Page 1

MODEL 5000
S E N T R Y
GAS MONITORING SYSTEM
Version 6
Sensors Service
APPLICABILITY & EFFECTIVITY
Effective for all Sentry systems manufactured after September 1, 1995.
Instruction Manual Part Number T12001-A1
Sierra Monitor Corporation
1991 Tarob Court, Milpitas, CA 95035
(408) 262-6611
Applicability & Effectivity
Page 2
SMC sierra monitor corporation Sentry Instruction Manual - Version 6
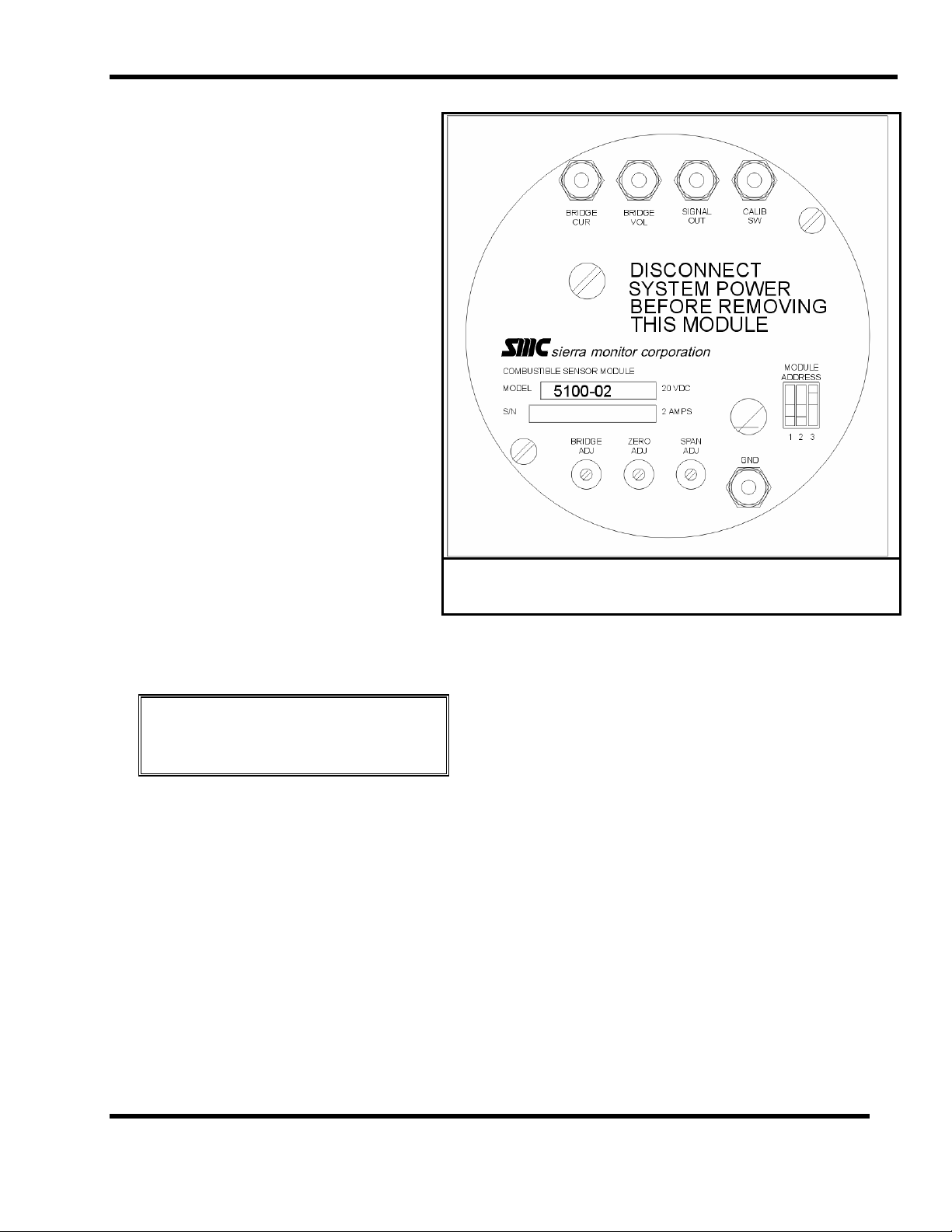
7.5 COMBUSTIBLE GAS SENSOR MODULE
(5100-02)
7.5.1 DESCRIPTION
The Combustible Gas Module includes the sensor
and electronic assembly installed in an explosion
proof housing. The sensor screws into one hub of
the enclosure and plugs into the bottom
electronics card via a six pin connector. Cabling
to the controller connects to a three pin spring
loaded terminal strip.
