Page 1

MODEL W1837
10" OPEN-STAND
HYBRID TABLE SAW
OWNER'S MANUAL
3092372
Phone: (360) 734-3482 • Online Technical Support: techsupport@woodstockint.com
COPYRIGHT © NOVEMBER, 2015 BY WOODSTOCK INTERNATIONAL, INC., REVISED OCTOBER, 2017 (BL)
WARNING: NO PORTION OF THIS MANUAL MAY BE REPRODUCED IN ANY SHAPE OR FORM WITHOUT
(FOR MODELS MANUFACTURED SINCE 9/17)
THE WRITTEN APPROVAL OF WOODSTOCK INTERNATIONAL, INC.
#17768BLWKMNJH Printed in China
Page 2

This manual provides critical safety instructions on the proper setup,
operation, maintenance, and service of this machine/tool. Save this
document, refer to it often, and use it to instruct other operators.
Failure to read, understand and follow the instructions in this manual
may result in fire or serious personal injury—including amputation,
electrocution, or death.
The owner of this machine/tool is solely responsible for its safe use.
This responsibility includes but is not limited to proper installation in
a safe environment, personnel training and usage authorization,
proper inspection and maintenance, manual availability and comprehension, application of safety devices, cutting/sanding/grinding tool
integrity, and the usage of personal protective equipment.
The manufacturer will not be held liable for injury or property
damage from negligence, improper training, machine modifications or
misuse.
Some dust created by power sanding, sawing, grinding, drilling, and
other construction activities contains chemicals known to the State of
California to cause cancer, birth defects or other reproductive harm.
Some examples of these chemicals are:
• Lead from lead-based paints.
• Crystalline silica from bricks, cement and other masonry products.
• Arsenic and chromium from chemically-treated lumber.
Your risk from these exposures varies, depending on how often you
do this type of work. To reduce your exposure to these chemicals:
Work in a well ventilated area, and work with approved safety equipment, such as those dust masks that are specially designed to filter
out microscopic particles.
Page 3

Contents
INTRODUCTION .....................................2
Contact Info
Manual Accuracy
Machine Specifications
Identification
Controls & Components
SAFETY ............................................... 8
Standard Machinery Safety Instructions
Additional Safety for Table Saws
Preventing Kickback
Protecting Yourself From Kickback
ELECTRICAL ....................................... 12
Circuit Requirements
Grounding Requirements
Extension Cords
Converting Voltage to 240V
SETUP .............................................. 15
Unpacking
Items Needed for Setup
Inventory
Hardware Recognition Chart
Cleaning Machine
Machine Placement
Assembly
Dust Collection
Test Run
Recommended Adjustments
OPERATIONS....................................... 30
General
Operation Overview
Workpiece Inspection
Non-Through & Through Cuts
Blade Size Requirements
Blade Selection
Blade Installation
Blade Guard Assembly
Riving Knife
Ripping
Crosscutting
Miter Cuts
Blade Tilt/Bevel Cuts
Dado Cutting
Rabbet Cutting
Resawing
....................................... 2
.................................. 2
.......................... 3
..................................... 6
......................... 7
...... 8
............ 10
........................... 11
.......... 11
.......................... 12
...................... 13
................................ 13
.................. 14
....................................... 15
....................... 15
........................................ 16
................. 18
............................... 19
............................ 20
......................................... 21
................................. 28
.......................................... 29
.................. 29
.......................................... 30
........................... 31
.......................... 31
................ 32
...................... 33
................................. 33
.............................. 35
......................... 36
..................................... 39
........................................... 41
..................................... 42
....................................... 43
.......................... 43
.................................... 44
................................. 47
......................................... 49
SHOP-MADE SAFETY ACCESSORIES ............ 54
Featherboards
Push Sticks
Push Blocks
Narrow-Rip Auxiliary Fence & Push Block
Outfeed & Support Tables
Crosscut Sled
ACCESSORIES ...................................... 62
Table Saw Accessories
MAINTENANCE .................................... 63
General
Cleaning & Protecting
Lubrication
SERVICE ............................................ 65
General
Blade Tilt Calibration
Miter Slot to Blade Parallelism
Spreader or Riving Knife Alignment
Adjusting Fence
Calibrating Fence to Blade
Fence Scale Calibration
Table/Dado Insert Adjustment
Miter Gauge Adjustments
Belt Tension & Replacement
Troubleshooting
Electrical Safety Instructions
Wiring Diagram
Electrical Components
PARTS .............................................. 83
Main
Cabinet & Stand
Fence & Rails
Blade Guard
Miter Guage
Labels & Cosmetics
WARRANTY ........................................ 93
.......................................... 63
.......................................... 65
.............................................. 83
.................................. 54
...................................... 57
...................................... 58
.. 59
.................... 61
.................................... 61
......................... 62
......................... 63
...................................... 64
.......................... 65
............... 67
......... 69
................................ 71
................... 73
....................... 74
............... 75
..................... 76
................. 77
................................. 78
................. 80
................................. 81
........................ 82
................................ 85
................................... 87
..................................... 88
..................................... 89
............................ 90
SAFETYINTRODUCTION
SET UPELECTRICAL MAINTENANCE
OPERATIONS
SERVICE PARTS
USE THE QUICK GUIDE PAGE LABELS TO SEARCH OUT INFORMATION FAST!
Page 4

INTRODUCTION
We are proud to provide a high-quality owner’s
manual with your new machine!
We
the
instructions, specifications, drawings, and photographs contained inside. Sometimes we make
mistakes, but our policy of continuous improvement
machine
you receive will be slightly different than what
is shown in the manual
If you find this to be the case, and the difference
between the manual and machine leaves you
confused about a procedure
check our website
for an updated version. W
manuals
and
on our website at
www.
Alternatively, you can call our Technical Support
for help. Before calling, make sure you write
down the
from the machine ID label (see below). Also, if
available, have a copy of your original purchase
receipt on hand. This information is required for
all Tech Support calls.
MODEL XXXX
MACHINE NAME
Motor:
Specification:
Specification:
Specification:
Specification:
Weight:
Specifications
To reduce risk of serious personal injury when using this
machine:
1. Read & understand owner’s manual before operating.
2. Always wear approved eye protection and respirator.
3. Only plug power cord into a grounded outlet.
4. Only use this machine to collect wood dust/chips—never
use to collect glass, metal, liquids, asbestos, silica,
animal parts, biohazards, burning material/ashes, etc.
5. Always disconnect power before servicing or cleaning.
6. Do not expose to rain or wet areas.
7. Keep hands, long hair, and loose clothing away from
inlet.
8. Never leave machine unattended while it is running.
9. Do not use if cord/plug becomes damaged—promptly
repair and protect cord from future damage.
10. Do not use without dust bag or filters in place.
11. Always wear a respirator when emptying bags.
12. Prevent unauthorized use by children or untrained users.
Date
Serial Number
Manufactured for Woodstock in Taiwan
WARNING!
We are committed to customer satisfaction. If
you have any questions or need help, use the
information below to contact us.
IMPORTANT: Before contacting, please get the
original purchase receipt, serial number, and
manufacture date of your machine. This information is required for all Technical Support
calls and it will help us help you faster.
We want your feedback on this manual. What did
you like about it? Where could it be improved?
Please take a few minutes to give us feedback.
Email: manuals@woodstockint.com
Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
INTRODUCTION
Contact Info
Woodstock International Technical Support
Phone: (360) 734-3482
Email: techsupport@woodstockint.com
Technical Documentation Manager
P.O. Box 2309
Bellingham, WA 98227
Manual Accuracy
made every effort to be exact with
also means that sometimes the
.
,
e post current
manual updates for free
woodstockint.com.
Manufacture Date and Serial Number
Manufacture
Date
Serial Number
-2-
Page 5

Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
MODEL W1837
10" 2 HP OPENSTAND HYBRID TABLE SAW
Product Dimensions
Weight.......................................................................................................... 243 lbs.
Width (side‐to‐side) x Depth (front‐to‐back) x Height........................ 57‐1/4 x 37‐1/2 x 35‐3/4 in.
Footprint (Length x Width)......................................................................... 21 x 19‐1/2 in.
Space Required for Full Range of Movement (Width x Depth)........................... 57‐1/4 x 37‐1/2 in.
Shipping Dimensions
Type.................................................................................................... Cardboard Box
Content........................................................................................................ Machine
Weight.......................................................................................................... 260 lbs.
Length x Width x Height........................................................................... 42 x 30 x 23 in.
INTRODUCTION
Electrical
Power Requirement.......................................................... 120V or 240V, Single‐Phase, 60 Hz
Prewired Voltage................................................................................................. 120V
Full‐Load Current Rating.............................................................. 15A at 120V, 7.5A at 240V
Minimum Circuit Size................................................................... 20A at 120V, 15A at 240V
Connection Type......................................................................................... Cord & Plug
Power Cord Included.............................................................................................. Yes
Power Cord Length............................................................................................... 6 ft.
Power Cord Gauge............................................................................................ 14 AWG
Plug Included....................................................................................................... Yes
Included Plug Type............................................................................. NEMA 5‐15 for 120V
Recommended Plug Type..................................................................... NEMA 6‐15 for 240V
Switch Type................................................................. ON/OFF Push Button w/Lockout Pin
Motors
Main
Horsepower................................................................................................. 2 HP
Phase.............................................................................................. Single‐Phase
Amps.............................................................................. 15A at 120V, 7.5A at 240V
Speed.................................................................................................. 3450 RPM
Type................................................................................ Capacitor‐Start Induction
Power Transfer ..................................................................................... Belt Drive
Bearings................................................................. Sealed & Permanently Lubricated
-3-
Page 6

Main Specifications
INTRODUCTION
Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
Main Information
Table Saw Type.......................................................................................... Hybrid
Maximum Blade Diameter............................................................................... 10 in.
Arbor Size................................................................................................ 5/8 in.
Arbor Speed.......................................................................................... 3450 RPM
Maximum Width of Dado............................................................................ 13/16 in.
Blade Tilt Direction........................................................................................ Left
Max Blade Tilt........................................................................................ 0–45 deg.
Maximum Depth of Cut At 90 Degrees............................................................ 3‐1/4 in.
Maximum Depth of Cut At 45 Degrees............................................................ 2‐1/4 in.
Max Rip Right of Blade w/Included Fence & Rails.................................................. 30 in.
Max Rip Left of Blade w/Included Fence & Rails.................................................... 15 in.
Additional Blade Information
Included Blade Information........................................................................ 10" x 40T
Riving Knife/Spreader Thickness................................................................... 0.090 in.
Required Blade Body Thickness........................................................... 0.060 – 0.086 in.
Required Blade Kerf Thickness............................................................ 0.094 – 0.126 in.
Rim Speed at Max Blade Diameter............................................................... 9,025 FPM
Table Information
Floor to Table Height.............................................................................. 35‐3/4 in.
Table Size with Extension Wings Width......................................................... 40‐1/4 in.
Table Size with Extension Wings Depth............................................................... 27 in.
Distance Front of Table to Center of Blade..................................................... 15‐1/2 in.
Distance Front of Table to Blade At Maximum Cut............................................ 11‐1/2 in.
Main Table Size Thickness.......................................................................... 1‐5/8 in.
Fence Information
Fence Type.......................................................... Camlock T‐Shape w/ Aluminum Face
Fence Size Length.................................................................................. 35‐3/4 in.
Fence Size Width..................................................................................... 3‐1/8 in.
Fence Size Height................................................................................... 2‐7/16 in.
Fence Rail Type......................................................................... Extruded Aluminum
Fence Rail Length........................................................................................ 64 in.
Fence Rail Width..................................................................................... 3‐1/8 in.
Fence Rail Height.................................................................................... 2‐1/4 in.
Miter Gauge Information
Miter Gauge Slot Type.................................................................................. T‐Slot
Miter Gauge Slot Size Width.......................................................................... 3/4 in.
Miter Gauge Slot Size Height.......................................................................... 3/8 in.
Construction
Table................................................................................................... Cast Iron
Wings................................................................................................... Stamped
Cabinet...................................................................................... Pre‐Formed Steel
Trunnions.............................................................................................. Cast Iron
Fence Assembly..................................................................................... Aluminum
Rails................................................................................................... Aluminum
Miter Guage Construction......................................................................... Aluminum
Guard...................................................................................... Aluminum & Plastic
Body/Cabinet Paint Type/Finish........................................................... Powder Coated
Arbor Bearings.......................................................... Sealed & Permanently Lubricated
-4-
Page 7

Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
Other Related Information
Number of Dust Ports......................................................................................... 1
Dust Port Size.............................................................................................. 4 in.
Other
Country of Origin ............................................................................................... China
Warranty ....................................................................................................... 2 Years
Approximate Assembly & Setup Time ...................................................................... 1 Hour
Serial Number Location ........................................................... ID Label on Front of Machine
Sound Rating ............................................................................................... 81 – 83 dB
ISO 9001 Factory .................................................................................................. Yes
Certified by a Nationally Recognized Testing Laboratory (NRTL) ......................................... Yes
Features
Precision‐Ground Cast‐Iron Table
Powder‐Coated Steel Extension Wings
Cast‐Iron Trunnions
Easy‐Glide Fence System
Quick‐Release Blade Guard Assembly
4" Dust Port
T‐Slot Miter Gauge
Included 10" x 40T Blade
Built‐In Mobile Base
INTRODUCTION
Accessories
Push Stick
Standard Table Insert
Dado Table Insert
Miter Gauge
-5-
Page 8
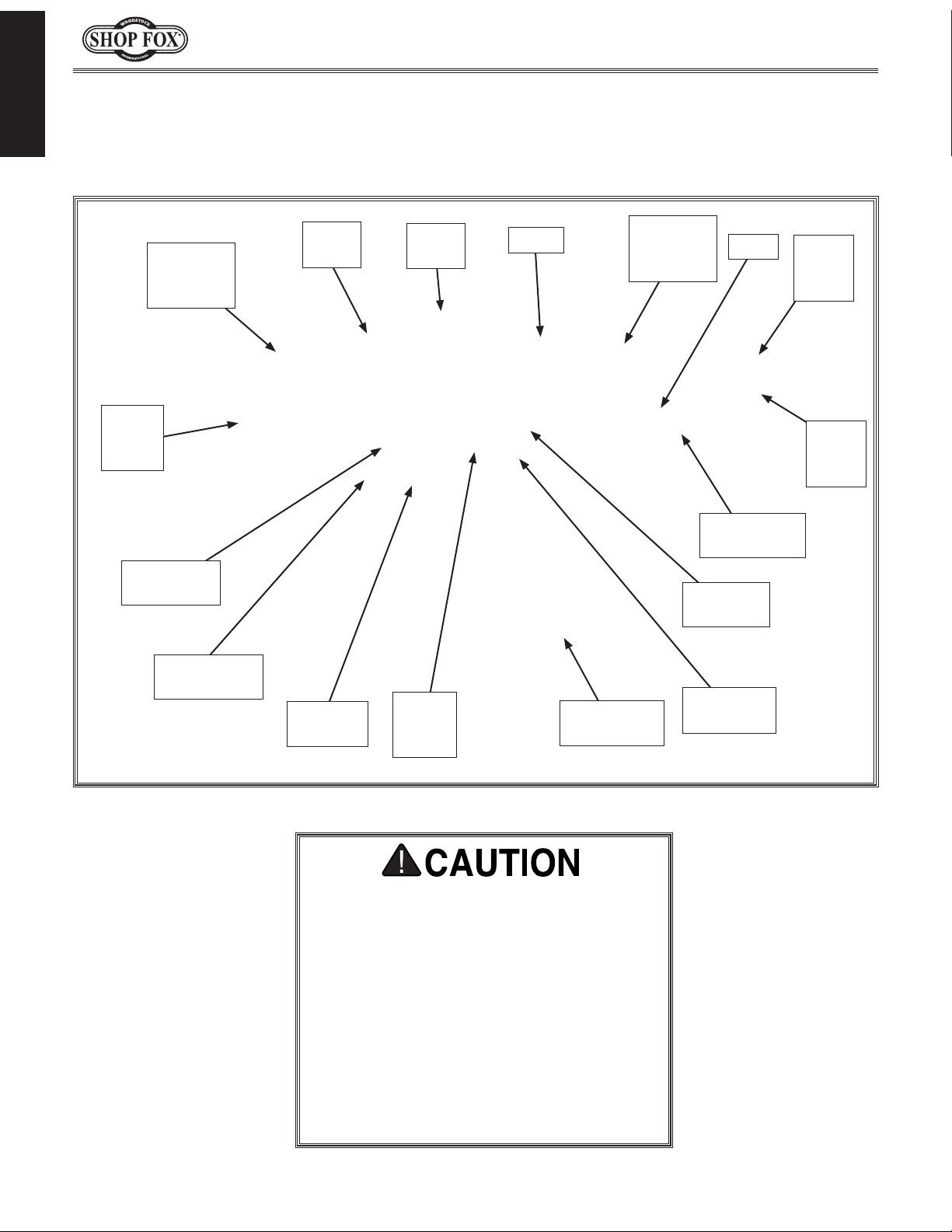
INTRODUCTION
Become familiar with the names and locations of the controls and features shown below to better
Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
Identification
Extension
START/
STOP
Switch
Blade
Height Lock
Blade Height
Left
Wing
Handwheel
Miter
Gauge
Blade Tilt
Scale
Blade
Guard
Fence
Lock
Handle
Fence
Extension
Mobile Base
Caster
Right
Wing
Blade Tilt
Handwheel
Scale
Front Fence
Rail
Lock
Blade Tilt
Rear
Fence
Rail
Fence
Rail
Brace
For Your Own Safety Read Instruction
Manual Before Operating Saw
a) Wear eye protection.
b) Use saw-blade guard and spreader for
every operation for which it can be
used, including all through sawing.
c) Keep hands out of the line of saw blade.
d) Use a push-stick when required.
e) Pay particular attention to instructions
on reducing risk of kickback.
f) Do not perform any operation freehand.
g) Never reach around or over saw blade.
-6-
Page 9
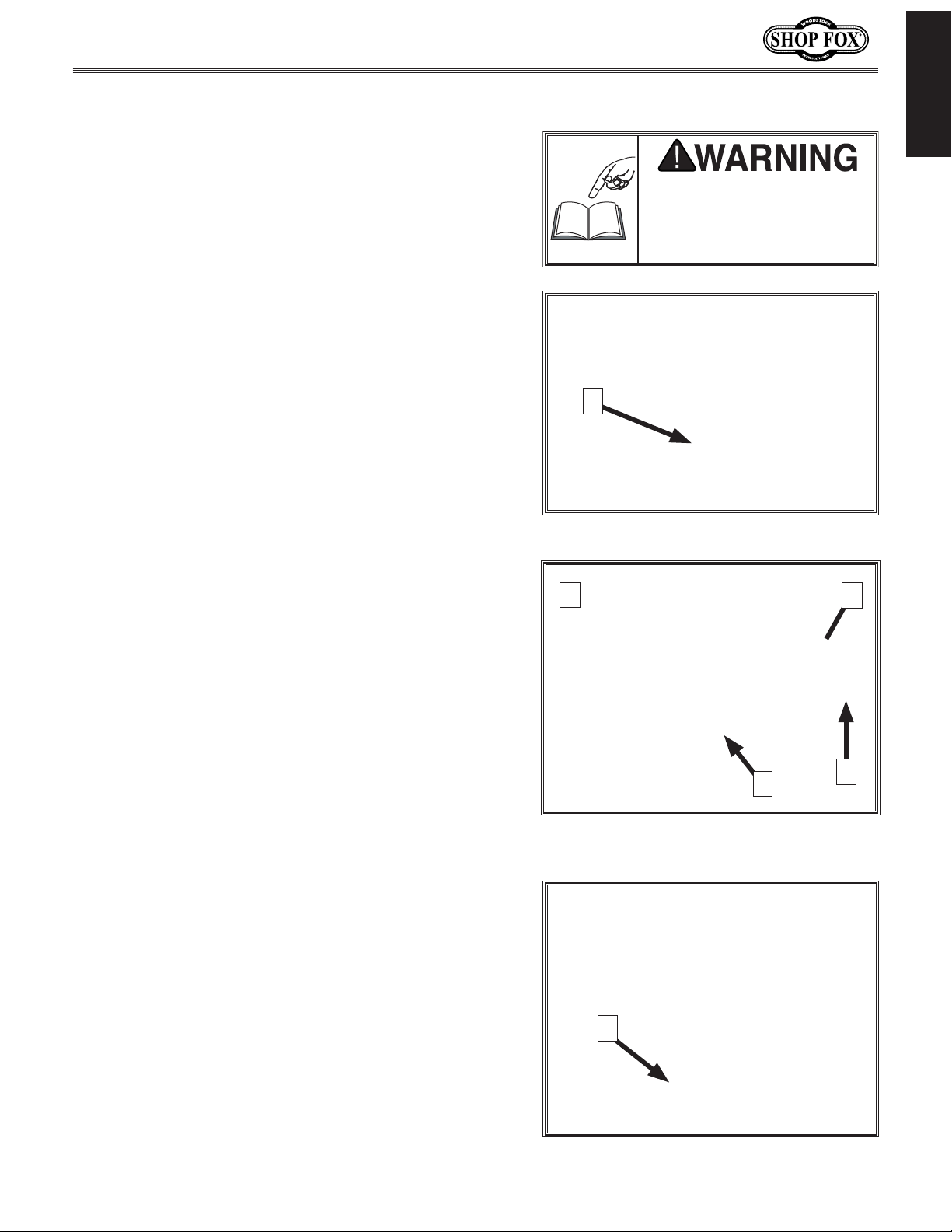
Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
Controls & Components
Refer to Figures 1–3 and the following descriptions to
become familiar with the basic controls and components
of this machine. Understanding these items and how they
work will help you understand the rest of the manual and
stay safe when operating this machine.
A. ON/OFF Switch: Starts and stops the motor. The
switch can be disabled for safety by inserting the
disabling pin or a padlock (not included) through the
START button.
INTRODUCTION
To reduce your risk of serious injury, read this entire
manual BEFORE using
machine.
Note: Paddle cover must be lifted to access ON
switch.
B. Handwheel Locks: Lock blade height and angle
when tightened (one on each handwheel).
Blade Height Handwheel: Adjusts blade height from
C.
. Blade Tilt Handwheel: Adjusts angle of blade tilt
D
1
⁄4".
0"–3
from 90°–45°.
A
Figure 1. Location of START/STOP switch.
B
C
Figure 2. Blade adjustment handwheels
and locks.
B
D
E. Fence Lock: Locks fence when pushed down, and
unlocks fence when pulled up.
-7-
E
Figure 3. Fence lock handle.
Page 10

Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
SAFETY
OWNER’S MANUAL.
TRAINED OPERATORS ONLY.
DANGEROUS ENVIRONMENTS.
MENTAL ALERTNESS REQUIRED.
electrical components or improperly grounded
manual uses a series of symbols and signal words intended to convey the level of importance of the
safety messages. The progression of symbols is described below. Remember that safety messages by
SAFETY
For Your Own Safety,
Read Manual Before Operating Machine
The purpose of safety symbols is to attract your attention to possible hazardous conditions. This
SAFETY
themselves do not eliminate danger and are not a substitute for proper accident prevention measures—this responsibility is ultimately up to the operator!
NOTICE
Standard Machinery Safety Instructions
Standard Machinery Safety Instructions
Indicates an imminently hazardous situation which, if not avoided,
WILL result in death or serious injury.
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided,
COULD result in death or serious injury.
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided,
MAY result in minor or moderate injury.
This symbol is used to alert the user to useful information about
proper operation of the equipment or a situation that may cause
damage to the machinery.
Read and understand this
owner’s manual BEFORE using machine.
have a higher risk of being hurt or killed. Only
allow trained/supervised people to use this
machine. When machine is not being used,
disconnect power, remove switch keys, or
lock-out machine to prevent unauthorized
use—especially around children. Make
workshop kid proof!
machinery in areas that are wet, cluttered,
or have poor lighting. Operating machinery
in these areas greatly increases the risk of
accidents and injury.
alertness is required for safe operation of
machinery. Never operate under the influence
of drugs or alcohol, when tired, or when
distracted.
Untrained operators
Do not use
Full mental
ELECTRICAL EQUIPMENT INJURY RISKS. You can
be shocked, burned, or killed by touching live
machinery. To reduce this risk, only allow an
electrician or qualified service personnel to
do electrical installation or repair work, and
always disconnect power before accessing or
exposing electrical equipment.
DISCONNECT POWER FIRST. Always disconnect
machine from power supply BEFORE making
adjustments, changing tooling, or servicing
machine. This eliminates the risk of injury
from unintended startup or contact with live
electrical components.
EYE PROTECTION. Always wear ANSI-approved
safety glasses or a face shield when operating
or observing machinery to reduce the risk of
eye injury or blindness from flying particles.
Everyday eyeglasses are not approved safety
glasses.
-8-
Page 11

Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
WEARING PROPER APPAREL. Do not wear
HAZARDOUS
HEARING PROTECTION.
REMOVE ADJUSTING TOOLS.
INTENDED USAGE.
AWKWARD POSITIONS.
CHILDREN & BYSTANDERS.
GUARDS & COVERS.
FORCING MACHINERY. Do not force machine. It
will do the job safer and better at the rate for
loss of control. Before starting, verify machine
malfunction, leading to serious personal injury
from heated surfaces, high traffic areas, harsh
clothing, apparel, or jewelry that can become
entangled in moving parts. Always tie back
or cover long hair. Wear non-slip footwear to
avoid accidental slips, which could cause loss
of workpiece control.
DUST. Dust created while using
machinery may cause cancer, birth defects,
or long-term respiratory damage. Be aware of
dust hazards associated with each workpiece
material, and always wear a NIOSH-approved
respirator to reduce your risk.
Always wear hearing
protection when operating or observing
loud machinery. Extended exposure to this
noise without hearing protection can cause
permanent hearing loss.
machinery can become dangerous projectiles
upon startup. Never leave chuck keys,
wrenches, or any other tools on machine.
Always verify removal before starting!
intended purpose—never make modifications
without prior approval from Woodstock
International. Modifying machine or using
it differently than intended will void the
warranty and may result in malfunction or
mechanical failure that leads to serious
personal injury or death!
balance at all times when operating machine.
Do not overreach! Avoid awkward hand
positions that make workpiece control difficult
or increase the risk of accidental injury.
bystanders at a safe distance from the work
area. Stop using machine if they become a
distraction.
Only use machine for its
Tools left on
Keep proper footing and
Keep children and
which it was designed.
NEVER STAND ON MACHINE. Serious injury may
occur if machine is tipped or if the cutting
tool is unintentionally contacted.
STABLE MACHINE. Unexpected movement during
operation greatly increases risk of injury or
is stable and mobile base (if used) is locked.
USE RECOMMENDED ACCESSORIES. Consult
this owner’s manual or the manufacturer for
recommended accessories. Using improper
accessories will increase risk of serious injury.
UNATTENDED OPERATION. To reduce the risk
of accidental injury, turn machine OFF and
ensure all moving parts completely stop
before walking away. Never leave machine
running while unattended.
MAINTAIN WITH CARE. Follow all maintenance
instructions and lubrication schedules to
keep machine in good working condition. A
machine that is improperly maintained could
or death.
CHECK DAMAGED PARTS. Regularly inspect
machine for any condition that may affect
safe operation. Immediately repair or replace
damaged or mis-adjusted parts before
operating machine.
MAINTAIN POWER CORDS. When disconnecting
cord-connected machines from power, grab
and pull the plug—NOT the cord. Pulling the
cord may damage the wires inside, resulting
in a short. Do not handle cord/plug with wet
hands. Avoid cord damage by keeping it away
chemicals, and wet/damp locations.
SAFETY
accidental contact with moving parts or flying
debris—make sure they are properly installed,
undamaged, and working correctly.
Guards and covers reduce
EXPERIENCING DIFFICULTIES. If at any time
you experience difficulties performing the
intended operation, stop using the machine!
-9-
Contact Technical Support at (360) 734-3482.
Page 12

INTRODUCTION
completely stop before removing cut-off pieces
insert. Never use your hands to move cut-off
deadly force at operator or bystanders. Only
Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
Additional Safety for Table Saws
Serious cuts, amputation, or death can occur from contact with rotating saw blade during
operation. Workpieces, broken blades, or flying particles thrown by blade can blind or strike
operators or bystanders with deadly force. To reduce the risk of these hazards, operator and
bystanders MUST completely heed the hazards and warnings below.
HAND & BODY POSITIONING. Keep hands away
from saw blade and out of blade path during
operation, so they cannot accidentally slip into
blade. Only operate at front of machine and
always stand to side of blade path. Never reach
behind or over blade.
BLADE GUARD. The blade guard protects operator from rotating saw blade. Make sure blade
guard is installed, adjusted correctly, and used
for all possible “through cuts.” Promptly repair or
replace if damaged. Re-install immediately after
operations that require its removal.
RIVING KNIFE. Use riving knife for all “nonthrough cuts.” Make sure it is aligned and positioned correctly. Promptly repair or replace it if
damaged.
KICKBACK. Kickback occurs when saw blade
ejects workpiece back toward operator. Know
how to reduce risk of kickback, and learn how to
protect yourself if it does occur.
FEEDING WORKPIECE. Feeding workpiece incorrectly increases risk of kickback. Always allow
blade to reach full speed before cutting, feed
workpiece from front of saw, making sure workpiece is flat against table and a fence, miter
gauge, or other guide is used to feed workpiece in
a straight line. Feed cuts through to completion.
Never start saw with workpiece touching blade
or pull workpiece from behind blade. Never back
workpiece out of cut, move it sideways, or perform a “freehand” operation. Never plunge cut.
PUSH STICKS/PUSH BLOCKS. To reduce risk of
accidental blade contact, use push sticks/push
blocks whenever possible. In event of an accident, these will often take damage that would
have occurred to hands/fingers.
FENCE. To reduce risk of kickback, make sure
fence remains properly adjusted and parallel with
blade. Always lock fence before using.
CUT-OFF PIECES. To avoid risk of injury due to
blade contact, turn saw OFF and allow blade to
near blade or trapped between blade and table
pieces away from blade while saw is running.
BLADE ADJUSTMENTS. Adjusting blade height
or tilt during operation increases risk of crashing
blade and sending metal fragments flying with
adjust blade height and tilt when blade is completely stopped and saw is OFF.
CHANGING BLADES. Accidental startup while
changing saw blade can result in serious injury.
To reduce risk of accidental blade contact, always
disconnect power before changing blades.
DAMAGED SAW BLADES. Damaged saw blade
teeth can become deadly projectiles. Never use
blades that have been dropped or damaged.
DADO AND RABBET OPERATIONS. Dado and
rabbeting operations require special attention
since they must be performed with blade guard
removed, which increases risk of blade contact.
DO NOT attempt dado or rabbeting operations
without first reading these sections in this manual.
CUTTING CORRECT MATERIAL. Cutting metal,
glass, stone, tile, etc., increases risk of operator
injury due to kickback or flying particles. Only cut
natural and man-made wood products, laminatecovered wood products, and some plastics. Never
cut materials not intended for this saw.
-10-
Page 13

Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
Preventing Kickback
Below are ways to avoid the most common
causes of kickback:
• Only cut workpieces with at least one smooth
and straight edge. DO NOT cut warped,
cupped or twisted wood.
• Keep the blade guard installed and working
correctly for all through-cuts.
• Never move the workpiece backwards or
try to back it out of a cut while the blade
is moving. If you cannot complete a cut for
some reason, stop the saw motor and allow
the blade to completely stop before backing
the workpiece out. Promptly fix the condition
that prevented you from completing the cut
before starting the saw again.
Protecting Yourself
SAFETY
• Never attempt freehand cuts. If the
workpiece is not fed parallel with the blade,
kickback will likely occur. Always use the
rip fence or miter gauge to support the
workpiece.
• Make sure the spreader or riving knife is
aligned with the blade. A misaligned spreader
or riving knife can cause the workpiece
to catch or bind, increasing the chance of
kickback.
• Take the time to check and adjust the rip
fence parallel with the blade; otherwise, the
chances of kickback are extreme.
• The spreader or riving knife maintains the
kerf in the workpiece, reducing the chance
of kickback. Always use the riving knife for
all non-through operations, unless using with
dado blade smaller than 10" in diameter.
Always use the spreader with the blade guard
for all through cuts.
• Feed cuts through to completion. Anytime
you stop feeding a workpiece in the middle
of a cut, the chance of kickback is greatly
increased.
From Kickback
Even if you know how to prevent kickback, it
may still happen. Here are some ways to protect
yourself if kickback DOES occur:
• Stand to the side of the blade during every
cut. If kickback does occur, the thrown
workpiece usually travels directly in front of
the blade.
• Wear safety glasses or a face shield. In the
event of kickback, your eyes and face are the
most vulnerable parts of your body.
• Never, for any reason, place your hand behind
the blade. Should kickback occur, your hand
will be pulled into the blade, which could
cause amputation.
• Use a push stick to keep your hands farther
away from the moving blade. If kickback
occurs, the push stick will most likely take
the damage your hand would have received.
• Use featherboards or anti-kickback devices to
assist with feeding and prevent or slow down
kickback.
• Keep the blade guard installed and in good
working order. Only remove it when performing
non-through cuts and immediately re-install
the blade guard when finished. Remember,
always use the riving knife for all non-through
operations, unless a dado blade is installed.
• Make multiple, shallow passes when performing a non-through cut. Making a deep nonthrough cut will greatly increase the chance of
kickback.
-11-
Statistics show that most common accidents
among table saw users can be linked to
kickback. Kickback is typically defined as the
high-speed expulsion of stock from the table
saw toward its operator. In addition to the
danger of the operator or others in the area
being struck by the flying stock, it is often the
case that the operator’s hands are pulled into
the blade during kickback.
Page 14
Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
This machine must be connected to the correct size and
type of power supply circuit, or fire or electrical damage
may occur. Read through this section to determine if an
adequate power supply circuit is available. If a correct
circuit is not available, a qualified electrician MUST install
one before you can connect the machine to power.
A power supply circuit includes all electrical equipment
between the breaker box or fuse panel in the building
and the machine. The power supply circuit used for
this machine must be sized to safely handle the fullload current drawn from the machine for an extended
period of time. (If this machine is connected to a circuit
protected by fuses, use a time delay fuse marked D.)
This machine can be converted to operate on a power
supply circuit that has a verified ground and meets the
requirements listed below. (Refer to
instructions for details.)
This machine is prewired to operate on a power supply
circuit that has a verified ground and meets the following
requirements:
The full-load current rating is the amperage a machine
draws at 100% of the rated output power. On machines
with multiple motors, this is the amperage drawn by the
largest motor or sum of all motors and electrical devices
that might operate at one time during normal operations.
or machine damage. To reduce this risk,
a dedicated circuit—
where only one machine will be running
multiple machines will be running at the
ELECTRICAL
Circuit Requirements
The machine must be properly set up
before it is safe to operate. DO NOT
connect this machine to the power
source until instructed to do so later in
this manual.
ELECTRICAL
Full-Load Current Rating
Full-Load Current Rating at 120V .................. 15 Am ps
Full-Load Current Rating at 240V ................. 7.5 A m p s
Circuit Requirements for 120V (Prewired)
Circuit Type ............... 110V/120V, 60 Hz, Single-Phase
Circuit Size ............................................. 20 Amps
Plug/Receptacle .................................... NEMA 5-15
Circuit Requirements for 240V
Circuit Type ...............220V/240V, 60 Hz, Single-Phase
Circuit Size ............................................. 15 Amps
Plug/Receptacle .................................... NE M A 6 -15
Voltage Conversion
Incorrectly wiring or grounding this
machine can cause electrocution, fire,
only an electrician or qualified service
personnel should do any required
electrical work on this machine.
NOTICE
The circuit requirements listed in this
manual apply to
at a time. If this machine will be
connected to a shared circuit where
same time, consult with an electrician
to ensure that the circuit is properly
sized for safe operation.
-12-
Page 15
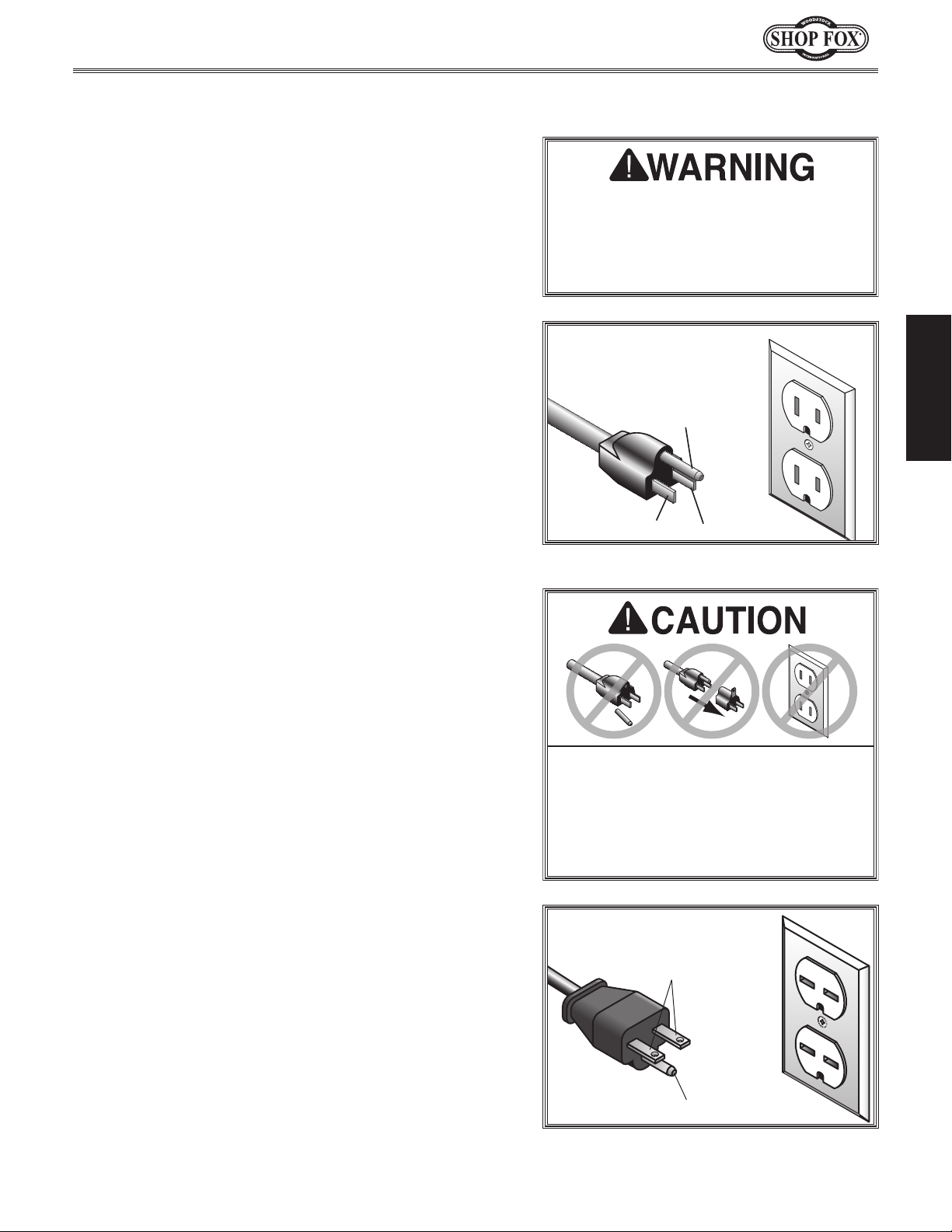
Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
This machine MUST be grounded. In the event of certain
types of
a path of least resistance for electric current
order
Improper connection of the equipment-grounding
will
increase
insulation
grounding
cord or plug is necessary, do not connect the equipmentgrounding
Check with a qualified electrician or service personnel
if
or if
properly grounded.
plug is damaged or worn, disconnect it from power, and
immediately replace it with a new one.
A NEMA 6-15 plug has a grounding prong that must be
attached to the equipment-grounding wire inside the
included power cord.
into a matching
installed and grounded in accordance with all local codes
and ordinances.
This machine is equipped with a power cord with an
equipment-grounding
plug
a matching
grounded in accordance with local codes and ordinances.
We do not recommend using an extension cord with
Any extension cord used with this machine must contain a
plug and receptacle, and
meet the following requirements:
Grounding Requirements
malfunctions or breakdowns, grounding provides
to travel—in
to reduce the risk of electric shock.
wire
the risk of electric shock. The wire with green
(with/without yellow stripes) is the equipment-
wire. If repair or replacement of the power
wire to a live (current carrying) terminal.
The machine must be properly set up
before it is safe to operate. DO NOT
connect this machine to the power
source until instructed to do so later in
this manual.
120V
GROUNDED
5-15 RECEPTACLE
ELECTRICAL
you do not understand these grounding requirements,
you are in doubt about whether the tool is
If you ever notice that a cord or
For 120V Connection (Prewired)
wire and NE M A 5-15 grounding
(see figure). The plug must only be inserted into
receptacle that is properly installed and
For 240V Connection
The plug must only be inserted
receptacle (see Figure) that is properly
this machine. Extension cords cause voltage drop, which
may damage electrical components and shorten motor
life. Voltage drop increases with longer extension cords
and smaller gauge sizes (higher gauge numbers indicate
smaller sizes).
ground wire
Minimum Gauge Size at 120V .......................14 AWG
Maximum Length (Shorter is Better) .................50 ft.
Extension Cords
, match the required
-13-
Grounding Prong
5-15 PLUG
Neutral Hot
Figure 4. NEMA 5-15 plug & receptacle.
DO NOT modify the provided plug or
use an adapter if the plug will not
fit the receptacle. Instead, have an
electrician install the proper receptacle
on a power supply circuit that meets
the requirements for this machine.
240V
Current Carrying Prongs
6-15 PLUG
Figure 5. NEMA 6-15 plug & receptacle.
GROUNDED
6-15 RECEPTACLE
Grounding Prong
Page 16
Converting Voltage to
Ground
Ground
or machine damage. To reduce this risk,
240V
The voltage conversion MUST be performed by an
electrician or qualified service personnel.
The voltage conversion procedure consists of rewiring the
motor and installing the correct plug. A wiring diagram is
provided on
IMPORTANT: If the diagram included on the motor
conflicts with the one on Page 81, the motor may have
changed since the manual was printed. Use the diagram
included on the motor instead.
Items Needed Qty
ELECTRICAL
• Phillips Head Screwdriver #2 ............................1
• Electrical Tape ................................. As Needed
• Wire Nut (14 AWG x 3) ....................................1
• Plug 6-15 ....................................................1
• Wire Cutters/Stripper.....................................1
Page 81 for your reference.
Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
Incorrectly wiring or grounding this
machine can cause electrocution, fire,
only an electrician or qualified service
personnel should do any required
electrical work on this machine.
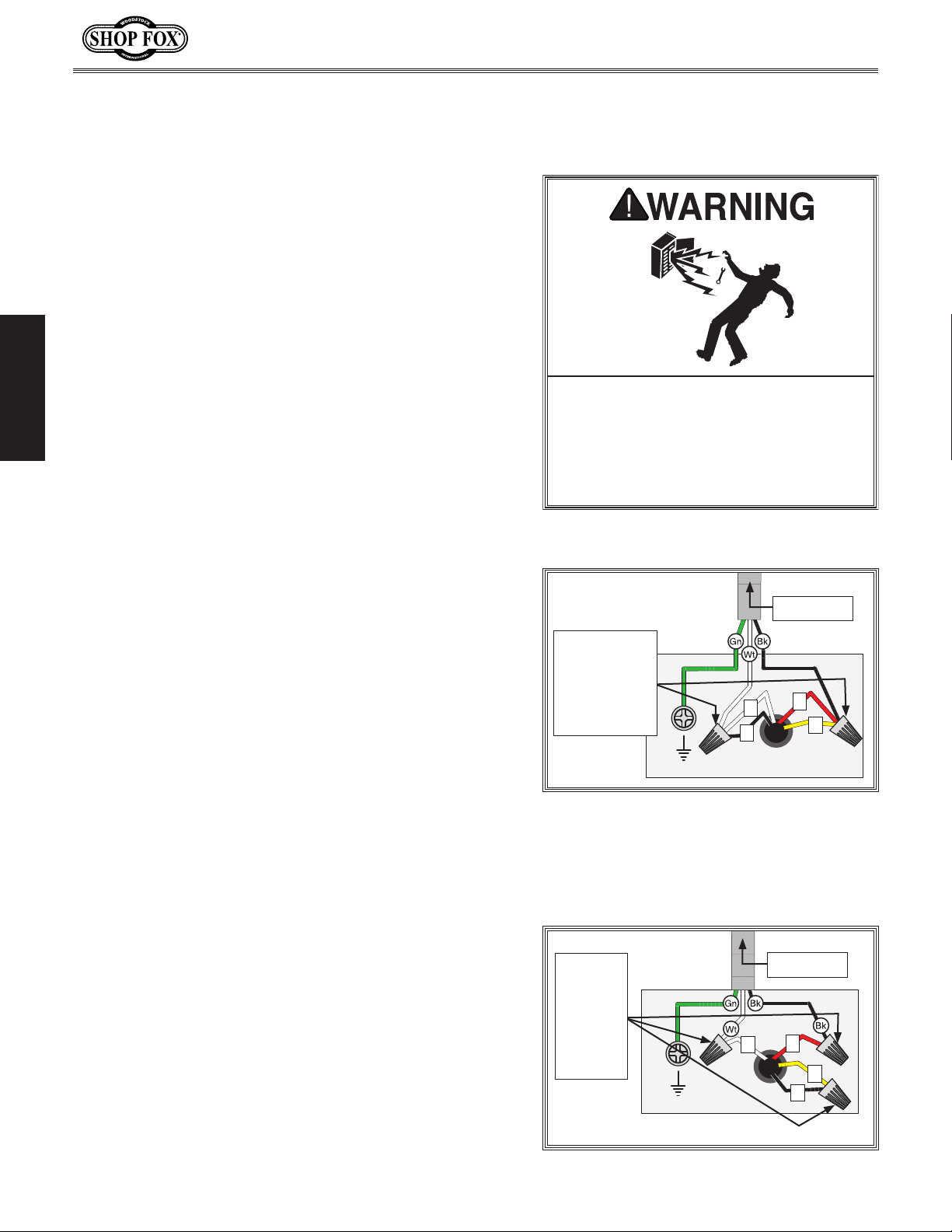
To convert the Model W1837 to 240V, do these steps:
1. DISCONNECT MACHINE FROM POWER!
Cut off existing 5-15 plug.
2.
3. Open motor junction box, remove two wire nuts
indicated in
4. Use wire nuts to connect wires as indicated in Figure
7. Twist wire nuts onto their respective wires and
wrap them with electrical tape so they will not come
loose.
Close and secure motor junction box.
5.
6. Install a 6-15 plug on the power cord, according
to plug manufacturer's instructions. If plug
manufacturer's instructions are not available, NEMA
standard 6-15 plug wiring is provided on Pa
Figure 6, and then disconnect wires.
ge 81.
To Switch
Remove
Wire Nuts
and
Disconnect
Wires
Figure 6. Inside motor junction box (motor
pre-wired to 120V).
Connect
Wires
and
Secure
with
Nuts
4
2
4
1
3
To Switch
1
3
2
Figure 7. Motor rewired to 240V.
-14-
Page 17
Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
This machine presents
serious injury hazards
to untrained users. Read
to become familiar with
tions before starting the
Immediately discard all
materials to eliminate
This machine has been carefully packaged for safe
transportation. If you notice the machine has been
damaged during shipping, please contact your authorized
Shop Fox dealer immediately.
The following items are needed, but not included, to set
up your machine.
SETUP
Unpacking
through this entire manual
Items Needed for Setup
Description Qty
• Additional People ..........................................1
• Safety Glasses for Each Person ..........................1
• Cleaner/Degreaser ............................ As Needed
• Disposable Shop Rags ......................... As Needed
• Straightedge 4' .............................................1
• Wrenches or Sockets 13mm ..............................2
• Phillips Head Screwdriver #2 ............................1
• Flat Head Screwdriver #2 ................................1
• Hex Wrench 8mm ..........................................1
• Dust Collection System ...................................1
• Dust Hose 4" ................................................1
• Hose Clamps 4" ............................................2
the controls and opera-
machine!
Wear safety glasses during entire setup process!
USE helpers or power
lifting equipment to lift
this machine. Otherwise,
serious personal injury
may occur.
SUFFOCATION HAZARD!
SETUP
plastic bags and packing
choking/suffocation
hazards for children and
animals.
-15-
Page 18
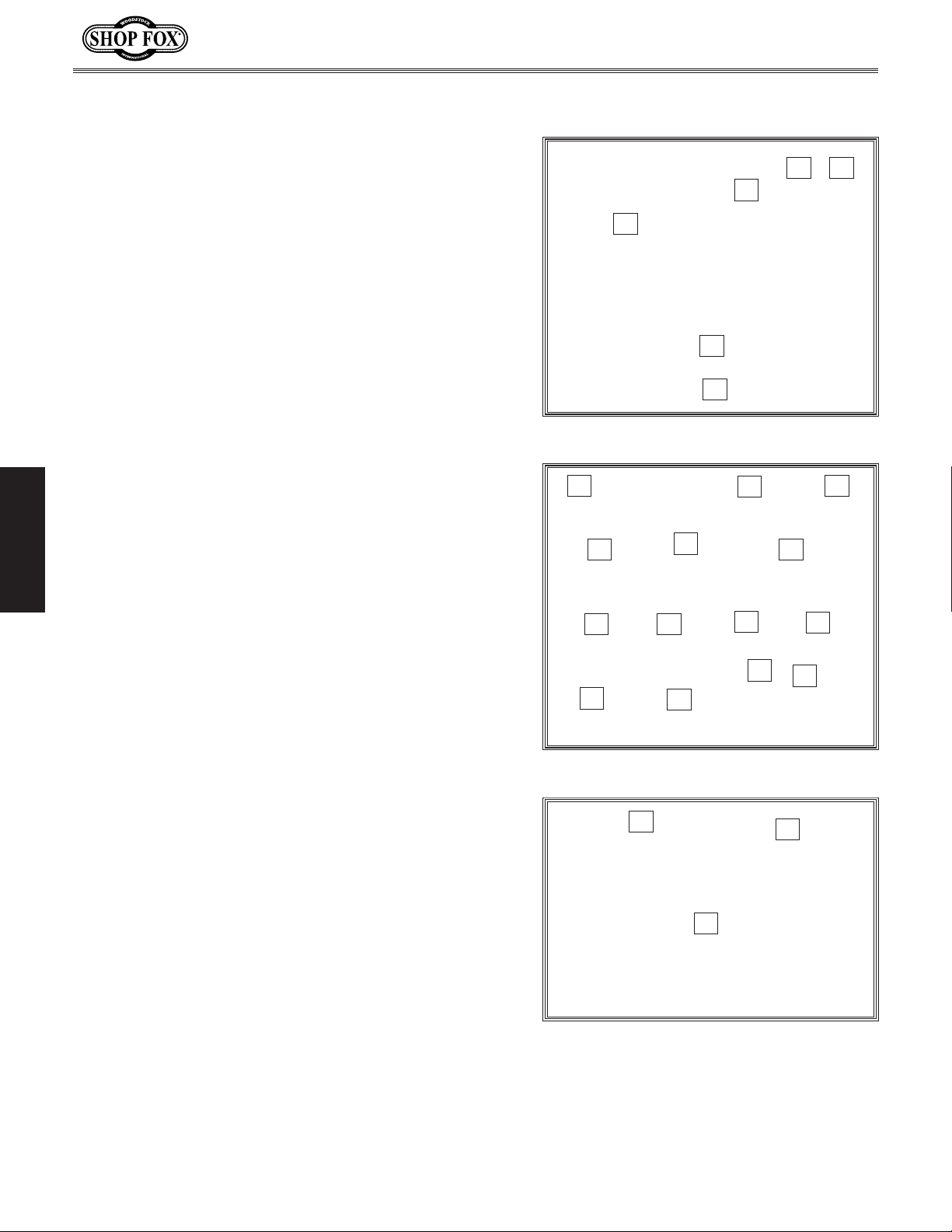
Inventory
The following is a list of items shipped with your machine.
Before beginning setup, lay these items out and inventory
them.
Note:
check around/inside the machine and packaging materials.
Often, these items get lost in packaging materials while
unpacking or they are pre-installed at the factory.
Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
D E
C
If you cannot find an item on this list, carefully
Box 1 Contents (Figure 8): Qty
A. Saw Body (Not Shown) ....................................1
Extension Wings ............................................2
B.
. Saw Blade 10" x 40T .......................................1
C
Dado Insert .................................................1
D.
Table Insert .................................................1
E.
Front Fence Rail ...........................................1
F.
. Rear Fence Rail .......................................1 Ea.
G
Box 2 Contents (Figure 9): Qty
H. Fence Assembly ............................................1
Blade Guard Assembly ....................................1
I.
SETUP
Push Stick ...................................................1
J.
Miter Gauge ................................................1
K.
Spreader/Riving Knife ....................................1
L.
. Fence Rail Brace ...........................................1
M
. Wrench 23mm Closed, 22mm Open ................1 Ea
N
Fence Rail End Caps ......................................4
O.
Miter Gauge Handle w/Washer ..........................1
P.
. Star Knobs ..................................................2
Q
Motor Cover ................................................1
R.
Access Panel ................................................1
S.
Hex Wrenches 3, 4, 5, 6, 8mm ......................1 Ea
T.
. Handwheels .................................................2
U
B
F
G
Figure 8. Box 1 contents.
H
K
R
Figure 9. Box 2 contents.
L
ON
S
I
M
P
T
J
Q
U
Box 3 Contents (Figure 10): Qty
V. Caster Foot Levers ........................................3
. Caster Support Brackets ..................................2
W
. Casters ......................................................3
X
-16-
V
X
Figure 10. Box 3 contents.
W
Page 19

Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
Hardware (See Hardware Recognition Chart) Qty
Button Head Cap Screws M8-1.25 X 16
(Legs/Caster Brackets) ...................................4
Flat Washers 8mm (Legs/Caster Brackets)
Lock Washers 8mm (Legs/Caster Brackets)
Hex Nuts M8-1.25 (Legs/Caster Brackets)
.................4
.................4
..................4
Hex Bolts M8-1.25 X 65 (Casters)
Lock Nuts M8-1.25 (Casters)
Hex Bolts M8-1.25 X 65 (Caster Foot Levers)...............3
Spacers 8mm (Caster Foot Levers)
Lock Nuts M8-1.25 (Caster Foot Levers)
Cap Screws M10-1.5 X 25 (Extension Wing/Table)
Flat Washers 10mm (Extension Wing/Table)
Lock Washers 10mm (Extension Wing/Table)
Hex Bolts M8-1.25 X 16 (Switch)
Lock Washers 8mm (Switch)
Hex Nuts M8-1.25 (Switch)
Hex Bolts M8-1.25 X 30 (Front Fence Rail/Table)
Hex Nuts M8-1.25 (Front Fence Rail/Table)
Cap Screws M8-1.25 X 25 (Rear Fence Rail/Table)
Hex Nuts M8-1.25 (Rear Fence Rail/Table)
Cap Screw M8-1.25 x 16 (Fence Rail Brace)
Hex Bolt M8-1.25 x 16 (Fence Rail Brace)
Hex Nuts M8-1.25 (Fence Rail Brace)
....................................2
............................3
..................................3
...........................6
....................3
.........6
...............6
...............6
.............................2
..................................2
.........8
................8
........8
.................4
................1
..................1
........................2
SETUP
Button Head Cap Screws M5-.8 X 12 (Rear Panel)
.........6
-17-
Page 20
Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
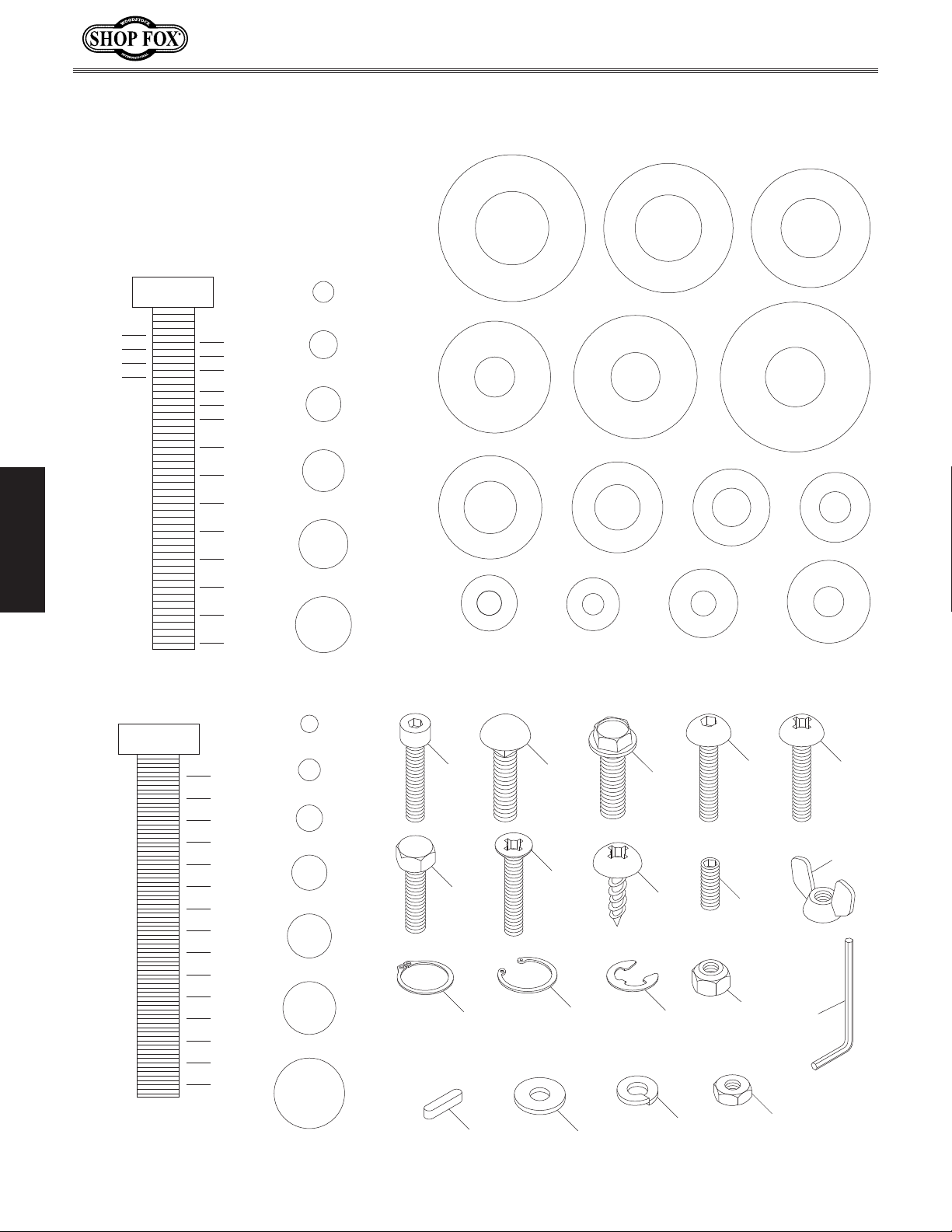
Hardware Recognition Chart
USE THIS CHART TO IDENTIFY
D
I
A
R
5
⁄8"
M
E
T
E
R
HARDWARE DURING THE
INVENTORY/ASSEMBLY
PROCESS.
A
W
E
H
S
#10
1
⁄4"
3
⁄8"
1
⁄2"
5
⁄8"
5
⁄16"
7
⁄16"
9
⁄16"
3
⁄4"
7
⁄8"
1
⁄4"
5
⁄16"
R
E
H
8mm
S
A
W
D
I
A
M
E
T
E
R
R
E
H
S
10mm
A
W
1
1
1
⁄4"
1
1
⁄2"
3
⁄4"
1
2
⁄16" INCH APART
1
SETUP
LINES ARE
1
2
⁄4"
1
2
⁄2"
3
2
⁄4"
3
3
⁄8"
7
⁄16"
1
⁄2"
D
I
A
R
E
7
R
E
H
S
A
#10
⁄16"
D
I
A
W
M
E
T
E
R
M
E
T
E
R
H
S
D
R
E
H
S
A
W
4mm
H
S
A
W
WASHERS ARE MEASURED BY THE INSIDE DIAMETER
D
R
E
3
⁄8"
A
W
I
A
M
E
T
E
R
D
I
A
R
E
A
E
T
9
⁄16"
M
E
T
E
R
M
E
T
E
R
H
S
A
A
I
D
M
R
S
I
A
R
5
⁄16"
A
M
E
T
E
E
T
E
R
W
E
H
D
R
E
H
S
A
W
E
H
S
A
W
D
I
I
A
M
R
5mm
E
H
S
A
W
R
E
12mm
W
R
D
1
⁄2"
I
A
H
D
I
A
M
E
R
E
H
1
S
⁄4"
A
W
D
R
E
S
A
W
6mm
M
E
T
E
R
T
E
R
D
I
A
M
E
T
E
R
I
A
M
E
T
E
R
5mm
10mm
15mm
20mm
25mm
30mm
35mm
MEASURE BOLT DIAMETER BY PLACING INSIDE CIRCLE
40mm
45mm
50mm
55mm
LINES ARE 1MM APART
60mm
65mm
70mm
75mm
4mm
5mm
6mm
8mm
10mm
12mm
16mm
Cap
Screw
Hex
Bolt
External
Retaining
Ring
Key
Carriage
Bolt
Flat
Head
Screw
Internal
Retaining
Ring
Flat Washer
Flange
Bolt
Tap
Screw
E-Clip
Lock
Washer
Button
Head
Screw
Set
Screw
Lock
Nut
Hex
Nut
Phillips
Head
Screw
Wing
Nut
Hex
Wrench
-18-
Page 21
Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
To prevent
machine, the factory has coated t
of your machine
compound
I
be difficult to
coating is as easy as possible, please gather the correct
cleaner, lubricant, and tools listed below:
• Cleaner/degreaser
and grease
• Safety glasses & disposable gloves
•
• Disposable Rags
To
1.
2.
3
4
5
6
immediately coat with a quality metal protectant.
Cleaning Machine
corrosion during shipment and storage of your
with a heavy-duty rust prevention
.
f you are unprepared or impatient, this compound can
remove. To ensure that the removal of this
designed to remove storage wax
Solvent brush or paint brush
remove rust preventative coating, do these steps:
DISCONNECT MACHINE FROM POWER!
he bare metal surfaces
Gasoline and petroleum
products have low flash
points and can explode
or cause fire if used to
clean machinery. Avoid
using these products
to clean machinery.
Many cleaning solvents
are toxic if inhaled.
Minimize your risk
by only using these
products in a well
ventilated area.
SETUP
Put on safety glasses and disposable gloves.
. Coat the rust preventative with a liberal amount of
cleaner/degreaser, then let it soak for 5–10 minutes.
. Wipe off surfaces. If your cleaner/degreaser is
effective, the coating will wipe off easily.
Tip: An easier way to clean off thick coats of rust
preventative from flat surfaces is to use a PLASTIC
paint scraper to scrape off the majority of the
coating before wiping it off with your rag. (Do
not use a metal scraper or you may scratch your
machine.)
. Repeat cleaning steps as necessary until all of the
compound is removed.
. To prevent rust on freshly cleaned surfaces,
In a pinch, automotive degreasers,
mineral spirits or WD•40 can be used
to remove rust preventative coating.
Before using these products, though,
test them on an inconspicuous area of
your paint to make sure they will not
damage it.
-19-
Page 22
Machine Placement
Weight Load
Refer to the
weight of your machine. Make sure that the
surface upon which the machine is placed will
bear the weight of the machine, additional
equipment that may be installed on the
machine, and the heaviest workpiece that will
be used. Additionally, consider the weight of
the operator and any dynamic loading that may
occur when operating the machine.
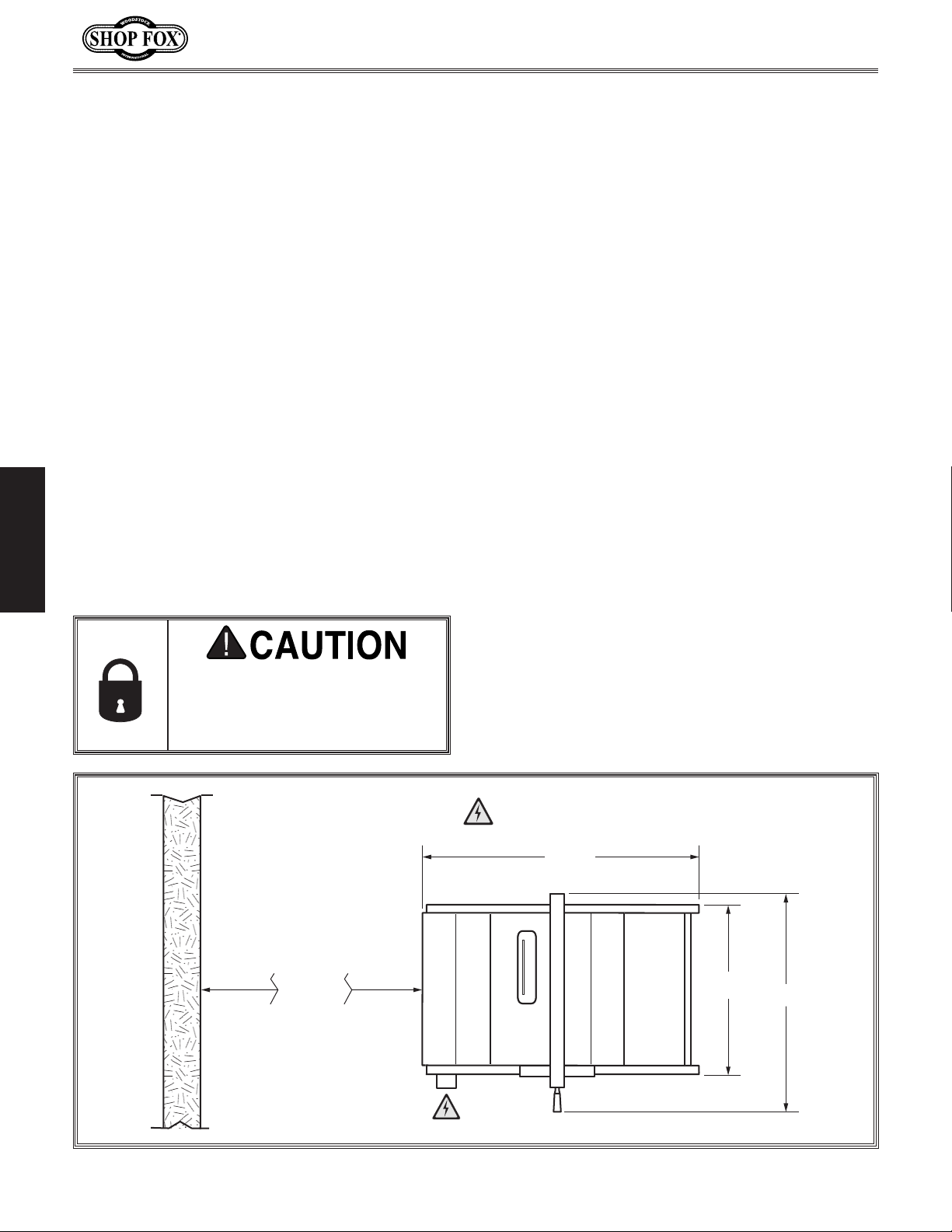
Space Allocation
Consider the largest size of workpiece that
will be processed through this machine and
provide enough space around the machine
for adequate operator material handling or
the installation of auxiliary equipment. With
permanent installations, leave enough space
around the machine to open or remove doors/
covers as required by the maintenance and
service described in this manual.
required space allocation.
Physical Environment
The physical environment where your machine is
operated is important for safe operation and the
ambient temperature range exceeds 41°–104°F;
(non-condensing); or the environment is subject
source. Make sure all power cords are protected
chemicals, or other hazards. Make sure to leave
Machine Specifications for the
Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
longevity of its components. For best results,
operate this machine in a dry environment
that is free from excessive moisture, hazardous
chemicals, airborne abrasives, or extreme
conditions. Extreme conditions for this type
of machinery are generally those where the
the relative humidity range exceeds 20–95%
to vibration, shocks, or bumps.
Electrical Installation
Place this machine near an existing power
SETUP
See below for
Children or untrained people
may be seriously injured by this
machine. Only install in an access
restricted location.
Wall
Min. 30"
from traffic, material handling, moisture,
access to a means of disconnecting the power
source or engaging a lockout/tagout device.
Lighting
Lighting around the machine must be adequate
enough that operations can be performed
safely. Shadows, glare, or strobe effects that
may distract or impede the operator must be
eliminated.
= Power Connection
571⁄4"
1
⁄4"
31
37
1
⁄2"
Figure 11. Working clearances.
-20-
Page 23
Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
Before beginning the assembly process, refer to Items
Needed for Setup
Ensure all parts have been properly cleaned of any
heavy-duty rust-preventative applied at the factory (if
applicable). Be sure to complete all steps in the assembly
procedure prior to performing the Tes t Run.
Assembly
and gather everything you need.
x 2
To assemble table saw, do these steps:
1. With help from another person, lift table saw unit
off of shipping pallet and onto floor.
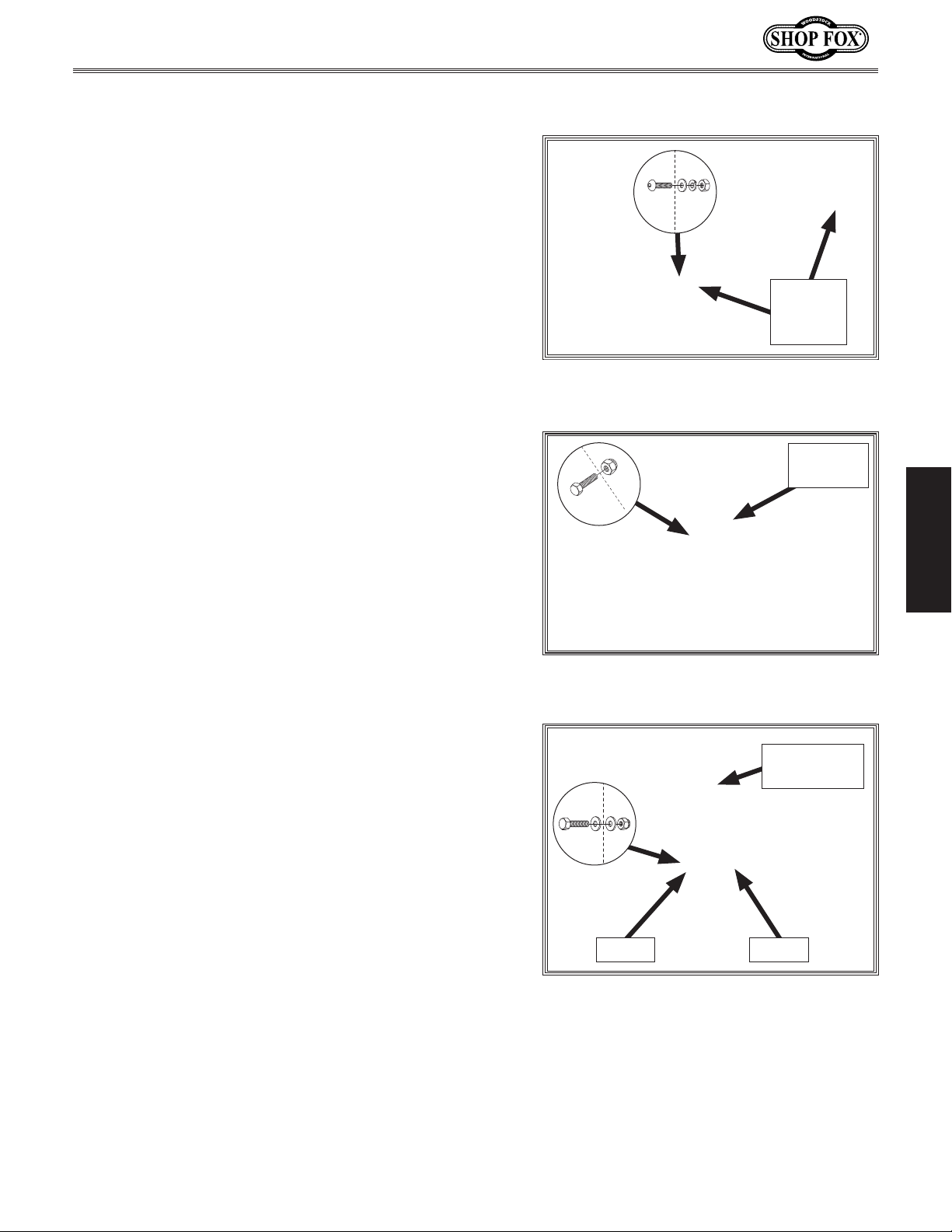
Install each of the two caster support brackets onto
2.
right front and rear stand legs using (2) M8-1.25 X
16 button head cap screws, (2) 8mm flat washers,
(2) 8mm lock washers, and (2) M8-1.25 hex nuts
Figure 12).
(see
3. Install casters onto caster support brackets and
mounting bracket using (3) M8-1.25 X 65 hex bolts
and (3) M8-1.25 lock nuts (see
Install caster foot levers onto support brackets
4.
and mounting bracket, each using (1) M8-1.25 X
65 hex bolt, (2) spacers, and (1) M8-1.25 lock nut
Figure 14).
(see
Figure 13).
Caster
Support
Brackets
Figure 12. Caster support brackets
installed on stand legs.
Mounting
Bracket
x 3
Figure 13. Caster installed onto mounting
bracket.
Caster Foot
Lever
SETUP
x 1
Spacer Spacer
Figure 14. Caster foot lever (1 of 3)
installed on front right support bracket.
-21-
Page 24
Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
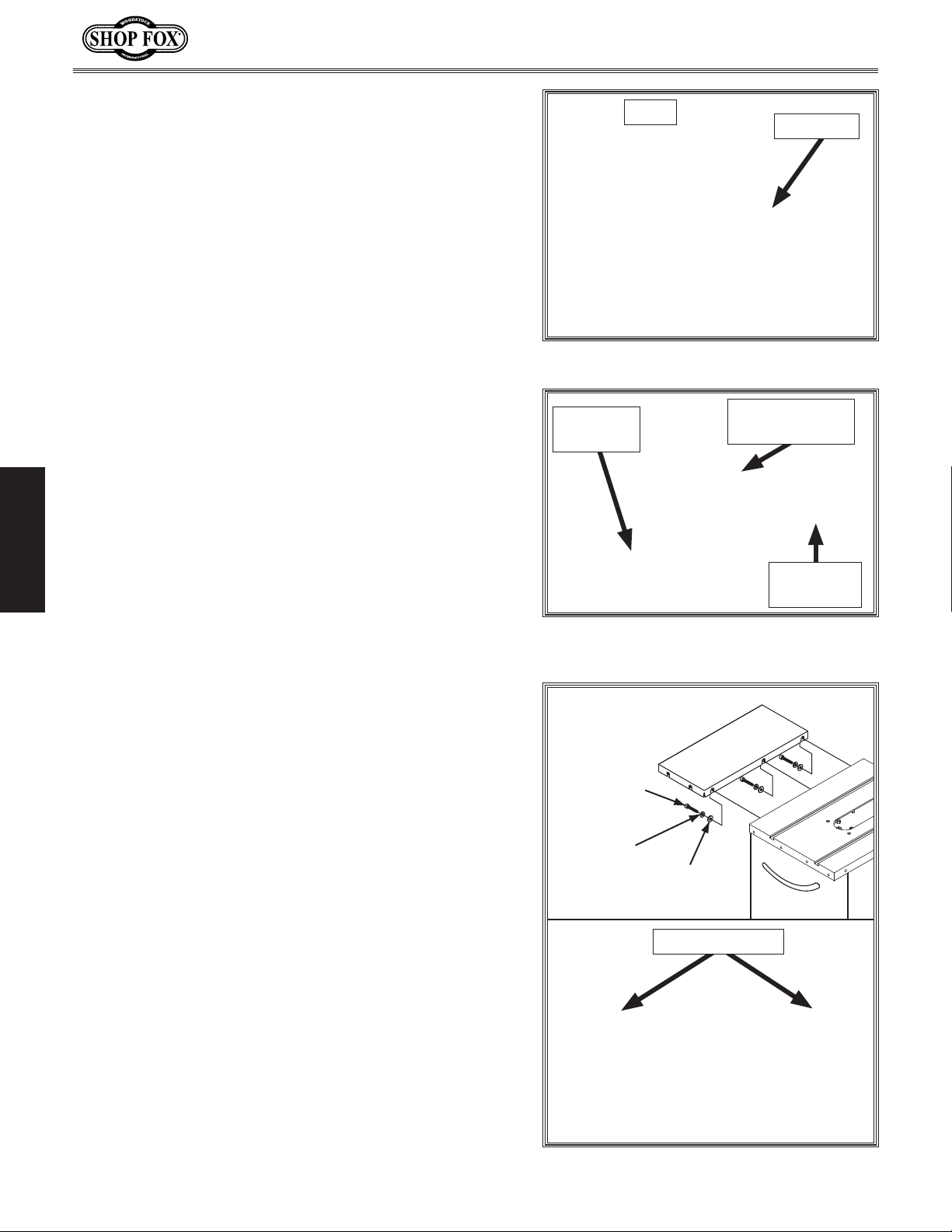
5. Install handwheels on shafts, making sure notch
in each handwheel fits over pin on each shaft, as
shown in
knobs.
6. Turn blade tilt handwheel until blade tilt indicator
points to 15° on blade angle scale (see Figure 16).
Figure 15, and then secure with star
Notch
Figure 15. Handwheel properly installed.
Blade Tilt
Indicator
Blade Elevation
Star Knob
Handwheel
SETUP
Inspect mating surfaces of cast iron table for burrs
7.
or foreign material that may inhibit installation of
extension wings.
Mating edges of table and wings must be clean,
smooth, and flat. If necessary, use a wire brush or
file to remove any flashing, dings, or high spots. This
step will ensure that wings will mount properly to
main table.
8. With another person to hold wings in place, attach
each extension wing to main table using (3) M10-1.5
x 25 cap screws, (3) 10mm lock washers, and (3)
10mm flat washers (see
Figure 17).
Blade Tilt
Handwheel
Figure 16. Blade tilt indicator and angle
scale.
Cap Screw
M10-1.5 x 25
Lock Washer
10mm
Flat Washer
10mm
Extension Wings
-22-
Figure 17. Extension wings installed.
Page 25
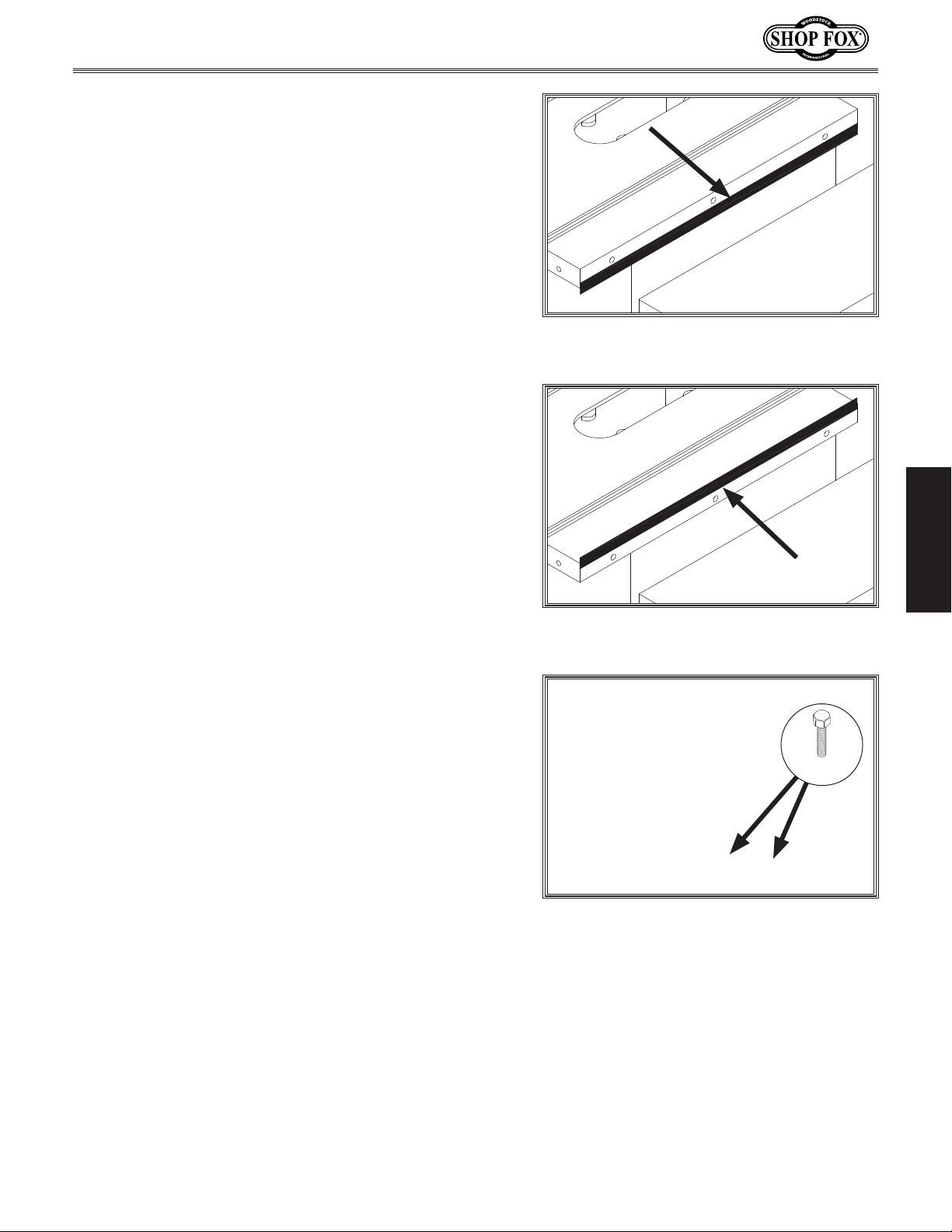
Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
9. Place straightedge across extension wings and main
table to ensure combined table surface is flat.
— If combined table surface is flat, skip to next step.
— If outside end of extension wing tilts down, remove
wing and place a strip of masking tape along bottom edge of main table to shim end of wing up
Figure 18).
(see
— If outside end of extension wing tilts up, remove
wing and place a strip of masking tape along top
edge of main table to shim end of extension wing
down (see Figure 19).
Note: After re-installing wings, remove all excess
masking tape with a razor blade.
Figure 18. Masking tape location for tilting
the extension wing up.
10. Remove (2) M8-1.25 x 16 hex bolts from switch and
insert into bottom slot on left end of fence rail (see
Figure 20). These will be used later for mounting
the switch.
SETUP
Figure 19. Masking tape location for tilting
the extension wing down.
x 2
Figure 20. Location of hex bolts for
mounting switch.
-23-
Page 26
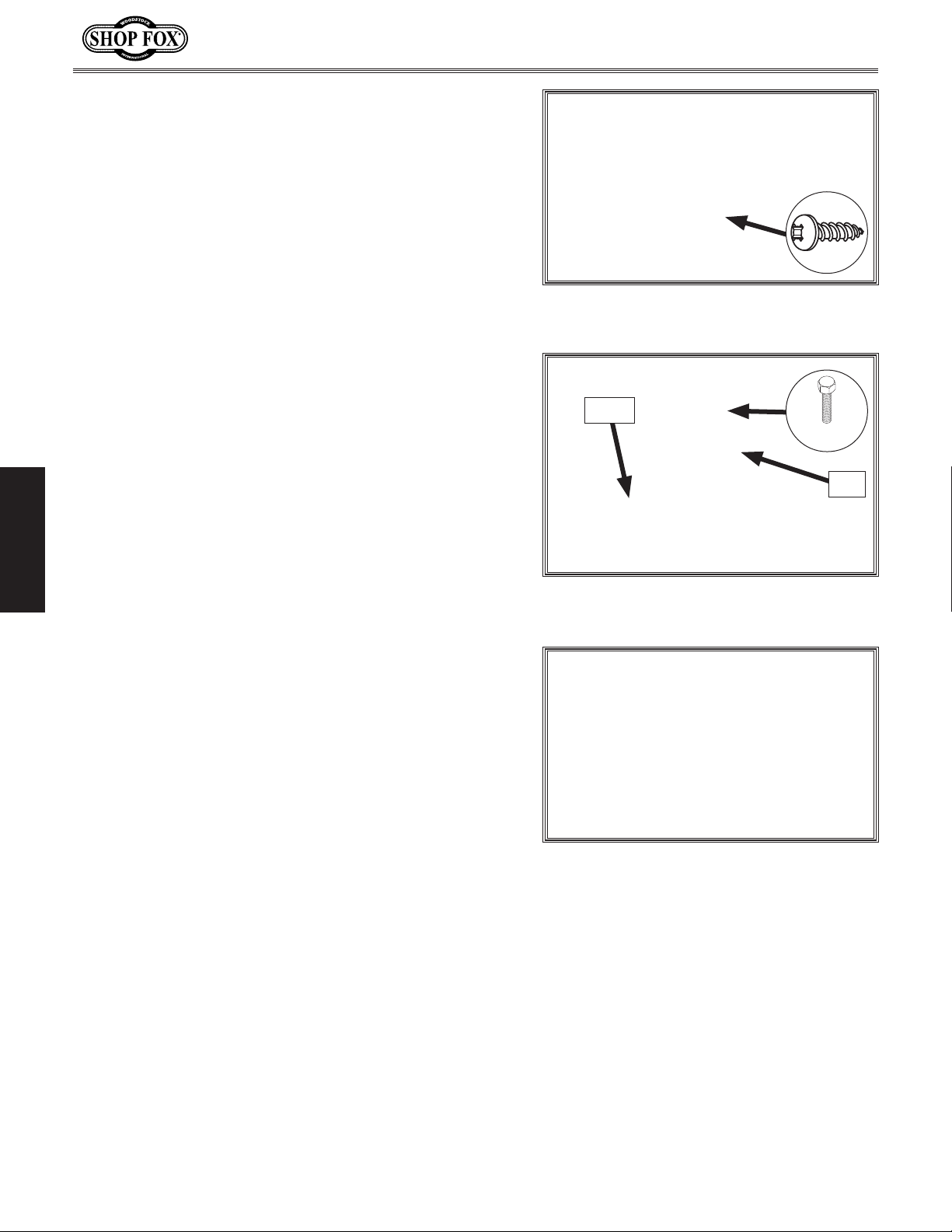
11
. Install end cap with (1) pre-installed tap screw on
left end of front fence rail (see Figure 21).
. Orient fence rail so scale faces you. Slide (8) M8-1.25
12
x 30 hex bolts into open slot (see Figure 22).
Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
x 1
Figure 21. Left end cap of front fence
rail.
Scale
x 8
Slot
SETUP
13. Align hex bolts in fence rail with holes in table, then
insert bolts into table. Be sure scale on fence rail is
facing up. Hand tighten (8) M8-1.25 hex nuts onto
hex bolts. Do not fully tighten yet (see Figure 23).
Figure 22. Hex bolt positioned in front
fence rail slot.
Figure 23. Mounting front fence rail.
-24-
Page 27
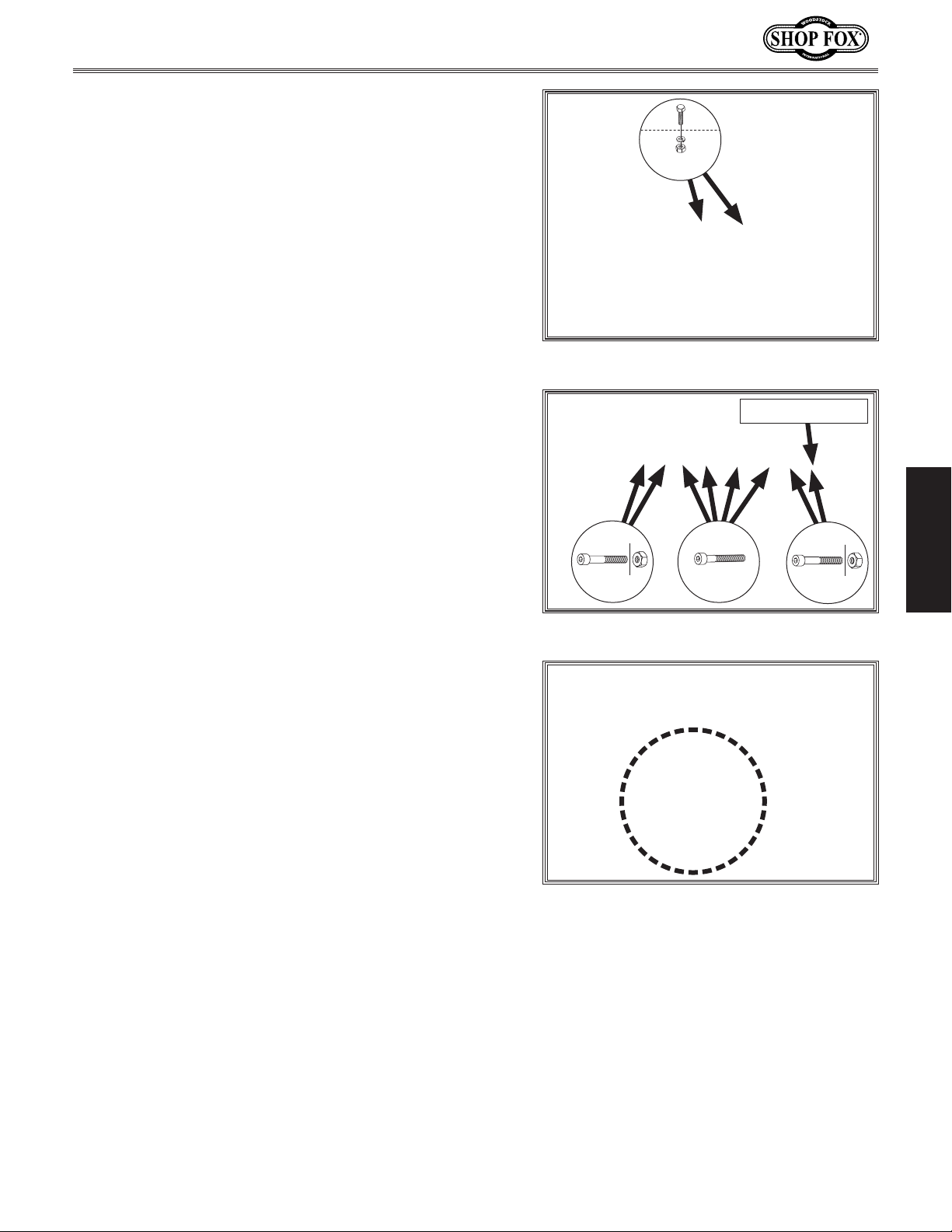
Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
14. Install switch onto hex bolts from Step 10 using
(2) M8-1.25 hex nuts and (2) 8mm lock washers
(see Figure 24).
Install rear fence rail on rear of table using (8)
15.
M8-1.25 x 25 cap screws, as shown in Figure 25.
Secure outer four cap screws with M8-1.25 hex nuts.
x 2
Figure 24. Switch installed.
Rear Fence Rail
16. Install saw blade as instructed in Blade Installation
on Page 34.
. Install table insert in table opening (see Figure 26).
17
Check to make sure it is flush and adjust if necessary
Table/Dado Insert Adjustment on Page 75 for
(see
more information).
x 2
Figure 25. Mounting rear fence rail.
Figure 26. Standard table insert installed.
x 4
x 2
SETUP
-25-
Page 28
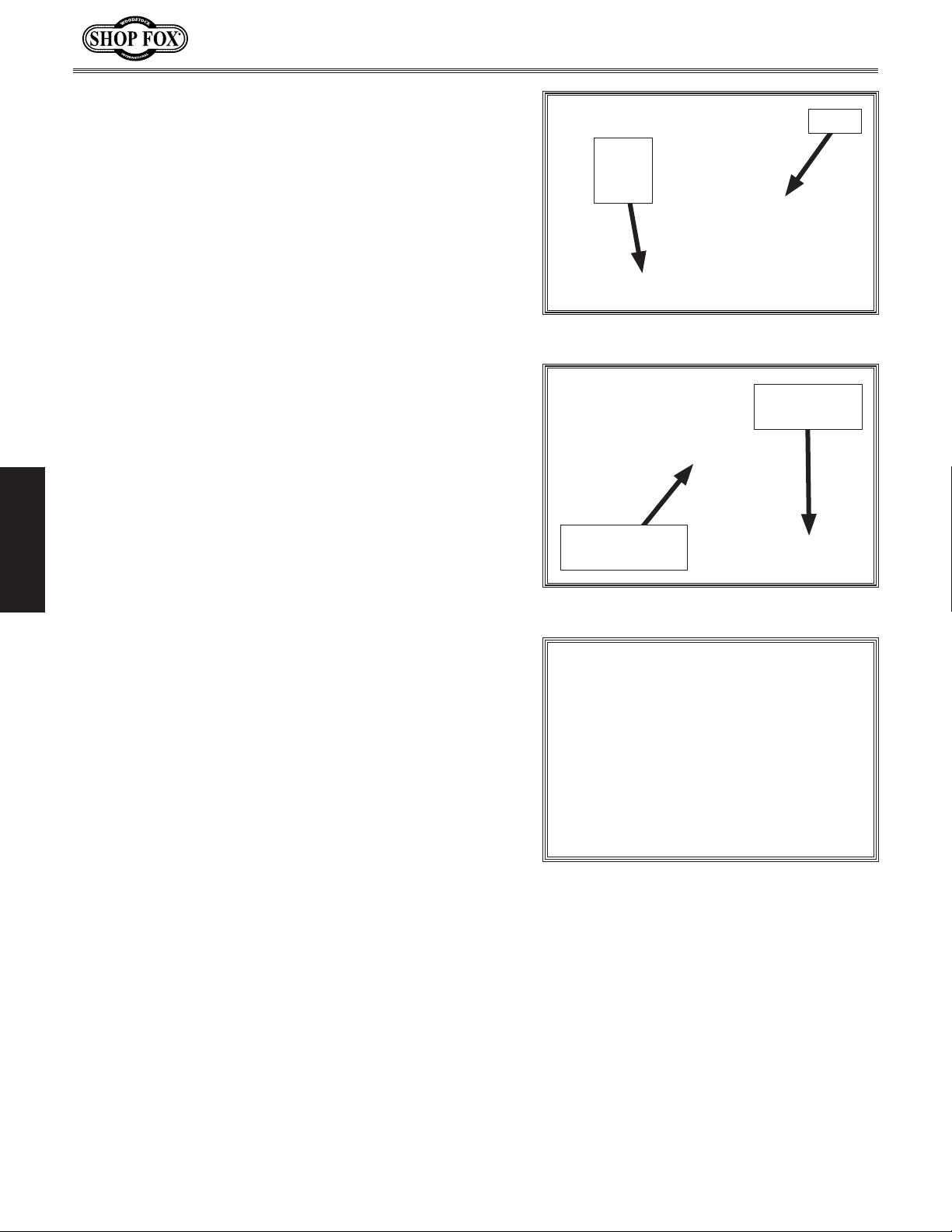
18. Place fence on front fence rail, as shown in
Figure 27. Press handle down to lock fence in
position.
Using blade height handwheel, raise blade 1–2
19.
inches.
Turn blade tilt handwheel until blade tilt indicator
20.
on front of machine points to 0° on blade angle
scale.
21. Slide fence so it lightly touches right side of blade
(see Figure 28). Do not yet lock fence.
. Nudge fence rail so zero mark of scale (on right)
22
lines up with cross-hair in fence scale window
(see Figure 28).
Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
Fence
Front
Fence
Rail
Figure 27. Fence installed on front rail.
Fence Scale
Window
. Tighten hex nuts to secure both fence rails.
23
SETUP
24. Check fence scale calibration by moving fence to 1"
mark on scale and measuring distance between blade
tooth (see Figure 29) and fence.
—If crosshair aligns exactly with 1" mark, no adjust-
ments need to be made.
—If crosshair does not align with 1" mark, loosen fence
scale window screws, move crosshair over 1" mark,
then tighten screws.
. Lift fence off of table and re-install to left of blade,
25
then slide fence so it lightly touches left side of
blade.
. Check left fence scale window.
26
Fence Lightly
Touching Blade
Figure 28. Fence scale calibration.
Figure 29. Checking calibration of fence
scale.
—If crosshair aligns with zero mark on left fence scale,
no adjustments need to be made.
—If crosshair does not align with zero mark on scale,
loosen fence scale window screws, move crosshair
over zero mark, then tighten screws.
-26-
Page 29
Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
27. Install blade guard as instructed on Page 35.
. Using a helper, mount fence rail brace to rear fence
28
rail with (1) M8-1.25 x 16 cap screw and (1) M8-1.25
hex nut (see Figure 30).
Note: Do not tighten cap screw yet.
29. Insert (1) M8-1.25 x 16 hex bolt into front
end of fence rail brace, then slide hex head
and tab of brace into slot in front fence rail
(see Figure 31). Tighten cap screw and hex nut on
rear end of fence rail brace.
Fence Rail
Brace
x 1
Rear
Fence Rail
Figure 30. Attaching rear end of fence rail
brace.
Slot
Front
Fence Rail
Ta b
. Measure distance (A) from table edge to rear end of
30
fence rail brace, then adjust front end of fence rail
brace so it is the same distance (B) from table edge
(see Figure 32).
. Secure hex bolt on front of rail brace with (1)
31
M8-1.25 hex nut.
SETUP
x 1
Figure 31. Attaching front end of fence
rail brace.
A
B
x 1
Figure 32. Fence rail brace installed.
-27-
Page 30

