Page 1

Graphing Calculator
EL-9450/9400
OPERATION GUIDE
Page 2
Built-in slide shows
Educational tools
(OHP/PC-link/Data collection)
Shift/Change function
Equation editor
Split display
Large display
Rapid graph
Rapid window
Rapid zoom
Easy to Teach
Easy to Learn
Easy to Use
Introduction
C
ontents
Sales points P 1
Basic operation P 2
Equation editor P 4
Features
Shift P 5
Change P 6
Slide show P 7
Slide show selections P 8
Graphing procedure P 10
Rapid graph P 11
Rapid window P 12
Rapid zoom P 13
System options
PC-link system P 14
Set to set communication P 15
OHP system P 16
Menu tree 1~6 P 17
Specifications P 23
The EL-9450/9400 was developed to meet the needs of an
expanding education market and is based on three concepts:
easy to teach, easy to learn and easy to use. The EL-9450/9400
has been designed with simplified operations and time-saving
features, allowing teachers to concentrate on actual teaching.
This manual was designed to introduce teachers to the unique
features of the EL-9450/9400 using detailed operation examples.
Page 3

1
Sales points
Graph Shift/Change shows
how "changing" the graph
affects the equation
Large 96 x 64-dot
display
Slide Shows reduce class
preparation time
Rapid zoom allows easy
adjustment of window size
Rapid graph/Rapid window
simplify graphing procedures
1
3
Equation Editor shows
equations just as in textbooks
2
4
5
6
Page 4
2
Basic operation
Use to enter equations
Use to draw graphs
Use to view table of function value
Use to set size of viewing window
