Page 1

Building Technologies
Fire Safety & Security Products
FDOOT241-9, FDOOT241-8,
FDOOT221, FDO241, FDO221,
FDT241, FDT221
Automatic fire detectors
Technical manual
Page 2

Technical specifications and availability subject to change without notice.
© 2006-2009 Copyright Siemens Building Technologies, Inc.
We reserve all rights in this document and in the subject thereof. By acceptance of the document the recipient acknowledges these rights
and undertakes not to publish the document nor the subject thereof in full or in part, nor to make them available to any third party without our
prior express written authorization, nor to use it for any purpose other than for which it was delivered to him.
Page 3

3
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
1
About this document ....................................................................................7
2 Safety............................................................................................................11
2.1 Safety notices................................................................................................11
2.2 Safety regulations for the method of operation .............................................13
2.3 Standards and directives complied with........................................................15
3 Structure and function................................................................................16
3.1 Overview .......................................................................................................16
3.1.1 Detectors with ASAtechnology (S-LINE) ....................................... 16
3.1.2 Detector with detection algorithms (C-LINE) .................................17
3.1.3 Details for ordering ........................................................................17
3.2 S-LINE and C-LINE.......................................................................................18
3.2.1 C-LINE ........................................................................................... 19
3.2.2 S-LINE ...........................................................................................20
3.3 Detectors .......................................................................................................22
3.3.1 Neural fire detector ........................................................................22
3.3.1.1 Variants of the FDOOT241-9 ....................................23
3.3.2 Wide-spectrum smoke detector .....................................................24
3.3.3 Heat detector .................................................................................25
3.4 Function.........................................................................................................26
3.4.1 Parameter sets...............................................................................26
3.4.2 Danger levels.................................................................................26
3.4.3 Diagnosis levels .............................................................................27
3.4.4 Line separator................................................................................29
3.4.5 Automatic recognition of the detector line protocol........................29
3.4.6 Internal alarm indicator ..................................................................29
3.4.7 Connection of external alarm indicators ........................................29
3.4.8 Renovation mode...........................................................................30
3.4.9 Test mode ......................................................................................30
3.4.10 Behavior in degraded mode...........................................................30
3.4.11 Interface to service devices ...........................................................31
3.4.12 Line tester ......................................................................................31
3.5 Mechanical setup ..........................................................................................32
3.6 Options ..........................................................................................................33
3.6.1 Detector base FDB221/FDB221-AA..............................................33
3.6.2 Detector base FDB201/FDB201-AA..............................................33
3.6.3 Detector base FDB222 ..................................................................34
3.6.4 Detector base FDB202 ..................................................................34
3.6.5 Sounder base FDSB291................................................................34
3.6.6 Sounder base FDSB292................................................................35
3.6.7 Base attachment FDB291..............................................................35
3.6.8 Base attachment humid FDB293...................................................35
3.6.9 Base adapter FDB281 ...................................................................36
3.6.10 Detector heating unit FDBH291.....................................................36
3.6.11 Designation plate FDBZ291...........................................................36
3.6.12 Designation plate DBZ1193A ........................................................37
3.6.13 Detector locking device FDBZ293 .................................................37
3.6.14 Dummy detector FDX291 ..............................................................37
3.6.15 Detector dust cap FDZ291............................................................. 37
3.6.16 Protective cage DBZ1194..............................................................38
Table of contents
Page 4

4
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
3.6.17 EMC-protective cage FDBZ294 .....................................................38
3.6.18 Micro terminal DBZ1190-AA ..........................................................38
3.6.19 Connection terminal DBZ1190-AB.................................................39
3.6.20 M20 x 1.5 metal cable gland ..........................................................39
4 Project engineering.....................................................................................40
4.1 Compatibility..................................................................................................40
4.2 Ambient features ...........................................................................................40
4.3 Parameter sets: Neural fire detector .............................................................42
4.3.1 Neural fire detector FDOOT241-x (sensor mode 0) ......................42
4.3.1.1 Description.................................................................42
4.3.1.2 Application .................................................................44
4.3.1.3 Specification ..............................................................45
4.3.2 Neural fire detector FDOOT241-x (sensor mode 1, 'Heat detector')46
4.3.3 Neural fire detector FDOOT241-x (sensor mode 2, 'Smoke
detector') ........................................................................................47
4.3.4 Neural fire detector FDOOT221.....................................................48
4.3.4.1 Description.................................................................48
4.3.4.2 Application .................................................................48
4.3.4.3 Specification ..............................................................48
4.4 Parameter sets: Wide-spectrum smoke detector..........................................49
4.4.1 Wide-spectrum smoke detector FDO241 ......................................49
4.4.1.1 Description.................................................................49
4.4.1.2 Application .................................................................49
4.4.1.3 Specifications ............................................................50
4.4.2 Wide-spectrum smoke detector FDO221 ......................................51
4.4.2.1 Description.................................................................51
4.4.2.2 Application .................................................................51
4.4.2.3 Specification ..............................................................51
4.5 Parameter sets: Heat detector ......................................................................52
4.5.1 Heat detector FDT241 ...................................................................52
4.5.1.1 Description.................................................................52
4.5.1.2 Specifications ............................................................53
4.5.2 Heat detector FDT221 ...................................................................54
4.5.2.1 Description.................................................................54
4.5.2.2 Specifications ............................................................54
4.6 Default settings..............................................................................................55
4.7 Application examples ....................................................................................56
5 Mounting / Installation ................................................................................57
5.1 Required space .............................................................................................57
5.2 Detector base FDB201/221...........................................................................58
5.3 Detector base FDB202/222...........................................................................59
5.4 Base attachment FDB291 .............................................................................60
5.5 Base attachment humid FDB293 ..................................................................61
5.6 Base adapter FDB281...................................................................................62
5.7 Detector locking device FDBZ293.................................................................63
5.8 Designation plate FDBZ291 ..........................................................................64
5.9 Designation plate DBZ1193A ........................................................................64
Page 5

5
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
5.10 Detector heating FDBH291 ...........................................................................65
5.10.1 Installation of the detector heating unit..........................................65
5.10.2 Connection of the detector heating unit.........................................66
5.11 Protective cages............................................................................................67
5.11.1 Installation of the protective cages ................................................67
5.11.2 Grounding of the EMC-protective cage FDBZ294.........................67
5.12 Cable entry....................................................................................................68
5.12.1 Auxiliary terminals DBZ1190-AA/-AB ............................................69
5.13 Detector lines ................................................................................................69
5.13.1 Connection diagram (addressed) ..................................................70
5.13.1.1 Use of unshielded cables .......................................... 70
5.13.1.2 Use of shielded cables ..............................................71
5.13.2 Connection diagram (collective) ....................................................73
5.13.2.1 Use of unshielded cables .......................................... 74
5.13.2.2 Use of shielded cables ..............................................75
5.13.3 Connection diagram (MS8)............................................................76
5.13.3.1 Use of unshielded cables .......................................... 76
5.13.3.2 Use of shielded cables ..............................................77
5.14 Detector dust cap FDZ291 ............................................................................78
6 Commissioning ...........................................................................................79
7 Maintenance / repair ...................................................................................80
7.1 Status polling with the detector exchanger and tester ..................................80
7.2 Performance check .......................................................................................80
7.3 Testing detectors...........................................................................................81
7.3.1 Testing detectors with detector exchanger and tester...................82
7.3.2 Testing detectors without detector exchanger and tester..............82
8 Specifications ..............................................................................................83
8.1 Technical data FDOOT241-x, FDOOT221 ...................................................83
8.1.1 General (irrespective of the detector line) .....................................83
8.1.2 Detector lines .................................................................................85
8.2 Technical data FDO221, FDO241.................................................................89
8.3 Technical data FDT221, FDT241.................................................................. 91
8.4 Dimensions....................................................................................................93
8.5 Environmental compatibility ..........................................................................93
9 Index .............................................................................................................94
Page 6

6
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
Page 7

About this document
7
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
1 About this document
Goal and purpose
This document contains information on automatic fire detectors. Consistent
compliance with the instructions guarantees correct and safe use.
Target groups
The information in this document is intended for the following target groups:
Target group Activity Qualification
Product Manager z Is responsible for information
passing between the manufacturer
and regional company.
z Coordinates the flow of information
between the individual groups of
people involved in a project.
z Has obtained suitable specialist training for
the function and for the products.
z Has attended the training courses for
Product Managers.
Project Manager z Coordinates the deployment of all
persons and resources involved in
the project according to the
schedule.
z Provides the information required to
run the project.
z Has obtained suitable specialist training for
the function and for the products.
z Has attended the training courses for Project
Managers.
Project Engineer z Parameterizes the product
according to country-specific and
customer-specific requirements.
z Checks operability and releases the
product for commissioning at the
place of installation.
z Searches for and corrects
malfunctions.
z Has obtained suitable specialist training for
the function and for the products.
z Has attended the training courses for Project
Engineers.
Installation personnel z Assembles and installs the product
components at the place of
installation.
z Carries out a performance check
following installation.
z Has received specialist training in the area of
building installation technology or electrical
installations.
Maintenance personnel z Carries out all maintenance work.
z Checks that the products are in
perfect working order.
z Searches for and corrects
malfunctions.
z Has obtained suitable specialist training for
the function and for the products.
Page 8

About this document
8
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
Document identification
Position Information
Title page z Product type
z Product designation
z Document type
Last page, bottom left z Document ID
ID_ModificationIndex_Language_COUNTRY
z Edition date
Last page, bottom right z Manual
z Register
Conventions for text marking
Markups
Special markups are shown in this document as follows:
⊳ Requirement for a behavior instruction
⇨ Intermediate result of a behavior instruction
⇨ End result of a behavior instruction
'Text' Quotation, reproduced identically
<Key> Identification of keys
Supplementary information
The
i
symbol identifies supplementary information such as a tip for an easier
way of working.
Supplementary information is labeled using the 'i' symbol.
Page 9

About this document
9
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
Technical terms
Term Explanation
AI Alarm indicator
ASA Advanced Signal Analysis
DA Detection algorithms
C-LINE Fire detector for standard applications
S-LINE Fire detector for sophisticated applications
ES Product version
FDnet Addressed detector line (field device net)
FET Field Effect Transistor
GMT Limit value detection technology (collective)
LED Light-emitting diode
MC link Maintenance and Commissioning Link; interface to the detector
exchanger and tester
MS8 Pulse detection technology (addressed); also known as PMT
PMT Pulse detection technology (addressed); also known as MS8
SIGMASYS Fire detection system
Reference documents
Document ID Title
008331 List of compatibility
007227 FDUD292 detector exchanger and tester
009718 FDUD293 intelligent detector tester
008250 FDUL221 line tester
010030 Fire detector application guideline
Page 10

About this document
10
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
History of changes
Document ID Edition date Brief description
007004_k_en_-- 04.2009 Sensitivities for FDOOT241-x with High
Suppression now 2.3 and 8 %/m.
Accessories with order no.
Detector base FDB2x1-AA with 1 micro terminal.
FDSB291 compatible with heat detector FDT2xx
(as of ES ≥43).
Connection diagram for shielded cables.
007004_j_de_-- 07.2008 Safety instructions revised
Technical data restructured
007004_i_de_-- 02.2008 Chap. 4.3.1.3: Only parameter set 8 doesn't satisfy
the EN 54-7 and CEA 4021 standards.
Parameters set 0 added to chaps. 4.3.2 and 4.3.3.
Index added.
007004_h_de_-- 02.2008 FM approvals supplemented.
IP protection category for FDB291/FDB293
corrected.
Structure in chap. 'Detector lines' uniform.
Various corrections to parameter sets of
FDOOT241-x, FDO241 and FDT241.
KMK in chap. 8.1.4: Par. sets specified more
precisely.
New chapters 'Default settings' and 'Protective
cages'.
New options:
- Detector base FDB202/FDB222
- Dummy detector FDX291
007004_g_de_-- 10.2007 Cross-reference list of detector names added in
chap. 'Overview'.
Display texts for detector exchanger and tester
added in 'Diagnosis levels' chapter.
Various corrections to FDOOT241-x parameter
sets.
EMC-protective cage FDBZ294 included in options.
'Mode' replaced by 'sensor mode'.
Supplements in the 'Technical data':
- Line separator
- IP protection categories
- LPCB approvals
- Standard EN 54-17
Images with language texts replaced by language-
neutral images
007004_f_de_-- 09.2006 Complete revision (devices with ES ≥ 30 included)
007004_e_de_-- 04.2005 Chapters 5.1, 5.3, 5.5.3, 5.7.2, 5.8.1, 5.8.2, 6.11.1,
6.11.2, 9.3.2, 9.3.3, 9.4, 9.5
007004_d_de_-- 01.2005 Chapters 4.4.1, 5, 9.3.1, 9.3.4, 9.3.6 and 9.4
adapted
007004_c_de_-- 12.2004 Text in chapter 0, titles 5.5.1, 5.5.2, 5.5.3 adapted
007004_b_de_-- 11.2004 Document layout adapted, parameter sets adapted,
various minor changes
007004_a_de_-- 06.2004 First edition
Page 11

Safety
11
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
2 Safety
2.1 Safety notices
The safety notices must be observed in order to protect people and property.
The safety notices in this document contain the following elements:
z Symbol for danger
z Signal word
z Nature and origin of the danger
z Consequences if the danger occurs
z Measures or prohibitions for danger avoidance
Symbol for danger
This is the symbol for danger. It warns of risks of injury.
Follow all measures identified by this symbol to avoid injury or death.
Additional danger symbols
These symbols indicate general dangers, the type of danger or possible
consequences, measures and prohibitions, examples of which are shown in the
following table:
General danger
Explosive atmosphere
Voltage/electric shock
Laser light
Battery
Heat
Page 12
Safety
12
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
Signal word
The signal word classifies the danger as defined in the following table:
Signal word Danger level
DANGER DANGER identifies a dangerous situation, which will result
directly in death or serious injury if you do not avoid this
situation.
WARNING WARNING identifies a dangerous situation, which may result
in death or serious injury if you do not avoid this situation.
CAUTION CAUTION identifies a dangerous situation, which could result
in slight to moderately serious injury if you do not avoid this
situation.
NOTICE
NOTICE
identifies possible damage to property that may
result from non-observance.
How risk of injury of presented
Information about the risk of injury is shown as follows:
WARNING
Nature and origin of the danger
Consequences if the danger occurs
z Measures / prohibitions for danger avoidance
How possible damage to property is presented
Information about possible damage to property is shown as follows:
NOTICE
Nature and origin of the danger
Consequences if the danger occurs
z Measures / prohibitions for danger avoidance
Page 13

