 mV.
11: Negative Hysteresis = 20 mV.
0x9B
60 Rev. 1.1
Page 61

C8051F320/1
Figure 7.5. CPT0MX: Comparator0 MUX Selection Register
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W Reset Value
- - CMX0N1 CMX0N0 - - CMX0P1 CMX0P0 00000000
Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0 SFR Address:
Bits7-6: UNUSED. Read = 00b, Write = don’t care.
Bits5-4: CMX0N1-CMX0N0: Comparator0 Negative Input MUX Select.
These bits select which Port pin is used as the Comparator0 negative input.
CMX0N1 CMX0N0 Negative Input
00 P1.1
01 P1.5
10 P2.1
11
Bits3-2: UNUSED. Read = 00b, Write = don’t care.
Bits1-0: CMX0P1-CMX0P0: Comparator0 Positive Input MUX Select.
These bits select which Port pin is used as the Comparator0 positive input.
P2.5
†
0x9F
CMX0P1 CMX0P0 Positive Input
00 P1.0
01 P1.4
10 P2.0
11
†
Note: P2.4 and P2.5 available only on C8051F320 devices; selection reserved on C8051F321
devices.
P2.4
†
Rev. 1.1 61
Page 62

C8051F320/1
Figure 7.6. CPT0MD: Comparator0 Mode Selection Register
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W Reset Value
- - CP0RIE CP0FIE - - CP0MD1 CP0MD0 00000010
Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0 SFR Address:
Bits7-6: UNUSED. Read = 00b. Write = don’t care.
Bit5: CP0RIE: Comparator0 Rising-Edge Interrupt Enable.
0: Comparator0 rising-edge interrupt disabled.
1: Comparator0 rising-edge interrupt enabled.
Bit4: CP0FIE: Comparator0 Falling-Edge Interrupt Enable.
0: Comparator0 falling-edge interrupt disabled.
1: Comparator0 falling-edge interrupt enabled.
Bits3-2: UNUSED. Read = 00b. Write = don’t care.
Bits1-0: CP0MD1-CP0MD0: Comparator0 Mode Select
These bits select the response time for Comparator0.
Mode CP0MD1 CP0MD0 CP0 Response Time (TYP)
0 0 0 100 ns
1 0 1 175 ns
2 1 0 320 ns
3 1 1 1050 ns
0x9D
62 Rev. 1.1
Page 63

C8051F320/1
Figure 7.7. CPT1CN: Comparator1 Control Register
R/W R R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W Reset Value
CP1EN CP1OUT CP1RIF CP1FIF CP1HYP1 CP1HYP0 CP1HYN1 CP1HYN0 00000000
Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0 SFR Address:
0x9A
Bit7: CP1EN: Comparator1 Enable Bit.
0: Comparator1 Disabled.
1: Comparator1 Enabled.
Bit6: CP1OUT: Comparator1 Output State Flag.
0: Voltage on CP1+ < CP1-.
1: Voltage on CP1+ > CP1-.
Bit5: CP1RIF: Comparator1 Rising-Edge Flag.
0: No Comparator1 Rising Edge has occurred since this flag was last cleared.
1: Comparator1 Rising Edge has occurred.
Bit4: CP1FIF: Comparator1 Falling-Edge Flag.
0: No Comparator1 Falling-Edge has occurred since this flag was last cleared.
1: Comparator1 Falling-Edge has occurred.
Bits3-2: CP1HYP1-0: Comparator1 Positive Hysteresis Control Bits.
00: Positive Hysteresis Disabled.
01: Positive Hysteresis = 5 mV.
10: Positive Hysteresis = 10 mV.
11: Positive Hysteresis = 20 mV.
Bits1-0: CP1HYN1-0: Comparator1 Negative Hysteresis Control Bits.
00: Negative Hysteresis Disabled.
01: Negative Hysteresis = 5 mV.
10: Negative Hysteresis = 10 mV.
11: Negative Hysteresis = 20 mV.
Rev. 1.1 63
Page 64

C8051F320/1
Figure 7.8. CPT1MX: Comparator1 MUX Selection Register
Bits7-6: UNUSED. Read = 00b, Write = don’t care.
Bits5-4: CMX1N1-CMX1N0: Comparator1 Negative Input MUX Select.
64 Rev. 1.1
Page 65

C8051F320/1
Figure 7.9. CPT1MD: Comparator1 Mode Selection Register
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W Reset Value
- - CP1RIE CP1FIE - - CP1MD1 CP1MD0 00000010
Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0 SFR Address:
Bits7-6: UNUSED. Read = 00b, Write = don’t care.
Bit5: CP1RIE: Comparator1 Rising-Edge Interrupt Enable.
0: Comparator1 rising-edge interrupt disabled.
1: Comparator1 rising-edge interrupt enabled.
Bit4: CP1FIE: Comparator1 Falling-Edge Interrupt Enable.
0: Comparator1 falling-edge interrupt disabled.
1: Comparator1 falling-edge interrupt enabled.
Bits1-0: CP1MD1-CP1MD0: Comparator1 Mode Select.
These bits select the response time for Comparator1.
Mode CP1MD1 CP1MD0 CP1 Response Time (TYP)
0 0 0 100 ns
1 0 1 175 ns
2 1 0 320 ns
3 1 1 1050 ns
0x9C
Rev. 1.1 65
Page 66

C8051F320/1
Tab le 7.1. Comparator Electrical Characteristics
VDD = 3.0 V, -40°C to +85°C unless otherwise noted.
All specifications apply to both Comparator0 and Comparator1 unless otherwise noted.
PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
Response Time:
Mode 0, Vcm† = 1.5 V
Response Time:
Mode 1, Vcm† = 1.5 V
Response Time:
Mode 2, Vcm† = 1.5 V
Response Time:
Mode 3, Vcm† = 1.5 V
Common-Mode Rejection Ratio 1.5 4 mV/V
Positive Hysteresis 1 CP0HYP1-0 = 00 0 1 mV
Positive Hysteresis 2 CP0HYP1-0 = 01 2 5 10 mV
Positive Hysteresis 3 CP0HYP1-0 = 10 7 10 20 mV
Positive Hysteresis 4 CP0HYP1-0 = 11 15 20 30 mV
Negative Hysteresis 1 CP0HYN1-0 = 00 0 1 mV
Negative Hysteresis 2 CP0HYN1-0 = 01 2 5 10 mV
Negative Hysteresis 3 CP0HYN1-0 = 10 7 10 20 mV
Negative Hysteresis 4 CP0HYN1-0 = 11 15 20 30 mV
Inverting or Non-Inverting Input
Voltage Range
Input Capacitance 3 pF
Input Bias Current 0.001 nA
Input Offset Voltage -5 +5 mV
POWER SUPPLY
Power Supply Rejection 0.1 mV/V
Power-up Time 10 µs
Supply Current at DC
†
Vcm is the common-mode voltage on CP0+ and CP0-.
CP0+ - CP0- = 100 mV 100 ns
CP0+ - CP0- = -100 mV 250 ns
CP0+ - CP0- = 100 mV 175 ns
CP0+ - CP0- = -100 mV 500 ns
CP0+ - CP0- = 100 mV 320 ns
CP0+ - CP0- = -100 mV 1100 ns
CP0+ - CP0- = 100 mV 1050 ns
CP0+ - CP0- = -100 mV 5200 ns
-0.25 VDD +
0.25
Mode 0 7.6 µA
Mode 1 3.2 µA
Mode 2 1.3 µA
Mode 3 0.4 µA
V
66 Rev. 1.1
Page 67

C8051F320/1
8. VOLTAGE REGULATOR (REG0)
C8051F320/1 devices include a 5 V- to -3 V voltage regulator (REG0). When enabled, the REG0 output appears on
the VDD pin and can be used to power external devices. REG0 can be enabled/disabled by software using bit
REGEN in register REG0CN. See
Note that the VBUS signal must be connected to the VBUS pin when using the device in a USB network. The VBUS
signal should only be connected to the REGIN pin when operating the device as a bus-powered function. REG0 con
figuration options are shown in Figure 8.1 - Figure 8.4.
Table 8.1 for REG0 electrical characteristics.
-
Rev. 1.1 67
Page 68

C8051F320/1
8.1. Regulator Mode Selection
REG0 offers a low power mode intended for use when the device is in suspend mode. In this low power mode, the
REG0 output remains as specified; however the REG0 dynamic performance (response time) is degraded. See
Table 8.1 for normal and low power mode supply current specifications. The REG0 mode selection is controlled via
the REGMOD bit in register REG0CN.
68 Rev. 1.1
Page 69

