Sharp LH28F160BGHR-TTL12, LH28F160BGHR-TTL10, LH28F160BGHR-BTL10, LH28F160BGHE-TTL12, LH28F160BGHE-TTL10 Datasheet
...
- 1 -
In the absence of confirmation by device specification sheets, SHARP takes no responsibility for any defects that may occur in equipment using any SHARP devices shown in catalogs, data books,
etc. Contact SHARP in order to obtain the latest device specification sheets before using any SHARP device.
PRELIMINARY
LH28F160BG-TL/BGH-TL
16 M-bit (1 MB x 16) Smart 3
Flash Memories
LH28F160BG-TL/BGH-TL
DESCRIPTION
The LH28F160BG-TL/BGH-TL flash memories with
Smart 3 technology are high-density, low-cost,
nonvolatile, read/write storage solution for a wide
range of applications. The LH28F160BG-TL/
BGH-TL can operate at V
CC and VPP = 2.7 V.
Their low voltage operation capability realizes
longer battery life and suits for cellular phone
application. Their boot, parameter and main-blocked
architecture, flexible voltage and enhanced cycling
capability provide for highly flexible component
suitable for portable terminals and personal
computers. Their enhanced suspend capabilities
provide for an ideal solution for code + data storage
applications. For secure code storage applications,
such as networking, where code is either directly
executed out of flash or downloaded to DRAM, the
LH28F160BG-TL/BGH-TL offer two levels of
protection : absolute protection with V
PP at GND,
selective hardware boot block locking. These
alternatives give designers ultimate control of their
code security needs.
FEATURES
• Smart 3 technology
– 2.7 to 3.6 V V
CC
– 2.7 to 3.6 V or 12 V VPP
• High performance read access time
LH28F160BG-TL10/BGH-TL10
– 100 ns (2.7 to 3.6 V)
LH28F160BG-TL12/BGH-TL12
– 120 ns (2.7 to 3.6 V)
• Enhanced automated suspend options
– Word write suspend to read
– Block erase suspend to word write
– Block erase suspend to read
• SRAM-compatible write interface
