Page 1

Series 820 Instruction Manual Table of Contents
Sierra 820 Series
Top-Trakª Mass Flow Meters
Instruction Manual
Part Number IM-82
Revision C 06-99
5 Harris Court, Building L Monterey, CA 93940
(831) 373-0200 (800) 866-0200 Fax (831) 373-4402
http://www.sierrainstruments.com
Sierra Instruments b.v. Bolstoen 30A 1046 AV Amsterdam The Netherlands
+31(0)20-6145810 Fax +31(0)20-6145815
IM-82-C 0-1
Page 2

Table of Contents Series 820 Instruction Manual
Customer Notice
Sierra Instruments, Inc. is not liable for any damage or personal injury, whatsoever,
resulting from the use of Sierra Instruments standard mass flow meters or controllers for oxygen gas. You are responsible for determining if this mass flow meter or
controller is appropriate for your oxygen application. You are responsible for
cleaning the mass flow meter or controller to the degree required for your oxygen
flow application.
© COPYRIGHT SIERRA INSTRUMENTS 1994
No part of this publication may be copied or distributed, transmitted, transcribed, stored in
a retrieval system, or translated into any human or computer language, in any form or by
any means, electronic, mechanical, manual, or otherwise, or disclosed to third parties
without the express written permission of Sierra Instruments. The information contained in
this manual is subject to change without notice.
TRADEMARKS
Top-Trakª and Cal-Benchª are trademarks of Sierra Instruments, Inc. Other product and
company names listed in this manual are trademarks or trade names of their respective
manufacturers.
All Sierra products are Year 2000 compliant.
0-2 IM-82-C
Page 3

Series 820 Instruction Manual Table of Contents
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Introduction
Introduction.............................................................1-1
Using this Manual .................................................1-1
Safety Information.................................................1-2
Receipt of System Components..................................1-2
Technical Assistance ..............................................1-2
Top Trak Features......................................................1-3
The 820 Series Flow Sensing Principle .............................1-4
Chapter 2 Installation
Installation Overview ..................................................2-1
Installing the Transducer ..............................................2-2
Compression Fittings .............................................2-2
VCO Fittings .......................................................2-2
VCR Fittings .......................................................2-3
All 1/2-inch Size Connections....................................2-3
Wiring the Transducer.................................................2-4
Standard 0-5 VDC Output Signal Wiring.......................2-5
Optional 4-20 mA Output Signal Wiring........................2-5
Remote Display Installation...........................................2-6
Chapter 3 Operation
Transducer Operation..................................................3-1
Transducer Accuracy..............................................3-1
Referencing the Transducer to Non-Standard Conditions ....3-2
Transducer Over-Ranging ........................................3-2
Zero and Span Adjustments ......................................3-3
Chapter 4 Maintenance and Repair
Transducer Cleaning...................................................4-1
Flow Path Cleaning Model 822/824 .................................4-2
Inlet and Outlet Screens...........................................4-2
Laminar Flow Element............................................4-3
Flow Path Cleaning Model 826/827 .................................4-4
Laminar Flow Element............................................4-4
Flow Path Cleaning Model 822-S/824-S............................4-5
Laminar Flow Element............................................4-5
Sensor Cleaning and Inspection .................................4-8
Transducer Calibration ................................................4-9
Transducer Troubleshooting............ . . . . . . ...................... 4-11
Returning Equipment to the Factory ............................... 4-12
IM-82-C 0-3
Page 4

Table of Contents Series 820 Instruction Manual
Appendix A Conversion Formulas and Gas Tables
Appendix B Production Specifications
List of Figures
1-1. Top-Trak Features (Typical)..................................1-3
1-2. Flow Paths through the Transducer..........................1-4
1-3. Flow Measuring Principle.....................................1-4
2-1. Piping Requirements for 1/2-inch Size Connections.......2-3
2-2. Transducer D-Connector Pin Assignments .. . . .............2-4
2-3. Standard 0-5 VDC Output Signal Wiring ...................2-5
2-4. Single Transducer Current Loop Connection...............2-5
2-5. Multiple Transducer Current Loop Connections ...........2-6
2-6. Mounting the Remote Display ................................2-6
4-1. Model 822/824 Flow Components.................. . . . . . . . . . 4-2
4-2. Correct LFE Position ..........................................4-3
4-3. Model 826/827 Flow Components.................. . . . . . . . . . 4-4
4-4. Low Flow Transducer LFE Cleaning........................4-5
4-5. Medium Flow Transducer LFE Cleaning ...................4-6
4-6. High Flow Transducer LFE Cleaning .......................4-7
4-7. Printed Circuit Board Component Locations ............. 4-10
0-4 IM-82-C
Page 5

Series 820 Instruction Manual Table of Contents
Cautions
Caution! Only qualified personnel should install the transducer.
Caution! Do not supply +DC power at the D-connector while using a power supply at
the power jack. Both supplies may be damaged.
Caution! Operating a 12 VDC transducer at 24 VDC will cause equipment damage.
Caution! Only qualified personnel should perform transducer service, calibration or
troubleshooting procedures.
Caution! When using toxic or corrosive gases, purge the unit thoroughly with inert
dry gas before disconnecting from the gas line.
Caution! Printed circuit boards are sensitive to electrostatic discharge. To avoid damaging the board, follow these precautions to minimize the risk of damage:
· before handling the assembly, discharge your body by touching a grounded,
metal object
· handle all cards by their edges unless otherwise required
· when possible, use grounded electrostatic discharge wrist straps when handling
sensitive components
IM-82-C 0-5
Page 6

Table of Contents Series 820 Instruction Manual
0-6 IM-82-C
Page 7

Series 820 Instruction Manual Chapter 1 Introduction
Chapter 1 Introduction
This instruction manual covers the installation, operation and maintenance of SierraÕs 820 Series product line including the following
Top-Trakª Models:
· 822 Mass Flow Meter with display (nylon flow body)
· 824 Mass Flow Meter without display (nylon flow body)
· 826 Hi-Flow Meter with display (aluminum flow body)
· 827 Hi-Flow without display (aluminum flow body)
· 822-S Mass Flow Meter with display (stainless steel flow body)
· 824-S Mass Flow Meter without display (stainless steel flow body)
SierraÕs Top-Trak
measurement of gas mass flow. The 820 Series offers a broad range
of sizes and process connections for flexibility and versatility. The
primary standard calibration ensures starting point accuracy and
NIST traceability. The meterÕs 0-5 VDC or 4-20 mA output signal is
provided for recording, data-logging or control. The optional display reads the mass flow rate directly in engineering units or percentage of full scale.
Using This Manual
This manual is organized into four chapters:
· Chapter 1 includes the introduction and theory of operation
· Chapter 2 provides installation and wiring instructions
· Chapter 3 describes transducer operation and features
· Chapter 4 covers maintenance, calibration and troubleshooting
Gas tables and conversion formulas are found in Appendix A.
The product specifications and dimensional drawings are found
in Appendix B.
Throughout this manual, we use the word transducer as a generic
term to represent all models of SierraÕs 820 Series Top-Trak
Mass Flow Meters.
ª
Mass Flow Meters are designed for precise
IM-82-C 1-1
Page 8

