Page 1

MODEL 4501-XX
2-Wire Series
TOXIC GAS SENSOR MODULE
APPLICABILITY & EFFECTIVITY
Effective for all Model 4501-XX Modules manufactured after September 1, 2006.
4501-03
4501-04
4501-05 FM Approved
4501-06
4501-08
4501-10
4501-12
4501-25
4501-26
Instruction Manual Part Number T13022
Rev. C
Page 2

Model 4501-XX Toxic Gas Sensor Module
FM PERFORMANCE APPROVAL
ONLY THE FOLLOWING ITEMS, FUNCTIONS AND OPTIONS ARE FM* APPROVED
Model 4501-05 Hydrogen Sulfide Gas Sensor Module
Sensor Module
Model 4501-05 Sensor Module - Hydrogen Sulfide
Calibration Equipment
Model 1250-01 Gas Sensor Calibration Kit, Type A
Model 1260-05 Hydrogen Sulfide in N2, 25 ppm Gas Cylinder
Model 1260-45 Hydrogen Sulfide in N2, 10 ppm Gas Cylinder
Model 5358-01 Calibration Adapter
Notes:
1) Apparatus must be installed in accordance with National Electrical Code.
2) FM Comments.
*FM Approvals, a subsidiary of FM Global
Project# 3028099
Page 3

Model 4501-XX Toxic Gas Sensor Module
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. PRODUCT DESCRIPTION ................................................................................................................................. 1
1.1 GENERAL ........................................................................................................................................................ 1
1.2 MOUNTING CONFIGURATION ...................................................................................................................... 1
1.3 THEORY OF OPERATION .............................................................................................................................. 1
1.4 MECHANICAL ................................................................................................................................................. 2
1.5 INTERCONNECT WIRING .............................................................................................................................. 2
1.6 POWER REQUIREMENTS ............................................................................................................................. 2
2. CAUTIONS & WARNINGS ................................................................................................................................. 4
2.1 INTRODUCTION ............................................................................................................................................. 4
2.2 GAS SENSOR MODULES - GENERAL ......................................................................................................... 4
2.3 WIRING ............................................................................................................................................................ 4
2.4 CALIBRATION FREQUENCY ......................................................................................................................... 4
3. QUICK START .................................................................................................................................................... 5
3.1 OVERVIEW ...................................................................................................................................................... 5
3.2 WIRING ............................................................................................................................................................ 5
3.3 MODULE INSTALLATION ............................................................................................................................... 5
3.4 TRANSMITTER INSTALLATION .................................................................................................................... 5
3.5 START-UP & OPERATION ............................................................................................................................. 5
3.6 ZERO STABILIZATION ................................................................................................................................... 5
4. INSTALLATION .................................................................................................................................................. 6
4.1 SENSOR MODULE LOCATIONS ................................................................................................................... 6
4.2 WIRING ............................................................................................................................................................ 7
4.3 ENCLOSURE INSTALLATION ........................................................................................................................ 7
4.4 TRANSMITTER AND SENSOR INSTALLATION ........................................................................................... 8
5. OPERATION ....................................................................................................................................................... 9
5.1 INTRODUCTION ..............................................................................................................
............................... 9
5.2 DATA ENTRY KEYPAD .................................................................................................................................. 9
5.3 MAIN MENU .................................................................................................................................................. 10
5.4 SETUP SUB-MENU ....................................................................................................................................... 11
6. CALIBRATION .................................................................................................................................................. 14
6.1 CALIBRATION FREQUENCY ....................................................................................................................... 14
6.2 CALIBRATION PREPARATION .................................................................................................................... 14
6.3 CALIBRATION
GAS DELIVERY METHODS ................................................................................................. 14
CALIBRATION PROCEDURE .................................................................................................................................. 14
6.4 SENSOR EXPOSURE TO GAS .................................................................................................................... 14
6.5 CALIBRATION SUB-MENU........................................................................................................................... 15
7. SERVICE ........................................................................................................................................................... 16
7.1 SENSOR
7.2 ENCLOSURE
MODULE CONFIGURATION ........................................................................................................ 16
REPLACEMENT .................................................................................................................... 16
7.3 TRANSMITTER REPLACEMENT ................................................................................................................. 17
7.4 SENSOR
REPLACEMENT ............................................................................................................................ 17
7.5 INSTALLATION INSPECTION ...................................................................................................................... 17
7.6 INSPECTION
AND TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE ....................................................................................... 18
Page 4

Model 4501-XX Toxic Gas Sensor Module
8. APPENDICES ................................................................................................................................................... 19
8.1 APPENDIX
A: SPECIFICATIONS.................................................................................................................. 19
8.2 APPENDIX B: MODEL NUMBERS & PARTS LIST ....................................................................................... 22
8.3 APPENDIX C: LIMITED WARRANTY ............................................................................................................ 23
8.4 APPENDIX
8.5 APPENDIX
D: 4501-25 & 4501-26 GAS SENSOR MODULE ........................................................................ 24
E: US FM APPROVAL. ............................................................................................................... 28
8.6 APPENDIX F: CANADIAN FM APPROVAL ................................................................................................... 30
8.7 APPENDIX G: ATEX CERTIFICATE ............................................................................................................. 32
8.8 APPENDIX H: PIPE MOUNTING FOR 4501-XX ALUMINUM ....................................................................... 34
LIST OF FIGURES
FIGURE 1 - 1: MODEL 4501-05 ALUMINUM HOUSING GAS SENSOR MODULE OUTLINE DIMENSIONS ....... 2
FIGURE 1 - 2: MODEL 4501-05 STAINLESS HOUSING GAS SENSOR MODULE OUTLINE DIMENSIONS ....... 3
FIGURE 1 - 3: MODEL 4501-XX HYDROGEN SULFIDE GAS SENSOR MODULE, ORIENTATION OPTIONS ... 3
FIGURE 4 - 1: TYPICAL MOUNTING OPTIONS ...................................................................................................... 6
FIGURE 4 - 2: 4-20 MA CONNECTION .................................................................................................................... 7
FIGURE 4 - 3: CONNECTOR LOCATIONS .............................................................................................................. 8
FIGURE 5 - 1: FACE PLATE WITH OPERATOR KEYPAD ..................................................................................... 9
FIGURE 6 - 1: MODEL 5358-01 CALIBRATION ADAPTER .................................................................................. 14
FIGURE 7 - 1: MODULE COMPONENTS .............................................................................................................. 16
FIGURE 8 - 1: MODULE COMPONENTS .............................................................................................................. 24
FIGURE 8 - 2: SENSOR ASSEMBLY – EXPLODED VIEW ................................................................................... 26
FIGURE 8 - 3: MODEL 4501-25-A1 AND 4501-26-A1 OUTLINE DIMENSIONS ................................................... 27
FIGURE 8 - 4: MODEL 4501-25-S1 AND 4501-26-S1 OUTLINE DIMENSIONS ................................................... 27
FIGURE 8 - 5: MODEL 4501-XX ALUMINUM ENCLOSURE PIPE MOUNT ......................................................... 34
FIGURE 8 - 6: PIPE MOUNT BRACKET FOR 4501-XX ALUMINUM ENCLOSURE ............................................ 34
LIST OF TABLES
TABLE 4 - 1: SPECIFIC GRAVITIES ........................................................................................................................ 6
TABLE 5 - 1: MASTER MENU
............................................................................................................................................. 10
TABLE 5 - 2: KEY OPERATIONAL DISPLAY ................................................................................................................... 10
TABLE 5 - 3: SET-UP CONFIGURATION ......................................................................................................................... 12
TABLE 5 - 4: MAINTENANCE SUB MENU ....................................................................................................................... 13
TABLE 6 - 1: CALIBRATION ................................................................................................................................................ 15
Page 5