• Optimized array blocking architecture
– Two 4 k-word boot blocks
– Six 4 k-word parameter blocks
– Thirty-one 32 k-word main blocks
– Top or bottom boot location
• Enhanced cycling capability
– 100 000 block erase cycles
• Low power management
– Deep power-down mode
– Automatic power saving mode decreases I
CC
in static mode
• Automated word write and block erase
– Command user interface
– Status register
• ETOX
TM
∗
V nonvolatile flash technology
• Packages
– 48-pin TSOP Type I (TSOP048-P-1220)
Normal bend/Reverse bend
– 60-ball CSP (FBGA060/048-P-0811)
∗ ETOX is a trademark of Intel Corporation.
VERSIONS BIT CONFIGURATION OPERATING TEMPERATURE
LH28F160BG-TL 1 MB x 16 0 to +70°C
LH28F160BGH-TL 1 MB x 16 – 25 to +85°C
LH28F160BV-TL
∗
2 MB x 8/1 MB x 16 0 to +70°C
LH28F160BVH-TL
∗
2 MB x 8/1 MB x 16 – 40 to +85°C
COMPARISON TABLE
∗ Refer to the datasheet of LH28F160BV-TL/BVH-TL.
PRELIMINARY
LH28F160BG-TL/BGH-TL
- 2 -
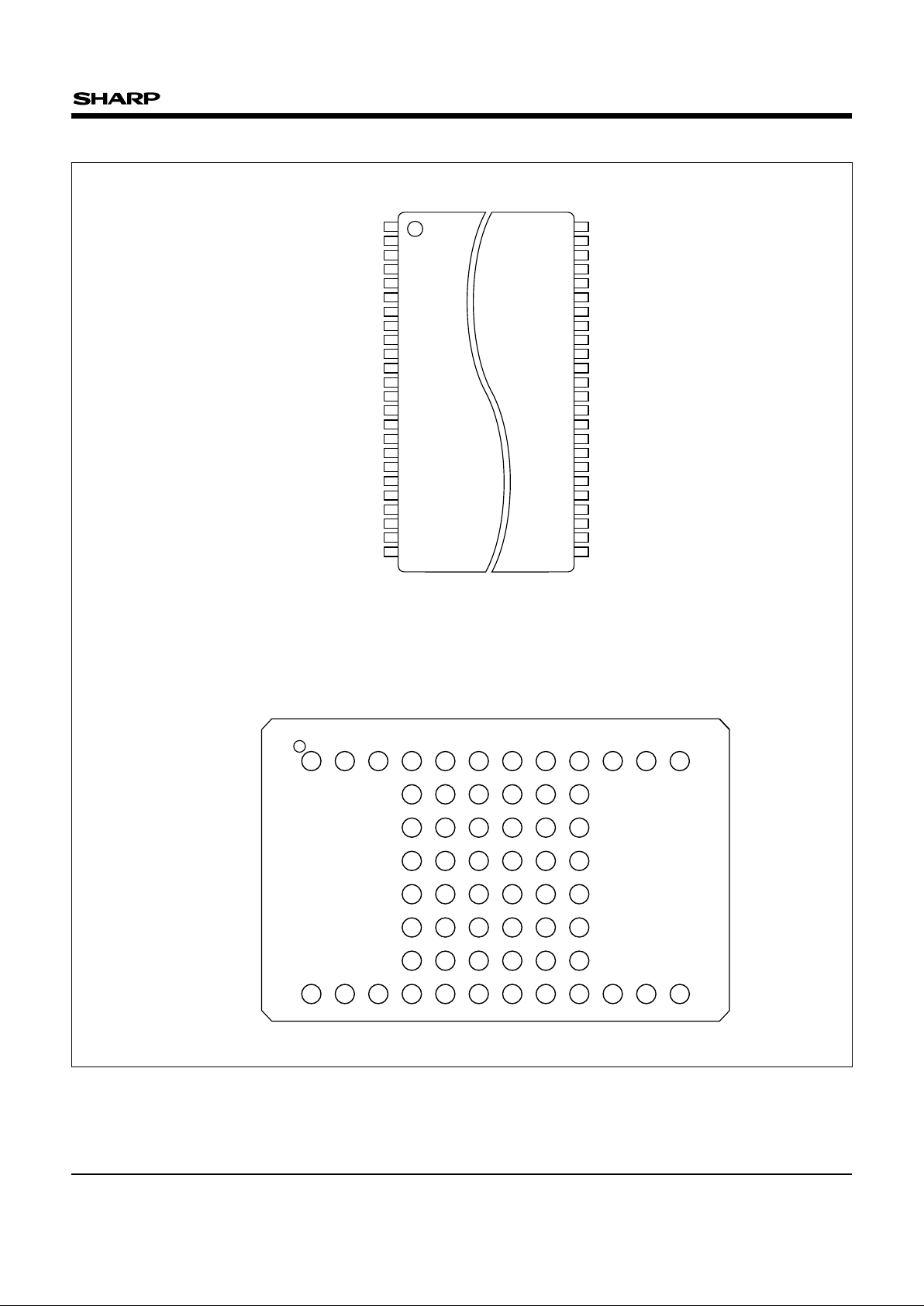
PIN CONNECTIONS
NC
1
A
B
C
D
E
NC2NC
A14 A13
34
A11
WE#
WP#
A17
5
A10
NC
RP#
VPP
A18
A15
6
A12
A9
RY/BY#
A19
A7
A16
7
DQ15
DQ6
DQ12
DQ10
DQ1
GND
8
DQ14
DQ5
VCC
DQ11
DQ2
F
G
NC NC NC NC NC NC
A5A2A6A3A4A1OE#A0DQ8
NC
9
DQ7
DQ13
DQ4
DQ3
DQ9
DQ0
NC10NC11NC
12
GND
CE#
H
A
8
(FBGA060/048-P-0811)
60-BALL CSP
48-PIN TSOP (Type I)
(TSOP048-P-1220)
A15
A14
A13
A12
A11
A10
A9
A8
NC
RY/BY#
WE#
RP#
V
PP
WP#
A
19
A18
A17
A7
A6
A5
A4
A3
A2
A1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
A16
NC
GND
DQ
15
DQ7
DQ14
DQ6
DQ13
DQ5
DQ12
DQ4
VCC
DQ11
DQ3
DQ10
DQ2
DQ9
DQ1
DQ8
DQ0
OE#
GND
CE#
A
0
TOP VIEW
NOTE :
Reverse bend available on request.
PRELIMINARY
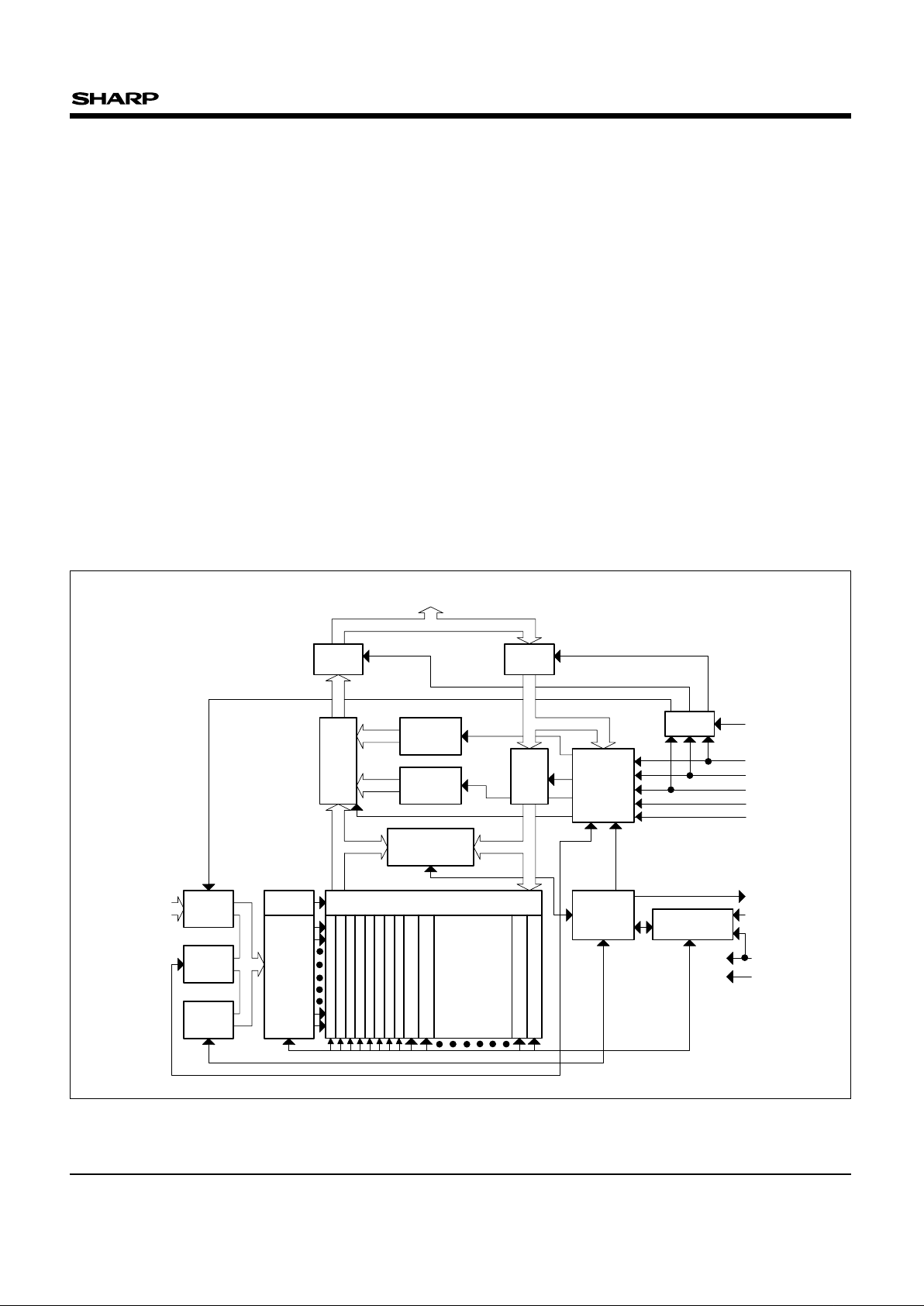
BLOCK ORGANIZATION
This product features an asymmetrically-blocked
architecture providing system memory integration.
Each erase block can be erased independently of
the others up to 100 000 times. For the address
locations of the blocks, see the memory map in
Fig. 1.