Use to adjust the viewing range
Use to trace graphs
Use to enter calculation mode
Use to enter slide show mode
Use to operate Rapid Graph/Rapid
Window and Rapid Zoom functions
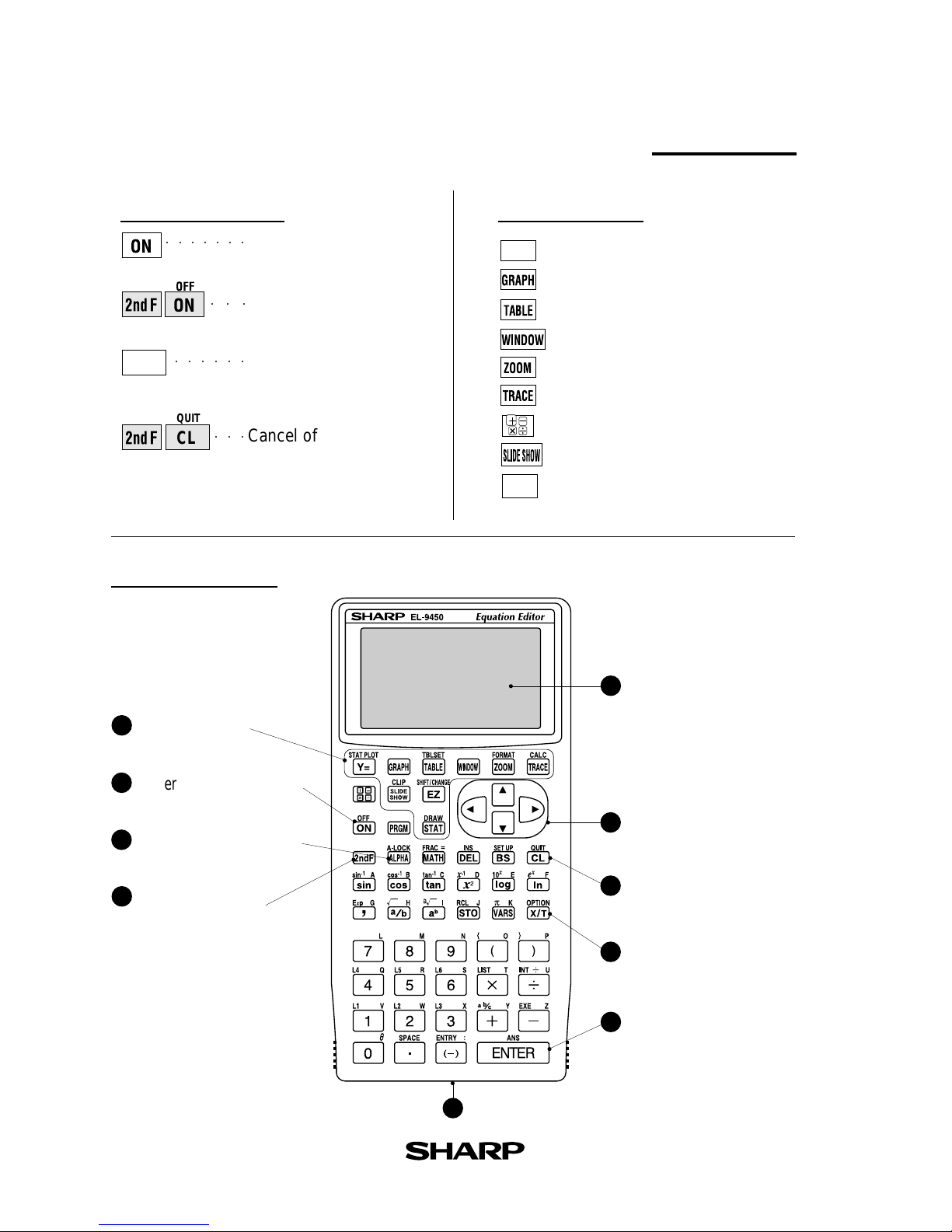
Function keys
Y =
EZ
Names of parts
Communication port for peripheral devices
Power off
Power on
CL
Erase equations and
remove error displays
Power ON/OFF
○○○○○○○
○○○
○○○○○○
QUIT
CL
Cancel of previous
function (Escape)
○○○
Graphing keys
Power supply ON/OFF key
Alphabet specification key
Secondary function
specification key
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Display screen
Cursor movement keys
Clear/Quit key
Variable enter key
Calculation execute key
10
Page 5
3
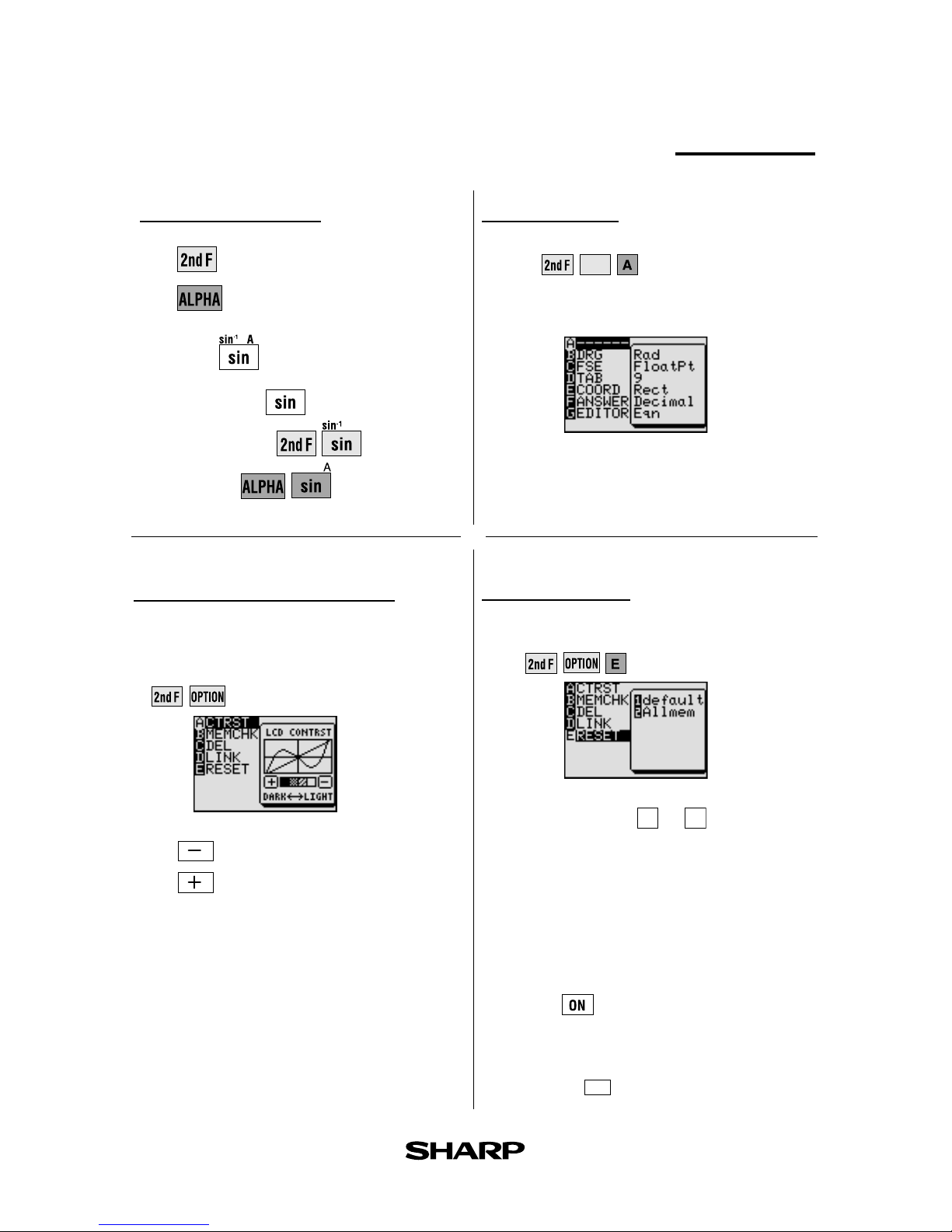
Reset function
1) When trouble occurs
Press to enter the reset mode.
• Use this function (1 or 2 ) to return all
settings to the default value or to delete all
data.
2) All RESET operation
• If trouble still occurs, proceed as follows:
1. Press the RESET switch on the back.
2. Press .
• Returns to the initial display.
CAUTION
Do not press CL in step 2. It will delete all data
stored in the calculator.
SET UP menu
Press
SET UP
.
• Contents displayed on the right side of
the screen are the current settings.
Adjusting screen contrast
• The contrast adjust screen will appear
when pressing
.
Press to lighten contrast.
Press to darken contrast.
Basic operation
Guide to key use
Press to use secondary functions (in yellow).
Press to use the alphabet keys (in blue).
Example:
