Page 1
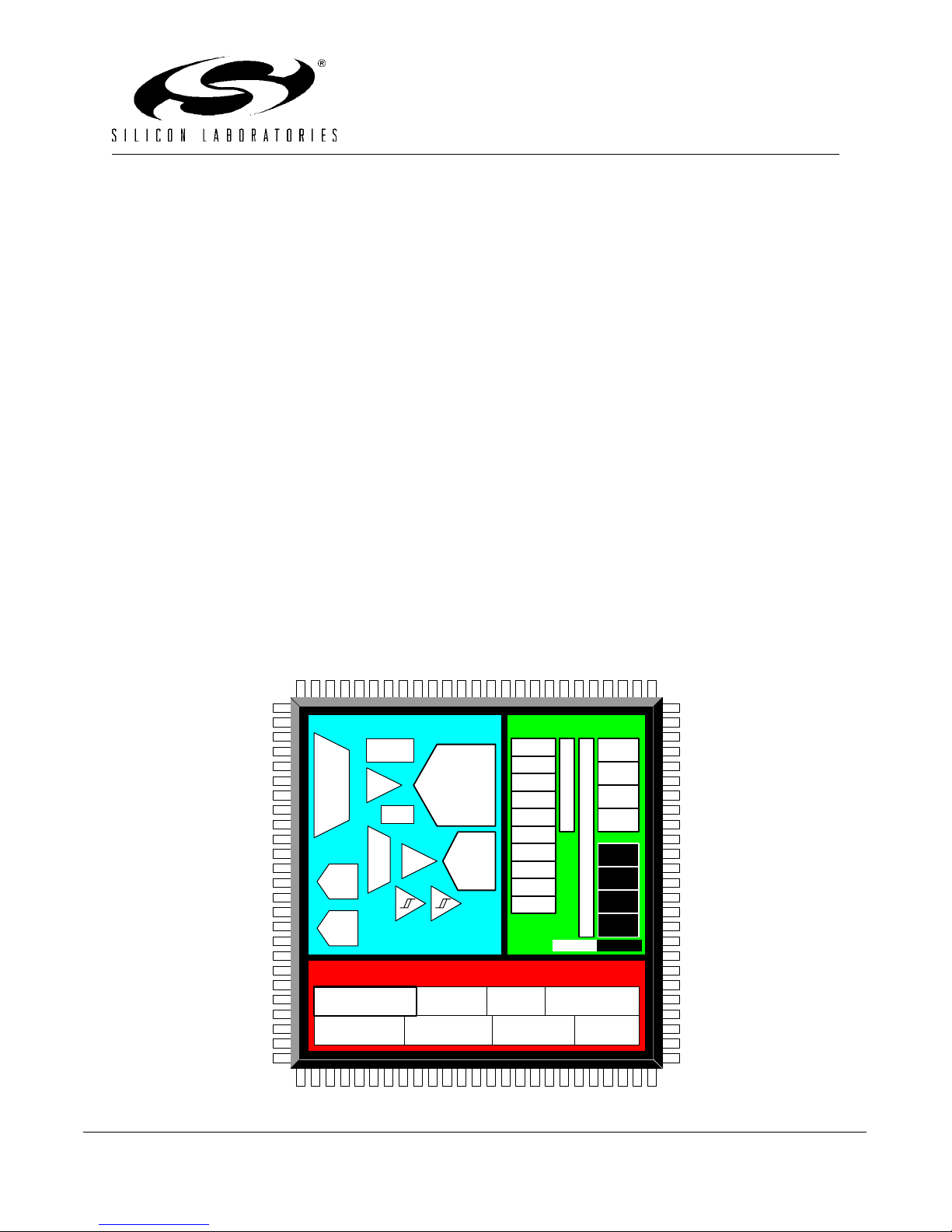
C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
High-Speed Mixed-Signal ISP FLASH MCU Family
ANALOG PERIPHERALS
-
SAR ADC
• 12-Bit (C8051F120/1/4/5)
• 10-Bit (C8051F122/3/6/7)
• ±1 LSB INL
• Programmable Throughput up to 100 ksps
• Up to 8 External Inputs; Programmable as Single-Ended or
Differential
• Programmable Amplifier Gain: 16, 8, 4, 2, 1, 0.5
• Data-Dependent Windowed Interrupt Generator
• Built-in Temperature Sensor
- 8-bit ADC
• Programmable Throughput up to 500 ksps
• 8 External Inputs (Single-Ended or Differential)
• Programmable Amplifier Gain: 4, 2, 1, 0.5
- Two 12-bit DACs
• Can Synchronize Outputs to Timers for Jitter-Free Wave-
- Two Analog Comparators
form Generation
- Voltage Reference
- VDD Monitor/Brown-Out Detector
ON-CHIP JTAG DEBUG & BOUNDARY SCAN
-
On-Chip Debug Circuitry Facilitates Full- Speed, NonIntrusive In-Circuit/In-System Debugging
- Provides Breakpoints, Single-Stepping, Watchpoints,
Stack Monitor; Inspect/Modify Memory and Registers
- Superior Performance to Emulation Systems Using ICE-
Chips, Target Pods, and Sockets
- IEEE1149.1 Compliant Boundary Scan
- Complete Development Kit
HIGH SPEED 8051 µC CORE
-
Pipelined Instruction Architecture; Executes 70% of
Instruction Set in 1 or 2 System Clocks
- Up to 100 MIPS (C8051F120/1/2/3) or 50 MIPS
(C8051F124/5/6/7) Throughput using Integrated PLL
- 2-cycle 16 x 16 MAC Engine (C8051F120/1/2/3)
- Flexible Interrupt Sources
MEMORY
-
8448 Bytes Internal Data RAM (8k + 256)
- 128k Bytes Banked FLASH; In-System programmable in
1024-byte Sectors
- External 64k Byte Data Memory Interface (programma-
ble multiplexed or non-multiplexed modes)
DIGITAL PERIPHERALS
-
8 Byte-Wide Port I/O (C8051F120/2/4/6); 5V tolerant
- 4 Byte-Wide Port I/O (C8051F121/3/5/7); 5V tolerant
- Hardware SMBus™ (I
Two UART Serial Ports Available Concurrently
2
C™ Compatible), SPI™, and
- Programmable 16-bit Counter/Timer Array with
6 Capture/Compare Modules
- 5 General Purpose 16-bit Counter/Timers
- Dedicated Watch-Dog Timer; Bi-directional Reset Pin
CLOCK SOURCES
- Internal Precision Oscillator: 24.5 MHz
- Flexible PLL technology
- External Oscillator: Crystal, RC, C, or Clock
POWER SUPPLIES
-
Supply Range: 2.7-3.6V (50 MIPS) 3.0-3.6V (100 MIPS)
- Power Saving Sleep and Shutdown Modes
100-PIN TQFP OR 64-PIN TQFP PACKAGING
-
Temperature Range: -40°C to +85°C
ANALOG PERIPHERALS
TEMP
AMUX
12-Bit
DAC
12-Bit
DAC
SENSOR
PGA
VREF
AMUX
10/12-bit
100ksps
ADC
PGA
500ksps
+
+
-
-
VOLTAGE
COMPARATORS
8-bit
ADC
DIGITAL I/O
UART0
UART1
SMBus
SPI Bus
PCA
Timer 0
Timer 1
Timer 2
Timer 3
Timer 4
CROSSBAR
64 pin
Port 0
Port 1
Port 2
Port 3
Port 4
Port 5
External Memory Interface
Port 6
Port 7
100 pin
HIGH-SPEED CONTROLLER CORE
8051 CPU
(50 or 100MIPS)
20
INTERRUPTS
128KB
ISP FLASH
DEBUG
CIRCUITRY
8448 B
SRAM
CLOCK / PLL
CIRCUIT
16 x 16 MAC
('F120/1/2/3)
JTAG
Preliminary Rev. 1.2 12/03 Copyright © 2003 by Silicon Laboratories C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7-DS12
This information applies to a product under development. Its characteristics and specifications are subject to change without notice.
Page 2

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
Notes
2 Rev. 1.2
Page 3

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. SYSTEM OVERVIEW .........................................................................................................19
1.1. CIP-51™ Microcontroller Core ......................................................................................25
1.1.1. Fully 8051 Compatible ..........................................................................................25
1.1.2. Improved Throughput ............................................................................................25
1.1.3. Additional Features................................................................................................26
1.2. On-Chip Memory ............................................................................................................27
1.3. JTAG Debug and Boundary Scan ...................................................................................28
1.4. 16 x 16 MAC (Multiply and Accumulate) Engine..........................................................29
1.5. Programmable Digital I/O and Crossbar .........................................................................30
1.6. Programmable Counter Array .........................................................................................31
1.7. Serial Ports.......................................................................................................................32
1.8. 12-Bit Analog to Digital Converter.................................................................................33
1.9. 8-Bit Analog to Digital Converter...................................................................................34
1.10.Comparators and DACs...................................................................................................35
2. ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS..................................................................................36
3. GLOBAL DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS ......................................................37
4. PINOUT AND PACKAGE DEFINITIONS........................................................................39
5. ADC0 (12-BIT ADC, C8051F120/1/4/5 ONLY) ..................................................................49
5.1. Analog Multiplexer and PGA..........................................................................................49
5.2. ADC Modes of Operation ...............................................................................................51
5.2.1. Starting a Conversion.............................................................................................51
5.2.2. Tracking Modes .....................................................................................................52
5.2.3. Settling Time Requirements ..................................................................................53
5.3. ADC0 Programmable Window Detector.........................................................................60
6. ADC0 (10-BIT ADC, C8051F122/3/6/7 ONLY) ..................................................................67
6.1. Analog Multiplexer and PGA..........................................................................................67
6.2. ADC Modes of Operation ...............................................................................................69
6.2.1. Starting a Conversion.............................................................................................69
6.2.2. Tracking Modes .....................................................................................................70
6.2.3. Settling Time Requirements ..................................................................................71
6.3. ADC0 Programmable Window Detector.........................................................................78
7. ADC2 (8-BIT ADC) ...............................................................................................................85
7.1. Analog Multiplexer and PGA..........................................................................................85
7.2. ADC2 Modes of Operation .............................................................................................86
7.2.1. Starting a Conversion.............................................................................................86
7.2.2. Tracking Modes .....................................................................................................86
7.2.3. Settling Time Requirements ..................................................................................88
7.3. ADC2 Programmable Window Detector.........................................................................94
7.3.1. Window Detector In Single-Ended Mode .............................................................94
7.3.2. Window Detector In Differential Mode.................................................................95
8. DACS, 12-BIT VOLTAGE MODE......................................................................................99
8.1. DAC Output Scheduling..................................................................................................99
Rev. 1.2 3
Page 4

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
8.1.1. Update Output On-Demand ...................................................................................99
8.1.2. Update Output Based on Timer Overflow...........................................................100
8.2. DAC Output Scaling/Justification.................................................................................100
9. VOLTAGE REFERENCE (C8051F120/2/4/6) .................................................................107
10. VOLTAGE REFERENCE (C8051F121/3/5/7) .................................................................109
11. COMPARATORS................................................................................................................111
12. CIP-51 MICROCONTROLLER........................................................................................119
12.1.Instruction Set................................................................................................................120
12.1.1. Instruction and CPU Timing................................................................................120
12.1.2. MOVX Instruction and Program Memory...........................................................120
12.2.Memory Organization ...................................................................................................125
12.2.1. Program Memory.................................................................................................125
12.2.2. Data Memory .......................................................................................................127
12.2.3. General Purpose Registers ...................................................................................127
12.2.4. Bit Addressable Locations ...................................................................................127
12.2.5. Stack .................................................................................................................127
12.2.6. Special Function Registers...................................................................................128
12.2.6.1.SFR Paging ..................................................................................................128
12.2.6.2.Interrupts and SFR Paging...........................................................................128
12.2.6.3.SFR Page Stack Example ............................................................................130
12.2.7. Register Descriptions...........................................................................................143
12.3.Interrupt Handler ...........................................................................................................146
12.3.1. MCU Interrupt Sources and Vectors ...................................................................146
12.3.2. External Interrupts ...............................................................................................146
12.3.3. Interrupt Priorities................................................................................................148
12.3.4. Interrupt Latency..................................................................................................148
12.3.5. Interrupt Register Descriptions............................................................................149
12.4.Power Management Modes ...........................................................................................155
12.4.1. Idle Mode.............................................................................................................155
12.4.2. Stop Mode............................................................................................................155
13. MULTIPLY AND ACCUMULATE (MAC0) ...................................................................157
13.1.Special Function Registers ............................................................................................157
13.2.Integer and Fractional Math ..........................................................................................158
13.3.Operating in Multiply and Accumulate Mode...............................................................159
13.4.Operating in Multiply Only Mode.................................................................................159
13.5.Accumulator Shift Operations .......................................................................................159
13.6.Rounding and Saturation ...............................................................................................160
13.7.Usage Examples ............................................................................................................160
14. RESET SOURCES ..............................................................................................................167
14.1.Power-on Reset..............................................................................................................168
14.2.Power-fail Reset ............................................................................................................168
14.3.External Reset................................................................................................................168
14.4.Missing Clock Detector Reset .......................................................................................169
14.5.Comparator0 Reset ........................................................................................................169
14.6.External CNVSTR0 Pin Reset.......................................................................................169
4 Rev. 1.2
Page 5

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
14.7.Watchdog Timer Reset ..................................................................................................169
14.7.1. Enable/Reset WDT ..............................................................................................169
14.7.2. Disable WDT .......................................................................................................170
14.7.3. Disable WDT Lockout.........................................................................................170
14.7.4. Setting WDT Interval...........................................................................................170
15. OSCILLATORS...................................................................................................................173
15.1.Programmable Internal Oscillator .................................................................................173
15.2.External Oscillator Drive Circuit...................................................................................175
15.3.System Clock Selection .................................................................................................175
15.4.External Crystal Example..............................................................................................177
15.5.External RC Example ....................................................................................................177
15.6.External Capacitor Example..........................................................................................177
15.7.Phase-Locked Loop (PLL) ............................................................................................178
15.7.1. PLL Input Clock and Pre-divider.........................................................................178
15.7.2. PLL Multiplication and Output Clock .................................................................178
15.7.3. Powering on and Initializing the PLL..................................................................179
16. FLASH MEMORY ..............................................................................................................185
16.1.Programming The Flash Memory .................................................................................185
16.1.1. Non-volatile Data Storage ...................................................................................185
16.1.2. Erasing FLASH Pages From Software ................................................................186
16.1.3. Writing FLASH Memory From Software ...........................................................187
16.2.Security Options ............................................................................................................188
17. BRANCH TARGET CACHE.............................................................................................193
17.1.Cache and Prefetch Operation .......................................................................................193
17.2.Cache and Prefetch Optimization ..................................................................................194
18. EXTERNAL DATA MEMORY INTERFACE AND ON-CHIP XRAM.......................199
18.1.Accessing XRAM..........................................................................................................199
18.1.1. 16-Bit MOVX Example.......................................................................................199
18.1.2. 8-Bit MOVX Example.........................................................................................199
18.2.Configuring the External Memory Interface .................................................................199
18.3.Port Selection and Configuration ..................................................................................200
18.4.Multiplexed and Non-multiplexed Selection.................................................................202
18.4.1. Multiplexed Configuration ..................................................................................202
18.4.2. Non-multiplexed Configuration...........................................................................203
18.5.Memory Mode Selection ...............................................................................................204
18.5.1. Internal XRAM Only ...........................................................................................204
18.5.2. Split Mode without Bank Select ..........................................................................204
18.5.3. Split Mode with Bank Select ...............................................................................205
18.5.4. External Only.......................................................................................................205
18.6.Timing .......................................................................................................................206
18.6.1. Non-multiplexed Mode........................................................................................207
18.6.1.1.16-bit MOVX: EMI0CF[4:2] = ‘101’, ‘110’, or ‘111’................................207
18.6.1.2.8-bit MOVX without Bank Select: EMI0CF[4:2] = ‘101’ or ‘111’. ...........208
18.6.1.3.8-bit MOVX with Bank Select: EMI0CF[4:2] = ‘110’. ..............................209
18.6.2. Multiplexed Mode................................................................................................210
Rev. 1.2 5
Page 6

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
18.6.2.1.16-bit MOVX: EMI0CF[4:2] = ‘001’, ‘010’, or ‘011’................................210
18.6.2.2.8-bit MOVX without Bank Select: EMI0CF[4:2] = ‘001’ or ‘011’. ...........211
18.6.2.3.8-bit MOVX with Bank Select: EMI0CF[4:2] = ‘010’. ..............................212
19. PORT INPUT/OUTPUT .....................................................................................................215
19.1.Ports 0 through 3 and the Priority Crossbar Decoder ....................................................217
19.1.1. Crossbar Pin Assignment and Allocation ............................................................217
19.1.2. Configuring the Output Modes of the Port Pins ..................................................218
19.1.3. Configuring Port Pins as Digital Inputs...............................................................219
19.1.4. Weak Pull-ups......................................................................................................219
19.1.5. Configuring Port 1 Pins as Analog Inputs ...........................................................219
19.1.6. External Memory Interface Pin Assignments......................................................220
19.1.7. Crossbar Pin Assignment Example......................................................................222
19.2.Ports 4 through 7 (C8051F120/2/4/6 only) ...................................................................231
19.2.1. Configuring Ports which are not Pinned Out.......................................................231
19.2.2. Configuring the Output Modes of the Port Pins ..................................................231
19.2.3. Configuring Port Pins as Digital Inputs...............................................................232
19.2.4. Weak Pull-ups......................................................................................................232
19.2.5. External Memory Interface..................................................................................232
20. SYSTEM MANAGEMENT BUS / I2C BUS (SMBUS0) .................................................237
20.1.Supporting Documents ..................................................................................................238
20.2.SMBus Protocol.............................................................................................................238
20.2.1. Arbitration............................................................................................................239
20.2.2. Clock Low Extension...........................................................................................239
20.2.3. SCL Low Timeout ...............................................................................................239
20.2.4. SCL High (SMBus Free) Timeout.......................................................................239
20.3.SMBus Transfer Modes.................................................................................................240
20.3.1. Master Transmitter Mode ....................................................................................240
20.3.2. Master Receiver Mode.........................................................................................240
20.3.3. Slave Transmitter Mode.......................................................................................241
20.3.4. Slave Receiver Mode ...........................................................................................241
20.4.SMBus Special Function Registers ...............................................................................242
20.4.1. Control Register...................................................................................................242
20.4.2. Clock Rate Register .............................................................................................244
20.4.3. Data Register........................................................................................................245
20.4.4. Address Register ..................................................................................................245
20.4.5. Status Register .....................................................................................................246
21. ENHANCED SERIAL PERIPHERAL INTERFACE (SPI0) .........................................249
21.1.Signal Descriptions........................................................................................................250
21.1.1. Master Out, Slave In (MOSI) ..............................................................................250
21.1.2. Master In, Slave Out (MISO) ..............................................................................250
21.1.3. Serial Clock (SCK) ..............................................................................................250
21.1.4. Slave Select (NSS)...............................................................................................250
21.2.SPI0 Master Mode Operation ........................................................................................251
21.3.SPI0 Slave Mode Operation ..........................................................................................253
21.4.SPI0 Interrupt Sources...................................................................................................253
6 Rev. 1.2
Page 7

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
21.5.Serial Clock Timing ......................................................................................................254
21.6.SPI Special Function Registers .....................................................................................256
22. UART0 ..................................................................................................................................263
22.1.UART0 Operational Modes ..........................................................................................264
22.1.1. Mode 0: Synchronous Mode................................................................................264
22.1.2. Mode 1: 8-Bit UART, Variable Baud Rate .........................................................265
22.1.3. Mode 2: 9-Bit UART, Fixed Baud Rate ..............................................................266
22.1.4. Mode 3: 9-Bit UART, Variable Baud Rate .........................................................267
22.2.Multiprocessor Communications...................................................................................268
22.2.1. Configuration of a Masked Address ....................................................................268
22.2.2. Broadcast Addressing ..........................................................................................268
22.3.Frame and Transmission Error Detection......................................................................269
23. UART1 ..................................................................................................................................275
23.1.Enhanced Baud Rate Generation...................................................................................276
23.2.Operational Modes ........................................................................................................277
23.2.1. 8-Bit UART .........................................................................................................277
23.2.2. 9-Bit UART .........................................................................................................278
23.3.Multiprocessor Communications...................................................................................279
24. TIMERS................................................................................................................................285
24.1.Timer 0 and Timer 1......................................................................................................285
24.1.1. Mode 0: 13-bit Counter/Timer.............................................................................285
24.1.2. Mode 1: 16-bit Counter/Timer.............................................................................286
24.1.3. Mode 2: 8-bit Counter/Timer with Auto-Reload.................................................287
24.1.4. Mode 3: Two 8-bit Counter/Timers (Timer 0 Only) ...........................................288
24.2.Timer 2, Timer 3, and Timer 4 ......................................................................................293
24.2.1. Configuring Timer 2, 3, and 4 to Count Down....................................................293
24.2.2. Capture Mode ......................................................................................................294
24.2.3. Auto-Reload Mode ..............................................................................................295
24.2.4. Toggle Output Mode (Timer 2 and Timer 4 Only)..............................................295
25. PROGRAMMABLE COUNTER ARRAY .......................................................................301
25.1.PCA Counter/Timer.......................................................................................................302
25.2.Capture/Compare Modules............................................................................................303
25.2.1. Edge-triggered Capture Mode .............................................................................304
25.2.2. Software Timer (Compare) Mode........................................................................305
25.2.3. High Speed Output Mode ....................................................................................306
25.2.4. Frequency Output Mode ......................................................................................307
25.2.5. 8-Bit Pulse Width Modulator Mode ....................................................................308
25.2.6. 16-Bit Pulse Width Modulator Mode ..................................................................309
25.3.Register Descriptions for PCA0 ....................................................................................310
26. JTAG (IEEE 1149.1)............................................................................................................315
26.1.Boundary Scan...............................................................................................................316
26.1.1. EXTEST Instruction ............................................................................................317
26.1.2. SAMPLE Instruction ...........................................................................................317
26.1.3. BYPASS Instruction ............................................................................................317
26.1.4. IDCODE Instruction ............................................................................................317
Rev. 1.2 7
Page 8

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
26.2.Flash Programming Commands ....................................................................................318
26.3.Debug Support...............................................................................................................321
8 Rev. 1.2
Page 9

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
LIST OF FIGURES
1. SYSTEM OVERVIEW .........................................................................................................19
Figure 1.1. C8051F120/124 Block Diagram..........................................................................21
Figure 1.2. C8051F121/125 Block Diagram..........................................................................22
Figure 1.3. C8051F122/126 Block Diagram..........................................................................23
Figure 1.4. C8051F123/127 Block Diagram..........................................................................24
Figure 1.5. On-Board Clock and Reset..................................................................................26
Figure 1.6. On-Chip Memory Map........................................................................................27
Figure 1.7. Development/In-System Debug Diagram ...........................................................28
Figure 1.8. MAC0 Block Diagram ........................................................................................29
Figure 1.9. Digital Crossbar Diagram....................................................................................30
Figure 1.10. PCA Block Diagram............................................................................................31
Figure 1.11. 12-Bit ADC Block Diagram................................................................................33
Figure 1.12. 8-Bit ADC Diagram ............................................................................................34
Figure 1.13. Comparator and DAC Diagram...........................................................................35
2. ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS..................................................................................36
3. GLOBAL DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS ......................................................37
4. PINOUT AND PACKAGE DEFINITIONS........................................................................39
Figure 4.1. TQFP-100 Pinout Diagram..................................................................................44
Figure 4.2. TQFP-100 Package Drawing...............................................................................45
Figure 4.3. TQFP-64 Pinout Diagram....................................................................................46
Figure 4.4. TQFP-64 Package Drawing.................................................................................47
5. ADC0 (12-BIT ADC, C8051F120/1/4/5 ONLY) ..................................................................49
Figure 5.1. 12-Bit ADC0 Functional Block Diagram............................................................49
Figure 5.2. Typical Temperature Sensor Transfer Function..................................................50
Figure 5.3. ADC0 Track and Conversion Example Timing ..................................................52
Figure 5.4. ADC0 Equivalent Input Circuits .........................................................................53
Figure 5.5. AMX0CF: AMUX0 Configuration Register.......................................................54
Figure 5.6. AMX0SL: AMUX0 Channel Select Register .....................................................55
Figure 5.7. ADC0CF: ADC0 Configuration Register ...........................................................56
Figure 5.8. ADC0CN: ADC0 Control Register.....................................................................57
Figure 5.9. ADC0H: ADC0 Data Word MSB Register.........................................................58
Figure 5.10. ADC0L: ADC0 Data Word LSB Register ..........................................................58
Figure 5.11. ADC0 Data Word Example.................................................................................59
Figure 5.12. ADC0GTH: ADC0 Greater-Than Data High Byte Register...............................60
Figure 5.13. ADC0GTL: ADC0 Greater-Than Data Low Byte Register................................60
Figure 5.14. ADC0LTH: ADC0 Less-Than Data High Byte Register....................................61
Figure 5.15. ADC0LTL: ADC0 Less-Than Data Low Byte Register .....................................61
Figure 5.16. 12-Bit ADC0 Window Interrupt Example: Right Justified Single-Ended Data .62
Figure 5.17. 12-Bit ADC0 Window Interrupt Example: Right Justified Differential Data.....63
Figure 5.18. 12-Bit ADC0 Window Interrupt Example: Left Justified Single-Ended Data....64
Figure 5.19. 12-Bit ADC0 Window Interrupt Example: Left Justified Differential Data.......65
6. ADC0 (10-BIT ADC, C8051F122/3/6/7 ONLY) ..................................................................67
Rev. 1.2 9
Page 10

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
Figure 6.1. 10-Bit ADC0 Functional Block Diagram............................................................67
Figure 6.2. Typical Temperature Sensor Transfer Function..................................................68
Figure 6.3. ADC0 Track and Conversion Example Timing ..................................................70
Figure 6.4. ADC0 Equivalent Input Circuits .........................................................................71
Figure 6.5. AMX0CF: AMUX0 Configuration Register.......................................................72
Figure 6.6. AMX0SL: AMUX0 Channel Select Register .....................................................73
Figure 6.7. ADC0CF: ADC0 Configuration Register ...........................................................74
Figure 6.8. ADC0CN: ADC0 Control Register.....................................................................75
Figure 6.9. ADC0H: ADC0 Data Word MSB Register.........................................................76
Figure 6.10. ADC0L: ADC0 Data Word LSB Register ..........................................................76
Figure 6.11. ADC0 Data Word Example.................................................................................77
Figure 6.12. ADC0GTH: ADC0 Greater-Than Data High Byte Register...............................78
Figure 6.13. ADC0GTL: ADC0 Greater-Than Data Low Byte Register................................78
Figure 6.14. ADC0LTH: ADC0 Less-Than Data High Byte Register....................................79
Figure 6.15. ADC0LTL: ADC0 Less-Than Data Low Byte Register .....................................79
Figure 6.16. 10-Bit ADC0 Window Interrupt Example: Right Justified Single-Ended Data .80
Figure 6.17. 10-Bit ADC0 Window Interrupt Example: Right Justified Differential Data.....81
Figure 6.18. 10-Bit ADC0 Window Interrupt Example: Left Justified Single-Ended Data....82
Figure 6.19. 10-Bit ADC0 Window Interrupt Example: Left Justified Differential Data.......83
7. ADC2 (8-BIT ADC) ...............................................................................................................85
Figure 7.1. ADC2 Functional Block Diagram.......................................................................85
Figure 7.2. ADC2 Track and Conversion Example Timing ..................................................87
Figure 7.3. ADC2 Equivalent Input Circuit...........................................................................88
Figure 7.4. AMX2CF: AMUX2 Configuration Register.......................................................89
Figure 7.5. AMX2SL: AMUX2 Channel Select Register .....................................................90
Figure 7.6. ADC2CF: ADC2 Configuration Register ...........................................................91
Figure 7.7. ADC2CN: ADC2 Control Register.....................................................................92
Figure 7.8. ADC2: ADC2 Data Word Register .....................................................................93
Figure 7.9. ADC2 Data Word Example.................................................................................93
Figure 7.10. ADC2 Window Compare Examples, Single-Ended Mode .................................94
Figure 7.11. ADC2 Window Compare Examples, Differential Mode ....................................95
Figure 7.12. ADC2GT: ADC2 Greater-Than Data Byte Register...........................................96
Figure 7.13. ADC2LT: ADC2 Less-Than Data Byte Register................................................96
8. DACS, 12-BIT VOLTAGE MODE......................................................................................99
Figure 8.1. DAC Functional Block Diagram.........................................................................99
Figure 8.2. DAC0H: DAC0 High Byte Register .................................................................101
Figure 8.3. DAC0L: DAC0 Low Byte Register ..................................................................101
Figure 8.4. DAC0CN: DAC0 Control Register...................................................................102
Figure 8.5. DAC1H: DAC1 High Byte Register .................................................................103
Figure 8.6. DAC1L: DAC1 Low Byte Register ..................................................................103
Figure 8.7. DAC1CN: DAC1 Control Register...................................................................104
9. VOLTAGE REFERENCE (C8051F120/2/4/6) .................................................................107
Figure 9.1. Voltage Reference Functional Block Diagram..................................................107
Figure 9.2. REF0CN: Reference Control Register ..............................................................108
10. VOLTAGE REFERENCE (C8051F121/3/5/7) .................................................................109
10 Rev. 1.2
Page 11