Boot Blocks : The two boot blocks are intended to
replace a dedicated boot PROM in a microprocessor or microcontroller-based system. The
boot blocks of 4 k words (4 096 words) feature
hardware controllable write-protection to protect the
crucial microprocessor boot code from accidental
modification. The protection of the boot blocks is
controlled using a combination of the V
PP, RP# and
WP# pins.
Parameter Blocks : The boot block architecture
includes parameter blocks to facilitate storage of
frequently update small parameters that would
normally require an EEPROM. By using software
techniques, the byte-rewrite functionality of
EEPROMs can be emulated. Each boot block
component contains six parameter blocks of 4 k
words (4 096 words) each. The parameter blocks
are not write-protectable.
Main Blocks : The reminder is divided into main
blocks for data or code storage. Each 16 M-bit
device contains thirty-one 32 k words (32 768
words) blocks.
LH28F160BG-TL/BGH-TL
INPUT
BUFFER
BUFFER
OUTPUT
MULTIPLEXER
VCC
CE#
RP#
OE#
IDENTIFIER
REGISTER
COMMAND
USER
INTERFACE
WRITE
STATE
MACHINE
PROGRAM/ERASE
VOLTAGE SWITCH
I/O
LOGIC
STATUS
REGISTER
DATA
REGISTER
DATA
COMPARATOR
X
DECODER
Y
DECODER
RY/BY#
VPP
VCC
GND
DQ0-DQ15
INPUT
BUFFER
ADDRESS
LATCH
ADDRESS
COUNTER
WP#
WE#
OUTPUT
A0-A19
BOOT BLOCK 0
BOOT BLOCK 1
PARAMETER BLOCK 0
PARAMETER BLOCK 1
PARAMETER BLOCK 2
PARAMETER BLOCK 3
PARAMETER BLOCK 4
PARAMETER BLOCK 5
MAIN BLOCK 0
MAIN BLOCK 1
MAIN BLOCK 29
MAIN BLOCK 30
31
32 k-WORD
MAIN BLOCKS
Y GATING
BLOCK DIAGRAM
- 3 -
- 4 -
PRELIMINARY
LH28F160BG-TL/BGH-TL
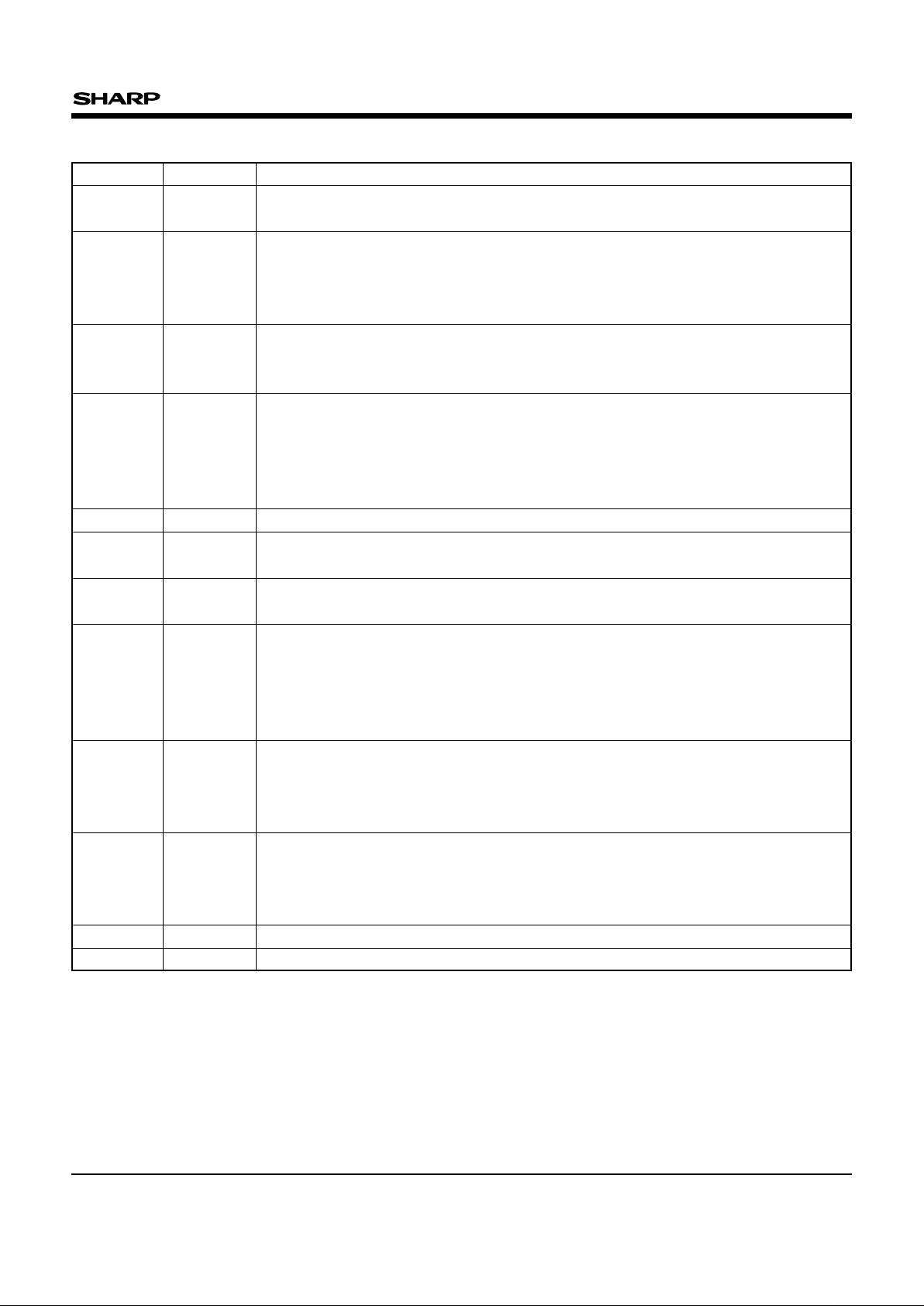
SYMBOL TYPE NAME AND FUNCTION
A0-A19 INPUT
ADDRESS INPUTS : Inputs for addresses during read and write operations. Addresses
are internally latched during a write cycle.
DATA INPUT/OUTPUTS : Inputs data and commands during CUI write cycles; outputs
data during memory array, status register and identifier code read cycles. Data pins float
to high-impedance when the chip is deselected or outputs are disabled. Data is
internally latched during a write cycle.
CE# INPUT
CHIP ENABLE : Activates the device’s control logic, input buffers, decoders and sense
amplifiers. CE#-high deselects the device and reduces power consumption to standby
levels.