Model 4501-XX Toxic Gas Sensor Module
1. PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
1.1 GENERAL
The Model 4501-XX Toxic Gas Sensor Module is a 2-wire transmitter with 4-20 mA output and it offers a broad
array of features including:
• 2-wire loop powered
• 180 day calibration interval
• Selectable ranges (if appropriate for gas type)
• Non-intrusive one-person calibration
• Integral LCD 2-line, 20-character display
• Stainless steel enclosure and sensor housing
• 4-20 mA output
• Long sensor life
• Rotatable faceplate enables multi-directional conduit
installation.
The 4501-XX is designed and approved for installation and
operation in hazardous locations.
Members of the 4501-XX Two-Wire Toxic Gas family include:
▪ 4501-03 Oxygen Gas Sensor Module
▪ 4501-04 Carbon Monoxide Gas Sensor Module
▪ 4501-05 Hydrogen Sulfide Gas Sensor Module
▪ 4501-06 Chlorine Gas Sensor Module
▪ 4501-08 Chlorine Dioxide Gas Sensor Module
▪ 4501-10 Sulfur Dioxide Gas Sensor Module
▪ 4501-12 Nitrogen Dioxide Gas Sensor Module
▪ 4501-25 Ammonia Gas Sensor Module
▪ 4501-26 Hydrogen Fluoride Gas Sensor Module
1.2 MOUNTING CONFIGURATION
Various module mounting configurations can be implemented without special fixtures. Where applicable,
these options are factory configured prior to shipment. Mounting configuration can be selected by the installer
or field technician and are fully described in this manual. Sensor must always be oriented downward.
1.3 THEORY OF OPERATION
Electrochemical sensors are fuel cell-like devices consisting of an anode, cathode, and electrolyte. The
components of the cell are selected so a subject gas, allowed to diffuse into the cell, will cause a chemical
reaction and generate a current. The cells are diffusion limited so the rate the gas enters the cell is solely
dependent on the gas concentration. The current generated is proportional to the rate of consumption of the
subject gas in the cell.
Page 1 of 35
Page 6
Model 4501-XX Toxic Gas Sensor Module
Sierra Monitor electrochemical sensors provide improved reliability by allowing the gas to diffuse into the
sensor through a capillary port, rather than diffusing through membranes. The result is an extremely stable
sensor with very low temperature and pressure coefficients and the capability to monitor gas as ppm.
1.4 MECHANICAL
The sensor module is comprised of the following three primary components:
1.4.1 ENCLOSURE
Explosion proof, rain-tight aluminum or stainless steel electrical housing with three ¾” FNPT conduit hubs.
The enclosure cover has a viewing window. The 3 conduit hubs combined with the rotatable faceplate
enable the user to mount the module in a variety of configurations. See Figure 1-2 for details.
1.4.2 TRANSMITTER ELECTRONICS
Electronic Assembly consisting of one printed circuit board assembly mounted under a cover plate. Wiring
connections for power and signal interface are located on the back side of the display.
1.4.3 SENSOR ASSEMBLY
The sensor assembly includes a stainless steel, explosion proof, housing containing the gas sensor and a
wiring harness for connection to the transmitter. The sensor assembly threads into one hub of the
enclosure. The exposed end of the sensor assembly is threaded to allow connection of a rain-shield or
calibration gas delivery fitting.
1.5 INTERCONNECT WIRING
Not supplied with the sensor module, but necessary to the installation and operation is the two conductor
wiring shielded which connects the module to its power source and controller. Before this wiring is installed it
is important to read and understand the control system installation instructions to determine wiring
requirements and alternatives.
1.6 POWER REQUIREMENTS
The 4501-XX module operates on DC power between 14 VDC and 30 VDC. The DC power must be supplied
by the loop controller.
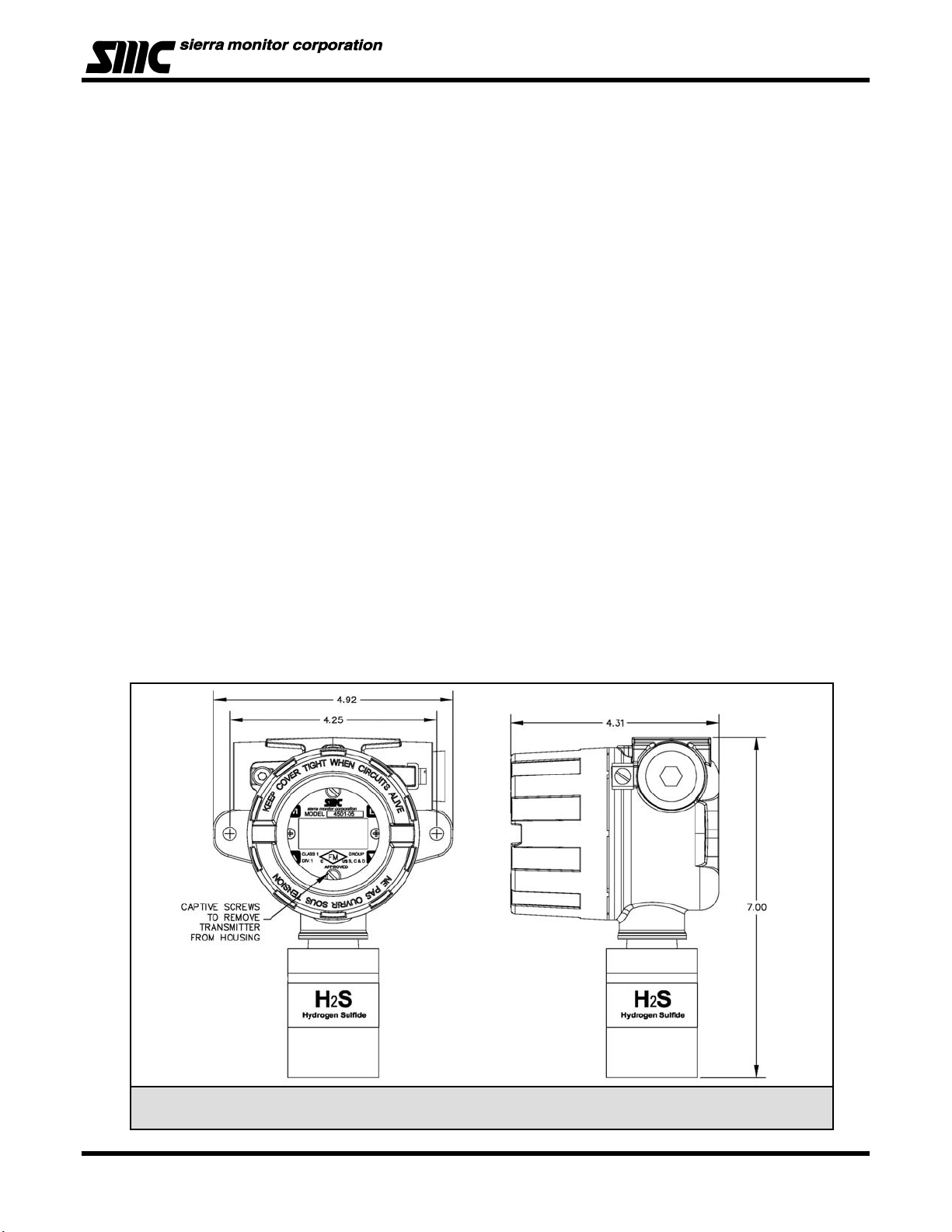
Figure 1 - 1: Model 4501-05 Aluminum Housing Gas Sensor Module Outline Dimensions
Page 2 of 35
Page 7
Model 4501-XX Toxic Gas Sensor Module
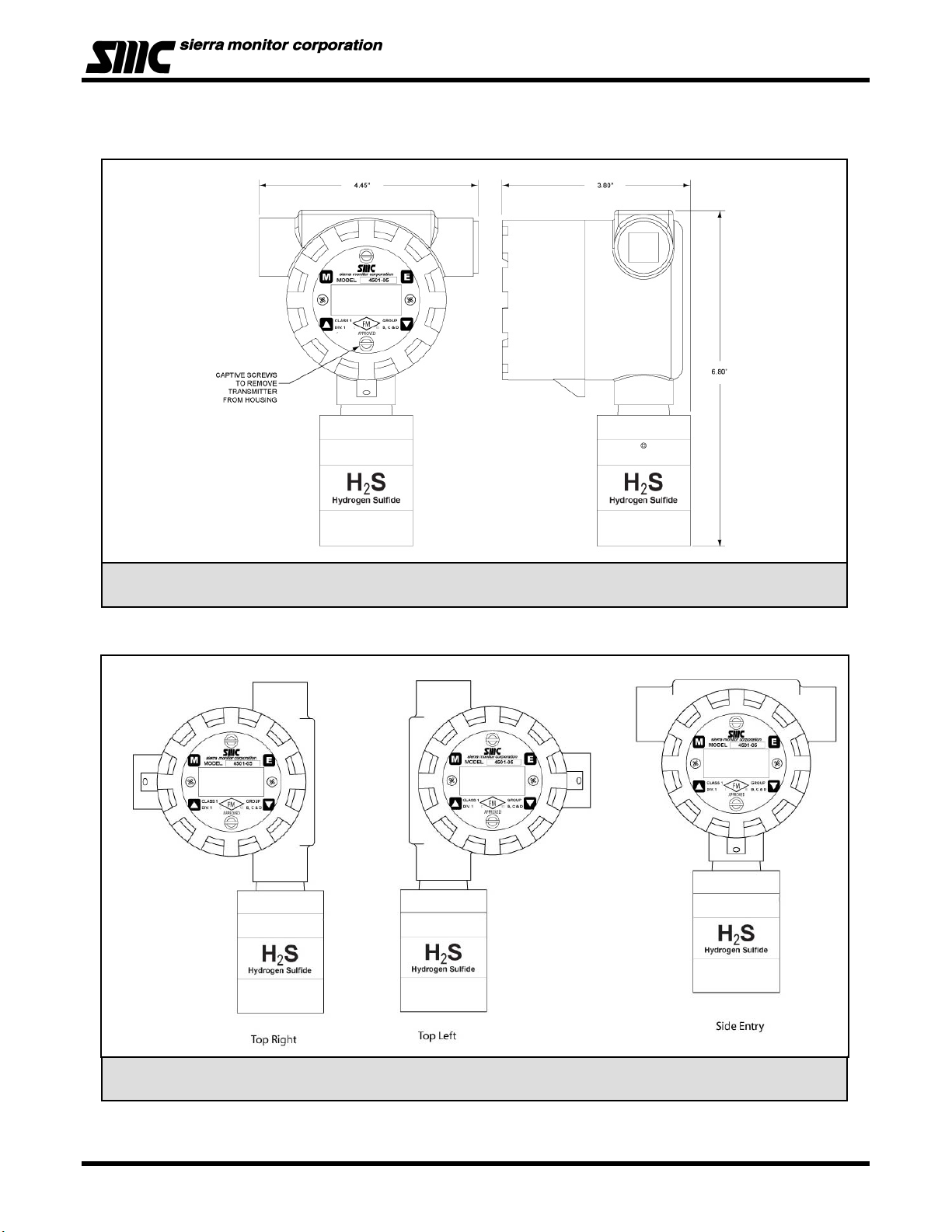
Figure 1 - 2: Model 4501-05 Stainless Steel Housing Gas Sensor Module Outline Dimensions
Figure 1 - 3: Model 4501-XX Hydrogen Sulfide Gas Sensor Module – Orientation Options
Page 3 of 35
Page 8
Model 4501-XX Toxic Gas Sensor Module
2. CAUTIONS & WARNINGS
2.1 INTRODUCTION
Although the 4501-XX Gas Sensor Module is designed and constructed for installation and operation in
industrial applications including hostile environments, caution should be taken to insure that the installation is
made in compliance with this instruction manual and that certain procedures and conditions are avoided. This
chapter discusses the necessary cautions. Read the entire chapter prior to installation of the equipment.
2.2 GAS SENSOR MODULES - GENERAL
Avoid installing sensor modules where they will be unnecessarily exposed to wind, dust, water (i.e. direct hose
down), shock, or vibration. Observe temperature range limitations.
Sensors may be adversely affected by prolonged exposure to certain materials. Loss of sensitivity, or
corrosion, may be gradual if such materials are present in low concentrations. These materials include:
Halides (compounds containing chlorine, fluorine, bromine, iodine), acid vapors, caustic liquids or mists.
Care has been taken by the manufacturer to ship modules in protective packaging to avoid contamination prior
to installation. It is recommended that the modules remain protected during installation and that the covering
be removed immediately prior to system start-up.
During normal use the O
, CO, H2S, SO2 and NO2 sensors are protected from dirt and oil contamination by a
2
sintered metal cover. If this cover becomes clogged, the response of the sensor will be reduced. Protect the
sensor from contamination by careful placement, or by use of rain shields and dust shields.
Sensor modules must not be painted. Paint may contain compounds which will contaminate the sensor. Paint
will cause clogging of the sintered metal cover and will cause difficulties during attachment of the calibration
head or other maintenance activity. It is recommended that the module be tagged
2.3 WIRING
"DO NOT PAINT".
The manufacturer recommends that extra caution be taken where the installation is near any sources of
electromagnetic or radio frequency interference. Precautions include:
• Avoid running sensor module cable close to high power cables, radio transmission lines, or cables
subject to pulses of high current.
• Avoid running cables near large electric motors or generators.
• Analog devices require shielded cable.
• In conduit installations and cable applications the shield should be connected to instrument ground.
• All splices must be via either a termination hardware system or soldered. Improperly spliced cable can