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
Figure 10.1. Voltage Reference Functional Block Diagram .................................................109
Figure 10.2. REF0CN: Reference Control Register ..............................................................110
11. COMPARATORS................................................................................................................111
Figure 11.1. Comparator Functional Block Diagram ............................................................111
Figure 11.2. Comparator Hysteresis Plot...............................................................................113
Figure 11.3. CPT0CN: Comparator0 Control Register .........................................................114
Figure 11.4. CPT0MD: Comparator0 Mode Selection Register ...........................................115
Figure 11.5. CPT1CN: Comparator1 Control Register .........................................................116
Figure 11.6. CPT1MD: Comparator1 Mode Selection Register ...........................................117
12. CIP-51 MICROCONTROLLER........................................................................................119
Figure 12.1. CIP-51 Block Diagram.....................................................................................119
Figure 12.2. Memory Map.....................................................................................................125
Figure 12.3. PSBANK: Program Space Bank Select Register ..............................................126
Figure 12.4. Address Memory Map for Instruction Fetches..................................................126
Figure 12.5. SFR Page Stack .................................................................................................129
Figure 12.6. SFR Page Stack While Using SFR Page 0x0F To Access Port 5 .....................130
Figure 12.7. SFR Page Stack After ADC2 Window Comparator Interrupt Occurs ..............131
Figure 12.8. SFR Page Stack Upon PCA Interrupt Occurring During an ADC2 ISR...........132
Figure 12.9. SFR Page Stack Upon Return From PCA Interrupt ..........................................133
Figure 12.10. SFR Page Stack Upon Return From ADC2 Window Interrupt.......................134
Figure 12.11. SFRPGCN: SFR Page Control Register..........................................................135
Figure 12.12. SFRPAGE: SFR Page Register .......................................................................135
Figure 12.13. SFRNEXT: SFR Next Register.......................................................................136
Figure 12.14. SFRLAST: SFR Last Register ........................................................................136
Figure 12.15. SP: Stack Pointer .............................................................................................143
Figure 12.16. DPL: Data Pointer Low Byte ..........................................................................143
Figure 12.17. DPH: Data Pointer High Byte .........................................................................143
Figure 12.18. PSW: Program Status Word ............................................................................144
Figure 12.19. ACC: Accumulator..........................................................................................145
Figure 12.20. B: B Register ...................................................................................................145
Figure 12.21. IE: Interrupt Enable .........................................................................................149
Figure 12.22. IP: Interrupt Priority ........................................................................................150
Figure 12.23. EIE1: Extended Interrupt Enable 1 .................................................................151
Figure 12.24. EIE2: Extended Interrupt Enable 2 .................................................................152
Figure 12.25. EIP1: Extended Interrupt Priority 1.................................................................153
Figure 12.26. EIP2: Extended Interrupt Priority 2.................................................................154
Figure 12.27. PCON: Power Control.....................................................................................156
13. MULTIPLY AND ACCUMULATE (MAC0) ...................................................................157
Figure 13.1. MAC0 Block Diagram ......................................................................................157
Figure 13.2. Integer Mode Data Representation....................................................................158
Figure 13.3. Fractional Mode Data Representation...............................................................158
Figure 13.4. MAC0 Pipeline..................................................................................................159
Figure 13.5. Multiply and Accumulate Example...................................................................160
Figure 13.6. Multiply Only Example.....................................................................................161
Figure 13.7. MAC0 Accumulator Shift Example ..................................................................161
Rev. 1.2 11
Page 12

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
Figure 13.8. MAC0CF: MAC0 Configuration Register ........................................................162
Figure 13.9. MAC0STA: MAC0 Status Register ..................................................................163
Figure 13.10. MAC0AH: MAC0 A High Byte Register .......................................................163
Figure 13.11. MAC0AL: MAC0 A Low Byte Register ........................................................164
Figure 13.12. MAC0BH: MAC0 B High Byte Register........................................................164
Figure 13.13. MAC0BL: MAC0 B Low Byte Register.........................................................164
Figure 13.14. MAC0ACC3: MAC0 Accumulator Byte 3 Register.......................................164
Figure 13.15. MAC0ACC2: MAC0 Accumulator Byte 2 Register.......................................165
Figure 13.16. MAC0ACC1: MAC0 Accumulator Byte 1 Register.......................................165
Figure 13.17. MAC0ACC0: MAC0 Accumulator Byte 0 Register.......................................165
Figure 13.18. MAC0OVR: MAC0 Accumulator Overflow Register....................................165
Figure 13.19. MAC0RNDH: MAC0 Rounding Register High Byte.....................................166
Figure 13.20. MAC0RNDL: MAC0 Rounding Register Low Byte......................................166
14. RESET SOURCES ..............................................................................................................167
Figure 14.1. Reset Sources ....................................................................................................167
Figure 14.2. Reset Timing .....................................................................................................168
Figure 14.3. WDTCN: Watchdog Timer Control Register ...................................................170
Figure 14.4. RSTSRC: Reset Source Register.......................................................................171
15. OSCILLATORS...................................................................................................................173
Figure 15.1. Oscillator Diagram ............................................................................................173
Figure 15.2. OSCICL: Internal Oscillator Calibration Register ............................................174
Figure 15.3. OSCICN: Internal Oscillator Control Register .................................................174
Figure 15.4. CLKSEL: System Clock Selection Register .....................................................175
Figure 15.5. OSCXCN: External Oscillator Control Register...............................................176
Figure 15.6. PLL Block Diagram ..........................................................................................178
Figure 15.7. PLL0CN: PLL Control Register........................................................................180
Figure 15.8. PLL0DIV: PLL Pre-divider Register ................................................................180
Figure 15.9. PLL0MUL: PLL Clock Scaler Register............................................................181
Figure 15.10. PLL0FLT: PLL Filter Register........................................................................181
16. FLASH MEMORY ..............................................................................................................185
Figure 16.1. FLASH Memory Map for MOVC Read and MOVX Write Operations...........186
Figure 16.2. FLASH Program Memory Map and Security Bytes .........................................189
Figure 16.3. FLACL: FLASH Access Limit .........................................................................190
Figure 16.4. FLSCL: FLASH Memory Control ....................................................................191
Figure 16.5. PSCTL: Program Store Read/Write Control .....................................................192
17. BRANCH TARGET CACHE.............................................................................................193
Figure 17.1. Branch Target Cache Data Flow .......................................................................193
Figure 17.2. Branch Target Cache Organiztion.....................................................................194
Figure 17.3. Cache Lock Operation.......................................................................................195
Figure 17.4. CCH0CN: Cache Control Register....................................................................196
Figure 17.5. CCH0TN: Cache Tuning Register ....................................................................197
Figure 17.6. CCH0LC: Cache Lock Control Register...........................................................197
Figure 17.7. CCH0MA: Cache Miss Accumulator................................................................198
Figure 17.8. FLSTAT: FLASH Status...................................................................................198
18. EXTERNAL DATA MEMORY INTERFACE AND ON-CHIP XRAM.......................199
12 Rev. 1.2
Page 13

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
Figure 18.1. EMI0CN: External Memory Interface Control .................................................201
Figure 18.2. EMI0CF: External Memory Configuration.......................................................201
Figure 18.3. Multiplexed Configuration Example.................................................................202
Figure 18.4. Non-multiplexed Configuration Example .........................................................203
Figure 18.5. EMIF Operating Modes.....................................................................................204
Figure 18.6. EMI0TC: External Memory Timing Control ....................................................206
Figure 18.7. Non-multiplexed 16-bit MOVX Timing ...........................................................207
Figure 18.8. Non-multiplexed 8-bit MOVX without Bank Select Timing............................208
Figure 18.9. Non-multiplexed 8-bit MOVX with Bank Select Timing.................................209
Figure 18.10. Multiplexed 16-bit MOVX Timing.................................................................210
Figure 18.11. Multiplexed 8-bit MOVX without Bank Select Timing .................................211
Figure 18.12. Multiplexed 8-bit MOVX with Bank Select Timing.......................................212
19. PORT INPUT/OUTPUT .....................................................................................................215
Figure 19.1. Port I/O Cell Block Diagram.............................................................................215
Figure 19.2. Port I/O Functional Block Diagram ..................................................................216
Figure 19.3. Priority Crossbar Decode Table ........................................................................217
Figure 19.4. Priority Crossbar Decode Table ........................................................................220
Figure 19.5. Priority Crossbar Decode Table ........................................................................221
Figure 19.6. Crossbar Example: ............................................................................................223
Figure 19.7. XBR0: Port I/O Crossbar Register 0 .................................................................224
Figure 19.8. XBR1: Port I/O Crossbar Register 1 .................................................................225
Figure 19.9. XBR2: Port I/O Crossbar Register 2 .................................................................226
Figure 19.10. P0: Port0 Data Register ...................................................................................227
Figure 19.11. P0MDOUT: Port0 Output Mode Register.......................................................227
Figure 19.12. P1: Port1 Data Register ...................................................................................228
Figure 19.13. P1MDIN: Port1 Input Mode Register .............................................................228
Figure 19.14. P1MDOUT: Port1 Output Mode Register.......................................................229
Figure 19.15. P2: Port2 Data Register ...................................................................................229
Figure 19.16. P2MDOUT: Port2 Output Mode Register.......................................................230
Figure 19.17. P3: Port3 Data Register ...................................................................................230
Figure 19.18. P3MDOUT: Port3 Output Mode Register.......................................................231
Figure 19.19. P4: Port4 Data Register ...................................................................................233
Figure 19.20. P4MDOUT: Port4 Output Mode Register.......................................................233
Figure 19.21. P5: Port5 Data Register ...................................................................................234
Figure 19.22. P5MDOUT: Port5 Output Mode Register.......................................................234
Figure 19.23. P6: Port6 Data Register ...................................................................................235
Figure 19.24. P6MDOUT: Port6 Output Mode Register.......................................................235
Figure 19.25. P7: Port7 Data Register ...................................................................................236
Figure 19.26. P7MDOUT: Port7 Output Mode Register.......................................................236
20. SYSTEM MANAGEMENT BUS / I2C BUS (SMBUS0) .................................................237
Figure 20.1. SMBus0 Block Diagram ...................................................................................237
Figure 20.2. Typical SMBus Configuration ..........................................................................238
Figure 20.3. SMBus Transaction ...........................................................................................239
Figure 20.4. Typical Master Transmitter Sequence...............................................................240
Figure 20.5. Typical Master Receiver Sequence ...................................................................240
Rev. 1.2 13
Page 14

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
Figure 20.6. Typical Slave Transmitter Sequence.................................................................241
Figure 20.7. Typical Slave Receiver Sequence .....................................................................241
Figure 20.8. SMB0CN: SMBus0 Control Register ...............................................................243
Figure 20.9. SMB0CR: SMBus0 Clock Rate Register..........................................................244
Figure 20.10. SMB0DAT: SMBus0 Data Register ...............................................................245
Figure 20.11. SMB0ADR: SMBus0 Address Register..........................................................245
Figure 20.12. SMB0STA: SMBus0 Status Register..............................................................246
21. ENHANCED SERIAL PERIPHERAL INTERFACE (SPI0) .........................................249
Figure 21.1. SPI Block Diagram............................................................................................249
Figure 21.2. Multiple-Master Mode Connection Diagram ....................................................252
Figure 21.3. 3-Wire Single Master and 3-Wire Single Slave Mode Connection Diagram ...252
Figure 21.4. 4-Wire Single Master Mode and 4-Wire Slave Mode Connection Diagram ....252
Figure 21.5. Master Mode Data/Clock Timing......................................................................254
Figure 21.6. Slave Mode Data/Clock Timing (CKPHA = 0) ................................................255
Figure 21.7. Slave Mode Data/Clock Timing (CKPHA = 1) ................................................255
Figure 21.8. SPI0CFG: SPI0 Configuration Register............................................................256
Figure 21.9. SPI0CN: SPI0 Control Register ........................................................................257
Figure 21.10. SPI0CKR: SPI0 Clock Rate Register..............................................................258
Figure 21.11. SPI0DAT: SPI0 Data Register ........................................................................259
Figure 21.12. SPI Master Timing (CKPHA = 0)...................................................................260
Figure 21.13. SPI Master Timing (CKPHA = 1)...................................................................260
Figure 21.14. SPI Slave Timing (CKPHA = 0) .....................................................................261
Figure 21.15. SPI Slave Timing (CKPHA = 1) .....................................................................261
22. UART0 ..................................................................................................................................263
Figure 22.1. UART0 Block Diagram.....................................................................................263
Figure 22.2. UART0 Mode 0 Timing Diagram .....................................................................264
Figure 22.3. UART0 Mode 0 Interconnect............................................................................264
Figure 22.4. UART0 Mode 1 Timing Diagram .....................................................................265
Figure 22.5. UART0 Modes 2 and 3 Timing Diagram..........................................................266
Figure 22.6. UART0 Modes 1, 2, and 3 Interconnect Diagram ............................................267
Figure 22.7. UART Multi-Processor Mode Interconnect Diagram .......................................269
Figure 22.8. SCON0: UART0 Control Register....................................................................271
Figure 22.9. SSTA0: UART0 Status and Clock Selection Register......................................272
Figure 22.10. SBUF0: UART0 Data Buffer Register............................................................273
Figure 22.11. SADDR0: UART0 Slave Address Register ....................................................273
Figure 22.12. SADEN0: UART0 Slave Address Enable Register ........................................273
23. UART1 ..................................................................................................................................275
Figure 23.1. UART1 Block Diagram.....................................................................................275
Figure 23.2. UART1 Baud Rate Logic ..................................................................................276
Figure 23.3. UART Interconnect Diagram ............................................................................277
Figure 23.4. 8-Bit UART Timing Diagram ...........................................................................277
Figure 23.5. 9-Bit UART Timing Diagram ...........................................................................278
Figure 23.6. UART Multi-Processor Mode Interconnect Diagram .......................................279
Figure 23.7. SCON1: Serial Port 1 Control Register.............................................................280
Figure 23.8. SBUF1: Serial (UART1) Port Data Buffer Register .........................................281
14 Rev. 1.2
Page 15

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
24. TIMERS................................................................................................................................285
Figure 24.1. T0 Mode 0 Block Diagram................................................................................286
Figure 24.2. T0 Mode 2 Block Diagram................................................................................287
Figure 24.3. T0 Mode 3 Block Diagram................................................................................288
Figure 24.4. TCON: Timer Control Register.........................................................................289
Figure 24.5. TMOD: Timer Mode Register...........................................................................290
Figure 24.6. CKCON: Clock Control Register......................................................................291
Figure 24.7. TL0: Timer 0 Low Byte ....................................................................................292
Figure 24.8. TL1: Timer 1 Low Byte ....................................................................................292
Figure 24.9. TH0: Timer 0 High Byte ...................................................................................292
Figure 24.10. TH1: Timer 1 High Byte .................................................................................292
Figure 24.11. T2, 3, and 4 Capture Mode Block Diagram ....................................................294
Figure 24.12. T2, 3, and 4 Auto-reload Mode Block Diagram..............................................295
Figure 24.13. TMRnCN: Timer 2, 3, and 4 Control Registers ..............................................297
Figure 24.14. TMRnCF: Timer 2, 3, and 4 Configuration Registers ....................................298
Figure 24.15. RCAPnL: Timer 2, 3, and 4 Capture Register Low Byte................................299
Figure 24.16. RCAPnH: Timer 2, 3, and 4 Capture Register High Byte ..............................299
Figure 24.17. TMRnL: Timer 2, 3, and 4 Low Byte .............................................................299
Figure 24.18. TMRnH Timer 2, 3, and 4 High Byte .............................................................300
25. PROGRAMMABLE COUNTER ARRAY .......................................................................301
Figure 25.1. PCA Block Diagram..........................................................................................301
Figure 25.2. PCA Counter/Timer Block Diagram.................................................................302
Figure 25.3. PCA Interrupt Block Diagram...........................................................................303
Figure 25.4. PCA Capture Mode Diagram ............................................................................304
Figure 25.5. PCA Software Timer Mode Diagram................................................................305
Figure 25.6. PCA High Speed Output Mode Diagram ..........................................................306
Figure 25.7. PCA Frequency Output Mode...........................................................................307
Figure 25.8. PCA 8-Bit PWM Mode Diagram ......................................................................308
Figure 25.9. PCA 16-Bit PWM Mode ...................................................................................309
Figure 25.10. PCA0CN: PCA Control Register ....................................................................310
Figure 25.11. PCA0MD: PCA0 Mode Register ....................................................................311
Figure 25.12. PCA0CPMn: PCA0 Capture/Compare Mode Registers .................................312
Figure 25.13. PCA0L: PCA0 Counter/Timer Low Byte .......................................................313
Figure 25.14. PCA0H: PCA0 Counter/Timer High Byte ......................................................313
Figure 25.15. PCA0CPLn: PCA0 Capture Module Low Byte ..............................................314
Figure 25.16. PCA0CPHn: PCA0 Capture Module High Byte .............................................314
26. JTAG (IEEE 1149.1)............................................................................................................315
Figure 26.1. IR: JTAG Instruction Register ..........................................................................315
Figure 26.2. DEVICEID: JTAG Device ID Register ............................................................317
Figure 26.3. FLASHCON: JTAG Flash Control Register.....................................................319
Figure 26.4. FLASHDAT: JTAG Flash Data Register..........................................................320
Figure 26.5. FLASHADR: JTAG Flash Address Register....................................................320
Rev. 1.2 15
Page 16

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
Notes
16 Rev. 1.2
Page 17

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
LIST OF TABLES
1. SYSTEM OVERVIEW ........................................................................................................19
Table 1.1. Product Selection Guide .......................................................................................20
2. ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS .................................................................................36
Table 2.1. Absolute Maximum Ratings* ...............................................................................36
3. GLOBAL DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS .....................................................37
Table 3.1. Global DC Electrical Characteristics (C8051F120/1/2/3) ....................................37
Table 3.2. Global DC Electrical Characteristics (C8051F124/5/6/7) ....................................38
4. PINOUT AND PACKAGE DEFINITIONS .......................................................................39
Table 4.1. Pin Definitions ......................................................................................................39
5. ADC0 (12-BIT ADC, C8051F120/1/4/5 ONLY) .................................................................49
Table 5.1. 12-Bit ADC0 Electrical Characteristics (C8051F120/1/4/5) ................................66
6. ADC0 (10-BIT ADC, C8051F122/3/6/7 ONLY) .................................................................67
Table 6.1. 10-Bit ADC0 Electrical Characteristics (C8051F122/3/6/7) ................................84
7. ADC2 (8-BIT ADC) ..............................................................................................................85
Table 7.1. ADC2 Electrical Characteristics ...........................................................................97
8. DACS, 12-BIT VOLTAGE MODE .....................................................................................99
Table 8.1. DAC Electrical Characteristics ...........................................................................105
9. VOLTAGE REFERENCE (C8051F120/2/4/6) ................................................................107
Table 9.1. Voltage Reference Electrical Characteristics .....................................................108
10. VOLTAGE REFERENCE (C8051F121/3/5/7) ................................................................109
Table 10.1.Voltage Reference Electrical Characteristics .....................................................110
11. COMPARATORS ...............................................................................................................111
Table 11.1.Comparator Electrical Characteristics ................................................................118
12. CIP-51 MICROCONTROLLER .......................................................................................119
Table 12.1.CIP-51 Instruction Set Summary ........................................................................121
Table 12.2.Special Function Register (SFR) Memory Map .................................................137
Table 12.3.Special Function Registers .................................................................................138
Table 12.4.Interrupt Summary ..............................................................................................147
13. MULTIPLY AND ACCUMULATE (MAC0) ..................................................................157
Table 13.1.MAC0 Rounding (MAC0SAT = 0) ....................................................................160
14. RESET SOURCES .............................................................................................................167
Table 14.1.Reset Electrical Characteristics ..........................................................................172
15. OSCILLATORS ..................................................................................................................173
Table 15.1.Oscillator Electrical Characteristics ...................................................................173
Table 15.2.PLL Frequency Characteristics ...........................................................................182
Table 15.3.PLL Lock Timing Characteristics ......................................................................182
16. FLASH MEMORY .............................................................................................................185
Table 16.1.FLASH Electrical Characteristics .......................................................................188
17. BRANCH TARGET CACHE ............................................................................................193
18. EXTERNAL DATA MEMORY INTERFACE AND ON-CHIP XRAM ......................199
Table 18.1.AC Parameters for External Memory Interface† ................................................213
19. PORT INPUT/OUTPUT ....................................................................................................215
Rev. 1.2 17
Page 18

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
Table 19.1.Port I/O DC Electrical Characteristics ................................................................215
20. SYSTEM MANAGEMENT BUS / I2C BUS (SMBUS0) ................................................237
Table 20.1.SMB0STA Status Codes and States ...................................................................247
21. ENHANCED SERIAL PERIPHERAL INTERFACE (SPI0) ........................................249
Table 21.1.SPI Slave Timing Parameters .............................................................................262
22. UART0 .................................................................................................................................263
Table 22.1.UART0 Modes ....................................................................................................264
Table 22.2.Oscillator Frequencies for Standard Baud Rates ................................................270
23. UART1 .................................................................................................................................275
Table 23.1.Timer Settings for Standard Baud Rates Using The Internal Oscillator ............282
Table 23.2.Timer Settings for Standard Baud Rates Using an External Oscillator ..............282
Table 23.3.Timer Settings for Standard Baud Rates Using an External Oscillator ..............283
Table 23.4.Timer Settings for Standard Baud Rates Using the PLL ....................................283
Table 23.5.Timer Settings for Standard Baud Rates Using the PLL ....................................284
24. TIMERS ...............................................................................................................................285
25. PROGRAMMABLE COUNTER ARRAY ......................................................................301
Table 25.1.PCA Timebase Input Options .............................................................................302
Table 25.2.PCA0CPM Register Settings for PCA Capture/Compare Modules ...................303
26. JTAG (IEEE 1149.1) ...........................................................................................................315
Table 26.1.Boundary Data Register Bit Definitions .............................................................316
18 Rev. 1.2
Page 19