7.5.2 TROUBLE ANALYSIS
Electrical adjustment, or replacement of the
sensor will be necessary under the following
conditions:
• Controller displays the following error
messages:
CHK BRIDGE VOLT
SENSOR FAILURE
LOW SENSITIVITY
• False readings or alarms are received
due to sensor inaccuracy.
Warning: : During sensor adjustments the
concentration reading on the controller will be
inaccurate and alarm level concentrations may be
displayed. If false activation of the alarm relays
will cause a problem disconnect the relay wiring
prior to adjustment or turn the module off using the
CHANGE MODULE mode.
NOTE
Although all the necessary data can be collected with a
voltmeter at the sensor module, some helpful information
can be displayed or printed. See diagnostic codes 0004
and 0008 in Appendix C.
7.5.3 ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURE
Prior to reading voltages and making adjustments perform
a visual inspection to confirm that there are no physical
problems such as water in the electronics enclosure,
wiring damage or corrosion.
Use Figure 7-6 to locate test points during the following
procedures:
Caution: The area must be free of flammable vapors or
gases during any adjustments or maintenance procedures.
7.5.3.1 BRIDGE VOLTAGE ADJUSTMENT
Confirm that no combustible gas is present and remove
sensor module cover.
Figure 7-6
Cover Plate - Combustible Gas Module
Comparing to the "GND" (ground) test point measure
"BRIDGE VOL" (bridge voltage) and adjust to 2.00 VDC
using "BRIDGE ADJ" potentiometer. Turn counterclockwise to increase.
7.5.3.2 ZERO ADJUSTMENT
Comparing to ground measure SIGNAL OUT and adjust to
0.18 VDC by turning
ZERO ADJ potentiometer. Turn
counter clock-wise to increase.
7.5.3.3 SPAN ADJUSTMENT
1. Determine the concentration of the calibration
gas (CG) in % LEL.
2. Use the following formula to determine the
response to the calibration gas at
SIGNAL OUT.
Voltage (Signal Out) = (CG+12)/60
For Example:
If CG = 50% L.E.L
Signal Out = (50+12)/60
= 1.03 volts
SERVICE
Page: 69
Page 3

SMC sierra monitor corporation Sentry Instruction Manual - Version 6
3. Using a Sierra Monitor Model 1200-26 Gas
Calibrator with a Sierra Monitor Model 535800 calibration adapter, or Model 5360 Gas
Delivery Fitting. Apply the calibration gas at a
flow rate of 100 cc/min. until the signal out
voltage stops changing (approx. 2 minutes).
Then adjust span adj. potentiometer to the
calculated value.
4. Remove the calibration gas and wait for the
voltage to drop. If the voltage is below 0.30
VDC the procedure is complete. If the voltage
is above 0.30 VDC repeat the zero and span
adjustments.
5. Calibrate the sensor using the instruction
manual procedure.
LOW SENSITIVITY message during
• A
calibration indicates one of the two
conditions for a combustible sensor:
• The zero gas voltage must be less than
.3 volts.
• The new span change (span voltage less
zero voltage) must exceed 30% of the
calculated span change.
For Example:
Zero gas voltage = .20 VDC
Span voltage = .43 VDC
Span change is .43-.2 = .23 VDC
As the calculated span value (from
step 5 above) is 1.03, the calculated
span change is: 1.03-.2 = .87
By calculation: 30% of .87 = .26
The new span change (.23) is less than
30% of the calculated span change so a
LOW SENSITIVITY message will be
displayed.
LOW SENSITIVITY calculation is made to insure that
The
the calibration does not adjust the electronics so that the
"gain" is large enough to cause false alarms due to minor
drift or due to minimal electronic noise.
PIN FUNCTION WIRE COLOR
1 DETECTOR WHITE
2 COMPENSATOR BROWN
3 CALIB. SW. RED
4 DETECTOR BLACK
5 DRAIN BARE
6 CALIB. SW. GREEN
Table 7-5
Combustible Gas Sensor
Wiring Pin Out
1. Detector element resistance should be between 1.5 to
2 ohms.
2. Compensator element resistance should be between
1.5 to 2 ohms.
3. Calibration switch should be open in normal
operation and should close when the calibration
magnet is applied.
If the sensor fails any of these tests it should be replaced.
If the sensor passes these tests the electronics are suspect
and BOTH the sensor and electronics should be replaced.
(The electronics and sensor which are removed should be
returned to the factory for evaluation).
When a new sensor is installed th e follo wing action s must
be taken:
• Make the bridge voltage adjustment
immediately to avoid over-voltage damage to
the sensor.
• Use diagnostic code 0020 to establish nominal
value calibration.
• Allow 24 hours for full stabilization of the
sensor, recheck the zero and span adjustments
and calibrate the sensor module.
7.5.4 SENSOR REPLACEMENT
If any of the above adjustments cannot be completed
successfully the sensor and/or electronics will require
replacement. To check the sensor unplug it from the
electronics and remove from the housing so that
continuity and resistance tests can be made. Table 7-4
provides the pin out for the sensor assembly.
