Siemens SIMATIC PROFINET Function Manual


PROFINET with STEP 7 V14
___________________
___________________
___________________
___________________
___________________
___________________
SIMATIC
PROFINET
PROFINET with STEP 7 V14
Function Manual
09/2016
A5E03444486
Preface
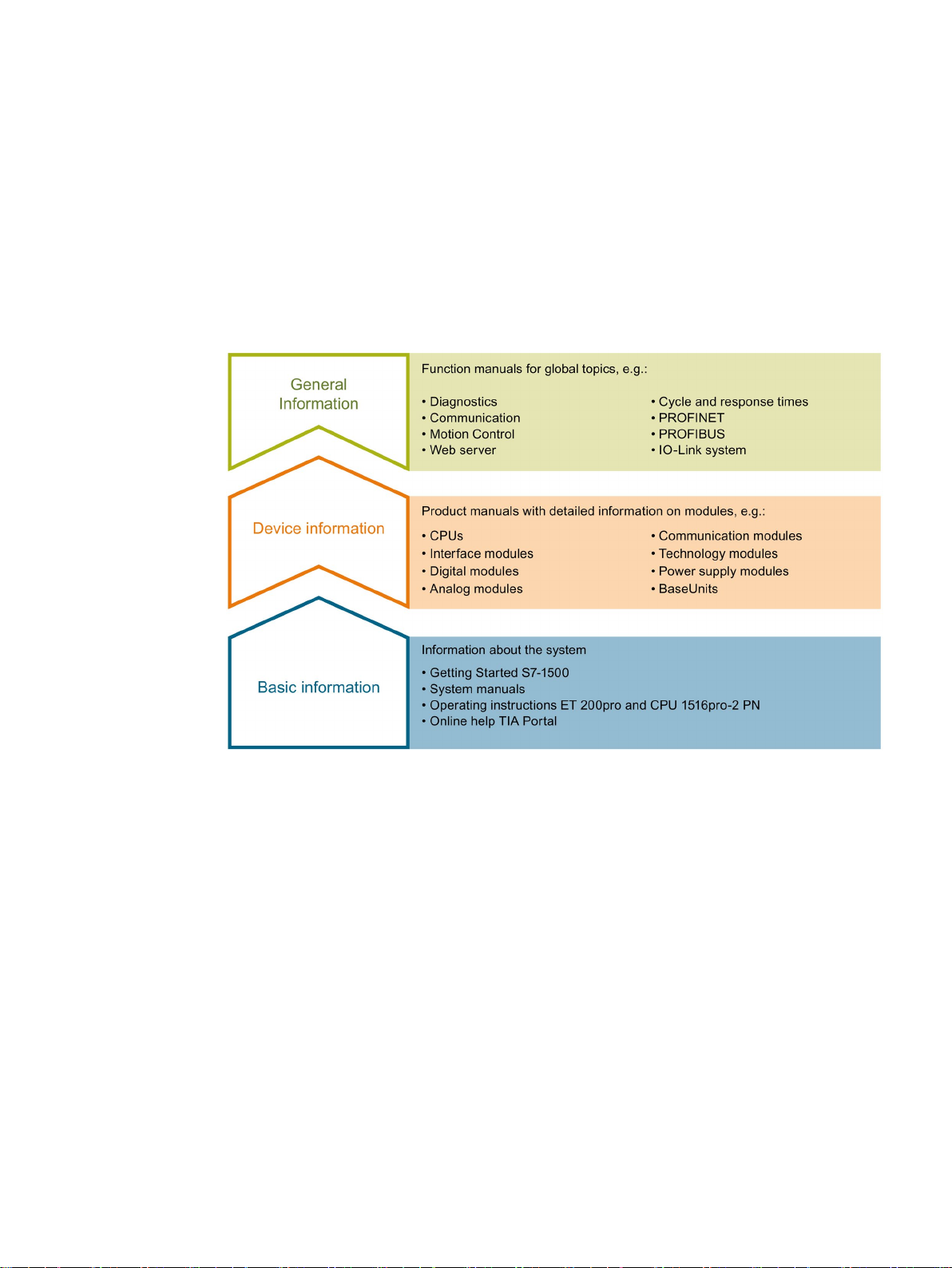
Documentation guide
1
Description
2
Parameter
assignment/addressing
3
Diagnostics
4
Functions
5
-AG

Siemens AG
Division Digital Factory
Postfach 48 48
90026 NÜRNBERG
GERMANY
A5E03444486-AG
Ⓟ
Copyright © Siemens AG 2013 - 2016.
All rights reserved
Legal information
Warning notice system
DANGER
indicates that death or severe personal injury will result if proper precautions are not taken.
WARNING
indicates that death or severe personal injury may result if proper precautions are not taken.
CAUTION
indicates that minor personal injury can result if proper precautions are not taken.
NOTICE
indicates that property damage can result if proper precautions are not taken.
Qualified Personnel
personnel qualified
Proper use of Siemens products
WARNING
Siemens products may only be used for the applications described in the catalog and in the relevant technical
ambient conditions must be complied with. The information in the relevant documentation must be observed.
Trademarks
Disclaimer of Liability
This manual contains notices you have to observe in order to ensure your personal safety, as well as to prevent
damage to property. The notices referring to your personal safety are highlighted in the manual by a safety alert
symbol, notices referring only to property damage have no safety alert symbol. These notices shown below are
graded according to the degree of danger.
If more than one degree of danger is present, the warning notice representing the highest degree of danger will
be used. A notice warning of injury to persons with a safety alert symbol may also include a warning relating to
property damage.
The product/system described in this documentation may be operated only by
task in accordance with the relevant documentation, in particular its warning notices and safety instructions.
Qualified personnel are those who, based on their training and experience, are capable of identifying risks and
avoiding potential hazards when working with these products/systems.
Note the following:
documentation. If products and components from other manufacturers are used, these must be recommended
or approved by Siemens. Proper transport, storage, installation, assembly, commissioning, operation and
maintenance are required to ensure that the products operate safely and without any problems. The permissible
All names identified by ® are registered trademarks of Siemens AG. The remaining trademarks in this publication
may be trademarks whose use by third parties for their own purposes could violate the rights of the owner.
We have reviewed the contents of this publication to ensure consistency with the hardware and software
described. Since variance cannot be precluded entirely, we cannot guarantee full consistency. However, the
information in this publication is reviewed regularly and any necessary corrections are included in subsequent
editions.
for the specific
08/2016 Subject to change

Preface
Purpose of the documentation
Basic knowledge required
Scope
This function manual provides an overview of the PROFINET communication system with
SIMATIC STEP 7 V14.
STEP 7 V14 is integrated into the powerful graphical Totally Integrated Automation Portal
(TIA Portal), the new integration platform for all automation software tools.
This function manual supports you in planning a PROFINET system. The manual is
structured into the following subject areas:
● PROFINET basics
● PROFINET diagnostics
● PROFINET functions
The following knowledge is required in order to understand the manual:
● General knowledge of automation technology
● Knowledge of the industrial automation system SIMATIC
● Knowledge about the use of Windows-based computers
● Knowledge about how to use STEP 7 (TIA Portal)
This documentation is the basic documentation for all SIMATIC products from the
PROFINET environment. The product documentation is based on this documentation.
The examples are based on the functionality of the S7-1500 automation system.
PROFINET with STEP 7 V14
4 Function Manual, 09/2016, A5E03444486-AG
Preface
Changes compared to previous version
Function
Applications
User benefits
line.
processing.
By sending the cyclic IO data in both directions in
with MRP.
performance.
demand.
Conventions
STEP 7:
Note
A note contains important information on the product, on handling of the product and on the
section of the documentation to which you
See also
This manual encompasses the following new functions compared to the previous version
(version 12/2014):
PROFINET IO on the 2nd
PROFINET interface
IRT with very short data cycle
times down to 125 µs
MRPD: Media Redundancy
with Planned Duplication of
frames
PROFINET performance
upgrade
Limitation of the data infeed
into the network
You can operate another
PROFINET IO system on the CPU or
connect additional IO devices.
You realize high-end applications with
IO communication which place very
high performance demands on the IO
PROFINET IO IRT enables you to
realize applications that place particularly high demands on the reliability
and accuracy (isochronous mode).
You can implement applications with
high speed and send clock requirements. This is interesting for applications with high demands on
You limit the network load for standard
Ethernet communication to a maximum
value.
You use a fieldbus type in the plant.
The CPU can perform fast and deterministic data
exchange as an I-device with a higher-level controller (PROFINET/Ethernet) through the second
You make PROFINET IO communication and
standard communication possible via one cable
even with a send clock of 125 µs.
the ring, the communication to the IO devices is
maintained even when the ring is interrupted and
does not result in device failure even with fast
update times. You achieve higher reliability than
Better utilization of the bandwidth results in short
reaction times.
You flatten peaks in the data feed.
You share the remaining bandwidth based on
programming software "STEP 7 as of V12 (TIA Portal)" and subsequent versions.
This documentation contains pictures of the devices described. The figures may differ
slightly from the device supplied.
You should also pay particular attention to notes such as the one shown below:
We refer to "STEP 7" in this documentation as a synonym for the configuration and
should pay particular attention.
PRODIS (http://www.siemens.com/simatic-tech-doku-portal)
Catalog (http://mall.industry.siemens.com)
PROFINET with STEP 7 V14
Function Manual, 09/2016, A5E03444486-AG
5
Preface
Security information
Siemens Industry Online Support
Product support
Application examples
Services
Forums
mySupport
Siemens provides products and solutions with industrial security functions that support the
secure operation of plants, systems, machines and networks.
In order to protect plants, systems, machines and networks against cyber threats, it is
necessary to implement – and continuously maintain – a holistic, state-of-the-art industrial
security concept. Siemens’ products and solutions only form one element of such a concept.
Customer is responsible to prevent unauthorized access to its plants, systems, machines
and networks. Systems, machines and components should only be connected to the
enterprise network or the internet if and to the extent necessary and with appropriate security
measures (e.g. use of firewalls and network segmentation) in place.
Additionally, Siemens’ guidance on appropriate security measures should be taken into
account. For more information about industrial security, please visit
(http://www.siemens.com/industrialsecurity
Siemens’ products and solutions undergo continuous development to make them more
secure. Siemens strongly recommends to apply product updates as soon as available and to
always use the latest product versions. Use of product versions that are no longer supported,
and failure to apply latest updates may increase customer’s exposure to cyber threats.
).
To stay informed about product updates, subscribe to the Siemens Industrial Security RSS
Feed under (http://www.siemens.com/industrialsecurity
You can find current information on the following topics quickly and easily here:
●
All the information and extensive know-how on your product, technical specifications,
FAQs, certificates, downloads, and manuals.
●
Tools and examples to solve your automation tasks – as well as function blocks,
performance information and videos.
●
Information about Industry Services, Field Services, Technical Support, spare parts and
training offers.
●
For answers and solutions concerning automation technology.
●
Your personal working area in Industry Online Support for messages, support queries,
and configurable documents.
).
This information is provided by the Siemens Industry Online Support in the Internet
(http://www.siemens.com/automation/service&support
PROFINET with STEP 7 V14
6 Function Manual, 09/2016, A5E03444486-AG
).