RESET/DEEP POWER-DOWN : Puts the device in deep power-down mode and resets
internal automation. RP#-high enables normal operation. When driven low, RP# inhibits
write operations which provide data protection during power transitions. Exit from deep
power-down sets the device to read array mode. Block erase or word write with V
IH <
RP# < VHH produce spurious results and should not be attempted.
OE# INPUT OUTPUT ENABLE : Gates the device’s outputs during a read cycle.
WE# INPUT
WRITE ENABLE : Controls writes to the CUI and array blocks. Addresses and data are
latched on the rising edge of the WE# pulse.
WP# INPUT
WRITE PROTECT : Master control for boot blocks locking. When VIL, locked boot
blocks cannot be erased and programmed.
READY/BUSY : Indicates the status of the internal WSM. When low, the WSM is
performing an internal operation (block erase or word write). RY/BY#-high-impedance
indicates that the WSM is ready for new commands, block erase is suspended, and
word write is inactive, word write is suspended, or the device is in deep power-down
mode.
BLOCK ERASE AND WORD WRITE POWER SUPPLY : For erasing array blocks or
writing words. With V
PP ≤ VPPLK, memory contents cannot be altered. Block erase and
word write with an invalid V
PP (see Section 6.2.3 "DC CHARACTERISTICS") produce
spurious results and should not be attempted.
DEVICE POWER SUPPLY : 2.7 to 3.6 V. Do not float any power pins. With V
CC ≤
VLKO, all write attempts to the flash memory are inhibited. Device operations at invalid
V
CC voltage (see Section 6.2.3 "DC CHARACTERISTICS") produce spurious results
and should not be attempted.
GND SUPPLY GROUND : Do not float any ground pins.
NC NO CONNECT : Lead is not internal connected; recommend to be floated.
PIN DESCRIPTION
DQ0-DQ15
INPUT/
OUTPUT
RP# INPUT
RY/BY# OUTPUT
V
PP SUPPLY
V
CC SUPPLY

PRELIMINARY
LH28F160BG-TL/BGH-TL
1 INTRODUCTION
This datasheet contains LH28F160BG-TL/BGH-TL
specifications. Section 1 provides a flash memory
overview. Sections 2, 3, 4 and 5 describe the
memory organization and functionality. Section 6
covers electrical specifications. LH28F160BG-TL/
BGH-TL flash memories documentation also
includes ordering information which is referenced in
Section 7.
1.1 New Features
Key enhancements of LH28F160BG-TL/BGH-TL
Smart 3 flash memories are :
• 2.7 V V
CC and VPP Write/Erase Operation
• Enhanced Suspend Capabilities
• Boot Block Architecture
Note following important differences :
•V
PPLK has been lowered to 1.5 V to support
2.7 V block erase and word write operations.
Designs that switch V
PP off during read
operations should make sure that the V
PP
voltage transitions to GND.
• To take advantage of Smart 3 technology, allow
V
PP connection to 2.7 V or 12 V.
1.2 Product Overview
The LH28F160BG-TL/BGH-TL are high-performance
16 M-bit Smart 3 flash memories organized as
1 024 k-word of 16 bits. The 1 024 k-word of data
is arranged in two 4 k-word boot blocks, six 4 kword parameter blocks and thirty-one 32 k-word
main blocks which are individually erasable insystem. The memory map is shown in Fig. 1.
V
PP at 2.7 V eliminates the need for a separate 12 V
converter, while V
PP = 12 V maximizes block erase
and word write performance. In addition to flexible
erase and program voltages, the dedicated V
PP pin
gives complete data protection when V
PP ≤ VPPLK.
A Command User Interface (CUI) serves as the
interface between the system processor and
internal operation of the device. A valid command
sequence written to the CUI initiates device
automation. An internal Write State Machine (WSM)
automatically executes the algorithms and timings
necessary for block erase and word write
operations.
A block erase operation erases one of the device’s
32 k-word blocks typically within 1.2 second (3.0 V
V
CC and VPP), independent of other blocks. Each
block can be independently erased 100 000 times.
Block erase suspend mode allows system software
to suspend block erase to read data from, or write
data to any other block.
Writing memory data is performed in word
increments of the device’s 32 k-word blocks
typically within 55 µs, 4 k-word blocks typically
within 60 µs (3.0 V V
CC and VPP). Word write
suspend mode enables the system to read data
from, or write data to any other flash memory array
location.
The boot block is located at either the top or the
bottom of the address map in order to
accommodate different micro-processor protect for
boot code location. The hardware-lockable boot
block provides complete code security for the
kernel code required for system initialization.
Locking and unlocking of the boot block is
controlled by WP# and/or RP# (see Section 4.9 for
details). Block erase or word write for boot block
must not be carried out by WP# to low and RP# to
V
IH.
The status register indicates when the WSM’s block
erase or word write operation is finished.
The RY/BY# output gives an additional indicator of
WSM activity by providing both a hardware signal
- 5 -

- 6 -
PRELIMINARY
LH28F160BG-TL/BGH-TL
of status (versus software polling) and status
masking (interrupt masking for background block
erase, for example). Status polling using RY/BY#
minimizes both CPU overhead and system power
consumption. When low, RY/BY# indicates that the
WSM is performing a block erase or word write.
RY/BY#-High-impedance indicates that the WSM is
ready for a new command, block erase is
suspended (and word write is inactive), word write
is suspended, or the device is in deep power-down
mode.
The access time is 100 ns or 120 ns (t
AVQV) at the
V
CC supply voltage range of 2.7 to 3.6 V over the
temperature range, 0 to +70°C (LH28F160BG-TL)/
– 25 to +85°C (LH28F160BGH-TL).
The Automatic Power Saving (APS) feature
substantially reduces active current when the
device is in static mode (addresses not switching).
In APS mode, the typical I
CCR current is 3 mA at
2.7 V V
CC.
When CE# and RP# pins are at V
CC, the ICC
CMOS standby mode is enabled. When the RP#
pin is at GND, deep power-down mode is enabled
which minimizes power consumption and provides
write protection during reset. A reset time (t
PHQV) is
required from RP# switching high until outputs are
valid. Likewise, the device has a wake time (t
PHEL)
from RP#-high until writes to the CUI are
recognized. With RP# at GND, the WSM is reset
and the status register is cleared.