SERVICE
Page: 70
Page 4

SMC sierra monitor corporation Sentry Instruction Manual - Version 6
7.5.5 COMBUSTIBLE GAS SCALING FACTORS
For combustible gas monitoring, a calibration standard of Methane or Propane my be used in conjunction with scaling
factors to cause Sentry concentration display and alarm function in %LEL scale of another gas as follows:
GAS METHANE PROPANE
FACTOR FACTOR
Acetaldehyde 60 109
Acetic Acid 54 98
Acetic Anhydride 46 83
Acetone 52 94
Acetylene 57 103
Alkyl Alcohol 51 92
Ammonia 126 229
n-Amyl Alcohol 33 59
Aniline 39 71
Benzene 41 74
Biphenyl 25 45
1,3-Butadiene 56 101
n-Butane 58 106
iso-Butane 52 94
Butene-1 45 82
cis-Butene-2 48 88
trans-Butene-2 51 92
n-Butyl Alcohol 34 62
iso-Butyl Alcohol 53 96
tert-Butyl-Alcohol 74 134
n-Butyl Benzene 31 57
iso-Butyl Benzene 32 58
n-Butyric Acid 38 69
Carbon Disulfide 18 32
Carbon Monoxide 75 137
Carbon Oxysulphide 93 169
Chlorobenzene 34 62
Cyanogen 89 162
Cyclohexane 41 74
Cyclopropane 62 113
n-Decane 33 59
Diethylamine 49 88
Dimethylamine 58 105
2,3-Dimethylpentane 40 72
2,3-Dimethylpropane 40 72
Dimethylsulphide 43 79
1,4-Dioxane 45 81
Epichlorohydrin 45 82
Ethane 68 123
Ethyl Acetate 51 93
Ethyl Alcohol 73 132
Ethylamine 53 95
Ethyl Benzene 36 65
Ethyl Bromide 91 165
Ethyl Chloride 57 103
Ethylcyclopentane 40 72
Ethylene 71 128
Ethylenedichloride 66 120
Ethyleneoxide 52 94
NOTES:
Diethyl Ether 46 84
Dimethoxyethane 42 75
Dimethyl Ether 63 113
Dimethylformamide 46 83
Ethyl Formate 44 80
Ethylmercaptan 56 102
n-Heptane 39 70
n-Hexane 37 67
Hydrazine 45 82
Hydrogencyanide 48 86
Hydrogen 77 139
Hydrogen Sulfide 41 74
Methane 100 181
Methyl Actetate 50 90
Methyl Alcohol 86 156
Methylamine 77 140
Methyl Bromide 90 162
Methyl Chloride 102 186
Methylcyclohexane 44 80
Methylenedichloride 93 168
Methylethylether 44 80
Methylethylketone 41 75
Methyl Formate 67 121
Methylmercaptan 61 110
Methylpropionate 51 93
Methyl n-propylketone 40 73
Napthalene 34 62
Nitromethane 34 62
n-Nonane 31 57
n-Octane 37 68
n-Pentane 46 83
i-Pentane 46 84
Propane 55 100
n-Propyl Alcohol 47 85
n-Propylamine 48 88
n-Propylchloride 50 90
Propylene 52 93
Propyleneoxide 46 83
iso-Propylether 44 79
Propyne 42 75
Toluene 40 73
Triethylamine 40 72
Trimethylamine 48 88
Vinylethylether 42 76
o-Xylene 36 65
m-Xylene 39 71
p-Xylene 39 71
JP-4 (Jet Fuel) 41 73
GAS METHANE PROPANE
FACTOR FACTOR
1. Scaling factors are not FMRC approved.
2. Base data source: EEV sensor specification catalog. (EEV claims some data is the result of specific tests, other
data is empirically derived.)