Chapter 1 Introduction Series 820 Instruction Manual
Safety Information
Caution and warning statements are used throughout this book to
draw your attention to important information.
Warning! Caution!
This statement appears with information that
is important to protect people and equipment
from damage. Pay very close attention to all
warnings that apply to your application.
This statement appears with information that is
important for protecting your equipment and performance. Read and follow all cautions that apply to your application.
Receipt of System Components
When receiving a Sierra transducer, carefully check the outside
packing carton for damage incurred in shipment. If the carton is
damaged, notify the local carrier and submit a report to the factory or
distributor. Remove the packing slip and check that all ordered components are present and match your specifications (as ordered).
Make sure any spare parts or accessories are not discarded with the
packing material. Do not return any equipment to the factory without
first contacting Sierra Customer Service.
Technical Assistance
If you encounter a problem with your transducer, review the configuration information for each step of the installation, operation and set
up procedures. Verify that your settings and adjustments are consistent with factory recommendations. Refer to Chapter 4, Troubleshooting, for specific information and recommendations.
If the problem persists after following the troubleshooting procedures
outlined in Chapter 4, contact Sierra Instruments by fax or by E-mail
(see inside front cover). For urgent phone support you may call (800)
866-0200 or (831) 373-0200 between 8:00 a.m. and 5:00 p.m. PST.
In Europe contact Sierra Instruments bv at +31 20 6145810. When
contacting Technical Support, make sure to include this information:
· the flow range, serial number, Sierra order number and
model number (all marked on the transducer nameplate)
· the problem you are encountering and any corrective action
taken
· application information (gas, pressure, temperature, pipe and
fitting configuration)
1-2 IM-82-C
Page 9
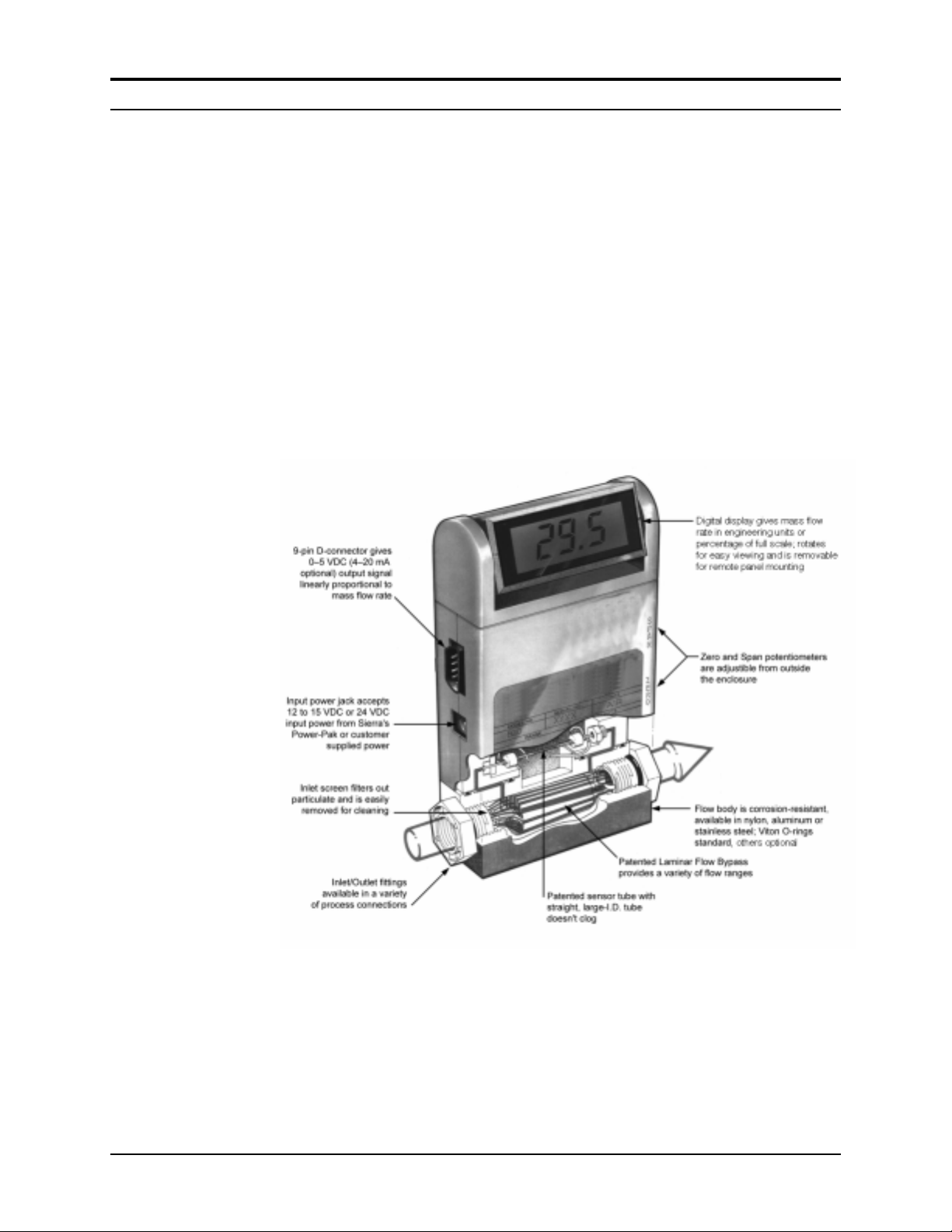
Series 820 Instruction Manual Chapter 1 Introduction
Top-Trak Features
Standard Top-Trak Mass Flow Meters require a 12 to 15 VDC external power source (24 VDC input power optional). The transducerÕs
0 to 5 VDC output signal allows for flow recording, data-logging or
control. A 4 to 20 mA output signal is optionally available. Input
power and output signal connections are made via the 9-pin sub-type
D-connector located on the side of the transducer. An additional input
power jack is located just below the D-connector. (It is important to
connect input power at only one location.)
The transducer shown below is a typical example of a 822 Series
Top-Trak Mass Flow Meter. Other models may vary slightly in their
appearance but are operationally equivalent.
Figure 1-1. Top-Trak Features (Typical)
IM-82-C 1-3
Page 10

Chapter 1 Introduction Series 820 Instruction Manual
The 820 Series Flow Sensing Principle
The operating principle of Top-Trak transducers is based on heat
transfer and the first law of thermodynamics. During operation
process gas enters the instrumentÕs flow body and divides into two
flow paths, one through the sensor tube, the other through the laminar flow element bypass. The laminar flow bypass generates a pressure drop, P1ÐP2, forcing a small fraction of the total flow to pass
through the sensor tube (m1).
Figure 1-2. Flow Paths through the Transducer
Two resistance temperature detector (RTD) coils around the sensor
tube direct a constant amount of heat (H) into the gas stream. In actual operation, the gas mass flow carries heat from the upstream coil
to the downstream coil. The resulting temperature difference (DT) is
detected by the RTD coils and gives the output signal. Since the
molecules of the gas carry away the heat, the output signal is linearly
proportional to gas mass flow.
Figure 1-3. Flow Measuring Principle
1-4 IM-82-C
Page 11

Series 820 Instruction Manual Chapter 2 Installation
Chapter 2 Installation
Installation Overview
To ensure a successful installation, inlet and outlet tubing should be
clean and free from burrs or rims caused by cutting prior to plumbing the transducer into the system. The protective caps covering the
inlet/outlet fittings should not be removed until immediately prior to
installation.
Before installing the transducer, verify the following:
1. Make sure the installation site meets the specific operating pa-
rameters recorded on the transducer’s nameplate. Each trans-
ducer is factory-configured for a specific gas and flow range. If
the operating pressure is more than 50 psi (3.4 bar) away from
the calibration pressure, it is advisable to return the unit to the
factory for re-calibration. (Adjusting zero may be sufficient to
remain within specification.)
2. Do not locate the transducer in areas subject to sudden tempera-
ture changes, moisture, drafts or near equipment radiating sig-
nificant amounts of heat. Make sure to allow adequate space for
cable connectors and wiring.
3. For 1/2-inch size inlet/outlet process connections on models 826
and 827 make sure the location meets the minimum number of
recommended pipe diameters upstream and downstream of the
transducer. A minimum of 5 inches (127 mm) upstream and 2-
1/2 inches (64 mm) downstream is always recommended. (not
necessary for other models)
4. Horizontal mounting is preferable. Vertical mounting is possible
with best results achieved when the factory calibration is specifi-
cally performed for vertical mounting. In vertical positions zero
shift will occur depending on the gas pressure at zero flow.
5. If the gas contains any particulate matter, install an in-line filter
prior to the transducer. Recommended filter size: 15 micron for
flows of 10 sccm to 30 slpm, 30 micron for above 30 slpm.
6. If a potential over-flow condition exists, insert a valve or critical
orifice in the line to limit flow to approximately 25 percent above
the full scale range of the meter.
7. Confirm that the transducer o-ring material is compatible with
the gas to be measured.
8. For remote displays, confirm the supplied cable is of sufficient
length to connect the components.
IM-82-C 2-1
Page 12