PRELIMINARY
LH28F160BG-TL/BGH-TL
- 7 -
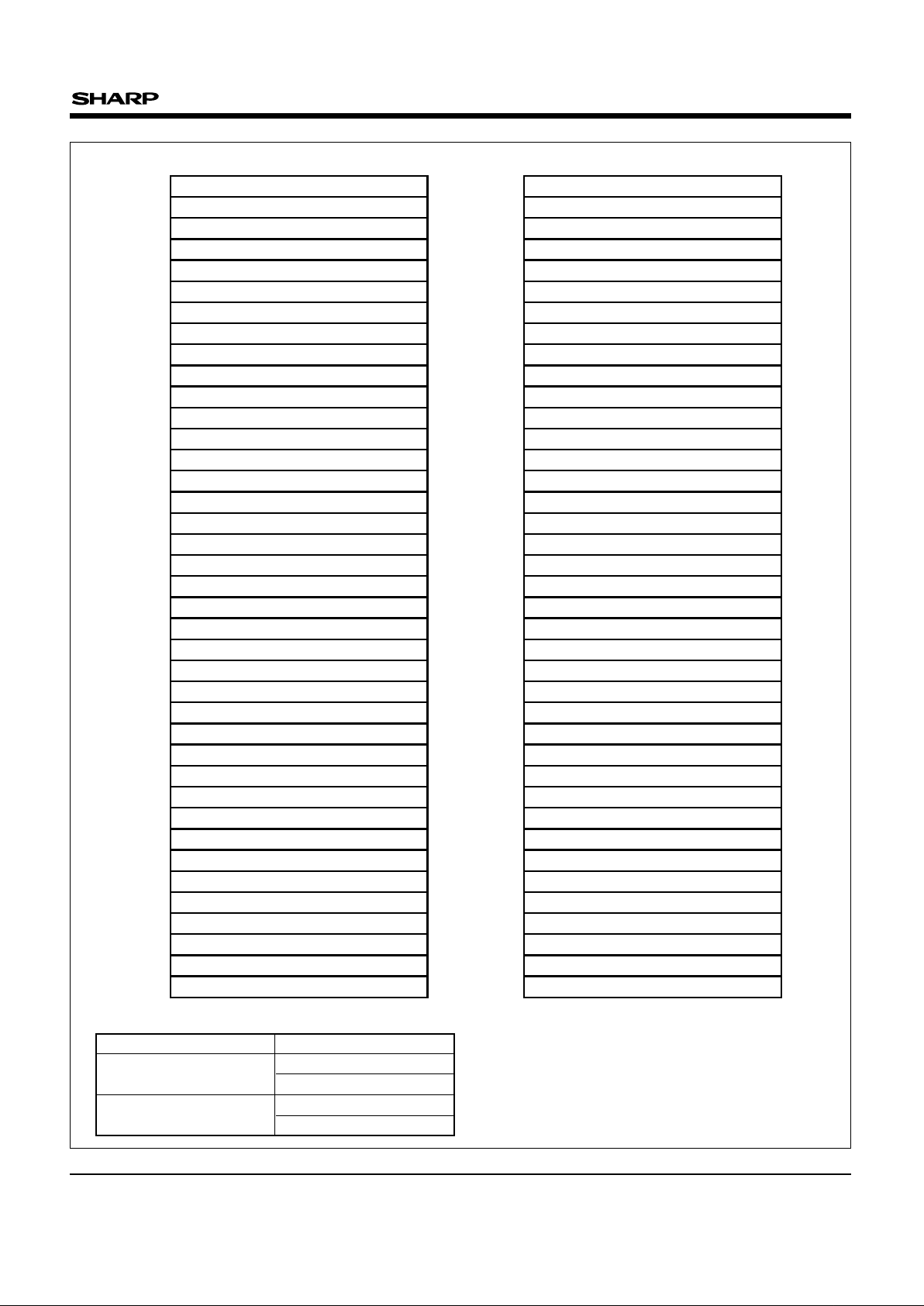
0
1
0
1
2
3
4
5
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
4 k-Word Boot Block
4 k-Word Boot Block
4 k-Word Parameter Block
4 k-Word Parameter Block
4 k-Word Parameter Block
4 k-Word Parameter Block
4 k-Word Parameter Block
4 k-Word Parameter Block
32 k-Word Main Block
32 k-Word Main Block
32 k-Word Main Block
32 k-Word Main Block
32 k-Word Main Block
32 k-Word Main Block
32 k-Word Main Block
32 k-Word Main Block
32 k-Word Main Block
32 k-Word Main Block
32 k-Word Main Block
32 k-Word Main Block
32 k-Word Main Block
32 k-Word Main Block
32 k-Word Main Block
32 k-Word Main Block
32 k-Word Main Block
32 k-Word Main Block
32 k-Word Main Block
32 k-Word Main Block
32 k-Word Main Block
32 k-Word Main Block
32 k-Word Main Block
32 k-Word Main Block
32 k-Word Main Block
32 k-Word Main Block
32 k-Word Main Block
32 k-Word Main Block
32 k-Word Main Block
32 k-Word Main Block
32 k-Word Main Block
Top Boot
FFFFF
FF000
FEFFF
FE000
FDFFF
FD000
FCFFF
FC000
FBFFF
FB000
FAFFF
FA000
F9FFF
F9000
F8FFF
F8000
F7FFF
F0000
EFFFF
E8000
E7FFF
E0000
DFFFF
D8000
D7FFF
D0000
CFFFF
C8000
C7FFF
C0000
BFFFF
B8000
B7FFF
B0000
AFFFF
A8000
A7FFF
A0000
9FFFF
98000
97FFF
90000
8FFFF
88000
87FFF
80000
7FFFF
78000
77FFF
70000
6FFFF
68000
67FFF
60000
5FFFF
58000
57FFF
50000
4FFFF
48000
47FFF
40000
3FFFF
38000
37FFF
30000
2FFFF
28000
27FFF
20000
1FFFF
18000
17FFF
10000
0FFFF
08000
07FFF
00000
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
5
4
3
2
1
0
1
0
32 k-Word Main Block
32 k-Word Main Block
32 k-Word Main Block
32 k-Word Main Block
32 k-Word Main Block
32 k-Word Main Block
32 k-Word Main Block
32 k-Word Main Block
32 k-Word Main Block
32 k-Word Main Block
32 k-Word Main Block
32 k-Word Main Block
32 k-Word Main Block
32 k-Word Main Block
32 k-Word Main Block
32 k-Word Main Block
32 k-Word Main Block
32 k-Word Main Block
32 k-Word Main Block
32 k-Word Main Block
32 k-Word Main Block
32 k-Word Main Block
32 k-Word Main Block
32 k-Word Main Block
32 k-Word Main Block
32 k-Word Main Block
32 k-Word Main Block
32 k-Word Main Block
32 k-Word Main Block
32 k-Word Main Block
32 k-Word Main Block
4 k-Word Parameter Block
4 k-Word Parameter Block
4 k-Word Parameter Block
4 k-Word Parameter Block
4 k-Word Parameter Block
4 k-Word Parameter Block
4 k-Word Boot Block
4 k-Word Boot Block
Bottom Boot
FFFFF
F8000
F7FFF
F0000
EFFFF
E8000
D7FFF
D0000
DFFFF
D8000
D7FFF
D0000
CFFFF
C8000
C7FFF
C0000
BFFFF
B8000
B7FFF
B0000
AFFFF
A8000
A7FFF
A0000
9FFFF
98000
97FFF
90000
8FFFF
88000
87FFF
80000
7FFFF
78000
77FFF
70000
6FFFF
68000
67FFF
60000
5FFFF
58000
57FFF
50000
4FFFF
48000
47FFF
40000
3FFFF
38000
37FFF
30000
2FFFF
28000
27FFF
20000
1FFFF
18000
17FFF
10000
0FFFF
08000
07FFF
07000
06FFF
06000
05FFF
05000
04FFF
04000
03FFF
03000
02FFF
02000
01FFF
01000
00FFF
00000
Fig. 1 Memory Map
BLOCK CONFIGURATION VERSIONS
Top Boot
LH28F160BG-TTL
LH28F160BGH-TTL
Bottom Boot
LH28F160BG-BTL
LH28F160BGH-BTL
NOTES :

PRELIMINARY
LH28F160BG-TL/BGH-TL
2 PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION
The LH28F160BG-TL/BGH-TL Smart 3 flash
memories include an on-chip WSM to manage
block erase and word write functions. It allows for :
fixed power supplies during block erasure and word
write, and minimal processor overhead with RAMlike interface timings.
After initial device power-up or return from deep
power-down mode (see Table 1 "Bus Operations"),
the device defaults to read array mode.
Manipulation of external memory control pins allow
array read, standby and output disable operations.
Status register and identifier codes can be
accessed through the CUI independent of the V
PP
voltage. High voltage on VPP enables successful
block erasure and word writing. All functions
associated with altering memory contents—block
erase, word write, status and identifier codes—are
accessed via the CUI and verified through the
status register.
Commands are written using standard microprocessor write timings. The CUI contents serve as
input to the WSM, which controls the block erase
and word write. The internal algorithms are
regulated by the WSM, including pulse repetition,
internal verification and margining of data.
Addresses and data are internally latched during