Safety
13
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
2.2 Safety regulations for the method of operation
National standards, regulations and legislation
Siemens products are developed and produced in compliance with the relevant
European and international safety standards. Should additional national or local
safety standards or legislation concerning the planning, assembly, installation,
operation or disposal of the product apply at the place of operation, then these
must also be taken into account together with the safety regulations in the product
documentation.
Electrical installations
WARNING
Electrical voltage
Electric shock
z Work on electrical installations may only be carried out by qualified
electricians or by instructed persons working under the guidance and
supervision of a qualified electrician, in accordance with the electrotechnical
regulations.
z Wherever possible disconnect products from the power supply when carrying
out commissioning, maintenance or repair work on them.
z Lock volt-free areas to prevent them being switched back on again by mistake.
z Label the connection terminals with external external voltage using a
'DANGER External voltage' sign.
z Route mains connections to products separately and fuse them with their own,
clearly marked fuse.
z Fit an easily accessible disconnecting device in accordance with IEC 60950-1
outside of installation.
z Produce earthing as stated in local safety regulations.
Assembly, installation, commissioning and maintenance
z If you require tools such as a ladder, these must be safe and must be intended
for the work in hand.
z When starting the fire control panel ensure that unstable conditions cannot
arise.
z Ensure that all points listed in the 'Testing the product operability' section below
are observed.
z You may only set controls to normal function when the product operability has
been completely tested and the system has been handed over to the customer.
Page 14

Safety
14
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
Testing the product operability
z Prevent the remote transmission from triggering erroneously.
z If testing building installations or activating devices from third-party companies,
you must collaborate with the people appointed.
z The activation of fire control installations for test purposes must not cause
injury to anyone or damage to the building installations. The following
instructions must be observed:
‒ Use the correct potential for activation; this is generally the potential of the
building installation.
‒ Only check controls up to the interface (relay with blocking option).
‒ Make sure that only the controls to be tested are activated.
z Inform people before testing the alarming control devices and allow for possible
panic responses.
z Inform people about any noise or mist which may be produced.
z Before testing the remote transmission, inform the corresponding alarm and
fault signal receiving stations.
Modifications to the system layout and products
Modifications to the system and to individual products may lead to faults,
malfunctioning and safety risks. Written confirmation must be obtained from
Siemens and the corresponding safety bodies for modifications or additions.
Modules and spare parts
z Components and spare parts must comply with the technical specifications
defined by Siemens. Only use products specified or recommended by
Siemens.
z Only use fuses with the specified fuse characteristics.
z Wrong battery types and improper battery changing lead to a risk of explosion.
Only use the same battery type or an equivalent battery type recommended by
Siemens.
z Batteries must be disposed of in an environmentally friendly manner. Observe
national guidelines and regulations.
Disregard of the safety regulations
Before they are delivered, Siemens products are tested to ensure they function
correctly when used properly. Siemens disclaims all liability for damage or injuries
caused by the incorrect application of the instructions or the disregard of danger
warnings contained in the documentation. This applies in particular to the following
damage:
z Personal injuries or damage to property caused by improper use and incorrect
application
z Personal injuries or damage to property caused by disregarding safety
instructions in the documentation or on the product
z Personal injury or damage to property caused by poor maintenance or lack of
maintenance
Page 15

Safety
15
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
Disclaimer
We have checked that the content of this document matches the hardware and
software described. Despite this, we cannot rule out deviations and cannot
therefore assume liability for them matching completely. The details in this
document are checked regularly and any corrections needed included in
subsequent editions.
We are grateful for any suggestions for improvement.
2.3 Standards and directives complied with
A list of the standards and directives complied with is available from your Siemens
contact.
Page 16
Structure and function
16
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
3 Structure and function
3.1 Overview
In this document the following detectors are summarized under the term
"Automatic fire detectors":
z Neural fire detector FDOOT2x1-x
z Wide-spectrum smoke detector FDO2x1
z Heat detector FDT2x1
The same detectors may have different names, depending on the document type.
Detector type Designation 1 (e.g. in technical documentation
etc.)
Designation 2 (e.g. in catalog sheets etc.)
FDOOT221 Neural fire detector Multi-sensor smoke detector, neural DA
FDOOT241-x Neural fire detector Multi-sensor smoke detector, neural ASA
FDO221 Wide-spectrum smoke detector Smoke detector, FDnet wide spectrum DA
FDO241 Wide-spectrum smoke detector Smoke detector, FDnet wide spectrum ASA
3.1.1 Detectors with ASAtechnology (S-LINE)
Neural fire detector
FDOOT241-9
Neural fire detector
FDOOT241-8
Wide-spectrum smoke
detector
FDO241
Heat detector
FDT241
Can be used either
addressed in FDnetor
collectively
Can be used either
addressed in MS8/PMT or in
FDnet
Can be used addressed on
the FDnet
Can be used addressed on
the FDnet
Can be set as neural fire detector, wide-spectrum smoke
detector or heat detector on the part of the software
Selectable detection behavior thanks to application-specific ASA parameter sets
Page 17

Structure and function
17
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
3.1.2 Detector with detection algorithms (C-LINE)
Neural fire detector
FDOOT221
Wide-spectrum smoke
detector FDO221
Heat detector FDT221
Can be used addressed on the FDnet
Selectable detection behavior thanks to different DA parameter sets
3.1.3 Details for ordering
Type Order no. Designation
FDOOT241-9 A5Q00004813 Neural fire detector
FDOOT241-8 A5Q00004663 Neural fire detector
FDO241 A5Q00004811 Wide-spectrum smoke detector
FDT241 A5Q00004812 Heat detector
FDOOT221 A5Q00001566 Neural fire detector
FDO221 A5Q00001565 Wide-spectrum smoke detector
FDT221 A5Q00001567 Heat detector
Page 18

Structure and function
18
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
3.2 S-LINE and C-LINE
Regarding the detectors, there are two product lines: S-LINE and C-LINE. They
differ regarding the different detector variants and functionalities in both the
detectors and control panels. The application range of the S-LINE detectors is
wider than that of the C-LINE detectors.
Application range
fast /
sensitive
Response behavior slow / insensitive
S-LINE
C-LINE
Few Deceptive phenomena Many
z
S-LINE detectors are suited to applications where many deceptive phenomena
have to be expected, or fast fire detection is required.
z C-LINE detectors are suited to applications where few deceptive phenomena
have to be expected.
FDnet devices of the S-LINE and C-LINE can be combined on the same detector
line.
Page 19
Structure and function
19
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
3.2.1 C-LINE
The C-LINE detectors are characterized by a very high detection reliability
combined with a high immunity to deceptive phenomena. The detectors have two
parameter sets, by means of which they can be adapted to the conditions
prevailing at the installation location.
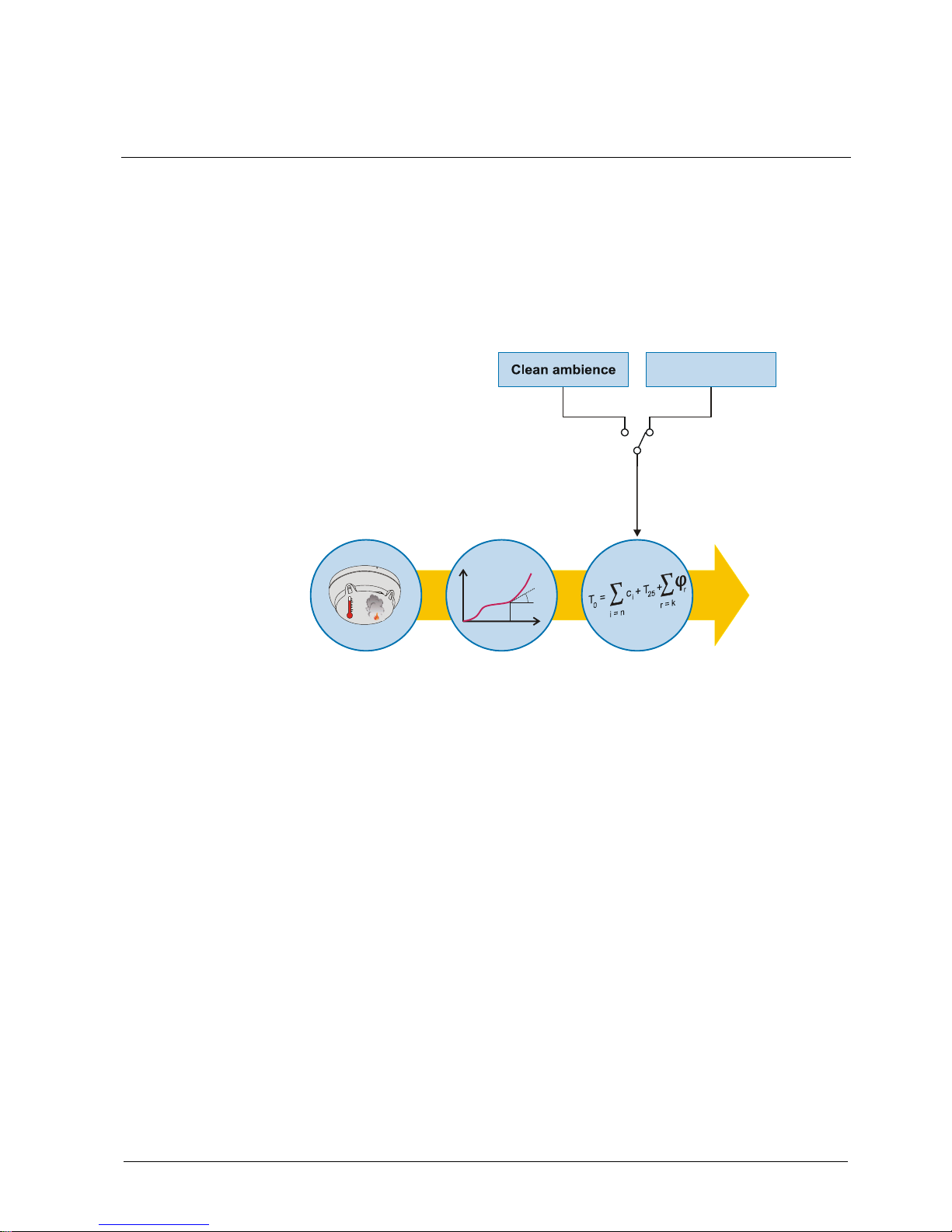
Operating mode: Signal processing with detection algorithms
The following figure shows signal processing with C-LINE detectors in a diagram.
C
Sensory
Signal analysis
Algorithms
Result
Danger
level
Standard ambience
Selection of parameter
The signals captured by the sensor technology are transmitted to the algorithm.
The algorithm analyses and evaluates the course of the signals (signal intensity,
rate of rise and fluctuation). The algorithms are set by selecting the parameter set,
which sets the detectors to the expected types of fire and ambient influences.
Page 20
Structure and function
20
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
3.2.2 S-LINE
Properties
In contrast to the C-LINE detectors, S-LINE detectors have the following features:
z Dynamic influence on the parameter sets
z Pattern recognition
z Real time interpretation of the situation
z Process- and time-controlled switchover of the parameter sets
Signal processing of the S-LINE detectors is based on ASAtechnology (ASA =
Advanced Signal Analysis). ASAtechnology can also be characterized as second
generation algorithms. Signal processing with ASAtechnology permits optimum
adaptation of the detector behavior to the particular ambient conditions.
S-LINE detectors are characterized by their unique detection reliability and high
immunity to deceptive phenomena.
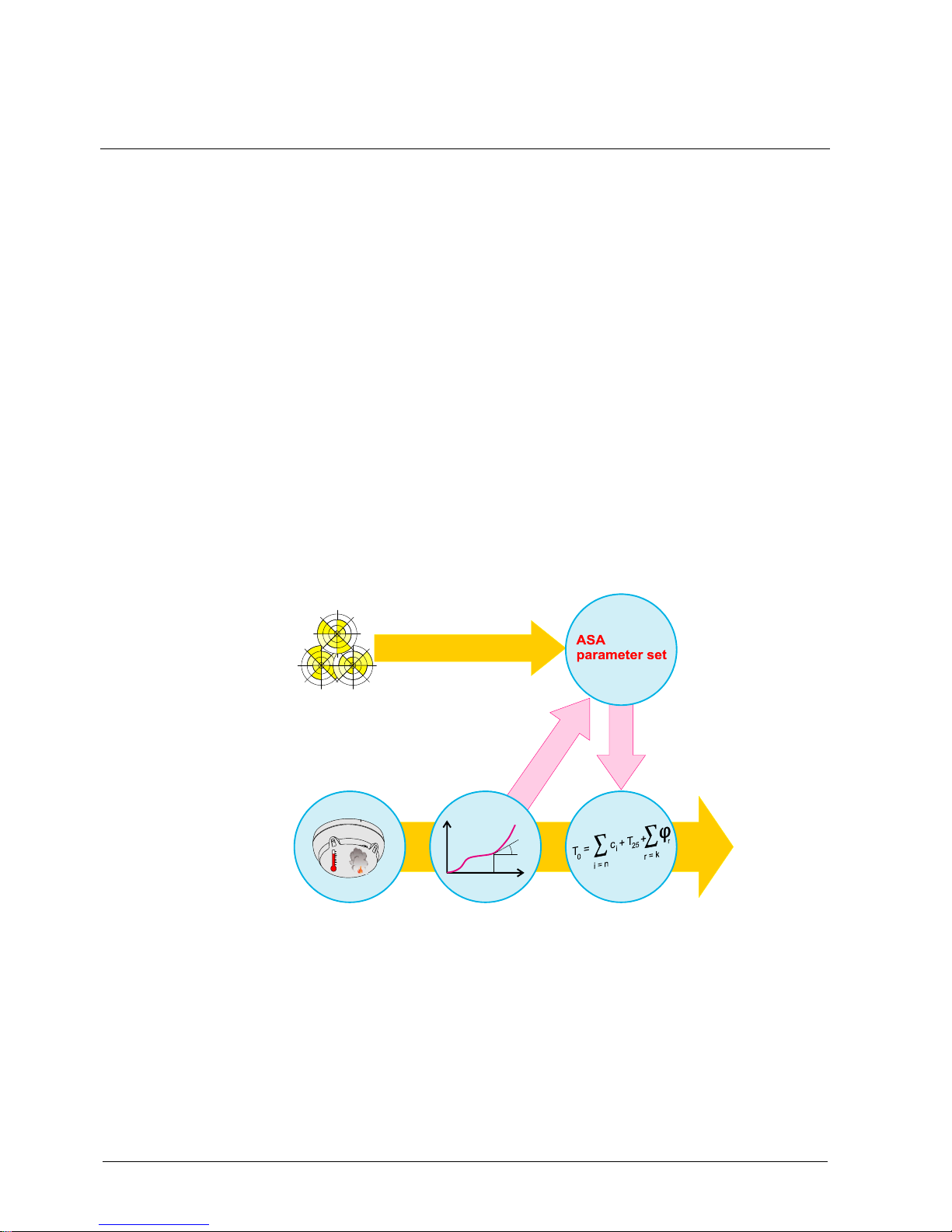
Operating mode: Signal processing with ASAtechnology
The following figure shows signal processing with S-LINE detectors in the form of a
diagram.
C
Dynamic influence
of parameter
Environment
Evaluation of the
situation
Danger
level
Result
Algorithms
Signal analysis
Sensory
Sensory
The signals captured by the sensory are transmitted to the algorithm. The
algorithms are set by selecting the parameter set.
Page 21

