Page 1
XV-Z2000
DT-400
SERVICE MANUAL
SERVICE-ANLEITUNG
SY4C6XV-Z2000
PROJECTOR
PROJEKTOR
XV-Z2000
MODELS
MODELLE
In the interests of user-safety (Required by safety regulations in some countries) the set should be restored to its original condition and only parts identical to those specified should be used.
Im lnteresse der Benutzersicherheit (erforderliche Sicherheitsregeln in einigen Ländern) muß das Gerät in seinen
Originalzustand gebracht werden. Außerdem dürfen für die spezifizierten Bauteile nur identische Teile verwendet
werden.
DT-400
SHARP CORPORATION
This document has been published to be used for
after sales service only.
The contents are subject to change without notice.
Page 2
XV-Z2000
DT-400
• SPECIFICATIONS ............................................ 3
• IMPORTANT SERVICE SAFETY
NOTES (for USA) .............................................. 4
• NOTE TO SERVICE PERSONNEL .................. 6
• OPERATION MANUAL ................................... 10
• DIMENSIONS ................................................. 16
• REMOVING OF MAJOR PARTS .................... 17
• RESETTING THE TOTAL LAMP TIMER ........ 22
• THE OPTICAL UNIT OUTLINE ....................... 24
• ELECTRICAL ADJUSTMENT ......................... 26
• TROUBLE SHOOTING TABLE ....................... 33
CONTENTS
Page Page
• BLOCK DIAGRAM .......................................... 88
• OVERALL WIRING DIAGRAM ....................... 90
• WAVEFORMS ................................................. 92
• PRINTED WIRING BOARD ASSEMBLIES .... 93
• PARTS LIST
Ë
ELECTRICAL PARTS...............................101
Ë
CABINET AND MECHANICAL PARTS .... 114
Ë
ACCESSORIES PARTS ........................... 118
Ë
PACKING PARTS..................................... 118
• PACKING OF THE SET ................................ 119
• SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM ....................... D1~D35
Seite Seite
• TECHNISCHE DATEN .................................... 47
• HINWEISE FÜR DAS
WARTUNGSPERSONAL................................48
• BEDIENUNGSANLEITUNG ............................ 50
• ABMESSUNGEN ............................................ 56
• ENTFERNEN DER HAUPTTEILE .................. 57
• RÜCKSTELLUN DES
LAMPEN-TIMERS .......................................... 62
• BESCHREIBUNG DER OPTIK-EINHEIT ....... 64
• ELEKTRISCHE EINSTELLUNG ..................... 66
• FEHLERSUCHTABELLE ................................ 74
• BLOCKSCHALTBILD ......................................88
INHALT
• GESAMTSCHALTPLAN..................................90
• WELLENFORMEN .......................................... 92
• LEITERPLATTENEINHEITEN ........................ 93
• ERSATZTEILLISTE
• VERPACKEN DES GERÄTS ........................ 119
• SCHEMATISCHER SCHALTPLAN....... D1~D35
Ë
ELEKTRISCHE BAUTEILE ....................... 101
Ë
GEHÄUSE UND MECHANISCHE
BAUTEILE ................................................. 114
Ë
ZUBEHÖRTEILE....................................... 118
Ë
VERPACKUNGSTEILE ............................. 118
2
Page 3