32. Install blade guard as instructed on Page 35.
Do not confuse this CFM recommendation with the rating
of the dust collector. To determine the CFM at the dust
port, you must consider these variables: (1) CFM rating of
the dust collector, (2) hose type and length between the
dust collector and the machine, (3) number of branches
or wyes, and (4) amount of other open lines throughout
the system. Explaining how to calculate these variables
is beyond the scope of this manual. Consult an expert or
purchase a good dust collection “how-to” book.
Install end cap on right end of front fence rail in
33.
same manner as you did on the left end (Step 11 on
Page 24).
Press end caps into rear fence rail.
34.
Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
x 6
35. Secure rear access panel and motor cover each
with (6) M5-.8 x 12 button head cap screws
Figure 33).
(see
Dust Collection
Recommended CFM at Dust Port: ................ 400 CFM
SETUP
Tools Needed Qty
Dust Collection System
Dust Hose 4"
Hose Clamps 4"
.....................................................1
..................................................2
........................................1
x 6
Figure
This machine creates substantial
amounts of dust during operation.
Breathing airborne dust on a regular
basis can result in permanent respiratory illness. Reduce your risk by wearing a respirator and capturing the dust
with a dust collection system.
33. Rear access panel installed.
To connect a dust collection hose, do these steps:
Fit 4" dust hose over dust port, as shown in Figure
1.
34, and secure it in place with hose clamp.
Tug hose to make sure it does not come off.
2.
Note: A tight fit is necessary for proper
performance.
Figure 34. Dust port connected to dust
collection system.
-28-
Page 31

Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
safety information. DO NOT operate, or
performed. Operating an improperly set
Once assembly is complete, test run the machine to
ensure it is properly connected to power and safety
components are functioning properly.
If you find an unusual problem during the test run,
immediately stop the machine, disconnect it from power,
and fix the problem BEFORE operating the machine again.
The
section of this
manual can help.
Test Run
Serious injury or death can result
from using this machine BEFORE
understanding its controls and related
Troubleshooting table in the SERVICE
To test run machine, do these steps:
1. Lower blade all the way down, and make sure all
tools and objects used during setup are cleared away
from machine.
Connect machine to power supply.
2.
3. Turn machine ON, verify motor operation, then turn
machine OFF.
The motor should run smoothly and without unusual
noises.
Insert switch disabling pin through green ON/START
4.
button (see example).
Press green ON/START button to test disabling
5.
feature on switch.The machine should not start.
— If machine does not start, the switch disabling
feature is working as designed.
— If machine does start, immediately stop the
machine. The switch disabling feature is not
working correctly. This safety feature must
work properly before proceeding with regular
operations. Call Tech Support for help.
allow others to operate, machine until
the information is understood.
DO NOT start machine until all
preceding setup instructions have been
up machine may result in malfunction
or unexpected results that can lead
to serious injury, death, or machine/
property damage.
Pin
ON / START
Button
OFF / STOP
Paddle
Figure 35. Removing switch key to disable
paddle switch.
SETUP
Recommended
Adjustments
For your convenience, the following adjustments have
been performed at the factory and no further setup is
required to operate this machine. However, because of
the many variables involved with shipping, we recommend
that you verify these adjustments to ensure that this saw
cuts safely and accurately.
-29-
Step-by-step instructions for these
adjustments can be found in
SERVICE.
Adjustments that should be verified:
. Blade Tilt Stop Accuracy (Page 65).
1
Miter Slot Parallel to Blade (Page 67).
2.
. Table/Dado Insert Adjustment
3
(Page 75).
SECTION 7:
Page 32

OPERATIONS
This machine will perform many types of operations
that are beyond the scope of this manual. Many of these
operations can be dangerous or deadly if performed
incorrectly.
The instructions in this section are written with the
understanding that the operator has the necessary
knowledge and skills to operate this machine. If at any
time you are experiencing difficulties performing any
operation, stop using the machine!
The overview below provides the novice machine operator
with a basic understanding of how the machine is used
during operation, so the machine controls/components
discussed later in this manual are easier to understand.
Due to its generic nature, this overview is NOT intended
this machine. Wear personal protective
General
Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
To reduce your risk of serious injury
or damage to the machine, read this
entire manual BEFORE using machine.
OPERATIONS
Eye injuries, respiratory problems, or
hearing loss can occur while operating
equipment to reduce your risk from
these hazards.
Children or untrained people can be
killed or seriously injured by this
machine. This risk increases with
unsupervised operation. To help
prevent unsupervised operation,
disable and lock the switch before
leaving machine unattended! Place key
in a well-hidden or secure location.
-30-
Page 33

Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
The purpose of this overview is to provide
the novice machine operator with a basic
understanding of how the machine is used
during operation, so the
components
easier to understand.
Due to the generic nature of this overview, it
is
To learn more about specific operations,
this entire manual and
from experienced
additional research outside of this manual by
reading "how-to" books, trade magazines, or
Operation Overview Workpiece Inspection
Some workpieces are not safe to cut on this
machine or may need to be modified before they
can be safely cut.
machine controls/
discussed later in this manual are
not intended to be an instructional guide.
read
seek additional training
machine operators, and do
To complete a typical operation, the operator
does the following:
1. Examines workpiece to make sure it is
suitable for cutting.
. Adjusts blade tilt, if necessary, to correct
2
angle of desired cut.
. Adjusts blade height approximately 1⁄4"
3
higher than thickness of workpiece.
Before beginning the cutting operation, inspect
all workpieces for the following:
• Material Type. This machine is intended
for cutting natural and man-made wood
products, laminate covered wood products,
and some plastics. Cutting drywall or
cementitious backer board creates extremely
fine dust and may reduce the life of the
motor bearings. This machine is NOT designed
to cut metal, glass, stone, tile, etc.; cutting
these materials with a table saw may lead to
injury.
• Foreign Objects. Nails, staples, dirt,
rocks and other foreign objects are often
embedded in wood. While cutting, these
objects can become dislodged and hit the
operator, cause kickback, or break the blade,
which might then fly apart. Always visually
inspect your workpiece for these items. If
they can’t be removed, DO NOT cut the
workpiece.
OPERATIONS
. Adjusts fence to desired width of cut, then
4
locks it in place.
. Checks outfeed side of machine for proper
5
support and to make sure workpiece can
safely pass all the way through blade without
interference.
. Puts on safety glasses, respirator, hearing
6
protection, and locates push sticks if needed.
. Starts saw.
7
8. Feeds workpiece all the way through blade
while maintaining firm pressure on workpiece
against table and fence, and keeping hands
and fingers out of blade path and away from
blade.
. Stops machine promptly after cut is complete.
9
• Large/Loose Knots. Loose knots can become
dislodged during the cutting operation.
Large knots can cause kickback and machine
damage. Choose workpieces that do not have
large/loose knots or plan ahead to avoid
cutting through them.
• Wet or “Green” Stock. Cutting wood
with a moisture content over 20% causes
unnecessary wear on the blades, increases
the risk of kickback, and yields poor results.
• Excessive Warping. Workpieces with
excessive cupping, bowing, or twisting are
dangerous to cut because they are unstable
and may move unpredictably when being cut.
• Minor Warping. Slightly cupped workpieces
can be safely supported with the cupped
side facing the table or fence; however,
workpieces supported on the bowed side
will rock during the cut, which could cause
kickback or severe injury.
-31-
Page 34

