Siemens BFQ82 Datasheet
NPN Silicon RF Transistor BFQ 82
● For low-noise, high-gain amplifiers up to 2 GHz.
● Linear broadband applications at collector currents
up to 40 mA.
● Hermetically sealed ceramic package.
● fT = 8 GHz
F = 1.1 dB at 800 MHz
ESD: Electrostatic discharge sensitive device, observe handling precautions!
Type Marking
Ordering Code
(tape and reel)
BFQ 82 Q62702-F118982 Cerec-X
Pin Configuration
1 2 3 4
B E C E
Package
Maximum Ratings
Parameter Symbol Values Unit
Collector-emitter voltage V
CE0 12 V
Collector-emitter voltage, VBE = 0 VCES 20
Collector-base voltage V
CB0 20
Emitter-base voltage VEB0 2
Collector current I
C 80 mA
Peak collector current, f ≥ 10 MHz ICM 80
Base current IB 10
Peak base current, f
Total power dissipation, T
≥ 10 MHz IBM 10
S ≤ 95 ˚C
3)
Ptot 500 mW
1)
Junction temperature Tj 175 ˚C
Ambient temperature range T
Storage temperature range T
A – 65 … + 175
stg – 65 … + 175
Thermal Resistance
Junction - ambient
Junction - case
1)
For detailed information see chapter Package Outlines.
2)
Package mounted on alumina 15 mm× 16.7 mm × 0.7 mm.
3)
TS is measured on the collector lead at the soldering point to the pcb.
2)
3)
Rth JA ≤ 240 K/W
Rth JS ≤ 160
Electrical Characteristics
A = 25 ˚C, unless otherwise specified.
at T
BFQ 82
Parameter Symbol
DC Characteristics
V
(BR)CE0 12 – –
C = 1 mA, IB = 0
I
I
CES – – 100
CE = 20 V, VBE = 0
V
Collector-base cutoff current
CB = 10 V, IE = 0
V
CB = 10 V, IE = 0, TA = 125 ˚C
V
Emitter-base cutoff current
V
EB = 1 V, IC = 0
C = 5 mA, VCE = 8 V
I
C = 30 mA, VCE = 8 V
I
CB0
I
I
EB0 ––1
FE
h
min. typ. max.
–
–
–
50
–
–
110
120
0.05
5
–
250
UnitValues
VCollector-emitter breakdown voltage
µACollector-emitter cutoff current
–DC current gain
Electrical Characteristics
A = 25 ˚C, unless otherwise specified.
at T
BFQ 82
Parameter Symbol
AC Characteristics
T
f
C = 5 mA, VCE = 8 V, f = 500 MHz
I
C = 30 mA, VCE = 8 V, f = 500 MHz
I
C
cb – 0.62 –
CB = 10 V, VBE = vbe = 0, f = 1 MHz
V
C
Collector-emitter capacitance
CE = 10 V, VBE = vbe = 0, f = 1 MHz
V
Input capacitance
EB = 0.5 V, IC = ic = 0, f = 1 MHz
V
Output capacitance
CE = 10 V, VBE = vbe = 0, f = 1 MHz
V
ce – 0.4 –
C
ibo – 2.5 –
C
obs – 1.0 –
F
I
C = 5 mA, VCE = 8 V, f = 10 MHz, ZS = 75 Ω
C = 30 mA, VCE = 8 V, f = 800 MHz, ZS = ZSopt
I
IC = 10 mA, VCE = 8 V, f = 2 GHz, ZS = ZSopt
min. typ. max.