SPECIFICATIONS
Product type
Model
Video system
Display method
DLP panel
Lens
Projection lamp
Video input signal
S-video input signal
Component input signal
(INPUT 1, 2)
Analog RGB/Digital
(INPUT 5/DIGITAL)
Horizontal resolution
Pixel clock
Vertical frequency
Horizontal frequency
Computer control signal
Rated voltage
Input current
Rated frequency
Power consumption
Power consumption (standby)
Heat dissipation
Operating temperature
Storage temperature
Cabinet
I/R carrier frequency
Dimensions (approx.)
Weight (approx.)
Supplied accessories
Replacement parts
Projector
XV-Z2000, DT-400
PAL/PAL 60/PAL-M/PAL-N/SECAM/NTSC 3.58/NTSC 4.43
DTV 480
I
/480P/540P/576I/576P/720P/1080
I
Single Panel Digital Micromirror Device (DMD™) by Texas Instruments
Panel size: 0.8"
Drive method: Digital Light Processing (DLP™)
No. of dots: 921,600 dots (1,280 [H] ⋅ 720 [V])
1–1.5 ⋅ zoom lens, F2.0–2.5 f=21.3–31.6 mm
275 W DC lamp
RCA Connector: VIDEO (INPUT 4), composite video, 1.0 Vp-p, sync negative, 75 Ω
terminated
4-pin Mini DIN connector (INPUT 3)
Y (luminance signal): 1.0 Vp-p, sync negative, 75 Ω terminated
C (chrominance signal): Burst 0.286 Vp-p, 75 Ω terminated
RCA Connector
Y: 1.0 Vp-p, sync negative, 75 Ω terminated
P
B (CB): 0.7 Vp-p, 75 Ω terminated
P
R (CR): 0.7 Vp-p, 75 Ω terminated
29-pin DVI-I terminal
<Digital>
Input impedance 50 Ω
Input level 250-1000 mV
<Analog>
Input impedance 75 Ω
Input level 0.7 Vp-p
Y: 1.0 Vp-p, sync negative, 75 Ω terminated
P
B (CB): 0.7 Vp-p, 75 Ω terminated
P
R (CR): 0.7 Vp-p, 75 Ω terminated
<Synchronization signal>
•
Separate sync/Composite sync
Input level TTL level
Input impedance 1 KΩ
• Green on sync
Input level (Synchronizing input) 0.286 Vp-p
Input impedance 75 Ω
720 TV lines (DTV 720P input)
12–80 MHz
43–75 Hz
15–70 kHz
9-pin D-sub connector (RS-232C Port)
AC 100–240 V
3.65 A (When using AC 100 V)
50/60 Hz
360 W (When using AC 100 V)
6 W (When using AC 100 V)
1,350 BTU/hour
41°F to 95°F (+5°C to +35°C)
–4°F to 140°F (–20°C to +60°C)
Plastic
38 kHz
12
7
/32" ⋅ 3 33/64" ⋅ 11 7/64" (310 (W) ⋅ 89 (H) ⋅ 282 (D) mm)
9.5 lbs. (4.3 kg)
Remote control, Two AA size batteries, Power cord, Lens cap (attached on the body),
Operation manual
Lamp unit (Lamp/cage module) (AN-K2LP), Remote control (RRMCGA334WJSA), AA
size batteries, Power cord (QACCBA036WJPZ:XV-Z2000, for U.K., Hong Kong and
Singapore), (QACCDA007WJPZ:XV-Z2000, for U.S.A., Canada and DT-400),
(QACCLA018WJPZ:XV-Z2000, for Australia and New Zealand),
(QACCVA011WJPZ:XV-Z2000, for Europe, except U.K.) Lens cap (PCAPHA021WJSA),
Operation manual (TINS-B529WJZZ:XV-Z2000, for U.S.A., and Canada),
(TINS-B530WJZZ:XV-Z2000, for European 7 Laguges),
(TINS-B531WJZZ:XV-Z2000, for Hong Kong and Korean), (TINS-B532WJZZ:DT-400)
Operation manual, for 21pin RCA Conversion Adaptor (TCADH1018CEN1:XV-Z2000,
for Europe) Video cable (QCNWGA001WJZZ:XV-Z2000, except U.S.A., Canada and
DT-400), 21pin RCA conversion adaptor (QSOCZ0361CEZZ:XV-Z2000, for Europe)
XV-Z2000
DT-400
As a part of policy of continuous improvement, SHARP reserves the right to make design and
specification changes for product improvement without prior notice. The performance specification figures indicated are nominal values of production units. There may be some deviations from
these values in individual units.
3
Page 4
XV-Z2000
DVM
AC SCALE
1.5k ohm
10W
TO EXPOSED
METAL PARTS
CONNECT TO
KNOWN EARTH
GROUND
0.15 µF
TEST PROBE
DT-400
IMPORTANT SERVICE SAFETY NOTES (for USA)
Ë Service work should be performed only by qualified service technicians who are
thoroughly familiar with all safety checks and servicing guidelines as follows:
WARNING
1. For continued safety, no modification of any circuit
should be attempted.
2. Disconnect AC power before servicing.
BEFORE RETURNING THE PROJECTOR:
(Fire & Shock Hazard)
Before returning the projector to the user, perform
the following safety checks:
1. Inspect lead wires are not pinched between the chassis
and other metal parts of the projector.
2. Inspect all protective devices such as non-metallic
control knobs, insulating materials, cabinet backs,
adjustment and compartment covers or shields,
isolation resistor-capacity networks, mechanical
insulators, etc.
3. To be sure that no shock hazard exists, check for
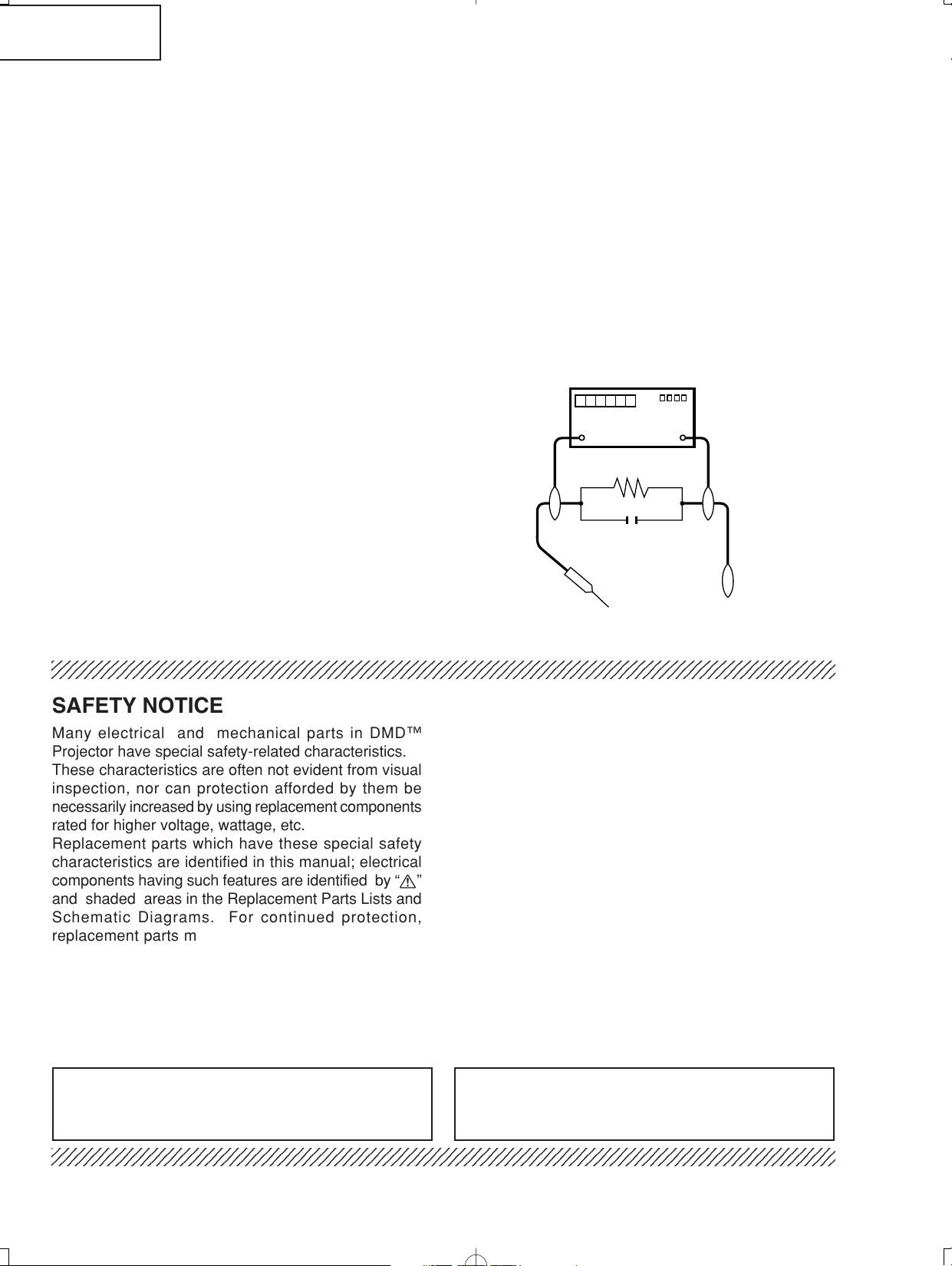
current leakage in the following manner:
» Plug the AC cord directly into a 100-240 volt AC outlet,
(Do not use an isolation transformer for this test).
» Using two clip leads, connect a 1.5k ohm, 10 watt
resistor paralleled by a 0.15µF capacitor in parallel
between all exposed metal cabinet parts and earth
ground.
» Use an AC voltmeter with sensitivity of 5000 ohm per
volt., or higher, sensitivity to measure the AC voltage
drop across the resistor (See Diagram).
» All checks must be repeated with the AC plug
connection reversed. (If necessary, a non-polarized
adapter plug must be used only for the purpose of
completing these checks.)
Any reading of 0.3 volts RMS (this corresponds to 0.2
milliamp. AC.) or more is excessive and indicates a
potential shock hazard which must be corrected before
returning the unit to the owner.
SAFETY NOTICE
Many electrical and mechanical parts in DMD™
Projector have special safety-related characteristics.
These characteristics are often not evident from visual
inspection, nor can protection afforded by them be
necessarily increased by using replacement components
rated for higher voltage, wattage, etc.
Replacement parts which have these special safety
characteristics are identified in this manual; electrical
components having such features are identified by “å”
and shaded areas in the Replacement Parts Lists and
Schematic Diagrams. For continued protection,
replacement parts must be identical to those used in
the original circuit. The use of a substitute replacement
parts which do not have the same safety characteristics
as the factory recommended replacement parts shown
in this service manual, may create shock, fire or other
hazards.
WARNING: The bimetallic component has the primary
conductive side exposed. Be very careful in
handling this component when the power is on.
AVIS POUR LA SECURITE
De nombreuses pièces, électriques et mécaniques, dans
les projecteur à DMD™ présentent des caractéristiques
spéciales relatives à la sécurité, qui ne sont souvent pas
évidentes à vue.
Le degré de protection ne peut pas être nécessairement
augmentée en utilisant des pièces de remplacement
étalonnées pour haute tension, puissance, etc.
Les pièces de remplacement qui présentent ces
caractéristiques sont identifiées dans ce manuel;
les pièces électriques qui présentent ces particularités
sont identifiées par la marque “å” et hachurées dans la
liste des pièces de remplacement et les diagrammes
schématiques. Pour assurer la protection, ces pièces
doivent être identiques à celles utilisées dans le circuit
d’origine. L’utilisation de pièces qui n’ont pas les mêmes
caractéristiques que les pièces recommandées par l’usine,
indiquées dans ce manuel, peut provoquer des
électrocutions, incendies ou autres accidents.
AVERTISSEMENT: La composante bimétallique dispose du
conducteur primaire dénudé. Faire attention
lors de la manipulation de cette
composante sous tension.
4
Page 5
XV-Z2000
DVM
ECHELLE CA
1.5k ohm
10W
0.15 µF
SONDE D'ESSAI
AUX PIECES
METALLIQUES
EXPOSEES
BRANCHER A UNE
TERRE CONNUE
DT-400
PRECAUTIONS A PRENDRE LORS DE LA REPARATION
Ë
Ne peut effectuer la réparation qu' un technicien spécialisé qui s'est parfaitement
accoutumé à toute vérification de sécurité et aux conseils suivants.
AVERTISSEMENT
1. N'entreprendre aucune modification de tout circuit.
C'est dangereux.
2. Débrancher le récepteur avant toute réparation.
PRECAUTION: POUR LA
PROTECTION CONTINUE CONTRE
LES RISQUES D'INCENDIE,
REMPLACER LE FUSIBLE
F701 (T6.3AH, AC250V)
VERIFICATIONS CONTRE L'INCEN-DIE ET
LE CHOC ELECTRIQUE
Avant de rendre le récepteur à l'utilisateur, effectuer
les vérifications suivantes.
1. Inspecter tous les faisceaux de câbles pour s'assurer
que les fils ne soient pas pincés ou qu'un outil ne soit
pas placé entre le châssis et les autres pièces
métalliques du récepteur.
2. Inspecter tous les dispositifs de protection comme les
boutons de commande non-métalliques, les isolants, le
dos du coffret, les couvercles ou blindages de réglage
et de compartiment, les réseaux de résistance-capacité,
les isolateurs mécaniques, etc.
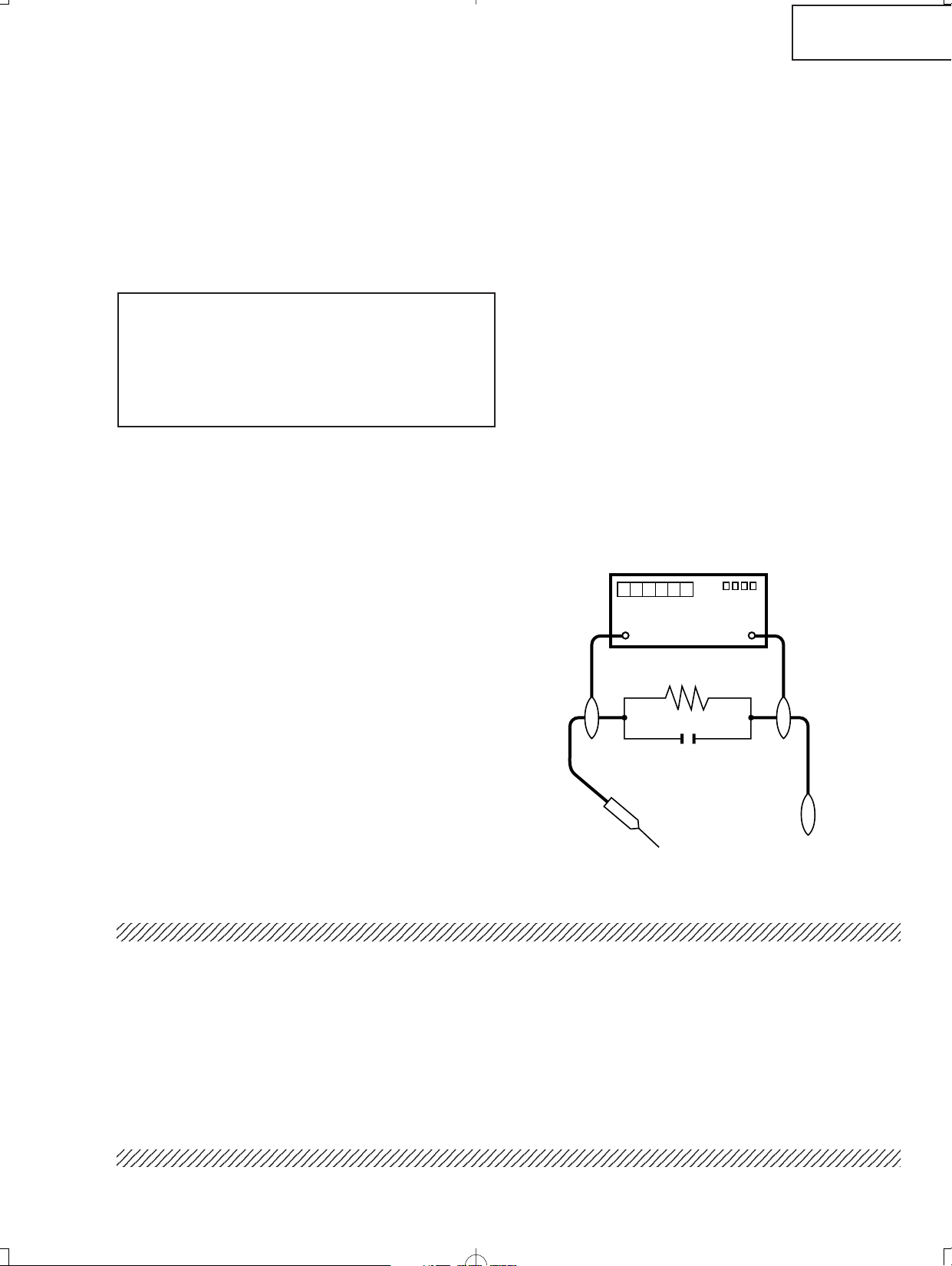
3. S'assurer qu'il n'y ait pas de danger d'électrocution en
vérifiant la fuite de courant, de la facon suivante:
• Brancher le cordon d'alimentation directem-ent à une
prise de courant de 100-240V. (Ne pas utiliser de
transformateur d'isolation pour cet essai).
• A l'aide de deux fils à pinces, brancher une résistance
de 1.5 kΩ 10 watts en parallèle avec un condensateur
de 0.15µF en série avec toutes les pièces métalliques
exposées du coffret et une terre connue comme une
conduite électrique ou une prise de terre branchée à la
terre.
• Utiliser un voltmètre CA d'une sensibilité d'au moins
5000Ω/V pour mesurer la chute de tension en travers
de la résistance.
• Toucher avec la sonde d'essai les pièces métalliques
exposées qui présentent une voie de retour au châssis
(antenne, coffret métallique, tête des vis, arbres de
commande et des boutons, écusson, etc.) et mesurer la
chute de tension CA en-travers de la résistance. Toutes
les vérifications doivent être refaites après avoir inversé
la fiche du cordon d'alimentation. (Si nécessaire, une
prise d'adpatation non polarisée peut être utilisée dans
le but de terminer ces vérifications.)
Tous les courants mesurés ne doivent pas dépasser 0.5
mA.
Dans le cas contraire, il y a une possibilité de choc
électrique qui doit être supprimée avant de rendre le
récepteur au client.
AVIS POUR LA SECURITE
De nombreuses pièces, électriques et mécaniques, dans les téléviseur ACL présentent des caractéristiques spéciales
relatives à la sécurité, qui ne sont souvent pas évidentes à vue. Le degré de protection ne peut pas être nécessairement
augmentée en utilisant des pièces de remplacement étalonnées pour haute tension, puissance, etc.
Les pièces de remplacement qui présentent ces caractéristiques sont identifiées dans ce manuel; les pièces électriques
qui présentent ces particularités sont identifiées par la marque " å " et hachurées dans la liste des pièces de
remplacement et les diagrammes schématiques.
Pour assurer la protection, ces pièces doivent être identiques à celles utilisées dans le circuit d'origine. L'utilisation
de pièces qui n'ont pas les mêmes caractéristiques que les pièces recommandées par l'usine, indiquées dans ce
manuel, peut provoquer des électrocutions, incendies, radiations X ou autres accidents.
5
Page 6
XV-Z2000
DT-400
NOTE TO SERVICE
PERSONNEL
UV-RADIATION PRECAUTION
The light source, metal halide lamp, in the projector
emits small amounts of UV-Radiation.
AVOID DIRECT EYE AND SKIN EXPOSURE.
To ensure safety please adhere to the following:
1. Be sure to wear sun-glasses when servicing the
projector with the lamp
turned “on” and the top
enclosure removed.
2. Do not operate the lamp outside of the lamp housing.
NOTE POUR LE PERSONNEL
D’ENTRETIEN
PRECAUTION POUR LES RADIATIONS UV
La source de lumière, la lampe métal halide, dans
le projecteur émet de petites quantités de
radiation UV.
EVITEZ TOUTE EXPOSITION DIRECTE DES
YEUX ET DE LA PEAU.
Pour votre sécurité, nous vous prions de respecter
les points suivants:
1. Toujours porter des lunettes de soleil lors d’un entretien
du projecteur
avec la lampe allumée
et le haut du coffret retiré.
2. Ne pas faire fonctionner la lampe à l’extérieur du boîtier
de lampe.
3. Do not operate for more than 2 hours with the enclosure
removed.
UV-Radiation and Medium Pressure
Lamp Precautions
1. Be sure to disconnect the AC plug when replacing the
lamp.
2. Allow one hour for the unit to cool down before
servicing.
3. Replace only with same type lamp. Type AN-K2LP
rated 275W.
4. The lamp emits small amounts of UV-Radiation, avoid
direct-eye contact.
5. The medium pressure lamp involves a risk of explosion.
Be sure to follow installation instructions described
below and handle the lamp with care.
3. Ne pas faire fonctionner plus de 2 heures avec le coffret
retiré.
Précautions pour les radiations UV
et la lampe moyenne pression
1. Toujours débrancher la fiche AC lors du remplacement
de la lampe.
2. Laisser l’unité refroidir pendant une heure avant de
procéder à l’entretien.
3. Ne remplacer qu’avec une lampe du même type. Type
AN-K2LP, caractéristique 275W.
4. La lampe émet de petites quantités de radiation UVéviter tout contact direct avec les yeux.
5. La lampe moyenne pression implique un risque
d’explosion. Toujours suivre les instructions
d’installation décrites ci-dessous et manipuler la lampe
avec soin.
6
Page 7
XV-Z2000
1
2
1
2
DT-400
UV-RADIATION PRECAUTION (Continued)
Lamp Replacement
Note:
Since the lamp reaches a very high temperature during
units operation replacement of the lamp should be
done at least one hour after the power has been turned
off. (to allow the lamp to cool off.)
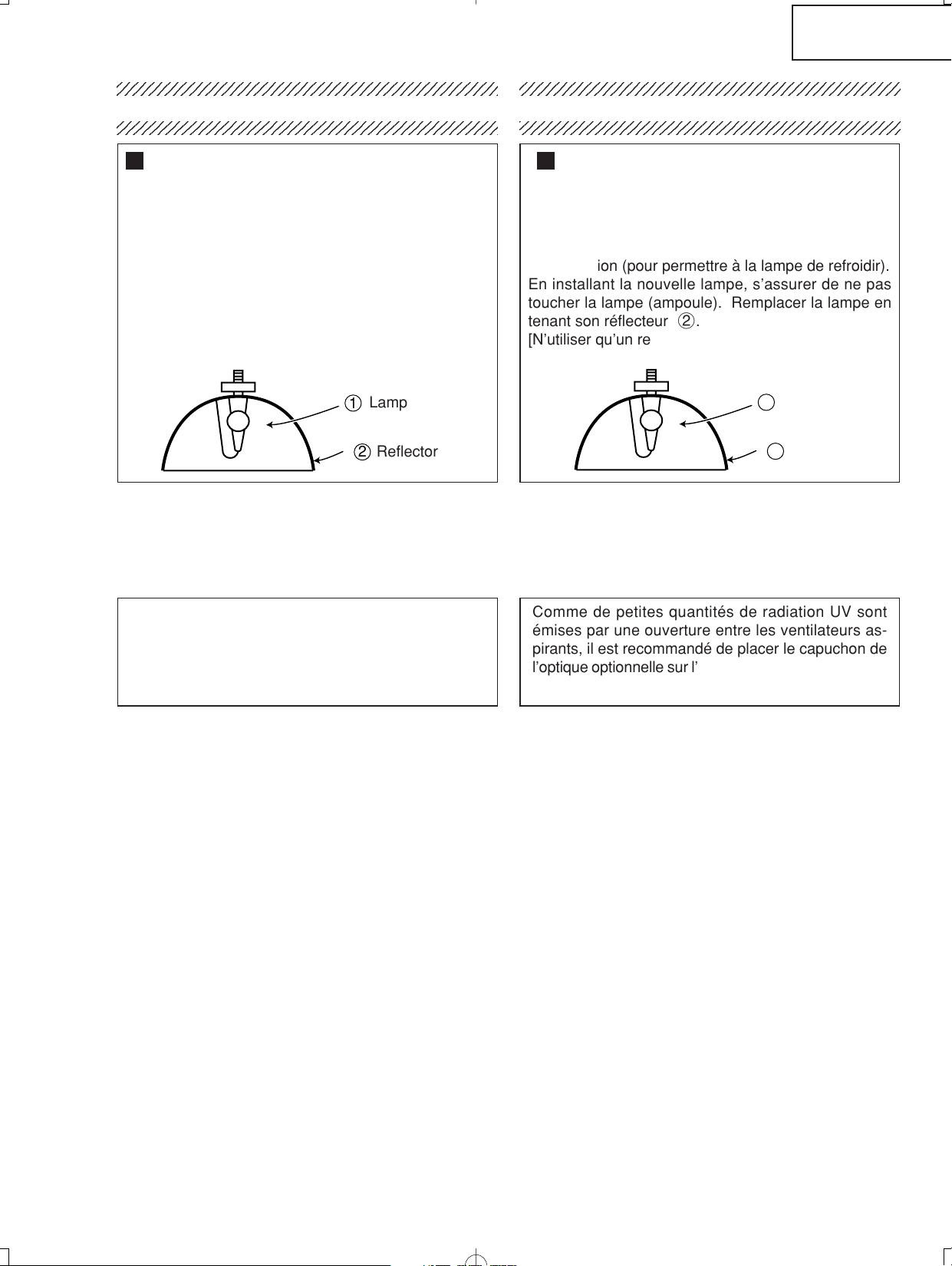
Installing the new lamp, make sure not to touch the
lamp (bulb) replace the lamp by holding its reflector
2.
[Use original replacement only.]
Lamp
Reflector
DANGER ! –– Never turn the power on without the
lamp to avoid electric-shock or damage of the devices
since the stabilizer generates high voltages at its start.
PRECAUTION POUR LES RADIATIONS UV (Suite)
Remplacement de la lampe
Remarque:
Comme la lampe devient très chaude pendant le
fonctionnement de l’unité, son remplacement ne doit
être effectué au moins une heure après avoir coupé
l’alimentation (pour permettre à la lampe de refroidir).
En installant la nouvelle lampe, s’assurer de ne pas
toucher la lampe (ampoule). Remplacer la lampe en
tenant son réflecteur 2.
[N’utiliser qu’un remplacement d’origine.]
Lampe
Reflecteur
DANGER ! –– Ne jamais mettre sous tension sans la
lampe pour éviter un choc électrique ou des
dommages des appareils car le stabilisateur génère
de hautes tensions à sa mise en route.
Since small amounts of UV-radiation are emitted
from an opening between the exhaust fans, it is recommended to place the cap of the optional lens on
the opening during servicing to avoid eye and skin
exposure.
Comme de petites quantités de radiation UV sont
émises par une ouverture entre les ventilateurs aspirants, il est recommandé de placer le capuchon de
l’optique optionnelle sur l’ouverture pendant l’entretien
pour éviter une exposition des yeux et la peau.
7
Page 8
XV-Z2000
DT-400
WARNING: High brightness light source, do not stare into the beam of light, or view directly. Be especially
careful that children do not stare directly in to the beam of light.
WARNING: TO REDUCE THE RISK OF FIRE OR ELECTRIC SHOCK, DO NOT EXPOSE THIS UNIT TO
MOISTURE OR WET LOCATIONS.
CAUTION
RISK OF ELECTRIC SHOCK.
DO NOT REMOVE SCREWS
EXCEPT SPECIFIED USER
SERVICE SCREW.
CAUTION: TO REDUCE THE RISK OF ELECTRIC SHOCK,
DO NOT REMOVE CABINET.
NO USER-SERVICEABLE PARTS EXCEPT LAMP UNIT.
REFER SERVICING TO QUALIFIED SERVICE
PERSONNEL.
The lighting flash with arrowhead within a
triangle is intended to tell the user that
parts inside the product are risk of electric
shock to persons.
The exclamation point within a triangle is
intended to tell the user that important
operating and servicing instructions are in
the manual with the projector.
CAUTION
(POWER Unit)
6.3A 250V
AVERTISSEMENT: Source lumineuse de grande intensité. Ne pas fixer le faisceau lumineux ou le regarder
For continued
protection against a
risk of fire, replace
only with same type
T6.3AH, AC250V
fuse.(F701)
directement. Veiller particulièrement à éviter que les enfants ne fixent directement le
faisceau lumineux.
AVERTISSEMENT: AFIN D’EVITER TOUT RISQUE D’INCENDIE OU D’ELECTROCUTION, NE PAS PLACER
CET APPAREIL DANS UN ENDROIT HUMIDE OU MOUILLE.
ATTENTION
RISQUE
D’ÉLECTROCUTION. NE
PASR ETIRER LES VIS Á
L’EXCEPTION DE LA VIS DE
REPARATION UTILISATEUR
SPECIFIEES
ATTENTION: POUR EVITER TOUT RISQUE
D’ELECTROCUTION, NE PAS RETIRER LE CAPOT.
AUCUNE DES PIECES INTERIEURES N’EST REPARABLE
PAR L’UTILISATEUR, A L’EXCEPTION DE L’UNITE DE
LAMPE. POUR TOUTE REPARATION, S’ADRESSER A UN
TECHNICIEN D’ENTRETIEN QUALIFIE.
L’éclair terminé d’une flèche à l’intérieur
d’un triangle indique à l’utilisateur que les
pi‘eces se trouvant dans l’appareil sont
susceptibles de provoquer une décharge
électrique.
Le point d’exclamation à l’intérieur d’un
triangle indique à l’utilisateur que les
instructions de fonctionnement et
d’entretien sont détaillées dans les
documents fournis avec le projecteur.
PRECAUTION
(Unité de PUTSSANCE)
6.3A 250V
Pour une protection
continue contre un
risques d’incendie, ne
remplacer qu’avec un
fusible T6.3AH,
AC250V du même
type. (F701)
8
Page 9
XV-Z2000
L Fa
DT-400
Precautions for using lead-free solder
1 Employing lead-free solder
"PWBs" of this model employs lead-free solder. The LF symbol indicates lead-free solder, and is attached on the
PWBs and service manuals. The alphabetical character following LF shows the type of lead-free solder.
Example:
Indicates lead-free solder of tin, silver and copper.
2 Using lead-free wire solder
When fixing the PWB soldered with the lead-free solder, apply lead-free wire solder. Repairing with conventional
lead wire solder may cause damage or accident due to cracks.
As the melting point of lead-free solder (Sn-Ag-Cu) is higher than the lead wire solder by 40°C, we recommend you
to use a dedicated soldering bit, if you are not familiar with how to obtain lead-free wire solder or soldering bit,
contact our service station or service branch in your area.
3 Soldering
As the melting point of lead-free solder (Sn-Ag-Cu) is about 220°C which is higher than the conventional lead solder
by 40°C, and as it has poor solder wettability, you may be apt to keep the soldering bit in contact with the PWB for
extended period of time. However, since the land may be peeled off or the maximum heat-resistance temperature
of parts may be exceeded, remove the bit from the PWB as soon as you confirm the steady soldering condition.
Lead-free solder contains more tin, and the end of the soldering bit may be easily corroded. Make sure to turn on
and off the power of the bit as required.
If a different type of solder stays on the tip of the soldering bit, it is alloyed with lead-free solder. Clean the bit after
every use of it.
When the tip of the soldering bit is blackened during use, file it with steel wool or fine sandpaper.
Be careful when replacing parts with polarity indication on the PWB silk.
Lead-free wire solder for servicing
Part No. ★ Description Code
ZHNDAi123250E J φ0.3mm 250g(1roll) BL
ZHNDAi126500E J φ0.6mm 500g(1roll) BK
ZHNDAi12801KE J φ1.0mm 1kg(1roll) BM
9
Page 10
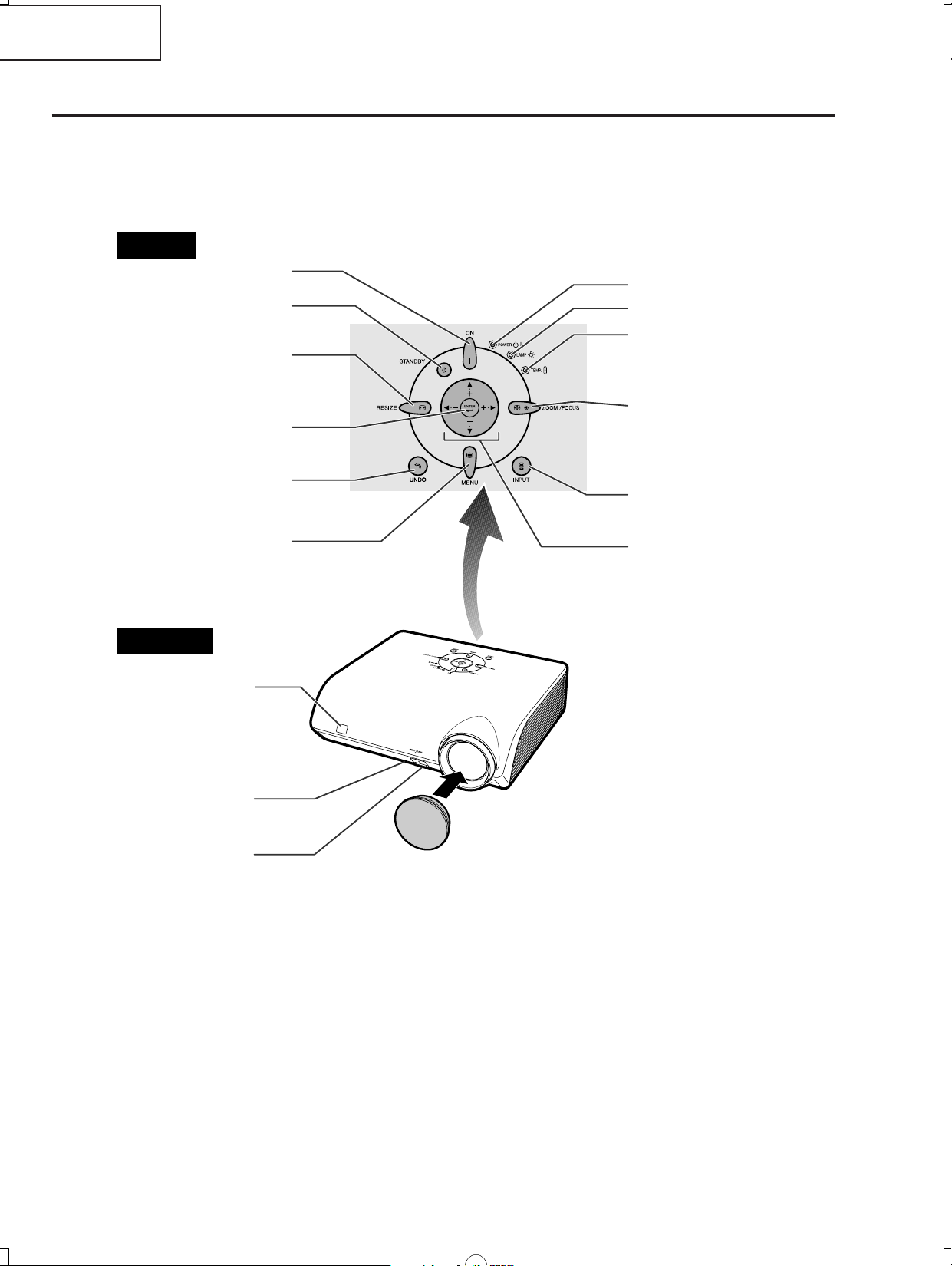
XV-Z2000
Adjustment buttons
('/"/\/|)
Select menu items and other
settings.
INPUT button
Switch input mode 1, 2, 3, 4,
5 or DIGITAL.
ZOOM/FOCUS button
Adjust the projected image
size or adjust the focus.
Temperature warning
indicator
Lamp indicator
Power indicator
Remote control sensor
HEIGHT ADJUST button
Front adjustment foot
(on the bottom of
the projector)
MENU button
Display adjustment and
setting screens.
ENTER button
Set items selected or
adjusted on the menu.
UNDO button
Undo an operation or
returning to the previous
display.
STANDBY button
Put the projector into standby
mode.
RESIZE button
Switch the picture display
(STRETCH, SIDE BAR, etc.).
ON button
Turn the power on.
Projector
• Attaching the lens cap
Push the lens cap on until it clicks
into position.
• Removing the lens cap
Pull the lens cap directly outward.
Top View
Front View
DT-400
OPERATION MANUAL
10
Page 11
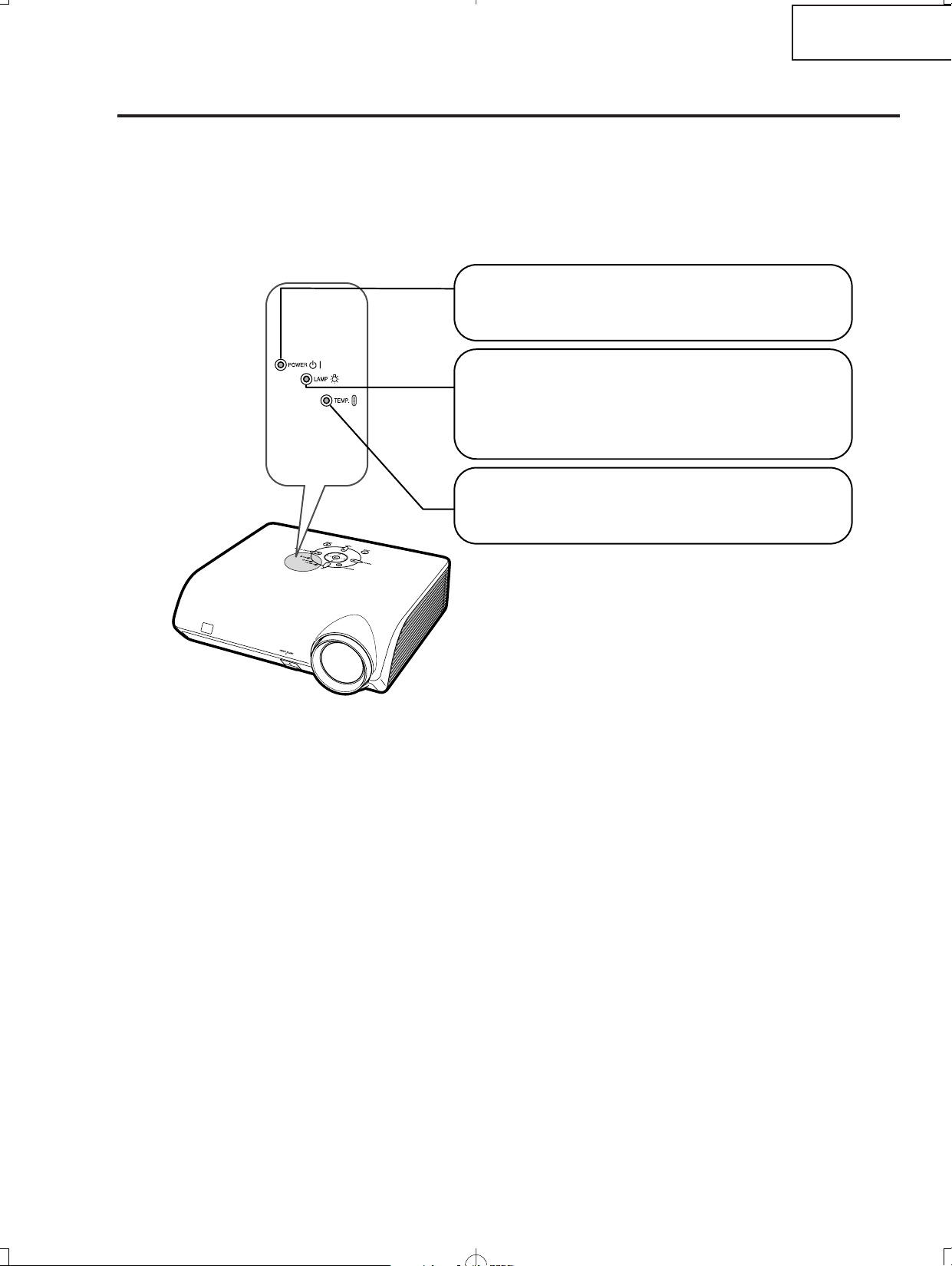
XV-Z2000
About the Indicators on the Projector
Power indicator
Red on
...
Normal (Standby)
Green on
...
Normal (Power on)
Temperature warning indicator
Off
...
Normal
Red on
...
The internal temperature is abnormally high.
Lamp indicator
Green on
...
Normal
Green blinks
...
The lamp is warming up or shutting down.
Red on
...
The lamp has been shut down abnormally or
needs to be changed.
DT-400
11
Page 12
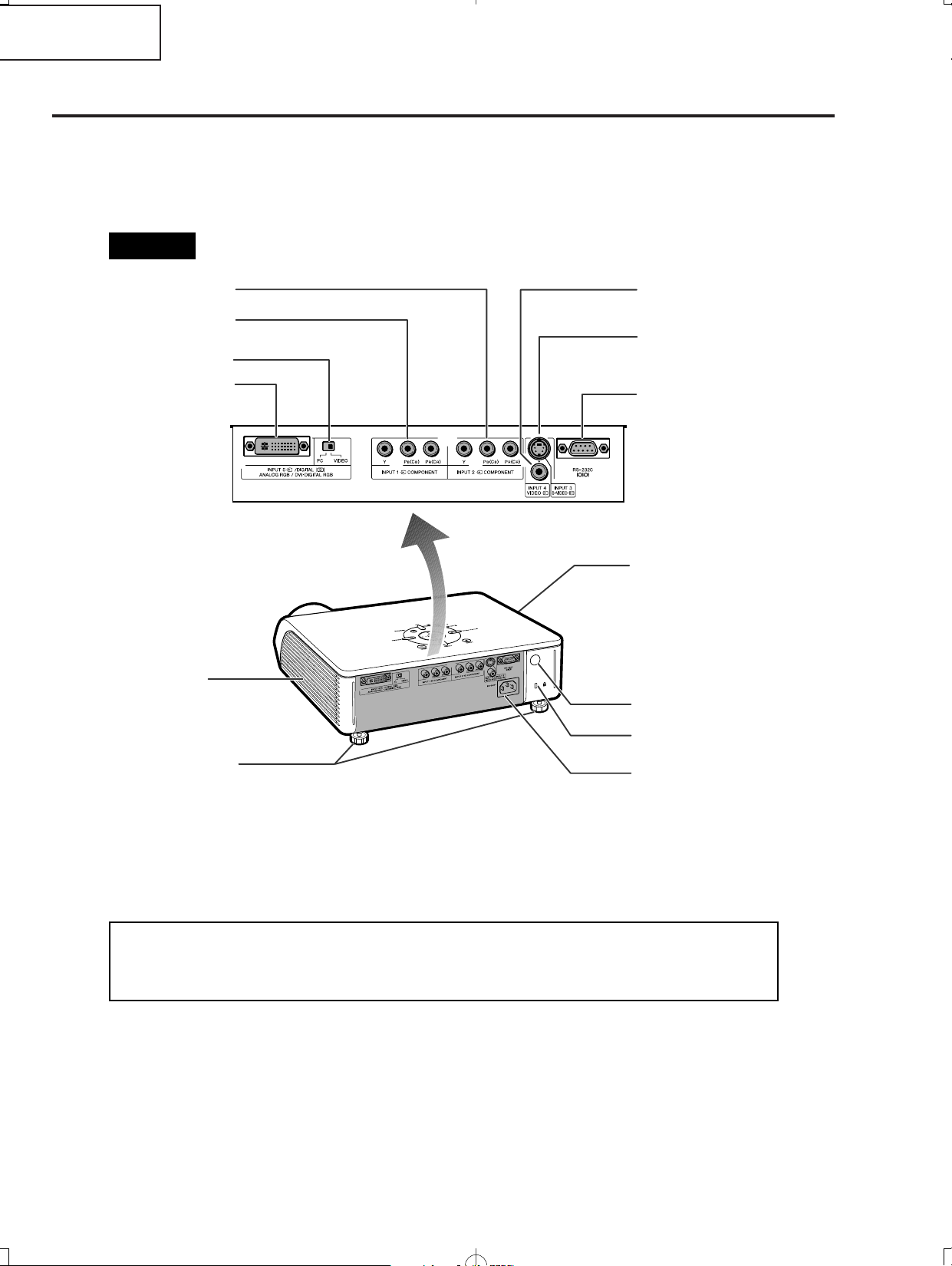
XV-Z2000
Projector (Rear View)
Using the Kensington Lock
• This projector has a Kensington Security Standard connector for use with a Kensington MicroSaver Security
System. Refer to the information that came with the system for instructions on how to use it to secure the
projector.
Remote control sensor
AC socket
Connect the supplied
Power cord.
Kensington Security
Standard connector
Rear adjustment feet
Intake vent
Exhaust vent
The speed and pitch of
the cooling fan may
change during operation
in response to internal
temperature changes.
This is normal operation
and does not indicate a
malfunction.
INPUT 2 terminal
Component signals.
Digital input type switch
INPUT 5/DIGITAL
terminal
INPUT 1 terminal
Component signals.
INPUT 4 terminal
Connect video
equipment.
INPUT 3 terminal
Connect video
equipment with an
S-video terminal.
RS-232C terminal
Control the projector using a
computer.
Terminals
DT-400
12
Page 13
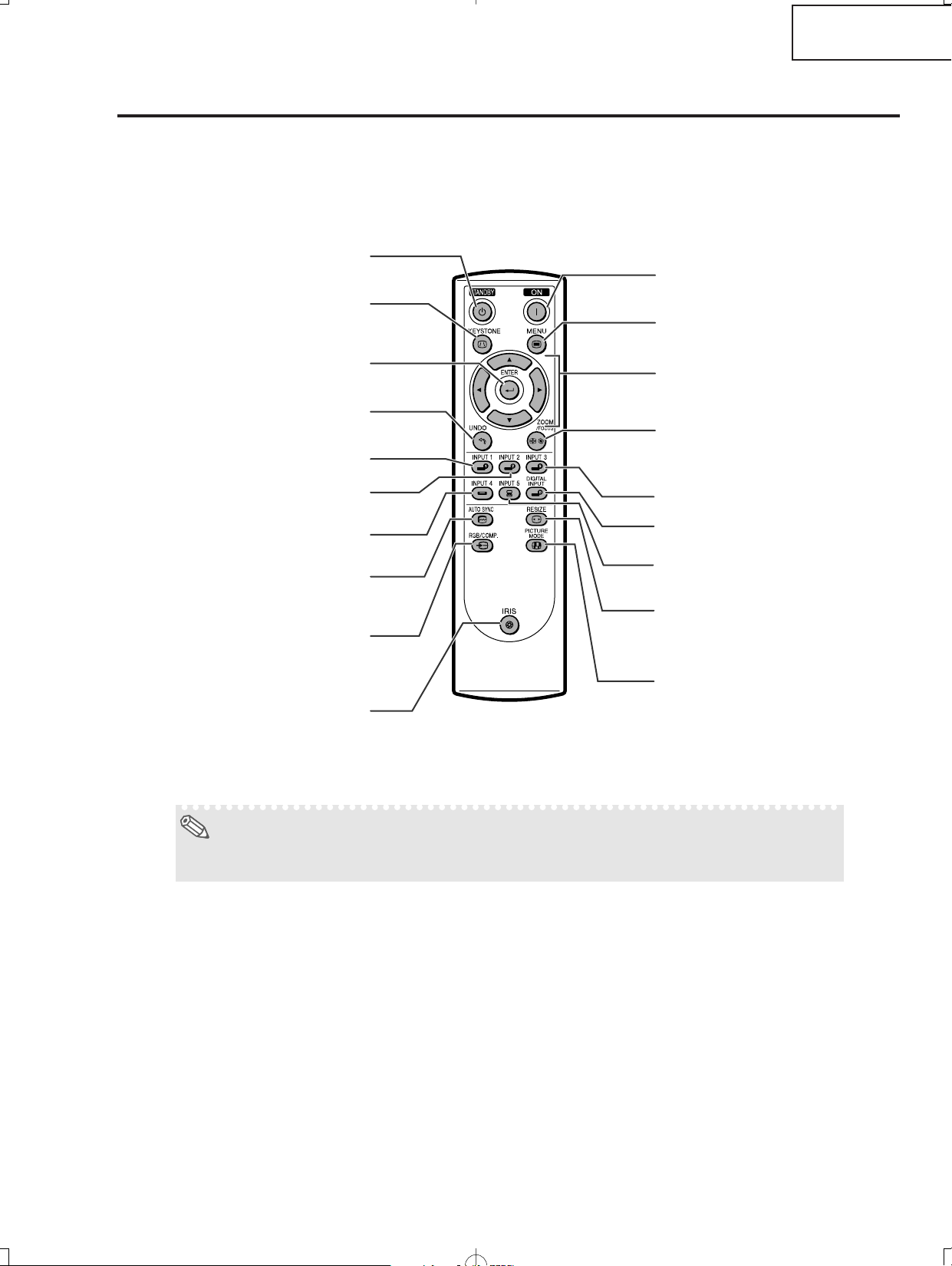
XV-Z2000
Remote Control
Adjustment buttons
('/"/\/|)
MENU button
Display adjustment and setting
screens.
ON button
Turn the power on.
ZOOM/FOCUS button
Adjust the projected image
size or adjusting the focus.
INPUT 3 button
INPUT 5 button
RESIZE button
Switch the picture display
(STRETCH, SIDE BAR, etc.).
DIGITAL INPUT button
PICTURE MODE button
Select the picture setting (Memory)
stored in “Picture Mode” on the
“Picture” menu.
STANDBY button
Put the projector into standby
mode.
KEYSTONE button
Enter the Keystone
Correction mode.
ENTER button
Set items selected or
adjusted on the menu.
UNDO button
Undo an operation or returning to
the previous display.
INPUT 1 button
INPUT 2 button
INPUT 4 button
AUTO SYNC button
Automatically adjust images when
connected to a computer.
RGB/COMP. button
Switch the signal type
(RGB or Component).
IRIS button
Switch “HIGH BRIGHTNESS
MODE” or “HIGH CONTRAST
MODE”.
Note
• All the buttons on the remote control are made of luminous material that is visible in the dark. Visibility will
diminish over time. Exposure to light will recharge the luminous buttons.
DT-400
13
Page 14
XV-Z2000
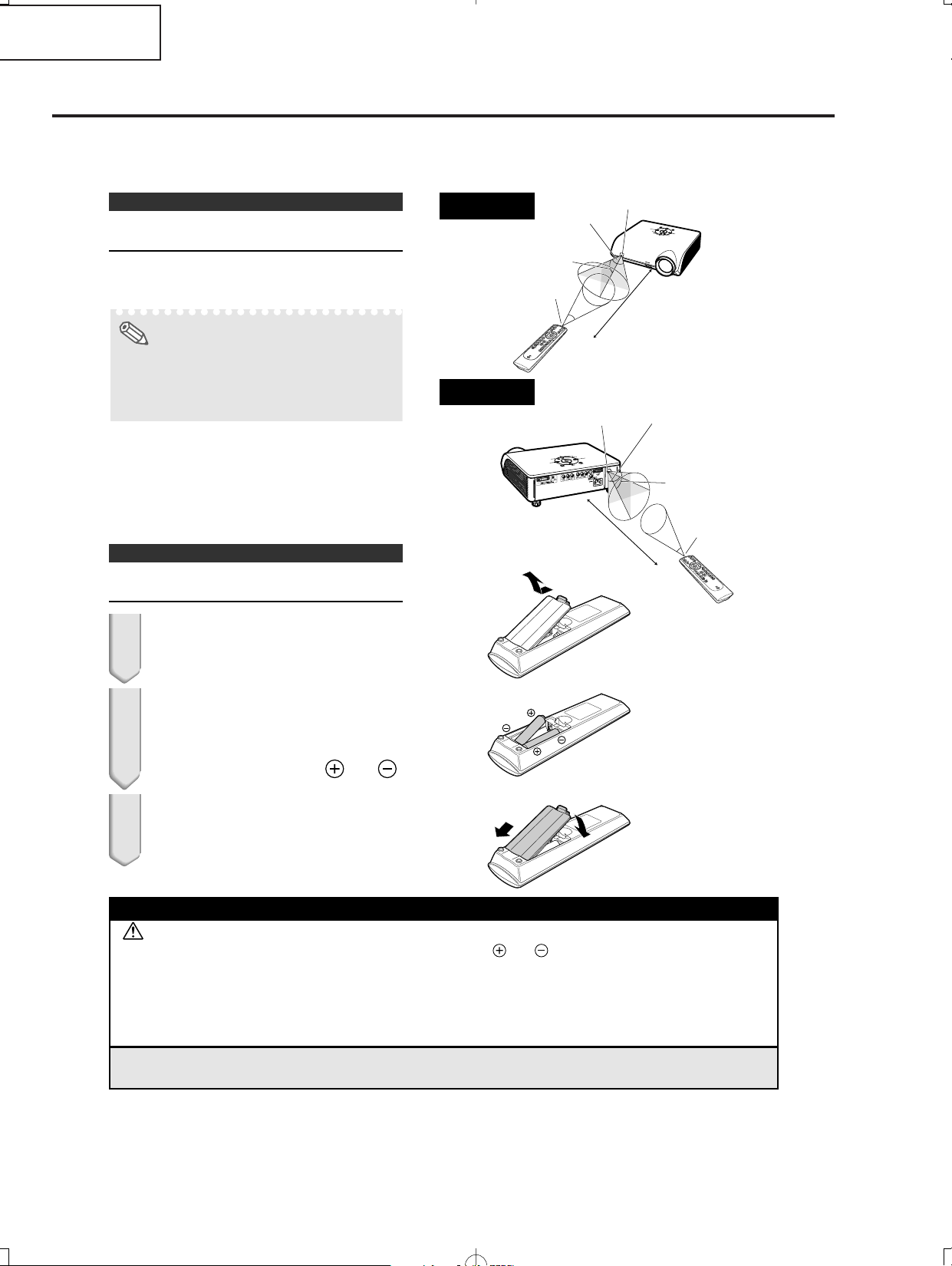
Inserting the Batteries
1
Pull down the tab on the cover
and remove the cover towards
the direction of the arrow.
2
Insert the included batteries
(two “AA” size).
• Insert the batteries making sure the polarities correctly match the
and
marks inside the battery compartment.
3
Insert the lower tab of the cover
into the opening, and lower the
cover until it clicks in place.
Incorrect use of the batteries may cause them to leak or explode. Please follow the precautions below.
Caution
• Insert the batteries making sure the polarities correctly match the and marks inside the battery compartment.
• Batteries of different types have different properties, therefore do not mix batteries of different types.
• Do not mix new and old batteries.
This may shorten the life of new batteries or may cause old batteries to leak.
• Remove the batteries from the remote control once they have run out, as leaving them in can cause them to leak.
Battery fluid from leaked batteries is harmful to skin, therefore ensure to first wipe them and then remove them using a cloth.
• The batteries included with this projector may run down in a short period, depending on how they are kept.
Ensure to replace them as soon as possible with new batteries.
Usable Range
The remote control can be used to control the
projector within the ranges shown in the
illustration.
Note
•
The signal from the remote control can be reflected off a screen for easy operation. However, the effective distance of the signal may
differ depending on the screen material.
When using the remote control:
• Ensure not to drop, expose to moisture or high
temperature.
• The remote control may malfunction under a
fluorescent lamp. In this case, move the projector away from the fluorescent lamp.
Remote control sensor
Remote
control
signal
transmitters
Remote control
23' (7 m)
30°
30°
30°
Front View
Remote control
30°
30°
Remote control sensor
23' (7 m)
Remote
control
signal
transmitters
30°
Rear View
DT-400
14
Page 15
Connection Pin Assignments
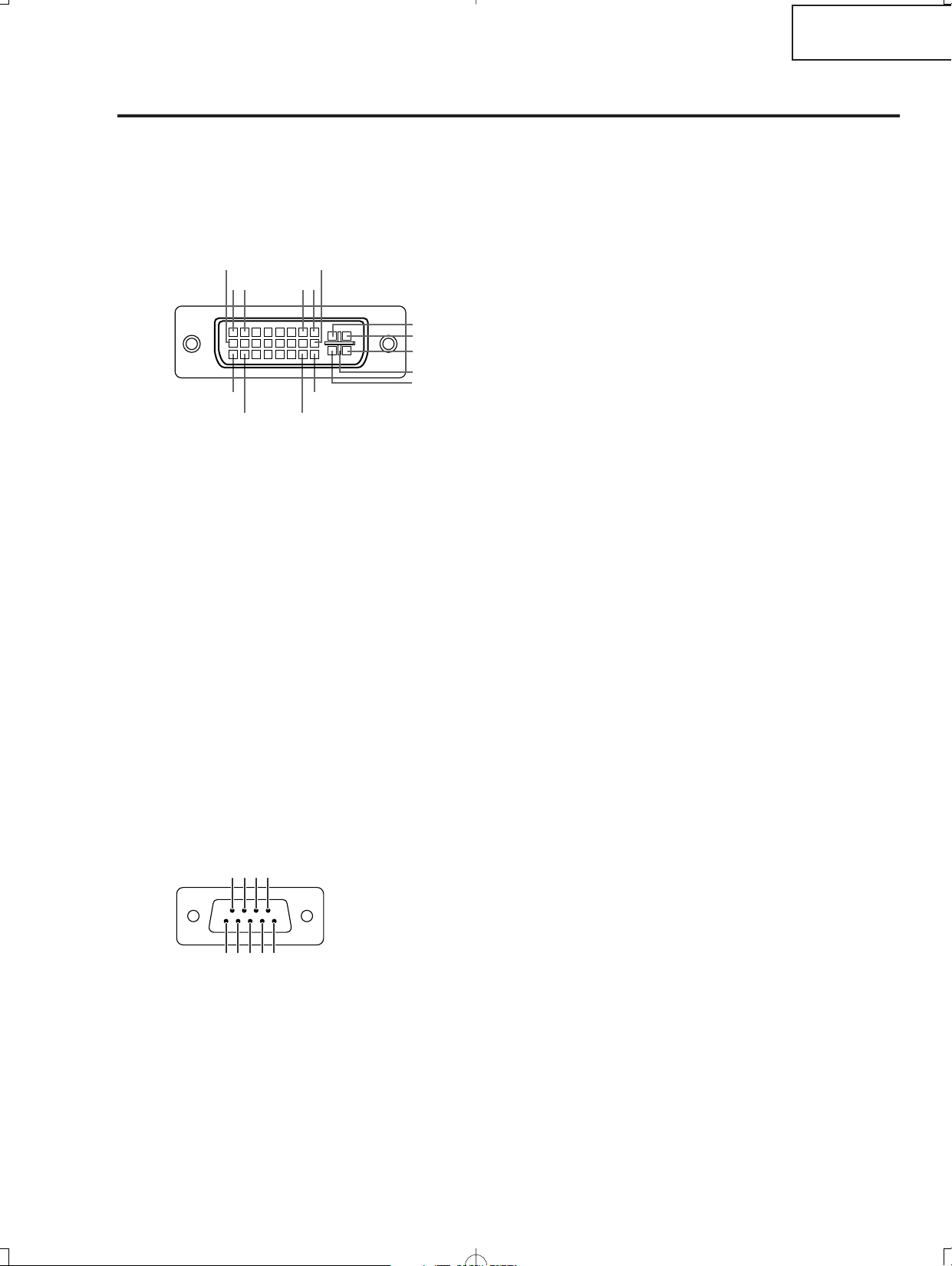
RS-232C Port: 9-pin D-sub male connector
Pin No. Signal Name I/O Reference
1 Not connected
2 RD Receive Data Input Connected to internal circuit
3 SD Send Data Output Connected to internal circuit
4 Reserved Connected to internal circuit
5 SG Signal Ground Connected to internal circuit
6 Reserved Connected to internal circuit
7 Reserved Connected to internal circuit
8 Reserved Connected to internal circuit
9 Not connected
DVI-I (INPUT 5) port : 29 pin connector
•
DVI Digital INPUT
Pin No. Signal Pin No. Signal
1 T.M.D.S data 2– 16 Hot plug detection
2 T.M.D.S data 2+ 17 T.M.D.S data 0–
3 T.M.D.S data 2 shield 18 T.M.D.S data 0+
4 Not connected 19 T.M.D.S data 0 shield
5 Not connected 20 Not connected
6 DDC clock 21 Not connected
7 DDC data 22 T.M.D.S clock shield
8 Not connected 23 T.M.D.S clock+
9 T.M.D.S data 1– 24 T.M.D.S clock–
10 T.M.D.S data 1+ C1 Not connected
11 T.M.D.S data 1 shield C2 Not connected
12 Not connected C3 Not connected
13 Not connected C4 Not connected
14 +5V power C5 Ground
15 Ground
•
DVI Analog RGB Input
Pin No. Signal Pin No. Signal
1 Not connected 16 Hot plug detection
2 Not connected 17 Not connected
3 Not connected 18 Not connected
4 Not connected 19 Not connected
5 Not connected 20 Not connected
6 DDC clock 21 Not connected
7 DDC data 22 Not connected
8 Vertical sync 23 Not connected
9 Not connected 24 Not connected
10 Not connected C1 Analog input Red
11 Not connected C2 Analog input Green
12 Not connected C3 Analog input Blue
13 Not connected C4 Horizontal sync
14 +5V power C5 Ground
15 Ground
•
DVI Analog Component Input
Pin No. Signal Pin No. Signal
1 Not connected 16 Not connected
2 Not connected 17 Not connected
3 Not connected 18 Not connected
4 Not connected 19 Not connected
5 Not connected 20 Not connected
6 Not connected 21 Not connected
7 Not connected 22 Not connected
8 Not connected 23 Not connected
9 Not connected 24 Not connected
10 Not connected C1 Analog input P
R/CR
11 Not connected C2 Analog input Y
12 Not connected C3 Analog input P
B/CB
13 Not connected C4 Not connected
14 Not connected C5 Ground
15 Ground
17
∞∞∞∞∞∞∞∞∞
~
∞∞∞∞∞∞∞∞∞
∞∞∞∞
~
∞∞∞∞
∞∞∞∞
~
∞∞∞∞
24
18 23
C3
21
9
16
C1
C2
C4
C5
87
6789
1
2345
XV-Z2000
DT-400
15
Page 16
XV-Z2000
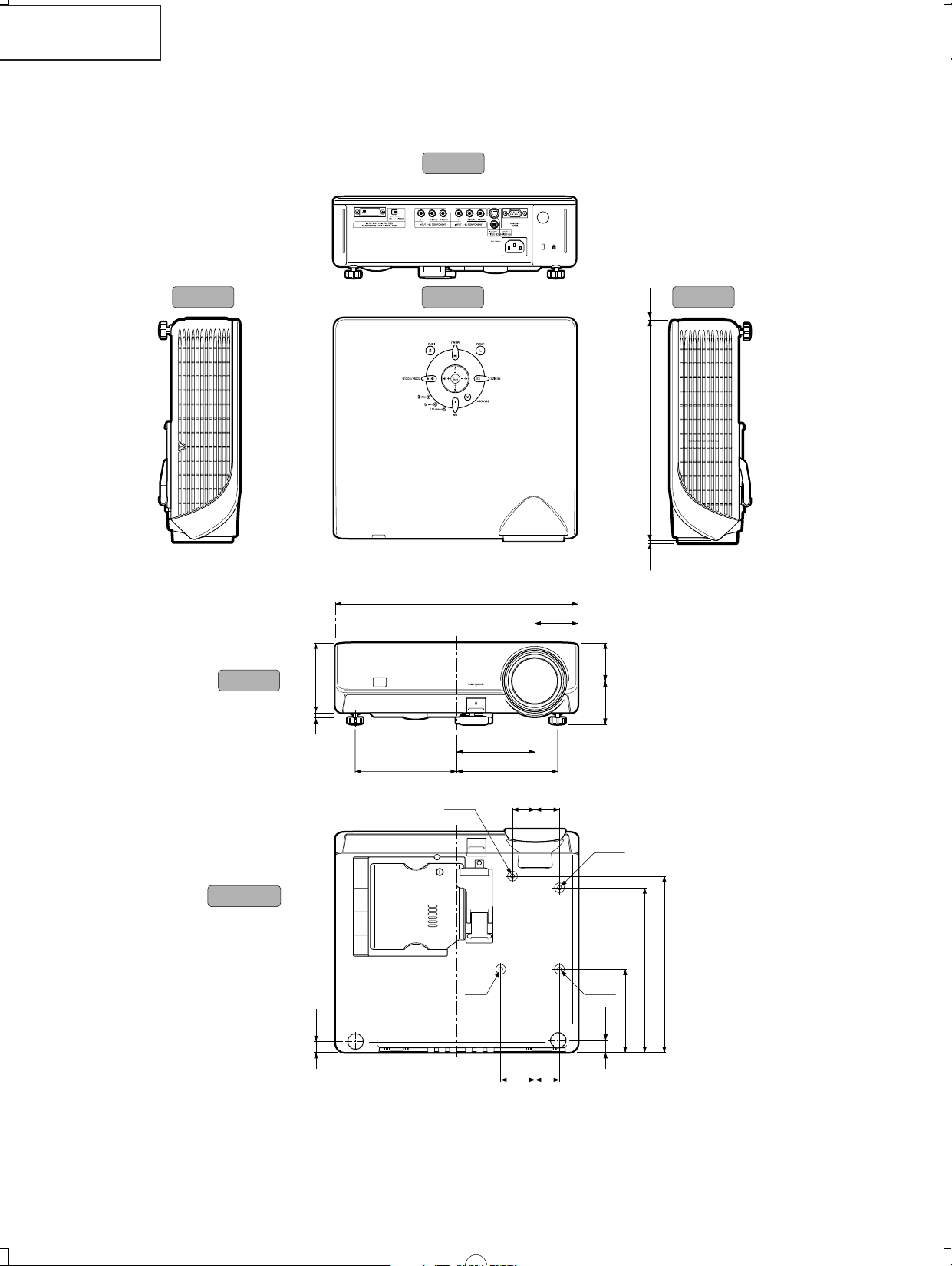
Units: inches (mm)
Side View Side View
Top View
Rear View
Front View
Bottom View
M4
M4
M4
M4
9
/
64
(3.25)
11
7
/
64
(282)
1
/
16
(1.5)
2
11
/64 (55.05)
12
7
/32 (310)
1
59
/
64
(48.5)
3
33
/
64
(89)
13
/
64
(5)
2
3
/
16
(55.5)
3
15
/16 (99.95)
5
7
/64 (129.5)5 7/64 (129.5)
5
/
8
(15.5)
9
/
16
(14)
4
3
/
16
(106.3)
8
9
/
32
(210.3)
8
7
/
8
(225.3)
1 7/
32
(30.9)
1
5
/
32
(29.1)
1
7
/
32
(30.9)
1
3
/
4
(44.1)
DT-400
DIMENSIONS
16
Page 17
XV-Z2000
Lamp Unit Cover
Lamp Unit
1-2
1-3
2-4
2-3
2-1
Thick paper such as a postcard.
To protect the lens barrel
against scratches.
Short side
(10cm)
Long side
(15cm)
Top Body
Bottom Body
2-2
2-2
DT-400
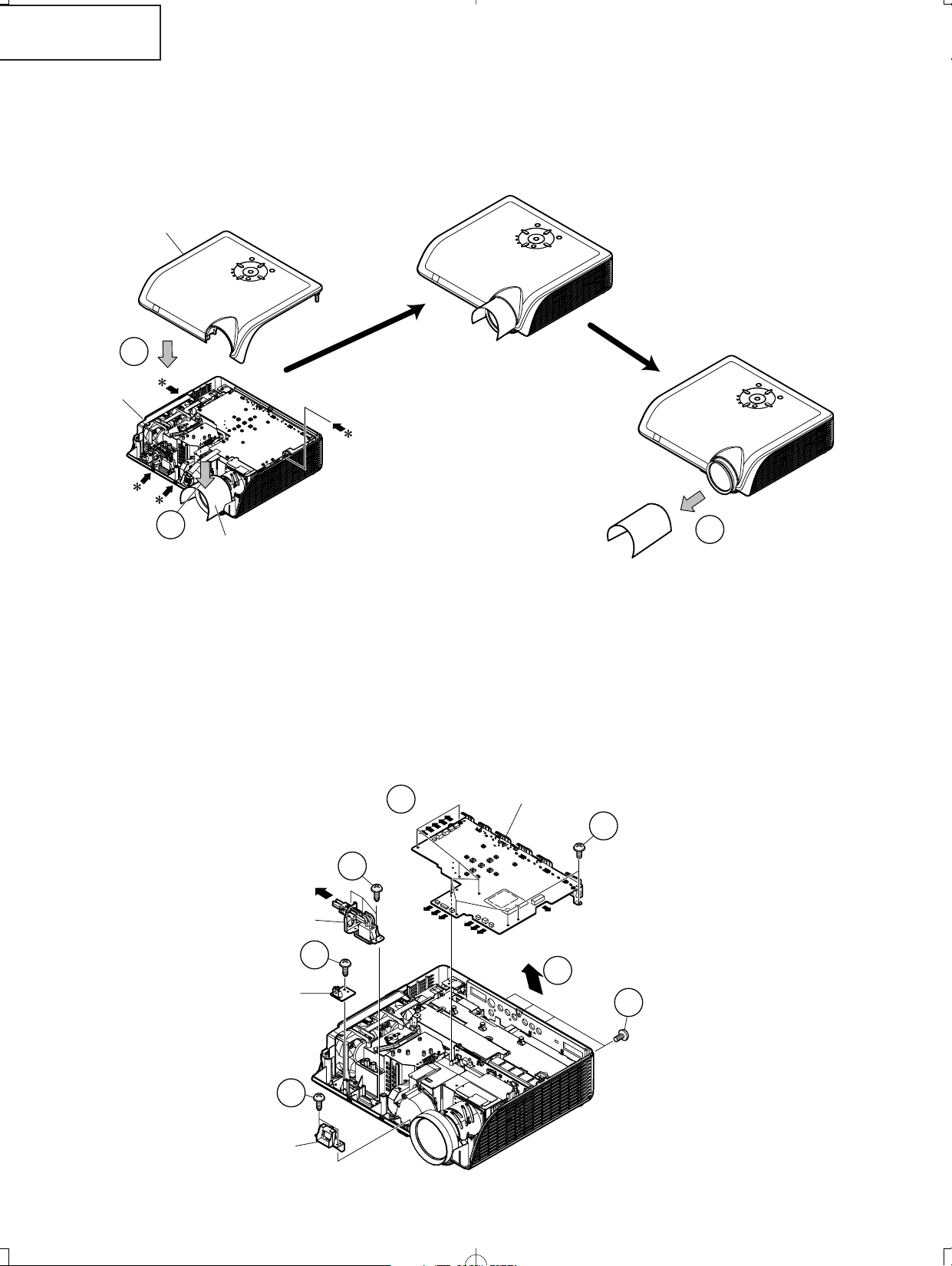
REMOVING OF MAJOR PARTS
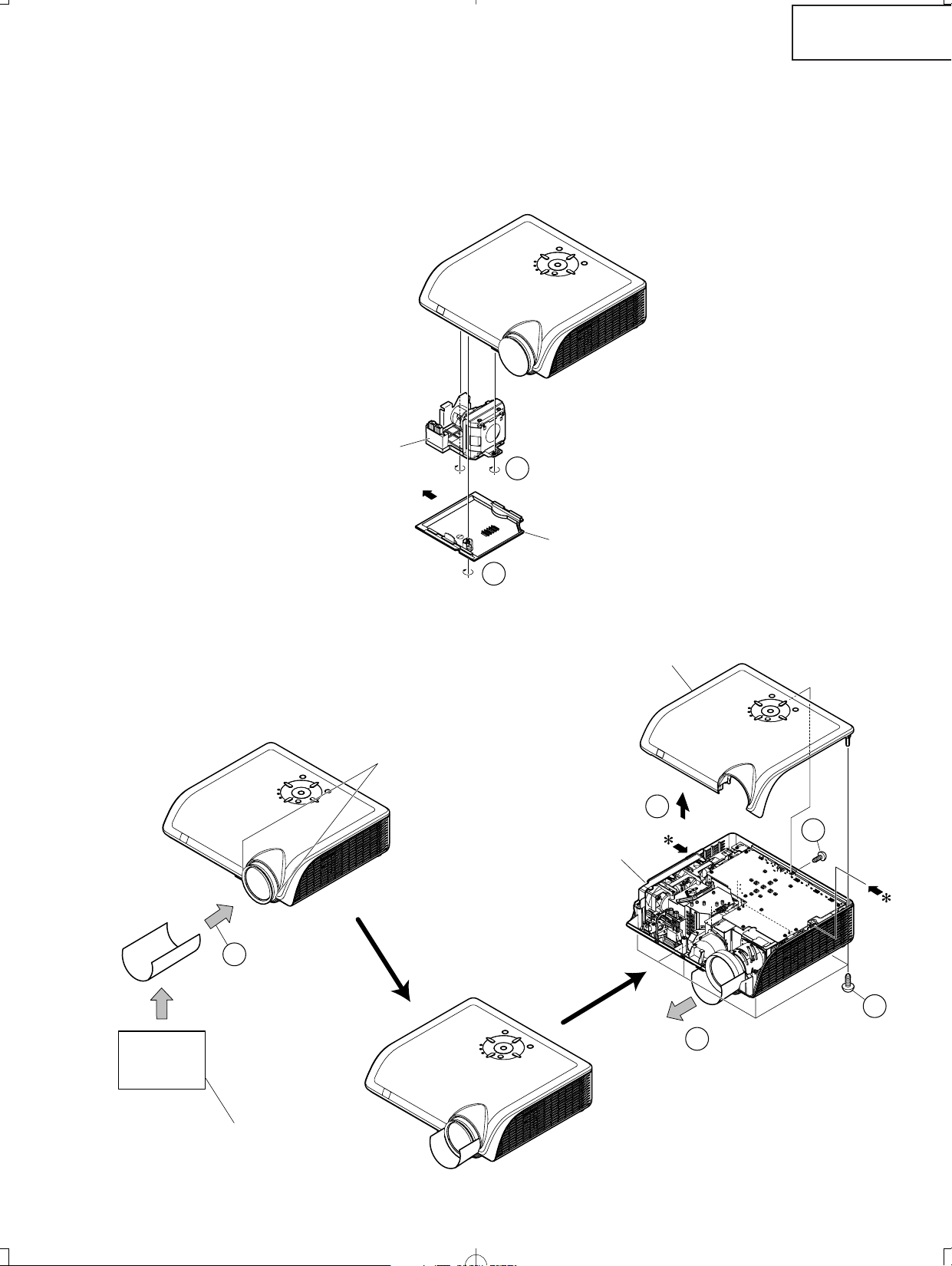
1. Removing the lamp unit cover and the lamp unit
1-1. Loosen the lamp unit cover fixing screw, slide the lamp unit cover in allow direction and lift off the lamp unit
cover.
1-2. Loosen 2 lamp unit fixing screws and lift off the lamp unit.
2. Removing the top body
2-1. Insert thick paper such as a postcard under the lens barrel.
2-2. Remove 7 fixing screws for the top and bottom bodies.
2-3. Press and hold the areas (marked with *) and disengage the claws on the top body to remove the top body.
2-4. Draw out a postcard.
17
Page 18
XV-Z2000
4-1
4-4
4-5
4-6
4-2
4-7
4-3
Main PWB
Button Holder
Switch Bracket
Front-R/C Unit
Top Body
Bottom Body
Thick paper such as postcard
3-2
3-1
3-3
DT-400
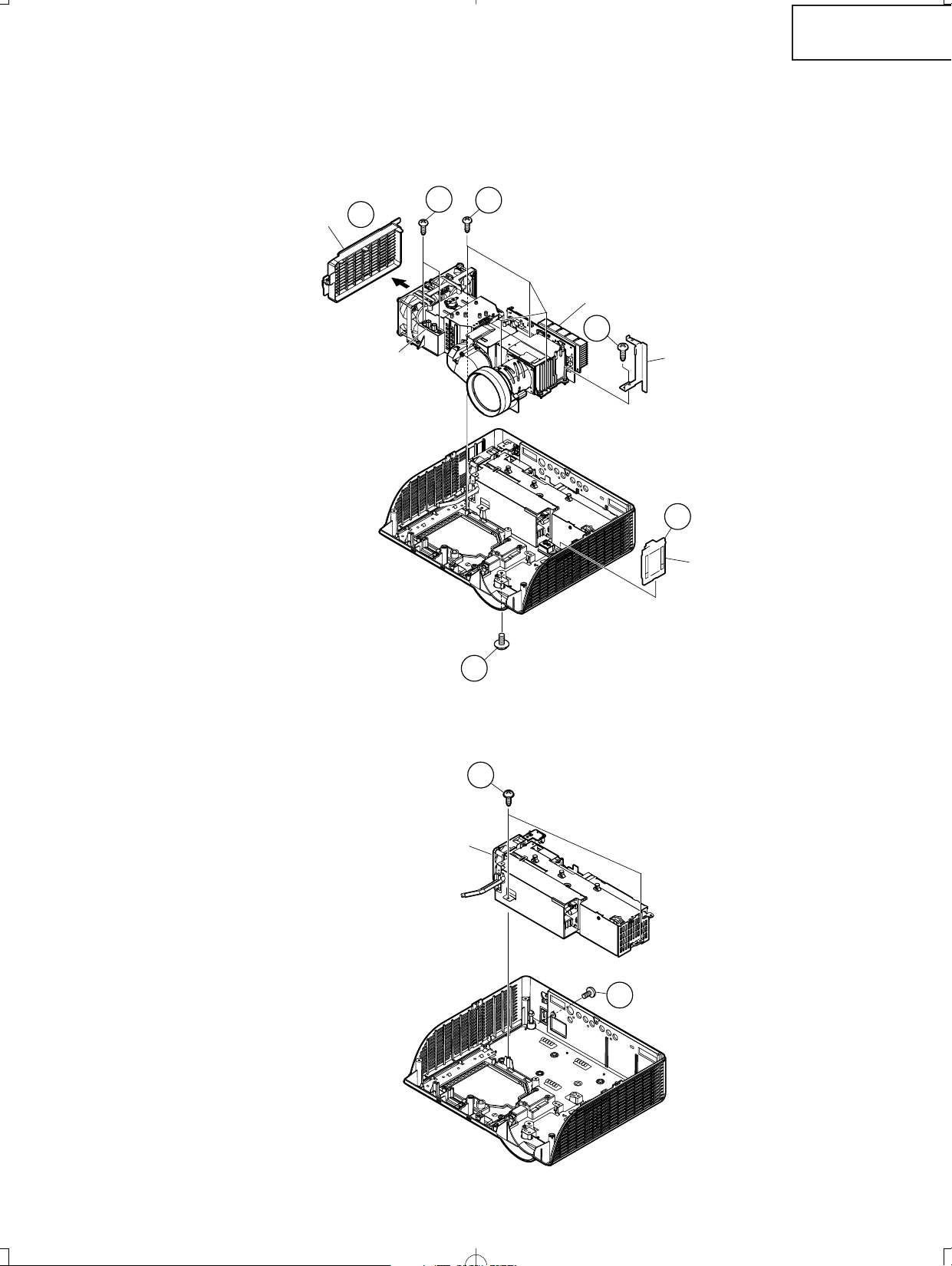
3. Attaching the top body (For the screws to apply, refer back to "2. Removing
the top body".)
3-1. Place the postcard over the lens barrel.
3-2. Place the top body in position. Make sure the four hooks are tightly caught.
3-3. Draw out the postcard.
4. Removing the main PWB unit and the peripheral units
4-1. Remove 4 main PWB fixing screws (terminal side).
4-2. Remove 9 main PWB fixing screws.
4-3. Remove 12 connectors from the main PWB.
4-4. Pull out the switch bracket connector and remove 3 fixing screws.
4-5. Remove the fixing screw for the front R/C PWB.
4-6. Remove 2 fixing screws for the button holder unit.
4-7. Lift off the main PWB in an oblique direction from the optical mechanism unit side.
18
Page 19
Power/Ballast Unit
6-1
6-1
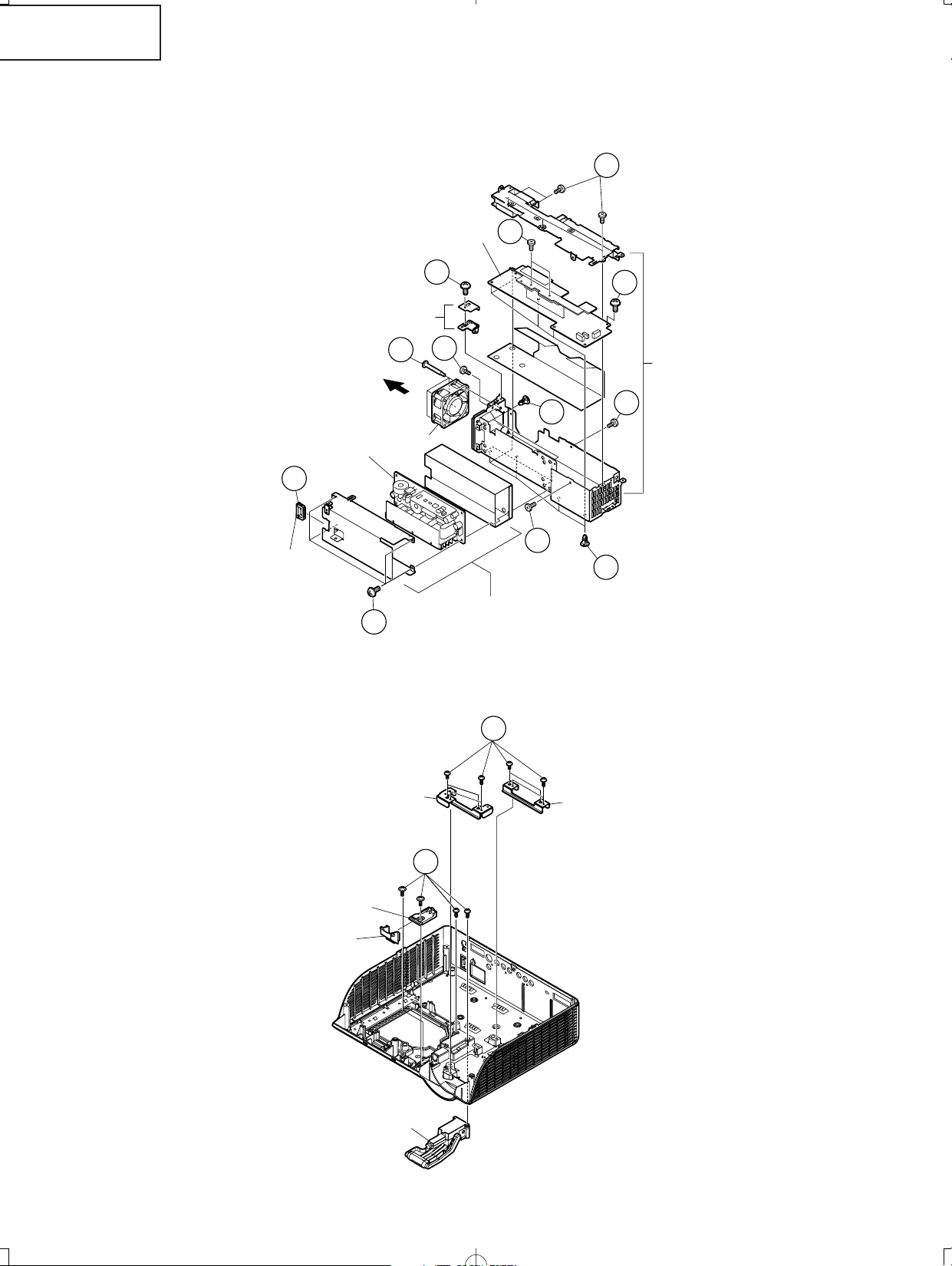
5. Removing the optical mechanism unit
Duct
Optical Mechanism Unit
5-3
5-3
5-2
5-4
Ballast Output Socket
5-1
PWB Bracket
Speaker Cover
5-5
5-1. Remove the fixing screw from the PWB bracket.
5-2. Remove 2 fixing screws for the ballast output socket, and remove the ballast output socket.
5-3. Remove 5 fixing screws for the optical mechanism unit, and remove the optical mechanism unit.
5-4. Remove the duct, pulling up the optical mechanism unit.
5-5. Remove the speaker cover.
XV-Z2000
DT-400
6. Removing the power/ballast unit
6-1. Remove 3 fixing screws for the power/ballast unit.
19
Page 20
XV-Z2000
Bracket-A
Bracket-B
Front Adjuster Foot
Front Adjuster Holder
Height Adjust Button
8-1
8-2
Power Unit
Fan
Air Flow
Ballast Unit
Ballast PWB
Rear-R/C PWB
Power PWB
Edge saddle
7-1
7-2
7-2
7-4
7-3
7-3
7-3
7-3
7-3
7-3
7-3
7-2
DT-400
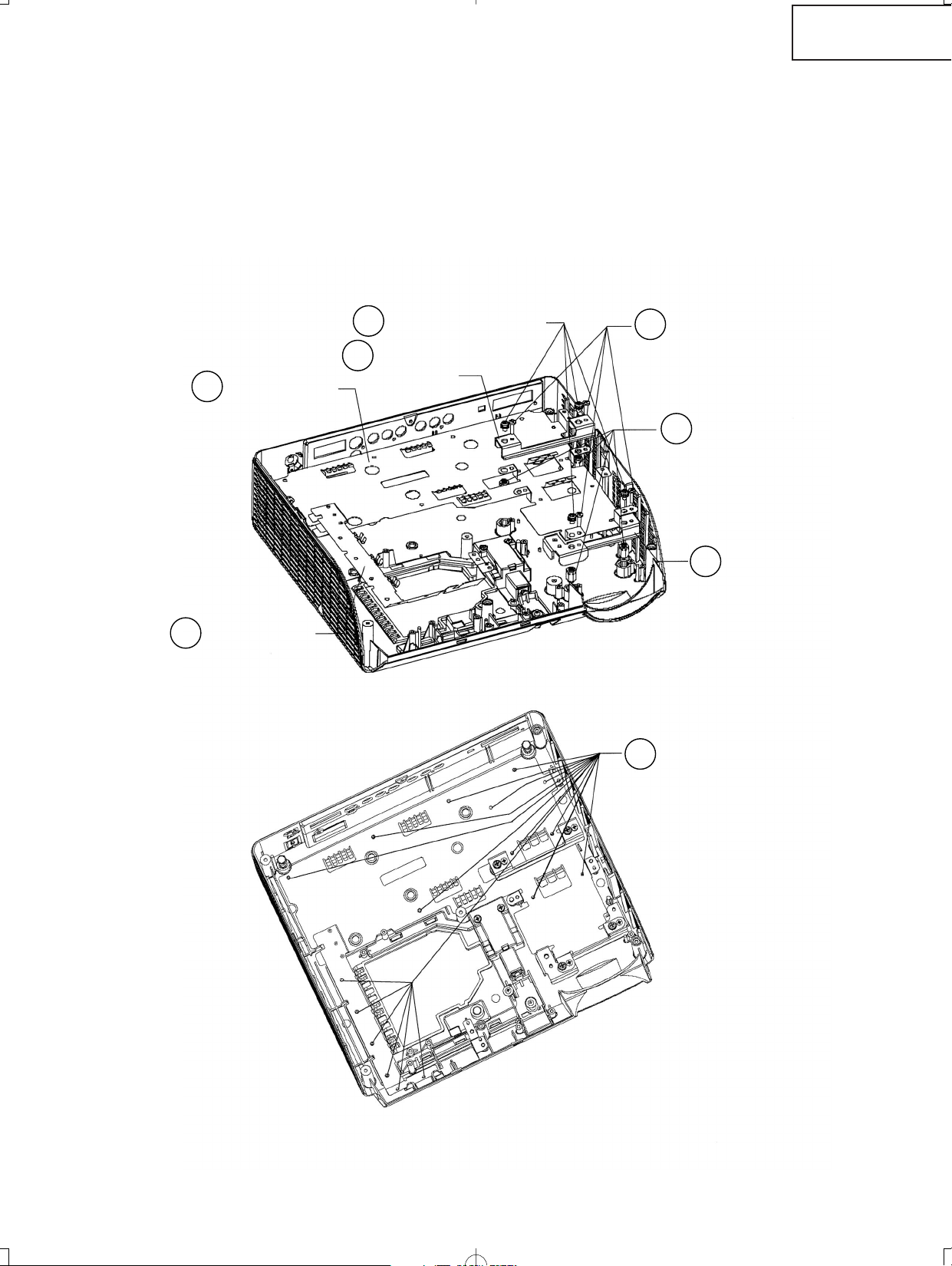
7. Removing the power/ballast unit
7-1. Remove the fixing screw for the rear-R/C PWB.
7-2. Remove 4 fixing screws, 4 WH bosses and the edge saddle for the ballast unit.
7-3. Remove 11 fixing screws and 5 WH bosses for the power unit.
7-4. Remove 4 fixing screws for the fan.
8. Removing the peripheral units
8-1. Remove 4 fixing screws for the front adjuster foot.
8-2. Remove 8 bracket fixing screws and remove the bracket-A and bracket-B.
20
Page 21
9-3
Earth Shield (L)
M4 screw (4 locations)
9-7
Earth Shield (S)
9-6
Reinforcement
(Bracket-B)
9-4
Reinforcement
(Bracket-A)
9-2
Melt the 17 pins.
Precaution
*Melt the pins with a soldering
iron to fix the earth shield.
Finally check for loosenes.
9-8
M3 screw (4 locations)
9-5
Nut (4 locations)
9-1
9. Fixing the earth shield
9-1. Install the four nuts.
9-2. Fit the reinforcement (bracket-A) in position.
9-3. Place the earth shield (L) as specified.
9-4. Fit the reinforcement (bracket-B) in position.
9-5. Tighten up the four M3 screws.
9-6. Tighten up the four M4 screws.
9-7. Place the earth shield (S) as specified.
9-8. Melt the 17 pins of the earth shield.
XV-Z2000
DT-400
21
Page 22
XV-Z2000
Power indicator
Lamp indicator
Temperature warning indicator
Maintenance Indicators
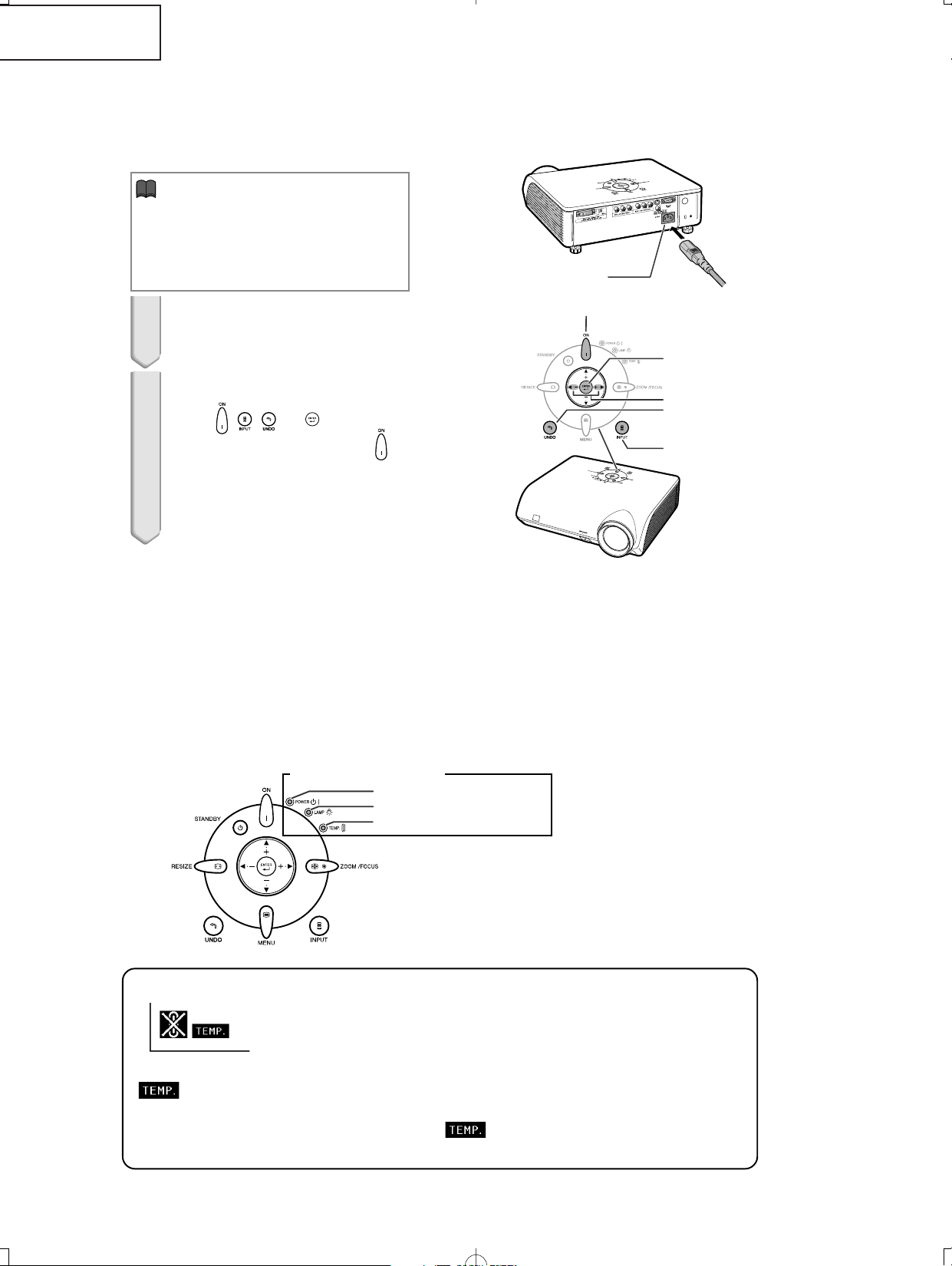
About the temperature warning indicator
If the temperature inside the projector increases, due to blockage of the air vents, or the setting location,
“ ” will illuminate in the lower left corner of the picture. If the temperature keeps on rising, the lamp will
turn off and the temperature warning indicator will blink, the cooling fan will run for a further 90 seconds, and
then the projector will enter the standby mode. After “
” appears, ensure to perform the measures
described on operation manual.
Info
• Make sure to reset the lamp timer only
when replacing the lamp. If you reset the
lamp timer and continue to use the same
lamp, this may cause the lamp to become
damaged or explode.
1 Connect the power cord.
• Plug the power cord into the AC socket
of the projector.
2 Reset the lamp timer.
• Press
, , ,
\\
\\
\,
and
||
||
| on the
projector in order, and then press
on
the projector.
•
“LAMP 0000H” is displayed on the lower
left of the screen, indicating that the lamp
timer is reset.
AC socket
\/|
buttons
ON button
ENTER button
UNDO button
INPUT button
DT-400
RESETTING THE TOTAL LAMP TIMER
● Resetting the total lamp timer
When replacing the lamp, reset the total lamp timer in the procedure below.
Lamp
■ It is recommended that the lamp (sold separately) be replaced when the remaining lamp life becomes 5% or less,
or when you notice a significant deterioration in the picture and color quality. The lamp life (percentage) can be
checked with the on-screen display.
■ Purchase a replacement lamp of type AN-K2LP from your place of purchase, nearest Sharp Projector Dealer or
Service Center.
■ The warning lights (ON/STANDBY button, lamp indicator and temperature warning indicator) on the projector
indicate problems inside the projector.
■ If a problem occurs, either the temperature warning indicator or the lamp indicator will illuminate red, and the
projector will enter the standby mode. After the projector has entered the standby mode, follow the procedures
given below.
22
Page 23
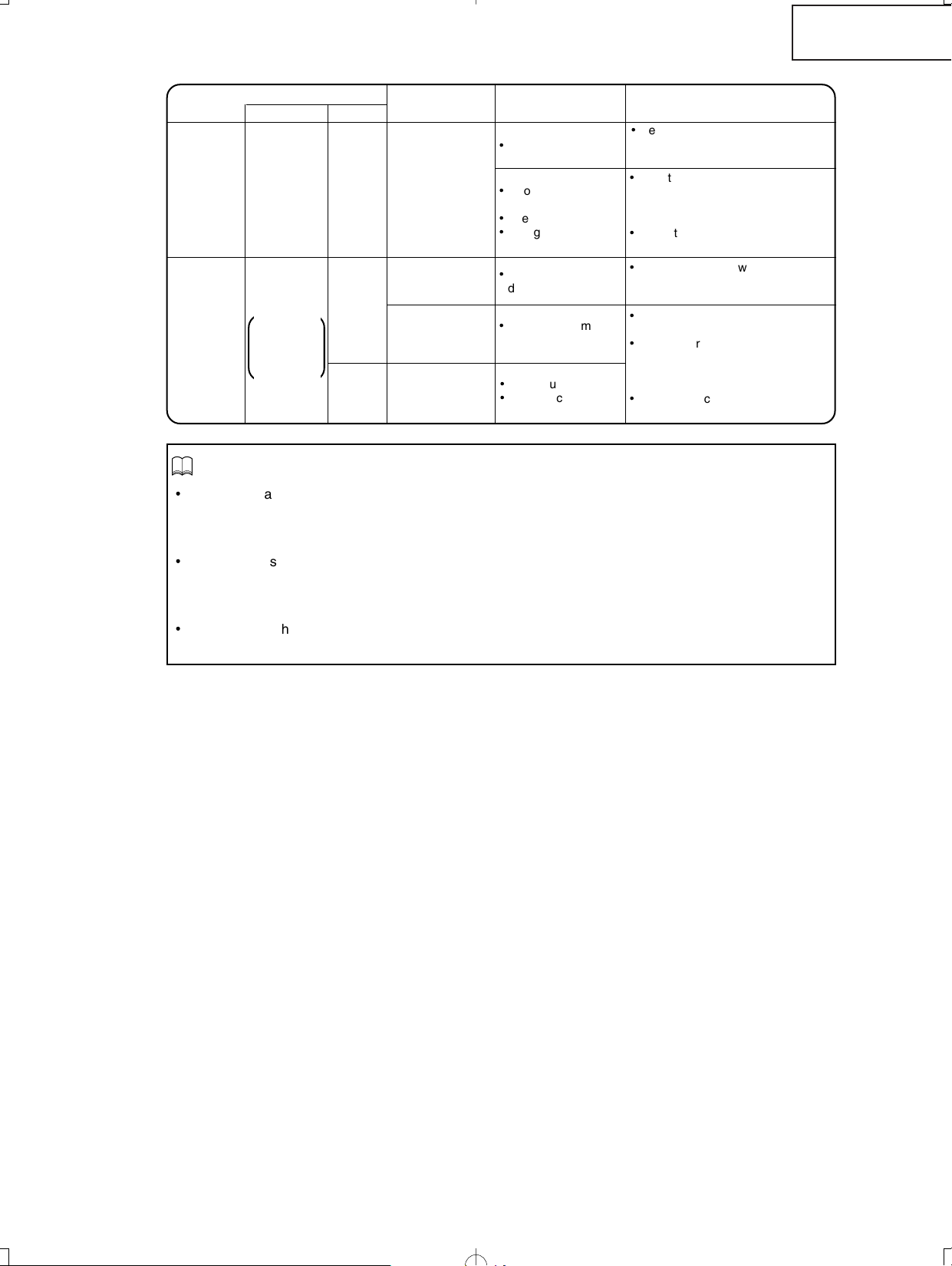
XV-Z2000
Maintenance indicator
Problem
Cause Possible solution
Temperature
warning
indicator
Normal
Abnormal
Off
Red on
(Standby)
The internal
temperature is
abnormally high.
Abnormal
•
Blocked air intake
•
Relocate the projector to an area
with proper ventilation
•
Cooling fan breakdown
•
Internal circuit failure
•
Clogged air intake
•
Take the projector to your nearest
Sharp Authorized Projector Dealer
or Service Center for repair.
•
Clean the exhaust and intake
vents.
Lamp
indicator
Red on
(Standby)
The lamp does
not illuminate.
•
Burnt-out lamp
•
Lamp circuit failure
•
Carefully replace the lamp.
•
Take the projector to your nearest
Sharp Authorized Projector Dealer
or Service Centerfor repair.
•
Please exercise care when
replacing the lamp.
Red on
Time to change
the lamp.
•
Remaining lamp life
becomes 5% or less.
Green on
Green blinks
when the lamp
is warming up
or shutting
down.
Info
•
If the temperature warning indicator illuminates and the projector enters the standby mode, check whether
any of the ventilation holes are blocked and then try turning the power back on. Wait until the projector has
cooled down completely before plugging in the power cord and turning the power back on.
(At least 10 minutes.)
•
If the power is turned off for a brief moment due to power outage or some other cause while using the
projector, and the power supply recovers immediately after that, the lamp indicator will illuminate in red
and the lamp may not be lit. In this case, unplug the power cord from the AC outlet, replace the power
cord in the AC outlet and then turn the power on again.
•
Do not unplug the power cord after the projector has entered the standby mode and while the cooling fan
is running. The cooling fan runs for about 90 seconds.
The lamp does
not illuminate.
•
The lamp is shut
down abnormally.
•
Disconnect the power cord from
the AC outlet, and then connect it
again.
DT-400
23
Page 24
XV-Z2000
DT-400
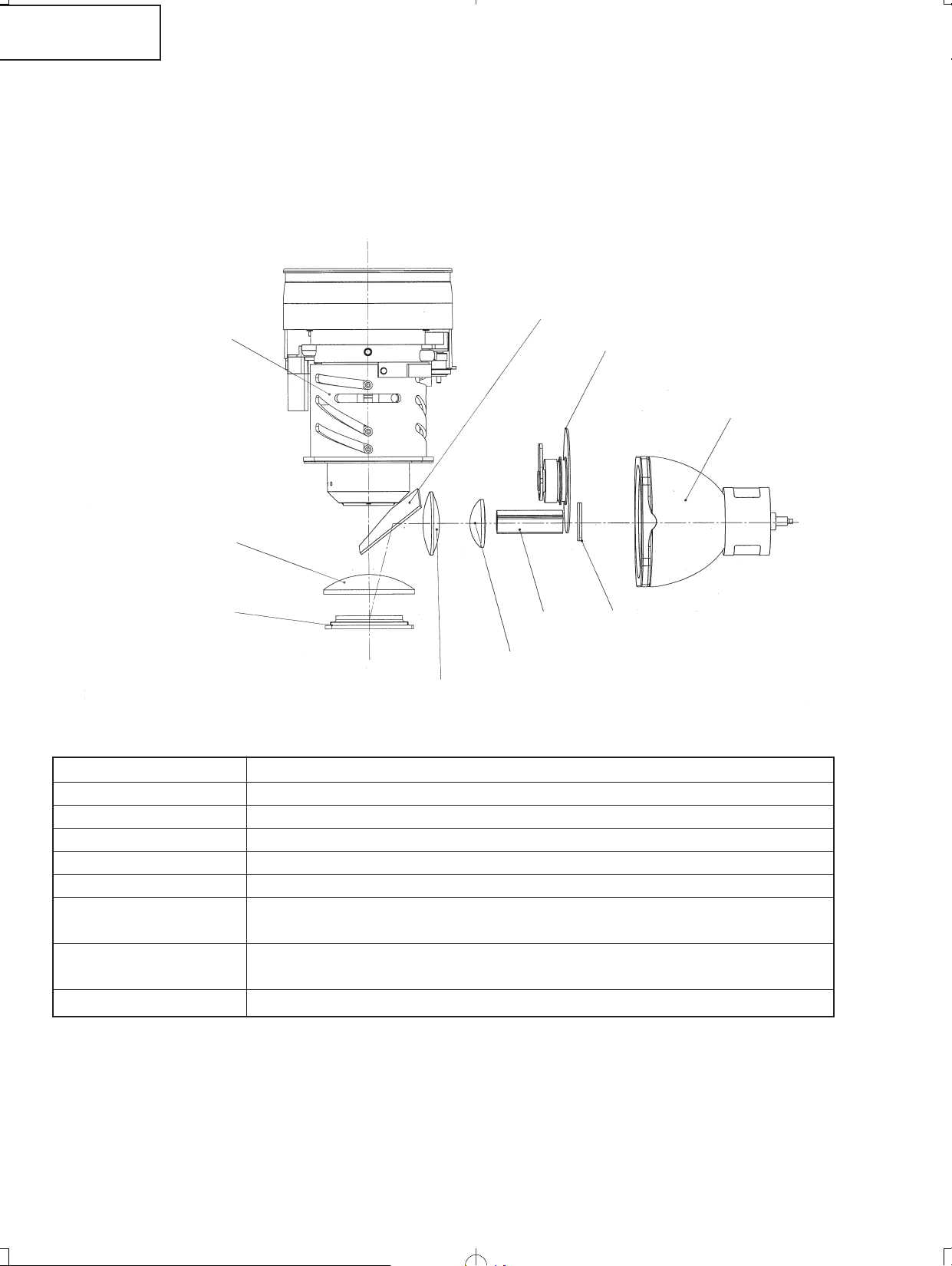
THE OPTICAL UNIT OUTLINE
Layout for proper setup of the optical components and parts (top view)
(Schematic diagram)
Reflection mirror
Projection lens
Field lens
DMD
Rod
Illumination lenses 1
Illumination lenses 2
Item Function
Lamp Light source. DC high-pressure mercury lamp.
Color wheel Splits light from the light source into R, G, B and W through a color filter.
Rod Assures uniform light ray.
Illumination lenses Focus light from the rod on DMD.
Reflection mirror Reflects light from the illumination lenses toward DMD.
Field lens Focuses light from the reflection mirror on DMD and then the light from DMD to
the projection lens.
DMD Turns the internal micromirror ON/OFF at the rate of color component of each dot
of the input source to reflect light.
Projection lens Enlarges light from DMD and projects it on a screen.
Color wheel
Lamp
UV Filter
24
Page 25
XV-Z2000
Air Flow
DT-400
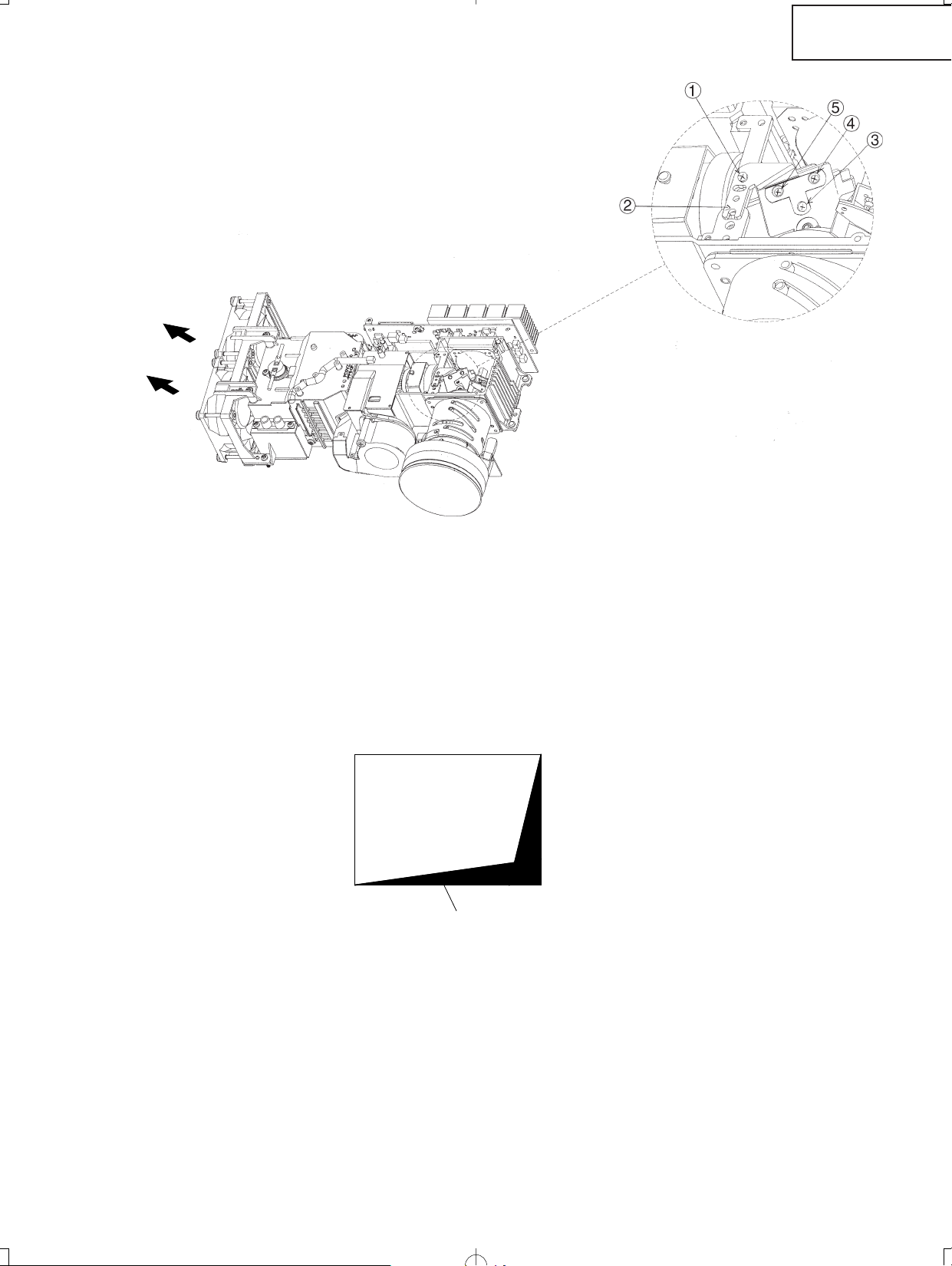
After replacing the DMD, if shading is present on the screen as shown in Figure 1, adjust the lighting area of the
DMD by turning the adjustment screws for the optical engine.
1. Loosen the fixing screw for the adjustment lever 1. Adjust the lighting area by adjustment lever 2 and
then tighten the fixing screw for the adjustment lever 1.
2. If the lightening area cannot be adjusted after the above procedure, loosen the fixing screw 3, adjust the
area with adjustment screws 4 and 5, and then tighten the fixing screw 3.
Shading
Fig. 1
25
Page 26
XV-Z2000
R
G
B
DT-400
ELECTRICAL ADJUSTMENT
No. Adjusting point Adjusting conditions Adjusting procedure
1 Initialization of
EEPROM
2 Adjustment of
CW index
3-1 R-Bright / R-
Contrast
1. Turn on the power (the
lamp lights up) and warm
up the system for 15 minutes.
1. Input the gradation pattern of RGB.
(SVGA60Hz or XGA)
2. Select the following
group and subject.
Group: DLP
Subject: INDEX DELAY
1. Group: AD
Subject: R-BRIGHT
(Black level)
R-CONTRAST
(White level)
2. Feed the window pattern
signal containing 91%
(0.64Vp-p) R signal and
0% level.
(Process/Gamma interaction)
(SVGA or XGA)
Input 5 RGB input
1. Carry out the following setting.
Using the remote controller or press S2002 to
enter the process mode, and execute SS2 on SS
menu.
1. Select subject and make adjustment so that the
lamp gradation patterns of R, G and B should be
smooth without noise.
1. Observe the 0% window pattern chromaticity on
CA100.
2. Starting with a bit dropout screen, vary the RBright setting until the bright red "x" setting turns
toward the black tone and stays there. Now raise
the setting by one point and adjust to the point
where the first bit dropout is encountered (the
setting changes over 5/1000).
3. Observe the 91% R signal chromaticity on CA100.
4. Starting with a bit dropout screen, vary the RContrast setting until the bright red "x" setting
turns toward the black tone and stays there. Now
raise the setting by one point and adjust to the
point where the first bit dropout is encountered
(the setting changes over 5/1000).
3-2 G-Bright / G-
Contrast
1. Group: AD
Subject: G-BRIGHT
(Black level)
G-CONTRAST
(White level)
2. Feed the window pattern
signal containing 91%
(0.64Vp-p) G signal and
0% level.
(Process/Gamma interaction)
(SVGA or XGA)
Input 5 RGB input
1. Observe the 0% window pattern chromaticity on
CA100.
2. Starting with a bit dropout screen, vary the GBright setting until the bright green "y" setting
turns toward the black tone and stays there. Now
raise the setting by one point and adjust to the
point where the first bit dropout is encountered
(the setting changes over 5/1000).
3. Observe the 91% G signal chromaticity on CA100.
4. Starting with a bit dropout screen, vary the RContrast setting until the bright green "y" setting turns toward the black tone and stays there.
Now raise the setting by one point and adjust to
the point where the first bit dropout is encountered (the setting changes over 5/1000).
26
Page 27
No. Adjusting point Adjusting conditions Adjusting procedure
XV-Z2000
DT-400
3-3 B-Bright / B-
Contrast
4-1 DTV Bright/
Contrast
Adjustment
4-2 DTV R-Bright/
Contrast
Adjustment
1. Group: AD
Subject: B-BRIGHT
(Black level)
B-CONTRAST
(White level)
2. Feed the window pattern
signal containing 91%
(0.64Vp-p) B signal and
0% level.
(Process/Gamma interaction)
(SVGA or XGA)
Input 5 RGB input
1. Group: DTV
Subject: BRIGHT
(Black level)
CONTRAST
(White level)
1. Group: DTV
Subject: R-BRIGHT
(Black level)
R-CONTRAST
(White level)
(Process/GAMMA interaction Input5 Color difference input)
1. Observe the 0% window pattern chromaticity on
CA100.
2. Starting with a bit dropout screen, vary the BBright setting until the bright blue "y" setting turns
toward the black tone and stays there. Now raise
the setting by one point and adjust to the point
where the first bit dropout is encountered (the
setting changes over 5/1000).
3. Observe the 91% G signal chromaticity on CA100.
4. Starting with a bit dropout screen, vary the BContrast setting until the bright blue "y" setting
turns toward the black tone and stays there. Now
raise the setting by one point and adjust to the
point where the first bit dropout is encountered
(the setting changes over 5/1000).
1. Check the fixed value.
Contrast: 5
Bright: 55
1. Observe the 0%black window pattern chromaticity on CA100.
2. Starting with a bit dropout screen, vary the Bright
setting until the bright red "x" setting turns toward the black tone and stays there. Now raise
the setting by one point and adjust to the point
where the first bit dropout is encountered (the
setting changes over 5/1000).
3. Observe the 100% W window pattern chromaticity on CA100.
4. Starting with a bit dropout screen, vary the Contrast setting until the bright red "x" setting turns
toward the black tone and stays there. Now raise
the setting by one point and adjust to the point
where the first bit dropout is encountered (the
setting changes over 5/1000).
4-3 DTV G-Bright/
Contrast
Adjustment
1. Group: DTV
Subject:G-BRIGHT
(Black level)
G-CONTRAST
(White level)
(Process/GAMMA interaction Input5 Color difference input)
1. Observe the 0%black window pattern chromaticity on CA100.
2. Starting with a bit dropout screen, vary the Bright
setting until the bright green "y" setting turns
toward the black tone and stays there. Now raise
the setting by one point and adjust to the point
where the first bit dropout is encountered (the
setting changes over 5/1000).
3. Observe the 100% W window pattern chromaticity on CA100.
4. Starting with a bit dropout screen, vary the Contrast setting until the bright green "y" setting turns
toward the black tone and stays there. Now raise
the setting by one point and adjust to the point
where the first bit dropout is encountered (the
setting changes over 5/1000).
27
Page 28
XV-Z2000
DT-400
No. Adjusting point Adjusting conditions Adjusting procedure
4-4 DTV B-Bright/
Contrast
Adjustment
5 DTV Tint 1. Group: DTV
6 DTV Color
Saturation
Level
1. Group: DTV
Subject: B-BRIGHT
(Black level)
B-CONTRAST
(White level)
(Process/GAMMA interaction Input5 Color difference input)
Subject: Tint
1. Group: DTV
Subject: Color
1. Observe the 0%black window pattern chromaticity on CA100.
2. Starting with a bit dropout screen, vary the Bright
setting until the bright blue "y" setting turns toward the black tone and stays there. Now raise
the setting by one point and adjust to the point
where the first bit dropout is encountered (the
setting changes over 5/1000).
3. Observe the 100% W window pattern chromaticity on CA100.
4. Starting with a bit dropout screen, vary the Contrast setting until the bright blue "y" setting turns
toward the black tone and stays there. Now raise
the setting by one point and adjust to the point
where the first bit dropout is encountered (the
setting changes over 5/1000).
1. Check the fixed value.
Tint: 8
1. Check the fixed value.
Color: 4
7 DVD Bright/
Contrast
Adjustment
8 DVD Tint 1. Check the fixed value.
9 DTV Color
Saturation Level
10 Video Bright/
Contrast
Adjustment
11 VIDEO Tint 1. Group: VIDEO
1. Group: DVD
Subject: BRIGHT
(Black level)
CONTRAST
(White level)
1. Group: DVD
Subject: Tint
1. Group: DVD
Subject: Color
1. Group: VIDEO
Subject: BRIGHT
(Black level)
CONTRAST
(White level)
Subject: N-Tint
P-Tint
S-Tint
1. Check the fixed value.
Contrast: 5
Bright: 55
Tint: 4
1. Check the fixed value.
Color: 5
1. Check the fixed value.
Contrast: 5
Bright: 55
1. Check the fixed values.
N-Tint: 8
P-Tint: 4
S-Tint: 4
12 VIDEO Color
Saturation Level
1. Group: VIDEO
Subject: N-Color
P-Color
S-Color
1. Check the fixed values.
N-Color: 7
P-Color: 4
S-Color: 7
28
Page 29
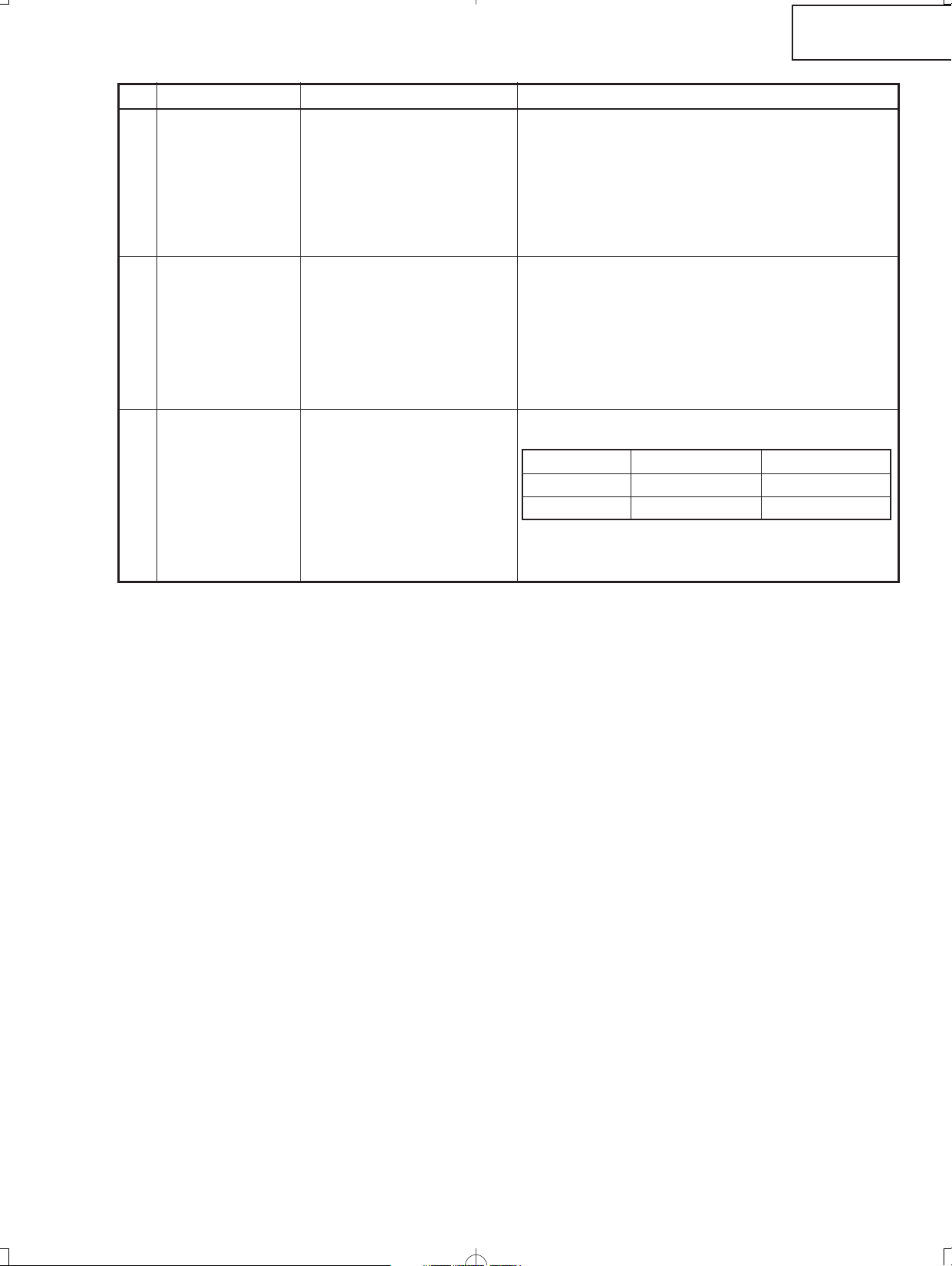
No. Adjusting point Adjusting conditions Adjusting procedure
XV-Z2000
DT-400
13 DVD White
balance
(Auto
adjustment)
14 DLP voltage
adjustment
15 Factory setting
1. Feed the component 75%
gray scale signal.
2. Group: PIXEL
Subject:R-GAIN (R)
B-GAIN (B)
Input 5 Color
difference input
1. Read the DLP-listed volt-
age rank.
2. Make the switch setting
corresponding to the readout rank.
(on the Formatter PWB)
1. Adjust the white balance by controlling R-GAIN and
B-GAIN.
(Adjust x=298 and y=319.)
1. Make this adjustment when the DLP chip has
been replaced or the combination of DLP chip
and Formatter PWB has been changed.
Ranking: D E
1. Make the following settings.
Destination Process adjustment
Europe SS3 Factory setting 3
North America SS4 Factory setting 4
Remote controller setting
29
29
Page 30
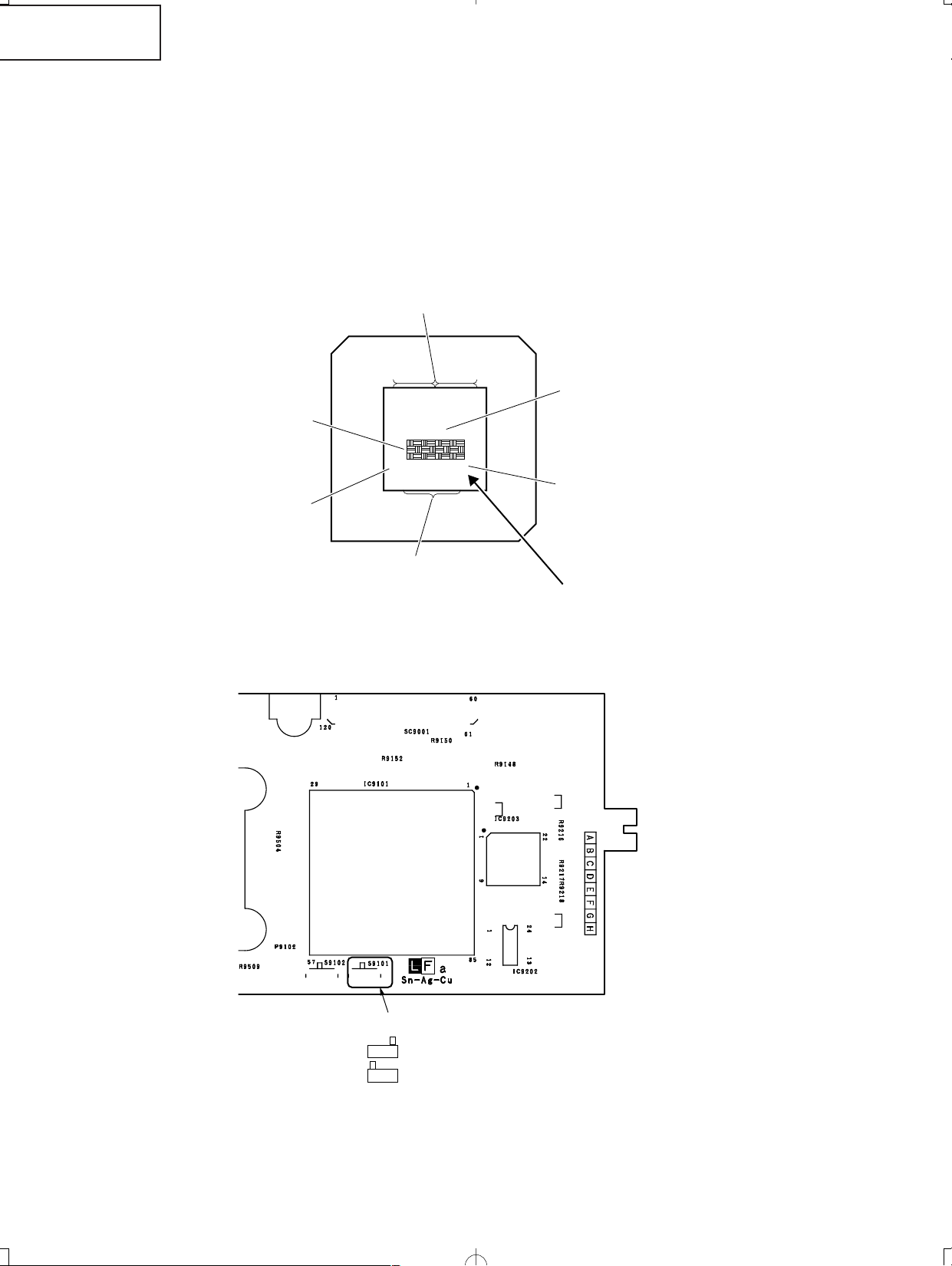
XV-Z2000
*1272-6bbc
CHXXXX
LLLLL
YYYYYYY
L LLL LM
TI Intenal Numbering
TI Intenal Numbering
2-Dimensional Matrix Code
(DMD Part Number and
Serial Number)
Part 1 of Serial Number
(7 characters)
Part 2 of Serial Number
(6 or 7 characters)
DMD Part Number
The last alphabet letter indicates the
Bin voltage setting (D. E).
1
DT-400
* Precautions in setting up the DMD (Digital Micromirror Device) unit
Before connecting the formatter PWB to the optical engine, take the following steps. Look at the voltage rank marking
that is on the DMD itself. Referring to this marking, set the DIP switches on the formatter PWB. And connect this PWB
to the optical engine. Wrong settings will adversely affect the system performance.
Set the formatter PWB switches according to the Bin voltage shown on the back face of the DMD.
2Based on Bin voltage, switch is set up as follows.
D:
E:
30
Page 31