write cycles. Writing the appropriate command
outputs array data, accesses the identifier codes or
outputs status register data.
Interface software that initiates and polls progress
of block erase and word write can be stored in any
block. This code is copied to and executed from
system RAM during flash memory updates. After
successful completion, reads are again possible via
the Read Array command. Block erase suspend
allows system software to suspend a block erase to
read/write data from/to blocks other than that which
is suspended. Word write suspend allows system
software to suspend a word write to read data from
any other flash memory array location.
2.1 Data Protection
Depending on the application, the system designer
may choose to make the V
PP power supply
switchable (available only when memory block
erases or word writes are required) or hardwired to
V
PPH1/2. The device accommodates either design
practice and encourages optimization of the
processor-memory interface.
When V
PP ≤ VPPLK, memory contents cannot be
altered. The CUI, with two-step block erase or word
write command sequences, provides protection
from unwanted operations even when high voltage
is applied to V
PP. All write functions are disabled
when V
CC is below the write lockout voltage VLKO
or when RP# is at VIL. The device’s blocks locking
capability provides additional protection from
inadvertent code or data alteration by gating erase
and word write operations.
3 BUS OPERATION
The local CPU reads and writes flash memory insystem. All bus cycles to or from the flash memory
conform to standard microprocessor bus cycles.
3.1 Read
Information can be read from any block, identifier
codes or status register independent of the V
PP
voltage. RP# can be at either VIH or VHH.
The first task is to write the appropriate read mode
command (Read Array, Read Identifier Codes or
Read Status Register) to the CUI. Upon initial
device power-up or after exit from deep powerdown mode, the device automatically resets to read
array mode. Five control pins dictate the data flow
in and out of the component : CE#, OE#, WE#,
RP# and WP#. CE# and OE# must be driven
active to obtain data at the outputs. CE# is the
- 8 -

- 9 -
PRELIMINARY
LH28F160BG-TL/BGH-TL
device selection control, and when active enables
the selected memory device. OE# is the data
output (DQ
0-DQ15) control and when active drives
the selected memory data onto the I/O bus. WE#
must be at V
IH and RP# must be at VIH or VHH.
Fig. 9 illustrates read cycle.
3.2 Output Disable
With OE# at a logic-high level (VIH), the device
outputs are disabled. Output pins (DQ
0-DQ15) are
placed in a high-impedance state.
3.3 Standby
CE# at a logic-high level (VIH) places the device in
standby mode which substantially reduces device
power consumption. DQ
0-DQ15 outputs are placed
in a high-impedance state independent of OE#. If
deselected during block erase or word write, the
device continues functioning, and consuming active
power until the operation completes.
3.4 Deep Power-Down
RP# at VIL initiates the deep power-down mode.
In read modes, RP#-low deselects the memory,
places output drivers in a high-impedance state and
turns off all internal circuits. RP# must be held low
for a minimum of 100 ns. Time t
PHQV is required
after return from power-down until initial memory
access outputs are valid. After this wake-up
interval, normal operation is restored. The CUI is
reset to read array mode and status register is set
to 80H.
During block erase or word write modes, RP#-low
will abort the operation. RY/BY# remains low until
the reset operation is complete. Memory contents
being altered are no longer valid; the data may be
partially erased or written. Time t
PHWL is required
after RP# goes to logic-high (V
IH) before another
command can be written.
As with any automated device, it is important to
assert RP# during system reset. When the system
comes out of reset, it expects to read from the flash
memory. Automated flash memories provide status
information when accessed during block erase or
word write modes. If a CPU reset occurs with no
flash memory reset, proper CPU initialization may
not occur because the flash memory may be
providing status information instead of array data.