result in corrosion, resistance changes and system errors.
Installation and wiring must be in accordance with the National Electrical Code.
Voltage AC conductors are not to be run in the same conduit as voltage DC
NOTE
conductors.
2.4 CALIBRATION FREQUENCY
The 4501-XX calibration frequency is six months (180 days). However, prudent gas detector maintenance
practices normally suggest a simple recalibration following incidences of exposure to high levels of gas that
would lead to alarm activation within any system utilizing the output of the gas sensor module.
Page 4 of 35
Page 9
Model 4501-XX Toxic Gas Sensor Module
3. QUICK START
3.1 OVERVIEW
The gas sensor module has been supplied factory calibrated and ready for immediate installation and
operation. An installer familiar with installation and operation of gas detection products can use this section to
begin immediate use of the module.
3.2 WIRING
Provide two conductor twisted shielded wiring from the power supply/control device to the sensor module
location. Use wire that is 18 AWG or larger.
3.3 MODULE INSTALLATION
The 4501-XX can be mounted in a variety of configurations supported by the conduit. See figure 1-2 to
determine which configuration is best for your specific application. The default configuration enables the
modules to be put in line with other modules with the sensor element below the transmitter. To change the
configuration simply remove the transmitter and rotate to the appropriate configuration and remount the
standoffs and transmitter.
The module is designed to be installed on a ¾” conduit. Two important warnings:
• The installation must meet any hazardous environment codes for electrical equipment.
• The sensor module enclosure mounting must be spaced far enough from any vertical surface
to allow removal and replacement of the sensor assembly which is threaded into one ¾”
conduit entry.
• Sensor housing must be oriented vertically pointing downward.
3.4 TRANSMITTER INSTALLATION
To install the transmitter printed circuit assembly into the housing, carefully turn the faceplate so that the
printing is in the correct horizontal position for the mounting configuration and slide the assembly over the two
stand-offs in the enclosure.
Hand tighten the two captive panel thumb screws into the stand-offs. Replace the enclosure cover prior to
providing power to the transmitter.
• If the transmitter is installed in a classified hazardous area, replace the threaded cover prior to
providing power.
3.5 START-UP & OPERATION
To begin operation of the sensor module activate the instrument loop with 14-30 VDC. Each time the sensor
module is powered up it will perform a warm-up for approximately 1.0 minutes (60 seconds). During this time
the display will read “Starting”. The loop output will be held at 4 mA.
NOTE: If the sensor is uncalibrated, the startup display will state “UNCALIB” instead of “STARTING”
NOTE: The 4501-06, 4501-08, 4501-25 and 4501-26 require 300 seconds warm-up period
After the warm-up period has expired, the display will indicate the gas concentration. Also, the instrument loop
will be released to output current in the range of 4 to 20 mA. The actual current is linear with the gas
concentration and depends on the selected range. For instance, when the range of 0 to 50 PPM has been
selected, a current of 4 mA corresponds to 0 PPM and a current of 20 mA corresponds to 50 PPM.
3.6 ZERO STABILIZATION
All electrochemical sensors require at least 30 minutes on power prior to calibration. This allows the electrode
potentials to equilibrate, resulting in a stable zero signal level.
Page 5 of 35
Page 10
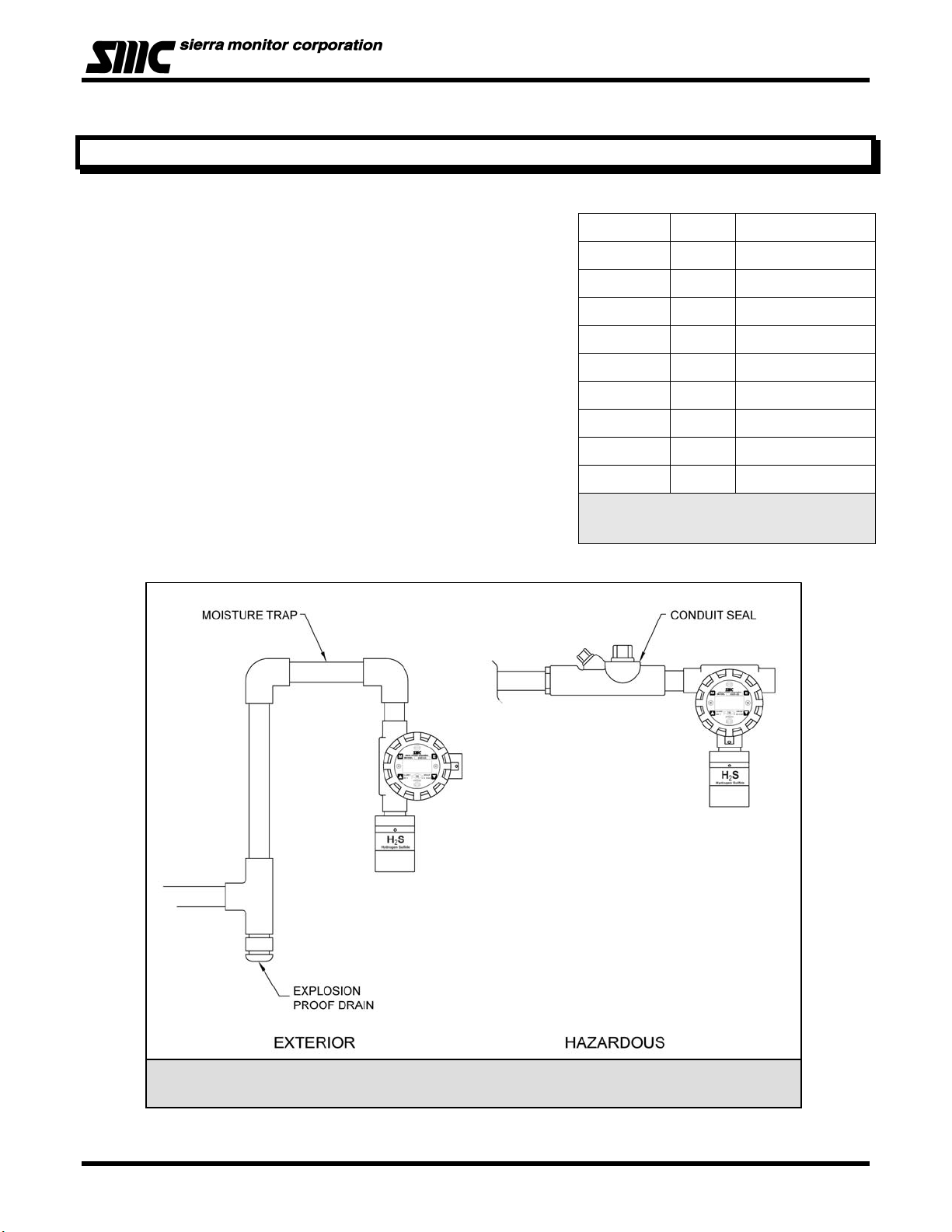
4. INSTALLATION
4.1 SENSOR MODULE LOCATIONS
The gas sensor module utilizes a diffusion type sensor which
should be located close to either the expected source or
destination of the gas hazard. If the gas is heavier than air, the
sensor module should be installed within 24 inches of the ground
or floor. If it is lighter than air, move it above 6’.
After optimum locations are determined based on the above
recommendations, consideration should be given to placing the
sensor modules in locations which are accessible for calibration
service. Slight adjustments to the location of the sensor module
may have little impact on effectiveness but major effect on
accessibility.
• Modules should be placed in areas accessible for
calibration.
• The cover should face out from the wall for easy access.
• Sensors should be pointed down and the conduit should
include an inverse trap to reduce moisture (condensation)
from accumulating in the electronics enclosure.
Model 4501-XX Toxic Gas Sensor Module
Model Gas Specific Gravity
N/A Air 1.00
4501-04 CO 0.97
4501-05 H2S 1.19
4501-06 Cl2 2.49
4501-08 ClO2 3.09
4501-10 SO2 2.26
4501-12 NO2 1.59
4501-25 NH3 0.60
4501-26 HF 1.86
Table 4 - 1: Specific Gravities
Figure 4 - 1: Typical Mounting Options
Page 6 of 35
Page 11
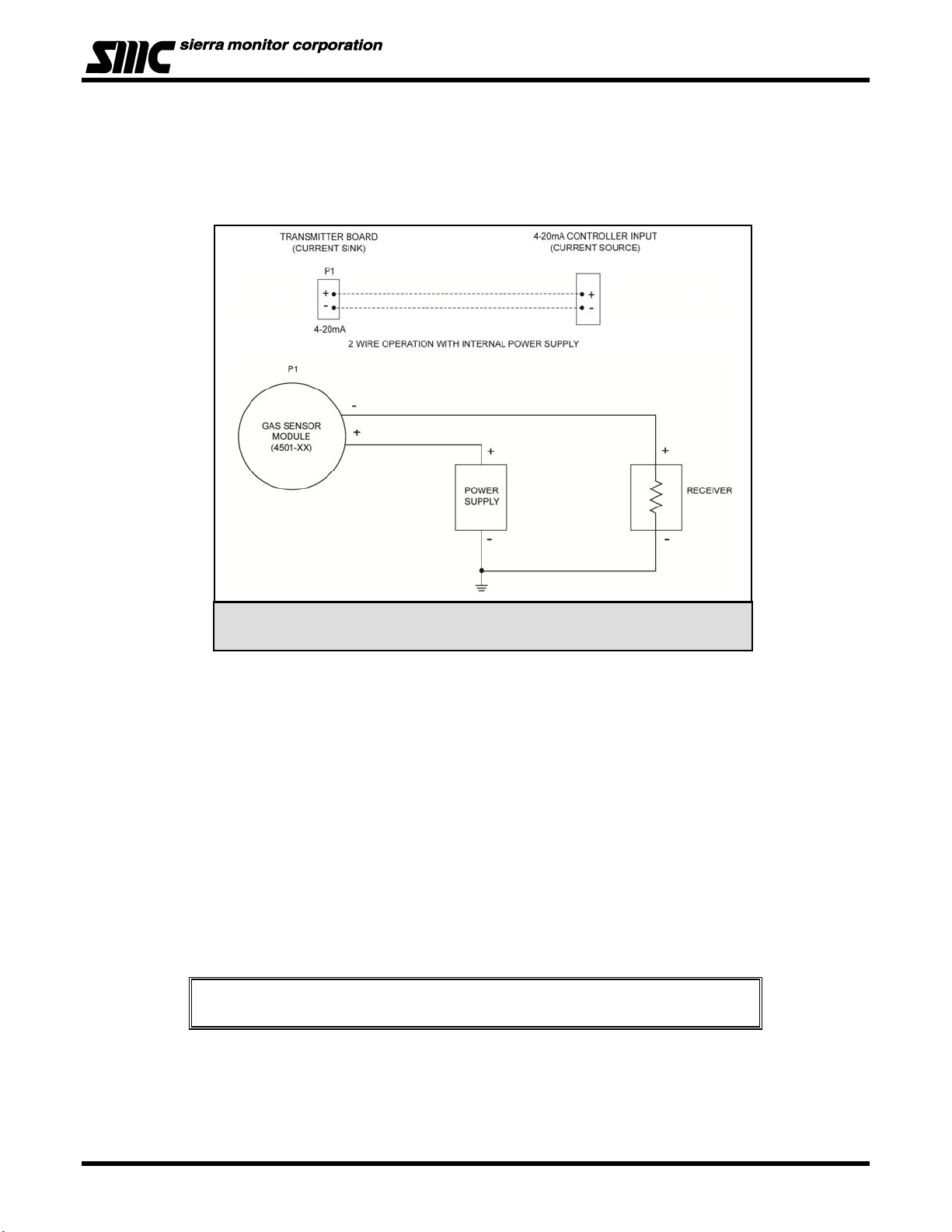
Model 4501-XX Toxic Gas Sensor Module
4.2 WIRING
• Wire should be 18 AWG minimum at a maximum distance is 5,000 feet. Install conduit as required by
local code or construction specifications.
• See figure 4-2 for typical 2 terminal and 4 terminal connections.
Figure 4 - 2: 4-20 mA Connection
4.3 ENCLOSURE INSTALLATION
To protect the transmitter and sensor assembly they should be removed from the enclosure and preserved
until final installation and wiring termination.
Prior to installation and wiring:
1. Remove the transmitter from the module housing by:
• Unscrew the two captive panel screws on the faceplate.
• Lift the transmitter out of the enclosure.
• Unplug the sensor cable from transmitter connector J1.
• Remove the sensor assembly from the enclosure hub.
2. Install the module enclosure onto the end of the supply conduit and/or bolt into position as required.
When enclosure earth grounding is required for the installation a grounding lug is located in
the base of the enclosure. Install the earth ground under the green ground screw.
NOTE
Page 7 of 35
Page 12
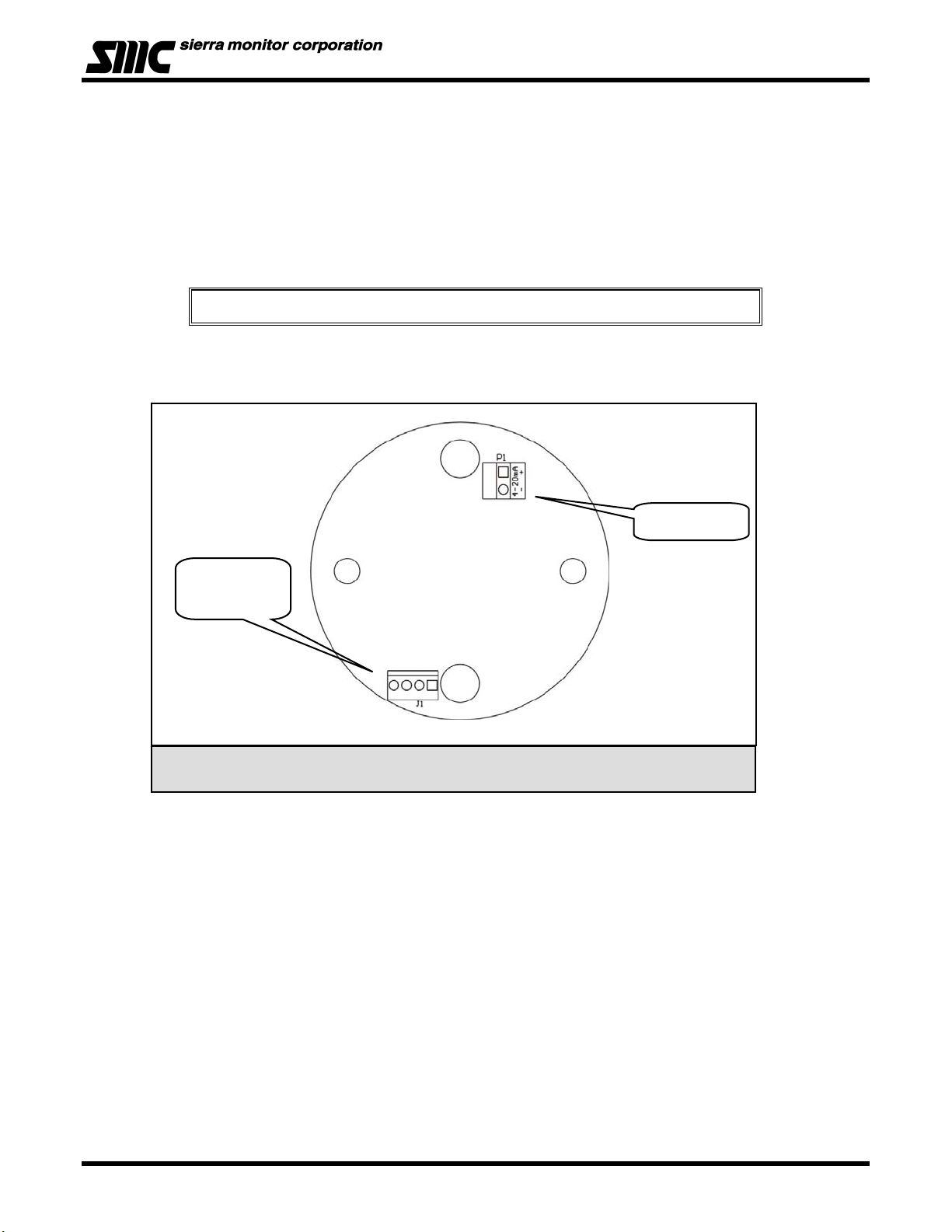
4.4 TRANSMITTER AND SENSOR INSTALLATION
When all pre-wiring is complete:
1. Install sensor assembly in the open hub on the module enclosure. The sensor assembly thread
must be fully seated into the hub and tightened to maintain explosion proof assembly.
2. Connect the sensor assembly cable to transmitter connector J1. (Figure 4-3)
3. Connect the loop wires (Loop + and Loop -) to transmitter connector P1 4-20 mA + and –
(Figure 4-3).
Model 4501-XX Toxic Gas Sensor Module
Conductor P1 is removable
NOTE
4. Carefully return the transmitter to the enclosure installing it over the two standoffs. Finger tighten
the retaining screws into the standoffs.
Loop Power
Sensor
Connector
Figure 4 - 3: Connector Locations
Page 8 of 35
Page 13