C8051F320/1
8.2. VBUS Detection
When the USB Function Controller is used (see section Section “15. Universal Serial Bus Controller (USB0)” on
page 143), the VBUS signal should be connected to the VBUS pin. The VBSTAT bit (register REG0CN) indicates
the current logic level of the VBUS signal. If enabled, a VBUS interrupt will be generated when the VBUS signal
matches the polarity selected by the VBPOL bit in register REG0CN. The VBUS interrupt is level-sensitive, and has
no associated interrupt pending flag. The VBUS interrupt will be active as long as the VBUS signal matches the
polarity selected by VBPOL. See
Important Note: When USB is selected as a reset source, a system reset will be generated when the VBUS signal
matches the polarity selected by the VBPOL bit. See
USB as a reset source.
Tab le 8.1. Voltage Regulator Electrical Specifications
VDD = 3.0 V; -40°C to +85°C unless otherwise specified
PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
Input Voltage Range 4.0 5.25 V
Output Voltage Output Current = 1 to 100 mA 3.0 3.3 3.6 V
VBUS Detection Input Threshold 1.0 1.8 4.0 V
Bias Current
Table 8.1 for VBUS input parameters.
Section “10. Reset Sources” on page 99 for details on selecting
Normal Mode (REGMOD = ‘0’)
Low Power Mode (REGMOD = ‘1’)
90
60
TBD
TBD
µA
Rev. 1.1 69
Page 70

C8051F320/1
Figure 8.1. REG0 Configuration: USB Bus-Powered
C8051F320/1
VBUS
From VBUS
To 3V
Power Net
From VBUS
From 5V
Power Net
VBUS Sense
REGIN
VDD
5V In
Voltage Regulator (REG0)
3V Out
Figure 8.2. REG0 Configuration: USB Self-Powered
C8051F320/1
VBUS
VBUS Sense
REGIN
5V In
Voltage Regulator (REG0)
3V Out
Device
Power Net
To 3V
Power Net
VDD
70 Rev. 1.1
Device
Power Net
Page 71

C8051F320/1
Figure 8.3. REG0 Configuration: USB Self-Powered, Regulator Disabled
C8051F320/1
From VBUS
From 3V
Power Net
From 5V
Power Net
VBUS
VBUS Sense
REGIN
VDD
5V In
Voltage Regulator (REG0)
3V Out
Figure 8.4. REG0 Configuration: No USB Connection
C8051F320/1
VBUS
VBUS Sense
REGIN
5V In
Voltage Regulator (REG0)
Device
Power Net
To 3V
Power Net
VDD
3V Out
Device
Power Net
Rev. 1.1 71
Page 72

C8051F320/1
Figure 8.5. REG0CN: Voltage Regulator Control
R/W R R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W Reset Value
REGDIS VBSTAT VBPOL REGMOD Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved 00000000
Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0 SFR Address:
Bit7: REGDIS: Voltage Regulator Disable.
0: Voltage Regulator Enabled.
1: Voltage Regulator Disabled.
Bit6: VBSTAT: VBUS Signal Status.
0: VBUS signal currently absent (device not attached to USB network).
1: VBUS signal currently preset (device attached to USB network).
Bit5: VBPOL: VBUS Interrupt Polarity Select.
This bit selects the VBUS interrupt polarity.
0: VBUS interrupt active when VBUS is low.
1: VBUS interrupt active when VBUS is high.
Bit4: REGMOD: Voltage Regulator Mode Select.
This bit selects the Voltage Regulator mode. When REGMOD is set to ‘1’, the voltage regulator oper-
ates in low power (suspend) mode.
0: USB0 Voltage Regulator in normal mode.
1: USB0 Voltage Regulator in low power mode.
Bits3-0: Reserved. Read = 0000b. Must Write = 0000b.
0xC9
72 Rev. 1.1
Page 73

C8051F320/1
9. CIP-51 MICROCONTROLLER
The MCU system controller core is the CIP-51 microcontroller. The CIP-51 is fully compatible with the MCS-51™
instruction set; standard 803x/805x assemblers and compilers can be used to develop software. The MCU family has
a superset of all the peripherals included with a standard 8051. Included are four 16-bit counter/timers (see descrip
tion in Section 19), an enhanced full-duplex UART (see description in Section 17), an Enhanced SPI (see description
in Section 18), 256 bytes of internal RAM, 128 byte Special Function Register (SFR) address space (Section 9.2.6),
and 25 Port I/O (see description in Section 14). The CIP-51 also includes on-chip debug hardware (see description in
Section 21), and interfaces directly with the analog and digital subsystems providing a complete data acquisition or
control-system solution in a single integrated circuit.
The CIP-51 Microcontroller core implements the standard 8051 organization and peripherals as well as additional
custom peripherals and functions to extend its capability (see
the following features:
Figure 9.1 for a block diagram). The CIP-51 includes
-
- Fully Compatible with MCS-51 Instruction Set
- 25 MIPS Peak Throughput with 25 MHz Clock
- 0 to 25 MHz Clock Frequency
- 256 Bytes of Internal RAM
- 25 Port I/O
Figure 9.1. CIP-51 Block Diagram
DATA BUS
RESET
CLOCK
STOP
IDLE
D8
ACCUMULATOR
PSW
D8
BUFFER
DATA POINTER
PC INCREMENTER
PROGRAM COUNTER (PC)
PRGM. ADDRESS REG.
CONTROL
LOGIC
POWER CONTROL
REGISTER
D8
TMP1 TMP2
PIPELINE
ALU
D8
- Extended Interrupt Handler
- Reset Input
- Power Management Modes
- On-chip Debug Logic
- Program and Data Memory Security
DATA BUS
D8
DATA BUS
D8
D8
DATA BUS
D8
B REGISTER
ADDRESS
REGISTER
D8
INTERFACE
D8
A16
INTERFACE
D8
INTERRUPT
INTERFACE
D8
D8
SRAM
D8
SFR
BUS
MEMORY
D8
STACK POINTER
SRAM
(256 X 8)
D8
SFR_ADDRESS
SFR_CONTROL
SFR_WRITE_DATA
SFR_READ_DATA
MEM_ADDRESS
MEM_CONTROL
MEM_WRITE_ DATA
MEM_READ_DATA
SYSTEM_IRQs
EMULATION_IRQ
Rev. 1.1 73
Page 74

C8051F320/1
Performance
The CIP-51 employs a pipelined architecture that greatly increases its instruction throughput over the standard 8051
architecture. In a standard 8051, all instructions except for MUL and DIV take 12 or 24 system clock cycles to exe
cute, and usually have a maximum system clock of 12 MHz. By contrast, the CIP-51 core executes 70% of its instructions in one or two system clock cycles, with no instructions taking more than eight system clock cycles.
With the CIP-51's maximum system clock at 25 MHz, it has a peak throughput of 25 MIPS. The CIP-51 has a total of
109 instructions. The table below shows the total number of instructions that for execution time.
Clocks to Execute 1 2 2/3 3 3/4 4 4/5 5 8
Number of Instructions 26 50 5 14 7 3 1 2 1
Programming and Debugging Support
In-system programming of the FLASH program memory and communication with on-chip debug support logic is
accomplished via the Silicon Labs 2-Wire Development Interface (C2). Note that the re-programmable FLASH can
also be read and changed a single byte at a time by the application software using the MOVC and MOVX instruc
tions. This feature allows program memory to be used for non-volatile data storage as well as updating program code
under software control.
The on-chip debug support logic facilitates full speed in-circuit debugging, allowing the setting of hardware breakpoints, starting, stopping and single stepping through program execution (including interrupt service routines), examination of the program's call stack, and reading/writing the contents of registers and memory. This method of on-chip
debugging is completely non-intrusive, requiring no RAM, Stack, timers, or other on-chip resources. C2 details can
be found in
Section “21. C2 Interface” on page 253.
-
-
The CIP-51 is supported by development tools from Silicon Labs and third party vendors. Silicon Labs provides an
integrated development environment (IDE) including editor, macro assembler, debugger and programmer. The IDE's
debugger and programmer interface to the CIP-51 via the C2 interface to provide fast and efficient in-system device
programming and debugging. Third party macro assemblers and C compilers are also available.
74 Rev. 1.1
Page 75

C8051F320/1
9.1. Instruction Set
The instruction set of the CIP-51 System Controller is fully compatible with the standard MCS-51™ instruction set.
Standard 8051 development tools can be used to develop software for the CIP-51. All CIP-51 instructions are the
binary and functional equivalent of their MCS-51™ counterparts, including opcodes, addressing modes and effect on
PSW flags. However, instruction timing is different than that of the standard 8051.
9.1.1. Instruction and CPU Timing
In many 8051 implementations, a distinction is made between machine cycles and clock cycles, with machine cycles
varying from 2 to 12 clock cycles in length. However, the CIP-51 implementation is based solely on clock cycle tim
ing. All instruction timings are specified in terms of clock cycles.
Due to the pipelined architecture of the CIP-51, most instructions execute in the same number of clock cycles as there
are program bytes in the instruction. Conditional branch instructions take one less clock cycle to complete when the
branch is not taken as opposed to when the branch is taken.
includes the mnemonic, number of bytes, and number of clock cycles for each instruction.
9.1.2. MOVX Instruction and Program Memory
The MOVX instruction is typically used to access external data memory (Note: the C8051F320/1 does not support
off-chip data or program memory). In the CIP-51, the MOVX write instruction is used to accesses external RAM
(XRAM) and the on-chip program memory space implemented as re-programmable FLASH memory. The FLASH
access feature provides a mechanism for the CIP-51 to update program code and use the program memory space for
non-volatile data storage. Refer to
Section “11. FLASH Memory” on page 107 for further details.
Tabl e 9.1 is the CIP-51 Instruction Set Summary, which
-
Tab le 9.1. CIP-51 Instruction Set Summary
Mnemonic Description Bytes
ARITHMETIC OPERATIONS
ADD A, Rn Add register to A 1 1
ADD A, direct Add direct byte to A 2 2
ADD A, @Ri Add indirect RAM to A 1 2
ADD A, #data Add immediate to A 2 2
ADDC A, Rn Add register to A with carry 1 1
ADDC A, direct Add direct byte to A with carry 2 2
ADDC A, @Ri Add indirect RAM to A with carry 1 2
ADDC A, #data Add immediate to A with carry 2 2
SUBB A, Rn Subtract register from A with borrow 1 1
SUBB A, direct Subtract direct byte from A with borrow 2 2
SUBB A, @Ri Subtract indirect RAM from A with borrow 1 2
SUBB A, #data Subtract immediate from A with borrow 2 2
INC A Increment A 1 1
INC Rn Increment register 1 1
INC direct Increment direct byte 2 2
INC @Ri Increment indirect RAM 1 2
DEC A Decrement A 1 1
DEC Rn Decrement register 1 1
DEC direct Decrement direct byte 2 2
DEC @Ri Decrement indirect RAM 1 2
INC DPTR Increment Data Pointer 1 1
Clock
Cycles
Rev. 1.1 75
Page 76