Chapter 2 Installation Series 820 Instruction Manual
Caution!
Only qualified
personnel should install
the transducer.
Installing the Transducer
Follow the installation instructions that apply to your transducer’s
process connection. For all 1/2-inch size process connections, observe
the piping recommendations given on page 2-3. Before operation, all
plumbing should be checked carefully for leaks and the transducer
purged with dry nitrogen.
Compression Fittings
1. Position the transducer with the flow direction arrow pointing
downstream in the direction of flow.
1. Verify the position of the front
and back ferrule. Insert the
tubing into the fitting. Make
sure that the tubing rests
firmly on the shoulder of the
fitting and that the nut is finger
tight. (Do not mix or interchange parts of tube fittings
made by different manufacturers.)
2. Hold the body steady with a backup wrench. For 1/2-
inch size, tighten the nut 1-1/4 turns from finger tight. For 1/8inch, 1/4-inch and 3⁄8-inch sizes, tighten only 3/4 turn from finger tight. Do not over-tighten!
3. Check the system’s entire flow path thoroughly for leaks. (Do
not use liquid leak detectors, instead monitor pressure decay.
Over-exposing the transducer to leak detector fluid may damage
the unit.)
VCO and VCR Fittings
1. Position the transducer with the flow direction arrow pointing
downstream in the direction of flow.
2. Install new o-rings compatible with the gas to be used. (Do not
mix or interchange parts of tube fittings made by different manufacturers.)
3. Hold the body steady with a backup wrench. Tighten
the nut finger tight and then 1/4 turn tighter with a wrench. Do
not over-tighten!
4. Check the system’s entire flow path thoroughly for leaks. (Do not
use liquid leak detectors, instead monitor pressure decay. Overexposing the transducer to leak detector fluid may damage the unit.)
2-2 IM-82-C
Page 13
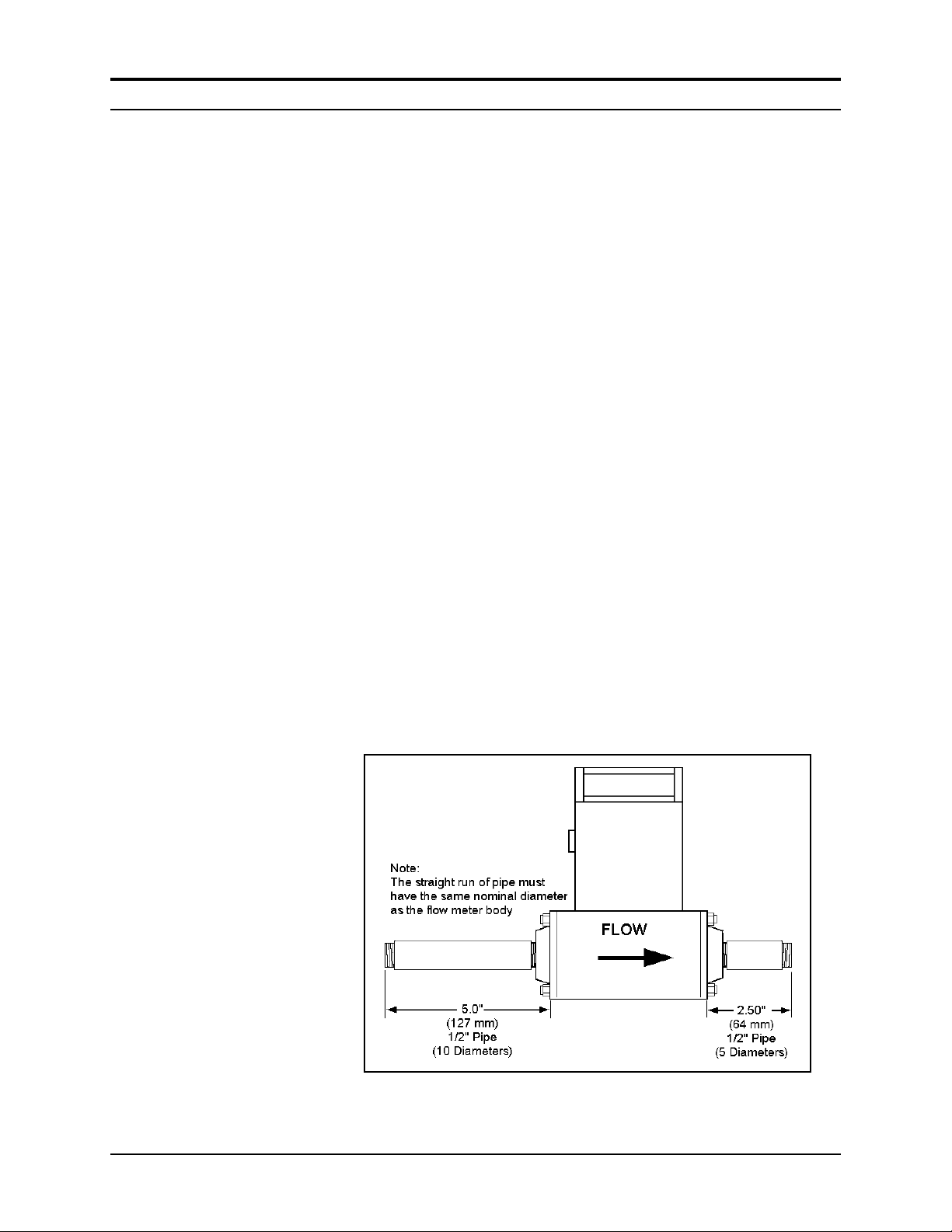
Series 820 Instruction Manual Chapter 2 Installation
1/4 Inch Female NPT (standard on nylon flow bodies)
1. Position the transducer with the flow direction arrow pointing
downstream in the direction of flow.
2. Use a good quality paste pipe thread sealant.
Apply to the pipe threads.
3. Tighten the pipe no more than 1 turn past hand-tight.
Caution! Do not over-tighten,
damage to the instrument may result.
4. Check the system’s entire flow path thoroughly for leaks. (Do not
use liquid leak detectors, instead monitor pressure decay. Over-
exposing the transducer to leak detector fluid may damage the unit.)
1/2-Inch Size NPT Connections (Models 826,827 only)
1. Install a section of straight pipe at least ten pipe diameters in length
upstream of the transducer. Also, allow at least five pipe diameters
downstream for accurate operation. DO NOT use reducers. If the
preceeding components in the flow path create disturbances extend
the upstream pipe length.
2. Position the transducer with the flow direction arrow pointing
downstream in the direction of flow.
3. Tighten fittings until leak tight (refer to published standards for
specific recommendations).
4. Check the system’s entire flow path thoroughly for leaks. (Do not
use liquid leak detectors, instead monitor pressure decay. Over-
exposing the transducer to leak detector fluid may damage the unit.)
Figure 2-1.
Piping Requirements for all 1/2-Inch Size Process Connections
IM-82-C 2-3
Page 14
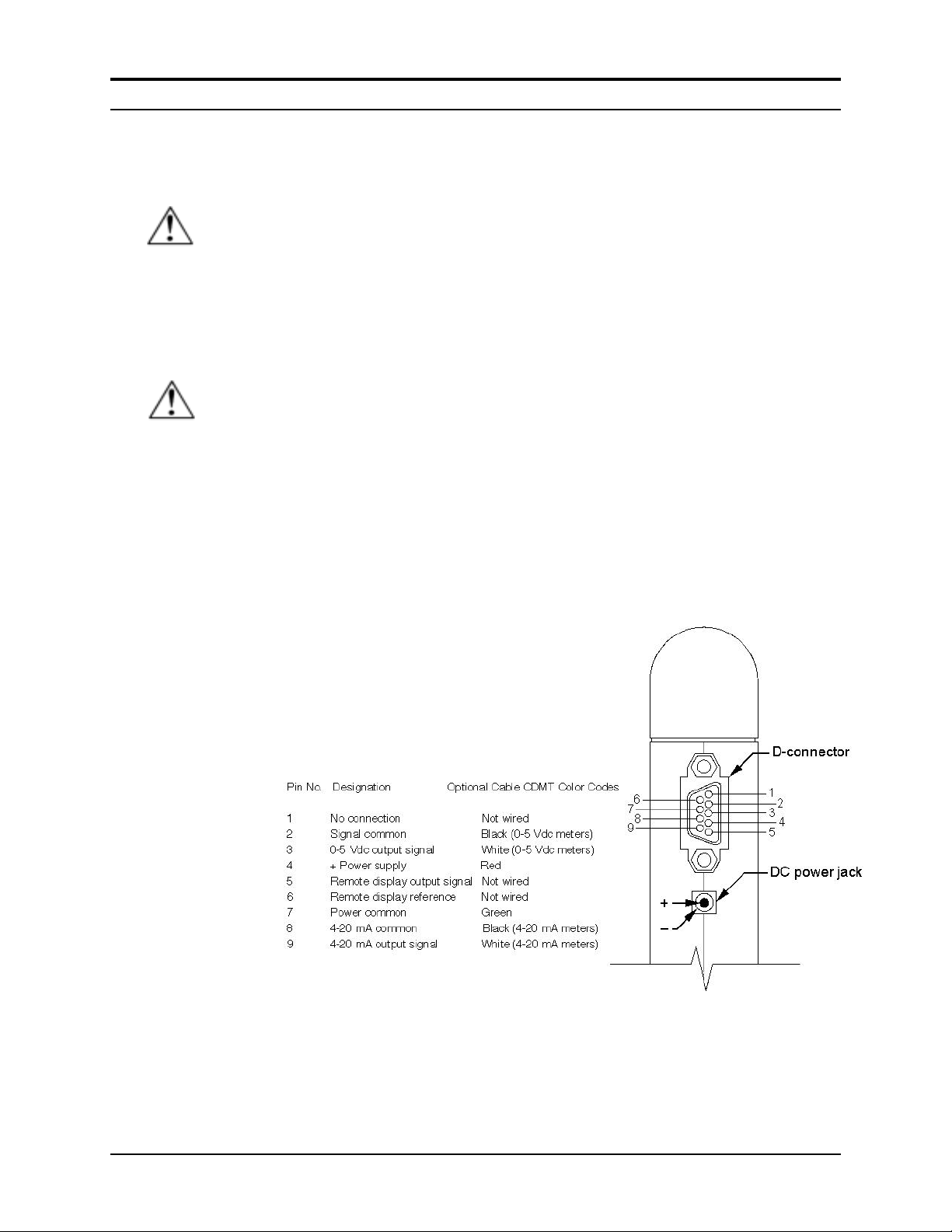
Chapter 2 Installation Series 820 Instruction Manual
Caution!
Do not supply +DC power
at the D-connector while
using a power supply at the
power jack. Both supplies
may be damaged.
Wiring the Transducer
Standard Top-Trak™ transducers require a 12 to 18 VDC power
supply (15 VDC nominal, 100 mA maximum). 24 VDC input power
is optional. Transducers are connected to the power supply through
either the dedicated DC power jack or through the 9-pin D-connector
located on the side of the enclosure. Before powering the unit, check
the transducer’s nameplate to confirm input power:
• PV1 = 12 to 18 VDC
• PV2 = 24 VDC
Note: operating a 24 VDC transducer at 12 to 18 VDC will result in
unreliable operation.
Caution!
Operating a 12 VDC trans-
ducer at 24 VDC will cause
equipment damage.
The transducer’s standard 0 to 5 VDC (4-20 mA optional) output
signal is available through the D-connector. The mating connector is
included with the transducer. Connection details are given on the
following pages.
When the transducer is configured for a remote display, signal connections are made via the 9-pin connector. Input power connections
are not included in the standard interface cable. Remote display
mounting dimensions are given at the end of this chapter.
Figure 2-2. Transducer D-Connector Pin Assignments
2-4 IM-82-C
Page 15