Non-Through & Through
Cuts
Non-Through Cuts
A non-through cut is a sawing operation where the blade
does not protrude above the top face of the wood stock,
as shown in
Examples of non-through cuts include dadoes and
rabbets. Non-through cuts have a higher risk of injury
from kickback because the blade guard must be removed.
However, the riving knife MUST be installed because it
still provides some protection. When making non-through
cuts with a dado blade, do not attempt to cut the full
depth in one pass. Instead, take multiple light passes to
reduce the load on the blade. A dado blade smaller than
10" will require removal of the riving knife, because the
riving knife will be higher than the blade.
Through Cuts
A through cut is a sawing operation in which the
workpiece is completely sawn through, as shown in
Figure
cuts, miter cuts, and beveled cuts. The blade guard
assembly MUST be used when performing through cuts.
Figure 36.
37. Examples of through cuts are rip cuts, cross
Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
Fence
Saw Blade
Workpiece
Figure 36. Example of a non-through cut.
Fence
Saw Blade
Workpiece
OPERATIONS
If you have never used this type of machine or
equipment before, seek training from an experienced
machine operator or read "how to" books before
beginning any projects. Regardless of the content
in this section, Shop Fox will not be held liable for
accidents caused by lack of training.
Figure 37. Example of a through cut
(blade guard not shown for illustrative
purposes).
-32-
Page 35

Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
Blade Size Requirements
The spreader/riving knife included with this machine is
0.090" (2.3mm) thick and is only designed for 10" diameter
blades.
When choosing a main blade, make sure the blade size
meets the requirements listed below. The thickness of the
blade body and teeth can be measured with calipers or
any precision measuring device.
Blade Size Requirements:
• Body Thickness: 0.060"-0.086" (1.5-2.1mm)
• Kerf (Tooth) Thickness: 0.094"-0.126"
(2.4-3.2mm)
Using a blade that does not meet the specified blade
size requirements presents a hazardous condition
that could cause kickback, operator injuries, or
property damage. ALWAYS use a blade that meets the
given blade size requirements.
Flat
Top
Blade
Figure 38. Example of a ripping blade.
Blade Selection
This section on blade selection is by no means
comprehensive. Always follow the saw blade
manufacturer's recommendations to ensure safe and
efficient operation of your table saw.
Ripping Blade Features (Figure 38):
• Best for cutting with the grain
• 20-40 teeth
• Flat-top ground tooth profile
• Large gullets for large chip removal
Crosscut Blade Features (Figure 39):
• Best for cutting across the grain
• 60-80 teeth
• Alternate top bevel tooth profile
• Small hook angle and a shallow gullet
Combination Blade Features (Figure 40):
• Designed to cut both with and across grain
• 40-50 teeth
• Alternate top bevel and flat, or alternate top bevel
and raker tooth profile
• Teeth are arranged in groups
• Gullets are small and shallow (similar to a cross-cut
blade), then large and deep (similar to a ripping
blade
OPERATIONS
Alternate
Top
Bevel
Figure 39. Example of a crosscut blade.
Alternate
Top
Bevel
and
Flat
Figure 40. Example of a combination
blade.
-33-
Page 36

Laminate Blade Features (Figure 41):
• Best for cutting plywood or veneer
• 40-80 teeth
• Triple chip tooth profile
• Very shallow gullet
Thin Kerf Blade: A blade with thinner kerf than a
standard blade. Since the spreader/riving knife included
with this table saw is sized for standard blades, thin kerf
blades cannot be used on this saw unless they meet the
Blade Requirements specified in this manual; otherwise,
they will increase the risk of kickback.
Dado Blades
Stacked Dado Blade (see Figure 42): Multiple blades are
stacked together to control the cutting width. Stacked
dado blades are more expensive than wobble blades, but
typically produce higher quality results.
Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
Triple
Chip
Blade
Figure 41. Example of a laminate blade.
Wobble Dado Blade: A single blade mounted at a slight
angle on an arbor hub. The blade angle is adjustable on
the hub, and the width of the dado cut is controlled by
the angle setting of the blade.
OPERATIONS
Figure 42. Stacked dado blade.
-34-
Page 37

Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
Blade Installation
Properly installing the blade is critical to safe cutting
operations that produce good results. Review this section,
even if your blade came pre-installed.
To install blade, do these steps:
1. DISCONNECT MACHINE FROM POWER!
. Raise blade arbor all the way up, remove blade
2
guard, table insert (leave Phillips head screws
mounted in table throat), and spreader/riving knife.
Note: Table insert is held in place by magnet.
. Use included arbor wrenches to loosen and remove
3
arbor nut, flange, and blade (see Figure 43). Arbor
nut has right-hand threads; turn counterclockwise to
loosen.
To reduce risk of injury,
always disconnect
power to saw before
changing blades. Since
the blade is sharp, use
extra care and wear
gloves when installing
it.
. Install new blade, flange, and arbor nut on arbor (as
4
shown in
5.
Re-install spreader/riving knife, table insert (see
Page 75), and blade guard.
Figure 44) with teeth facing front of saw.
Figure 43. Example of removing table saw
blade.
OPERATIONS
-35-
Figure 44. Correct order of installation
with teeth facing the correct direction.
Page 38

Blade Guard Assembly
The term "blade guard" refers to the assembly that
consists of the clear polycarbonate shield, the spreader,
and the anti-kickback pawls on each side of the spreader
Figure 45). Each of these components has important
(see
safety functions during the operation of the saw.
Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
Clear Shield
Guard
The clear polycarbonate guard allows the operator to
watch the blade cut the workpiece during operation.
This guard is designed to lift as the workpiece is pushed
into the blade and remain in contact with the workpiece
throughout the entire cut.
The guard reduces injury risk by providing a barrier
around the blade that prevents accidental contact and
contains flying wood chips.
To ensure that the guard does its job effectively, the
guard must always be in the downward position against
the table during idle operation, and the hinge mechanism
must be maintained in good working condition so the
guard can freely pivot up and down to accommodate the
height of the workpiece and return to the table surface.
Spreader/Riving Knife
The spreader/riving knife is a metal plate that prevents
the newly cut kerf of the workpiece from pinching the
back side of the blade, causing kickback.
The spreader/riving knife also acts as a barrier behind the
OPERATIONS
blade, which can help prevent hand from being pulled into
the blade in certain situations if a kickback occurs.
Spreader
Anti-Kickback
Pawl
Figure 45. Blade guard assembly
components.
In order to work properly, the spreader
cannot be bent or misaligned with
the blade. If the spreader accidentally
gets bent, take the time to straighten
it or just replace it. Using a bent or
misaligned spreader will increase the
risk of kickback! Refer to Page 69 to
check or adjust alignment if necessary.
Installing Blade Guard & Spreader/Riving
Knife
DISCONNECT MACHINE FROM POWER!
1.
Remove table insert, but leave Phillips head screws
2.
mounted in table throat.
Raise blade all the way up.
3.
4. Insert lower set of holes on spreader/riving knife
into bracket slot, and tighten lock lever to secure
spreader (see Figure 46).
Note: Do not insert upper set of holes on spreader
into bracket slot. Doing so will result in improper
installation of blade guard.
-36-
Spreader
Figure 46. Lock lever used to secure
spreader/riving knife.
Bracket
Slot
Lock Lever
Page 39

Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
5. Re-install table insert (refer to Table/Dado Insert
Adjustment on Page 75).
Tug spreader upward to verify it is locked.
6.
. Push guard lever toward front of saw.
7
8.
Insert rear pin on blade guard into rear slot of
spreader (see Figure 47), then push down on blade
guard assembly so forward pin slides into forward
slot of spreader.
9. Push guard lever toward rear of saw, locking blade
guard.
Tug upward on blade guard assembly to verify that it
10.
is locked into spreader.
When properly installed, the blade guard should be
set up similarly to
Figure 48. It should pivot freely
up and down and return to table in resting position.
It should also swing up high enough to accommodate
workpiece.
Pin
Guard Lever
Figure 47. Blade guard installation.
. Swing one side of blade guard up and out of the way.
11
. While lifting up on right spreader pawl, place a
12
straightedge against blade and spreader, making sure
straightedge does not touch a blade tooth.
When properly aligned, spreader/riving knife will be
in "Alignment Zone," shown in
Figure 49, and will be
parallel with blade.
Figure 48. Blade guard installed.
Alignment
Zone
Spreader or
Riving Knife
Blade
Straightedge
Figure 49. Spreader in the "Alignment
Zone."
OPERATIONS
-37-
Page 40

Anti-Kickback Pawls
The anti-kickback pawls allow the workpiece to travel in
only one direction. If the workpiece moves backwards,
such as during a kickback, the pawls will dig into the
workpiece to slow or stop it.
To work properly, the pawls must return to their resting
position after pivoting, shown in
If the pawls fail to return to the resting position, the pivot
area may need to be cleaned or the spring may have been
dislodged or broken and will need to be fixed/replaced.
Disabling Pawls
You might disable the pawls if you are concerned
about them scratching a delicate workpiece, or if you
believe that they will obstruct a narrow workpiece and
cause feeding difficulty or loss of control. Use your
best judgment before retracting the pawls, as they are
provided for your safety.
To disable pawls, do these steps:
. DISCONNECT MACHINE FROM POWER!
1
Figure 50.
Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
Pawl
Figure 50. Pawls in resting position.
We do not recommend disabling pawls
during normal operations unless absolutely necessary. In most situations,
disabling pawls will increase your risk
of serious personal injury in the event
of a kickback.
. Remove cap screw, locking hex nut, washers, pawls,
2
and retaining spring from blade guard assembly (see
Figure 51).
Enabling Pawls
To enable the pawls, re-install retaining spring, pawls,
washers, cap screw, and locking hex nut onto blade guard
OPERATIONS
assembly. Do not overtighten.
When to Use Blade Guard
The blade guard assembly MUST always be installed on
the saw for all normal through cuts (those where the
blade cuts all the way through the thickness of the
workpiece). If the blade guard is removed for specific
operations, always immediately replace it after those
operations are complete.
When Not to Use Blade Guard
The blade guard cannot be used on any non-through
cuts (those in which the blade does not cut all the way
through the thickness of the workpiece).
Pawls are sharp and can cut fingers or
hands. Use caution, and wear leather
gloves when handling pawls to reduce
risk of injury.
Figure 51. Pawls Removed.
Sometimes the blade guard or its components can get in
the way when cutting very narrow workpieces or other
specialized cuts. Because the blade guard is provided to
decrease your risk of injury, it should not be used if it
gets in the way of making a safe cut. Use good judgment!
-38-
Whenever blade guard cannot be used,
spreader/riving knife must be installed.
Page 41

Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
Riving Knife
The spreader also functions as a riving knife, which works
in the same manner as the spreader, but is used for nonthrough cuts. It is a metal plate that prevents the newly
cut workpiece from pinching the backside of the blade and
causing kickback.
The key difference between a spreader and a riving knife
is that a riving knife mounts below the blade's highest
point of rotation, as shown in
The height difference between a riving knife and a blade
allows the workpiece to pass over the blade during nonthrough cuts (those in which the blade does not cut all
the way through the thickness of the workpiece).
Figure 52.
Minimum 1mm
Maximum 5mm
Figure 52. Example of height difference
between riving knife and blade.
Height Difference
Riving
Knife
Similar to the spreader, the riving knife acts as a barrier
behind the blade to reduce the risk of hands being pulled
into the blade if kickback occurs.
When used as a riving knife, the spreader/riving knife
must be kept within the range shown in
that reason, a 10" blade is required for operations that
use a riving knife.
To install riving knife, do these steps:
DISCONNECT MACHINE FROM POWER!
1.
Remove table insert, but leave Phillips head screws
2.
mounted in table throat.
Note: Table insert is held in place by magnet.
Raise blade all the way up.
3.
4. Insert upper set of holes on spreader/riving knife
into bracket slot and tighten lock lever to secure
spreader/riving knife (see Figure 54).
Figure 53. For
Top Distance
Minimum 3mm
Maximum 8mm
Riving
Bottom Distance
Minimum 3mm
Maximum 8mm
Table
Figure 53. Example of allowable top and
bottom distances between riving knife and
blade.
Spreader/
Riving Knife
Bracket
Slot
Upper Holes
Knife
OPERATIONS
Re-install table insert (refer to Page 75).
5.
Tug upward on top of spreader/riving knife to verify
6.
it is locked.
-39-
Lock Lever
Figure 54. Lock lever used to secure
spreader.
Page 42

When to Use the Riving Knife
Use the riving knife for all non-through cuts made with a
standard table saw blade (i.e., dadoes or rabbet cuts, and
when using a tenoning jig), or when using a 10" diameter
dado blade.
Also, use the riving knife for those special operations
where the blade guard or its components get in the way
of safe operation, such as with very narrow cuts.
When Not to Use the Riving Knife
Do not use the riving knife with a dado blade that has
a diameter smaller than 10" in diameter. Otherwise, the
riving knife height will exceed the blade height and the
workpiece will hit the riving knife during the cut, forcing
the operator into a dangerous situation of trying to turn
the saw off with the workpiece stuck halfway through the
cut.
Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
To ensure riving knife works safely, it
MUST be aligned with and correctly
adjusted to blade. Refer to Page 69 to
check or adjust riving knife alignment.
In addition, although it is possible to use the riving knife
for through cutting operations, the blade guard assembly
offers far more injury protection and risk reduction than
the riving knife. Therefore,
you use the blade guard assembly for through cuts.
we strongly recommend that
OPERATIONS
-40-
Page 43

Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
Ripping
Ripping means cutting with the grain of a natural wood
workpiece. In man-made materials such as MDF or
plywood, ripping simply means cutting lengthwise.
To make a rip cut, do these steps:
. Review Preventing Kickback on Page 11 and take
1
necessary precautions to reduce likelihood of
kickback.
. If using natural wood, joint one long edge of
2
workpiece on a jointer.
. DISCONNECT MACHINE FROM POWER!
3
Ensure that blade guard/spreader is installed.
4.
. Set fence to desired width of cut on scale.
5
Serious injury can be caused by
kickback. Kickback is a high-speed
ejection of stock from table saw
toward an operator. The operator or
bystanders may be struck by flying
stock, or the operator’s hands can be
pulled into blade during kickback.
6. Adjust blade height so highest saw tooth protrudes
no more than 1⁄4" above workpiece.
. Set up safety devices such as featherboards or other
7
anti-kickback devices, making sure no safety devices
are contacting blade.
. Plug saw into power source, turn it ON, and allow it
8
to reach full speed.
Note: Jointed edge of workpiece must slide against
fence during cutting operation.
Use a push stick to feed workpiece through saw blade,
9.
as shown in Figure 55, until workpiece is completely
beyond saw blade.
OPERATIONS
Figure 55. Typical ripping operation.
Turn saw OFF and allow blade to come
to a complete stop before removing
cutoff piece. Failure to follow this
warning could result in severe cuts or
amputation.
-41-
Keep blade guard installed and in down
position. Failure to do this could result
in serious personal injury or death.
Page 44

Crosscutting
"Crosscutting" means cutting across the grain of a natural
wood workpiece, usually with a miter saw In other manmade materials, such as MDF or plywood, crosscutting
means cutting across the width of the workpiece.
To make a crosscut using miter gauge, do these steps:
DISCONNECT MACHINE FROM POWER!
1.
Ensure that blade guard/spreader is installed.
2.
. Move rip fence aside and position miter gauge,
3
adjusted to 90°, in a miter slot.
. Adjust blade height so teeth protrude no more than
4
1
⁄4" above workpiece.
. Slide miter gauge near blade and adjust workpiece
5
so blade will cut on waste side of line.
. Plug in table saw, turn it ON, and allow it to reach
6
full speed.
. Hold workpiece firmly against face of miter gauge
7
(as shown in Figure 56), and ease it through blade
until workpiece is completely past saw blade.
Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
Figure 56. Typical crosscutting operation.
Turn saw OFF and allow blade to come
to a complete stop before removing
cutoff piece. Failure to follow this
warning could result in severe cuts or
amputation.
OPERATIONS
-42-
Page 45

Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
Miter Cuts
A miter cut is an angled crosscut. Miters are usually cut in
the same manner as crosscuts, using the miter gauge and
a predetermined mark on the workpiece.
To perform a miter cut, do these steps:
DISCONNECT MACHINE FROM POWER!
1.
Ensure that blade guard/spreader is installed.
2.
Determine angle of cut. If angle needs to be very
3.
precise, use a protractor to set miter gauge to
blade.
Place face of miter gauge against edge of workpiece
4.
and place bar across face of workpiece. Use bar as a
guide to mark your cut, as shown in
Figure 57.
Figure 57. Example of marking miter line.
Place miter gauge back into slot and hold workpiece
5.
firmly against miter gauge body. Slide miter gauge
near blade and adjust workpiece so blade will cut on
waste side of line.
Proceed to make cut in same manner as described in
6.
Crosscutting instructions.
Blade Tilt/Bevel Cuts
When the blade tilt adjustment bolts are properly
adjusted (as described on
handwheel allows the operator to tilt the blade to the
left, between 0° and 45°. This is used most often when
cutting bevels, compound miters, or chamfers.
shows an example of the blade when tilted to 45°.
Page 65), the blade tilt
Figure 58
OPERATIONS
-43-
Figure 58. Example of blade tilted to
45° for bevel cutting (blade guard only
removed for clarity.
Page 46

Dado Cutting
Commonly used in furniture joinery, a dado is a straight
channel cut in the face of the workpiece. Dadoes are
"non-through" cuts that can be made with a dado blade or
a standard saw blade. Figure
a dado cut being made with a dado blade.
59 shows a cutaway view of
Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
Dado Blade
The Model W1837 can accommodate dado blades up to 10"
in diameter. However, you MUST install the included riving
knife while using a 10" diameter dado blade, as it provides
a barrier behind the blade and reduces the risk of hands
being pulled into the blade if kickback occurs.
DO NOT use the riving knife if you install a dado blade
smaller than 10" in diameter. Otherwise, the riving knife
height will exceed the blade height and the workpiece will
hit the riving knife during the cut, forcing the operator into
a dangerous situation and trying to turn the saw OFF with
the workpiece stuck halfway through the cut.
Installing Dado Blade
1. DISCONNECT MACHINE FROM POWER!
. Remove table insert, blade guard assembly,
2
spreader/riving knife, and saw blade.
. Attach and adjust dado blade system according to
3
dado blade manufacturer’s instructions.
Workpiece
Fence
Figure 59. Example of a dado being cut
with a dado blade.
DO NOT make through cuts with a dado
blade. The extra width of a dado blade
will increase risk of kickback during
a through cut. Dado blades are only
intended for non-through cuts. Failure
to heed this warning could result in
serious injury.
OPERATIONS
. Install included dado table insert.
4
-44-
Page 47

Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
Cutting Dadoes with a Dado Blade
Because dado blades are much wider than standard
blades, they place a greater amount of force against the
workpiece when cutting. This additional force increases
the risk of kickback, requiring the operator to take
additional steps when cutting to keep their injury risk at
an acceptable level.
Never try to cut a warped board by
holding it down against the table. If
kickback occurs, your hand could be
pulled into blade, resulting in accidental contact with rotating blade, causing severe cuts or amputation.
Dado blades have a higher risk of kickback than
normal blades because their larger size applies
stronger forces to the workpiece. This risk increases
relative to depth and width of cut. To minimize your
risk of serious personal injury, ensure that stock is
flat and straight, and make multiple light cuts (rather
than one deep cut) to achieve desired cutting depth.
Figure 60 demonstrates the sequential process of making
multiple, light cuts that get progressively deeper. The
actual number of cuts used should be determined by
workpiece hardness, total dado depth, and feed rate. In
general, if you hear the motor slow down during the cut,
you are cutting too deep or feeding too fast. Slow down!
To cut dado with dado blade, do these steps:
. DISCONNECT MACHINE FROM POWER!
1
Adjust dado blade to desired depth of cut.
2.
Adjust distance between fence and inside edge of
3.
blade, as shown in Figure 59 on Page 43, to dado
length of a workpiece
.
Dado Blade
Workpiece
Cut 1
Fence
Cut 2
Workpiece
Fence
Cut 3
Workpiece
Finished
Dado Cut
Workpiece
Figure 60. Example of dado being cut with
multiple light cuts, instead of one deep
cut.
Fence
Fence
OPERATIONS
— If dadoing across workpiece, use miter gauge and
carefully line up desired cut with dado blade. DO
NOT use fence in combination with miter gauge.
Reconnect saw to power source.
4.
5. Turn saw ON. Blade should run smoothly, with no
vibrations.
When blade has reached full speed, perform test cut
6.
with scrap piece of wood.
— If cut is satisfactory, repeat cut with actual
workpiece.
-45-
Page 48

Cutting Dadoes with a Standard Blade
A ripping blade (described on Page 32) is typically the
best blade to use when cutting dadoes with a standard
blade because it removes sawdust very efficiently.
To use standard saw blade to cut dadoes, do these
steps:
DISCONNECT MACHINE FROM POWER!
1.
. Mark width of dado cut on workpiece. Include marks
2
on edge of workpiece so cut path can be aligned
when workpiece is lying on table.
Raise blade up to desired depth of cut (depth of
3.
dado channel desired).
Set saw up for type of cut you need to make,
4.
depending on whether it is a rip cut (Page 40) or
crosscut (Page
Align blade to cut one side of dado, as shown in
5.
Figure 61.
41).
Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
Cut 1
Workpiece
Figure 61. First cut for a single-blade
Cut 2
Workpiece
Figure 62. Second cut for a single-blade
Blade
Fence
dado.
Blade
Fence
dado.
OPERATIONS
. Reconnect saw to power source and turn saw ON.
6
Allow blade to reach full speed, then perform
cutting operation.
. Repeat cutting operation on other side of dado, as
7
shown in Figure 62.
. Make additional cuts (see Figure 63) in center
8
of dado to clear out necessary material. Dado is
complete when channel is completely cleared out.
Cuts 3+
Fence
Workpiece
Figure 63. Additional single-blade dado
cuts.
-46-
Page 49

Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
Rabbet Cutting
Commonly used in furniture joinery, a rabbet cut is
an L-shaped groove cut in the edge of the workpiece.
Rabbets can be cut with either a dado blade or a standard
saw blade.
Rabbet cutting along the edge of a workpiece with a dado
blade requires a sacrificial fence (see
the sacrificial fence the same length as the fence and
3
⁄4" thick. Attach it to the fence with screws or clamps,
making sure they are all secure and tight. Raise the blade
into the sacrificial fence to the height needed.
When using a dado blade, the included dado table insert
must be installed and used during rabbeting operations.
Cutting Rabbets with a Dado Blade
1. DISCONNECT MACHINE FROM POWER!
Figure 64). Make
Dado blades have a higher risk of
kickback than normal blades because
their larger size applies stronger forces
to the workpiece. This risk increases
relative to the depth and width of the
cut. To minimize your risk of serious
personal injury, ensure that stock is
flat and straight, and make multiple
light cuts (rather than one deep cut) to
achieve the desired cutting depth.
Rip Fence
. Adjust dado blade to height needed for rabbeting
2
operation. When cutting deep rabbets, take more
than one pass to reduce risk of kickback.
Adjust fence and align workpiece to perform cutting
3.
operation, as shown in
Reconnect saw to power source and turn saw ON.
4.
When blade has reached full speed, perform a test
cut with a scrap piece of wood.
—If cut is satisfactory, repeat cut with workpiece.
Figure 65.
Sacrificial Fence
Dado Insert
Blade Cut-Out
OPERATIONS
Figure 64. Example of sacrificial fence.
Sacrificial Fence
Dado Blade
Fence
Workpiece
Figure 65. Rabbet cutting.
-47-
Page 50

Cutting Rabbets with a Standard Blade
A ripping blade is typically the best blade to use for
cutting rabbets when using a standard blade because it
removes sawdust very efficiently. (See
details.) Also, a sacrificial fence is not required when
cutting rabbets with a standard blade.
To cut rabbets with standard blade, do these steps:
DISCONNECT MACHINE FROM POWER!
1.
Ensure that riving knife and standard table insert are
2.
installed.
. Mark width of rabbet cut on edge of workpiece,
3
so you can clearly identify intended cut while it is
laying flat on saw table.
. Raise blade up to desired depth of cut (depth of
4
rabbet channel desired).
. Stand workpiece on edge, as shown in Figure 66,
5
then adjust fence so blade is aligned with inside of
your rabbet channel.
Page 32 for blade
Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
45
30
15
DO NOT place a tall board on edge to
perform a rabbet cut with a standard
blade. Workpieces that are too tall
to properly support with fence can
easily shift during operation and cause
kickback. Instead, place stock flat on
saw and perform rabbet cut with a
dado blade, as instructed on Page 46.
— If workpiece is very tall, or is unstable when placed
against fence, lay it flat on table and use a dado
blade to perform rabbet cut.
. Reconnect saw to power source, then perform cut.
6
7. Lay workpiece flat on table, as shown in Figure 67,
OPERATIONS
adjust saw blade height to intersect with first cut,
then perform second cut to complete rabbet.
Blade
Workpiece
Fence
Figure 66. Example of rabbet cutting with
a standard blade.
Blade
Fence
Workpiece
-48-
Figure 67. Example of second cut to cre-
ate a rabbet.
Page 51

Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
Resawing
Resawing is the process of cutting a thick piece of stock
into one or more thinner pieces. Although resawing can
be done with a table saw, we strongly recommend that
you use a bandsaw instead.
A bandsaw is the ideal machine for resawing, and
resawing with one is fairly easy and safe. A table saw
is not intended for resawing, and resawing with one
is difficult and dangerous due to the increased risk of
kickback from binding and deep cuts, and the increased
risk of injury from having to remove the guard.
If you insist on resawing with a table saw, DO NOT do
so without using a resaw barrier and wearing a full face
shield. The following instructions describe how to build a
resaw barrier and add an auxiliary fence to your standard
fence, to reduce the risk injury from resawing on a table
saw.
Resawing operations require proper
procedures to avoid serious injury
and prevent kickback. Any tilting or
movement of workpiece away from
fence will likely cause kickback. Be
certain that stock is flat and straight.
Failure to follow these warnings could
result in serious personal injury or
amputation.
Note: To determine the maximum resawing height for this
table saw, find the maximum blade height, then double it
and subtract
1
⁄8".
Making a Resaw Barrier
When resawing, the resaw barrier (see Figure 68) acts in
tandem with the rip fence to provide tall support for the
workpiece. This minimizes the probability of it binding
against the blade and causing kickback.
Tools Needed: Qty
Table Saw ........................................................1
Jointer and Planer
Clamps
Drill ...............................................................1
Drill Bits
Countersink Bit
Components Needed for Resaw Barrier:
Wood* 3⁄4" x 5 1⁄2" x Length of Fence ........................1
Wood*
Wood Screws #8 x 2" ...........................................4
Wood Glue
................................................2 Minimum
1
⁄8", 9⁄64" ....................................... 1 Each
3
⁄4" x 3" x Length of Fence ............................1
........................................... As Needed
............................. Recommended
..................................................1
OPERATIONS
Figure 68. Example of resaw barrier.
* Only use furniture-grade plywood, kiln dried hardwood,
or HDPE plastic to prevent warping.
-49-
Page 52

To build a resaw barrier, do these steps:
. Cut your wood pieces to specified size. If you are
1
using hardwood, cut pieces oversize, then joint and
plane them to correct size to make sure they are
square and flat.
Pre-drill and countersink four holes approximately
2.
3
⁄8" from bottom of 51⁄2" tall wood piece.
Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
#8 x 2"
Wood Screw
3
⁄4"
Glue the end of the 3" board, then clamp the boards
3.
at a 90° angle with the larger board in the vertical
position, as shown in
Figure 69, and fasten them
together with the wood screws.
Making Auxiliary Fence
An auxiliary fence is necessary if you are resawing a
workpiece that is taller than it is wide. The fence should
be no less than
The fence should be similar to the one in
when installed.
Tools Needed: Qty
Clamps ............................................................2
Drill ...............................................................1
1
Drill Bit
⁄4" .....................................................1
Countersink Drill Bit
Hex Wrench 5mm
..............................................................1
Ruler
Components Needed for Auxiliary Fence:
OPERATIONS
Hex Nuts M6-1
Flat Head Cap Screws M6-1 (length varies)
3
Wood*
⁄4" x 4" x Length of Fence ................ 1
1
⁄2" shorter than the board to be resawn.
Figure 70
............................................1
...............................................1
................................................ 3–6
... 3–6
3
⁄4"
Figure 69. Resaw barrier.
Auxiliary Fence
M6-1 Flat
Head Cap Screw
Assembled
Resaw Barrier
M6-1 Hex Nut
Fence
* Only use furniture-grade plywood, kiln dried hardwood,
or HDPE plastic to prevent warping.
-50-
Assembled Auxiliary Fence
Figure 70. Example illustration of an
auxiliary fence installed.
Page 53

Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
Fence
Auxiliary Fence
M6-1 Flat
Head Cap Screw
M6-1 Hex Nut
To build an auxiliary fence, do these steps:
Remove fence cap from fence face on which you will
1.
mount auxiliary fence (see Figure 71).
Slide (3) M6-1 hex nuts into either the upper or
2.
lower T-slot.
Note: For additional mounting strength, attach
auxiliary board with (6) hex nuts and flat head cap
screws using upper and lower T-slots.
Place auxiliary fence board against fence face.
3.
Place a thin metal shim (such as a ruler) between
table and bottom of auxiliary fence board to ensure
adequate clearance between fence board and table.
Clamp in position.
Measure depth of board plus depth of T-slot, to
4.
determine maximum length of M6-1 flat head cap
screws needed to mount auxiliary fence board to
fence face.
Upper T-SlotFence Cap
Lower T-Slot
Figure 71. Auxiliary fence mounts on
upper or lower T-slots of fence face.
. Measure centerline of fence T-slot and transfer to
5
auxiliary fence board to determine where to drill
holes in board for flat head cap screws.
6. Set auxiliary fence board aside, and using 1⁄4" drill
bit, drill mounting holes in auxiliary fence board.
1
Countersink holes
⁄16" deep so head of cap screw
sits slightly beneath face of auxiliary fence board.
Insert cap screws through holes in auxiliary fence
7.
board (see Figure 72).
Align cap screw threads with hex nuts and tighten
8.
(see Figure 72).
Replace fence cap.
9.
OPERATIONS
x 3
Figure 72. Example auxiliary fence
attached to included fence.
-51-
Page 54

Resawing Operations
The table saw motor is pushed to its limits when
resawing. If the motor starts to bog down, slow down
your feed rate. Motor overloading and blade wear can
be reduced by using a ripping blade. Ripping blades are
designed to clear the sawdust quickly.
Components Needed for Resawing:
Zero-clearance Table Insert ...................................1
Ripping Blade 10"
Clamps
............................................................2
Shop-Made Auxiliary Fence
Shop-Made Resaw Barrier
To perform resawing operations, do these steps:
. DISCONNECT MACHINE FROM POWER!
1
. Remove standard table insert and blade guard
2
assembly.
...............................................1
....................................1
......................................1
Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
You may experience kickback during
this procedure. Stand to the side of the
blade and wear safety glasses and a
full face shield to prevent injury when
resawing.
. Install ripping blade, install riving knife, lower blade
3
below table surface, then install zero-clearance
table insert.
. Attach auxiliary fence and set it to desired width.
4
Note: When determining correct width, don't forget
to account for blade kerf and inaccuracy of fence
scale while auxiliary fence is installed.
OPERATIONS
resaw barrier against workpiece, as shown in Figure
Place workpiece against auxiliary fence and slide
5.
73. Now clamp resaw barrier to top of table saw at
both ends, making sure it is parallel to fence.
Lower blade completely below table-top, and
6.
slide workpiece over blade to make sure it moves
smoothly and fits between resaw barrier and fence.
Raise blade approximately an inch, or close to half
7.
the height of workpiece, whichever is less.
Workpiece
Resaw
Barrier
(Front View)
Auxiliary
Fence
Fence
-52-
Figure 73. Example illustration of a resaw
setup.
Page 55

Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
8. Plug in table saw, turn it ON, and use a push stick or
push block to feed workpiece through blade, using a
slow and steady feed rate.
Note: We recommend making a series of light cuts
that get progressively deeper, to reduce the chance
of stalling the motor.
Flip workpiece end for end, keeping same side
9.
against fence, and run workpiece through blade
again.
Repeat Steps 7–9 until blade is close to half the
10.
height of board to be resawn. The ideal completed
1
resaw cut will leave an
resawing is complete, as shown in
1
Leaving an
⁄8" connection will reduce risk of
⁄8" connection when
Figure 74.
kickback.
Turn OFF table saw, then separate parts of
11.
workpiece and hand plane remaining ridge to remove
it.
When finished resawing, remove resaw barrier and
12.
auxiliary fence, then re-install blade guard/spreader
or riving knife and standard table insert.
The danger of kickback increases
relative to the depth of a cut. Reduce
risk of kickback by making multiple
passes to achieve the desired depth of
cut. Failure to follow these warnings
could result in serious personal injury.
Always use push sticks or push paddles
to increase safety and control during
operations which require that blade
guard and spreader must be removed
from saw. ALWAYS replace blade guard
after resawing is complete.
Workpiece
Auxiliary
Fence
Resaw
Barrier
1
/8" Connection
Fence
OPERATIONS
-53-
Figure 74. Ideal completed resaw
operation.
Page 56

SHOP-MADE SAFETY ACCESSORIES
Featherboards
Easily made from scrap stock, featherboards provide an
added degree of protection against kickback, especially
when used together with push sticks. They also maintain
pressure on the workpiece to keep it against the fence
or table while cutting, which makes the operation easier
and safer because the cut can be completed without the
operator’s hands getting near the blade. The angled ends
and flexibility of the fingers allow the workpiece to move
in only one direction.
Making a Featherboard
This sub-section covers the two basic types of
featherboards: 1) Those secured by clamps, and 2) those
secured with the miter slot.
Material
Hardwood 3⁄4" x 3" x 10" (Minimum) .........................1
Hardwood
Additional Material Needed for Mounting Featherboard:
Hardwood 3⁄8" x (Miter Slot Width) x 5"L ...................1
Wing Nut
Flat Head Screw
Flat Washer
To make a featherboard, do these steps:
OPERATIONS
1. Cut a hardwood board that is approximately 3⁄4"
Needed for Featherboard:
3
⁄4" x 6" x 28" (Maximum) .........................1
1
⁄4"-20 .................................................1
1
⁄4"-20 x 2" ..................................1
1
⁄4"-20 .............................................1
thick to size. The length and width of the board can
vary according to your design. Most featherboards
are 10"–28" long and 3"–6" wide. Make sure wood
grain runs parallel with length of featherboard, so
fingers you will create in
Step 3 will bend without
breaking.
Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
We recommend using a bandsaw
for making fingers in the next step
because it tends to be safer. A table
saw can be used, but it will over-cut
the underside of the ends, produce a
thicker kerf, and require you to stop
the blade half-way through the cut,
which can be dangerous.
10" (Minimum)
30°
3
/8"
A
Initial Cut
2"-3"
3
/8"
B
Kerf
1
/16"-1/8"
2"-3"
Kerf
1
/16"-1/8"
Progressively
Longer Cuts
Figure 75. Patterns for making
featherboards.
IM P O R TANT: Cuts made across grain result
in weak fingers that easily break when
flexed. When made correctly, fingers
should withstand flexing from moderate
pressure. To test finger flexibility, push
firmly on ends with your thumb. If fingers
do not flex, they are likely too thick (cuts
are too far apart).
Cut 30º angle at one end of board.
2.
Make a series of end cuts with the grain 3⁄8"– 1⁄4"
3.
apart and 2"–3" long, as shown in
Figure 75
(A). Alternatively, start cuts at 2"–3" deep, then
make them progressively deeper, as shown in
Figure 75 (B).
Only Steps 1–3 are required to make a
clamp-mounted featherboard. Refer to
Page 55 for instructions on clamping.
-54-
Page 57

Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
4. Rout a 1⁄4"–3⁄8" wide slot 4"–5" long in workpiece and
1"–2" from short end of featherboard (see
Figure
76).
Cut a miter bar approximately 5" long that will fit in
5.
table miter slot, as shown in
Figure 77.
1
/4"-3/8" Slot
1"-2"
Tip: Consider making miter bar longer for larger
featherboards—approximately half the length of
total featherboard—to support force applied to the
featherboard during use.
Drill a 1⁄4" hole in center of bar, then countersink
6.
bottom to fit a
Mark a 4" line through center of countersunk hole in
7.
1
⁄4"-20 flat head screw.
center, then use a jig saw with a narrow blade to cut
it out.
Assemble miter bar and featherboard with a 1⁄4"-20
8.
x flat head screw, flat washer, and a wing nut or
a star knob (see
Figure 78). Congratulations! Your
featherboard is complete.
Note: The routed slot, countersink hole, and flat
head screw are essential for miter bar to clamp into
miter slot. When wing nut is tightened, it will draw
flat head screw upward into countersunk hole. This
will spread sides of miter bar and force them into
walls of miter slot, locking featherboard in place.
Tip: The length of the flat head screw depends on
the thickness of the featherboard—
though 1 1⁄2" to 2"
lengths usually work.
9. Now, proceed to Mounting Featherboard in Miter
Slot on Page 55.
4"-5"
Figure 76. Slot routed in featherboard.
(Top View)
5"
3
/8"
1
/4" Hole
Countersink on Bottom
4" Slot
(Side View)
5"
Figure 77. Miter bar pattern.
Wing Nut
(Side View)
Flat Washer
Featherboard
Miter Bar
Flat Head Screw
Figure 78. Assembling miter slot
featherboard components.
OPERATIONS
-55-
Page 58

Mounting Featherboard w/Clamps
1. Lower saw blade, then adjust fence to desired width
and secure it.
. Place workpiece against fence, making sure it is 1" in
2
front of the blade.
. Place a featherboard on table away from blade so
3
all fingers point forward and contact workpiece (see
Figure 79).
Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
Fence Featherboard
. Secure featherboard to table with a clamp.
4
5. Check featherboard by pushing it with your thumb to
ensure it is secure.
— If featherboard moves, tighten clamp more.
6. Optional: If cutting long workpieces, it may be
beneficial to use another featherboard to keep board
firmly against table while feeding.
Mounting Featherboard in Miter Slot
1. Lower saw blade, then adjust fence to desired width
and secure it.
. Place workpiece evenly against fence, making sure it
2
is 1" in front of blade.
. Slide featherboard miter bar into miter slot, making
3
sure fingers slant toward blade, as shown in Figure
OPERATIONS
80.
Clamp
Clamp
Table
Featherboard
Figure 79. Example of featherboards
secured with clamps.
Blade
Featherboard
. Position fingered edge of featherboard against edge
4
of workpiece, so that all fingers contact workpiece.
Slide featherboard toward blade until first finger is
nearly even with end of workpiece, which should be
1" away from blade.
. Double check workpiece and featherboard to
5
ensure they are properly positioned, as described in
Step 4. Then secure featherboard to table. Check
featherboard by hand to make sure it is tight.
Note: The featherboard should be placed firmly
enough against workpiece to keep it against
fence but not so tight that it is difficult to feed
workpiece.
-56-
Workpiece
Figure 80. Featherboard installed in miter
slot and supporting workpiece for ripping
cut.
The featherboard should be placed
firmly enough against the workpiece
to keep it against the fence but not
so tight that it is difficult to feed the
workpiece.
Page 59

Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
Push Sticks
When used correctly, push sticks reduce the risk of injury
by keeping hands away from the blade while cutting. In
the event of an accident, a push stick can absorb damage
that would have otherwise happened to hands or fingers.
Use push sticks whenever your hands will get within 12"
of the blade. To maintain control when cutting large
workpieces, start the cut by feeding with your hands then
use push sticks to finish the cut, so your hands are not on
the end of the workpiece as it passes through the blade.
Feeding: Place the notched end of the push stick
against the end of the workpiece (see inset
and move the workpiece into the blade with steady
downward and forward pressure.
Supporting: A second push stick can be used to keep the
workpiece firmly against the fence while cutting. When
using a push stick in this manner, only apply pressure
before the blade; otherwise, pushing the workpiece
against or behind the blade will increase the risk of
kickback (see "Push Stick Prohibition Zone" in
Figure 81),
Figure 81).
Push Stick
Prohibition
Zone
Push Stick
Supporting
Blade
Path
Feeding
Store Push
Stick Here
for Easy
Access
Push Stick
Figure 81. Using push sticks to rip narrow
stock.
Figure 82. Side view of push stick in use.
Making a Push Stick
Use this template to make
90º
Cut here to
1
push
Cut here to push 1⁄2" stock
Notch for placing on
corners of workpieces
MATERIAL: Only use hardwood, sturdy plywood, or
high-density plastic. Do not
use softwood that may break
under pressure or metal that
1
⁄2" Grid
can break teeth from the
blade!
your own push stick.
⁄4" stock
Notch to help
prevent hand
from slipping
15
3
/
4
" Minimum Length
SANDING: Sand
edges to remove
rough edges and
increase comfort.
SIZING: Push stick must
be at least 15
1
⁄2"–3⁄4" thick
Use
material.
3
⁄4" long.
OPERATIONS
Figure 83. Template for a basic shop-made push stick (not shown at actual size).
-57-
Page 60

Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
Push Blocks
When used correctly, a push block reduces the risk of
injury by keeping hands away from the blade while
cutting. In the event of an accident, a push block often
takes the damage that would have otherwise happened
to hands or fingers.
A push block can be used in place of or in addition to
a push stick for feeding workpieces into the blade. Due
to their design, push blocks allow the operator to apply
firm downward pressure on the workpiece that could not
otherwise be achieved with a push stick.
The push block design on this page (see
be used in two different ways (see
the bottom of the push block is used until the end of the
workpiece reaches the blade.
The notched end of the push block is then used to push
the workpiece the rest of the way through the cut,
keeping the operator's hands at a safe distance from the
blade. A push stick is often used at the same time in the
other hand to support the workpiece during the cut.
Figure 86) can
Figure 85). Typically,
Push Stick
Prohibition
Zone
Push Stick
Supporting
Blade
Path
Feeding
Push
Block
Figure 84. Using a push block and push
stick to make a rip cut.
Figure 85. Side view of push block in use.
OPERATIONS
Making a Push Block
Use this template to make your own push block.
Notch for use
as a push stick
CAUTION: Only use hardwood, sturdy plywood, or
high-density plastic. Do not use softwood that
may break under pressure or metal that can break
teeth from the blade!
Handle for
firm grip
Make push block with
1
⁄2"–3⁄4" thick material
CAUTION: Bottom
of handle must be
at least 4" above
bottom of push
block to keep
hand away from
blade.
4"
1
⁄4"–1⁄2"
1
⁄2" Grid
Lip for pushing workpiece
9"−10" Minimum Length
Figure 86. Template for a basic shop-made push block (shown at 50% full size).
-58-
Page 61

Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
3
⁄4" Plywood
Completed
Fence
3
⁄4" Hardwood
#8 x 1
1
⁄2"
Wood Screw
Narrow-Rip Auxiliary
Fence & Push Block
There are designs for hundreds of specialty jigs that can
be found in books, trade magazines, and on the internet.
These types of jigs can greatly improve the safety and
consistency of cuts. They are particularly useful during
production runs when dozens or hundreds of the same
type of cut need to be made. The narrow-rip auxiliary
fence and push block system shown in this section is an
example of a specialty jig that can be made to increase
the safety of very narrow rip cuts.
Material
Block
Hardwood
Plywood
Wood Screws #8 x 1
Needed for Narrow Rip Auxiliary Fence & Push
3
⁄4" x 3" x Length of Fence .......................1
3
⁄4" x 5 1⁄4" x Length of Fence ......................1
1
⁄2" ........................................8
3
Length of Table
Saw Rip Fence
⁄4" Hardwood
3
⁄4" Plywood
3"
Length of Table
Saw Rip Fence
1
⁄4"
5
Figure 87. Auxiliary fence dimension.
Material
Hardwood or Plywood 3⁄4" x 15" x 5 5⁄8" .....................1
Hardwood or Plywood
Cyanoacrylate Wood Glue
Wood Screws #8 x 1 1⁄2" ............................ As Needed
Making a Narrow-Rip Push Block for an
Auxiliary Fence
1. Cut a piece of 3⁄4" thick plywood 5 1⁄4" wide and as
Note: We recommend cutting the hardwood board
2.
3.
Needed for Push Block
3
⁄4" x 10" x 5"–9" ....................1
...............................Varies
3
long as your table saw fence; cut a piece of
⁄4"
thick hardwood 3" wide and as long as your table
saw fence, as shown in
Figure 87.
oversize, then jointing and planing it to the correct
size to make sure the board is square and flat. Only
use furniture-grade plywood or kiln dried hardwood
to prevent warping.
Pre-drill and countersink eight pilot holes 3⁄8"
from bottom of 3" wide board, then secure boards
together with (8) #8 x 1 1⁄2" wood screws, as shown
Figure 88.
in
Using 3⁄4" material you used in previous steps, cut
out pieces for push block per the dimensions shown
Figure 89; for handle, cut a piece 10" long by
in
5"–9" high and shape it as desired to fit your hand.
Figure 88. Location of pilot holes.
5
5
⁄8"
15"
1
⁄2"
3
⁄8"
1
⁄4"
5
1
12
⁄2"
2
3
⁄8"
3
⁄8"
Handle
Lip
1
⁄2"
2
Figure 89. Push block dimensions and
construction.
OPERATIONS
. Attach handle to base with #8 x 11⁄2" wood screws,
4
and attach lip to base with cyanoacrylate-type wood
glue.
-59-
Page 62

Using Auxiliary Fence and Push Block
1. Place auxiliary fence on table and clamp it to
fence at both ends, then adjust distance between
auxiliary fence and blade—this determines how wide
workpiece will be ripped (see
. Install blade guard, then remove right spreader
2
pawl, as explained on Page 37, so it does not
interfere with push block lip.
. Place workpiece 1" behind blade and evenly against
3
table and auxiliary fence (see Figure 91).
Figure 90).
Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
Auxilliary Fence
Blade
Workpiece
Cutting
Width
Figure 90. Adjusting ripping distance
between blade and auxiliary fence.
Auxilliary Fence
Keep blade guard installed and in down position.
Failure to do this could result in serious personal
injury or death.
4. Turn saw ON, then begin ripping workpiece using a
push stick for side support.
. As workpiece nears end of cut, place push block on
5
auxiliary fence with lip directly behind workpiece,
OPERATIONS
then release push stick just before blade.
Guide workpiece rest of the way through cut with
6.
push block, as shown in Figure 92.
. Re-install right spreader pawl when finished using
7
auxiliary fence and push block.
Turn OFF saw and allow blade to come to a complete
stop before removing cut-off piece. Failure to follow
this warning could result in serious personal injury.
Blade
Push Stick
for Side
Support
Push
Block
Workpiece
Blade Path
Figure 91. Push block in position to push
workpiece through blade.
Release
Push Stick
Before Blade
-60-
Figure 92. Ripping with push block.
Page 63

Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
Outfeed & Support Tables
One of the best accessories for improving the safety and
ease of using a table saw is simply placing a large table
(outfeed table) behind the saw to catch the workpiece
Figure 93). Additionally, another table to the left
(see
of the saw (support table) can also help support large
workpieces so they can be cut safely and accurately.
Crosscut Sled
A crosscut sled (see Figure 94) is a fantastic way to
improve the safety and accuracy of crosscutting on the
table saw. Most expert table saw operators use a crosscut
sled when they have to crosscut a large volume of work,
because the sled offers substantial protection against
kickback when crosscutting.
Support
Table
Figure 93. Example of support and
outfeed tables.
Outfeed
Table
OPERATIONS
-61-
Crosscut
Sled
Figure 94. Example of a crosscut sled.
Page 64

Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
ACCESSORIES
Table Saw Accessories
The following table saw accessories may be available through your local Woodstock International Inc.
Dealer. If you do not have a dealer in your area, these products are also available through online
dealers. Please call or e-mail Woodstock International Inc. Customer Service to get a current listing of
dealers at: 1-800-840-8420 or at sales@woodstockint.com.
D2271—Shop Fox Roller Table
Use this versatile roller table wherever you need extra workpiece
support. Features all-steel welded construction and measures 19" x
65". Comes with 9 ball bearing rollers and has four independently
adjustable legs for any leveling requirement. Adjustable in height from
6 3⁄8" to 4 1⁄8". 1,000 lb. capacity!
W1727—1 HP Dust Collector
Specifications: • 1 HP, 120V/240V, single-phase motor • 800 CFM air
suction capacity • 5.67" static pressure • One 4" intake hole • 9"
balanced steel, radial fin impeller • 2.1 cubic feet bag capacity • 15 3⁄4"
x 39 3⁄4" base on casters for portability • 2.5 micron bag filtration •
Power-coated finish for durability • 54 1⁄2" height with bag inflated.
OPERATIONS
W1500 —Right Angle Jig
This jig is constructed using top quality aluminum castings and
plates which are machined to exacting tolerances. It has the perfect
weight-use ratio to dampen vibration, yet is still light enough to
easily slide the workpiece through the machining process. Its quality
and precision are evident from the first cut. Cut tenons, dadoes, rail
ends, and finger joints safely and with complete accuracy.
D3246—Tenoning Jig
This jig can help you produce perfect tenons for mortise and tenon
joinery. This tenoning jig also adjusts for angled tenon cutting set-ups.
Standard
3
/8" x 3/4" miter bar fits all miter gauge slots including T-slots.
-62-
Page 65

Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
MAINTENANCE
General
For optimum performance from your machine, follow
this maintenance schedule and refer to any specific
instructions given in this section.
Daily Check:
• Inspect blades for damage or wear.
Check for loose mounting bolts/arbor nut.
•
Check cords, plugs, and switch for damage.
•
• Check for the proper function of the blade guard
(see Blade Guard Assembly on Page 35).
Check for any other condition that could hamper the
•
safe operation of this machine.
• Wipe the table clean after every use—this ensures
moisture from wood dust does not remain on bare
metal surfaces.
MAKE SURE that your machine is
unplugged during all maintenance
procedures! If this warning is ignored,
serious personal injury may occur.
Weekly Maintenance:
• Wipe down the table surface and grooves with a
lubricant and rust preventive such as SLIPIT®.
• Vacuum dust buildup from the motor housing and
trunnions.
• Clean the pitch and resin from the saw blade with a
cleaner like OxiSolv® Blade & Bit Cleaner.
Monthly Maintenance:
• Check/tighten the belt tension (Page 77).
Every 6–12 Months:
• Lubricate trunnion slides (Page 64).
• Lubricate worm gear (Page 64).
• Lubricate leadscrew (Page 64).
Cleaning & Protecting
Cleaning the Model W1837 is relatively easy. Vacuum excess
wood chips and sawdust, and wipe off the remaining dust
with a dry cloth. If any resin has built up, use a resindissolving cleaner to remove it.
MAINTENANCE
Protect the unpainted cast iron table by wiping it clean
after every use—this ensures moisture from wood dust does
not remain on bare metal surfaces. Keep your table r u s tfree with regular applications of quality lubricants.
-63-
Page 66