SHARP’s flash memories allow proper CPU
initialization following a system reset through the
use of the RP# input. In this application, RP# is
controlled by the same RESET# signal that resets
the system CPU.
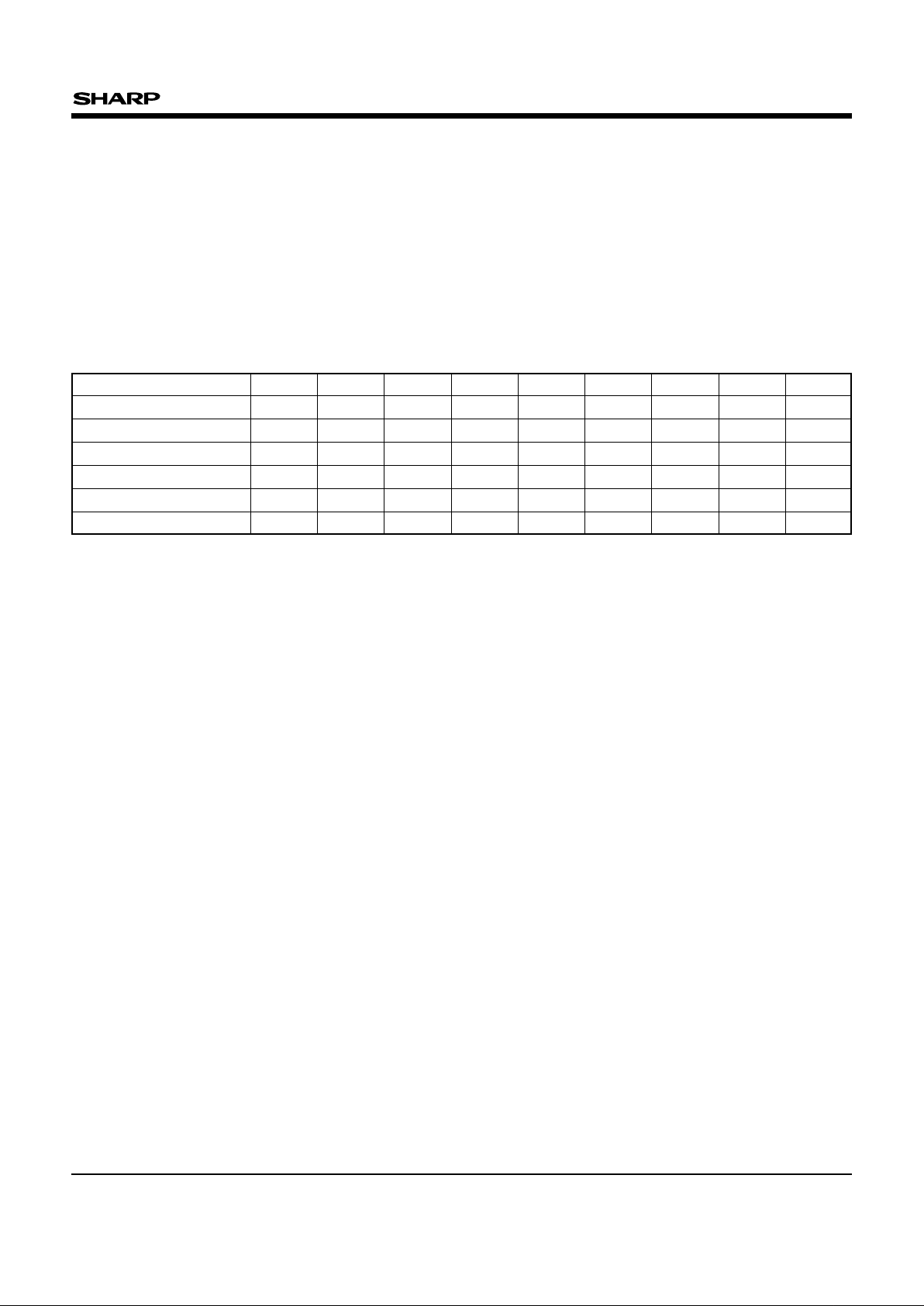
3.5 Read Identifier Codes
The read identifier codes operation outputs the
manufacture code and device code (see Fig. 2).
Using the manufacture and device codes, the
system CPU can automatically match the device
with its proper algorithms.
Fig. 2 Device Identifier Code Memory Map
3.6 Write
Writing commands to the CUI enable reading of
device data and identifier codes. They also control
inspection and clearing of the status register.
The Block Erase command requires appropriate
command data and an address within the block to
be erased. The Word Write command requires the
command and address of the location to be written.
FFFFF
00002
00001
00000
Reserved for
Future Implementation
Device Code
Manufacture Code
- 10 -
PRELIMINARY
LH28F160BG-TL/BGH-TL
The CUI does not occupy an addressable memory
location. It is written when WE# and CE# are
active. The address and data needed to execute a
command are latched on the rising edge of WE# or
CE# (whichever goes high first). Standard
microprocessor write timings are used. Fig. 10 and
Fig. 11 illustrate WE# and CE# controlled write
operations.
4 COMMAND DEFINITIONS
When the VPP ≤ VPPLK, read operations from the
status register, identifier codes, or blocks are
enabled.
Device operations are selected by writing specific
commands into the CUI. Table 2 defines these
commands.
