Page 1
SER VICE MANU AL
AIR CONDITIONER
AF-05CML
S3209AF05CML/
MODEL
In the interests of user-safety (Required by safety regulations in some
countries) the set should be restored to its original condition and only
parts identical to those specified should be used.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
SPECIFICATIONS ................................................................................................................................................ 2
EWIRING DIAGRAM ............................................................................................................................................ 3
EXTERNAL DIMENSIONS ................................................................................................................................... 3
HOW TO OPERATE ............................................................................................................................................. 4
INSTALLATIOIN INSTRUCTIONS ........................................................................................................................5
DISASSEMBLING PROCEDURE......................................................................................................................... 7
HOW TO REPAIR REFRIGERATION ................................................................................................................ 10
ELECTRICAL COMPONENT TEST .................................................................................................................... 12
TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE ............................................................................................................................13
COOLING LOAD ESTIMATE FORM ...................................................................................................................16
RUNNING CONDITION .......................................................................................................................................18
PACKING AND ACCESSORIES ......................................................................................................................... 19
REPLACEMENT PARTS LIST ............................................................................................................................20
AF-05CML
Page
SHARP CORPORATION This document has been published to be used for after
sales service only.
The contents are subject to change without notice.
1
Page 2

AF-05CML
SPECIFICATIONS
Models AF-05CML
Cooling capacity BTU/h 5000
Moisture removal Pints/h 1.0
ELECTRICAL DATA
Phase Single
Rared frequency Hz 60
Rated voltage Volts 115
Rated current Amps 4.6
Rated input Watts 500
Power factor % 95
EER BTU/Wh 10.0
COMPRESSOR
Type (Hermetically sealed rotary type)
Model, Motor output
REFRIGERANT SYSTEM
Evaporator Louver fin, Grooved tube, 7mm, Hair pin
Condenser Louver fin, Grooved tube, 7mm, Hair pin
Control O.D. x I.D. x Length x Q'ty(mm) 2.7 x 1.1 x 400 x 1
(Capillary tube)
Refrigerant volume R-22(OZ) 8.5
(Factory change)
NET DIMENSIONS
Width Height Depth
inches(mm)
Net Weight lbs 47