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
1. SYSTEM OVERVIEW
The C8051F12x devices are fully integrated mixed-signal System-on-a-Chip MCUs with 64 digital I/O pins
(C8051F120/2/4/6) or 32 digital I/O pins (C8051F121/3/5/7). Highlighted features are listed below; refer to Table 1.1
for specific product feature selection.
• High-Speed pipelined 8051-compatible CIP-51 microcontroller core (up to 100 MIPS for C8051F120/1/2/3 and
50 MIPS for C8051F124/5/6/7)
• In-system, full-speed, non-intrusive debug interface (on-chip)
• True 12-bit (C8051F120/1/4/5) or 10-bit (C8051F122/3/6/7) 100 ksps ADC with PGA and 8-channel analog
multiplexer
• True 8-bit 500 ksps ADC with PGA and 8-channel analog multiplexer
• Two 12-bit DACs with programmable update scheduling
• 2-cycle 16 by 16 Multiply and Accumulate Engine (C8051F120/1/2/3)
• 128k bytes of in-system programmable FLASH memory
• 8448 (8k + 256) bytes of on-chip RAM
• External Data Memory Interface with 64k byte address space
•SPI, SMBus/I
• Five general purpose 16-bit Timers
• Programmable Counter/Timer Array with 6 capture/compare modules
• On-chip Watchdog Timer, VDD Monitor, and Temperature Sensor
2
C, and (2) UART serial interfaces implemented in hardware
With on-chip VDD monitor, Watchdog Timer, and clock oscillator, the C8051F12x devices are truly stand-alone System-on-a-Chip solutions. All analog and digital peripherals are enabled/disabled and configured by user firmware.
The FLASH memory can be reprogrammed even in-circuit, providing non-volatile data storage, and also allowing
field upgrades of the 8051 firmware.
On-board JTAG debug circuitry allows non-intrusive (uses no on-chip resources), full speed, in-circuit debugging
using the production MCU installed in the final application. This debug system supports inspection and modification
of memory and registers, setting breakpoints, watchpoints, single stepping, run and halt commands. All analog and
digital peripherals are fully functional while debugging using JTAG.
Each MCU is specified for operation over the industrial temperature range (-45° C to +85° C). The Port I/Os, /RST,
and JTAG pins are tolerant for input signals up to 5 V. The C8051F120/2/4/6 are available in a 100-pin TQFP package (see block diagrams in Figure 1.1 and Figure 1.3). The C8051F121/3/5/7 are available in a 64-pin TQFP package
(see block diagrams in Figure 1.2 and Figure 1.4).
Rev. 1.2 19
Page 20
C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
Table 1.1. Product Selection Guide
C
2
MIPS (Peak)
FLASH Memory
C8051F120 100 128k 8448
C8051F121 100 128k 8448
C8051F122 100 128k 8448
C8051F123 100 128k 8448
C8051F124 50 128k 8448
C8051F125 50 128k 8448
C8051F126 50 128k 8448
C8051F127 50 128k 8448
RAM
2-cycle 16 by 16 MAC
External Memory Interface
3333
3333
3333
3333
333
333
333
333
SPI
SMBus/I
UARTS
Timers (16-bit)
Programmable Counter Array
25364 8 - 8
25332 8 - 8
25364 - 8 8
25332 - 8 8
25364 8 - 8
25332 8 - 8
25364 - 8 8
25332 - 8 8
Package
Digital Port I/O’s
12-bit 100ksps ADC Inputs
10-bit 100ksps ADC Inputs
Voltage Reference
Temperature Sensor
8-bit 500ksps ADC Inputs
33
33
33
33
33
33
33
33
DAC Outputs
DAC Resolution (bits)
12 2 2 100TQFP
12 2 2 64TQFP
12 2 2 100TQFP
12 2 2 64TQFP
12 2 2 100TQFP
12 2 2 64TQFP
12 2 2 100TQFP
12 2 2 64TQFP
Analog Comparators
20 Rev. 1.2
Page 21
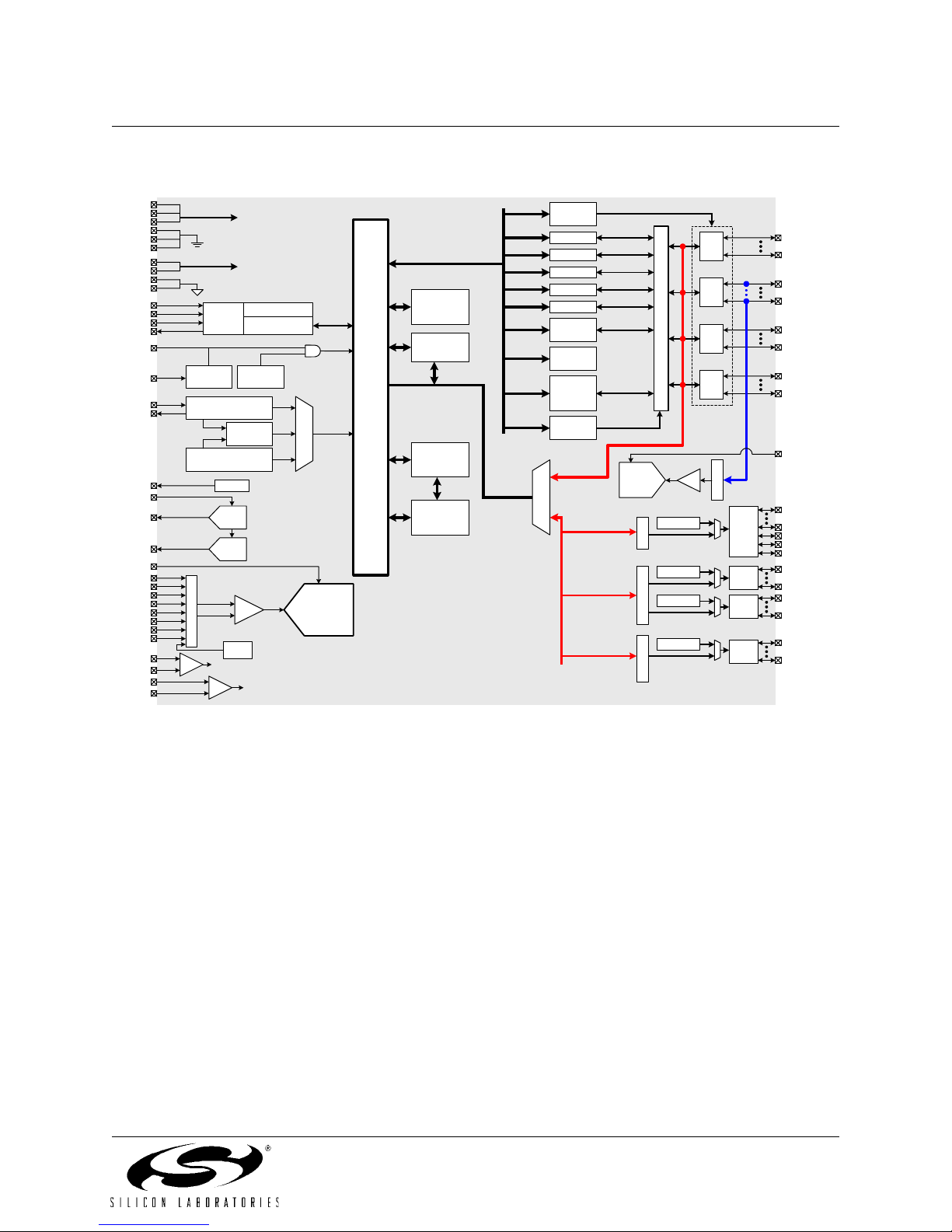
C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
Figure 1.1. C8051F120/124 Block Diagram
VDD
VDD
VDD
DGND
DGND
DGND
AV+
AV+
AGND
AGND
TCK
TMS
TDI
TDO
/RST
MONEN
XTAL1
XTAL2
VREF
VREFD
DAC1
DAC0
VREF0
AIN0.0
AIN0.1
AIN0.2
AIN0.3
AIN0.4
AIN0.5
AIN0.6
AIN0.7
CP0+
CP0CP1+
CP1-
Digital Power
Analog Power
JTAG
Logic
VDD
Monitor
External Oscillator
Circuit
Circuitry
Calibrated Internal
Oscillator
VREF
DAC1
(12-Bit)
DAC0
(12-Bit)
A
M
U
X
TEMP
SENSOR
CP0
CP1
Boundary Scan
Debug HW
WDT
PLL
Prog
Gain
Reset
System
Clock
ADC
100ksps
(12-Bit)
8
0
5
1
C
o
r
e
SFR Bus
256 byte
RAM
8kbyte
XRAM
External Data
Memory Bus
128kbyte
FLASH
64x4 byte
cache
Port I/O
Config.
UART0
UART1
SMBus
SPI Bus
PCA
Timers 0,
1, 2, 4
Timer 3/
RTC
P0, P1,
P2, P3
Latches
Crossbar
Config.
Bus Control
Address Bus
Data Bus
ADC
500ksps
(8-Bit)
C
T
L
A
d
d
r
D
a
a
t
C
R
O
S
S
B
A
R
P4 Latch
P5 Latch
P6 Latch
P7 Latch
P0
Drv
P1
Drv
P2
Drv
P3
Drv
A
8:1
M
Prog
Gain
U
X
P4
DRV
P5
DRV
P6
DRV
P7
DRV
P0.0
P0.7
P1.0/AIN2.0
P1.7/AIN2.7
P2.0
P2.7
P3.0
P3.7
VREF2
P4.0
P4.4
P4.5/ALE
P4.6/RD
P4.7/WR
P5.0/A8
P5.7/A15
P6.0/A0
P6.7/A7
P7.0/D0
P7.7/D7
Rev. 1.2 21
Page 22
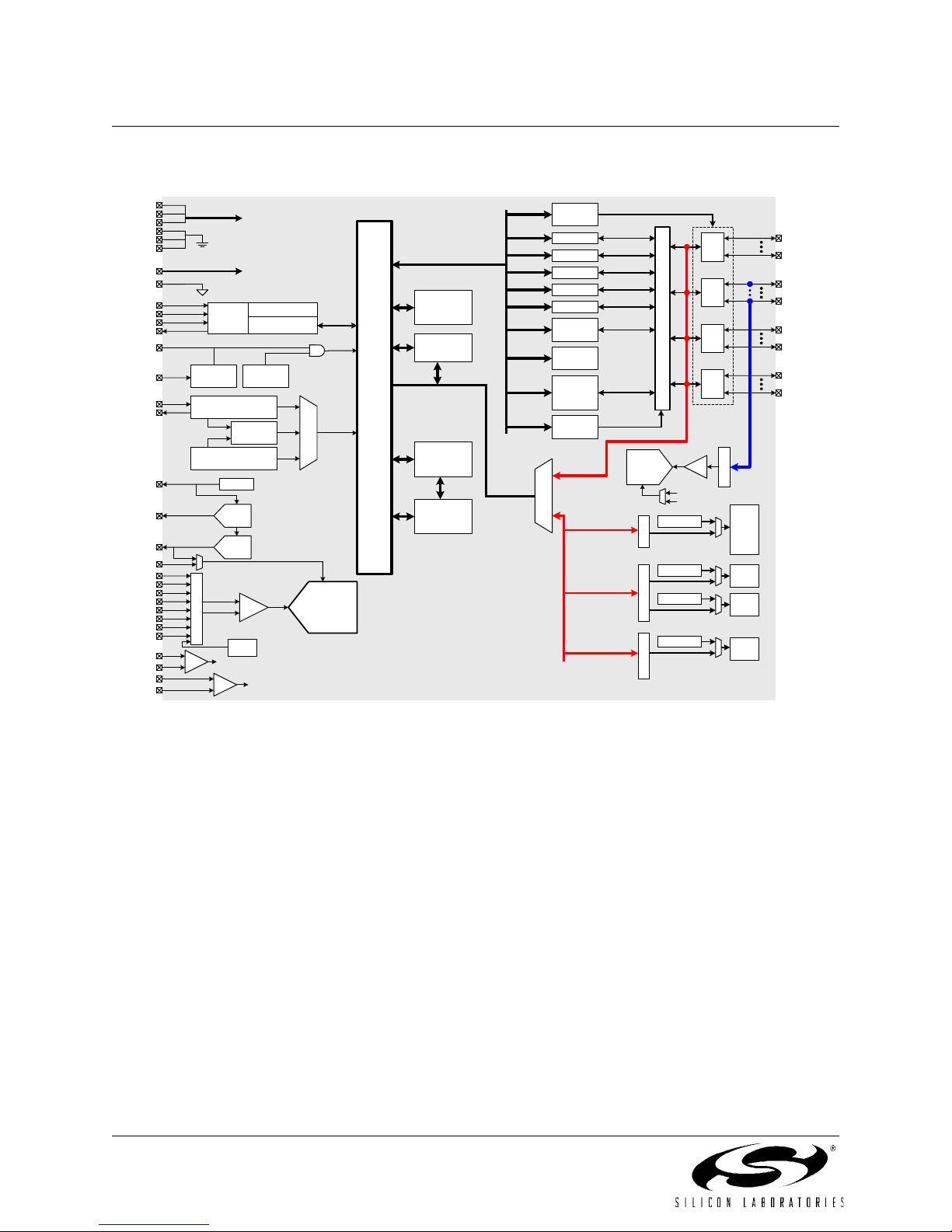
C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
Figure 1.2. C8051F121/125 Block Diagram
VDD
VDD
VDD
DGND
DGND
DGND
AV+
AGND
TCK
TMS
TDI
TDO
/RST
MONEN
XTAL1
XTAL2
VREF
DAC1
DAC0
VREFA
AIN0.0
AIN0.1
AIN0.2
AIN0.3
AIN0.4
AIN0.5
AIN0.6
AIN0.7
CP0+
CP0CP1+
CP1-
Digital Power
Analog Power
JTAG
Logic
VDD
Monitor
External Oscillator
Calibrated Internal
Oscillator
A
M
U
X
CP0
CP1
Circuit
VREF
DAC1
(12-Bit)
DAC0
(12-Bit)
SENSOR
Circuitry
TEMP
Boundary Scan
Debug HW
WDT
PLL
Prog
Gain
Reset
System
Clock
ADC
100ksps
(12-Bit)
8
0
5
1
C
o
r
e
SFR Bus
256 byte
RAM
8kbyte
XRAM
External Data
Memory Bus
128kbyte
FLASH
64x4 byte
cache
Port I/O
Config.
UART0
UART1
SMBus
SPI Bus
PCA
Timers 0,
1, 2, 4
Timer 3/
RTC
P0, P1,
P2, P3
Latches
Crossbar
Config.
Bus Control
Address Bus
Data Bus
ADC
500ksps
(8-Bit)
C
T
L
A
d
d
r
D
a
t
a
C
R
O
S
S
B
A
R
P4 Latch
P5 Latch
P6 Latch
P7 Latch
AV+
VREFA
P0
Drv
P1
Drv
P2
Drv
P3
Drv
A
8:1
M
Prog
Gain
U
X
P4
DRV
P5
DRV
P6
DRV
P7
DRV
P0.0
P0.7
P1.0/AIN2.0
P1.7/AIN2.7
P2.0
P2.7
P3.0
P3.7
22 Rev. 1.2
Page 23
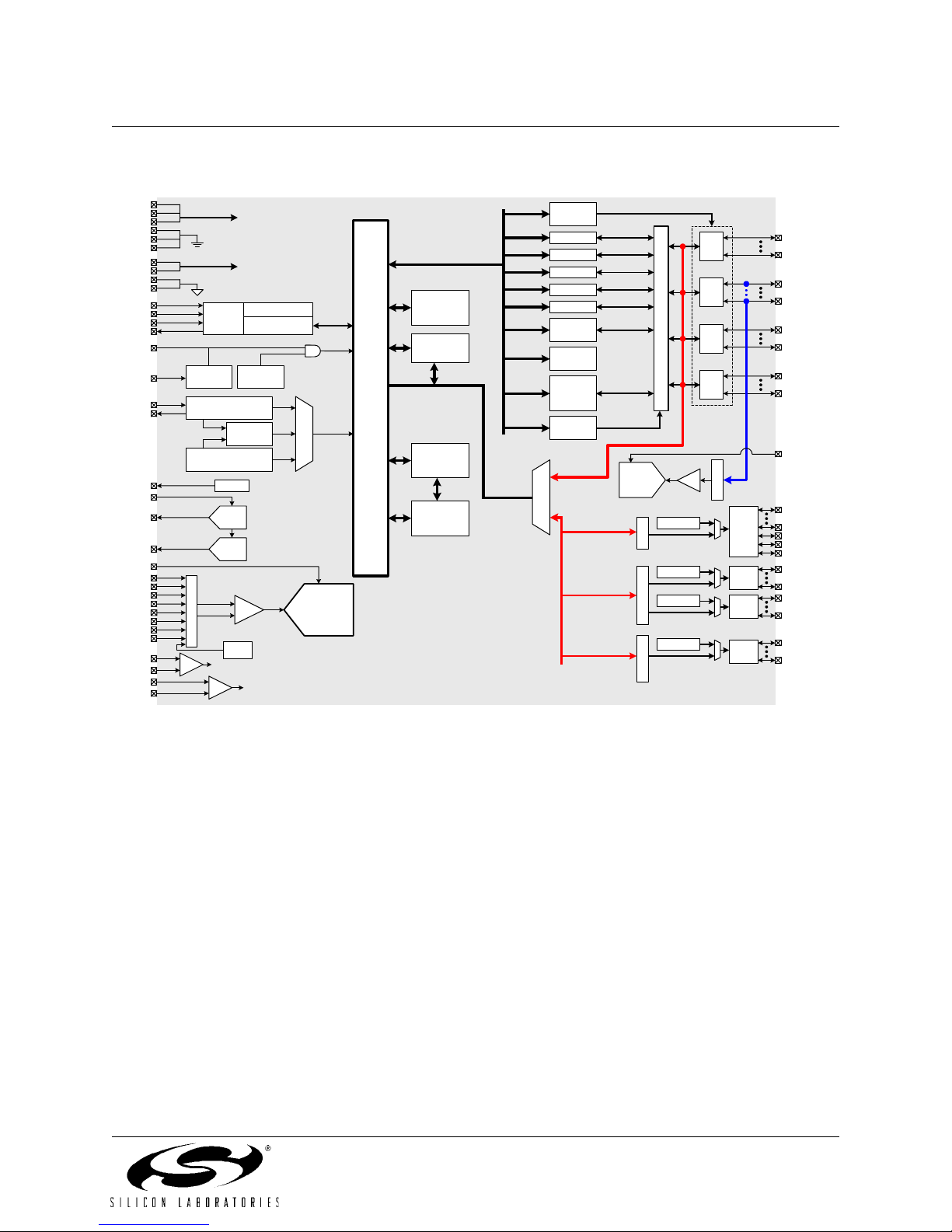
C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
Figure 1.3. C8051F122/126 Block Diagram
VDD
VDD
VDD
DGND
DGND
DGND
AV+
AV+
AGND
AGND
TCK
TMS
TDI
TDO
/RST
MONEN
XTAL1
XTAL2
VREF
VREFD
DAC1
DAC0
VREF0
AIN0.0
AIN0.1
AIN0.2
AIN0.3
AIN0.4
AIN0.5
AIN0.6
AIN0.7
CP0+
CP0CP1+
CP1-
Digital Power
Analog Power
JTAG
Logic
VDD
Monitor
External Oscillator
Circuit
Circuitry
Calibrated Internal
Oscillator
VREF
DAC1
(12-Bit)
DAC0
(12-Bit)
A
M
U
X
TEMP
SENSOR
CP0
CP1
Boundary Scan
Debug HW
WDT
PLL
Prog
Gain
Reset
System
Clock
ADC
100ksps
(10-Bit)
8
0
5
1
C
o
r
e
SFR Bus
256 byte
RAM
8kbyte
XRAM
External Data
Memory Bus
128kbyte
FLASH
64x4 byte
cache
Port I/O
Config.
UART0
UART1
SMBus
SPI Bus
PCA
Timers 0,
1, 2, 4
Timer 3/
RTC
P0, P1,
P2, P3
Latches
Crossbar
Config.
Bus Control
Address Bus
Data Bus
ADC
500ksps
(8-Bit)
C
T
L
A
d
d
r
D
a
a
t
C
R
O
S
S
B
A
R
P4 Latch
P5 Latch
P6 Latch
P7 Latch
P0
Drv
P1
Drv
P2
Drv
P3
Drv
A
8:1
M
Prog
Gain
U
X
P4
DRV
P5
DRV
P6
DRV
P7
DRV
P0.0
P0.7
P1.0/AIN2.0
P1.7/AIN2.7
P2.0
P2.7
P3.0
P3.7
VREF2
P4.0
P4.4
P4.5/ALE
P4.6/RD
P4.7/WR
P5.0/A8
P5.7/A15
P6.0/A0
P6.7/A7
P7.0/D0
P7.7/D7
Rev. 1.2 23
Page 24
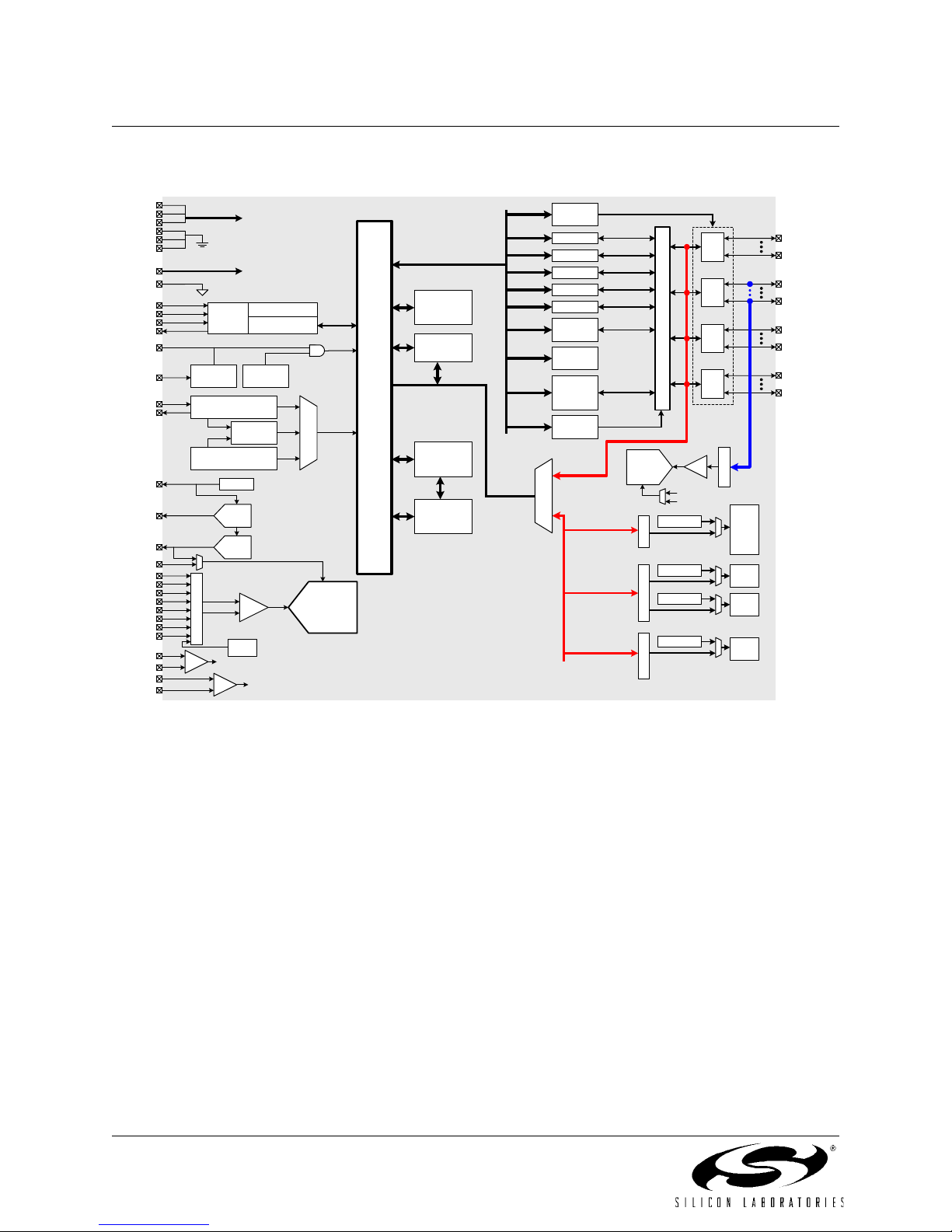
C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
Figure 1.4. C8051F123/127 Block Diagram
VDD
VDD
VDD
DGND
DGND
DGND
AV+
AGND
TCK
TMS
TDI
TDO
/RST
MONEN
XTAL1
XTAL2
VREF
DAC1
DAC0
VREFA
AIN0.0
AIN0.1
AIN0.2
AIN0.3
AIN0.4
AIN0.5
AIN0.6
AIN0.7
CP0+
CP0CP1+
CP1-
Digital Power
Analog Power
JTAG
Logic
VDD
Monitor
External Oscillator
Calibrated Internal
Oscillator
A
M
U
X
CP0
CP1
Circuit
VREF
DAC1
(12-Bit)
DAC0
(12-Bit)
SENSOR
Circuitry
TEMP
Boundary Scan
Debug HW
WDT
PLL
Prog
Gain
Reset
System
Clock
ADC
100ksps
(10-Bit)
8
0
5
1
C
o
r
e
SFR Bus
256 byte
RAM
8kbyte
XRAM
External Data
Memory Bus
128kbyte
FLASH
64x4 byte
cache
Port I/O
Config.
UART0
UART1
SMBus
SPI Bus
PCA
Timers 0,
1, 2, 4
Timer 3/
RTC
P0, P1,
P2, P3
Latches
Crossbar
Config.
Bus Control
Address Bus
Data Bus
ADC
500ksps
(8-Bit)
C
T
L
A
d
d
r
D
a
t
a
C
R
O
S
S
B
A
R
P4 Latch
P5 Latch
P6 Latch
P7 Latch
AV+
VREFA
P0
Drv
P1
Drv
P2
Drv
P3
Drv
A
8:1
M
Prog
Gain
U
X
P4
DRV
P5
DRV
P6
DRV
P7
DRV
P0.0
P0.7
P1.0/AIN2.0
P1.7/AIN2.7
P2.0
P2.7
P3.0
P3.7
24 Rev. 1.2
Page 25
C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
1.1. CIP-51™ Microcontroller Core
1.1.1. Fully 8051 Compatible
The C8051F12x family utilizes Silicon Labs’ proprietary CIP-51 microcontroller core. The CIP-51 is fully compatible with the MCS-51™ instruction set; standard 803x/805x assemblers and compilers can be used to develop software. The core has all the peripherals included with a standard 8052, including five 16-bit counter/timers, two fullduplex UARTs, 256 bytes of internal RAM, 128 byte Special Function Register (SFR) address space, and 8/4 bytewide I/O Ports.
1.1.2. Improved Throughput
The CIP-51 employs a pipelined architecture that greatly increases its instruction throughput over the standard 8051
architecture. In a standard 8051, all instructions except for MUL and DIV take 12 or 24 system clock cycles to execute with a maximum system clock of 12-to-24 MHz. By contrast, the CIP-51 core executes 70% of its instructions in
one or two system clock cycles, with only four instructions taking more than four system clock cycles.
The CIP-51 has a total of 109 instructions. The table below shows the total number of instructions that require each
execution time.
Clocks to Execute 1 2 2/3 3 3/4 4 4/5 5 8
Number of Instructions 26 50 5 14 7 3 1 2 1
With the CIP-51's maximum system clock at 100 MHz, the C8051F120/1/2/3 have a peak throughput of 100 MIPS
(the C8051F124/5/6/7 have a peak throughput of 50 MIPS).
Rev. 1.2 25
Page 26
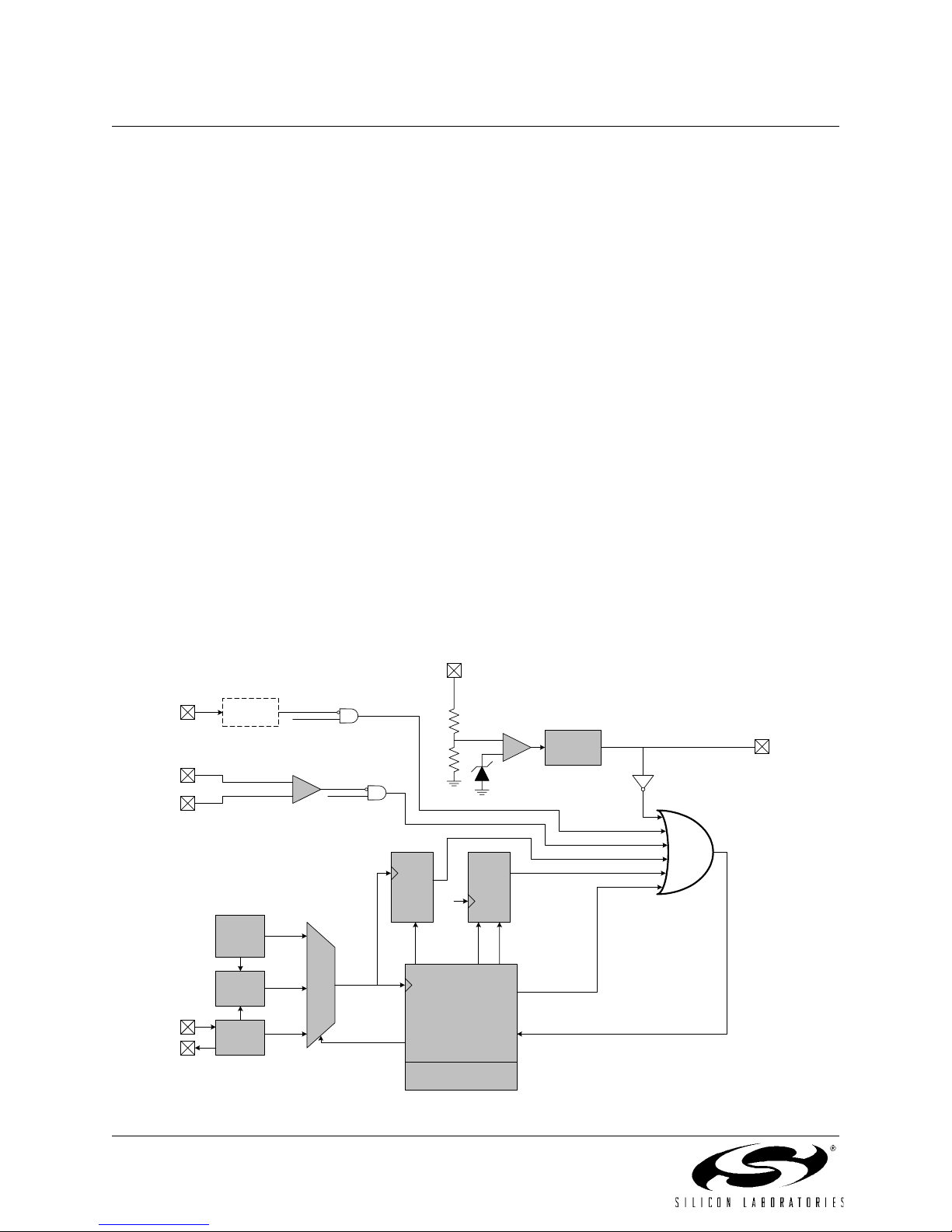
C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
1.1.3. Additional Features
The C8051F12x MCU family includes several key enhancements to the CIP-51 core and peripherals to improve overall performance and ease of use in end applications.
The extended interrupt handler provides 20 interrupt sources into the CIP-51 (as opposed to 7 for the standard 8051),
allowing the numerous analog and digital peripherals to interrupt the controller. An interrupt driven system requires
less intervention by the MCU, giving it more effective throughput. The extra interrupt sources are very useful when
building multi-tasking, real-time systems.
There are up to seven reset sources for the MCU: an on-board VDD monitor, a Watchdog Timer, a missing clock
detector, a voltage level detection from Comparator0, a forced software reset, the CNVSTR0 input pin, and the /RST
pin. The /RST pin is bi-directional, accommodating an external reset, or allowing the internally generated POR to be
output on the /RST pin. Each reset source except for the VDD monitor and Reset Input pin may be disabled by the
user in software; the VDD monitor is enabled/disabled via the MONEN pin. The Watchdog Timer may be permanently enabled in software after a power-on reset during MCU initialization.
The MCU has an internal, stand alone clock generator which is used by default as the system clock after any reset. If
desired, the clock source may be switched on the fly to the external oscillator, which can use a crystal, ceramic resonator, capacitor, RC, or external clock source to generate the system clock. This can be extremely useful in low power
applications, allowing the MCU to run from a slow (power saving) external crystal source, while periodically switching to the 24.5 MHz internal oscillator as needed. Additionally, an on-chip PLL is provided to achieve higher system
clock speeds for increased throughput.
(Port
I/O)
CP0+
CP0-
XTAL1
XTAL2
Crossbar
Internal
Clock
Generator
PLL
Circuitry
OSC
Figure 1.5. On-Board Clock and Reset
CNVSTR
(CNVSTR
reset
enable)
Comparator0
+
-
(CP0
reset
enable)
System
Clock
Clock Select
VDD
Missing
Clock
Detector
(one-
shot)
EN
MCD
WDT
Enable
CIP-51
Microcontroller
Core
Extended Interrupt
Handler
WDT
EN
Enable
Supply
Monitor
+
-
PRE
WDT
Supply
Reset
Timeout
Strobe
Software Reset
System Reset
(wired-OR)
Reset
Funnel
/RST
26 Rev. 1.2
Page 27

