Siemens LMU54 Series,LMU64 Series Basic Documentation

HVAC Products
LMU54... / LMU64...
Boiler Management Unit (BMU)
Basic Documentation
Software version 2. 08
CC1P7494en
07.11.2002
Siemens Building Technologies

Safety notes
Caution: The present Basic Documentation describes the broad range of applications and functions
offered by the LMU... and shall serve as a guideline. The correct functioning of the unit must
be checked and confirmed by functional tests on the boiler and / or on the relevant plant!
• Degree of protection IP 40 to EN 60 529 for burner controls must be ensured by the burner or boiler
manufacturer by adequately mounting the LMU...
• In the geographical areas where DIN standards apply, mounting and installation must be in compliance
with the relevant VDE requirements, especially DIN / VDE 0100, 0550 and DIN / VDE 0722!
• The electrical wiring inside the boiler must conform to country-specific and local regulations!
• Where (S)LTs are required, refer to the safety-related notes given in section «Electronic (S)LT»!
• It must be ensured that spliced individual wires cannot get in contact with adjacent terminals.
Use adequate ferrules!
• Prior to commissioning, check wiring and parameterization carefully!
The boiler manufacturer is responsible for the correct parameterization of the LMU..., which must be in
compliance with the relevant standards and regulations!
• When commissioning the plant, check all safety functions!
• Before performing any wiring changes or other work in the connection area of the LMU…, completely
isolate the unit from the mains supply!
• Lay high-voltage ignition cable completely separate from all other cables!
• Ensure protection against electric shock hazard on the LMU… and on all electrical connections
through appropriate mounting!
• There is no absolute protection against incorrect use of the RAST5 connectors.
For this reason, check the correct connector assignments prior to commissioning the plant!
• The burner manufacturer must ensure protection against electric shock hazard on all AC 230 V terminals
by fitting dummy plugs!
• When wiring the unit, AC 230 V mains voltage and extra low-voltage must always be run strictly
separate to warrant protection against electric shock hazard!
− DIN EN 60335
− DIN EN 60730-2-5
• Protect the mains-powered ionization probe against electric shock hazard!
The LMU… is a safety device!
• Do not open, interfere with or modify the unit!
• Siemens is not liable for damage resulting from unauthorized interference!
• In the event of blown fuses inside the LMU..., return the unit to Siemens!
(Customer may replace mains fuse F1 only once)
• Electromagnetic emissions must be checked on an application-specific basis!
To ensure the safety and reliability of the LMU..., the following points must also be observed:
− Condensation, formation of ice and ingress of water are not permitted!
If such conditions have occurred, make certain the unit is completely dry before switching on!
− Static charges must be avoided as they can damage the unit’s electronic components when touching them
Recommendation: Use ESD equipment !
2/171
Siemens Building Technologies Basic Documentation LMU54... / LMU64... CC1P7494en
HVAC Products 07.11.2002

Contents
1 Overview ..........................................................................................10
− Brief description..........................................................................10
1.1 System concept ..................................................................................10
1.2 Features............................................................................................11
− Safety functions ..........................................................................11
− Supervision / protective functions for the plant .................................11
− Auxiliary modules (clip-in) .............................................................11
− DHW .........................................................................................12
− Heating circuit.............................................................................12
− System application ......................................................................12
− Operation / service......................................................................12
− Parameterization.........................................................................13
− Mains transformer........................................................................13
− Other features .............................................................................13
1.3 Product range.....................................................................................13
1.4 Field of use ........................................................................................13
− Target market .............................................................................13
− Heating plants .............................................................................13
− Heat generating equipment ...........................................................13
1.5 Notes on product liability......................................................................14
1.6 Notes on environmental protection........................................................14
− Disposal notes ............................................................................14
2 Product range overview ....................................................................15
3 Functions ..........................................................................................17
3.1 Burner control ....................................................................................17
− Program selection .......................................................................17
− EEPROM...................................................................................17
− Forced intermittent operation ........................................................17
− Burner control program ................................................................17
− Sequence diagram ......................................................................18
− Capacity range < 70 kW ............................................................18
− Capacity range 70...120 kW.......................................................18
− Capacity range > 120 kW..........................................................19
− Description of sequence diagrams..............................................19
− Sequence times.......................................................................20
− Standby..................................................................................20
− Startup ...................................................................................20
− Shutdown................................................................................22
− Home run ................................................................................22
− Special cases (deviations).........................................................22
− LMU... plausibility checks of the speed parameters .......................24
− Parameterization of speed feedback signal..................................24
− Fan parameters accessible via QAA ...........................................25
− The different capacity ranges .....................................................26
− Setting the fan parameters during startup and shutdown................27
− Speed readjustment .................................................................28
3.2 Selection of the compensation variants..................................................30
3/171
Siemens Building Technologies Basic Documentation LMU54... / LMU64... CC1P7494en
HVAC Products Contents 07.11.2002

− Heating circuits ...........................................................................30
− Room setpoint ............................................................................ 32
− Configuration of the heating circuits ...............................................34
− DHW circuit................................................................................ 35
3.3 Acquisition of actual values .................................................................. 37
− Assignment of analog sensors ...................................................... 37
− Temperatures ............................................................................. 37
− Display of ionization current ..........................................................38
3.4 Supervisory functions .......................................................................... 39
− Temperature limiter function......................................................... 39
− Flue gas temperature supervision.................................................. 39
− Plausibility check of sensor ....................................................... 39
− Function................................................................................. 39
− Electronic (S)LT ..........................................................................40
− Handling faults ........................................................................ 40
− Flow switch / water pressure supervision ........................................42
− Function of flow switch.............................................................. 42
− Function of pressure switch....................................................... 42
− Pressure sensor.......................................................................... 42
− Static supervision..................................................................... 43
− Dynamic supervision ................................................................ 44
− Load limitation............................................................................ 45
− Speed limitation.......................................................................... 48
− Limitation of ionization current....................................................... 48
3.5 Boiler control...................................................................................... 49
− Frost protection for the boiler........................................................ 49
− Controller delay .......................................................................... 49
− Controller delay due to parameterization..................................... 49
− Controller delay due to SLT criterion........................................... 50
− Controller configuration ................................................................50
− Transfer of setpoint / actual value ...............................................50
− Determining the controller coefficients ........................................ 50
− Heat output limits..................................................................... 51
− Boiler temperature control............................................................ 52
− 2-position control ..................................................................... 52
− Minimum boiler pause time........................................................ 52
− Boiler cycling protection............................................................... 52
− Dynamic switch-off differential.................................................... 53
− Modulating control, conventional................................................ 54
3.6 Hydraulic system management (HSM)................................................... 55
− Frost protection for the plant ......................................................... 55
3.7 Consumer management (CM) .............................................................. 56
− Determining the demands for heat .................................................56
− Priorization of demands for heat ................................................ 56
− Determining the temperature demand............................................ 57
− Temperature limitation ..............................................................58
− Summer / winter (S / W) changeover.............................................. 59
3.8 Electronically controlled PWM heating circuit pump .................................61
− General...................................................................................... 61
− Introduction................................................................................ 61
− Notes ..................................................................................... 61
4/171
Siemens Building Technologies Basic Documentation LMU54... / LMU64... CC1P7494en
HVAC Products Contents 07.11.2002

− Task of ∆T control with PWM pump ...............................................61
− First stage Maximum limitation of the flow temperature..................62
− Second stage ∆T limitation........................................................62
− Third stage ∆T supervision ........................................................63
− PWM pump control......................................................................63
− H-Q chart (example) .................................................................63
− Adaption of modulating pump to the heating plant.........................64
− Parametes of the PWM pump (OEM).............................................64
− Preset parameters .......................................................................64
− Activation of PWM pump via a configuration byte.............................65
− Parameters of the PWM pump (installer) ........................................66
− Parameters for temperatures ........................................................66
− PID controller coefficients of delta-T supervision ..............................67
− Summary of all ∆T parameters ......................................................67
− Behavior in different operating modes ............................................68
− Pump overrun..........................................................................68
− Normal operation (heating operation) ..........................................68
− Reduced (setback) operation .....................................................68
− Shutdown mode.......................................................................68
− Heating up phase.....................................................................68
− DHW operation ........................................................................69
3.9 Heating circuit control..........................................................................70
− Attenuated outside temperature .................................................70
− Composite outside temperature ...................................................71
− Type of building construction .....................................................71
− Heating curves .........................................................................72
− Generating the demands for heat ..................................................73
− Time switch.............................................................................74
− Room thermostat .....................................................................75
− RU .........................................................................................75
− Combinations of RU and room thermostat / time switch.................76
− ECO functions ............................................................................77
− S / W changeover.....................................................................77
− Automatic 24-hour heating limit ..................................................77
− Quick setback constant (KON) ......................................................78
− Generating the temperature demands .............................................78
− With fixed value control or emergency operation...........................78
− With weather compensation.......................................................78
4 Clip-in AGU2.500... for additional heating circuit.................................79
− Functions ...................................................................................79
− General...................................................................................79
− Hydraulic diagrams......................................................................79
− Sensor inputs (analog inputs)........................................................79
− Inputs / outputs...........................................................................79
− Interfaces for the LMU... ...............................................................80
− Sensor.......................................................................................80
− Frost protection ...........................................................................80
− Overtemperature protection..........................................................80
− Mixing circuits..........................................................................80
− Determining the flow temperature setpoint ......................................80
− Handling the locking signal........................................................80
5/171
Siemens Building Technologies Basic Documentation LMU54... / LMU64... CC1P7494en
HVAC Products Contents 07.11.2002

− Handling the forced signal......................................................... 80
− Flow temperature control.............................................................. 80
− Pump control.............................................................................. 81
− Pump control with pump circuits .................................................81
− Pump control with mixing circuits ............................................... 81
− Pump overrun ..........................................................................81
− Pump kick............................................................................... 81
− Mixing valve control .....................................................................81
− Position of mixing valve in the idle state...................................... 81
− Functional test ............................................................................ 81
5 Clip-in module OCI420... for communication via LPB.......................... 82
− Functions ................................................................................... 82
− General .................................................................................. 82
− Inputs / outputs ...........................................................................82
− Interfaces to LMU... .....................................................................82
5.1 Connection of LMU... to ALBATROS via OCI420 (LPB clip-in) .................. 82
5.1.1 Additional heating circuit extensions via ALBATROS controllers................ 82
− Automatic changeover of operating mode .......................................83
− Giving consideration to heat demand from the RVA… ......................83
− Locking and forced signals when connecting to the LPB................... 83
5.1.2 External DHW heating by ALBATROS controllers ................................... 83
− Type of priority of DHW heating .................................................... 84
5.1.3 Multiboiler plants with LMU (cascade applications).................................. 84
− Separate DHW circuit in cascade applications................................. 85
− Operation with the RVA65... ......................................................... 85
5.1.4 System functions ................................................................................ 86
− Uniform system time.................................................................... 86
− Error / diagnostic messages from the LMU...................................... 86
− Outside sensor, outside temperature sensor................................... 88
− Assignment of address numbers................................................ 88
− Setting the LPB device and segment address................................. 88
6 Clip-in function module AGU2.51x ..................................................... 89
− Functions ................................................................................... 89
− General .................................................................................. 89
− Outputs...................................................................................... 89
− Number of available outputs ......................................................89
− Inputs........................................................................................ 90
− Digital input ............................................................................. 90
− Analog input ............................................................................ 90
− Predefined setpoint (temperature demand) ..................................90
− Predefined output .................................................................... 91
− Sensor input “Pressureless header”............................................ 91
7 DHW control (BWR) .......................................................................... 93
− Boiler temperature setpoint during DHW heating with storage tank
systems ..................................................................................... 93
− DHW temperature control............................................................. 94
− Compensation variants............................................................. 94
− Position of diverting valve.......................................................... 95
− Storage tank systems............................................................... 95
− Stratification storage tank.......................................................... 96
6/171
Siemens Building Technologies Basic Documentation LMU54... / LMU64... CC1P7494en
HVAC Products Contents 07.11.2002