GROSS DIMENSIONS
Width Height Depth
inches(mm)
Gross Weight lbs 52
FAN SYSTEM
Indoor side(Evaporator) Centrifugal fan
Outdoor side(Condenser) Propeller fan
Air flow rate(indoor side) CFM High / Med / Low
OTHERS
Safety devices Compressor: Overload relay
Air filter Polypropylene net
Power cord length ft 6.0
Power plug type 125V, 10A
ELECTRICAL PARTS
Running capacitor 250V-40µF
Fan capacitor 250V-6µF
Selector switch 2109
Thermistor No. APPLI- COLD COLD WARM WARM
Fan motor OBM-2016K1 (MLA998)
Overload relay MRA99484
RM5455GQ86, 400W
17-23/32(450) x 14-9/16(370) x 14-7/8(378)
20-7/8(530) x 18-1/8(460) x 18-3/8(467)
195 / 175 / 150
Fan motor: Internal thermal protector
. CAUTION CUT-IN CUT-OUT CUT-IN CUT-OUT
MM1-A001 Cooling 66.2˚F 61.7˚F 86.0˚F 82.5˚F
2
Page 3
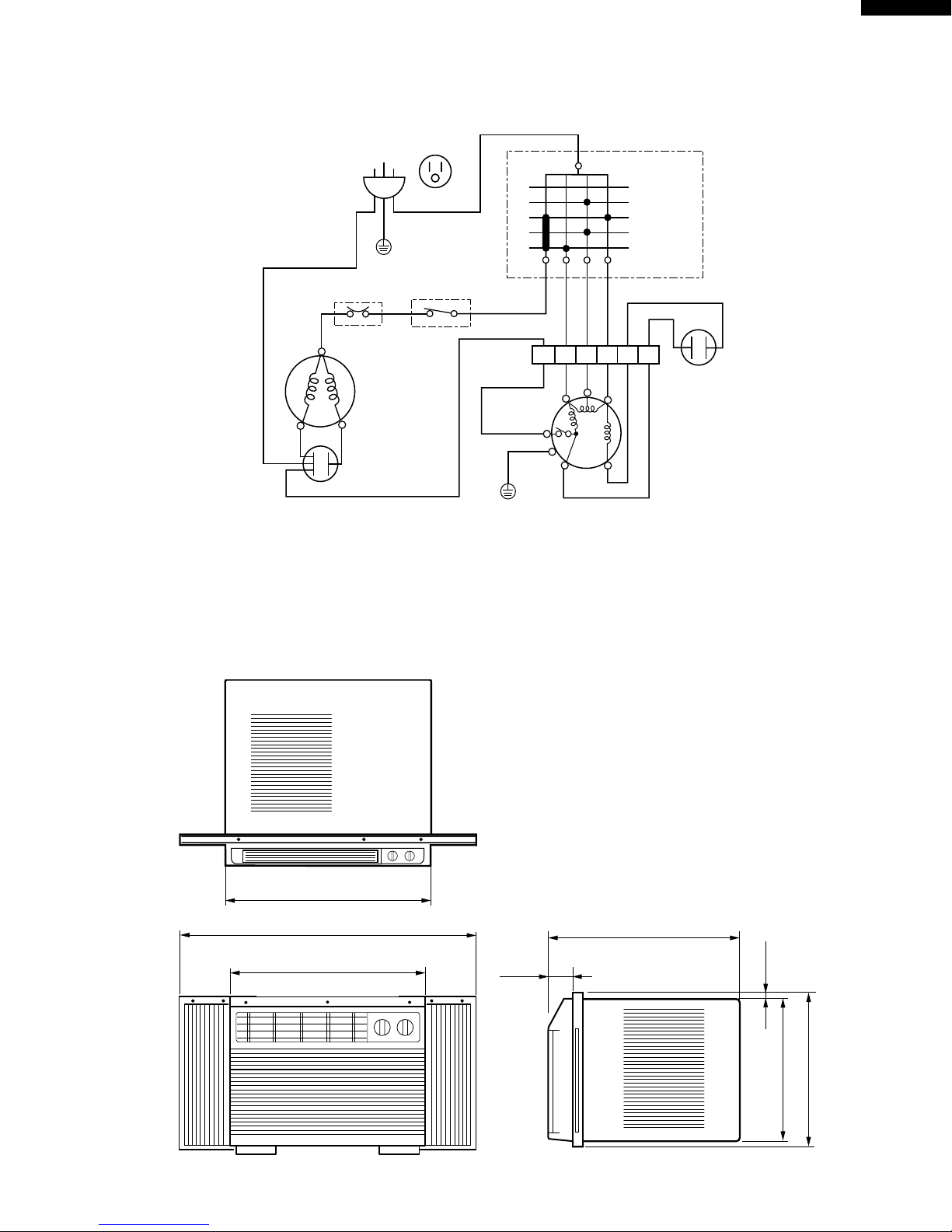
:
BLACK
BK
:
BLUE
BL
:
RE
RED
:
WHITE
WH
OR
:ORANGE
:
GR
GRAY
G
: GREEN
RIBBED
RE
BK
R
GR
WIRING DIAGRAM
POWER SUPPLY CORD
115V 60Hz
NON RIBBED
G
EARTH
OVERLOAD
RELAY
C
COMPRESSOR
S
WH
THERMOSTAT
BK
MOTOR
GR
RUNNING
CAPACITOR
250V 40µF
CONNECTOR
PROTECTOR
G
8
BK
GR
THERMAL
H
EARTH
M.C
SELECTOR SWITCH
1
OFF
FAN
LOW-COOL
MED-COOL
HIGH-COOL
642
RE
WH
OR
BK
214563
RE
M
OR
L
WH
FAN MOTOR
BK
BL
CAPACITOR
250V 6µF
BL
A.C
BK
FAN MOTOR
AF-05CML
BL
EXTERNAL DIMENSIONS
17-23/32"
33-7/16" (full opened)
21-21/32" (full closed)
Figure W-1
14-7/8"
4-1/8"
1-15/32"
13-5/8"
15-11/16"
3
Page 4
AF-05CML
SELECTOR
WAIT THREE MINUTES BEFORE RESTARTING
THERMOSTAT
COOLER
SELECTOR
COOLER
HOW TO OPERA TE
HOW TO OPERATE
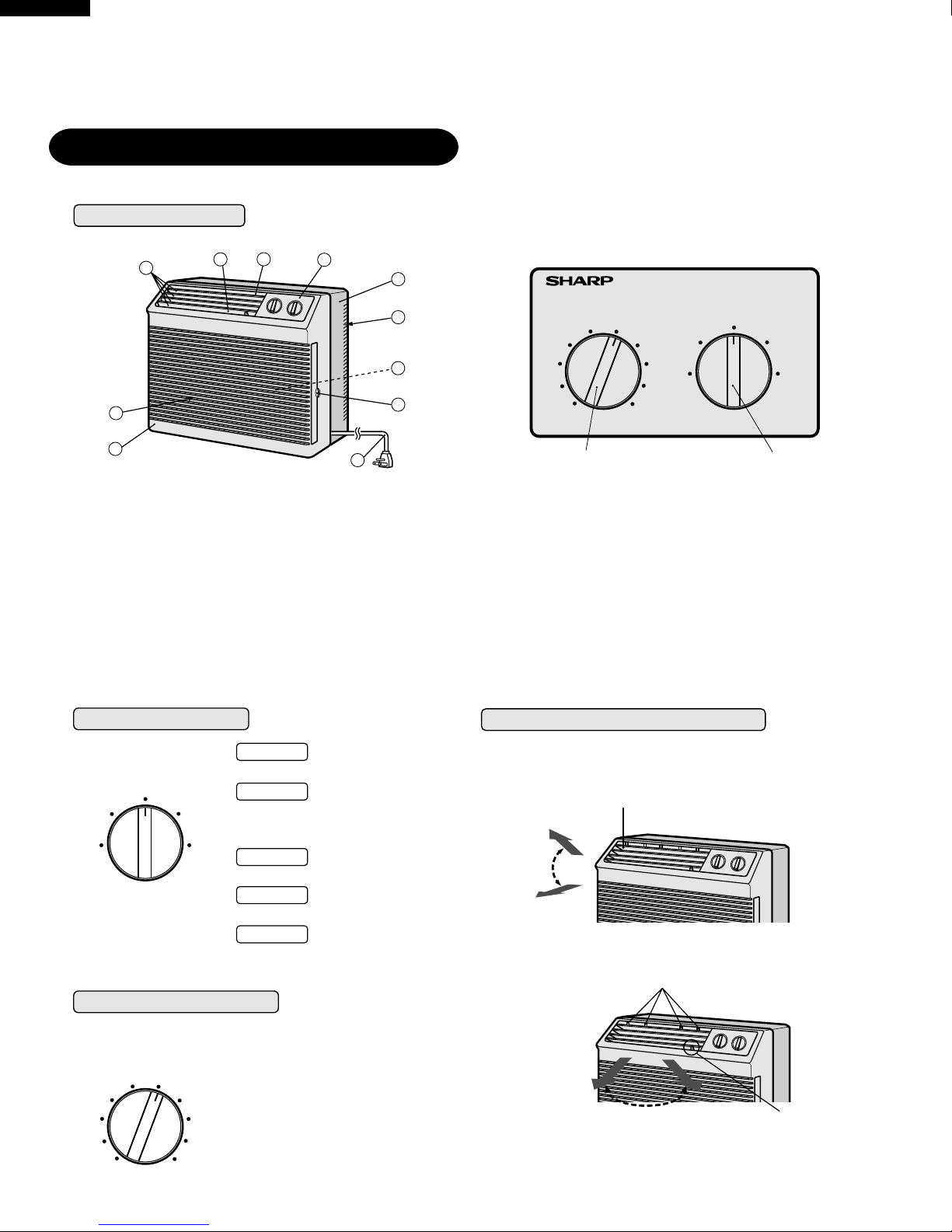
PARTS NAMES
UNIT CONTROL PANEL
3
2
1
1 Front Cabinet
2 Air Inlet (Indoor Side)
3 Horizontal Louvers
4 Vertical Louvers
5 Air Outlet (Indoor Side)
6 Control Panel
7 Rear Cabinet
8 Air Inlet (Outdoor Side)
9 FiIter (Pull the filter handle to the right to remove.)
0 Filter Handle
q Power Cord
5
4
6
7
8
4
9
3
2
10
1
11
1 Thermostat Knob
2 Selector Knob
THERMOSTAT
5
6
7
8
OFF
9
1
0
COOLER
WAIT THREE MINUTES BEFORE RESTARTING
1
FAN
SELECTOR
LOW
COOL
MED
COOL
2
HIGH
COOL
SELECTOR KNOB
Both the fan and cooling
operationare off.
This setting can be used to
circulate air whenever cooling
is not desired. The fan will
operate at medium speed.
Cooling for sleeping comfort
with low fan speed.
Fan operates at medium speed;
cooling power at medium.
Fan and cooling at maximum
performance.
FAN
OFF
SELECTOR
LOW
COOL
MED
COOL
HIGH
COOL
OFF
FAN
LOW COOL
MED COOL
HIGH COOL
THERMOSTAT KNOB
This knob is used to adjust the desired room temperature.
You can adjust the cooling performance of
5
6
4
7
3
1
0
9
COOLER
2
1
your air conditioner by resetting the thermostat
control to a higher number for maximum cooling.
The lower the number, the warmer the room
temperature.
8
You will need to experiment to find the setting
which suits you best.
CHANGING AIR DIRECTION
The horizontal louvers are used to adjust the UP/DOWN direction of air flow,
and the vertical louvers are used to adjust the LEFT/RIGHT direction of air flow
for uniform and efficient cooling of the room.
Horizontal louvers
Adjusts UP / DOWN
air flow.
Vertical louvers
Adjusts LEFT / RIGHT air flow.