XV-Z2000
DT-400
Calling and quitting the process mode with the control keys on this model.
∗ Although it is possible for the process OUT to exit using the process menu, the IN/OUT toggle command is also
available considering the existing specification.
1. Calling and quitting
With the menu not displayed, press the "'", "'", """, """, "|", "\" and "ENTER" keys on main unit.
2. Others
Press the S2002 process key (toggle) on the main PWB to call and quit the process menu.
Note: When adjusting in the process mode, set a signal with a vertical frequency of 60 Hz or no signal. (May not be
properly adjusted with other signals.)
» Adjustment mode process menu
Adjustment mode process menu 1
* Adjust only the shaded items below.
Adjustment Process Menu
First layer DTV VERSION
DVD SS
VIDEO TEMP
AD OPTION
DLP PATTERN
VIDEO1 LAMP
PIXEL LINE
Pedestal EXIT
second layer Initial Value
DTV Contrast 5
Tint 8
Color 4
Sharpness 1
Bright 55
R-Bright 20
G-Bright 20
B-Bright 20
R-Contrast 120
G-Contrast 120
B-Contrast 120
EXIT
DVD Contrast 5
Tint 4
Color 5
Sharpness 1
CTi-Level 1
LTi-Level 0
CB-Offset 7
CR-Offset 7
Bright 55
B-DRIVE 41
R-DRIVE 41
EXIT
VIDEO Contrast 5
N-Tint 7
P-Tint 4
S-Tint 4
N-Color 7
P-Color 4
S-Color 7
Sharpness 2
CTi-Level 1
LTi-Level 0
CB-Offset 7
CR-Offset 7
Bright 55
B-DRIVE 41
R-DRIVE 41
EXIT
31
Page 32