Preface
Industry Mall
The Industry Mall is the catalog and order system of Siemens AG for automation and drive
solutions on the basis of Totally Integrated Automation (TIA) and Totally Integrated Power
(TIP).
Catalogs for all the products in automation and drives are available on the Internet
(https://mall.industry.siemens.com
).
PROFINET with STEP 7 V14
Function Manual, 09/2016, A5E03444486-AG
7

Table of contents
Preface ................................................................................................................................................... 4
1 Documentation guide ............................................................................................................................ 11
2 Description ............................................................................................................................................ 15
3 Parameter assignment/addressing ........................................................................................................ 41
4 Diagnostics ........................................................................................................................................... 69
2.1 Introduction to PROFINET ..................................................................................................... 15
2.1.1 PROFINET terms ................................................................................................................... 17
2.1.2 Basic terminology of communication ..................................................................................... 20
2.1.3 PROFINET interface .............................................................................................................. 23
2.1.4 Implementation of the PROFINET device model in SIMATIC ............................................... 26
2.2 Setting up PROFINET ............................................................................................................ 27
2.2.1 Active Network Components .................................................................................................. 28
2.2.2 Cabling technology ................................................................................................................ 30
2.2.3 Wireless design ...................................................................................................................... 33
2.2.3.1 Basics ..................................................................................................................................... 33
2.2.3.2 Tips on assembly ................................................................................................................... 35
2.2.4 Network security..................................................................................................................... 36
2.2.4.1 Basics ..................................................................................................................................... 36
2.2.4.2 Network components and software........................................................................................ 38
2.2.4.3 Application example ............................................................................................................... 39
3.1 Assigning an IO device to an IO controller ............................................................................ 42
3.2 Device name and IP address ................................................................................................. 44
3.2.1 Device name .......................................................................................................................... 45
3.2.2 IP address .............................................................................................................................. 46
3.2.3 Assigning a device name and IP address .............................................................................. 49
3.2.4 Assign device name via communication table ....................................................................... 54
3.2.5 Permitting changes to the device name and IP address directly on the device .................... 57
3.3 Configuring topology .............................................................................................................. 59
3.3.1 Topology view in STEP 7 ....................................................................................................... 61
3.3.2 Interconnecting ports in the topology view ............................................................................. 64
3.3.3 Interconnecting ports - Inspector window .............................................................................. 65
3.3.4 Automatic assignment of devices by offline/online comparison ............................................ 66
3.3.5 Apply the port interconnections identified online manually to the project .............................. 67
3.3.6 Include the devices identified online manually in the project ................................................. 68
3.3.7 Automatic assignment of devices by advanced offline/online comparison ............................ 68
4.1 Diagnostics mechanisms of PROFINET IO ........................................................................... 69
4.1.1 Diagnostics levels in PROFINET IO ...................................................................................... 71
4.1.2 I&M data (identification and maintenance) ............................................................................ 73
4.1.3 Loading I&M data to PROFINET IO devices and your modules ............................................ 73
4.2 Diagnostics using status LEDs .............................................................................................. 75
PROFINET with STEP 7 V14
8 Function Manual, 09/2016, A5E03444486-AG

Table of contents
5 Functions .............................................................................................................................................. 93
4.3 Diagnostics via the display of the S7-1500 CPUs .................................................................. 76
4.4 Diagnostics via Web server .................................................................................................... 80
4.5 Diagnostics in STEP 7 ............................................................................................................ 83
4.6 Extended maintenance concept ............................................................................................. 86
4.7 Diagnostics of the network topology ....................................................................................... 88
4.8 Diagnostics in the user program ............................................................................................. 89
4.8.1 Diagnostics and configuration data records ........................................................................... 89
4.8.2 Evaluate diagnostics in the user program .............................................................................. 91
5.1 Connecting other bus systems ............................................................................................... 94
5.1.1 Connecting other bus systems ............................................................................................... 94
5.1.2 Linking PROFINET and PROFIBUS ....................................................................................... 95
5.1.3 Connect the DP slave via the IE/PB Link to a PROFINET IO system .................................... 96
5.2 Intelligent IO devices (I-devices) ............................................................................................. 98
5.2.1 I-device functionality ............................................................................................................... 98
5.2.2 Properties and Advantages of the I-Device ............................................................................ 99
5.2.3 Characteristics of an I-Device ............................................................................................... 100
5.2.4 Data Exchange between higher- and lower-level IO system ................................................ 104
5.2.5 Configuring the I-device ........................................................................................................ 106
5.2.6 Program examples ................................................................................................................ 109
5.2.7 Diagnostics and interrupt characteristics .............................................................................. 112
5.2.8 Rules for the Topology of a PROFINET IO System with I-Device ........................................ 114
5.2.9 Boundary conditions when using I-devices .......................................................................... 118
5.2.10 Configuring PROFIenergy with I-devices.............................................................................. 118
5.3 Shared device ....................................................................................................................... 121
5.3.1 Useful information on shared devices ................................................................................... 121
5.3.2 Configuring shared device .................................................................................................... 124
5.3.3 Configuring an I-device as a shared device.......................................................................... 128
5.3.4 Module-internal shared input/shared output (MSI/MSO) ...................................................... 137
5.4 Media redundancy (ring topologies) ..................................................................................... 144
5.4.1 Media Redundancy Protocol (MRP) ..................................................................................... 145
5.4.2 Configuring media redundancy ............................................................................................. 148
5.4.3 Media Redundancy with Planned Duplication of frames (MRPD) ........................................
5.
4.4 Multiple rings ......................................................................................................................... 152
150
5.5 Real-time communication ..................................................................................................... 157
5.5.1 Introduction ........................................................................................................................... 157
5.5.2 RT ......................................................................................................................................... 158
5.5.3 IRT ........................................................................................................................................ 159
5.5.4 Comparison of RT and IRT ................................................................................................... 162
5.5.5 Configuring PROFINET IO with IRT ..................................................................................... 162
5.5.6 Setting the bandwidth usage for the send clock ................................................................... 166
5.5.7 Setup recommendations for optimizing PROFINET ............................................................. 167
5.5.8 Limitation of the data infeed into the network ....................................................................... 171
PROFINET with STEP 7 V14
Function Manual, 09/2016, A5E03444486-AG
9