Model 4501-XX Toxic Gas Sensor Module
5. OPERATION
5.1 INTRODUCTION
The 4501-XX Toxic Gas Sensor Module utilizes a visual menu system operated by means of a magnet with
the cover in place. A magnet stick is supplied for this purpose. Access the menu system to calibrate the
sensor module, and for maintenance and diagnostic procedures.
The following adjustments can be made to the sensor module:
Range adjustments (see section 5.4)
4mA and 20mA calibration adjustments (see section 5.4)
Span adjustment (see section 6.3)
5.2 DATA ENTRY KEYPAD
The module menu system is operated by means of directing the magnet stick toward each of four independent
hall-effect magnetic switches. Each switch functions as if it is a manually activated panel key. The keys are
located under the faceplate above and below the LCD and are labeled
Figure 5-1.
M , E , and as shown in
• Key
: MODE
• Key ENTER
• Key : UP (+)
• Key : DOWN (-)
Figure 5 - 1: Face Plate with Operator Keypad
Page 9 of 35
Page 14

Model 4501-XX Toxic Gas Sensor Module
5.3 MAIN MENU
Key
Function Display Description Reference
M E
M E
ME
ME
M E
ME
ME
ME
Table 5-2 defines the key operational displays on the operator interface.
Mode Switch [M]
Enter Switch [E]
Up Switch [▲] Previous Menu
Down Switch [▼] Next Menu
Mode
Down
Down
Down
4501-XX
CAL 180
4501-XX
Version
4501-XX
Starting
H2S
XXX.PPM
H2S
CALIB:
H2S
SETUP:
H2S
MAINT:
H2S
Exit-?
First screen at power-up, Model and days to
calibration
Second screen at start-up, Version (e.g. V300aA)
Third screen at start-up, will remain for 60 seconds
(4501-05)
Default Display (example 4501-05)
Mode Function: Calibration (example 4501-05) Table 6-1
Mode Function: Setup (example 4501-05) Table 5-3
Mode Function: Maintenance (example 4501-05) Table 5-4
Exit Mode (example 4501-05)
Table 5 - 1: Master Menu
Display Description
- H2S -
STARTING
SENSOR
FAIL
NO
SENSOR
Warm-up at start-up (example 4501-05)
Sensor failure
Sensor not found or plugged in
C.## PPM Calibration Mode
F.## PPM Failure detected, sensor is attempting recovery
XXX
DONE
Table 5 - 2: Key Operational Display
Finished with step
Page 10 of 35
Page 15