To select “sin”:
To select “sin-1”:
To select A:
There may be differences in the results
of calculations and graph plotting
depending on the SET UP settings.
]
]
Page 6
NotesKey Operation
Display
Example
4
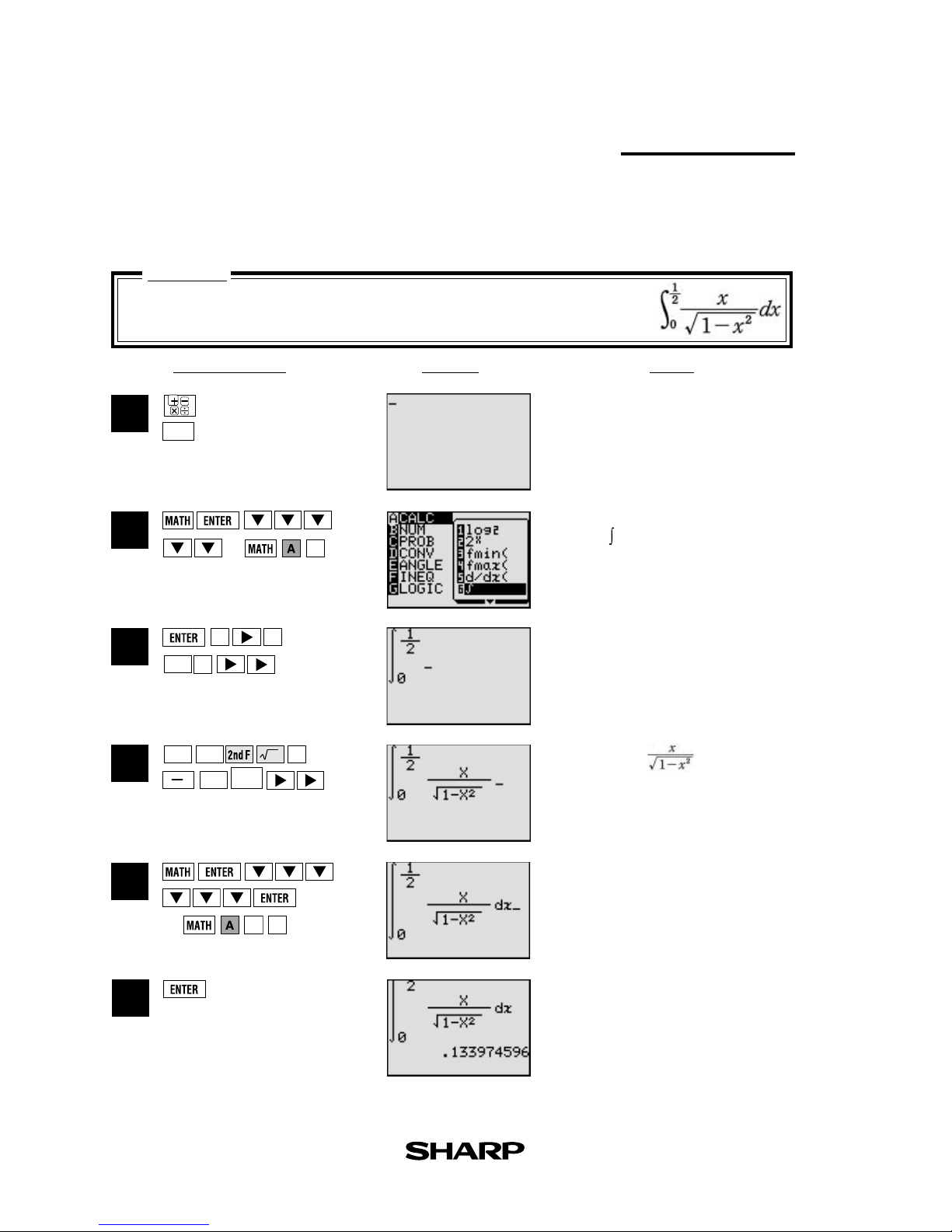
Equation editor
1
2
5
4
3
6
Input the equation and see how it can be easily
viewed with the equation editor.
CL
0
1
a/b
2
a/b
1
x
2
Clear the display.
Select CALC and
Enter the range of the integral.
Complete equation input.
Calculate the expression.
The blinking mark in the upper right
side of the display indicates the
expression is being calculated.
Enter
(or 6 )
(or
0 7 )
]
]
X/T
X/T
(Integral function)
The equation editor allows equations to be viewed just as they are written in textbooks. This
aids student comprehension and allows mistakes to be found quickly.
Page 7
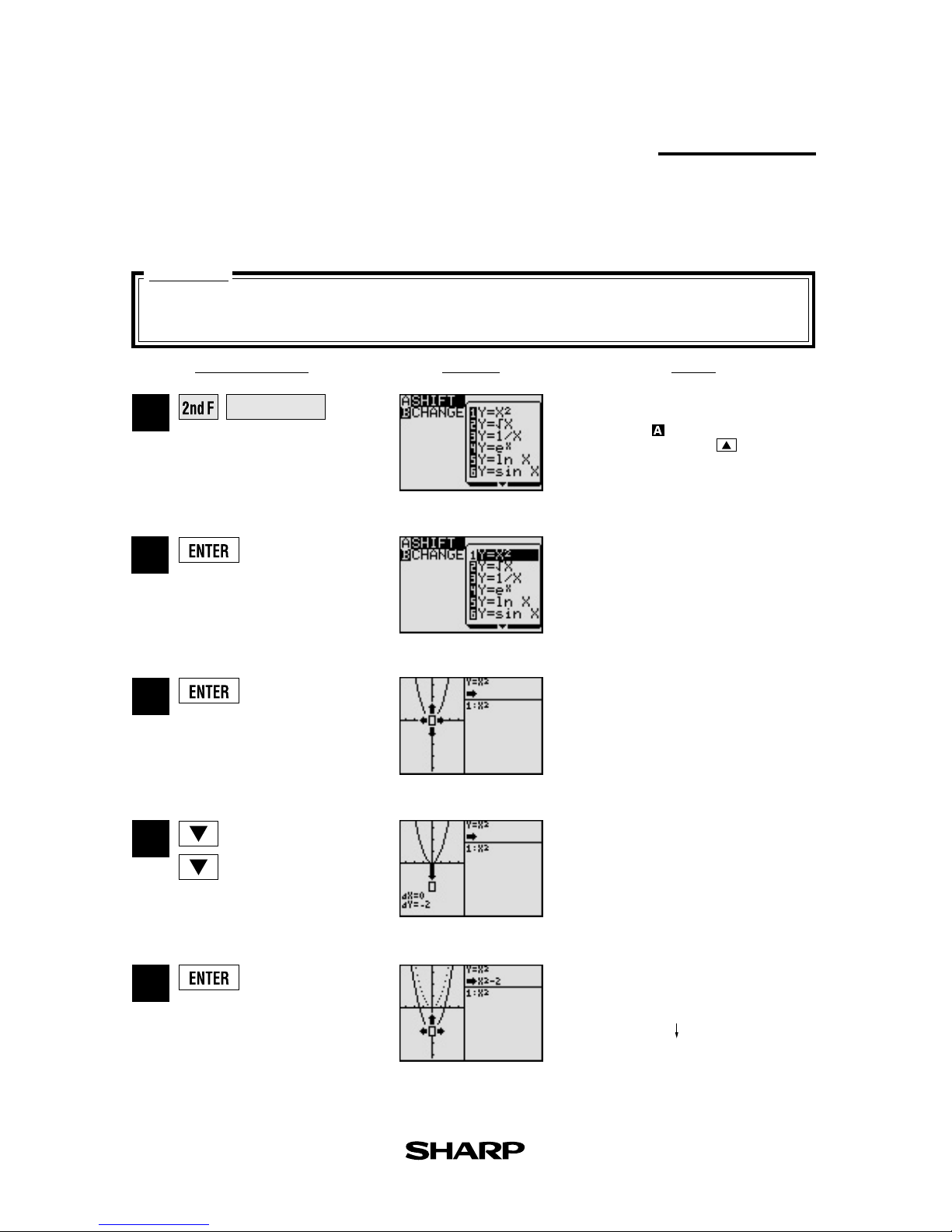
NotesKey Operation Display
Example
5
SHIFT/CHANGE
]
]
]
]
Shift
(Change the location of graphs)
Graph shift function helps students grasp the relationship between an equation and its graph.
Shift the graph’s location without changing its shape, and the change is immediately reflected
in the equation on the right side of the display.
When the graph of y = x2 is shifted downward,
how does this affect the equation?
View the result of the shift.
Select the location of the shift:
move cursor down twice.
Select the equation: y = x
2
and
draw the graph.
Select shift. Cursor moves to the
equation menu.
y = x
2
y = x2-2
Enter
SHIFT/CHANGE
mode.
If
SHIFT