Table of contents
Glossary .............................................................................................................................................. 242
Index ................................................................................................................................................... 255
5.6 PROFINET with performance upgrade ................................................................................ 172
5.6.1 Dynamic frame packing ....................................................................................................... 173
5.6.2 Fragmentation ...................................................................................................................... 175
5.6.3 Fast forwarding .................................................................................................................... 176
5.6.4 Configuration of IRT with high performance ........................................................................ 177
5.6.5 Sample configuration for IRT with high performance........................................................... 181
5.7 Isochronous mode ............................................................................................................... 182
5.7.1 What is isochronous mode? ................................................................................................. 182
5.7.2 Use of isochronous mode .................................................................................................... 183
5.7.3 Isochronous applications ..................................................................................................... 183
5.7.4 Time sequence of synchronization ...................................................................................... 185
5.7.5 Basics of Programming ........................................................................................................ 186
5.7.6 Program processing according to the IPO model with application cycle = 1 ....................... 187
5.7.7 Program execution according to the IPO model with application cycle > 1 ......................... 188
5.7.8 Configuring isochronous mode ............................................................................................ 189
5.7.9 Setting the application cycle and delay time ........................................................................ 192
5.8 Device replacement without exchangeable medium ........................................................... 193
5.8.1 Device replacement without exchangeable medium/PG function ....................................... 194
5.8.2 Replacing an IO device without exchangeable medium ...................................................... 196
5.8.3 Permit overwriting of PROFINET device name ................................................................... 197
5.9 Standard machine projects .................................................................................................. 199
5.9.1 Multiple use IO systems ....................................................................................................... 200
5.9.1.1 What you should know about multiple use IO systems ....................................................... 200
5.9.1.2 Configuring multiple use IO systems ................................................................................... 204
5
.9.1.3 Adapt multiple use IO systems locally ................................................................................. 207
5.9.2 Configuration control for IO systems ................................................................................... 209
5.9.2.1 Information about configuration control of IO systems ........................................................ 209
5.9.2.2 Configuring IO devices as optional ...................................................................................... 212
5.9.2.3 Enabling optional IO devices in the program ....................................................................... 213
5.9.2.4 Configuring flexible order of IO devices ............................................................................... 219
5.9.2.5 Customizing arrangement of IO devices in the program ..................................................... 222
5.9.2.6 System behavior and rules .................................................................................................. 225
5.10 Saving energy with PROFIenergy........................................................................................ 227
5.11 Docking systems .................................................................................................................. 229
5.11.1 Configuring docking systems ............................................................................................... 232
5.12 Accelerating startup ............................................................................................................. 234
5.12.1 Options for accelerating the startup of IO devices ............................................................... 234
5.12.2 Prioritized startup ................................................................................................................. 236
5.12.3 Configuring prioritized startup .............................................................................................. 237
5.12.4 Optimize the port settings .................................................................................................... 239
5.12.5 Optimize the cabling of the ports ......................................................................................... 240
5.12.6 Measures in the user program ............................................................................................. 241
PROFINET with STEP 7 V14
10 Function Manual, 09/2016, A5E03444486-AG
1
Basic information
Device information
The documentation for the SIMATIC S7-1500 automation system, for CPU 1516pro-2 PN
based on SIMATIC S7-1500, and for the distributed I/O systems SIMATIC ET 200MP,
ET 200SP and ET 200AL is divided into three areas.
This division allows you easier access to the specific information you require.
System manuals and Getting Started manuals describe in detail the configuration,
installation, wiring and commissioning of the SIMATIC S7-1500, ET 200MP, ET 200SP and
ET 200AL systems; use the corresponding operating instructions for CPU 1516pro-2 PN.
The STEP 7 online help supports you in configuration and programming.
Product manuals contain a compact description of the module-specific information, such as
properties, terminal diagrams, characteristics and technical specifications.
PROFINET with STEP 7 V14
Function Manual, 09/2016, A5E03444486-AG
11

Documentation guide
General information
Manual Collections
"mySupport"
"mySupport" - Documentation
The function manuals contain detailed descriptions on general topics such as diagnostics,
communication, Motion Control, Web server, OPC UA.
You can download the documentation free of charge from the Internet
http://w3.siemens.com/mcms/industrial-automation-systems-simatic/en/manual-
(
overview/Pages/Default.aspx).
Changes and additions to the manuals are documented in product information sheets.
You will find the product information on the Internet:
● S7-1500/ET 200MP (https://support.industry.siemens.com/cs/us/en/view/68052815
● ET 200SP (https://support.industry.siemens.com/cs/us/en/view/73021864)
● ET 200AL (https://support.industry.siemens.com/cs/us/en/view/99494757)
The Manual Collections contain the complete documentation of the systems put together in
one file.
You will find the Manual Collections on the Internet:
● S7-1500/ET 200MP (https://support.industry.siemens.com/cs/ww/en/view/86140384
● ET 200SP (https://support.industry.siemens.com/cs/ww/en/view/84133942)
● ET 200AL (https://support.industry.siemens.com/cs/ww/en/view/95242965)
With "mySupport", your personal workspace, you make the best out of your Industry Online
Support.
In "mySupport", you can save filters, favorites and tags, request CAx data and compile your
personal library in the Documentation area. In addition, your data is already filled out in
support requests and you can get an overview of your current requests at any time.
)
)
You must register once to use the full functionality of "mySupport".
You can find "mySupport" on the Internet (https://support.industry.siemens.com/My/ww/en
).
In the Documentation area in "mySupport" you can combine entire manuals or only parts of
these to your own manual.
You can export the manual as PDF file or in a format that can be edited later.
You can find "mySupport" - Documentation on the Internet
(http://support.industry.siemens.com/My/ww/en/documentation
PROFINET with STEP 7 V14
12 Function Manual, 09/2016, A5E03444486-AG
).
Documentation guide
"mySupport" - CAx data
Application examples
TIA Selection Tool
In the CAx data area in "mySupport", you can access the current product data for your CAx
or CAe system.
You configure your own download package with a few clicks.
In doing so you can select:
● Product images, 2D dimension drawings, 3D models, internal circuit diagrams, EPLAN
macro files
● Manuals, characteristics, operating manuals, certificates
● Product master data
You can find "mySupport" - CAx data on the Internet
(http://support.industry.siemens.com/my/ww/en/CAxOnline
).
The application examples support you with various tools and examples for solving your
automation tasks. Solutions are shown in interplay with multiple components in the system separated from the focus on individual products.
You will find the application examples on the Internet
(https://support.industry.siemens.com/sc/ww/en/sc/2054
With the TIA Selection Tool, you can select, configure and order devices for Totally
Integrated Automation (TIA).
This tool is the successor of the SIMATIC Selection Tool and combines the known
configurators for automation technology into one tool.
With the TIA Selection Tool, you can generate a complete order list from your product
selection or product configuration.
You can find the TIA Selection Tool on the Internet
(http://w3.siemens.com/mcms/topics/en/simatic/tia-selection-tool
).
).
PROFINET with STEP 7 V14
Function Manual, 09/2016, A5E03444486-AG
13
Documentation guide
SIMATIC Automation Tool
PRONETA
You can use the SIMATIC Automation Tool to run commissioning and maintenance activities
simultaneously on different SIMATIC S7 stations as a bulk operation, independently of the
TIA Portal.
The SIMATIC automation tool provides a variety of functions:
● Scanning of a PROFINET/Ethernet plant network and identification of all connected CPUs
● Address assignment (IP, subnet, gateway) and station name (PROFINET device) to a
CPU
● Transfer of the date and programming device/PC time converted to UTC time to the
module
● Program download to CPU
● Operating mode switchover RUN/STOP
● CPU localization by means of LED flashing
● Reading out CPU error information
● Reading of CPU diagnostic buffer
● Reset to factory settings
● Updating the firmware of the CPU and connected modules
You can find the SIMATIC Automation Tool on the Internet
(https://support.industry.siemens.com/cs/ww/en/view/98161300
With SIEMENS PRONETA (PROFINET network analysis), you analyze the plant network
during commissioning. PRONETA features two core functions:
● The topology overview independently scans PROFINET and all connected components.
● The IO check is a fast test of the wiring and the module configuration of a plant.
You can find SIEMENS PRONETA on the Internet
(https://support.industry.siemens.com/cs/ww/en/view/67460624
).
).
PROFINET with STEP 7 V14
14 Function Manual, 09/2016, A5E03444486-AG