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
1.2. On-Chip Memory
The CIP-51 has a standard 8051 program and data address configuration. It includes 256 bytes of data RAM, with the
upper 128 bytes dual-mapped. Indirect addressing accesses the upper 128 bytes of general purpose RAM, and direct
addressing accesses the 128 byte SFR address space. The lower 128 bytes of RAM are accessible via direct and indirect addressing. The first 32 bytes are addressable as four banks of general purpose registers, and the next 16 bytes
can be byte addressable or bit addressable.
The CIP-51 in the C8051F12x MCUs additionally has an on-chip 8k byte RAM block and an external memory interface (EMIF) for accessing off-chip data memory. The on-chip 8k byte block can be addressed over the entire 64k
external data memory address range (overlapping 8k boundaries). External data memory address space can be
mapped to on-chip memory only, off-chip memory only, or a combination of the two (addresses up to 8k directed to
on-chip, above 8k directed to EMIF). The EMIF is also configurable for multiplexed or non-multiplexed address/data
lines.
The MCU’s program memory consists of 128k bytes of banked FLASH memory. This memory may be reprogrammed in-system in 1024 byte sectors, and requires no special off-chip programming voltage. The 1024 bytes from
addresses 0x1FC00 to 0x1FFFF are reserved. There are also two 128 byte sectors at addresses 0x20000 to 0x200FF,
which may be used by software. See Figure 1.6 for the MCU system memory map.
PROGRAM/DATA MEMORY
(FLASH)
0x200FF
0x20000
0x1FFFF
0x1FC00
0x1FBFF
0x00000
Scrachpad Memory
(DATA only)
RESERVED
FLASH
(In-System
Programmable in 1024
Byte Sectors)
Figure 1.6. On-Chip Memory Map
DATA MEMORY (RAM)
INTERNAL DATA ADDRESS SPACE
0xFF
0x80
0x7F
0x30
0x2F
0x20
0x1F
0x00
0xFFFF
Upper 128 RAM
(Indirect Addressing
Only)
(Direct and Indirect
Addressing)
Bit Addressable
General Purpose
Registers
Special Function
(Direct Addressing Only)
Lower 128 RAM
(Direct and Indirect
Addressing)
EXTERNAL DATA ADDRESS SPACE
Off-chip XRAM space
Registers
0
1
2
3
Up To
256 SFR Pages
0x2000
0x1FFF
0x0000
XRAM - 8192 Bytes
(accessable using MOVX
instruction)
Rev. 1.2 27
Page 28
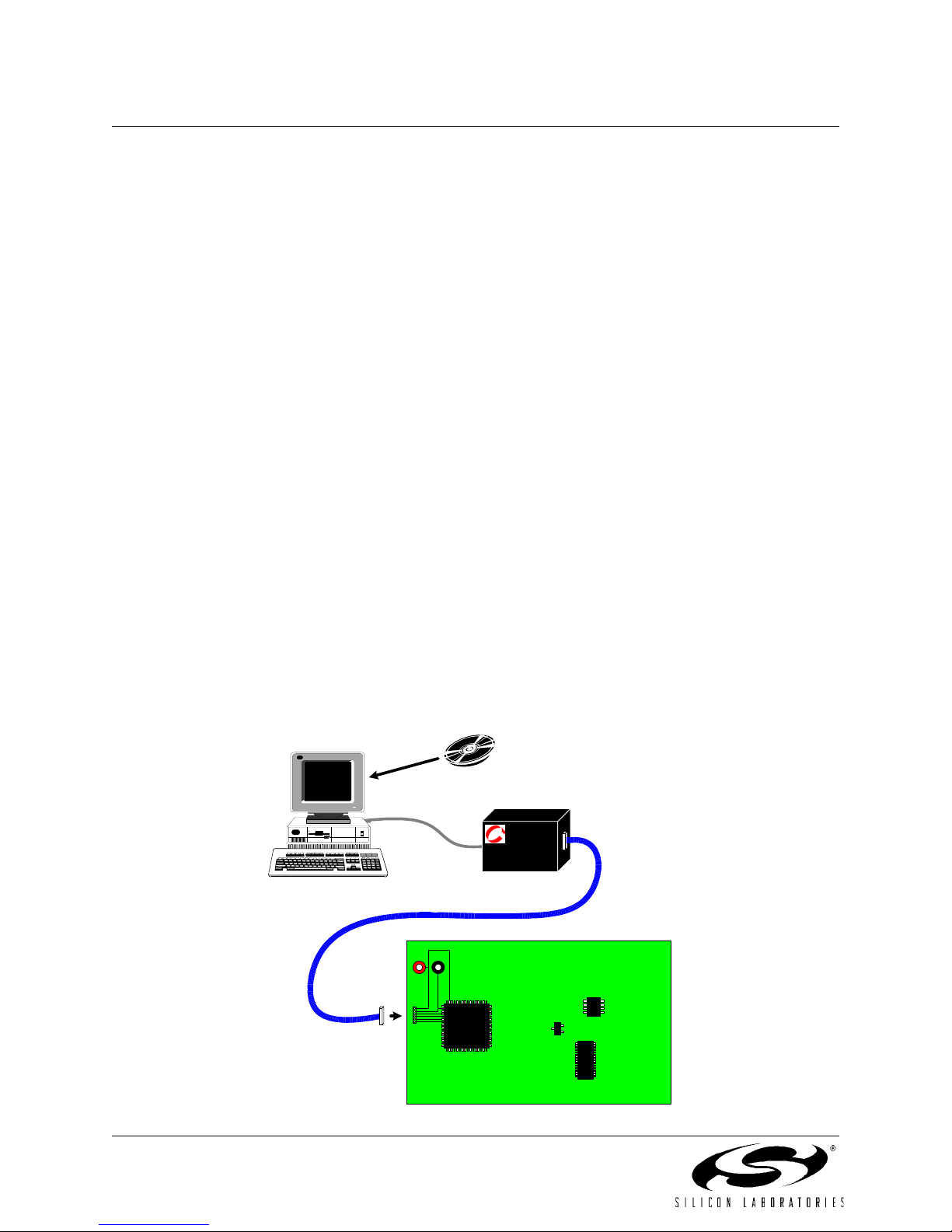
C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
1.3. JTAG Debug and Boundary Scan
The C8051F12x device family has on-chip JTAG boundary scan and debug circuitry that provides non-intrusive, full
speed, in-circuit debugging using the production part installed in the end application, via the four-pin JTAG inter-
face. The JTAG port is fully compliant to IEEE 1149.1, providing full boundary scan for test and manufacturing purposes.
Silicon Labs' debugging system supports inspection and modification of memory and registers, breakpoints, watchpoints, a stack monitor, and single stepping. No additional target RAM, program memory, timers, or communications
channels are required. All the digital and analog peripherals are functional and work correctly while debugging. All
the peripherals (except for the ADC and SMBus) are stalled when the MCU is halted, during single stepping, or at a
breakpoint in order to keep them synchronized.
The C8051F120DK development kit provides all the hardware and software necessary to develop application code
and perform in-circuit debugging with the C8051F12x MCUs. The kit includes software with a developer's studio and
debugger, an integrated 8051 assembler, and an RS-232 to JTAG serial adapter. It also has a target application board
with the associated MCU installed, plus the RS-232 and JTAG cables, and wall-mount power supply. The Development Kit requires a Windows 95/98/NT/ME computer with one available RS-232 serial port. As shown in Figure 1.7,
the PC is connected via RS-232 to the Serial Adapter. A six-inch ribbon cable connects the Serial Adapter to the
user's application board, picking up the four JTAG pins and VDD and GND. The Serial Adapter takes its power from
the application board. For applications where there is not sufficient power available from the target system, the provided power supply can be connected directly to the Serial Adapter.
Silicon Labs’ debug environment is a vastly superior configuration for developing and debugging embedded applications compared to standard MCU emulators, which use on-board "ICE Chips" and target cables and require the MCU
in the application board to be socketed. Silicon Labs' debug environment both increases ease of use and preserves the
performance of the precision analog peripherals.
Figure 1.7. Development/In-System Debug Diagram
CYGNAL Integrated
Development Environment
WINDOWS 95/98 /NT/ME/2000
RS-232
Serial
Adapter
JTAG (x4), VDD, GND
C8051
F12x
TARGET PCB
VDD GND
28 Rev. 1.2
Page 29
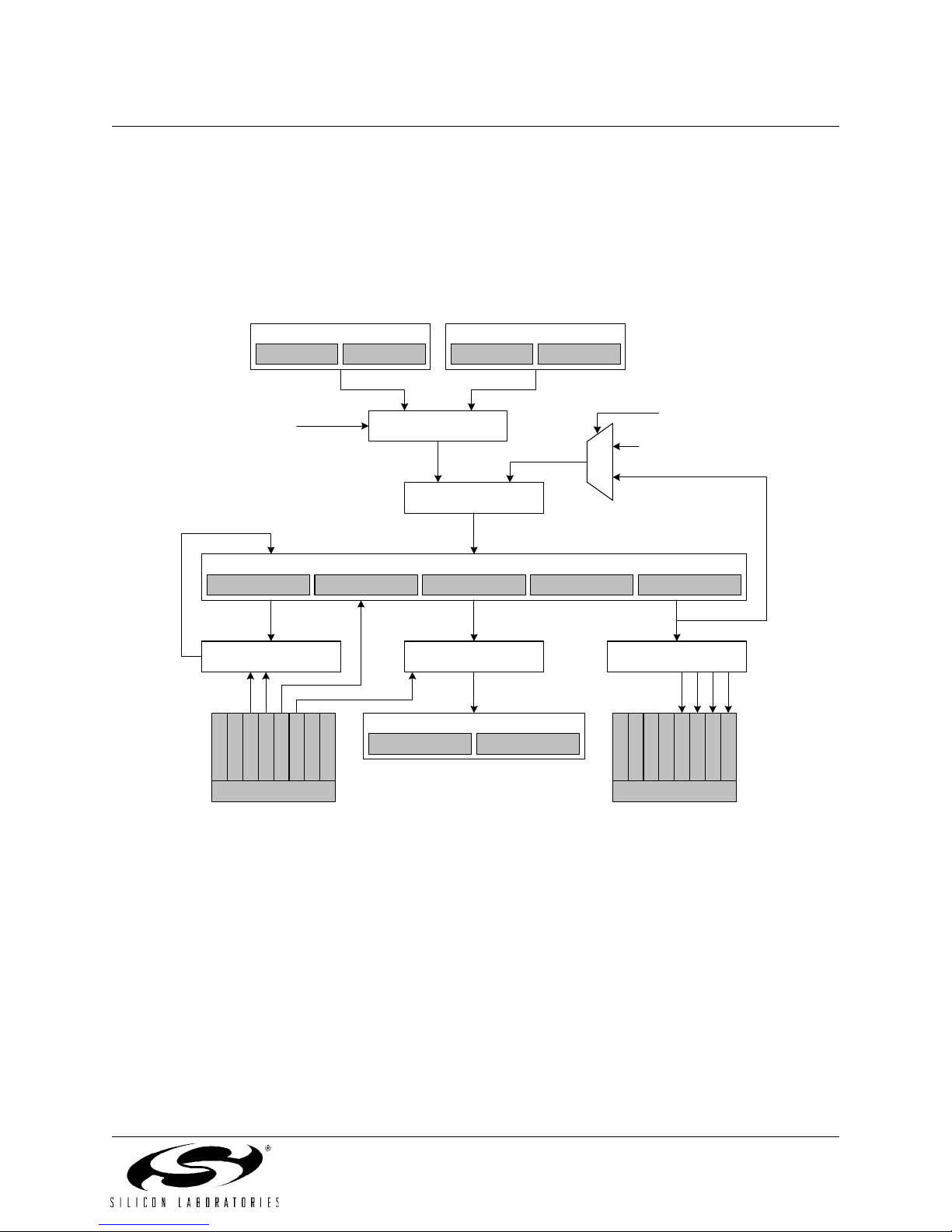
C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
1.4. 16 x 16 MAC (Multiply and Accumulate) Engine
The C8051F120/1/2/3 devices include a multiply and accumulate engine which can be used to speed up many mathematical operations. MAC0 contains a 16-by-16 bit multiplier and a 40-bit adder, which can perform integer or fractional multiply-accumulate and multiply operations on signed input values in two SYSCLK cycles. A rounding
engine provides a rounded 16-bit fractional result after an additional (third) SYSCLK cycle. MAC0 also contains a 1bit arithmetic shifter that will left or right-shift the contents of the 40-bit accumulator in a single SYSCLK cycle.
Figure 1.8. MAC0 Block Diagram
MAC0 A Register
MAC0AH MAC0AL
MAC0FM
16 x 16 Multiply
MAC0 B Register
MAC0BH MAC0BL
MAC0MS
1
0
0
40 bit Add
MAC0 Accumulator
MAC0OVR MAC0ACC3 MAC0ACC2 MAC0ACC1 MAC0ACC0
Rounding Engine1 bit Shift
Flag Logic
MAC0 Rounding Register
MAC0RNDH MAC0RNDL
MAC0MS
MAC0FM
MAC0SAT
MAC0CA
MAC0SD
MAC0SC
MAC0CF
MAC0STA
MAC0HO
MAC0SO
MAC0Z
MAC0N
Rev. 1.2 29
Page 30
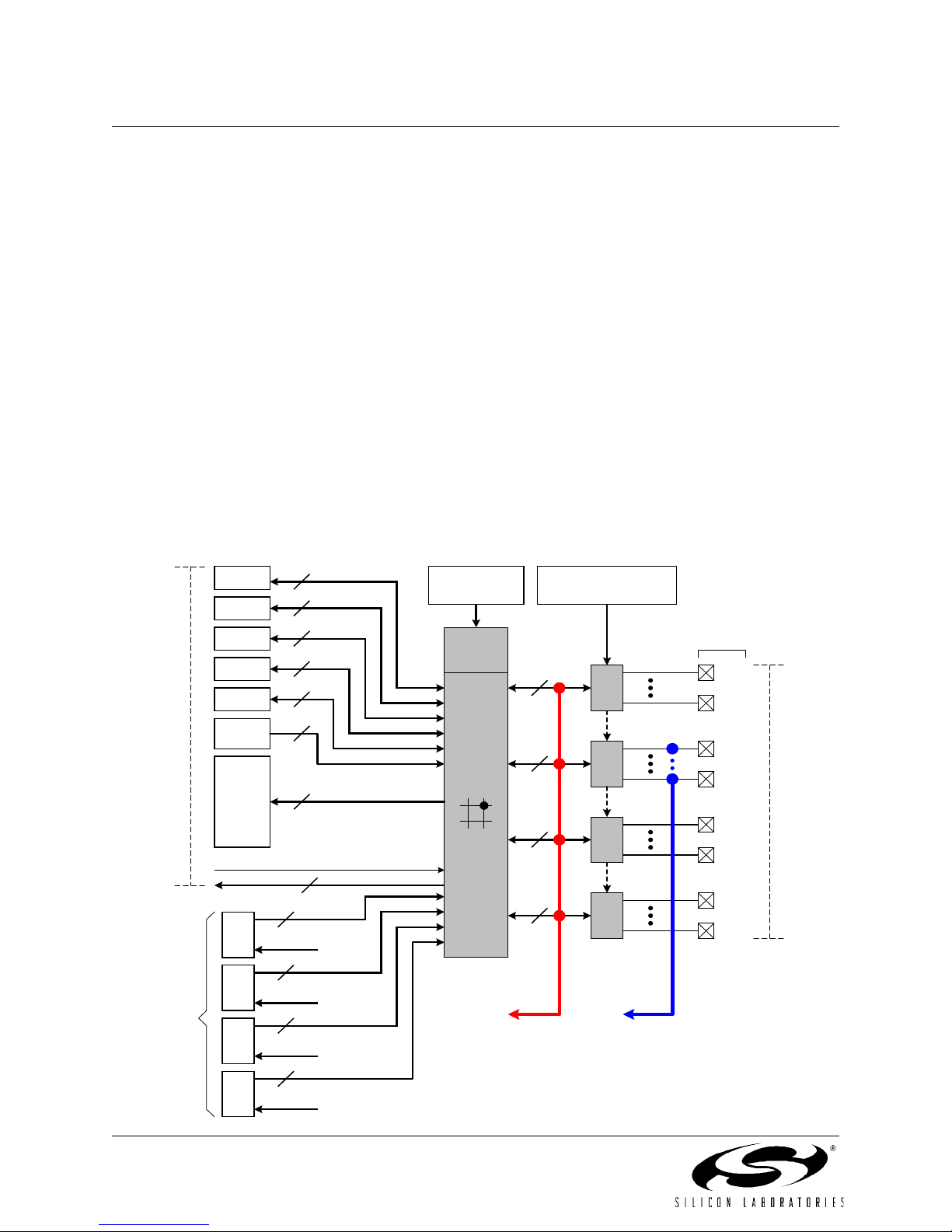
C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
1.5. Programmable Digital I/O and Crossbar
The standard 8051 Ports (0, 1, 2, and 3) are available on the MCUs. The C8051F120/2/4/6 have 4 additional ports (4,
5, 6, and 7) for a total of 64 general-purpose port I/O. The Port I/O behave like the standard 8051 with a few enhancements.
Each Port I/O pin can be configured as either a push-pull or open-drain output. Also, the "weak pull-ups" which are
normally fixed on an 8051 can be globally disabled, providing additional power saving capabilities for low-power
applications.
Perhaps the most unique enhancement is the Digital Crossbar. This is a large digital switching network that allows
mapping of internal digital system resources to Port I/O pins on P0, P1, P2, and P3. (See Figure 1.9) Unlike microcontrollers with standard multiplexed digital I/O, all combinations of functions are supported.
The on-chip counter/timers, serial buses, HW interrupts, ADC Start of Conversion inputs, comparator outputs, and
other digital signals in the controller can be configured to appear on the Port I/O pins specified in the Crossbar Control registers. This allows the user to select the exact mix of general purpose Port I/O and digital resources needed for
the particular application.
Highest
Priority
Lowest
Priority
Port
Latches
UART0
SPI
SMBus
UART1
PCA
Comptr.
Outputs
(Internal Digital Signals)
T0, T1,
T2, T2EX,
T4,T4EX
/INT0,
/INT1
/SYSCLK divided by 1,2,4, or 8
CNVSTR0/2
8
P0
(P0.0-P0.7)
8
P1
(P1.0-P1.7)
8
P2
(P2.0-P2.7)
8
P3
(P3.0-P3.7)
Figure 1.9. Digital Crossbar Diagram
2
4
2
2
7
2
XBR0, XBR1,
XBR2, P1MDIN
Registers
Priority
Decoder
Digital
Crossbar
8
2
To External
Memory
Interface
(EMIF)
P0MDOUT, P1MDOUT,
8
8
8
8
P2MDOUT, P3MDOUT
Registers
P0
I/O
Cells
P1
I/O
Cells
P2
I/O
Cells
P3
I/O
Cells
To
ADC2
Input
External
Pins
P0.0
P0.7
P1.0
P1.7
P2.0
P2.7
P3.0
P3.7
Highest
Priority
Lowest
Priority
30 Rev. 1.2
Page 31

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
1.6. Programmable Counter Array
The C8051F12x MCU family includes an on-board Programmable Counter/Timer Array (PCA) in addition to the five
16-bit general purpose counter/timers. The PCA consists of a dedicated 16-bit counter/timer time base with 6 programmable capture/compare modules. The timebase is clocked from one of six sources: the system clock divided by
12, the system clock divided by 4, Timer 0 overflow, an External Clock Input (ECI pin), the system clock, or the
external oscillator source divided by 8.
Each capture/compare module can be configured to operate in one of six modes: Edge-Triggered Capture, Software
Timer, High Speed Output, Frequency Output, 8-Bit Pulse Width Modulator, or 16-Bit Pulse Width Modulator. The
PCA Capture/Compare Module I/O and External Clock Input are routed to the MCU Port I/O via the Digital Crossbar.
Figure 1.10. PCA Block Diagram
SYSCLK/12
SYSCLK/4
Timer 0 Overflow
ECI
SYSCLK
External Clock/8
PCA
CLOCK
MUX
16-Bit Counter/Timer
ECI
Capture/Compare
Module 0
CEX0
Capture/Compare
Module 1
CEX1
Capture/Compare
Module 2
CEX2
Crossbar
Port I/O
Capture/Compare
Module 3
CEX3
Capture/Compare
Module 4
CEX4
Capture/Compare
Module 5
CEX5
Rev. 1.2 31
Page 32

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
1.7. Serial Ports
The C8051F12x MCU Family includes two Enhanced Full-Duplex UARTs, SPI Bus, and SMBus/I2C. Each of the
serial buses is fully implemented in hardware and makes extensive use of the CIP-51's interrupts, thus requiring very
little intervention by the CPU. The serial buses do not "share" resources such as timers, interrupts, or Port I/O, so any
or all of the serial buses may be used together with any other.
32 Rev. 1.2
Page 33

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
1.8. 12-Bit Analog to Digital Converter
The C8051F120/1/4/5 have an on-chip 12-bit SAR ADC (ADC0) with a 9-channel input multiplexer and programmable gain amplifier. With a maximum throughput of 100 ksps, the ADC offers true 12-bit linearity with an INL of
±1LSB. C8051F122/3/6/7 devices include a 10-bit SAR ADC with similar specifications and configuration options.
The ADC0 voltage reference is selected between the DAC0 output and an external VREF pin. On C8051F120/2/4/6
devices, ADC0 has its own dedicated VREF0 input pin; on C8051F121/3/5/7 devices, the ADC0 shares the VREFA
input pin with the 8-bit ADC2. The on-chip 15 ppm/°C voltage reference may generate the voltage reference for other
system components or the on-chip ADCs via the VREF output pin.
The ADC is under full control of the CIP-51 microcontroller via its associated Special Function Registers. One input
channel is tied to an internal temperature sensor, while the other eight channels are available externally. Each pair of
the eight external input channels can be configured as either two single-ended inputs or a single differential input.
The system controller can also put the ADC into shutdown mode to save power.
A programmable gain amplifier follows the analog multiplexer. The gain can be set in software from 0.5 to 16 in
powers of 2. The gain stage can be especially useful when different ADC input channels have widely varied input
voltage signals, or when it is necessary to "zoom in" on a signal with a large DC offset (in differential mode, a DAC
could be used to provide the DC offset).
Conversions can be started in four ways; a software command, an overflow of Timer 2, an overflow of Timer 3, or an
external signal input. This flexibility allows the start of conversion to be triggered by software events, external HW
signals, or a periodic timer overflow signal. Conversion completions are indicated by a status bit and an interrupt (if
enabled). The resulting 10 or 12-bit data word is latched into two SFRs upon completion of a conversion. The data
can be right or left justified in these registers under software control.
Window Compare registers for the ADC data can be configured to interrupt the controller when ADC data is within
or outside of a specified range. The ADC can monitor a key voltage continuously in background mode, but not interrupt the controller unless the converted data is within the specified window.
Figure 1.11. 12-Bit ADC Block Diagram
AIN0.0
AIN0.1
AIN0.2
AIN0.3
AIN0.4
AIN0.5
AIN0.6
AIN0.7
Analog Multiplexer
TEMP
SENSOR
AGND
+
-
+
-
+
-
+
-
9-to-1
AMUX
(SE or
DIFF)
Configuration, Control, and Data
Programmable Gain
Amplifi er
AV+
+
X
-
External VREF
DAC0 Output
Registers
Pin
12-Bit
SAR
ADC
VREF
Start
Conversion
Window Compare
Logic
12
Write to AD0BUSY
Timer 3 Overflow
CNVSTR0
Timer 2 Overflow
Compare
ADC Data
Registers
Conversion
Complete
Window
Interrupt
Interrupt
Rev. 1.2 33
Page 34

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
1.9. 8-Bit Analog to Digital Converter
The C8051F12x Family have an on-board 8-bit SAR ADC (ADC2) with an 8-channel input multiplexer and programmable gain amplifier. This ADC features a 500 ksps maximum throughput and true 8-bit linearity with an INL of
±1LSB. Eight input pins are available for measurement. The ADC is under full control of the CIP-51 microcontroller
via the Special Function Registers. The ADC2 voltage reference is selected between the analog power supply (AV+)
and an external VREF pin. On C8051F120/2/4/6 devices, ADC2 has its own dedicated VREF2 input pin; on
C8051F121/3/5/7 devices, ADC2 shares the VREFA input pin with the 12/10-bit ADC0. User software may put
ADC2 into shutdown mode to save power.
A programmable gain amplifier follows the analog multiplexer. The gain stage can be especially useful when different ADC input channels have widely varied input voltage signals, or when it is necessary to "zoom in" on a signal
with a large DC offset (in differential mode, a DAC could be used to provide the DC offset). The PGA gain can be set
in software to 0.5, 1, 2, or 4.
A flexible conversion scheduling system allows ADC2 conversions to be initiated by software commands, timer
overflows, or an external input signal. ADC2 conversions may also be synchronized with ADC0 software-commanded conversions. Conversion completions are indicated by a status bit and an interrupt (if enabled), and the
resulting 8-bit data word is latched into an SFR upon completion.
AIN2.0
AIN2.1
AIN2.2
AIN2.3
AIN2.4
AIN2.5
AIN2.6
AIN2.7
Analog Multiplexer
8-to-1
AMUX
Figure 1.12. 8-Bit ADC Diagram
Configuration, Control, and Data Registers
Programmable Gain
Amplifier
X
AV+
+
-
8-Bit
SAR
ADC
External VREF
Pin
AV+
VREF
Start Conversion
8
Window
Compare
Logic
Window
Compare
Interrupt
ADC Data
Register
Conversion
Complete
Interrupt
Write to AD2BUSY
Timer 3 Overflow
CNVSTR2 Input
Timer 2 Overflow
Write to AD0BUSY
(synchronized with
ADC0)
34 Rev. 1.2
Page 35

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
1.10. Comparators and DACs
Each C8051F12x MCU has two 12-bit DACs and two comparators on chip. The MCU data and control interface to
each comparator and DAC is via the Special Function Registers. The MCU can place any DAC or comparator in low
power shutdown mode.
The comparators have software programmable hysteresis and response time. The response time of the comparators
can be adjusted to minimize power consumption, or to maximize speed. Each comparator can generate an interrupt on
its rising edge, falling edge, or both; these interrupts are capable of waking up the MCU from sleep mode. The comparators' output state can also be polled in software. The comparator outputs can be programmed to appear on the Port
I/O pins via the Crossbar.
The DACs are voltage output mode, and include a flexible output scheduling mechanism. This scheduling mechanism allows DAC output updates to be forced by a software write or a Timer 2, 3, or 4 overflow. The DAC voltage
reference is supplied via the dedicated VREFD input pin on C8051F120/2/4/6 devices or via the internal voltage reference on C8051F121/3/5/7 devices. The DACs are useful as references for the comparators or offsets for the differential inputs of the ADC.
(Port I/O)
(Port I/O)
CP0+
CP0-
CP1+
CP1-
DAC0
Figure 1.13. Comparator and DAC Diagram
CP0
CP1
+
CP0
-
+
CP1
-
REF
DAC0
REF
CROSSBAR
CP0
CP1
SFR's
(Data
and
Cntrl)
CIP-51
and
Interrupt
Handler
DAC1
DAC1
Rev. 1.2 35
Page 36

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
2. ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Table 2.1. Absolute Maximum Ratings
PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
Ambient temperature under bias -55 125 °C
Storage Temperature -65 150 °C
Voltage on any Pin (except VDD and Port I/O) with
respect to DGND
Voltage on any Port I/O Pin or /RST with respect to
DGND
Voltage on VDD with respect to DGND -0.3 4.2 V
Maximum Total current through VDD, AV+, DGND,
and AGND
Maximum output current sunk by any Port pin 100 mA
Maximum output current sunk by any other I/O pin 50 mA
Maximum output current sourced by any Port pin 100 mA
Maximum output current sourced by any other I/O pin 50 mA
*
Stresses above those listed under “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. This
is a stress rating only and functional operation of the devices at those or any other conditions above those indicated
in the operation listings of this specification is not implied. Exposure to maximum rating conditions for extended
periods may affect device reliability.
*
-0.3 VDD +
0.3
-0.3 5.8 V
800 mA
V
36 Rev. 1.2
Page 37