XV-Z2000
DT-400
Adjustment mode process menu 2
second layer Initial Value
AD R-Bright 40
G-Bright 40
B-Bright 40
R-Contrast 120
G-Contrast 120
B-Contrast 120
EXIT
DLP Index Delay 325
R-Bright 128
G-Bright 128
B-Bright 128
R-Contrast 100
G-Contrast 100
B-Contrast 100
EXIT
VIDEO1 N-Contrast 14
P-Contrast 14
S-Contrast 15
Color 17
NT3.58Delay 0
NT4.43Delay 1
PAL Delay 5
SECAM Delay 0
Shapness2 1
EXIT
PIXEL R-GAIN 128
G-GAIN 128
B-GAIN 128
EXIT
Pedestal R-Bright -10
G-Bright -10
B-Bright -10
R-Contrast +10
G-Contrast +10
B-Contrast +10
EXIT
second layer Initial Value
VERSION Build
Boot Code
Config
RomCode
GUI
DLP
EXIT
SS SS2
SS3 EU
SS4 US
SS5 JPN
SS6 CHIN
EXIT
TEMP Temp1 Parameter of sensor1
Temp2 Parameter of sensor2
Temp3
Temp4
EXIT
OPTION
PATTERN Cross Hatch
LAMP Current Time Current time of use
LINE OFF
PW365 Gamma
DLP Gamma 8
EXIT
Color bar
EXIT
History1 One Earlier
History2 Two Earlier
History3 Three Earlier
History4 Four Earlier
TOTAL TIME Total operating hours
EXIT
LED CHECK
EXIT
Standard VIDEO
32
Page 33