C8051F320/1
Table 9.1. CIP-51 Instruction Set Summary
Mnemonic Description Bytes
MUL AB Multiply A and B 1 4
DIV AB Divide A by B 1 8
DA A Decimal adjust A 1 1
LOGICAL OPERATIONS
ANL A, Rn AND Register to A 1 1
ANL A, direct AND direct byte to A 2 2
ANL A, @Ri AND indirect RAM to A 1 2
ANL A, #data AND immediate to A 2 2
ANL direct, A AND A to direct byte 2 2
ANL direct, #data AND immediate to direct byte 3 3
ORL A, Rn OR Register to A 1 1
ORL A, direct OR direct byte to A 2 2
ORL A, @Ri OR indirect RAM to A 1 2
ORL A, #data OR immediate to A 2 2
ORL direct, A OR A to direct byte 2 2
ORL direct, #data OR immediate to direct byte 3 3
XRL A, Rn Exclusive-OR Register to A 1 1
XRL A, direct Exclusive-OR direct byte to A 2 2
XRL A, @Ri Exclusive-OR indirect RAM to A 1 2
XRL A, #data Exclusive-OR immediate to A 2 2
XRL direct, A Exclusive-OR A to direct byte 2 2
XRL direct, #data Exclusive-OR immediate to direct byte 3 3
CLR A Clear A 1 1
CPL A Complement A 1 1
RL A Rotate A left 1 1
RLC A Rotate A left through Carry 1 1
RR A Rotate A right 1 1
RRC A Rotate A right through Carry 1 1
SWAP A Swap nibbles of A 1 1
DATA TRANSFER
MOV A, Rn Move Register to A 1 1
MOV A, direct Move direct byte to A 2 2
MOV A, @Ri Move indirect RAM to A 1 2
MOV A, #data Move immediate to A 2 2
MOV Rn, A Move A to Register 1 1
MOV Rn, direct Move direct byte to Register 2 2
MOV Rn, #data Move immediate to Register 2 2
MOV direct, A Move A to direct byte 2 2
MOV direct, Rn Move Register to direct byte 2 2
MOV direct, direct Move direct byte to direct byte 3 3
MOV direct, @Ri Move indirect RAM to direct byte 2 2
MOV direct, #data Move immediate to direct byte 3 3
MOV @Ri, A Move A to indirect RAM 1 2
MOV @Ri, direct Move direct byte to indirect RAM 2 2
MOV @Ri, #data Move immediate to indirect RAM 2 2
Clock
Cycles
76 Rev. 1.1
Page 77

Table 9.1. CIP-51 Instruction Set Summary
C8051F320/1
Mnemonic Description Bytes
MOV DPTR, #data16 Load DPTR with 16-bit constant 3 3
MOVC A, @A+DPTR Move code byte relative DPTR to A 1 3
MOVC A, @A+PC Move code byte relative PC to A 1 3
MOVX A, @Ri Move external data (8-bit address) to A 1 3
MOVX @Ri, A Move A to external data (8-bit address) 1 3
MOVX A, @DPTR Move external data (16-bit address) to A 1 3
MOVX @DPTR, A Move A to external data (16-bit address) 1 3
PUSH direct Push direct byte onto stack 2 2
POP direct Pop direct byte from stack 2 2
XCH A, Rn Exchange Register with A 1 1
XCH A, direct Exchange direct byte with A 2 2
XCH A, @Ri Exchange indirect RAM with A 1 2
XCHD A, @Ri Exchange low nibble of indirect RAM with A 1 2
BOOLEAN MANIPULATION
CLR C Clear Carry 1 1
CLR bit Clear direct bit 2 2
SETB C Set Carry 1 1
SETB bit Set direct bit 2 2
CPL C Complement Carry 1 1
CPL bit Complement direct bit 2 2
ANL C, bit AND direct bit to Carry 2 2
ANL C, /bit AND complement of direct bit to Carry 2 2
ORL C, bit OR direct bit to carry 2 2
ORL C, /bit OR complement of direct bit to Carry 2 2
MOV C, bit Move direct bit to Carry 2 2
MOV bit, C Move Carry to direct bit 2 2
JC rel Jump if Carry is set 2 2/3
JNC rel Jump if Carry is not set 2 2/3
JB bit, rel Jump if direct bit is set 3 3/4
JNB bit, rel Jump if direct bit is not set 3 3/4
JBC bit, rel Jump if direct bit is set and clear bit 3 3/4
PROGRAM BRANCHING
ACALL addr11 Absolute subroutine call 2 3
LCALL addr16 Long subroutine call 3 4
RET Return from subroutine 1 5
RETI Return from interrupt 1 5
AJMP addr11 Absolute jump 2 3
LJMP addr16 Long jump 3 4
SJMP rel Short jump (relative address) 2 3
JMP @A+DPTR Jump indirect relative to DPTR 1 3
JZ rel Jump if A equals zero 2 2/3
JNZ rel Jump if A does not equal zero 2 2/3
CJNE A, direct, rel Compare direct byte to A and jump if not equal 3 3/4
CJNE A, #data, rel Compare immediate to A and jump if not equal 3 3/4
CJNE Rn, #data, rel Compare immediate to Register and jump if not equal 3 3/4
Clock
Cycles
Rev. 1.1 77
Page 78

C8051F320/1
Table 9.1. CIP-51 Instruction Set Summary
Mnemonic Description Bytes
CJNE @Ri, #data, rel Compare immediate to indirect and jump if not equal 3 4/5
DJNZ Rn, rel Decrement Register and jump if not zero 2 2/3
DJNZ direct, rel Decrement direct byte and jump if not zero 3 3/4
NOP No operation 1 1
Notes on Registers, Operands and Addressing Modes:
Rn - Register R0-R7 of the currently selected register bank.
@Ri - Data RAM location addressed indirectly through R0 or R1.
rel - 8-bit, signed (two’s complement) offset relative to the first byte of the following instruction. Used by SJMP
and all conditional jumps.
direct - 8-bit internal data location’s address. This could be a direct-access Data RAM location (0x00-0x7F) or an
SFR (0x80-0xFF).
#data - 8-bit constant
#data16 - 16-bit constant
Clock
Cycles
bit - Direct-accessed bit in Data RAM or SFR
addr11 - 11-bit destination address used by ACALL and AJMP. The destination must be within the same 2K-byte
page of program memory as the first byte of the following instruction.
addr16 - 16-bit destination address used by LCALL and LJMP. The destination may be anywhere within the 8Kbyte program memory space.
There is one unused opcode (0xA5) that performs the same function as NOP.
All mnemonics copyrighted © Intel Corporation 1980.
78 Rev. 1.1
Page 79

C8051F320/1
9.2. Memory Organization
The memory organization of the CIP-51 System Controller is similar to that of a standard 8051. There are two separate memory spaces: program memory and data memory. Program and data memory share the same address space but
are accessed via different instruction types. The CIP-51 memory organization is shown in
Figure 9.2. Memory Map
Figure 9.2.
PROGRAM/DATA MEMORY
(FLASH)
0x3E00
0x3DFF
0x0000
RESERVED
16K FLASH
(In-System
Programmable in 512
Byte Sectors)
0xFF
0x80
0x7F
0x30
0x2F
0x20
0x1F
0x00
0xFFFF
0x0800
0x07FF
0x0400
0x03FF
0x0000
DATA MEMORY (RAM)
INTERNAL DATA ADDRESS SPACE
Upper 128 RAM
(Indirect Addressing
Only)
(Direct and Indirect
Addressing)
Bit Addressable
General Purpose
Registers
Special Function
Register's
(Direct Addressing Only)
Lower 128 RAM
(Direct and Indirect
Addressing)
EXTERNAL DATA ADDRESS SPACE
Same 2048 bytes as from
0x0000 to 0x07FF, wrapped
on 2K-byte boundaries
USB FIFOs
1024 Bytes
XRAM - 1024 Bytes
(accessable using MOVX
instruction)
9.2.1. Program Memory
The CIP-51 core has a 64k-byte program memory space. The C8051F320/1 implements 16k bytes of this program
memory space as in-system, re-programmable FLASH memory, organized in a contiguous block from addresses
0x0000 to 0x3FFF. Addresses above 0x3DFF are reserved.
Program memory is normally assumed to be read-only. However, the CIP-51 can write to program memory by setting
the Program Store Write Enable bit (PSCTL.0) and using the MOVX instruction. This feature provides a mechanism
for the CIP-51 to update program code and use the program memory space for non-volatile data storage. Refer to
tion “11. FLASH Memory” on page 107 for further details.
Rev. 1.1 79
Sec-
Page 80