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
3. GLOBAL DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Table 3.1. Global DC Electrical Characteristics (C8051F120/1/2/3)
-40°C TO +85°C, 100 MHZ SYSTEM CLOCK UNLESS OTHERWISE SPECIFIED.
PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
Analog Supply Voltage (Note 1) SYSCLK = 0 to 50 MHz
SYSCLK > 50 MHz
Analog Supply Current Internal REF, ADC, DAC, Compar-
ators all active
Analog Supply Current with
analog sub-systems inactive
Analog-to-Digital Supply Delta
(|VDD - AV+|)
Digital Supply Voltage SYSCLK = 0 to 50 MHz
Digital Supply Current with
CPU active
Digital Supply Current with
CPU inactive (not accessing
FLASH)
Digital Supply Current (shutdown)
Internal REF, ADC, DAC, Comparators all disabled, oscillator disabled
SYSCLK > 50 MHz
VDD=3.0 V, Clock=100 MHz
VDD=2.7 V, Clock=50 MHz
VDD=2.7 V, Clock=1 MHz
VDD=2.7 V, Clock=32 kHz
VDD=3.0 V, Clock=100 MHz
VDD=2.7 V, Clock=50 MHz
VDD=2.7 V, Clock=1 MHz
VDD=2.7 V, Clock=32 kHz
Oscillator not running TBD µA
2.7
3.0
2.7
3.0
3.0
3.3
1.7 TBD mA
0.2 TBD µA
3.0
3.3
TBD
25
0.6
16
TBD
TBD
TBD
TBD
3.6
3.6
0.5 V
3.6
3.6
V
V
V
V
mA
mA
mA
µA
mA
mA
mA
µA
Digital Supply RAM Data
Retention Voltage
SYSCLK (System Clock)
(Notes 2 and 3)
Specified Operating Temperature Range
Note 1: Analog Supply AV+ must be greater than 1 V for VDD monitor to operate.
Note 2: SYSCLK is the internal device clock. For operational speeds in excess of 25 MHz, SYSCLK must be
derived from the Phase-Locked Loop (PLL).
Note 3: SYSCLK must be at least 32 kHz to enable debugging.
VDD, AV+ = 2.7 V to 3.6 V
VDD, AV+ = 3.0 V to 3.6 V
Rev. 1.2 37
0
0
-40 +85 °C
1.5 V
50
100
MHz
MHz
Page 38

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
Table 3.2. Global DC Electrical Characteristics (C8051F124/5/6/7)
-40°C TO +85°C, 50 MHZ SYSTEM CLOCK UNLESS OTHERWISE SPECIFIED.
PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
Analog Supply Voltage (Note 1) 2.7 3.0 3.6 V
Analog Supply Current Internal REF, ADC, DAC, Compar-
ators all active
Analog Supply Current with
analog sub-systems inactive
Analog-to-Digital Supply Delta
(|VDD - AV+|)
Digital Supply Voltage 2.7 3.0 3.6 V
Digital Supply Current with
CPU active
Digital Supply Current with
CPU inactive (not accessing
FLASH)
Digital Supply Current (shutdown)
Digital Supply RAM Data
Retention Voltage
SYSCLK (System Clock)
(Notes 2 and 3)
Internal REF, ADC, DAC, Comparators all disabled, oscillator disabled
VDD=2.7 V, Clock=50 MHz
VDD=2.7 V, Clock=1 MHz
VDD=2.7 V, Clock=32 kHz
VDD=2.7 V, Clock=50 MHz
VDD=2.7 V, Clock=1 MHz
VDD=2.7 V, Clock=32 kHz
Oscillator not running 0.4 µA
050MHz
1.7 TBD mA
0.2 TBD µA
0.5 V
25
0.6
16
16
0.3
TBD
1.5 V
mA
mA
µA
mA
mA
µA
Specified Operating Temperature Range
Note 1: Analog Supply AV+ must be greater than 1 V for VDD monitor to operate.
Note 2: SYSCLK is the internal device clock. For operational speeds in excess of 25 MHz, SYSCLK must be
derived from the Phase-Locked Loop (PLL).
Note 3: SYSCLK must be at least 32 kHz to enable debugging.
38 Rev. 1.2
-40 +85 °C
Page 39

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
4. PINOUT AND PACKAGE DEFINITIONS
Table 4.1. Pin Definitions
Pin Numbers
Name
F120/
2/4/6
F121/
3/5/7
Type
Description
VDD 37, 64, 9024, 41,
57
DGND 38, 63, 8925, 40,
56
AV+ 11, 14 6 Analog Supply Voltage. Must be tied to +2.7 to +3.6 V.
AGND 10, 13 5 Analog Ground. Must be tied to Ground.
TMS 1 58 D In JTAG Test Mode Select with internal pull-up.
TCK 2 59 D In JTAG Test Clock with internal pull-up.
TDI 3 60 D In JTAG Test Data Input with internal pull-up. TDI is latched on the
TDO 4 61 D Out JTAG Test Data Output with internal pull-up. Data is shifted out on
/RST 5 62 D I/O Device Reset. Open-drain output of internal VDD monitor. Is driven
XTAL1 26 17 A In Crystal Input. This pin is the return for the internal oscillator circuit
Digital Supply Voltage. Must be tied to +2.7 to +3.6 V.
Digital Ground. Must be tied to Ground.
rising edge of TCK.
TDO on the falling edge of TCK. TDO output is a tri-state driver.
low when VDD is < V
can initiate a system reset by driving this pin low.
for a crystal or ceramic resonator. For a precision internal clock,
connect a crystal or ceramic resonator from XTAL1 to XTAL2. If
overdriven by an external CMOS clock, this becomes the system
clock.
and MONEN is high. An external source
RST
XTAL2 27 18 A Out Crystal Output. This pin is the excitation driver for a crystal or
MONEN 28 19 D In VDD Monitor Enable. When tied high, this pin enables the internal
VREF 12 7 A I/O Bandgap Voltage Reference Output (all devices).
VREFA 8 A In ADC0 and ADC2 Voltage Reference Input.
VREF0 16 A In ADC0 Voltage Reference Input.
VREF2 17 A In ADC2 Voltage Reference Input.
VREFD 15 A In DAC Voltage Reference Input.
ceramic resonator.
VDD monitor, which forces a system reset when VDD is < V
When tied low, the internal VDD monitor is disabled.
This pin must be tied high or low.
DAC Voltage Reference Input (C8051F121/3/5/7 only).
Rev. 1.2 39
RST
.
Page 40

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
Table 4.1. Pin Definitions
Pin Numbers
Name
AIN0.0 18 9 A In ADC0 Input Channel 0 (See ADC0 Specification for complete
AIN0.1 19 10 A In ADC0 Input Channel 1 (See ADC0 Specification for complete
AIN0.2 20 11 A In ADC0 Input Channel 2 (See ADC0 Specification for complete
AIN0.3 21 12 A In ADC0 Input Channel 3 (See ADC0 Specification for complete
AIN0.4 22 13 A In ADC0 Input Channel 4 (See ADC0 Specification for complete
F120/
2/4/6
F121/
3/5/7
description).
description).
description).
description).
description).
Type
Description
AIN0.5 23 14 A In ADC0 Input Channel 5 (See ADC0 Specification for complete
description).
AIN0.6 24 15 A In ADC0 Input Channel 6 (See ADC0 Specification for complete
description).
AIN0.7 25 16 A In ADC0 Input Channel 7 (See ADC0 Specification for complete
description).
CP0+ 9 4 A In Comparator 0 Non-Inverting Input.
CP0- 8 3 A In Comparator 0 Inverting Input.
CP1+ 7 2 A In Comparator 1 Non-Inverting Input.
CP1- 6 1 A In Comparator 1 Inverting Input.
DAC0 100 64 A Out Digital to Analog Converter 0 Voltage Output. (See DAC Specifica-
tion for complete description).
DAC1 99 63 A Out Digital to Analog Converter 1 Voltage Output. (See DAC Specifica-
tion for complete description).
P0.0 62 55 D I/O Port 0.0. See Port Input/Output section for complete description.
P0.1 61 54 D I/O Port 0.1. See Port Input/Output section for complete description.
P0.2 60 53 D I/O Port 0.2. See Port Input/Output section for complete description.
P0.3 59 52 D I/O Port 0.3. See Port Input/Output section for complete description.
P0.4 58 51 D I/O Port 0.4. See Port Input/Output section for complete description.
ALE/P0.5 57 50 D I/O ALE Strobe for External Memory Address bus (multiplexed mode)
40 Rev. 1.2
Port 0.5
See Port Input/Output section for complete description.
Page 41

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
Table 4.1. Pin Definitions
Pin Numbers
Name
/RD/P0.6 56 49 D I/O /RD Strobe for External Memory Address bus
/WR/P0.7 55 48 D I/O /WR Strobe for External Memory Address bus
F120/
2/4/6
F121/
3/5/7
Port 0.6
See Port Input/Output section for complete description.
Port 0.7
See Port Input/Output section for complete description.
Type
Description
AIN2.0/A8/P1.0 36 29 A In
D I/O
AIN2.1/A9/P1.1 35 28 A In
D I/O
AIN2.2/A10/P1.2 34 27 A In
D I/O
AIN2.3/A11/P1.3 33 26 A In
D I/O
AIN2.4/A12/P1.4 32 23 A In
D I/O
AIN2.5/A13/P1.5 31 22 A In
D I/O
AIN2.6/A14/P1.6 30 21 A In
D I/O
AIN2.7/A15/P1.7 29 20 A In
D I/O
ADC2 Input Channel 0 (See ADC2 Specification for complete
description).
Bit 8 External Memory Address bus (Non-multiplexed mode)
Port 1.0
See Port Input/Output section for complete description.
Port 1.1. See Port Input/Output section for complete description.
Port 1.2. See Port Input/Output section for complete description.
Port 1.3. See Port Input/Output section for complete description.
Port 1.4. See Port Input/Output section for complete description.
Port 1.5. See Port Input/Output section for complete description.
Port 1.6. See Port Input/Output section for complete description.
Port 1.7. See Port Input/Output section for complete description.
A8m/A0/P2.0 46 37 D I/O Bit 8 External Memory Address bus (Multiplexed mode)
A9m/A1/P2.1 45 36 D I/O Port 2.1. See Port Input/Output section for complete description.
A10m/A2/P2.2 44 35 D I/O Port 2.2. See Port Input/Output section for complete description.
A11m/A3/P2.3 43 34 D I/O Port 2.3. See Port Input/Output section for complete description.
A12m/A4/P2.4 42 33 D I/O Port 2.4. See Port Input/Output section for complete description.
A13m/A5/P2.5 41 32 D I/O Port 2.5. See Port Input/Output section for complete description.
A14m/A6/P2.6 40 31 D I/O Port 2.6. See Port Input/Output section for complete description.
Bit 0 External Memory Address bus (Non-multiplexed mode)
Port 2.0
See Port Input/Output section for complete description.
Rev. 1.2 41
Page 42

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
Table 4.1. Pin Definitions
Pin Numbers
Name
A15m/A7/P2.7 39 30 D I/O Port 2.7. See Port Input/Output section for complete description.
AD0/D0/P3.0 54 47 D I/O Bit 0 External Memory Address/Data bus (Multiplexed mode)
AD1/D1/P3.1 53 46 D I/O Port 3.1. See Port Input/Output section for complete description.
AD2/D2/P3.2 52 45 D I/O Port 3.2. See Port Input/Output section for complete description.
AD3/D3/P3.3 51 44 D I/O Port 3.3. See Port Input/Output section for complete description.
AD4/D4/P3.4 50 43 D I/O Port 3.4. See Port Input/Output section for complete description.
F120/
2/4/6
F121/
3/5/7
Bit 0 External Memory Data bus (Non-multiplexed mode)
Port 3.0
See Port Input/Output section for complete description.
Type
Description
AD5/D5/P3.5 49 42 D I/O Port 3.5. See Port Input/Output section for complete description.
AD6/D6/P3.6 48 39 D I/O Port 3.6. See Port Input/Output section for complete description.
AD7/D7/P3.7 47 38 D I/O Port 3.7. See Port Input/Output section for complete description.
P4.0 98 D I/O Port 4.0. See Port Input/Output section for complete description.
P4.1 97 D I/O Port 4.1. See Port Input/Output section for complete description.
P4.2 96 D I/O Port 4.2. See Port Input/Output section for complete description.
P4.3 95 D I/O Port 4.3. See Port Input/Output section for complete description.
P4.4 94 D I/O Port 4.4. See Port Input/Output section for complete description.
ALE/P4.5 93 D I/O ALE Strobe for External Memory Address bus (multiplexed mode)
Port 4.5
See Port Input/Output section for complete description.
/RD/P4.6 92 D I/O /RD Strobe for External Memory Address bus
Port 4.6
See Port Input/Output section for complete description.
/WR/P4.7 91 D I/O /WR Strobe for External Memory Address bus
Port 4.7
See Port Input/Output section for complete description.
A8/P5.0 88 D I/O Bit 8 External Memory Address bus (Non-multiplexed mode)
A9/P5.1 87 D I/O Port 5.1. See Port Input/Output section for complete description.
A10/P5.2 86 D I/O Port 5.2. See Port Input/Output section for complete description.
A11/P5.3 85 D I/O Port 5.3. See Port Input/Output section for complete description.
42 Rev. 1.2
Port 5.0
See Port Input/Output section for complete description.
Page 43

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
Table 4.1. Pin Definitions
Pin Numbers
Name
A12/P5.4 84 D I/O Port 5.4. See Port Input/Output section for complete description.
A13/P5.5 83 D I/O Port 5.5. See Port Input/Output section for complete description.
A14/P5.6 82 D I/O Port 5.6. See Port Input/Output section for complete description.
A15/P5.7 81 D I/O Port 5.7. See Port Input/Output section for complete description.
A8m/A0/P6.0 80 D I/O Bit 8 External Memory Address bus (Multiplexed mode)
A9m/A1/P6.1 79 D I/O Port 6.1. See Port Input/Output section for complete description.
F120/
2/4/6
F121/
3/5/7
Bit 0 External Memory Address bus (Non-multiplexed mode)
Port 6.0
See Port Input/Output section for complete description.
Type
Description
A10m/A2/P6.2 78 D I/O Port 6.2. See Port Input/Output section for complete description.
A11m/A3/P6.3 77 D I/O Port 6.3. See Port Input/Output section for complete description.
A12m/A4/P6.4 76 D I/O Port 6.4. See Port Input/Output section for complete description.
A13m/A5/P6.5 75 D I/O Port 6.5. See Port Input/Output section for complete description.
A14m/A6/P6.6 74 D I/O Port 6.6. See Port Input/Output section for complete description.
A15m/A7/P6.7 73 D I/O Port 6.7. See Port Input/Output section for complete description.
AD0/D0/P7.0 72 D I/O Bit 0 External Memory Address/Data bus (Multiplexed mode)
Bit 0 External Memory Data bus (Non-multiplexed mode)
Port 7.0
See Port Input/Output section for complete description.
AD1/D1/P7.1 71 D I/O Port 7.1. See Port Input/Output section for complete description.
AD2/D2/P7.2 70 D I/O Port 7.2. See Port Input/Output section for complete description.
AD3/D3/P7.3 69 D I/O Port 7.3. See Port Input/Output section for complete description.
AD4/D4/P7.4 68 D I/O Port 7.4. See Port Input/Output section for complete description.
AD5/D5/P7.5 67 D I/O Port 7.5. See Port Input/Output section for complete description.
AD6/D6/P7.6 66 D I/O Port 7.6. See Port Input/Output section for complete description.
AD7/D7/P7.7 65 D I/O Port 7.7. See Port Input/Output section for complete description.
Rev. 1.2 43
Page 44

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
Figure 4.1. TQFP-100 Pinout Diagram
DAC0
DAC1
P4.0
P4.1
P4.2
P4.3
P4.4
ALE/P4.5
/RD/P4.6
/WR/P4.7
VDD
DGND
A8/P5.0
A9/P5.1
A10/P5.2
A11/P5.3
A12/P5.4
A13/P5.5
A14/P5.6
A15/P5.7
A8m/A0/P6.0
A9m/A1/P6.1
A10m/A2/P6.2
A11m/A3/P6.3
A12m/A4/P6.4
TMS
TCK
TDI
TDO
/RST
CP1-
CP1+
CP0-
CP0+
AGND
AV+
VREF
AGND
AV+
VREFD
VREF0
VREF2
AIN0.0
AIN0.1
AIN0.2
AIN0.3
AIN0.4
AIN0.5
AIN0.6
AIN0.7
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
9998979695949392919089888786858483828180797877
100
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
C8051F120
C8051F122
C8051F124
C8051F126
76
75
A13m/A5/P6.5
74
A14m/A6/P6.6
73
A15m/A7/P6.7
72
AD0/D0/P7.0
71
AD1/D1/P7.1
70
AD2/D2/P7.2
69
AD3/D3/P7.3
68
AD4/D4/P7.4
67
AD5/D5/P7.5
66
AD6/D6/P7.6
65
AD7/D7/P7.7
64
VDD
63
DGND
62
P0.0
61
P0.1
60
P0.2
59
P0.3
58
P0.4
57
ALE/P0.5
56
/RD/P0.6
55
/WR/P0.7
54
AD0/D0/P3.0
53
AD1/D1/P3.1
52
AD2/D2/P3.2
51
AD3/D3/P3.3
262728293031323334353637383940
XTAL1
XTAL2
MONEN
AIN2.7/A15/P1.7
AIN2.6/A14/P1.6
44 Rev. 1.2
AIN2.5/A13/P1.5
AIN2.4/A12/P1.4
AIN2.3/A11/P1.3
AIN2.2/A10/P1.2
41
424344454647484950
VDD
DGND
AD7/D7/P3.7
AD6/D6/P3.6
AD5/D5/P3.5
A9m/A1/P2.1
A15m/A7/P2.7
A14m/A6/P2.6
A13m/A5/P2.5
A12m/A4/P2.4
AIN2.1/A9/P1.1
AIN2.0/A8/P1.0
A11m/A3/P2.3
A10m/A2/P2.2
A8m/A0/P2.0
AD4/D4/P3.4
Page 45

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
Figure 4.2. TQFP-100 Package Drawing
100
PIN 1
DESIGNATOR
D
D1
E1 E
1
A
A1
A2
b
D
D1
e
E
E1
MIN
(mm)
-
0.05
0.95
0.17
-
-
-
-
-
NOM
(mm)
-
-
1.00
0.22
16.00
14.00
0.50
16.00
14.00
MAX
(mm)
1.20
0.15
1.05
0.27
-
-
-
-
-
A2
e
A
b
Rev. 1.2 45
A1
Page 46

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
Figure 4.3. TQFP-64 Pinout Diagram
DAC0
DAC1
/RST
TDO
TDI
TCK
64
63
62
61
60
59
TMS
58
VDD
57
DGND
56
P0.0
55
P0.1
54
P0.2
53
P0.3
52
P0.4
51
ALE/P0.5
/RD/P0.6
50
49
CP1-
CP1+
CP0-
CP0+
AGND
AV+
VREF
VREFA
AIN0.0
AIN0.1
AIN0.2
AIN0.3
AIN0.4
AIN0.5
AIN0.6
AIN0.7
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
C8051F121
C8051F123
C8051F125
C8051F127
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
48
/WR/P0.7
47
AD0/D0/P3.0
46
AD1/D1/P3.1
45
AD2/D2/P3.2
44
AD3/D3/P3.3
43
AD4/D4/P3.4
42
AD5/D5/P3.5
41
VDD
40
DGND
39
AD6/D6/P3.6
38
AD7/D7/P3.7
37
A8m/A0/P2.0
36
A9m/A1/P2.1
35
A10m/A2/P2.2
34
A11m/A3/P2.3
33
A12m/A4/P2.4
XTAL1
XTAL2
46 Rev. 1.2
MONEN
AIN2.7/A15/P1.7
AIN2.6/A14/P1.6
AIN2.5/A13/P1.5
AIN2.4/A12/P1.4
VDD
DGND
A15m/A7/P2.7
A14m/A6/P2.6
AIN2.3/A11/P1.3
AIN2.1/A9/P1.1
AIN2.2/A10/P1.2
AIN2.0/A8/P1.0
A13m/A5/P2.5
Page 47

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
Figure 4.4. TQFP-64 Package Drawing
D
D1
64
PIN 1
DESIGNATOR
A2
MIN
(mm)
A
A1
0.05
E1
E
A2
b
0.95
0.17
D
D1
1
e
A
e
E
E1
b
A1
NOM
(mm)
-
0.22
-
12.00
-
10.00
-
0.50
-
12.00
-
10.00
MAX
(mm)
-
1.20
-
0.15
-
1.05
0.27
-
-
-
-
-
Rev. 1.2 47
Page 48

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
48 Rev. 1.2
Page 49

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
5. ADC0 (12-BIT ADC, C8051F120/1/4/5 ONLY)
The ADC0 subsystem for the C8051F120/1/4/5 consists of a 9-channel, configurable analog multiplexer (AMUX0), a
programmable gain amplifier (PGA0), and a 100 ksps, 12-bit successive-approximation-register ADC with integrated
track-and-hold and Programmable Window Detector (see block diagram in Figure 5.1). The AMUX0, PGA0, Data
Conversion Modes, and Window Detector are all configurable under software control via the Special Function Registers shown in Figure 5.1. The voltage reference used by ADC0 is selected as described in Section “9. VOLTAGE
REFERENCE (C8051F120/2/4/6)” on page 107 for C8051F120/2/4/6 devices, or Section “10. VOLTAGE REFERENCE (C8051F121/3/5/7)” on page 109 for C8051F121/3/5/7 devices. The ADC0 subsystem (ADC0, track-
and-hold and PGA0) is enabled only when the AD0EN bit in the ADC0 Control register (ADC0CN) is set to logic 1.
The ADC0 subsystem is in low power shutdown when this bit is logic 0.
Figure 5.1. 12-Bit ADC0 Functional Block Diagram
ADC0LTLADC0LTHADC0GTLADC0GTH
24
AIN0.0
AIN0.1
AIN0.2
AIN0.3
AIN0.4
AIN0.5
AIN0.6
AIN0.7
TEMP
SENSOR
AGND
+
-
+
-
+
-
+
-
9-to-1
AMUX
(SE or
DIFF)
X
+
-
AD0EN
AV+
AGND
AV+
12-Bit
SAR
ADC
SYSCLK
AD0CM
REF
12
Start Conversion
Comb.
Logic
12
ADC0L ADC0H
00
01
10
11
AD0WINT
AD0BUSY (W)
Timer 3 Overflow
CNVSTR0
Timer 2 Overflow
AIN01IC
AIN23IC
AIN45IC
AIN67IC
AMX0CF
5.1. Analog Multiplexer and PGA
Eight of the AMUX channels are available for external measurements while the ninth channel is internally connected
to an on-chip temperature sensor (temperature transfer function is shown in Figure 5.2). AMUX input pairs can be
programmed to operate in either differential or single-ended mode. This allows the user to select the best measurement technique for each input channel, and even accommodates mode changes "on-the-fly". The AMUX defaults to
all single-ended inputs upon reset. There are two registers associated with the AMUX: the Channel Selection register
AMX0SL (Figure 5.6), and the Configuration register AMX0CF (Figure 5.5). The table in Figure 5.6 shows AMUX
functionality by channel, for each possible configuration. The PGA amplifies the AMUX output signal by an amount
determined by the states of the AMP0GN2-0 bits in the ADC0 Configuration register, ADC0CF (Figure 5.7). The
PGA can be software-programmed for gains of 0.5, 2, 4, 8 or 16. Gain defaults to unity on reset.
AMX0AD3
AMX0SL
AMX0AD1
AMX0AD2
AMX0AD0
AD0SC4
AD0SC3
ADC0CF
AD0INT
AD0TM
AD0EN
ADC0CN
AD0BUSY
AD0LJST
AD0WINT
AD0CM0
AD0CM1
AD0CM
AMP0GN0
AMP0GN1
AMP0GN2
AD0SC0
AD0SC1
AD0SC2
Rev. 1.2 49
Page 50

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
The Temperature Sensor transfer function is shown in Figure 5.2. The output voltage (V
) is the PGA input when
TEMP
the Temperature Sensor is selected by bits AMX0AD3-0 in register AMX0SL; this voltage will be amplified by the
PGA according to the user-programmed PGA settings.
Figure 5.2. Typical Temperature Sensor Transfer Function
(Volts)
1.000
0.900
0.800
V
= 0.00286(TEMPC) + 0.776
0.700
0.600
0.500
0-50 50 100
TEMP
for PGA Gain = 1
(Celsius)
50 Rev. 1.2
Page 51

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
5.2. ADC Modes of Operation
ADC0 has a maximum conversion speed of 100 ksps. The ADC0 conversion clock is derived from the system clock
divided by the value held in the ADCSC bits of register ADC0CF.
5.2.1. Starting a Conversion
A conversion can be initiated in one of four ways, depending on the programmed states of the ADC0 Start of Conversion Mode bits (AD0CM1, AD0CM0) in ADC0CN. Conversions may be initiated by:
1. Writing a ‘1’ to the AD0BUSY bit of ADC0CN;
2. A Timer 3 overflow (i.e. timed continuous conversions);
3. A rising edge detected on the external ADC convert start signal, CNVSTR0;
4. A Timer 2 overflow (i.e. timed continuous conversions).
The AD0BUSY bit is set to logic 1 during conversion and restored to logic 0 when conversion is complete. The falling edge of AD0BUSY triggers an interrupt (when enabled) and sets the AD0INT interrupt flag (ADC0CN.5). Converted data is available in the ADC0 data word MSB and LSB registers, ADC0H, ADC0L. Converted data can be
either left or right justified in the ADC0H:ADC0L register pair (see example in Figure 5.11) depending on the programmed state of the AD0LJST bit in the ADC0CN register.
When initiating conversions by writing a ‘1’ to AD0BUSY, the AD0INT bit should be polled to determine when a
conversion has completed (ADC0 interrupts may also be used). The recommended polling procedure is shown below.
Step 1. Write a ‘0’ to AD0INT;
Step 2. Write a ‘1’ to AD0BUSY;
Step 3. Poll AD0INT for ‘1’;
Step 4. Process ADC0 data.
When CNVSTR0 is used as a conversion start source, it must be enabled in the crossbar, and the corresponding pin
must be set to open-drain, high-impedance mode (see Section “19. PORT INPUT/OUTPUT” on page 215 for more
details on Port I/O configuration).
Rev. 1.2 51
Page 52

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
5.2.2. Tracking Modes
The AD0TM bit in register ADC0CN controls the ADC0 track-and-hold mode. In its default state, the ADC0 input is
continuously tracked when a conversion is not in progress. When the AD0TM bit is logic 1, ADC0 operates in lowpower track-and-hold mode. In this mode, each conversion is preceded by a tracking period of 3 SAR clocks (after
the start-of-conversion signal). When the CNVSTR0 signal is used to initiate conversions in low-power tracking
mode, ADC0 tracks only when CNVSTR0 is low; conversion begins on the rising edge of CNVSTR0 (see
Figure 5.3). Tracking can also be disabled (shutdown) when the entire chip is in low power standby or sleep modes.
Low-power track-and-hold mode is also useful when AMUX or PGA settings are frequently changed, to ensure that
settling time requirements are met (see Section “5.2.3. Settling Time Requirements” on page 53).
Figure 5.3. ADC0 Track and Conversion Example Timing
A. ADC Timing for External Trigger Source
CNVSTR0
(AD0CM[1:0]=10)
12345678910111213141516
SAR Clocks
ADC0TM=1
ADC0TM=0
Timer 2, Timer 3 Overflow;
Write '1' to AD0BUSY
(AD0CM[1:0]=00, 01, 11)
SAR Clocks
ADC0TM=1
SAR Clocks
ADC0TM=0
Low Power
or Convert
Track Or Convert Convert Track
Track Convert Low Power Mode
B. ADC Timing for Internal Trigger Sources
1234567891011121314151617 18 19
Low Power
or Convert
Track or
Convert
Track Convert Low Power Mode
12345678910111213141516
Convert Track
52 Rev. 1.2
Page 53