SERVICE
Page: 71
Page 5
SMC sierra monitor corporation Sentry Instruction Manual - Version 6
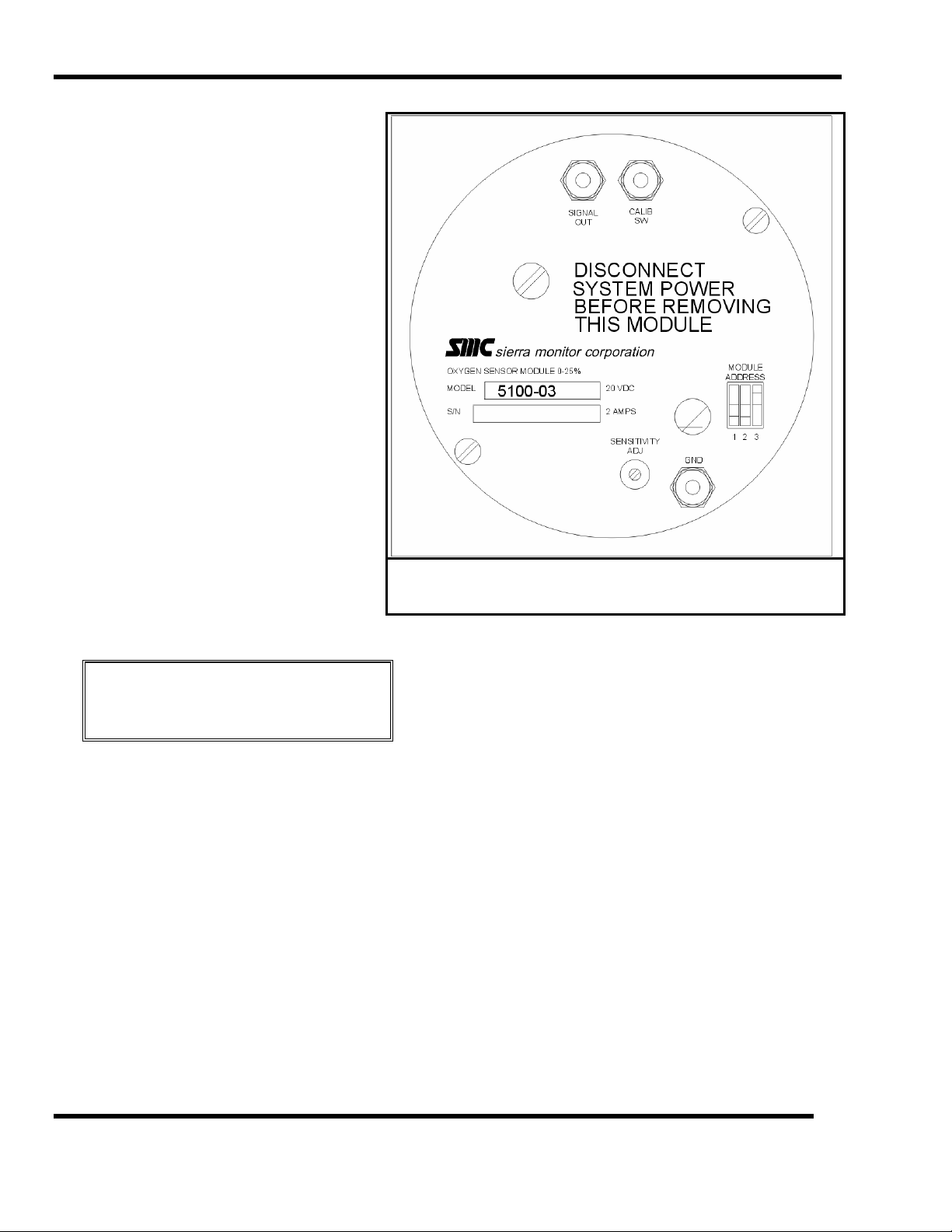
7.6 OXYGEN MODULE (5100-03)
7.6.1 DESCRIPTION
The Oxygen Module includes the electronic
assembly installed in an explosion proof housing
and the electrochemical sensor connected to one
hub of the enclosure. Cabling from the controller
connects to a three pin spring loaded terminal
strip.
7.6.2 TROUBLE ANALYSIS
Electrical adjustment, or replacement of the
sensor will be necessary under the following
conditions:
• Controller displays the following error
messages:
CHANGE SENSOR
SENSOR FAILURE
REPLACE SENSOR
• False readings or alarms are received due to
sensor inaccuracy.
Warning: During sensor adjustments the
concentration reading on the controller will be
inaccurate and alarm level concentrations may be
displayed. If false activation of the alarm relays
will cause a problem disconnect the relay wiring
prior to adjustment or turn the module off using
the "Change Module" mode.
NOTE
Although all the necessary data can be collected with a
voltmeter at the sensor module, some helpful information
can be displayed on the controller or printed. See
diagnostic codes 0004 and 0008 in Appendix C.
7.6.3 ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURE
Prior to reading voltages and making adjustments perform
a visual inspection to confirm that there are no physical
problems such as water in the electronics enclosure,
wiring damage or corrosion.
Use Figure 7-7 to locate test points during the following
procedures.
7.6.3.1 SIGNAL ADJUSTMENT
It is unlikely that any electrical adjustment will be
required except when a new sensor is installed.
To make the electrical adjustment connect a voltmeter to
SIGNAL OUT (pos) and GND (ground) and use
SENSITIVITY ADJ potentiometer to set the voltage equal to
1/10 of the actual oxygen concentration. In clean air the
concentration is 20.9% so the voltage should be set at
2.09 VDC.
Figure 7-7
Cover Plate - Oxygen Module
7.6.4 SENSOR REPLACEMENT
The oxygen sensor should be replaced when it can no
longer be calibrated correctly or when the signal output
drops to zero. Generally this is every twelve to eighteen
months. The Sentry clock keeps track of the age of the
sensor if it is correctly initialized in the "change module"
mode.