C8051F320/1
9.2.2. Data Memory
The CIP-51 includes 256 of internal RAM mapped into the data memory space from 0x00 through 0xFF. The lower
128
bytes of data memory are used for general purpose registers and scratch pad memory. Either direct or indirect
addressing may be used to access the lower 128
as four banks of general purpose registers, each bank consisting of eight byte-wide registers. The next 16
tions 0x20 through 0x2F, may either be addressed as bytes or as 128 bit locations accessible with the direct addressing mode.
The upper 128 bytes of data memory are accessible only by indirect addressing. This region occupies the same
address space as the Special Function Registers (SFR) but is physically separate from the SFR space. The addressing
mode used by an instruction when accessing locations above 0x7F determines whether the CPU accesses the upper
128
bytes of data memory space or the SFRs. Instructions that use direct addressing will access the SFR space.
Instructions using indirect addressing above 0x7F access the upper 128
the data memory organization of the CIP-51.
9.2.3. General Purpose Registers
The lower 32 bytes of data memory, locations 0x00 through 0x1F, may be addressed as four banks of general-purpose
registers. Each bank consists of eight byte-wide registers designated R0 through R7. Only one of these banks may be
enabled at a time. Two bits in the program status word, RS0 (PSW.3) and RS1 (PSW.4), select the active register bank
(see description of the PSW in
rupt service routines. Indirect addressing modes use registers R0 and R1 as index registers.
Figure 9.6). This allows fast context switching when entering subroutines and inter-
bytes of data memory. Locations 0x00 through 0x1F are addressable
bytes, loca-
bytes of data memory. Figure 9.2 illustrates
9.2.4. Bit Addressable Locations
In addition to direct access to data memory organized as bytes, the sixteen data memory locations at 0x20 through
0x2F are also accessible as 128
the byte at 0x20 has bit address 0x00 while bit7 of the byte at 0x20 has bit address 0x07. Bit 7 of the byte at 0x2F has
bit address 0x7F. A bit access is distinguished from a full byte access by the type of instruction used (bit source or
destination operands as opposed to a byte source or destination).
The MCS-51™ assembly language allows an alternate notation for bit addressing of the form XX.B where XX is the
byte address and B is the bit position within the byte. For example, the instruction:
MOV C, 22h.3
moves the Boolean value at 0x13 (bit 3 of the byte at location 0x22) into the Carry flag.
individually addressable bits. Each bit has a bit address from 0x00 to 0x7F. Bit 0 of
9.2.5. Stack
A programmer's stack can be located anywhere in the 256-byte data memory. The stack area is designated using the
Stack Pointer (SP, 0x81) SFR. The SP will point to the last location used. The next value pushed on the stack is placed
at SP+1 and then SP is incremented. A reset initializes the stack pointer to location 0x07. Therefore, the first value
pushed on the stack is placed at location 0x08, which is also the first register (R0) of register bank 1. Thus, if more
than one register bank is to be used, the SP should be initialized to a location in the data memory not being used for
data storage. The stack depth can extend up to 256
bytes.
80 Rev. 1.1
Page 81

C8051F320/1
9.2.6. Special Function Registers
The direct-access data memory locations from 0x80 to 0xFF constitute the special function registers (SFRs). The
SFRs provide control and data exchange with the CIP-51's resources and peripherals. The CIP-51 duplicates the SFRs
found in a typical 8051 implementation as well as implementing additional SFRs used to configure and access the
sub-systems unique to the MCU. This allows the addition of new functionality while retaining compatibility with the
MCS-51™ instruction set.
The SFR registers are accessed anytime the direct addressing mode is used to access memory locations from 0x80 to
0xFF. SFRs with addresses ending in 0x0 or 0x8 (e.g. P0, TCON, SCON0, IE, etc.) are bit-addressable as well as
byte-addressable. All other SFRs are byte-addressable only. Unoccupied addresses in the SFR space are reserved for
future use. Accessing these areas will have an indeterminate effect and should be avoided. Refer to the corresponding
pages of the datasheet, as indicated in
F8 SPI0CN PCA0L PCA0H PCA0CPL0 PCA0CPH0 PCA0CPL4 PCA0CPH4 VDM0CN
F0
E8
E0
D8
D0
C8
C0
B8
B0
A8
A0
98
90
88
80
B P0MDIN P1MDIN P2MDIN P3MDIN EIP1 EIP2
ADC0CN PCA0CPL1 PCA0CPH1 PCA0CPL2 PCA0CPH2 PCA0CPL3 PCA0CPH3 RSTSRC
ACC XBR0 XBR1 IT01CF EIE1 EIE2
PCA0CN PCA0MD PCA0CPM0 PCA0CPM1 PCA0CPM2 PCA0CPM3 PCA0CPM4
PSW REF0CN P0SKIP P1SKIP P2SKIP USB0XCN
TMR2CN REG0CN TMR2RLL TMR2RLH TMR2L TMR2H
SMB0CN SMB0CF SMB0DAT ADC0GTL ADC0GTH ADC0LTL ADC0LTH
IP CLKMUL AMX0N AMX0P ADC0CF ADC0L ADC0H
P3 OSCXCN OSCICN OSCICL FLSCL FLKEY
IE CLKSEL EMI0CN
P2 SPI0CFG SPI0CKR SPI0DAT P0MDOUT P1MDOUT P2MDOUT P3MDOUT
SCON0 SBUF0 CPT1CN CPT0CN CPT1MD CPT0MD CPT1MX CPT0MX
P1 TMR3CN TMR3RLL TMR3RLH TMR3L TMR3H USB0ADR USB0DAT
TCON TMOD TL0 TL1 TH0 TH1 CKCON PSCTL
P0 SP DPL DPH PCON
0(8) 1(9) 2(A) 3(B) 4(C) 5(D) 6(E) 7(F)
(bit addressable)
Tabl e 9.2 lists the SFRs implemented in the CIP-51 System Controller.
Table 9.3, for a detailed description of each register.
Table 9.2. Special Function Register (SFR) Memory Map
Tab le 9.3. Special Function Registers
SFRs are listed in alphabetical order. All undefined SFR locations are reserved
Register Address Description Page
ACC 0xE0 Accumulator 86
ADC0CF 0xBC ADC0 Configuration 47
ADC0CN 0xE8 ADC0 Control 49
ADC0GTH 0xC4 ADC0 Greater-Than Compare High 50
ADC0GTL 0xC3 ADC0 Greater-Than Compare Low 50
ADC0H 0xBE ADC0 High 47
ADC0L 0xBD ADC0 Low 48
ADC0LTH 0xC6 ADC0 Less-Than Compare Word High 51
Rev. 1.1 81
Page 82

C8051F320/1
Table 9.3. Special Function Registers
Register Address Description Page No.
ADC0LTL 0xC5
AMX0N 0xBA AMUX0 Negative Channel Select 46
AMX0P 0xBB AMUX0 Positive Channel Select 45
B 0xF0 B Register 86
CKCON 0x8E Clock Control 223
CLKSEL 0xA9 Clock Select 125
CPT0CN 0x9B Comparator0 Control 60
CPT0MD 0x9D Comparator0 Mode Selection 62
CPT0MX 0x9F Comparator0 MUX Selection 61
CPT1CN 0x9A Comparator1 Control 63
CPT1MD 0x9C Comparator1 Mode Selection 65
CPT1MX 0x9E Comparator1 MUX Selection 64
DPH 0x83 Data Pointer High 84
DPL 0x82 Data Pointer Low 84
EIE1 0xE6 Extended Interrupt Enable 1 92
EIE2 0xE7 Extended Interrupt Enable 2 94
EIP1 0xF6 Extended Interrupt Priority 1 93
EIP2 0xF7 Extended Interrupt Priority 2 94
EMI0CN 0xAA External Memory Interface Control 115
FLKEY 0xB7 FLASH Lock and Key 111
FLSCL 0xB6 FLASH Scale 111
IE 0xA8 Interrupt Enable 90
IP 0xB8 Interrupt Priority 91
IT01CF 0xE4 INT0/INT1 Configuration 95
OSCICL 0xB3 Internal Oscillator Calibration 119
OSCICN 0xB2 Internal Oscillator Control 119
OSCXCN 0xB1 External Oscillator Control 122
P0 0x80 Port 0 Latch 135
P0MDIN 0xF1 Port 0 Input Mode Configuration 135
P0MDOUT 0xA4 Port 0 Output Mode Configuration 136
P0SKIP 0xD4 Port 0 Skip 136
P1 0x90 Port 1 Latch 137
P1MDIN 0xF2 Port 1 Input Mode Configuration 137
P1MDOUT 0xA5 Port 1 Output Mode Configuration 138
P1SKIP 0xD5 Port 1 Skip 138
P2 0xA0 Port 2 Latch 139
P2MDIN 0xF3 Port 2 Input Mode Configuration 139
P2MDOUT 0xA6 Port 2 Output Mode Configuration 140
P2SKIP 0xD6 Port 2 Skip 140
P3 0xB0 Port 3 Latch 141
P3MDIN 0xF4 Port 3 Input Mode Configuration 141
P3MDOUT 0xA7 Port 3 Output Mode Configuration 142
PCA0CN 0xD8 PCA Control 248
PCA0CPH0 0xFC PCA Capture 0 High 252
PCA0CPH1 0xEA PCA Capture 1 High 252
PCA0CPH2 0xEC PCA Capture 2 High 252
ADC0 Less-Than Compare Word Low 51
82 Rev. 1.1
Page 83