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
5.2.3. Settling Time Requirements
When the ADC0 input configuration is changed (i.e., a different MUX or PGA selection is made), a minimum tracking time is required before an accurate conversion can be performed. This tracking time is determined by the ADC0
MUX resistance, the ADC0 sampling capacitance, any external source resistance, and the accuracy required for the
conversion. Figure 5.4 shows the equivalent ADC0 input circuits for both Differential and Single-ended modes.
Notice that the equivalent time constant for both input circuits is the same. The required settling time for a given settling accuracy (SA) may be approximated by Equation 5.1. When measuring the Temperature Sensor output, R
reduces to R
. An absolute minimum settling time of 1.5 µs is required after any MUX or PGA selection. Note
MUX
that in low-power tracking mode, three SAR clocks are used for tracking at the start of every conversion. For most
applications, these three SAR clocks will meet the tracking requirements.
Equation 5.1. ADC0 Settling Time Requirements
n
2
t
-------
×ln=
SA
R
TOTALCSAMPLE
TOTAL
Where:
SA is the settling accuracy, given as a fraction of an LSB (for example, 0.25 to settle within 1/4 LSB)
t is the required settling time in seconds
R
is the sum of the ADC0 MUX resistance and any external source resistance.
TOTAL
n is the ADC resolution in bits (12).
Figure 5.4. ADC0 Equivalent Input Circuits
AIN0.x
Differential Mode
MUX Select
R
= 5k
MUX
RC
= R
MUX
* C
SAMP LE
Input
C
SAMPLE
C
SAMPLE
= 10pF
= 10pF
Single-Ended Mode
MUX Select
AIN0.x
RC
Input
= R
MUX
R
* C
MUX
SAMPL E
= 5k
C
SAMPLE
= 10pF
AIN0.y
MUX Select
R
= 5k
MUX
Rev. 1.2 53
Page 54

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
Figure 5.5. AMX0CF: AMUX0 Configuration Register
SFR Page:
SFR Address:
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W Reset Value
Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0
Bits7-4: UNUSED. Read = 0000b; Write = don’t care.
Bit3: AIN67IC: AIN0.6, AIN0.7 Input Pair Configuration Bit.
Bit2: AIN45IC: AIN0.4, AIN0.5 Input Pair Configuration Bit.
Bit1: AIN23IC: AIN0.2, AIN0.3 Input Pair Configuration Bit.
Bit0: AIN01IC: AIN0.0, AIN0.1 Input Pair Configuration Bit.
NOTE: The ADC0 Data Word is in 2’s complement format for channels configured as differential.
0
0xBA
- - - - AIN67IC AIN45IC AIN23IC AIN01IC 00000000
0: AIN0.6 and AIN0.7 are independent single-ended inputs.
1: AIN0.6, AIN0.7 are (respectively) +, - differential input pair.
0: AIN0.4 and AIN0.5 are independent single-ended inputs.
1: AIN0.4, AIN0.5 are (respectively) +, - differential input pair.
0: AIN0.2 and AIN0.3 are independent single-ended inputs.
1: AIN0.2, AIN0.3 are (respectively) +, - differential input pair.
0: AIN0.0 and AIN0.1 are independent single-ended inputs.
1: AIN0.0, AIN0.1 are (respectively) +, - differential input pair.
54 Rev. 1.2
Page 55

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
Figure 5.6. AMX0SL: AMUX0 Channel Select Register
SFR Page:
SFR Address:
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W Reset Value
0
0xBB
- - - - AMX0AD3 AMX0AD2 AMX0AD1 AMX0AD0 00000000
Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0
Bits7-4: UNUSED. Read = 0000b; Write = don’t care.
Bits3-0: AMX0AD3-0: AMX0 Address Bits.
0000-1111b: ADC Inputs selected per chart below.
AMX0AD3-0
0000 0001 0010 0011 0100 0101 0110 0111 1xxx
0000
0001
0010
0011
0100
0101
0110
0111
1000
1001
AMX0CF Bits 3-0
1010
1011
1100
1101
1110
1111
AIN0.0 AIN0.1 AIN0.2 AIN0.3 AIN0.4 AIN0.5 AIN0.6 AIN0.7
+(AIN0.0)
-(AIN0.1)
AIN0.0 AIN0.1
+(AIN0.0)
-(AIN0.1)
AIN0.0 AIN0.1 AIN0.2 AIN0.3
+(AIN0.0)
-(AIN0.1)
AIN0.0 AIN0.1
+(AIN0.0)
-(AIN0.1)
AIN0.0 AIN0.1 AIN0.2 AIN0.3 AIN0.4 AIN0.5
+(AIN0.0)
-(AIN0.1)
AIN0.0 AIN0.1
+(AIN0.0)
-(AIN0.1)
AIN0.0 AIN0.1 AIN0.2 AIN0.3
+(AIN0.0)
-(AIN0.1)
AIN0.0 AIN0.1
+(AIN0.0)
-(AIN0.1)
AIN0.2 AIN0.3 AIN0.4 AIN0.5 AIN0.6 AIN0.7
+(AIN0.2)
-(AIN0.3)
+(AIN0.2)
-(AIN0.3)
AIN0.2 AIN0.3
+(AIN0.2)
-(AIN0.3)
+(AIN0.2)
-(AIN0.3)
AIN0.2 AIN0.3 AIN0.4 AIN0.5
+(AIN0.2)
-(AIN0.3)
+(AIN0.2)
-(AIN0.3)
AIN0.2 AIN0.3
+(AIN0.2)
-(AIN0.3)
+(AIN0.2)
-(AIN0.3)
AIN0.4 AIN0.5 AIN0.6 AIN0.7
AIN0.4 AIN0.5 AIN0.6 AIN0.7
+(AIN0.4)
-(AIN0.5)
+(AIN0.4)
-(AIN0.5)
+(AIN0.4)
-(AIN0.5)
+(AIN0.4)
-(AIN0.5)
AIN0.4 AIN0.5
AIN0.4 AIN0.5
+(AIN0.4)
-(AIN0.5)
+(AIN0.4)
-(AIN0.5)
+(AIN0.4)
-(AIN0.5)
+(AIN0.4)
-(AIN0.5)
AIN0.6 AIN0.7
AIN0.6 AIN0.7
AIN0.6 AIN0.7
AIN0.6 AIN0.7
+(AIN0.6)
-(AIN0.7)
+(AIN0.6)
-(AIN0.7)
+(AIN0.6)
-(AIN0.7)
+(AIN0.6)
-(AIN0.7)
+(AIN0.6)
-(AIN0.7)
+(AIN0.6)
-(AIN0.7)
+(AIN0.6)
-(AIN0.7)
+(AIN0.6)
-(AIN0.7)
TEMP
SENSOR
TEMP
SENSOR
TEMP
SENSOR
TEMP
SENSOR
TEMP
SENSOR
TEMP
SENSOR
TEMP
SENSOR
TEMP
SENSOR
TEMP
SENSOR
TEMP
SENSOR
TEMP
SENSOR
TEMP
SENSOR
TEMP
SENSOR
TEMP
SENSOR
TEMP
SENSOR
TEMP
SENSOR
Rev. 1.2 55
Page 56

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
Figure 5.7. ADC0CF: ADC0 Configuration Register
SFR Page:
SFR Address:
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W Reset Value
AD0SC4 AD0SC3 AD0SC2 AD0SC1 AD0SC0 AMP0GN2 AMP0GN1 AMP0GN0 11111000
Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0
Bits7-3: AD0SC4-0: ADC0 SAR Conversion Clock Period Bits.
Bits2-0: AMP0GN2-0: ADC0 Internal Amplifier Gain (PGA).
0
0xBC
The SAR Conversion clock is derived from system clock by the following equation, where AD0SC
refers to the 5-bit value held in AD0SC4-0, and CLK
(Note: the ADC0 SAR Conversion Clock should be less than or equal to 2.5 MHz).
AD0SC
When the AD0SC bits are equal to 00000b, the SAR Conversion clock is equal to SYSCLK to facilitate faster ADC conversions at slower SYSCLK speeds.
000: Gain = 1
001: Gain = 2
010: Gain = 4
011: Gain = 8
10x: Gain = 16
11x: Gain = 0.5
SYSCLK
--------------------------------1–= AD0SC 00000b>()
2 C× LK
SAR0
refers to the desired ADC0 SAR clock
SAR0
56 Rev. 1.2
Page 57

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
Figure 5.8. ADC0CN: ADC0 Control Register
SFR Page:
SFR Address:
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W Reset Value
AD0EN AD0TM AD0INT AD0BUSY AD0CM1 AD0CM0 AD0WINT AD0LJST 00000000
Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0
Bit7: AD0EN: ADC0 Enable Bit.
Bit6: AD0TM: ADC Track Mode Bit.
Bit5: AD0INT: ADC0 Conversion Complete Interrupt Flag.
Bit4: AD0BUSY: ADC0 Busy Bit.
Bits3-2: AD0CM1-0: ADC0 Start of Conversion Mode Select.
Bit1: AD0WINT: ADC0 Window Compare Interrupt Flag.
Bit0: AD0LJST: ADC0 Left Justify Select.
0
0xE8 (bit addressable)
0: ADC0 Disabled. ADC0 is in low-power shutdown.
1: ADC0 Enabled. ADC0 is active and ready for data conversions.
0: When the ADC is enabled, tracking is continuous unless a conversion is in process.
1: Tracking Defined by ADCM1-0 bits.
This flag must be cleared by software.
0: ADC0 has not completed a data conversion since the last time this flag was cleared.
1: ADC0 has completed a data conversion.
Read:
0: ADC0 Conversion is complete or a conversion is not currently in progress. AD0INT is set to
logic 1 on the falling edge of AD0BUSY.
1: ADC0 Conversion is in progress.
Write:
0: No Effect.
1: Initiates ADC0 Conversion if AD0CM1-0 = 00b.
If AD0TM = 0:
00: ADC0 conversion initiated on every write of ‘1’ to AD0BUSY.
01: ADC0 conversion initiated on overflow of Timer 3.
10: ADC0 conversion initiated on rising edge of external CNVSTR0.
11: ADC0 conversion initiated on overflow of Timer 2.
If AD0TM = 1:
00: Tracking starts with the write of ‘1’ to AD0BUSY and lasts for 3 SAR clocks, followed by conversion.
01: Tracking started by the overflow of Timer 3 and lasts for 3 SAR clocks, followed by conversion.
10: ADC0 tracks only when CNVSTR0 input is logic low; conversion starts on rising CNVSTR0
edge.
11: Tracking started by the overflow of Timer 2 and lasts for 3 SAR clocks, followed by conversion.
This bit must be cleared by software.
0: ADC0 Window Comparison Data match has not occurred since this flag was last cleared.
1: ADC0 Window Comparison Data match has occurred.
0: Data in ADC0H:ADC0L registers are right-justified.
1: Data in ADC0H:ADC0L registers are left-justified.
Rev. 1.2 57
Page 58

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
Figure 5.9. ADC0H: ADC0 Data Word MSB Register
SFR Page:
SFR Address:
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W Reset Value
Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0
0
0xBF
Bits7-0: ADC0 Data Word High-Order Bits.
For AD0LJST = 0: Bits 7-4 are the sign extension of Bit3. Bits 3-0 are the upper 4 bits of the 12-bit
ADC0 Data Word.
For AD0LJST = 1: Bits 7-0 are the most-significant bits of the 12-bit ADC0 Data Word.
Figure 5.10. ADC0L: ADC0 Data Word LSB Register
SFR Page:
SFR Address:
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W Reset Value
Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0
Bits7-0: ADC0 Data Word Low-Order Bits.
0
0xBE
For AD0LJST = 0: Bits 7-0 are the lower 8 bits of the 12-bit ADC0 Data Word.
For AD0LJST = 1: Bits 7-4 are the lower 4 bits of the 12-bit ADC0 Data Word. Bits3-0 will always
read ‘0’.
00000000
00000000
58 Rev. 1.2
Page 59

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
Figure 5.11. ADC0 Data Word Example
12-bit ADC0 Data Word appears in the ADC0 Data Word Registers as follows:
ADC0H[3:0]:ADC0L[7:0], if AD0LJST = 0
(ADC0H[7:4] will be sign-extension of ADC0H.3 for a differential reading, otherwise =
0000b).
ADC0H[7:0]:ADC0L[7:4], if AD0LJST = 1
(ADC0L[3:0] = 0000b).
Example: ADC0 Data Word Conversion Map, AIN0.0 Input in Single-Ended Mode
(AMX0CF = 0x00, AMX0SL = 0x00)
AIN0.0-AGND
(Volts)
VREF * (4095/4096) 0x0FFF 0xFFF0
VREF / 2 0x0800 0x8000
VREF * (2047/4096) 0x07FF 0x7FF0
0 0x0000 0x0000
ADC0H:ADC0L
(AD0LJST = 0)
ADC0H:ADC0L
(AD0LJST = 1)
Example: ADC0 Data Word Conversion Map, AIN0.0-AIN0.1 Differential Input Pair
(AMX0CF = 0x01, AMX0SL = 0x00)
AIN0.0-AIN0.1
(Volts)
VREF * (2047/2048) 0x07FF 0x7FF0
VREF / 2 0x0400 0x4000
VREF * (1/2048) 0x0001 0x0010
0 0x0000 0x0000
-VREF * (1/2048) 0xFFFF (-1d) 0xFFF0
-VREF / 2 0xFC00 (-1024d) 0xC000
-VREF 0xF800 (-2048d) 0x8000
For AD0LJST = 0:
Code Vin
× 2n×=
ADC0H:ADC0L
(AD0LJST = 0)
Gain
---------------
VREF
ADC0H:ADC0L
(AD0LJST = 1)
; ‘n’ = 12 for Single-Ended; ‘n’=11 for Differential.
Rev. 1.2 59
Page 60

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
5.3. ADC0 Programmable Window Detector
The ADC0 Programmable Window Detector continuously compares the ADC0 output to user-programmed limits,
and notifies the system when an out-of-bound condition is detected. This is especially effective in an interrupt-driven
system, saving code space and CPU bandwidth while delivering faster system response times. The window detector
interrupt flag (AD0WINT in ADC0CN) can also be used in polled mode. The high and low bytes of the reference
words are loaded into the ADC0 Greater-Than and ADC0 Less-Than registers (ADC0GTH, ADC0GTL, ADC0LTH,
and ADC0LTL). Reference comparisons are shown starting on page 62. Notice that the window detector flag can be
asserted when the measured data is inside or outside the user-programmed limits, depending on the programming of
the ADC0GTx and ADC0LTx registers.
Figure 5.12. ADC0GTH: ADC0 Greater-Than Data High Byte Register
SFR Page:
SFR Address:
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W Reset Value
Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0
0
0xC5
Bits7-0: High byte of ADC0 Greater-Than Data Word.
Figure 5.13. ADC0GTL: ADC0 Greater-Than Data Low Byte Register
SFR Page:
SFR Address:
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W Reset Value
Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0
Bits7-0: Low byte of ADC0 Greater-Than Data Word.
0
0xC4
11111111
11111111
60 Rev. 1.2
Page 61

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
Figure 5.14. ADC0LTH: ADC0 Less-Than Data High Byte Register
SFR Page:
SFR Address:
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W Reset Value
Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0
0
0xC7
Bits7-0: High byte of ADC0 Less-Than Data Word.
Figure 5.15. ADC0LTL: ADC0 Less-Than Data Low Byte Register
SFR Page:
SFR Address:
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W Reset Value
Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0
Bits7-0: Low byte of ADC0 Less-Than Data Word.
0
0xC6
00000000
00000000
Rev. 1.2 61
Page 62

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
Figure 5.16. 12-Bit ADC0 Window Interrupt Example: Right Justified Single-Ended Data
Input Voltage
(AD0.0 - AGND)
REF x (4095/4096)
REF x (512/4096)
REF x (256/4096)
0
ADC Data
Word
0x0FFF
0x0201
0x0200
0x01FF
0x0101
0x0100
0x00FF
0x0000
AD0WINT
not affected
ADC0LTH:ADC0LTL
AD0WINT=1
ADC0GTH:ADC0GTL
AD0WINT
not affected
Given:
AMX0SL = 0x00, AMX0CF = 0x00
AD0LJST = ‘0’,
ADC0LTH:ADC0LTL = 0x0200,
ADC0GTH:ADC0GTL = 0x0100.
An ADC0 End of Conversion will cause an ADC0
Window Compare Interrupt (AD0WINT = ‘1’) if
the resulting ADC0 Data Word is < 0x0200 and
> 0x0100.
Input Voltage
(AD0.0 - AGND)
REF x (4095/4096)
REF x (512/4096)
REF x (256/4096)
0
ADC Data
Word
0x0FFF
0x0201
0x0200
0x01FF
0x0101
0x0100
0x00FF
0x0000
AD0WINT=1
ADC0GTH:ADC0GTL
AD0WINT
not affected
ADC0LTH:ADC0LTL
AD0WINT=1
Given:
AMX0SL = 0x00, AMX0CF = 0x00,
AD0LJST = ‘0’,
ADC0LTH:ADC0LTL = 0x0100,
ADC0GTH:ADC0GTL = 0x0200.
An ADC0 End of Conversion will cause an ADC0
Window Compare Interrupt (AD0WINT = ‘1’) if
the resulting ADC0 Data Word is > 0x0200 or
< 0x0100.
62 Rev. 1.2
Page 63

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
Figure 5.17. 12-Bit ADC0 Window Interrupt Example: Right Justified Differential Data
Input Voltage
(AD0.0 - AD0.1)
REF x (2047/2048)
REF x (256/2048)
REF x (-1/2048)
-REF
ADC Data
Word
0x07FF
0x0101
0x0100
0x00FF
0x0000
0xFFFF
0xFFFE
0xF800
AD0WINT
not affected
ADC0LTH:ADC0LTL
AD0WINT=1
ADC0GTH:ADC0GTL
AD0WINT
not affected
Given:
AMX0SL = 0x00, AMX0CF = 0x01,
AD0LJST = ‘0’,
ADC0LTH:ADC0LTL = 0x0100,
ADC0GTH:ADC0GTL = 0xFFFF.
An ADC0 End of Conversion will cause an ADC0
Window Compare Interrupt (AD0WINT = ‘1’) if
the resulting ADC0 Data Word is < 0x0100 and
> 0xFFFF. (In two’s-complement math,
0xFFFF = -1.)
Input Voltage
(AD0.0 - AD0.1)
REF x (2047/2048)
REF x (256/2048)
REF x (-1/2048)
-REF
ADC Data
Word
0x07FF
0x0101
0x0100
0x00FF
0x0000
0xFFFF
0xFFFE
0xF800
AD0WINT=1
ADC0GTH:ADC0GTL
AD0WINT
not affected
ADC0LTH:ADC0LTL
AD0WINT=1
Given:
AMX0SL = 0x00, AMX0CF = 0x01,
AD0LJST = ‘0’,
ADC0LTH:ADC0LTL = 0xFFFF,
ADC0GTH:ADC0GTL = 0x0100.
An ADC0 End of Conversion will cause an ADC0
Window Compare Interrupt (AD0WINT = ‘1’) if
the resulting ADC0 Data Word is < 0xFFFF or
> 0x0100. (In two’s-complement math,
0xFFFF = -1.)
Rev. 1.2 63
Page 64

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
Figure 5.18. 12-Bit ADC0 Window Interrupt Example: Left Justified Single-Ended Data
Input Voltage
(AD0.0 - AGND)
REF x (4095/4096)
REF x (512/4096)
REF x (256/4096)
0
ADC Data
Word
0xFFF0
0x2010
0x2000
0x1FF0
0x1010
0x1000
0x0FF0
0x0000
AD0WINT
not affected
ADC0LTH:ADC0LTL
AD0WINT=1
ADC0GTH:ADC0GTL
AD0WINT
not affected
Given:
AMX0SL = 0x00, AMX0CF = 0x00,
AD0LJST = ‘1’,
ADC0LTH:ADC0LTL = 0x2000,
ADC0GTH:ADC0GTL = 0x1000.
An ADC0 End of Conversion will cause an ADC0
Window Compare Interrupt (AD0WINT = ‘1’) if
the resulting ADC0 Data Word is < 0x2000 and
> 0x1000.
Input Voltage
(AD0.0 - AGND)
REF x (4095/4096)
REF x (512/4096)
REF x (256/4096)
0
ADC Data
Word
0xFFF0
0x2010
0x2000
0x1FF0
0x1010
0x1000
0x0FF0
0x0000
AD0WINT=1
ADC0GTH:ADC0GTL
AD0WINT
not affected
ADC0LTH:ADC0LTL
AD0WINT=1
Given:
AMX0SL = 0x00, AMX0CF = 0x00,
AD0LJST = ‘1’
ADC0LTH:ADC0LTL = 0x1000,
ADC0GTH:ADC0GTL = 0x2000.
An ADC0 End of Conversion will cause an ADC0
Window Compare Interrupt (AD0WINT = ‘1’) if
the resulting ADC0 Data Word is < 0x1000 or
> 0x2000.
64 Rev. 1.2
Page 65

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
Figure 5.19. 12-Bit ADC0 Window Interrupt Example: Left Justified Differential Data
Input Voltage
(AD0.0 - AD0.1)
REF x (2047/2048)
REF x (256/2048)
REF x (-1/2048)
-REF
ADC Data
Word
0x7FF0
0x1010
0x1000
0x0FF0
0x0000
0xFFF0
0xFFE0
0x8000
AD0WINT
not affected
ADC0LTH:ADC0LTL
AD0WINT=1
ADC0GTH:ADC0GTL
AD0WINT
not affected
Given:
AMX0SL = 0x00, AMX0CF = 0x01,
AD0LJST = ‘1’,
ADC0LTH:ADC0LTL = 0x1000,
ADC0GTH:ADC0GTL = 0xFFF0.
An ADC0 End of Conversion will cause an ADC0
Window Compare Interrupt (AD0WINT = ‘1’) if
the resulting ADC0 Data Word is < 0x1000 and
> 0xFFF0. (Two’s-complement math.)
Input Voltage
(AD0.0 - AD0.1)
REF x (2047/2048)
REF x (256/2048)
REF x (-1/2048)
-REF
ADC Data
Word
0x7FF0
0x1010
0x1000
0x0FF0
0x0000
0xFFF0
0xFFE0
0x8000
AD0WINT=1
ADC0GTH:ADC0GTL
AD0WINT
not affected
ADC0LTH:ADC0LTL
AD0WINT=1
Given:
AMX0SL = 0x00, AMX0CF = 0x01,
AD0LJST = ‘1’,
ADC0LTH:ADC0LTL = 0xFFF0,
ADC0GTH:ADC0GTL = 0x1000.
An ADC0 End of Conversion will cause an ADC0
Window Compare Interrupt (AD0WINT = ‘1’) if
the resulting ADC0 Data Word is < 0xFFF0 or
> 0x1000. (Two’s-complement math.)
Rev. 1.2 65
Page 66

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
Table 5.1. 12-Bit ADC0 Electrical Characteristics (C8051F120/1/4/5)
VDD = 3.0V, AV+ = 3.0V, VREF = 2.40V (REFBE=0), PGA Gain = 1, -40°C to +85°C unless otherwise specified
PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
DC ACCURACY
Resolution 12 bits
Integral Nonlinearity ±1 LSB
Differential Nonlinearity Guaranteed Monotonic ±1 LSB
Offset Error -3±1 LSB
Full Scale Error Differential mode -7±3 LSB
Offset Temperature Coefficient ±0.25 ppm/°C
DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE (10 kHz sine-wave input, 0 to 1 dB below Full Scale, 100 ksps
Signal-to-Noise Plus Distortion 66 dB
Total Harmonic Distortion
Spurious-Free Dynamic Range 80 dB
CONVERSION RATE
SAR Clock Frequency 2.5 MHz
Conversion Time in SAR Clocks 16 clocks
Track/Hold Acquisition Time 1.5 µs
Throughput Rate 100 ksps
ANALOG INPUTS
Input Voltage Range Single-ended operation 0 VREF V
*Common-mode Voltage Range Differential operation AGND AV+ V
Input Capacitance 10 pF
TEMPERATURE SENSOR
Linearity Note 1 ±0.2 °C
Gain Note 2 2.86
Offset Note 1, Note 2, (Temp = 0 °C) 776
POWER SPECIFICATIONS
Power Supply Current (AV+ supplied to ADC)
Power Supply Rejection ±0.3 mV/V
Note 1: Includes ADC offset, gain, and linearity variations.
Note 2: Represents one standard deviation from the mean.
Up to the 5
Operating Mode, 100 ksps 450 900 µA
th
harmonic
-75 dB
mV / °C
±0.034
mV
±8.5
66 Rev. 1.2
Page 67

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
6. ADC0 (10-BIT ADC, C8051F122/3/6/7 ONLY)
The ADC0 subsystem for the C8051F122/3/6/7 consists of a 9-channel, configurable analog multiplexer (AMUX0), a
programmable gain amplifier (PGA0), and a 100 ksps, 10-bit successive-approximation-register ADC with integrated
track-and-hold and Programmable Window Detector (see block diagram in Figure 6.1). The AMUX0, PGA0, Data
Conversion Modes, and Window Detector are all configurable under software control via the Special Function Registers shown in Figure 6.1. The voltage reference used by ADC0 is selected as described in Section “9. VOLTAGE
REFERENCE (C8051F120/2/4/6)” on page 107 for C8051F120/2/4/6 devices, or Section “10. VOLTAGE REFERENCE (C8051F121/3/5/7)” on page 109 for C8051F121/3/5/7 devices. The ADC0 subsystem (ADC0, track-
and-hold and PGA0) is enabled only when the AD0EN bit in the ADC0 Control register (ADC0CN) is set to logic 1.
The ADC0 subsystem is in low power shutdown when this bit is logic 0.
Figure 6.1. 10-Bit ADC0 Functional Block Diagram
ADC0LTLADC0LTHADC0GTLADC0GTH
20
AIN0.0
AIN0.1
AIN0.2
AIN0.3
AIN0.4
AIN0.5
AIN0.6
AIN0.7
TEMP
SENSOR
AGND
+
-
+
-
+
-
+
-
9-to-1
AMUX
(SE or
DIFF)
X
+
-
AD0EN
AV+
AGND
AV+
10-Bit
SAR
ADC
SYSCLK
AD0CM
REF
10
Start Conversion
Comb.
Logic
10
ADC0L ADC0H
00
01
10
11
AD0WINT
AD0BUSY (W)
Timer 3 Overflow
CNVSTR0
Timer 2 Overflow
AIN01IC
AIN23IC
AIN45IC
AIN67IC
AMX0CF
6.1. Analog Multiplexer and PGA
Eight of the AMUX channels are available for external measurements while the ninth channel is internally connected
to an on-chip temperature sensor (temperature transfer function is shown in Figure 6.2). AMUX input pairs can be
programmed to operate in either differential or single-ended mode. This allows the user to select the best measurement technique for each input channel, and even accommodates mode changes "on-the-fly". The AMUX defaults to
all single-ended inputs upon reset. There are two registers associated with the AMUX: the Channel Selection register
AMX0SL (Figure 6.6), and the Configuration register AMX0CF (Figure 6.5). The table in Figure 6.6 shows AMUX
functionality by channel, for each possible configuration. The PGA amplifies the AMUX output signal by an amount
determined by the states of the AMP0GN2-0 bits in the ADC0 Configuration register, ADC0CF (Figure 6.7). The
PGA can be software-programmed for gains of 0.5, 2, 4, 8 or 16. Gain defaults to unity on reset.
AMX0AD3
AMX0SL
AMX0AD1
AMX0AD2
AMX0AD0
AD0SC4
AD0SC3
ADC0CF
AD0INT
AD0TM
AD0EN
ADC0CN
AD0BUSY
AD0LJST
AD0WINT
AD0CM0
AD0CM1
AD0CM
AMP0GN0
AMP0GN1
AMP0GN2
AD0SC0
AD0SC1
AD0SC2
Rev. 1.2 67
Page 68