Checking the basic operation
Does the power LED light up or flash in
red or green?
Go to "Checking the power supply system"
and "Checking the power unit".
Does the set function with its keys or the
remote controller?
Go to "Checking the peripheral circuits of
the microprocessor".
Does the cooling fan rotate, and the lamp
turn on?
Go to "Checking the lamp light-up".
Is the user menu displayed?
Go to "Checking the peripheral circuits of
the formatter".
Does the analog RGB input function
normally?
Go to "Checking the RGB input".
Does the component input function
normally?
Go to "Checking the component".
Does the VIDEO input function normally?
Go to "
Checking of
VIDEO input ".
Does the DVI input function normally?
Check the DVI circuit and its peripheral
circuits.
Does the RS-232C function?
Go to "Checking RS-232C".
Does the autofocus function?
Go to "Checking the IRIS, FOCUS and
ZOOM motors".
End.
NO
YES
NO
YES
NO
YES
NO
YES
NO
YES
NO
YES
NO
YES
NO
YES
NO
YES
NO
YES
XV-Z2000
DT-400
TROUBLESHOOTING TABLE
33
Page 34

XV-Z2000
Checking the power supply system
Is 13V outputted to pins (9) and (11) of
P1707?
Is 6V outputted to pins (1) and (3) of
P1707?
Go to "Checking the power unit".
Go to "Checking the power unit".
Is the connector of P1707 fully inserted?
Is the voltage of 6V applied to both ends?
Replace the thermal fuse.
Is B+5VA outputted from IC1707?
Check IC1707 and its peripheral circuits.
Is Bu+5V outputted from IC1701?
Check IC1701 and its peripheral circuits.
Is Bu+3.3V outputted from IC1702?
Check IC1702 and its peripheral circuits.
Is Bu+2.5V outputted from IC1703?
Check IC1703 and its peripheral circuits.
Go to "Checking the peripheral circuits of
the microprocessor".
NO
YES
NO
YES
NO
YES
NO
YES
NO
YES
NO
YES
YES
NO
DT-400
34
Page 35

XV-Z2000
NO
YES
NO
YES
NO
YES
NO
YES
NO
YES
NO
NO
ABNORMAL
YES
YES
Checking the power unit
Is each connector of the power unit
fully inserted?
Securely insert the connectors.
Is the lamp door closed completely?
Fix the lamp door with screws.
Is the bimetal broken?
Replace the bimetal switch or restore
by pressing the red button.
Is AC voltage applied to both AC input
ends of DB701?
Replace F701. If other parts are
damaged, replace them.
Is DC voltage of approx. 6.25V
outputted to both ends of C726?
Check D707 and the peripheral circuits
of IC702 on the primary side. If
defective, replace them.
Is DC voltage of approx. 370V
outputted to the cathode of D701?
Replace the subunit or check the
primary side circuit.
if defective, replace them.
Replace the ballast power supply.
Is the specified voltage outputted to
each output terminal of EA701?
Check the secondary-side circuits of
T701. If defective, replace them.
Check the PWB circuits on each output
side.
DT-400
35
Page 36

XV-Z2000
Checking the peripheral circuits of the
microprocessor
Are the voltages of approx. 3.3V and 2.5V
applied to both ends of C8001 and C8056
respectively?
Go to "Checking the power supply
system".
Are the oscillations of 133MHz and
74.25MHz outputted from pin (3) of
X8003 and pin (3) of X8007 respectively?
Check X8001, X8003 and their peripheral
circuits.
Does each terminal of R8038, R8039,
R8041, R8042 and R8050 change?
Check IC8202 or IC8001 is defective.
Do pins (15) and (16) of IC2002 change?
Check IC8203 or IC2002 is defective. The
I2C bus does not function normally.
Do pins (46) to (49) and (4) to (7) of
IC2002 change when any key is
operated?
IC2002 is defective. The keys do not
function normally.
When the power button is pressed, does
the voltage of pin (7) of IC8006 become
3.3V?
IC8001 is defective.
Do pulse-shaped waveforms appear at
pins (1), (2), (5) and (6) of IC8006?
IC8006 is defective.
Does the voltage of pins (3) and (6) of
IC8003 change?
IC8003 is defective.
Is the voltage of pin (2) of Q8002 5V?
Q8002 is defective.
Does the fan rotate?
Check the power supply circuit or fan
circuit on the main circuit.
Go to "Checking the lamp light-up".
NO
YES
NO
YES
NO
YES
NO
YES
NO
YES
NO
YES
NO
YES
NO
YES
NO
YES
NO
YES
DT-400
36
Page 37

XV-Z2000
Checking the lamp light-up
Does each cooling fan
function?
Check the power supply circuit
or fan circuit on the main circuit.
Is the rotating sound of the
color wheel heard?
Check Q9401 to Q9403,
IC9401(motor driver IC)
and their peripheral circuits.
Go to "Checking the
peripheral circuits of
the formatter".
Replace the color wheel.
Is the discharging sound
heard?
Is the lamp tight in the
socket?
Replace the lamp.
Securely insert the
connectors.
Is DC voltage of approx.
370V applied to both ends
of the ballast power supply?
Is pin (2) of P1707 at the
"H" level?
Go to "Checking the
power unit".
Go to "Checking the
peripheral circuits of the
formatter".
Check Q8002, Q8006 and
their peripheral circuits.
NO
YES
NO
ABNORMAL
YES
NORMAL
YES NO
YES
NO
NO YES
YES
NO
DT-400
37
Page 38

XV-Z2000
Adjustment by "Process
Menu"
→
"DLP"
→
"INDEX". The failure state
remains unchanged.
Display in trouble
Screen with spectral
colors
Color production of R,
G and B is not correct.
Black screen
Are the sockets SC2001
and SC9001 connected
correctly?
Are the socket SC2001
and SC9001 connected
correctly?
Are the contact terminals
of the DMD, formatter
PWB and cLGA dirty?
Are the SC2001 and
SC9001 connected
correctly?
Does the color wheel
turn?
Does P9402 have the
correct motor drive
voltage waveform?
Is the waveform at pins
(18) and (20) of IC9202
the 400MHz sine wave?
IC9202, IC9101, X9101
or their peripheral
circuits are faulty.
Does the pin (3) of
IC9201 have the correct
voltage +1.8V?
Are the signals fed to the
terminating resistance
(39W) of RDRAM
(IC9203)?(DQA8 and
DQB8 are unused.)
Re-assemble the DMD,
the optical mechanism
and the formatter unit.
Do the colors return to
correct colors when the
process menu is
entered?
Poor adjustment should
be a likely cause.
Perform readjustment
according to the
adjustment method.
Color wheel is faulty.
IC2002 is faulty.
IC9401 or its peripheral
circuits are faulty.
Is the lamp lit on?
Check the color wheel
sensor unit.
IC2001, IC2007 or their
peripheral circuits are
faulty.
Is the correct voltage is
supplied to the each
connector of power and
ballast unit?
Check the ballast unit
and the power unit.
Does pin (2) of P2004
have 150Hz pulse signal
in no-signal state?
Does pin (9) of IC9301
have the correct voltage
(+23~+26V)?
Is pulse wave in voltage
at pin (14) of P1701?
IC9301 or its peripheral
circuits are faulty.
Miscellaneous
Equally spaced white or
black vertical stripes
Black horizontal band
IC9203, IC9101 or their
peripheral circuits are
faulty.
IC2007, IC2002 or their
peripheral circuits are
faulty.
Does pin (13) of IC9301
have the correct voltage
(-26V)?
Does pin (49) of IC9301
have the correct voltage
(+7V)?
Is the fan rotating?
Check the fan circuit.
Double-check DMD and
cLGA units.
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
NO
NO
NO
NO
NO
NO
NO
NO
NO
NO
NO
YES
DT-400
» Formatter Unit Troubleshooting
38
Page 39

XV-Z2000
Input the digital signal from INPUT5.
Select digital with the keys on the main body or the
remote control.
Check the Formatter unit.
Is the picture disturbed?
Is picture outputted?
Is the signal coming to pins (10)(77) of IC502?
YES NO
Check between the input terminals
and IC502.
NO
NO
YES
YES
Is the signal coming to pins (26)(54) and (66)-(94) of SC2001?
Check IC8001 and its peripheral
circuits.
NO
YES
Checking the digital input
End.
1
Input the analog RGB signal from INPUT5.
Select INPUT5 with the keys on the main body or the
remote control.
Check IC3102 and its peripheral
circuits.
Are pins (76), (77) and (78) of
IC3102 outputting and the signals
inputted to pins (73), (74) and (75)?
Is the picture disturbed?
Is picture outputted?
YES NO
NO
YES
NO
Is the picture signal coming to
pins (3), (4) and (5) of IC3102?
Check between the input terminals
and IC3102.
NO
YES
YES
Checking the analog RGB input
End.
1
3
DT-400
39
Page 40

XV-Z2000
YES
NO
Check IC3102, IC3106 and
their peripheral circuits.
Check IC3104 and its
peripheral circuits.
Check IC3102 and its
peripheral circuits.
NO
NO
Check IC6004 and its
peripheral circuits.
NO
Check IC8001 and its
peripheral circuits.
NO
Checking the Component
Send component signals to
INPUT1 or INPUT2. Use keys
on the main unit or remote
control to select INPUT1 or
INPUT2.
Is video signal inputted into
pins (3) to (5) of IC3102 at the
time of INPUT1 selection, and
is inputted into pins (15) to
(17), respectively at the time of
INPUT2 selection?
Are video signals inputted to
pins (1), (3) and (5) of
IC3104?
YES
Are video signals inputted to
pins (43), (48) and (54) of
IC6004?
YES
Are video signals outputted
from pins (2)-(9), (12)-(19)
and (70)-(77) of IC6004?
YES
Is signal outputted to each
even number pin of pins (21)(54) and (66)-(94) of SC2001?
YES
Check Formatter unit again.
YES
DT-400
40
Page 41

Feed the composite video signal to
INPUT 4. Select INPUT 4 using the
set's key or the remote controller.
Does the picture appear? Is the picture disturbed?
End.
YES
YES
NO
NO
Is the video signal inputted to the
pin (1) of IC3105?
YES
Check the VIDEO-IN signal
line of Q3505.
NO
Is there any input to pins (1), (3) and (5) of IC3104?
YES
Check IC3102 and its peripheral circuits.
NO
Is there any output from pins (16), (18) and (20) of IC3104?
YES
Check IC3104 and its peripheral circuits.
NO
Is the video signal inputted to pins (43), (48) and (54) of
IC6004 and the synchronized signal inputted to pins (30)
and (31)?
YES
Check IC3104, IC6001, IC6002 and their
peripheral circuits.
NO
Is each digital output coming on pins (64), (65), (66) and
(67) of IC6004?
YES
Check IC6004 and its peripheral circuits.
NO
Is there any output from IC8001 (DPORT)?
Check the formatter PWB.
YES
Check IC8001 and its peripheral circuits.
NO
YES
Check IC3501 and its
peripheral circuits.
YES
Checking the Video Input
Check IC3102 and its
peripheral circuits.
1
3
NOYES
Is synchronized signal
coming to pins (28) and
(29) of IC3102?
2
Memo
The composite video signal is Y/C-separated by IC3506 (3 Line
COM) and the resulting signals are inputted to pins (39) and
(41) of IC3105.
The video signal is outputted from color-difference pins (21),
(22) and (23) of IC3105.
Are the video signals inputted to
pins (39) and (41) of IC3105?
YES
YES
Is the video signal outputted from
pins (21), (22) and (23) of IC3105
inputted to pins (67), (68) and (69)
of IC3102?
Check IC3504, IC3506 and
their peripheral circuits.
XV-Z2000
DT-400
41
Page 42

XV-Z2000
Checking the SOG Circuit
Measure the pin (7) of IC5001
with an oscilloscope.
This is the failure of the SOG
synchronization separator circuit.
Is there the Y signal including sync
signal?
Measure the pin (2) of Q5001
with an oscilloscope.
Is the composite synchronized
signal regenerated at proper timing?
NO
Is there any output from the pin
(25) of IC3102?
NO
The SOG circuit is normal.
End.
YES
YES YES
Check Q3110 and its
peripheral circuits.
NO
DT-400
42
Page 43

XV-Z2000
Input the S terminal (Y, C) signal to
INPUT 3. Select INPUT 3 with the
keys on the main body or the
remote controller.
Does the picture appear? Is the picture disturbed? End.
Is the video signal inputted to the
pins (43) and (44) of IC3105?
YES NO
NO
NO YES
NO
YES
Check the input side and its
peripheral circuits.
Check the Y,C signal line.
Checking the S terminal input.
Check IC3105 and its
peripheral circuits.
1
YES
3
Is the video signal outputted
from pins (21), (22) and (23)
of IC3105 inputted into pins
(67), (68) and (69) of IC3102?
DT-400
43
Page 44

XV-Z2000
Checking the Sync Signal
Is the horizontal synchronized
signal on pin (6) of IC6003?
Is the vertical synchronized signal
on pin (6) of IC6009?
Is the synchronized signal
outputted from IC5009, IC5005,
IC5006, IC5007 and IC5008?
Are the timing of both vertical and
horizontal synchronized signals
correct?
Is the horizontal synchronized
signal on pin (30) of IC6004?
Is the vertical synchronized signal
on pin (31) of IC6004?
The sync signal is normal.
End of checking.
YES
NO
Check the of the signal input part.
NO
YES
YES
YES
YES
NO
YES
Check each IC and their peripheral
circuits.
NO
Check IC6001, IC6002 and their
peripheral circuits.
NO
Set the signal source appropriately.
NO
2
Is the signal generator (input
source) correct?
YES
IC8001 and its periphery is
defective.
NO
Is the horizontal synchronized
signal on pin (66) of IC6004?
Is the vertical synchronized signal
on pin (64) of IC6004?
YES
YES
NO
Failure of IC6004 and its
peripheral circuit.
NO
DT-400
44
Page 45

Checking RS-232C
Communication is disabled even though
connecting the control PC and projector
with a RS-232C cable.
Is the connecting cable connected
correctly? (cross cable)
Replace the connecting cable.
Is there any signal at pin (8) of IC8002?
Check SC3501, R2039 and their peripheral circuits.
Is there any signal at pin (106) of IC2201? Check IC2006 and its peripheral circuits.
Check IC2002 and its peripheral circuits.
NO
YES
NO
YES
NO
YES
XV-Z2000
DT-400
45
Page 46

XV-Z2000
Checking the IRIS, FOCUS and
ZOOM motors
Do all the motors function?
Check the optical mechanism.
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
NO
NO
YES
YES
NO
NO
NO
NO
Is there I2C signal at pins (2) and
(3) of IC8201?
Is there any signal at the following
cases?
Zoom:Pin (3) and (7) of IC8205
Focus:Pin (11) and (15) of IC8205
Iris:Pin (2) and (4) of IC8206
Is there signal at pins (1) thru (4)
of P8201 and pins (1) and (2) of
P8202?
Check the connection cable and
optical mechanism unit.
Check IC8205, IC8206 and their
peripheral circuits.
Check IC8201 and its peripheral
circuits.
Check IC2002 and its peripheral
circuits.
Is 3.3V of IC8204 outputted as
specified?
Check the B+6V input line, IC8204
and its peripheral circuits.
Check the line up to the input
section and the remote control
receiver.
Check pins (16) and (17) of
IC2002 and their peripheral
circuits.
Are there remote control receiver
and key signals at pin (9) of
IC2002, pins (4) thru (7) as well as
(47) thru (49) of IC2002?
DT-400
46
Page 47

