Page 1

SIMATIC NET
SPC3 Siemens PROFIBUS Controller
Hardware Description
Date 2003/04/09
Page 2

Page 3

SPC3
Hardware Description
SIMATIC - NET
(Siemens PROFIBUS Controller
according to IEC 61158)
Version: 1.3
Date: 2003/04
Page 4

PROFIBUS Interface Center
SPC3
Liability Exclusion
We have tested the contents of this document regarding agreement with the
hardware and software described. Nevertheless, there may be deviations, and
we don’t guarantee complete agreement. The data in the document is tested
periodically, however. Required corrections are included in subsequent
versions. We gratefully accept suggestions for improvement
Copyright
Copyright © Siemens AG 2003. All Rights Reserved.
Unless permission has been expressly granted, passing on this document or
copying it, or using and sharing its content are not allowed. Offenders will be
held liable. All rights reserved, in the event a patent is granted or a utility model
or design is registered.
Subject to technical changes.
Page 2 V1.3 SPC3 Hardware Description
2003/04 Copyright (C) Siemens AG 2003. All rights reserved.
Page 5
Included the specification of the different manufacturers in
Included the specification of the different manufacturers in
SPC3 PROFIBUS Interface Center
Versions
Release Date Changes
V 1.1 12/23/99 Chapter 8.2 Current consumption without bus accesses
Chapter 10.1 Contact persons
V 1.2 09/25/02
Chap. 8.1, 8.3, 8.5 and 10.3 Order numbers
chap 10.1 contact persons
V 1.3 2003/04
Chap. 8.1, 8.3, 8.5 and 10.3
SPC3 Hardware Description V1.3 Page 3
Copyright (C) Siemens AG 2003 All rights reserved. 2003/04
Page 6

PROFIBUS Interface Center
SPC3
Directory
1 INTRODUCTION 7
2 FUNCTION OVERVIEW 8
3 PIN DESCRIPTION 9
4 MEMORY ALLOCATION 11
4.1 Memory Area Distribution in the SPC3 11
4.2 Processor Parameters (Latches/Register) 13
4.3 Organizational Parameters (RAM) 15
5 ASIC INTERFACE 17
5.1 Mode Register 17
5.1.1 Mode Register 0 17
5.1.2 Mode Register 1 (Mode-REG1, writable): 19
5.2 Status Register 20
5.3 Interrupt Controller 22
5.4 Watchdog Timer 25
5.4.1 Automatic Baud Rate Identification 25
5.4.2 Baud Rate Monitoring 25
5.4.3 Response Time Monitoring 25
6 PROFIBUS-DP INTERFACE 26
6.1 DP_Buffer Structure 26
6.2 Description of the DP Services 29
6.2.1 Set_Slave_Address (SAP55) 29
6.2.2 Set_Param (SAP61) 30
6.2.3 Check_Config (SAP62) 31
6.2.4 Slave_Diagnosis (SAP60) 32
6.2.5 Write_Read_Data / Data_Exchange (Default_SAP) 33
6.2.6 Global_Control (SAP58) 35
6.2.7 Read_Inputs (SAP56) 36
6.2.8 Read_Outputs (SAP57) 36
6.2.9 Get_Config (SAP59) 36
7 HARDWARE INTERFACE 37
7.1 Universal Processor Bus Interface 37
7.1.1 General Description 37
7.1.2 Bus Interface Unit (BIU) 37
7.1.3 Switching Diagram Principles 39
7.1.4 Application with the 80 C 32 41
7.1.5 Application with th 80 C 165 42
Page 4 V1.3 SPC3 Hardware Description
2003/04 Copyright (C) Siemens AG 2003. All rights reserved.
Page 7

7.1.6 Interface Signals 43
SPC3 PROFIBUS Interface Center
7.2 UART 43
7.3 ASIC Test 43
8 TECHNICAL DATA 44
8.1 Maximum Limit Values 44
8.2 Permitted Operating Values 44
8.3 DC-Specifikation of the I/O- Drivers 44
8.4 AC-Specification for the Output Drivers 45
8.5 Timing Characteristics 46
8.5.1 SYS Bus Interface 46
8.5.2 Timing in the Synchronous C32-Mode: 47
8.5.3 Timing in the Asynchronous Intel Mode (X86 Mode) : 49
8.5.4 Timing in the Synchronous Motorola Mode (E_Clock-Mode, for example, 68HC11) : 50
8.5.5 Timing in the Asynchronous Motorola-Mode (for example, 68HC16) : 52
8.5.6 Serial Bus Interface 54
8.5.7 Housing 55
8.5.8 Processing Instructions 56
9 PROFIBUS INTERFACE 57
9.1 Pin Assignment 57
9.2 Example for the RS 485 Interface 58
10 APPENDIX 59
10.1 Addresses 59
10.2 General Definition of Terms 60
10.3 Ordering of ASICs 60
10.3.1 SPC3 (AMI) 60
10.3.2 SPC3 (ST) 60
11 APPENDIX A: DIAGNOSTICS PROCESSING IN PROFIBUS DP 61
11.1 Introduction 61
11.2 Diagnostics Bits and Expanded Diagnostics 61
11.2.1 STAT_DIAG 61
11.2.2 EXT_DIAG 61
11.2.3 EXT_DIAG_OVERFLOW 63
11.3 Diagnostics Processing from the System View 63
12 APPENDIX B: USEFUL INFORMATION 64
12.1 Data format in the Siemens PLC SIMATIC 64
SPC3 Hardware Description V1.3 Page 5
Copyright (C) Siemens AG 2003 All rights reserved. 2003/04
Page 8

PROFIBUS Interface Center
SPC3
Page 6 V1.3 SPC3 Hardware Description
2003/04 Copyright (C) Siemens AG 2003. All rights reserved.
Page 9

SPC3 PROFIBUS Interface Center
1 Introduction
For simple and fast digital exchange between programmable logic controllers, Siemens offers its users
several ASICs. These ASICs are based on and are completely handled on the principles of the EN 50170
Vol. 2, of data traffic between individual programmable logic controller stations.
The following ASICs are available to support intelligent slave solutions, that is, implementations with a
microprocessor.
The ASPC2 already has integrated many parts of Layer 2, but the ASPC2 also requires a processor’s
support. This ASIC supports baud rates up to 12 Mbaud. In its complexity, this ASIC is conceived primarily
for master applications.
Due to the integration of the complete PROFIBUS-DP protocol, the SPC3 decisively relieves the processor
of an intelligent PROFIBUS slave. The SPC3 can be operated on the bus with a baud rate of up to 12
MBaud.
However, there are also simple devices in the automation engineering area, such as switches and
thermoelements, that do not require a microprocessor to record their states.
There are two additional ASICs available with the designations SPM2 (Siemens Profibus Multiplexer,
Version 2 ) and LSPM2 (Lean Siemens PROFIBUS Multiplexer) for an economical adaptation of these
devices. These blocks work as a DP slave in the bus system (according to DIN E 19245 T3) and work with
baud rates up to 12 Mbaud. A master addresses these blocks by means of Layer 2 of the 7 layer model.
After these blocks have received an error-free telegram, they independently generate the required response
telegrams.
The LSPM2 has the same functions as the SPM2, but the LSPM2 has a decreased number of I/O ports and
diagnostics ports.
SPC3 Hardware Description V1.3 Page 7
Copyright (C) Siemens AG 2003 All rights reserved. 2003/04
Page 10

PROFIBUS Interface Center
SPC3
2 Function Overview
The SPC3 makes it possible to have a price-optimized configuration of intelligent PROFIBUS-DP slave
applications.
The processor interface supports the following processors:
Intel: 80C31, 80X86
Siemens: 80C166/165/167
Motorola: HC11-,HC16-,HC916 types
In SPC3, the transfer technology is integrated (Layer 1), except for analog functions (RS485 drivers), the
FDL transfer protocol (Fieldbus Data Link) for slave nodes (Layer 2a), a support of the interface utilities
(Layer 2b), some Layer 2 FMA utilities, and the complete DP slave protocol (USIF: User Interface, which
makes it possible for the user to have access to Layer 2). The remaining functions of Layer 2 (software
utilities and management) must be handled via software.
The integrated 1.5k Dual-Port-RAM serves as an interface between the SPC3 and the
software/application. The entire memory is subdivided into 192 segments, with 8 bytes each. Addressing
from the user takes place directly and from the internal microsequencer (MS) by means of the so-alled base
pointer. The base-pointer can be positioned at any segment in the memory. Therefore, all buffers must
always be located at the beginning of a segment.
If the SPC3 carries out a DP communication the SPC3 automatically sets up all DP-SAPs. The various
telegram information is made available to the user in separate data buffers (for example, parameter setting
data and configuration data). Three change buffers are provided for data communication, both for the
output data and for the input data. A change buffer is always available for communication. Therefore, no
resource problems can occur. For optimal diagnostics support, SPC3 has two diagnostics change buffers
into which the user inputs the updated diagnostics data. One diagnostics buffer is always assigned to SPC3
in this process.
The bus interface is a parameterizable synchronous/asynchronous 8-bit interface for various Intel and
Motorola microcontrollers/processors. The user can directly access the internal 1.5k RAM or the parameter
latches via the 11-bit address bus.
After the processor has been switched on, procedural-specific parameters (station address, control bits, etc.)
must be transferred to the Parameter Register File and to the mode registers.
The MAC status can be scanned at any time in the status register.
Various events (various indications, error events, etc.) are entered in the interrupt controller. These
events can be individually enabled via a mask register. Acknowledgement takes place by means of the
acknowledge register. The SPC3 has a common interrupt output.
The integrated Watchdog Timer is operated in three different states: ‘Baud_Search’, ‘Baud_Control,’ and
‘DP_Control’.
The Micro Sequencer (MS) controls the entire process.
Procedure-specific parameters (buffer pointer, buffer lengths, station address, etc.) and the data buffer are
contained in the integrated 1.5kByte RAM that a controller operates as Dual-Port-RAM.
In UART, the parallel data flow is converted into the serial data flow, or vice-versa. The SPC3 is capable of
automatically identifying the baud rates (9.6 kBd - 12 MBd).
The Idle Timer directly controls the bus times on the serial bus cable.
Page 8 V1.3 SPC3 Hardware Description
2003/04 Copyright (C) Siemens AG 2003. All rights reserved.
Page 11
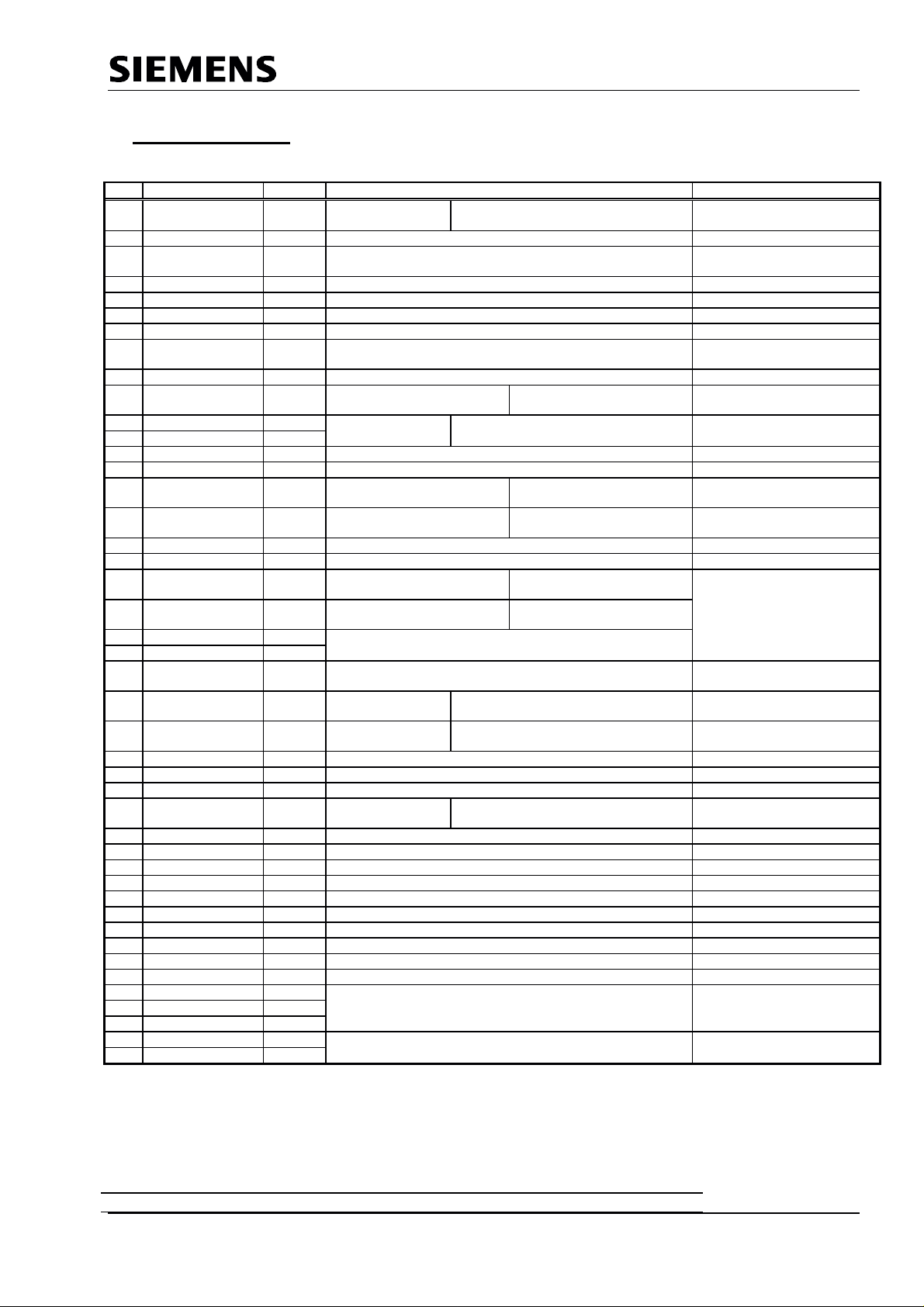
SPC3 PROFIBUS Interface Center
3 Pin Description
The SPC3 has a 44-pin PQFP housing with the following signals:
Pin Signal Name In/Out Description Source / Destination
1 XCS I© Chip-Select C32 Mode: place on VDD.
2 XWR/E_Clock I© Write signal /EI_Clock for Motorola CPU
3 DIVIDER I© Setting the scaler factor for CLK2OUT2/4.
4 XRD/R_W I© Read signal / Read_Write for Motorola CPU
5 CLK I(TS) Clock pulse input System
6 VSS
7 CLKOUT2/4 O Clock pulse divided by 2 or 4 System, CPU
8 XINT/MOT I© <log> 0 = Intel interface
9 X/INT O Interrupt CPU, Interrupt-Contr.
10 AB10 I(CPD) Address bus C32 mode: <log> 0
11 DB0 I©/O Data bus C32 Mode: Data/address bus multiplexed CPU, memory
12 DB1 I©/O C165 Mode: Data/address bus separated
13 XDATAEXCH O Data_Exchange state for PROFIBUS-DP LED
14 XREADY/XDTACK O Ready for external CPU System, CPU
15 DB2 I©/O Data bus C32 mode: data bus/address
16 DB3 I©/O C165 mode: data/address bus
17 VSS
18 VDD
19
DB4
20 DB5 I©/O C165 mode: data bus/address
21 DB6 I©/O
22 DB7 I©/O
23 MODE I <log> 0 = 80C166 Data bus/address bus separated; ready signal
24 ALE/AS I© Address latch enable C32 mode: ALE
25 AB9 I Address bus C32 mode: <log> 0
26 TXD O Serial send port RS 485 sender
27 RTS O Request to Send RS 485 sender
28 VSS
29 AB8 I© Address bus C32 Mode : <log> 0
30 RXD I© Serial receive port RS 485 receiver
31 AB7 I© Address bus System, CPU
32 AB6 I© Address bus System, CPU
33 XCTS I© Clear to send <log> 0 = send enable FSK modem
34 XTEST0 I© Pin must be placed fixed at VDD.
35 XTEST1 I© Pin must be placed fixed at VDD.
36 RESET I(CS) Connect reset input with CPU’s port pin.
37 AB4 I© Address bus System, CPU
38 VSS
39 VDD
40 AB3 I©
41 AB2 I© Address bus System, CPU
42 AB5 I©
43 AB1 I© Address bus System, CPU
44 AB0 I©
I©/O Data bus C32 mode: data bus/address
low potential means divided through 4
<log> 1 = Motorola interface
<log> 1 = 80C32 data bus/address bus multiplexed, fixed timing
C165 Mode: CS-Signal
C165 mode: address bus
bus multiplexed
separate
bus multiplexed
bus separate
C165 mode: <log> 0
C165 mode: address bus
C165 Mode: address bus
Figure 3.1: SPC3 Pin Assignment
Note: •••• All signals that begin with X.. are LOW active
• VDD = +5V, VSS = GND
Input levels: I ©: CMOS
I (CS): CMOS Schmitt trigger
CPU (80C165)
System
CPU, memory
CPU, memory
System
CPU (80C32)
CPU (C165), memory
SPC3 Hardware Description V1.3 Page 9
Copyright (C) Siemens AG 2003 All rights reserved. 2003/04
Page 12