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
The Temperature Sensor transfer function is shown in Figure 6.2. The output voltage (V
) is the PGA input when
TEMP
the Temperature Sensor is selected by bits AMX0AD3-0 in register AMX0SL; this voltage will be amplified by the
PGA according to the user-programmed PGA settings.
Figure 6.2. Typical Temperature Sensor Transfer Function
(Volts)
1.000
0.900
0.800
V
= 0.00286(TEMPC) + 0.776
0.700
0.600
0.500
0-50 50 100
TEMP
for PGA Gain = 1
(Celsius)
68 Rev. 1.2
Page 69

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
6.2. ADC Modes of Operation
ADC0 has a maximum conversion speed of 100 ksps. The ADC0 conversion clock is derived from the system clock
divided by the value held in the ADCSC bits of register ADC0CF.
6.2.1. Starting a Conversion
A conversion can be initiated in one of four ways, depending on the programmed states of the ADC0 Start of Conversion Mode bits (AD0CM1, AD0CM0) in ADC0CN. Conversions may be initiated by:
1. Writing a ‘1’ to the AD0BUSY bit of ADC0CN;
2. A Timer 3 overflow (i.e. timed continuous conversions);
3. A rising edge detected on the external ADC convert start signal, CNVSTR0;
4. A Timer 2 overflow (i.e. timed continuous conversions).
The AD0BUSY bit is set to logic 1 during conversion and restored to logic 0 when conversion is complete. The falling edge of AD0BUSY triggers an interrupt (when enabled) and sets the AD0INT interrupt flag (ADC0CN.5). Converted data is available in the ADC0 data word MSB and LSB registers, ADC0H, ADC0L. Converted data can be
either left or right justified in the ADC0H:ADC0L register pair (see example in Figure 6.11) depending on the programmed state of the AD0LJST bit in the ADC0CN register.
When initiating conversions by writing a ‘1’ to AD0BUSY, the AD0INT bit should be polled to determine when a
conversion has completed (ADC0 interrupts may also be used). The recommended polling procedure is shown below.
Step 1. Write a ‘0’ to AD0INT;
Step 2. Write a ‘1’ to AD0BUSY;
Step 3. Poll AD0INT for ‘1’;
Step 4. Process ADC0 data.
When CNVSTR0 is used as a conversion start source, it must be enabled in the crossbar, and the corresponding pin
must be set to open-drain, high-impedance mode (see Section “19. PORT INPUT/OUTPUT” on page 215 for more
details on Port I/O configuration).
Rev. 1.2 69
Page 70

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
6.2.2. Tracking Modes
The AD0TM bit in register ADC0CN controls the ADC0 track-and-hold mode. In its default state, the ADC0 input is
continuously tracked when a conversion is not in progress. When the AD0TM bit is logic 1, ADC0 operates in lowpower track-and-hold mode. In this mode, each conversion is preceded by a tracking period of 3 SAR clocks (after
the start-of-conversion signal). When the CNVSTR0 signal is used to initiate conversions in low-power tracking
mode, ADC0 tracks only when CNVSTR0 is low; conversion begins on the rising edge of CNVSTR0 (see
Figure 6.3). Tracking can also be disabled (shutdown) when the entire chip is in low power standby or sleep modes.
Low-power track-and-hold mode is also useful when AMUX or PGA settings are frequently changed, to ensure that
settling time requirements are met (see Section “6.2.3. Settling Time Requirements” on page 71).
Figure 6.3. ADC0 Track and Conversion Example Timing
A. ADC Timing for External Trigger Source
CNVSTR0
(AD0CM[1:0]=10)
12345678910111213141516
SAR Clocks
ADC0TM=1
ADC0TM=0
Timer 2, Timer 3 Overflow;
Write '1' to AD0BUSY
(AD0CM[1:0]=00, 01, 11)
SAR Clocks
ADC0TM=1
SAR Clocks
ADC0TM=0
Low Power
or Convert
Track Or Convert Convert Track
Track Convert Low Power Mode
B. ADC Timing for Internal Trigger Sources
1234567891011121314151617 18 19
Low Power
or Convert
Track or
Convert
Track Convert Low Power Mode
12345678910111213141516
Convert Track
70 Rev. 1.2
Page 71

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
6.2.3. Settling Time Requirements
When the ADC0 input configuration is changed (i.e., a different MUX or PGA selection is made), a minimum tracking time is required before an accurate conversion can be performed. This tracking time is determined by the ADC0
MUX resistance, the ADC0 sampling capacitance, any external source resistance, and the accuracy required for the
conversion. Figure 6.4 shows the equivalent ADC0 input circuits for both Differential and Single-ended modes.
Notice that the equivalent time constant for both input circuits is the same. The required settling time for a given settling accuracy (SA) may be approximated by Equation 6.1. When measuring the Temperature Sensor output, R
reduces to R
. An absolute minimum settling time of 1.5 µs is required after any MUX or PGA selection. Note
MUX
that in low-power tracking mode, three SAR clocks are used for tracking at the start of every conversion. For most
applications, these three SAR clocks will meet the tracking requirements.
Equation 6.1. ADC0 Settling Time Requirements
n
2
t
-------
×ln=
SA
R
TOTALCSAMPLE
TOTAL
Where:
SA is the settling accuracy, given as a fraction of an LSB (for example, 0.25 to settle within 1/4 LSB)
t is the required settling time in seconds
R
is the sum of the ADC0 MUX resistance and any external source resistance.
TOTAL
n is the ADC resolution in bits (10).
Figure 6.4. ADC0 Equivalent Input Circuits
AIN0.x
Differential Mode
MUX Select
R
= 5k
MUX
RC
= R
MUX
* C
SAMP LE
Input
C
SAMPLE
C
SAMPLE
= 10pF
= 10pF
Single-Ended Mode
MUX Select
AIN0.x
RC
Input
= R
MUX
R
* C
MUX
SAMPL E
= 5k
C
SAMPLE
= 10pF
AIN0.y
MUX Select
R
= 5k
MUX
Rev. 1.2 71
Page 72

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
Figure 6.5. AMX0CF: AMUX0 Configuration Register
SFR Page:
SFR Address:
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W Reset Value
Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0
Bits7-4: UNUSED. Read = 0000b; Write = don’t care.
Bit3: AIN67IC: AIN0.6, AIN0.7 Input Pair Configuration Bit.
Bit2: AIN45IC: AIN0.4, AIN0.5 Input Pair Configuration Bit.
Bit1: AIN23IC: AIN0.2, AIN0.3 Input Pair Configuration Bit.
Bit0: AIN01IC: AIN0.0, AIN0.1 Input Pair Configuration Bit.
NOTE: The ADC0 Data Word is in 2’s complement format for channels configured as differential.
0
0xBA
- - - - AIN67IC AIN45IC AIN23IC AIN01IC 00000000
0: AIN0.6 and AIN0.7 are independent single-ended inputs.
1: AIN0.6, AIN0.7 are (respectively) +, - differential input pair.
0: AIN0.4 and AIN0.5 are independent single-ended inputs.
1: AIN0.4, AIN0.5 are (respectively) +, - differential input pair.
0: AIN0.2 and AIN0.3 are independent single-ended inputs.
1: AIN0.2, AIN0.3 are (respectively) +, - differential input pair.
0: AIN0.0 and AIN0.1 are independent single-ended inputs.
1: AIN0.0, AIN0.1 are (respectively) +, - differential input pair.
72 Rev. 1.2
Page 73

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
Figure 6.6. AMX0SL: AMUX0 Channel Select Register
SFR Page:
SFR Address:
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W Reset Value
0
0xBB
- - - - AMX0AD3 AMX0AD2 AMX0AD1 AMX0AD0 00000000
Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0
Bits7-4: UNUSED. Read = 0000b; Write = don’t care.
Bits3-0: AMX0AD3-0: AMX0 Address Bits.
0000-1111b: ADC Inputs selected per chart below.
AMX0AD3-0
0000 0001 0010 0011 0100 0101 0110 0111 1xxx
0000
0001
0010
0011
0100
0101
0110
0111
1000
1001
AMX0CF Bits 3-0
1010
1011
1100
1101
1110
1111
AIN0.0 AIN0.1 AIN0.2 AIN0.3 AIN0.4 AIN0.5 AIN0.6 AIN0.7
+(AIN0.0)
-(AIN0.1)
AIN0.0 AIN0.1
+(AIN0.0)
-(AIN0.1)
AIN0.0 AIN0.1 AIN0.2 AIN0.3
+(AIN0.0)
-(AIN0.1)
AIN0.0 AIN0.1
+(AIN0.0)
-(AIN0.1)
AIN0.0 AIN0.1 AIN0.2 AIN0.3 AIN0.4 AIN0.5
+(AIN0.0)
-(AIN0.1)
AIN0.0 AIN0.1
+(AIN0.0)
-(AIN0.1)
AIN0.0 AIN0.1 AIN0.2 AIN0.3
+(AIN0.0)
-(AIN0.1)
AIN0.0 AIN0.1
+(AIN0.0)
-(AIN0.1)
AIN0.2 AIN0.3 AIN0.4 AIN0.5 AIN0.6 AIN0.7
+(AIN0.2)
-(AIN0.3)
+(AIN0.2)
-(AIN0.3)
AIN0.2 AIN0.3
+(AIN0.2)
-(AIN0.3)
+(AIN0.2)
-(AIN0.3)
AIN0.2 AIN0.3 AIN0.4 AIN0.5
+(AIN0.2)
-(AIN0.3)
+(AIN0.2)
-(AIN0.3)
AIN0.2 AIN0.3
+(AIN0.2)
-(AIN0.3)
+(AIN0.2)
-(AIN0.3)
AIN0.4 AIN0.5 AIN0.6 AIN0.7
AIN0.4 AIN0.5 AIN0.6 AIN0.7
+(AIN0.4)
-(AIN0.5)
+(AIN0.4)
-(AIN0.5)
+(AIN0.4)
-(AIN0.5)
+(AIN0.4)
-(AIN0.5)
AIN0.4 AIN0.5
AIN0.4 AIN0.5
+(AIN0.4)
-(AIN0.5)
+(AIN0.4)
-(AIN0.5)
+(AIN0.4)
-(AIN0.5)
+(AIN0.4)
-(AIN0.5)
AIN0.6 AIN0.7
AIN0.6 AIN0.7
AIN0.6 AIN0.7
AIN0.6 AIN0.7
+(AIN0.6)
-(AIN0.7)
+(AIN0.6)
-(AIN0.7)
+(AIN0.6)
-(AIN0.7)
+(AIN0.6)
-(AIN0.7)
+(AIN0.6)
-(AIN0.7)
+(AIN0.6)
-(AIN0.7)
+(AIN0.6)
-(AIN0.7)
+(AIN0.6)
-(AIN0.7)
TEMP
SENSOR
TEMP
SENSOR
TEMP
SENSOR
TEMP
SENSOR
TEMP
SENSOR
TEMP
SENSOR
TEMP
SENSOR
TEMP
SENSOR
TEMP
SENSOR
TEMP
SENSOR
TEMP
SENSOR
TEMP
SENSOR
TEMP
SENSOR
TEMP
SENSOR
TEMP
SENSOR
TEMP
SENSOR
Rev. 1.2 73
Page 74

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
Figure 6.7. ADC0CF: ADC0 Configuration Register
SFR Page:
SFR Address:
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W Reset Value
AD0SC4 AD0SC3 AD0SC2 AD0SC1 AD0SC0 AMP0GN2 AMP0GN1 AMP0GN0 11111000
Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0
Bits7-3: AD0SC4-0: ADC0 SAR Conversion Clock Period Bits.
Bits2-0: AMP0GN2-0: ADC0 Internal Amplifier Gain (PGA).
0
0xBC
SAR Conversion clock is derived from system clock by the following equation, where AD0SC refers
to the 5-bit value held in AD0SC4-0, and CLK
ADC0 SAR Conversion Clock should be less than or equal to 2.5 MHz).
AD0SC
When the AD0SC bits are equal to 00000b, the SAR Conversion clock is equal to SYSCLK to facilitate faster ADC conversions at slower SYSCLK speeds.
000: Gain = 1
001: Gain = 2
010: Gain = 4
011: Gain = 8
10x: Gain = 16
11x: Gain = 0.5
SYSCLK
--------------------------------1–= AD0SC 00000b>()
2 C× LK
SAR0
refers to the desired ADC0 SAR clock (Note: the
SAR0
74 Rev. 1.2
Page 75

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
Figure 6.8. ADC0CN: ADC0 Control Register
SFR Page:
SFR Address:
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W Reset Value
AD0EN AD0TM AD0INT AD0BUSY AD0CM1 AD0CM0 AD0WINT AD0LJST 00000000
Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0
Bit7: AD0EN: ADC0 Enable Bit.
Bit6: AD0TM: ADC Track Mode Bit.
Bit5: AD0INT: ADC0 Conversion Complete Interrupt Flag.
Bit4: AD0BUSY: ADC0 Busy Bit.
Bits3-2: AD0CM1-0: ADC0 Start of Conversion Mode Select.
Bit1: AD0WINT: ADC0 Window Compare Interrupt Flag.
Bit0: AD0LJST: ADC0 Left Justify Select.
0
0xE8 (bit addressable)
0: ADC0 Disabled. ADC0 is in low-power shutdown.
1: ADC0 Enabled. ADC0 is active and ready for data conversions.
0: When the ADC is enabled, tracking is continuous unless a conversion is in process.
1: Tracking Defined by ADCM1-0 bits.
This flag must be cleared by software.
0: ADC0 has not completed a data conversion since the last time this flag was cleared.
1: ADC0 has completed a data conversion.
Read:
0: ADC0 Conversion is complete or a conversion is not currently in progress. AD0INT is set to
logic 1 on the falling edge of AD0BUSY.
1: ADC0 Conversion is in progress.
Write:
0: No Effect.
1: Initiates ADC0 Conversion if AD0CM1-0 = 00b.
If AD0TM = 0:
00: ADC0 conversion initiated on every write of ‘1’ to AD0BUSY.
01: ADC0 conversion initiated on overflow of Timer 3.
10: ADC0 conversion initiated on rising edge of external CNVSTR0.
11: ADC0 conversion initiated on overflow of Timer 2.
If AD0TM = 1:
00: Tracking starts with the write of ‘1’ to AD0BUSY and lasts for 3 SAR clocks, followed by conversion.
01: Tracking started by the overflow of Timer 3 and lasts for 3 SAR clocks, followed by conversion.
10: ADC0 tracks only when CNVSTR0 input is logic low; conversion starts on rising CNVSTR0
edge.
11: Tracking started by the overflow of Timer 2 and lasts for 3 SAR clocks, followed by conversion.
This bit must be cleared by software.
0: ADC0 Window Comparison Data match has not occurred since this flag was last cleared.
1: ADC0 Window Comparison Data match has occurred.
0: Data in ADC0H:ADC0L registers are right-justified.
1: Data in ADC0H:ADC0L registers are left-justified.
Rev. 1.2 75
Page 76

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
Figure 6.9. ADC0H: ADC0 Data Word MSB Register
SFR Page:
SFR Address:
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W Reset Value
Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0
0
0xBF
Bits7-0: ADC0 Data Word High-Order Bits.
For AD0LJST = 0: Bits 7-4 are the sign extension of Bit3. Bits 3-0 are the upper 4 bits of the 10-bit
ADC0 Data Word.
For AD0LJST = 1: Bits 7-0 are the most-significant bits of the 10-bit ADC0 Data Word.
Figure 6.10. ADC0L: ADC0 Data Word LSB Register
SFR Page:
SFR Address:
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W Reset Value
Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0
Bits7-0: ADC0 Data Word Low-Order Bits.
0
0xBE
For AD0LJST = 0: Bits 7-0 are the lower 8 bits of the 10-bit ADC0 Data Word.
For AD0LJST = 1: Bits 7-4 are the lower 4 bits of the 10-bit ADC0 Data Word. Bits3-0 will always
read ‘0’.
00000000
00000000
76 Rev. 1.2
Page 77

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
Figure 6.11. ADC0 Data Word Example
10-bit ADC0 Data Word appears in the ADC0 Data Word Registers as follows:
ADC0H[1:0]:ADC0L[7:0], if AD0LJST = 0
(ADC0H[7:2] will be sign-extension of ADC0H.1 for a differential reading, otherwise =
000000b).
ADC0H[7:0]:ADC0L[7:6], if AD0LJST = 1
(ADC0L[5:0] = 00b).
Example: ADC0 Data Word Conversion Map, AIN0.0 Input in Single-Ended Mode
(AMX0CF = 0x00, AMX0SL = 0x00)
AIN0.0-AGND
(Volts)
VREF * (1023/1024) 0x03FF 0xFFC0
VREF / 2 0x0800 0x8000
VREF * (511/1024) 0x01FF 0x7FC0
0 0x0000 0x0000
ADC0H:ADC0L
(AD0LJST = 0)
ADC0H:ADC0L
(AD0LJST = 1)
Example: ADC0 Data Word Conversion Map, AIN0.0-AIN0.1 Differential Input Pair
(AMX0CF = 0x01, AMX0SL = 0x00)
AIN0.0-AIN0.1
(Volts)
VREF * (511/512) 0x01FF 0x7FC0
VREF / 2 0x0100 0x4000
VREF * (1/512) 0x0001 0x0040
0 0x0000 0x0000
-VREF * (1/512) 0xFFFF (-1d) 0xFFC0
-VREF / 2 0xFF00 (-256d) 0xC000
-VREF 0xFE00 (-512d) 0x8000
For AD0LJST = 0:
Code Vin
× 2n×=
ADC0H:ADC0L
(AD0LJST = 0)
Gain
---------------
VREF
ADC0H:ADC0L
(AD0LJST = 1)
; ‘n’ = 10 for Single-Ended; ‘n’= 9 for Differential.
Rev. 1.2 77
Page 78

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
6.3. ADC0 Programmable Window Detector
The ADC0 Programmable Window Detector continuously compares the ADC0 output to user-programmed limits,
and notifies the system when an out-of-bound condition is detected. This is especially effective in an interrupt-driven
system, saving code space and CPU bandwidth while delivering faster system response times. The window detector
interrupt flag (AD0WINT in ADC0CN) can also be used in polled mode. The high and low bytes of the reference
words are loaded into the ADC0 Greater-Than and ADC0 Less-Than registers (ADC0GTH, ADC0GTL, ADC0LTH,
and ADC0LTL). Reference comparisons are shown starting on page 80. Notice that the window detector flag can be
asserted when the measured data is inside or outside the user-programmed limits, depending on the programming of
the ADC0GTx and ADC0LTx registers.
Figure 6.12. ADC0GTH: ADC0 Greater-Than Data High Byte Register
SFR Page:
SFR Address:
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W Reset Value
Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0
0
0xC5
Bits7-0: High byte of ADC0 Greater-Than Data Word.
Figure 6.13. ADC0GTL: ADC0 Greater-Than Data Low Byte Register
SFR Page:
SFR Address:
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W Reset Value
Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0
Bits7-0: Low byte of ADC0 Greater-Than Data Word.
0
0xC4
11111111
11111111
78 Rev. 1.2
Page 79

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
Figure 6.14. ADC0LTH: ADC0 Less-Than Data High Byte Register
SFR Page:
SFR Address:
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W Reset Value
Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0
0
0xC7
Bits7-0: High byte of ADC0 Less-Than Data Word.
Figure 6.15. ADC0LTL: ADC0 Less-Than Data Low Byte Register
SFR Page:
SFR Address:
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W Reset Value
Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0
Bits7-0: Low byte of ADC0 Less-Than Data Word.
0
0xC6
00000000
00000000
Rev. 1.2 79
Page 80

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
Figure 6.16. 10-Bit ADC0 Window Interrupt Example: Right Justified Single-Ended Data
Input Voltage
(AD0.0 - AGND)
REF x (1023/1024)
REF x (512/1024)
REF x (256/1024)
0
ADC Data
Word
0x03FF
0x0201
0x0200
0x01FF
0x0101
0x0100
0x00FF
0x0000
ADWINT
not affected
ADC0LTH:ADC0LTL
ADWINT=1
ADC0GTH:ADC0GTL
ADWINT
not affected
Given:
AMX0SL = 0x00, AMX0CF = 0x00
AD0LJST = ‘0’,
ADC0LTH:ADC0LTL = 0x0200,
ADC0GTH:ADC0GTL = 0x0100.
An ADC0 End of Conversion will cause an ADC0
Window Compare Interrupt (AD0WINT = ‘1’) if
the resulting ADC0 Data Word is < 0x0200 and
> 0x0100.
Input Voltage
(AD0.0 - AGND)
REF x (1023/1024)
REF x (512/1024)
REF x (256/1024)
0
ADC Data
Word
0x03FF
0x0201
0x0200
0x01FF
0x0101
0x0100
0x00FF
0x0000
ADWINT=1
ADC0GTH:ADC0GTL
ADWINT
not affected
ADC0LTH:ADC0LTL
ADWINT=1
Given:
AMX0SL = 0x00, AMX0CF = 0x00,
AD0LJST = ‘0’,
ADC0LTH:ADC0LTL = 0x0100,
ADC0GTH:ADC0GTL = 0x0200.
An ADC0 End of Conversion will cause an ADC0
Window Compare Interrupt (AD0WINT = ‘1’) if
the resulting ADC0 Data Word is > 0x0200 or
< 0x0100.
80 Rev. 1.2
Page 81

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
Figure 6.17. 10-Bit ADC0 Window Interrupt Example: Right Justified Differential Data
Input Voltage
(AD0.0 - AD0.1)
REF x (511/512)
REF x (256/512)
REF x (-1/512)
-REF
ADC Data
Word
0x01FF
0x0101
0x0100
0x00FF
0x0000
0xFFFF
0xFFFE
0xFE00
ADWINT
not affected
ADC0LTH:ADC0LTL
ADWINT=1
ADC0GTH:ADC0GTL
ADWINT
not affected
Given:
AMX0SL = 0x00, AMX0CF = 0x01,
AD0LJST = ‘0’,
ADC0LTH:ADC0LTL = 0x0100,
ADC0GTH:ADC0GTL = 0xFFFF.
An ADC0 End of Conversion will cause an ADC0
Window Compare Interrupt (AD0WINT = ‘1’) if
the resulting ADC0 Data Word is < 0x0100 and
> 0xFFFF. (In two’s-complement math,
0xFFFF = -1.)
Input Voltage
(AD0.0 - AD0.1)
REF x (511/512)
REF x (256/512)
REF x (-1/512)
-REF
ADC Data
Word
0x01FF
0x0101
0x0100
0x00FF
0x0000
0xFFFF
0xFFFE
0xFE00
ADWINT=1
ADC0GTH:ADC0GTL
ADWINT
not affected
ADC0LTH:ADC0LTL
ADWINT=1
Given:
AMX0SL = 0x00, AMX0CF = 0x01,
AD0LJST = ‘0’,
ADC0LTH:ADC0LTL = 0xFFFF,
ADC0GTH:ADC0GTL = 0x0100.
An ADC0 End of Conversion will cause an ADC0
Window Compare Interrupt (AD0WINT = ‘1’) if
the resulting ADC0 Data Word is < 0xFFFF or
> 0x0100. (In two’s-complement math,
0xFFFF = -1.)
Rev. 1.2 81
Page 82

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
Figure 6.18. 10-Bit ADC0 Window Interrupt Example: Left Justified Single-Ended Data
Input Voltage
(AD0.0 - AGND)
REF x (1023/1024)
REF x (512/1024)
REF x (256/1024)
0
ADC Data
Word
0xFFC0
0x8040
0x8000
0x7FC0
0x4040
0x4000
0x3FC0
0x0000
ADWINT
not affected
ADC0LTH:ADC0LTL
ADWINT=1
ADC0GTH:ADC0GTL
ADWINT
not affected
Given:
AMX0SL = 0x00, AMX0CF = 0x00,
AD0LJST = ‘1’,
ADC0LTH:ADC0LTL = 0x2000,
ADC0GTH:ADC0GTL = 0x1000.
An ADC0 End of Conversion will cause an ADC0
Window Compare Interrupt (AD0WINT = ‘1’) if
the resulting ADC0 Data Word is < 0x2000 and
> 0x1000.
Input Voltage
(AD0.0 - AGND)
REF x (1023/1024)
REF x (512/1024)
REF x (256/1024)
0
ADC Data
Word
0xFFC0
0x8040
0x8000
0x7FC0
0x4040
0x4000
0x3FC0
0x0000
ADWINT=1
ADC0GTH:ADC0GTL
ADWINT
not affected
ADC0LTH:ADC0LTL
ADWINT=1
Given:
AMX0SL = 0x00, AMX0CF = 0x00,
AD0LJST = ‘1’
ADC0LTH:ADC0LTL = 0x1000,
ADC0GTH:ADC0GTL = 0x2000.
An ADC0 End of Conversion will cause an ADC0
Window Compare Interrupt (AD0WINT = ‘1’) if
the resulting ADC0 Data Word is < 0x1000 or
> 0x2000.
82 Rev. 1.2
Page 83

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
Figure 6.19. 10-Bit ADC0 Window Interrupt Example: Left Justified Differential Data
Input Voltage
(AD0.0 - AD0.1)
REF x (511/512)
REF x (128/512)
REF x (-1/512)
-REF
ADC Data
Word
0x7FC0
0x2040
0x2000
0x1FC0
0x0000
0xFFC0
0xFF80
0x8000
ADWINT
not affected
ADC0LTH:ADC0LTL
ADWINT=1
ADC0GTH:ADC0GTL
ADWINT
not affected
Given:
AMX0SL = 0x00, AMX0CF = 0x01,
AD0LJST = ‘1’,
ADC0LTH:ADC0LTL = 0x2000,
ADC0GTH:ADC0GTL = 0xFFC0.
An ADC0 End of Conversion will cause an ADC0
Window Compare Interrupt (AD0WINT = ‘1’) if
the resulting ADC0 Data Word is < 0x2000 and
> 0xFFC0. (Two’s-complement math.)
Input Voltage
(AD0.0 - AD0.1)
REF x (511/512)
REF x (128/512)
REF x (-1/512)
-REF
ADC Data
Word
0x7FC0
0x2040
0x2000
0x1FC0
0x0000
0xFFC0
0xFF80
0x8000
ADWINT=1
ADC0GTH:ADC0GTL
ADWINT
not affected
ADC0LTH:ADC0LTL
ADWINT=1
Given:
AMX0SL = 0x00, AMX0CF = 0x01,
AD0LJST = ‘1’,
ADC0LTH:ADC0LTL = 0xFFC0,
ADC0GTH:ADC0GTL = 0x2000.
An ADC0 End of Conversion will cause an ADC0
Window Compare Interrupt (AD0WINT = ‘1’) if
the resulting ADC0 Data Word is < 0xFFC0 or
> 0x2000. (Two’s-complement math.)
Rev. 1.2 83
Page 84

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
Table 6.1. 10-Bit ADC0 Electrical Characteristics (C8051F122/3/6/7)
VDD = 3.0V, AV+ = 3.0V, VREF = 2.40V (REFBE=0), PGA Gain = 1, -40°C to +85°C unless otherwise specified
PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
DC ACCURACY
Resolution 10 bits
Integral Nonlinearity ±1 LSB
Differential Nonlinearity Guaranteed Monotonic ±1 LSB
Offset Error ±0.5 LSB
Full Scale Error Differential mode -1.5±0.5 LSB
Offset Temperature Coefficient ±0.25 ppm/°C
DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE (10 kHz sine-wave input, 0 to 1 dB below Full Scale, 100 ksps
Signal-to-Noise Plus Distortion 59 dB
Total Harmonic Distortion
Spurious-Free Dynamic Range 80 dB
CONVERSION RATE
SAR Clock Frequency 2.5 MHz
Conversion Time in SAR Clocks 16 clocks
Track/Hold Acquisition Time 1.5 µs
Throughput Rate 100 ksps
ANALOG INPUTS
Input Voltage Range Single-ended operation 0 VREF V
*Common-mode Voltage Range Differential operation AGND AV+ V
Input Capacitance 10 pF
TEMPERATURE SENSOR
Linearity Note 1 ±0.2 °C
Gain Note 2 2.86
Offset Note 1, Note 2, (Temp = 0 °C) 776
POWER SPECIFICATIONS
Power Supply Current (AV+ supplied to ADC)
Power Supply Rejection ±0.3 mV/V
Note 1: Includes ADC offset, gain, and linearity variations.
Note 2: Represents one standard deviation from the mean.
Up to the 5
Operating Mode, 100 ksps 450 900 µA
th
harmonic
-70 dB
mV / °C
±0.034
mV
±8.5
84 Rev. 1.2
Page 85