Series 820 Instruction Manual Chapter 2 Installation
Standard 0-5 VDC Output Signal Wiring
The standard 0-5 VDC output signal flows from Pin 3 (0-5 VDC
Out) through the load (1K Ohm minimum) to Pin 7 (Power Common). The figure below is a typical example of input power and
output signal connections.
Figure 2-3. Standard 0-5 VDC Output Signal Wiring
Optional 4-20 mA Output Signal Wiring
The optional 4-20 mA output signal flows from Pin 9 (4-20 mA Out)
through the load (50 to 500 Ohms maximum) to Pin 7 (Power Common). The figure below is a typical example of input power and output signal connections. (Multiple transducer current loop output connections are given on the next page.)
Figure 2-4. Single Transducer Current Loop Connection
IM-82-C 2-5
Page 16

Chapter 2 Installation Series 820 Instruction Manual
Figure 2-5. Multiple Transducer Current Loop Connections
Remote Display Installation
Mount the remote display at a convenient location within reach of the
supplied interface cable. The maximum cable length is 100 feet (30 m).
Figure 2-6. Mounting the Remote Display
2-6 IM-82-C
Page 17

Series 820 Instruction Manual Chapter 3 Operation
Chapter 3 Operation
The output signal of the transducer is either 0-5 VDC (standard) or
4-20 mA (optional). The output signal is linear and proportional to
the gas mass flow rate. For example, for a 0-5 VDC output signal,
5.00 VDC is the output signal for the full scale listed on the transducer’s nameplate, 2.50 VDC is for one-half of full scale, and 0.00
VDC is for zero flow. For a 4-20 mA output signal, 20.00 mA is the
output signal for the full scale, 12.00 mA is for one-half of full
scale, and 4.00 mA is for zero flow.
Transducer Operation
When the transducer is installed and the system has undergone a
complete leak check:
1. Apply power. The output signal will be at a high level for the
first 10 to 20 seconds while the sensor warms up to its normal
operating temperature range. Assuming zero flow, the output
signal will then drop to zero (or 4 mA, depending on output con-
figuration). Allow at least thirty minutes of warm-up time.
2. For first-time start ups, perform an initial zero output check as
described on page 3-3. After checking the initial zero setting, the
transducer is ready to monitor the gas mass flow rate.
Transducer Accuracy
The standard accuracy of Top-Trak is ±1.5% of full scale. The
±1.5% of full scale accuracy means that the 0-5 VDC output signal
is accurate to within ±0.1 VDC. The 4-20 mA output is accurate to
within ±0.4 mA.
For example, the output signal for zero flow can be as much as
+0.1 VDC or +0.4 mA. If the transducer has an output signal at
zero flow, as long as it is within either of these two ranges, it does
not mean it is malfunctioning.
For transducers with a digital display, the accuracy is simply 1.5
times the full scale flow rate stated on the nameplate. For example,
if the full scale is 10 slpm, the digital display will be accurate to
±0.2 slpm. The reading at zero flow may be as much as +0.2 slpm
and still be within the stated accuracy specification.
IM-82-C 3-1
Page 18

Chapter 3 Operation Series 820 Instruction Manual
Referencing the Transducer to Non-Standard Conditions
The gas flow rate output of your transducer is referenced to “standard”
conditions of 21°C (70°F) and 760 mm of mercury (1 atmosphere)
unless otherwise specified on the certificate of calibration. Check the
stated reference conditions of your transducer. If you are comparing
your transducer’s output with another type of flow meter, different
reference conditions could cause a discrepancy between the flow
readings.
For example, the output reading of a Top-Trak will be approximately
7% lower when referenced to 0°C rather than 21°C. To find the flow
rate referenced to other standard conditions or the actual temperature
and pressure conditions in the pipe where your transducer is located,
see Appendix A.
Transducer Over-Ranging
If the flow rate exceeds the full scale value listed on the transducer
nameplate, the output signal and digital display (if so equipped) will
read a higher value. The transducer is not calibrated for over-ranged
flows and will probably be both non-linear and inaccurate. Overrange conditions are indicated by the display and/or output signal
going to a level above the full scale range. When the over-range
condition is removed, it may take several seconds for the transducer
to recover and resume normal operation.
If the supply voltage is only 12 VDC, the over-ranged reading may
exceed the full scale value by 10% maximum. If the supply voltage
is higher, as with the 24 VDC option, then the output can exceed the
full scale by as much as 50%, or more. Digital displays cannot exceed 3-1/2 digits (1999). If the flow rate exceeds 1999, the rightmost digits will blank and only the left-hand “1” will appear on the
display.
3-2 IM-82-C
Page 19

Series 820 Instruction Manual Chapter 3 Operation
Zero and Span Adjustments
The zero and span potentiometers are
accessed through the ports marked on
the side of the transducer. Normally,
span adjustments are not made unless
you are calibrating the transducer. The
span adjustment should not be used
unless you have a known, precise nonzero flow rate that you wish to match.
Before making any zero adjustments,
confirm that the system has reached its
normal operating temperature and pressure and the transducer is mounted in
its final position.
For transducers without the digital display:
1. Power the transducer and allow at least 30 minutes of warm up
time before attempting any adjustments. Set gas flow to zero.
Confirm that no flow exists.
2. Connect a digital multimeter to Pin 3 (0-5 Out) or, Pin 9 (4-20 Out)
and Pin 7 (Power Common). Check the reading. If it does not indi-
cate 0± .05 VDC, (or 4.0± .016mA) adjust the zero potentiometer.
Since the output does not indicate negative numbers, it is neces-
sary to adjust down from a slightly positive reading. Begin by
slowly rotating the zero pot clockwise until a positive reading is
indicated. To complete the zero adjustment, slowly turn the pot
counterclockwise until zero is achieved.
For transducers with the digital display:
1. Power the transducer and allow at least 30 minutes of warm up
time before attempting any adjustments. Set gas flow to zero.
Confirm that no flow exists.
2. Observe the reading on the digital display. If the reading is
greater than 1.5% of full scale, adjust the zero potentiometer.
IM-82-C 3-3
Page 20

Chapter 3 Operation Series 820 Instruction Manual
3-4 IM-82-C
Page 21

Series 820 Instruction Manual Chapter 4 Maintenance & Repair
Chapter 4 Maintenance and Repair
Top-Trak™ transducers essentially require no scheduled maintenance
other than periodic flow path cleaning if the gas is dirty. If an in-line
Caution!
It is important that this
transducer be serviced
and/or calibrated by
qualified personnel.
filter is used, the filtering element should be periodically replaced or
ultrasonically cleaned.
Calibration of Sierra Instruments flow meters and controllers requires a calibrating standard of at least equal accuracy and preferably
an order of magnitude better than the transducer, and a skilled factory technician familiar with the Top-Trak. It is recommended that
Top-Trak meters be returned to the factory for annual evaluation and
calibration.
Included in this chapter are general instructions for:
• Transducer Cleaning Instructions..........................page 4-1
• Transducer Calibration......................................page 4-9
• Transducer Troubleshooting..............................page 4-11
• Returning Equipment to the Factory.....................page 4-12
Transducer Cleaning
Due to transducer design variations, separate cleaning instructions
are given in this chapter for each of the following models:
• Model 822/824 with nylon flow body
• Model 826/827 with aluminum flow body
• Model 822-S/824-S with stainless steel flow body
When toxic or corrosive gases are used, the transducer must be
thoroughly purged with inert dry gas before disconnecting from the
gas line. If a transducer used with toxic or corrosive gas is returned
to the factory, the transducer must first be purged clean. A Material
Safety Data Sheet must be enclosed with the unit upon its return.
IM-82-C 4-1
Page 22

Chapter 4 Maintenance & Repair Series 820 Instruction Manual
Flow Path Cleaning Model 822/824
Caution!
When using toxic or cor-
rosive gases, purge the
unit thoroughly with inert
dry gas before disconnect-
ing from the gas line.
Figure 4-1. Model 822/824 Flow Components
Inlet and Outlet Screens
1. Remove the transducer from the system.
1. Remove inlet and outlet fittings.
2. Pull out the laminar flow element (LFE) holddowns.
3. Replace or clean the inlet and outlet screens.
4. Re-assemble components. When the transducer is installed in the
system, leak test the connection.
5. To be within the original accuracy, calibrate the transducer (see
page 4-9).
4-2 IM-82-C
Page 23

Series 820 Instruction Manual Chapter 4 Maintenance & Repair
Laminar Flow Element
The laminar flow element (LFE) is a precision flow divider which
diverts a preset amount of flow through the sensor tube. The LFE is
made of precision machined 316 stainless steel. The particular LFE
used depends on the gas and flow range of the instrument. To clean
or inspect the LFE:
1. Remove the transducer from the system.
Caution!
When using toxic or cor-
rosive gases, purge the
unit thoroughly with inert
dry gas before disconnect-
ing from the gas line.
1. Remove the inlet and outlet fittings. Pull out the LFE holddowns
and inlet/outlet screens.
2. The LFE has a slightly tapered shape with the larger diameter on
the upstream (inlet) side. To remove, use a blunt object which
does not mar the flow channels to push the LFE from the outlet
side to the inlet side. A 3/8-inch (9 mm) nut driver works well.
3. Clean the LFE using a suitable solvent. Make sure to carefully
clean all active flow channels in the LFE.
4. Re-install the LFE making sure to press it in the correct distance
as shown below.
5. Re-assemble remaining components. When the transducer is in-
stalled in the system, leak test the connection. Re-zero the trans-
ducer (see Chapter 3).
Figure 4-2. Correct LFE Position
IM-82-C 4-3
Page 24