C8051F320/1
Table 9.3. Special Function Registers
Register Address Description Page No.
PCA0CPH3 0xEE PCA Capture 3High 252
PCA0CPH4 0xFE PCA Capture 4 High 252
PCA0CPL0 0xFB PCA Capture 0 Low 252
PCA0CPL1 0xE9 PCA Capture 1 Low 252
PCA0CPL2 0xEB PCA Capture 2 Low 252
PCA0CPL3 0xED PCA Capture 3Low 252
PCA0CPL4 0xFD PCA Capture 4 Low 252
PCA0CPM0 0xDA PCA Module 0 Mode Register 250
PCA0CPM1 0xDB PCA Module 1 Mode Register 250
PCA0CPM2 0xDC PCA Module 2 Mode Register 250
PCA0CPM3 0xDD PCA Module 3 Mode Register 250
PCA0CPM4 0xDE PCA Module 4 Mode Register 250
PCA0H 0xFA PCA Counter High 251
PCA0L 0xF9 PCA Counter Low 251
PCA0MD 0xD9 PCA Mode 249
PCON 0x87 Power Control 97
PSCTL 0x8F Program Store R/W Control 110
PSW 0xD0 Program Status Word 85
REF0CN 0xD1 Voltage Reference Control 56
RSTSRC 0xEF Reset Source Configuration/Status 104
SBUF0 0x99 UART0 Data Buffer 199
SCON0 0x98 UART0 Control 198
SMB0CF 0xC1 SMBus Configuration 182
SMB0CN 0xC0 SMBus Control 184
SMB0DAT 0xC2 SMBus Data 186
SP 0x81 Stack Pointer 85
SPI0CFG 0xA1 SPI Configuration 210
SPI0CKR 0xA2 SPI Clock Rate Control 212
SPI0CN 0xF8 SPI Control 211
SPI0DAT 0xA3 SPI Data 213
TCON 0x88 Timer/Counter Control 221
TH0 0x8C Timer/Counter 0 High 224
TH1 0x8D Timer/Counter 1 High 224
TL0 0x8A Timer/Counter 0 Low 224
TL1 0x8B Timer/Counter 1 Low 224
TMOD 0x89 Timer/Counter Mode 222
TMR2CN 0xC8 Timer/Counter 2 Control 228
TMR2H 0xCD Timer/Counter 2 High 229
TMR2L 0xCC Timer/Counter 2 Low 229
TMR2RLH 0xCB Timer/Counter 2 Reload High 229
TMR2RLL 0xCA Timer/Counter 2 Reload Low 229
TMR3CN 0x91 Timer/Counter 3Control 233
TMR3H 0x95 Timer/Counter 3 High 234
TMR3L 0x94 Timer/Counter 3Low 234
TMR3RLH 0x93 Timer/Counter 3 Reload High 234
TMR3RLL 0x92 Timer/Counter 3 Reload Low 234
Rev. 1.1 83
Page 84

C8051F320/1
Table 9.3. Special Function Registers
Register Address Description Page No.
VDM0CN 0xFF VDD Monitor Control 101
XBR0 0xE1 Port I/O Crossbar Control 0 132
XBR1 0xE2 Port I/O Crossbar Control 1 133
0x84-0x86, 0xAB-0xAF, 0xB4,
0xB5, 0xBF, 0xC7, 0xCE,
0xCF, 0xD2, 0xD3, 0xDF,
0xE3, 0xE5, 0xF5
9.2.7. Register Descriptions
Following are descriptions of SFRs related to the operation of the CIP-51 System Controller. Reserved bits should not
be set to logic
of the bit will be logic
in the sections of the datasheet associated with their corresponding system function.
l. Future product versions may use these bits to implement new features in which case the reset value
0, selecting the feature's default state. Detailed descriptions of the remaining SFRs are included
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W Reset Value
Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0 SFR Address:
Reserved
Figure 9.3. DPL: Data Pointer Low Byte
00000000
0x82
Bits7-0: DPL: Data Pointer Low.
The DPL register is the low byte of the 16-bit DPTR. DPTR is used to access indirectly addressed
memory.
Figure 9.4. DPH: Data Pointer High Byte
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W Reset Value
Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0 SFR Address:
Bits7-0: DPH: Data Pointer High.
The DPH register is the high byte of the 16-bit DPTR. DPTR is used to access indirectly addressed
memory.
00000000
0x83
84 Rev. 1.1
Page 85

C8051F320/1
Figure 9.5. SP: Stack Pointer
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W Reset Value
Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0 SFR Address:
Bits7-0: SP: Stack Pointer.
The Stack Pointer holds the location of the top of the stack. The stack pointer is incremented before
every PUSH operation. The SP register defaults to 0x07 after reset.
Figure 9.6. PSW: Program Status Word
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R Reset Value
CY AC F0 RS1 RS0 OV F1 PARITY 00000000
Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0 SFR Address:
(bit addressable)
00000111
0x81
0xD0
Bit7: CY: Carry Flag.
This bit is set when the last arithmetic operation resulted in a carry (addition) or a borrow (subtraction). It is cleared to logic 0 by all other arithmetic operations.
Bit6: AC: Auxiliary Carry Flag
This bit is set when the last arithmetic operation resulted in a carry into (addition) or a borrow from
(subtraction) the high order nibble. It is cleared to logic 0 by all other arithmetic operations.
Bit5: F0: User Flag 0.
This is a bit-addressable, general purpose flag for use under software control.
Bits4-3: RS1-RS0: Register Bank Select.
These bits select which register bank is used during register accesses.
RS1 RS0 Register Bank Address
0 0 0 0x00 - 0x07
0 1 1 0x08 - 0x0F
1 0 2 0x10 - 0x17
1 1 3 0x18 - 0x1F
Bit2: OV: Overflow Flag.
This bit is set to 1 under the following circumstances:
• An ADD, ADDC, or SUBB instruction causes a sign-change overflow.
• A MUL instruction results in an overflow (result is greater than 255).
• A DIV instruction causes a divide-by-zero condition.
The OV bit is cleared to 0 by the ADD, ADDC, SUBB, MUL, and DIV instructions in all other cases.
Bit1: F1: User Flag 1.
This is a bit-addressable, general purpose flag for use under software control.
Bit0: PARITY: Parity Flag.
This bit is set to logic 1 if the sum of the eight bits in the accumulator is odd and cleared if the sum is
even.
Rev. 1.1 85
Page 86

C8051F320/1
Figure 9.7. ACC: Accumulator
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W Reset Value
ACC.7 ACC.6 ACC.5 ACC.4 ACC.3 ACC.2 ACC.1 ACC.0 00000000
Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0 SFR Address:
(bit addressable)
Bits7-0: ACC: Accumulator.
This register is the accumulator for arithmetic operations.
Figure 9.8. B: B Register
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W Reset Value
B.7 B.6 B.5 B.4 B.3 B.2 B.1 B.0 00000000
Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0 SFR Address:
(bit addressable)
Bits7-0: B: B Register.
This register serves as a second accumulator for certain arithmetic operations.
0xE0
0xF0
86 Rev. 1.1
Page 87