PROFIBUS Interface Center
I (CPD): CMOS with pull down
I (TS): TTLt Schmitt trigger
SPC3
Page 10 V1.3 SPC3 Hardware Description
2003/04 Copyright (C) Siemens AG 2003. All rights reserved.
Page 13
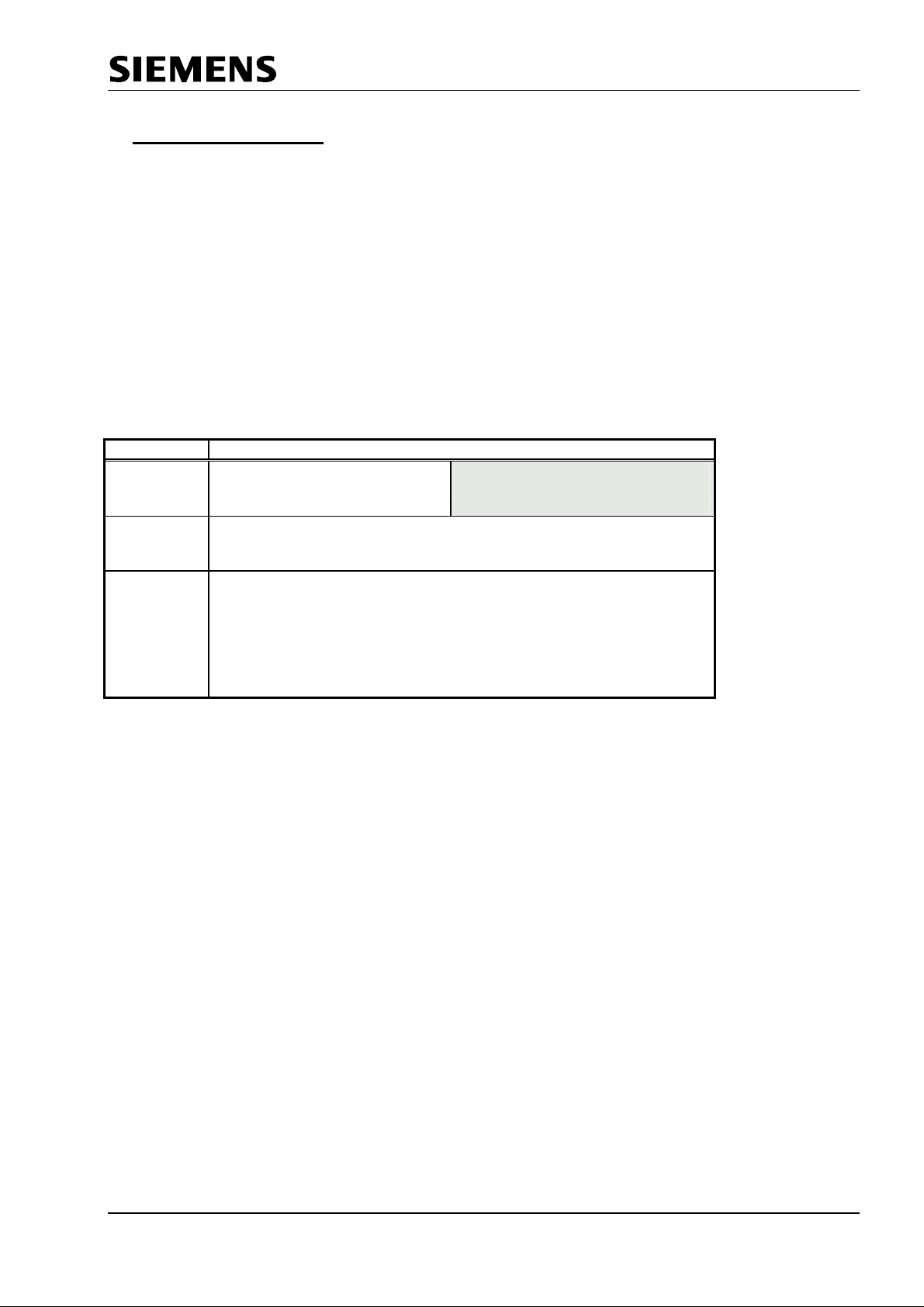
SPC3 PROFIBUS Interface Center
4 Memory Allocation
4.1 Memory Area Distribution in the SPC3
The figure displays the division of the SPC3 1.5k internal address area.
The internal latches/register are located in the first 21 addresses. The internal latches/register either come
from the controller or influence the controller. Certain cells can be only read or written. The internal work
cells to which the user has no access are located in RAM at the same addresses.
The organizational parameters are located in RAM beginning with address 16H. The entire buffer structure
(for the DP-SAPS) is written based on these parameters. In addition, general parameter setting data
(station address, Ident no., etc.) are transferred in these cells and the status displays are stored in these
cells (global control command, etc.).
Corresponding to the parameter setting of the organizational parameters, the user-generated buffers are
located beginning with address 40H. All buffers or lists must begin at segment addresses (48 bytes
segmentation).
Address Function
000H Processor parameters internal work cells
Latches/register
(22 bytes)
016H Organizational
parameters
(42 bytes)
040H DP- buffer: Data In (3) *
Data Out (3) *
Diagnostics (2)
Parameter setting data (1)
5FFH Configuration data (2)
Figure 4.1: SPC3 Memory Area Distribution
Auxiliary buffer (2)
SSA-buffer(1)
Caution:
The HW prohibits overranging the address area. That is, if a user writes or reads past the memory
end, 400H is subtracted from this address and the user therefore accesses a new address. This
prohibits overwriting a process parameter. In this case, the SPC3 generates the RAM access
violation interrupt. If the MS overranges the memory end due to a faulty buffer initialization, the
same procedure is executed.
* Data In is the input data from PROFIBUS slave to master
Data out is the output data from PROFIBUS master to slave
SPC3 Hardware Description V1.3 Page 11
Copyright (C) Siemens AG 2003 All rights reserved. 2003/04
Page 14
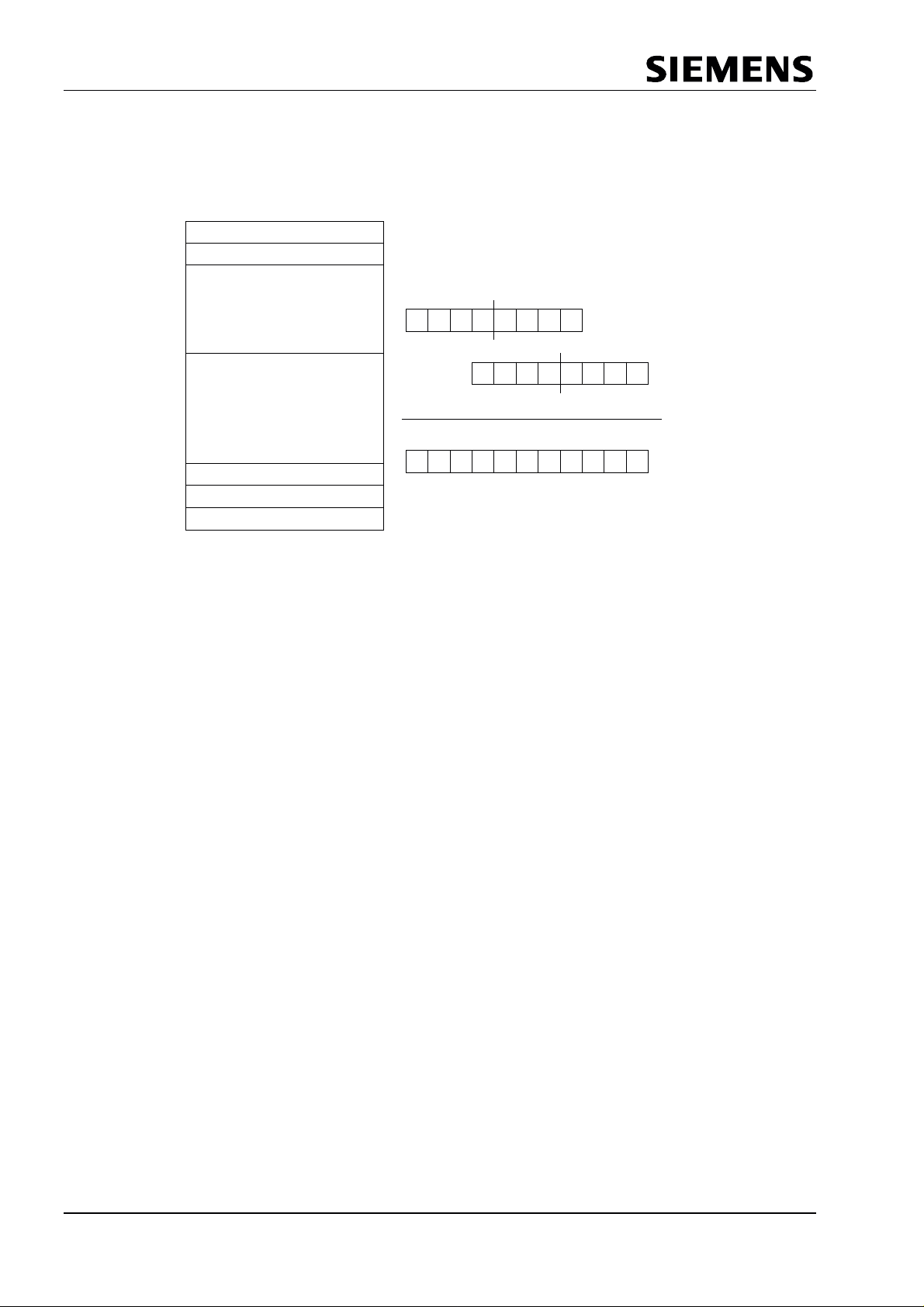
PROFIBUS Interface Center
SPC3
The complete internal RAM of the SPC 3 is divided logically into 192 segments. Each segment consists of 8
bytes. For more informations about the contents of the 3 memory areas see previous chapter.The physical
address is build by multiplikation with 8.
internal SPC 3 RAM (1.5 kByte)
Segment 0
Segment 1
Segment 2
8 Bit Segmentaddresses
(Pointer to the buffers
+
Segment 190
Segment 191
07
010
Page 12 V1.3 SPC3 Hardware Description
2003/04 Copyright (C) Siemens AG 2003. All rights reserved.
Page 15
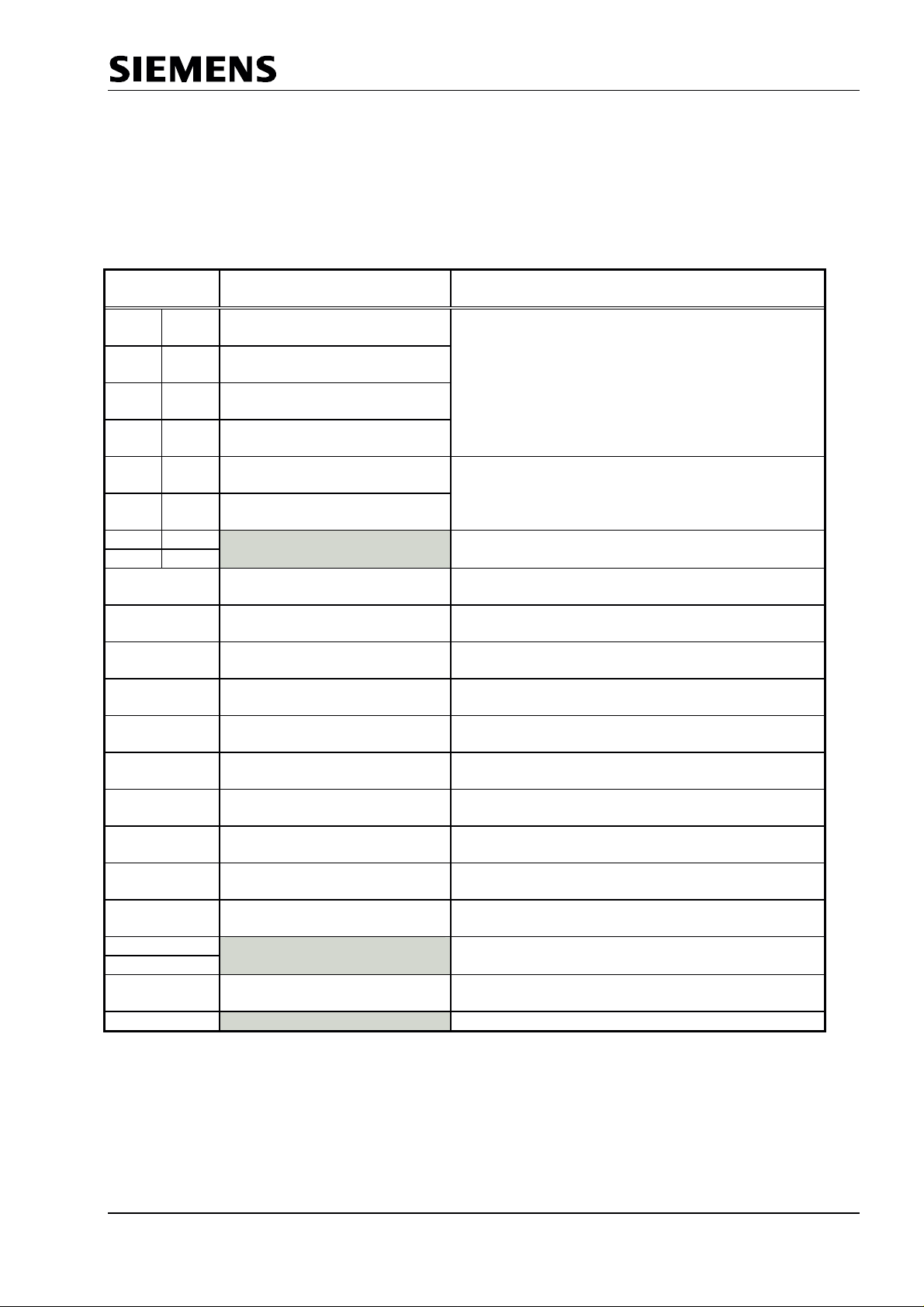
SPC3 PROFIBUS Interface Center
4.2 Processor Parameters (Latches/Register)
These cells can be either read only or written only. SPC3 carries out “address swapping” for an access to
the address area 00H - 07H (word register) in the Motorola mode. That is, the SPC3 exchanges
address bit 0 (generated from an even address, one uneven, and vice-versa). The following sections more
clearly explain the significance of the individual registers.
Address
Intel / Motorla
00H 01H Int-Req-Reg
01H 00H Int-Req-Reg
02H 03H Int—Reg
03H 02H Int—Reg
04H 05H Status-Reg
05H 04H Status-Reg
06H 07H Reserved
07H 06H
08H DIN_Buffer_SM
09H New_DIN_Buffer_Cmd
0AH DOUT_Buffer_SM
0BH Next_DOUT_Buffer_Cmd
0CH DIAG_Buffer_SM
0DH New_DIAG_Puffer_Cmd
0EH User_Prm_Data_OK
0FH UserPrmDataNOK
10H User_Cfg_Data_OK
11H User_Cfg_Data_NOK 1..0 The user negatively acknowledges the configuration
12H Reserved
13H
14H SSA_Bufferfreecmd The user has fetched the data from the SSA buffer
15H Reserved
Name Bit
No.
7..0
15..8
7..0
15..8
7..0
15..8
7..0
1..0
7..0
1..0
3..0
1..0
1..0
1..0
1..0
Significance (Read Access!)
Interrupt Controller Register
Status Register
Buffer assignment of the
DP_Din_Buffer_State_Machine
The user makes a new DP Din buffer available in
the N state.
Buffer assignment of the
DP_Dout_Puffer_State_Machine
The user fetches the last DP Dout-Buffer from the N
state.
Buffer assignment for the
DP_Diag_Puffer_State_Machine
The user makes a new DP Diag Buffer available to
the SPC3.
The user positively acknowledges the user
parameter setting data of a Set_Param-Telegram.
The user negatively acknowledges the user
parameter setting data of a Set_Param-Telegram.
The user positively acknowledges the configuration
data of a Check_Config-Telegram.
data of a Check_Config-Telegram.
and enables the buffer again.
Figure 4.2: Assignment of the Internal Parameter Latches for READ
SPC3 Hardware Description V1.3 Page 13
Copyright (C) Siemens AG 2003 All rights reserved. 2003/04
Page 16
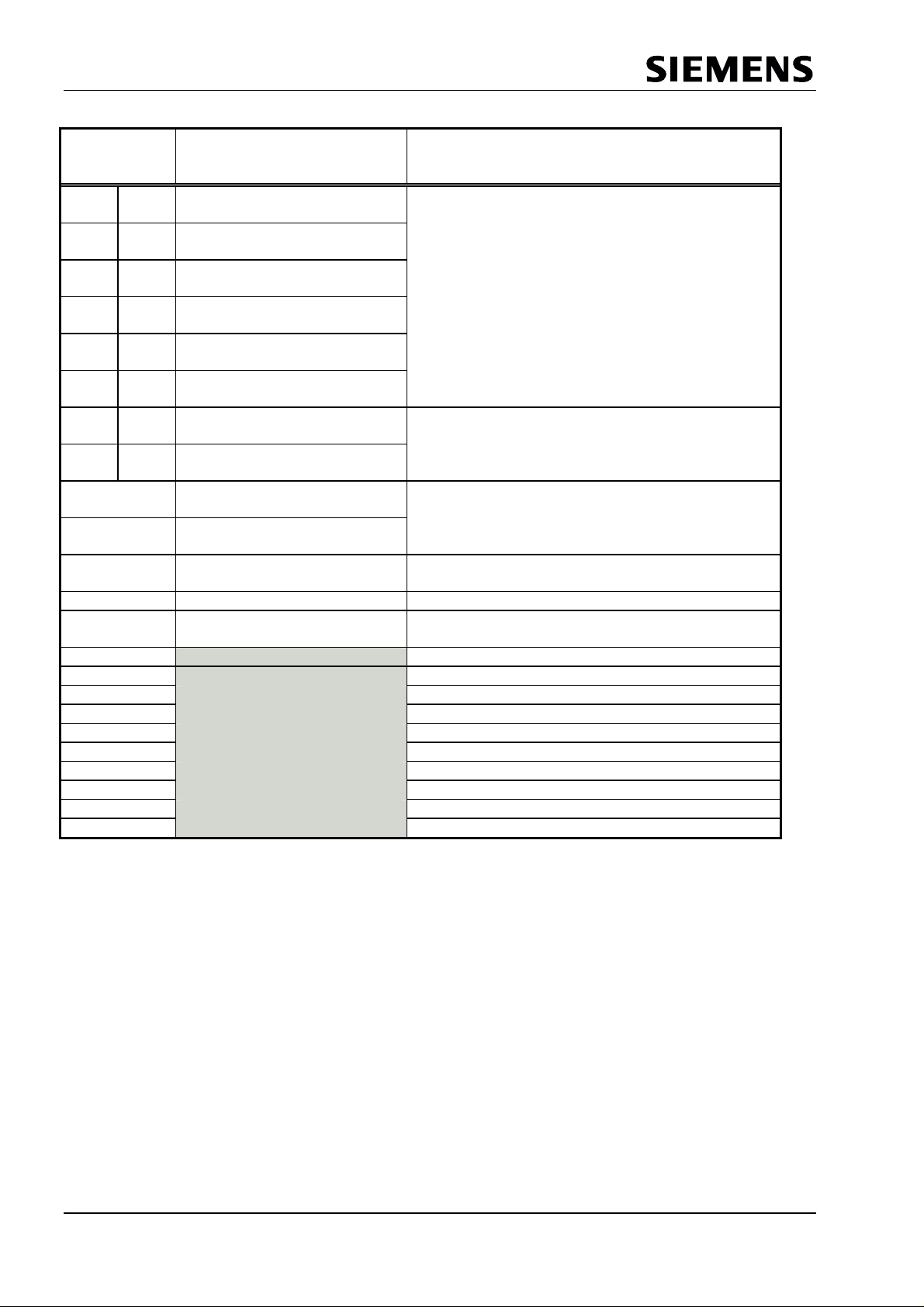
PROFIBUS Interface Center
Val
Address
Intel
/Motorola
00H 01H Int-Req-Reg
01H 00H Int-Req_Reg
02H 03H Int-Ack-Reg
03H 02H Int-Ack-Reg
04H 05H Int—Mask-Reg
05H 04H Int—Mask-Reg
06H 07H Mode-Reg0
07H 06H Mode-Reg0-S
08H Mode-Reg1-S
09H Mode-Reg1-R
0AH WD Baud Ctrl -
0BH MinTsdr_Val
OCH
0DH Reserved
0EH
0FH
10H
11H
12H
13H
14H
15H
Figure 4.3: Assignment of the Internal Parameter Latches for WRITE
Name Bit
No.
7..0
15..8
7..0
15..8
7..0
15..8
7..0
15..8
7..0
7..0
7..0
7..0
SPC3
Significance (Write Access !)
Interrupt- Controller - Register
Setting parameters for individual bits
Root value for baud rate monitoring
MinTsdr time
Page 14 V1.3 SPC3 Hardware Description
2003/04 Copyright (C) Siemens AG 2003. All rights reserved.
Page 17