TECHNISCHE DATEN
Produkttyp
Modell
Videosystem
Display-Verfahren
DLP-Feld
Linse
Projektionslampe
Videoeingangssignal
S-Videoeingangssignal
Komponenten-Eingangssignal
(INPUT 1, 2)
Analog-RGB/Digital
(INPUT 5/DIGITAL)
Horizontal-Auflösung
Punktetakt
Vertikale Frequenz
Horizontale Frequenz
Computersteuerungs-Signal
Nennspannung
Eingangsspannung
Nennfrequenz
Stromaufnahme
Stromaufnahme(Bereitschaft)
Wärmeabgabe
Betriebstemperatur
Lagertemperatur
Gehäuse
I/R-Trägerfrequenz
Abmessungen (ca.)
Gewicht (ca.)
Mitgeliefertes Zubehör
Ersatzteile
Projector
XV-Z2000, DT-400
PAL/PAL 60/PAL-M/PAL-N/SECAM/NTSC 3.58/NTSC 4.43
Einzel-Bedienungsfeld-Digital Micromirror Device (DMDTM) von Texas Instruments
Feldformat: 0,8"
Ansteuerungsmethode: Digital Light Processing (DLP
TM
)
Anzahl der Punkte: 921.600 Punkte (1.280[H] ⋅ 720 [V])
1 –1,5 X Zoom-Linse, F2,0 –2,5, f=21,3 –31,6 mm
Gleichstromlampe 275 W
RCA-Stecker: VIDEO (INPUT 4), Gemischtes Video, 1,0 Vp-p, Synch. negativ, 75 Ω
terminiert
4-Pin Mini DIN-Stecker (INPUT 3)
Y (Luminanz-Signal): 1,0 Vp-p, Synch. negativ, 75 Ω terminiert
C (Chrominanz-Signal): Stoß 0,286 Vp-p, 75 Ω terminiert
RCA-Stecker
Y: 1,0 Vp-p, Synch. negativ, 75 Ω terminiert
P
B (CB): 0,7 Vp-p, 75 Ω terminiert
PR (CR): 0,7 Vp-p, 75 Ω terminiert
29-Pin DVI-I-Terminal
<Digital>
Eingangsimpedanz 50 Ω
Eingangspegel 250-1000 mV
<Analog>
Eingangsimpedanz 75 Ω
Eingangspegel 0,7 Vp-p
Y: 1,0 Vp-p, Synch. negativ, 75 Ω terminiert
P
B (CB): 0,7 Vp-p, 75 Ω terminiert
P
R (CR): 0,7 Vp-p, 75 Ω terminiert
<Synchronisationssignal>
•Separates Synch./Komposit-Synch.
Eingangspegel TTL-Pegel
Eingangsimpedanz 1 KΩ
•Grün auf Synch.
Eingangspegel (Synchronisierungseingang) 0,286Vp-p
Eingangsimpedanz 75 Ω
720 TV-Zeilen (DTV 720P)
12–80 MHz
43–75 Hz
15–70 kHz
9-Pin D-Sub-Steckanschluß (RS-232C-Eingangs-Port)
100–240 V Wechselstrom (Hongkong: 220 V)
3,65 A(Bei 100 V Wechselstrom)/(Hongkong: 1,6 A)
50/60 Hz(Hongkong: 50 Hz)
360 W(Bei 100 V Wechselstrom)/(Hongkong: 345W)
6W(Bei 100 V Wechselstrom)
1.350 BTU/Stunde
+5°C bis +35°C
–20°C bis +60°C
Kunststoff
38 kHz
310× 89 × 282 mm (B × H × T)
4,3 kg
Fernbedienung, Zwei AA-Batterien, Netzkabel, 21-Pin RCA- Konvertierungsadapter,
Video-Kabel, Linsenkappe (am Gehäuse befestigt), Bedienungsanleitung
Bedingt durch fortlaufende technische Verbesserungen behält sich SHARP das Recht
vor, das Design und die Spezifikationen ohne vorherige Ankündigung ändern zu können.
Die angegebenen Leistungswerte stellen die Nennwerte einer in Serienherstellung
produzierten Einheit dar. Geringe Abweichungen bei einzelnen Geräten sind möglich.
DTV 480I/480P/540P/576I/576P/720P/1080I
Lampeneinheit (Lampe/Gehäusemodul) (AN-K2LP), Fernbedienung (RRMCGA334WJSA),
AA-Batterien, Netzkabel (QACCDA007WJPZ:XV-Z2000 für USA, Kanada und DT-400) (für
Europa, ausgenommen Großbritannien) (QACCVA011WJPZ:XV-Z2000 für Europa,
ausgenommen Großbritannien) (QACCBA036WJPZ:XV-Z2000 für Großbritannien,Hongkong
und Singapur) (QACCLA018WJPZ:XV-Z2000 für Australien und Neuseeland)21-Pin RCAKonvertierungsadapte (QSOCZ0361CEZZ:XV-Z2000 für Europe), Video-Kabel
(QCNWGA001WJZZ:Ausgenommen XV-Z2000 für USA, Kanada und DT-400), Linsenkappe
(PCAPHA021WJSA), Bedienungsanleitungen (TINS-B529WJZZ:XV-Z2000 für USA und Kanada)
(TINS-B530WJZZ:XV-Z2000 für 7 europäische Sprachen) (TINS-B531WJZZ:XV-Z2000 für
Hongkong und Koreanisch) (TINS-B532WJZZ:DT-400)
XV-Z2000
DT-400
47
Page 48

XV-Z2000
1
2
DT-400
HINWEISE FÜR DAS
WARTUNGSPERSONAL
ACHTUNG: UV-STRAHLUNG
Die Beleuchtungsquelle des LCD-Projektors, eine
UHP-Lampe, emittiert eine geringe Menge
UV-Strahlung.
DIREKTE BESTRAHLUNG AUF AUGEN
UND HAUT MUSS VERMIEDEN WERDEN.
Zur Gewährleistung der Sicherheit muß folgendes
beachtet werden:
1. Bei Arbeiten am Projektor bei eingeschalteter
Lampe und abgenommenem oberen Gehäuse muß
unbedingt eine Sonnenbrille getragen werden.
2. Die Lampe darf nicht außerhalb des
Lampengehäuses eingeschaltet werden.
Auswechseln der Lampe
Hinweis:
Da die Lampe während des Betriebs sehr heiß wird, sollte
die Lampe erst ausgewechselt werden, nachdem das
Gerät mindestens eine Stunde ausgeschaltet war, damit
die Lampe ausreichend abkühlen kann.
Beim Installieren der neuen Lampe muß darauf
geachtet werden, die Lampe selbst (Glaskolben)
nicht zu berühren. Vielmehr muß die Lampe am
Reflektor 2 gehalten werden.
[Es darf nur ein Original-Ersatzteil verwendet
werden.]
Lampe
Reflektor
GEFAHR! — Niemals die Spannungsversorgung
einschalten, ohne daß eine Lampe vorhanden ist, um
elektrische Schläge und Schäden am Gerät zu
vermeiden, da der Stabilisator anfangs hohe
Spannungen erzeugt.
3. Betrieb für länger als 2 Stunden bei
abgenommenem Gehäuse ist nicht zulässig.
Zur Beachtung bei UV-Strahlung
und Mitteldruck-Lampen
1. Vor dem Auswechseln der Lampe muß der Netzstecker
gezogen werden.
2. Vor Durchführung von Wartungsarbeiten muß das
Gerät eine Stunde abkühlen.
3. Die Lampe darf nur gegen eine der gleichen Art
ausgewechselt werden. Typ AN-K2LP bemessen für
275W.
4. Die Lampe gibt eine geringe UV-Strahlung ab, daher
muß direkter Augenkontakt vermieden werden.
5. Die Mitteldruck-Lampe weist ein Explosionsrisiko auf.
Daher mü ssen die nachstehenden
Installationsanweisungen beachtet werden, und die
Lampe muß vorsichtig behandelt werden.
Da eine geringe Menge UV-Strahlung an der Öffnung
zwischen den Lüftern austritt, wird empfohlen, während
der Wartungsarbeiten die Abdeckkappe des Zusatzobjektivs an dieser Öffnung anzubringen, um Augen
und Haut vor den UV-Strahlen zu schützen.
48
Page 49

XV-Z2000
L Fa
DT-400
Vorsichtsmaßregeln für bleifreien Lötzinn
1 Verwendung von bleifreiem Lötzinn
Bei den Platinen für dieses Modells wird bleifreies Lot verwendet. Das Symbol LF kennzeichnet bleifreies Lot und
findet sich an den Platinen und in den Wartungshandbüchern. Der Buchstabe hinter LF bezieht sich auf die Art des
bleifreien Lots.
Beispiel:
Zeigt bleifreien Lötzinn aus Zinn, Silber und Kupfer an.
2 Bei Reparatur der mit bleifreiem Lötzinn gelöteten Platine immer bleifreien Lötzinn verwenden. Reparatur mit
herkömmlichem Lötzinn kann zu Schäden oder Unfällen aufgrund von Rissen führen.
Da der Schmelzpunkt bleifreien Lvtzinns (Sn-Ag-Cu) um 40°C höher als der von Bleidraht-Lötzinn ist, empfehlen
wir die Verwendung einer speziellen Lötspitze. Wenn Fragen über den Beschaffung leitfreien Lötzinns oder spezieller
Lötspitzen bestehen, wenden Sie sich an unsere Kundendienstvertretung in Ihrem Gebiet.
3Löten
Da der Schmelzpunkt bleifreien Lötzinns (Sn-Ag-Cu) etwa 220°C beträgt, was um 40°C höher als der von bleihaltigem
Lötzinn ist, und außerdem schlechte Löt-Benetzbarkeit aufweist, kann es erforderlich werden, die Lötspitze längere
Zeit in Kontakt mit der Platine zu halten. Da die Lötlauge abfliessen kann oder der maximale Hitzewiderstand von
Teilen überschritten werden kann, die Lötspitze sofort von der Platine nehmen, sobald eine gute Lötung erzielt ist.
Bleifreier Lötzinn enth_lt mehr Zinn, und das Ende der Lötspitze kann leicht angegriffen werden. Immer sicherstellen,
dass der Lötkolben nur bei Bedarf eingeschaltet wird.
Wenn ein anderer Typ von Lötzinn an der Lötspitze haften bleibt, verschmilzt er mit dem bleifreien Lötzinn. Die
Lötspitze nach jeder Verwendung reinigen.
Wenn die Lötspitze bei der Verwendung geschwärzt wird, die Spitze mit Stahlwolle oder feinem Sandpapier
abschmirgeln.
Immer beim Austausch von Teilen vorsichtig sein, und die Polaritätsanzeige auf der Platinenbeschriftung beachten.
Bleifreier Lötzinn zur Wartung
Teile-Nr. ★ Beschreibung Code
ZHNDAi123250E J φ0.3mm 250g(1roll) BL
ZHNDAi126500E J φ0.6mm 500g(1roll) BK
ZHNDAi12801KE J φ1.0mm 1 Rolle BM
49
Page 50

XV-Z2000
Projektor
Draufsicht
Vorderansicht
• Anbringen der Objektivkappe
Drücken Sie die Objektivkappe
auf, bis diese in Position einrastet.
• Abnehmen der Objektivkappe
Ziehen Sie die Objektivkappe
nach außen.
Einstelltasten
('/"/\/|)
Für das Auswählen von
Menüpunkten und anderen
Einstellungen.
INPUT-Taste
Wählen Sie zwischen den
Eingangsmodi 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
oder DIGITAL
ZOOM/FOCUS-Taste
Für das Einstellen der
projizierten Bildgröße oder
das Einstellen des Fokus.
TemperaturwarnAnzeige
Lampen-Anzeige
Netz-Anzeige
Fernbedienungssensor
HEIGHT ADJUST-Taste
Vorderer Einstellfuß
(auf der Unterseite des
Projektors)
MENU-Taste
Für die Anzeige des Justierungs-
und Einstellungsbildschirms.
ENTER-Taste
Für das Einstellen der
ausgewählten oder eingestellten
Menüpunkte.
UNDO-Taste
Für das Rückgängigmachen eines
Bedienschrittes oder für die Rückkehr
zur vorherigen Anzeige.
STANDBY-Taste
Schaltet den Projektor in den
Standby-Modus.
RESIZE-Taste
Für das Umschalten der Bildanzeige
(STRECKEN, SEITENBALKEN, usw.).
ON-Taste
Schaltet die Stromversorgung ein.
DT-400
BEDIENUNGSANLEITUNG
50
Page 51

XV-Z2000
Netz-Anzeige
Rot leuchtend
...
Normal (Standby)
Grün leuchtend
...
Normal (Eingeschaltet)
Lampen-Anzeige
Grün leuchtend
...
Normal
Grün blinkend
...
Die Lampe wird aufgewärmt oder wird
ausgeschaltet.
Rot leuchtend
...
Die Lampe wurde auf unnormale
Weise ausgeschaltet oder muss
ausgewechselt werden.
Temperaturwarn-Anzeige
Aus
...
Normal
Rot leuchtend
...
Die Temperatur im Inneren des
Gerätes ist zu hoch.
Informationen über die Anzeigen des Projektors
DT-400
51
Page 52

XV-Z2000
Verwendung der Kensington-Sperre
• Dieser Projektor ist mit einem Kensington-Sicher-heitsstandardanschluss für die Verwendung des Kensington
MicroSaver-Sicherheits-systems ausgestattet. Lesen Sie hinsichtlich dessen Verwen-dung die Informationen,
die dem System beiliegen, um den Projektor zu sichern.
Digitaler Eingangstyp-
Schalter
INPUT 5/DIGITAL-
Anschluss
INPUT 2-Anschluss
Anschluss für
Komponentensignale.
INPUT 1-Anschluss
Anschluss für
Komponentensignale.
INPUT 4-Anschluss
Anschluss für ein
Videogerät.
INPUT 3-Anschluss
Anschluss für ein Videogerät
mit einem
S-Video-Anschluss.
RS-232C-Anschluss
Anschluss für die Bedienung des
Projektors unter Verwendung eines
Computers.
Luftaustrittöffnung
Die Geschwindigkeit und das
Geräusch des Kühlventilators kann
sich abhängig von internen
Temperaturschwankungen während
des Betriebes verändern. Dies ist
ein normaler Vorgang und kein
Zeichen für eine Fehlfunktion.
Einsaugöffnung
Fernbedienungssensor
Netzanschluss
Schließen Sie das
mitgelieferte Netzkabel an.
Kensington-Sicherheitsstandardanschlus
Projektor (Rückansicht)
Anschlüsse Beachten Sie die Erläuterungen unter „INPUT (EINGANG)-Anschlüsse und
Hauptausrüstung zum Anschließen“ .
Hinterer Einstellfuß
DT-400
52
Page 53

XV-Z2000
Fernbedienung
Einstelltasten
('/"/\/|)
MENU-Taste
Für die Anzeige des Justierungs- und
Einstellungsbildschirms.
ON-Taste
Schaltet die Stromversorgung ein.
ZOOM/FOCUS-Taste
Für das Einstellen der
projizierten Bildgröße oder
das Einstellen des Fokus.
INPUT 3-Taste
INPUT 5-Taste
RESIZE-Taste
Für das Umschalten der Bildanzeige
(STRECKEN, SEITENBALKEN, usw).
DIGITAL INPUT-Taste
PICTURE MODE-Taste
Wählen Sie die Bildeinstellung
(Speicher) aus, die in “Bildmodus” im
“Bild”-Menü gespeichert ist.
STANDBY-Taste
Schaltet den Projektor in den
Standby-Modus.
KEYSTONE-Taste
Für das Aktivieren des Trapezverzerrungs-
Korrekturmodus.
ENTER-Taste
Für das Einstellen der ausgewählten
oder eingestellten Menüpunkte.
UNDO-Taste
Für das Rückgängigmachen eines Bedienschrittes
oder für die Rückkehr zur vorherigen Anzeige.
INPUT 1-Taste
INPUT 2-Taste
INPUT 4-Taste
AUTO SYNC-Taste
Für das automatische Einstellen von Bildern,
wenn ein Computer angeschlossen ist.
RGB/COMP.-Taste
Zum Umschalten des Signaltyps
(RGB oder Komponente).
IRIS-Taste
Zum Umschalten zwischen „HOHE
HELLIGKEITS-MODUS“ und
„HOHER KONTRAST-MODUS“.
Hinweis
• Alle Tasten der Fernbedienung bestehen aus fluoreszierendem Gummi, das im Dunkeln leuchtet. Der
Leuchteffekt lässt mit der Zeit nach. Die selbstleuchtenden Tasten werden wieder aufgeladen, wenn Sie
Licht ausgesetzt werden.
DT-400
53
Page 54

XV-Z2000
Einlegen der Batterien
1
Ziehen Sie die Lasche an der
Abdeckung herunter und entfernen
Sie die Abdeckung in Pfeilrichtung.
2
Die beiliegenden Batterien
(zwei
Batterien der Größe “AA”)
einlegen.
•
Die Batterien einlegen und sicherstellen,
dass die Pole mit der Markierung
und
im Batteriefach übereinstimmen.
3
Führen Sie die untere Lasche
der Abdeckung in die Öffnung
ein und senken Sie die
Abdeckung bis sie einrastet.
Reichweite
Der Projektor kann mittels der Fernbedienung
innerhalb der in der Abbildung dargestellten
Bereiche gesteuert werden.
Hinweis
•
Das Signal von der Fernbedienung kann für eine
einfache Bedienung von der Bildwand reflektiert
werden. Die tatsächliche Reichweite des Signals
kann je nach Bildwandmaterial unterschiedlich sein.
Bei Verwendung der Fernbedienung:
•
Nicht fallen lassen, keiner Feuchtigkeit oder hohen
Temperatur aussetzen.
•
Die Fernbedienung funktioniert unter Umständen
nicht unter einer Fluoreszenzlampe. Unter diesen
Umständen den Projektor von der Fluoreszenzlampe
entfernt aufstellen.
Fernbedienungssensor
Signalsender für
Fernbedienung
Fernbedienung
7 m
30°
30°
30°
30°
30°
Fernbedienungssensor
7 m
Signalsender für
Fernbedienung
30°
Fernbedienung
Falsche Verwendung der Batterien kann eine Leckage oder Explosion zur Folge haben. Bitte befolgen
Sie die unten stehenden Vorsichtsmaßnahmen.
Achtung
•
Die Batterien einlegen und sicherstellen, dass die Pole mit den Markierungen und im Batteriefach übereinstimmen.
•
Batterien unterschiedlichen Typs haben unterschiedliche Eigenschaften, verwenden Sie deshalb keine Batterien
unterschiedlichen Typs zusammen.
•
Verwenden Sie keine neuen und alten Batterien zusammen.
Dadurch könnte die Lebensdauer der neuen Batterien reduziert oder ein Auslaufen der Batterien verursacht werden.
•
Nehmen Sie leere Batterien aus der Fernbedienung heraus, da sie ansonsten auslaufen könnten.
Aus den Batterien ausgelaufene Batterieflüssigkeit ist für Ihre Haut schädlich, wischen Sie die Batterien deshalb unbedingt
zuerst ab und nehmen Sie sie dann mit einem Tuch heraus.
•
Die diesem Projektor beiliegenden Batterien können unter Umständen, je nach Handhabung, nach kurzer Zeit
aufgebraucht sein. Stellen Sie sicher, dass sie so bald wie möglich durch neue Batterien ersetzt werden.
Vorderansicht
Rückansicht
DT-400
54
Page 55

Verbindungs-Pin-Zuweisungen
17
∞∞∞∞∞∞∞∞∞
~
∞∞∞∞∞∞∞∞∞
∞∞∞∞
~
∞∞∞∞
∞∞∞∞
~
∞∞∞∞
24
18 23
C3
21
9
16
C1
C2
C4
C5
87
6789
1
2345
RS-232C-Port: 9-Pin D-Sub-Stecker
Pin Nr. Signal Name E/A Referenz
1 Nicht angeschlossen
2 RD Daten empfangen Eingang An internen Schaltkreis angeschlossen
3 SD Daten senden Ausgang An internen Schaltkreis angeschlossen
4 Reserviert An internen Schaltkreis angeschlossen
5 SG Signalerdung An internen Schaltkreis angeschlossen
6 Reserviert An internen Schaltkreis angeschlossen
7 Reserviert An internen Schaltkreis angeschlossen
8 Reserviert An internen Schaltkreis angeschlossen
9 Nicht angeschlossen
DVI-I (INPUT 5)-Anschluss: 29-pol. Stecker
•
DVI-Digital-Eingang
Pin Nr. Signal Pin Nr. Signal
1 T.M.D.S.-Daten 2- 16 Zündkerzenerkennung
2 T.M.D.S.-Daten 2+ 17 T.M.D.S.-Daten 03 T.M.D.S.-Daten 2-Schutz 18 T.M.D.S.-Daten 0+
4 Nicht angeschlossen 19 T.M.D.S.-Daten 0-Schutz
5 Nicht angeschlossen 20 Nicht angeschlossen
6 DDC-Takt 21 Nicht angeschlossen
7 DDC-Daten 22 T.M.D.S.-Taktschutz
8 Nicht angeschlossen 23 T.M.D.S.-Takt+
9 T.M.D.S.-Daten 1- 24 T.M.D.S.-Takt10 T.M.D.S.-Daten 1+ C1 Nicht angeschlossen
11 T.M.D.S.-Daten 1-Schutz C2 Nicht angeschlossen
12 Nicht angeschlossen C3 Nicht angeschlossen
13 Nicht angeschlossen C4 Nicht angeschlossen
14 Stromversorgung + 5 V C5 Erde
15 Erde
•
DVI-Analog-RGB-Eingang
Pin Nr. Signal Pin Nr. Signal
1 Nicht angeschlossen 16 Zündkerzenerkennung
2 Nicht angeschlossen 17 Nicht angeschlossen
3 Nicht angeschlossen 18 Nicht angeschlossen
4 Nicht angeschlossen 19 Nicht angeschlossen
5 Nicht angeschlossen 20 Nicht angeschlossen
6 DDC-Takt 21 Nicht angeschlossen
7 DDC-Daten 22 Nicht angeschlossen
8 Vertikales Synch. 23 Nicht angeschlossen
9 Nicht angeschlossen 24 Nicht angeschlossen
10 Nicht angeschlossen C1 Analog-Eingang Rot
11 Nicht angeschlossen C2 Analog-Eingang Grün
12 Nicht angeschlossen C3 Analog-Eingang Blau
13 Nicht angeschlossen C4 Horizontales Synch.
14 Stromversorgung + 5 V C5 Erde
15 Erde
•
DVI-Analog-Komponenten-Eingang
Pin Nr. Signal Pin Nr. Signal
1 Nicht angeschlossen 16 Nicht angeschlossen
2 Nicht angeschlossen 17 Nicht angeschlossen
3 Nicht angeschlossen 18 Nicht angeschlossen
4 Nicht angeschlossen 19 Nicht angeschlossen
5 Nicht angeschlossen 20 Nicht angeschlossen
6 Nicht angeschlossen 21 Nicht angeschlossen
7 Nicht angeschlossen 22 Nicht angeschlossen
8 Nicht angeschlossen 23 Nicht angeschlossen
9 Nicht angeschlossen 24 Nicht angeschlossen
10 Nicht angeschlossen C1 Analog-Eingang P
R/CR
11 Nicht angeschlossen C2 Analog-Eingang Y
12 Nicht angeschlossen C3 Analog-Eingang P
B/CB
13 Nicht angeschlossen C4 Nicht angeschlossen
14 Nicht angeschlossen C5 Erde
15 Erde
XV-Z2000
DT-400
55
Page 56

XV-Z2000
Einheiten: mm
Ansicht
von hinten
Ansicht von
der Seite
Ansicht von
vorne
Ansicht von
unten
Ansicht von
oben
Ansicht von
der Seite
2823,25 1,5
55,05
310
48,5
895
55,5
99,95
129,5129,5
15,5
14
106,3
210,3
225,3
30,9
M4
M4
29,1
30,944,1
M4
M4
DT-400
ABMESSUNGEN
56
Page 57

ENTFERNEN DER HAUPTTEILE
Lampentür
Lampeneinheit
1-2
1-3
2-4
2-3
2-1
Dickes papier wie
eine Postkarte
Um den Objektivtubus gegen
Kratzer zu sch
ützen
Kurze Seite
(10cm)
Lange Seite
(15cm)
Oberes Gehäuse
Unteres Gehäuse
2-2
2-2
1. Ausbau der Lampentür und der Lampeneinheit
1-1. Die Lampentür-Befestigungsschraube herausdrehen, dann die Lampentür abnehmen.
1-2. Die 2 Lampeneinheits-Befestigungsschrauben herausdrehen, dann die Lampeneinheit abheben.
XV-Z2000
DT-400
2. Ausbau des oberen Gehäuses
2-1. Eine Postkarte oder ein dickes papier unter dem objektivtubus einzuführen.
2-2. Die 6 Befestigungsschrauben für das obere und das untere Gehäuse herausdrehen.
2-3. Die mit * bezeichneten Teile gedrückt halten und die Klauen am oberen Gehäuse freigeben, um das obere
Gehäuse abzunehmen.
2-4. Die Postkarte wieder herausziehen.
57
Page 58

XV-Z2000
Oberes Gehäuse
Unteres Gehäuse
Dickes Papier wie z.B.
eine Postkarte
3-2
3-1
3-3
4-1
4-4
4-5
4-6
4-2
4-7
4-3
Hauptleiterplatten
Knopf-Halter
Schalterhalterung
Voedere R/C einheit
DT-400
3. Anbringen der oberen Gehäuses (Für die geeigneten Schrauben ist auf den
Abschnitt "2. Aubau des oberen Gehäuses" Bezug zu nehmen.)
3-1. Die Postkarte über dem Objektivtubus einführen.
3-2. Die obere Gehäuse aufsetzen. Sicherstellen, daß die vier Haken gut einrasten.
3-3. Die Postkarte wieder herausziehen.
4. Ausbau der Hauptleiterplatteneinheit und der peripheren Einheiten
4-1. Die 4 Hauptleiterplatten-Befestigungsschrauben (Klemmenseite) herausdrehen.
4-2. Die 9 Hauptleiterplatten-Befestigungsschrauben herausdrehen.
4-3. Die 12 Anschlüsse aus der Hauptleiterplatte entfernen.
4-4. Den Anschluss an der Schalterhalterung herausziehen, dann die 3 Befestigungsschrauben herausdrehen.
4-5. Die Befestigungsschrauben für die vordere R/C-Leiterplatte herausdrehen.
4-6. Die 2 Befestigungsschrauben für die knopf-Halter herausdrehen.
4-7. Die Hauptleiterplatte in querer Richtung von der Optische Laufwerkeinheitseite abheben.
58
Page 59

5. Ausbau der optischen Laufwerkeinheit
Kanal
Optische Laufwerkeinheit
5-3
5-3
5-2
5-4
Lampenfassung
5-1
Halterung
Lautsprecherhalter
5-5
Vorschaltgerät/Netz-Einheit
6-1
6-1
5-1. Die Befestigungsschrauben für die Halterung.
5-2. Die zwei Sperrschrauben vom Lampenfassung entfernen.
5-3. Die 5 Befestigungsschrauben für die optische Laufwerkeinheit herausdrehen.
5-4. Den Kanal abnehmen.
5-5. Die Lautsprecherhalter abnehmen.
XV-Z2000
DT-400
6. Ausbau der Vorschaltgerät/Netz-Einheit
6-1. Die 3 Befestigungsschrauben für die Vorschaltgerät/Netz-Einheit herausdrehen.
59
Page 60

XV-Z2000
Netzteil
Gebläse
Voeschaltgerätteil
Vorshaltgerat-einheit
Hintere-R/C-einheit
Netzeinheit
Randhalter
7-1
7-2
7-2
7-4
7-3
7-3
7-3
7-3
7-3
7-3
7-2
Luftfluß
Halterungen-A
Halterungen-B
Vorder Einstellfuß
Vorder Einstellfuß Halter
Height Adjust-Taste
8-1
8-2
DT-400
7. Ausbau der Vorschaltgerät/Netz-Einheit
7-1. Die Befestigungsschraube für die hintere R/C-einheit herausdrehen.
7-2. Die 4 Befestigungsschrauben, 4 WH-Naben und den Randhalter für die Vorschaltgerätteil entfernen.
7-3. Die 11 Befestigungsschrauben und 5 WH-Naben für das Netzteil entfernen.
7-4. Die 4 Befestigungsschrauben für das Gebläse herausdrehen.
8. Ausbau der peripheren Einheiten
8-1. Die 4 Befestigungsschrauben für die Vorder Einstellfuß herausdrehen.
8-2. Die 8 Befestigungsschrauben herausdrehen, dann die Halterungen A und B sowie die Erdplatte abnehmen.
60
Page 61

9-3
Erdungsplatte
M4-Schrauben
(4 Stellen)
9-7
Erdungs platte
9-6
Verstärkung
(Halterung B)
9-4
Muttem (4 Stellen)
9-2
Die 17 Stifte schmelzen.
Vorsichtsmaßnahme:
*Die Stifte mit eniem Lötkolben
schmelzen, um die
Erdungsplatte zu befestigen.
Zum Schluß auf Lockerheit
überprüfen.
9-8
M3-Schrauben (4 Stellen)
9-5
Verstärkung
(Halterung A)
9-1
9. Befestigen der Erdungsplatte
9-1. Die vier Muttern anbringen.
9-2. Die Verstärkung (Halterung A) aufsetzen.
9-3. Die Erdungsplatte wie gezeigt ansetzen.
9-4. Die Verstärkung (Halterung B) aufsetzen.
9-5. Die vier M3-Schrauben festziehen.
9-6. Die vier M4-Schrauben festziehen.
9-7. Die Erdungsplatte wie gezeigt ansetzen.
9-8. Die sechs 17 der Erdungsplatte schmelzen.
XV-Z2000
DT-400
61
Page 62