− Instantaneous DHW system ........................................................ 100
− Notes ................................................................................... 100
− Hydraulic diagram.................................................................. 100
− Operating mode........................................................................ 100
− Outlet temperature control (FS-DHW is closed).......................... 100
− Comfort control (after FS-DHW opening)................................... 100
− Aqua-booster system.................................................................. 103
− Hydraulic diagram.................................................................. 103
− Operating mode........................................................................ 103
− Outlet temperature control .......................................................103
− Comfort control ......................................................................103
− Legionella function .................................................................... 104
7.1 Special functions .............................................................................. 105
− Forced signals .......................................................................... 105
− Parameterization....................................................................... 105
− Via PC tool ACS420 and OCI490... .......................................... 105
− Via QAA73... / AGU2.310........................................................ 105
− Via AGU2.361 / AGU2.303...................................................... 106
− Programmable input of the LMU... ............................................... 106
− Modem function..................................................................... 106
− Warm air curtain function ........................................................ 106
− Programmable output of the LMU... ............................................. 107
− Status output......................................................................... 107
− Alarm output ..........................................................................107
− Operational status signal......................................................... 107
− Switching off the external transformer ....................................... 108
− Pump output second heating circuit.......................................... 108
− DHW circulating pump............................................................ 108
− Actuating device with warm air curtain function activated............. 108
− Pump of pressureless header .................................................. 108
− Basic function of controller clip-in module.................................. 108
− Actuating device with full DHW charging activated...................... 108
− Actuating device when analog signal exceeds threshold ..............109
− Power concept.......................................................................... 109
8 Basic diagram................................................................................. 110
8.1 LMU... ............................................................................................. 110
9 Connection diagrams...................................................................... 111
9.1 LMU... ............................................................................................. 111
9.2 DHW stepper motor (bipolar).............................................................. 112
9.3 AGU2.104A109................................................................................ 112
9.4 AGU2.500A109................................................................................ 113
9.5 AGU2.500A209................................................................................ 114
9.6 OCI420A109 .................................................................................... 115
9.7 OCI420A209 .................................................................................... 116
9.8 AGU2.51x ........................................................................................ 117
9.9 Connecting cable between OCI490... and PC .......................................118
9.10 Mounting, electrical installation and service.......................................... 119
− Mounting (general) .................................................................... 119
− Mounting the LMU5x............................................................... 119
7/171
Siemens Building Technologies Basic Documentation LMU54... / LMU64... CC1P7494en
HVAC Products Contents 07.11.2002

− Ignition device...........................................................................119
− Terminals and wiring .................................................................119
− Testing by the customer.............................................................120
10 Technical data ................................................................................121
10.1 LMU................................................................................................121
− General....................................................................................121
− Electrical connection data ........................................................... 122
− Cable lengths (LMU... Ö HMI and LMU... Ö Clip-in).................126
− Connectors ..............................................................................126
10.2 Clip-in .............................................................................................127
10.2.1 AGU2.500........................................................................................127
− Outputs....................................................................................127
− Electrical connections................................................................127
− Input........................................................................................127
10.2.2 AGU2.51x........................................................................................127
− Outputs....................................................................................127
− Electrical connections................................................................127
− Input........................................................................................127
10.3 External components ........................................................................128
− RAST5 connectors ....................................................................128
− Mains transformer .....................................................................128
− Fan with DC 24 V motor.............................................................128
− Fan with DC motor operating on mains voltage..............................128
11 Dimensions....................................................................................129
11.1 LMU5x... .........................................................................................129
11.2 LMU6x... .........................................................................................130
11.3 AGU2.500A109 / AGU2.51xA109 .......................................................131
11.4 AGU2.500A209................................................................................132
11.5 OCI420A109....................................................................................133
11.6 OCI420A209....................................................................................134
11.7 Mounting plate for clip-in module ........................................................135
12 Parameter list / legend of parameter bit fields LMU... ........................ 136
12.1 Parameter list...................................................................................136
− Parameter list LMU....................................................................136
− Temperatures........................................................................136
− Switching differentials.............................................................137
− Controller functions ................................................................137
− Controller times .....................................................................138
− Controller coefficients.............................................................138
− Pressures .............................................................................138
− Burner control fan ..................................................................139
− Burner control sequence.........................................................139
− Burner control identification.....................................................140
− Operating data......................................................................140
− MCI......................................................................................140
− LPB .....................................................................................140
12.2 Lockout position storage....................................................................141
− Phase designations / numbers ....................................................141
8/171
Siemens Building Technologies Basic Documentation LMU54... / LMU64... CC1P7494en
HVAC Products Contents 07.11.2002

12.3 Legend of parameter bit fields LMU..................................................... 142
− Controller functions ................................................................ 142
− Burner control program........................................................... 145
− Operating modes ................................................................... 147
− LPB...................................................................................... 147
13 Glossary of abbreviations ................................................................148
− Constants................................................................................. 148
− Variables.................................................................................. 148
14 Addendum: Hydraulic diagrams BMU............................................... 149
14.1 Hydraulic diagrams ........................................................................... 149
− Basic diagrams......................................................................... 149
− Pump circuit extensions via AGU2.500......................................... 151
− Mixing circuit extensions via AGU2.500... ..................................... 153
− Zone extensions........................................................................ 156
− Heat generation manager........................................................... 162
14.2 Assignment of hydraulic diagrams to the outputs of the LMU…............... 166
9/171
Siemens Building Technologies Basic Documentation LMU54... / LMU64... CC1P7494en
HVAC Products Contents 07.11.2002
1 Overview
Brief description
QAA73...
LMU... are Boiler Management Units (BMUs) of digital design for use with gas-fired
appliances equipped with premix burners.
They are used for the startup, control and supervision of premix burners having the
capacity ranges < 70 kW, 70 - 120 kW or > 120 kW in intermittent operation and with
direct ignition of the main flame.
The LMU... provide all supervisory and control functions required for burner, heating and
DHW operation and make possible modular system extensions via integrated
communication interfaces.
Output modulation is accomplished via a PWM-controlled fan, and pneumatic fuel / air
ratio control with the help of a gas valve.
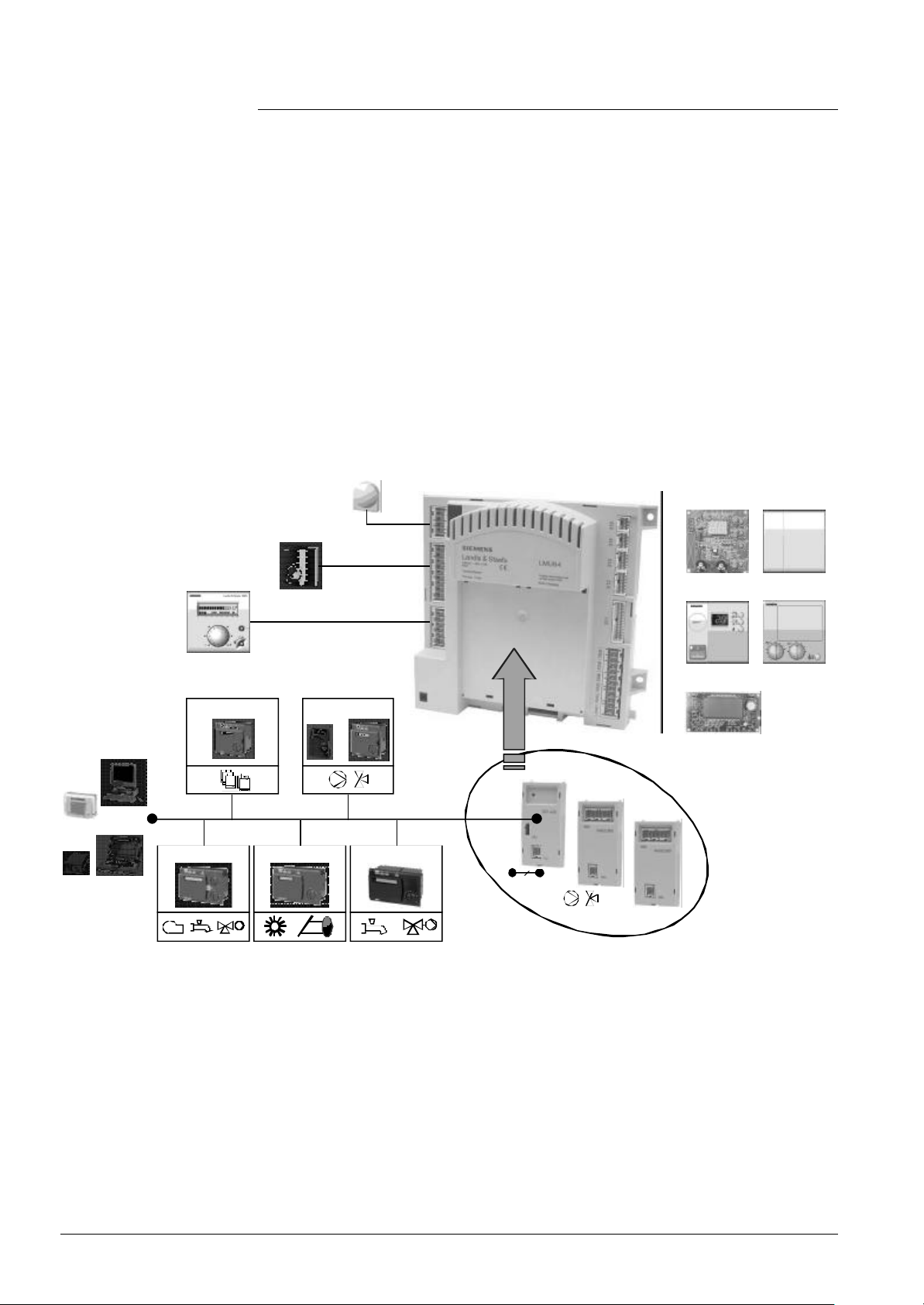
1.1 System concept
LMU...
QAC34...
Room thermostat /
time switch
Human Machine Interface
AGU2.303...
(HMI)
AGU2.350...
Building automation /
remote management
OCI / ACS
Service tool
Modulating room unit
RVA47... RVA46...
LPB
RVA65...RVA63... RVA66...
LPB
Clip-in
Auxiliary modules
OCI420
AGU2.500
AGU2.51x
0...10 V
4...20 mA
AGU2.361...
AGU2.310...
AGU2.362...
7494b01E/0702
10/171
Siemens Building Technologies Basic Documentation LMU54... / LMU64... CC1P7494en
HVAC Products 1 Overview 07.11.2002