SPC3 PROFIBUS Interface Center
4.3 Organizational Parameters (RAM)
The user stores the organizational parameters in RAM under the specified addresses. These parameters
can be written and read.
SPC3 Hardware Description V1.3 Page 15
Copyright (C) Siemens AG 2003 All rights reserved. 2003/04
Page 18
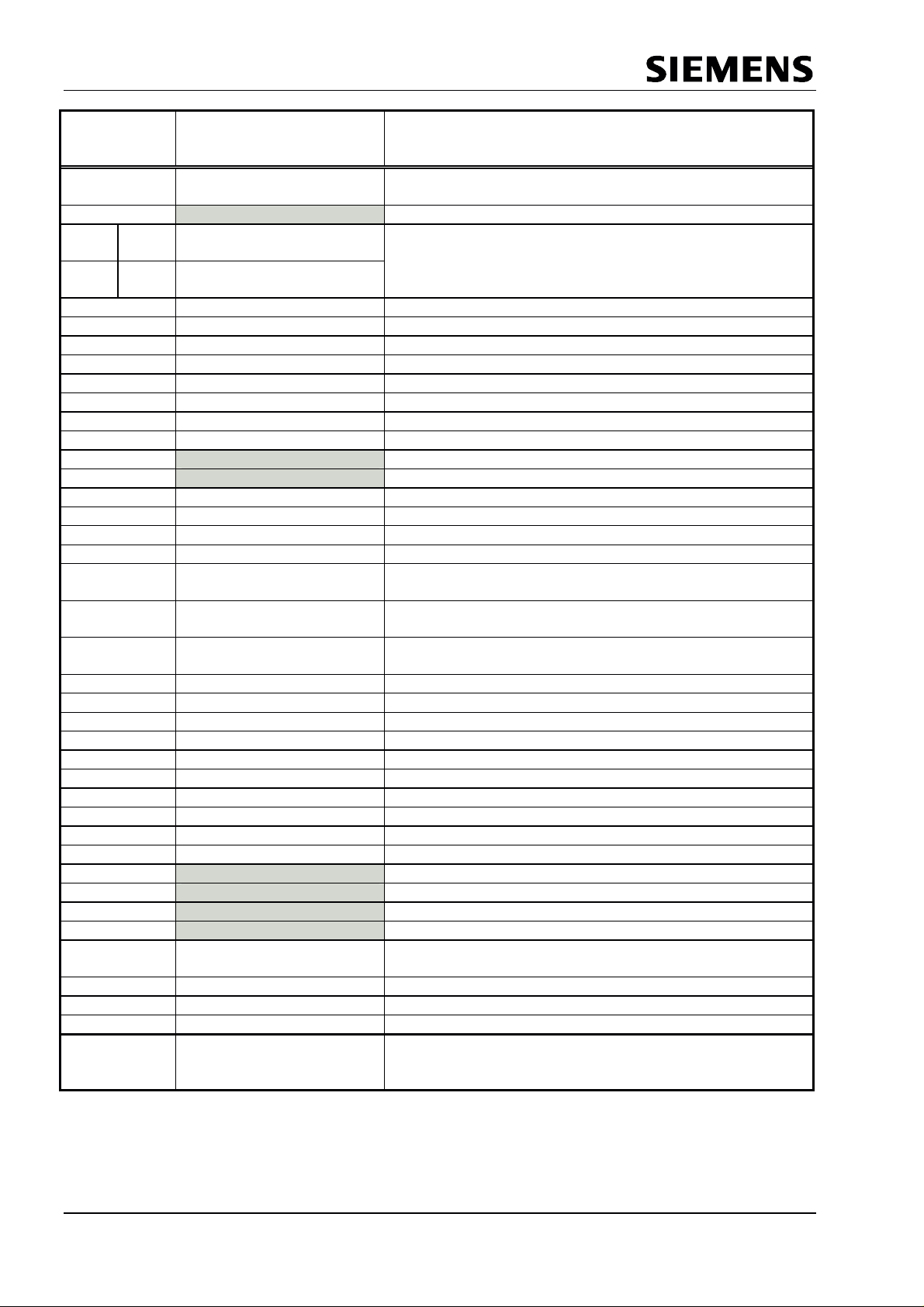
PROFIBUS Interface Center
bit wachdog timer, the user is
If parameters are set for the Spec_Prm_Buffer_Mode (see
mode register 0), this cell defines the length of the param
Address
Intel
/Motorola
16H R_TS_Adr
17H reserved Pointer to a RAM address which is presetted with 0FFH
18H 19H R_User_Wd_Value
19H 18H R_User_Wd_Value 15
1AH R_Len_Dout_Puf Length of the 3 Dout buffers
1BH R_Dout_buf_Ptr1 Segment base address of Dout buffer 1
1CH R_Dout_buf_Ptr2 Segment base address of Dout buffer 2
1DH R_Dout_buf_Ptr3 Segment base address of Dout buffer 3
1EH R_Len_Din_buf Length of the 3 Din buffers
1FH R_Din_buf_Ptr1 Segment base address of Din buffer 1
20H R_Din_buf_Ptr2 Segment base address of Din buffer 2
21H R_Din_buf_Ptr3 Segment base address of Din buffer 3
22H reserved Preset with 00H.
23H reserved Preset with 00H.
24H R Len Diag buf1 Length of Diag buffer 1
25H R Len Diag buf2 Length of Diag buffer 2
26H R_Diag_Puf_Ptr1 Segment base address of Diag buffer 1
27H R_Diag_Puf_Ptr2 Segment base address of Diag buffer 2
28H R Len Cntrl Pbuf1 Length of Aux buffer 1 and the control buffer belonging to it,
29H R Len Cntrl Puf2 Length of Aux-Buffer 2 and the control buffer belonging to
2AH R Aux Puf Sel Bit array, in which the assignments of the Aux-buffers ½ are
2BH R_Aux_buf_Ptr1 Segment base address of auxiliary buffer 1
2CH R_Aux_buf_Ptr2 Segment base address of auxiliary buffer 2
2DH R_Len_SSA_Data Length of the input data in the Set_Slave_Address-buffer
2EH R SSA buf Ptr Segment base address of the Set_Slave_Address-buffer
2FH R_Len_Prm_Data Length of the input data in the Set_Param-buffer
30H R_Prm_buf_Ptr Segment base address of the Set_Param-buffer
31H R_Len_Cfg_Data Length of the input data in the Check_Config-buffer
32H R Cfg Buf Ptr Segment base address of the Check_Config-buffer
33H R_Len_Read_Cfg_Data Length of the input data in the Get_Config-buffer
34H R_Read_Cfg_buf_Ptr Segment base address of the Get_Config-buffer
35H reserved Preset with 00H.
36H reserved Preset with 00H
37H reserved Preset with 00H.
38H reserved Preset with 00H.
39H R_Real_No_Add_Change This parameter specifies whether the DP slave address may
3AH R_Ident_Low The user sets the parameters for the Ident_Low value.
3BH R_Ident_High The user sets the parameters for the Ident_High value.
3CH R_GC_Command The Global_Control_Command last received
3DH R_Len_Spec_Prm_buf
Name Bit No. Significance
7..0
7..0
..8
Set up station address of the relevant SPC3
Based on an internal 16monitored in the DP_Mode.
for example, SSA-Buf, Prm-Buf, Cfg-Buf, Read-Cfg-Buf
it, for example, SSA-Buf, Prm-Buf, Cfg-Buf, Read-Cfg-Buf
defined to the control buffers, SSA-Buf, Prm-Buf, Cfg-Buf
again be changed at a later time point.
SPC3
buffer.
Figure 4.4: Assignment of the Organizational Parameters
Page 16 V1.3 SPC3 Hardware Description
2003/04 Copyright (C) Siemens AG 2003. All rights reserved.
Page 19
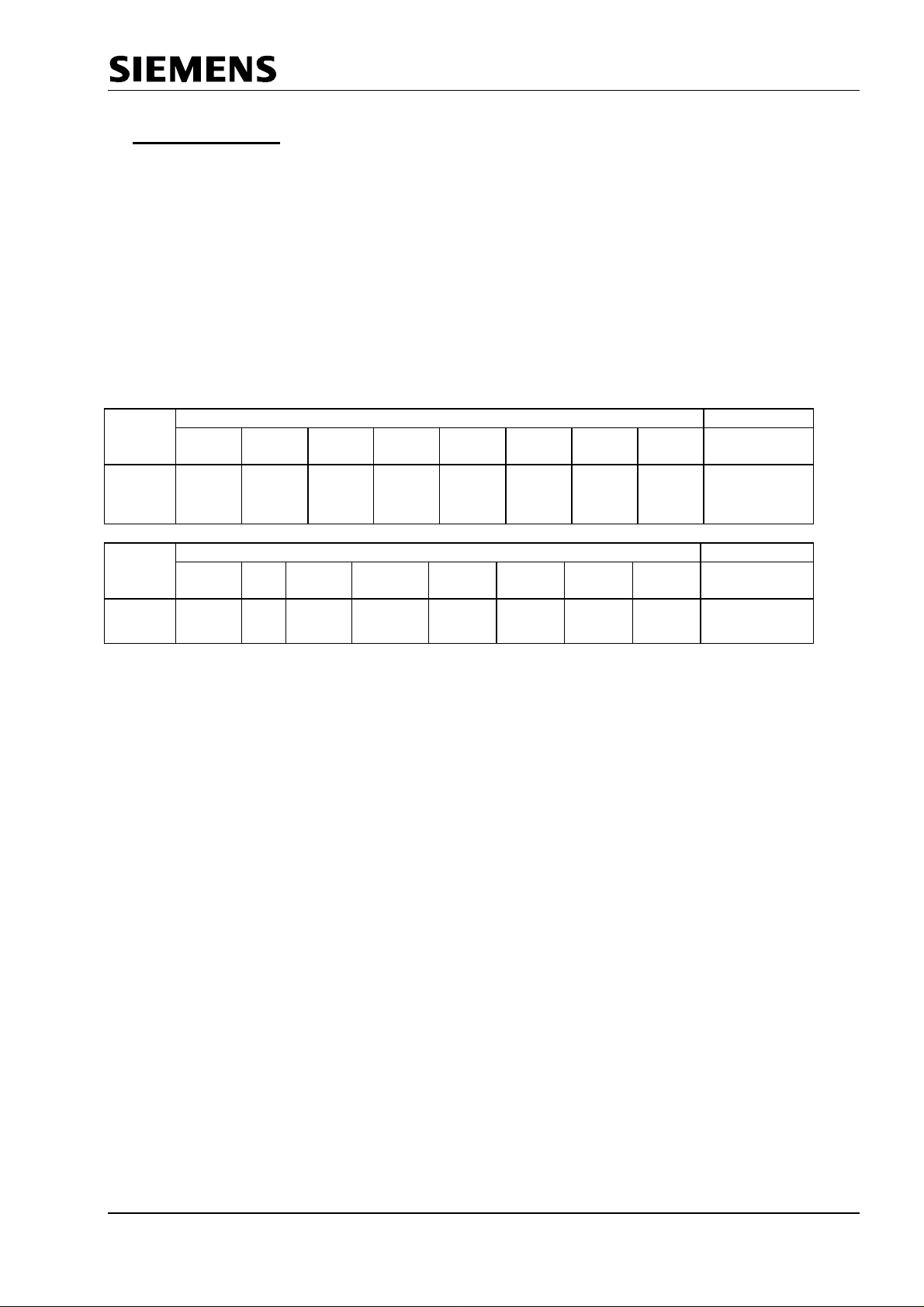
SPC3 PROFIBUS Interface Center
5 ASIC Interface
The registers that determine both the hardware function of the ASIC as well as telegram processing are
described in the following.
5.1 Mode Register
Parameter bits that access the controller directly or which the controller directly sets are combined in two
mode registers (0 and 1) in the SPC3.
5.1.1 Mode Register 0
Setting parameters for Mode Register 0 takes place in the offline state only (for example, after
switching on). The SPC3 may not exit offline until Mode Register 0, all processor parameters, and
organizational parameters are loaded (START_SPC3 = 1, Mode-Register 1).
Address Bit Position Designation
Control
Register
06H
(Intel)
Address Bit Position Designation
Control
Register
07H
(Intel)
*) When Spec_Clear_Mode (Fail Safe Mode ) = 1 the SPC3 will accept data telegramm with a data unit=0 in
the state Data Exchange. The reaction to the outputs can be parameterized f.e. in the parameterization
telegram ( only available from version Step C).
**) When using a big number of parameters to be transmitted from the PROFIBUS-Master to the slave the
Auxiliary buffer ½ has to have the same size like the Parameterization buffer. Sometimes this could reach
the limit of the available memory space in the SPC3. When Spec_Prm_Puf_Mode = 1 the parameterization
data are processed directly in this special buffer and the Auxiliary buffers can be held compact.
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Freeze_
Support-
ed
Sync_
Support-
ed
EARLY_
RDY
INT_
POL MinTSDR
DIS_
STOP_
CON
TROL
DIS_
START_
CON
TROL
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8
Spec_Cle
ar_Mode
*)
Spec_Prm_
Puf_Mode
**)
WD
Test
User
Time
base
EOI
Time
base
DP
Mode
Mode Reg0
7..0
Mode-Reg0
13 .. 8
SPC3 Hardware Description V1.3 Page 17
Copyright (C) Siemens AG 2003 All rights reserved. 2003/04
Page 20

PROFIBUS Interface Center
ram telegram overwrites this memory cell in the DP mode.
SPC3
Bit 0 DIS_START_CONTROL
Monitoring the following start bit in UART. Set-Param Telegram overwrites this memory cell in
the DP mode. (Refer to the user-specific data.)
0 = Monitoring the following start bit is enabled.
1 = Monitoring the following start bit is switched off.
Bit 1 DIS_STOP_CONTROL
Stop bit monitoring in UART. Set-Pa
(Refer to the user-specific data.)
0 = Stop bit monitoring is enabled.
1 = Stop bit monitoring is switched off.
Bit 2 EN_FDL_DDB
Reserved
0 = The FDL_DDB receive is disabled.
Bit 3 MinTSDR
Default setting for the MinTSDR after reset for DP operation or combi operation
0 = Pure DP operation (default configuration!)
1 = Combi operation
Bit 4 INT_POL
Polarity of the interrupt output
0 = The interrupt output is low-active.
1 = The interrupt output is high-active.
Bit 5 EARLY_RDY
Moved up ready signal
0 = Ready is generated when the data are valid (read) or when the data are accepted
(write).
1 = Ready is moved up by one clock pulse.
Bit 6 Sync_Supported
Sync_Mode support
0 = Sync_Mode is not supported.
1 = Sync_Mode is supported.
Bit 7 Freeze_Supported
Freeze_Mode support
0 = Freeze_Mode is not supported.
1 = Freeze_Mode is supported.
Bit 8 DP_MODE
DP_Mode enable
0 = DP_Mode is disabled.
1 = DP_Mode is enabled. SPC3 sets up all DP_SAPs.
Bit 9 EOI_Time base
Time base for the end of interrupt pulse
0 = The interrupt inactive time is at least 1 usec long.
1 = The interrupt inactive time is at least 1 ms long.
Bit 10 User_Time base
Time base for the cyclical User_Time_Clock-Interrupt
0 = The User_Time_Clock-Interrupt occurs every 1 ms.
1 = The User_Time_Clock-Interrupt occurs every 10 ms.
Bit 11 WD_Test
Test mode for the Watchdog-Timer, no function mode
0 = The WD runs in the function mode.
1 = Not permitted
Bit 12 Spec_Prm_Puf_Mode
Special parameter buffer
0 = No special parameter buffer.
1 = Special parameter buffer mode .Parameterization data will be stored directly in the
special parameter buffer.
Bit 13 Spec_Clear_Mode
Special Clear Mode (Fail Safe Mode)
0 = No special clear mode.
1 = Special clear mode. SPC3 will accept datea telegramms with data unit = 0.
Figure 5.1: Mode-Register 0 Bit 12 .. 0.(can be written to, can be changed in offline only)
Page 18 V1.3 SPC3 Hardware Description
2003/04 Copyright (C) Siemens AG 2003. All rights reserved.
Page 21
SPC3 PROFIBUS Interface Center
5.1.2 Mode Register 1 (Mode-REG1, writable):
Some control bits must be changed during operation. These control bits are combined in Mode-Register 1
and can be set independently of each other (Mode_Reg_S) or can be deleted independently of each other
(Mode_Reg_R). Various addresses are used for setting and deleting. Log ‘1’ must be written to the bit
position to be set or deleted.
Address Bit Position Designation
Control
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Register
08H
09H
Res_
User_WD
Res_
User_WD
EN_
Change_
Cfg_
Puffer
EN_
Change_
Cfg_
Puffer
User_
Leave_
Master
User_
Leave_
Master
Go_
Offline
Go_
Offline
EOI START_
SPC3
EOI START_
SPC3
Mode-Reg_S
7..0
Mode-Reg_R
7..0
Bit 0 START_SPC3
Exiting the Offline state
1 = SPC3 exits offline and goes to passive-idle. In addition, the idle timer and
Wd timer are started and ‘Go_Offline = 0’ is set.
Bit 1 EOI
End of Interrupt
1 = End of Interrupt: SPC3 switches the interrupt outputs to inactive and again
sets EOI to log.’0.’
Bit 2 Go_Offline
Going into the offline state
1 = After the current requests ends, SPC3 goes to the offline state and again
sets Go_Offline to log.’0.’
Bit 3 User_Leave_Master
Request to the DP_SM to go to ‘Wait_Prm.’
1 = The user causes the DP_SM to go to ‘Wait_Prm.’ After this action, SPC3
sets User_Leave_Master to log.’0.’
Bit 4 En_Change_Cfg_Puffer
Enabling buffer exchange (Cfg buffer for Read_Cfg buffer)
0 = With ‘User_Cfg_Data_Okay_Cmd,’ the Cfg buffer may not be exchanged for
the Read_Cfg buffer.
1 = With ‘User_Cfg_Data_Okay_Cmd,’ the Cfg buffer must be exchanged for
the Read_Cfg buffer.
Bit 5 Res_User_Wd
Resetting the User_WD_Timers
1 = SPC3 again sets the User_Wd_Timer to the parameterized value
‘User_Wd_Value
15..0.
’ After this action, SPC3 sets Res_User_Wd to log.’0.’
Figure 5..2: Mode Register1 S and Mode Register1 R Bit7..0.(writable)
SPC3 Hardware Description V1.3 Page 19
Copyright (C) Siemens AG 2003 All rights reserved. 2003/04
Page 22