C8051F320/1
9.3. Interrupt Handler
The CIP-51 includes an extended interrupt system supporting a total of 16 interrupt sources with two priority levels.
The allocation of interrupt sources between on-chip peripherals and external inputs pins varies according to the spe
cific version of the device. Each interrupt source has one or more associated interrupt-pending flag(s) located in an
SFR. When a peripheral or external source meets a valid interrupt condition, the associated interrupt-pending flag is
set to logic
If interrupts are enabled for the source, an interrupt request is generated when the interrupt-pending flag is set. As
soon as execution of the current instruction is complete, the CPU generates an LCALL to a predetermined address to
begin execution of an interrupt service routine (ISR). Each ISR must end with an RETI instruction, which returns pro
gram execution to the next instruction that would have been executed if the interrupt request had not occurred. If
interrupts are not enabled, the interrupt-pending flag is ignored by the hardware and program execution continues as
normal. (The interrupt-pending flag is set to logic
Each interrupt source can be individually enabled or disabled through the use of an associated interrupt enable bit in
an SFR (IE-EIE2). However, interrupts must first be globally enabled by setting the EA bit (IE.7) to logic
individual interrupt enables are recognized. Setting the EA bit to logic 0 disables all interrupt sources regardless of
the individual interrupt-enable settings.
Some interrupt-pending flags are automatically cleared by the hardware when the CPU vectors to the ISR. However,
most are not cleared by the hardware and must be cleared by software before returning from the ISR. If an interruptpending flag remains set after the CPU completes the return-from-interrupt (RETI) instruction, a new interrupt
request will be generated immediately and the CPU will re-enter the ISR after the completion of the next instruction.
1.
1 regardless of the interrupt's enable/disable state.)
1 before the
-
-
9.3.1. MCU Interrupt Sources and Vectors
The MCU supports 16 interrupt sources. Software can simulate an interrupt by setting any interrupt-pending flag to
logic
1. If interrupts are enabled for the flag, an interrupt request will be generated and the CPU will vector to the ISR
address associated with the interrupt-pending flag. MCU interrupt sources, associated vector addresses, priority order
and control bits are summarized in
on-chip peripheral for information regarding valid interrupt conditions for the peripheral and the behavior of its interrupt-pending flag(s).
Table 9.4 on page 89. Refer to the datasheet section associated with a particular
Rev. 1.1 87
Page 88

C8051F320/1
9.3.2. External Interrupts
The /INT0 and /INT1 external interrupt sources are configurable as active high or low, edge or level sensitive. The
IN0PL (/INT0 Polarity) and IN1PL (/INT1 Polarity) bits in the IT01CF register select active high or active low; the
IT0 and IT1 bits in TCON (
table below lists the possible configurations.
IT0 IN0PL /INT0 Interrupt IT1 IN1PL /INT1 Interrupt
10
11Active high, edge sensitive 11Active high, edge sensitive
00Active low, level sensitive 00Active low, level sensitive
01Active high, level sensitive 01Active high, level sensitive
/INT0 and /INT1 are assigned to Port pins as defined in the IT01CF register (see Figure 9.15). Note that /INT0 and
/INT0 Port pin assignments are independent of any Crossbar assignments. /INT0 and /INT1 will monitor their
assigned Port pins without disturbing the peripheral that was assigned the Port pin via the Crossbar. To assign a Port
pin only to /INT0 and/or /INT1, configure the Crossbar to skip the selected pin(s). This is accomplished by setting the
associated bit in register XBR0 (see
on configuring the Crossbar).
IE0 (TCON.1) and IE1 (TCON.3) serve as the interrupt-pending flags for the /INT0 and /INT1 external interrupts,
respectively. If an /INT0 or /INT1 external interrupt is configured as edge-sensitive, the corresponding interruptpending flag is automatically cleared by the hardware when the CPU vectors to the ISR. When configured as level
sensitive, the interrupt-pending flag remains logic 1 while the input is active as defined by the corresponding polarity
bit (IN0PL or IN1PL); the flag remains logic 0 while the input is inactive. The external interrupt source must hold the
input active until the interrupt request is recognized. It must then deactivate the interrupt request before execution of
the ISR completes or another interrupt request will be generated.
Section “19.1. Timer 0 and Timer 1” on page 217) select level or edge sensitive. The
Active low, edge sensitive 10Active low, edge sensitive
Section “14.1. Priority Crossbar Decoder” on page 129 for complete details
9.3.3. Interrupt Priorities
Each interrupt source can be individually programmed to one of two priority levels: low or high. A low priority interrupt service routine can be preempted by a high priority interrupt. A high priority interrupt cannot be preempted. Each
interrupt has an associated interrupt priority bit in an SFR (IP or EIP2) used to configure its priority level. Low prior
ity is the default. If two interrupts are recognized simultaneously, the interrupt with the higher priority is serviced
first. If both interrupts have the same priority level, a fixed priority order is used to arbitrate, given in
Tabl e 9.4.
9.3.4. Interrupt Latency
Interrupt response time depends on the state of the CPU when the interrupt occurs. Pending interrupts are sampled
and priority decoded each system clock cycle. Therefore, the fastest possible response time is 5 system clock cycles:
1
clock cycle to detect the interrupt and 4 clock cycles to complete the LCALL to the ISR. If an interrupt is pending
when a RETI is executed, a single instruction is executed before an LCALL is made to service the pending interrupt.
Therefore, the maximum response time for an interrupt (when no other interrupt is currently being serviced or the
new interrupt is of greater priority) occurs when the CPU is performing an RETI instruction followed by a DIV as the
next instruction. In this case, the response time is 18
cycles to execute the RETI, 8
to the ISR. If the CPU is executing an ISR for an interrupt with equal or higher priority, the new interrupt will not be
serviced until the current ISR completes, including the RETI and following instruction.
Note that the CPU is stalled during FLASH write/erase operations and USB FIFO MOVX accesses (see Section
“12.2. Accessing USB FIFO Space” on page 114). Interrupt service latency will be increased for interrupts occuring
while the CPU is stalled. The latency for these situations will be determined by the standard interrupt service procedure (as described above) and the amount of time the CPU is stalled.
clock cycles to complete the DIV instruction and 4 clock cycles to execute the LCALL
system clock cycles: 1 clock cycle to detect the interrupt, 5 clock
-
88 Rev. 1.1
Page 89

Tab le 9.4. Interrupt Summary
C8051F320/1
Interrupt Source
Reset 0x0000 Top None N/A N/A
External Interrupt 0
(/INT0)
Timer 0 Overflow 0x000B 1 TF0 (TCON.5) Y Y ET0 (IE.1) PT0 (IP.1)
External Interrupt 1
(/INT1)
Timer 1 Overflow 0x001B 3 TF1 (TCON.7) Y Y ET1 (IE.3) PT1 (IP.3)
UART0 0x0023 4
Timer 2 Overflow 0x002B 5
SPI0 0x0033 6
SMB0 0x003B 7 SI (SMB0CN.0) Y N
USB0 0x0043 8 Special N N
ADC0 Window Compare 0x004B 9
ADC0 Conversion
Complete
Programmable Counter
Array
Comparator0 0x0063 12
Comparator1 0x006B 13
Timer 3 Overflow 0x0073 14
VBUS Level 0x007B 15 N/A N/A N/A
Interrupt
Vector
0x0003 0 IE0 (TCON.1) Y Y EX0 (IE.0) PX0 (IP.0)
0x0013 2 IE1 (TCON.3) Y Y EX1 (IE.2) PX1 (IP.2)
0x0053 10 AD0INT (ADC0CN.5) Y N
0x005B 11
Priority
Order
Pending Flag
RI0 (SCON0.0)
TI0 (SCON0.1)
TF2H (TMR2CN.7)
TF2L (TMR2CN.6)
SPIF (SPI0CN.7)
WCOL (SPI0CN.6)
MODF (SPI0CN.5)
RXOVRN (SPI0CN.4)
AD0WINT
(ADC0CN.3)
CF (PCA0CN.7)
CCFn (PCA0CN.n)
CP0FIF (CPT0CN.4)
CP0RIF (CPT0CN.5)
CP1FIF (CPT1CN.4)
CP1RIF (CPT1CN.5)
TF3H (TMR3CN.7)
TF3L (TMR3CN.6)
Enable
Flag
Bit addressable?
Cleared by HW?
Always
Enabled
Y N ES0 (IE.4) PS0 (IP.4)
Y N ET2 (IE.5) PT2 (IP.5)
Y N
Y N
Y N
N N
N N
N N
ESPI0
(IE.6)
ESMB0
(EIE1.0)
EUSB0
(EIE1.1)
EWADC0
(EIE1.2)
EADC0
(EIE1.3)
EPCA0
(EIE1.4)
ECP0
(EIE1.5)
ECP1
(EIE1.6)
ET3
(EIE1.7)
EVBUS
(EIE2.0)
Priority
Control
Always
Highest
PSPI0
(IP.6)
PSMB0
(EIP1.0)
PUSB0
(EIP1.1)
PWADC0
(EIP1.2)
PA DC 0
(EIP1.3)
PPCA0
(EIP1.4)
PCP0
(EIP1.5)
PCP1
(EIP1.6)
PT3
(EIP1.7)
PVBUS
(EIP2.0)
Rev. 1.1 89
Page 90