Chapter 4 Maintenance & Repair Series 820 Instruction Manual
Flow Path Cleaning Model 826/827
Laminar Flow Element
The laminar flow element (LFE) is a precision flow divider which
diverts a preset amount of flow through the sensor tube. The particular LFE used depends on the gas and flow range of the instrument. To clean or inspect the LFE:
Caution!
When using toxic or cor-
rosive gases, purge the
unit thoroughly with inert
dry gas before disconnect-
ing from the gas line.
1. Remove the transducer from the system.
2. Remove the 6-32 hex nuts and washers. Remove the end caps.
Note the position of the three (3) LFE elements.
3. To remove the LFE, use a blunt object which does not mar the
flow channels to push the LFE from the flow body.
4. Clean the LFE using a suitable solvent. Make sure to carefully
clean all active flow channels in the LFE.
5. Re-install the LFE making sure to position it with both ends
even with the transducer flow body.
6. Re-assemble remaining components. When the transducer is in-
stalled in the system, leak test the connection. Re-zero the transducer (see Chapter 3).
Figure 4-3. Model 826/827 Flow Components
4-4 IM-82-C
Page 25

Series 820 Instruction Manual Chapter 4 Maintenance & Repair
Flow Path Cleaning Model 822-S/824-S
Laminar Flow Element
The laminar flow element (LFE) is a precision flow divider which
diverts a preset amount of flow through the sensor tube. The LFE is
made of precision machined 316 stainless steel. The particular LFE
used depends on the gas and flow range of the instrument. Should
the LFE require cleaning or inspection due to deposition, use the appropriate cleaning procedure which is specific to flow body size.
Caution!
When using toxic or cor-
rosive gases, purge the
unit thoroughly with inert
dry gas before disconnect-
ing from the gas line.
Figure 4-4. Low Flow Transducer LFE Cleaning
Low Flow Transducers:
The LFE is accessed by unscrewing the main inlet fitting and removing it from the flow body. The LFE is screwed into the inlet fitting, which has been specially machined for this purpose. To access
the components:
1. Remove the transducer from the system.
1. The inlet filter screen is held in place in the inlet fitting by the
LFE. Disassemble by holding the fitting steady with a wrench
and unscrewing the LFE with a medium flat-tipped screwdriver.
2. Remove the LFE assembly taking care not to bend the inlet
screen. Inspect the sealing O-ring and replace if necessary. In-
spect the inlet screen and replace if corroded or damaged. Light
to medium particulate contamination can be cleaned by back
washing with a suitable solvent. Air dry thoroughly.
3. Inspect the LFE for damage and replace if necessary. Replacement
of the LFE or inlet screen requires transducer re-calibration.
4. Re-assemble components. When the transducer is installed in the
system, leak test the connection. Re-zero the transducer (see
Chapter 3).
IM-82-C 4-5
Page 26

Chapter 4 Maintenance & Repair Series 820 Instruction Manual
Figure 4-5. Medium Flow Transducer LFE Cleaning
Medium Flow Transducers:
In the medium flow body, the LFE assembly consists of the honeycomb laminar flow element, inlet screen, 0.63 inch long standoff,
two ranging washers, 2-1⁄4 inch long 4-40 screw and 4-40 nut.
Range changes in the honeycomb element are made with various diameter ranging washers. To access the components:
Caution!
When using toxic or cor-
rosive gases, purge the
unit thoroughly with inert
dry gas before disconnect-
ing from the gas line.
1. Remove the unit from the system.
2. Access the LFE by unscrewing the four 10-32 socket head cap
screws from the inlet side of the flow body and remove the inlet
end cap. (Note the position of the screws, one has a shorter
length.)
3. Remove the LFE assembly taking care not to bend the inlet
screen. Inspect the sealing O-ring and replace if necessary. Inspect the inlet screen and replace if corroded or damaged. Light
to medium particulate contamination can be cleaned by back
washing with a suitable solvent. Air dry thoroughly.
4. Inspect the honeycomb element for damage and replace if neces-
sary. Replacement of the LFE or inlet screen requires transducer
re-calibration.
5. Re-assemble components. When the transducer is installed in the
system, leak test the connection.
6. To be within the original accuracy, calibrate the transducer (see
page 4-9).
4-6 IM-82-C
Page 27

Series 820 Instruction Manual Chapter 4 Maintenance & Repair
Figure 4-6. High Flow Transducer LFE Cleaning
High Flow Transducers:
The high flow LFE is similar to the honeycomb element used in the
medium flow body but larger in diameter. The high flow body consists
of four parts: inlet tube, inlet cap, main flow body and end cap. The
inlet tube is only removed to inspect and replace the sealing O-ring
between the inlet tube and inlet cap. To access the components:
Caution!
When using toxic or cor-
rosive gases, purge the
unit thoroughly with inert
dry gas before disconnect-
ing from the gas line.
1. Remove the unit from the system.
2. To remove the inlet screen, remove the four 1⁄4-28 socket head
cap screws on the inlet side of the flow body and separate the
inlet cap from the main flow body.
3. Inspect the inlet screen for damage and corrosion and replace if nec-
essary. Light to medium particulate contamination can be cleaned by
back washing with a suitable solvent. Air dry thoroughly.
4. Inspect the sealing O-ring for damage and replace if necessary.
The inlet screen is mounted with the fine mesh side facing the inlet.
5. To remove the LFE loosen and remove the four threaded rods
holding the end cap to the main flow body. Separate the end cap
from the main flow body and remove the LFE assembly. The LFE
assembly consists of: 6-32 x 31⁄8 inch long screw, a #6 washer,
two ranging washers, honeycomb laminar flow element, LFE,
spacer, inlet filter, and 6-32 nut.
6. Inspect the honeycomb element for damage and replace if neces-
sary. Replacement of the LFE or inlet screen requires transducer
re-calibration.
7. Re-assemble components. When the transducer is installed in the
system, leak test the connection.
8. To be within the original accuracy, calibrate the transducer (see
page 4-9).
IM-82-C 4-7
Page 28

Chapter 4 Maintenance & Repair Series 820 Instruction Manual
Sensor Cleaning and Inspection
Due to sensor design variations, the following sensor cleaning instructions are for Model 822-S/824-S only. All other transducer
models must be returned to the factory.
Sensor cleaning is accomplished by simply rodding out the sensor
with the Sensor Cleaning Stylette, part number “CK” available
from Sierra. A 0.028 inch diameter piano wire may also be used.
To access the sensor for inspection or cleaning:
Caution!
When using toxic or cor-
rosive gases, purge the
unit thoroughly with inert
dry gas before disconnect-
ing from the gas line.
1. Remove the transducer from the system. Remove the two socket
head access port plugs with a 1⁄4-inch Allen wrench. Visually
inspect the sensing ports and sensor.
1. Use a hemostat or tweezers to
push the cleaning wire into the
downstream opening of the
sensor tube. Do not force the
cleaning wire, move it back and
forth–DO NOT TWIST OR
ROTATE.
2. Flush the sensor tube with a
non-residuous solvent compatible with the O-ring material. In cases where solids are deposited
in sensor, units should be returned to factory for complete
cleaning and re-calibration.
3. Blow dry all parts with dry nitrogen and re-assemble. When the
transducer is installed in the system, leak test the connection.
Re-zero the transducer (see Chapter 3).
4-8 IM-82-C
Page 29

Series 820 Instruction Manual Chapter 4 Maintenance & Repair
Caution!
It is important that this
transducer be calibrated
only by qualified personnel.
Transducer Calibration
Calibration of Sierra’s flow meters requires a calibration standard of
at least four times the accuracy of the transducer. Sierra’s Cal-Bench
Automated Primary Calibration System is the preferred method of
calibration and is used at the factory for all calibrations from 10 sccm
up to 50 slpm. Most calibrations can be performed with a digital
voltmeter (DVM) or multimeter with 0.25% accuracy and four digits,
dry nitrogen and the K-factor tables included in this manual. Flow
meters require a metering valve for setting a constant flow rate.
The following procedures are offered as guidelines for calibration.
It is always best to return the transducer to the factory for calibration. Calibration checks and minor adjustments to the zero and full
scale are made via the access ports in the enclosure. If the linearity
needs adjustment (when installing a different bypass to change the
range) skip Step 2 and Step 3. If linearity does not need adjustment,
complete only Steps 1 through 3.
Step 1. Warm Up
Plug in the unit to be calibrated and allow at least 30 minutes warm
up time before attempting any adjustments.
Step 2. Zero Adjust
Slide open the zero and span access doors. Connect a DVM or multimeter to the transducer output pins. Adjust the zero potentiometer
for 0.0 volts (4 mA) at zero flow.
Step 3. Check Full Scale
Generate full scale flow using a metering valve in-line with the unit
under test. Compare the indicated flow rate with the flow standard
reading. If they agree to within ±10%, adjust the span potentiometer
for exact agreement. If the readings do not agree within ±10%, attempt to determine the cause of disagreement. Possibilities are:
• leaks in the system or in the transducer
• wrong or improper use of K-factor
• wrong or improper correction for temperature and pressure
• partially clogged or dirty sensor tube
• replacement of components in the flow path do not exactly match
the original parts
This completes transducer calibration. To adjust linearity, continue
with Step 4.
IM-82-C 4-9
Page 30