PROFIBUS Interface Center
SPC3
5.2 Status Register
The status register mirrors the current SPC3 status and can be read only.
Address Bit Position Designation
Control
Register
04H
(Intel)
1 0 1 0
Address Bit Position Designation
Control
Register
05H
(Intel)
3 2 1 0 3 2 1 0
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
WD_State DP_State
RAM
access
violation
Diag_
Flag
FDL_
IND_ST
Offline/
Passive-
Idle
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8
SPC3 Release Baud Rate Status-Reg
Status-Reg
7..0
15 .. 8
Page 20 V1.3 SPC3 Hardware Description
2003/04 Copyright (C) Siemens AG 2003. All rights reserved.
Page 23

SPC3 PROFIBUS Interface Center
Bit 0 Offline/Passive-Idle
Offline-/Passive-Idle state
0 = SPC3 is in offline.
1 = SPC3 is in passive idle.
Bit 1 FDL_IND_ST
FDL indication is temporarily buffered.
0 = No FDL indication is temporarily buffered.
1 = No FDL indication is temporarily buffered.
Bit 2 Diag_Flag
Status diagnostics buffer
0 = The DP master fetches the diagnostics buffer.
1 = The DP master has not yet fetched the diagnostics buffer.
Bit 3 RAM Access Violation
Memory access > 1.5kByte
0 = No address violation
1 = For addresses > 1536 bytes, 1024 is subtracted from the current address,
and there is access to this new address.
Bits
DP-State
1..0
4,5
DP-State Machine state
00 = ’Wait_Prm’ state
01= ’Wait_Cfg’ state
10 = ’DATA_EX’ state
11= Not possible
Bits
WD-State
1..0
6,7
Watchdog-State-Machine state
00 = ’Baud_Search’ state
01= ’Baud_Control’ state
10 = ’DP_Control’ state
11= Not possible
Bits
Baud rate
3..0
:
8,9
10,11 The baud rates SPC3 found
0000 = 12 MBaud
0001 = 6 MBaud
0010 = 3 MBaud
0011 = 1.5 MBaud
0100 = 500 kBaud
0101 = 187.5 kBaud
0110 = 93.75 kBaud
0111 = 45.45 kBaud
1000 = 19.2 kBaud
1001 = 9.6 kBaud
Rest = Not possible
Bit 12 SPC3-Release
3..0
:
13,14, Release no. for SPC3
15 0000 = Release 0
Rest = Not possible
Figure 5.3: Status Register Bit15 .. 0.(readable)
SPC3 Hardware Description V1.3 Page 21
Copyright (C) Siemens AG 2003 All rights reserved. 2003/04
Page 24

PROFIBUS Interface Center
uP
SPC3
5.3 Interrupt Controller
The processor is informed about indication messages and various error events via the interrupt controller.
Up to a total of 16 events are stored in the interrupt controller. The events are carried out on an interrupt
output. The controller does not have a prioritization level and does not provide an interrupt vector (not
8259A compatible!).
The controller consists of an Interrupt Request Register (IRR), an Interrupt Mask Register (IMR), an Interrupt
Register (IR), and an Interrupt Acknowledge Register (IAR).
uP uP uP
SEP_INT
IR
SPC3
uP
S
IRR IMR
R
S
R
X/INT
FF
INT_Pol
IAR
Each event is stored in the IRR. Individual events can be suppressed via the IMR. The input in the IRR is
independent of the interrupt masks. Event signals not masked out in the IMR generate the X/INT interrupt
via a sum network. The user can set each event in the IRR for debugging.
Each interrupt event the processor processed must be deleted via the IAR (except for New_Prm_Data,
New_DDB_Prm_Data, and New_Cfg_Data). Log ‘1’ must be written on the relevant bit position. If a new
event and an acknowledge from the previous event are present at the IRR at the same time, the event
remains stored. If the processor subsequently enables a mask, it must be ensured that no prior input is
present in the IRR. For safety purposes, the position in the IRR must be deleted prior to the mask enable.
uP
Prior to exiting the interrupt routine, the processor must set the “end of interrupt signal (E01) = 1” in the
mode register. The interrupt cable is switched to inactive with this edge change. If another event must be
stored, the interrupt output is not activated again until after an interrupt inactive time of at least 1 usec or 12 ms. This interrupt inactive time can be set via ‘EOI_Timebase.’ This makes it possible to again come into
the interrupt routine when an edge-triggered interrupt input is used.
The polarity for the interrupt output is parameterized via the INT_Pol mode bit. After the hardware reset,
the output is low-active.
Address Bit Position Designation
Control
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Register
00H
(Intel)
Res Res Res User_
Timer_
Clock
WD_DP_
Mode_
Timeout
Baud_
rate_
Detect
Go/Leave
Data_
EX
MAC_
Reset
Int-Req-Reg
7..0
Address Bit Position Designation
Control
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8
Register
01H
(Intel)
Res Res DX_OUT Diag_
Puffer_
Changed
New_
Prm_
Data
New_
Cfg_
Data
New_
SSA_
Data
New_GC
Com
mand
Int-Req-Reg 7
15..8
Page 22 V1.3 SPC3 Hardware Description
2003/04 Copyright (C) Siemens AG 2003. All rights reserved.
Page 25

Bit 0 MAC_Reset
After it processes the current request, the SPC3 has arrived at the offline state (through
setting the ‘Go_Offline bit’ or through a RAM access violation).
Bit 1 Go/Leave_DATA_EX
The DP_SM has entered or exited the ‘DATA_EX’ state.
Bit 2 Baudrate_Detect
The SPC3 has exited the ‘Baud_Search state’ and found a baud rate.
Bit 3 WD_DP_Control_Timeout
The watchdog timer has run out in the ‘DP_Control’ WD state.
Bit 4 User_Timer_Clock
The time base for the User_Timer_Clocks has run out (1/10ms).
Bit 5 Res
For additional functions
Bit 6 Res
For additional functions
Bit 7 Res
For additional functions
Bit 8 New_GC_Command
The SPC3 has received a ‘Global_Control telegram’ with a changed ‘GC_Command-
Byte,’ and this byte is stored in the ‘R_GC_Command’ RAM cell.
Bit 9 New_SSA_Data
The SPC3 has received a ‘Set_Slave_Address telegram’ and made the data available
in the SSA buffer.
Bit 10 New_Cfg_Data
The SPC3 has received a ‘Check_Cfg telegram’ and made the data available in the Cfg
buffer.
Bit 11 New_Prm_Data
The SPC3 has received a ‘Set_Param telegram’ and made the data available in the
Prm buffer.
Bit 12 Diag_Puffer_Changed
Due to the request made by ‘New_Diag_Cmd,’ SPC3 exchanged the diagnostics buffer
and again made the old buffer available to the user.
Bit 13 DX_OUT
The SPC3 has received a ‘Write_Read_Data telegram’ and made the new output data
available in the N buffer. For a ‘Power_On’ or for a ‘Leave_Master,’ the SPC3 deletes
the N buffer and also generates this interrupt.
Bit 14 Res
For additional functions
Bit 15 Res
For additional functions
Figure 5.4: Interrupt Request Register, IRR Bit 15..0 (writable and readable)
SPC3 PROFIBUS Interface Center
SPC3 Hardware Description V1.3 Page 23
Copyright (C) Siemens AG 2003 All rights reserved. 2003/04
Page 26

PROFIBUS Interface Center
The other interrupt controller registers are assigned in the bit positions, like the IRR.
Address Register Reset State Assignment
02H /
03H
04H /
05H
02H /
03H
Figure 5.5: Additional Interrupt Registers
The ‘New_Prm_Data’, ‘New_Cfg_Data’ inputs may not be deleted via the Interrupt Acknowledge Register.
The relevant state machines delete these inputs through the user acknowledgements (for example,
‘User_Prm_Data_Okay’ etc.).
Interrupt Register
(IR)
Interrupt Mask
Register
(IMR)
Interrupt
Acknowledge
Register
(IAR)
Readable
only
Writable, can
be changed
during
operation
Writable, can
be changed
during
operation
All bits deleted
All bits set Bit =
All bits deleted Bit =
SPC3
1
Bit =
0
1
Bit =
0
Mask is set and the interrupt
is disabled.
Mask is deleted and the
interrupt is enabled.
The IRR bit is deleted.
The IRR bit remains
unchanged.
Page 24 V1.3 SPC3 Hardware Description
2003/04 Copyright (C) Siemens AG 2003. All rights reserved.
Page 27

SPC3 PROFIBUS Interface Center
5.4 Watchdog Timer
5.4.1 Automatic Baud Rate Identification
The SPC3 is able to identify the baud rate automatically. The „baud search“ state is located after each
RESET and also after the watchdog (WD) timer has run out in the ‘Baud_Control_state.’
As a rule, SPC3 begins the search for the set rate with the highest baud rate. If no SD1 telegram, SD2
telegram, or SD3 telegram was received completely and without errors during the monitoring time, the
search continues with the next lowest baud rate.
After identifying the correct baud rate, SPC3 switches to the “Baud_Control” state and monitors the baud
rate. The monitoring time can be parameterized (WD_Baud_Control_Val). The watchdog works with a
clock of 100 Hz (10 msec). The watchdog resets each telegram received with no errors to its own station
address. If the timer runs out, SPC3 again switches to the baud search state.
5.4.2 Baud Rate Monitoring
The located baud rate is constantly monitored in ‘Baud_Control.’ The watchdog is reset for each error-free
telegram to its own station address. The monitoring time results from multiplying both
‘WD_Baud_Control_Val’ (user sets the parameters) by the time base (10 ms). If the monitoring time runs
out, WD_SM again goes to ‘Baud_Search’. If the user carries out the DP protocol (DP_Mode = 1, see Mode
register 0) with SPC3, the watchdog is used for the “DP_Control’ state, after a ‘Set_Param telegram’ was
received with an enabled response time monitoring ‘WD_On = 1.’ The watchdog timer remains in the baud
rate monitoring state when there is a switched off ‘WD_On = 0’ master monitoring. The PROFIBUS DP
state machine is also not reset when the timer runs out. That is, the slave remains in the DATA_EXchange
state, for example.
5.4.3 Response Time Monitoring
The ‘DP_Control’ state serves response time monitoring of the DP master (Master_Add). The set
monitoring times results from multiplying both watchdog factors and multiplying the result with the
momentarily valid time base (1 ms or 10 ms):
TWD = (1 ms or 10 ms) * WD_Fact_1 * WD_Fact_2 (See byte 7 of the parameter setting telegram.)
The user can load the two watchdog factors (WD_Fact_1, and WD_Fact_2) and the time base that
represents a measurement for the monitoring time via the ‘Set_Param telegram’ with any value between 1
and 255.
EXCEPTION: The WD_Fact_1=WD_Fact_2=1 setting is not permissible. The circuit does not check
this setting.
Monitoring times between 2 ms and 650 s - independent of the baud rate - can be implemented with the
permisible watchdog factors.
If the monitoring time runs out, the SPC3 goes again to ‘Baud_Control,’ and the SPC3 generates the
‘WD_DP_Control_Timeout-Interrupt’. In addition, the DP_State machine is reset, that is, generates the
reset states of the buffer management.
If another master accepts SPC3, then there is either a switch to ‘Baud_Control” (WD_On = 0), or there is a
delay in ‘DP_Control’ (WD_On = 1), depending on the enabled response time monitoring (WD_On = 0).
SPC3 Hardware Description V1.3 Page 25
Copyright (C) Siemens AG 2003 All rights reserved. 2003/04
Page 28

PROFIBUS Interface Center
SPC3
6 PROFIBUS-DP Interface
6.1 DP_Buffer Structure
The DP mode is enabled in the SPC3 with ‘DP_Mode = 1’ (see mode Register0). In this process, the
following SAPS are fixed reserved for the DP mode:
`
Default SAP: Data exchange (Write_Read_Data)
`
SAP53: reserved
`
SAP55: Changing the station address (Set_Slave_Address)
`
SAP56: Reading the inputs (Read_Inputs)
`
SAP57: Reading the outputs (Read_Outputs)
`
SAP58: Control commands to the DP-Slave (Global_Control)
`
SAP59: Reading configuration data (Get_Config)
`
SAP60: Reading diagnostics information (Slave_Diagnosis)
`
SAP61: Sending parameter setting data (Set_Param)
`
SAP62: Checking configuration data (Check_Config)
The DP Slave protocol is completely integrated in the SPC3 and is handled independently. The user must
correspondingly parameterize the ASIC and process and acknowledge transferred messages. Except for
the default SAP, SAP56, SAP57, and SAP58, all SAPS are always enabled. The remaining SAPS are not
enabled until the the DP Slave Machine (DP_SM) goes into the ‘DATA_EX’ state. The user has the
possibility of disabling SAP55. The relevant buffer pointer R_SSA_Puf_Ptr must be set to ‘00H’ for this
purpose. The DDB utility is disabled by the already described initialization of the RAM cells.
The DP_SAP buffer structure is displayed in Figure 6.1. The user configures all buffers (length and buffer
beginning) in the ‘offline state.’ During operation, the buffer configuration must not be changed, except for
the length of the Dout-/Din buffers.
The user may still adapt these buffers in the ‘Wait_Cfg’ state after the configuration telegram
(Check_Config). Only the same configuration may be accepted in the ‘DATA_EX’ state.
The buffer structure is divided into the data buffer, diagnostics buffer, and the control buffer.
Both the output data and the input data have three buffers each available with the same length. These
buffers function as change buffers. One buffer is assigned to the ‘D’ data transfer, and one buffer is
assigned to the ‘U’ user. The third buffer is either in a Next ‘N’ state or Free ‘F’ state, whereby one of the
two states is always unoccupied.
Two diagnostics buffers that can have varying lengths are available for diagnostics. One diagnostics buffer
is always the ‘D’ assigned to SPC3 for sending. The other diagnostics buffer belongs to the user for
preparing new diagnostics data, ‘U.’
The SPC3 first reads the different parameter setting telegrams (Set_Slave_Address, and Set_Param) and
the configuring telegram (Check_Config) into Aux-Puffer1 or Aux-Puffer 2.....
Page 26 V1.3 SPC3 Hardware Description
2003/04 Copyright (C) Siemens AG 2003. All rights reserved.
Page 29

SPC3 PROFIBUS Interface Center
N- U is changed by the userD-Nis changed by SPC 3
UART
D N
D N
Aux1/2-buffer
U
Dout-buffer
U
Din-buffer
D U
Diagnosticsbuffer
ReadConfigbuffer
User
Configbuffer
SSA-buffer
Aux1/2-buffer
Parambuffer
Figure 6.1: DP_SAP Buffer Structure
Data exchanged with the corresponding target buffer (SSA buffer, Prm buffer, and Cfg buffer). Each of the
buffers to be exchanged must have the same length. The user defines which Aux_buffers are to be used
for the above-named telegrams in the ‘R_Aux_Puf_Sel’ parameter cell. The Aux- buffer1 must always be
available. The Aux-buffer2 is optional. If the data profiles of these DP telegrams are very different, such as
the data amount in the Set_Param telegram is significantly larger than for the other telegrams, it is
suggested to make an Aux-Buffer2 available (Aux_Sel_Set_Param = 1) for this telegram. The other
telegrams are then read via Aux-Buffer 1 (Aux_Sel_..=0). If the buffers are too small, SPC3 responds with
“no resources”!
SPC3 Hardware Description V1.3 Page 27
Copyright (C) Siemens AG 2003 All rights reserved. 2003/04
Page 30

PROFIBUS Interface Center
SPC3
Address Bit Position Designation
RAM
7 6 5 4 3 2 0
Register
2AH 0 0 0 0 0
Set_
Slave_
Adr
Cfg
Set_
R_Aux_Puf_Sel
Prm
Check_
X1 X1 X1 See below for coding.
X1 Coding
0 Aux_Buffer1
1 Aux_Buffer2
Figure 6.2: Aux-Buffer Management
The user makes the configuration data (Get_Config) available in the Read_Cfg buffer for reading. The
Read_Cfg buffer must have the same length as the Cfg_buffer.
The Read_Input_Data telegram is operated from the Din buffer in the ‘D state’, and the Read_Output_Data
telegram is operated from the Dout buffer in the ‘U state.’
All buffer pointers are 8-bit segment addresses, because the SPC3 internally has only 8-bit address
registers. For a RAM access, SPC3 adds an 8-bit offset address to the segment address shifted by 3 bits
(result: 11-bit physical address). As regards the buffer start addresses, this results in an 8-byte graunularity
from this specification.
Page 28 V1.3 SPC3 Hardware Description
2003/04 Copyright (C) Siemens AG 2003. All rights reserved.
Page 31