2
2.1
Introduction to PROFINET
What is PROFINET IO?
Objectives of PROFINET
Within the framework of Totally Integrated Automation (TIA), PROFINET IO is the logical
further development of:
● PROFIBUS DP, the established fieldbus and
● Industrial Ethernet
PROFINET IO is based on 20 years of experience with the successful PROFIBUS DP and
combines the normal user operations with the simultaneous use of innovative concepts of
Ethernet technology. This ensures the integration of PROFIBUS DP into the PROFINET
world.
PROFINET IO as the Ethernet-based automation standard of PROFIBUS/PROFINET
International defines a cross-vendor communication, automation, and engineering model.
The objectives of PROFINET:
● Industrial networking, based on Industrial Ethernet (open Ethernet standard)
● Compatibility of Industrial Ethernet and standard Ethernet components
● High robustness due to Industrial Ethernet devices. Industrial Ethernet devices are suited
to the industrial environment (temperature, noise immunity, etc.).
● Use of IT standards such as TCP/IP, http.
● Real-time capability
● Seamless integration of other fieldbus systems
PROFINET with STEP 7 V14
Function Manual, 09/2016, A5E03444486-AG
15
Description
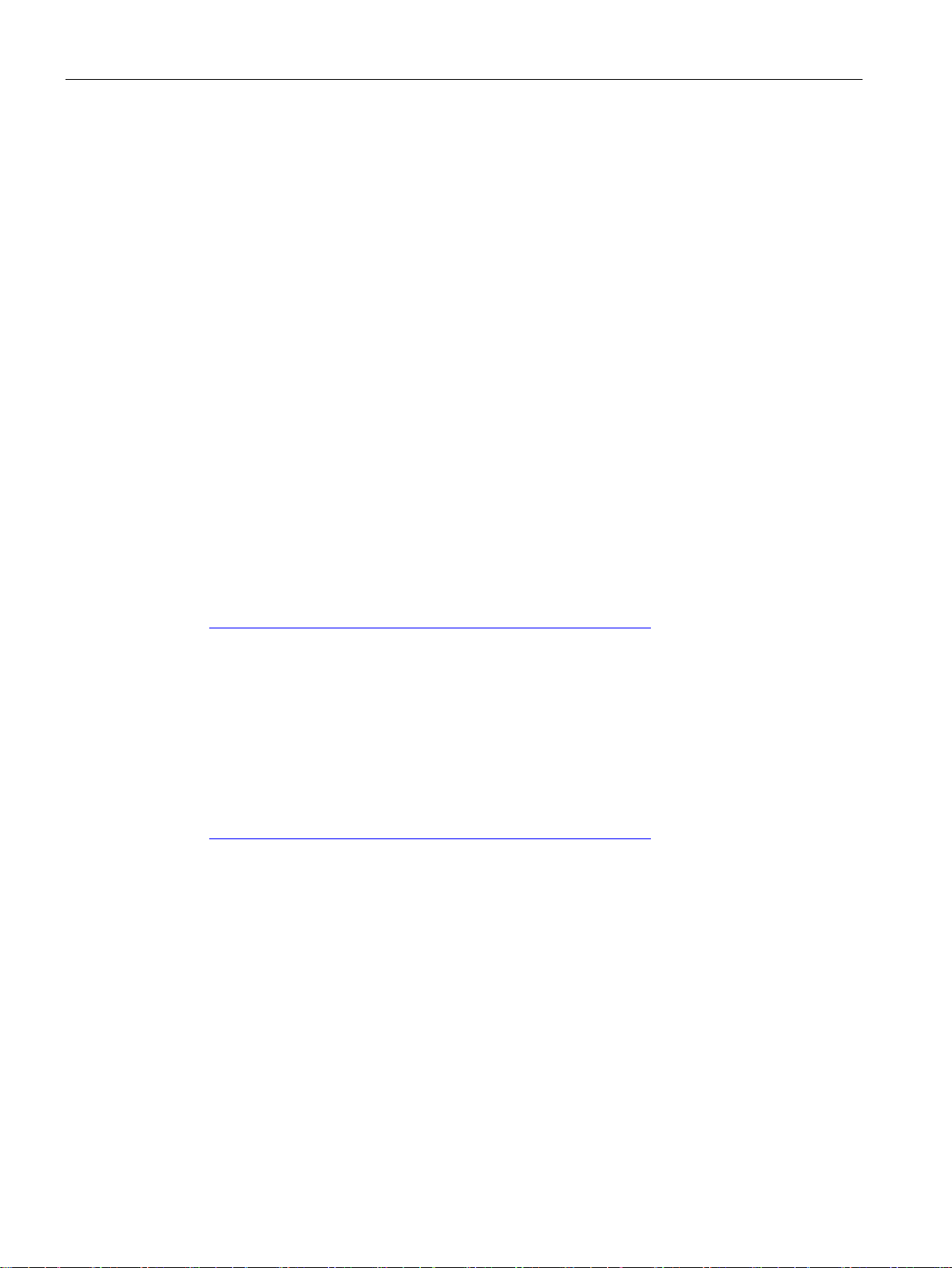
Implementation of PROFINET in SIMATIC
PROFINET IO
STEP 7
2.1 Introduction to PROFINET
PROFINET is implemented in SIMATIC as follows:
● We have implemented communication between field devices in SIMATIC with
● Installation technology and network components are available as SIMATIC NET products.
● Ethernet standard protocol and procedures (e.g., SNMP = Simple Network Management
Protocol for network parameter assignment and diagnostics) are used for remote
maintenance and network diagnostics.
.
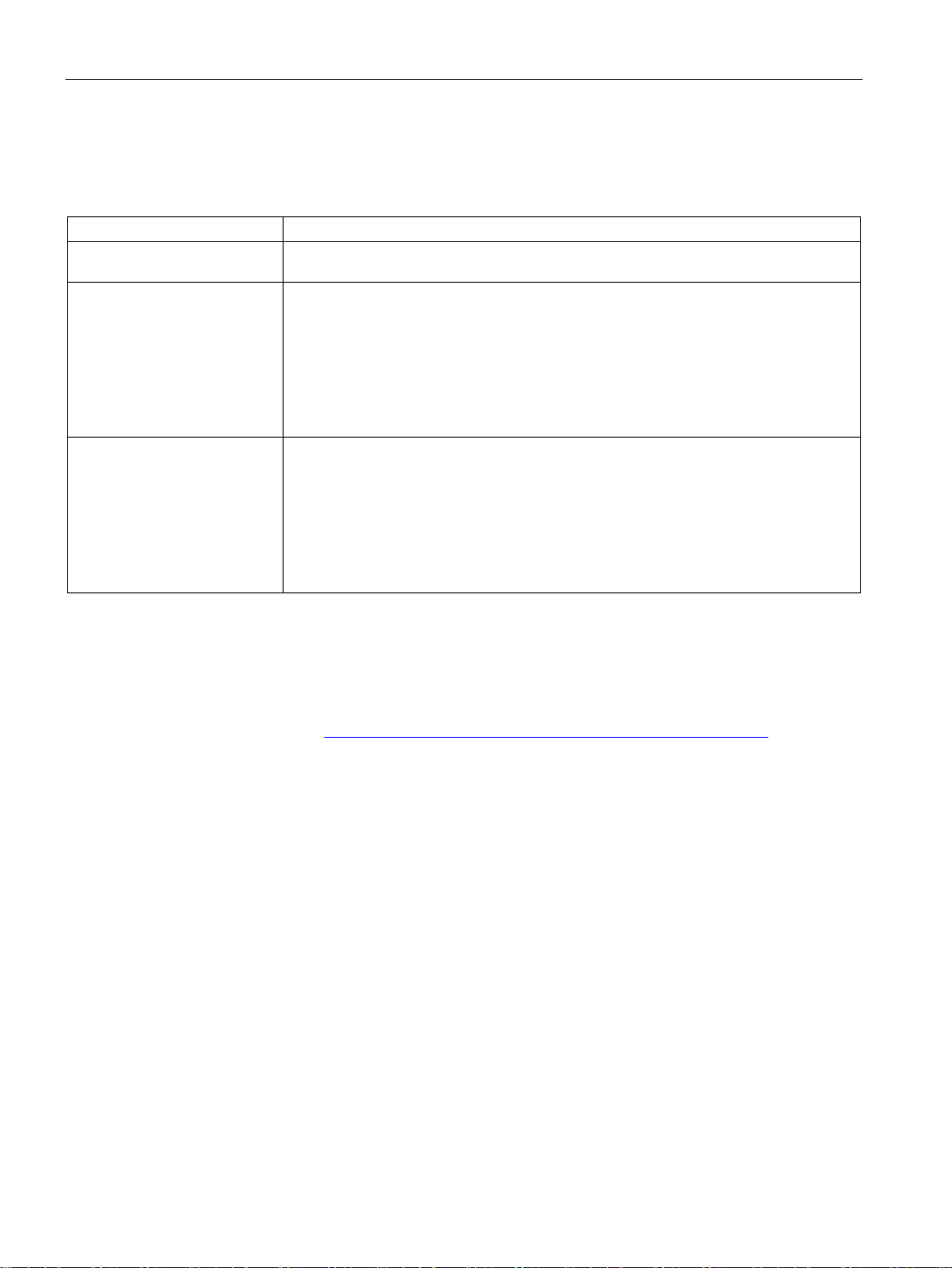
Figure 2-1 PROFINET overview configuration
The STEP 7 engineering tool supports you in setting up and configuring an automation
solution. STEP 7 provides a uniform application view over all bus systems.
PROFINET with STEP 7 V14
16 Function Manual, 09/2016, A5E03444486-AG