XV-Z2000
Netz-Anzeige
Lampen-Anzeige
Temperaturwarn-Anzeige
Wartungsanzeigen
Über die Temperaturwarn-Anzeige
Wenn der Monitor sich infolge nicht ordnungsgemäßer Aufstellung oder blockierter Belüftungsöffnungen
überhitzt, leuchtet am unteren linken Rand des Bildes „
“ auf. Wenn die Temperatur weiterhin steigt,
wird die Lampe ausgeschaltet. Die Temperaturwarn-Anzeige auf dem Projektor beginnt zu blinken. Nachdem
der Lüfter weiterläuft, schaltet sich der Projektor in den Standby-Modus. Nachdem „
“ erscheint,
führen Sie auf jeden Fall die Maßnahmen aus wie beschrieben.
Netzanschluss
ON-Taste
ENTER-Taste
\/|
Tasten
UNDO-Taste
INPUT-Taste
Info
•
Stellen Sie sicher, dass Sie den Lampen-Timer
nur nach dem Austausch der Lampe zurücksetzen.
Wenn Sie den Lampen-Timer zurückstellen und
dieselbe Lampe weiterhin verwenden, könnte die
Lampe beschädigt werden oder explodieren.
1
Das Netzkabel anschließen.
• Das Netzkabel am Netzanschluss des
Projektors anschließen.
2
Den Lampen-Timer zurückstellen.
•Drücken Sie auf dem Projektor in folgender
Reihenfolge die Tasten
, , ,\, und
|
dr
ücken Sie anschlie
ßend die Tste
.
•
„LAMP 0000H“ wird im unteren linken Teil des
Bildschirms angezeigt und weist darauf hin,
dass der Lampen-Timer zurückgesetzt wurde.
DT-400
RÜCKSTELLUNG DES LAMPEN-TIMERS
● Rückstellung des Lampen-Timers
Den Lampen-Timer nach dem Lampenaustausch zurückzustellen.
Lampe
■ Es wird empfohlen, die Lampe (separat erhältlich) auszutauschen, wenn die Lampenlebensdauer 5 % oder weniger
beträgt, oder wenn Sie eine deutliche Verschlechterung der Bild- und Farbqualität feststellen. Die
Lampenlebensdauer (Prozentsatz) kann auf der Bildschirmanzeige überprüft werden.
■ Erwerben Sie über einen Sharp-Projektor-Händler oder Kundendienstbetrieb in Ihrer Nähe eine Lampe des Typs
AN-K2LP.
■ Die Warnanzeigen (ON/STANDBY-Taste, Lampen-Anzeige und Temperatur-Warnanzeige) auf dem Projektor weisen
auf Funktionsstörungen hin.
■ Wenn eine Funktionsstörung auftritt, beginnt die Temperatur-Warnanzeige oder die Lampen- Anzeige zu leuchten,
und der Projektor wechselt in den Standby-Modus. Fürhren Sie die folgenden Schritte aus, nachdem der Projektor
in den Standby-Modus gewechselt ist.
62
Page 63

XV-Z2000
DT-400
63
Page 64

XV-Z2000
DT-400
BESCHREIBUNG DER OPTIK-EINHEIT
Erläuterungen für das korrekte Setup der optischen Komponenten und Baugruppen (Ansicht von oben)
(Schematische Darstellung)
Projektionslinse
Feldlinse
DMD
Reflektorspiegel
Stab
Beleuchtungslinsen 1
Beleuchtungslinsen 2
Farbrad
Lampe
UV-Filter
Objekt Funktion
Lampe Lichtquelle. Gleichstrom-Hochdruck-Quecksilberlampe
Farbrad Teilt durch den Farbfilter das Licht aus der Lichtquelle in R, G, B und W auf.
Stab Entwickelt einen gleichmäßigen Lichtstrahl.
Beleuchtungslinsen Fokussieren das Licht aus dem Stab auf DMD.
Reflektorspiegel Reflektiert das Licht aus den Beleuchtungslinsen gegen DMD.
Feldlinse Fokussiert das Licht aus dem Reflektorspiegel auf DMD und das Licht aus DMD
auf Projektionslinse.
DMD Schaltet im Verhältnis von Farbkomponente jedes Bildpunktes der Eingangsquelle
den internen Mikrospiegel ein/aus, um das Licht zu reflektieren.
Projektionslinse Vergrößert das Licht aus DMD und projiziert es auf eine Leinwand.
64
Page 65

XV-Z2000
Luftfluß
DT-400
Wenn nach dem Austausch von DMD eine Abschattung auf der Leinwand erscheint (siehe Abbildung 1), den
Beleuchtungsbereich von DMD einstellen, indem man die Einstellschrauben für den optischen Motor dreht.
1. Die Befestigungsschraube für den Einstellhebel 1 lösen. Den Beleuchtungsbereich mit dem Einstellhebel 2
einstellen, dann die Befestigungsschraube für den Einstellhebel 1 anziehen.
2. Wenn der Beleuchtungsbereich nach dem obigen Verfahren nicht eingestellt werden kann, die Befestigungsschraube
3 lösen, und den Bereich mit den Einstellschrauben 4 und 5 einstellen; danach die Befestigungsschraube 3
anziehen.
Abschattung
Abb. 1
65
Page 66

XV-Z2000
R
G
B
DT-400
ELEKTRISCHE EINSTELLUNG
Nr. Einstellpunkt Einstellbedingungen Einstellverfahren
1 Initialisieren
von EEPROM
2 Einstellung von
CW-Index
1. DieBetriebsstromversorgung einschalten (die
Lampe leuchtet auf), und
das System 15 Minuten
lang warmlaufen lassen.
1. Gradationsmuster von
RGB eingeben.
(SVGA60Hz oder XGA)
2. Die folgende Gruppe und
Gegenstand wählen.
Gruppe: DLP
Gegenstand: INDEX DELAY wählen.
1. Die folgende Einstellung ausführen. Das
Fernbedienungsteil verwenden oder S2002
drücken, um auf Prozessmodus zu schalten, und
SS2 im SS-Menü ausführen.
1. Gegenstand wählen und Einstellungen
vornehmen, so dass die Lampengradationsmuster
R, G und B glatt und ohne Rauschen sind.
3-1 R-Helligkeit/R-
Kontrast
1.
Gruppe: AD
Gegenstand: R-BRIGHT
(Schwarzpegel)
R-CONTRAST (Weißpegel)
2.
Das Fenstermustersignal mit
einem Anteil von 91% (0,64
Vs-s)
R-Signal und 0% Pegel.
(Prozess/GammaInteraktion)
(SVGA oder XGA)
Eingang 5 RGB Eingang
1. Die 0%-Fenster-Chromatik von CA100
beobachten.
2. Beginnend mit einem Bit-Bildschirmaussetzer ist
die R-Helligkeitseinstellung so zu variieren, bis
die hellrote "x"-Einstellung zu einem schwarzen
Farbton übergeht und dort verweilt. Nun die
Einstellung um einen Punkt anheben und den
Punkt auf die Position einstellen, wo der erste
Bit-Aussetzer festgestellt wird. (Die Einstellung
verändert sich über 5/1000).
3. Die 91% R-Signal-Chromatik am von CA100
beobachten.
4. Beginnend mit einem Bit-Bildschirmaussetzer ist
die R-Kontrasteinstellung so zu variieren, bis die
hellrote "x"-Einstellung zu einem schwarzen
Farbton übergeht und dort verweilt. Nun die
Einstellung um einen Punkt anheben und den
Punkt auf die Position einstellen, wo der erste
Bit-Aussetzer festgestellt wird. (Die Einstellung
verändert sich über 5/1000).
66
Page 67

Nr. Einstellpunkt Einstellbedingungen Einstellverfahren
XV-Z2000
DT-400
3-2 G-Helligkeit/G-
Kontrast
1.
Gruppe: AD
Gegenstand: G-BRIGHT
(Schwarzpegel)
G-CONTRAST (Weißpegel)
2.
Das Fenstermustersignal mit
einem Anteil von 91% (0,64
Vs-s)
G-Signal und 0% Pegel.
(Prozess/GammaInteraktion)
(SVGA oder XGA)
Eingang 5 RGB Eingang
1. Die 0%-Fenster-Chromatik von CA100
beobachten.
2. Beginnend mit einem Bit-Bildschirmaussetzer ist
die G-Helligkeitseinstellung so zu variieren, bis
die hellgrün "y"-Einstellung zu einem schwarzen
Farbton übergeht und dort verweilt. Nun die
Einstellung um einen Punkt anheben und den
Punkt auf die Position einstellen, wo der erste
Bit-Aussetzer festgestellt wird. (Die Einstellung
verändert sich über 5/1000).
3. Die 91% G-Signal-Chromatik am von CA100
beobachten.
4. Beginnend mit einem Bit-Bildschirmaussetzer ist
die R-Kontrasteinstellung so zu variieren, bis die
hellgrune "y"-Einstellung zu einem schwarzen
Farbton übergeht und dort verweilt. Nun die
Einstellung um einen Punkt anheben und den
Punkt auf die Position einstellen, wo der erste
Bit-Aussetzer festgestellt wird. (Die Einstellung
verändert sich über 5/1000).
3-3 B-Helligkeit/B-
Kontrast
1.
Gruppe: AD
Gegenstand: B-BRIGHT
(Schwarzpegel)
B-CONTRAST (Weißpegel)
2.
Das Fenstermustersignal mit
einem Anteil von 91% (0,64
Vs-s)
B-Signal und 0% Pegel.
(Prozess/GammaInteraktion)
(SVGA oder XGA)
Eingang 5 RGB Eingang
1. Die 0%-Fenster-Chromatik von CA100
beobachten.
2. Beginnend mit einem Bit-Bildschirmaussetzer ist
die B-Helligkeitseinstellung so zu variieren, bis
die hellblaue "y"-Einstellung zu einem schwarzen
Farbton übergeht und dort verweilt. Nun die
Einstellung um einen Punkt anheben und den
Punkt auf die Position einstellen, wo der erste
Bit-Aussetzer festgestellt wird. (Die Einstellung
verändert sich über 5/1000).
3. Die 91% G-Signal-Chromatik am von CA100
beobachten.
4. Beginnend mit einem Bit-Bildschirmaussetzer ist
die B-Kontrasteinstellung so zu variieren, bis die
hellblaue "y"-Einstellung zu einem schwarzen
Farbton übergeht und dort verweilt. Nun die
Einstellung um einen Punkt anheben und den
Punkt auf die Position einstellen, wo der erste
Bit-Aussetzer festgestellt wird. (Die Einstellung
verändert sich über 5/1000).
67
Page 68

XV-Z2000
DT-400
Nr. Einstellpunkt Einstellbedingungen Einstellverfahren
4-1 DTV-Helligkeit/
KontrastEinstellung
4-2 DTV-Helligkeit/
Kontrast
1. Gruppe: DTV
Gegenstand:BRIGHT
(Schwarzpegel)
CONTRAST
(Weißpegel)
1. Das 480P 100%/0%
Schwarz/Weiß-FensterMustersignal anlegen.
2. Gruppe: DTV
Gegenstand: R-BRIGHT
(Schwarzpegel)
R-CONTRAST
(Weißpegel)
(Prozess/GammaInteraktion)
Eingang 5-Farb-Differenz
Eingang
1. Den festen Wert prüfen.
Kontrast: 5
Helligkeit: 55
1. Die 0%-Schwarz-Fenster-Chromatik von CA100
beobachten.
2. Beginnend mit einem Bit-Bildschirmaussetzer ist
die Helligkeitseinstellung so zu variieren, bis die
hellrote "x"-Einstellung zu einem schwarzen
Farbton übergeht und dort verweilt. Nun die
Einstellung um einen Punkt anheben und den
Punkt auf die Position einstellen, wo der erste
Bit-Aussetzer festgestellt wird. (Die Einstellung
verändert sich über 5/1000).
3. Die 100% Weiß-fenster-Chromatik am von CA100
beobachten.
4. Beginnend mit einem Bit-Bildschirmaussetzer ist
die Kontrasteinstellung so zu variieren, bis die
hellrote "x"-Einstellung zu einem schwarzen
Farbton übergeht und dort verweilt. Nun die
Einstellung um einen Punkt anheben und den
Punkt auf die Position einstellen, wo der erste
Bit-Aussetzer festgestellt wird. (Die Einstellung
verändert sich über 5/1000).
4-3 DTV-Helligkeit/
Kontrast
1. Das 480P 100%/0%
Schwarz/Weiß-FensterMustersignal anlegen.
2. Gruppe: DTV
Gegenstand: G-BRIGHT
(Schwarzpegel)
G-CONTRAST
(Weißpegel)
(Prozess/GammaInteraktion)
Eingang 5-Farb-Differenz
Eingang
1. Die 0%-Schwarz-Fenster-Chromatik von CA100
beobachten.
2. Beginnend mit einem Bit-Bildschirmaussetzer ist
die Helligkeitseinstellung so zu variieren, bis die
hellgrün "y"-Einstellung zu einem schwarzen
Farbton übergeht und dort verweilt. Nun die
Einstellung um einen Punkt anheben und den
Punkt auf die Position einstellen, wo der erste
Bit-Aussetzer festgestellt wird. (Die Einstellung
verändert sich über 5/1000).
3. Die 100% Weiß-fenster-Chromatik am von CA100
beobachten.
4. Beginnend mit einem Bit-Bildschirmaussetzer ist
die Kontrasteinstellung so zu variieren, bis die
hellgrün "y"-Einstellung zu einem schwarzen
Farbton übergeht und dort verweilt. Nun die
Einstellung um einen Punkt anheben und den
Punkt auf die Position einstellen, wo der erste
Bit-Aussetzer festgestellt wird. (Die Einstellung
verändert sich über 5/1000).
68
Page 69

Nr. Einstellpunkt Einstellbedingungen Einstellverfahren
4-4 DTV-Helligkeit/
Kontrast
1. Das 480P 100%/0%
Schwarz/Weiß-FensterMustersignal anlegen.
2. Gruppe: DTV
Gegenstand: B-BRIGHT
(Schwarzpegel)
B-CONTRAST
(Weißpegel)
(Prozess/GammaInteraktion)
Eingang 5-Farb-Differenz
Eingang
1. Die 0%-Schwarz-Fenster-Chromatik von CA100
beobachten.
2. Beginnend mit einem Bit-Bildschirmaussetzer ist
die Helligkeitseinstellung so zu variieren, bis die
hellblaue "y"-Einstellung zu einem schwarzen
Farbton übergeht und dort verweilt. Nun die
Einstellung um einen Punkt anheben und den
Punkt auf die Position einstellen, wo der erste
Bit-Aussetzer festgestellt wird. (Die Einstellung
verändert sich über 5/1000).
3. Die 100% Weiß-fenster-Chromatik am von CA100
beobachten.
4. Beginnend mit einem Bit-Bildschirmaussetzer ist
die Kontrasteinstellung so zu variieren, bis die
hellblaue "y"-Einstellung zu einem schwarzen
Farbton übergeht und dort verweilt. Nun die
Einstellung um einen Punkt anheben und den
Punkt auf die Position einstellen, wo der erste
Bit-Aussetzer festgestellt wird. (Die Einstellung
verändert sich über 5/1000).
XV-Z2000
DT-400
5 DTV-Farbton
6 DTV-
Farbsättigungspegel
7 DVD-Helligkeit/
KontrastEinstellung
8 DVD-Farbton
9 DTV-
Farbsättigungspegel
1. Gruppe: DTV
Gegenstand: Farbton
1. Gruppe: DTV
Gegenstand: Farbe
1. Gruppe: DVD
Gegenstand:BRIGHT
(Schwarzpegel)
CONTRAST
(Weißpegel)
1. Gruppe: DVD
Gegenstand: Farbton
1. Gruppe: DVD
Gegenstand: Farbe
1. Den festen Wert prüfen.
Farbton: 8
1. Den festen Wert prüfen.
Farbe: 4
1. Den festen Wert prüfen.
Kontrast: 5
Helligkeit: 55
1. Den festen Wert prüfen.
Farbton: 4
1. Den festen Wert prüfen.
Farbe: 5
10 Video-
Helligkeit/
KontrastEinstellung
1. Gruppe: VIDEO
Gegenstand:BRIGHT
(Schwarzpegel)
CONTRAST
(Weißpegel)
1. Den festen Wert prüfen.
Kontrast: 5
Helligkeit: 55
69
Page 70

XV-Z2000
DT-400
Nr. Einstellpunkt Einstellbedingungen Einstellverfahren
11 VIDEO-Farbton
12 VIDEO-
Farbsättigungspegel
13 DVD-
Weißabgleich
(automatische
Einstellung)
1. Gruppe: VIDEO
Gegenstand: N-Farbton
P-Farbton
S-Farbton
1. Gruppe: VIDEO
Gegenstand: N-Farbe
P-Farbe
S-Farbe
1. Das Komponenten 75%Grauskalensignal
einspeisen.
2. Gruppe: PIXEL
Gegenstand: R-GAIN (R)
B-GAIN (B)
(Prozess/GammaInterktion)
Eingang 5-Farb-Differenz
Eingang
1. Die festen Werte prüfen.
N-Farbton: 8
P-Farbton: 4
S-Farbton: 4
1. Die festen Werte prüfen.
N-Farbe: 7
P-Farbe: 4
S-Farbe: 7
1. Den Weißabgleich durch Steuerung von R-GAIN
und B-GAIN einstellen. (x=298 und y=319
einstellen.)
14 DLP-
Spannungeinstellung
15 Werkseitige
Einstellungen
1. Die DLP-gelistete
Spannungsrangordnung
lesen.
2. Die Schaltereinstellung
gemäß der SpannungsLeserangordnung
einstellen (auf der
Formatierer-Platine).
1. Die Einstellung vornehmen, wenn der DLP-Chip
ersetzt wurde, oder wenn die Kombination des
DLP-Chips und der Formatierer-Platine verändert
wurde.
2. Rangordnung: D E
1. Die folgenden Einstellungen vornehmen.
Ziel Prozesseinstellung
Europa SS3
Nordmerika SS4
Fernbedienungseinstellung
Werkseitige Einstellung 3
Werkseitige Einstellung 4
70
Page 71

XV-Z2000
*1272-6bbc
CHXXXX
LLLLL
YYYYYYY
L LLL LM
1
TI interne Nummerierung
TI interne Nummerierung
2-dimensionaler Matrixcode
(DMD-Teilenummer und
Seriennummer)
Teil 1 der Seriennummer
(7 Zeichen)
Teil 2 der Seriennummer
(6 oder 7 Zeichen)
DMD-Teilenummer
Der letzte Alphabetbuchstabe zeigt die
Bin-Spannungseinstellung (D.E) an.
DT-400
* Vorsichtsmaßregeln bei Einrichtung der DMD (Digital Micromirror Device)-Einheit
Vor dem Anschließen der Formatierleiterplatte an der Optikengine die folgenden Schritte ausführen. Die
Spannungsrangmarkierung am DMD selber beachten. Unter
bezug auf diese Markierung die DIP-Schalter an der Formatierleiterplatte einstellen. Dann diese Leiterplatte an die
Optikengine anschließen. Falsche Einstellungenbeeinträchtigen die Systemleistung.
Die Schalter der Formatierleiterplatte entsprechend der Bin-Spannung wie auf der Rückseite des DMD gezeigt einstellen.
2Gegründet auf Soltierfachspannung, wird
schalter wie folgt aufgestellt.
D:
E:
71
Page 72

XV-Z2000
DT-400
1. Aktivieren und Deaktivieren des Prozeßmodus unter Verwendung der Steuertasten dieses
Modells.
∗ Für den Prozess OUT ist es möglich, unter dem Prozessmenü zu verlassen, jedoch ist auch der IN/OUT-
Umschaltbefehl mit Rücksicht auf die vorhandene Spezifikation verfügbar.
1. Aktivieren und Deaktivieren
Bei nicht angezeigtem Menü die Tasten ""'", "'", """, """, "|", "\" und "ENTER" auf dem Hauptgerät drücken.
2. Andere Modelle
Die Prozeßtaste S2002 (Kippschalter) an der Hauptleiterplatte drücken, um das Prozeßmenü zu aktivieren bzw.
zu deaktivieren.
Hinweis: Im Prozessmodus ist eine Einstellung mit einem Signal, dessen vertikale Frequenz 60 Hz beträgt, oder
unter keinen Signal vorzunehmen. (Kann mit anderen Signalen nicht richtig eingestellt werden.)
» Prozeßmenü
Prozeßmenü 1
* Nur die schattierten Punkte in den folgenden Tabellen einstellen.
Prozeßmenü
1. Schicht DTV VERSION
DVD SS
VIDEO TEMP
AD OPTION
DLP PATTERN
VIDEO1 LAMP
PIXEL LINE
Pedestal EXIT
2. Schicht Ausgangswert
DTV Contrast 5
Tint 8
Color 4
Sharpness 1
Bright 55
R-Bright 20
G-Bright 20
B-Bright 20
R-Contrast 120
G-Contrast 120
B-Contrast 120
EXIT
DVD Contrast 5
Tint 4
Color 5
Sharpness 1
CTi-Level 1
LTi-Level 0
CB-Offset 7
CR-Offset 7
Bright 55
B-DRIVE 41
R-DRIVE 41
EXIT
VIDEO Contrast 5
N-Tint 7
P-Tint 4
S-Tint 4
N-Color 7
P-Color 4
S-Color 7
Sharpness 2
CTi-Level 1
LTi-Level 0
CB-Offset 7
CR-Offset 7
Bright 55
B-DRIVE 41
R-DRIVE 41
EXIT
72
Page 73

Prozeßmenü 2
XV-Z2000
DT-400
2. Schicht Ausgangswert
AD R-Bright 40
G-Bright 40
B-Bright 40
R-Contrast 120
G-Contrast 120
B-Contrast 120
EXIT
DLP Index Delay 325
R-Bright 128
G-Bright 128
B-Bright 128
R-Contrast 100
G-Contrast 100
B-Contrast 100
EXIT
VIDEO1 N-Contrast 14
P-Contrast 14
S-Contrast 15
Color 17
NT3.58Delay 0
NT4.43Delay 1
PAL Delay 5
SECAM Delay 0
Shapness2 1
EXIT
PIXEL R-GAIN 128
G-GAIN 128
B-GAIN 128
EXIT
Pedestal R-Bright -10
G-Bright -10
B-Bright -10
R-Contrast +10
G-Contrast +10
B-Contrast +10
EXIT
2. Schicht Ausgangswert
VERSION Build
Boot Code
Config
RomCode
GUI
DLP
EXIT
SS SS2
SS3 EU
SS4 US
SS5 JPN
SS6 CHIN
EXIT
TEMP Temp1 Parameter von sensor1
Temp2 Parameter von sensor2
Temp3
Temp4
EXIT
OPTION
PATTERN Cross Hatch
LAMP Current Time
LINE OFF
PW365 Gamma
DLP Gamma 8
EXIT
Color bar
EXIT
History1 Ein früher
History2 Zwei früher
History3 Drei früher
History4 Vier früher
TOTAL TIME
EXIT
LED CHECK
EXIT
Standa VIDEO
Aktuelle Uhrzeit des Gebrauches.
Funktioniernde Gesamtstunden
73
Page 74

XV-Z2000
Überprüfung der grund-legenden
Funktionen
Ist die POWER LED eingeschaltet, oder
blinkt sie rot oder grün?
Zu den Abschnitten "Überprüfen des
Stromversorgungssystems" und "Überprüfen
der Energieversorgung" gehen.
Kann das Gerät mit der Einschalttaste oder
über die Fernbedienungseinheit
eingeschaltet werden?
Mit dem Abschnitt "Überprüfung der
peripheren Schaltkreise des
Mikroprozessors" fortfahren.
Läuft das Kühlgebläse und leuchtet die
Lampe?
Mit dem Abschnitt "Überprüfung der
Lampenfunktion" fortfahren.
Wird das Benutzermenü angezeigt?
Mit dem Abschnitt "Überprüfung der peripheren
Schaltkreise des Formatters" fortfahren.
Funktioniert der Analog-RGB-Eingang
normal?
Mit dem Abschnitt "Überprüfung des RGBEingangs" fortfahren.
Funktioniert der Komponenten-Eingang
normal?
Mit dem Abschnitt "Überprüfung der
Komponente" fortfahren.
Funktioniert der VIDEO-Eingang?
Mit dem Abschnitt "Überprüfung des
VIDEO-Eingangs" fortfahren.
Funktioniert der DVI-Eingang normal?
Den DVI-Schaltkreis und seine peripheren
Schaltkreise überprüfen.
Funktioniert die RS-232C-Schnittstelle?
Zum Abschnitt "Überprüfen der RS-232CSchnittstelle" gehen.
Funktioniert die automatische
Fokuseinstellung?
Zum Abschnitt "Überprüfen des Blenden-,
Fokus- und Zoommotors.
Ende.
NEIN
JA
NEIN
JA
NEIN
JA
NEIN
JA
NEIN
JA
NEIN
JA
NEIN
JA
NEIN
JA
NEIN
JA
NEIN
JA
DT-400
FEHLERSUCHTABELLE
74
Page 75

Überprüfung des Stromversorgungssystems
Wird 13V dem Stift (9) und (11) von
P1707 zugeführt?
Wird 6 V dem Stift (1) und (3) von P1707
zugeführt?
Mit dem Abschnitt "Überprüfung des
Netzteils" fortfahren.
Ist der Anschluss von P1707 fest
eingesetzt? Liegt 6 V an den beiden
Enden an
Die Temperatursicherung ersetzen.
Wird B+5VA aus IC1707 zugeführt?
IC1707 und die peripheren Schaltkreise
überprüfen.
Wird Bu+5V aus IC1701 zugeführt?
IC1701 und die peripheren Schaltkreise
überprüfen.
Wird Bu+3.3V aus IC1702 zugeführt?
IC1702 und die peripheren Schaltkreise
überprüfen.
Wird Bu+2.5V aus IC1703 zugeführt?
IC1703 und die peripheren Schaltkreise
überprüfen.
Mit dem Abschnitt "Überprüfung der
peripheren Schaltkreise des
Mikroprozessors" fortfahren.
Mit dem Abschnitt "Überprüfung des
Netzteils" fortfahren.
NEIN
JA
NEIN
JA
NEIN
JA
NEIN
JA
NEIN
JA
NEIN
JA
JA
NEIN
XV-Z2000
DT-400
75
Page 76

XV-Z2000
NEIN
JA
NEIN
JA
NEIN
JA
NEIN
JA
NEIN
JA
NEIN
NEIN
FEHLERHAFT
JA
JA
Überprüfen des Netzteils
Sind die Anschlüsse des Netzteils fest
eingesetzt?
Den Anschluss fest einsetzen.
Ist die Lampentür vollständig
geschlossen?
Die Lampentür vollständig mit Schrauben
schließen.
Ist das Bimetall durchgebrannt?
Den Bimetall-Schalter ersetzen oder die
rote Taste zum Wiederherstellen
drücken.
Liegt eine Wechselspannung an den
beiden Enden des WechselstromEingangs von DB701 an?
F701 ersetzen. Wenn andere Teile
defekt sind, diese ersetzen.
Wird eine Gleichspannung von ca. 6,25 V
den beiden Enden von C726 zugeführt?
D707 und die peripheren Schaltkreise
von IC702 an der Primärseite überprüfen.
Wenn defekt, diese ersetzen.
Wird eine Gleichspannung von ca. 370
V der Kathode von D701 zugeführt?
Die Primärseiten-
Schaltkreise
von IC701
usw. prüfen.
Wenn defekt, diese ersetzen.
Den Vorschaltgeräte-Netzteil ersetzen.
Wird eine angegebene Spannung den
Anschlüssen von EA701 zugeführt?
Die Sekundärseiten-Schaltkreise von T701
überprüfen. Wenn defekt, diese ersetzen.
Die Leiterplattenschaltungen an jeder
Ausgangsseite überprüfen.
DT-400
76
Page 77

Überprüfung der peripheren Schaltkreise
des Mikroprozessors
Liegen ca. 3,3 V und ca. 2,5 V an den
beiden Enden von C8001 bzw. C8056 an?
Mit dem Abschnitt "Überprüfung des
Stromversorgungssystems" fortfahren.
Werden die Oszillationen von 133 Hz und
74,25 Hz aus dem Stift (3) von X8003 und
stift (3) von X8001 zugeführt?
X8001, X8003 und die peripheren
schaltkreise überprüfen.
Ändern sich die Anschlüsse von R8038,
R8039, R8041, R8042 und R8050?
IC8202 überprüfen oder IC8001 ist
defekt.
Ändern sich die Stifte (15) und (16) von
IC2002?
IC8203 überprüfen. IC2002 ist defekt. Der
I2C-Bus funktioniert nicht normal.
Ändern sich die Stifte (46) bis (49) und (4)
bis (7) von IC2002 beim Tastendruck?
IC2002 ist defekt. Die Tasten
funktionieren nicht normal.
Erreicht die Spannung des Stiftes (7) von
IC8006 3,3 V, wenn die Netztaste
gedrückt wird?
IC8001 ist defekt.
Erscheint eine impulsförmige Wellenform auf
dem Stift (1), (2), (5) und (6) von IC8006?
IC8006 ist defekt.
Ändert sich die Spannung des Stiftes (3)
und (6) von IC8006?
IC8003 ist defekt.
Beträgt die Spannung des Stiftes (6) von
Q8002 5 V?
Q8002 ist defekt.
Läuft das Gebläse?
Den Stromversorgungskreis oder
Gebläse-Schaltkreis am Hauptschaltkreis
Überprüfen.
Mit dem Abschnitt "Überprüfung der
Lampenfunktion" fortfahren.
NEIN
JA
NEIN
JA
NEIN
JA
NEIN
JA
NEIN
JA
NEIN
JA
NEIN
JA
NEIN
JA
NEIN
JA
NEIN
JA
XV-Z2000
DT-400
77
Page 78