SPC3 PROFIBUS Interface Center
6.2 Description of the DP Services
6.2.1 Set_Slave_Address (SAP55)
6.2.1.1 Sequence for the Set_Slave_Address Utility
The user can disable this utility by setting the ‘R_SSA_Puf_Ptr = 00H’ buffer pointer. The slave address
must then be determined, for example, by reading a switch, and written in the R_TS_Adr. RAM register.
The user must make a retentive memory possibility available (for example, EEPROM) to support this utility.
It must be possible to store the ‘station address’ and the ‘Real_No_Add_Change’ (‘True’ = FFH) parameter
in this external EEPROM. After each restart caused by a power failure, the user must again make these
values available to SPC3 in the R_TS_Adr und R_Real_No_Add_Change RAM register.
If SAP55 is enabled and the Set_Slave_Address telegram is correctly accepted, SPC3 enters all net data in
the Aux-Puffer1/2, exchanges the Aux buffer1/2 for the SSA buffer, stores the entered data length in
‘R_Len_SSA_Data’, generates the ‘New_SSA_Data’ interrupt and internally stores the new ‘station address’
and the new ‘Real_No_Add_Change’ parameter. The user does not need to transfer this changed
parameter to SPC3 again. After the user has read the buffer, the user generates the
‘SSA_Puffer_Free_Cmd’ (read operation on address 14H). This makes SPC3 again ready to receive an
additional Set Slave Address telegram (such as from another master).
SPC3 reacts independently when there are errors.
Address Bit Position Designation
Control
Register
14H 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 SSA_Puffer_Free_Cmd
don´t care
Figure 6.3: Coding SSA_Buffer_Free_Cmd
6.2.1.2 Structure of the Set_Slave_Address Telegram
The net data are stored as follows in the SSA buffer:
Byte Bit Position Designation
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
0 New_Slave_Address
1 Ident_Number_High
2 Ident_Number_Low
3 No_Add_Chg
4-243 Rem_Slave_Data additional application-
Figure 6.4: Data Format for the Set_Slave_Address Telegram
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
specific data
SPC3 Hardware Description V1.3 Page 29
Copyright (C) Siemens AG 2003 All rights reserved. 2003/04
Page 32

PROFIBUS Interface Center
SPC3
6.2.2 Set_Param (SAP61)
6.2.2.1 Parameter Data Structure
SPC3 evaluates the first seven data bytes (without user prm data), or the first eight data bytes (with user
prm data). The first seven bytes are specified according to the standard. The eighth byte is used for SPC3specific characteristics. The additional bytes are available to the application.
Byte Bit Position Designation
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Lock
Unlo.
Sync
Free
WD
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8-243
Req
Req
Req
Req
0 0 0 0 0 WD_
Res Res Res
on
Base
Dis
Stop
Station status
WD_Fact_1
WD_Fact_2
MinTSDR
Ident_Number_High
Ident_Number_Low
Group_Ident
Dis
Spec_User_Prm_Byte
Start
User_Prm_Data
Byte 7 Spec_User_Prm_Byte
Bit Name Significance Default State
0 Dis_Startbit The start bit monitoring in the
receiver is switched off with this bit.
Dis_Startbit= 1 ,
that is, start bit monitoring is
switched off.
1 Dis_Stopbit Stop bit monitoring in the receiver is
switched off with this bit.
Dis_Stopbit= 0,
that is, stop bit monitoring is not
switched off.
2 WD_Base This bit specifies the time base used
to clock the watchdog.
WD_Base= 0,
that is, the time base is 10 ms
WD_Base = 0: time base 10 ms
WD_Base = 1: time base 1 ms
3-7 res to be parameterized with 0 0
Figure 6.5: Data Format for the Set_Param_Telegram
6.2.2.2 Parameter Data Processing Sequence
In the case of a positive validatation for more than seven data bytes, SPC3 carries out the following
reaction, among others:
SPC3 exchanges Aux-Puffer1/2 (all data bytes are input here) for the Prm buffer, stores the input data
length in ‘R_Len_Prm_Data’, and triggers the ‘New_Prm_Data Interrupt’. The user must then check the
‘User_Prm_Data’ and either reply with the ‘User_Prm_Data_Okay_Cmd’ or with
‘User_Prm_Data_Not_Okay_Cmd.’ The entire telegram is input in the buffer, that is, application-specific
parameter data are stored beginning with data byte 8 only.
The user response (User_Prm_Data_Okay_Cmd or User_Prm_Data_Not_Okay_Cmd) again takes
back the ‘New_Prm_Data’ interrupt. The user may not acknowledge the ‘New_Prm_Data’ interrupt in
the IAR register.
The relevant diagnostics bits are set with the ‘User_Prm_Data_Not_Okay_Cmd’ message and are branched
to ‘Wait_Prm.’
The ‘User_Prm_Data_Okay’ and ‘User_Prm_Data_Not_Okay’ acknowledgements are reading accesses to
defined registers with the relevant signals:
• ‘User_Prm_Finished’: No additional parameter telegram is present.
• ‘Prm_Conflict’ : An additional parameter telegram is present, processing again
• ‘Not_Allowed’, Access not permitted in the current bus state
Page 30 V1.3 SPC3 Hardware Description
2003/04 Copyright (C) Siemens AG 2003. All rights reserved.
Page 33

Address Bit Position Designation
Control
Register
0EH 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 User_Prm_Finished
0 1 PRM_Conflict
1 1 Not_Allowed
Address Bit Position Designation
Control
Register
0FH 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 User_Prm_Finished
0 1 PRM_Conflict
1 1 Not_Allowed
Figure 6.6: Coding User_Prm_Data_Not/_Okay_Cmd
If an additional Set-Param telegram is supposed to be received in the meantime, the signal ‘Prm_Conflict’ is
is returned for the acknowledgement of the first Set_Param telegram, whether positive or negative. Then
the user must repeat the validation because the SPC3 has made a new Prm buffer available.
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
SPC3 PROFIBUS Interface Center
User_Prm_Data_Okay
User_Prm_Data_Not_Okay
6.2.3 Check_Config (SAP62)
The user takes on the evaluation of the configuration data. After SPC3 has received a validated
Check_Config-Telegram, SPC3 exchanges the Aux-Puffer1/2 (all data bytes are entered here) for the Cfg
buffer, stores the input data length in ‘R_Len_Cfg-Data,’ and generates ‘New_Cfg_Data-Interrupt’.
The user must then check the ‘User_Config_Data’ and either respond with ‘User_Cfg_Data_Okay_Cmd’ or
with ‘User_Cfg_Data_Not_Okay_Cmd’ (acknowledgement to the Cfg_SM). The net data is input in the
buffer in the format regulation of the standard.
The user response (User_Cfg_Data_Okay_Cmd or the User_Cfg_Data_Not_Okay_Cmd response)
again takes back the ‘New_Cfg_Data’ interrupt and may not be acknowledged in the IAR.
If an incorrect configuration is signalled back, various diagnostics bits are changed, and there is branching
to ‘Wait_Prm.“
For a correct configuration, the transition to ‘DATA_EX’ takes place immediately, if no Din_buffer is present
(R_Len_Din_Puf = 00H) and trigger counters for the parameter setting telegrams and configuration
telegrams are at 0. Otherwise, the transition does not take place until the first ‘New_DIN_Puffer_Cmd’ with
which the user makes the first valid ‘N buffer” available. When entering into ‘DATA_EX,’ SPC3 also
generates the ‘Go/Leave_Data_Exchange-Interrupt.
If the received configuration data from the Cfg buffer are supposed to result in a change of the Read-Cfgbuffer ( the change contains the data for the Get_Config telegram), the user must make the new Read_Cfg
data available in the Read-Cfg buffer before the ‘User_Cfg_Data_Okay_Cmd” acknowledgement. After
receiving the acknowledgement, SPC3 exchanges the Cfg buffer with the Read-Cfg buffer, if
‘EN_Change_Cfg_buffer = 1’ is set in mode register1.
During the acknowledgement, the user receives information about whether there is a conflict or not. If an
additional Check_Config telegram was supposed to be received in the meantime, the user receives the
‘Cfg_Conflict” signal during the acknowledgement of the first Check_Config telegram, whether positive or
negative. Then the user must repeat the validation, because SPC3 has made a new Cfg buffer available.
The ‘User_Cfg_Data_Okay_Cmd’ and ‘User_Cfg_Data_Not_Okay_Cmd’ acknowledgements are read
accesses to defined memory cells (see Section 2.2.1) with the relevant ‘Not_Allowed’, ‘User_Cfg_Finished,’
or ‘Cfg_Conflict’ signals (see Figure 3.7). If the ‘New_Prm_Data’and ‘New_Cfg_Data’ are supposed to
be present simultaneously during power up, the user must maintain the Set_Param and then the
Check_Config. acknowledgement sequence.
SPC3 Hardware Description V1.3 Page 31
Copyright (C) Siemens AG 2003 All rights reserved. 2003/04
Page 34

PROFIBUS Interface Center
SPC3
Address Bit Position Designation
Control
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Register
10H 0 0 0 0 0 0
User_Cfg_Data_Okay
0 0 User_Cfg_Finished
0 1 Cfg_Conflict
1 1 Not_Allowed
Address Bit Position Designation
Control
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Register
11H 0 0 0 0 0 0
User_Cfg_Data_Not_Okay
0 0 User_Cfg_Finished
0 1 Cfg_Conflict
1 1 Not_Allowed
Figure 6.7: Coding of the User_Cfg_Data_Not/_Okay_Cmd
6.2.4 Slave_Diagnosis (SAP60)
6.2.4.1 Diagnostics Processing Sequence
Two buffers are available for diagnostics. The two buffers can have varying lengths. SPC3 always has one
diagnostics buffer assigned to it, which is sent for a diagnostics call-up. The user can pre-process new
diagnostics data in parallel in the other buffer. If the new diagnostics data are to be sent now, the user uses
the ‘New_Diag_Cmd’ to make the request to exchange the diagnostics buffers. The user receives
confirmation of the exchange of the buffers with the ‘Diag_Puffer_Changed Interrupt.’
When the buffers are exchanged, the internal ‘Diag_Flag’ is also set. For an activated ‘Diag_Flag,’ SPC3
responds during the next Write_Read_Data with high-priority response data that signal the relevant master
that new diagnostics data are present at the slave. Then this master fetches the new diagnostics data with a
Slave_Diagnosis telegram. Then the ‘Diag_Flag” is reset again. If the user signals ‘Diag.Stat_Diag = 1,’
however (static diagnosis, see the structure of the diagnostics buffer), then ‘Diag_Flag’ still remains
activated after the relevant master has fetched the diagnosis. The user can poll the ‘Diag_Flag’ in the
status register to find out whether the master has already fetched the diagnostics data before the old data is
exchanged for the new data.
Status coding for the diagnostics buffers is stored in the‘Diag_bufferSM’ processor parameter. The user can
read this cell with the possible codings for both buffers: ‘User,’ ‘SPC3,’ or ‘SPC3_Send_Mode.’
Address Bit Position Designation
Control
7 6 5 4 3 2 0
Register
0CH 0 0 0 0 D_Puf2 D_Puf1 Diag_Puffer_SM
X1 X2 X1 X2 See below for coding.
X1 X2 Coding
0 0 Each for the D_Buf2 or D_Buf1
0 1 User
1 0 SPC3
1 1 SPC3_Send_Mode
Figure 6.8: Diag_Buffer Assignment
The ‘New_Diag_Cmd’ is also a read access to a defined processor parameter with the signal as to which
diagnostics buffer belongs to the user after the exchange, or whether both buffers are currently assigned to
SPC3 (‘no Puffer’, ‘Diag_Puf1’, ‘Diag_Puf2’).
Page 32 V1.3 SPC3 Hardware Description
2003/04 Copyright (C) Siemens AG 2003. All rights reserved.
Page 35

SPC3 PROFIBUS Interface Center
Address Bit Position Designation
Control
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Register
0DH 0 0 0 0 0 0
New_Diag_Cmd
0 0 no Puffer
0 1 Diag_Puf1
1 0 Diag_Puf2
Figure 6.9: Coding Diag_Puffer_SM, New_Diag_Cmd
6.2.4.2 Structure of the Diagnostics Buffer:
The user transfers the diagnostics buffer displayed in the figure below to SPC3. The first 6 bytes are space
holders, except for the three least significant bit positions in the first byte. The user stores the diagnostics
bits, ‘Diag.Ext_Diag’ ‘Diag.Stat_Diag,” and Diag.Ext.Diag_Overflow’ in these three bit positions. The
remaining bits can be assigned in any order. When sending, SPC3 pre-processes the first six bytes
corresponding to the standard.
Byte Bit Position Designation
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
0
1
2
3
4
5
6-n
Ext_
The user must input
Diag
Overf
Stat
Diag
Ext_
Spaceholder
Diag
Spaceholder
Spaceholder
Spaceholder
Spaceholder
Spaceholder
Ext_Diag_Data (n = max 243)
Figure 6.10: Structure of the Diagnostics Buffer for Transfer to the SPC3
The ‘Ext-Diag_Data’ the user must enter into the buffers follow after the SPC3-internal diagnostics data.
The three different formats are possible here (device-related, ID-related, and port-related). In addition to the
‘Ext_Diag_Data,’ the buffer length also includes the SPC3 diagnostics bytes (R_Len_Diag_Puf1,
R_Len_Diag_Puf2).
6.2.5 Write_Read_Data / Data_Exchange (Default_SAP)
6.2.5.1 Writing Outputs
SPC3 reads the received output data in the D buffer. After error-free receipt, SPC3 shifts the newly filled
buffer from ‘D’ to ‘N.’ In addition, the ‘DX_Out_Interrupt’ is generated. The user now fetches the current
output data from ‘N.’ The buffer changes from ‘N’ to ‘U’ with the ‘Next_Dout_Buffer_Cmd,’ so that the
current data of the application can be sent back for the master’s Read_Outputs.
If the user’s evaluation cycle time is shorter than the bus cycle time, the user does not find any new buffers
with the next ‘Next_Dout_Buffer_Cmd’ in ‘N.’ Therefore, the buffer exchange is omitted, At a 12 Mbd baud
rate, it is more likely, however, that the user’s evaluation cycle time is larger than the bus cycle time. This
makes new output data available in ‘N’ several times before the user fetches the next buffer. It is
guaranteed, however, that the user receives the data last received.
For ‘Power_On’, ‘Leave_Master’ and the Global_Control-Telegram ‘Clear,’ SPC3 deletes the D buffer and
then shifts it to ‘N.’ This also takes place during the power up (entering into ‘Wait_Prm’). If the user fetches
this buffer, he receives the ‘U_buffer cleared’ display during the ‘Next_Dout_Buffer_Cmd.’ If the user is still
supposed to enlarge the output data buffer after the Check_Config telegram, the user must delete this delta
in the N buffer himself (possible only during the power-up phase in the ‘Wait_Cfg’ state).
If ‘Diag.Sync_Mode = 1’, the D buffer is filled but not exchanged with the Write_Read_Data-Telegram, but
rather exchanged at the next Sync or Unsync.
SPC3 Hardware Description V1.3 Page 33
Copyright (C) Siemens AG 2003 All rights reserved. 2003/04
Page 36

PROFIBUS Interface Center
SPC3
The user can read the buffer management state with the following codes for the four states: ‘Nil’,
‘Dout_Puf_Ptr1-3’. The pointer for the current data is in the “N” state.
Address Bit Position Designation
Control
7 6 5 4 3 2 0
Register
0AH F U N D Dout_Puffer_SM
X1 X2 X1 X2 X1 X2 X1 X2 See below for coding.
X1 X2 Coding
0 0 Nil
0 1 Dout_Puf_Ptr1
1 0 Dout_Puf_Ptr2
1 1 Dout_Puf_Ptr3
Figure 6.11: Dout_Buffer Management
When reading the ‘Next_Dout_Buffer_Cmd’ the user gets the information which buffer (U-buffer) belongs to
the user after the change, or whether a change has taken place at all.
Address Bit Position Designation
Control
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Register
0BH 0 0 0 0
U_
Buffer
Cleared
State_
U_
Buffer
Ind_U_
Buffer
Next_Dout_Buf_Cmd
0 1 Dout_Buf_Ptr1
1 0 Dout_Buf_Ptr2
1 1 Dout_Buf_Ptr3
0 No new U buffer
1 New U buffer
0 U buffer contains data
1 U buffer was deleted
Figure 6.12: Next_Dout_Puffer_Cmd
The user must delete the U buffer during initialization so that defined (deleted) data can be sent for a
Read_Output Telegram before the first data cycle.
6.2.5.2 Reading Inputs
SPC3 sends the input data from the D buffer. Prior to sending, SPC3 fetches the Din buffer from ‘N’ to ‘D.’
If no new buffer is present in ‘N,’ there is no change.
The user makes the new data available in ‘U’. With the ‘New_Din_buffer_Cmd,’ the buffer changes from ‘U’
to ‘N’. If the user’s preparation cycle time is shorter than the bus cycle time, not all new input data are sent,
but just the most current. At a 12 Mbd baud rate, it is more probable, however, that the user’s preparation
cycle time is larger than the bus cycle time. Then SPC3 sends the same data several times in succession.
During start-up, SPC3 first goes to ‘DATA_EX’ after all parameter telegrams and configuration telegrams
are acknowledged, and the user then makes the first valid Din buffer available in ‘N’ with the
‘New_Din_Buffer_Cmd.
If ‘Diag.Freeze_Mode = 1’, there is no buffer change prior to sending.
The user can read the status of the state machine cell with the following codings for the four states: ‘Nil’,
‘Dout_Puf_Ptr1-3.’ (See Figure 3.13.) The pointer for the current data is in the “N” state.
Page 34 V1.3 SPC3 Hardware Description
2003/04 Copyright (C) Siemens AG 2003. All rights reserved.
Page 37