Description
Documentation from PROFIBUS & PROFINET International on the Internet
Overview of the most important documents and links
2.1.1
PROFINET terms
Definition: Devices in the PROFINET environment
2.1 Introduction to PROFINET
You will find numerous documents on the topic of PROFINET at the Internet address
(http://www.profibus.com
organization, which is also responsible for PROFINET.
Additional information can be found on the Internet (http://www.siemens.com/profinet).
) of the "PROFIBUS & PROFINET International" PROFIBUS user
A compilation of the most important PROFINET application examples, FAQs and other
contributions in the Industry Online Support is available in this FAQ
).
(https://support.industry.siemens.com/cs/ww/en/view/108165711
In the PROFINET environment, "device" is the generic term for:
● Automation systems (PLC, PC, for example)
● Distributed I/O systems
● Field devices (for example, hydraulic devices, pneumatic devices)
● Active network components (for example, switches, routers)
● Gateways to PROFIBUS, AS interface or other fieldbus systems
PROFINET with STEP 7 V14
Function Manual, 09/2016, A5E03444486-AG
17
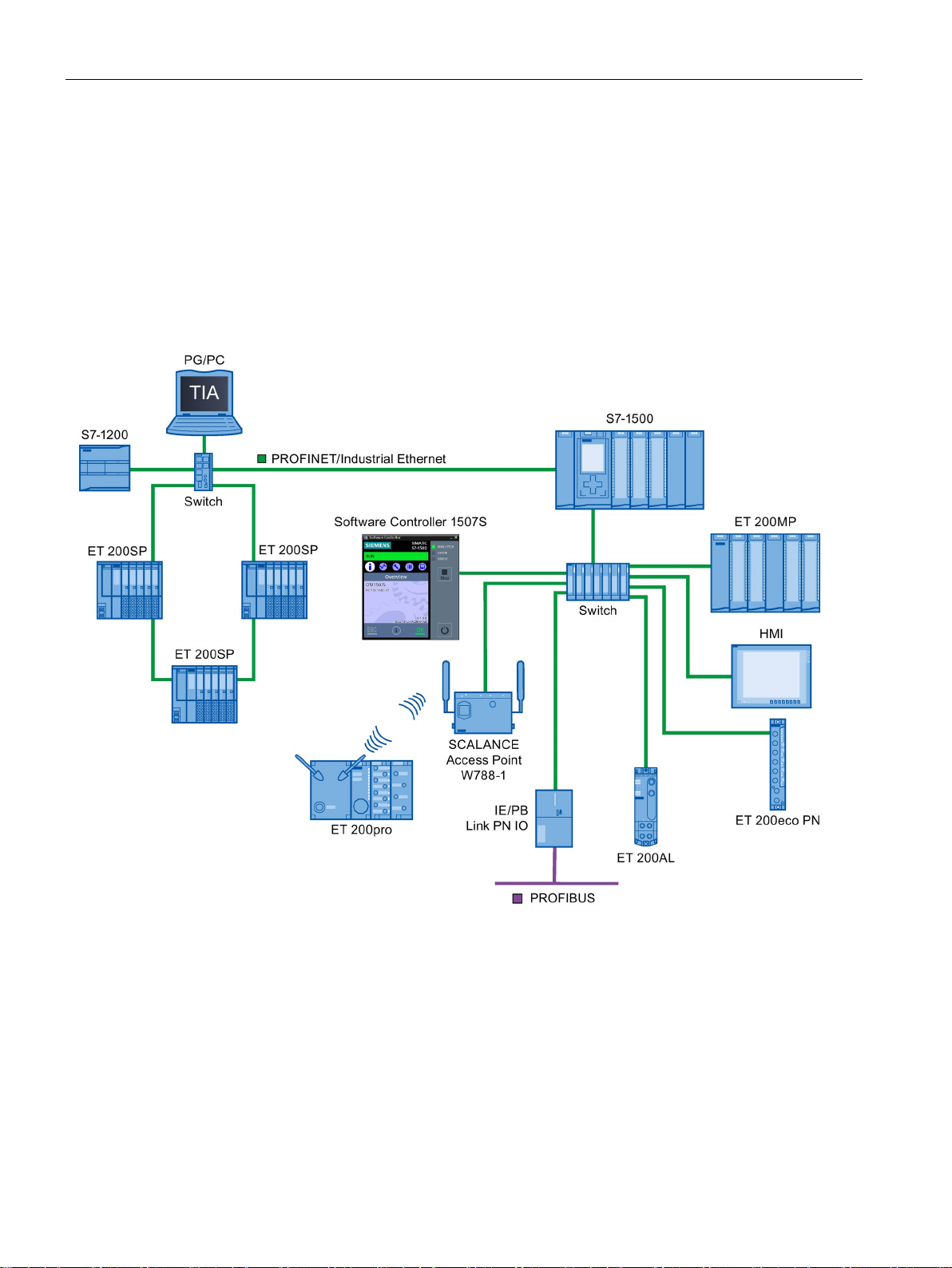
Description
PROFINET IO devices
Number
PROFINET
Explanation
①
PROFINET IO System
②
and output signals with field devices.
③
(PROFINET IO supervisor)
diagnostics
④
PROFINET/Industrial Ethernet
Network infrastructure
⑤
HMI (Human Machine Interface)
Device for operating and monitoring functions.
⑥
ed PROFINET IO functionality)
⑦
I-device
Intelligent IO device
2.1 Introduction to PROFINET
The following graphic shows the general names used for the most important devices in
PROFINET. In the table below the graphic you can find the names of the individual
components in the PROFINET IO context.
IO controller Device used to address the connected IO devices.
This means that: The IO controller exchanges input
Programming device / PC
IO device A distributed field device that is assigned to one of
Figure 2-2 PROFINET devices
PG/PC/HMI device used for commissioning and for
the IO controllers (e.g., Distributed IO, valve terminals, frequency converters, switches with integrat-
PROFINET with STEP 7 V14
18 Function Manual, 09/2016, A5E03444486-AG
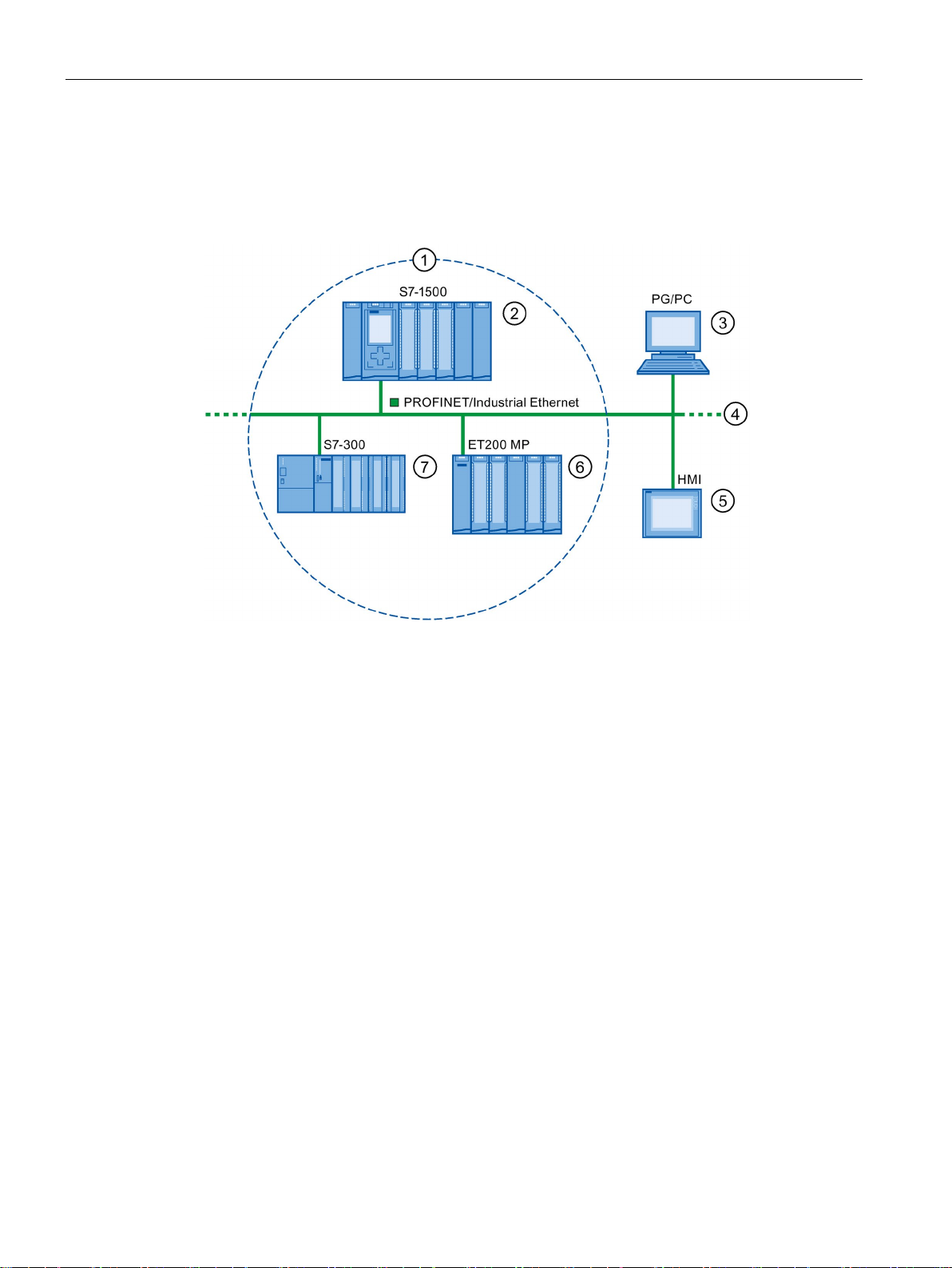
Description
IO communication via PROFINET IO
A
IO controller - IO controller communication via PN/PN coupler
B
IO controller - I-device communication
C
IO controller - IO-device communication
2.1 Introduction to PROFINET
The inputs and outputs of distributed I/O devices are read and written by means of
PROFINET IO using what is referred to as IO communication. The following figure provides
an overview of IO communication by means of PROFINET IO.
Figure 2-3 IO communication via PROFINET IO
PROFINET with STEP 7 V14
Function Manual, 09/2016, A5E03444486-AG
19
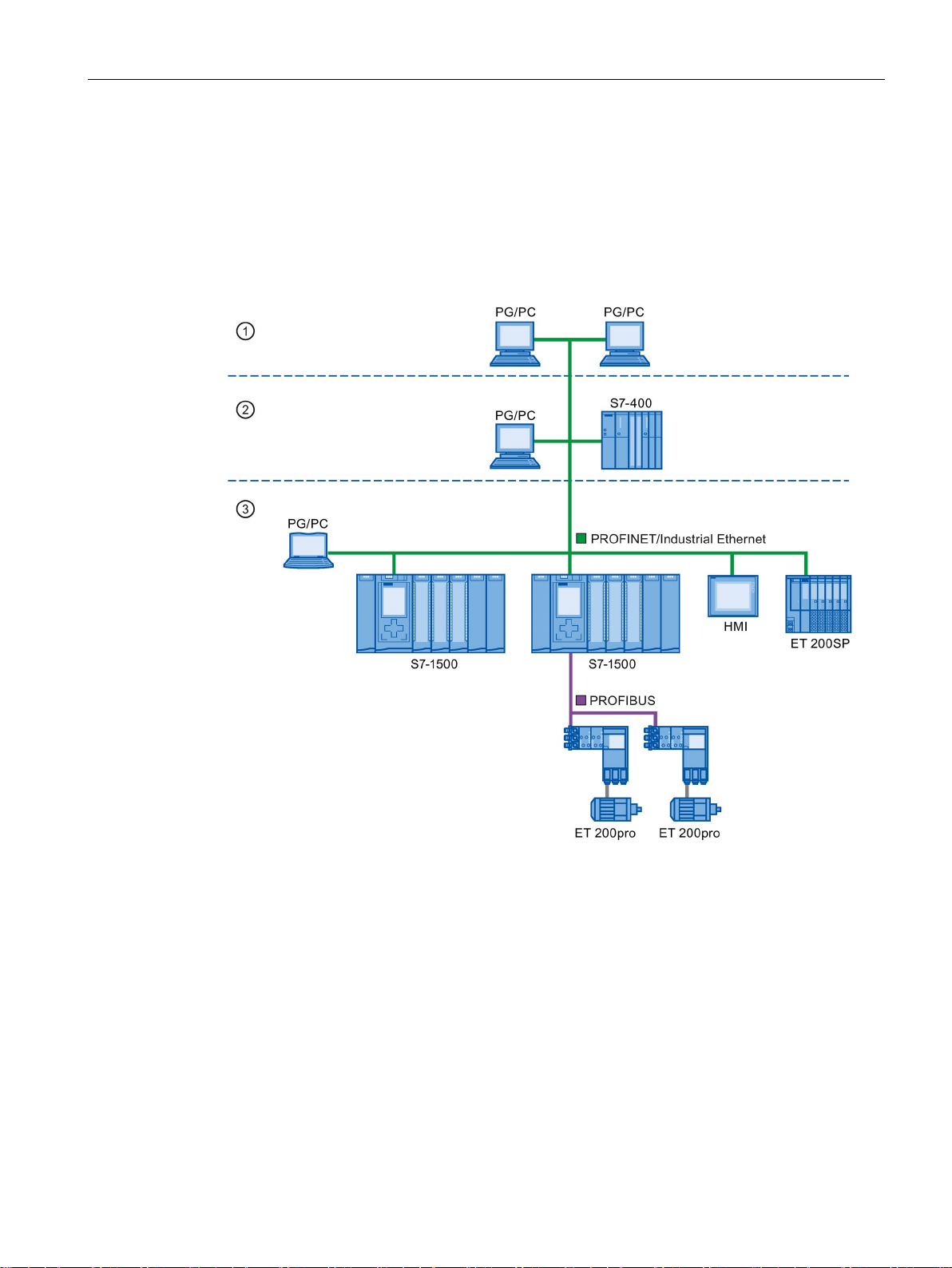
Description
IO communication via PROFINET IO
Communication between ...
Explanation
receives data from these devices.
A fixed quantity of data is transferred cyclically between the user programs in CPUs of IO
via direct access.
A fixed quantity of data is cyclically transferred between the user programs in CPUs of IO
via direct access.
See also
2.1.2
Basic terminology of communication
PROFINET communication
2.1 Introduction to PROFINET
Table 2- 1 IO communication via PROFINET IO
IO controllers and IO devices The IO controller sends data cyclically to the IO devices of its PROFINET IO system and
IO controller and I-device
controllers and I-devices.
The IO controller does not access the I/O module of the I-device, but instead accesses
configured address ranges, i.e. transfer ranges, which may be located inside our outside
the process image of the CPU of the I-device. If parts of the process image are used as
transfer ranges, it is not permitted to use these for real I/O modules.
Data transfer takes place using load- and transfer operations via the process image or
IO controller and IO controller
controllers. A PN/PN coupler is required as additional hardware.
The IO controllers mutually access configured address ranges, i.e. transfer ranges,
which may be located inside or outside the process image of the CPU. If parts of the
process image are used as transfer ranges, it is not permitted to use these for real I/O
modules.
Data transfer takes place using load- and transfer operations via the process image or
Network security (Page 36)
Functions (Page 93)
Communication (http://support.automation.siemens.com/WW/view/en/59192925
PROFINET communication takes place via Industrial Ethernet. The following transmission
types are supported:
● Acyclic transmission of engineering and diagnostics data and interrupts
● Cyclic transmission of user data
The PROFINET-IO communication takes place in real-time.
For additional information on the real-time communication, refer to chapter Real-time
communication (Page 157).
)
PROFINET with STEP 7 V14
20 Function Manual, 09/2016, A5E03444486-AG
Description
Transparent data access
①
Management level
②
Control level
③
Production level
2.1 Introduction to PROFINET
Access to process data from different levels of the factory is supported by PROFINET
communication. By using Industrial Ethernet, standard mechanisms of communication and
information technology such as OPC/XML can now be used along with standard protocols
such as UDP/TCP/IP and HTTP in automation engineering. This allows transparent access
from company management level directly to the data from the automation systems at the
control level and production level.
PROFINET with STEP 7 V14
Function Manual, 09/2016, A5E03444486-AG
Figure 2-4 Access to process data
21