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
7. ADC2 (8-BIT ADC)
The ADC2 subsystem for the C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7 consists of an 8-channel, configurable analog multiplexer
(AMUX2), a programmable gain amplifier (PGA2), and a 500 ksps, 8-bit successive-approximation-register ADC
with integrated track-and-hold (see block diagram in Figure 7.1). The AMUX2, PGA2, and Data Conversion Modes
are all configurable under software control via the Special Function Registers shown in Figure 7.1. The ADC2 subsystem (8-bit ADC, track-and-hold and PGA) is enabled only when the AD2EN bit in the ADC2 Control register
(ADC2CN) is set to logic 1. The ADC2 subsystem is in low power shutdown when this bit is logic 0. The voltage reference used by ADC2 is selected as described in Section “9. VOLTAGE REFERENCE (C8051F120/2/4/6)” on
page 107 for C8051F120/2/4/6 devices, or Section “10. VOLTAGE REFERENCE (C8051F121/3/5/7)” on
page 109 for C8051F121/3/5/7 devices.
Figure 7.1. ADC2 Functional Block Diagram
PIN67IC
AMX2CF
+
-
+
-
8-to-1
AMUX
+
-
+
-
PIN01IC
PIN23IC
PIN45IC
X
AMX2SL ADC2CN
AIN2.0 (P1.0)
AIN2.1 (P1.1)
AIN2.2 (P1.2)
AIN2.3 (P1.3)
AIN2.4 (P1.4)
AIN2.5 (P1.5)
AIN2.6 (P1.6)
AIN2.7 (P1.7)
7.1. Analog Multiplexer and PGA
AD2EN
AV+
AV+
ADC2LTHADC2GTH
REF
SYSCLK
8
16
Dig
Comp
AD2WINT
8-Bit
+
SAR
-
AD2SC0
ADC
AMP2GN0
AMP2GN1
AD2BUSY
AD2INT
AD2TM
AD2EN
AGND
AMX2AD0
AMX2AD1
AMX2AD2
AD2SC3
AD2SC4
ADC2CF
AD2SC1
AD2SC2
8
Start Conversion
AD2CM
AD2WINT
AD2CM0
AD2CM1
AD2CM2
8
ADC2
000
001
010
011
1xx
AD2CM
Write to AD2BUSY
Timer 3 Overflow
CNVSTR2
Timer 2 Overflow
Write to AD0BUSY
(synchronized with
ADC0)
Eight ADC2 channels are available for measurement, as selected by the AMX2SL register (see Figure 7.5). The PGA
amplifies the ADC2 output signal by an amount determined by the states of the AMP2GN2-0 bits in the ADC2 Configuration register, ADC2CF (Figure 7.6). The PGA can be software-programmed for gains of 0.5, 1, 2, or 4. Gain
defaults to 0.5 on reset.
Important Note: AIN2 pins also function as Port 1 I/O pins, and must be configured as analog inputs when used as
ADC2 inputs. To configure an AIN2 pin for analog input, set to ‘0’ the corresponding bit in register P1MDIN. Port 1
pins selected as analog inputs are skipped by the Digital I/O Crossbar. See Section “19.1.5. Configuring Port 1 Pins
as Analog Inputs” on page 219 for more information on configuring the AIN2 pins.
Rev. 1.2 85
Page 86

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
7.2. ADC2 Modes of Operation
ADC2 has a maximum conversion speed of 500 ksps. The ADC2 conversion clock (SAR2 clock) is a divided version
of the system clock, determined by the AD2SC bits in the ADC2CF register. The maximum ADC2 conversion clock
is 7.5 MHz.
7.2.1. Starting a Conversion
A conversion can be initiated in one of five ways, depending on the programmed states of the ADC2 Start of Conversion Mode bits (AD2CM2-0) in ADC2CN. Conversions may be initiated by:
1. Writing a ‘1’ to the AD2BUSY bit of ADC2CN;
2. A Timer 3 overflow (i.e. timed continuous conversions);
3. A rising edge detected on the external ADC convert start signal, CNVSTR2;
4. A Timer 2 overflow (i.e. timed continuous conversions);
5. Writing a ‘1’ to the AD0BUSY of register ADC0CN (initiate conversion of ADC2 and ADC0 with a
single software command).
During conversion, the AD2BUSY bit is set to logic 1 and restored to 0 when conversion is complete. The falling
edge of AD2BUSY triggers an interrupt (when enabled) and sets the interrupt flag in ADC2CN. Converted data is
available in the ADC2 data word, ADC2.
When a conversion is initiated by writing a ‘1’ to AD2BUSY, it is recommended to poll AD2INT to determine when
the conversion is complete. The recommended procedure is:
Step 1. Write a ‘0’ to AD2INT;
Step 2. Write a ‘1’ to AD2BUSY;
Step 3. Poll AD2INT for ‘1’;
Step 4. Process ADC2 data.
When CNVSTR2 is used as a conversion start source, it must be enabled in the crossbar, and the corresponding pin
must be set to open-drain, high-impedance mode (see Section “19. PORT INPUT/OUTPUT” on page 215 for more
details on Port I/O configuration).
7.2.2. Tracking Modes
The AD2TM bit in register ADC2CN controls the ADC2 track-and-hold mode. In its default state, the ADC2 input is
continuously tracked, except when a conversion is in progress. When the AD2TM bit is logic 1, ADC2 operates in
low-power track-and-hold mode. In this mode, each conversion is preceded by a tracking period of 3 SAR clocks
(after the start-of-conversion signal). When the CNVSTR2 signal is used to initiate conversions in low-power tracking mode, ADC2 tracks only when CNVSTR2 is low; conversion begins on the rising edge of CNVSTR2 (see
Figure 7.2). Tracking can also be disabled (shutdown) when the entire chip is in low power standby or sleep modes.
Low-power Track-and-Hold mode is also useful when AMUX or PGA settings are frequently changed, due to the settling time requirements described in Section “7.2.3. Settling Time Requirements” on page 88.
86 Rev. 1.2
Page 87

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
Figure 7.2. ADC2 Track and Conversion Example Timing
A. ADC Timing for External Trigger Source
CNVSTR2
(AD2CM[2:0]=010)
123456789
SAR Clocks
AD2TM=1
Write '1' to AD2BUSY,
Timer 3 Overflow,
Timer 2 Overflow,
Write '1' to AD0BUSY
(AD2CM[2:0]=000, 001, 011, 1xx)
SAR Clocks
AD2TM=1
SAR Clocks
AD2TM=0
Low Power
or Convert
Track or Convert Convert TrackAD2TM=0
Track Convert Low Power Mode
B. ADC Timing for Internal Trigger Source
123456789101112
Low Power
or Convert
Track or
Convert
Track Convert Low Power Mode
123456789
Convert Track
Rev. 1.2 87
Page 88

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
7.2.3. Settling Time Requirements
When the ADC2 input configuration is changed (i.e., a different MUX or PGA selection), a minimum tracking time is
required before an accurate conversion can be performed. This tracking time is determined by the ADC2 MUX resistance, the ADC2 sampling capacitance, any external source resistance, and the accuracy required for the conversion.
Figure 7.3 shows the equivalent ADC2 input circuit. The required ADC2 settling time for a given settling accuracy
(SA) may be approximated by Equation 7.1. Note: An absolute minimum settling time of 800 ns required after any
MUX selection. Note that in low-power tracking mode, three SAR2 clocks are used for tracking at the start of every
conversion. For most applications, these three SAR2 clocks will meet the tracking requirements.
Equation 7.1. ADC2 Settling Time Requirements
n
2
t
-------
SA
Where:
SA is the settling accuracy, given as a fraction of an LSB (for example, 0.25 to settle within 1/4 LSB)
t is the required settling time in seconds
R
is the sum of the ADC2 MUX resistance and any external source resistance.
TOTAL
n is the ADC resolution in bits (8).
R
×ln=
TOTALCSAMPLE
AIN2.x
AIN2.y
Figure 7.3. ADC2 Equivalent Input Circuit
Differential Mode
MUX Select
R
= 5k
MUX
RC
= R
MUX
* C
SAMPL E
R
= 5k
MUX
Note: When the PGA gain is set to 0.5, C
Input
MUX Select
C
SAMPLE
C
SAMPLE
= 5pF
= 5pF
Single-Ended Mode
MUX Select
AIN2.x
RC
Input
SAMPLE
= R
MUX
= 3pF
R
* C
MUX
SAMPLE
= 5k
C
SAMPLE
= 5pF
88 Rev. 1.2
Page 89

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
Figure 7.4. AMX2CF: AMUX2 Configuration Register
SFR Page:
SFR Address:
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W Reset Value
Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0
Bits7-4: UNUSED. Read = 0000b; Write = don’t care.
Bit3: PIN67IC: AIN2.6, AIN2.7 Input Pair Configuration Bit.
Bit2: PIN45IC: AIN2.4, AIN2.5 Input Pair Configuration Bit.
Bit1: PIN23IC: AIN2.2, AIN2.3 Input Pair Configuration Bit.
Bit0: PIN01IC: AIN2.0, AIN2.1 Input Pair Configuration Bit.
NOTE: The ADC2 Data Word is in 2’s complement format for channels configured as differential.
2
0xBA
- - - - PIN67IC PIN45IC PIN23IC PIN01IC 00000000
0: AIN2.6 and AIN2.7 are independent single-ended inputs.
1: AIN2.6 and AIN2.7 are (respectively) +, - differential input pair.
0: AIN2.4 and AIN2.5 are independent single-ended inputs.
1: AIN2.4 and AIN2.5 are (respectively) +, - differential input pair.
0: AIN2.2 and AIN2.3 are independent single-ended inputs.
1: AIN2.2 and AIN2.3 are (respectively) +, - differential input pair.
0: AIN2.0 and AIN2.1 are independent single-ended inputs.
1: AIN2.0 and AIN2.1 are (respectively) +, - differential input pair.
Rev. 1.2 89
Page 90

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
Figure 7.5. AMX2SL: AMUX2 Channel Select Register
SFR Page:
SFR Address:
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W Reset Value
2
0xBB
- - - - AMX2AD2 AMX2AD1 AMX2AD0 00000000
Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0
Bits7-3: UNUSED. Read = 00000b; Write = don’t care.
Bits2-0: AMX2AD2-0: AMX2 Address Bits.
000-111b: ADC Inputs selected per chart below.
AMX2AD2-0
000 001 010 011 100 101 110 111
0000
0001
0010
0011
0100
0101
0110
0111
1000
1001
AMX2CF Bits 3-0
1010
1011
1100
1101
1110
1111
AIN2.0 AIN2.1 AIN2.2 AIN2.3 AIN2.4 AIN2.5 AIN2.6 AIN2.7
+(AIN2.0)
-(AIN2.1)
AIN2.0 AIN2.1
+(AIN2.0)
-(AIN2.1)
AIN2.0 AIN2.1 AIN2.2 AIN2.3
+(AIN2.0)
-(AIN2.1)
AIN2.0 AIN2.1
+(AIN2.0)
-(AIN2.1)
AIN2.0 AIN2.1 AIN2.2 AIN2.3 AIN2.4 AIN2.5
+(AIN2.0)
-(AIN2.1)
AIN2.0 AIN2.1
+(AIN2.0)
-(AIN2.1)
AIN2.0 AIN2.1 AIN2.2 AIN2.3
+(AIN2.0)
-(AIN2.1)
AIN2.0 AIN2.1
+(AIN2.0)
-(AIN2.1)
AIN2.2 AIN2.3 AIN2.4 AIN2.5 AIN2.6 AIN2.7
+(AIN2.2)
-(AIN2.3)
+(AIN2.2)
-(AIN2.3)
AIN2.2 AIN2.3
+(AIN2.2)
-(AIN2.3)
+(AIN2.2)
-(AIN2.3)
AIN2.2 AIN2.3 AIN2.4 AIN2.5
+(AIN2.2)
-(AIN2.3)
+(AIN2.2)
-(AIN2.3)
AIN2.2 AIN2.3
+(AIN2.2)
-(AIN2.3)
+(AIN2.2)
-(AIN2.3)
AIN2.4 AIN2.5 AIN2.6 AIN2.7
AIN2.4 AIN2.5 AIN2.6 AIN2.7
+(AIN2.4)
-(AIN2.5)
+(AIN2.4)
-(AIN2.5)
+(AIN2.4)
-(AIN2.5)
+(AIN2.4)
-(AIN2.5)
AIN2.4 AIN2.5
AIN2.4 AIN2.5
+(AIN2.4)
-(AIN2.5)
+(AIN2.4)
-(AIN2.5)
+(AIN2.4)
-(AIN2.5)
+(AIN2.4)
-(AIN2.5)
AIN2.6 AIN2.7
AIN2.6 AIN2.7
AIN2.6 AIN2.7
AIN2.6 AIN2.7
+(AIN2.6)
-(AIN2.7)
+(AIN2.6)
-(AIN2.7)
+(AIN2.6)
-(AIN2.7)
+(AIN2.6)
-(AIN2.7)
+(AIN2.6)
-(AIN2.7)
+(AIN2.6)
-(AIN2.7)
+(AIN2.6)
-(AIN2.7)
+(AIN2.6)
-(AIN2.7)
90 Rev. 1.2
Page 91

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
A
Figure 7.6. ADC2CF: ADC2 Configuration Register
SFR Page:
SFR Address:
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W Reset Value
AD2SC4 AD2SC3 AD2SC2 AD2SC1 AD2SC0 - AMP2GN1 AMP2GN0 11111000
Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0
Bits7-3: AD2SC4-0: ADC2 SAR Conversion Clock Period Bits.
Bit2: UNUSED. Read = 0b; Write = don’t care.
Bits1-0: AMP2GN1-0: ADC2 Internal Amplifier Gain (PGA).
2
0xBC
SAR Conversion clock is derived from system clock by the following equation, where AD2SC refers
to the 5-bit value held in AD2SC4-0, and CLK
ADC2 SAR Conversion Clock should be less than or equal to 7.5 MHz).
D2SC
00: Gain = 0.5
01: Gain = 1
10: Gain = 2
11: Gain = 4
SYSCLK
-----------------------1–=
CLK
SAR2
refers to the desired ADC2 SAR clock (Note: the
SAR2
Rev. 1.2 91
Page 92

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
Figure 7.7. ADC2CN: ADC2 Control Register
SFR Page:
SFR Address:
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W Reset Value
AD2EN AD2TM AD2INT AD2BUSY AD2CM2 AD2CM1 AD2CM0 AD2WINT 00000000
Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0
Bit7: AD2EN: ADC2 Enable Bit.
Bit6: AD2TM: ADC2 Track Mode Bit.
Bit5: AD2INT: ADC2 Conversion Complete Interrupt Flag.
Bit4: AD2BUSY: ADC2 Busy Bit.
Bits3-1: AD2CM2-0: ADC2 Start of Conversion Mode Select.
Bit0: AD2WINT: ADC2 Window Compare Interrupt Flag.
2
0xE8 (bit addressable)
0: ADC2 Disabled. ADC2 is in low-power shutdown.
1: ADC2 Enabled. ADC2 is active and ready for data conversions.
0: Normal Track Mode: When ADC2 is enabled, tracking is continuous unless a conversion is in process.
1: Low-power Track Mode: Tracking Defined by AD2CM2-0 bits (see below).
This flag must be cleared by software.
0: ADC2 has not completed a data conversion since the last time this flag was cleared.
1: ADC2 has completed a data conversion.
Read:
0: ADC2 Conversion is complete or a conversion is not currently in progress. AD2INT is set to
logic 1 on the falling edge of AD2BUSY.
1: ADC2 Conversion is in progress.
Write:
0: No Effect.
1: Initiates ADC2 Conversion if AD2CM2-0 = 000b
AD2TM = 0:
000: ADC2 conversion initiated on every write of ‘1’ to AD2BUSY.
001: ADC2 conversion initiated on overflow of Timer 3.
010: ADC2 conversion initiated on rising edge of external CNVSTR2.
011: ADC2 conversion initiated on overflow of Timer 2.
1xx: ADC2 conversion initiated on write of ‘1’ to AD0BUSY (synchronized with ADC0 softwarecommanded conversions).
AD2TM = 1:
000: Tracking initiated on write of ‘1’ to AD2BUSY and lasts 3 SAR2 clocks, followed by conversion.
001: Tracking initiated on overflow of Timer 3 and lasts 3 SAR2 clocks, followed by conversion.
010: ADC2 tracks only when CNVSTR2 input is logic low; conversion starts on rising CNVSTR2
edge.
011: Tracking initiated on overflow of Timer 2 and lasts 3 SAR2 clocks, followed by conversion.
1xx: Tracking initiated on write of ‘1’ to AD0BUSY and lasts 3 SAR2 clocks, followed by conversion.
This bit must be cleared by software.
0: ADC2 Window Comparison Data match has not occurred since this flag was last cleared.
1: ADC2 Window Comparison Data match has occurred.
92 Rev. 1.2
Page 93

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
Figure 7.8. ADC2: ADC2 Data Word Register
SFR Page:
SFR Address:
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W Reset Value
Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0
Bits7-0: ADC2 Data Word.
2
0xBE
Figure 7.9. ADC2 Data Word Example
Single-Ended Example:
8-bit ADC Data Word appears in the ADC2 Data Word Register as follows:
Example: ADC2 Data Word Conversion Map, Single-Ended AIN2.0 Input
(AMX2CF = 0x00; AMX2SL = 0x00)
AIN2.0-AGND
(Volts)
VREF * (255/256) 0xFF
VREF * (128/256) 0x80
VREF * (64/256) 0x40
00x00
ADC2
00000000
Gain
Code Vin
Differential Example:
8-bit ADC Data Word appears in the ADC2 Data Word Register as follows:
Example: ADC2 Data Word Conversion Map, Differential AIN2.0-AIN2.1 Input
(AMX2CF = 0x01; AMX2SL = 0x00)
AIN2.0-AIN2.1
(Volts)
VREF * (127/128) 0x7F
VREF * (64/128) 0x40
00x00
-VREF * (64/128) 0xC0 (-64d)
-VREF * (128/128) 0x80 (-128d)
Code Vin
---------------
× 256×=
VREF
Gain
-------------------------
× 256×=
2 V× REF
ADC2
Rev. 1.2 93
Page 94

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
7.3. ADC2 Programmable Window Detector
The ADC2 Programmable Window Detector continuously compares the ADC2 output to user-programmed limits,
and notifies the system when a desired condition is detected. This is especially effective in an interrupt-driven system,
saving code space and CPU bandwidth while delivering faster system response times. The window detector interrupt
flag (AD2WINT in register ADC2CN) can also be used in polled mode. The ADC2 Greater-Than (ADC2GT) and
Less-Than (ADC2LT) registers hold the comparison values. Example comparisons for Differential and Single-ended
modes are shown in Figure 7.11 and Figure 7.10, respectively. Notice that the window detector flag can be programmed to indicate when measured data is inside or outside of the user-programmed limits, depending on the contents of the ADC2LT and ADC2GT registers.
7.3.1. Window Detector In Single-Ended Mode
Figure 7.10 shows two example window comparisons for Single-ended mode, with ADC2LT = 0x20 and
ADC2GT = 0x10. Notice that in Single-ended mode, the codes vary from 0 to VREF*(255/256) and are represented
as 8-bit unsigned integers. In the left example, an AD2WINT interrupt will be generated if the ADC2 conversion
word (ADC2) is within the range defined by ADC2GT and ADC2LT (if 0x10 < ADC2 < 0x20). In the right example,
and AD2WINT interrupt will be generated if ADC2 is outside of the range defined by ADC2GT and ADC2LT
(if ADC2 < 0x10 or ADC2 > 0x20).
Input Voltage
(AIN2.x - AGND)
REF x (255/256)
REF x (32/256)
REF x (16/256)
0
Figure 7.10. ADC2 Window Compare Examples, Single-Ended Mode
ADC2 ADC2
Input Voltage
(AIN2.x - AGND)
0xFF
0x21
0x20
0x1F
0x11
0x10
0x0F
0x00
AD2WINT
not affected
ADC2LT
ADC2GT
AD2WINT
not affected
REF x (255/256)
REF x (32/256)
AD2WINT=1
REF x (16/256)
0
0xFF
0x21
0x20
0x1F
0x11
0x10
0x0F
0x00
ADC2GT
AD2WINT
not affected
ADC2LT
AD2WINT=1
AD2WINT=1
94 Rev. 1.2
Page 95

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
7.3.2. Window Detector In Differential Mode
Figure 7.11 shows two example window comparisons for differential mode, with ADC2LT = 0x10 (+16d) and
ADC2GT = 0xFF (-1d). Notice that in Differential mode, the codes vary from -VREF to VREF*(127/128) and are
represented as 8-bit 2’s complement signed integers. In the left example, an AD2WINT interrupt will be generated if
the ADC2 conversion word (ADC2L) is within the range defined by ADC2GT and ADC2LT (if 0xFF (-1d) < ADC2
< 0x0F (16d)). In the right example, an AD2WINT interrupt will be generated if ADC2 is outside of the range
defined by ADC2GT and ADC2LT (if ADC2 < 0xFF (-1d) or ADC2 > 0x10 (+16d)).
Figure 7.11. ADC2 Window Compare Examples, Differential Mode
ADC2ADC2
Input Voltage
(AIN2.x - AIN2.y)
REF x (127/128)
0x7F (127d)
Input Voltage
(AIN2.x - AIN2.y)
REF x (127/128)
0x7F (127d)
REF x (16/128)
REF x (-1/256)
-REF
0x11 (17d)
0x10 (16d)
0x0F (15d)
0x00 (0d)
0xFF (-1d)
0xFE (-2d)
0x80 (-128d)
AD2WINT
not affected
ADC2LT
ADC2GT
AD2WINT
not affected
AD2WINT=1
REF x (16/128)
REF x (-1/256)
-REF
0x11 (17d)
0x10 (16d)
0x0F (15d)
0x00 (0d)
0xFF (-1d)
0xFE (-2d)
0x80 (-128d)
ADC2GT
AD2WINT
not affected
ADC2LT
AD2WINT=1
AD2WINT=1
Rev. 1.2 95
Page 96

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
Figure 7.12. ADC2GT: ADC2 Greater-Than Data Byte Register
SFR Page:
SFR Address:
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W Reset Value
Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0
2
0xC4
Bits7-0: ADC2 Greater-Than Data Word.
Figure 7.13. ADC2LT: ADC2 Less-Than Data Byte Register
SFR Page:
SFR Address:
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W Reset Value
Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0
Bits7-0: ADC2 Less-Than Data Word.
2
0xC6
11111111
00000000
96 Rev. 1.2
Page 97

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
Table 7.1. ADC2 Electrical Characteristics
VDD = 3.0 V, AV+ = 3.0 V, VREF2 = 2.40 V (REFBE=0), PGA gain = 1, -40°C to +85°C unless otherwise specified
PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
DC ACCURACY
Resolution 8 bits
Integral Nonlinearity ±1 LSB
Differential Nonlinearity Guaranteed Monotonic ±1 LSB
Offset Error 0.5±0.3 LSB
Full Scale Error Differential mode -1±0.2 LSB
Offset Temperature Coefficient TBD ppm/°C
DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE (10 kHz sine-wave input, 1 dB below Full Scale, 500 ksps
Signal-to-Noise Plus Distortion TBD 47 dB
Total Harmonic Distortion
Spurious-Free Dynamic Range 52 dB
CONVERSION RATE
SAR Clock Frequency 7.5 MHz
Conversion Time in SAR Clocks 8 clocks
Track/Hold Acquisition Time 800 ns
Throughput Rate 500 ksps
ANALOG INPUTS
Input Voltage Range 0 VREF V
Input Capacitance 5 pF
POWER SPECIFICATIONS
Power Supply Current (AV+ supplied to ADC2)
Power Supply Rejection ±0.3 mV/V
Up to the 5
Operating Mode, 500 ksps 420 TBD µA
th
harmonic
51 dB
Rev. 1.2 97
Page 98

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
98 Rev. 1.2
Page 99

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
8. DACS, 12-BIT VOLTAGE MODE
Each C8051F12x device includes two on-chip 12-bit voltage-mode Digital-to-Analog Converters (DACs). Each
DAC has an output swing of 0 V to (VREF-1LSB) for a corresponding input code range of 0x000 to 0xFFF. The
DACs may be enabled/disabled via their corresponding control registers, DAC0CN and DAC1CN. While disabled,
the DAC output is maintained in a high-impedance state, and the DAC supply current falls to 1 µA or less. The voltage reference for each DAC is supplied at the VREFD pin (C8051F120/2/4/6 devices) or the VREF pin (C8051F121/
3/5/7 devices). Note that the VREF pin on C8051F121/3/5/7 devices may be driven by the internal voltage reference
or an external source. If the internal voltage reference is used it must be enabled in order for the DAC outputs to be
valid. See Section “9. VOLTAGE REFERENCE (C8051F120/2/4/6)” on page 107 or Section “10. VOLTAGE
REFERENCE (C8051F121/3/5/7)” on page 109 for more information on configuring the voltage reference for the
DACs.
8.1. DAC Output Scheduling
Each DAC features a flexible output update mechanism which allows for seamless full-scale changes and supports
jitter-free updates for waveform generation. The following examples are written in terms of DAC0, but DAC1 operation is identical.
8.1.1. Update Output On-Demand
In its default mode (DAC0CN.[4:3] = ‘00’) the DAC0 output is updated “on-demand” on a write to the high-byte of
the DAC0 data register (DAC0H). It is important to note that writes to DAC0L are held, and have no effect on the
DAC0 output until a write to DAC0H takes place. If writing a full 12-bit word to the DAC data registers, the 12-bit
data word is written to the low byte (DAC0L) and high byte (DAC0H) data registers. Data is latched into DAC0 after
Figure 8.1. DAC Functional Block Diagram
DAC0EN
DAC0H
Timer 3
Timer 4
Timer 2
DAC0MD1
DAC0MD0
DAC0DF2
DAC0CN
DAC0DF1
DAC0DF0
DAC1EN
DAC1MD1
DAC1MD0
DAC1DF2
DAC1CN
DAC1DF1
DAC1DF0
8
DAC0HDAC0L
8
DAC1H
8
DAC1HDAC1L
8
8
8
Latch Latch
Timer 3
Timer 4
Timer 2
8
8
Latch Latch
REF
AV+
12
DAC0
Dig. MUX
AGND
REF
AV+
12
DAC1
Dig. MUX
AGND
DAC0
DAC1
Rev. 1.2 99
Page 100

C8051F120/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
a write to the corresponding DAC0H register, so the write sequence should be DAC0L followed by DAC0H if the
full 12-bit resolution is required. The DAC can be used in 8-bit mode by initializing DAC0L to the desired value (typically 0x00), and writing data to only DAC0H (also see Section 8.2 for information on formatting the 12-bit DAC
data word within the 16-bit SFR space).
8.1.2. Update Output Based on Timer Overflow
Similar to the ADC operation, in which an ADC conversion can be initiated by a timer overflow independently of the
processor, the DAC outputs can use a Timer overflow to schedule an output update event. This feature is useful in
systems where the DAC is used to generate a waveform of a defined sampling rate by eliminating the effects of variable interrupt latency and instruction execution on the timing of the DAC output. When the DAC0MD bits
(DAC0CN.[4:3]) are set to ‘01’, ‘10’, or ‘11’, writes to both DAC data registers (DAC0L and DAC0H) are held until
an associated Timer overflow event (Timer 3, Timer 4, or Timer 2, respectively) occurs, at which time the
DAC0H:DAC0L contents are copied to the DAC input latches allowing the DAC output to change to the new value.
8.2. DAC Output Scaling/Justification
In some instances, input data should be shifted prior to a DAC0 write operation to properly justify data within the
DAC input registers. This action would typically require one or more load and shift operations, adding software overhead and slowing DAC throughput. To alleviate this problem, the data-formatting feature provides a means for the
user to program the orientation of the DAC0 data word within data registers DAC0H and DAC0L. The three
DAC0DF bits (DAC0CN.[2:0]) allow the user to specify one of five data word orientations as shown in the DAC0CN
register definition.
DAC1 is functionally the same as DAC0 described above. The electrical specifications for both DAC0 and DAC1 are
given in Table 8.1.
100 Rev. 1.2
 Loading...
Loading...