1.2 Features
Below, the full functionality of the LMU... is described. For information on the scope of
functions of a specific unit, refer to the relevant version / configuration.
Safety functions
Supervision / protective
functions for the plant
• Gas burner control conforming to EN 298 for intermittent operation
• Integrated boiler / burner control for space heating and DHW operation
• Sequence control depending on the boiler’s capacity: < 70 kW, 70 - 120 kW, or > 120 kW.
Boiler capacities up to about 600 kW can be handled (depending on the type of fan /
gas valve used)
• Integrated electronic (safety) limit thermostat
• Integrated limit thermostat function
• Direct ignition of the main flame by means of
− integrated single-pole high-voltage ignition (with the choice of single-electrode
operation)
− external AC 230 V ignition control (optional)
• Continuous (analog) ionization current supervision with optional indication of flame
intensity
• Gas valve control AC 230 V (RAC optional)
• Number of start repetitions can be programmed
• Quick startup (especially in connection with instantaneous DHW systems)
• Fan supervision
• Optimization of combustion (optional)
• Control of an AC 230 V fan (DC 24 V fan optional)
• Ignition load precontrol via speed readjustment
• Adaptive postpurge level of fan speed
• Load limitation (fan limitation by minimum / maximum speed and / or flame signal)
• Number of fan feedback pulses can be selected
• Flame stabilization time
• Boiler cycling protection via minimum boiler off time
• Dynamic switch-off differentials for space heating (Hz) and DHW (Bw) operation
• Pump and diverting valve kick
• Frost protection functions for the plant, the boiler, DHW and the room
• Water pressure supervision (pressure sensor with static and / or dynamic supervision,
contact for pressure switch, flow switch)
• Flue gas temperature supervision
Auxiliary modules
(clip-in)
• OCI420 clip-in for communication, LPB interface for ALBATROS system world
• AGU2.500 clip-in for additional heating circuit
• AGU2.51x clip-in function module
- inputs: NTC, 10 kΩ
digital input
0(4)...20 mA
DC 0...10 V
- outputs: max. 3 relays AC 230 V
11/171
Siemens Building Technologies Basic Documentation LMU54... / LMU64... CC1P7494en
HVAC Products 1 Overview 07.11.2002

DHW
• Integrated DHW systems with specific algorithms for storage tank, stratification
storage tank, instantaneous and aquabooster systems
• Instantaneous DHW heating systems with optional comfort function
• DHW heating with charging pump / diverting valve
• Diverting valve control via stepper motor control, N.O. contact with continuous phase
or changeover contact
• DHW control with sensor or thermostat
• Control of DHW circulating pump with QAA73...-V1.4
Heating circuit
System application
• Integrated weather-compensated pump heating circuit
• PWM-controlled heating circuit pump with specific algorithms to ensure most effective
condensation, improved overall efficiency and enhanced room comfort (optional)
• Additional weather-compensated heating circuit for single-user applications via
modular clip-in add-on module AGU2.500 (pump or mixing heating circuit) with
independent minimum / maximum limitation and heating curve.
Independent time switch program in connection with the QAA73...
• Automatic summer / winter changeover
• Automatic 24-hour heating limit (with no RU connected)
• Quick setback (with no RU connected)
• Compensation variants with room thermostat / time switch (single- or dual-channel
time switch)
• Compensation variants with room controls via integrated interface based on
OpenTherm (QAA73... / QAA53...)
• Integrated interface on OpenTherm basis
• Communication capability via the Local Process Bus (LPB) by means of clip-in
module
• Consistent system architecture of RVA… controllers
• Optional remote supervision
• Connection via LPB clip-in module to
− RVA46... zone controllers
− RVA47... cascade controllers
− RVA63... boiler and heating circuit controllers
− RVA65... energy managers for solar, wood, etc.
− RVA66... boiler and heating circuit controllers
− OCI6... communication interface for remote supervision (in connection with
appropriate ACS… software)
1)
Operation / service
• Modular and flexible concept of operating units AGU2.3...; optionally with housings for
flush panel mounting, degree of protection IPX4D (splash-proof) and LCD model with
clock function and backlit display
• Chimney sweep function
• Controller stop function for output adjustment
• Error messages with lockout storage and fault history
• Display and interrogation of all relevant process parameters via operating units,
QAA73... and PC tool
• Counter for the number of startups and the number of operating hours
• Maintenance functions with service message
1)
• Automatic plant configuration (identification of RU, connected HMI, sensors, etc.)
1) Planned; on request
12/171
Siemens Building Technologies Basic Documentation LMU54... / LMU64... CC1P7494en
HVAC Products 1 Overview 07.11.2002

Parameterization
• Via PC tool ACS420
• Via room unit QAA73...
• Via operating units AGU2.3...
• Via specific final production test tool ACS421
Mains transformer
Other features
• Mains transformer integrated in the unit
An additional external transformer is not absolutely required (only when using a fan
operating on DC 24 V, or in the case of stepper motor control).
• Multifunctional housing with mechanical attachment facility for maximum 2 clip-in
modules
− Integrated exchangeable main fuse AC 230 V
− Integrated installer interface via RAST5 connector
• Optional extensions with up to 2 flexible clip-in modules that can be matched to
individual customer needs
• Programmable relay output (AC 230 V) for specific functions
• Programmable digital input for specific functions
• Housing / clip-in modules of advanced design made of recyclable plastic
1.3 Product range
Target market
Heating plants
Heat generating
equipment
Refer to chapter 2, «Product range overview».
1.4 Field of use
The LMU... are designed for use by OEMs. They are supplied directly to the boiler
manufacturer and enhance both the functionality and the level of outfit of gas-fired
boilers.
Suited for all types of standard heating systems such as radiator or underfloor heating
systems in the residential sector (one-family houses or blocks of flats).
Primarily for use with:
• Premixing or condensing gas-fired appliances with modulating burners using PWM
DC fans and pneumatic fuel / air ratio control, in intermittent operation and with direct
ignition of the main flame
• Capacity ranges < 70 kW, 70...120 kW, or > 120 kW
• Heating boilers or combi boilers with DHW storage tanks or instantaneous DHW
heaters
13/171
Siemens Building Technologies Basic Documentation LMU54... / LMU64... CC1P7494en
HVAC Products 1 Overview 07.11.2002

1.5 Notes on product liability
• The units may only be used in building services plant in accordance with the
applications and features described above
• When using the products, all requirements specified in chapter «Technical data» must
be observed
• The local safety regulations must be complied with
1.6 Notes on environmental protection
Disposal notes
The LMU... contains electrical and electronic components and may not be disposed of
together with household waste. Local and currently valid legislation must be
observed!
14/171
Siemens Building Technologies Basic Documentation LMU54... / LMU64... CC1P7494en
HVAC Products 1 Overview 07.11.2002
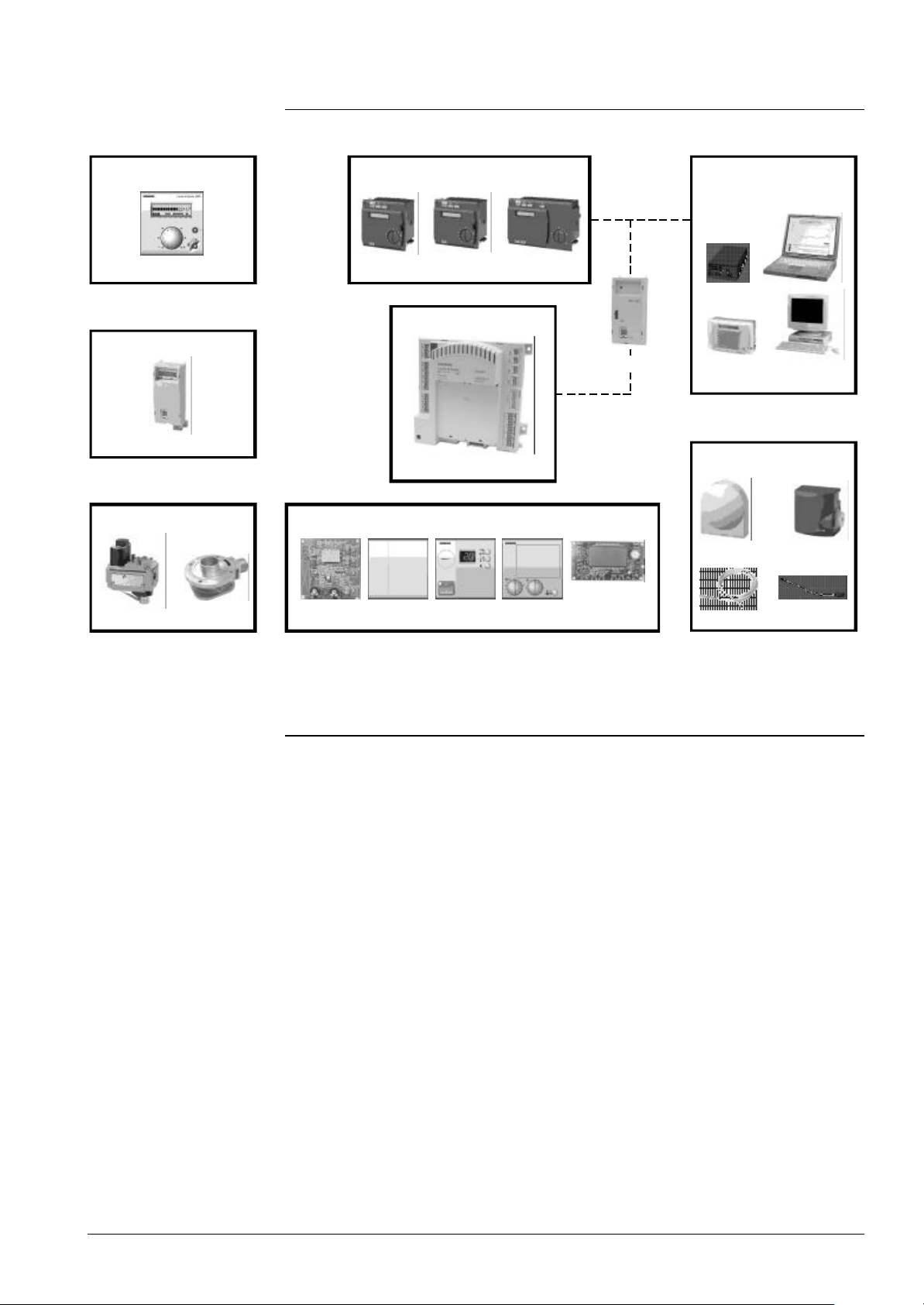
2 Product range overview
7494b02E/0802
Room units
QAA73...
Clip-in modules
AGU2.5xx
Gas valves / Mixer
AGU3.6...
Controllers
RVA46... RVA47... RVA...
BMU
OCI420...
LMU...
HMI
AGU2.350 AGU2.361 AGU2.362AGU2.303 AGU2.310
Service remote
management
ACS6... / OCI6...
Temp. sensors
QAC34...
QAZ36...
QAL36...VDU...
QAD36...
BMU
Controller
Service tool
The following units and accessories are designed for use with the ALBATROS range:
Type of unit Description Documentation no.
LMU54... BMU (without housing, without combustion optimization) CC1P7494
LMU64... BMU (with housing, without combustion optimization) CC1P7494
1)
1)
REA02... Room thermostat (RAA20) CE1N3002
REA11... Room temperature controller CE1P2274
RVA46... Heating controller CE1P2372
RVA47... Cascade controller for modulating gas-fired CE1P2379
heating boilers
RVA63... Heating circuit controller CE1P2373
RVA65... Heat energy manager CE1P2392
RVA66... Heating circuit or primary controller with DHW control CE1P2378
2)
2)
2)
OCI490A109 PC interface for ACS42X... -ACS420 Software for OCI490A109
ACS421 Final production test software
Remote supervision
ACS... Operating software CE1B2530
OCI6... Central communication unit CE1N2530 / 2531
15/171
Siemens Building Technologies Basic Documentation LMU54... / LMU64... CC1P7494en
HVAC Products 2 Product range overview 07.11.2002
2)
2)