C8051F320/1
9.3.5. Interrupt Register Descriptions
The SFRs used to enable the interrupt sources and set their priority level are described below. Refer to the datasheet
section associated with a particular on-chip peripheral for information regarding valid interrupt conditions for the
peripheral and the behavior of its interrupt-pending flag(s).
Figure 9.9. IE: Interrupt Enable
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W Reset Value
EA ESPI0 ET2 ES0 ET1 EX1 ET0 EX0 00000000
Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0 SFR Address:
(bit addressable)
Bit7: EA: Enable All Interrupts.
This bit globally enables/disables all interrupts. It overrides the individual interrupt mask settings.
0: Disable all interrupt sources.
1: Enable each interrupt according to its individual mask setting.
Bit6: ESPI0: Enable Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI0) Interrupt.
This bit sets the masking of the SPI0 interrupts.
0: Disable all SPI0 interrupts.
1: Enable interrupt requests generated by SPI0.
Bit5: ET2: Enable Timer 2 Interrupt.
This bit sets the masking of the Timer 2 interrupt.
0: Disable Timer 2 interrupt.
1: Enable interrupt requests generated by the TF2L or TF2H flags.
Bit4: ES0: Enable UART0 Interrupt.
This bit sets the masking of the UART0 interrupt.
0: Disable UART0 interrupt.
1: Enable UART0 interrupt.
Bit3: ET1: Enable Timer 1 Interrupt.
This bit sets the masking of the Timer 1 interrupt.
0: Disable all Timer 1 interrupt.
1: Enable interrupt requests generated by the TF1 flag.
Bit2: EX1: Enable External Interrupt 1.
This bit sets the masking of External Interrupt 1.
0: Disable external interrupt 1.
1: Enable interrupt requests generated by the /INT1 input.
Bit1: ET0: Enable Timer 0 Interrupt.
This bit sets the masking of the Timer 0 interrupt.
0: Disable all Timer 0 interrupt.
1: Enable interrupt requests generated by the TF0 flag.
Bit0: EX0: Enable External Interrupt 0.
This bit sets the masking of External Interrupt 0.
0: Disable external interrupt 0.
1: Enable interrupt requests generated by the /INT0 input.
0xA8
90 Rev. 1.1
Page 91

C8051F320/1
Figure 9.10. IP: Interrupt Priority
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W Reset Value
- PSPI0 PT2 PS0 PT1 PX1 PT0 PX0 10000000
Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0 SFR Address:
(bit addressable)
Bit7: UNUSED. Read = 1, Write = don't care.
Bit6: PSPI0: Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI0) Interrupt Priority Control.
This bit sets the priority of the SPI0 interrupt.
0: SPI0 interrupt set to low priority level.
1: SPI0 interrupt set to high priority level.
Bit5: PT2: Timer 2 Interrupt Priority Control.
This bit sets the priority of the Timer 2 interrupt.
0: Timer 2 interrupt set to low priority level.
1: Timer 2 interrupts set to high priority level.
Bit4: PS0: UART0 Interrupt Priority Control.
This bit sets the priority of the UART0 interrupt.
0: UART0 interrupt set to low priority level.
1: UART0 interrupts set to high priority level.
Bit3: PT1: Timer 1 Interrupt Priority Control.
This bit sets the priority of the Timer 1 interrupt.
0: Timer 1 interrupt set to low priority level.
1: Timer 1 interrupts set to high priority level.
Bit2: PX1: External Interrupt 1 Priority Control.
This bit sets the priority of the External Interrupt 1 interrupt.
0: External Interrupt 1 set to low priority level.
1: External Interrupt 1 set to high priority level.
Bit1: PT0: Timer 0 Interrupt Priority Control.
This bit sets the priority of the Timer 0 interrupt.
0: Timer 0 interrupt set to low priority level.
1: Timer 0 interrupt set to high priority level.
Bit0: PX0: External Interrupt 0 Priority Control.
This bit sets the priority of the External Interrupt 0 interrupt.
0: External Interrupt 0 set to low priority level.
1: External Interrupt 0 set to high priority level.
0xB8
Rev. 1.1 91
Page 92

C8051F320/1
Figure 9.11. EIE1: Extended Interrupt Enable 1
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W Reset Value
ET3 ECP1 ECP0 EPCA0 EADC0 EWADC0 EUSB0 ESMB0 00000000
Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0 SFR Address:
Bit7: ET3: Enable Timer 3 Interrupt.
This bit sets the masking of the Timer 3 interrupt.
0: Disable Timer 3 interrupts.
1: Enable interrupt requests generated by the TF3L or TF3H flags.
Bit6: ECP1: Enable Comparator1 (CP1) Interrupt.
This bit sets the masking of the CP1 interrupt.
0: Disable CP1 interrupts.
1: Enable interrupt requests generated by the CP1RIF or CP1FIF flags.
Bit5: ECP0: Enable Comparator0 (CP0) Interrupt.
This bit sets the masking of the CP0 interrupt.
0: Disable CP0 interrupts.
1: Enable interrupt requests generated by the CP0RIF or CP0FIF flags.
Bit4: EPCA0: Enable Programmable Counter Array (PCA0) Interrupt.
This bit sets the masking of the PCA0 interrupts.
0: Disable all PCA0 interrupts.
1: Enable interrupt requests generated by PCA0.
Bit3: EADC0: Enable ADC0 Conversion Complete Interrupt.
This bit sets the masking of the ADC0 Conversion Complete interrupt.
0: Disable ADC0 Conversion Complete interrupt.
1: Enable interrupt requests generated by the AD0INT flag.
Bit2: EWADC0: Enable Window Comparison ADC0 Interrupt.
This bit sets the masking of ADC0 Window Comparison interrupt.
0: Disable ADC0 Window Comparison interrupt.
1: Enable interrupt requests generated by ADC0 Window Compare flag (AD0WINT).
Bit1: EUSB0: Enable USB0 Interrupt.
This bit sets the masking of the USB0 interrupt.
0: Disable all USB0 interrupts.
1: Enable interrupt requests generated by USB0.
Bit0: ESMB0: Enable SMBus (SMB0) Interrupt.
This bit sets the masking of the SMB0 interrupt.
0: Disable all SMB0 interrupts.
1: Enable interrupt requests generated by SMB0.
0xE6
92 Rev. 1.1
Page 93

C8051F320/1
Figure 9.12. EIP1: Extended Interrupt Priority 1
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W Reset Value
PT3 PCP1 PCP0 PPCA0 PADC0 PWADC0 PUSB0 PSMB0 00000000
Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0 SFR Address:
Bit7: PT3: Timer 3 Interrupt Priority Control.
This bit sets the priority of the Timer 3 interrupt.
0: Timer 3 interrupts set to low priority level.
1: Timer 3 interrupts set to high priority level.
Bit6: PCP1: Comparator1 (CP1) Interrupt Priority Control.
This bit sets the priority of the CP1 interrupt.
0: CP1 interrupt set to low priority level.
1: CP1 interrupt set to high priority level.
Bit5: PCP0: Comparator0 (CP0) Interrupt Priority Control.
This bit sets the priority of the CP0 interrupt.
0: CP0 interrupt set to low priority level.
1: CP0 interrupt set to high priority level.
Bit4: PPCA0: Programmable Counter Array (PCA0) Interrupt Priority Control.
This bit sets the priority of the PCA0 interrupt.
0: PCA0 interrupt set to low priority level.
1: PCA0 interrupt set to high priority level.
Bit3: PADC0 ADC0 Conversion Complete Interrupt Priority Control.
This bit sets the priority of the ADC0 Conversion Complete interrupt.
0: ADC0 Conversion Complete interrupt set to low priority level.
1: ADC0 Conversion Complete interrupt set to high priority level.
Bit2: PWADC0: ADC0 Window Comparator Interrupt Priority Control.
This bit sets the priority of the ADC0 Window interrupt.
0: ADC0 Window interrupt set to low priority level.
1: ADC0 Window interrupt set to high priority level.
Bit1: PUSB0: USB0 Interrupt Priority Control.
This bit sets the priority of the USB0 interrupt.
0: USB0 interrupt set to low priority level.
1: USB0 interrupt set to high priority level.
Bit0: PSMB0: SMBus (SMB0) Interrupt Priority Control.
This bit sets the priority of the SMB0 interrupt.
0: SMB0 interrupt set to low priority level.
1: SMB0 interrupt set to high priority level.
0xF6
Rev. 1.1 93
Page 94

C8051F320/1
Figure 9.13. EIE2: Extended Interrupt Enable 2
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W Reset Value
- - - - - - - EVBUS 00000000
Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0 SFR Address:
Bits7-1: UNUSED. Read = 0000000b. Write = don’t care.
Bit0: EVBUS: Enable VBUS Level Interrupt.
This bit sets the masking of the VBUS interrupt.
0: Disable all VBUS interrupts.
1: Enable interrupt requests generated by VBUS level sense.
Figure 9.14. EIP2: Extended Interrupt Priority 2
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W Reset Value
- - - - - - - PVBUS 00000000
Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0 SFR Address:
0xE7
0xF7
Bits7-1: UNUSED. Read = 0000000b. Write = don’t care.
Bit0: PVBUS: VBUS Level Interrupt Priority Control.
This bit sets the priority of the VBUS interrupt.
0: VBUS interrupt set to low priority level.
1: VBUS interrupt set to high priority level.
94 Rev. 1.1
Page 95