Chapter 4 Maintenance & Repair Series 820 Instruction Manual
Step 4. Adjusting Linearity
First gain access to the printed circuit board inside the enclosure:
1. For units with the digital display, carefully rotate the display un-
til it hits the top plate. Slide the display’s two side panels up and
remove. Move the display aside taking care not to damage the
connecting cable.
2. Remove the two Phillips head screws from the top of the trans-
ducer enclosure. Remove the two Phillips head screws from the
back of the transducer enclosure. Pull the enclosure panels off.
3. Orient the transducer with the component side of the circuit
board facing you. Plug in the transducer and allow to warm up
for at least 30 minutes.
Step 5. Zero Adjust
Connect a DVM to the transducer output pins. Adjust the zero potentiometer for 0.0 volts (4 mA) at zero flow.
Step 6. Calibrate 25%
Use the calibration standard to set a flow rate of 25% of full scale.
Adjust the span potentiometer for 1.25 volts (8 mA) at the output of
the transducer.
Step 7. Calibrate 50%
Increase the flow rate to 50% of full scale. If the output is within
+0.05 V (0.2 mA), no adjustment is necessary. If the output is beyond these limits, install a jumper block at J1 in the appropriate position (see Figure 4-7). Adjust R25 for the proper reading.
Step 8. Calibrate 75% and 100%
Set the flow to 75% of full scale. If the output is outside the limits
set in Step 7, install a jumper block in J2 in the appropriate position.
Adjust R27 for the correct reading. Repeat this procedure for 100%
flow using R29. Repeat Steps 6 through 8 at least one more time.
Figure 4-7. Printed Circuit Board Component Locations
4-10 IM-82-C
Page 31

Series 820 Instruction Manual Chapter 4 Maintenance & Repair
Transducer Troubleshooting
When you suspect that the transducer is not operating correctly,
there are a few simple checks that can be made before taking the unit
out of service:
1. Make certain that there are no leaks in the gas line.
2. Check that all cables are connected and are in good condition.
3. Verify that the power supply is in the correct range and
properly connected to the transducer.
4. Double check connector pin outs when replacing another manu-
facturer’s transducer.
This information is provided to help locate the cause of a transducer
failure. It is not intended to be an all inclusive repair guide. For most
repairs, the unit should be returned to the factory for service.
Problem Possible Cause Solution
No output No power
Inlet filter screen clogged
Clogged sensor
PCB defective
Unit will not zero Gas leak
Application requires high pressure and non-horizontal mounting
PCB defective
Reads full scale
with no flow
Output too high Incorrect calibration or K-factor
Out of calibration
*Model 822-S/824-S see sensor cleaning instructions
Gas leak
Liquid present in system
Defective sensor
Liquid present in system
Defective sensor
Dirty or clogged sensor
Change in composition of gas
Gas leak
LFE dirty
Inlet filter screen clogged
Incorrect inlet conditions
(1/2-inch size models)
PCB defective
Plug in power supply
Clean or replace screen
Return to factory for cleaning*
Return to factory for repair
Find and correct leaks
Re-zero transducer
(see Chapter 3)
Return to factory for repair
Find and correct leaks
Check for liquid in flow path
Return to factory for repair
Correct calibration/k-factor
Check for liquid in flow path
Return to factory for repair
Return to factory for cleaning*
See K-factory tables
Find and correct leaks
Clean LFE
Clean or replace screen
Re-plumb transducer correctly
(See Chapter 2)
Return to factory for repair
IM-82-C 4-11
Page 32

Chapter 4 Maintenance & Repair Series 820 Instruction Manual
Returning Equipment to the Factory
Factory Calibration—All Models
Sierra Instruments maintains a fully-equipped calibration laboratory. All
measuring and test equipment used in the calibration of Sierra transducers
are traceable to NIST Standards. Sierra is ISO-9001 registered and conforms to the requirements of ANSI/NCSL-Z540 and ISO/IEC Guide 25.
Instructions for Returning Your Instrument for Service
The following information will help you return your instrument to Sierra
Instruments' Factory Service Center and will ensure that your order is
processed promptly. Prices may vary depending on the flow range, type
of gas and operating pressure of your unit. To request detailed pricing contact your local Sierra Instruments distributor or contact one of our offices
directly. Our expedite fees are: three-day turnaround 25%, two-day turnaround 40%.
Please follow these easy steps to return your instrument for factory
service:
1. Obtain a Return Materials Authorization Form (RMA) with assigned
number from Sierra Instruments. You may obtain this from the
factory by calling (800) 866 0200 between 8:00 a.m. and 5:00 p.m.
PST Monday through Friday. You may also obtain this number via
e-mail by contacting service@sierrainstruments.com.
2. Once you have obtained an RMA number, complete the form (one
form can be used for multiple units). If you require service beyond
calibration, but do not know which service(s) will be required, describe the symptoms as accurately as possible on the RMA form.
Submit electronically or by fax to (831) 373-2414.
3. Pack your instrument carefully (bubble wrap or molded foam sug-
gested-NOT PEANUTS) and include a copy of the RMA form
(complete with Sierra supplied RMA number) with the unit(s).
4. Ship the unit(s) to the following address:
4-12 IM-82-C
Page 33

Series 820 Instruction Manual Chapter 4 Maintenance & Repair
RETURN ADDRESS:
Sierra Instruments, Inc.
Caution!
Always fully neutralize
any toxic gas trapped in-
side the instrument before
removing it from the gas
line.
CUSTOMER SERVICE AND SUPPORT INFORMATION:
Email Technical Support: service@sierrainstruments.com
Email Sales: sales@sierrainstruments.com
FACTORY USA (recommended):
TOLL FREE: 800-866-0200
European Sales & Service Center:
Attention: Factory Service Center
5 Harris Court, Building L
Monterey, CA 93940 USA
PHONE: 831-373-0200
FAX: 831-373-4402
EMAIL: service@sierrainstruments.com
PHONE: +31 72 5071400
FAX: +31 72 5071401
EMAIL: service@sierra-instruments.nl
Asia Sales & Service Center:
PHONE: + 86 203435 4870
FAX: +86 203435 4872
IMPORTANT SAFETY NOTE ABOUT PURGING
WARNING: When toxic or corrosive gases are used, purge
unit thoroughly with inert dry gas before disconnecting
from the gas line to prevent personnel from being injured
when coming in contact with the instrument.
WARNING: If an instrument used with a toxic or corrosive
gas is returned to the factory, a Material Safety Data Sheet
(MSDS) must be enclosed & attached to the outside of the
box to alert Sierra personnel of the potential hazard. Also,
make sure the inlet & outlet are solidly plugged off.
IM-82-C 4-13
Page 34

Series 820 Instruction Manual Appendix A
Appendix A Conversion Formulas and Gas Tables
Conversion of Flow Rate to Other T and P Conditions
The flow rate of your transducer is referenced to certain ÒstandardÓ
conditions of temperature and pressure. Unless otherwise specified in
your order, these standard conditions are 21°C (70°F) and 760 mm of
mercury (1 atmosphere). If you wish to convert to other ÒstandardÓ
conditions or to find the ÒactualÓ conditions in the pipe where your instrument is installed, use the following relationship:
P
Q2 = Q
P
T
1
2
2
T
1
1
(1)
( )1 = The standard conditions under which your instrument
was calibrated,
= The new standard conditions or the actual temperature
( )
2
and pressure conditions in the pipe,
= The gas mass flow rate referenced to the calibrated standard
Q
1
conditions (sccm or slm),
= The gas mass flow rate referenced to the new standard or
Q
2
actual conditions (sccm or slmÑÒSÓ means Òstandard,Ó
accm or almÑÒAÓ means ÒactualÓ),
P = Absolute pressure (kg/cm
or psia), and
2
T = Absolute temperature (°K or °R) (°K = °C + 273, °R = °F + 460).
Example 1: Changing ÒStandardÓ Conditions
If your transducer has a flow rate reading of 10.00 slm and was calibrated
at standard conditions of 70°F (21°C) and 1 atmosphere (14.7 psia), and if
you wish to convert this reading to standard conditions of 32°F (0°C) and
1 atmosphere, then you would use Equation (1) as follows:
14.7 460 + 32
= (10.0) = 9.28 slm
Q
2
14.7 460 + 70
The flow rate referenced to 0°C will be approximately 7% lower than
when referenced to standard conditions of 21°C.
Example 2: Finding the ÒActualÓ Flow Rate
If the flow rate and calibrated standard conditions are as given in
Example 1 and you wish to find the actual flow rate at 100°F and 30
psig, then you would use Equation (1) as follows:
14.7 460 + 100
= (10.00) = 3.47 slm
Q
2
14.7 + 30 460 + 70
IM-82-C A-1
Page 35

Appendix A Series 820 Instruction Manual
Calculating For a Single Gas
The following tables provide K-factors and thermodynamic properties of gases commonly used with mass flow meters and controllers.
The purpose of these tables is two-fold:
1. Calibrating an ÒactualÓ gas with a reference gas. This is particularly useful if the actual gas is not a common gas or if it is toxic,
flammable, corrosive, etc.
2. Interpreting the reading of a flow meter or flow controller which
has been calibrated with a gas other than the actual gas.
In applying the tables, the following fundamental relationship is used:
Q1/Q2 = K1/K
2
(1)
Where:
Q = The volumetric flow rate of the gas referenced to standard
conditions of 0°C and 760 mm Hg (sccm or slm),
K = The K-factor defined in equation (6),
( ) 1 = Refers to the ÒactualÓ gas, and
( ) 2 = Refers to the ÒreferenceÓ gas.
The K-factor is derived from the first law of thermodynamics applied to the sensor tube, as described in Chapter 1:
¥
mC DT
H =
p
N
(2)
A-2 IM-82-C
Page 36