Model 4501-XX Toxic Gas Sensor Module
5.4 SETUP SUB-MENU
The sensor module set-points menu is used to initially set-up the range and 4-20 mA calibration.
• Range: Once the Set-up menu is selected, press key [▼] twice and press [E] to activate the Range Set-
up menu. Use the [▲] or [▼] keys to select Range menu and press [E]. When “Range” is selected menu
provides any choices of ranges available for the gas type selected. Use the [▲] or [▼] keys to select the
desired range. If the “User” range is selected, use the [▲] or [▼] keys to adjust the high end of the range
desired. See specifications below for optional ranges.
Model Range Other Available
4501-03 5-25% 0-25%
4501-04 0-500 PPM Variable
4501-05 0-100 PPM Variable
4501-06 0-10 PPM None
Factory Range Set-up
4501-08 0-3 PPM None
4501-10 0-100 PPM Variable
4501-12 0-20 PPM None
4501-25 0-100 PPM Variable
4501-26 0-10 PPM None
• 4-20mA: Once the Set-up menu is selected, press key [▼] three times and press [E] to activate the 4-
20mA Set-up menu. Use the [▲] or [▼] keys to select Calib menu and press [E]. The “Calib” section of
the menu allows the user to calibrate the 4 mA and 20 mA outputs. To calibrate the 4 mA and 20 mA
outputs it is necessary to have an amp meter connected to the 4501-XX and upon selecting the 4 mA
output calibration then the [▲] or [▼] keys can be used to adjust the 4 mA reading on the amp meter until it
reads 4 mA. Similar steps can then be performed for the 20 mA output.
Page 11 of 35
Page 16

Model 4501-XX Toxic Gas Sensor Module
M
E
Function Display Description
Key
M E
ME
Mode
Down
H2S
XX PPM
H2S
CALIB:
H2S
SETUP:
Default Display (example 4501-05)
Gas Range Adjustment Example
M E
ME
ME
M E
Enter Range S.P. Function - Range Adjust
Enter
Down
Down
Enter
H2S
*100 PPM
H2S
10 PPM
H2S
USER
H2S
100 PPM
Select [E] to select or or to select another and press [E]
Press [E] if selecting 0-10 PPM range
Press [E] if selecting User adjustable range
Select [E] to select or or to select another and press [E]
4-20 mA Adjustment Example
ME
M E
M E
M E
M E
Down
Enter
Enter
Enter
Enter
H2S
4-20mA
H2S
Calib
H2S
Out: 4mA
H2S
4mA
H2S
ACK
S.P Function 4-20 mA Calibrator
S.P. Function - Calib Adjust
Use or keys to select 4 mA or 20mA
Selects 4 mA
Momentary Acknowledge of new Set Point
Reference
Table 5 - 3: Set-up Configuration
Page 12 of 35
Page 17

Model 4501-XX Toxic Gas Sensor Module
MAINTENANCE SUB-MENU
The maintenance menu enables the operator to view sensor and software versions. Sierra Monitor technical
support has access to other values as needed. The maintenance menu operation is described in Table 5-4.
Function Display
Key
M E
Mode
M E
Enter
ME
Down
ME
Down
M E
Enter
M E
Enter
H2S
XXX PPM
H2S
CALIB
H2S
SETUP:
H2S
MAINT:
H2S
VX.XX
H2S:
CCC001
Default Display(example 4501-05)
Go to previous maintenance menu item
Version number of firmware
Configuration Version
Table 5 - 4: Maintenance Sub Menu
Description
Reference
Page 13 of 35
Page 18

Model 4501-XX Toxic Gas Sensor Module
6. CALIBRATION
6.1 CALIBRATION FREQUENCY
The sensor module must be calibrated every 180 days at a minimum. Periodic functional tests are advisable
for critical applications and hostile environments.
The sensor module microprocessor software includes high-level self checking algorithms which provide
continuous sensor diagnostic and self adjustment.
6.2 CALIBRATION PREPARATION
Calibration of the sensor is accomplished by simple menu based steps and application of span gas.
If an error is made during any stage of the calibration process, hold the magnet stick at the
[M] for 10 seconds. A scrolling display will indicate “calibration aborted” and the sensor
module will exit the calibration activity and return to normal operating mode. The calibration
procedure can then be restarted.
NOTE
Calibration must be performed only when the area is known to be clear of the gas of interest. When in doubt,
use a portable instrument to confirm that there is no background.
For compliance with Factory Mutual (FM) Approvals, the Sierra Monitor Model 1250-01, 1260 -05 and 1260-45
are the FM Approved calibration gas delivery devices. Use the Model 5358-01 Calibration Adapter delivery
fitting.
NOTE: Refer to Appendix D for information on use of permeation tube for 4501-25 calibration.
6.3 CALIBRATION GAS DELIVERY METHODS
Calibration gas can be delivered to the sensors via the Model 5358-01:
Calibration Adapter (Figure 6-1) - used with portable calibrators.
CALIBRATION PROCEDURE
The Calibration Menu is described on Table 6-1:
The procedure requires that the menu “keys” be activated using the magnet stick.
Each key press steps through the process of setting the zero value for clean air
and then setting the span value.
Sample Gas In
At each of these steps, apply calibration gas of the value corresponding to
the setting accepted on the sensor module display.
6.4 SENSOR EXPOSURE TO GAS
Calibration gas must be delivered to the sensor using the flow rate and
duration listed in below:
Model Calibration Gas Flow Period
Figure 6 - 1: Model
5358-01 Calibration
Adapter
4501-03 Air 300 cc of Zero Air or exposure to Ambient Air (3 minutes)
4501-04 Carbon Monoxide 300 cc/min Until Stable (minimum 3 minutes)
4501-05 Hydrogen Sulfide 300 cc/min Until Stable (minimum 3 minutes)
4501-06 Chlorine 300 cc/min Until Stable (minimum 3 minutes)
4501-08* Chlorine 300 cc/min Until Stable (minimum 3 minutes)
4501-10 Sulfur Dioxide 300 cc/min Until Stable (minimum 3 minutes)
4501-12 Nitrogen Dioxide 300 cc/min Until Stable (minimum 3 minutes)
4501-25 Ammonia See Appendix D
4501-26** Chlorine 500 cc/min Until Stable (minimum 6 minutes)
* Note: Use 10 PPM Cl2 to calibrate, equivalent reading = 3.0 PPM ClO2
** Note: Use 5 PPM Cl
to calibrate equivalent reading = 8.0 PPM HF
2
Page 14 of 35
Page 19