When a new sensor is installed use the
CHANGE MODULE
menu selection to answer yes to the "new sensor?"
question. After nine months the
CHANGE SENSOR
message will be displayed to warn that a new sensor
should be installed.
SENSOR FAILURE message for Oxygen sensors does
The
not indicate a specific failure of the sensor but indicates
that the sensor is not correctly connected to the
electronics. If this message appears check that the sensor
harness is correctly installed to the connector on the
bottom electronics board.
When sensor replacement is required, open the cover of
the sensor module, remove the transmitter and disconnect
the sensor wiring harness from the back of the transmitter.
SERVICE
Page: 72
Page 6

SMC sierra monitor corporation Sentry Instruction Manual - Version 6
Unscrew the old sensor from the conduit hub, screw in
the new sensor and connect the wiring harness to the
transmitter electronics. Replace the transmitter into the
enclosure, make signal adjustments as described above,
and replace the enclosure cover.
After the sensor is installed:
• Update "new sensor" status in the change
module mode.
• Allow one hour of stabilization of the new
sensor.
• Make the electrical sensitivity adjustment as
described above.
• Calibrate the sensor module.
SERVICE
Page: 73
Page 7

SMC sierra monitor corporation Sentry Instruction Manual - Version 6
7.7 CARBON MONOXIDE MODULE (5100-04)
7.7.1 DESCRIPTION
The Carbon Monoxide Module includes the
sensor and electronic assembly installed in an
explosion proof housing.
The sensor screws into one hub of the enclosure
and plugs into the bottom electronics card via a
six pin connector. Cabling from the controller
connects to a three pin spring loaded terminal
strip.
7.7.2 TROUBLE ANALYSIS
Electrical adjustment, or replacement of the
sensor will be necessary under the following
conditions:
• Controller displays the following error
messages
SENSOR FAILURE
LOW SENSITIVITY
• False readings or alarms are received
due to sensor inaccuracy.
Warning: During sensor adjustments the
concentration reading on the controller will be
inaccurate and alarm level concentrations may be
displayed. If false activation of the alarm relays
will cause a problem disconnect the relay wiring
prior to adjustment or turn the module off using the
"Change Module" mode.
Note
Although all the necessary data can be collected with a
voltmeter at the sensor module, some helpful information
can be displayed on the controller or printed. See
diagnostic codes 0004 and 0008 in Appendix C.
7.7.3 ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURE
Prior to reading voltages and making adjustments perform
a visual inspection to confirm that there are no physical
problems such as water in the electronics enclosure,
wiring damage or corrosion.
Use Figure 7-8 to locate test points during the following
procedures.
Cover Plate - Carbon Monoxide Module
• 1 ppm CO = 0.004 VDC.
• 100 ppm CO = 0.40 VDC.
• 250 ppm CO = 1.00 VDC.
7.7.3.2 SENSOR REPLACEMENT
The carbon monoxide sensor should be replaced when it
can no longer be calibrated correctly. Generally this is
every twenty four to thirty months.
The "SENSOR FAILURE" message for Carbon
Monoxide sensors does not indicate a specific failure of
the sensor but indicates that the sensor is not correctly
connected to the electronics. If this message appears
check that the sensor harness is correctly installed to the
connector on the bottom electronics board.
Figure 7-8
7.7.3.1 SIGNAL ADJUSTMENT
It is unlikely that any electrical adjustment will be
required except when a new sensor is installed.
To make the electrical adjustment connect a voltmeter to
SIGNAL OUT (pos) and GND (ground) and use
SENSITIVITY ADJ potentiometer to adjust the voltage
based on the following:
SERVICE
Page: 74
Page 8

SMC sierra monitor corporation Sentry Instruction Manual - Version 6
If sensor replacement is necessary remove the electronics
from the housing and unplug the old sensor from the
bottom board, remove it from the enclosure hub and
reverse the procedure to install the new sensor.
After the sensor is installed:
• Allow one hour of stabilization of the new
sensor.
• Make the electrical sensitivity adjustment as
described above.
• Calibrate the sensor using the instruction
manual procedure.
SERVICE
Page: 75
Page 9

SMC sierra monitor corporation Sentry Instruction Manual - Version 6
7.8 HYDROGEN SULFIDE MODULE (5100-05)
7.8.1 DESCRIPTION
Model 5100-05 Hydrogen Sulfide Sensor Module
includes a sensor assembly and electronic
assembly installed in an explosion proof housing.