Series 820 Instruction Manual Appendix A
Where:
H = The constant amount of heat applied to the sensor tube,
¥
m = The mass flow rate of the gas (gm/min)
Cr = The coefficient of specific heat of the gas (Cal/gm);
Cr is given in the Table (at 0°C),
DT = The temperature difference between the downstream and
upstream coils, and
N = A correction factor for the molecular structure of the gas
given by the following table:
Number of Atoms in the Gas Molecule N
Monatomic 1.040
Diatomic 1.000
Triatomic 0.941
Polyatomic 0.880
The mass flow rate, m, can also be written as:
¥
m = Q
¥
(3)
r
Where:
r = The gas mass density at standard conditions (g/l); r is given
in the tables (at 0°C, 760 mm Hg).
Furthermore, the temperature difference, DT, is proportional to the
output voltage, E, of the mass flow meter, or
DT = aE (4)
where:
a = A constant.
If we combine equations (3) and (4), insert them into equation (2),
and solve for Q, we get
Q = (bN/rC
) (5)
p
where:
b = H/aE = a constant if the output voltage is constant.
IM-82-C A-3
Page 37

Appendix A Series 820 Instruction Manual
For our purposes, we want the ratio of the flow rate, Q1, for an actual gas to the flow rate of a reference gas, Q2, which will produce
the same output voltage in a particular mass flow meter or controller.
We get this by combining equations (1) and (5):
Q1/Q2 = K1/K2 = (N1/ r1Cp1)/(N2/r2CP2) (6)
Please note that the constant b cancels out. Equation (6) is the fundamental relationship used in the accompanying tables. For convenience,
the tables give ÒrelativeÓ K-factors, which are the ratios K
1/K2
, instead
of the K-factors themselves. In the tables, the relative K-factor is
K
/KN2 where the reference gas is the commonly used gas, nitrogen
actual
(N2). The remaining columns give Cp and r, enabling you to calculate
K1/K2 directly using Equation (6). In some instances, K1/K2 from the
tables may be different from that which you calculate directly. The value
from the tables is preferred because in many cases it was obtained by
experiment. Sierra calibrates every transducer with primary standards
using the actual gas or a molecular equivalent reference gas. The calibration certificate accompanying the transducer cites the reference gas
used.
Example 1:
A transducer is calibrated for nitrogen (N
), and the flow rate is
2
1000 sccm for a 5.000 VDC output signal. The flow rate for carbon
dioxide at a 5.000 VDC output is:
Q
CO2/QN2
Q
CO2
= K
CO2/K N2
= (0.74/1.000)1000 = 740 sccm
, or
Example 2:
A transducer is calibrated for hydrogen (H
), and the flow rate is
2
100 sccm for a 5.000 VDC output signal. The flow rate for nitrous
oxide (N2O) is found as follows:
Q
N2O/QH2
Q
N2O
= K
N2O/K H2
= (0.71/1.01) 100 = 70.3 sccm
Note that the K-factors relative to nitrogen must be used in each case.
, or
Example 3:
We want a transducer to be calibrated for use with dichlorosilane
(SiH2Cl2) at a 100 sccm full scale flow. We wish to use the preferred reference gas Freon-14 (CF4). What flow of CF4 must we
generate to do the calibration?
Q
SiH2CL2 /QCF4
100/Q
CF4
= 100/0.869 = 115 sccm
Q
CF4
= K
= 0.869
SiH2CL2 /K CF4
A-4 IM-82-C
Page 38

Series 820 Instruction Manual Appendix A
Calculating Dual Gas Mixtures
Equation (6) is used for gas mixtures, but we must calculate N/rC
for the mixture. The equivalent values of r, Cp, and N for a dual
gas mixture are given as follows:
The equivalent gas density is:
¥
r
¥
= ( / ) + ( / )
m
1T
m
r
¥
¥
m
m
2
1
Tr2
Where:
¥
m = m
( )
¥
¥
m
T
= Refers to gas #1, and
1
+ = Total mass flow rate (gm/min),
1
2
( )2 = Refers to gas #2
The equivalent specific heat is:
= F1Cp1 + F2C
C
p
p2
Where:
p
¥
F = ( )/( ) and
F = ( )/( )
m
1
¥
m
2
2
¥
r
m
1r1
T
¥
m
r
T
r
2
The equivalent value of N is:
¥
N = ( / ) N + ( / ) Nm
¥
m
1T1
¥
m
m
2
¥
T2
The equivalency relationships for r, Cp, and N for mixtures of
more than two gases have a form similar to the dual-gas relation-
ship given above.
IMPORTANT NOTE ABOUT K-FACTORS:
Please note that if you have a transducer calibrated for a gas such as
methane and wish to use the K-factors to measure a gas such as air,
that the inaccuracy of the measurement can range from ±5 to 10%.
The use of K-factors is, at best, only a rough
approximation and
should not be used in applications that require a better than ±5 to
10% accuracy.
It should also be noted that certain gases, in similar Òfamilies,Ó will
work exceptionally well with K-factors; however, those instances
are only true when similar thermal properties of the gas are present.
IM-82-C A-5
Page 39

Appendix A Series 820 Instruction Manual
Gas Tables and K-factors
Actual Gas
Symbol
Acetylene C2H
Chemical
2
K-factor
Relative N2Cp(Cal/g)
.58 .4036 1.162
Density
(g/l) @ 0°C
Air 1.00 .240 1.293
Allene (Propadiene) C
3H4
Ammonia NH
3
.43 .352 1.787
.73 .492 .760 NEO
Argon Ar 1.45 .1244 1.782
Arsine AsH
Boron Trichloride BCl
Boron Trifluoride BF
Bromine Br
Boron Tribromide Br
Bromine Pentafluoride BrF
Bromine Trifluoride BrF
Bromotrifloromethane
CBrF
3
3
3
2
3
5
3
3
.67 .1167 3.478
.41 .1279 5.227 KR
.51 .1778 3.025
.81 .0539 7.130
.38 .0647 11.18
.26 .1369 7.803
.38 .1161 6.108
.37 .1113 6.644
(Freon-13 B1)
1,3-Butadiene C4H
Butane C
4H10
1-Butane C4H
2-Butane C
2-Butane
4H8
C4H8 TRANS .291 .374 2.503
Carbon Dioxide CO
Carbon Disulfide CS
6
8
CIS .324 .336 2.503 NEO
2
2
.32 .3514 2.413
.26 .4007 2.593 NEO
.30 .3648 2.503 NEO
.74 .2016 1.964
.60 .1428 3.397
Carbon Monoxide CO 1.00 .2488 1.250
Carbon Tetrachloride CCl
Carbon Tetrafluoride
CF
4
4
.31 .1655 6.860
.42 .1654 3.926
(Freon-14)
Carbonyl Fluoride COF
2
.54 .1710 2.945
Carbonyl Sulfide COS .66 .1651 2.680
Chlorine CL
Chlorine Trifluoride CIF
Chlorodifluoromethane
CHClF
2
3
2
.86 .114 3.163
.40 .1650 4.125
.46 .1544 3.858
(Freon-22)
Chloroform CHCI
Chloropentafluoroethane
C2CIF
3
5
.39 .1309 5.326
.24 .164 6.892
(Freon-115)
Chlorotrifluromethane
CCIF
3
.38 .153 4.660
(Freon-13)
Cyanogen C2N
2
.61 .2613 2.322
Cyanogen Chloride CICN .61 .1739 2.742
Cychlopropane C3H
Deuterium D
Diborane B
2
2H6
Dibromodifluoromethane CBr2F
5
2
.46 .3177 1.877
1.00 .1722 1.799
.44 .508 1.235
.19 .15 9.362
Dibromethane .47 .075 7.76
Dichlorodifluoromethane
CCI
2F2
.35 .1432 5.395
(Freon-12)
Dichlorofluoromethane
CHCl2F .42 .140 4.952
(Freon-21)
Elastomer
O-ring*
* If no O-ring material is specified then O-ring to be used is Viton
A-6 IM-82-C
Page 40