Structure and function
21
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
Algorithms
In comparison to the detection algorithms (DA), the individual parameters of the
selected parameter set can be adapted with ASAtechnology. A real time
interpretation of the situation leads to a dynamic influence on the algorithm. This
results in a broadening of the application range of the parameter set and thus of
the detector. The detector reacts more sensitively in the event of fire, and more
robustly in the event of deceptive phenomena.
Switching over the parameter set
In addition to the selection of the parameter set, the S-LINE detectors enable timeor process-controlled switching over of the parameter sets (Manned/Unmanned
switchover). Thanks to this function, the detector can be used in places where the
situation changes regularly and frequently (e.g. kitchen, production hall).
Downloadable parameter sets
Detectors of the S-LINE have several permanently programmed parameter sets.
For special applications new, additional parameter sets can be downloaded in the
field (depending on the control panel).
Page 22

Structure and function
22
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
3.3 Detectors
3.3.1 Neural fire detector
The neural fire detector is a multiple criteria fire detector and is equipped with two
optical and two thermal sensors. The following neural fire detectors are available:
z FDOOT241-9
z FDOOT241-8
z FDOOT221
The following table shows the most important differences between the neural fire
detectors.
Parameter FDOOT241-9 FDOOT241-8 FDOOT221
Signal processing ASAtechnology ASAtechnology Detection algorithms
Communication protocol z FDnet
z Collective
z FDnet
z MS8
z FDnet
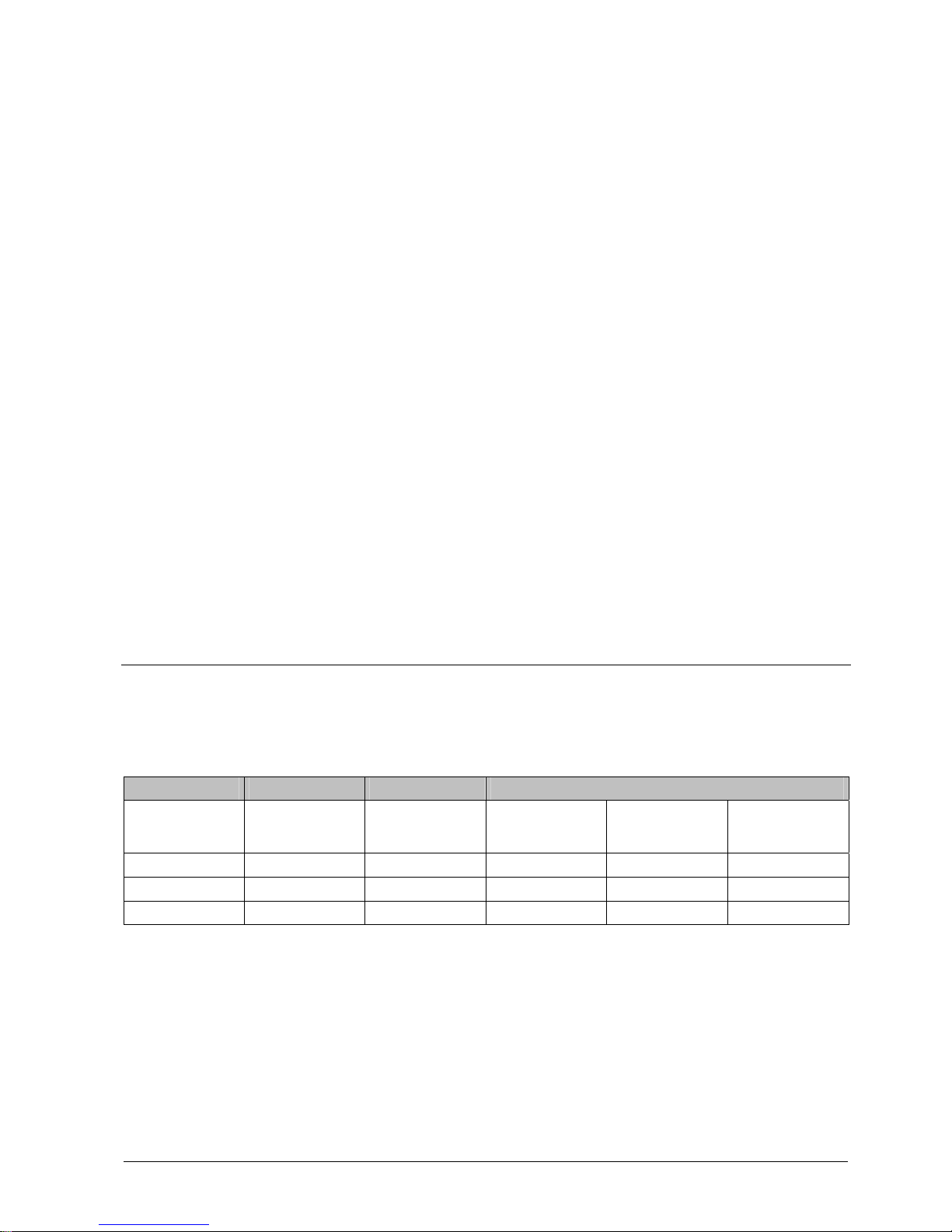
Structure and function
1 2
3
4
1 Heat sensors 3 Forward scatterer
2 Backward scatterer 4 Labyrinth
The detector has a sophisticated opto-electronic measuring chamber with two
optical emitters, an optical receiver and two thermal sensors.
The transmitters illuminate the smoke particles from different angles. One sensor
acts as forward scatterer, the other as backward scatterer. The scattered light then
hits the receiver (photodiode) and generates a measurable electric signal.
The combination of a forward and backward scatterer facilitates an optimum
detection and the differentiation of light and dark particles, which leads to a
homogenous response behavior and optimizes the differentiation of wanted signals
and deceptive phenomena.
Page 23
Structure and function
23
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
In addition, the heat sensors make it possible to detect fires without smoke
generation.
The combination of optical and thermal sensor signals optimizes detection
reliability. This has the following advantages:
z Early detection of all types of fire, whether they generate light or dark smoke, or
no smoke at all.
z The neural fire detector can be operated at a lower sensitivity level and thus
achieves a higher immunity against false alarms which may otherwise be
caused by cold aerosols (e.g. by smoking, electrical welding, etc.). In the case
of an open fire, the smoke sensitivity is heightened by the temperature
increase, which means that a detection reliability level that is comparable to
that of the wide-spectrum smoke detector can be achieved.
The neural fire detectors FDOOT241-8/9 may as well be applied either as optical
smoke detectors or as out-and-out heat detectors. This is possible by selecting one
of the following sensor modes (with the detector exchanger and tester or on the
control panel):
z Sensor mode 0: Application as neural fire detector
z Sensor mode 1: Application as heat detector
z Sensor mode 2: Application as smoke detector
In sensor mode 1 or 2 the parameter sets of the heat detector FDT241 or of the
wide-spectrum smoke detector FDO241, respectively, can be selected. Then,
these neural fire detectors behave like the heat detector FDT241 or smoke detector
FDO241.
3.3.1.1 Variants of the FDOOT241-9
The neural fire detector FDOOT241-9 is available in three different variants A, B
and C. The compatibility differs depending on the variant. The following table
provides an overview of the compatibility of the different variants. Refer to
document 008331 'List of compatibility' for compatibility details.
Variants Part number Product version Compatibility
FDnet Collective control
panels from
Germany
Collective control
panels from
Switzerland
A A5Q00004813 < 13 X X –
B A5Q00015955 13 ≤ ES < 30 X – only CZ10
C A5Q00004813 ≥ 30 X X X
Notes
z Variant B has been available only as kit (FDOOT241-9M) consisting of the
neural fire detector and the detector base FDB201.
z The specifications of variant B largely correspond to those of variant A. Any
possible deviations are marked accordingly in this document.
z Variant C is available both as single detector and as kit (FDOOT241-9M).
Page 24

Structure and function
24
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
The following figure shows how the different variants are marked (to the left:
Variant B; to the right: Variants A and C).
3.3.2 Wide-spectrum smoke detector
The wide-spectrum smoke detector is an optical smoke detector with an optical
sensor. It works according to the principle of forward scattering. This detector
reacts with extreme sensitivity to light fire aerosols. The following wide-spectrum
smoke detectors are available:
z FDO241 (with ASAtechnology)
z FDO221 (with detection algorithms)
Structure and function
1
2
1 Labyrinth 2 Forward scatterer
The wide-spectrum smoke detector has the same measuring chamber as the
neural fire detector, however, it has only a forward scatterer. The increased
sensitivity makes the early detection of smoldering and open fires possible.
Page 25

Structure and function
25
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
3.3.3 Heat detector
The heat detector is a pure heat detector with two thermal sensors. The following
heat detectors are available:
z FDT241
z FDT221
The following table indicates the most important differences between the two heat
detectors.
Parameters FDT241 FDT221
Signal processing ASAtechnology Detection algorithms
Alarm activation by: z Temperature increase
z Reaching the maximum
temperature
z Temperature increase
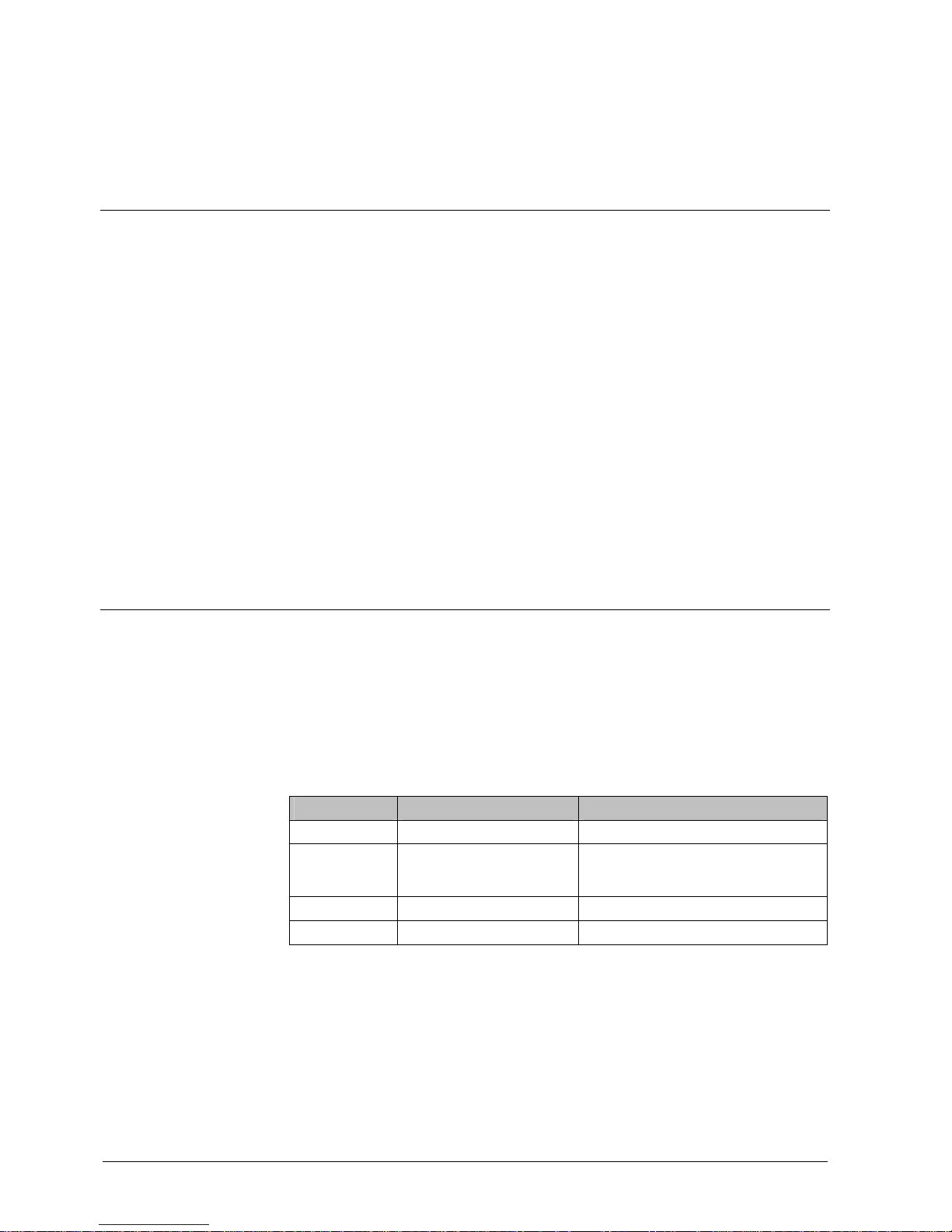
Setup and function
1
1 Heat sensors
Thanks to the two sensors, a total failure can be avoided if one of the two sensors
fails or breaks down.
Page 26
Structure and function
26
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
3.4 Function
3.4.1 Parameter sets
The parameter sets influence the detection behavior of the detectors and
specifically set them to the expected fire phenomena and ambient influences in the
environment to be monitored.
All parameter sets are programmed in the detectors. During commissioning, the
optimum parameter set must be selected for the conditions at the place of
installation. On a FDnet detector line, this is carried out at the control panel. On a
collective or MS8 detector line this is done with the detector exchanger and tester.
On a FDnet detector line, the parameter set must always be set explicitly. Unless a
parameter set is selected in collective or MS8 operation, the detector works with
the default parameter set '0'. In this case the number of the selected parameter set
is always '0'.
See also
Parameter sets: Neural fire detec
tor [J 42]
Parameter sets: Wide-spectrum s
moke detector [J 49]
Parameter sets: Heat detector [J 52]
3.4.2 Danger levels
The detector's signal processing efficiently distinguishes between fire events and
deceptive phenomena. The basis for reaching a danger level is not only given by
measured values exceeding a "response threshold"; moreover, the smoke density
progression is observed over a longer period of time and assessed by the
algorithms.
Fire detectors can transmit the following danger levels to the control panel:
Danger level Meaning Comment
0 No danger Normal condition
1 Check situation A different parameter set should
potentially be selected (inappropriate
application)
2 Warning Possible danger
3 Alarm Fire
Notes
z The evaluation of the danger level and the decisions to be taken (e.g. activation
of remote transmission) are configured in the control panel.
z On a collective line only the danger levels 0 and 3 can be transmitted to the
control panel.
Page 27