Description
Update time
Watchdog time
Send clock
Relationship between the update time and send clock
Send clock
Update time
Reduction ratios
250 μs
250 μs to 128 ms
1,2, ..., 512
1 ms
1 ms to 512 ms
1,2, ..., 512
2 ms
2 ms to 512 ms
1,2, ..., 256
4 ms
4 ms to 512 ms
1,2, ..., 128
Additional information
2.1 Introduction to PROFINET
The update time is a time interval. IO controller and IO device/I-device exchange IO data
cyclically in the IO system within this time interval. The update time can be configured
separately for each IO device and determines the interval at which output data is sent from
the IO controller to the IO device (output module/submodule) as well as input data from the
IO device to the IO controller (input module/submodule).
STEP 7 calculates the update time automatically in the default setting for each IO device of
the PROFINET IO system, taking into account the volume of data to be exchanged as well
as the set send clock.
For additional information on the update time, refer to section Real-time communication
(Page 157).
The watchdog time is the time interval that an IO controller or IO device permits, without
receiving IO data. If the IO device is not supplied by the IO controller with data within the
watchdog time, the device detects the missing frames and outputs substitute values. This is
reported in the IO controller as a station failure.
In STEP 7, the watchdog time is made up from an integral multiple of the update time and
can be set by the user.
The period of time between two consecutive communication cycles. The send clock is the
shortest possible interval in data exchange.
The calculated update times are reduction ratios (1, 2, 4, 8, ..., 512) of the send clock. The
minimum possible update time thus depends on the minimum send clock of the IO controller
that can be set and the efficiency of the IO controller and IO device. Depending on the send
clock, it can be that only some of the reduction ratios are available (STEP 7 guarantees this
through a pre-selection).
The following tables illustrate the dependency of the update time that can be set on the send
clock, using an example of the CPU 1516-3 PN/DP. The update times satisfy the
requirements of the PROFINET standard IEC 61158.
Table 2- 2 With real-time communication the following applies:
500 μs 500 μs to 256 ms 1,2, ..., 512
PROFINET with STEP 7 V14
22 Function Manual, 09/2016, A5E03444486-AG
For information on real-time communication, refer to the section Real-Time Communication
(RT) (Page 158).