is not already
highlighted press .
1
2
4
3
5
Page 8
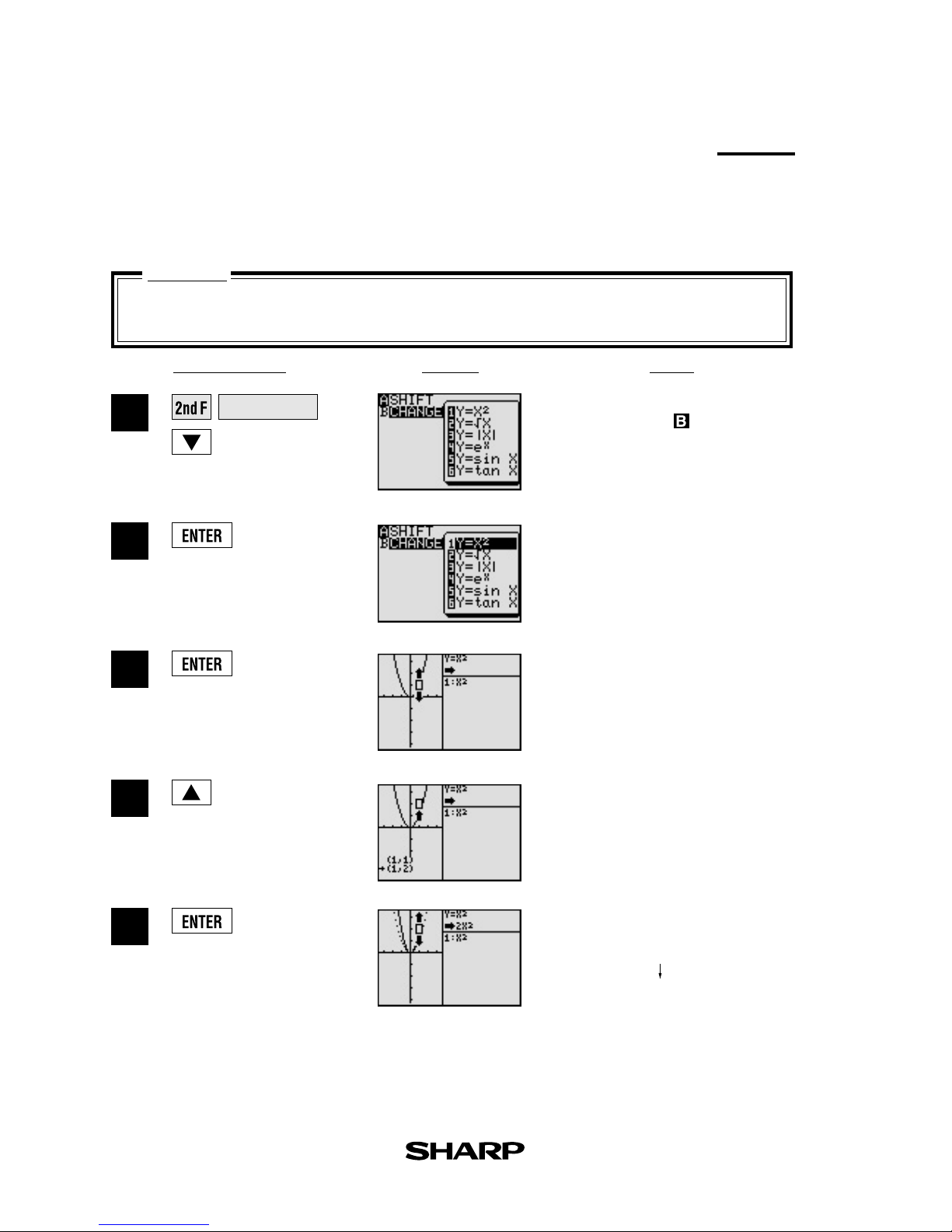
NotesKey Operation
Display
Example
6
When the graph of y = x2 is changed,
how does it affect the equation?
Change
Graph change function helps students grasp the relationship between an equation and its
graph. Change the shape of the graph, and the change is immediately reflected in the equation
on the right side of the display.
Enter
SHIFT/CHANGE
mode
and specified (
CHANGE
).
1
3
4
5
2
Select change. Cursor will move
to the equation menu.
Select the equation: y = x
2
and
draw the graph.
View the result of the change.
Select the location of the
change: increase the value of ycoordinates.
SHIFT/CHANGE
(Change the shape of the graphs)
Features
y = x
2
y = 2x
2
]
]
Page 9
NotesKey Operation Display
Example
7
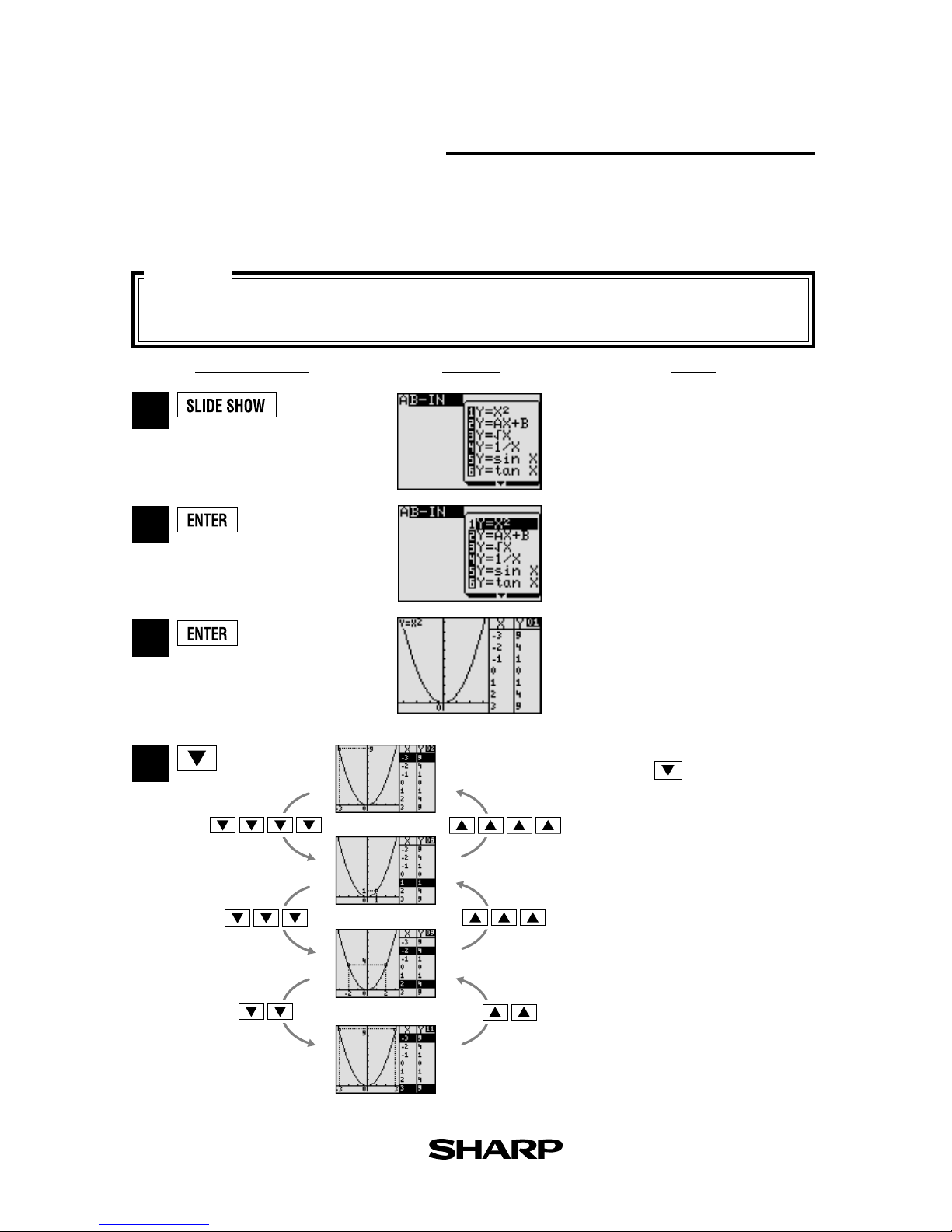
Slide sho w
Slide show assists with teacher preparation. By selecting from the built-in options or creating your own series of slides, you can demonstrate lessons with minimum preparation
time.
Use the built-in slide show of y = x2 to show how the
coordinates change as you move along the graph.
Select y = x2 and the first slide
appears.
Moving between the values you
can follow the changes in the
graph’s coordinates, making the
nature of the graph easier to
understand.
Specified
SLIDE SHOW
mode.
1
2
4
3
Begin the slide show by pressing the cursor key.
Select the built-in menu.
Features
* View the selection of built-in slide shows
on the following pages.
Page 10