Room units
QAA73... RU for boiler control with OpenTherm interface CE1P2284
QAA53... RU for boiler control with OpenTherm interface CE1Q2282
Clip-in modules
Gas valve
Sensor
AGU2.500A109 Clip-in for additional heating circuit
AGU2.500A209 Clip-in for additional heating circuit (printed circuit board version)
AGU2.511A109 Clip-in function module, voltage relay
AGU2.513A109 Clip-in function module, current relay
AGU2.514A109 Clip-in function module, sensor relay
AGU2.515A109 Clip-in function module, digital input relay
OCI420A109 Clip-in for communication LPB interface
OCI420A209 Clip-in for communication LPB interface (printed circuit board version)
VDUxxx Compact gas control loop with pneumatic fuel / air CC1N7662
ratio control
AGU3.6... Gas / air mixing device (pressure side) --
QAC34/101 Outside sensor NTC 1kΩ CE1Q1811
QAD36/101 Strap-on temperature sensor NTC 10 kΩ -QAK36... Screwed immersion temperature sensor NTC 10 kΩ --
QAL36.225 Universal temperature sensor NTC 10 kΩ CE1Q1842
QAZ36.522/109 Cable temperature sensor NTC 10 kΩ, cable length 2 m CE1Q1843
QAZ36.526/109 Cable temperature sensor NTC 10 kΩ, cable length 6 m CE1Q1843
2)
2)
Operating section
Cable
AQL21.30 Holding spring for QAL36.225, 30 mm -AQL21.42 Holding spring for QAL36.225, 42 mm --
AGU2.350A109 Dummy cover, housing for flush panel mounting,
degree of protection IPx4D
AGU2.361A109 Operating section for boiler, housing for flush panel mounting,
degree of protection IPx4D
AGU2.362A109 Operating section for heating circuit, housing for flush panel mounting,
degree of protection IPx4D
AGU2.303B109 Operating section, type of printed circuit board
AGU2.310A109 Operating unit with LCD (printed circuit board version)
AGU2.100A109 Connecting cable LMU... Ö AGU2.303 / AGU2.361 / AGU2.310
AGU2.101A109 Connecting cable AGU2.361 Ö AGU2.362
AGU2.102A109 Connecting cable AGU2.361 Ö control panel mounting QAA73...
AGU2.103A109 Connecting cable service interface AGU2.361 Ö QAA73...
1) 2)
1) 2)
1) 2)
1) 2)
AGU2.104A109 Connecting cable LMU... Ö Clip-in module AGU2.500 / OCI420
1)
1)
1)
1)
1)
2)
1)
Refer to Operating Instructions CC1B7494
2)
On request
16/171
Siemens Building Technologies Basic Documentation LMU54... / LMU64... CC1P7494en
HVAC Products 2 Product range overview 07.11.2002

3 Functions
3.1 Burner control
Program selection
EEPROM
Forced intermittent
operation
Parameterization enables certain parts of the burner control program to be changed,
thus permitting a number of different burner control sequences.
The burner control sequences are distinguished by their capacity ranges in which the
boilers shall operate.
In accordance with the standards, there are 3 different capacity ranges:
• < 70 kW
• 70...120 kW
• > 120 kW
For all capacity ranges, there are additional parameterization choices available,
enabling the burner control’s sequence and times to be matched to specific
requirements.
The EEPROM of the LMU... is used to store the burner control’s program sequence and
lockout positions.
Also, control parameters and other setting values are filed in EEPROM.
Forced intermittent operation ensures that the burner control initiates shutdown after no
more than 24 hours of continuous operation.
This enables the burner control to perform the internal self-tests included in the startup
and shutdown sequence.
Burner control program
The burner control’s program ensures orderly operation of the unit including startup and
shutdown as well as flame supervision.
The sequence can be altered by changing certain parameters.
If there are deviations from the defined sequence, or in the case of a reset, the program
initiates safety shutdown (home run) and then - depending on the setting made lockout, restart or start prevention.
The program sequence is controlled in accordance with the program’s phases. The
individual phases are grouped and include startup, operation, shutdown and home run.
After a reset (power on), the burner starts its home run. Depending on the available
(parameterized) input / output signals or program times (e.g. prepurging), the individual
program phases will be either executed or skipped.
The burner control’s program is designed for intermittent operation. To verify orderly
functioning (detection of faults), a complete program cycle is required.
In the «Standby» position, the burner control is ready to operate and waits for a heat
demand signal from the controller, or it demands start prevention (no release).
The burner control maintains the «Operation» position until no more heat is demanded
by the controller - but for no more than 24 hours. On completion of that period of time,
the burner control will automatically enforce intermittent operation.
17/171
Siemens Building Technologies Basic Documentation LMU54... / LMU64... CC1P7494en
HVAC Products 3 Functions 07.11.2002
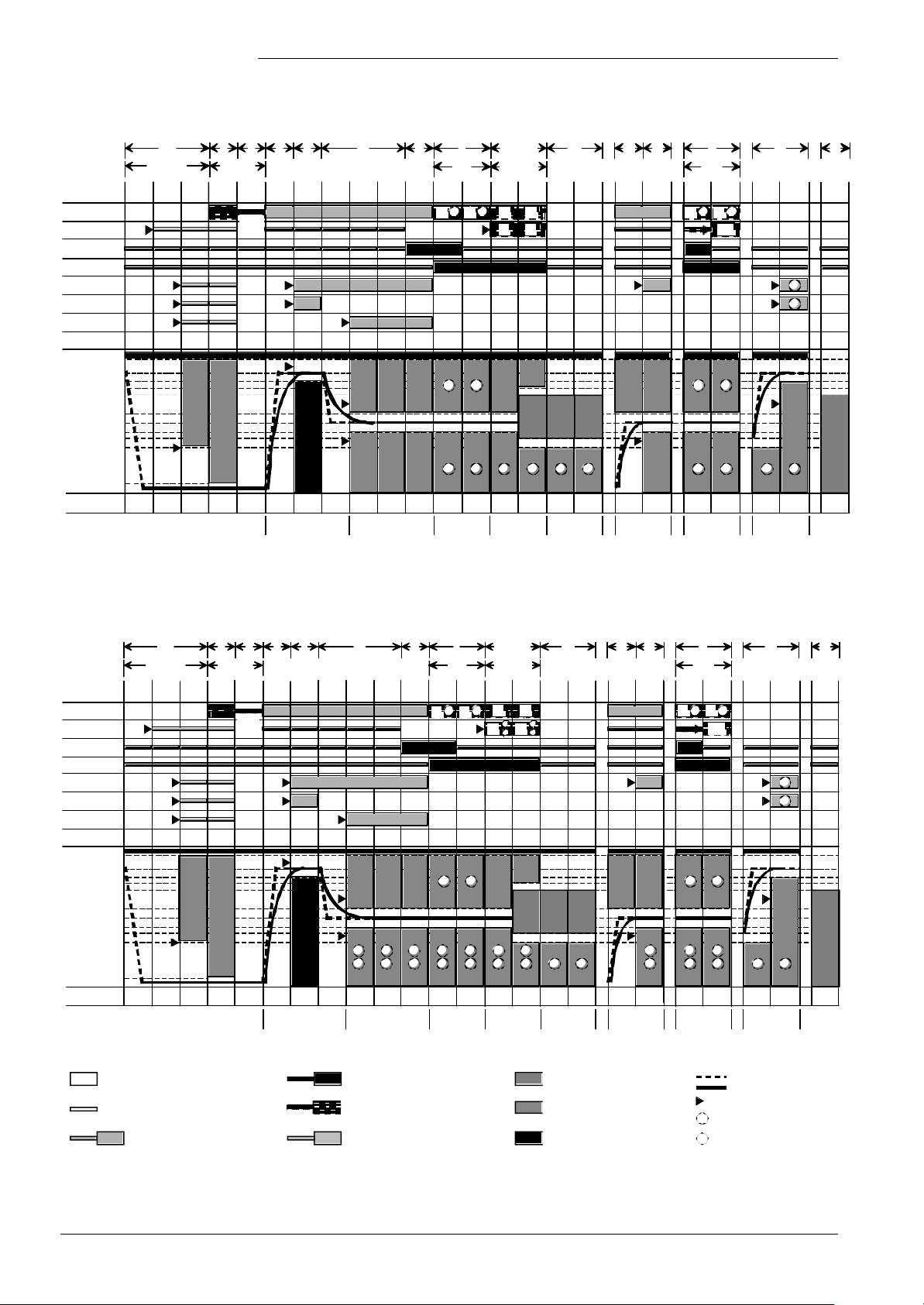
Sequence diagram
Capacity range < 70 kW
HMI
display:
Phase
Heat demand
Flame
Ignition
BV
LP (2)
LP (3)
LP (4)
NoG_Max
N_Vor
-N_Vor_Delta
+N_VL_Delta
N_VL
+N_ZL_Delta
N_ZL
-N_ZL_Delta
N_TL
-N_TL_Delta
NoG_Null
7494f01e/0801
22 0 1 2 3 654
PH_TNB
Home run
TLOTNB
PH_TLO PH_TNN
Standby
TNN tsa1 tsa2
PH_
STANDBY
PH_
STARTVER
PH_
STANDBY
THL1
PH_
THL1_1
dependent on
10 Hz
11 Bw
12 Hz+Bw
tsa
Operation
tv TBRE TW1 TW2 tvz tsa1 tsa2 tn
PH_TV PH_TBRE PH_TW1 PH_TW2 PH_TVZ
PH_
TSA1_1
PH_
THL2
PH_
TSA2_1
PH_
Z
THL2
PH_
ti
MODULATION
PH_
THL2
PH_
THL2
PH_
THL2_1
PH_TI
PH_
Z
THL2
PH_
THL2
ZZ
ZZ
parameter
setting
dependent on
parameter
setting
dependent on
20 2 4 7 21 99
tsa
PH_TN_1
THL1 (TW1)
PH_
PH_TW1
THL1_2
PH_
TSA1_2
PH_
THL2
Z Z
PH_
THL2
PH_
TSA2_2
PH_
TSA1_2
THL2 tn
PH_
PH_TN_2
THL2_2
Z
Z
ZZ
parameter
setting
ZZZZ
dependent on
parameter
setting
dependent on
parameter
setting
dependent on
parameter
setting
ZZZZ
PH_
STOER
Capacity range 70...120 kW
HMI
display:
Phase
Heat demand
Flame
Ignition
BV
LP (2)
LP (3)
LP (4)
NoG_Max
N_Vor
-N_Vor_Delta
+N_VL_Delta
N_VL
+N_ZL_Delta
N_ZL
-N_ZL_Delta
N_TL
-N_TL_Delta
NoG_Null
7494f02e/0201
PH_TNB
22
Home run
TLOTNB
PH_TLO PH_TNN
0 1
Standby
TNN tsa1 tsa2
PH_
STANDBY
PH_
STARTVER
PH_
STANDBY
3
2
tv TBRE
THL1
PH_
PH_TV PH_TBRE PH_TW1 PH_TW2 PH_TVZ
THL1_1
TW1
Z
R
dependent on
parameter
setting
10 Hz
11 Bw
654
12 Hz+Bw
tsa
Operation
TW2 tvz tsa1 tsa2 tn
PH_
TSA1_1
PH_
THL2
Z
PH_
TSA2_1
PH_
THL2
ti
PH_TI
PH_
THL2
Z
Z
PH_
PH_
THL2
THL2
R
PH_
MODULATION
PH_
THL2
20 2 4 7 21 99
PH_
PH_TN_1
THL2_1
Z
R
ZZ
RR
dependent on
parameter
setting
ZZ
ZZ
R
ZZ
RR
dependent on
parameter
setting
ZZ
THL1 (TW1)
PH_
PH_TW1
THL1_2
dependent on
parameter
setting
tsa
PH_
TSA1_2
PH_
THL2
Z Z
TSA2_2
PH_
THL2
PH_
TSA1_2
PH_
THL2_2
PH_TN_2
PH_
STOER
THL2 tn
PH_
Z
Z
ZZ
R
dependent on
parameter
setting
ZZ
dependent on
parameter
setting
ZZ
R
Z
RR
Logic on
Logic off
On deviation
transition to home run
Deviation leads to lockout
On deviation transition to
specified or following
phase
Control
Permitted range
Prohibited range
-> Home run
Prohibited range
-> Lockout
Control signal
Ideal signal
Transition criterion
Triggering forced prepurging
Z
Repetition can be parameterized,
R
then lockout
18/171
Siemens Building Technologies Basic Documentation LMU54... / LMU64... CC1P7494en
HVAC Products 3 Functions 07.11.2002