Lever
4
Page 5
y
INSTALLATION INSTALLATIONS
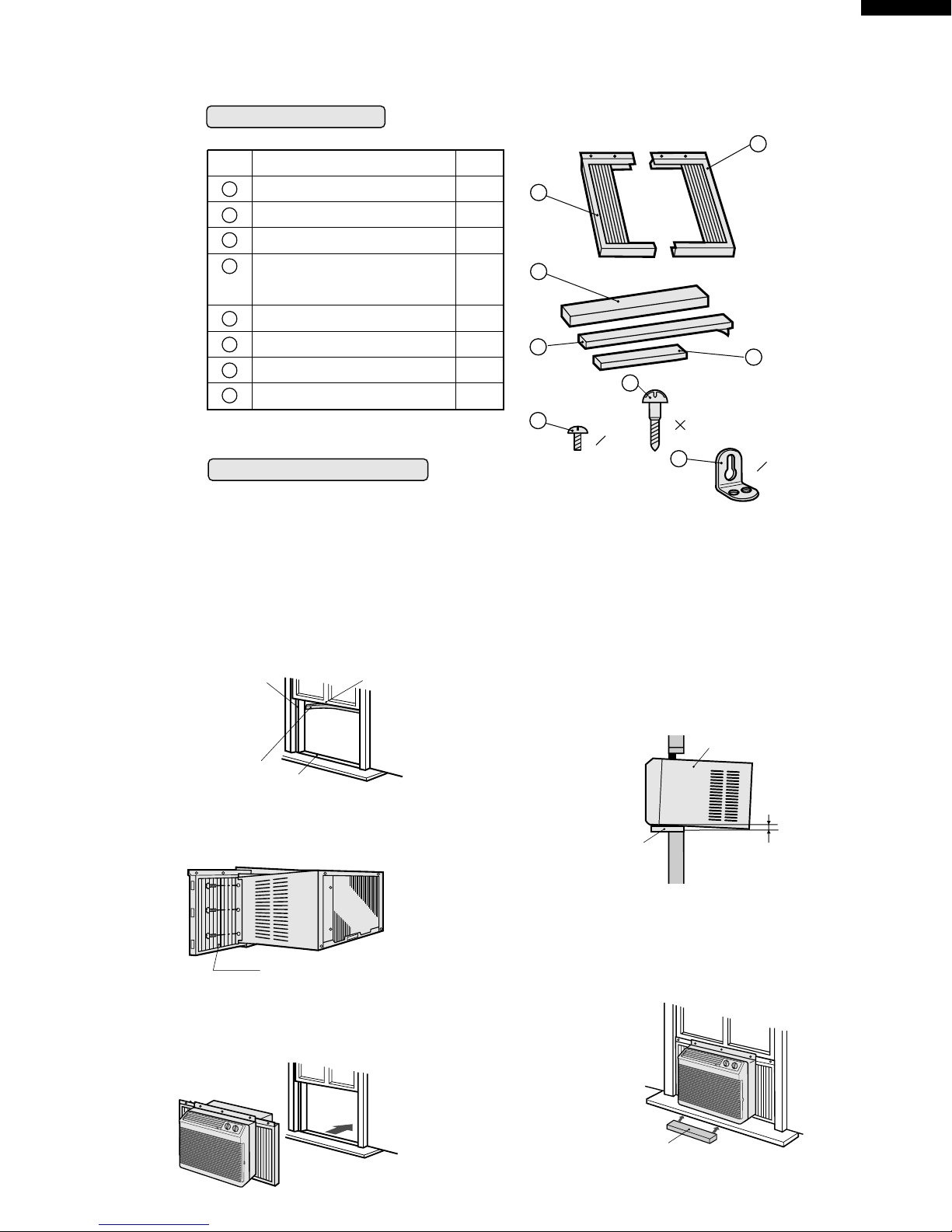
ACCESSORIES
No. Accessories
Right closure assembly
1
Left closure assembly
2
Window sash foam seal
3
Window sash foam seal
4
(adhesive type)
Bottom gasket
5
Screws(L=1",25.4mm)
6
13
Screws(L=
7
Base pan angle
8
SUGGESTED TOOLS
1. Screw driver (medium size Phillips)
2. Tape measure or ruler
3. Knife or scissors
/32",10mm)
Q'ty
1
1
1
1
1
7
6
2
AF-05CML
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
6
7
8
2
INSTALLATION
WARNING: Make sure the unit is turned off and unplugged before working.
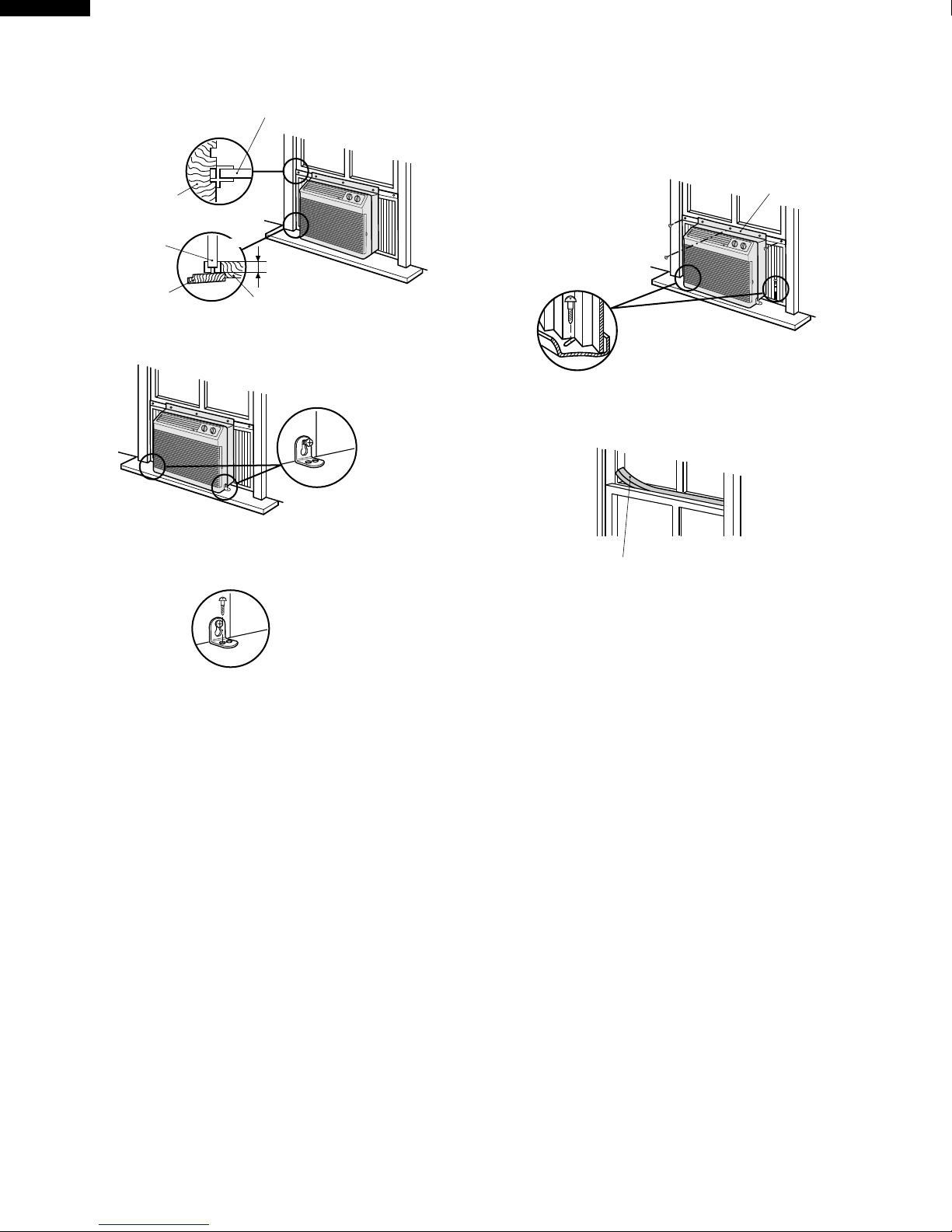
1. Cut the window sash foam seal (adhesive type) to the
proper length and attach it to the underside of the
window sash.
Jamb
Window sash foam seal
(adhesive type)
Sill
Sash
2. Insert the right closure assembly and the left closure
assembly into the top angle and the bottom channels.