Model 4501-XX Toxic Gas Sensor Module
6.5 CALIBRATION SUB-MENU
* 4501-03 –
Oxygen Calibration: If area is known to be safe with adequate air flow, you may use the surrounding air as the calibration gas.
If Oxygen levels are unknown, it is recommended to use a Zero Air gas standard.
When calibrating an Oxygen module, there is no zero gas process in the calibration procedure. Only span adjustments can be
made. Normal ambient Air = 20.9% Oxygen.
Begin calibration procedure using the magnet on the Mode key until CALIB is displayed.
Enter to begin procedure. Select cal gas value (20.9), Enter to confirm.
Apply span gas for 3 minutes or use surrounding air if acceptable.
Select Enter when done, and procedure is complete.
Function Display Description Reference
Key
XXXPPM Default Display
M E
M E
M E
M E
M E
Mode
Enter
Enter
Enter
Enter
H2S
CALIB:--
H2S
Cal Zero
H2S
ACK
H2S
10PPM-SP
H2S
CXXX PPM
H2S
CXXX PPM
H2S
CXXXPPM
H2S
CAL-OK
H2S
WAIT-300
Mode Function - Calibrate
Banner: Apply zero gas, enter <E> when done
Operation: Confirm area clear of gas, or apply zero air to
sensor.
Zero gas setting acknowledged
Banner: Select span, enter <E> when done*
Banner: Apply span gas, then enter <E> to calibrate gas sensor
Operation: Apply calbration gas .
Operation: As gas is applied the reading w ill increase - wait 3
minutes
Calibration Passed - now remove gas
Operation: Five minute time out before sensor is returned to
service.
Sub-Routines
ME
ME
M E
M E
M E
M E
Down
Down
Enter
Enter
Enter
Mode
H2S
10PPM-SP
H2S
25PPM-SP
H2S
Adj-SPAN
H2S
25PPM-SP
H2S
C 25PPM
H2S
C 25PPM
H2S
CAL-FAIL
H2S
WAIT-300
(Any)
H2S
XXXPPM
Banner: Select span, enter <E> when done
Operation: Change Span Gas Value to 25PP M
Operation: User adjustable value
Operation: Ready for user adjust ment
Banner: Apply 25PPM gas, then enter <E> to calibrate gas
sensor
Operation: Apply calbration gas .
Operation: No calibration gas applied, or s ensor did not respond
correctly.
Operation: Five minute time out before sensor is returned to
service.
Operation: Hold magnet over Mode Switch for ten senconds to
abort calibration
Banner: Calibration Aborted
Default Display
Table 6 - 1: Calibration
Sub A
Sub B
Sub A
Sub B
Sub C
The Analog output values to be transmitted during the calibration procedure are selected in
the maintenance configuration. Normal 20.9% value provides 17.3 mA.
NOTE
Page 15 of 35
Page 20

Model 4501-XX Toxic Gas Sensor Module
7. SERVICE
7.1 SENSOR MODULE CONFIGURATION
The gas sensor module is comprised of the following sub-assemblies (Figure 7-1):
4501-XX Gas Sensor Module
SPL27077 Stainless Steel Enclosure (SPL 27085 for Aluminum Enclosure)
SPM27071 Transmitter Assembly
XXXXXXX Sensor Assembly (see Appendix B)
XXXXXXX Sensor (see Appendix B)
There are no field serviceable components below the sub assembly level.
Area must be determined to be non-hazardous before opening enclosure.
7.2 ENCLOSURE REPLACEMENT
The enclosure should be replaced if the cover threads or conduit threads have been damaged, or if the
enclosure has been damaged sufficiently that it no longer meets the required NEMA classification.
To replace the enclosure follow the transmitter and sensor assembly removal instructions, remove the
damaged enclosure from its conduit, install a new enclosure and continue the transmitter and sensor assembly
replacement instructions.
Figure 7 - 1: Module Components
NOTE
Page 16 of 35
Page 21

Model 4501-XX Toxic Gas Sensor Module
7.3 TRANSMITTER REPLACEMENT
The transmitter assembly should be replaced when it is determined that it is unreliable, noisy or cannot be
adjusted for calibration. This may occur due to age, corrosion or failed components.
To replace the transmitter assembly:
a. Remove the cover of the main enclosure.
b. Unscrew the two thumb screws in the top of the cover plate, lift the assembly and rotate 90
wiring service loop.
c. Remove the two wires from P1 terminals (see figure 4-3).
d. Unplug the sensor connector from the transmitter.
e. Reverse the preceding steps to install the new transmitter.
f. Restore power and allow a minimum of 30 minutes for stabilization before re-calibration.
7.4 SENSOR REPLACEMENT
NOTE: Refer to Appendix D for information on sensor electrolyte replacement for 4501-25.
The gas sensor which is located inside the sensor assembly housing can be replaced without replacement of
the housing. The gas sensor needs replacement when:
It is no longer possible to obtain correct Zero and Span values.
The “LOW SENS” message appears after calibration.
The sensor output signal is noisy, causing erroneous gas level readings.
To replace the sensor:
a. Confirm that system power has been removed.
b. Remove the gas sensor module enclosure cover.
c. Unscrew the two thumb screws in the top of the faceplate, lift the transmitter assembly and rotate 90
relieve the wiring service loop.
d. Unplug the sensor connector from the transmitter.
e. Unscrew the old sensor assembly from the enclosure conduit hub. Remove the sensor assembly with its
harness.
f. Unscrew sensor housing cover from the sensor.
g. Carefully pull the old sensor straight up from the socket.
h. Press the new sensor into the socket.
i. Reverse the preceding steps to install the sensor assembly.
j. Allow the new sensor to stabilize for a minimum of 30 minutes and then calibrate using the procedure in
Section 6.
7.5 INSTALLATION INSPECTION
o
to relieve the
o
to
Prior to system start-up or trouble shooting, the entire system should be visually inspected. The following are
guidelines for that inspection:
7.5.1 CONTROLLER INSTALLATION
• Controller installed in conformance to manufacturer’s instruction manual recommendations.
7.5.2 CABLING INSTALLATION
• All splices are soldered or via terminal block.
• Cabling is away from sources of electrical noise or RFI where possible.
7.5.3 SENSOR MODULE INSTALLATION
• Module installation in conformance with this manual.
• Modules accessible for calibration.
• Wiring terminations clean and correct.
Page 17 of 35
Page 22

Model 4501-XX Toxic Gas Sensor Module
7.5.4 MOISTURE TRAPS AND RAINSHIELDS
• Conduit seals and drains installed to avoid moisture build up in electronics enclosure. Water
accumulation in sensor module enclosures is a major cause of damage and system failures - take
precautions to seal electrical conduits and provide moisture traps and drains to avoid water damage.
• Rain-shields installed where applicable.
7.5.5 STANDARD VOLTAGES
• Loop voltage to be applied to the sensor module must be between 14 VDC and 30 VDC.
7.6 INSPECTION AND TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE
The inspection and troubleshooting guide can be used to step through the system start-up and to determine
the corrective action if a fault occurs.
7.6.1 IF MODULE DOES NOT RESPOND TO GAS
1. Repeat calibration procedure.
2. Remove the gas and wait for the timer to completely count down.
3. Apply calibration gas and verify that the sensor sees calibration gas after calibration.
4. If the sensor still does not see gas, power cycle the unit and repeat calibration.
7.6.2 IF THE MODULE DISPLAYS “STARTING” FOR MORE THAN 1 HOUR
1. Make sure the sensor is place in an ambient room temperature environment.
2. Power cycle the sensor.
3. Ensure that the sensor is not exposed to the gas of interest during warm-up.
7.6.3 IF THE MODULE DOES NOT DISPLAY THE CORRECT PPM
1. Power cycle the unit.
2. Recalibrate the sensor.
7.6.4 IF THE DISPLAY SHOWS ‘F’ OR “NO SENSOR”
1. Power down the unit.
2. Open the enclosure and unplug the sensor assembly from the transmitter board.
3. Plug the sensor back into the transmitter board carefully and ensure a secure fit.
4. Check all wire connections.
5. Power up the unit.
6. If the system still shows ‘F’, apply magnet to ‘M’ key, then ‘E’ key. The module will start scrolling an
error message. Please write that message down and contact Sierra Monitor for assistance.
7.6.5 IF THE DISPLAY SHOWS ‘C’
1. Complete calibration and exit to operating mode.
Page 18 of 35
Page 23

8.1 APPENDIX A: SPECIFICATIONS
Sensor:
Type: Electrochemical
Model 4501-XX Toxic Gas Sensor Module
8. APPENDICES
4501-03 O2
4501-04 CO
4501-05 H2S
4501-06 Cl2
4501-08 ClO2
4501-10 SO2
4501-12 NO2
4501-25 NH3
4501-26 HF
Max Range (1) Zero Drift Repeatability Linearity Resolution Response Time (2) Sensor Life (3)
0-25% Vol. +/- 0.5 Vol. +/- 0.1 % +/- 0.1 % 0.2% Vol. <10 seconds 20 months
0-1200 PPM +/- 1 PPM +/- 1 PPM +/- 1 PPM 0.5 PPM <25 seconds 2 years
0-100 PPM +/- 0.5 PPM +/- 1 PPM +/- 1 PPM 0.1 PPM <30 seconds 2 years
0-10 PPM +/- 0.5 PPM +/- 0.5 PPM +/- 0.5 PPM 0.1 PPM <60 seconds 2 years
0-3 PPM +/- 0.5 PPM +/- 0.5 PPM +/- 0.5 PPM 0.1 PPM <60 seconds 2 years
0-100 PPM +/- 0.5 PPM +/- 1 PPM +/- 1 PPM 0.5 PPM <20 seconds 2 years
0-20 PPM +/- 0.5 PPM +/- 0.5 PPM +/- 0.5 PPM 0.2 PPM <35 seconds 2 years
0-100 PPM +/- 1.0 PPM +/- 1.0 PPM +/- 1.0 PPM +/- 1 PPM <30 seconds (4)
0-10 PPM +/- 0.5 PPM +/- 0.5 PPM +/- 0.5 PPM +/- 0.5 PPM <90 seconds (4)
(1) Optional ranges available
(2) Response time to 90% full signal value for applied concentration
(3) Sensor life typical for use at standard temperature and pressure with occasional exposure to gas of interest
(4) Sensor electrolyte needs to be recharged every six months
Output:
Display: LCD, 2-line, 16-characters
Signal Output: 2-wire sensor powered analog 4-20 mA (Trouble: 3.6 mA)
Loop Resistance 800 ohm
Electrical Data:
Power consumption: 0.2 watts
Connection type: 2 wire loop-powered
Input voltage: 24 VDC nominal: 14-30VDC
RFI/EMI Protection: EN50081-2, EN50082-2
Operating Range:
o
Extended Range Sensor and 4-20 mA will continue to operate to -40
Operation: LCD display will decay over time if exposed to temperatures below -4
4501-03 O2
4501-04 CO
4501-05 H2S
4501-06 Cl2
4501-08 ClO2
4501-10 SO2
4501-12 NO2
4501-25 NH3
4501-26 HF
Ambient Temp (oF) Ambient Temp (oC) Relative Humidity
-4 to 122 oF -20 to 50 oC 15 – 90%
-4 to 122 oF -20 to 50 oC 15 – 90%
-4 to 122 oF -20 to 50 oC 15 – 90%
-4 to 122 oF -20 to 50 oC 15 – 90%
-4 to 122 oF -20 to 50 oC 15 – 90%
-4 to 122 oF -20 to 50 oC 15 – 90%
-4 to 122 oF -20 to 50 oC 15 – 90%
+14 to 113 oF -10 to 45 oC 20 – 90%
+14 to 113 oF -10 to 45 oC 20 – 90%
F (-40o C) but the
o
C) for
(-20
significant time (not
applicable to 4501-
25)
o
Storage Temperature: -4
o
o
to 122
F(-20o to 50o C)
Page 19 of 35
Page 24