Structure and function
27
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
3.4.3 Diagnosis levels
For the most part, the detector monitors its function by itself. The signals of all
sensors are permanently monitored. In particular, the temperature sensors, light
emitters, and light receivers are monitored to ensure that they are functioning
correctly. Signal processing takes account of the monitoring results and adapts its
behavior accordingly.
The following diagnosis levels are derived from the different control measurements:
z Normal
z Observe information
z Replacement recommended
z Replacement necessary
z Fault
See the table below for details.
A fault message is signaled in the event of a fatal error that makes the proper
function of the detector impossible. To correct the cause of the fault, additional
information is available in the detector. This information may be displayed, for
example, by the detector exchanger and tester FDUD29x (for details see
documents 007227 and 009718).
Page 28

Structure and function
28
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
Information displayed on the
detector exchanger and
tester
Meaning Measures
'No deviation' Normal, no fault is present
The detector is fully functional
None
'maybe excha.' 1 Observe information
The detector is fully functional
z FDOOT:
– Slightly soiled
Check cause during periodic maintenance
'advice excha.' 1 Replacement recommended
Detector is still functional, in spite of minor
problems
z FDOOT:
– Average soiling
– Untypical sensor values caused by
environmental influence
z FDO:
– Average soiling
z Remedy the cause during the next
maintenance
z Replace detector if necessary
'needed excha.' 1 Replacement necessary
Detection possibly restricted; alarming is
still possible
z FDOOT:
– Heavily soiled, failure of one optical
sensor
– Failure of one or both thermal sensors
z FDO:
– Heavily soiled
z Call maintenance service
z Replace detector
Fault present
Detection is no longer guaranteed, or
invalid parameter setting
z FDOOT:
– Failure of both optical sensors
z FDO:
– Failure of the optical sensor
z FDT:
– Failure of one or both thermal sensors
z Remedy cause
z Adjust parameter setting
z Replace detector
Supply fault z Check detector line voltage
z Replace detector
Software error (watchdog error) Replace detector
Memory error Replace detector
Any fault message 2
Communication error involving detector and
control panel
Remedy cause
1
The information displayed on the detector exchanger and tester is always in
English; no translation into the corresponding language.
2
This status can be displayed together with another status, e.g. 'needed excha.'
(replacement necessary).
Page 29

Structure and function
29
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
3.4.4 Line separator
All FDnet devices are equipped with a line separator.
The FDnet device is equipped with electronic switches which isolate the defective
part in case of a short-circuit on the detector line. The rest of the detector line
remains serviceable. On a loop line all FDnet devices remain fully functional after a
simple error.
3.4.5 Automatic recognition of the detector line protocol
The two multiple protocol detectors FDOOT241-9 and -8 may communicate via
different detector line protocols. These detectors recognize the protocol on the
detector line (e.g. FDnet or collective) and automatically switch to the protocol in
question. This functionality facilitates commissioning in case of modernization, as
no actions need to be taken on the detector itself. See document 008331 'List of
compatibility' for exceptions.
3.4.6 Internal alarm indicator
The detectors have an internal alarm indicator. The internal alarm indicator shows
the operating condition of the detector (see table).
Operating condition Flashing mode of the AI
Normal AI flashes weakly every 4 seconds
Test AI flashes weakly every 0.5 seconds
Alarm AI lights up every second
3.4.7 Connection of external alarm indicators
Two external alarm indicators can be connected to every detector. In the FDnet the
alarm indicator can be connected to any detector; activation of the alarm indicator
can be programmed in the control panel.
Instead of an optical alarm indicator that flashes in the event of an alarm, the
sounder base is provided with an acoustic alarm indicator.
See also
Connection diagram (addressed) [J 70]
Connection diagram (collective) [J 73]
Connection diagram (MS8) [J 76]
Page 30

Structure and function
30
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
3.4.8 Renovation mode
Renovation mode should be selected when work that generates a lot of dust or
aerosols is being performed in the room.
In renovation mode, the neural fire detector and the heat detector only trigger alarm
when the temperature exceeds 80 °C for 20 seconds.
The wide-spectrum smoke detector does not trigger alarms in renovation mode
but continues to work normally.
3.4.9 Test mode
For testing purposes the detectors can be set to test mode. In test mode the
detectors react faster and with a higher sensitivity level. All detectors can be tested
with the detector exchanger and tester FDUD29x. Optical detectors may also be
tested with the test gas REF 8 or REF 8-S. Heat detectors can be tested with a hot
air fan.
See also
Testing detectors [J 81]
3.4.10 Behavior in degraded mode
If the main processor of the fire control panel fails, the control panel enters
degraded mode operation. Depending on the control panel, the fire control panel
may continue to provide the main alarming functions and signaling functions in
degraded mode operation.
Characteristics of degraded mode operation on control panels supporting degraded
mode operation:
z Alarming is still ensured in degraded mode operation. However, in degraded
mode operation, only collective alarming is possible. This means that in the
event of an alarm, it is possible to identify the detector line but not the exact
location of the detector triggering the alarm.
z If a sounder base is connected to the output for the external alarm indicator, it
is activated in degraded mode operation if there is a fire alarm (only with
detectors and sounder bases with ES ≥ 30); configuration for a specific control
panel is possible.
z When the connection for the external alarm indicator is used for a control
function (e.g. hold-open system), the output assumes the configured fail-safe
position (only with detectors with ES ≥ 30); configuration for a specific control
panel is possible.
Degraded mode operation on the FDnet is not supported in the same way by all
control panels. During planning, observance of the information in document
008331 'List of compatibility' and the respective control panel documentation is
therefore mandatory.
Page 31

Structure and function
31
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
3.4.11 Interface to service devices
All point detectors have a non-contact interface to the detector exchanger and
tester FDUD29x (service device for commissioning and maintenance). The
detector exchanger and tester communicates with the detector via this interface
(MC link). Detailled information is listed in the operating instructions for the detector
exchanger and tester (see documents 007227 and 009718).
See also
Status polling with the detector e
xchanger and tester [J 80]
3.4.12 Line tester
The line tester FDUL221 is able to recognize and localize the following errors on
the FDnet:
z Wiring error
z Open line
z Short-circuit
z Ground fault
In addition, the line tester recognizes the devices connected to the FDnet detector
line. For details, see document 008250.
Page 32

Structure and function
32
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
3.5 Mechanical setup
To install a point detector, a detector base is always required. After mounting the
detector base the point detector is simply screwed into the base by hand with the
detector exchanger or with the detector exchanger and tester.
Properties
z Quick installation and reliable contact due to screwless terminals
z Insertion of the insulated wires without any tools
z The centered alarm indicator makes an alignment of the detector base
superfluous
z Space for up to 6 auxiliary terminals for detector heating units etc.
A wide range of accessories that can be combined for the corresponding
application is available for the different applications.
See also
Options [J 33]
Mounting / Installation [J 57]
Page 33

Structure and function
33
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
3.6 Options
3.6.1 Detector base FDB221/FDB221-AA
z For the installation of point detectors and alarm
sounders
z For the recess-mounted cable entry
z For the surface-mounted cable entry, up to 6 mm
cable diameter
z Addressed
z Orange terminal block
z Detector base FDB221-AA additionally with a micro
terminal
z Compatible with:
– Point detector
– Alarm sounder FDS221
– Alarm sounder with beacon FDS229
z Order no. FDB221: A5Q00001664
z Order no. FDB221-AA: A5Q00012741
See also
Detector base FDB201/221 [J 58]
3.6.2 Detector base FDB201/FDB201-AA
z For the installation of point detectors
z For the recess-mounted cable entry
z For the surface-mounted cable entry, up to 6 mm
cable diameter
z Collective
z Gray terminal block
z Detector base FDB201-AA additionally with a micro
terminal
z Compatible with:
– Neural fire detector FDOOT2419-9
z Order no. FDB201: A5Q00003814
z Order no. FDB201-AA: A5Q00012742
See also
Detector base FDB201/221 [J 58]
Page 34

Structure and function
34
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
3.6.3 Detector base FDB222
z For the installation of point detectors and alarm
sounders
z For the recess-mounted cable entry
z Directly attached to the mounting surface
z Addressed
z Orange terminal block
z Compatible with:
– Point detector
– Alarm sounder FDS221
– Alarm sounder with beacon FDS229
z Order no.: A5Q00016447
See also
Detector base FDB202/222 [J 59]
3.6.4 Detector base FDB202
z For the installation of point detectors
z For the recess-mounted cable entry
z Directly attached to the mounting surface
z Collective
z Gray terminal block
z Compatible with:
– Neural fire detector FDOOT2419-9
z Order no.: A5Q00016446
See also
Detector base FDB202/222 [J 59]
3.6.5 Sounder base FDSB291
z For acoustic alarming in the case of an event
z For the FDnet detector line
z Orange terminal block
z With two micro terminals
z For the recess-mounted cable entry
z For the surface-mounted cable entry, up to 6 mm
cable diameter
z Compatible with:
– Neural fire detector FDOOT2xx
– Neural fire detector FDOOTC2xx
– Wide-spectrum smoke detector FDO2xx
– Heat detector FDT2xx (as of ES ≥43)
z For details, see document 007025
z Order no.: A5Q00001647
Page 35

Structure and function
35
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
3.6.6 Sounder base FDSB292
z For acoustic alarming in the case of an event
z For the collective detector line
z Gray terminal block
z With two micro terminals
z For the recess-mounted cable entry
z For the surface-mounted cable entry, up to 6 mm
cable diameter
z Compatible with:
– Neural fire detector FDOOT241-9
z For details, see document 009769
z Order no.: A5Q00013755
3.6.7 Base attachment FDB291
z For the installation of detector bases
z For the surface-mounted cable entry, as of 6 mm
cable diameter
z Compatible with:
– Detector base FDB2x1
– Detector base FDB2x2
z Order no.: A5Q00001603
See also
Base attachment FDB291 [J 60]
3.6.8 Base attachment humid FDB293
z For installation in wet rooms
z Compatible with:
– Detector base FDB2x1
– Detector base FDB2x1-AA
– Detector base FDB2x2
– Detector heating unit FDBH291
– Designation plate DBZ1193A
– M20 x 1.5 metal cable gland
z Order no.: A5Q00003945
See also
Base attachment humid FDB293 [J 61]
Page 36

Structure and function
36
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
3.6.9 Base adapter FDB281
z For adapting MS8 to Sinteso
TM
detector systems
z With fitted detector base FDB221
z Compatible with:
– MS8 detector base
– Neural fire detector FDOOT2419-8
z Order no.: A5Q00004929
See also
Base adapter FDB281 [J 62]
3.6.10 Detector heating unit FDBH291
z For applications where there is danger of moisture
condensation or icing
z Compatible with:
– Base attachment humid FDB293
z Order no.: A5Q00004439
See also
Detector heating FDBH291 [J 65]
3.6.11 Designation plate FDBZ291
z To identify the location
z Compatible with:
– Detector base FDB2x1
– Detector base FDB2x2
– Sounder base FDSB29x
– Base attachment FDB291
– Base adapter FDB281
z Order no.: A5Q00002621
See also
Designation plate FDBZ291 [J 64]
Page 37

Structure and function
37
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
3.6.12 Designation plate DBZ1193A
z To identify the location
z Compatible with:
– Base attachment humid FDB293
z Order no.: BPZ:4864330001
See also
Designation plate DBZ1193A [J 64]
3.6.13 Detector locking device FDBZ293
z For protection against theft
z Compatible with:
– Point detector
– Alarm sounder FDS221
– Alarm sounder with beacon FDS229
z Order no.: A5Q00005035
See also
Detector locking device FDBZ293 [J 63]
3.6.14 Dummy detector FDX291
F
D
X
2
9
1
S
5
4
3
1
9
-
F
2
-
A
1
z To protect the detector base from dirt
z External labelling for identification
z Does not open the contact in the detector base
z Compatible with:
– Detector base FDB2xx
– Sounder base FDSB29x
z Order no.: S54319-F2-A1
3.6.15 Detector dust cap FDZ291
z To protect the detector from dust
z Compatible with:
– Point detector
– Alarm sounder FDS221
– Alarm sounder with beacon FDS229
z Order no.: A5Q00004814
See also
Detector dust cap FDZ291 [J 78]
Page 38

Structure and function
38
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
3.6.16 Protective cage DBZ1194
z To protect the devices against mechanical damage
z Compatible with:
– Base attachment humid FDB293
z Order no.: BPZ:4677110001
See also
Protective cages [J 67]
3.6.17 EMC-protective cage FDBZ294
z To protect the devices against mechanical damage
and electromagnetic fields
z Must be connected with earth connection
z Compatible with:
– Base attachment humid FDB293
z Order no.: A5Q00023040
See also
Protective cages [J 67]
3.6.18 Micro terminal DBZ1190-AA
z For connecting cables
z For T-branches of additional cabling for detector
heating units, sounder base, external alarm
indicators, etc.
z For wire diameters of 0.28 … 0.5 mm
2
z 4-pin
z Order no.: BPZ:4677080001
See also
Auxiliary terminals DBZ1190-AA/-AB [J 69]
Page 39

Structure and function
39
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
3.6.19 Connection terminal DBZ1190-AB
z For connecting cables
z For T-branches of additional cabling for detector
heating units, sounder base, external alarm
indicators, etc.
z For wire diameters of 1 … 0.10 in
2
z 3-pin
z Order no.: BPZ:4942340001
See also
Auxiliary terminals DBZ1190-AA/-AB [J 69]
3.6.20 M20 x 1.5 metal cable gland
z For introducing a cable into a housing
z Compatible with:
– M20 x 1.5 metal counter nut
z Order no.: A5Q00004478
Page 40