Secure the right and left closure to the cabinet with six
of the provided screws. (L= 13/32",10mm)
Closure assembl
3. Open the window sash and place the air conditioner on
the sill.
Balance the unit on the sill and close the window
sash securely behind the top angle.
WARNING:
At this step, make sure the unit is inclinedapproximately
1 cm (3/8") to the back. If the unit is not properly
inclined, the water collected in the bottom tray during
operation will not drain properly and may flow into the
room where the air conditioner is installed.
4. Insert the bottom gasket into the space between the
window sill and the bottom of the unit to seal outside
air.
If there is space between the bottom channel and
the sill, fill the gap with a thin board or other hard filler.
Sill
Unit
incline backwards about 1cm
3
/8")
(
Bottom gasket
5
Page 6
AF-05CML
Window sash foam seal
5. Insert the closure assemblieson both sides into the
rails of the jamb.
Closure assembly
(Left)
Indoor
Jamb
(Left)
Closure assembly
(Left)
Sill
side
Indoor
side
Stool
1
/2 inches
(13mm)
6. Loosen screws on both sides of the cabinet, then hang
the base pan angle on and secure the screws again.
8. Secure the top angle of the unit and the top of the
closure assemblies to the sash with three of the
provided screws. (L=1",25.4mm)
And secure the bottom of the closure assemblies to
the sill with two of theprovided screws.
(L=1",25.4mm)
Top angle
9. Cut the window sash foam seal to the proper length
and seal the opening between the top of the inside
window sash and the outside window sash.
7. Secure the base pan angle to the sill by using the hole
of the front side on the angle with one screw.
(L=1",25.4mm)
6
Page 7
DISASSEMBLING PROCEDURE
AF-05CML
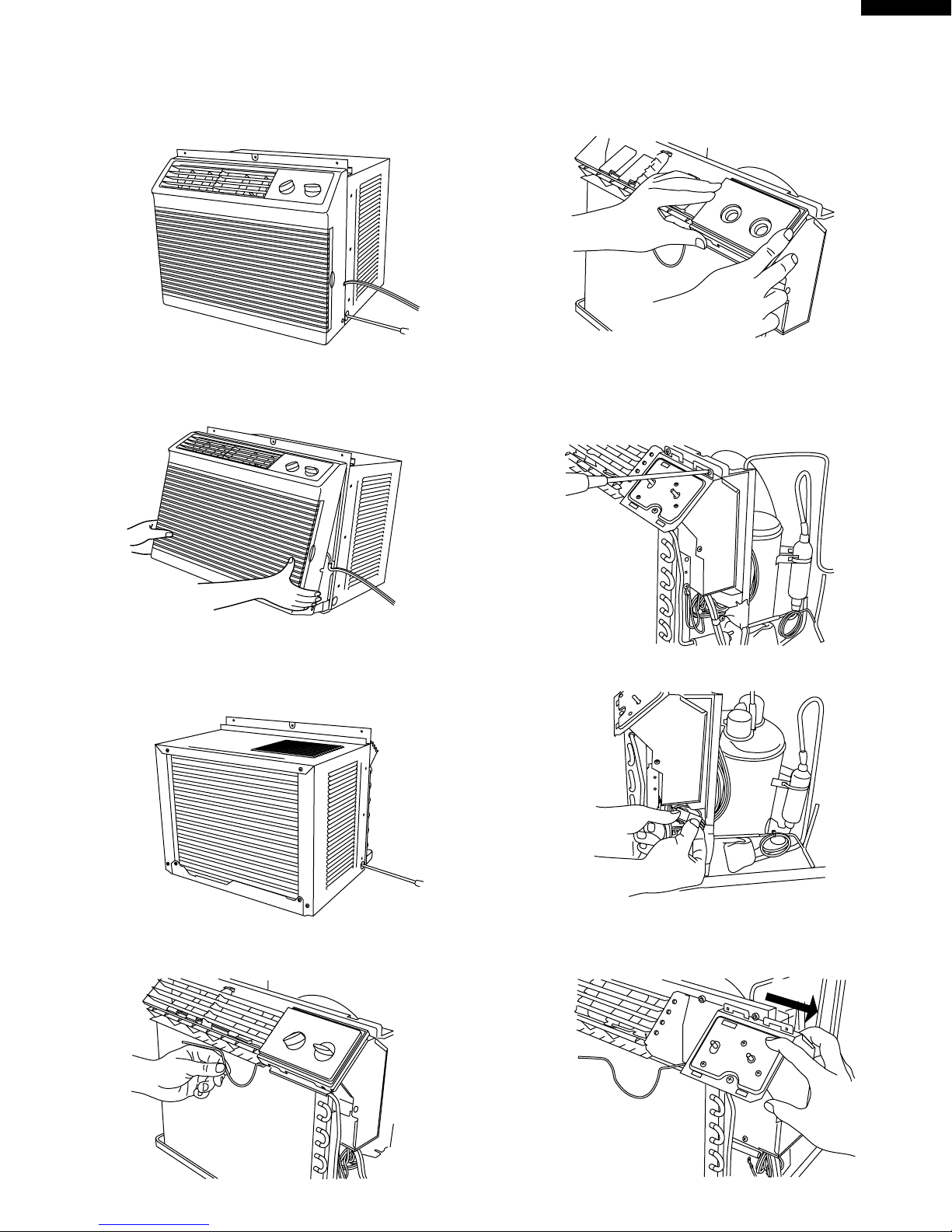
1. Unscrew the 2 screws holding the front panel on each
side.
2. Remove the front panel by pulling the front panel at the
lower corner toward you about one inch.
Next lift up and pull it toward you.
5. Remove the control knob and control panel.
6. Unscrew the 5 screws.
3 screws are holding the control box at the top and right
side.
1 screw is holding the power supply cord.
1 screw each screw on the evaporator.
3. Unscrew the 9 screws holding the cabinet.
2 screws are on each side.
4 screws are on back side.
3 screws are on top side.
4. Remove the thermostat.
7. Take off the fan motor connector.
8. Cut the wire fixing band, slide the control box rightward
and remove.