Repetition can be parameterized,
Sequence diagram
Capacity range > 120 kW
HMI
display:
Phase
Heat demand
Flame
Ignition
BV
LP (2)
LP (3)
LP (4)
NoG_Max
N_Vor
-N_Vor_Delta
+N_VL_Delta
N_VL
+N_ZL_Delta
N_ZL
-N_ZL_Delta
N_TL
-N_TL_Delta
NoG_Null
7494f03e/0201
PH_TNB
Logic on
Logic off
On deviation
transition to home run
PH_
THL2
PH_
TSA2_1
ZZ
Z
10 Hz
11 Bw
12 Hz+Bw
Operation
PH_
ti
MODU-
PH_TI
LATION
PH_
THL2
20 2 4 7 21 99
PH_
THL2
PH_
THL2_1
dependent on
parameter
setting
PH_TN_1
ZZ
THL1 (TW1)
PH_
THL1_2
dependent on
parameter
setting
Permitted range
Prohibited range
-> Home run
Prohibited range
-> Lockout
22
Home run
TLOTNB
PH_TLO PH_TNN
0 1
Standby
TNN tsa1 tsa2
PH_
PH_
STANDBY
STARTVER
PH_
STANDBY
3
2
tv TBRE
THL1
PH_
PH_TV PH_TBRE PH_TW1 PH_TW2 PH_TVZ
THL1_1
dependent on
parameter
setting
TW1
654
tsa
TW2 tvz tsa1 tsa2 tn
PH_
TSA1_1
PH_
Z
THL2
dependent on
parameter
setting
Deviation leads to lockout
On deviation transition to
specified or following
phase
Control
PH_TW1
tsa
PH_
TSA1_2
PH_
Z Z
THL2
dependent on
parameter
setting
Z
R
THL2 tn
PH_
PH_
TSA2_2
THL2_2
PH_
THL2
PH_
TSA1_2
ZZ
dependent on
parameter
setting
Control signal
Ideal signal
Transition criterion
Triggering forced prepurging
then lockout
PH_TN_2
PH_
STOER
Z
Z
ZZ
Description of sequence
diagrams
The burner control’s program is subdivided into different phases. Each phase is
identified by a certain output and input configuration of the burner control.
For the precise sequence of signals, refer to the sequence diagrams.
Signal sequences not shown in the sequence diagrams are summarized under «Special
cases».
The times given in the sequence diagrams are distinguished as follows:
UPPERCASE LETTERS (e.g. «THL1») constants stored in ROM
Lowercase letters (e.g. «tsa») parameters stored in EEPROM
With regard to the speed feedback signal, the following nominal levels are used:
N_Vor, N_VL, N_ZL, N_TL
Prepurging Nominal load
1)
Previously «Full load» (VL)
1)
Ignition load Partial load
Siemens Building Technologies Basic Documentation LMU54... / LMU64... CC1P7494en
HVAC Products 3 Functions 07.11.2002
19/171
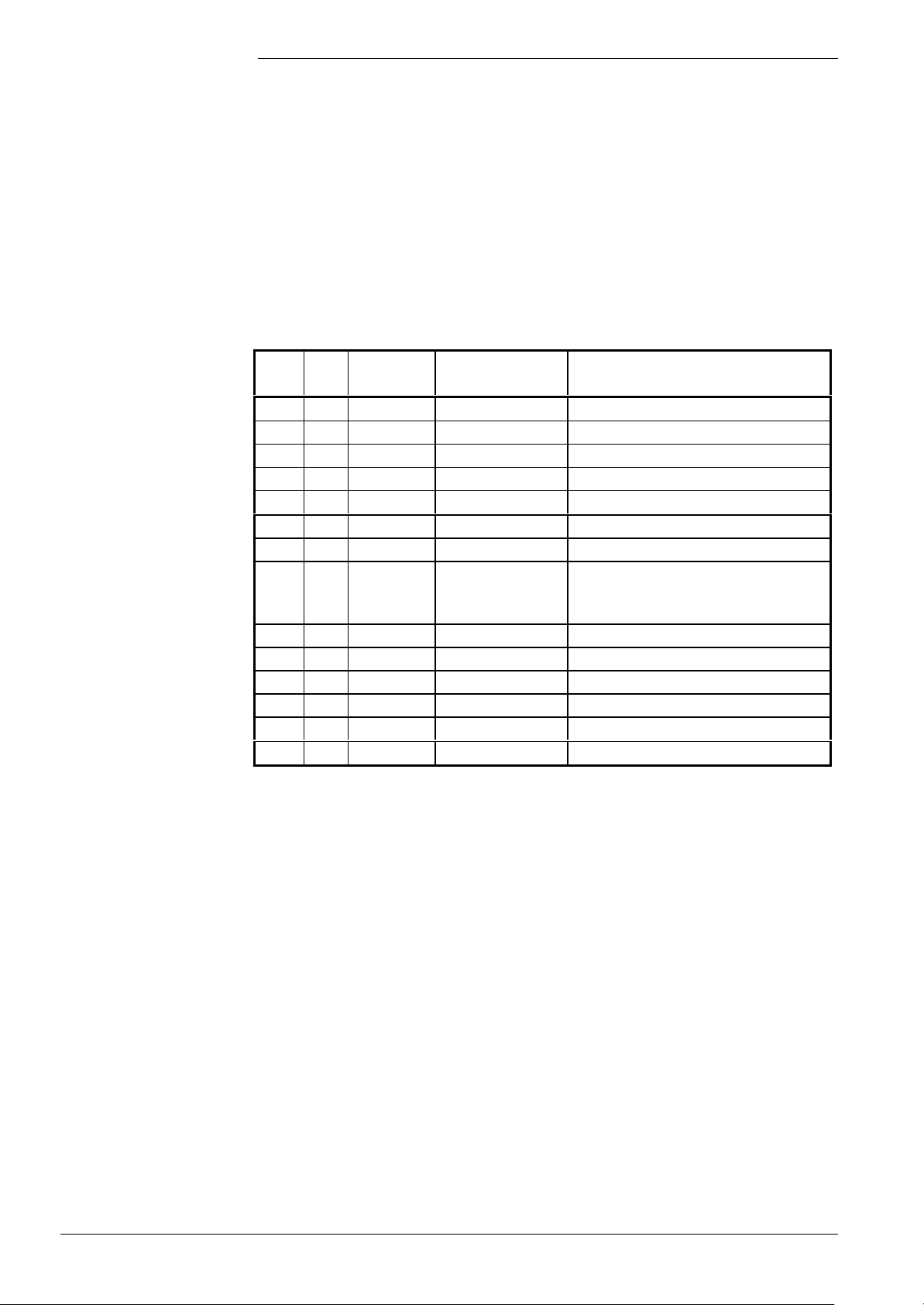
According to the sequence diagram, there is a permitted tolerance band with an upper
and a lower limit for each level (e.g. «N_ZL»), which is defined via parameter
«N_XX_Delta».
The relevant sequence phases (refer to the sequence diagrams) are queried for these
limits.
Example: Ignition load upper limit = «N_ZL» + «N_ZL_Delta»
lower limit = «N_ZL» - «N_ZL_Delta»
These limit values are complemented by «NoG_Null» and «NoG_Max» (refer to the
sequence diagrams).
«NoG_Max» is the maximum speed that must never be reached. «NoG_Null» is the low
speed that must be crossed when changing to standby.
Sequence times
Time
Min.
(s)
TNB 0.2 21.0 Lockout position Afterburn time
TLO 0.2 51.0 Lockout position Open LP
TNN 0.2 51.0 Lockout position Down to speed = 0
THL1 0.2 51.0 Lockout position First fan runup time
THL2 0.2 51.0 Lockout position Second fan runup time
tv 0 51.0 Switching Prepurging
TBRE 0.2 51.0 Lockout position Brake time until ignition load is reached
TW1 0.2 51.0 Lockout position
tvz 0.2 5.0 Switching Preignition time
TSA 1.8 9.8
tsa1 0.2 9.6
tsa2 0.2 TSA-tsa1
ti 0.2 10 Switching Interval operation
tn 0 51.0 Switching Postpurging
1)
Lockout position or start repetition, depending on the flame signal and the parameter;
various parameterization choices (refer to relevant description)
2)
With parameterization with abortion of safety time in the case of flame detection, the times
of «tsa1» and «tsa2» are derived from the time of establishment of flame. It should be
noted, however, that «TSA» can never be exceeded
Max.
(s)
Response
Description
at end of
Waiting for internal sequence, speed
readjustment and optimization of
combustion
1)
2)
1)
2)
1)
Ignition safety time
Ignition safety time with ignition
Ignition safety time without ignition
The following phases (with associated times in parentheses) are relevant with one
startup / shutdown cycle:
Standby
• PH_STANDBY (unlimited): Burner control waits for a heat demand signal from the
controller
• PH_STARTVER: No external or internal release, relevant diagnostic code is delivered
Startup
The change from «Standby» to «Operation» is the startup triggered by a heat demand
signal from the controller.
If startup takes place with prepurging, startup will commence with the «PH_THL1_1»
phase; if no prepurging is used, with the «PH_THL1_2» phase.
20/171
Siemens Building Technologies Basic Documentation LMU54... / LMU64... CC1P7494en
HVAC Products 3 Functions 07.11.2002