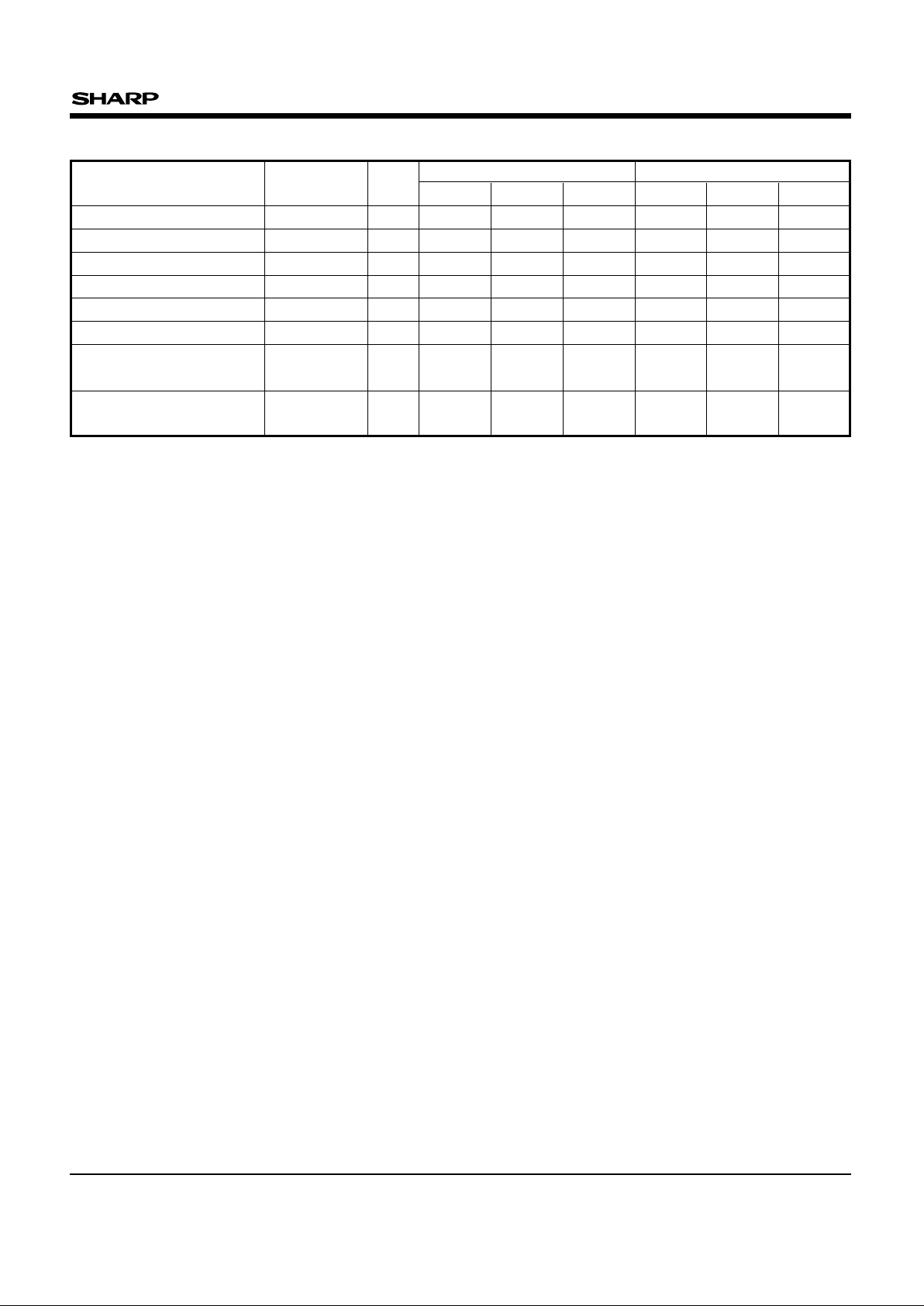
Table 1 Bus Operations
MODE NOTE RP# CE# OE# WE#
ADDRESS
V
PP
DQ
0-15
RY/BY#
Read 1, 2, 3, 8
VIHor V
HH
V
IL
V
IL
V
IH
XXD
OUT
X
Output Disable 3
VIHor V
HH
V
IL
V
IH
V
IH
X X High Z X
Standby 3
VIHor V
HH
V
IH
XXXXHigh Z X
Deep Power-Down 4 VIL XXXXXHigh Z High Z
Read Identifier Codes 8
VIHor V
HH
V
IL
V
IL
V
IH
See Fig. 2
X(
NOTE 5)
High Z
Write 3, 6, 7, 8
VIHor V
HH
V
IL
V
IH
V
IL
XXDINX
NOTES :
1. Refer to Section 6.2.3 "DC CHARACTERISTICS".
When V
PP ≤ VPPLK, memory contents can be read, but
not altered.
2. X can be V
IL or VIH for control pins and addresses, and
V
PPLK or VPPH1/2 for VPP. See Section 6.2.3 "DC
CHARACTERISTICS" for V
PPLK and VPPH1/2 voltages.
3. RY/BY# is V
OL when the WSM is executing internal
block erase or word write algorithm. It is high-impedance
when the WSM is not busy, in block erase suspend
mode (with word write inactive), word write suspend
mode or deep power-down mode.
4. RP# at GND±0.2 V ensures the lowest deep powerdown current.
5. See Section 4.2 for read identifier code data.
6. V
IH < RP# < VHH produce spurious results and should
not be attempted.
7. Refer to Table 2 for valid D
IN during a write operation.
8. Don’t use the timing both OE# and WE# are V
IL.
- 11 -
PRELIMINARY
LH28F160BG-TL/BGH-TL
COMMAND
BUS CYCLES
NOTE
FIRST BUS CYCLE SECOND BUS CYCLE
REQ’D.
Oper
(NOTE 1)
Addr
(NOTE 2)
Data
(NOTE 3)
Oper
(NOTE 1)
Addr
(NOTE 2)
Data
(NOTE 3)
Read Array/Reset 1 Write X FFH
Read Identifier Codes ≥ 2 4 Write X 90H Read IA ID
Read Status Register 2 Write X 70H Read X SRD
Clear Status Register 1 Write X 50H
Block Erase 2 5 Write BA 20H Write BA D0H
Word Write 2 5, 6 Write WA
40H or 10H
Write WA WD
Block Erase and
1 5 Write X B0H
Word Write Suspend
Block Erase and
1 5 Write X D0H
Word Write Resume
Table 2 Command Definitions
(NOTE 7)
NOTES :
1. Bus operations are defined in Table 1.
2. X = Any valid address within the device.
IA = Identifier code address : see Fig. 2.
BA = Address within the block being erased.
WA = Address of memory location to be written.
3. SRD = Data read from status register. See Table 5 for a
description of the status register bits.
WD = Data to be written at location WA. Data is latched
on the rising edge of WE# or CE# (whichever
goes high first).
ID = Data read from identifier codes.
4. Following the Read Identifier Codes command, read
operations access manufacture and device codes. See
Section 4.2 for read identifier code data.
5. If the block is boot block, WP# must be at V
IH or RP#
must be at V
HH to enable block erase or word write
operations. Attempts to issue a block erase or word write
to a boot block while WP# is V
IH or RP# is VIH.
6. Either 40H or 10H is recognized by the WSM as the
word write setup.
7. Commands other than those shown above are reserved
by SHARP for future device implementations and should
not be used.
 Loading...
Loading...