SLIDE
7
Page 8
AF-05CML
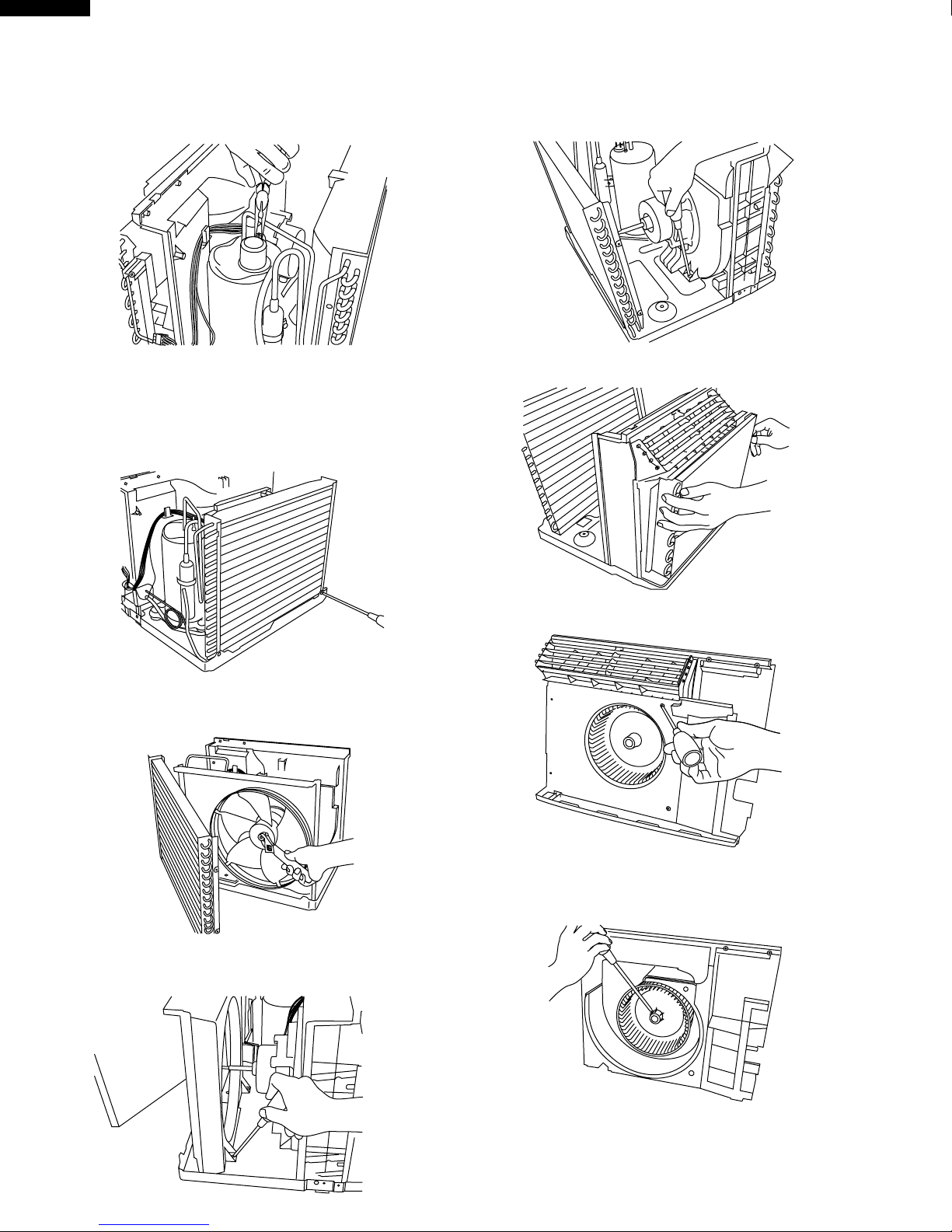
9. Unfasten the one nut at the top of the compressor
holding the terminal cover.
Then remove the wiring connector of the compressor
cord.
10. Unscrew the 6 screws holding the condenser.
2 screws are on right side.
2 screws are on left side.
2 screws are on back side.
And remove the condenser from the unit.
13. Unscrew the 5 screws.
2 screws are holding the evaporator on each side.
3 screws are holding the bulkhead to the base pan on
each side and back side.
14. Lift up and take out the bulkhead.
11. Unfasten the nut holding the propeller fan by rotating it
counter-clockise. And remove the propeller fan.
12. Unscrew the 3 screws holding the condenser shround.
And remove the condenser shround.
15. Unscrew the 2 screws holding the orifice.
16. Unscrew the screw holding the centrifugal fan.
(Remove by using a driver or a wrench)
8
Page 9

17. Remove the caseing. 18. Unscrew the 4 screws holding fan motor.
DISASSEMBLING THE CONTROL BOX
AF-05CML
1 Unscrew the 2 screws holding the control box cover.
CAUTION:
DISCHARGE THE FAN MOTOR CAPACITOR
AND RUNNING CAPACITOR BEFORE
TOUCHING THOSE CAPACITORS OR OTHER
COMPONENTS OR WIRING.
2 Cut the wire fixing bands holding the fan motor lead
wires, the compressor cord and the power supply cord.
3 Unscrew the 3 screw holding the selector switch and
thermostat. And take off the wiring connector of the
compressor cord, the fan motor cord and the power
supply cord.
4 Unscrew the 1 screw holding the capacitor clamp and
the fan motor capacitor, and take off each connector.
And unscrew 2 earth screws.
9
Page 10

AF-05CML
INNER CONE
TORCH STEM
SILVER ALLOY
Figure 3
Directing Torch Flame to Copper Tubing.
3/8"
;;
;;
;;
HOW TO REPAIR REFRIGERATION
Before sealed system work can be preformed a refrigerant recovery EPA and LOCALLY approved certification is
required, additionally, EPA and LOCALLY approved refrigerant recovery equipment is required.
SEALED SYSTEM REPAIR
Sealed system repairs should be properly diagnosed before entering into a repair of the system.
It is important to follow proper procedures when doing a system repair for safety reasons and that the repair will result in a
restoration of the system to proper factory standards.
SAFETY REMINDERS
1) Do not heat any system component with an open flame for any reason.
2) Do not solder until you are sure that all refrigerant has been removed from the system.
3) Do not heat the charging cylinder with an open flame. Use warm water only and do not exceed 125˚F (not too hot to keep
your hand in.)
4) Do not over fill any charging cylinders, as they could explode when over filled.
5) Use proper wrenches.
6) Use safety goggles when working with refrigerants.
7) Keep a fire extinguisher within easy reach.
8) Watch flame direction when soldering so as not to burn clothing, wiring or other components.
9) Solder in a well ventilated area. If a high concentration of freon is present, an open flame will create phosgene gas which
can be harmful.
PROPER SOLDERING
Joint clearances should be maintained so that the brazing alloy will flow between
the closely mated surfaces rather than forming large fillets.
This films make the strongest joints, capillary attraction also work best with close
tolerance.
The best clearance is between 0.01" to 0.03", the amount of lap will be
approximately 3/8" depending on the sweging tool used. (Figure 1.)
CLEANING TUBING
To make a sound, leak tight joint, the brazing alloy when raised to brazing
temperature, must wet and flow freely over the entire surface of the tubing in the
joint area.
To assure this, the tubing surfaces must be free of all dirt, grease, oil and oxides
otherwise the alloy will not wet and flow properly over any surface with these
elements present. Cleaning can be done with an abrasive cloth or steel wool.
Never blow into the tubing because this will introduce a lot of moisture into the
system. Open tubing joints should be covered if exposed for long periods of time.
GOOD FIT
PROPER
JOINT FIT
CLEARANCE
.001"TO .003"
Joint Clearance.
Figure 1
EMERY CLOTH
KEEP TUBE IN
DOWNWARD POSITION
Cleaning Tubing.
Figure 2
POOR FIT
PROPER FLUXING
Flux is necessary when using silver solder; it is not required when using silfos
on copper to copper joints.
To do a good job the flux should cover the tube surface completely. Be careful
not to introduce any flux inside the tubing.
Fluxing should be done after the tubing is mated together and just before brazing
is done.
Do not allow it to dry out.
When brazing, the flux should become entirely liquid and clear, like water. The
temperature will be at 1100˚F and only a little more heat will allow the alloy to
flow freely into the joint.3
10
Page 11

AF-05CML
HEATING THE TUBING
Direct the torch flame so that the larger tube receives most of the heat. Silver
solder flows at 1200˚F and silfos flows at 1300˚F.
Heat all around the tubing.
The flame is composed of two cones, a smaller inner cone (pale blue) in colour
and a much larger outer cone. The hottest part of the flame is at the tip of the
inner cone. The flame should be directed at the joint with the tip of the cone just
touching the surface of the tubing. Figure 3 and 4.
OUTER CONE
HOTTEST PART
OF FLAME
INNER CONE
TORCH STEM
Composition of Torch Flame.