Description
2.1.3
PROFINET interface
Overview
Properties
Identification and numbering of the interfaces and ports
Element
Symbol
Interface number
Interface
X
In ascending order starting from number 1
(for each interface)
Ring port
R
Examples of identification
Sample labeling
Interface number
Port number
X2 P1
2
1
X1 P2
1
2
X1 P1 R
1
1 (ring port)
2.1 Introduction to PROFINET
PROFINET devices of the SIMATIC product family have one or more PROFINET interfaces
(Ethernet controller/interface). The PROFINET interfaces have one or more ports (physical
connection options).
In the case of PROFINET interfaces with multiple ports, the devices have an integrated
switch.
PROFINET devices with two ports on one interface allow you to configure the system in a
line or ring topology. PROFINET devices with three or more ports on one interface are also
ideal for setting up tree topologies.
Properties and rules for naming the PROFINET interface and its representation in STEP 7
are explained in the following.
Every PROFINET device on the network is uniquely identified via its PROFINET interface.
For this purpose, each PROFINET interface has:
● A MAC address (factory default)
● An IP address
● A PROFINET device name
Interfaces and ports for all modules and devices in the PROFINET system are identified with
the following characters:
Table 2- 3 Identification for interfaces and ports of PROFINET devices
Port P In ascending order starting from number 1
Three examples illustrate the rules for identifying PROFINET interfaces:
Table 2- 4 Examples for identifying PROFINET interfaces
PROFINET with STEP 7 V14
Function Manual, 09/2016, A5E03444486-AG
23
Description
Representation of PROFINET Interfaces in the Topology Overview in STEP 7
Number
Description
①
PROFINET interface of an IO controller in STEP 7
②
PROFINET interface of an IO device in STEP 7
③
These lines represent the PROFINET interface.
④
These lines represent the "ports" of a PROFINET interface.
Schematic Representation of a PROFINET Interface with Integrated Switch
2.1 Introduction to PROFINET
You can find the PROFINET interface in the topology overview in STEP 7. The PROFINET
interface for an IO controller and an IO device is represented as follows in STEP 7:
Figure 2-5 Representation of the PROFINET interfaces in STEP 7
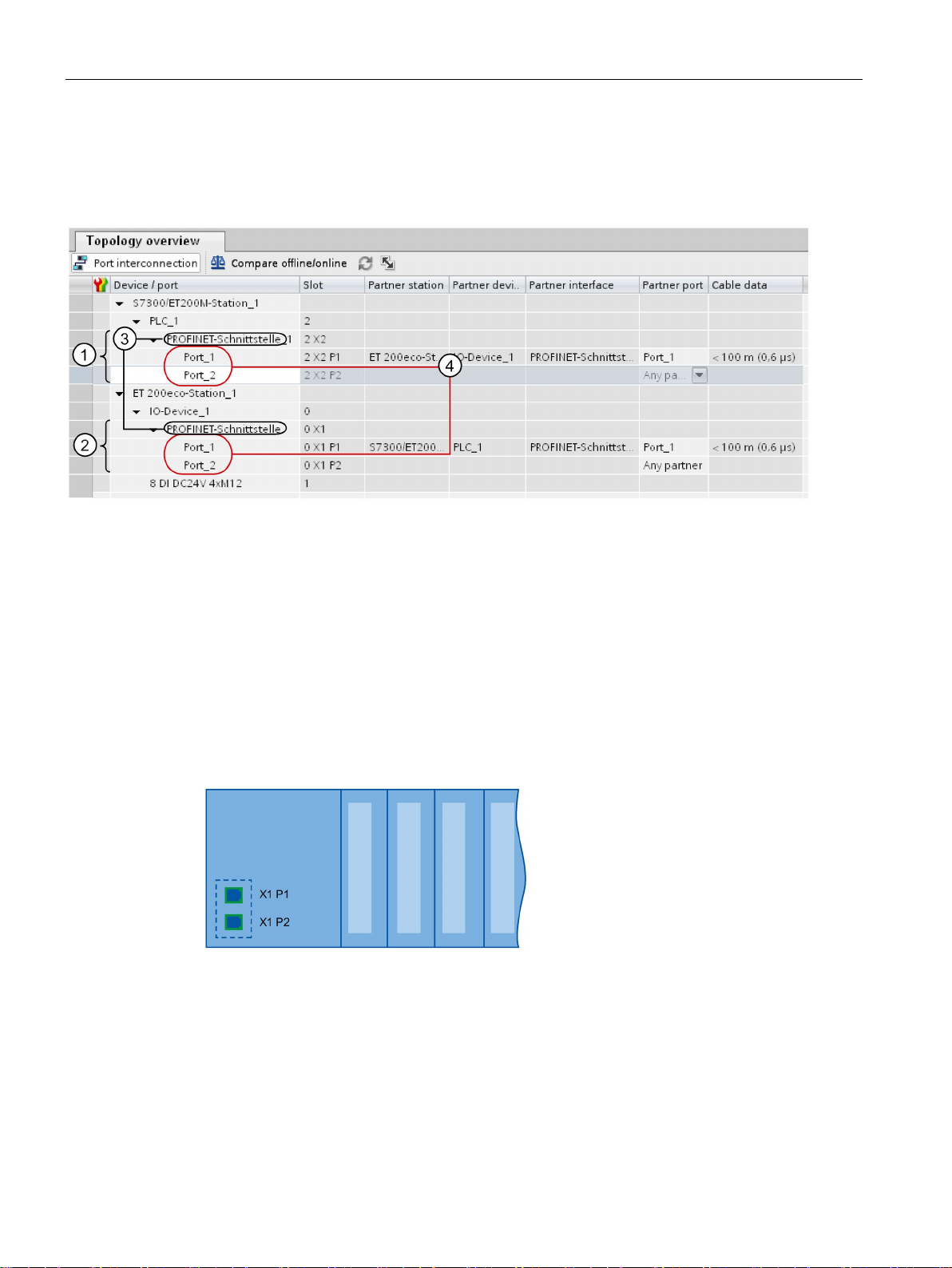
The following schematic diagram shows the PROFINET interface with integrated switch and
its ports for all PROFINETdevices.
Figure 2-6 PROFINET interface with integrated switch
PROFINET with STEP 7 V14
24 Function Manual, 09/2016, A5E03444486-AG