• PH_THL1_1 (THL1): Maximum fan runup time to prepurging level. With «tv» > 0 or in
case of demanded forced prepurging
• PH_THL1_2 (THL1): Maximum fan runup time to ignition level. With «tv» = 0 and no
demanded forced prepurging
• PH_TV (tv): Prepurging phase
• PH_TBRE (TBRE): Maximum period of time for reaching the ignition level after
prepurging (reaching the speed band for the ignition load)
• PH_TW1 (TW1): Maximum waiting time until the following functions are performed:
− Internal safety tests: These tests are started the moment the startup phase
commences and already run in the background during the preceding phases
− Combustion optimization: Optimization of combustion deactivated or stepper motor
in start position
− Speed readjustment: Checkback signal delivered when the required speed for the
ignition load is reached for the first time
• PH_TVZ (tvz): Preignition time (can be parameterized, but minimum is 0.2 seconds)
• PH_TSA1_1; PH_TSA2_1; PH_TSA1_2; PH_TSA2_2; (TSA): Ignition safety time. If,
on completion of this period of time, there is no flame (also after several reignition
attempts), the burner control will initiate lockout or make a restart, depending on the
parameter settings made.
With parameterization with abortion of the safety time in the case of flame detection,
«TSA» can be shortened via flame establishment (refer to «PH_TSA1_2»,
«PH_TSA2_2»).
Parameterization choice 1:
• PH_TSA1_1 (tsa1, max. TSA): First part of the safety time with ignition switched on.
The fuel valve is open
• PH_TSA2_1 (TSA - tsa1, max. TSA): Second part of the safety time with ignition
switched off. The fuel valve is open
Parameterization choice 2:
• PH_TSA1_2 (max. TSA): First part of the safety time with ignition switched on.
Once a flame signal is detected, the change to the «PH_TSA2_2» phase (switching
ignition off) takes place. If there is no establishment of flame, the burner control stays
in the «PH_TSA1_2» phase until the end of «TSA» is reached
• PH_TSA2_2 (0.2 seconds, can be run through several times during «TSA»):
Second part of the safety time with ignition switched off. The fuel valve is open. 0.2
seconds after the change to the «PH_TSA2_2» phase, the flame signal is checked. If,
in that case, the flame has been lost, an immediate reignition attempt is made by
returning to the «PH_TSA1_2» phase.
This procedure can repeat itself until the end of «TSA» is reached.
If the flame is still present, the change to the «PH_TI» phase takes place.
Operation:
Start of the operating position is the «PH_TI» phase. If interval «ti» is not required, it
cannot be parameterized to 0 but only to a minimum of 0.2 seconds.
• PH_TI; (ti), interval required for stabilization of the flame
• PH_MODULATION; (unlimited), controller operation. In this phase, the controller
result is output
21/171
Siemens Building Technologies Basic Documentation LMU54... / LMU64... CC1P7494en
HVAC Products 3 Functions 07.11.2002