8
Built-in slide show selections
1) Y=X
2
2) Y=AX+B 4) Y=1/X
Features
3) Y= X
Page 11

9
5) Y=sinX 6) Y=tanX 7) Y=cos-1X 8) Y=lnX
Features
Built-in slide show selections
Page 12

10
Graphing Procedures
Following outlines graphing procedures and indicates the steps where Sharp's unique functions can
be used to simplify operations. These functions are introduced on the following pages.
Step 1
Input equation
Step 2
Set X, Y range
Xmin =
Xmax =
Xscl =
Ymin =
Ymax =
Yscl =
Step 3
Draw graph
Step 4
Adjust viewing
window
Manual Input
Graphing Procedure
Y =
EZ
EZ
EZ
Rapid Graph
Manual Input
Rapid Window
Manual Input
Rapid Zoom
Press Graph button to draw graph.
Simply select from
built-in menu to
modify desired type of equation .
Simply select from
built-in menu to set
window size.
Use arrows to adjust window
size while viewing graph.
Go back to Step 2 to
readjust window size.
Features
3
a
b
x
2
2
1
5
(–)
3 3
1
(–)
5
1 5
Amending
range size
X/T X/T
X/T
The EL-9450/9400 has three unique functions that simplify graphing procedures: Rapid Graph,
Rapid Window and Rapid Zoom. Of course, the EL-9450/9400 supports conventional graphing
procedures as well.
Page 13