The sensor assembly includes a reuseable housing
and disposable electrochemical sensor. The
assembly screws into one hub of the sensor
module enclosure and plugs into the bottom
electronics card via a six pin connector.
Cabling from the controller connects to a three
pin spring loaded terminal strip on the electronics
assembly.
7.8.2 TROUBLE ANALYSIS
Electrical adjustment, or replacement of the
sensor will be necessary under the following
conditions:
• Controller displays the following error
messages
SENSOR FAILURE
LOW SENSITIVITY
• False readings or alarms are received
due to sensor inaccuracy.
Cover Plate - Hydrogen Sulfide Module
Figure 7-9
Warning: During sensor adjustments the
concentration reading on the controller will be
inaccurate and alarm level concentrations may be
displayed. If false activation of the alarm relays will
cause a problem disconnect the relay wiring prior to
adjustment or turn the module off using the "Change
Module" mode.
NOTE
Although all the necessary data can be collected with a
voltmeter at the sensor module, some helpful information
can be displayed on the controller or printed. See
diagnostic codes 0004 and 0008 in Appendix C.
7.8.3 ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURE
Prior to reading voltages and making adjustments perform
a visual inspection to confirm that there are no physical
problems such as water in the electronics enclosure,
wiring damage or corrosion.
Use Figure 7-9 to locate test points during the following
procedures.
7.8.3.1 SIGNAL ADJUSTMENT
It is unlikely that any electrical adjustment will be
required except when a new sensor is installed.
To make the electrical adjustment connect a voltmeter to
SIGNAL OUT (pos) and GND (ground) and use SPAN ADJ
potentiometer to adjust the voltage based on the
following:
• 1 ppm H
• 100 ppm H
7.8.3.2 SENSOR REPLACEMENT
S = 0.02 VDC.
2
S = 2.00 VDC.
2
The Hydrogen Sulfide sensor should be replaced when it
can no longer be calibrated correctly. Generally this is
every twenty four to thirty months.
SENSOR FAILURE message for Hydrogen Sulfide
The
sensors does not indicate a specific failure of the sensor
but indicates that the sensor is not correctly connected to
the electronics. If this message appears check that the
sensor harness is correctly installed to the connector on
the bottom electronics board.
The gas sensor which is located inside the sensor
assembly housing can be replaced without replacement of
the housing. To replace the sensor:
SERVICE
Page: 76
Page 10

SMC sierra monitor corporation Sentry Instruction Manual - Version 6
1. Confirm that system power has been
removed.
2. Remove the transmitter electronics board
from the main housing and unplug the
sensor harness from the transmitter
electronics.
3. Unscrew the sensor housing from the
bottom of the enclosure
4. Hold the sensor assembly so that the
harness faces down and the sensor faces
up. Unscrew and remove the round
section of the housing from the hex
section. Be careful not to lose the spacer
washer which will be sitting on top of th e
exposed sensor.
5. Carefully pull the old sensor straight up
from the socket.
6. Orient the new sensor so that the sensor
pin labeled “
“C” which is on the far side of the board
from the vertical reed switch. The reed
switch will slide into a hole on the side of
the new sensor. Press the new sensor’s
pins into the three sockets.
7. Carefully replace the cover on the sensor
assembly including the spacer washer.
8. Install the sensor assembly into the enclosure and
tighten firmly.
9. Reconnect the sensor harness to the transmitter,
install the transmitter into the housing and restore
power.
10. Allow one hour for the sensor to stabilize prior to
recalibration.
11. Recalibrate the sensor module.
7.8.3.3 SENSOR OUTPUT ADJUSTMENT
The following procedure is to be used when, during
normal calibration of a new sensor, the span voltage
cannot be adjusted to a high enough level.
1. Adjust the span potentiometer so that it is
approximately mid range. (Twenty turns
clockwise and tens turns counter-clockwise).
2. Remove system power and remove both the
transmitter and the sensor assembly from the
enclosure. Remove the sensor assembly cover so
that the sensor is visible.
3. Plug the sensor harness into the transmitter
assembly and check that no components are
touching the enclosure. Restore power and allow
a minimum of 30 minutes for stabilization before
adjustment.
C” faces the socket labeled
Figure 7-10
Hydrogen Sulfide Transmitter Component Locator
4. Connect a DVM across TP10 and GT1 on the
transmitter assembly. Figure 7-10
5. Locate the gain potentiometer which is on the
sensor electronics directly behind one of the holes
in the sensor body. The potentiometer is
accessible by inserting a jewelers screwdriver
through the hole in the sensor.
6. Determine the correct value to be read at TP10
based on the following formula:
= 2 (C/R) , where C = concentration of span gas,
V
TP10
and R = range of detection (100 PPM).
7. Apply span gas. Adjust the gain potentiometer
until TP10 = correct value as described above.
To increase voltage at TP10 turn the gain
potentiometer counter clockwise.