–
–
–
–
–
3.6
8
0.7
1.6
2.3
–
–
–
–
–
UnitValues
GHzTransition frequency
pFCollector-base capacitance
dBNoise figure
Power gain
C = 30 mA, VCE = 8 V, f = 1 GHz, Z0 = 50 Ω
I
C = 30 mA, VCE = 8 V, f = 2 GHz, Z0 = 50 Ω
I
Transducer gain
C = 30 mA, VCE = 8 V, f = 1 GHz, Z0 = 50 Ω
I
two-tone intermodulation test
C = 40 mA, VCE = 8 V, dIM = 60 dB,
I
1 = 806 MHz, f2 = 810 MHz, ZS = ZL = 50 Ω
f
C = 40 mA, VCE = 8 V, f = 800 MHz
I
1)
S21e
(k
–
k2–1)
√
S12e
1)
ma
G
I S
21e I
–
–
2
– 13.5 –
17
11
–
–
Vo1 = Vo2 – 280 –
IP
3 –32–
mVLinear output voltage
dBmThird order intercept point
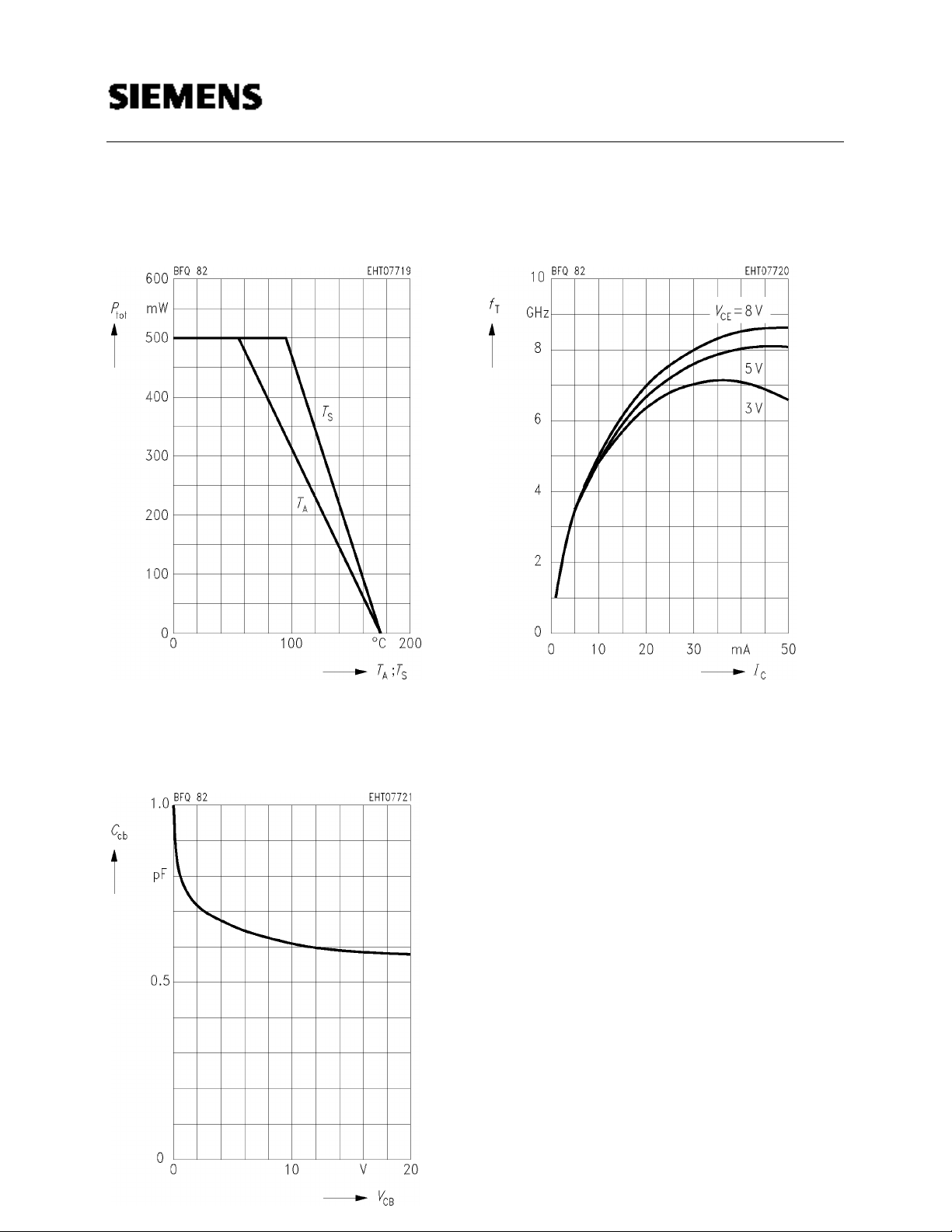
BFQ 82
Total power dissipation Ptot = f (TA*; TS)
* Package mounted on alumina
Transition frequency fT = f (IC)
f = 500 MHz
Collector-base capacitance C
BE = vbe = 0, f = 1 MHz
V
cb = f (VCB)
BFQ 82
Common Emitter Noise Parameters
Γ
f
Fmin Gp(Fmin) RN NF50 Ω
opt
GHz dB dB MAG ANG Ω –dBdB
IC = 10 mA, VCE = 8 V, Z0 = 50 Ω
G
p(F50 Ω)
0.01
0.8
2.0
C = 30 mA, VCE = 8 V, Z0 = 50 Ω
I
0.01
0.8