Project engineering
40
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
4 Project engineering
4.1 Compatibility
All detectors can be operated on the FDnet detector line. The neural fire detector
FDOOT241-9 may also be operated on a collective detector line and the
FDOOT241-8 may be operated on an MS8 detector line (for details, please refer to
document 008331).
4.2 Ambient features
In selecting the optimum parameter set, the following factors must be taken into
account:
z Risk of injury to persons
z Concentration of valuable items
z Room geometry
z Deceptive phenomena
z Risk of fire
z Critical fire size
Risk of injury to persons
People are extremely endangered in localities such as concert halls, nursing
homes or hospitals. The risk of damage to persons is thus very high in these
localities. In canteen kitchens the situation is different. Few people work in such
facilities and are able to save themselves in the event of timely alarms. The risk of
injury to persons is thus rather low in this case.
Concentration of valuable items
Irreplaceable cultural assets are often on display in museums. Computer centers
house servers with large data volumes. The concentration of valuable items is
rather high. In a normal hotel room the concentration of valuable items must be
classified as low.
Room geometry
High ceilings, complex room shapes or well ventilated rooms have a complex room
geometry. This aggravates early fire detection, as it is difficult for the fire
phenomenon to reach the fire detector. An office room with normal ceiling height
has a simple room geometry.
Page 41

Project engineering
41
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
Deceptive phenomena
Deceptive phenomena can deceive a fire detector and bring about a false alarm.
Depending on the fire detector in question, the deceptive phenomena may be e.g.
vapor, cigarette smoke, dust, dry ice in discotheques, exhaust fumes, aerosols
occurring during welding or heat sources such as radiant heaters or hot engines.
In a small hotel room with a rather low ceiling where vapor from the bathroom may
penetrate the room, or in operating facilities where a lot of dust is generated, many
deceptive phenomena must be taken into consideration. In a clean room where
electronic modules are fabricated the risk of deceptive phenomena is rather low.
Risk of fire
In production facilities where highly combustible materials such as flammable
liquids, cotton, paper etc. are processed and where electrical machines are
operated, the fire risk is very high. Minor overheating or sparks may cause a fire. In
a storehouse where steel is stored and where no electrical installation is provided
with the exception of lighting, the fire risk is very low.
Critical fire size
When a waste paper basket in a metal-processing facility catches fire, the
consequential damage is usually rather low. Here we are talking about a critical,
medium fire size that can still be tolerated. The situation is completely different in
pharmaceutical production facilities where even the lowest smoke concentration
may impair the process and where combustible materials are processed. Even the
smallest fire must be detected immediately. In this case, we speak of a small
admissible critical fire size.
Page 42

Project engineering
42
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
4.3 Parameter sets: Neural fire detector
4.3.1 Neural fire detector FDOOT241-x (sensor mode 0)
4.3.1.1 Description
(Parameter set numbers in brackets)
High Suppression (8):
To cover applications with permanent, optical deceptive phenomena (dry ice in
discotheques, welding), this parameter set only reacts when a temperature rise of
approx. 8 K is detected in addition to the optical signal. Due to the combination of
optical and thermal signals, it is better suited than a pure heat detector. This
parameter set is also suited for applications that can otherwise only be covered
with special detectors.
Suppression (5):
Thanks to its very robust behavior, the 'Suppression' parameter set is particularly
suited for rooms where deceptive phenomena such as cigarette smoke or exhaust
fumes can be expected. It reacts in a very robust way to the deceptive
phenomenon vapor.
High Compensation (7):
This parameter set reacts in the same way as the 'Robust' parameter set; however,
the compensation range is twice as large. This parameter set is thus especially
suited for rooms in which a lot of dust and other deposits can be expected during
longer periods.
Robust (2):
The priority of the 'Robust' parameter set is to a robust response. The sensitivity is
the same as with the 'Suppression' parameter set; however, deceptive phenomena
are not explicitly analyzed and suppressed. It is thus particularly suited for us in
rooms where deceptive phenomena such as cigarette smoke or dust can be
expected. The 'Robust (2)' parameter set is suitable for higher rooms in
comparison to the 'Suppression (5)' parameter set.
Insensitive (0):
This parameter set is only available with the FDOOT2419-9 (ES <13) in collective
operation. Regarding visible aerosols the priority is on robust response. The
response behavior regarding open fires is sensitive and fast.
Balanced (4):
The 'Balanced' parameter set reveals a balanced response behavior regarding
reaction to fires and robustness to deceptive phenomena. It reacts faster with open
fires. It reacts slower with vapor, cigarette smoke or smoldering fires.
Page 43

Project engineering
43
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
Sensitive (0):
This parameter set is only available with the FDOOT241-8 in MS8 operation. It has
been specially developed for the migration of ionization detectors to MS8 control
panels.
Regarding sensitivity and response time, the FDOOT2418 with the 'Sensitive'
parameter set reacts in a similar way to an MS8 ionization detector. The difference
in the response behavior of an optical and an ionization detector must be taken into
account.
When the detector is migrated to an FDnet detector line the parameter setting
should be changed to 'Fast Response'.
Fast Response (6):
This parameter set reacts in a fast and highly sensitive manner. It is thus especially
suited for rooms without deceptive phenomena, where the priority is on detecting
the fire as early as possible.
High Sensitive Fast (9):
This parameter set is suited for applications requiring very high sensitivity levels. It
reveals a significantly higher optical and thermal sensitivity than 'Fast Response'.
This parameter set is also suited for applications that can otherwise only be
covered with special detectors.
Download 1 (14) / Download 2 (15):
Application-specific parameter sets that can be loaded on site (depending on the
control panel).
Page 44

Project engineering
44
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
4.3.1.2 Application
Risk of injury to
persons
Concentration
of valuable
items
Room
geometry
Deceptive
phenomena
Risk of fire Critical fire size No. Name
small …
large
low…
high
simple…
complex
few…
many
small …
large
small …
medium
8 High
Suppression
5 Suppression
7 High
Compensation
2 Robust
0 Insensitive
4 Balanced
0 Sensitive
6 Fast Response
9 High Sensitive
Fast
Comment
The 'High Suppression' and 'High Sensitive Fast' parameter sets are only suited for
special applications.
Page 45

Project engineering
45
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
4.3.1.3 Specification
The following table shows the characteristics and application fields of the
parameter sets of the neural fire detectors FDOOT241-9 and FDOOT241-8.
Optical Thermal
Typ. response
time
from - typ. - to
Sensitivity,
open fire
Sensitivity,
smoldering fire
Static
activation
temperature
Differential
activation
temperature3
Differential
activation
possible from:
No. Name
[s] [%/m] [%/m] [°C] ∆T [K] [°C]
8 High Suppression
(as of ES ≥30)
2
60 - 80 - 360 2,3 8 80 25 30
5 Suppression 90 -160 - 760 3,2 11,4 80 29 30
7 High Compensation 80 3,2 11,4 80 29 30
0 1 High Compensation
(only FDnet
operation)
80 3,2 11,4 80 29 30
0 1 High Compensation
(only collective
operation from ES ≥
13)
80 3,2 11,4 80 29 30
2 Robust 80 3,2 11,4 80 29 30
0 1 Insensitive
(only collective
operation up to ES <
13)
30 3,2 11,4 80 29 30
4 Balanced 40 - 64 - 300 2,3 8 80 25 30
0 1 Sensitive
(only MS8 operation)
30 1,6 5,6 80 22 30
6 Fast Response 20 - 30 1,6 5,6 80 22 3
9 High Sensitive Fast
(from ES ≥ 30)
20 - 30 0,8 2,8 60 16 3
14
15
Application-specific parameter sets
1
= Delivery status; only selectable in collective operation and MS8 operation.
2
Note chapter '4.3.1.1 Description', 'High Suppression (8)' paragraph.
3
Applicable with fast temperature increases >10 K/min.
All parameter sets except for 8 comply with standards EN 54-7 and CEA 4021.
Page 46

Project engineering
46
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
4.3.2 Neural fire detector FDOOT241-x (sensor mode 1, 'Heat detector')
This sensor mode is especially suited for applications where the detector should
only react thermally.
No. Name at ES <30 Name at ES ≥ 30
0 1 A2R A1R
1 A2R A1R
2 BR BR
3 A2S A1S
4 BS BS
1
= Delivery status; only selectable in collective operation and MS8 operation.
All parameter sets meet the criteria of standard EN 54-5.
See also
Description [J 52]
Page 47

Project engineering
47
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
4.3.3 Neural fire detector FDOOT241-x (sensor mode 2, 'Smoke
detector')
This mode should be selected when fast temperature changes may occur which
are not caused by fire (e.g. radiant heaters, hot engines). In this sensor mode the
detector only reacts optically; this is comparable with a wide-spectrum smoke
detector. Thanks to a second optical sensor, however, it reveals a balanced
response behavior in relation to the different types of fire.
Robust (2):
This parameter set reacts to aerosols in a similar way as the neural fire detector
FDOOT241 in sensor mode 0 with the 'Robust' parameter set, without taking into
account the temperature.
Universal (1):
With 'Universal' the sensitivity and response time to aerosols are between 'Robust'
and 'Sensitive'.
Sensitive (3):
With regard to aerosols, this parameter set reacts in a way that is comparable to
'Fast Response' in sensor mode 0 without temperature influence.
No. Name Response time [s] Sensitivity
open fire / smoldering fire
[%/m]
0 1 Universal 50 2,3 / 8
2 Robust 80 2,3 / 8
1 Universal 50 2,3 / 8
3 Sensitive 30 1,6 / 5,6
1
= Delivery status; only selectable in collective operation and MS8 operation.
All parameter sets meet the criteria of standard EN 54-7.
Page 48

Project engineering
48
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
4.3.4 Neural fire detector FDOOT221
4.3.4.1 Description
Standard (2):
The priority of the 'Standard' parameter set is set to robust response. It is thus
particularly suited for us in rooms where deceptive phenomena such as cigarette
smoke or dust can be expected.
Standard Plus (4):
This parameter set is fast and highly sensitive. It is thus especially suited to rooms
without deceptive phenomena, where the priority is on early fire detection.
4.3.4.2 Application
Risk of injury to
persons
Concentration of
valuable items
Room geometry Deceptive
phenomena
Risk of fire Critical fire size No. Name
small …
large
low…
high
simple…
complex
few…
many
small …
large
small …
medium
2 Standard
4 Standard Plus
4.3.4.3 Specification
Optical Thermal
Response time Sensitivity, open
fire
Sensitivity,
smoldering fire
Static activation
temperature
Differential activation
temperature1
No. Name
[s] [%/m] [%/m] [°C] ∆T [K]
2 Standard 64 3,2 11,4 80 29
4 Standard Plus 50 2,3 8 80 25
1
Applicable with fast temperature increases >10 K/min.
All parameter sets meet the criteria of standard EN 54-7.
Page 49

Project engineering
49
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
4.4 Parameter sets: Wide-spectrum smoke detector
4.4.1 Wide-spectrum smoke detector FDO241
4.4.1.1 Description
Robust (2):
The priority of the 'Robust' parameter set is to a robust response. It is thus
particularly suited for the application in rooms where deceptive phenomena such
as cigarette smoke can be expected.
Universal (1):
With the 'Universal' parameter set the sensitivity and response time are between
'Robust' and 'Sensitive'.
Sensitive (3):
This parameter set is both fast and sensitive. It is thus especially suited for rooms
without deceptive phenomena, where the priority is on possibly early fire detection.
Download 1 (14) / Download 2 (15):
Application-specific parameter sets that can be loaded on site (depending on the
control panel).
4.4.1.2 Application
Risk of injury to
persons
Concentration
of valuable
items
Room
geometry
Deceptive
phenomena
Risk of fire Critical fire size No. Name
small …
large
low…
high
simple…
complex
few…
many
small …
large
small …
medium
2 Robust
1 Universal
3 Sensitive
Page 50

Project engineering
50
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
4.4.1.3 Specifications
No. Name Response time [s] Sensitivity [%/m]
2 Robust 70 2.8
1 Universal 50 2.0
3 Sensitive 30 1.4
14
15
Application-specific parameter sets
All parameter sets meet the standard EN 54-7.
Page 51

Project engineering
51
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
4.4.2 Wide-spectrum smoke detector FDO221
4.4.2.1 Description
Standard (2):
The priority of the 'Standard' parameter set is set to robust response. It is thus
particularly suited to application in rooms where few deceptive phenomena such as
cigarette smoke can be expected.
Standard Plus (3):
This parameter set is both fast and sensitive. It is thus especially suited to rooms
without deceptive phenomena, where the priority is on early fire detection.
4.4.2.2 Application
Risk of injury to
persons
Concentration
of valuable
items
Room
geometry
Deceptive
phenomena
Risk of fire Critical fire size No. Name
small …
large
low…
high
simple…
complex
few…
many
small …
large
small …
medium
2 Standard
3 Standard Plus
4.4.2.3 Specification
No. Name Response time [s] Sensitivity [%/m]
2 Standard 60 2.8
3 Standard Plus 50 2
All parameter sets meet the standard EN 54-7.
Page 52

Project engineering
52
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
4.5 Parameter sets: Heat detector
4.5.1 Heat detector FDT241
4.5.1.1 Description
The heat detector FDT241 has the following parameter sets:
z A1R (1)
z BR (2)
z A1S (3)
z BS (4)
z Download 1 (14) / Download 2 (15)
Application-specific parameter sets that can be loaded on site (depending on
the control panel).
Notes on the designations A1 and B
z A1-parameter sets should be applied at an ambient temperature of
approximately 25 ℃. However, they can be applied at temperatures up to 50℃.
The static response temperature is 60°C.
z B-parameter sets are normally applied at temperatures around 40 °C. They can
be applied at temperatures up to 65°C. The static response temperature is
80°C.
Notes on the designations R and S
In comparison to the S-parameter sets, R-parameter sets additionally trigger
alarms in the case of a temperature increase (e.g. from 20 °C to 50 °C within a few
minutes).
Page 53

Project engineering
53
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
4.5.1.2 Specifications
Operating temperature
typ. / max.
Static activation
temperature1
Differential activation
temperature2
Differential activation
possible from:
No. Name
[°C] [°C] ∆T [K] [°C]
1 A1R
60℃ rate of rise
25 / 50 60 25 3
2 BR
80 ℃ rate of rise
40 / 65 80 29 30
3 A1S
60℃ maximum
25 / 50 60 – –
4 BS
80 ℃ Maximum
40 / 65 80 – –
14
15
Application-specific parameter sets
1
Applicable with slow temperature increases <1 K/min.
2
Applicable with fast temperature increases >10 K/min. With slow temperature
increases of <10 K/min, this value increases by several degrees.
All parameter sets meet the criteria of standard EN 54-5.
Page 54