Shutdown
The change from the operating position to «Standby» is made when there is no more
demand for heat and is divided into «Shutdown» and «Home run».
«Shutdown» consists of postpurging, which can be deactivated.
With postpurging, there is a choice of 2 operating modes the difference being the way
the fan is controlled.
Parameterization choice 1:
• PH_THL2_1 (0.2 s): Change during postpurging, to the level of the last operating
command
• PH_TN1 (tn): Postpurging to the level of the last operating command
Parameterization choice 2:
• PH_THL2_2 (THL2): Change during postpurging, to the level of prepurging
• PH_TN2 (tn): Postpurging to the level of prepurging
Home run
Special cases (deviations)
The home run is used to bring about the change to the «Standby» position.
Normally, the home run is made on completion of «Shutdown».
After extraordinary events (refer to the sequence diagram), or in the case of a reset, the
home run brings the unit back to its basic position («Standby»).
In the case of a new demand for heat, the home run triggers a faster startup sequence.
This is accomplished by a shorter «TNN» followed by a direct change from the
«PH_TNN» phase to the «PH_THL1_1/2» phase. This means that the «Standby» state
will be skipped.
• PH_TNB (TNB): Permitted afterburn time
• PH_TLO (TLO): Permitted period of time with «LP» closed (if present) or speed >
«N_TL-N_TL_Delta»
• PH_TNN (TNN): Permitted period of time at speed > «NoG_Null»
• Forced prepurging: In the case of a reset after lockout and after power ON, forced
prepurging with the «LmodVOr» parameter is initiated, which takes place in the
«PH_TV» phase and which lasts 21 seconds, or «tv», if «tv» > 21 seconds.
The deviations marked with «Z» in the sequence diagram cause the burner control to
perform forced prepurging in the next startup phase.
• Repetition at the end of «TSA»: In the event no flame is established at the end of
«TSA», there is a choice of lockout or repetition can be triggered by changing to the
home run. The number of repetitions is limited and can be selected via the
«RepZaehler» parameter.
However, the general conditions of the different adjustable capacity ranges must be
observed (refer to the table further below).
• In the event of loss of flame during operation, the burner control initiates lockout or
changes to home run with restart, depending on the capacity range (refer to the table
further below)
• Prepurging: Can be deactivated by using the setting 0 seconds. In that case - as
shown on the sequence diagram - a change from the «PH_THL1_1» phase to the
«PH_TW1» phase will take place
• Preignition time: If parameter «tvz» is set to 0 (no ignition prior to «TSA»), the
«PH_TVZ» phase takes no more than 0.2 seconds (minimum time)
• Forced intermittent operation: After 24 hours of continuous operation at the latest,
forced intermittent operation is triggered, which ensures a regular shutdown to the
«PH_STANDBY» phase.
The timer for forced intermittent operation is reset in the «PH_STANDBY» phase.
Quick startup with forced intermittent operation is not possible.
22/171
Siemens Building Technologies Basic Documentation LMU54... / LMU64... CC1P7494en
HVAC Products 3 Functions 07.11.2002
• Safety time (TSA): As described above, the behavior of the burner control in the 2
1 SW run
different modes can be parameterized: Abortion of the safety time with flame
detection, and evaluation of the flame at the end of the safety time.
It must be noted that in the case of single-electrode operation, it is always «Evaluation of
the flame at the end of the safety time» that must be parameterized.
• Postpurging: Can be parameterized in 2 different ways, namely as postpurging on
the prepurging level, or as postpurging with the control used last. The duration of
postpurging is adjusted via «tn» (also see above)
• Start prevention: Certain internal or external events can trigger start prevention. In
that case, the burner control changes to the «PH_STARTVER» phase. The reason for
start prevention is given via the diagnostic code
The reason can be one of the following (examples):
− Open-circuit or short-circuit of flame detector
− No «GP» signal (depending on the parameterization)
− Open «LP» input (depending on the parameterization)
− Temperature limiter has cut out
Some of the functions that give rise to start prevention can be deactivated via
parameterization.
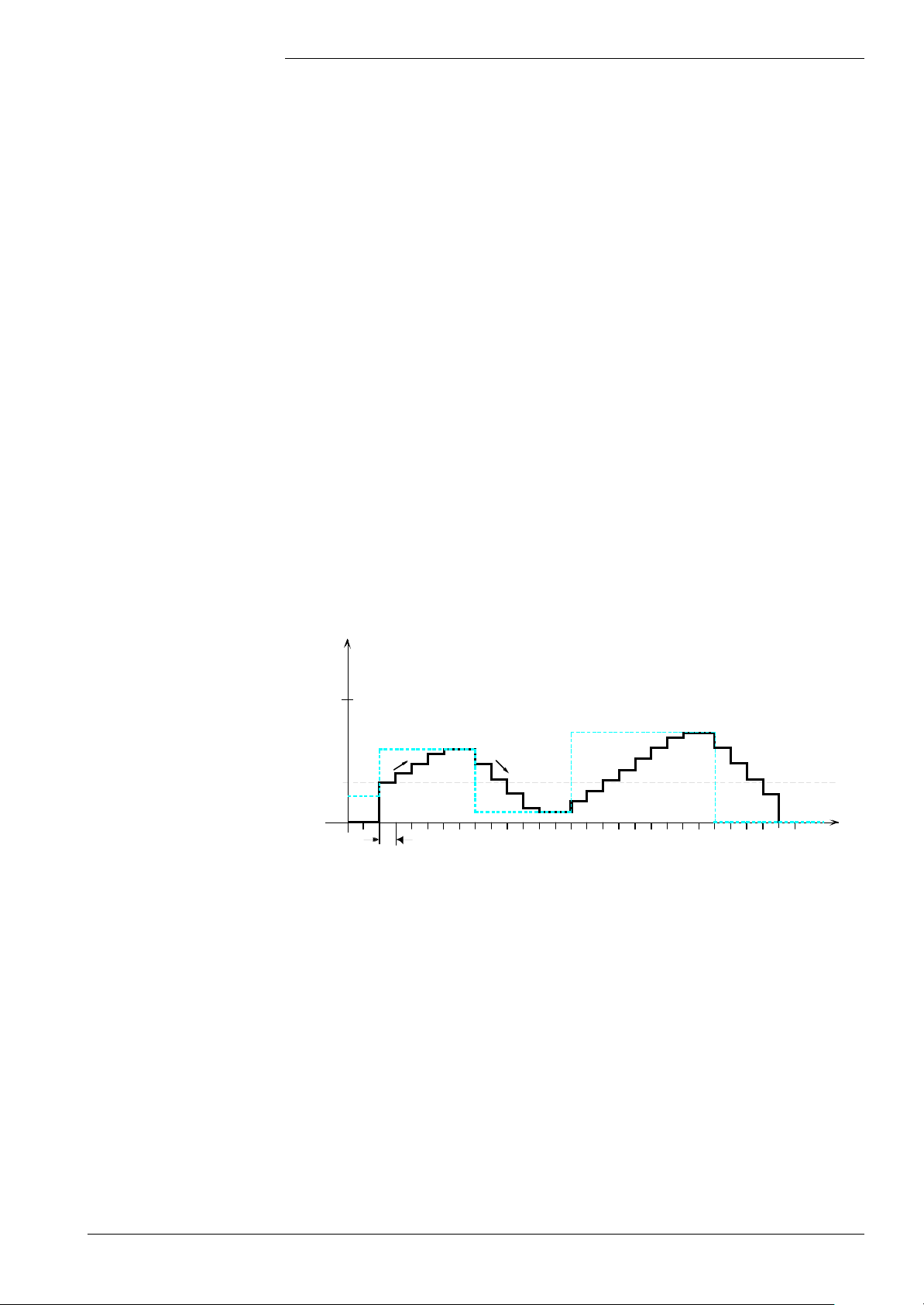
• Ramps: Fan control can be limited by a ramp. To do this, a number of
parameterization choices are available.
The rate of signal change towards a higher or lower speed is limited via parameter
(VmLauf, VmLaufBetr, VmLab, VmLabBetr).
In all phases - with the exception of «PH_MODULATION» - parameters «VmLauf»
and «VmLab» apply to the rate of change of fan control up or down.
PWM
100 %
Setpoint
Ramp (DOWN)
Threshold
value
Control value following the setpoint while considering the threshold value and the ramps
Ramp (UP)
7494d21E
In the «PH_MODULATION» phase, the increase of fan control is limited by the smaller
of the 2 parameters «VmLaufBetr» and «VmLauf».
The decrease is limited by the smaller of the 2 parameters «VmLab» and «VmLabBetr».
Also, when controlling the fan, a threshold value is to be considered. It is predefined by
the «LmodStart» parameter.
As long as the setpoint is lower than the threshold value, the fan will not be controlled. It is
controlled only - using the threshold value - when the setpoint is at least equal to the
threshold value.
23/171
Siemens Building Technologies Basic Documentation LMU54... / LMU64... CC1P7494en
HVAC Products 3 Functions 07.11.2002
If the setpoint lies above the threshold value, starting from the threshold value, the
control value will approach the setpoint in accordance with the maximum slope (ramp)
defined by parameters «VmLauf» and «VmLaufBetr».
If the setpoint lies below the current control value, the control value will approach the
setpoint in accordance with the ramp (VmLab, VmLabBetr). This also applies in the case
the setpoint is lower than the threshold value.
If the setpoint equals zero, which means that the fan shall be switched off, first the
control value will be reduced in accordance with the ramp until it is smaller than or equal
to the threshold value. Only then will the control value be reduced to zero.
LMU... plausibility checks
of the speed parameters
Fault Display of fault on the
PC tool
Check PWM control values of the fan for plausibility in relation to other parameters:
LmodZL > LmodVL 218
LmodTL > LmodZL 219
LmodNull > LmodTL 220
Check speed parameters of the fan for plausibility in relation to other parameters:
N_TL > N_VL 221
N_VOr > NoG_Max 222
N_VL + N_VL_Delta > NoG_Max 223
N_ZL + N_ZL_Delta > N_VL + N_VL_Delta 224
N_VOr - N_VOr_Delta < NoG_Null 225
N_ZL - N_ZL_Delta < N_TL - N_TL_Delta 226
N_TL - N_TL_Delta < NoG_Null 227
N_Nachstell_Delta ≥ N_ZL_Delta
or N_Nachstell_Delta ≥ N_Vor_Delta
503
Parameterization of
speed feedback signal
24/171
The fan’s speed feedback signal can be parameterized.
Parameter: Fan pulses (in «FaEinstellFlags3»)
Available choices : 2, 3 or 4 pulses per revolution
Siemens Building Technologies Basic Documentation LMU54... / LMU64... CC1P7494en
HVAC Products 3 Functions 07.11.2002
Fan parameters
accessible via QAA
Under certain conditions, the fan parameters for ignition load, partial load and full load
can also be set via the QAA73... (parameter «FaEinstellFlags3»).
Since these fan parameters are safety-related and – as a general rule – safety-related
values cannot be readjusted via the QAA73..., following applies:
• The relevant parameters will be copied and the new parameters filed in the nonsafety-related range
• Changeover between the 2 parameter groups can be parameterized via a safetyrelated flag (FaEinstellFlags3)
Changeover to the QAA fan parameters is only permitted under certain preconditions:
1. Capacity range < 70 kW.
2. Changeover only possible on the OEM level or higher.
For the new parameters, the usual fan parameter checks are made (same as with the
previous parameter group).
Listing of both parameter groups:
Parameters on QAA Safety-related parameters
LmodZL_QAA LmodZL
LmodTL_QAA LmodTL
LmodVL_QAA LmodVL
Note
N_ZL_QAA N_ZL
N_TL_QAA N_TL
N_VL_QAA N_VL
When setting these parameters, the following general conditions must be observed:
QAA parameters : CRC-protected parameter:
LmodZL_QAA ≤ LmodZL
LmodVL_QAA ≤ LmodVL
LmodTL_QAA ≥ LmodTL
N_ZL_QAA ≤ N_ZL
N_VL_QAA ≤ N_VL
N_TL_QAA ≥ N_TL
When, in the following, reference is made to one of the safety-related parameters, it is
also possible that the corresponding QAA parameter is meant (depending on the
parameterization).
25/171
Siemens Building Technologies Basic Documentation LMU54... / LMU64... CC1P7494en
HVAC Products 3 Functions 07.11.2002
The different capacity
ranges
In compliance with the standards, a differentiation must be made with regard to the
responses in the sequence diagram for the different boiler capacity ranges.
Parameter «FaProgFlags1» can be used to select the 3 following ranges:
FaProgFlags1 (Bit7) FaProgFlags1 (Bit6) Capacity range
0 0 < 70 kW
0 1 70...120 kW
1 0 > 120 kW
From these 3 capacity ranges, the following differences emerge:
Capacity range
Subject < 70 kW 70 - 120 kW > 120 kW
Air supply failure during
prepurging, ignition or in
operation:
1)
Failure during
establishment of flame:
2)
Response:
Home run; during the safety time and
in operation also forced prepurging.
During prepurging, immediate lockout.
Response:
Shutdown on first occurrence, restart
permitted (number of restarts can be
parameterized). Then lockout; also
forced prepurging.
Repetition counter is reset in phase
Response:
Home run on first occurrence, one restart permitted
(number 0 / 1 can be parameterized). Then lockout;
also forced prepurging.
During prepurging, immediate lockout.
Repetition counter is reset in the «PH_TI » phase.
Response:
Shutdown on first occurrence, one restart permitted
(number 0 / 1 can be parameterized). Then lockout;
also forced prepurging.
Repetition counter is reset in the «PH_TI » phase.
Response:
Lockout
position
4)
Response:
Lockout
position
4)
«PH_TI ».
Loss of flame during
operation:
3)
Response:
Shutdown
Response:
Shutdown on first occurrence, one restart permitted
(number 0 / 1 can be parameterized). Then lockout;
also forced prepurging.
Repetition counter is reset in the «PH_TI » phase.
Response:
Lockout
position
4)
1)
With the LMU...: Failure of speed supervision or speed feedback signal below the valid
range.
Relevant phases: PH_TV, PH_TW1, PH_TW2, PH_TVZ, PH_TSA1_1, PH_TSA2_1,
PH_TSA1_2, PH_TSA2_2, PH_TI, PH_MODULATION
2)
With the LMU...: No flame at the end of the safety time. Relevant phases: PH_TSA1_1,
PH_TSA2_1, PH_TSA1_2, PH_TSA2_2
3)
With the LMU...: Loss of flame during phases «PH_TI» and «PH_MODULATION»
4)
Accomplished by parameterizing the specified value for the start repetitions to 0
26/171
Siemens Building Technologies Basic Documentation LMU54... / LMU64... CC1P7494en
HVAC Products 3 Functions 07.11.2002
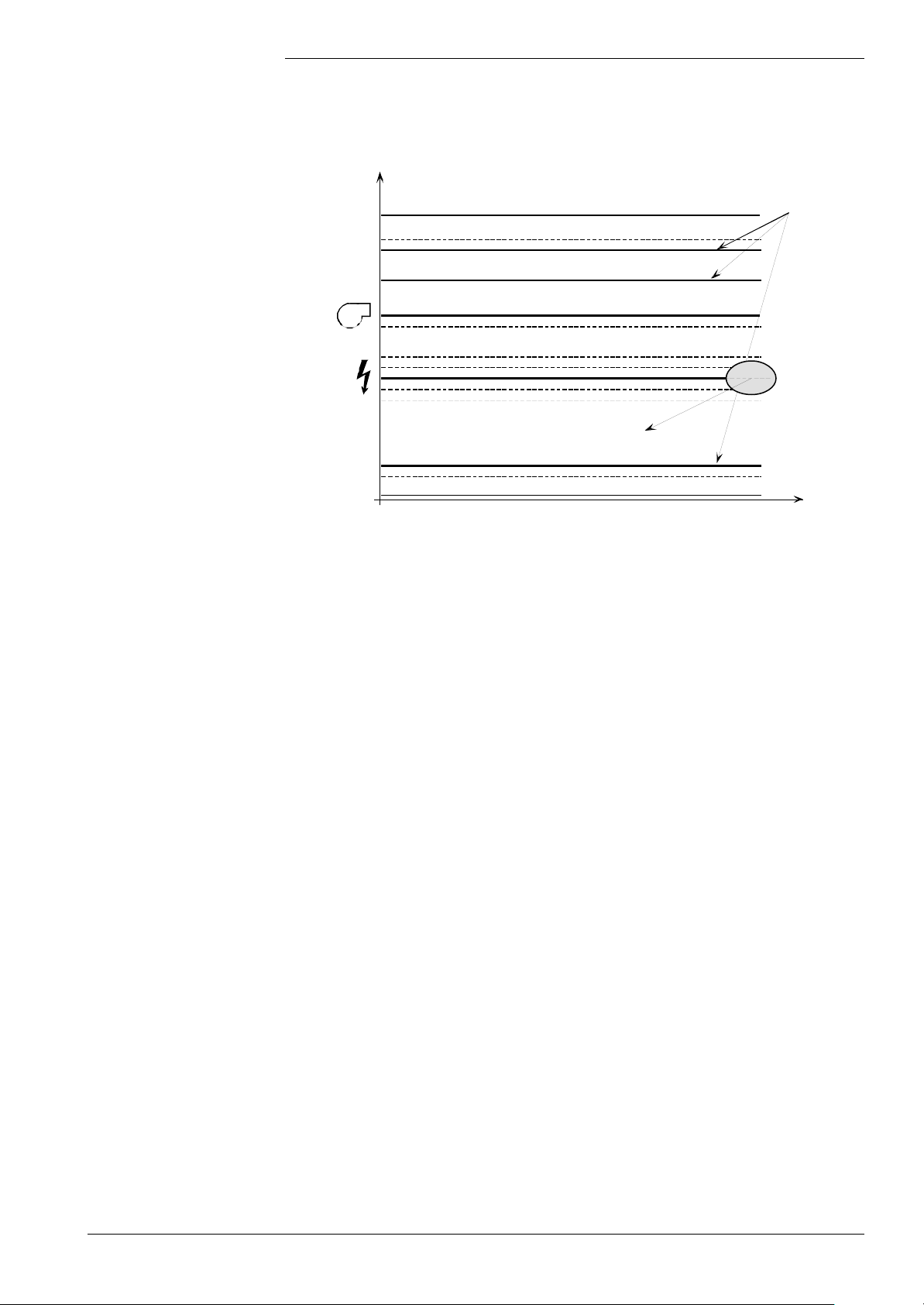
Setting the fan parameters
during startup and shutdown
Parameter LMU...
Speed
[min-1]
NoG_MAX
Signal
PWM [%]
To visualize the following description, also refer to the sequence diagram of the LMU…
and the following graph.
Speed limitation
KonfigRg5)
N_VL*
(N_VL_Delta)
N_VL_QAA*
NhzMax
N_Vor
(N_Vor_Delta)
(N_ZL_Delta)
N_Nachstell_Delta
N_ZL* LmodZL*
N_Nachstell_Delta
(N_ZL_Delta)
N_ZL_QAA*
N_TL*
(N_TL_Delta)
N_TL_QAA*
NoG_Null
* Depending on parameter «FaEinstellFlags3»
LmodVL*
LmodVL_QAA*
PhzMax
LmodVor
LmodZL_QAA*
LmodTL*
LmodTL_QAA*
LmodNull
Fan control and speed parameters
First, set the speed limits while speed readjustment is switched off.
For that purpose, set the fan control parameters («LmodZL», «LmodVor», etc.) to the
values required from the combustion point of view (with the medium flueway and at
mains voltage).
Then, also determine the associated fan speeds from the fan characteristic and
parameterize them accordingly («N_ZL», «N_Vor», etc.).
In a first approach, set the limit values for the permitted bands very wide
(«N_ZL_Delta», «N_Vor_Delta», etc.).
The values of fan control and fan speed can now be optimized.
MAX
MAX
MIN
Boiler
Boiler
Heating
OFF
Extra function «Speed readjustment»
(optional)
N_Nachstell Kon1
N_Nachstell_Lern
7494d31E
Speed limits
First, the speed readjustment should be set to the required or parameterized speed
readjustment.
When the optimization or setting is completed, proceed to the next step and determine
and set the speed limits.
For that purpose, use the PC tool and record the speed (Gebl_F_Drehz) in a startup and
shutdown cycle under the following boundary conditions:
1. With the minimum flueway and undervoltage (AC 195 V)
2. With the maximum flueway and overvoltage (AC 253 V)
Now, set the speed bands (speed limits about the selected speeds, that is, «N_ZLV +/N_ZL_Delta», etc.) such that in all possible worst cases, the measured speed lies within
the valid band (see above).
Faults outside these worst cases give rise to a violation of the speed limits and lead to
appropriate reactions (refer to sequence diagram).
27/171
Siemens Building Technologies Basic Documentation LMU54... / LMU64... CC1P7494en
HVAC Products 3 Functions 07.11.2002