Description
Functional differences of the PROFINET interfaces
PROFINET interface (X1)
PROFINET interface (X2)
2 ports with PROFINET IO functionality:
1 port with PROFINET IO functionality:
PG communication
HMI communication
S7 communication
Time-of-day synchronization
Web server
Open communication
OPC UA server
IO controller
I-device
RT
IRT
-
Isochronous mode
-
Media redundancy
-
Prioritized startup
-
Additional Information on the Functionality of PROFINET interfaces
2.1 Introduction to PROFINET
PROFINET interfaces can provide different functions. PROFINET interface functions include
identification, configuration, diagnostics and communication services (e.g., open
communication). PROFINET interfaces that provide PROFINET IO functions and network
security functions are also available.
The following table illustrates the differences using the example of the CPU 1516-3 PN/DP
(as of firmware version V2.0), which features two PROFINET interfaces with different
functionality.
Table 2- 5 Differences between the PROFINET interfaces of the CPU 1516-3 PN/DP (as of firm-
ware version V2.0)
Identification, configuration and diagnostics
You can find information on the number and functionality of the interfaces of a PROFINET
device in the documentation for the specificPROFINET device.
PROFINET communication services are described in the Communication function manual.
In the Network security section you can find components that are used to protect networks
against hazards.
The Functions section describes the PROFINET IO functions.
PROFINET with STEP 7 V14
Function Manual, 09/2016, A5E03444486-AG
25
Description
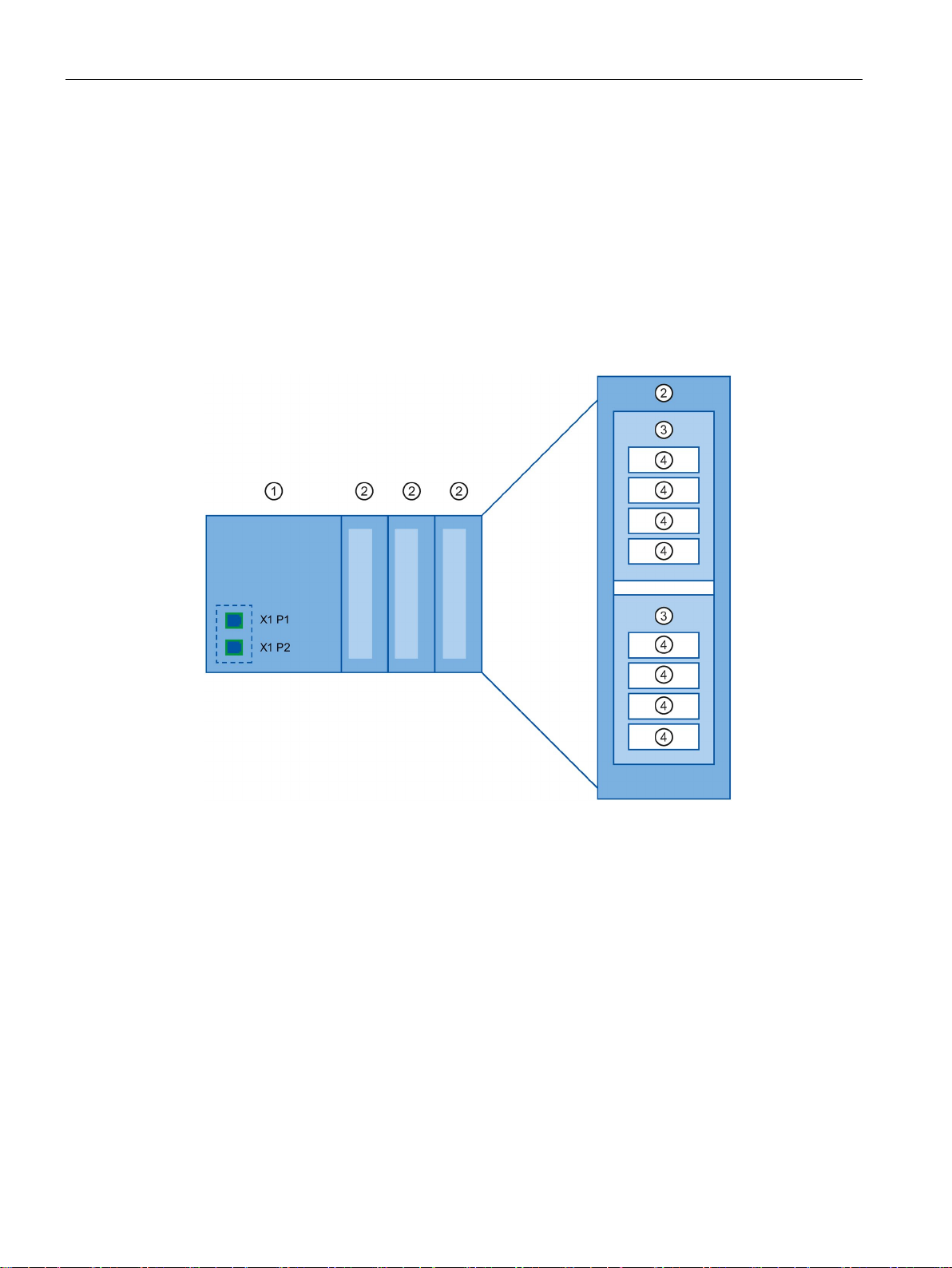
2.1.4
Implementation of the PROFINET device model in SIMATIC
Slots and modules
Number
Description
①
Slot with bus interface
②
Slot with module
③
Subslot with submodule
④
Channel
2.1 Introduction to PROFINET
A PROFINET device can have a modular and compact structure. A modular PROFINET
device consists of slots into which the modules are inserted. The modules have channels
which are used to read and output process signals. A compact device has the same design
and can include modules, however, it cannot be physically expanded, which means that no
modules can be inserted.
This is illustrated by the following graphic.
PROFINET with STEP 7 V14
26 Function Manual, 09/2016, A5E03444486-AG
Figure 2-7 Configuration of a PROFINET device
A module can contain multiple submodules.

Description
Representation of PROFINET Device Model in the Device View of STEP 7
2.2
Setting up PROFINET
Contents of this chapter
Physical connections of industrial networks
2.2 Setting up PROFINET
The following figure shows the representation of the PROFINET device model in the device
view of STEP 7, based on the example of a distributed I/O system ET 200MP:
Figure 2-8 PROFINET device model in the device view of STEP 7
The following chapter provides background information on building your communication
network.
● Overview of the most important passive network components: These are network
components that forward a signal without the possibility of actively influencing it, for
example, cables, connectors, etc.
● Overview of the most important active network components: These are network
components that actively affect a signal, for example switches, routers, etc.
● Overview of the most common network structures (topologies).
PROFINET devices can be networked in industrial systems in two different physical ways:
● Connected line
– By means of electrical pulses via copper cables
– By means of optical pulses via fiber-optic cables
● Wireless via wireless network using electromagnetic waves
PROFINET with STEP 7 V14
Function Manual, 09/2016, A5E03444486-AG
27

Description
Fast Ethernet
Industrial Ethernet
2.2.1
Active Network Components
Introduction
Switched Ethernet
Switches
2.2 Setting up PROFINET
PROFINET devices and cabling technology in SIMATIC are suited for industrial use, as they
are based on Fast Ethernet and Industrial Ethernet.
●
You can use Fast Ethernet to transfer data at a speed of 100 Mbps. This transmission
technology uses the 100 Base-T standard for this.
●
Structure of Ethernet in industrial environment.
The biggest difference from standard Ethernet is the mechanical current carrying capacity
and noise immunity of the individual components.
The following active network components are available for PROFINET:
● Switch
● Router
PROFINET IO is based on switched Ethernet with full-duplex operation and a bandwidth of
100 Mbps. In this way, the network can be used much more efficiently through the
simultaneous data transfer of several devices. The PROFINET IO frames are processed with
high priority.
Switches are network components used to connect several terminal devices or network
segments in a local network (LAN).
For the communication of a device with several other devices on PROFINET, the device is
connected to the port of a switch. Other communication devices (including switches) can
then be connected to the other ports of the switch. The connection between a
communication device and the switch is a point-to-point connection.
A switch has the task of receiving and distributing frames. The switch "learns" the Ethernet
address(es) of a connected PROFINET device or additional switches and only forwards
those frames that are intended for the connected PROFINET device or the connected
switch.
PROFINET with STEP 7 V14
28 Function Manual, 09/2016, A5E03444486-AG

Description
Switch variants
Selection Guide for Switches
Switches of the SCALANCE product family
2.2 Setting up PROFINET
Switches are available in two models:
● Integrated into a PROFINET device
For PROFINET devices with multiple ports (two or more), we are dealing with devices
with an integrated switch (for example, CPU 1516-3 PN/DP).
● As autonomous device (for example, switches of the SCALANCE product family)
To use PROFINET with the RT class "RT", you can use any switch of "PROFINET
Conformance Class A" or higher. All switches of the SCALANCE product family meet these
requirements.
If you want to use PROFINET functions that provide an additional value, such as topology
recognition, diagnostics, device exchange without exchangeable medium/programming
device, you have to use a switch of the "PROFINET Conformance Class B" or higher.
To use PROFINET with the RT class "IRT", you must use a switch of "PROFINET
Conformance Class C". With switches of the SCALANCE product family, watch out for the
catalog feature "IRT PROFINET IO switch".
To select appropriate switches, we recommend the SIMATIC NET Selection Tool on the
Internet (http://support.automation.siemens.com/WW/view/en/39134641
Use the switches of the SCALANCE product family if you want to use the full scope of
PROFINET. They are optimized for use in PROFINET IO.
In the SCALANCE X device family, you will find switches with electrical and optical ports and
with a combination of both variants. SCALANCE X202-2IRT, for example, has two electrical
ports and two optical ports and supports IRT communication.
Beginning with the SCALANCE X200, you can configure, diagnose and address switches of
the SCALANCE X device series as PROFINET IO devices using STEP 7.
).
PROFINET with STEP 7 V14
Function Manual, 09/2016, A5E03444486-AG
29
Description
Router
Note
If devices need to communicate beyond the limits of a network, you must configure
router so that it allows this communication to take place.
2.2.2
Cabling technology
Cables for PROFINET
Simple method for the prefabrication of twisted pair cables
Note
A maximum of four plug
2.2 Setting up PROFINET
A router connects separated network segments with each other (e.g. management level and
control level). The volume of data volume must be coordinated with the services of the
respective network segment. A router also separates two networks and acts as a mediator
between both networks. It thus reduces the network load. Routing functionality is provided in
the SCALANCE X device family, with SCALANCE X300 or higher.
Communication devices on different sides of a router can only communicate with one
another if you have explicitly enabled communication between them via the router.
If you want to access manufacturing data directly from SAP, for example, use a router to
connect your Industrial Ethernet in the factory with the Ethernet in your office.
the
Information on routing with STEP 7 is available in the function manual Communication
(http://support.automation.siemens.com/WW/view/en/59192925
).
Electrical and optical cables are available for PROFINET. The type of cable depends on the
data transfer requirements and on the ambient conditions.
When you set up your PROFINET system, you can cut the twisted-pair cable to the required
length on site, strip it with the
Ethernet Fast Connect RJ45 plugs
stripping tool
using the cut-and-clamp method. For more information on
installation, refer to the installation instructions in the "SIMATIC NET Industrial Ethernet
Network Manual" (http://support.automation.siemens.com/WW/view/en/8763736
-in pairs are allowed between two switches per Ethernet path.
(for Industrial Ethernet), and fit the
Industrial
).
PROFINET with STEP 7 V14
30 Function Manual, 09/2016, A5E03444486-AG
 Loading...
Loading...