Series 820 Instruction Manual Appendix A
Actual Gas
Symbol
Dichloromethylsilane (CH
Dichlorosilane SiH
Chemical
Dichlorotetrafluoroethane
C
SiCl
3) 2
2Cl2
2Cl2F4
2
K-factor
Relative N2Cp(Cal/g)
.25 .1882 5.758
.40 .150 4.506
.22 .1604 7.626
Density
(g/l) @ 0°C
Elastomer
O-ring*
(Freon-114)
1,1-Difluoroethylene
C
2H2F2
.43 .224 2.857
(Freon-1132A)
Dimethylamine (CH3) 2NH .37 .366 2.011
Dimethyl Ether (CH
2,2-Dimethylpropane C3H
Ethane C
Ethanol C
EthylAcetylene C4H
Ethyl Chloride C
Ethylene C
O .39 .3414 2.055
3) 2
12
2H6
O .39 .3395 2.055
2H6
6
CI .39 .244 2.879
2H5
2H4
.22 .3914 3.219
.50 .4097 1.342
.32 .3513 2.413
.60 .1365 1.251
Ethylene Oxide C2H4O .52 .268 1.965
Fluorine F
Fluoroform (Freon-23) CHF
2
3
.980 .1873 1.695
.50 .176 3.127
Freon-11 CCI3F .33 .1357 6.129
Freon-12 CCI
2F2
Freon-13 CCIF
Freon-13 B1 CFrF
Freon-14 CF
Freon-21 CHCI
4
2
Freon-22 CHCIF
Freon-113
Freon-114 C
CCI2FCCIF
2Cl2F4
Freon-115 C2ClF
Freon-C318 C
Germane GeH
4F6
4
Germanium Tetrachloride GeCL
3
3
F .42 .140 4.952
2
2
5
4
.35 .1432 5.395
.38 .153 4.660
.37 .1113 6.644
.42 .1654 3.926
.46 .1544 3.858
.20 .161 8.360
.22 .160 7.626
.24 .164 6.892
.17 .185 8.397
.57 .1404 3.418
.27 .1071 9.565
Helium He 1.454 1.241 .1786
Hexafluoroethane
C
2F6
.24 .1834 6.157
(Freon-116)
Hexane C6H
Hydrogen H
14
2
.18 .3968 3.845
1.01 3.419 .0899
Hydrogen Bromide HBr 1.000 .0861 3.610
Hydrogen Chloride HCl 1.000 .1912 1.627 KR
Hydrogen Cyanide HC N 1.070 .3171 1.206
Hydrogen Fluoride HF 1.000 .3479 .893 KR
Hydrogen Iodide HI 1.000 .0545 5.707
Hydrogen Selenide H
Se .79 .1025 3.613
2
Hydrogen Sulfide H2S .80 .2397 1.520
Iodine Pentafluoride IF
Isobutane CH(CH
Isobutylene C4H
5
3)3
8
.25 .1108 9.90
.27 .3872 3.593
.29 .3701 2.503
Krypton Kr 1.453 .0593 3.739
Methane CH
4
.72 .5328 .715
Methanol CH3OH .58 .3274 1.429
Methyl Acetylene C
Methyl Bromide CH
3H4
Br .58 .1106 4.236
2
.43 .3547 1.787
Methyl Chloride CH3Cl .1926 2.253
Methyl Fluoride CH
F .68 .3221 1.518
3
* If no O-ring material is specified then O-ring to be used is Viton
IM-82-C A-7
Page 41

Appendix A Series 820 Instruction Manual
Actual Gas
Chemical
Symbol
K-factor
Relative N2Cp(Cal/g)
Density
(g/l) @ 0°C
Elastomer
O-ring*
Methyl Mercaptan CH3SH .52 .2459 2.146
Methyl Trichlorosilane (CH
Molybdenum Hexafluoride MoF
Monoethylamine C
Monomethylamine CH3NH
) SiCl
3
6
2H5NH2
3
.25 .164 6.669
.21 .1373 9.366
.35 .387 2.011
2
.51 .4343 1.386
Neon NE 1.46 .245 .900
Nitric Oxide NO .990 .2328 1.339
Nitrogen N
Nitrogen Dioxide NO
Nitrogen Trifluoride NF
2
2
3
1.000 .2485 1.25
.74 .1933 2.052
.48 .1797 3.168
Nitrosyl Chloride NOCl .61 .1632 2.920
Nitrous Oxide N
Octafluorocyclobutane
O .71 .2088 1.964
2
C
4F6
.17 .185 8.397
(Freon-C318)
Oxygen Difluoride OF
Oxygen O
Ozone O
Pentaborane B
Pentane C
5H9
5HI2
2
2
3
.63 .1917 2.406
1.000 .2193 1.427
.446 .3 2.144
.26 .38 2.816
.21 .398 3.219
Perchloryl Fluoride CIO3F .39 .1514 4.571
Perfluoropropane C
3F8
Phosgene COCl
2
.174 .197 8.388
.44 .1394 4.418
PhosphinePH3 .76 .237 1.517
Phosphorous Oxychloride POCl
Phosphorous Pentafluoride PH
Phosphorous Trichloride PCl
Propane C
Propylene C
3H8
3H6
Silane SiH
Silicon Tetrachloride SiCl
Silicon Tetrafluoride SiF
Sulfur Dioxide So
Sulfur Hexafluoride SF
Sulfuryl Fluoride SO
2F2
3
5
5
4
4
4
2
6
.36 .1324 6.843
.30 .1610 5.620
.30 .1250 6.127
.36 .3885 1.967
.41 .3541 1.877
.60 .3189 1.433
.28 .1270 7.580
.35 .1691 4.643
.69 .1488 2.858
.26 .1592 6.516
.39 .1543 4.562
Teos .090 KR
Tetrafluorahydrazine N
Trichlorofluormethane
CCl
2F4
F .33 .1357 6.129
3
.32 .182 4.64
(Freon-11)
Trichlorisilane SiHCl
1,1,2-Trichloro-1,2,2
CCl2FCClF
3
2
.33 .1380 6.043
.20 .161 8.360
Trifluorethane (Freon-113)
Trisobutyl Aluminum (C
Titanium Tetrachloride TiCl
Trichloro Ethylene C2HCl
Trimethylamine (CH
Tungsten Hexasfuoride WF
Uranium Hexafluoride UF
Vinyl Bromide CH
Vinyl Chloride CH
)Al .061 .508 8.848
4H9
4
3
N .28 .3710 2.639
3)3
6
6
CHBr .46 .1241 4.772
2
CHCl .48 .12054 2.788
2
.27 .120 8.465
.32 .163 5.95
.25 .0810 13.28 KR
.20 .0888 15.70
Xenon Xe 1.44 .0378 5.858
* If no O-ring material is specified then O-ring to be used is Viton
A-8 IM-82-C
Page 42

Series 820 Instruction Manual Appendix B Specifications
Appendix B Product Specifications
Operating Specifications
Gases Most gases; check compatibility with wetted materials; specify when ordering
Mass Flow Rates Models 822/824: 0 to 10 sccm to 0 to 50 slpm;
Gas Pressure Models 822/824:150 psig ( 10 barg) maximum, 20 psig (1.4 barg) optimum
Gas & Ambient Temperature
Leak Integrity Models 822/824, 826/827: 1 X 10-4 atm cc/sec of helium maximum
Pressure Drop Models 822/824:
Models 826/827: 0 to 75 slpm to 0 to 175 slpm;
Models 822-S/824-S: 0 to 10 sccm to 0 to 500 slpm;
flow ranges specified are for an equivalent flow of nitrogen at 760 mm Hg
and 21°C (70°F); other ranges in other units are available (e.g. scfh or
nm3/h)
Models 826/827: 150 psig ( 10 barg) maximum, 20 psig (1.4 barg) optimum
Models 822-S/824-S: 1000 psig (68.9 barg) maximum for low flow bodies only;
500 psig (34 barg) maximum; 20 psig (1.4 barg) optimum
32° to 122°F (0 to 50°C); higher available on special order
Models 822-S/824-S: 5 X 10-9 atm cc/sec of helium maximum
Flow Rate cm of Water mbar in H2O
100 sccm 0.06 0.06 0.024
1 slpm 0.6 0.59 0.236
10 slpm 6.0 5.88 2.36
20 slpm 24.0 23.5 9.45
30 slpm 54.0 53 21.3
40 slpm 96.0 94.7 37.8
50 slpm 130.0 127.4 51.2
Models 826/827: Two inches of mercury maximum at 175 slpm
822/824-S (low).........0.08 psi (0.006 bar or 6 cm of water) differential max;
822/824-S (med).......0.08 psi (0.006 bar or 6 cm of water) differential max;
822/824-S (high)........0.08 psi (6 mbar or 6 cm of water) differential max;
Power Requirements 12 to 18 VDC nominal, 100 mA maximum; 24 VDC optional
Output Signal Linear 0-5 VDC, 1000 Ohms minimum load resistance
Linear 4-20 mA, 30-500 Ohms maximum loop resistance
Display 3.5 digit LCD (0.6 in H); remote mounting option available
15 slpm: 1.5 psi (0.10 bar or 105 cm of water) differential max
100 slpm: 1.5 psi (0.10 bar or 105 cm of water) differential max
300, 400 and 500 slpm: 2 psi (0.14 bar or 140 cm of water)
differential maximum
IM-82-C B-1
Page 43

Appendix B Specifications Series 820 Instruction Manual
Performance Specifications
Accuracy ±1.5% of full scale including linearity over 15 to 25°C and 5 to 60 psia (0.3 to 4 bara)
Repeatability ±0.5% of full scale
Temperature Coefficient 0.08% of full scale per °F (0.15% of full scale per °C), or better
Pressure Coefficient 0.01% of full scale per psi (0.15% of full scale per bar), or better
Response Time 800 ms time constant; six seconds (typical) to within ±2% of final value over 25 to
100% of full scale
Physical Specifications
Wetted Materials 822/824: 10% glass-filled Nylon® 6/6, 316 stainless steel, nickel plating, Viton
o-rings standard, Neoprene® and 4079 Kal-Rez® (or equivalent) o-rings optional
826/827: Anodized aluminum, 316 stainless steel, nickel plating, Viton® o-rings
standard, Neoprene® and 4079 Kal-Rez® (or equivalent) o-rings optional
822-S/824-S: 316 stainless steel, nickel plating, Viton® o-rings standard, Neoprene
and 4079 Kal-Rez® (or equivalent) o-rings optional
®
®
B-2 IM-82-C
Page 44

Series 820 Instruction Manual Appendix B Specificati
ons
IM-82-C B-3
Page 45

Appendix B Specifications Series 820 Instruction Manual
B-4 IM-82-C
 Loading...
Loading...