C8051F320/1
Figure 9.15. IT01CF: INT0/INT1 Configuration Register
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W Reset Value
IN1PL IN1SL2 IN1SL1 IN1SL0 IN0PL IN0SL2 IN0SL1 IN0SL0 00000001
Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0 SFR Address:
0xE4
Note: Refer to Figure 19.4 for INT0/1 edge- or level-sensitive interrupt selection.
Bit7: IN1PL: /INT1 Polarity
0: /INT1 input is active low.
1: /INT1 input is active high.
Bits6-4: IN1SL2-0: /INT1 Port Pin Selection Bits
These bits select which Port pin is assigned to /INT1. Note that this pin assignment is independent of
the Crossbar; /INT1 will monitor the assigned Port pin without disturbing the peripheral that has been
assigned the Port pin via the Crossbar. The Crossbar will not assign the Port pin to a peripheral if it is
configured to skip the selected pin (accomplished by setting to ‘1’ the corresponding bit in register
P0SKIP).
IN1SL2-0 /INT1 Port Pin
000 P0.0
001 P0.1
010 P0.2
011 P0.3
100 P0.4
101 P0.5
110 P0.6
111 P0.7
Bit3: IN0PL: /INT0 Polarity
0: /INT0 interrupt is active low.
1: /INT0 interrupt is active high.
Bits2-0: INT0SL2-0: /INT0 Port Pin Selection Bits
These bits select which Port pin is assigned to /INT0. Note that this pin assignment is independent of
the Crossbar. /INT0 will monitor the assigned Port pin without disturbing the peripheral that has been
assigned the Port pin via the Crossbar. The Crossbar will not assign the Port pin to a peripheral if it is
configured to skip the selected pin (accomplished by setting to ‘1’ the corresponding bit in register
P0SKIP).
IN0SL2-0 /INT0 Port Pin
000 P0.0
001 P0.1
010 P0.2
011 P0.3
100 P0.4
101 P0.5
110 P0.6
111 P0.7
Rev. 1.1 95
Page 96

C8051F320/1
9.4. Power Management Modes
The CIP-51 core has two software programmable power management modes: Idle and Stop. Idle mode halts the CPU
while leaving the peripherals and clocks active. In Stop mode, the CPU is halted, all interrupts, are inactive, and the
internal oscillator is stopped (analog peripherals remain in their selected states; the external oscillator is not affected).
Since clocks are running in Idle mode, power consumption is dependent upon the system clock frequency and the
number of peripherals left in active mode before entering Idle. Stop mode consumes the least power. Figure 1.15
describes the Power Control Register (PCON) used to control the CIP-51's power management modes.
Although the CIP-51 has Idle and Stop modes built in (as with any standard 8051 architecture), power management
of the entire MCU is better accomplished through system clock and individual peripheral management. Each analog
peripheral can be disabled when not in use and placed in low power mode. Digital peripherals, such as timers or serial
buses, draw little power when they are not in use. Turning off the oscillators lowers power consumption considerably;
however a reset is required to restart the MCU.
The internal oscillator can be placed in Suspend mode (see Section “13. Oscillators” on page 117). In Suspend
mode, the internal oscillator is stopped until a non-idle USB event is detected, or the VBUS input signal matches the
polarity selected by the VBPOL bit in register REG0CN (
9.4.1. Idle Mode
Setting the Idle Mode Select bit (PCON.0) causes the CIP-51 to halt the CPU and enter Idle mode as soon as the
instruction that sets the bit completes execution. All internal registers and memory maintain their original data. All
analog and digital peripherals can remain active during Idle mode.
Figure 8.5 on Page 72).
Idle mode is terminated when an enabled interrupt is asserted or a reset occurs. The assertion of an enabled interrupt
will cause the Idle Mode Selection bit (PCON.0) to be cleared and the CPU to resume operation. The pending inter
rupt will be serviced and the next instruction to be executed after the return from interrupt (RETI) will be the instruction immediately following the one that set the Idle Mode Select bit. If Idle mode is terminated by an internal or
external reset, the CIP-51 performs a normal reset sequence and begins program execution at address 0x0000.
If enabled, the Watchdog Timer (WDT) will eventually cause an internal watchdog reset and thereby terminate the
Idle mode. This feature protects the system from an unintended permanent shutdown in the event of an inadvertent
write to the PCON register. If this behavior is not desired, the WDT may be disabled by software prior to entering the
Idle mode if the WDT was initially configured to allow this operation. This provides the opportunity for additional
power savings, allowing the system to remain in the Idle mode indefinitely, waiting for an external stimulus to wake
up the system. Refer to
and configuration of the WDT.
Section “10.6. PCA Watchdog Timer Reset” on page 102 for more information on the use
9.4.2. Stop Mode
Setting the Stop Mode Select bit (PCON.1) causes the CIP-51 to enter Stop mode as soon as the instruction that sets
the bit completes execution. In Stop mode the internal oscillator, CPU, and all digital peripherals are stopped; the
state of the external oscillator circuit is not affected. Each analog peripheral (including the external oscillator circuit)
may be shut down individually prior to entering Stop Mode. Stop mode can only be terminated by an internal or
external reset. On reset, the CIP-51 performs the normal reset sequence and begins program execution at address
0x0000.
If enabled, the Missing Clock Detector will cause an internal reset and thereby terminate the Stop mode. The Missing
Clock Detector should be disabled if the CPU is to be put to in STOP mode for longer than the MCD timeout of
100
µsec.
-
96 Rev. 1.1
Page 97

C8051F320/1
Figure 9.16. PCON: Power Control Register
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W Reset Value
GF5 GF4 GF3 GF2 GF1 GF0 STOP IDLE 00000000
Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0 SFR Address:
Bits7-2: GF5-GF0: General Purpose Flags 5-0.
These are general purpose flags for use under software control.
Bit1: STOP: Stop Mode Select.
Setting this bit will place the CIP-51 in Stop mode. This bit will always be read as 0.
1: CPU goes into Stop mode (internal oscillator stopped).
Bit0: IDLE: Idle Mode Select.
Setting this bit will place the CIP-51 in Idle mode. This bit will always be read as 0.
1: CPU goes into Idle mode. (Shuts off clock to CPU, but clock to Timers, Interrupts, Serial Ports,
and Analog Peripherals are still active.)
0x87
Rev. 1.1 97
Page 98

C8051F320/1
Notes
98 Rev. 1.1
Page 99

C8051F320/1
10. RESET SOURCES
Reset circuitry allows the controller to be easily placed in a predefined default condition. On entry to this reset state,
the following occur:
• CIP-51 halts program execution
• Special Function Registers (SFRs) are initialized to their defined reset values
• External Port pins are forced to a known state
• Interrupts and timers are disabled.
All SFRs are reset to the predefined values noted in the SFR detailed descriptions. The contents of internal data memory are unaffected during a reset; any previously stored data is preserved. However, since the stack pointer SFR is
reset, the stack is effectively lost even though the data on the stack is not altered.
The Port I/O latches are reset to 0xFF (all logic ones) in open-drain mode. Weak pull-ups are enabled during and after
the reset. For VDD Monitor and Power-On Resets, the /RST pin is driven low until the device exits the reset state.
On exit from the reset state, the program counter (PC) is reset, and the system clock defaults to the internal oscillator.
Refer to
source. The Watchdog Timer is enabled with the system clock divided by 12 as its clock source (Section
“20.3. Watchdog Timer Mode” on page 246 details the use of the Watchdog Timer). Program execution begins at
location 0x0000.
Section “13. Oscillators” on page 117 for information on selecting and configuring the system clock
XTAL1
XTAL2
Internal
Oscillator
Clock
Multiplier
External
Oscillator
Drive
Px.x
Px.x
System
Clock
Clock Select
Figure 10.1. Reset Sources
VDD
Supply
Comparator 0
+
-
Missing
Clock
Detector
(one-
shot)
EN
MCD
Enable
Microcontroller
Extended Interrupt
C0RSEF
CIP-51
Core
Handler
PCA
WDT
EN
WDT
Monitor
Enable
+
-
System Reset
Enable
Power On
Reset
Software Reset (SWRSF)
Errant
FLASH
Operation
'0'
USB
Controller
(wired-OR)
Enable
Reset
Funnel
VBUS
Transition
/RST
Rev. 1.1 99
Page 100

C8051F320/1
10.1. Power-On Reset
During power-up, the device is held in a reset state and the /RST pin is driven low until VDD settles above V
Power-On Reset delay (T
ms. Figure 10.2. plots the power-on and VDD monitor reset timing.
0.3
PORDelay
) occurs before the device is released from reset; this delay is typically less than
RST
. A
On exit from a power-on reset, the PORSF flag (RSTSRC.1) is set by hardware to logic 1. When PORSF is set, all of
the other reset flags in the RSTSRC Register are indeterminate (PORSF is cleared by all other resets). Since all resets
cause program execution to begin at the same location (0x0000) software can read the PORSF flag to determine if a
power-up was the cause of reset. The content of internal data memory should be assumed to be undefined after a
power-on reset. The VDD monitor is enabled following a power-on reset.
Software can force a power-on reset by writing ‘1’ to the PINRSF bit in register RSTSRC.
Figure 10.2. Power-On and VDD Monitor Reset Timing
VDD
2.70
2.4
2.0
1.0
volts
V
RST
D
D
V
Logic HIGH
Logic LOW
/RST
Power-On
Reset
T
PORDelay
t
VDD
Monitor
Reset
100 Rev. 1.1
 Loading...
Loading...