Project engineering
54
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
4.5.2 Heat detector FDT221
4.5.2.1 Description
The heat detector FDT221 has the following parameter sets:
z A1R (1)
z BR (2)
See also
Description [J 52]
4.5.2.2 Specifications
Operating temperature
typ. / max.
Static activation
temperature1
Differential activation
temperature2
Differential activation
possible from:
No. Name
[°C] [°C] ∆T [K] [°C]
1 A1R
60℃ rate of rise
25 / 50 60 25 3
2 BR
80 ℃ rate of rise
40 / 65 80 29 30
1
Applicable with slow temperature increases <1 K/min.
2
Applicable with fast temperature increases >10 K/min. With slow temperature
increases of <10 K/min, this value increases by several degrees.
All parameter sets meet the criteria of standard EN 54-5.
Page 55

Project engineering
55
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
4.6 Default settings
The default parameter set (parameter set 0) is set in all fire detectors when
delivered.
The following table shows the default parameter set of the various fire detectors.
Fire detector Default parameter set
FDOOT241-x in FDnet operation:
z Sensor mode 0 (neural fire detector) High Compensation
z Sensor mode 1 (heat detector) A1R
z Sensor mode 2 (smoke detector) Universal
FDOOT241-9 in collective operation:
z Sensor mode 0 (neural fire detector) ES <13 = Insensitive / ES ≥13 = High
Compensation
z Sensor mode 1 (heat detector) A1R
z Sensor mode 2 (smoke detector) Universal
FDOOT241-8 in MS8 operation:
z Sensor mode 0 (neural fire detector) Sensitive
z Sensor mode 1 (heat detector) A1R
z Sensor mode 2 (smoke detector) Universal
FDOOT221 Standard
FDO241 Robust
FDO221 Standard
FDT241 A1R
FDT221 A1R
Upon commissioning of the fire detection system, the optimum parameter set must
be selected based on the existing risk and the ambient conditions.
If the fire detectors are operated on the FDnet (addressed), the fire detectors are
automatically set to the basic setting for the country in question when the control
panel is started up for the first time. Individual adaptation is made using the
commissioning tool of the corresponding control panel.
If the fire detectors are operated in collective or MS8 operation, the detectors
operate with their default setting on first commissioning. In this operating mode,
individual adaptation of the detector behavior is performed using the detector
exchanger and tester FDUD292.
Page 56

Project engineering
56
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
4.7 Application examples
Application recommendations such as the selection of the detector type and its
settings for the various applications are described in document 010030 'Fire
detector application guideline'.
The following table includes examples regarding the selection of the detector and
the parameter set. These examples cannot be used universally but serve only as
typical examples.
Environment Detector Parameter set
Normal office room without
any particular deceptive
phenomena
No special requirements
⇨ FDOOT221 or FDO221
Standard
Possible deceptive
phenomena, e.g. electric
kettle
Vapor as deceptive phenomenon
⇨ FDOOT241
Balanced or Suppression
Kitchen A lot of vapor as deceptive phenomenon
⇨ FDOOT241 or FDT241
FDOOT241: Suppression or BS
FDT241: BS
Hospital room, museum Quick response needed, no deceptive
phenomena expected
⇨ FDOOT241 or FDO241
FDOOT241: Fast Response
FDO241: Sensitive
Clean room Fast and very sensitive reaction required
⇨ FDOOT241
High Sensitive
Page 57

Mounting / Installation
57
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
5 Mounting / Installation
5.1 Required space
z Upon insertion of the detector, the detector base is stressed by compression,
tension and torsion. The fixing must thus be designed accordingly.
z Detector bases must be placed flat on the ceiling.
z Avoid mounting on steps, concrete ribs, etc.
z Mount the detector base directly on the recessed box, or together with a base
attachment, when the feeding main is surface-mounted and the cable diameter
is more than 6 mm.
z There must be at least 50 cm below and at least 2 cm of free space to the
sides of the detector, so that the detector can be extracted or tested with the
detector exchanger and tester.
z Contorted detector bases complicate or even impede the insertion of the
detectors with the detector exchanger.
* = min. 2 cm
*
*
*
Minimum spacing when installing detector bases
Page 58

Mounting / Installation
58
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
5.2 Detector base FDB201/221
z The cables are routed surface-mounted (up to cable diameter 6 mm) or recess-
mounted through detector base FDB201/221 or FDB201/221-AA.
z The cables must be placed flat on the bottom of the detector base so that they
do not hamper detector insertion.
FDB201/FDB221
FDB201-AA/
FDB221-AA
max. 4m
m
Ø
max. 6mmØ
min. 46
max. 79
1
Installation of detector bases FDB201/FDB201-AA and FDB221/FDB221-AA
1 Detector base
Page 59

Mounting / Installation
59
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
5.3 Detector base FDB202/222
z The cables are routed recess-mounted through detector base FDB202/222.
z The cables must be placed flat on the bottom of the detector base so that they
do not hamper detector insertion.
FDB202/FDB22
2
max. 4mm
Ø
min. 46
max. 79
1
Installation of detector base FDB202/FDB222
1 Detector base
Page 60

Mounting / Installation
60
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
5.4 Base attachment FDB291
z When the cable diameter is more than 6 mm, the base attachment FDB291
must be used.
z The required cable entries must be broken out on the base attachment
FDB291.
119
25
max. 90
min. 46
max. Ø 4mm
FDB291
max. Ø 21m
m
FDB2x1
FDB2x1-AA
FDB2x2
1
2
3
Installation of detector base on base attachment FDB291
1 Identification 3 Detector base
2 Base attachment
Page 61

Mounting / Installation
61
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
5.5 Base attachment humid FDB293
z For installation in wet rooms, the base attachment humid FDB293 is used.
z To seal the cables, especially tight cable glands are used.
max. 4mm
Ø
max. 4mm
Ø
FDB293
FDB2x1
FDB2x1-AA
FDB2x2
1
2
Installation of detector base on base attachment humid FDB293
1 Base attachment humid 2 Detector base
Page 62

Mounting / Installation
62
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
5.6 Base adapter FDB281
z For the adaptation of MS8 bases on the FDnet the base adapter FDB281 is
required.
z The base adapter is screwed into the MS8 base.
FDOOT241-8
FDB281
1
2
3
Installation of base adapter FDB281 on MS8 detector base
1 MS8 detector base 3 Neural fire detector
2 Base adapter
Page 63

Mounting / Installation
63
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
5.7 Detector locking device FDBZ293
The detector can be protected against theft with the detector locking device
FDBZ293.
Installation of detector locking device FDBZ293
A Detector base C Detector locking device
B Detector
1. Place the grub screw with a hexagon socket screw in the detector.
2. Insert the detector in the detector base.
3. Insert the hexagonal wrench provided in the bore hole on the detector housing
and tighten the grub screw.
Page 64

Mounting / Installation
64
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
5.8 Designation plate FDBZ291
To provide the detector with a location address, the address is inscribed on the
designation plate FDBZ291 and placed on the detector base or base attachment.
Installation of designation plate FDBZ291
1 Designation plate FDBZ291 3 Identification
2 Base attachment FDB291 4 Detector base
5.9 Designation plate DBZ1193A
To identify a detector on a base attachment humid, the detector designation plate
DBZ1193A is labelled and placed on the detector base humid FDB293.
FDB29
3
DBZ1193A
1
2
Installation of designation plate DBZ1193A
1 Designation plate DBZ1193A 2 Base attachment humid FDB293
Page 65

Mounting / Installation
65
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
5.10 Detector heating FDBH291
5.10.1 Installation of the detector heating unit
When the detector is exposed to icing or moisture condensation (e.g. in cooling
rooms, attics, loading ramps) the detector heating unit FDBH291 is installed in the
base. The detector heating unit increases the detector temperature by
approximately 2 °C over the ambient temperature and thus avoids moisture
condensation on the detector.
To ensure IP protection, the base is always mounted together with the base
attachment humid FDB293.
FDB293
FDBH291
FDB2x1
FDB2x1-A
A
FDB2x2
DBZ1190-AA
1
2
3
4
Installation of the detector heating unit FDBH291
1 Micro terminals 3 Detector base
2 Base attachment humid 4 Detector heating unit
Page 66

Mounting / Installation
66
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
5.10.2 Connection of the detector heating unit
z Connect the cables for the monitored supply from the control panel and the
detector heating unit to the supplied micro terminals DBZ1190-AA.
z The cables can be placed in the same cable harness as the detector line or
separately.
z Several detector heating units can be connected in parallel.
z Detector heating units require a separate supply.
The detector must be checked periodically for possible icing.
+-+-+
-
+
-
DBZ1190-AA
+
LINE
FDBH291
+-+-+
-
-
+
FDBH291
-
+
DBZ1190-A
A
FDB221/FDB221-A
A
FDB222
FDB221
/
FDB221-A
A
FDB222
1
2
1
2
33
4
5
Connection diagram for detector heating unit FDBH291
1 Detector base 4 Control panel
2 Micro terminals 5 Control panel supply (monitored)
3 Detector heating unit
Page 67

Mounting / Installation
67
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
5.11 Protective cages
Protective cage DBZ1194 protects the detector against mechanical damage.
EMC-protective cage FDBZ294 protects the detector against mechanical damage
and electromagnetic fields.
5.11.1 Installation of the protective cages
The protective cages can only be installed on the base attachment humid FDB293.
Installation of the protective cages
1 Base attachment humid 4 Flat plug 6.3 x 0.8 mm
2 Break out and screw protective cage
on firmly
5 EMC-protective cage
3 Protective cage
5.11.2 Grounding of the EMC-protective cage FDBZ294
The EMC-protective cage must be connected to the shielding of the detector line
cable at the flat plug.
If the detector line cable is not shielded then the EMC-protective cage must be
grounded using a separate cable.
For optimum grounding in the presence of powerful electromagnetic fields, the
ground line must be shorter than 10 m and have a cross section of at least
1.5 mm
2
.
See also
Installation of the protective cages [J 67]
Page 68

Mounting / Installation
68
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
5.12 Cable entry
The detector bases include a spring clip (admissible wire/strand cross-section
0.28... 1.5 mm
2
). Only one wire is allowed to be connected per terminal. This is the
only way in which a faultless connection can be guaranteed.
!
30°
1
3
4
5
6
7
2
Cable entry in detector base
1 The conductor loops must be placed flat in the base
bottom.
5 Contact for test tips
2 The conductor loops must not be placed over this
zone, as otherwise the detector cannot be inserted
correctly.
6 Turn the screwdriver 90° in the direction of the arrow
(left) to only loosen the conductors and insert the strand.
3 Screwless connection terminals 7 Optimum insertion of the wire without tool, at an angle of
approx. 30°
4 Bare length 6.5 ... 7.5 mm
Page 69

Mounting / Installation
69
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
5.12.1 Auxiliary terminals DBZ1190-AA/-AB
Corresponding auxiliary terminals are available for multiple connections.
z DBZ1190-AB Connection terminal 1... 2.5 mm
2
z DBZ1190-AA Micro terminal 0.28... 0.5 mm
2
DBZ1190-A
B
DBZ1190-AA
FDB2x1
FDB2x1-A
A
FDB2x2
1
2
3
Installation of auxiliary terminals in detector base
1 Connection terminals 3 Micro terminals
2 Detector base
5.13 Detector lines
General cabling information
z Preferably, twisted and non-shielded cables should be used. This also applies
to connecting the external alarm indicators.
z Shielded cables are only required in special cases, such as strong high-
frequency fields.
See also
Detector lines [J 85]
Page 70

Mounting / Installation
70
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
5.13.1 Connection diagram (addressed)
General
z Loop lines and stub lines as well as T-branches are possible.
z Note document 001508 for installation (calculation of the capacity layer)!
z External alarm indicators may only be connected to one detector.
z Permissible cables for detectors with more than one external alarm indicator
according to the collective connection diagram may be migrated to FDnet
without any changes.
5.13.1.1 Use of unshielded cables
Guideline
z The connection is established from base to base using twisted or non-twisted
wire pairs.
+-+-+
-
+-+-+
-
LINE
+-+-+
-
+-+-+
-
+
-
+
+-+-+
-
1
2
3
4
2
+
4
+
Connection diagram for addressed detector line with and without external alarm indicators
(without shielded cables)
1 Control panel 3 Auxiliary terminals
DBZ1190-AA/DBZ1190-AB
2 Detector base FDB221/FDB221-AA,
FDB222
4 External alarm indicator DJ119x
Page 71

Mounting / Installation
71
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
5.13.1.2 Use of shielded cables
The shielding of the FDnet line must be connected through in the detector base
with auxiliary terminals DBZ1190-xx.
If a shielded cable is used, there are two possible ways of connecting external
alarm indicators:
+-+-+
-
+-+-+
-
LINE
+-+-+
-
1
2
3
+-+-+
-
+-+-+
-
2
4
A
B
4
+
+
3
3
Connection diagram for addressed detector line with and without external alarm indicators
(with shielded cables)
1 Control panel 3 Auxiliary terminals
DBZ1190-AA/DBZ1190-AB
2 Detector base FDB221/FDB221-AA,
FDB222
4 External alarm indicator DJ119x
Page 72

Mounting / Installation
72
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
Variant A:
1. Connect the positive pole of the alarm indicator to the positive pole for the
alarm indicator on the detector.
2. Connect the negative pole of the alarm indicator to the negative pole for the
alarm indicator on the detector.
3. Connect the shielding of the connection cable between the alarm indicator and
detector on the detector side to the positive pole with an auxiliary terminal
DBZ1190-xx.
Variant B:
1. Connect the positive pole of the alarm indicator to the positive pole for the
alarm indicator on the detector.
2. Leave the negative pole for the alarm indicator on the detector unoccupied.
3. Connect each of the two negative poles of the alarm indicator separately to
both negative terminals of the FDnet line.
The two negative connections of the alarm indicator are decoupled internally in
the alarm indicator by diodes.
4. Connect the shielding of the FDnet line with the shielding of the connection
cable to the alarm indicator with an auxiliary terminal DBZ1190-xx.
Page 73