Speed readjustment
Speed readjustment is active during startup and shutdown (not during controller
operation where speed limitation can be activated).
The basic task of speed readjustment is to act on the fan control in such a way that the
resultant speed (after a certain settling time) will lie within an accepted speed band.
Hence, external effects (over- or undervoltage, minimum or maximum flueway, etc.) can
largely be offset.
The following parameters must be considered:
• N_NachstellKon1 (in «FaEinstellFlags2»)
This parameter is used to activate or deactivate the function during startup.
• N_NachstellKon2 (in «FaEinstellFlags2»)
This parameter is used to activate or deactivate the function during shutdown.
• N_Nachstell_lern (in «FaEinstellFlags2»)
This parameter is used to activate or deactivate the learning function of fan control.
• N_Nachstell_Delta
This parameter predefines the band (+/-) to which the speed will be readjusted (neutral
band).
• Nachstell_Zaehler
This parameter is used to define the time when ignition shall be started (depending on
the fan speed settling time à more or less overshoot on ignition permitted).
Description
Learning function
If the function is activated (N_NachstellKon1 + N_NachstellKon2), the fan output signal
will be readjusted in order to get the speed back into the predefined band (e.g. N_ZL +/N_Nachstell_Delta).
If speed readjustment is used, the actual speed will be readjusted to nearly the required
speed until ignition takes place.
Since with this readjustment, the fan speed requires a certain settling time, it is very
advisable to parameterize prepurging and ignition at the same level, so that the
prepurging time can be used for settling process.
If, for example, prepurging > ignition, a second settling process will take place, that is,
the deviation at the time of ignition will be greater.
In that case, the prepurging time should be changed and the level of prepurging and
ignition should be the same.
During startup, the fan output will be changed in order to readjust the resulting actual
speed.
To ensure that this practically fixed offset does not need to be readjusted on each
startup, the fan output signal will be acquired at the end of startup, and the value
learned will be used next time the burner is started up.
This means that the settling process will be accelerated.
The learning function can be deactivated with flag «N_Nachstell_lern» (in
«FaEinstellFlags2»).
28/171
Siemens Building Technologies Basic Documentation LMU54... / LMU64... CC1P7494en
HVAC Products 3 Functions 07.11.2002

Reinitialization
In the following cases, a reinitialization will be made or the parameterized control values
learned:
• In the event of a fault in connection with the fan
• In the event of a reset
• After power ON
Tolerance of settling
process during startup
Especially in cases where the prepurge level deviates from the ignition level, the fan
speed needs a certain time to settle out just prior to ignition. Depending on the
application, this speed variation can give rise to more or less disturbance.
Parameter «Nachstell_Zaehler» can be used to adjust the permitted degree of fan
speed settling, or from when the change to ignition shall take place.
If a small value is parameterized (e.g. 1), ignition is effected immediately. The greater
the value, the less overshoot is permitted on ignition.
It should be noted that greater values extend the startup phase.
29/171
Siemens Building Technologies Basic Documentation LMU54... / LMU64... CC1P7494en
HVAC Products 3 Functions 07.11.2002
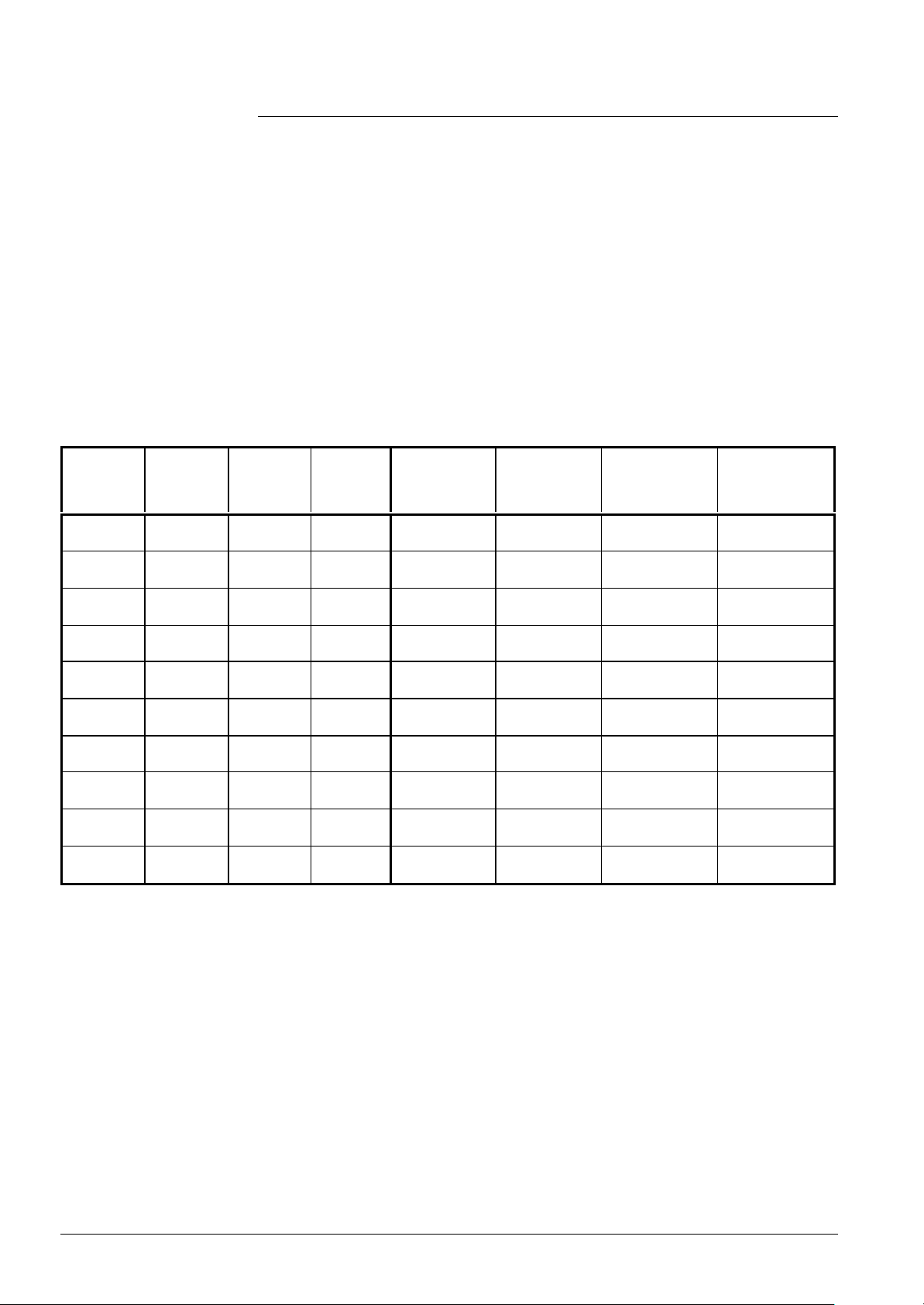
3.2 Selection of the compensation variants
Legend
Different types of compensation are used for the heating and the DHW circuit, depending
on the types of plant components. On completion of a certain startup time, during which
the connected components are queried, the relevant compensation variant is selected.
If plant components are connected or removed during operation, the compensation variant
changes after the new plant state is identified.
Heating circuits
The plant components decisive for the compensation variant of heating circuits 1 and 2
or the following:
• The RU
• The outside sensor
• The HMI (none / cannot be parameterized / can be parameterized)
External heat demand signals (via the RVA...) are received directly and are not included
in the following table.
Without HMI
RU
QAA53 /
QAA73
Not present – – Not present
Not present – – Present TvSollWf1 TvSollWf2
Present No No Not present
Present No No Present TvSollWf1 TvSollWf2
Present Yes No Not present Tset / Tset2
Present Yes No Present Tset / Tset2 TvSollWf2
Present Yes Yes Not present Tset / Tset2 Tset / Tset2
Present Yes Yes Present Tset / Tset2 Tset / Tset2
Present No Yes Not present
Present No Yes Present TvSollWf1 Tset / Tset2
RU for Hk1
active
RU for Hk2
active
Outside
sensor
Setpoint Hk1
TkSoll
TvSollWf1 at
TaGem = 0 °C
TvSollWf1 at
TaGem = 0 °C
TvSollWf1 at
TaGem = 0 °C
Setpoint Hk2
TvSoll
TvSollWf2 at
TaGem = 0 °C
TvSollWf2 at
TaGem = 0 °C
TvSollWf2 at
TaGem = 0 °C
Tset / Tset2
Compensation
variant heating
circuit 1
Emergency
operation
Weather compensation LMU
Emergency
operation
Weather compensation LMU
Room compensation RU
Weather compensation RU
Room compensation RU
Weather compensation RU
Emergency
operation
Weather compensation LMU
Compensation
variant heating
circuit 2
Emergency
operation
Weather compensation LMU
Emergency
operation
Weather compensation LMU
Emergency
operation
Weather compensation LMU
Room compensation RU
Weather compensation RU
Room compensation RU
Weather compensation RU
TvSollWf1 Flow temperature setpoint resulting from weather compensation for heating circuit 1
TvSollWf2 Flow temperature setpoint resulting from weather compensation for heating circuit 2
TsRaumMmi Room temperature setpoint of HMI
TSet Flow temperature setpoint of RU for heating circuit 1
Tset2 Flow temperature setpoint of RU for heating circuit 2
TrSet Room temperature setpoint of RU for heating circuit 1
RT / SU Room thermostat / time switch
SU program Hz1 Time switch program on the AGU2.310 for heating circuit 1
RU1 / V Heat demand from RU for heating circuit 1/ heating circuit 2
– Will not be evaluated
30/171
Siemens Building Technologies Basic Documentation LMU54... / LMU64... CC1P7494en
HVAC Products 3 Functions 07.11.2002
 Loading...
Loading...