NotesKey Operation Display
Example
11
Rapid graph
Graphing has never been easier. With its full range of preset equations, rapid graph simplifies
equation input. Use in conjunction with the rapid window function or with any graph
created.
Draw the graph for y = 2sin (-2x+ ) + 2
using the rapid graph function.
Enter the equation entry mode.
Enter Rapid Graph mode and view
the equation-type menu.
Select the sin equation format and
view the sin equation style.
Select the type of equation: Trigonometric, and view the equation
format menu.
Draw the graph.
(Note: Previous range values may affect
the viewing window. To reset range
values, use Rapid Window.)
1
2
3
4
5
6
Select the second equation style and
input. If necessary, make changes to
the coefficients.
Y =
EZ
Features
Page 14

NotesKey Operation
Display
Example
12
Rapid windo w
Rapid window simplifies setting window size with a range of preset values. Use in conjunction with the rapid graph function or with any graph created.
After using Rapid Graph to draw the graph of y = 2sin (-2x+ ) + 2 (refer
p. 11), set the viewing window using the rapid window function.
1
2
3
4
5
7
Select the No. 3 style and view the
X-range menu.
Enter Rapid Window mode.
Select the Y-range and draw the
graph.
Move the cursor to No. 5:
(-0.5 < Y < 5 scl=0.5)
Enter viewing window setup mode.
EZ
(Five times)
Select X-range No. 4:
(-1 < X < 10 scl=1), and
view the Y-range menu.
Features
(or
5
)
(or
5
)
(Six times)
Page 15

NotesKey Operation Display
Example
13
Rapid zoom
Rapid zoom offers one-touch adjustment of window size while viewing the graph.
No more
guessing or wasting class time to find optimal values for window size.
Adjust the viewing window for y = x3 + x2 - 2x
to show the entire graph.
1
2
3
4
Create the graph y = x3 + x2 - 2x
using the following conditions:
X-range: xmin = -3
xmax = 3
xscl = 1
Y-range: ymin = -1.5
ymax = 1.5
yscl = 0.5
View display (adjusted).
Enter Rapid Zoom mode.
5
Change X-range from Ymax = 1.5 to
Ymax=2. Draw the graph.
EZ
Features
Y =
1
5
(–)
3
3
1
(–)
51
5
Repeat: Change Y-range from Ymax
= 2 to Ymax=2.5. Draw the graph
3
a
b
x
2
2
X/T X/T
X/T
Page 16

14
PC-LINK
System options
1
2
3
Procedure
Connect the EL-9450/9400 to the PC by using the
CE-450L, PC-Link adaptor and PC connector
(see above diagram).
Make sure that the RS-232C (serial port) is connected
to the PC. Use of the connector is determined by the
shape of the PC serial port (see below chart).
4
5
6
Operate according to the instructions on the
screen.
PC-Link
Software
PC-Link
Software
PC conversion
connector for
IBM-PC
PC conversion
connector for
Macintosh
CE-450L
IBM PC
or Compatibles
R
R
Macintosh
Shape of PC serial port
Connecting procedure
25 pin (male) Connect the other side (25-pin side) of PC LINK
adaptor to the serial
port for the PC.
Connect the other side (25-pin side) of PC LINK
adaptor to the 25-pin
9 pin (male) terminal of a converting adaptor. Also connect the
other side (9-pin side) of the converting adaptor to
the serial port for the PC.
8 pin (female) For Macintosh
What is PC LINK?
Connect the EL-9450/9400 with a PC or Macintosh computer to expand the possibilities of
data exchange using PC-Link software.
• Creates and edits EL-9450/9400 programs on a PC.
• Receives and saves programs and various data from EL-9450/9400.
• Makes a backup of all the contents of EL-9450/9400.
• Sends programs and various data to EL-9450/9400.
• Loads image data of EL-9450/9400.
• Converts programs and various data files into a Text File. Converts
program text files into a Program File.
• Prints out programs and various data files.
Turn off the EL-9450/9400.
Switch on EL-9450/9400.
Open PC-Link Software.
*
It is essential to use the same port for both the PC
and the PC-Link Software.
CE-LK1P (PC-link system)
Page 17

15
CE-450L
Communication cable
EL-9450/9400 EL-9450/9400
*
mark desired data to be
sent.
]
]
S
et to set communication
5
7
8
9
Sender
Communication Procedure
( or )
A SELECT ....................... Sends files individually as described below.
1 ALL .............................. Selects and displays all files.
2 List............................... Selects and displays all list files.
3 GraphEq....................... Selects and displays all graph equations.
4 Program ....................... Selects and displays all program files.
5 G_Data......................... Selects and displays all graph data files.
6 L_Data ......................... Selects and displays all list data files.
7 Picture .........................Selects and displays all picture data files.
8 A~Z, Ø.......................... Selects and displays all fixed memory of A to Z, and Ø
B BACKUP ...................... Menu to send all file data. Use this
feature to send the entire content.
List of the SEND menu
Receiver
3
4
( or )
6
2
1
Plug the cable into both calculators.
Turn power on.
Specified LINK.
Select LINK/SEND.
Select SEND/ALL.
( or 2 )
( or 1 )
Select ‘LI’, ‘YI’
Execute Sending function.
Select LINK/RECEIVE.
Specified LINK.
List of sendable data will
appear on screen.
]
]
Transfer data between two EL-9450/9400 calculators using the communication cable
(CE-450L).
Page 18