Mounting / Installation
73
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
5.13.2 Connection diagram (collective)
General
z A control-panel specific end-of-line element (EOL) must be connected at the
end of the collective detector line.
Connecting external alarm indicators
The following points must be noted when connecting external alarm indicators:
z If the external alarm indicator is connected to only one detector, there is no
limitation.
z If the external alarm indicator is connected to more than one detector, this is
only admissible on the following conditions:
‒ The detectors are of the FD20 generation (they are not to be mixed with
older detector generations, e.g. AlgoRex detectors)
‒ No sounder base is used
‒ The detectors must have the part number and product version (ES) in
question (see table)
Part number
FDOOT241-9
Product version (ES)
FDOOT241-9
External alarm indicator connected to
several collective detectors
A5Q00004813 < 13
1
not admissible
A5Q00004813 ≥ 30 1 permissible2
A5Q00015955 13 ≤ ES < 30 permissible2
1
This also applies to the flame detector FDF2x1-9 and the linear smoke detector
FDL2x1-9
2
The cabling of the external alarm indicators can be migrated to FDnet without
any changes.
Page 74

Mounting / Installation
74
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
5.13.2.1 Use of unshielded cables
Guideline
z The connection is established from base to base using twisted or non-twisted
wire pairs.
+-+-+
-
+-+-+
-
LINE
+
-
+-+-+
-
1
2
C
4
B
3
A
+
Connection diagram for collective detector line with and without external alarm indicators
(without shielded cables)
1 Control panel 3 External alarm indicator DJ119x
2 Detector base FDB201/FDB201-AA,
FDB202
4 End-of-line depending on control
panel
Notes
z Standard wiring:
The external alarm indicator is connected to the positive and negative poles of
each detector.
z Wire-saving cabling:
The external alarm indicators are connected as follows:
‒ The external alarm indicator must be connected to the positive and negative
poles of at least one detector (A).
‒ The external alarm indicator must be connected to the positive pole of every
other detector (B).
‒ The external alarm indicator need not be connected to the negative pole of
each other detector (C).
The wire-saving cabling for external alarm indicators is not admissible for new
installations.
Page 75

Mounting / Installation
75
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
5.13.2.2 Use of shielded cables
The shielding of the collective line must be connected through in the detector base
with auxiliary terminals DBZ1190-xx.
If a shielded cable is used, there are two possible ways of connecting external
alarm indicators:
+-+-+
-
+-+-+
-
LINE
+-+-+
-
1
2
3
B
4
++
A
+-+-+
-
5
4
Connection diagram for collective detector line with and without external alarm indicators
(with shielded cables)
1 Control panel 4 External alarm indicator DJ119x
2 Detector base FDB201/FDB201-AA, FDB202 5 End-of-line depending on control panel
3 Auxiliary terminals DBZ1190-AA/DBZ1190-AB
Variant A:
1. Connect the positive pole of the external alarm indicator to the positive pole for
the alarm indicator on the detector.
2. Connect the negative pole of the external alarm indicator to the negative pole
for the alarm indicator on the detector.
3. Connect the shielding of the connection cable between the alarm indicator and
detector on the detector side to the positive pole for the external alarm indicator
via an auxiliary terminal DBZ1190-xx.
Page 76

Mounting / Installation
76
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
Variant B:
1. Connect the positive pole of the external alarm indicator to the positive pole for
the alarm indicator on the detector.
2. Leave the negative pole for the alarm indicator on the detector unoccupied.
3. Connect the negative pole of the external alarm indicator with the negative
terminal on the input side of the collective line on the detector via an auxiliary
terminal DBZ1190-xx.
4. Connect the shielding of the collective line with the shielding of the connection
cable to the external alarm indicator via an auxiliary terminal DBZ1190-xx.
5.13.3 Connection diagram (MS8)
On an MS8 detector line an external alarm indicator may be connected to only one
detector.
5.13.3.1 Use of unshielded cables
Guideline
z The connection is established from base to base using twisted or non-twisted
wire pairs.
+-+-+
-
+-+-+
-
LINE
+
-
+-+-+
-
1
2
3
+
Connection diagram for MS8 detector line with and without external alarm indicators (without
shielded cables)
1 Control panel 3 External alarm indicator DJ119x
2 Base adapter FDB281 (with fitted
detector base FDB221)
Page 77

Mounting / Installation
77
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
5.13.3.2 Use of shielded cables
The shielding of the MS8 line must be connected through in the base adapter
auxiliary terminals DBZ1190-xx.
If a shielded cable is used, there are two possible ways of connecting external
alarm indicators:
+-+-+
-
+-+-+
-
LINE
+-+-+
-
1
2
3
B
4
++
A
+-+-+
-
4
Connection diagram for MS8 detector line with and without external alarm indicators (with
shielded cables)
1 Control panel 3 External alarm indicator DJ119x
2 Base adapter FDB281 (with fitted
detector base FDB221)
Variant A:
1. Connect the positive pole of the external alarm indicator to the positive pole for
the alarm indicator on the detector.
2. Connect the negative pole of the external alarm indicator to the negative pole
for the alarm indicator on the detector.
3. Connect the shielding of the connection cable between the alarm indicator and
detector on the detector side to the positive pole for the external alarm indicator
via an auxiliary terminal DBZ1190-xx.
Variant B:
1. Connect the positive pole of the external alarm indicator to the positive pole for
the alarm indicator on the detector.
2. Leave the negative pole for the alarm indicator on the detector unoccupied.
3. Connect the negative pole of the external alarm indicator with the negative
terminal on the input side of the MS8 line on the detector via an auxiliary
terminal DBZ1190-xx.
4. Connect the shielding of the Ms8 line with the shielding of the connection cable
to the external alarm indicator via an auxiliary terminal DBZ1190-xx.
Page 78

Mounting / Installation
78
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
5.14 Detector dust cap FDZ291
During the construction phase the detector may be covered with a detector dust
cap FDZ291 to protect it from dust and dirt.
FDZ291
1
2
3
Installation / removal of detector dust cap FDZ291
1 Detector 3 Remove the detector dust cap either
manually by turning it to the right, or
by using a detector exchanger and
tester.
2 Detector dust cap
Page 79

Commissioning
79
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
6 Commissioning
Commissioning on FDnet
The control panel is used to commission the detectors. The exact procedure is
described in the control panel documentation.
Commissioning on collective or MS8 detector line
The commissioning of the collective detector line is performed on the control panel.
The exact procedure is described in the control panel documentation.
After commissioning the detector line, the parameter sets can be set with the
detector exchanger and tester FDUD292.
Changing over from collective to FDnet
When changing from a collective detector line with FD20 detectors to an FDnet
detector line, the following must be taken into account:
z There is no need to exchange the detector base FDB201 by a detector base
FDB221.
z It is not necessary to replace the sounder base FDSB292, either. On an FDnet
detector line the sounder base FDSB292 behaves in the same way as the
sounder base FDSB291 with product version ES ≥30.
z When a detector is removed from an FDnet detector line and that detector is
located on a collective detector base (FDB201 or FDSB292), the
communication between the control panel and the next detector is interrupted.
In this case, alarming by the subsequent detectors is no longer possible. A fault
is indicated on the control panel.
Changing over from FDnet to collective
When changing from an FDnet detector line with FD20 detectors on a collective
line, or when new detectors are used on a collective detector line for the first time,
new, collective detector bases are mandatory!
WARNING
Removal of the devices cannot be recognized when the wrong detector bases
are used.
Fire may spread unhindered.
z Only detector bases FDB201 and FDB201-AA as well as sounder bases
FDSB292 must be operated on a collective detector line.
Changeover is normally performed automatically. With some detectors, a
temporary fault or alarm may occur during changeover. For details, see Document
008331.
Page 80

Maintenance / repair
80
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
7 Maintenance / repair
7.1 Status polling with the detector exchanger and tester
All detectors have an interface to the detector exchanger and tester. With this
interface, proximity data exchange is possible between the detector and the
detector exchanger and tester FDUD29x. Depending on the authorization level of
the user and the control panel type, the following actions can be performed:
z Device test (Go / No Go or detailed by status polling)
z Activation of a test alarm
z Reading out the identification number, customer text and measure text
z Localization and parameter setting of the detector (parameter setting not in
FDnet mode)
z Switching off the detector
z Resetting the control panel
For detailed information, please refer to the operating instructions of the detector
exchanger and tester (see documents 007227 and 009718).
7.2 Performance check
Through the self-test, the detectors are automatically subjected to an electrical
performance check. Regular performance checks are nevertheless required on the
detectors. This may be done with the detector exchanger and tester, test gas or by
the hot air fan.
Recommendation:
z Subject all detectors to an annual visual check. Detectors that are heavily
soiled or mechanically damaged must be replaced.
z All detectors should be replaced after 6 to 8 years of service, regardless of the
ambient conditions.
Page 81

Maintenance / repair
81
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
7.3 Testing detectors
Depending on the detector, testing may be performed with one or more of the
following accessories:
z Detector exchanger and tester FDUD29x (recommended)
z Test gas
‒ REF 8-S (recommended)
‒ REF 8
z Hot air fan
The following table shows which detectors may be tested with which test aids.
Detector Detector
exchanger and
tester
Test gas Hot air fan
FDOOT241-9/-8 (sensor mode 0) X X X
FDOOT241-9/-8 (sensor mode 1) X – X
FDOOT241-9/-8 (sensor mode 2) X X –
FDOOT221 X X X
FDO2x1 X X –
FDT2x1 X – X
Depending on the detector, the following must be taken into account:
Detector in
test mode
To be considered
FDOOT z The FDOOT with ES < 13 reveals the same optical and thermal
sensitivity level in all parameter sets.
z From ES 13, the detector reacts in correspondence with the
parameter set in test mode. This means when the neural fire detector
is operated as a heat detector (sensor mode 1), it must be thermally
checked as well.
FDO z The detector reacts optically with medium sensitivity (2 %/m).
FDT z The detector reacts when a temperature of 60 °C is reached or at a
temperature increase of 22 K/min.
When the detector is in alarm condition, the internal alarm indicator flashes
brightly every second.
Page 82

Maintenance / repair
82
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
7.3.1 Testing detectors with detector exchanger and tester
Testing detectors on a collective or addressed (FDnet, MS8) line is easiest with the
detector exchanger and tester FDUD29x. With the detector exchanger and tester,
the detectors can also be tested in operating mode without any problems.
A detector can also be switched to test mode with the detector exchanger and
tester. Detectors on a collective line or on an MS8 line automatically revert to
normal operating mode after 60 seconds in this case.
For detailed information, please refer to the operating instructions of the detector
exchanger and tester (documents 007227 and 009718).
7.3.2 Testing detectors without detector exchanger and tester
The fire detectors are highly resistant to deceptive phenomena. Optical fire
detectors thus recognize the immediate occurrence of smoke, as typically occurs
when testing with test gas, as a deceptive phenomenon and do not trigger an
alarm. This is desirable in normal operation; however, it does make testing with test
gas problematical.
To enable detector testing with test gas or with a hot air fan, the detector must be
switched to test mode. Testing with test gas or the hot air fan differs with
addressed and collective detector lines.
Addressed detector lines (FDnet)
On addressed detector lines, the detector or detector zones can be switched to test
mode on the control panel. Testing with test gas is then possible without problems.
Addressed detector lines (MS8)
Detectors on an MS8 line cannot be set to test mode from the control panel. Unlike
with the collective detector line, the detector is not allowed to be removed briefly
from the detector line and reinserted, otherwise all subsequent detectors will be
disconnected. Testing without a detector exchanger and tester is difficult,
specifically with smoke detectors.
Collective detector lines
Detectors on a collective line are automatically switched to test mode for 3 minutes
during startup and reset. A detector that has been newly inserted (or that has been
briefly removed from the detector line and re-inserted) is thus automatically in test
mode during the first 3 minutes.
To trigger a detector with test gas, normally 2 … 4 gas discharges at intervals of
approx. 2 seconds are required. When the detector is in test mode, activation
takes place after approximately 10 seconds.
Page 83

Specifications
83
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
8 Specifications
Unless otherwise mentioned, the following data applies:
Temperature = 25°C
Air pressure = 1000 hPa (750 Torr)
8.1 Technical data FDOOT241-x, FDOOT221
8.1.1 General (irrespective of the detector line)
Device characteristics Response sensitivity (typ.):
z FDOOT221 6 … 12 %/m (depending on the
parameter set)
z FDOOT241-x 3 … 12 %/m (depending on the
parameter set)
Compensation speed ≤ 1/45 voltage increase for
detection/h
Detector diagnosis With detector exchanger and tester
FDUD29x
Ambient conditions Permitted ambient temperature:
z FDOOT221 -10 … +60 ℃
z FDOOT241-x -25 … +70 °C
Storage temperature -30 … +75 °C
Air humidity ≤ 95 % rel.
Protection categories according to
EN 60529/IEC 60529:
z Base FDB201/FDB221/
FDB202/FDB222
IP43
z Base attachment FDB291 with base
FDB201/FDB221/
FDB202/FDB222
IP43
z Base attachment humid FDB293 with
base FDB201/FDB221/
FDB202/FDB222:
– FDOOT241-8
– FDOOT241-9
IP54
IP44
z Sounder base FDSB29x IP43
Electromagnetic compatibility:
z 1 MHz … 2 GHz 50 V/m
Permissible wind speed:
z FDOOT221 Max. 5 m/s
z FDOOT241-x Max. 20 m/s
Page 84

Specifications
84
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
Mechanical data Colour ∼RAL 9010 pure white
Standards Standards
z FDOOT221 CEA 4021, EN 54-7, EN 54-17
z FDOOT241-x CEA 4021, EN 54-7, EN 54-17,
EN 54-5
VdS approvals:
z FDOOT221 G204006
z FDOOT241-9 G204007
z FDOOT241-8 G204133
FM approvals:
z FDOOT221 3029351
z FDOOT241-9 3029351
z FDOOT241-8 3029351
Certificates:
z FDOOT221 0786-CPD-20006
z FDOOT241-9 0786-CPD-20007
0786-CPD-20010
z FDOOT241-8 0786-CPD-20008
0786-CPD-20009
CE conformity mark Yes
QA Standards Siemens Standard SN 36350
Page 85