8. Remove system power and re-install the sensor
and transmitter in the enclosure. Restore power
and calibrate.
SERVICE
Page: 77
Page 11

SMC sierra monitor corporation Sentry Instruction Manual - Version 6
7.9 TOXIC GAS SENSOR MODULE
7.9.1 DESCRIPTION
Toxic Gas Sensor Modules include the following
models and default ranges:
5100-06 Chlorine -10 PPM
5100-07 Hydrogen - 2000 PPM
5100-12 Nitrogen Dioxide - 20 PPM
5100-13 Carbon Monoxide, High Range -
1,000 PPM
5100-10 Sulfur Dioxide - 100 PPM
5100-16 Carbon Monoxide, H2 Tolerant -
2,000 PPM
5100-19 Nitric Oxide - 20 PPM
5100-21 Hydrogen Chloride - 20 PPM
5100-22 Hydrogen Cyanide - 20 PPM
5100-27 Ethylene Oxide - 20 PPM
The Toxic Sensor Module includes a sensor
assembly and electronic assembly installed in an
explosion proof housing.
The sensor assembly includes a reuseable housing
and disposable electrochemical sensor. The
assembly screws into one hub of the sensor
module enclosure and plugs into the bottom
electronics card via a six pin connector.
Cabling from the controller connects to a three pin spring
loaded terminal strip on the electronics assembly.
7.9.2 TROUBLE ANALYSIS
Electrical adjustment, or replacement of the sensor will be
necessary under the following conditions:
• Controller displays the following error
messages
SENSOR FAILURE
LOW SENSITIVITY
• False readings or alarms are received due to
sensor inaccuracy.
Warning: During sensor adjustments the concentration
reading on the controller will be inaccurate and alarm
level concentrations may be displayed. If false activation
of the alarm relays will cause a problem disconnect the
relay wiring prior to adjustment or turn the module off
using the "Change Module" mode.
NOTE
Although all the necessary data can be collected with a
voltmeter at the sensor module, some helpful information
can be displayed on the controller or printed. See
diagnostic codes 0004 and 0008 in Appendix C.
Cover Plate - Toxic Gas Module
7.9.3 ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURE
Prior to reading voltages and making adjustments perform
a visual inspection to confirm that there are no physical
problems such as water in the electronics enclosure,
wiring damage or corrosion.
Use Figure 7-11 to locate test points during the following
procedures.
7.9.3.1 SIGNAL ADJUSTMENT
It is unlikely that any electrical adjustment will be
required except when a new sensor is installed.
To make the electrical adjustment connect a voltmeter to
SIGNAL OUT (pos) and GND (ground) and use SPAN ADJ
potentiometer to adjust the voltage based on the
following:
• 1% of full scale = 0.02 VDC.
• 100% of full scale = 2.00 VDC.
7.9.3.2 SENSOR REPLACEMENT
The toxic gas sensor should be replaced when it can no
longer be calibrated correctly. Generally this is every
twenty four to thirty months.
Figure 7-11
SERVICE
Page: 78
Page 12

SMC sierra monitor corporation Sentry Instruction Manual - Version 6
The
SENSOR FAILURE message for toxic gas
sensors does not indicate a specific failure of the
sensor but indicates that the sensor is not correctly
connected to the electronics. If this message
appears check that the sensor harness is correctly
installed to the connector on the bottom
electronics board.
The gas sensor which is located inside the sensor
assembly housing can be replaced without
replacement of the housing. To replace the
sensor:
1. Confirm that system power has been
removed.
2. Remove the transmitter electronics board
from the main housing and unplug the
sensor harness from the transmitter
electronics.
3. Unscrew the sensor housing from the
bottom of the enclosure
4. Hold the sensor assembly so that the
harness faces down and the sensor faces
up. Unscrew and remove the round
section of the housing from the hex
section. Be careful not to lose the spacer
washer which will be sitting on top of th e
exposed sensor.
5. Carefully pull the old sensor straight up from the
socket.
6. Orient the new sensor so that the sensor pin
labeled “
C” faces the socket labeled “C” which is
on the far side of the board from the vertical reed
switch. The reed switch will slide into a hole on
the side of the new sensor. Press the new
sensor’s pins into the three sockets.
7. Carefully replace the cover on the sensor
assembly including the spacer washer.
8. Install the sensor assembly into the enclosure and
tighten firmly.
9. Reconnect the sensor harness to the transmitter,
install the transmitter into the housing and restore
power.
10. Allow one hour for the sensor to stabilize prior to
recalibration.
11. Recalibrate the sensor module.
7.9.3.3 SENSOR OUTPUT ADJUSTMENT
The following procedure is to be used when, during
normal calibration of a new sensor, the span voltage
cannot be adjusted to a high enough level.