XV-Z2000
Überprüfung der Lampenfunktion
Laufen die Kühlgebläse?
Den Stromversorgungskreis oder GebläseSchaltkreis am Hauptschaltkreis überprüfen.
Wird das Betriebsgeräusch
des Farbrades gehört?
Q9401-Q9403, IC9401
(Motortriber-IC) und die
peripheren schaltkreise
überprüfen.
Mit dem Abschnitt
"Überprüfung der
peripheren Schaltkreise
des Formatters" fortfahren.
Das Farbrad auswechseln.
Wird das
Entladungsgeräusch
gehört?
Ist die Lampenfassung
locker?
Die Lamp auswechseln.
Die Anschlüsse fest
einsetzen.
Liegt eine Gleichspannung
von ca. 370 V an den beiden
Enden des VorschaltgeräteNetzteils an?
Liegt der Stift (2) von
P1707 auf H-Pegel?
Mit dem Abschnitt
"Überprüfung des
Netzteils" fortfahren.
Mit dem Abschnitt
"Überprüfung der peripheren
Schaltkreise des
Formatters" fortfahren.
Q8002, Q8006 und die
peripheren Schaltkreise
überprüfen.
NEIN
JA
NEIN
FEHLERHAFT
JA
NORMAL
JA NEIN
JA
NEIN
NEIN JA
JA
NEIN
DT-400
78
Page 79

» Formatiereinheit-Störungssuche
Störung an Display
Bildschirm mit
Spektralfarben
Farbproduktion bei R, G
und B ist nicht korrekt.
Einstellung mit
"Prozessmenü"→"DLP"
→"INDEX". Der
Fehlerstatus bleibt
unverändert.
Schwarzer Bildschirm
Sind die Buchsen
SC2001 und SC9001
richtig angeschlossen?
Sind die Bucsen
SC2001 und SC9001
richtig angeschlossen?
Sind die
Kontaktklemmen von
DMD, FormatierLeiterplatte und cLGA
verschmutzt?
Sind die Buchsen
SC9101 und SC9001
richtig angeschlossen?
Dreht das Farbrad?
Hat P9402 die richtige
MotortreiberspannungWellenform?
Ist die Wellenform an
Stiften (18) und (20) von
IC9202 die 400-MHzSinuswelle?
IC9202, IC9101, X9101
oder ihre
Peripheriekreise sind
fehlerhaft.
Hat Stift (3) von IC9201
die richtige Spannung
(+1,8 V)?
Werden die Signale zum
Abschlusswiderstand
(39W) von RDRAM
(IC9203) angelegt?
(DQA8 und DQB8
werden nicht verwendet.)
DMD,
Optikmechanismus und
Formatiereinheit neu
montieren.
Kehren die Farben bei
Abruf des
Prozessmenüs auf die
richtigen Farben
zurück?
Schlechte Einstellung
ist eine wahrscheinliche
Ursache.
Neueinstellung
entsprechend dem
Einstellverfahren
Farbrad ist fehlerhaft.
Fehler von IC2002.
IC9401 und seine
Peripheriekreise sind
fehlerhaft.
Leuchtet die Lampe?
Die FarbradSensoreinheit prüfen.
IC2001, IC2007 und
ihre peripheren
Schaltkreise
überprüfen.
Wird die korrekte
Spannung jedem
Anschluß des
Stomversorgungsaggre
gats und dem
Vorschaltgerät
zugeführt?
Hat Stift (2) von P2004
ein 150 Hz-Impulssignal
im Kein-Signal-Status?
Hat Stift (9) von IC9301
die richtige Spannung
(+23 - +26 V)?
Liegt die Impulswelle in
der Spannung am Stift
(14) von P1701 an?
IC9301 und seine
Peripheriekreise sind
fehlerhaft.
Verschiedenes
Gleichmäßig verteilte
weiße oder schwarze
senkrechte Streifen
Schwarzer horizontaler
Balken.
IC9203, IC9101 oder
ihre Peripheriekreise
sind fehlerhaft.
IC2007, IC2002 oder
ihre peripheren
Schaltkreise sind
defekt.
Hat Stift (13) von
IC9301 die richtige
Spannung (-26 V)?
Hat Stift (49) von
IC9301 die richtige
Spannung (+7 V)?
Läuft das Gebläse?
Den Gebläseschaltkreis
überprüfen.
DMD und cLGA-Einheiten
doppelt prüfen.
JA
JA
JA
JA
JA
JA
JA
JA
JA
JA
JA
JA
JA
JA
JA
JA
JA
NEIN
NEIN
NEIN
NEIN
NEIN
NEIN
NEIN
NEIN
NEIN
NEIN
NEIN
JA
Das
Stomversorgungsaggreg
at und das
Vorschaltgerät
überprüfen.
XV-Z2000
DT-400
79
Page 80

XV-Z2000
Das Digitalsignal vom INPUT5 zuführen.
Das Digitalsignal mit den Tasten am Gerät oder auf der
Fernbedienung anwählen.
Die Formatierer-Einheit überprüfen.
Liegen Bildstörungen vor?
Wird ein Bild ausgegeben?
Wird das Signal den Stiften (10)(77) von IC502 zugeführt?
JA
NEIN
Zwischen den
Eingangsanschlüssen und dem
IC502 überprüfen.
NEIN
NEIN
JA
JA
Wird das Signal den Stiften (26)(54) und (66)-(94) von SC2001
zugeführt?
IC8001 und seine peripheren
Schaltkreise überprüfen.
NEIN
JA
Überprüfen des Digitaleingangs
Ende
1
Das Analog-RGB-Signal vom INPUT5 zuführen.
INPUT5 mit den Tasten am Gerät oder auf der
Fernbedienung anwählen.
IC3102 und seine peripheren
Schaltkreise überprüfen.
Werden an den Stiften (76), (77)
und (78) von IC3102 Signale
ausgegeben und den Stiften (73),
(74) und (75) zugeführt?
Liegen Bildstörungen vor?
Wird ein Bild ausgegeben?
JA NEIN
NEIN
JA
NEIN
Wird das Signal den Stiften (3), (4)
und (5) von IC3102 zugeführt?
Zwischen den
Eingangsanschlüssen und dem
IC3102 überprüfen.
NEIN
JA
JA
Überprüfen des Analog-
RGB-Eingangs
Ende
1
3
DT-400
80
Page 81

JA
NEIN
IC3102, IC3106 und ihre
peripheren Schaltkreise
überprüfen.
IC3104 und seine peripheren
Schaltkreise überprüfen.
IC3102 und seine peripheren
Schaltkreise überprüfen.
NEIN
NEIN
IC6004 und seine peripheren
Schaltkreise überprüfen.
NEIN
IC8001 und seine peripheren
Schaltkreise überprüfen.
NEIN
Überprüfen der
Komponenten
Komponenten-Signale an
INPUT1 oder INPUT2
weiterleiten. Die Tasten am
Gerät oder auf der
Fernbedienung benutzen, um
INPUT1 oder INPUT2
anzuwählen.
Wird das zum Zeitpunkt der
INPUT1-Wahl den Stiften (3)
bis (5) von IC3102 zugeführte
Videosignal den Stiften (15) bis
(17) zugeführt (zum Zeitpunkt
der INPUT2-Wahl)?
Werden Videosignale den
Stiften (1), (3) und (5) von
IC3104 zugeführt?
JA
Werden Videosignale den
Stiften (43), (48) und (54) von
IC6004 zugeführt?
JA
Werden Videosignale an den
Stiften (2)-(9), (12)-(19) und
(70)-(77) von IC6004
ausgegeben?
JA
Werden Signale an jeden
geradzahligen Anschluß der
Stifte (21)-(54) und (66)-(94)
von SC2001 ausgegeben?
JA
Die Formatierer-Einheit
erneut überprüfen.
JA
XV-Z2000
DT-400
81
Page 82

XV-Z2000
Ende.
JA
JA
NEIN
NEIN
JA
NEIN
JA
NEIN
JA
NEIN
JA
NEIN
JA
NEIN
JA
NEIN
JA
JA
Prüfen des Videoeingangs
1
3
NEINJA
Liegt das synchronisierte
Signal an den Stiften (28)
und (29) von IC3102 an?
Die Peripherieschaltkreise
von IC3102 prüfen.
2
Memo
Das BAS-Videosignal ist Y/C-separiert durch IC3506 (3 Line
COM), und die resultierenden Signale werden an die Stifte (39)
und (41) von IC3105 angelegt.
Das Videosignal wird von den Farbdifferenz-Stiften (21), (22)
und (23) von IC3105 ausgegeben.
JA
JA
Das FBAS-Videosignal an INPUT4
einspeisen. INPUT4 mit den
Tasten am Gerät oder an der
Fernbedienung wählen.
Erscheint das Bild?
Liegt Eingang an den Stiften (1), (3) und (5) von IC3104 an?
Liegt Eingang an den Stiften (16), (18) und (20) von IC3104 an?
Kommt digitaler Ausgang von Stiften (64), (65), (66) und
(67) von IC6004?
Kommt Ausgang von IC8001 (DPORT)?
Die Formatierleiterplatte prüfen.
Liegt das Videosignale an den Stiften (43), (48) und (54)
von IC6004 und das synchronisierte Signal an den Stiften
(30) und (31) an?
Die Peripherieschaltkreise von IC3102 prüfen.
Die Peripherieschaltkreise von IC3104 prüfen.
Die Peripherieschaltkreise von IC6004 prüfen.
Die Peripherieschaltkreise von IC8001 prüfen.
In der Umgebung von IC3104, IC6001 und IC6002
prüfen.
Liegt das videosignal an Stift (1)
von IC3105 an?
Werden die Videosignale an Stifte
(39) und (41) von IC3105
angelegt?
Werden die Videosignale von den
Stiften (21), (22) und (23) von
IC3105 ausgegeben und an Stifte
(67), (68) und (69) von IC3102
angelegt?
Ist das Bild gestört?
IC3501 und seine
Peripheriekreise prüfen.
Die Signalleitung VIDEO-IN
von Q3505 prüfen.
IC3504, IC3506 und ihre
Peripheriekreise prüfen.
DT-400
82
Page 83

XV-Z2000
Prüfen der SOG-Schaltung
NEIN
NEIN
JA
JA JA
Q3110 und die peripheren
Schaltkreise überprüfen.
NEIN
Den Stift (7) von IC5001 mit einem
Oszilloskop prüfen.
Wird das FBAS-Signal mit richtiger
Zeitgabe regeneriert?
Den Stift (2) von Q5001 mit einem
Oszilloskop prüfen.
Ist das Y-Signal einschließlich SynSignal vorhanden?
Dies ist ein Fehler in der SOGSynchronisationsSeparatorschaltung.
Gibt es Ausgang von Stift (25) von
IC3102?
Die SOG-Schaltung ist normal.
Ende.
DT-400
83
Page 84

XV-Z2000
Ende.
JA NEIN
NEIN
NEIN JA
NEIN
JA
1
JA
3
Prüfung des Eingangs der SKlemme.
Erscheint das Bild?
Wird das Bildsignal an die Stifte
(43) und (44) von IC3105?
Die eingangsseitige Leiterplatte
prüfen. Und überprüfen Sie das Y,
C Leitungssignal.
Ist das Bild gestört?
Werden die Videosignale von
den Stiften (21), (22) und (23)
von IC3105 ausgegeben und
an Stifte (67), (68) und (69)
von IC3102 angelegt?
IC3105 und die
peripheren Schaltkreise
überprüfen.
Das S-Klemmen-Signal (Y, C) von
INPUT3 eingeben. INPUT3 mit
den Tasten am Hauptgerät oder
an der Fernbedienung wählen.
DT-400
84
Page 85

Prüfen des Sync-Signals
JA
NEIN
NEIN
JA
JA
JA
JA
NEIN
JA
NEIN
NEIN
NEIN
2
JA
NEIN
JA
JA
NEIN
NEIN
Wird das horizontal synchronisierte
Signal auf Stift (6) von IC6003
ausgegeben?
Wird das vertikal synchronisierte
Signal auf Stift (6) von IC6009
ausgegeben?
Wird das synchronisierte Signal von
IC5009, IC5005, IC5006, IC5007
und IC5008 ausgegeben?
Wird das vertikal synchronisierte
Signal auf Stift (31) von IC6004
ausgegeben?
Liegt das horizontale
synchronisierte Signal auf Stift (30)
von IC6004 an?
Wird das vertikal synchronisierte
Signal auf Stift (64) von IC6004?
ausgegeben?
Liegt das horizontale
synchronisierte Signal auf Stift (66)
von IC6004 an?
Sind die Zeitangaben von sowohl
vertikal als auch horizontal
synchronisierten Signalen korrekt?
Ist der Signalgenerator
(Eingangsquelle) korrekt?
IC8001 und seine Umgebung ist
defekt.
Die Leiterplatte des
Signaleingangsteils prüfen.
Jeden IC und die
Peripherieschaltung des ICs prüfen.
IC6001, IC6002 und die ICPeripheriekreise prüfen.
Fehler von IC6004 und dem ICPeripherieschaltkreis.
Das Sync-Signal ist normal. Ende
der Prüfung.
Die Signalquelle richtig einstellen.
XV-Z2000
DT-400
85
Page 86

XV-Z2000
Überprüfung von RS-232C
Eine Kommunikation ist nicht möglich,
selbst wenn der Steuer-PC und der
Projektor mit einem RS-232C-Kabel
verbunden werden.
st das Anschlusskabel richtig
angeschlossen? (Crosskabel)
Das Anschlusskabel ersetzen.
Empfängt der Stift (8) von IC2006 ein
Signal?
SC3501, R2039 und die peripheren Schaltkreise
überprüfen.
Empfängt der Stift (106) von IC2201 ein
Signal?
IC2006 und die peripheren Schaltkreise überprüfen.
IC2002 und die peripheren Schaltkreise
überprüfen.
JA
NEIN
JA
NEIN
JA
NEIN
JA
DT-400
86
Page 87

Überprüfen des Blenden-,
Fokus- und Zoommotors
Funktionieren alle Motoren?
Den Optik-Mechanismus
überprüfen.
JA
JA
JA
JA
JA
NEIN
NEIN
JA
JA
NEIN
NEIN
NEIN
NEIN
Liegt das I2C-Signal an den Stiften
(2) und (3) von IC8201 an?
Gibt es irgendein Signal an den
folgenden Fällen?
Zoom:Stiften (3) und (7) von
IC8205
Fokus:Stiften (11) und (15) von
IC8205
Blenden:Stiften (2) und (4) von
IC8206
Liegen Signale an den Stiften (1)
bis (4) von P8201 und den Stiften
(1) und (2) von P8202 an?
Das Anschlußkabel und OptikMechanismus überprüfen.
IC8205, IC8206 und ihre
peripheren Schaltkreise
überprüfen.
IC8201 und seine peripheren
Schaltkreise überprüfen.
IC2002 und seine peripheren
Schaltkreise überprüfen.
Liegen am IC8204 3,3 V an, wie
spezifiziert?
Die B+6V-Eingangsleitung, den
IC8204 und seine peripheren
Schaltkreise überprüfen.
Die Leitung bis zum
Eingabebereich und dem
Fernbedienungs-Empfänger
überprüfen.
Die Stifte (16) und (17) von IC2002
und ihre peripheren Schaltkreise
überprüfen.
Liegen Tastensignale des Geräts
und des FernbedienungsEmpfängers am Stift (9) von
IC2002 an, sowie den Stiften (4)
bis (7) und (47) bis (49) von
IC2002?
XV-Z2000
DT-400
87
Page 88

87109654321
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
XV-Z2000
VIDEO
IC502
HDCP
PANEL LINK
RECEIVER
SII169G
EDID
IC501
EDID
IC506
IC507
BU4053V
A/D AMP PLL
IC6004
MAIN VIDEO CHROMA
IC3105
3LINE DIGITAL
IC3506
TC90A69F
RGB DECODER
IC3101
CXA2101Q
I/O EXPANDER
IC2002
TE7780
RS232C
RECEIVER
IC2006
ISL83220
HSYNC
VSYNC
IC6001,
2
7WH157
TL712CPW
HSYNC SLICE
TL712CPW
SYNC PROCES
HC4538PW
HC1G00GW
HC1G32G
W
TC7W74U
IC8202
HSYNC
VSYNC
SYNC PROCES
IC5004
SD/HD
PC/VIDEO
IC3104
AD8186
LEVEL ADJ
IC3106
CLAMP
IC5019
HC1G32GW
IC5003
HC4538PW
AB
VHS,VVS
GGAIN
Y1-IN
CB1-IN
CR1-IN
LPF AMP
IC3504
TK15420
COMB-Y
COMB-C
VIDEO_IN
S-Y
S-C
IN3 1~3
IN4 1~3
IN2 1~3
Y1-IN
CB1-IN
CR1-IN
H1-IN
V1-IN
IN3 H V
INV
IC3101
SN2G04CT
HS-OUT
VS-OUT
DVI-V,DVI-H,DE
SOGOUT
GPEN
GHS
GVS
GFBK
GRE0~7,GBE0~7,GBE0~7,
GRO0~7,GBO0~7,GBO0~7
GRO0~7,GBO0~7,GBO0~7
GRE0~7,GBE0~7,GBE0~7,
GCLK
DVIR+,DVIG+,DVIB+.-
DVICL+,-
DDCDATA,DDCCLK
TX
RX
KEY
LED
FRONT R/C
DUNTKC754WEF*
REAR R/C
DUNTKC755WEF*
EXHAUST FAN1 EXHAUST FAN2
LAMP BLOW FAN
POWER FAN
FAN3 REG
IC1710
FAN1 REG
IC1708
FAN2 REG
IC1709
FAN4 REG
IC1711
DA
IC5014
FRONT R/C
REAR R/C
IRIS DRIVE
IC8206
LB1638M
I/ O
IC8201
ZOOM/FOCUS
IC8205
LB1831M
IC8204
PQ1L333M
MAIN
DC-DC 3.3V
IC1713
MP1410E S
DC-DC 2.5V
IC1712
MP1410E S
12
IC
PQ1
9V
IC
PQ0
B+5VA REG
IC1707
PQ050DZ1
BU5V REG
IC1701
PQ050DZ1
BU3.3V REG
IC1702
PQ033DZ1
BU2.5V REG
IC1703
PQ025EZ5
5V REG
IC1704
PQ050DZ1
LAMP_POW
LAMPLIT
DDP LIGHT
FA1~19
IC6005
SNCL257P
FD0~15
32KbitEEPROM
IC8203
BR24L32F
14.7456MHz
I2C
SDA3_EEP
SCL3_EEP
DUNTKC753WEF*
THERMISTOR
FOCUS
M
IRIS
M
ZOOM
M
FAN ERROR
PULSE
TB1274AF
M62334FP
PQ20WZ11 PQ20WZ11
PQ20WZ11
PQ20WZ11
C0141TA
M52347FP
RGB/COMP
IXA202WJN1
Y/G ON SYNC
SEP
IXB351WJ
IXB350WJ
PLUG&PLAY
PLUG&PLAY
EDID SEL
VSYNC SLICE
PVSYNC1,PHSYNC1
GGHS,GGVS
CBLKSPL
LV4053AT
BLACK
WRØ,CSØ,RDØ
8M FLASH MEMORY
IXB196WJ
IXB197WJ
ROMOE
ROMWE
BOOTWE
SEL
AD9883A1
DRIVER/
COMB FILTER
SEL
SEL
RESETH
VSOUT
HSOUT
3.3 REG
M62320FP
FA1~5
FD0~7
DT-400
BLOCK DIAGRAM/BLOCK SCHALTBILD
88
Page 89

1716 1918151413121110
DC-DC
PFC-ON/OFF
B+13V
LINE FILTER
B+6V
LAMP_LIT
LAMP_EN
ECO/LPS
BI-METAL
LAMP
DC-DC
IC8001
PW365
DDP1010P
IC9301
A384WJN1(DAD1000)
8M FLASH
IXB194WJ
IXB195WJ
IC9203
CLOCK GENERATOR
IC9202
TCDCR83D
C/W MOTOR
CONTROLLER
IC9401
SH6742C
X8001
GPEN
GHS
GVS
GFBK
ZOOM/FOCUS
IC8205
LB1831M
BALLAST UNIT RDENCA088WJZZ
COLOR WHEEL
SENSOR
6V
13V
3.3V
SENSOR
IC1713
IC1712
12V REG
IC1705
PQ12DZ1U
9V REG
IC1706
PQ09DZ1U
5V REG
IC1704
LAMP_LITZ
LAMP_LITC
LAMP_EN
ECO/LPS
PFC-ON/OFF
DRE[9;0
DBE[9;0]
DGE[9;0]
DCLK
DVS
DHS
RV[9;0
GY[9;0
BU[9;0 ]
HSYNC
VSYNC
ACTDAT
CLKIN
RESETZ
PWRGOOD
D
RESETZ
LAMP_EN
FA1~19
X8003
IC6005
IC8002 PST6001M
IC8004 TC7W14U
IC8005 TC7S00U
FD0~15
DUNTKC757WEF*
FOCUS
M
M
POWER UNIT RDENCA082WJZZ
ZOOM
M
PCON0
LAMP-DOOR SW
AC CORD
PFC
PRIMARY
PRIMARY
IGNITER
SECONDARY
SECONDARY
DMD
DMDPA015WJ
WAVEFORM GENERATOR
DLP DATA PROCESSOR
IC9101
100MzOSC
X9101
UAA041WJ
IC9102
FORMATTER
K4R271F8
RDRAM
74.25MzOSC
UAA046WJ
UAA013WJ
133MzOSC
ROMOE
ROMWE
BOOTWE
RESET
DENR
SEL
XV-Z2000
DT-400
89
Page 90

87109654321
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
XV-Z2000
123
123
4
123
123
4
123
123
4
BDK
+-+
-
BDK
B
DCK
BDK
BDC
K
+
N
C
M
M
S
S
+
N
C
+NN
C
+
N
C
+NN
C
G
O
OOU
U
G
O
G
O
G
O
G
O
L
O
O
C
C
L
L
L
L
Z
Z
O
O
P1706
F
F
P1706 P1705 P1704 P1703
P8201
1SDA
2 SCL P2005
3GND
4 B'+3.3V
5 L AMPFAIL
6GND
CR
V
T
5
N
P1551
+
O
D
URN
BFG
123
1
BU+5V
2
FRONT R/C
P2011
3GND
4
BU+5V
5
REAR R/C
6GND
123
VCD
5RN
P1501
+
G
U
R
B
AER
P1701
2 PFC-ON/OFF 6V 1
4 GND 6V 3
6 PROTECTOR GND 5
8 LAMP_LITC GND 7
10 LAMP_LITE 13V 9
12 3.3V 13V 11
14 LAMP_EN GND 13
16 ECO/LPS GND 15
1234567
8
1234567
8
BLACK EA702 EA701
ORANGE
GRAY
WHITE
FAFBFC
FD
RDENCA082WJZZ
DUNTKC753WEF0
AZ
ZOOM
MOTOR
FOCUS
MOTOR
AI
IRIS
MOTOR
RAB
RA
DUNTKC755WEF0
DUNTKC754WEF0
RB
LAMP-DOOR SW &BIMETAL
QCNW-C671WJPZ
IRIS MOTOR
RMOTBA006WJZZ
ZOOM/FOCUS MOTOR
RMOTBA005WJZZ
LAMP FAN
NFANSA017WJZZ
EXHAUST FAN1
NFANSA035WJZZ
EXHAUST FAN2
NFANSA034WJZZ RUN
EA
REAR R/C UNIT
QCNW-C667WJPZ
FRONT R/C UNIT
FMT
POWER FAN
PHO
MAIN UNIT
AC-CORD
QACCDA007WJPZ
QACCVA011WJPZ
QACCBA036WJPZ
QACCLA018WJPZ
POWER UNIT
DT-400
OVERALL WIRING DIAGRAM/GESAMTSCHALTPLAN
90
Page 91

1716 1918151413121110
123
4
123
1
234
BDC
K
VXD
)))
C
+NN
C
5EN
UUU
N
G
O
+DG
(((
1 5V 5V
L
B
N
123
2 GND
YYY
3 GND
P1703
W
OOO
4 12V 12V
C
MMM
5 12V 12V
P2004 P2003 6 GND
7 3.3V 3.3V
8 3.3V 3.3V
9 GND
10 GND
11 2.5V 2.5V
12 2.5V 2.5V
13 GND
14 CW-W CW-U
15 CW-W CW-U
16
CW-C
17
CW-C
18 GND
19
CWINDEX
SDA
20
CW-BREAK
SCL
21
BOOT_LOAD
LAMP_LITZ
22
ASIC_READY
LAMP_EN
99
23
LAMP_SYNC
RESETZ
98
SC2001 24 TEMP1
POWRGOOD
97
SC9001
25 GND
96
26 RV0
95
27 GND
94
28 RV2
93
29 GND
92
30 RV4
91
31 GND
90
32 RV6
89
33 GND
88
34 RV8
87
35 GND
86
36 GY0
85
37 GND
84
38 GY2
83
39 GND
82
40 GY4
81
41 GND
80
42 GY6
79
43 GND
78
44 GY8
77
45 GND
76
46 BU0
75
47 GND
74
48 BU2
73
49 GND
72
50 BU4
71
51
GND
70
69
68
67
V
P1707 55 GND
66
3
56
ACT_DATA
65
.
1
57 GND
64
3
P
58 H_SYNC
63
+
M
59 GND W_CLK
62
U
E
C
60 SYNC_VAL
61
BTN
123
1
2
RCORFA008WJZZ
34567
8
EA701
LAMP-LIT
(C)
CN2 WHITE
LAMP-LIT(E) 2 2
3.3V
BLACK
LAMP-EN/SYNC
5
CN1
AN-K2LP
WHITE
1 +DC
2
NC
BLACK
3 0V
DMD
DUNTKC757WEF0
FA
BALLAST UNIT
RDENCA088WJZZ
LAMP
DD
CW
TF
TO
EXHAUST FAN2
NFANSA034WJZZ
COLOR WHEEL
CFILWA081WJ0 1
RUNTKA091WJZZ
THERMAL FUSE
QCNW-D074WJZZ
THERMAL SENSOR
QCNW-B114WJZZ
BC
PHOTO SENSOR UNIT
M0039CE
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
RV1
RV3
RV5
RV7
RV9
GY1
GY3
GY5
GY7
GY9
BU1
BU3
BU5
BU7
BU9
2.5V
W0031CE
V_SYNC
11
3
3
44
5
ECO
FORMATTER UNIT
XV-Z2000
DT-400
91
Page 92

XV-Z2000
DT-400
WAVEFORMS / WELLENFORMEN
1 IC3102 (28) pin
(VS-OUT)
H : 5m sec/div
V : 1V/div
5 IC3102 (37) pin
(2YO)
H : 20µ sec/div
V : 1V/div
9 IC3506 (7) pin
(YCIN)
H : 20µ sec/div
V : 1V/div
2 IC3102 (29) pin
(HS-OUT)
H : 20µ sec/div
V : 1V/div
6 IC3102 (39) pin
(1YO)
H : 20µ sec/div
V : 1V/div
0 IC3506 (19) pin
(FSC)
H : 200n sec/div
V : 1V/div
3 IC3102 (31) pin
(SCP-IN)
H : 20µ sec/div
V : 1V/div
7 IC3105 (43) pin
(C2-IN)
H : 20µ sec/div
V : 1V/div
q IC3506 (25) pin
(YOUT)
H : 20µ sec/div
V : 1V/div
4 IC3102 (35) pin
(3YO)
H : 20µ sec/div
V : 1V/div
8 IC3105 (44) pin
(CVBS/Y2-IN)
H : 20µ sec/div
V : 1V/div
w IC3506 (27) pin
(COUT)
H : 20µ sec/div
V : 1V/div
e Q2006 (Colector)
(LAMP_EN)
H : 1m sec/div
V : 1V/div
u IC3104 (18) pin
(OUT 1)
H : 20µ sec/div
V : 1V/div
r P2004 (2) pin
(CWINDEX)
H : 2m sec/div
V : 1V/div
i IC3104 (16) pin
(OUT 2)
H : 20µ sec/div
V :1V/div
t SC2003 (1) pin
(MDY1(U))
H : 500µ sec/div
V : 2V/div
92
y IC3104 (20) pin
(OUT 0)
H : 20µ sec/div
V : 1V/div
Page 93

654321
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
XV-Z2000
DT-400
PRINTED WIRING BOARD ASSEMBLIES
LEITERPLATTENEINHEITEN
FRONT R/C Unit (Side-A)/
Vordere R/C-Einheit (Seite-A)
FRONT R/C Unit (Side-B)/
Vordere R/C-Einheit (Seite-B)
REAR R/C Unit (Side-A)/
Hintere R/C-Einheit (Seite-A)
REAR R/C Unit (Side-B)/
Hintere R/C-Einheit (Seite-B)
93
Page 94

87109654321
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
XV-Z2000
DT-400
MAIN Unit (Side-A)
HAUPT-Einheit (Seite-A)
94
Page 95

1716 1918151413121110
XV-Z2000
DT-400
95
Page 96

87109654321
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
XV-Z2000
DT-400
MAIN Unit (Side-B)
HAUPT-Einheit (Seite-B)
96
Page 97

1716 1918151413121110
XV-Z2000
DT-400
97
Page 98

654321
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
XV-Z2000
DT-400
FORMATTER Unit (Side-A)
FORMATTER-Einheit (Seite-A)
98
Page 99

654321
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
XV-Z2000
DT-400
FORMATTER Unit (Side-B)
FORMATTER-Einheit (Seite-B)
99
Page 100

654321
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
XV-Z2000
DT-400
POWER Unit (Side-A)
NETZ-Einheit (Seite-A)
POWER Unit (Side-B)
NETZ-Einheit (Seite-B)
100
 Loading...
Loading...