16
AC adaptor (optional)
OHP Projection Panel
OHP Panel
Controller
CE-450L
The CE-450L is included
for separate use
(see page 15)
OHP System
1
2
3
4
5
Procedure
Plug the cable connector of the OHP Projection Panel straight into the connection terminal of the
OHP Panel Controller.
(The optional AC adaptor is recommended for extended use of the OHP Projection Panel.)
Turn on the power to the overhead projector.
Operating the OHP Panel Controller.
The OHP Projection Panel display is synchronized with the display of the OHP Panel Controller.
Place the OHP Projection Panel on top of the overhead projector to project images onto the screen.
Switch on the OHP Panel Controller.
Switch off the OHP Panel Controller.
Use the EL-9450/9400 OHP system with the overhead projector to make classroom
presentations convenient for the whole class to see.
EL-945T/94T (OHP system)
Page 19

17
Menu tree 1
SET UP
( )
Rad 1 Deg
FloatPt 2 Rad
1 FloatPt
2 Fix
1 1 1 Rect
2 Param2 2
3 3
4 4
5 5
6 6
7 7
8 8
9 9
0 0
9 3 Grad
Rect
Decimal
Eqn
2nd F SET UP
A
1 Decimal
2 Mixed
3 Improp
1 Eqn
2 Oneline
B DRG
F AMSWER G EDITOR
C FSE D TAB
E COORD
FORMAT
( )
OFF 1 ON
OFF 2 OFF
1 ON
2 OFF
1 Connect
2 Dot
Connect
Sequen
2nd F FORMAT
A
1 Sequen
2 Simul
B EXPRES
E STYLE 2
C Y
1
D STYLE1
MATH
( )
1 log2 1 abs(
2 2
x
2 round(
3 ipart
4 fpart
5 int
6 min(
7 max(
8 lcm(
9 gcd(
1 random
2 nPr
3 nCr
4!
3 fmin(
4 fmax(
5 d/dx(
6
∫
7 dx
MATH
B NUMA CALC C PROB
1
2 '
3 "
4
r
5
g
3 >
1
2
4 ≥
5 <
6 ≤
E ANGLE
F INEQ
1 and
2 or
3 not
4 xor
5 xnor
G LOGIC
4 xy (
5 r x(
6 r y(
3 xy r(
2 dms
1 deg
D CONV
Page 20

18
Menu tree 2
CALC
CALC
When coordinate system is Rect When coordinate system is Param
( ) ( )
1 Value
2 Intsct
3 Minimum
4 Maximum
5 X_Incpt
6 Y_Incpt
7 Inflec
2nd F CALC
( )
2nd F DRAW
LIST
A OPE
( )
1 sortA(
2 sortD(
3 dim(
4 fill(
5 seq(
6 cumul
7 df_list
8 aug...(
A DRAW
1 ClrDraw
2 Line(
3 H_Line
4 V_Line
5 T_Line(
6 Draw
7 Shade(
8 DrawInv
9 Circle(
0 Text(
B POINT
1 PntON(
2 PntOFF(
3 PntCHG(
4 PxlON(
5 PxlOFF(
6 PxlCHG(
7 PxlTST(
B MATH
1 min(
2 max(
3 mean(
4 median(
5 sum(
6 prod(
7 stdDv(
8 varian(
D REG
01 Med Med
02 ax+b
03 a+bx
04 x
2
05 In
06 log
07 ab
x
08 ae
bx
09 x
-1
10 ax
b
11 x'
12 y'
C L_DATA
1 stoLD
2 RclLD
2nd F LIST
CALC
CALC
1 Value
2nd F CALC
STAT
A EDIT
( )
edit list
Press
B OPE
1 sortA(
2 sortD(
3 SetList
4 ClrList
C CALC
1 1_Stats
2 2_Stats
STAT
ENTER
D LINE
select
line type
Press
ENTER
DRAW
C ON/OFF
1 DrawON
2 DrawOFF
F PICT
1 StoPict
2 RclPict
G SHADE
1 SET
2 INITIAL
E G_DATA
1 StoGD
2 RclGD
Page 21

19
Menu tree 3
ZOOM
A ZOOM B FACTOR D EXP E TRIG
( )
1 Auto
2 Box
3 In
4 Out
5 Default
6 Square
7 Dec
8 Int
9 Stat
F STO
1 StoWin
G RCL
1 StoWin
2 PreWin
1 10
x
2 e
x
3 log x
4 In x
1 sin x
2 cos x
3 tan x
4 sin
-1
x
5 cos
-1
x
6 tan
-1
x
Set factor
of zoom
Press
ZOOM
ENTER
PROGM-COM
A PRGM D I/O E COORD
( on Program screen)
1 Print
2 "
3 Input
4 Wait
5 Rem
6 End
B BRNCH
1 Label
2 Goto
3 If
4 Gosub
5 Return
C SCRN
1 ClrT
2 ClrG
3 DispT
4 DispG
F FORM
1 ExprON
2 ExprOFF
3 Y' ON
4 Y' OFF
5 Connect
6 Dot
7 Sequen
8 Simul
G S_PLOT
1 Plt1(
2 Plt2(
3 Plt3(
H COPY
1 StoLine
2 RclLine
1 Get
2 Send
1 Rect
2 Param
2nd F PRGM
VARS
A EQVARS D L_DATA E G_DATA
( )
B WINDOW C STOWIN
F PICTUR
1 Pict1
2 Pict2
3 Pict3
4 Pict4
5 Pict5
6 Pict6
7 Pict7
8 Pict8
9 Pict9
0 Pict0
G TABLE
1 TBLStrt
2 TBLStep
3 TBLList
H STAT
1 L_Data 1
2 L_Data 2
3 L_Data 3
4 L_Data 4
5 L_Data 5
6 L_Data 6
7 L_Data 7
8 L_Data 8
9 L_Data 9
0 L_Data 0
1 G_Data 1
2 G_Data 2
3 G_Data 3
4 G_Data 4
5 G_Data 5
6 G_Data 6
7 G_Data 7
8 G_Data 8
9 G_Data 9
0 G_Data 0
VARS
Graph equation
Press
Value of
window
Press
Value of
stored window
Press
stat
Press
ENTER
ENTER ENTER
ENTER
C POWER
1
X
2
2
X
-1
3
X
Page 22