2.0
1
1.15
2.3
1.65
1.6
2.6
–
15.7
9.5
–
17
10
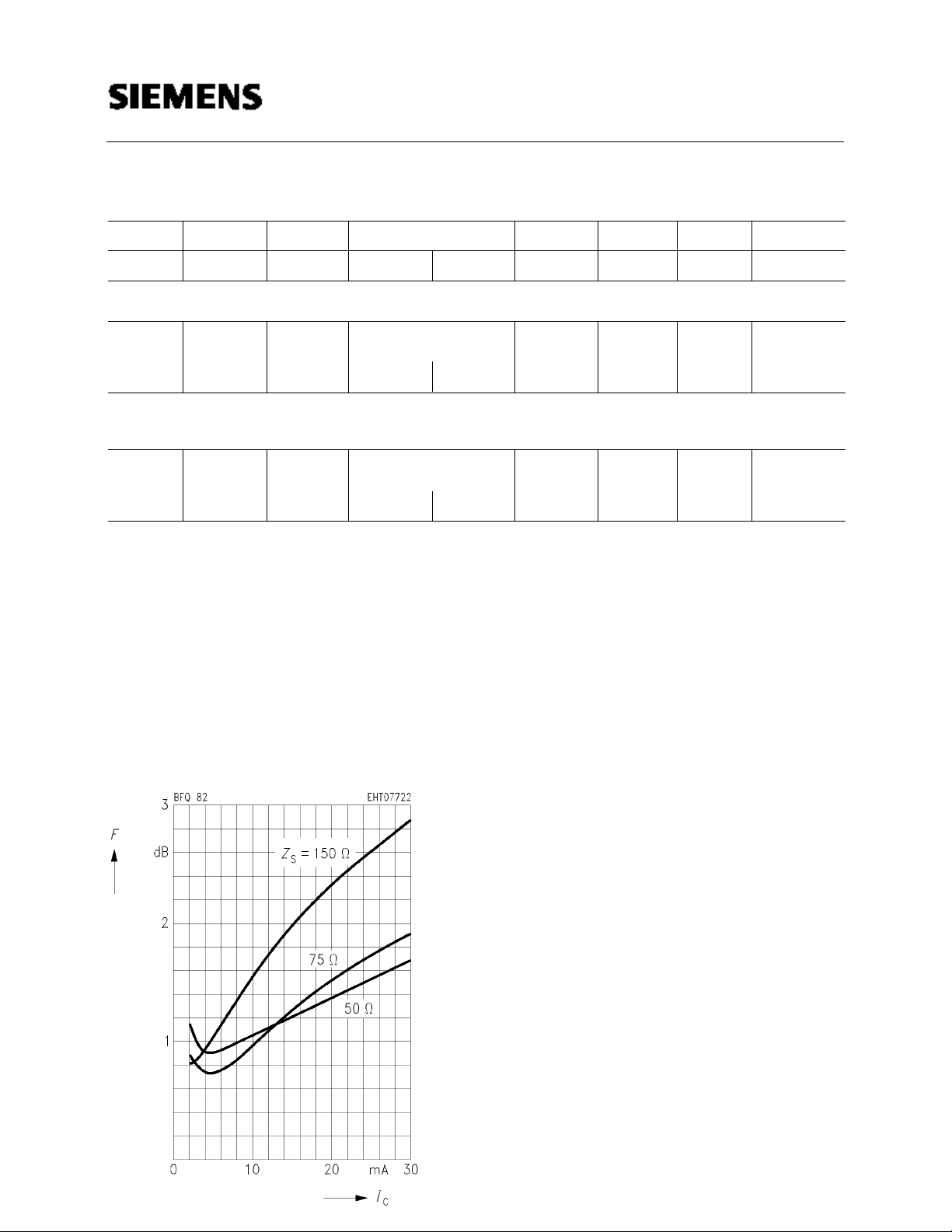
Noise figure F = f (IC)
CE = 8 V, f = 10 MHz
V
S = 75 Ω)
(Z
–
–
(Z
–
–
–
–
S = 50 Ω)
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
1.05
1.35
2.8
1.65
1.95
3.3
–
14.7
7.5
–
15.8
8
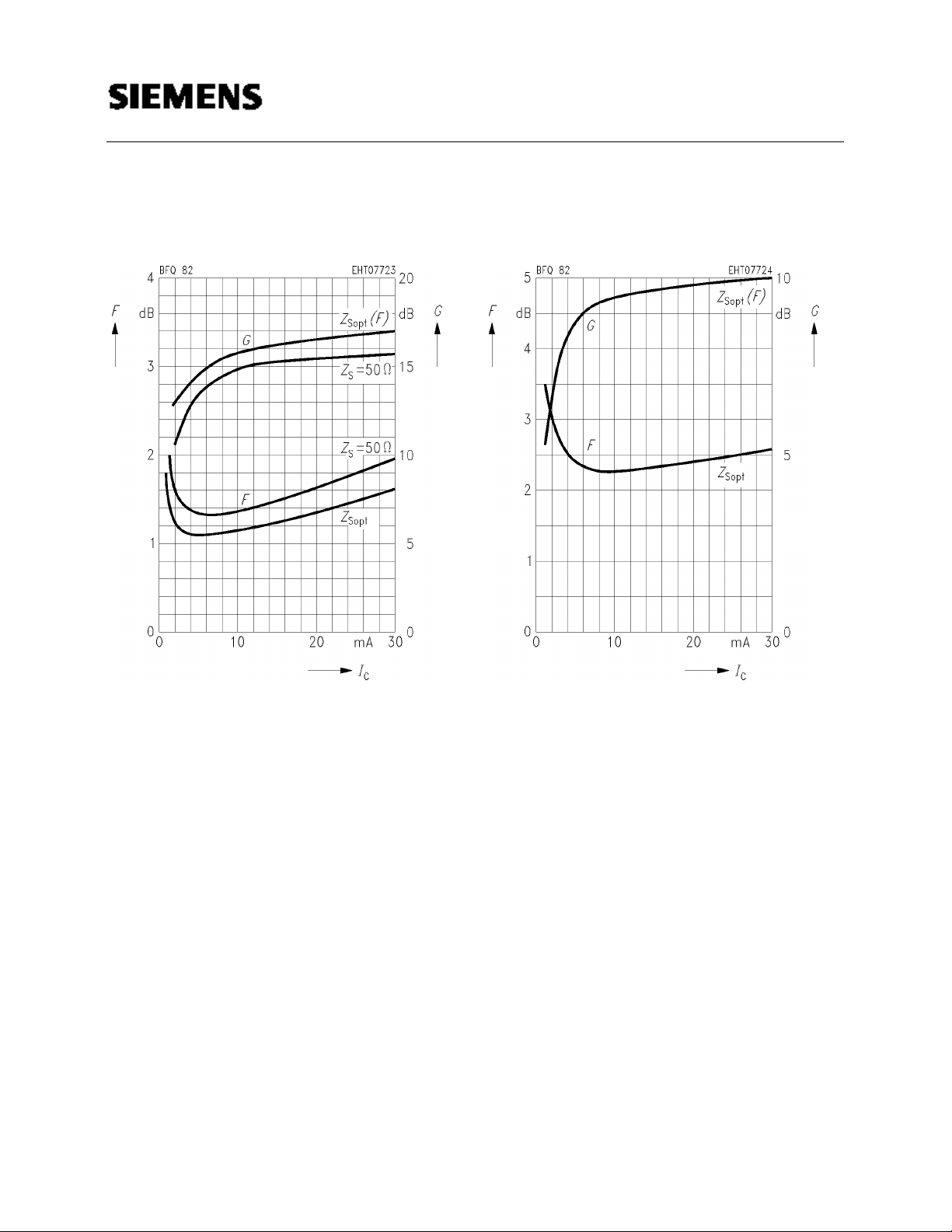
BFQ 82
Noise figure F = f (IC)
Power gain G = f (I
CE = 8 V, f = 800 MHz, ZLopt (G)
V
C)
Noise figure F = f (IC)
Power gain G = f (I
CE = 8 V, f = 2 GHz, ZLopt (G)
V
C)
 Loading...
Loading...