Figure 4
DEHYDRATING SEALED SYSTEM
Many services feel that since air conditioners run with evaporator temperatures above 33˚F, moisture will not present a
problem. Nothing is further from the truth. Oxygen in moisture plus the heat produced during compression will react with the
refrigerant oil to produce harmful acids in the system which will break down motor winding insulation, create sludge and pit
component parts, reducing efficiency of the air conditioner and shortening the life of compressors.
There it becomes mandatory that good dehydrating practices be adhered to at all times.
Proper hook up procedures as shown in Figure 5 must be used in order to pull and good vacuum from the system.
The use of a good vacuum pump is very important so that the boiling point of any water in the system will be lowered to a
point where it will vaporize and be expelled from the system in the form of vapour.
Type of evacuation methods
1. Piston Type Compressor No good.
System parts must be above 110 ˚F.
2. Rotary Vacuum Pump Disadvantages.
Low CFMC. 4 oil gets dirty.
3. Single State Vacuum Pump will not clean oil.
Oil must be changed often.
4. Two Stage Vacuum Pump will reach 50 microns.
First stage is below atmospheric pressure.
Moisture is removed into second stage which works
up to atmospheric pressure thus keeping oil clean.
Manometer cannot be read to 1/2 mm. Micron
gauge reads from 25,400 microns to 0.
ELECTRIC
VACUUM
GAUGE
TO RELATED SERVICE
VALVE OR PROCESS
TUBES OF THE UNIT.
LARGE DIAMETER
BRAIDED VACUUM
HOSES
Hook up for Evacuation and charging
HIGH VACUUM
MANIFOLD
HIGH VACUUM PUMP
Figure 5
DIAL-CHARGE
CHARGING CYLINDER
LOW SIDE
GAUGE
HIGH SIDE
GAUGE
11
Page 12

AF-05CML
It becomes clear that good equipment and maintained properly must be used in order to remove air and moisture from the
system.
When a vacuum of 1,000 to 500 microns is reached, block off the vacuum pump from the system.
This is done by closing the value between the pump and system. If the micron gauge does not increase above 1,000, the
system is free of moisture and no leak exists. If the micron gauge increases to higher levels moisture or a leak exists.
LEAKS
Several methods are used to detect leaks in systems.
Electronic Leak Detectors are very sensitive and are able to detect leaks down to 1/2 ounce per year.
A good electronic leak detector is generally far better in locating very small leaks.
Halide Torch be sure the room is free from refrigerant vapours. Watch the flame for the slightest change in colour.
A very faint green indicates a small leak. The flame will be unmistakably changed to green or purple when large leaks
are encountered. To simplify leak detection pressurize the system to approximately 75 lbs.
Some leaks can be located by a visual inspection of the system components and solder joints and if oil is found at
any given location it generally is a sign that a leak exists at that point due to the fact that flame does carry oil with it
travels through the system.
Soap Bubbles
Liquid detergents can sometimes assist in finding small leaks by brushing detergent on the suspect area and watching
for bubbles. Before applying detergent be sure that the system is pressurized.
Tap line devices are permissible for diagnosis only they are not suitable when evacuating the system. After the diagnosis
has been made they must be removed so that the system will be restored to a hermetical sealed condition.
ELECTRICAL COMPONENT TEST
SELECTOR SWITCH
(1) Remove the lead wires from the selector switch.
(2) Using a volt-ohm-meter set on resistance range, check continuity
between terminals as indicated below.
FAN OPERATION 1-4
LOW-COOL OPERATION 1-2, 1-8
MED-COOL OPERATION 1-4, 1-8
HIGH-COOL OPERATION 1-6, 1-8
1
OFF
FAN
LOW-COOL
MED-COOL
HIGH-COOL
2468
INSULATION TEST
Check the resistance between the terminal and SWITCH shaft.
Reading must be more than 10MΩ at DC 500V.
THERMOSTAT
(1) Take the wires off the thermostat terminals.
2
6
8
1
4
(2) Set the selector switch of a volt-ohm-meter (or a tester) on the
resistance range.
(3) Connect the probes to the thermostat terminals and check continuity between terminals.
(4) Turn the shaft of the thermostat clockwise. Continuity between terminals: OFF ON
Turn the shaft of the thermostat counter-clockwise. Continuity between terminals: ON OFF
(When ambient temperature is more than 86˚F, continuity between terminals may not change to OFF.)
INSULATION TEST
Check the resistance between the terminals and thermostat shaft. Reading must be more than 10MΩ at DC 500V.
1
2468
RUNNING CAPACITOR AND FAN CAPACITOR
CAUTION:DISCHARGE THE RUNNING CAPACITOR AND FAN CAPACITOR BEFORE TOUCHING CAPACITOR
OR WIRING.
(1) Discharge capacitor by shorting terminals.
(2) Take the wires off the capacitor terminals.
(3) Set the selector switch of a volt-ohm-meter (or a tester) on the resistance range.
(4) Connect the probes to the capacitor terminals and watch the indicator swing.
The indicator does not swing at all ..... Open.
The indicator swings but does not return ..... Shorted.
The indicator swings, then returns a moment later ..... Good.
12
Page 13

INSULATION TEST
RUNNING CAPACITOR
FAN CAPACITOR
Neither fan motor not
compressor operate
In sufficient cooling
No cooling
1) Check power supply switch or
plug and measure the voltage
1) Fuse open or circuit braker
open
1) If fuse or breaker are normal,
ask the power supply
company for check.
2) Plug disconnected
3) Plug connected properly but
contact defective.
2) Connect properly.
1) Knob position not properly
adjusted
3) Change power supplym cord
with plug.
1) Move thermostat knob to a
higher number (toward 10).
2) Defective thermostat 2) Replace
2) Change compressor
2) Outside air too high temp.
1) Equipment defective if no
temp. difference
3) Air conditioner normal but
heat leak excessive
1) Change or repair defect
2) Improve ventilation, avoid
sunshine
3) Calculate cooling load and
change or remove heat
source
1) Change capillary tube
2) Check for gas leak and
repair, recharge
1) Capillary tube restricted
2) Gas leak
1) Gas leak
2) Compressor defective
2) Check if temp.difference
between inlet and outlet air of
indoor unit is over 14˚F
1) No temperature difference
between discharge pipe and
suction pipe of compressor
3) Check indoor exchanger
inlet/outlet piping temp.
Sweat is less than half of coil
or frost sticks to capillary tube
2) Check air filter
1) Check thermostat
Air filter clogged Clean
3) Check for a high heat source
4) Check doors and windows
5) Check if condenser and evaporator are clean
6) Check if any object is restricting heat radiation from the
condenser.
7) Undersized air conditioner
8) Sealed system
Remove the added heat source
Windows and doors must be
kept closed
Clean them with steam cleaner
or another method
Remove the object or move the
air conditioner
Use Cooling Load Estimate
Form (Refer to page 16).
Check sealed system
1) Repair gas leak
Symptom Check Defect Remedy
Check the resistance between the terminals and case.
Reading must be more than 10MΩ at DC 500V.
OVERLOAD RELAY
Check continuity between terminals with volt-ohm-meter.
INSULATION TEST
Check resistance between terminals and the relay case.
Reading must be more than 10MΩ at DC 500V.
COMPRESSOR
(1) Take the wires off compressor terminals.
(2) Set selector switch of volt-ohm-meter on the resistance range.
(3) Put the probes on the terminals of the compressor and check continuity between each terminal.
INSULATION TEST
Check the resistance between the terminals and the copper tube.