Model 4501-XX Toxic Gas Sensor Module
Enclosure:
Dimensions: 7.0 x 3.6 x 4.0 inches (H x W x D)
(17.8 x 9.1 x 11.2 cm)
Weight: 2.2 lb. (1.0Kg) Al
4.6 lb. (2.1 Kg) SS
Material of Construction: 316 Stainless Steel, Aluminum
Housing: NEMA 4X, NEMA 7
Electrical Approvals:
Factory Mutual (FM):
Hazardous Locations: FM Standards 3600, 3615, 3810
(All Models) Class 1 Div I, Groups B, C, D
Class II, Div I, Groups E, F, G
NEMA 4X1
CSA Class I, Div I, Groups B, C, D
Class II, Div I, Groups E, F, G
NEMA 4X
UL UL Standard 508A
ATEX: II 2 G Ex d IIB+H2 T6 Gb Ta = -20
Performance Approvals:
FM Performance Approval: Approval Standards: ISA-92.0.01, Part I-1998 and FM 3600
(4501-05 only)
Warranty:
Limited Warranty: 2 years
Specifications subject to change without notice
o
C to +50oC
Page 20 of 35
Page 25

Cross Sensitivity Data:
4501-04 Carbon Monoxide
Gas Conc. Response
H
S 15 PPM ~38 PPM
2
SO
5 PPM ~3 PPM
2
NO 35 PPM ~10 PPM
NO
5 PPM ~-3 PPM
2
H
100 PPM <60 PPM
2
C
100 PPM <100 PPM
2H4
HCN 10 PPM ~5 PPM
HCl 5 PPM 0 PPM
4501-05 Hydrogen Sulfide
Gas Conc. Response
CO 400 PPM <.1 PPM
SO
20 PPM <10 PPM
2
NO 50 PPM <3 PPM
NO
10 PPM <-30 PPM
2
Cl
10 PPM <-25 PPM
2
H
400 PPM 1 PPM
2
C
NH
400 PPM <0.1 PPM
2H4
20 PPM <0.1 PPM
3
4501-06 Chlorine
Gas Conc. Response
CO 300 PPM 0 PPM
H
S 15 PPM 0 to -3.38 PPM
2
SO
5 PPM -0.05 PPM
2
NO 35 PPM 0 PPM
NO
5 PPM ~5 PPM
2
H
100 PPM 0 PPM
2
C
100 PPM 0 PPM
2H4
HCN 10 PPM 0 PPM
HCl 5 PPM 0 PPM
4501-08 Chlorine Dioxide
Gas Conc. Response
Cl
3.1 PPM 10 PPM
2
Model 4501-XX Toxic Gas Sensor Module
4501-10 Sulfur Dioxide
Gas Conc. Response
H
S 15 PPM 0 PPM
2
NO 35 PPM -7 to 0 PPM
NO
5 PPM -5 PPM
2
Cl
5 PPM -1.5 to 0 PPM
2
NO
5 PPM ~5 PPM
2
H
100 PPM 0 PPM
2
HCN 10 PPM <5 PPM
HCl 5 PPM 0 PPM
C
100 PPM 0 PPM
2H4
4501-12 Nitrogen Dioxide
Gas Conc. Response
CO 300 PPM 0 PPM
H
S 15 PPM -1.5 to 0 PPM
2
SO
5 PPM -0.05 to 0 PPM
2
NO 35 PPM 0 PPM
Cl
1 PPM ~1 PPM
2
H
100 PPM 0 PPM
2
HCN 10 PPM 0 PPM
HCl 5 PPM 0 PPM
C
100 PPM 0 PPM
2H4
4501-25 Ammonia
Gas Conc. Response
CO 1000 PPM 0 PPM
SO
15 PPM >40 PPM
2
NO 100 PPM 0 PPM
NO
60 PPM 0 PPM
2
H
4% 0 PPM
2
CH
4% 0 PPM
4
HCN 10 PPM 75 PPM
H
S 3 PPM 75 PPM
2
4501-26 Hydrogen Fluoride
Gas Conc. Response
Cl
5 PPM 8 PPM
2
HCl 5 PPM 9 PPM
NH
75 PPM 0 PPM
3
SiH
15 PPM 0 PPM
4
CO 1000 PPM 0 PPM
SO
5 PPM 9 PPM
2
NO 100 PPM 0 PPM
NO
15 PPM 2 PPM
2
H
4% 0 PPM
2
H
S 30 PPM 0 PPM
2
Page 21 of 35
Page 26

8.2 APPENDIX B: MODEL NUMBERS & PARTS LIST
Model 4501-XX Toxic Gas Sensor Module
Sensor Module
Options
Model Gas Enclosure Sensor Protection ATEX
4501 - XX - XX - X - X
4501 Series - 03 = O
- 04 = CO - A2 = AL M20 x 1.5 - 1 = Conformal Sensor - C = ATEX/IECEx
- 05 = H2S - S1 = SS ¾” NPT
- 06 = Cl2- S2 = SS M20 x 1.5
- 08 = ClO
- 10 = SO
- 12 = NO
- 25 = NH
- 26 = HF
- A1 = AL ¾” NPT - 0 = Standard - 0 = Standard
2
2
2
2
3
5311-00 Rainshield
5311-02 Rainshield, with calibration port
Calibration Items
Gas Sensor Calibration Kit, Type A (CO
1250-01 Gas Sensor Calibration Kit, Type B (SO
1250-03 Gas Sensor Calibration Kit, Type C (Cl
, H2
S)
, NO2)
2
)
2
1260-00 Gas Cylinder, Air, (Type A), 105 liters
1260-04 Gas Cylinder, CO 100 PPM, (Type A) 57 liters
1260-05 Gas Cylinder, H
1260-06 Gas Cylinder, Cl
1260-10 Gas Cylinder, SO
1260-12 Gas Cylinder, NO
S in N2, 25 PPM, (Type A) 57 liters
2
, 5 PPM, (Type C) 104 liters
2
, 50 PPM, (Type B) 74 liters
2
, 10 PPM, (Type B) 74 liters
2
1260-13 Gas Cylinder, CO, 1000 PPM, (Type A), 105 liters
5360-00 Calibrator Head Standard
1256-01 Regulator Type A Calibrator
1256-02 Regulator Type B Calibrator
1265-03 Regulator Type C Calibrator
5358-01 Calibration Adapter - Direct, Standard
5358-51 Calibration/Configuration Magnetic Tool, 4501-XX
9210-00 Calibrator, Permeation Tube
9211-09 Permeation Tube, Ammonia, NH
3
SPX27057 Kit, Sensor Recharge, for 4501-25
SPX27061 Kit, Sensor Recharge, for 4501-26
Spare Parts
SPM21834 Sensor Assy, Aluminum, 4501-03
SPM21832 Sensor Assy, Aluminum, 4501-04
SPM21830 Sensor Assy, Aluminum, 4501-05
SPM21833 Sensor Assy, Aluminum, 4501-06/4501-08
SPM21844 Sensor Assy, Aluminum, 4501-10
SPM21845 Sensor Assy, Aluminum, 4501-12
SPM21840 Sensor Assy, Plastic, 4501-25
SPM21878 Sensor Assy, Plastic, 4501-26
SPM27071 Transmitter for 4501-XX
SPM27082 Sensor Assy, 316SS, 4501-03
SPM27083 Sensor Assy, 316SS, 4501-04
SPM27074 Sensor Assy, 316SS, 4501-05
SPM27084 Sensor Assy, 316SS, 4501-06/4501-08
SPM27087 Sensor Assy, 316SS, 4501-10
SPM27088 Sensor Assy, 316SS, 4501-12
SPM33044 Sensor for 4501-03
SPM33030 Sensor for 4501-04
SPM33041 Sensor for 4501-05
SPM33050 Sensor for 4501-06 & 4501-08
SPM33052 Sensor for 4501-10
SPM33054 Sensor for 4501-12
SPL27085 Module Enclosure AL
SPL27077 Module Enclosure SS
(4501-05 only)
Page 22 of 35
Page 27