SPC3 PROFIBUS Interface Center
Address Bit Position Designation
Control
7 6 5 4 3 2 0
Register
08H F U N D Din_Buffer_SM
X1 X2 X1 X2 X1 X2 X1 X2 See below for coding.
X1 X2 Coding
0 0 Nil
0 1 Din_Buf_Ptr1
1 0 Din_Buf_Ptr2
1 1 Din_Buf_Ptr3
Figure 6.13: Din_Buffer Management
When reading the ‘New_Din_Buffer_Cmd’ the user gets the information which buffer (U-buffer) belongs to
the user after the change (Din_Buf_Ptr 1-3).
Address Bit Position Designation
Control
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Register
09H 0 0 0 0 0 0
New_Din_Buf_Cmd
0 1 Din_Buf_Ptr1
1 0 Din_Buf_Ptr2
1 1 Din_Buf_Ptr3
Figure 6.14: Next_Din_Buffer_Cmd
6.2.5.3 User_Watchdog_Timer
After power-up (‘DATA_EX’ state), it is possible that SPC3 continually answers Write_Read_Data-telegrams
without the user fetching the received Din buffers or making new Dout buffers available. If the user
processor ‘hangs up,’ the master would not receive this information. Therefore, a ‘User_Watchdog_Timer’
is implemented in SPC3.
This User_Wd_Timer is an internal 16-bit RAM cell that is started from a ‘R_User_Wd_Value
15..0
’ value the
user parameterizes and is decremented with each received Write_Read_Data telegram from SPC3. If the
timer attains the ‘0000hex’ value, SPC3 transitions to the ‘Wait_Prm’ state, and the DP_SM carries out a
‘Leave_Master.’ The user must cyclically set this timer to its start value. Therefore, ‘Res_User_Wd = 1’
must be set in mode register 1. Upon receipt of the next Write_Read_Data telegram, SPC3 again loads the
User_Wd_Timer to the parameterized value ‘R_User_Wd_Value
15..0
’ and sets ‘Res_User_Wd = 0’ (Mode
Register 1). During power-up, the user must also set ‘Res_User_Wd = 1’, so that the User_Wd_Timer is
even set at its parameterized value.
6.2.6 Global_Control (SAP58)
SPC3 itself processes the Global_Control-Telegrams in the manner already described. In addition, this
information is available to the user.
The first byte of a valid Global_Control command is stored in the R_GC_Comand RAM cell. The second
telegram byte (Group_Select) is processed internally.
Address Bit Position Designation
RAM
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Cell
3CH
Res Res Sync Un
sync
Freeze Un
freeze
Clear_
Data
Res
R_GC_Command
SPC3 Hardware Description V1.3 Page 35
Copyright (C) Siemens AG 2003 All rights reserved. 2003/04
Page 38

PROFIBUS Interface Center
Bit Designation Significance
0 Reserved
1 Clear_Data With this command, the output data is deleted in ‘D’ and is changed
to ‘N.’
2 Unfreeze With „Unfreeze,“ freezing input data is cancelled.
3 Freeze The input data is fetched from ‘N’ to ‘D’ and „frozen“. New input data
is not fetched again until the master sends the next ‘Freeze’
command.
4 Unsync The „Unsync“ command cancels the „Sync“ command.
5 Sync The output data transferred with a WRITE_READ_DATA telegram is
changed from ‘D’ to ‘N.’ The following transferred output data is kept
in ‘D’ until the next ‘Sync’ command is given.
6,7 Reserved The „Reserved“ designation specifies that these bits are reserved for
future function expansions.
Figure 6.15: Data Format for the Global_Control Telegram
If the Control_Comand byte changed at the last received Global_Control telegram, SPC3 additionally
generates the ‘New_GC_Command’ interrupt. During initialization, SPC3 presets the ‘R_GC_Command’
RAM cell with 00H. The user can read and evaluate this cell.
So that Sync and Freeze can be carried out, these functions must be enabled in the mode register.
SPC3
6.2.7 Read_Inputs (SAP56)
SPC3 fetches the input data like it does for the Write_Read_Data Telegram. Prior to sending, ‘N’ is shifted
to ‘D,’ if new input data are available in ‘N.’ For ‘Diag.Freeze_Mode = 1,’ there is no buffer change.
6.2.8 Read_Outputs (SAP57)
SPC3 fetches the output data from the Dout buffer in ‘U’. The user must preset the output data with ‘0’
during start-up so that no invalid data can be sent here. If there is a buffer change from ‘N’ to ‘U’ (through
the Next_Dout_Buffer_Cmd) between the first call-up and the repetition, the new output data is sent during
the repetition.
6.2.9 Get_Config (SAP59)
The user makes the configuration data available in the Read_Cfg buffer. For a change in the configuration
after the Check_Config telegram, the user writes the changed data in the Cfg buffer, sets
‘EN_Change_Cfg_buffer = 1’ (see Mode-Register1), and SPC3 then exchanges the Cfg buffer for the
Read_Cfg buffer. (See Section 3.2.3.) If there is a change in the configuration data (for example, for the
modular DP systems) during operation, the user must return with ‘Go Offline’ (see Mode Register1) to
‘Wait_Prm’ to SPC3.
Page 36 V1.3 SPC3 Hardware Description
2003/04 Copyright (C) Siemens AG 2003. All rights reserved.
Page 39

SPC3 PROFIBUS Interface Center
7 Hardware Interface
7.1 Universal Processor Bus Interface
7.1.1 General Description
SPC3 has a parallel 8-bit interface with an 11-bit address bus. SPC3 supports all 8-bit processors and
microcontrollers based on the 80C51/52 (80C32) from Intel, the Motorola HC11 family, as well as 8-/16-bit
processors or microcontrollers from the Siemens 80C166 family, X86 from Intel, and the HC16 and HC916
family from Motorola. Because the data formats from Intel and Motorola are not compatible, SPC3
automatically carries out ‘byte swapping’ for accesses to the following 16-bit registers (interrupt register,
status register, and mode register0) and the 16-bit RAM cell (R-User_Wd_Value). This makes it possible for
a Motorola processor to read the 16-bit value correctly. Reading or writing takes place, as usual, through
two accesses (8-bit data bus).
Due to the 11-bit address bus, SPC3 is no longer fully compatible to SPC2 (10-bit address bus). However,
AB(10) is located on the XINTCI output of the SPC2 that was not used until now. For SPC3, the AB(10)
input is provided with an internal pull-down resistor. If SPC3 is to be connected into existing SPC2
hardware, the user can use only 1 kByte of the internal RAM. Otherwise, the AB(10) cable on the modules
must be moved to the same place.
The Bus Interface Unit (BIU) and the Dual Port RAM Controller (DPC) that controls accesses to the internal
RAM belong to the processor interface of the SPC3.
In addition, a clock rate divider is integrated that the clock pulse of an external clock pulse generator divided
by 2 (Pin: DIVIDER = High-Potential) or 4 (Pin: DIVIDER = Low-Potential) makes available on the pin
CLKOUT2/4 as the system clock pulse so that a slower controller can be connected without additional
expenditures in a low-cost application. SPC3 is supplied with a clock pulse rate of 48MHz.
7.1.2 Bus Interface Unit (BIU)
The BIU forms the interface to the connected processor/microcontroller. This is a synchronous or
asynchronous 8-bit interface with an 11-bit address bus. The interface is configurable via 2 pins
(XINT/MOT, MODE). The connected processor family (bus control signals such as XWR, XRD, or R_W,
and the data format) is specified with the XINT/MOT pin. Synchronous (rigid) or asynchronous bus timing is
specified with the MODE pin.
Various Intel system configurations are displayed in the figures in Section 7.1.3. The internal address latch
and the integrated decoder must be used in the C32 mode. One figure displays the minimum configuration
of a system with SPC3, whereby the block is connected to an EPROM version of the controller. Only a
pulse generator is necessary as an additional block in this configuration. If a controller is to be used without
an integrated program memory, the addresses must once again be latched off for the external memory.
The connection schematic in the next figure is applicable for all Intel/Siemens processors that offer
asynchronous bus timing and evaluate the ready signal.
Notes:
If the SPC3 is connected to an 80286 processor, or others, it must be taken into consideration that the
processor carries out word accesses. That is, either a “swapper” is necessary that switches the characters
out of the SPC3 at the relevant byte position of the 16-bit data bus during reading, or the least significant
address bit is not connected, and the 80286 must read word accesses and evaluate only the lower byte, as
displayed in the figure.
SPC3 Hardware Description V1.3 Page 37
Copyright (C) Siemens AG 2003 All rights reserved. 2003/04
Page 40

PROFIBUS Interface Center
dresses AB7..0 externally
For microcontrollers with chip select logic (K, F1, HC16, and HC916), the chip select
address range, the priority, the polarity, and
For microcontrollers without chip select logic (N and M), and others, an external chip
The SPC3 output clock (CLKOUT2/4) must be four times larger than the E_CLOCK.
The SPC3 input clock (CLK) must be at least 10 times larger than the desired system
r 4), and it results in an
All other HC11 types with a multiplexed bus must externally select addresses AB7..0
Intel microcontroller CPU basis is 80C51/52/32, microcontrollers from various
The address decoder is switched on in SPC3. The CS signal is generated for SPC3
d with the ALE signal in an internal address
latch. The internal CS decoder is activated in SPC3 that generates its own CS signal
XINT/MO MODE The SPC3 interface supports the following processors/microcontrollers.
1 1 Motorola microcontroller with the following characteristics:
synchron-ous
Motorola
The following can be connected:
The address decoder is switched off in the SPC3. The CS signal is fed to SPC3.
Condition:
1 0 Motorola microcontroller with the following characteristics:
asynchron-ous
Motorola
The following can be connected:
The address decoder is switched off in SPC3. The CS signal is fed into SPC3.
0 1
synchron-ous
Intel
The following can be connected:
• Synchronous (rigid) bus timing without evaluation of the XREADY signal
• 8-bit non-multiplexed bus: DB7..0, AB10..0
• HC11 types: K, N, M, F1
• HC16- und HC916 types with programmable E clock timing
• All other HC11 types with a multiplexed bus must select ad
from DB7..0 data.
•
signals are programmable as regards the
the window width in the write cycle or read cycle.
•
select logic is required. This means additional hardware and a fixed assignment.
•
clock (E_Clock). The divider pin must be placed at „low“ (divide
E_CLOCK of 3 MHz
• Asychronous bus timing with evaluation of the XREADY signal
• 8-bit non-multiplexed bus: DB7..0, AB10..0
• HC16 and HC916 types
•
from data DB7..0.
• Chip select logic is available and programmable in all microcontrollers.
manufacturers:
• Sychronous (rigid) bus timing without evaluation of the XREADY signal
• 8-bit multiplexed bus: ADB7..0
• Microcontroller families from Intel, Siemens, and Philips, for example
internally.
• The lower address bits AB7..0 are store
SPC3
from the AB10..0 addresses.
• The internal address decoder is fixed wired, so that SPC3 must always be addressed
under the fixed addresses AB7..0 = 00000xxxb. SPC3 selects relevant address
window from the AB2..0 signals. In this mode, the CS-Pin (XCS) must be located at
VDD (high potential).
0 1 Intel- and Siemens 16-/8-bit microcontroller families
asynchron.
Intel
The following can be connected:
Address decoder is switched off in SPC3. The CS signal is fed in to the SPC3.
Figure 7.1: Bus Interface
Page 38 V1.3 SPC3 Hardware Description
2003/04 Copyright (C) Siemens AG 2003. All rights reserved.
• Asychronous bus timing with evaluation of the XREADY signal
• 8 bit non-multiplexed bus: DB7..0, AB10..0
• Microcontroller families from Intel x86 and Siemens 80C16x, for example
• External address decoding is always necessary.
• External chip select logic if the microcontroller is not present
Page 41

GND
VDD
7.1.3 Switching Diagram Principles
SPC3 PROFIBUS Interface Center
80C32/
C501
CLK
WR
INT0
Port 0
ALE
Port 2
Reset
RD
Low Cost System with 80C32
A / D 7...0
AB 15...8
(0000 00XXBIN)
12/24 MHz
1K 1K
1K
Pulse Generator
48MHz
Divider :2/4
XW R
XRD
X/INT
DB 7..0
Data
DB 7..0
Address Latch
AB 7..0
Address
decoder
AB8
AB9
AB10
Mode
3K3
GND VDD
RTS
TxD
RxD
XCTS
SPC3
SPC3
Reset
DIVIDER
1K
GND
CLK
80C32
20/16MHz
PSEN
WR
INT0
ALE
Port 0
Port 2
Reset
RD
A / D 7...0
AB 15...8
80C32 System with Ext. Memory (C32-Mode)
Address
Latch
(0000 00XXBIN)
AB 15...0
EPROM
64kB
RAM
32kB
RD WR
Address
Decoder
12/24 MHz
XW R
XRD
X/INT
DB 7..0
Data
DB 7..0
Address Latch
AB 7....0
Addressdecoder
AB8
AB9
AB10
1K 1K 3K3
1K
Pulse Generator
48 MHz
Scaler:2/4
SPC3
Mode
RTS
TxD
RxD
XCTS
SPC3
Reset
DIVIDER
1K
GND
SPC3 Hardware Description V1.3 Page 39
Copyright (C) Siemens AG 2003 All rights reserved. 2003/04
Page 42

PROFIBUS Interface Center
GND
GND
80286-System (X86-Mode)
SPC3
Clock -Generator
48 MHz
12/24 MHz
DIVIDER
CLK
80286
+
Buscontr.
(82288) +
82244
WR
RD
INTR
READYLogic
DB
AB
Reset
DB 15...0
Driver, Control-logic
EPROM
64kB
AB 23...0
RD WR
RAM
32kB
DB 7...0
AB 12...1
CSRAM
CSEPROM
Address
Decoder
CS
XWR
XRD
X/INT
XREADY
DB
(7..0)
AB
(10..0
XCS
Teiler
Mode
3K3
XCTS
SPC3
RTS
TxD
RxD
SPC3
Reset
1K
Page 40 V1.3 SPC3 Hardware Description
2003/04 Copyright (C) Siemens AG 2003. All rights reserved.
Page 43

SPC3 PROFIBUS Interface Center
7.1.4 Application with the 80 C 32
uC
uC
uC
uC
ADB(8:15)
uC
5
CLK
48 MHz
M
P5 XCS
P5 MODE
P5
P5
M
M
Px.x
ALE
XWR
XRD
AB8
AB9
AB10
AB11
AB12
AB13
AB14
AB15
1K
3k3
3k3
3k3
3k3
5V or
GND
1
1K
1K
8
36
1
23
24
2
4
34
35
3
44
43
41
40
37
42
32
31
29
25
XINT/MOT
RESET
ALE
XWR
XRD
XTEST0
XTEST1
DIVIDER
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
AB
SPC3
CLK2
XHOLDT.
XREADY
AB 10
X/INT
XCTS
RXD 30
RTS
TXD
DB
7
13
14
10
1K
9
33
27
26
0
11
1
12
2
15
3
16
4
19
5
20
6
21
7
22
1K
M
INT0/1
RXD
RTS
TXD
ADB0
ADB1
ADB2
ADB3
ADB4
ADB5
ADB6
ADB7
uC
RS485
RS485
RS485
DB(0:7)
uC
The pull up / pull down resistances in the drawing above are only relevant for a in circuit tester.The internal
chip select logic is activated when the address pins A 11 .. A 15 are set to „0“ . In the example above the
starting address of the SPC3 is set to 0x1000 .
Processor
ALE
AD 0 ..7
A8 .. 10
A 11..15 alle 0
Addreßlatch
AD 0 ..7
SPC 3
A 0..10
1,5 kByte RAM
in the SPC 3
CS
SPC3 Hardware Description V1.3 Page 41
Copyright (C) Siemens AG 2003 All rights reserved. 2003/04
Page 44
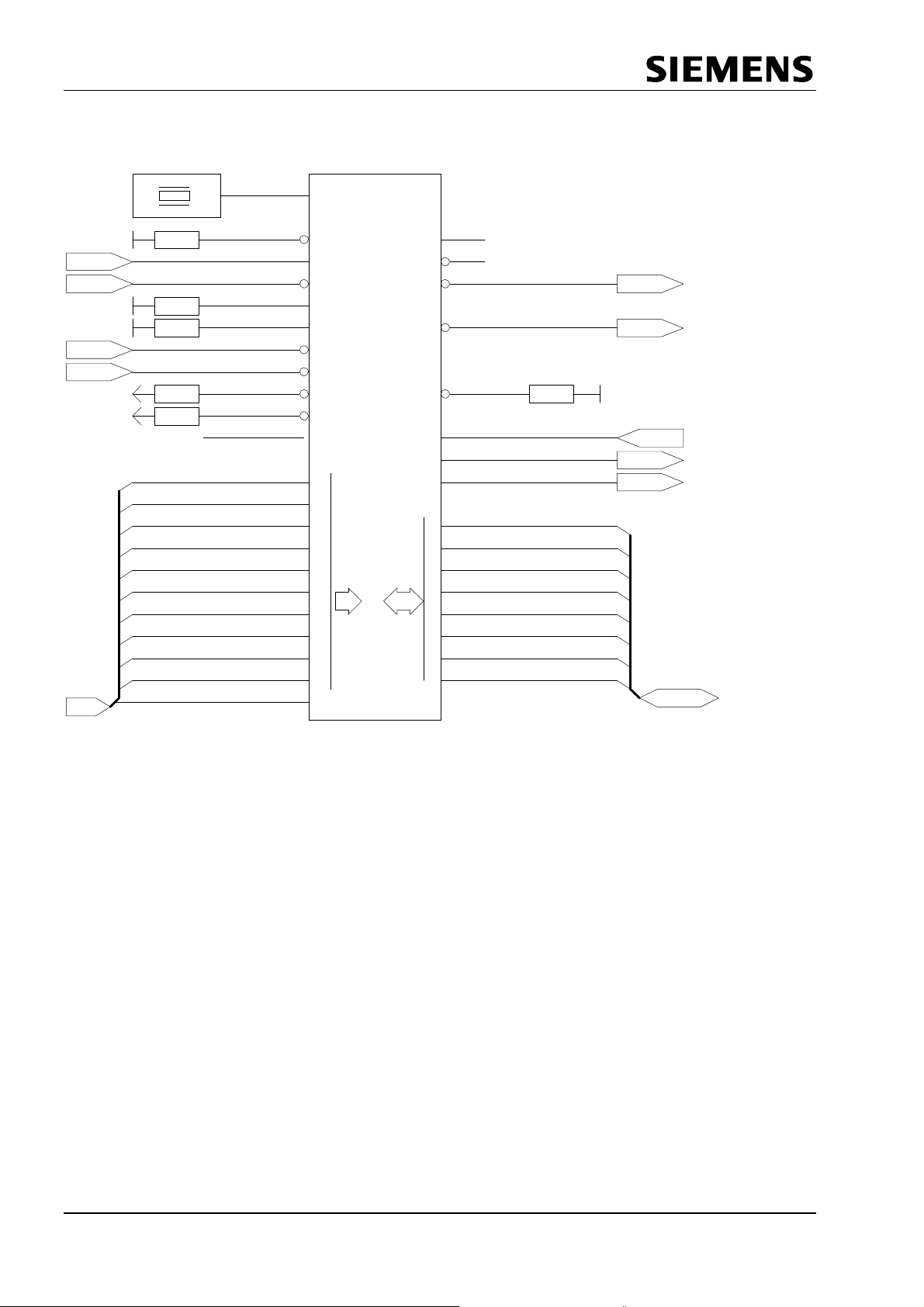
PROFIBUS Interface Center
SPC3
7.1.5 Application with th 80 C 165
uC
uC
uC
uC
uC
AB(0:10)
uC
48 MHz
M
M
M
P5
P5
1K
XSPC3CS
1K
1K
XWRL
XRD
3k3
3k3
5V or
ground
AB0
AB1
AB2
AB3
AB4
AB5
AB6
AB7
AB8
AB9
AB10 10
5
8
36
1
23
24
2
4
34
35
3
44
43
41
40
37
42
32
31
29
25
CLK
XINT/MOT
RESET
XCS
MODE
ALE
XWR
XRD
XTEST0
XTEST1
DIVIDER
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
AB
SPC3
CLK2
XDATAEX.
XREADY
XINT
XCTS
RXD 30
RTS
TXD
DB
7
13
14
9
33
27
26
0
11
1
12
2
15
3
16
4
19
5
20
6
21
7
22
1K
XREADY
XEXxIN
RXD
RTS
TXD
DB0
DB1
DB2
DB3
DB4
DB5
DB6
DB7
uC
uC
RS485
RS485
RS485
DB(0:7)
uC
The pull up / pull down resistances in the drawing above are only relevant for a in circuit tester.
Dual Port RAM Controller
The internal 1.5k RAM of the SPC3 is a Single Port RAM. Due to an integrated Dual Port RAM controller,
the controller, however, permits an almost simultaneous access of both ports (bus interface and
microsequencer interface). When there is a simultaneous access of both ports, the bus interface has
priority. This provides for the shortest possible access time. If SPC3 is connected to a microcontroller with
an asynchronous interface, SPC3 can evaluate the Ready signal.
Page 42 V1.3 SPC3 Hardware Description
2003/04 Copyright (C) Siemens AG 2003. All rights reserved.
Page 45