Reading must be more than 10MΩ at DC 500V.
TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE
AF-05CML
13
Page 14

AF-05CML
Symptom Check Defect Remedy
Fan motor runs but
compressor doesn't
operate
1) No current runs.
(Compressor circuit)
1) Slector switch defective
2) Thermostat defective
3) Overload relay defective
4) Compressor coil burnt out
5) Wiring disconnected or burnt
1) Change switch
1) Change thermostat
2) Change overload relay
3) Change compressor
4) Connect or change wiring
out
2) Current runs.
(Below operating current,
capacitor normal)
3) High current draw
1) Compressor (main winding)
burn out
2) Switch contact defective
1) Compressor locked
2) Compressor (Auxiliary
1) Change compressor
2) Change switch
1) Change compressor
2) Change compressor
winding) burn out
3) Overload relay contact burn
3) Change overload relay
out
4) High current draw
compressor operates but
stops immediately
4) Capacitor defective
5) Compressor winding short
1) Compressor winding short
2) Heat source near to air
conditioner
3) Partial restriction in sealed
4) Change capacitor
5) Change compressor
1) Change compressor
2) Remove heat source
3) Check sealed system
system
Compressor trys to start
With switch set for cooling,
fuse or circuit breaker
open
1) Check power source voltage,
start voltage drop
1) Check power line fuse or
circuit breaker
2) Check power source voltage
1) Power source voltage too
low
2) Wiring for power supply
equipment too small
1) Insufficient capacity of fuse
2) Circuit breaker "OFF"
Power source cut off or contact
1) Improve the power supply
equipment
2) Improve the power supply
equipment
1) Change to rated fuse
2) Circuit breaker "ON"
Repair
defective
3) Check compressor
1) Compressor locked
2) One connection terminal of
1) Change compressor
2) Solder
compressor burn out
3) One core of lead wire of
3) Change lead wire
compressor burn out
Fan motor doesn't operate
with "Selector switch" set
at "Fan only"
4) Insulation test on compressor
5) Insulation test on switch
1) Check select switch or micro
switch contact
Insulation defective
Insulation defective
1) Switch contact burn out
2) Switch contact defective
3) Switch cam defective
4) Wiring to terminal defective
Change compressor
Change switch
1) Change switch
2) Polish contact
3) Change switch
4) Change or correct wiring
or improper
2) Check
a. Fan capacitor
b. Power cord
c. Fan motor
3) Check
a. Current exceeds rated one
1) Fan capacitor defective
2) Power supply voltage is too
low
3) Fan motor defective
1) Fan motor bearing locked
2) Fan motor lead wire burn out
1) Change capacitor
2) Improve power supply
equipment
3) Change fan motor
1) Change motor
2) Change or repair lead wire
b. Motor lead wire
14
Page 15

Symptom Check Defect Remedy
Fan motor operates but
supplies no air when
"Selector switch" set at
"Fan"
Compressor starts
but stops soon
1)
Check motor rotating direction
1) Check air filter and fan
elements
1) Measure power supply
voltage
Motor rotating wrong
1) Dirty air filter
2) Fan screw or nut loose and
only motor rotating
1) Voltage is low and overcurrent runs, overload relay or
Change motor
1) Clean
2) Tighten up
1) Improve the power supply
equipment
internal thermostat operates
2) Improve the power supply
equipment
1) Change switch
Check electric circuit (fan)
2) Tighten up
2) Check if air is delivered
2) Wiring for power supply
equipment too small
1) Overload relay operates as
fan is not rotating
2) Overload relay operates as
fan nut is loose
3) Check the temp. of air at
condensor
1) Overload relay operates as
outdoor air temp. is too high
1) Ventilate well for outdoor
exchanger, avoid sun light,
remove heat source from
around outdoor unit
AF-05CML
Compressor operates
in cooling but fan doesn't
rotate
Noise
Excessive vibration
and noise
4) Rated current is normal but
overload relay or internal
thermostat cuts out
1) Check switch mechanism
2) Check fan capacitor
3) Check fan motor
1) Vibrating noise
2) Metallic sound
3) Noise created by fan
4) Check mounting of
compressor
Check noise source
2) Improper ventilation for
outdoor heat exchanger.
Overload relay operates as
the temp. of outdoor unit is
too high
Overload relay defective
Switch defective
Capacitor defective
Fan motor defective
1) Insulation unstable
2) Cabinet screw loose
Piping touches cabinet or other
parts
1) Fan cracked or deformed
2) Screw or nut loose causing
vibrating noise
Compressor mounts defective
1) Compressor
2) Electric parts
3) Piping touched
4) Cabinet or parts set-screws
loosened
5) Fan touching
6) Insulation unstable
2) Clean the outdoor unit
Improve ventilation for outlet
port of outdoor exchanger
Change overload relay
Change switch
Change capacitor
Change motor
1) Secure
2) Tighten up
Repair
1) Change fan
2) Secure
Replace
1) Change compressor
2) Repair or change
3) Repair
4) Tighten up
5) Adjust
6) Secure
15
Page 16

AF-05CML
COOLING LOAD ESTIMATE FORM
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USING COOLING LOAD ESTIMATE FORM FOR ROOM AIR CONDITIONERS
(AHAM PUB. NO. RAC-1)
A. This cooling load estimate form is suitable for estimating the cooling load for comfort air conditioning installations
which do not require specific conditions of inside temperature and humidity.
B. The form is based on an outside design temperature of 95˚F dry bulb and 75˚F wet bulb. It can be used for areas in
the continental United States having other outside design temperature by applying a correction factor for the
particular locality as determined from the map.
C. The form includes "day" factors for calculating cooling loads in rooms where daytime comfort (such as living rooms,
offices, etc.).
D. The numbers of the following paragraphs refer to the correspondingly numbered item on the form:
1. Multiply the square feet of window area for each exposure by the applicable factor. The window area is the area
of the wall opening in which the window is installed. For windows shaded by inside shades or venetian blinds, use
the factor for "Inside Shades". For windows shades by outside awnings or by both outside awnings and inside
shades (or venetian blinds), use the factor for "Outside Awnings". "Single Glass" includes all types of single
thickness windows, and "Double Glass" includes sealed air space types, storm windows, and glass block. Only
one number should be entered in the right-hand column for item 1, and this number should represent only the
exposure with the largest load.
2. Multiply the total square feet of all windows in the room by the applicable factor.
3a. Multiply the total length (linear feet) of all walls exposed to the outside by the applicable factor. Doors should be
considered as being part of the wall. Outside walls facing due north should be calculated separately from outside
walls facing other directions. Walls which are permanently shaded by adjacent structures should be considered
as being "North Exposure". Do not consider trees and shrubbery as providing permanent shading. An insulated
frame wall or a masonry wall 8 inches or less in thickness is considered "Light Construction". An insulated frame
wall or a masonry wall over 8 inches in thickness is considered "Heavy Construction".
3b. Multiply the total length (linear feet) of all inside walls between the space to be conditioned and any unconditioned
spaces by the given factor. Do not include inside walls which separate other air conditioned rooms.
4. Multiply the total square feet of roof or ceiling area by the factor given for the type of construction most nearly
describing the particular application. (Use one line only.)
5. Multiply the total square feet of floor area by the factor given. Disregard this item if the floor is directly on the
ground or over a basement.
6. Multiply the number of people who normally occupy the space to be air conditioned by the factory given. Use a
minimum of 2 people.
7. Determine the total number of watts for lights and electrical equipment, except the air conditioner itself, that will
be in use when the room air conditioning is operating. Multiply the total wattage by the factor given.