Toxic Gas Transmitter Component Locator
1. Adjust the span potentiometer so that it is
approximately mid range. (Twenty turns
clockwise and tens turns counter-clockwise).
2. Remove system power and remove both the
transmitter and the sensor assembly from the
enclosure. Remove the sensor assembly cover so
that the sensor is visible.
3. Plug the sensor harness into the transmitter
assembly and check that no components are
touching the enclosure. Restore power and allow
a minimum of 30 minutes for stabilization before
adjustment.
4. Connect a DVM across TP10 and GT1 on the
transmitter assembly. Figure 7-12
5. Locate the gain potentiometer which is on the
sensor electronics directly behind one of the holes
in the sensor body. The potentiometer is
accessible by inserting a jewelers screwdriver
through the hole in the sensor.
6. Determine the correct value to be read at TP10
based on the following formula:
= 2 (C/R) , where C = concentration of span gas,
V
TP10
and R = range of detection (100 PPM). The value
is negative for all models except 5100-06, and
5100-19.
Figure 7-12
SERVICE
Page: 79
Page 13

SMC sierra monitor corporation Sentry Instruction Manual - Version 6
7. Apply span gas. Adjust the gain potentiometer
until TP10 = correct value as described above.
To increase voltage at TP10 turn the gain
potentiometer counter clockwise.
8. Remove system power and re-install the sensor
and transmitter in the enclosure. Restore power
and calibrate.
SERVICE
Page: 80
Page 14

SMC sierra monitor corporation Sentry Instruction Manual - Version 6
7.10 AMMONIA SENSOR MODULE (5100-25)
7.10.1 DESCRIPTION
The Ammonia Sensor Module includes a sensor
assembly and electronic assembly installed in an
explosion proof housing.
The sensor assembly includes a rechargeable
electrochemical sensor. The assembly screws into
one hub of the sensor module enclosure and plugs
into the bottom electronics card via a six pin
connector.
Cabling from the controller connects to a three
pin spring loaded terminal strip on the electronics
assembly.
7.10.2 TROUBLE ANALYSIS
Electrical adjustment, recharge, or replacement of
the sensor will be necessary under the following
conditions:
• Controller displays the following error
messages
SENSOR FAILURE
LOW SENSITIVITY
• False readings or alarms are received
due to sensor inaccuracy.
Cover Plate - Ammonia Module
Figure 7-13
Warning: During sensor adjustments the
concentration reading on the controller will be
inaccurate and alarm level concentrations may be
displayed. If false activation of the alarm relays will
cause a problem disconnect the relay wiring prior to
adjustment or turn the module off using the "Change
Module" mode.
NOTE
Although all the necessary data can be collected with a
voltmeter at the sensor module, some helpful information
can be displayed on the controller or printed. See
diagnostic codes 0004 and 0008 in Appendix C.
7.10.3 ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURE
Prior to reading voltages and making adjustments perform
a visual inspection to confirm that there are no physical
problems such as water in the electronics enclosure,
wiring damage or corrosion.
Use Figure 7-13 to locate test points during the following
procedures.
7.10.3.1 SIGNAL ADJUSTMENT
It is unlikely that any electrical adjustment will be
required except when a new sensor is installed.
To make the electrical adjustment connect a voltmeter to
SIGNAL OUT (pos) and GND (ground) and use SPAN ADJ
potentiometer to adjust the voltage based on the
following:
• 1% of full scale = 0.02 VDC.
• 100% of full scale = 2.00 VDC.
7.10.3.2 SENSOR RECHARGE
The Ammonia sensor can be recharged by removing it
from service, draining electrolyte, cleaning electrodes and
replacing the electrolyte and membrane.
Step by step instructions for sensor recharge are supplied
with the recharge kit.
7.10.3.3 SENSOR REPLACEMENT
The Ammonia sensor assembly should be replaced when
it can no longer be recharged and calibrated correctly.
SERVICE
Page: 81
Page 15

SMC sierra monitor corporation Sentry Instruction Manual - Version 6
The
SENSOR FAILURE message for ammonia sensors does
not indicate a specific failure of the sensor but indicates
that the sensor is not correctly connected to the
electronics. If this message appears check that the sensor
harness is correctly installed to the connector on the
bottom electronics board.
To replace the sensor assembly:
1. Confirm that system power has been removed.
2. Remove the transmitter electronics board from
the main housing and unplug the sensor harness
from the transmitter electronics.
3. Unscrew the sensor housing from the bottom of
the enclosure
4. Install the new sensor assembly into the enclosure
and tighten firmly.
5. Reconnect the sensor harness to the transmitter,
install the transmitter into the housing and restore
power.
6. Allow one hour for the sensor to stabilize prior to
recalibration.
7. Recalibrate the sensor module.
SERVICE
Page: 82
 Loading...
Loading...