Model 4501-XX Toxic Gas Sensor Module
8.3 APPENDIX C: LIMITED WARRANTY
SIERRA MONITOR CORPORATION warrants its products to be free from defects in workmanship or material
under normal use and service for two years after date of shipment. SMC will repair or replace without charge
any equipment found to be defective during the warranty period. Final determination of the nature and
responsibility for defective or damaged equipment will be made by SMC personnel.
All warranties hereunder are contingent upon proper use in the application for which the product was intended
and do not cover products which have been modified or repaired without SMC approval or which have been
subjected to accident, improper maintenance, installation or application, or on which original identification
marks have been removed or altered. This Limited Warranty also will not apply to interconnecting cables or
wires, consumables (i.e. calibration gases, batteries, sensors), nor to any damage resulting from battery
leakage.
In all cases SMC’s responsibility and liability under this warranty shall be limited to the cost of the equipment.
The purchaser must obtain shipping instructions for the prepaid return of any item under this warranty
provision and compliance with such instruction shall be a condition of this warranty.
Except for the express warranty stated above, SMC disclaims all warranties with regard to the products sold
hereunder including all implied warranties of merchantability and fitness and the express warranties stated
herein are in lieu of all obligations or liabilities on the part of SMC for damages including, but not limited to,
consequential damages arising out of/or in connection with the use or performance of the product.
Page 23 of 35
Page 28

Model 4501-XX Toxic Gas Sensor Module
8.4 APPENDIX D: 4501-25 & 4501-26 GAS SENSOR MODULE
1. Calibration of 4501-26 (Follow instructions in Section 6)
2. Calibration of 4501-25 (See below)
3. Equipment Required
The following tools and equipment will be required for calibration:
- Permeation Device Calibrator (Model 9210-00), with
Ammonia Permeation Tube (Model 9211-09).
- Calibration Adapter (Model 5358-01).
4. Permeation Device Calibrator Operation
The calibrator is a portable device with a pump that operates from a 1.5 V
alkaline size D battery. A fresh battery should allow 8 hours of continuous
operation. The permeation device will probably be shipped separately,
usually in a pipe with screw cap ends, one of which will be marked for
opening. The permeation device should come fitted with a scrubber, but, as a
precaution, open the pipe and remove the permeation device in a
well ventilated area.
1. Remove the scrubber from the permeation device and attach the device
to the stainless steel “Tee” assembly inside the calibrator box. Tighten
the connection with a wrench, with the device resting inside one of the
openings in the rack.
Figure 8 - 1: Module
Components
2. Close the door of the calibrator and turn on the pump switch.
3. Set the flow rate for the desired ppm of ammonia. The desired flow rate for calibration of the Model
4501-25 is 300-500 cc/min. and the concentration range should be set between the high alarm point and
100 ppm full scale.
The carrier gas flow rate can be calculated from the formula:
P = (CxF)/K
Where P = the permeation rate in nanograms/min., and C = ppm of span gas, F = carrier gas flow rate in
ml./min. and K = 1.437 for ammonia. The permeation rate for the temperature read on the front of the
calibrator can be obtained from permeation rate vs. temperature chart.
4. Run the gas calibrator for 30 min. before attaching the output hose to the ammonia sensor.
5. When the use of the calibrator is completed, do not turn off the pump unit until the permeation device
has been removed from the “Tee” and the gas scrubber reattached. Failure to remove the permeation
device when the pump has been turned off will contaminate the system with high amounts of the
permeating gas and result in erroneous concentrations. The device, with scrubber, can be stored in the
storage rack overnight, but should not stay in the gas calibrator for longer storage periods.
5. Calibration Procedure
Follow procedures outlined in Section 6.0
Page 24 of 35
Page 29

Model 4501-XX Toxic Gas Sensor Module
Electrolyte/Membrane Replacement (See Fig. 8-2) – Models 4501-25 and 4501-26
The electrolyte needs to be replaced at least every six months, or if there is evidence of low sensor
output. The membrane and O-Ring should be replaced at the same time that the electrolyte is
replaced.
1. Equipment Required
- Electrolyte Recharge Kit (SPX27057 for Model 4501-25 NH
and SPX27061 for Model 4501-26
3
HF) consisting of the electrolyte, package of 5 membranes, one (1) 0-Ring and alcohol wipes to
clean the electrode.
- Tweezers to aid in removing and replacing the membrane.
2. Preparation
a. Transfer the necessary electrolyte into a plastic wash bottle.
b. Confirm that system power has been removed.
c. Remove the transmitter electronics board from the main housing and unplug the sensor harness
from the transmitter electronics.
d. Unscrew the sensor assembly from the bottom of the enclosure.
e. Remove the assembly cover from the sensor assembly.
CAUTION: Only remove the sensor cover from the assembly, DO NOT attempt to unscrew the
sensor from the mounting assembly or you could damage the wiring.
3. Electrolyte Replacement (See Fig. 8-1)
a. Invert the sensor assembly so that the membrane is upward.
b. Insert the sensor assembly in a clamp, if available, and unscrew the box nut counterclockwise, and take
out the hold-down ring, membrane and O-Ring. Then pour out the old electrolyte into a beaker for
disposal.
CAUTION: Avoid contact of the electrolyte with skin, eyes and clothing. In case of contact wash
immediately - rubber gloves and safety glasses are recommended.
c. Clean the electrode with the alcohol wipes included in the electrolyte replacement kit. All oxidation
residue must be removed before re-assembly. When dirt is found inside the sensor assembly, wash the
dirt off with electrolyte.
d. Hold the sensor assembly with the sensing electrode up. Close the pressure compensation port with a
tissue. Pour approximately 10cc of fresh electrolyte from the wash bottle into the sensor, and rinse the
inside of the sensor. Empty the electrolyte into the beaker.
e. Place the O-ring on top of the washer. Then transfer one drop of electrolyte from the plastic wash bottle
to the exposed electrode surface.
f. Place a new membrane into the hold-down ring and carefully place the plastic hold-down ring on top of
the sensor body with the ring ears in the slots of the sensor body. Then fasten the sensor cover over the
assembly.
CAUTION: Never touch the membrane with your hands. Use rubber gloves or tweezers.
g. Invert the sensor so that the membrane is down. If this is the first time that electrolyte has been replace,
there should be a round Mili Seal covering the pressure compensation screw. This Mili-Seal prevented
loss of electrolyte during shipment. Remove and discard the round Mili Seal and remove the screw to
expose the electrolyte supply port.
h. Transfer electrolyte from the plastic wash bottle into the electrolyte supply port (see Fig. 8-1) until the
level is at the maximum level line on the side of the sensor body.
Page 25 of 35
Page 30

Model 4501-XX Toxic Gas Sensor Module
i. Replace the pressure compensation screw into the electrolyte supply port.
j. Replace the sensor housing cover.
k. Install the sensor assembly into the enclosure hub and tighten firmly.
l. Reconnect the sensor harness to the transmitter, carefully install the transmitter into the housing and
restore system power.
m. Recalibrate the transmitter following the instructions in Section 6.
Figure 8 - 2: Sensor Assembly – Exploded View
(WHITE)
Page 26 of 35
Page 31

Model 4501-XX Toxic Gas Sensor Module
Figure 8 - 3: Model 4501-25-A1 and 4501-26-A1 Outline Dimensions
Figure 8 - 4: Model 4501-25-S1 and 4501-26-S1 Outline Dimensions
Page 27 of 35
Page 32

8.5 APPENDIX E: US FM APPROVAL.
.
Model 4501-XX Toxic Gas Sensor Module
Page 28 of 35
Page 33

Model 4501-XX Toxic Gas Sensor Module
8.6
Page 29 of 35
Page 34

APPENDIX F: CANADIAN FM APPROVAL
.
Model 4501-XX Toxic Gas Sensor Module
Page 30 of 35
Page 35

Model 4501-XX Toxic Gas Sensor Module
Page 31 of 35
Page 36

8.7 APPENDIX G: ATEX CERTIFICATE
Model 4501-XX Toxic Gas Sensor Module
Page 32 of 35
Page 37

Model 4501-XX Toxic Gas Sensor Module
Special Conditions for Safe Use:
Contact the original manufacturer for information on the dimensions of the flameproof joints.
Page 33 of 35
Page 38

8.8 APPENDIX H: PIPE MOUNTING FOR 4501-XX ALUMINUM
Model 4501-XX Toxic Gas Sensor Module
Figure 8 - 5: Model 4501-XX Aluminum Enclosure Pipe Mount
Figure 8 - 6: Pipe Mount Bracket for 4501-XX Aluminum Enclosure
Page 34 of 35
Page 39

INDEX
Model 4501-XX Toxic Gas Sensor Module
4-20MA ............................................................... 1, 11
AMMONIA ............................................................... 24
APPROVALS .......................................................... 20
CALIBRATION ............................. 1, 4, 14, 15, 22, 24
DATA ENTRY KEYPAD ........................................... 9
ENCLOSURE ........................................... 2, 7, 16, 20
FM ................................................................. 1, 28, 30
INSTALLATION .......................................... 5, 7, 8, 17
MAINTENANCE ...................................................... 13
MOUNTING .............................................................. 1
POWER .................................................................... 2
RANGE .................................................................. 11
SENSOR .................................. 2, 4, 6, 14, 16, 17, 22
SET-UP .............................................................. 5, 11
SPARE PARTS ...................................................... 22
SPECIFICATIONS ................................................. 19
THEORY OF OPERATION ...................................... 1
TRANSMITTER ......................................... 2, 5, 8, 17
TROUBLESHOOTING ........................................... 18
WARRANTY .................................................... 20, 23
WIRING .................................................... 1, 2, 4, 5, 7
Page 35 of 35
 Loading...
Loading...