7.1.6 Interface Signals
The data bus outputs are high-resistance during the reset phase. All outputs are switched to high-resistance
in the test mode. (See block test.)
SPC3 PROFIBUS Interface Center
Name Input/
Output
DB(7..0) I/O Tristate High-resistance for RESET
AB(10..0) I AB(10) has a pull down resistor.
MODE I Setting: syn/async interface
XWR/E_CLOCK I Intel: Write /Motorola: E-Clk
XRD/R_W I Intel: Read /Motorola: Read/Write
XCS I Chip Select
ALE/AS I Intel/Motorola: Address Latch Enable
DIVIDER I Scaling factor 2/4 for CLKOUT 2/4
X/INT O Tristate Polarity programmable
XRDY/XDTACK O Tristate Intel/Motorola: Ready-Signal
CLK I 48 MHz
XINT/MOT I Setting: Intel/Motorola
CLKOUT2/4 O Tristate 24/12 MHz
RESET I Schmitt-Trigger Minimum of 4 clock pulse cycles
Figure 7.2: Microprocessor Bus Signals
Type Comments
7.2 UART
The transmitter converts the parallel data structure into a serial data flow. Request-to-Send (RTS) is
generated before the first character. The XCTS input is available for connecting a modem. After RTS
active, the transmitter must hold back the first telegram character until the XCTS modem activates.
The receiver converts the serial data flow into the parallel data structure. The receiver scans the serial data
flow with the four-fold transmission speed. Stop bit testing can be switched off for test purposes
(„DIS_STOP_CONTROL = 1“, in mode register 0 or ‘Set_Param-Telegram’ for DP). One requirement of the
PROFIBUS protocol is that no rest states are permitted between the telegram characters. The SPC3
transmitter ensures that this specification is maintained. This following start bit test is switched off with the
parameter setting „DIS_START_CONTROL = 1“ (in mode register 0 or ‘Set_Param telegram’ for DP).
Specified by the four-fold scan, a maximum distortion of the serial input signal of X = -47% to y = +22% is
permissible.
7.3 ASIC Test
All output pins and I/O pins can be switched in the high-resistance state via the XTESTO test pin. An
additional XTEST1 input is provided (more information upon request) to test the block internally with test
automatic devices (not in the target hardware environment!).
Pin No. Name Function
34 XTEST0 VSS (GND) All outputs high-resistance
VDD (+5V) Normal SPC3 function
35 XTEST1 VSS (GND) Various test modes
VDD (+5V) Normal SPC3 function
Figure 7.3: Test Support
XTEST0 and XTEST1 must be placed on VDD (+5V) via external pull-up resistors.
SPC3 Hardware Description V1.3 Page 43
Copyright (C) Siemens AG 2003 All rights reserved. 2003/04
Page 46

PROFIBUS Interface Center
Parameter
Designation
Unit
AMI-Vers.
ST-Vers.
AMI-Vers.
ST-Vers.
DD
I
Stg
0
0
0
C
(Soldering, 10 sec)
Parameter
Designation
Unit
AMI-Vers.
AMI-Vers.
DD
Schmitt-Trigger (CMOS)
IHC
ILC
DD
h
Schmitt-Trigger (TTL)
IHC
ILC
h
Parameter
Design.
Unit
AMI-Vers.
ST-Vers.
AMI-Vers.
ST-Vers.
AMI-Vers.
ST-Vers.
OLVDD
OLVDD
8 Technical Data
8.1 Maximum Limit Values
SPC3
Min Max
Supply Voltage V
Input Voltage
V
I
Input Current I
Storage Temperature T
Ambient Temperature TA -40
-0,3 -0,5 6 7 V
-0,3 -0,5 VDD+0,3
V
DD
-10 k.A. 10 k.A. mA
-55 -40 150 125
-40
85
85
Lead Temp. TL k.A k.A. 300 k.A.
Tabel 8.1: Maximum Limit Values
8.2 Permitted Operating Values
Min Max
Supply Voltage V
Input High Voltage
Input Low Voltage
ST-Vers.
4,5 4,75 5,5 5,25 V
V
IHC
V
ILC
0,7 V
DD
k.A. 0
0,7 V
DD
k.A.
0,3 V
DD
ST-Vers.
V
DD
0,3 V
DD
+0,5
V
C
C
V
V
Input High Voltage VP / V
Input Low Voltage Vn / V
Hysteresis Voltage V
Input High Voltage VP / V
Input Low Voltage Vn / V
Hysteresis Voltage V
k.A. k.A. 0,8 VDD 4 V
0,2 V
1 k.A. k.A. k.A. V
k.A. k.A. 2,1 2,4 V
0,7
0,4 k.A. k.A. k.A. V
Tabel 8. 2: -Permitted Operating Values
8.3 DC-Specifikation of the I/O- Drivers
Condition Min Max
Output High Voltage
Output High Voltage V
Output Low Voltage V
Output Low Voltage V
V
* at an output load of 4mA
** at an output load of 8mA
OH
OH
VDD=4,5V
VDD=4,5V
=4,5V
=4,5V
k.A.
k.A.
k.A.
k.A.
1 k.A. k.A. V
0,6
VDD-0.5 * VDD-0,5
3.65 ** VDD-0,5 k.A.
k.A.
k.A.
k.A.
k.A.
k.A.
k.A.
k.A.
0,4*
0,55**
k.A.
k.A.
0,4
0,4
V
V
V
V
V
Page 44 V1.3 SPC3 Hardware Description
2003/04 Copyright (C) Siemens AG 2003. All rights reserved.
Page 47

AMI-Vers.
AMI-Vers.
AMI-Vers.
Input capacity
CIN
n.c
510n.c.
n.c.pFOutput capacity
COUT
n.c
510n.c.
n.c.pFI/O-capacity
CI/O
n.c.
510n.c.
n.c.
pF
Signal lineeitung
Driver type
Unit
kap. Last
AMI-Vers.
ST-Vers.
DB(7:0)
Tristate
88mA
TXD
Tristate
88mA
RTS
Tristate
88mA
X/INT
Tristate
84mA
XREADY/XDSACK
Tristate
84mA
XDATAEXCH
Tristate
88mA
CLKOUT2/4
Tristate
88mA
SPC3 PROFIBUS Interface Center
Tabel 8.3: DC-Specifikation of the I/O- Drivers
ST-Vers.
n.c.
n.c.
n.c.
ST-Vers.
ST-Vers.
Tabel 8.4: Capacity of the I/O drivers
Parameter Des Min Max unit
Input leakage current
Tristate output leakage
I
I
IOZ
AMI-Vers.
-1
-10
ST-Vers.
-1
-10
AMI-Vers.
1
10
ST-Vers.
1
10
current
Tabelle 8.5: Leakage current of the output drivers
µA
µA
8.4 AC-Specification for the Output Drivers
Driver power
100pF
50pF
50pF
50pF
50pF
50pF
100pF
Hint:
The output power of the AMI-drivers is entspricht 8mA under the circumstances described in Tabel 8.3
Tabel 8.6: AC-Specifikation of the output drivers
SPC3 Hardware Description V1.3 Page 45
Copyright (C) Siemens AG 2003 All rights reserved. 2003/04
Page 48

PROFIBUS Interface Center
SPC3
8.5 Timing Characteristics
The following is generally applicable: All signals beginning with ‘X’ are ‘low active’.
All signal runtimes are based on the capacitive loads specified in the table above.
8.5.1 SYS Bus Interface
Clock Pulse:
No. Parameter MIN MAX Unit
Clock pulse 48 Mhz :
1 Clock High Time 6.25 14.6 ns
2 Clock Low Time 6.25 14.6 ns
3 Rise Time 4 ns
4 Fall Time 4 ns
Clock Pulse Timing:
TCLH TCLL
1
CLK
2,4V
0,6V
3 4
Distortions in the clock pulse signal are permitted up to a ratio of 40:60. At a threshold of 1.5 or 3.5 V:
Interrupts:
No. Parameter MIN MAX Unit
2
1 Interrupt Inactive Time (for EOI_Timebase = 0) 1 1
µs
Interrupt Inactive Time 1 1 ms
X/INT 1
EOI
After acknowledging an interrupt with EO1, a min. of 1 us or 1 ms is expected in SPC3 before a new
interrupt is output.
Page 46 V1.3 SPC3 Hardware Description
2003/04 Copyright (C) Siemens AG 2003. All rights reserved.
Page 49

SPC3 PROFIBUS Interface Center
Reset:
SPC3 requires a minimum of 400 clock pulse cycles during the reset phase so that it can be reset correctly.
Reset
8.5.2 Timing in the Synchronous C32-Mode:
If SPC3 is operated at 48MHz, an 80C32 with a maximum clock pulse rate of 20MHz can be connected.
In the C32 mode, SPC3 saves the least significant addresses with the negative edge of ALE. At the same
time, SPC3 expects the more significant address bits on the address bus. SPC3 generates a chipselect
signal from the more significant address bits. The request for an access to SPC3 is generated from the
negative edge of the read signal and from the positive edge of the write signal.
AMI-Vers.
ST-Vers.
No. Parameter Min Max Min Max Unit
1
Address to ALE ↓ Setuptime
2
Address (AB
3
XRD ↓ to Data Out (Zugriff auf RAM)
XRD ↓ to Data Out (Zugriff auf die Register)
4
ALE ↓ to XRD ↓
5
Data Holdtime after XRD ↑
6
Data Holdtime after XWR ↑
7
Data Setuptime to XWR ↑
8
XRD ↑ to ALE ↑
10 XRD-Pulse-Width 6T - 10
11 XWR-Pulse-Width 4T
12
Address-Holdtime after ALE ↓
13 ALE-Puls-Width 10
14 XRD, XWR Cycletime 6T + 30
15
ALE ↓ to XWR ↓
16
XWR ↑ to ALE ↑
) Holdtime after XRD ↑ or XWR ↑
8..15
10
5
4T + 5
(88,3)
4T + 18
(101,3)
20
2 6
10
10
10
10
20
10
10
5
3T+42.5
4T+20.2
20
3.1 10.2
10
10
10
6T
−
10
4T
10
10
6T + 30
20
10
(105)
(103,5)
Explanations:
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
T = Clock pulse cycle (48MHz)
TBD = to be defined
(1
= Access to the RAM
(2
= Access to the registers/latches
(3)
= for T = 48MHz
SPC3 Hardware Description V1.3 Page 47
Copyright (C) Siemens AG 2003 All rights reserved. 2003/04
Page 50

PROFIBUS Interface Center
13
1281
243510
14
AB(7..0
Synchronous Intel-Mode, Processor-Read-Timing
ALE
SPC3
AB(7..0)
DB(7..0)
Adressen
VALID
XRD
Synchronous Intel-Mode, Processor-Write-Timing
13
ALE
)
DB(7..0)
12
1
VALID
Data InAdressen
15
Data Out
16
67
VALID
Adressen
XWR = log.'1'
2
VALID
Adressen
XWR
11
14
XRD = log.'1'
Page 48 V1.3 SPC3 Hardware Description
2003/04 Copyright (C) Siemens AG 2003. All rights reserved.
Page 51

SPC3 PROFIBUS Interface Center
8.5.3 Timing in the Asynchronous Intel Mode (X86 Mode) :
In 80X86 operation, SPC3 acts like memory with ready logic. The access times depend on the type of
accesses.
The request for an access to SPC3 is generated from the negative edge of the read signal or the positive
edge of the write signal.
SPC3 generates the Ready signal synchronously to the fed in pulse. The Ready signal is reset when the
read signal or write signal is deactivated. The data bus is switched to the Tristate with XRD = 1.
AMI-Vers.
ST-Vers.
No. Parameter Min Max Min Max Unit
20
Address-Setuptime to RXD ↓ or XWR ↓
21
XRD ↓ to Data valid (Zugriff auf RAM)
XRD ↓ to Data valid (Zugriff auf die Register)
22
Address (AB
23
XCS ↓ Setuptime to XRD ↓ or XWR ↓
24 XRD-Puls-Width 6T – 10
25
Data Holdtime after XRD ↑
26 Read/Write-Inactive-Time 10
27
XCS Holdtime after XRD ↑ or XWR ↑
28
XRD/XWR ↓ to XRDY ↓ (Normal Ready)
29
XRD/XWR ↓ to XRDY ↓ (Early Ready)
30 XREADY-Holdtime after XRD or XWR 4.3 12.8
31
Data Setuptime to XWR ↑
32
Data Holdtime after XWR ↑
33 XWR-Pulse-Width * 4T
34 XRD, XWR Cycletime 6T
35
last XRD
36
XCS
to next XWR
37
to next XWR (XCS don’t care)
XWR
) Holdtime after XRD or XWR ↑
10..0
to XCS
0
4T+5
(88,3)
4T+18
(101,3)
0
- 5
(115)
2 6
0
4T + 5 5T+ 14
3T + 5 4T+ 14
10
10
4T + 10
2T + 10
6T
0
3T+42.5
4T+20.2
0
-5
6T
−
10
(115)
3.1 10.2
10
0
5T + 16
4T + 12
6 22
10
10
4T
6T
4T + 10
2T + 10
6T
(105)
(103,5)
Explanations:
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
T = Clock pulse cycle (48MHz)
TBD = to be defined
(1
= Access to the RAM
(2
= Access to the registers/latches
(3
= For T = 48 MHz
SPC3 Hardware Description V1.3 Page 49
Copyright (C) Siemens AG 2003 All rights reserved. 2003/04
Page 52

PROFIBUS Interface Center
XREADY
XREADY
Asynchronous Intel-Mode, Processor-Read-Timing
SPC3
AB(10..0)
VALID
20
21
DB(7..0)
XRD
35
23
XCS
(normal)
28
29
(early)
Asynchronous Intel-Mode, Processor-Write-Timing
Data Out
24
22
25
26
27
30
34
XWR = log.'1'
AB(10..0)
DB(7..0)
XWR
XCS
XREADY
(normal)
VALID
20
26
22
Data In
31
33
23
28
29
32
27
30
36
XREADY
(early)
34
37
XRD = log.'1'
8.5.4 Timing in the Synchronous Motorola Mode (E_Clock-Mode, for example, 68HC11) :
For a CPU clockline through the SPC3, the output clock pulse (CLKOUT2/4) must be 4 times larger than the
E_CLOCK. That is, a clock pulse signal must be present at the CLK input that is at least 10 times larger
than the desired system clock pulse (E_CLOCK). The Divider-Pin must be placed on <log. 0> (divider 4).
This results in an E_CLOCK of 3MHz.
Page 50 V1.3 SPC3 Hardware Description
2003/04 Copyright (C) Siemens AG 2003. All rights reserved.
Page 53

8.5.4.1.1.1
T +
SPC3 PROFIBUS Interface Center
The request for a read access to SPC3 is derived from the positive edge of the E clock (in addition: XCS =
0, R W = 1). The request for a write access is derived from the negative edge of the E clock (in addition:
XCS = 0, R W = 0).
AMI-Vers.
ST-Vers.
No. Parameter Min Max Min Max Unit
40 E_Clock-Pulse-Width
3T + 74.2
74.2
41
Address (AB
42
Address (AB
43
E_Clock ↑ to Data Active Delay
44
E_Clock ↑ to Data valid (Zugriff auf RAM)
E_Clock ↑ to Data valid (Zugriff auf die Register)
45
Data Holdtime after E_Clock ↓
46
R_W Setuptime to E_Clock ↑
47
R_W Holdtime after E_Clock ↓
48
XCS Setuptime to E_Clock ↑
49
XCS Holdtime after E_Clock ↓
50
Data Setuptime to E_Clock ↓
51
Data Holdtime after E_Clock ↓
Explanations:
) Setuptime to E_Clock ↑
10..0
) Holdtime after E_Clock ↓
10..0
10
5
5.7 17
4T + 5
(88,3)
4T + 18
(101,3)
2 6.3
10
5
0
0
10
10
10
5
5
3T + 44.2
(107)
4T + 21.9
(105,2)
4 12
10
5
0
0
10
10
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
T = Clock pulse cycle (48MHz)
TBD = to be defined
(1
= Access to the RAM
(2
= Access to the registers/latches
(3
= For T = 48 MHz
Synchronous Motorola-Mode, Processor-Read-Timing
E_Clock
41
AB(10..0)
43
DB(7..0)
46
R_W
48 49
XCS
44
VALID
Data Invalid
40
42
45
Data Valid
47
AS = log.'1'
SPC3 Hardware Description V1.3 Page 51
Copyright (C) Siemens AG 2003 All rights reserved. 2003/04
Page 54