Specifications
85
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
8.1.2 Detector lines
FDnet
Detector line Operating voltage (modulated) 12 … 33 V DC
Operating current (quiescent) Typ. 230 μA
Maximum current connection factor 1
Quiescent current connection factor 1
Address connection factor 1
Separator connection factor 1
Protocol FDnet
Compatibility See document 008331 'List of
compatibility'
Line separator Line voltage:
z Nominal 32 V DC (= V
nom
)
z Minimum 12 V DC (= V
min
)
z Maximum 33 V DC (= V
max
)
Voltage at which the separator opens:
z Minimum 7.5 V DC (= V
SO min
)
z Maximum 10.5 V DC (= V
SO max
)
Permanent current when switches are
closed:
Max. 0.5 A (= I
C max
)
Switching current (e.g. in the event of a
short-circuit):
Max. 1 A (= I
S max
)
Leakage current when switches are open: Max. 1 mA (= I
L max
)
Serial impedance when switches are
closed:
Max. 0.5 Ω (= Z
C max
)
External alarm indicators External alarm indicators that can be
connected
2 external alarm indicators and 1
sounder base
Voltage 10 … 17 V DC
Power 9 … 15 mA
Length of line
z Max. 30 m with unshielded
cables, or when the shielding is
connected to the detector's
positive pole
z Max. 5 m, if the shielding is
connected to earth
Flashing interval times:
z Bright 15 ms
z Dark 1 s
Page 86

Specifications
86
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
Collective detector line (FDOOT241-9)
Detector line Operating voltage 14 ... 28 V DC
Maximum current connection factor 1.25 … 2 (depending on the
parameter set and ES)
Quiescent current at:
z Maximum current connection factor =
1,25
80 … 120 μA
z Maximum current connection factor =
1.5
100 … 150 μA
z Maximum current connection factor = 2
For details, please refer to the following
chapter
130 … 200 μA
Current peak at:
z Maximum current connection factor =
1,25
180 μA
z Maximum current connection factor =
1.5
225 μA
z Maximum current connection factor = 2
For details, please refer to the following
chapter
300 μA
Alarm voltage at:
z Alarm current = 1 ... 15 mA 5 … 10 V DC
z Alarm current = 35 mA 18 … 22 V DC
z Alarm current = 50 mA 26 … 28 V DC
Alarm current at UB = 5 ... 28 V DC 4 … 50 mA
Reset voltage UR:
z Alarm is reliably reset 0 ... 2 V DC
z Alarm may possibly not be reset 2 ... 4 V DC
Reset time at UR ≤ 2 V DC:
z Alarm is reliably reset > 2 s
z Alarm may possibly not be reset 1 ... 2 s
Protocol Collective (with and without current
limitation)
Compatibility See document 008331 'List of
compatibility'
External alarm indicators External alarm indicators which can be
connected
z 2 external alarm indicators
- OR -
z 1 external alarm indicator and 1
FDSB292
Voltage Typ. 6 … 17 V DC
Power 9 … 15 mA
Length of line
z Max. 30 m with unshielded
cables, or when the shielding is
connected to the detector's
positive pole
z Max. 5 m, if the shielding is
connected to earth
Flashing interval times: Depending on the control panel
Page 87

Specifications
87
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
Collective maximum current connection factor / Alarm verification
(FDOOT241-9)
The default parameter set (parameter set 0) is set in all fire detectors when
delivered.
Use as Parameter
set no.
Parameter set name Maximum
current
connection
factor for ES
<30
Maximum
current
connection
factor for ES
<30 1
Alarm verification on
control panel
permitted with
detector ES < 13
(verification time at
the control panel
≥ 50 s)
Alarm verification on
control panel
permitted with
detector ES ≥13
(verification time at
the control panel ≥
30 s)
2 Robust
4 Balanced
5 Suppression
2
1,5
No
Yes
6 Fast Response 2 1,5 Yes Yes
7 High Compensation 2 1,5 2 No Yes
0 (ES ≥ 13) High Compensation – 1,25 2 Yes Yes
0 (ES < 13) Insensitive 1,5 – No Yes
8 High Suppression – 1,5 – Yes
Neural fire
detector
(FDOOT)
9 High Sensitive Fast – 1,5 – Yes
0 Universal
1 Universal
2 Robust
2 1,5 No Yes
Wide-spectrum
smoke detector
(FDO)
3 Sensitive 2 1,5 Yes Yes
Heat detector
(FDT)
0 … 4 all parameter sets 2 1,5 No Yes
1
For CS1115 the maximum current connection factor values in the column
apply for ES < 30
2
Different load factors due to the different measuring cycles
Page 88

Specifications
88
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
MS8/PMT detector line (FDOOT241-8)
Detector line Operating voltage (modulated) 14 … 28 V DC
Operating current (quiescent) 200 μA
Maximum current connection factor 2
Protocol MS8/PMT
Compatibility See document 008331 'List of
compatibility'
External alarm indicators Number of external alarm indicators that
can be connected:
z With ES < 30 0 (not supported)
z With ES ≥ 30 Max. 2
Voltage Typ. 6 … 17 V DC
Power 9 … 15 mA
Length of line
z Max. 30 m with unshielded
cables, or when the shielding is
connected to the detector's
positive pole
z Max. 5 m, if the shielding is
connected to earth
Flashing interval times:
z Bright 15 ms
z Dark 1 s
Page 89

Specifications
89
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
8.2 Technical data FDO221, FDO241
Detector line Operating voltage (modulated) 12 … 33 V DC
Operating current (quiescent) Typ. 220 μA
Maximum current connection factor 1
Quiescent current connection factor 1
Address connection factor 1
Separator connection factor 1
Protocol FDnet
Compatibility See document 008331 'List of
compatibility'
Line separator Line voltage:
z Nominal 32 V DC (= V
nom
)
z Minimum 12 V DC (= V
min
)
z Maximum 33 V DC (= V
max
)
Voltage at which the separator opens:
z Minimum 7.5 V DC (= V
SO min
)
z Maximum 10.5 V DC (= V
SO max
)
Permanent current when switches are
closed:
Max. 0.5 A (= I
C max
)
Switching current (e.g. in the event of a
short-circuit):
Max. 1 A (= I
S max
)
Leakage current when switches are open: Max. 1 mA (= I
L max
)
Serial impedance when switches are
closed:
Max. 0.5 Ω (= Z
C max
)
External alarm indicators External alarm indicators that can be
connected
2 external alarm indicators and 1
sounder base
Voltage 10 … 17 V DC
Power 9 … 15 mA
Length of line
z Max. 30 m with unshielded
cables, or when the shielding is
connected to the detector's
positive pole
z Max. 5 m, if the shielding is
connected to earth
Flashing interval times:
z Bright 15 ms
z Dark 1 s
Page 90

Specifications
90
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
Device characteristics Response sensitivity:
z FDO221 Typ. 2 ... 3.5 %/m (depending on
the parameter set)
z FDO241 Typ. 1.4 ... 3.5 %/m (depending on
the parameter set)
Compensation, zone 'normal' ≤ 1 voltage increases for detection
Compensation, zone
'Information/Impairment'
≤ 1.5 voltage increases for
detection
Compensation speed ≤ 1/45 voltage increase for
detection/h
Detector diagnosis With detector exchanger and tester
FDUD29x
Ambient conditions Permitted ambient temperature
z FDO221 -10 … +60 ℃
z FDO241 -25 … +70 °C
Storage temperature -30 … +75 °C
Air humidity ≤95 % rel.
Protection categories according to
EN 60529/IEC 60529:
z Base FDB221/FDB222 IP43
z Base attachment FDB291 with base
FDB221/FDB222
IP43
z Base attachment humid FDB293 with
base FDB221/FDB222
IP44
z Sounder base FDSB29x IP43
Electromagnetic compatibility:
z 1 MHz ... 2 GHz 50 V/m
Permissible wind speed Max. 5 m/s
Mechanical data Colour ∼RAL 9010 pure white
Standards Standards EN 54-7, EN 54-17
VdS approvals:
z FDO221 G204018
z FDO241 G204017
LPCB approvals:
z FDO221 126ab/02
z FDO241 126ab/01
FM approvals:
z FDO221 3029351
z FDO241 3029351
Certificates:
z FDO221 0786-CPD-20001
z FDO241 0786-CPD-20002
CE conformity mark Yes
QA Standards Siemens Standard SN 36350
Page 91

Specifications
91
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
8.3 Technical data FDT221, FDT241
Detector line Operating voltage (modulated) 12 … 33 V DC
Operating current (quiescent) Typ. 165 μA
Maximum current connection factor 1
Quiescent current connection factor 1
Address connection factor 1
Separator connection factor 1
Protocol FDnet
Compatibility See document 008331 'List of
compatibility'
Line separator Line voltage:
z Nominal 32 V DC (= V
nom
)
z Minimum 12 V DC (= V
min
)
z Maximum 33 V DC (= V
max
)
Voltage at which the separator opens:
z Minimum 7.5 V DC (= V
SO min
)
z Maximum 10.5 V DC (= V
SO max
)
Permanent current when switches are
closed:
Max. 0.5 A (= I
C max
)
Switching current (e.g. in the event of a
short-circuit):
Max. 1 A (= I
S max
)
Leakage current when switches are open: Max. 1 mA (= I
L max
)
Serial impedance when switches are
closed:
Max. 0.5 Ω (= Z
C max
)
External alarm indicators Number of external alarm indicators that
can be connected
2
Voltage 10 … 17 V DC
Power 9 … 15 mA
Length of line
z Max. 30 m with unshielded
cables, or when the shielding is
connected to the detector's
positive pole
z Max. 5 m, if the shielding is
connected to earth
Flashing interval times:
z Bright 15 ms
z Dark 1 s
Device characteristics Response sensitivity Depending on parameter set
Detector diagnosis With detector exchanger and tester
FDUD29x
Page 92

Specifications
92
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
Ambient conditions Permitted ambient temperature Depending on parameter set
Storage temperature -30 … +75 °C
Air humidity ≤95 % rel.
Protection categories according to
EN 60529/IEC 60529:
z Base FDB221/FDB222 IP43
z Base attachment FDB291 with base
FDB221/FDB222
IP43
z Base attachment humid FDB293 with
base FDB221/FDB222
IP54
Electromagnetic compatibility:
z 1 MHz ... 2 GHz 50 V/m
Static response temperature:
z Parameter set BR and BS 78 … 82 ℃
z Parameter set A1R and A1S 58 … 62 ℃
Mechanical data Colour ∼RAL 9010 pure white
Standards Standards EN 54-5, EN 54-17
VdS approvals:
z FDT221 G204020
z FDT241 G204019
LPCB approvals:
z FDT221 126aa/02
z FDT241 126aa/01
FM approvals:
z FDT221 3029351
z FDT241 3029351
Certificates:
z FDT221 0786-CPD-20003
z FDT241 0786-CPD-20004
CE conformity mark Yes
QA Standards Siemens Standard SN 36350
Page 93

Specifications
93
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
8.4 Dimensions
FDB201/FDB201-AA FDB202/FDB222
FDB221/FDB221-AA
45,7
54,6
2
1
100
45,7
50
3
100
Dimensions with detector bases at distance or directly attached
1 Suitable for surface-mounted cables
up to Ø 6 mm.
3 Detector base directly attached to the
mounting surface
2 Detector base at a distance
8.5 Environmental compatibility
z Environmentally friendly detector-testing without gas
z Recyclable materials
z Electronic parts and synthetic materials can be easily separated
z Halogen-free synthetic materials, marked by embossed code
z The synthetic materials used do not generate any toxic substances during
combustion.
Larger synthetic material parts are marked according to DIN 4840 and
ISO/DIS 1469. The short names of the basic polymers are in accordance with
DIN 728 or ISO 043, which makes separation for recycling possible.
Page 94

Index
94
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
9 Index
A
Application as heat detector
Sensor mode 1, 23
Application as neural fire detector
Sensor mode 0, 23
Application as smoke detector
Sensor mode 2, 23
ASAtechnology
S-LINE, 20
C
C-LINE
Detection algorithms, 19
FDOOT221, FDO221, FDT221, 17
D
Danger level
Signal evaluation of the detector, 27
Default parameter set 0
Delivery, 56
Degraded mode operation
Failure of fire control panel, 31
Delivery
Default parameter set 0, 56
Detection algorithms
C-LINE, 19
Detection behavior of the detector
Parameter set, 27
Detector base FDB201/FDB221
Surface-mounted or recess-mounted feed line,
59
Detector base FDB202/222
Recess-mounted feed line, 60
Detector exchanger and tester
Status polling, 81
Test tools, 31
Diagnosis levels
Display on detector exchanger and tester, 28
Display on detector exchanger and tester
Diagnosis levels, 28
F
Failure of fire control panel
Degraded mode operation, 31
FDO221
Wide-spectrum smoke detector, 24
FDO241
Wide-spectrum smoke detector, 24
FDOOT221
Neural fire detector, 22
FDOOT221, FDO221, FDT221
C-LINE, 17
FDOOT241-8
Neural fire detector, 22
FDOOT241-9
Neural fire detector, 22
FDOOT241-9, FDOOT241-8, FDO241, FDT241
S-LINE, 16
FDT221
Heat detector, 26
FDT241
Heat detector, 26
H
Heat detectors
FDT241, FDT221, 26
Hot air fan
Test tools, 31
I
Interface
MC-Link, 32
Page 95

Index
95
Building Technologies 007004_k_en_--
Fire Safety & Security Products 16.04.2009
M
Major renovation work
Renovation mode, 31
MC-Link
Interface, 32
N
Neural fire detector
Multi-sensor smoke detector, neural DA or ASA,
16
Neural fire detectors
FDOOT241-9, FDOOT241-8, FDOOT221, 22
P
Parameter set
Detection behavior of the detector, 27
R
Recess-mounted feed line
Detector base FDB202/222, 60
Renovation mode
Major renovation work, 31
S
Sensor mode 0
Application as neural fire detector, 23
Sensor mode 1
Application as heat detector, 23
Sensor mode 2
Application as smoke detector, 23
Signal evaluation of the detector
Danger level, 27
S-LINE
ASAtechnology, 20
FDOOT241-9, FDOOT241-8, FDO241, FDT241,
16
Status polling
Detector exchanger and tester, 81
Surface-mounted or recess-mounted feed line
Detector base FDB201/221, 59
T
Test gases REF 8 and REF 8-S
Test tools, 31
Test tools
Detector exchanger and tester, 31
Hot air fan, 31
Test gases REF 8 and REF 8-S, 31
W
Wide-spectrum smoke detector
Smoke detector, FDnet wide-spectrum DA or
ASA, 16
Wide-spectrum smoke detectors
FDO241, FDO221, 24
Page 96

Issued by
Siemens Switzerland Ltd
Industry Sector
Building Technologies Division
International Headquarters
Gubelstrasse 22
CH-6301 Zug
Tel. +41 41-724 24 24
Fax +41 41-724 35 22
www.siemens.com/buildingtechnologies
© 2006-2009 Copyright Siemens Building Technologies, Inc.
Technical specifications and availability subject to change without notice.
Document ID 007004_k_en_-- Manual FD20
Edition 16.04.2009 Register 2
 Loading...
Loading...