Lubrication
It is essential to clean components before lubricating
them because dust and chips build up on lubricated
components and make them hard to move. Simply adding
more grease to them will not yield smooth moving
components.
Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
Clean the components in this section with mineral spirits
or other oil/grease solvent cleaner and shop rags.
If you thoroughly clean the components in this section
before lubricating them, the result will be silky smooth
movement when turning the handwheels, which will result
in much higher enjoyment on your part!
The following are the main components that need to be
lubricated:
• Trunnion Slides and Orientation Gears
• Worm Gears, Trunnion, and Bearing Housing Teeth
Trunnion Slides
Clean out the front and rear trunnion slides with mineral
spirits and a rag, then apply lithium grease into each
groove. Move the blade tilt back-and-forth to spread the
grease (see
Figure 95).
Worm Gear, Bull Gear, Leadscrew
Clean away any built up grime and debris from the
worm gear, bull gear, and leadscrew (see
with a wire brush, rags, and mineral spirits. Allow the
components to dry, then apply a thin coat of white
lithium grease.
Figures 96–97)
Front
Trunnion
Slide
Figure 95. Trunnion slide (only front slide
shown).
Bull Gear
Worm Gear
Figure 96. Location of the bull and worm
gears.
Leadscrew
MAINTENANCE
Figure 97. Location of the leadscrew.
-64-
Page 67

Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
This section covers the most common service adjustments
or procedures that may need to be made during the life
of your machine.
If you require additional machine service not included
in this section, please contact Woodstock International
Technical Support at (360) 734-3482 or send e-mail to:
techsupport@woodstockint.com.
SERVICE
General
Blade Tilt Calibration
The blade tilt settings for this saw have been set at
the factory and should not require adjustment during
assembly. However, after prolonged use, or if the saw
does not cut accurate bevels, the settings should be
checked and adjusted accordingly.
Note: The tilt scale reads "0" when the blade is 90° to the
table.
Tools Needed Qty
90° Square .......................................................1
45° Square
Hex Wrench 4mm
Setting 90° Stop
1. DISCONNECT MACHINE FROM POWER!
Raise blade as high as it will go, then tilt it toward
2.
90° until it stops and cannot be tilted any more.
3.
Place a 90° square against table and blade so it
contacts blade evenly from bottom to top, as shown
in
obstruct placement of square.
— If blade is 90° to table, then no adjustments are
— If blade is not 90° to table, you will need to adjust
.......................................................1
...............................................1
Figure 98. Make sure a blade tooth does not
necessary. Make sure tilt indicator arrow shown in
Figure 99 points to 0° mark on scale. Adjust position by loosening Phillips head screws, moving indicator with your fingers, then tightening screws.
90° stop nuts. Proceed to
Step 4.
-65-
MAKE SURE that your machine is
unplugged during all service procedures! If this warning is ignored, serious personal injury may occur.
Blade
Table
Figure 98. Checking blade at 90°.
Figure 99. Tilt indicator arrow location.
90° Square
SERVICE
Page 68

4. Remove motor cover.
Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
5. Loosen (2) M8-1.25 hex nuts on leadscrew (see Figure
100).
6. Tilt blade to about 5° so there is room for stop nuts
to move.
Loosen stop nuts and adjust according to how far
7.
off blade was from 90°. Recheck blade and repeat
adjustment as necessary until blade stops at 90°,
then tighten stop nuts against each other and
replace motor cover.
Note: Turning stop nuts clockwise adjusts blade fur-
ther to right; turning them counterclockwise adjusts
blade to left.
Setting 45° Stop
1. DISCONNECT MACHINE FROM POWER!
2. Raise blade as high as it will go, then tilt it towards
45° until it stops and cannot be tilted any more.
Leadscrew
x 2
Figure 100. Location of 90° stop nuts.
3. Place a 45° square against table and blade so it
contacts blade evenly from bottom to top, as shown
Figure 101. Make sure a blade tooth does not
in
obstruct placement of square.
— If blade is 45° to table, then no adjustments need
to be made. Proceed to
— If blade is not 45° to table, you will need to adjust
45° limiting block. Proceed to
Remove rear access panel.
4.
5.
Loosen (2) M5-.8 x 10 cap screws in 45° limiting
block (see Figure 102).
Tilt blade away from 45° by about 5°, so there is
6.
room for limiting block to move.
Adjust 45° limiting block according to how far off
7.
blade was from 45°, then recheck blade and repeat
SERVICE
adjustment as necessary until blade stops at 45°, then
tighten cap screws and replace rear access panel.
Step 8.
Step 4.
45° Square
Blade
Table
Figure 101. Checking blade at 45°.
x 2
45° Limiting
Block
. Make sure tilt indicator arrow points to 45° mark on
8
scale. If it doesn't, adjust indicator arrow as described
Page 65.
on
-66-
Figure 102. Location of 45° limiting block.
Page 69

Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
Miter Slot to Blade
Parallelism
Your table saw will give the best results if the miter slot
and the rip fence are adjusted parallel to the blade. If
either of these are not exactly parallel, your cuts and your
finished work will be lower in quality, but more importantly, the risk of kickback will be increased.
Tools Needed Qty
Adjustable Square ..............................................1
Marker
Metal Shim Stock
Open-End Wrench 12mm.......................................1
To adjust blade parallel to miter slot, do these steps:
1. DISCONNECT MACHINE FROM POWER!
2.
............................................................1
.................................... As Needed
Tilt blade to 0°, then use an adjustable square to
measure distance from miter slot to a carbide tip on
blade, as shown in Figure 103. Make sure that face of
adjustable square is even along miter slot.
STEP A
Blade tilted to 90º
3. With end of adjustable square just touching tip, lock
square in place. Now, mark carbide tip with a marker
where you made this measurement.
4. Rotate marked blade tip to other end of table insert.
5.
Slide adjustable square down to other end of table
insert and compare distance from marked blade tip
to end of adjustable square, as shown in
—If blade tip measurement is same on both sides, go
Step 8.
to
If blade tip does not touch end of adjustable square
—
similar to first measurement, table will need to be
adjusted. Proceed to
Step 6.
Figure 104.
Front
A
Figure 103. Making first slot-to-blade
measurement at 90°.
STEP B
Blade tilted to 90º
SERVICE
Front
B
-67-
Figure 104. Making second slot-to-blade
measurement at 90°.
Page 70

6. Loosen (4) table mounting bolts securing table top
to base (see
direction needed to square table to blade.
7. Repeat Steps 2–6 until blade and miter slot are
parallel, then retighten table mounting bolts.
8. Tilt blade to 45° and recheck miter slot-to-blade
parallelism.
— If blade is still parallel with miter slot, no additional
adjustments need to be made.
If blade was parallel with miter slot at 0° but not
—
at 45°, one end of table will need to be shimmed
higher with metal shim stock. Continue to
Loosen (4) table mounting bolts from Step 6.
9.
Figure 105), and lightly tap table in
Step 9.
Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
Mounting
Bolts
Figure 105. Location of table mounting
bolts (table omitted for clarity).
10
. Refer to Figures 106–107 for shim placement. If
distance A is shorter than B, shim(s) will need to be
placed under corners #1 and #2. If the distance of B is
shorter than A, shim(s) will need to be placed under
corner #3. Very thin shim stock works well.
11. Tighten one table mounting bolt a small amount and
then repeat with the others, tightening each down
the same amount. Continue this process with all the
bolts, tightening them a little each time until they
are all secure.
Now recheck blade to miter slot at 0° and 45° by
12.
repeating
— If distance of A and B are equal, continue to Step
13.
— If distances are still off, repeat Steps 9–12.
Once miter slot is adjusted to blade, recheck all
13.
measurements and be sure table mounting bolts are
secure.
Steps 2-5.
STEP A
Blade tilted to 45°
#1
Front
#3
#2
Figure 106. Shim procedure diagram A.
STEP B
Blade tilted to 45°
#1
Note: If you remove the table in the future, note the
shim placements and reassemble them exactly how
they came apart.
SERVICE
-68-
Front
#3
#2
Figure 107. Shim procedure diagram B.
Page 71

Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
Table
Riving
Knife
Top Alignment
Bottom Alignment
Spreader or Riving Knife
Alignment
Checking Alignment
The blade guard spreader/riving knife must be aligned
with the blade when installed. If the spreader/riving knife
is not aligned with the blade, then the workpiece will be
forced sideways during the cut, which will increase the
risk of kickback.
Tools Needed Qty
Straightedge (min. 12") ........................................1
To check spreader/riving knife alignment, do these
steps:
. DISCONNECT MACHINE FROM POWER!
1
. Raise saw blade to maximum height so you have easy
2
working access.
. Place straightedge against top and bottom of blade
3
and spreader/riving knife, as shown in Figure 108.
Spreader/riving knife should be parallel with blade
at both positions and in the "Alignment Zone," as
shown in
— If spreader is in alignment zone no adjustments
need to be made.
— If spreader/riving knife is not parallel with blade and
inside alignment zone, then it needs to be adjusted.
Proceed to Adjusting
— If spreader/riving knife is not parallel with blade
at either top or bottom, it may be bent.
spreader/riving knife, place it on a flat surface and
check to see if spreader/riving knife lies evenly
along its length.
— If spreader/riving knife does not lie evenly, pro-
ceed to
procedure.
Figure 109.
Alignment instructions.
Remove
Adjusting Bent Spreader/Riving Knife
Figure 108. Example of checking top and
bottom riving knife parallelism with blade.
Alignment
Zone
Spreader or
Riving Knife
Blade
SERVICE
Figure 109. Spreader/riving knife
alignment zone.
-69-
Page 72

Adjusting Alignment
The spreader/riving knife mounting position can be
adjusted into alignment with the blade using the cap
screws on the spreader/riving knife "L" bracket.
Possible Tools Needed Qty
Hex Wrench 4mm ...............................................1
To adjust spreader/riving knife position, do these steps:
DISCONNECT MACHINE FROM POWER!
1.
Remove table insert, but leave Phillips head screws
2.
mounted in table throat.
Note: Table insert is held in place by a magnet.
. Loosen two cap screws on the "L" bracket (see
3
Figure 110), then slide spreader/riving knife as
needed to move it into alignment with blade.
Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
4
. Follow Checking Alignment, Steps 1–3 on Page 69.
— If spreader/riving knife is in alignment zone, no
additional steps are necessary.
— If spreader/riving knife is still not in alignment
zone, continue adjusting position of "L" bracket as
necessary to correctly align spreader/riving knife.
Tighten two cap screws on mounting block to secure
5.
spreader/riving knife adjustment.
. Replace table insert (refer to Page 75).
6
Adjusting Bent Spreader/Riving Knife
1. DISCONNECT MACHINE FROM POWER!
. Bend spreader/riving knife by hand while installed,
2
then follow
determine if it is parallel with blade and inside
"Alignment Zone" (refer to
Page 69).
Steps 1–3 in Checking Alignment to
Checking Alignment on
"L" Bracket
Cap
Screws
Figure 110. Cap screws for adjusting
spreader/riving knife position.
— If this does not work, remove spreader/riving knife
SERVICE
to straighten.
— If you cannot straighten spreader/riving knife prop-
erly, replace it.
-70-
Page 73

Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
Adjusting Fence
There are three main adjustments for the fence: (1)
square, (2) height, and (3) clamping pressure. Keep in
mind that these adjustments are interconnected and some
trial-and-error may be needed to achieve satisfactory
results.
Tools Needed Qty
Wrench 19mm ...................................................1
Hex Wrench 6mm
Machinist's Square
...............................................1
..............................................1
Fence Squareness and Height
The fence face must be square to the table in order
to produce accurate cuts. The fence is adjustable with
two set screws where the fence slot sits in the front rail
(see Figure 111).
Also, the fence should be adjusted evenly above the table
to ensure it does not drag across the surface, as shown in
Figure 112 .
To check/adjust fence squareness and height to table,
do these steps:
DISCONNECT MACHINE FROM POWER!
1.
Place square on table against face of fence (see
2.
Figure 113) to check if fence is square to table.
— If fence is not square to table, proceed to Step 3.
— If fence is square to table, skip to Step 4.
Knurled Lock Nuts
and Set Screws
Figure
screws for adjusting fence squareness and
Front Set
111. Location of lock nuts and set
height.
1
/16" Gap
Screws
(1 of 2)
(Side View)
Table
Rear
Bearing
Shaft
Fence
3.
Loosen knurled lock nuts and adjust set screws (see
Figure 111) on top of fence bracket to ensure fence
face is 90° to table. Tighten lock nuts when fence is
square to table.
-71-
Figure 112. Fence height is adjusted by
two front set screws and rear bearing
shaft.
SERVICE
90° Square
Fence
Table
Figure 113. Example of checking fence
squareness to table.
Page 74

Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
4. Measure gap between fence and table top at front
and rear of fence.
— If gap is approximately 1⁄16" and even from front of
table to back (see
Figure 114), then no additional
adjustments are necessary. Proceed to Fence
Handle
If gap is uneven, or if fence height is not
—
approximately
with Step
5.
Remove fence assembly and lay it upside down.
Clamping Pressure below.
1
⁄16" above table, then continue
5.
6. Remove fence assembly cap as shown in Figure 115,
then loosen inner and outer jam nuts that secure
bearing shaft.
Note: Wrench clearance for inner jam nut is tight
inside fence assembly. If necessary, hold inner jam
nut with wrench and twist bearing shaft to loosen.
1
/16" Gap
(Side View)
Fence
Table
Figure 114. Example of even gap between
1
fence and table approximately
⁄16" front
to back.
Assembly Cap
Bearing Shaft
Roller
Bearing
Re-install fence assembly.
7.
8. Reach inside fence and adjust height of bearing
shaft. Turn shaft clockwise to decrease shaft height;
turn shaft counterclockwise to raise shaft height.
9. When satisfied with position of bearing shaft,
remove fence and tighten inner and outer jam nuts.
Keep roller bearing parallel with rear fence rail.
Re-install fence. Repeat Steps 4–9 until gap between
10.
table and fence is approximately
1
⁄16" and even from
front to back of table.
Fence Handle Clamping Pressure
1. Remove fence and lay it upside down.
2. Loosen knurled lock nut (see Figure 116).
Adjust set screw clockwise to increase clamping
3.
pressure of lock handle or counterclockwise to
decrease clamping pressure.
SERVICE
Tighten knurled lock nut.
4.
Outer
Jam Nut
Figure 115. Rear adjustment area for
leveling fence.
Knurled Lock
Nut and Set
Screw
5. Re-install fence and check clamping pressure of lock
handle.
Repeat Steps 1–5 as necessary until satisfied.
6.
-72-
Figure 116. Set screw for adjusting fence
handle clamping pressure.
Page 75

Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
Calibrating Fence to
Blade
Two set screws at the front of the fence position it
parallel with the blade (see
procedures below to check the fence/blade parallelism
and adjust the fence if necessary. Perform this step only
after Adjusting Fence on Page 66.
Tools Needed Qty
Hex Wrench 4mm ...............................................1
Framing Square 24"
To check and adjust fence parallelism, do these steps:
.............................................1
Figure 117). Follow the
Fence
Adjustment
Set Screws
1. DISCONNECT MACHINE FROM POWER!
Slide fence against right edge of miter slot, lock it in
2.
place, then raise blade fully. Using a ruler, examine
how fence lines up with miter slot and blade (see
Figure 118).
— If fence is parallel with blade, no further
adjustments need to be made.
— If fence is not parallel with blade, proceed to
Step 3.
Remove fence assembly from front rail.
3.
4. Adjust two set screws on front of fence, as shown
Figure 117. Each set screw adjustment affects
in
opposite side of fence.
Re-install fence assembly and measure parellism
5.
with blade. Repeat Step 4 as needed.
Figure 117. Location of set screws to
adjust fence parallelism (shown upside
down).
Fence
Miter Slot
Blade
Figure 118. Checking fence parallelism
Fence is
Parallel to
Miter Slot,
which is
Parallel to
Blade
with blade.
Offsetting Fence
Some woodworkers prefer to offset the rear of the fence
1
/64" from the blade, as shown in Figure 119.
The reason for this wider gap at the back side of the
blade is to help prevent the chance of kickback and the
blade burning the workpiece because a workpiece may be
inconsistent. H owe v e r, t h e trade-off is less accurate cuts,
and if the fence is placed on the other side of the blade
for other table saw operations, the potential of workpiece
burning and kickback can be increased. Whenever using
a fence, make sure that if an offset has been adjusted in
the fence alignment, you use the fence on the side of the
blade where the offset creates the wide gap.
-73-
X = Your Measurement
1
/64"
X" +
X"
Extra Space
to Prevent Binding
Figure 119. Example of adjusting fence
with a
1
⁄64" offset.
SERVICE
Page 76

Fence Scale Calibration
The fence scale windows, shown in Figure 120, can be
calibrated with the fence scale by loosening the mounting
screws and sliding them in the desired direction.
The indicator window on the right side is used when the
fence is positioned to the right side of the blade. The
indicator window on the left is used when the fence is
positioned on the left side of the blade.
IM P O R TANT: Do not use the fence on the left side of the
blade if it has been purposely offset, and is not adjusted
parallel with the blade.
Tools Needed Qty
Phillips Head Screwdriver #2 ..................................1
Scrap Piece of Wood
To calibrate fence scale indicator windows, do these
steps:
............................................1
Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
Left Indicator
Window
Figure 120. Fence indicator windows.
Right Indicator
Window
Lock fence at 13" and cut your scrap piece of wood.
1.
. Reposition and lock fence at 12", as indicated by the
2
scale.
. Flip over your scrap piece of wood, placing side that
3
was cut in
. Measure width of freshly cut workpiece at both ends
4
with a tape measure. Workpiece width should be
exactly 12" at front and back. If it is not, then adjust
indicator window to match width of workpiece.
Step 1 against fence, then make your cut.
SERVICE
-74-
Page 77

Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
Table/Dado Insert
Adjustment
The table/dado insert must sit perfectly flush with the
table to provide a smooth, continuous surface for the
workpiece to slide over. The insert is held in place by a
magnet and sits on top of five adjustment screws (see
Figure 121). The insert should be checked and adjusted
any time it is removed and replaced, after prolonged
use, or any time you notice the workpiece does not slide
smoothly across the insert.
Tools Needed Qty
Phillips Head Screwdriver #2 ..................................1
Straight Edge
To check and adjust insert, do these steps:
1. DISCONNECT MACHINE FROM POWER!
....................................................1
Figure 121. Location of table/dado insert
holes with adjustment screws.
2. Place straightedge across insert and check to make
sure insert is flush with table at front and back of
throat.
— If insert is flush with table, no adjustments are nec-
essary.
— If insert is not flush with table, proceed to Step 3.
. Insert screwdriver through holes shown in Figure 121
3
and either loosen screws to raise insert, or tighten
screws to lower it. Repeat Steps 2–3 until insert is
perfectly flush with surface of table.
SERVICE
-75-
Page 78

Miter Gauge Adjustments
The miter gauge is equipped with stop screws that allow
you to easily adjust the miter gauge 0°– 30° left, 90°, and
0°–45° right. The stop screws contact the shaft, which
moves in or out of the way for adjustments.
Tools Needed Qty
Phillips Head Screwdriver .....................................1
90° Square
45° Square
30° Square
Wrench 8mm
Checking/Setting 90° Stops
1. DISCONNECT MACHINE FROM POWER!
.......................................................1
.......................................................1
.......................................................1
.....................................................1
Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
2. Slide miter gauge into T-slot on table.
3. Place square evenly against face of miter gauge and
blade, as shown in Figure 122.
— If square touches miter body and body of blade
evenly at same time, then it is square to blade. No
adjustments are necessary.
— If square does not touch miter body and blade
evenly, then proceed to
Remove miter gauge from miter slot.
4.
5. Loosen two Phillips head screws that secure 90° stop
plate (see
Using a square, position miter shaft at 90° to miter
6.
gauge body.
Tighten stop plate screws, then repeat Step 3.
7.
Figure 123).
Step 5.
Checking/Setting 45° Stops
Follow the same process with the 45° and 30° stops that
you followed with the 90°, except using a 45° square or
adjustable square to verify that the miter body is 45° to
the blade.
Square
Blade
Miter Gauge
Figure 122. Checking 90° stop on miter
gauge.
Miter Gauge
Shaft
Adjustment
Stop Plate
Figure 123. Checking 45° stop on miter
gauge.
Screws
SERVICE
-76-
Page 79

Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
Belt Tension &
Replacement
The drive belt stretches slightly as the saw is used. Most
stretching will happen during the first 16 hours of use,
but it may slightly continue with further use. If you notice
that the saw is losing power in the middle of a cut, the
belt may be slipping and will need to be tensioned.
If, upon inspection, you find that the belt is cracked,
frayed, or shows other signs of excessive wear or other
damage, replace it immediately to ensure proper power
transmission from the motor to the blade.
Tools Needed Qty
Open-End or Socket Wrench 13mm ..........................1
Tensioning Belt
1. DISCONNECT SAW FROM POWER!
2. Remove motor cover from side of machine.
3. Set blade to 0° on tilt scale, then raise or lower
blade to approximately 2" above table.
Loosen blade tension hex bolt shown in Figure 124.
4.
5.
Use blade height handwheel to lower motor. When
motor starts to pull blade down with it, belt is
tensioned.
. Retighten blade tension hex bolt, then re-install
6
motor cover.
Replacing Belt
1. DISCONNECT MACHINE FROM POWER!
Remove motor cover from side of machine.
2.
3. Set blade to 0° on tilt scale, then raise or lower
blade to approximately 2" above table.
Loosen blade tension hex bolt, shown in Figure 124.
4.
Blade Tension
Hex Bolt
Motor
Belt
Figure 124. Components used to tension
or remove belt.
SERVICE
. Use blade height handwheel to raise motor and
5
loosen belt, then remove belt.
Install new belt onto pulleys. Lower motor until it
6.
begins to pull blade down with it, then retighten
blade tension hex bolt.
Re-install motor cover.
7.
-77-
Page 80

Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
The following troubleshooting tables cover common problems that may occur with this machine. If you
need replacement parts or additional troubleshooting help, contact our Technical Support.
Note:
available, your original purchase receipt. This information is required to properly assist you.
Troubleshooting
Before contacting Tech Support, find the machine serial number and manufacture date, and if
Motor & Electrical
PROBLEM POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTIVE ACTION
Machine does not
start or a breaker
trips.
Machine stalls or
is underpowered.
Machine has
vibration or noisy
operation.
1. Switch disabling key not installed.
2. Wall circuit breaker tripped or fuse blown.
3. Power supply switched OFF or at fault.
4. Plug/receptacle at fault/wired wrong.
5. Motor wired incorrectly.
6. Wiring open/has high resistance.
7. Motor ON/OFF switch at fault.
8. Start capacitor at fault.
9. Motor at fault.
1. Feed rate/cutting speed too fast.
2. Workpiece material unsuitable for machine.
3. Workpiece crooked; fence mis-adjusted.
4. Machine undersized for task; wrong blade.
5. Run capacitor at fault.
6. Belt slipping.
7. Motor wired incorrectly for voltage.
8. Plug/receptacle at fault.
9. Pulley slipping on shaft.
10. Motor bearings at fault.
11. Motor overheated.
12. Motor at fault.
1. Blade at fault.
2. Belt worn or loose.
3. Pulley loose.
4. Motor mount loose/broken.
5. Motor fan cover dented.
6. Arbor bearings at fault.
7. Motor bearings at fault.
1. Insert switch disabling key into ON/OFF switch.
2. Ensure circuit size is correct; replace weak breaker
or blown fuse.
3. Ensure power supply is on/has correct voltage.
4. Test for good contacts; correct the wiring.
5. Correct motor wiring connections.
6. Check/fix broken, disconnected, or corroded wires.
7. Replace switch.
8. Test/replace if faulty.
9. Test/repair/replace.
1. Decrease feed rate/cutting speed.
2. Only cut wood; ensure moisture is below 20%.
3. Straighten or replace workpiece; adjust fence.
4. Use correct blade; reduce feed rate or depth of
cut.
5. Test/repair/replace.
6. Tension/replace belt (Page 77).
7. Wire motor correctly for power supply voltage.
8. Test for good contacts/correct wiring.
9. Secure loose pulley; replace if damaged.
10. Test/repair/replace.
11. Clean motor, let cool, and reduce workload.
12. Test/repair/replace.
1. Replace warped/bent blade; resharpen dull blade.
2. Tension/replace belt (Page 77).
3. Realign/replace shaft, pulley, set screw, and key.
4. Tighten/replace.
5. Fix dent; re-adjust position of fan cover.
6. Replace arbor housing bearings; replace arbor.
7. Test by rotating shaft; grinding/loose shaft requires
bearing replacement.
SERVICE
-78-
Page 81

Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
PROBLEM POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTIVE ACTION
Rip fence
does not move
smoothly.
Material moves
away from fence
when ripping.
1. Rip fence or rails mounted incorrectly.
2. Rails dirty or sticky.
3. Clamp screw is out of adjustment.
1. Rip fence misaligned. 1. Check and adjust rip fence.
1. Remount rip fence or rails.
2. Clean rails.
3. Adjust clamp screw.
Blade is not
aligned with
miter slot or
fence.
Blade does not
r e a c h 9 0 °.
Blade hits insert
at 45°, or blade
too close to
insert.
Board binds or
burns when feeding through saw.
Handwheel binds
or is difficult to
move.
Blade will not go
beneath table
sur face.
Blade will not
move up or down.
1. Blade is warped.
2. Table top is not parallel with blade.
3. Fence is not parallel with blade.
1. 90° stop nuts are out of adjustment.
2. Sawdust or debris stuck in trunnion slides or
on stop nuts.
1. 45° limiting block is out of adjustment.
2. Slot in table insert is too small.
3. Table out of alignment/adjustment with
blade.
4. Blade position on arbor is incorrect.
1. Dull blade.
2. Blade is warped.
3. Fence is not parallel with blade.
4. Table top is not parallel with blade.
1. Lock knob is engaged.
2. Handwheel shaft pins are wedged.
1. Roll pin/set screw in worm gear contacting
geared trunnion.
2. Debris lodged between trunnion castings.
1. Set screw on worm gear is loose or missing. 1. Tighten or replace set screw.
1. Replace blade (Page 34).
2. Adjust table parallel with blade (Page 67).
3. Adjust fence parallel with blade (Page 73).
1. Adjust 90° stop nuts (Page 65).
2. Clean sawdust or debris out of trunnion slides or off
stop nuts.
1. Adjust 45° limiting block (Page 66).
2. File/mill slot in table insert; use dedicated zero
clearance for 45° cuts.
3. Align table to the blade (Page 67).
4. Verify that blade arbor washers are correct and in
the required position.
1. Replace blade (Page 34).
2. Replace blade (Page 34).
3. Adjust fence parallel with blade (Page 73).
4. Adjust table parallel with blade (Page 67).
1. Loosen lock knob.
2. Remove handwheel and adjust shaft pins.
1. Tighten roll pins and set screws in the worm gear.
2. Remove debris.
Too much sawdust blown back
toward operator.
Workpiece catches on table insert
when cutting.
1. Blade guard has been removed.
2. Too many air leaks in cabinet for proper dust
collection.
3. Dust collection system clogged or airflow CFM
is insufficient; too weak.
4. Fence not parallel with blade (pressure at
blade backside).
5. Miter slot/fence not parallel with blade at
90°.
1. Table/dado insert out of adjustment. 1. Adjust table/dado insert so it is perfectly flush with
1. Re-install blade guard for maximum safety and dust
control.
2. Seal leaks in cabinet or around dust chute.
3. Remove clog; revise ducting layout for improved
suction; use a stronger dust collector.
4. Adjust fence parallel with blade (Page 73).
5. Adjust table so miter slot is parallel with blade at
90° (Page 67).
table surface (Page 75).
-79-
SERVICE
Page 82

Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
These pages are current at the time of printing. However, in the spirit of improvement, we may make
changes to the electrical systems of future machines. Compare the manufacture date of your machine to
If there are differences between your machine and what is shown in this section, call Technical Support
for assistance BEFORE making any changes to the wiring on your machine. An updated
machine before calling. This information can be found on the main machine label.
Electrical Safety Instructions
the one stated in this manual, and study this section carefully.
at (360) 734-3482
wiring diagram may be available. Note: Please gather the serial number and manufacture date of your
SHOCK HAZARD. Working on wiring that is
connected to a power source is extremely
dangerous. Touching electrified parts will
result in personal injury including but not
limited to severe burns, electrocution,
or death. Disconnect the power from
the machine before servicing electrical
components!
QUALIFIED ELECTRICIAN. Due to the inherent
hazards of electricity, only a qualified
electrician should perform wiring tasks on
this machine. If you are not a qualified
electrician, get help from one before
attempting any kind of wiring job.
WIRE CONNECTIONS. All connections must
be tight to prevent wires from loosening
during machine operation. Double-check all
wires disconnected or connected during any
wiring task to ensure tight connections.
WIRE/COMPONENT DAMAGE. Damaged wires
or components increase the risk of serious
personal injury, fire, or machine damage. If
you notice that any wires or components are
damaged while performing a wiring task,
replace those wires or components before
completing the task.
MODIFICATIONS. Using aftermarket parts or
modifying the wiring beyond what is shown
in the diagram may lead to unpredictable
results, including serious injury or fire.
MOTOR WIRING. The motor wiring shown
in these diagrams is current at the time
of printing, but it may not match your
machine. Always use the wiring diagram
inside the motor junction box.
CAPACITORS/INVERTERS. Some capacitors
and power inverters store an electrical
charge for up to 10 minutes after being
disconnected from the power source.
To reduce the risk of being shocked,
wait at least this long before working on
capacitors.
CIRCUIT REQUIREMENTS. You MUST follow
the requirements at the beginning of this
manual when connecting your machine to a
power source.
EXPERIENCING DIFFICULTIES. If you are
experiencing difficulties understanding
the information included in this section,
contact our Technical Support at
(360) 734-3482.
WIRING DIAGRAM COLOR KEY
SERVICE
The photos and diagrams
included in this section are
best viewed in color. You
can view these pages in
color at www.shopfox.biz.
BLACK
WHITE
GREEN
RED
BLUE
BROWN
GRAY
ORANGE
-80-
YELLOW
YELLOW
GREEN
PURPLE
PINK
LIGHT
BLUE
BLUE
WHITE
TURQUOISE
Page 83

Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
Ground
Ground
Read
Page 80
Wiring Diagram
STOP
Before
Wiring
ON/OFF Switch
(viewed from behind)
120
VAC
240
VAC
LINELOAD
Re-wired for 240V
KEDU HY56
4
2
Ground
1
3
5-15 Plug
(Pre-wired)
Re-wired for 240V
Motor
Pre-wired for 120V
Run
Capacitor
CBB60 30MFD
350VAC
Start
Start
Capacitor
Capacitor
150MFD
CD60
250VAC
250VAC
6-15 Plug
(As Recommended)
Motor
1
4
3
2
Re-wired for 240V
SERVICE
Run
Capacitor
CBB60 30MFD
350VAC
Read
Page 80
Start
Start
Capacitor
STOP
Capacitor
Before
150MFD
Wiring
CD60 200MFD
250VAC
250VAC
-81-
Page 84

KEDU
HY56
Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
Electrical Components
Read
Page 80
STOP
Before
Wiring
Figure 128. Motor wiring at 120V.
Figure 125. Switch wiring.
Figure 129. Motor wiring label inside junction
box.
The motor wiring diagram is current at the
Figure 126. Capacitors.
time of printing; however, always use the
diagram on the inside of the junction box
cover when rewiring your motor!
SERVICE
Figure 127. Motor label.
-82-
Page 85

Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
PARTS
Main
29
27
28
29-2
29-3
24
29-1
25
30
41
26
53
40
31
29-4
29-5
29-6
39
37
54
34
79
50
77
56
38
36
35
29-7
29-8
29-9
29-10
78
43
55
57
51
44
76
58
46
45
42
123
113
93
96
100
86
122
63
104
106
109
75
62
120
74
119
99
99
89
47
115
98
99
95
92
97
71
116
105
81
72
71
49
117
88
87
80
70
69
68
118
98
121
91
90
82
84
83
111
48
59
60
6059
125
114
85
64
121
67
102
73
66
65
61
103
101
94
93
54
52
97
98
99
100
99
57
124
96
105
51
50
53
-83-
PARTS
Page 86

Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
68 X1837068 TILT SHAFT 125 X1837125 HEX WRENCH 2.5MM
Main Parts List
REF PART # DESCRIPTION REF PART # DESCRIPTION
24 X1837024 HEX BOLT M8-1.25 X 30 69 X1837069 RIVING GUIDE
25 X1837025 LOCK WASHER 8MM 70 X1837070 MAIN TRUNNION
26 X1837026 FLAT WASHER 8MM 71 X1837071 HEX NUT M8-1.25
27 X1837027 LOCK NUT M16-2 72 X1837072 HEX BOLT M8-1.25 X 40
28 X1837028 FLAT WASHER 16MM 73 X1837073 ARBOR NUT 5/8-18
29 X1837029 MOTOR 2HP 110V/220V 1-PH 74 X1837074 BLADE FLANGE
29-1 X1837029-1 MOTOR FAN COVER 75 X1837075 BLADE 10" X 5/8" X 40T
29-2 X1837029-2 MOTOR FAN 76 X1837076 ARBOR
29-3 X1837029-3 MOTOR JUNCTION BOX 77 X1837077 KEY 5 X 5 X 12
29-4 X1837029-4 R CAPACITOR 30M 350V 1-5/8 X 3-1/8 78 X1837078 BALL BEARING 6203ZZ
29-5 X1837029-5 S CAPACITOR 200M 150V 1-3/8 X 2-11/16 79 X1837079 BALL BEARING 6202ZZ
29-6 X1837029-6 CAPACITOR COVER 80 X1837080 EXT RETAINING RING 52MM
29-7 X1837029-7 CENTRIFUGAL SWITCH L19-15 4S 81 X1837081 CAP SCREW M5-.8 X 6
29-8 X1837029-8 CONTACT PLATE 82 X1837082 MOUNTING PLATE
29-9 X1837029-9 BALL BEARING 6203-2RS 83 X1837083 BUSHING
29-10 X1837029-10 BALL BEARING 6202ZZ 84 X1837084 SHAFT PIN
30 X1837030 BULL GEAR 85 X1837085 CLAMP LOCK BOLT M8-1.25 X 54
31 X1837031 CAP SCREW W/WASHER M6-1 X 25 86 X1837086 RIVING KNIFE LOCK LEVER
34 X1837034 SET SCREW M5-.8 X 8 87 X1837087 RIVING KNIFE CLAMP PLATE
35 X1837035 MOTOR PULLEY J6 X 5/8" BORE 88 X1837088 RIVING KNIFE MOUNTING BLOCK
36 X1837036 KEY 5 X 5 X 30 89 X1837089 COMPRESSION SPRING 8 X 18MM
37 X1837037 V-BELT 355J6 POLYFLEX 90 X1837090 BUSHING 8 X 10 X 12MM
38 X1837038 BLADE BRACKET 91 X1837091 LOCK NUT M8-1.25
39 X1837039 ARBOR BUSHING 92 X1837092 SET SCREW M5-.8 X 10
40 X1837040 ARBOR PULLEY J6 93 X1837093 FLAT WASHER 5MM
41 X1837041 LOCK NUT M12-1.5 94 X1837094 LOCK WASHER 5MM
42 X1837042 SHIM WASHER 95 X1837095 CAP SCREW W/WASHER M5-.8 X 16
43 X1837043 PHLP HD SCR M4-.7 X 6 96 X1837096 EXTENSION WING
44 X1837044 BEVEL INDICATOR 97 X1837097 CAP SCREW M10-1.5 X 40
45 X1837045 CAP SCREW M5-.8 X 8 98 X1837098 LOCK WASHER 10MM
46 X1837046 POINTER SEAT 99 X1837099 FLAT WASHER 10MM
47 X1837047 BEVEL NUT 100 X1837100 TRUNNION
48 X1837048 SHIM WASHER 101 X1837101 MAIN TABLE
49 X1837049 MAIN TRUNNION SHAFT 102 X1837102 FLAT HD SCR 8-32 X 1/2
50 X1837050 SHOULDER SCREW M8-1.25 X 14, 9 X 100 103 X1837103 TABLE INSERT
51 X1837051 HANDWHEEL HANDLE 106MM SS 104 X1837104 TABLE INSERT MAGNET
52 X1837052 CAP SCREW M5-.8 X 16 105 X1837105 CAP SCREW M10-1.5 X 25
53 X1837053 LOCK HANDLE KNOB M8-1.25 3 LOBE 106 X1837106 FLANGE BOLT M8-1.25 X 16
54 X1837054 HANDWHEEL TYPE-01 180D X 11K X M8-1.25 109 X1837109 FLAT WASHER 8MM
55 X1837055 COMPRESSION SPRING 111 X1837111 90° LIMITING BLOCK
56 X1837056 ELEVATION BUSHING 113 X1837113 BEVEL LABEL
57 X1837057 ROLL PIN 3 X 20 114 X1837114 HEX WRENCH 3MM
58 X1837058 ELEVATION SHAFT 115 X1837115 HEX WRENCH 4MM
59 X1837059 E-CLIP 14MM 116 X1837116 HEX WRENCH 5MM
60 X1837060 SPACER 117 X1837117 HEX WRENCH 6MM
61 X1837061 BEVEL PLATE 118 X1837118 HEX WRENCH 8MM
62 X1837062 E-CLIP 9MM 119 X1837119 SET SCR M8-1.25 X 20 CUP-PT NYLOCK
63 X1837063 BALL BEARING 6201ZZ 120 X1837120 SET SCR M8-1.25 X 25 CUP-PT NYLOCK
64 X1837064 BEARING SEAT 121 X1837121 HEX NUT M10-1.5
65 X1837065 HEX NUT M5-.8 122 X1837122 CAP SCREW W/WASHER M5-.8 X 10
66 X1837066 CAP SCREW M5-.8 X 10 123 X1837123 CAP SCREW M5-.8 X 10
67 X1837067 BLADE GUARD 124 X1837124 DADO TABLE INSERT
PARTS
-84-
Page 87

Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
Cabinet & Stand
237
206
238
219
219
219
235
210
210
222
218
205
220
216
239
213
221
217
223
210
201
202
203
204
203
202
204
207
202
204
208
241
219
240
224
210
219
210
212
204
202
219
203
234
209
221
217
215
236
222
237
238
231
232
233
216
223
220
218
220
223
213
216
219
219
221
222
218
211
220
219
225
223
219
PARTS
214
-85-
Page 88

Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
218 X1837218 CASTER 241 X1837241 HEX NUT M5-.8
Cabinet & Stand Parts List
REF PART # DESCRIPTION REF PART # DESCRIPTION
201 X1837201 CAP SCREW M8-1.25 X 25 219 X1837219 CAP SCREW M6-1 X 12
202 X1837202 LOCK WASHER 8MM 220 X1837220 HEX BOLT M8-1.25 X 65
203 X1837203 FLAT WASHER 8MM 221 X1837221 LOCK NUT M8-1.25
204 X1837204 HEX NUT M8-1.25 222 X1837222 FLAT WASHER 8MM
205 X1837205 DUST CHUTE 223 X1837223 BUTTON HD CAP SCREW M8-1.25 X 16
206 X1837206 SUPPORT LEG BACK LEFT 224 X1837224 LOCK NUT M3-.5
207 X1837207 SUPPORT LEG BACK RIGHT 225 X1837225 PHLP HD SCR M3-.5 X 16
208 X1837208 SUPPORT LEG FRONT LEFT 231 X1837231 ARBOR WRENCH 16 X 23MM OPEN-END
209 X1837209 SUPPORT LEG FRONT RIGHT 232 X1837232 ARBOR WRENCH 13 X 22MM CLOSED-ENDS
210 X1837210 LEG BRACE 233 X1837233 PUSH STICK
211 X1837211 LEG BRACE W/CASTER MOUNT 234 X1837234 CABINET
212 X1837212 SHOP FOX LEG BRACE 235 X1837235 MOTOR COVER
213 X1837213 RUBBER FOOT BACK LEFT/RIGHT 236 X1837236 REAR ACCESS PANEL
214 X1837214 RUBBER FOOT FRONT LEFT 237 X1837237 BUTTON HD CAP SCREW M5-.8 X 12
215 X1837215 RUBBER FOOT FRONT RIGHT 238 X1837238 FLAT WASHER 5MM
216 X1837216 FOOT LEVER 239 X1837239 STRAIN RELIEF 1/2"-3/8" SNAP-IN ST
217 X1837217 CASTER SUPPORT BRACKET 240 X1837240 CAP SCREW M5-.8 X 25
PARTS
-86-
Page 89

Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
Fence & Rails
357
300V2-5
300V2-15
339V2
359
361
360
300V2-2
300V2-6
304
306
312V2
311V2
358
300V2-8
300V2-9
300V2-7
300V2-10
305
310
308V2
300V2-29
300V2-25
356
307
364
300V2-3
300V2-7
300V2-11
300V2-12
300V2-14
300V2-28
300V2-6
300V2-39
300V2-40
300V2-21
300V2-38
300V2-35
300V2-26
300V2-1
300V2-4
300V2-5
300V2-13
300V2-6
300V2-39
300V2-4
300V2-2
300V2-31
300V2-33
300V2-40
300V2-43
300V2-15
300V2-30
300V2-37
300V2-15
300V2-44
300V2-4
300V2-21
300V2-32
300V2-36
300V2-14
300V2-39
300V2-40
300V2-38
300V2-34
300V2-20
300V2-21
300V2-24
300V2-46
300V2-4
300V2-45
300V2-16
300V2-17
300V2-18
300V2-19
300V2-22
300V2
300V2-2
300V2-42
300V2-43
300V2-15
300V2-23
300V2-27
300V2-25
REF PART # DESCRIPTION REF PART # DESCRIPTION
304 X1837304 HEX BOLT M8-1.25 X 16 300V2-16 X1837300V2-16 CAP SCREW M8-1.25 X 85
305 X1837305 LOCK WASHER 8MM 300V2-17 X1837300V2-17 FENCE HANDLE END COVER
306 X1837306 HEX NUT M8-1.25 300V2-18 X1837300V2-18 FENCE HANDLE 90L X 32OD X 19ID
307 X1837307 SWITCH BRACKET 300V2-19 X1837300V2-19 HANDLE BASE SCR M8-1.25 X 8, 11 X 11
308V2 X1837308V2 SWITCH BOX V2.09.17 300V2-20 X1837300V2-20 FENCE HANDLE CAM
310 X1837310 TAP SCREW M4 X 14 300V2-21 X1837300V2-21 SET SCREW M8-1.25 X 8
311V2 X1837311V2 SWITCH PADDLE V2.09.17 300V2-22 X1837300V2-22 COMPRESSION SPRING 0.8 X 5 X 15MM
312V2 X1837312V2 SWITCH KEDU HY56-3 V2.09.17 300V2-23 X1837300V2-23 STEEL BALL 6MM
339V2 X1837339V2 TAP SCREW M4 X 25 300V2-24 X1837300V2-24 SCALE LABEL (L)
356 X1837356 STRAIN RELIEF 1/2"-3/8" SNAP-IN ST 300V2-25 X1837300V2-25 TAP SCREW 3.5 X 8
357 X1837357 POWER CORD 14G 3W 72" 5-15P 300V2-26 X1837300V2-26 HEX BOLT M8-1.25 X 25
358 X1837358 MOTOR CORD 14G 3W 39" 300V2-27 X1837300V2-27 FRONT RAIL CAP (R)
359 X1837359 PHLP HD SCR M5-.8 X 8 300V2-28 X1837300V2-28 FRONT RAIL
360 X1837360 LOCK WASHER 5MM 300V2-29 X1837300V2-29 FRONT RAIL CAP (L)
361 X1837361 INT TOOTH WASHER 5MM 300V2-30 X1837300V2-30 INDICATOR
364 X1837364 ADJUSTABLE CABLE CLAMP 300V2-31 X1837300V2-31 PHLP HD SCR M6-1 X 8
300V2 X1837300V2 FENCE & RAIL ASSEMBLY V2.06.17 300V2-32 X1837300V2-32 HEX BOLT M10-1.5 X 45
300V2-1 X1837300V2-1 REAR RAIL 300V2-33 X1837300V2-33 LOCK NUT M10-1.5
300V2-2 X1837300V2-2 REAR RAIL CAP 300V2-34 X1837300V2-34 HEX BOLT M6-1 X 40
300V2-3 X1837300V2-3 CAP SCREW M8-1.25 X 25 300V2-35 X1837300V2-35 LOCK NUT M6-1
300V2-4 X1837300V2-4 HEX NUT M8-1.25 300V2-36 X1837300V2-36 SPRING PLATE
300V2-5 X1837300V2-5 HEX BOLT M6-1 X 20 300V2-37 X1837300V2-37 SLIDE PLATE 30 X 24 X 2
300V2-6 X1837300V2-6 FLAT WASHER 6MM 300V2-38 X1837300V2-38 SLIDE PLATE 50 X 20 X 2
300V2-7 X1837300V2-7 HEX NUT M6-1 300V2-39 X1837300V2-39 KNURLED NUT M10-1.5
300V2-8 X1837300V2-8 FENCE ASSEMBLY CAP 300V2-40 X1837300V2-40 SET SCREW M10-1.5 X 18, NYLON TIP
300V2-9 X1837300V2-9 HEX NUT M12-1.75 THIN 300V2-41 X1837300V2-41 SCALE LABEL (R)
300V2-10 X1837300V2-10 LIMIT SHAFT M12-1.75 X 25, 40L 300V2-42 X1837300V2-42 HEX BOLT M8-1.25 X 16
300V2-11 X1837300V2-11 BALL BEARING 696-2RS 300V2-43 X1837300V2-43 CAP SCREW M8-1.25 X 16
300V2-12 X1837300V2-12 CAP SCREW M6-1 X 12 300V2-44 X1837300V2-44 CONNECTION PLATE (L)
300V2-13 X1837300V2-13 FENCE BASE ASSEMBLY 300V2-45 X1837300V2-45 CONNECTION PLATE (R)
300V2-14 X1837300V2-14 FENCE FACE 300V2-46 X1837300V2-46 RAIL BRACE
300V2-15 X1837300V2-15 FENCE FACE CAP
PARTS
-87-
Page 90

Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
412 X1837412 PHLP HD SCR M5-.8 X 25 426 X1837426 BLADE GUARD WINDOW COVER
Blade Guard
410
408
407
423
410
408 407
408
409
424
408
401
413
422
416
404
403
418
404
406
417
410
402
422
413
408
426
420
408
423
409
421
414
415
405
409
412
411
401
409
408
407
406
408
401
407
408
410
408
410
REF PART # DESCRIPTION REF PART # DESCRIPTION
401 X1837401 LOCK NUT M5-.8 413 X1837413 FLAT WASHER 5MM
402 X1837402 SET PIN 414 X1837414 BLADE GUARD LOCK LEVER
403 X1837403 TORSION SPRING 415 X1837415 BLADE GUARD LOCK LEVER SCREW
404 X1837404 SCREW CAP 416 X1837416 ANTI-KICKBACK PAWL (L)
405 X1837405 BLADE GUARD BODY 417 X1837417 ANTI-KICKBACK PAWL (R)
406 X1837406 BARRIER 418 X1837418 SPREADER/RIVING KNIFE
407 X1837407 BARRIER CONNECTING BAR 420 X1837420 COMPRESSION SPRING
408 X1837408 FLAT WASHER 5MM 421 X1837421 STEEL BALL 4MM
409 X1837409 HEX BOLT M5-.8 X 10 422 X1837422 FLAT WASHER 3MM
410 X1837410 PHLP HD SCR M5-.8 X 10 423 X1837423 TAP SCREW M3 X 6
411 X1837411 GUARD RAIL 424 X1837424 CAP SCREW M5-.8 X 30
PARTS
-88-
Page 91

Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
512 X1837512 MITER HANDLE
Miter Guage
508
506
512
523
521
504
503
514
522
509
516
507
501
513
520
510
519
505
515
502
511
517
518
REF PART # DESCRIPTION REF PART # DESCRIPTION
501 X1837501 FLAT PLATE 513 X1837513 RIVET 2 X 5MM
502 X1837502 SPRING PLATE COVER 514 X1837514 MITER PIN
503 X1837503 MITER GAUGE BODY 515 X1837515 FLAT HD SCR 4-40 X 3/16
504 X1837504 MITER BAR 516 X1837516 SET SCREW 10-24 X 1/2
505 X1837505 ANGLE INDICATOR 517 X1837517 THREADED STOP PIN
506 X1837506 UPPER HANDLE CAP 518 X1837518 FLAT WASHER 3MM
507 X1837507 LOWER HANDLE CAP 519 X1837519 PHLP HD SCR 10-32 X 1/4
508 X1837508 CAP SCREW M8-1.25 X 50 520 X1837520 PHLP HD SCR 6-32 X 7/16
509 X1837509 HANDLE WASHER 6 X 20 521 X1837521 FLAT HD SCR 1/4-28 X 5/16
510 X1837510 MITER SCALE 522 X1837522 SET SCREW 10-32 X 1/4
511 X1837511 SPRING PLATE 523 X1837523 MITER BAR GUIDE WASHER
PARTS
-89-
Page 92

Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
605 X1837605 EYE/LUNG HAZARD LABEL 610 X1837610 KICKBACK HAZARD LABEL
Labels & Cosmetics
610
601
609
602
603
604
605
608
607
REF PART # DESCRIPTION REF PART # DESCRIPTION
601 X1837601 ELECTRICITY LABEL 606 X1837606 SHOP FOX NAMEPLATE
602 X1837602 DISCONNECT POWER LABEL 607 X1837607 MODEL NUMBER LABEL
603 X1837603 BLADE GUARD LABEL 608 X1837608 READ MANUAL LABEL
604 X1837604 MACHINE ID LABEL 609 X1837609 TABLE SAW WARNING LABEL
606
Safety labels warn about machine hazards and how to prevent serious personal injury. The owner
of this machine MUST maintain the original location and readability of all labels on this machine.
If any label is removed or becomes unreadable, REPLACE that label before allowing machine to
be operated again. Contact us at (360) 734-3482 or www.shopfoxtools.com to order new labels.
PARTS
-90-
Page 93

Model W1837 (For Machines Mfd. Since 9/17)
Page 94

FOLD ALONG DOTTED LINE
FOLD ALONG DOTTED LINE
Place
Stamp
Here
Woodstock international inc.
p.o. box 2309
bellingham, Wa 98227-2309
TAPE ALONG EDGES--PLEASE DO NOT STAPLE
Page 95

WARRANTY
Woodstock International, Inc. warrants all Shop Fox machinery to be free of defects from workmanship
and materials for a period of two years from the date of original purchase by the original owner.
This warranty does not apply to defects due directly or indirectly to misuse, abuse, negligence or
accidents, lack of maintenance, or reimbursement of third party expenses incurred.
Woodstock International, Inc. will repair, replace, or arrange for a dealer refund, at its expense and
option, the Shop Fox machine or machine part proven to be defective for its designed and intended
use, provided that the original owner returns the product prepaid to an authorized warranty or repair
facility as designated by our Bellingham, Washington office with proof of their purchase of the product
within two years, and provides Woodstock International, Inc. reasonable opportunity to verify the
alleged defect through inspection. If it is determined there is no defect, or that the defect resulted
from causes not within the scope of Woodstock International Inc.'s warranty, then the original owner
must bear the cost of storing and returning the product.
This is Woodstock International, Inc.’s sole written warranty and any and all warranties that may be
implied by law, including any merchantability or fitness, for any particular purpose, are hereby limited
to the duration of this written warranty. We do not warrant that Shop Fox machinery complies with
the provisions of any law, acts or electrical codes. We do not reimburse for third party repairs. In no
event shall Woodstock International, Inc.’s liability under this limited warranty exceed the purchase
price paid for the product, and any legal actions brought against Woodstock International, Inc. shall be
tried in the State of Washington, County of Whatcom. We shall in no event be liable for death, injuries
to persons or property or for incidental, contingent, special or consequential damages arising from the
use of our products.
Every effort has been made to ensure that all Shop Fox machinery meets high quality and durability
standards. We are commited to continuously improving the quality of our products, and
right to change specifications at any time
WARRANTY
.
reserve the
Page 96

 Loading...
Loading...