PROFIBUS Interface Center
SPC3
Synchronous Motorola-Mode, Processor-Write-Timing
E_Clock
41
40
42
AB(10..0)
DB(7..0)
46
VALID
50 51
Data Valid
47
R_W
48
49
XCS
AS = log.'1'
8.5.5 Timing in the Asynchronous Motorola-Mode (for example, 68HC16) :
In the asynchronous Motorola mode, the SPC3 acts like memory with Ready logic, whereby the access
times depend on the type of accesses.
The request for an access of SPC3 is generated from the positive edge of the AS signal (in addition:
XCS=´0´, R_W=´1´). The request for a write access is generated from the positive edge of the AS signal (in
addition: XCS=´0´, R_W=´0´).
AMI-Vers.
ST-Vers.
No. Parameter Min Max Min Max Unit
60
Address-Setuptime to AS ↓
61
AS ↓ to Data valid (Zugriff auf RAM)
AS ↓ to Data valid (Zugriff auf die Register)
62
Address (AB
63
R_W ↓ Setuptime to AS ↓
64 AS-Puls-Width (Read) 6T - 10
65
Data Holdtime after AS ↑
66 AS-Inactive-Time 10
67
R_W Holdtime after AS ↑
68
XCS ↓ Setuptime to AS ↓
69
XCS Holdtime after AS ↑
70
AS ↓ to XDSACK ↓ (Read, Normal Ready)
71
AS ↓ to XDSACK ↓ (Read, Early Ready)
72
XDSACK-Holdtime after AS ↑
73 AS Cycletime 6T
74
Data Setuptime to AS ↑
75
Data Holdtime after AS ↑
76 AS-Pulse-Width (Write) * 4T
77
last AS
78
79
to next AS (Write)
XCS
AS
to next AS (Write, XCS don’t care)
) Holdtime after AS ↑
10..0
(Read) to XCS
0
4T + 5
(88,3)
4T + 18
(101,3)
10
10
2 6.3
10
-5
0
4T + 5 5T + 14
3T + 5 4T + 14
4.3 12.7
10
10
4T + 10
2T + 10
6T
0
3T + 45.2
4T + 22.9
10
10
6T
−
10
4 12
10
10
-5
0
5T + 16
4T + 16
6 22
6T
10
10
4T
4T + 10
2T + 10
6T
(108)
(106,2)
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
Explanations:
Page 52 V1.3 SPC3 Hardware Description
2003/04 Copyright (C) Siemens AG 2003. All rights reserved.
Page 55

SPC3 PROFIBUS Interface Center
T = Pulse cycle (48MHz)
TBD = To Be Defined
(1
= Access to the RAM
(2
= Access to the register/latches
(3
= For T = 48MHz
Asynchronous Motorola-Mode, Processor-Read-Timing
AB(10..0)
DB(7..0)
AS
VALID
60
61
Data Out
63
64
R_W
6877
XCS
XDSACK
(normal)
70
71
XDSACK
(early)
Asynchronous Motorola-Mode, Processor-Write-Timing
62
65
66
67
69
72
73
E_Clock = log.'0'
DB(7..0)
R_W
XCS
XDSACK
(normal)
XDSACK
(early)
AS
VALID
60
66
62
Data In
74
76
63
68
70
71
73
75
67
69
72
79
E_Clock = log.'0'
78
SPC3 Hardware Description V1.3 Page 53
Copyright (C) Siemens AG 2003 All rights reserved. 2003/04
Page 56

PROFIBUS Interface Center
SPC3
8.5.6 Serial Bus Interface
No. Parameter MIN MAX Unit
1
2
Pulse 48 MHz:
RTS ↑ to TxD Setup Time
RTS ↓ to TxD Hold Token
T = Clock pulse cycle (48MHz)
RTS
1 2
TxD
4T
4T
Page 54 V1.3 SPC3 Hardware Description
2003/04 Copyright (C) Siemens AG 2003. All rights reserved.
Page 57

8.5.7 Housing
PQFP-44 Housing
SPC3 PROFIBUS Interface Center
SPC3 Hardware Description V1.3 Page 55
Copyright (C) Siemens AG 2003 All rights reserved. 2003/04
Page 58

PROFIBUS Interface Center
Symbol
AMI-Vers.
A A1 0.10
A2 1.95
D 13.65
D1 9.90
E 13.65
E1 9.90
L 0.65
e BASIC -
B 0.30
c 0.13
αααα°
ββββ°
γγγγ°
G 0.13
H -
J -
K 0.40
2H (Footprint) -
Min Typ Max
12
0
0
ST-Vers.
-
0.25
1.90
13.65
9.90
13.65
9.90
0.78
-
0.30
-
0
1
-
-
-
-
-
SPC3
AMI-Vers.
2.13
0.15
2.00
13.90
10.00
13.90
10.00
0.80
0.80
-
-
-
-
-
-
1.95
0.30
-
3.90
ST-Vers.
-
-
2.00
13.90
10.00
13.90
10.00
0.88
0.80
0.35
-
10
-
5
0.20
-
0.30
-
3.90
AMI-Vers.
2.35
0.25
2.10
14.15
10.10
14.15
10.10
0.95
-
0.45
0.23
16
7
-
-
-
-
-
-
ST-Vers.
2.45
-
2.10
14.15
10.10
14.15
10.10
1.03
-
0.40
0.17
7
9
-
-
-
-
-
8.5.8 Processing Instructions
ESD protective measures must be maintained for all electronic components.
SPC3 is a cracking-endangered component that must be handled as such.
A drying process must be carried out before SPC3 is processed. The component must be dried at 125o C
for 24 hours and then be processed within 48 hours. This drying process may be carried out once only
because the component is soldered.
It must also be ensured that the SPC3’s connections are not bent. Flawless processing can be guaranteed
only if a planity of less than 0.1 mm is ensured. SPC3 is released for infrared soldering with a soldering
profile according to CECC00802.
Page 56 V1.3 SPC3 Hardware Description
2003/04 Copyright (C) Siemens AG 2003. All rights reserved.
Page 59

SPC3 PROFIBUS Interface Center
9 PROFIBUS Interface
9.1 Pin Assignment
The data transmission is performed in RS 485 operating mode (i.e., physical RS 485).
The SPC3 is connected via the following signals to the galvanically isolated interface drivers.
Signal Name Input/
Output
RTS Output Request to send
TXD Output Sending data
RXD Input Receiving data
The PROFIBUS interface is a 9-way, sub D, plug connector with the following pin assignment.
Pin 1 - Free
Pin 2 - Free
Pin 3 - B line
Pin 4 - Request to send (RTS)
Pin 5 - Ground 5V (M5)
Pin 6 - Potential 5V (floating P5)
Pin 7 - Free
Pin 8 - A line
Pin 9 - Free
The cable shield must be connected to the plug connector housing.
The free pins are described as optional in EN 50170 Vol. 2. If used, they should conform to the
specifications in DIN192453.
CAUTION:
The designations A and B of the lines on the plug connector refer to the designations in the RS 485
standard, and not the pin designation of driver ICs.
Keep the cable from driver to connector as short as possible.
Use of higher baud rates )i.e., 3 to 12 Mbaud) requires the use of new plug connectors. These connectors
compensate for line interferences on all possible combinations of cables.
6ES7 972-0BB10-0XA0 with PG socket
6ES7 972-0BA10-0XA0 without PG socket
Function
SPC3 Hardware Description V1.3 Page 57
Copyright (C) Siemens AG 2003 All rights reserved. 2003/04
Page 60

PROFIBUS Interface Center
9.2 Example for the RS 485 Interface
SPC3
2
1
100
K
R
0
0
3
2
3
1
C
H
&
4
7
2
HCPL0601
R
0
0
3
EN
M
2P5
300R
680R
680R
2P5
U+
EN1
SN65ALS1176
2
K
1
n
8
6
2M
2P5
2M
68n
680R
U-
U+
EN
T
U
O
HCPL7101 / 7721 / 0721
U+
U-
IN
5
6
7
3
4
e
n
S
i
l
B
GND
5
M
T
P
2
R
2
1
1
2
EN2
R
0
8
6
2P5
1K2
68n
U+
HCPL7101 / 7721 / 0721
U+
9
8
e
n
i
l
A
100
K
2M
V
2
>
e
g
a
t
l
:
o
t
v
c
l
e
a
l
i
t
e
n
s
e
r
r
e
e
v
f
i
f
i
r
D
D
s
u
b
o
t
n
o
i
t
a
l
o
s
i
l
a
c
i
r
t
c
e
l
e
:
t
n
a
t
r
o
p
m
I
d
l
e
i
h
S
5
P
2
d
n
a
5
P
2M
.
e
1
M
F
n
2
2
.
V
.
0
2
.
0
2
5
U-
IN
T
U
U-
EN
O
l
b
i
s
s
o
p
s
a
t
r
o
h
s
s
a
t
p
e
k
e
b
t
s
u
m
s
e
n
i
l
:
t
u
o
y
a
L
R
M
n
8
6
M
R
0
0
3
S
T
R
S
T
C
P5
20K
D
X
T
P5
0
8
6
n
8
6
M
D
X
R
Explanations of the circuitry:
The bus driver input EN2 has to be connected to low potential to ensure that after transmission of a
telegram the ASIC is able to listen to the transmitted data.
To minimize the capacity of the bus lines the user should avoid additional capacities. The typical capacity of
a bus station should be 15 ... 25 pF.
Page 58 V1.3 SPC3 Hardware Description
2003/04 Copyright (C) Siemens AG 2003. All rights reserved.
Page 61

SPC3 PROFIBUS Interface Center
10 Appendix
10.1 Addresses
PROFIBUS User Organisation
PNO
Office
Mr. Dr. Wenzel
Haid- und Neu- Straße 7
76131 Karlsruhe
Tel.: (0721) 9658-590
Technical contact person at ComDeC in Germany
Siemens AG
A&D SE RD73
Mr. Putschky
Address:
Postfach 2355
90713 Fürth
Tel.: (0911) 750 - 2078
Fax: (0911) 750 - 2100
email: Gerd.Putschky@siemens.com
Technical contact person at the PROFIBUS Interface Center in the United States
PROFIBUS Interface Center
One Internet Plaza
PO Box 4991
Johnson City, TN 37602-4991
Fax : (423) - 262 - 2103
Your Partner: Ron Mitchell
Tel.: (423) - 262 - 2687
email: Ron.Mitchell@sea.siemens.com
SPC3 Hardware Description V1.3 Page 59
Copyright (C) Siemens AG 2003 All rights reserved. 2003/04
Page 62

PROFIBUS Interface Center
SPC3
10.2 General Definition of Terms
ASPC2 Advanced Siemens PROFIBUS Controller, 2nd generation
SPC2 Siemens PROFIBUS Controller, 2nd generation
SPC3 Siemens PROFIBUS Controller, 3rd generation
SPM2 Siemens PROFIBUS Multiplexer, 2nd generation
LSPM2 Lean Siemens PROFIBUS Multiplexer, 2nd generation
DP Distributed I/Os
FMS Fieldbus Message Specification
MS MicroSequenzer
SM State Machine
10.3 Ordering of ASICs
For Ordering SPC3 ASICs please refer to your contact person in the Siemens local branch office and use
one of the ordering numbers depending on the amount you want to order.
10.3.1 SPC3 (AMI)
ASIC SPC 3 6ES7 195-0BD02-0XA0 Small amount 5
(STEP C) 6ES7 195-0BD12-0XA0 Single-Tray 96
6ES7 195-0BD22-0XA0 Tray-Box 576
6ES7 195-0BD32-0XA0 8 Tray-Box 4608
6ES7 195-0BD42-0XA0 17 Tray-Box 9792
10.3.2 SPC3 (ST)
ASIC SPC 3 6ES7 195-0BD01-0XA0 Kleinverpack. 5
(STEP C) 6ES7 195-0BD11-0XA0 Einzel-Tray 96
6ES7 195-0BD21-0XA0 Tray-Box 576
6ES7 195-0BD31-0XA0 8 Tray-Box 4608
6ES7 195-0BD41-0XA0 17 Tray-Box 9792
Page 60 V1.3 SPC3 Hardware Description
2003/04 Copyright (C) Siemens AG 2003. All rights reserved.
Page 63

SPC3 PROFIBUS Interface Center
11 Appendix A: Diagnostics Processing in PROFIBUS DP
11.1 Introduction
PROFIBUS DP offers a convenient and multi-layer possibility for processing diagnostics messages on the
basis of error states.
As soon as a diagnostics request is required, the slave will respond in the current data exchange with a high
priority reply message. In the next bus cycle, the master then requests a diagnostics from this slave,
instead of executing normal data exchange.
Likewise, any master (not only the assigned master!) can request a diagnostics from the slave. The
diagnostics information of the DP slave consists of standard diagnostics information (6 bytes), and can be
supplemented by user-specific diagnostics information.
In the case of the ASICs, SPM2, and LSPM2, extensive diagnostics is possible through corresponding
wiring. In the case of the intelligent SPCx solution, adapted and convenient diagnostics processing can be
carried out through programming.
11.2 Diagnostics Bits and Expanded Diagnostics
Parts of the standard diagnostics information are permanently specified in the firmware and in the microprogram of the ASICs through the state machine.
Request diagnostics only once („update_diag(..)“) if an error is present or changes. By no means should
diagnostics be requested cyclically in the data exchange state; otherwise, the system will be burdened by
redundant data.
Three information bits can be influenced by the application:
11.2.1 STAT_DIAG
Because of a state in the application, the slave can’t make valid data available. Consequently, the master
only requests diagnostics information until this bit is removed again. The PROFIBUS DP state is, however,
Data_Exchange, so that immediately after the cancellation of the static diagnostics, data exchange can
start.
Example: failure of supply voltage for the output drivers
11.2.2 EXT_DIAG
If this bit is set, a diagnostics entry must be present in the user-specific diagnostics area. If this bit is not
set, a status message can be present in the user-specific diagnostics area.
User-Specific Diagnostics
The user-specific diagnostics can be filed in three different formats:
Device-Specific Diagnostics:
The diagnostics information can be coded as required.
Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5-0
Header Byte
Diagnostics Field Coding of diagnostics is device-specific
..... Can be specified as required
SPC3 Hardware Description V1.3 Page 61
Copyright (C) Siemens AG 2003 All rights reserved. 2003/04
0 0
Block length in bytes, including header
Page 64

PROFIBUS Interface Center
Identifier-Related Diagnostics:
For each identifier byte assigned during configuration (for example, 0 x 10 for 1 byte input), a bit is
reserved.
In the case of a modular system with an identifier byte each per module, module-specific diagnostics can be
indicated. One bit respectively will then indicate diagnostics per module.
Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5-0
Header Byte
Bit Structure 1 1
Identifier Byte 7 has etc. Identifier Byte 0 has
diagnostics diagnostics
Channel-Related Diagnostics:
In this block, the diagnosed channels and the diagnostics cause are entered in sequence. Three bits are
required per entry.
Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 - 0
Header Byte
Channel Number Coding
Type of Diagnostics Coding
Coding of the error type is in part manufacturer-specific; other codings are specified in the Standard.
0 1
1 0
Input/Output
Channel Type
Block length in bytes including header
Identification Number
Channel Number
Coding
Error Type
SPC3
Example:
0 0 0 1 0 0
0 0
Device-specific Meaning of the bits
diagnostics field of is specified
length 3 manufacturer-specific.
0 0 0 1 0 1
0 1
1 Identification number 0 has diagnostics.
1
1 Identification number 18 has diagnostics.
0 0 0 0 0 0
1 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 Channel 2.
0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 Overload, channel organized bit by bit.
0 0 1 1 0 0
1 0
0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 Channel 6.
1 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 Upper limit evalue xceeded, channel organized word by word.
Status
If the Bit EXT_DIAG is set to 0 , data is viewed as status info from the system view. f.e. cancellation of the
error triggering the diagnostics.
Device-related diagnostics.
Identifier-related diagnostics.
Channel-related diagnostics, identification number 0.
Channel-related diagnostics identification number 12.
Page 62 V1.3 SPC3 Hardware Description
2003/04 Copyright (C) Siemens AG 2003. All rights reserved.
Page 65

11.2.3 EXT_DIAG_OVERFLOW
This bit is set if more diagnostics data is present than will fit in the available diagnostics data area. For
example, more channel diagnostics could be present than the send buffer or the receive buffer makes
possible.
SPC3 PROFIBUS Interface Center
11.3 Diagnostics Processing from the System View
Inasmuch as it is bus-specific, the diagnostics information of the slaves is managed solely by the master
interface (for example, IM308B).
All diagnostics from the application are made available to the S6 program via corresponding data bytes. If
the External Diagnostics bit is set, the slaves to be diagnosed can already be evaluated in the diagnostics
overview. Then, a special error routine can be called up, whereby the standard diagnostics information and
the user-specific information can be evaluated.
After eliminating the current diagnostics situation, this can be signalled as a status message from the slave
without setting the external diagnostics bit.
With the COM ET200, a comfortable diagnostics tool is available on-line. At the present time, identificationrelated diagnostics information can be displayed with it in plain text. In later phases, channel-related
diagnostics will also be supported. User-specific diagnostics are only displayed if the EXT_DIAG bit is set.
The figure below shows a screen during data processing, for example:
Set Program File C:PNO4..ET.200 SIMATIC S5 / COM ET 200
SINGLE DIAGNOSTICS
Station Number: 30 Station Type: ET 200U-
COMBI
Station Designation: Station4
Station Status: Slave not ready for data
exchange
External diagnostics
Configuration error
Device-Related Diagnostics
KH = 01
Identification-Related
Diagnostics
Slot
3
Active
F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 F8
In the type file for the COM ET200 and in the GSD [device master data] file, fields are already provided for
referencing device-specific bits and pertinent plain text messages (for example, Bit 7: „I have had it; good
night!“).
EXIT
SPC3 Hardware Description V1.3 Page 63
Copyright (C) Siemens AG 2003 All rights reserved. 2003/04
Page 66

PROFIBUS Interface Center
SPC3
12 Appendix B: Useful Information
12.1 Data format in the Siemens PLC SIMATIC
The SPC3 always sends data from the beginning of the buffer till the end. 16Bit values are shown in the
Motorola format. For example:
Buffer pointer high byte
Buffer pointer +1 low byte
Page 64 V1.3 SPC3 Hardware Description
2003/04 Copyright (C) Siemens AG 2003. All rights reserved.
Page 67

Page 68

Siemens AG
Division Automation Engineering
Combination Engineering
PO Box 23 55, D-90713 Fuerth/Germany
SIEMENS Aktiengesellschaft
Siemens AG
Subject to change without prior notice
Printed in the Fed. Rep. of Germany
 Loading...
Loading...