20
Menu tree 4
EQ VAR
A XY
( )
1 Y1
2 Y2
3 Y3
4 Y4
5 Y5
6 Y6
7 Y7
8 Y8
9 Y9
0 Y0
B REGEQN
1 RegEqn
2 a
3 b
4 c
5 r
6 r
2
7 R
2
8 resid
C POINTS
1 x1
2 x2
3 x3
4 y1
5 y2
6 y3
7 Q1
8 Med
9 Q3
B XYT
01 X1T
02 Y1T
03 X2T
04 Y2T
05 X3T
06 Y3T
VARS A
WIN VAR
A XY
( )
1 Xmin
2 Xmax
3 Xscl
4 Ymin
5 Ymax
6 Yscl
7 X_Fact
8 Y_Fact
B T
1 Tmin
2 Tmax
3 Tstep
VARS B
ZOOM VAR
A STOXY
( )
1 Zm_Xmin
2 Zm_Xmax
3 Zm_Xscl
4 Zm_Ymin
5 Zm_Ymax
6 Zm_Yscl
B STOT
1 Zm_Tmin
2 Zm_Tmax
3 Zm_Tstp
VARS C
STAT VAR
( )
VARS H
A XY
01 n
03 sx
04 x
05 xmin
06 xmax
10 y
11 sy
12 y
13 ymin
14 ymax
15 ∑y07 ∑x
16 ∑y
2
08 ∑x
2
09 ∑xy
02 x
A EXEC
01
02
03
04
05
06
01
02
03
04
Cleate
new program
05
06
B EDIT C NEW
PRGM
07 X4T
08 Y4T
09 X5T
10 Y5T
11 X6T
12 Y6T
( )
PRGM
Press
ENTER
Page 23

21
Menu tr ee 5
1 Y X
2
5 Y sinX
6 Y tanX
2 Y X
3 Y 1/X
4 Y e
x
4 Y e
x
5 Y lnX
6 Y sinX
7 Y tanX
8 Y X
B CHANGE
A SHIFT
1 Y X
2
2 Y X
3 Y X
1 Y X
2
2 Y AX+B
3 Y
4 Y 1/X
5 Y sinX
6 Y tanX
7 Y cos
-1
X
8 Y lnX
A B-IN
X
1 MBox
•
2 MBox+
3 MBox
1 Scattr
•
2 Scattr+
3 Scattr
F MBOX
G S.D.
1 xyLine
•
2 xyLine+
3 xyLine
H XYLINE
1 Broken
•
2 Broken+
3 Broken
1 Norm
•
X
2 Norm+_X
3 Norm _X
4 Norm
•
_Y
5 Norm+_Y
6 Norm _Y
B B.L. C N.P.
STAT PLOT
Stat plot1 Stat plot2 Stat plot3 1 SET 1 PlotON
2 PlotOFF2 LimON
3 LimOFFPress Press
Press
2nd F STATPLOT
B PLOT2A PLOT1 C PLOT3 D LIMIT
E ON/OFF
OPTION
( )
Remain
12345bytes
Press
1 List
2 GraphEq
3 Program
4 Picture
5 G-Data
6 L-Data
7 Entry
1 SEND 1 default
2 All mem2 RECEIVE
2nd F OPTION
B MEMCHKA CTRST C DEL D LINK E RESET
STAT GRAPH
( )
1 Hist 1 NormDis 1 Box
2nd F STATPLOT on PLOT1-3screen
A HIST D N.D. E BOX
SLIDE
( )
SLIDESHOW
SHIFT/CHANGE
( )
SHIFT/CHANGE
(
)
2nd F
ENTER ENTER
ENTER
ENTER
Page 24

22
Menu tree 6
Y=
( )
RECT MODE
Y1=
Y2=
Y3=
Y4=
Y5=
Y6=
Y7=
Y8=
Y9=
Y0=
PAR MODE
X1T=
Y1T=
X2T=
Y2T=
X3T=
Y3T=
X4T=
Y4T=
X5T=
Y5T=
X6T=
Y6T=
Y=
( 1)
2nd F DOPTION
LINK
ENTER
B BACKUP
back up
Press
A SELECT
1 All
2 List
3 GraphEq
4 Program
5 G_Data
6 L_Data
7 Picture
8 A Z,
Page 25

23
Dimensions W x D x H (mm) 163 x 76 x 19.5 (without hardcase)
Power R03 (AAA) x 4
Backup Battery CR2032 x 1
Size (dot) 96 x 64
Line x Characters 8 x 16
Character Size (dot) 5 x 7
Digits (mantissa + exponent) 10 + 2
Display
Total Memory Size 32 KB
Constant Memory 27 + last answer memory
Protective hard case
Memory
CE-450L Unit-to-unit communications cable
CE-LK1P PC-Link (Print screen/Data storage)
EL-945T/94T OHP system (includes controller)
Peripheral
Accessory
Equation editor, Shift/Change, Slide show (Built-in), Rapid graph,
Rapid window, Rapid zoom, List grouping
Function graphing Up to 10
Parametric graphing Up to 6
Zoom, Trace
Table of function values
GraphingStandard
Features
Regression models 10
Scatter Plots and Histograms
Box-and-Whisker Diagrams
Statistics
List Up to 6 (Maximum length : 999)
Programming
Trigonometry functions (including sec, csc, cot)
Fraction/Decimal conversions
Last entry recall
Last answer recall
Other
Features
unique to
Sharp
* Design and specifications are subject to change without notice.
* Some
p
roducts may not be available in some countries.
Specifications
Specifications
Page 26

EL-9450/9400 Graphing Calculator
Page 27

SHARP CORPORATION
OSAKA, JAPAN
Distributed by:
 Loading...
Loading...