8. Multiply the total width (linear feet) of any doors or arches which are continually open to an unconditioned space
by the applicable factor.
NOTE: Where the width of the doors or arches is more than 5 feet, the actual load may exceed the calculated
value. In such cases, both adjoining rooms should be considered as a single large room, and the room air
conditioner unit or units should be selected according to a calculation made on this new basis.
9. Total the loads estimated for the foregoing 8 items.
10. Multiply the sub total obtained in item 9 by the proper correction factor, selected from the map, for the particular
locality. The result is the total estimated design cooling load in BTU per hour.
E. For best results a room air conditioner unit or units having a cooling capacity rating (determined in accordance with
the NEMA Standards Publication for Room Air Conditioners, CN 1-1960) as close as possible to the estimated load
should be selected. In general, a greatly oversized unit which would operate intermittently will be much less
satisfactory than one which is slightly undersized and which would operate more nearly continuously.
F. Intermittent loads such as kitchen and laundry equipment are not included in this form.
16
Page 17

AF-05CML
HEAT GAIN FROM QUANTITY
FACTORS
DAY
BTU/Hr
(Quantity
x Factor)
1. WINDOWS: Heat gain from sun.
Southeast
Northeast
South
Southwest
Southeast
West
Northwest
North
sq ft
sq ft
sq ft
sq ft
sq ft
sq ft
sq ft
No
Shades
Inside
Shades
Outside
Shades
(Area a
Factor)
60
80
75
75
110
150
120
0
25
40
30
35
45
65
50
0
20
25
20
20
30
45
35
0
Use
only
the
largest
load
Use
only
only
These factors are for single glass only. For glass block, multiply the above factors
by 0.5: for double-glass or storm windows, multiply the above factors by 0.8.
2. WINDOWS: Heat gain by conduction.
(Total of all windows)
Single glass
Double glass or glass block
sq ft
sq ft
sq ft
sq ft
sq ft
sq ft
sq ft
sq ft
ft
ft
ft
ft
watts
30
60
30
19
12
20
30
14
7
8
3
3
3
5
600
300
Light Construction Heavy Construction
x x x x x x x x x x
(Item 9) x (Factor from Map) =
3. WALLS: (Based on linear feet of wall.)
4. ROOF OR CEILING: (Use one only.)
5. FLOOR: (Disregard if floor is directly
on ground or over basement.)
6. NUMBER OF PEOPLE:
7. LIGHTS AND ELECTRICAL
EQUIPMENT IN USE
8. DOORS AND ARCHES
CONTINUOUSLY OPENED TO
UNCONDITIONED SPACE:
(Linear feet of width.)
9. SUB-TOTAL
10. TOTAL COOLING LOAD:
(BTU per hour to be used for selection
of room air conditioner(s).)
a. Outside walls
Noth exposure
Other than North exposure
b. Inside Walls (between conditioned
and unconditioned spaces only)
a. Roof, uninsulated
b. Roof, 1 inch or more insulation
c. Ceiling, occupied space above.
d. Ceiling, insulated with attic space
above
e. Ceiling, uninsulated, with attic space
above
FARGO
EUGENE
RENO
SACRAMENT
FRESNO
LAS VEGAS
PHOENIX
PUEBLO
WICHITA
SAN ANTONIO
GREEN BAY
BIRMINGHAM
ATLANTA
COLUMBIA
ROCHESTER
ALBANY
NEW HAVEN
17
Page 18

AF-05CML
RUNNING CONDITION
Note:
1. Select mode of the Running Condition of a Room Air Conditioner.
SELECTOR .................................................................................................... HIGH COOL
THERMOSTAT .............................................................................................. 64˚F
2. Data of Performance Curve is measured between 40%RH and 70%RH.
If you measure the Room Air Conditioner above or below this rating, the data may miss the range of the
performance curve.
3. Outlet air temp. is influenced by the method of measurement. Measurement examples are shown.
4. Use power input data when checking the Running Condition.
RUNNING CONDITION FOR
PERFORMANCE CURVE
600
40%RH
500
400
300
5
4
Line current(Amp.) Power input (W)
3
30
(86)
20
(68)
10
(50)
Outlet air temp˚C (˚F)
25 30 35
(77) (86) (95) (104)
Outside air temp.˚C (˚F)
70%RH
40%RH
70%RH
70%RH
40%RH
40
18
Page 19

PACKING AND ACCESSORIES
TOP PAD ASSEMBLY (DPADBA004JBFZ)
Top pad L
4
3
5
6
AF-05CML
Top pad R
Accessories
Operation manual
Window sash foam seal
Window sash seal
Bottom gasket
6
Screws
Base pan angle
Right closure assembly
Left closure assembly
5
Enegry card
(TLAB-C217JBEZ)
"Front side" mark
Packing case
(SPAKCB001JBEZ)
Front side
2
Protect
(SSAKHA245YDE0)
Power supply cord
Detail is assembling
Energy card
1
Bottom pad assembly
(CPADBA046JBKZ)
19
Page 20

AF-05CML
REPLACEMENT PARTS LIST
REF. NO. PART NO. DESCRIPTION Q'TY CODE
CABINET AND UNIT PARTS
1- 1 DCHS-A439JBTA Base pan ass’y 1 AZ
1- 2 CCAB-A316JBKZ Cabinet ass’y 1 BB
1- 3 LANG-A503JBTA Top inst. angle 1 BP
1- 4 PSEL-C357JBEZ Cabinet insulator 1 AC
1- 5 HPNLCA812JBRA Control panel 1 AK
1- 6 JKNB-A045JBKZ Control knob ass’y 2 AE
1- 7 PKESPA091JBFZ Condenser shroud 1 AS
1- 8 PSEL-C351JBEZ Condenser indulator 1 AC
1- 9 NFANPA106JBFZ Propeller fan 1 AR
1-10 CMOTLA998JBEZ Fan motor 1 BK
1-11 PSEL-A828JBE0 Motor insulator 1 AB
1-12 PSKR-A239JBFA Bulkhead 1 AX
1-13 PKESSA067JBFZ Caseing 1 AH
1-14 NFANSA027JBF0 Centrifugal fan 1 AU
1-15 PKESSA066JBFA Orifice 1 AH
1-16 MLOV-A321JBFA Vertical louver A 1 AC
1-17 MLOV-A322JBFA Vertical louver B 3 AC
1-18 MJNTPA089JBFA Louver joint 1 AC
1-19 MLOV-A323JBFA Horizontal louver 4 AC
1-20 MJNTPA090JBFA Louver link 1 AC
1-21 MSPR-A148JBEZ Louver spring 2 AF
1-22 GWAKPA150JBFA Front panel 1 AV
1-23 PFILMA162JBEA Air filter 1 AK
1-24 PSEL-C254JBEZ Tube insulator 1 AC
1-25 LHLDW0364JBE0 Wire holder 1 AA
1-26 LHLDW0366JBE0 Wire holder 1 AA
1-27 TSPC-E077JBRZ Name badge 1 AC
1-28 TLAB-C217JBEZ Energy card 1 AC
1-29 TLABBA110JBRA Sharp badge 1 AB
1-30 TLABKA564JBE0 Number card 1 AC
1-31 LBND-A042JBE0 Wire fixing band 2 AC
1-32 DSKR-A126JBKZ Bulkhead ass'y 1 AW
1-33 DKES-A029JBKZ Orifice ass'y 1 AW
CONTROL BOX PARTS
2- 1 DPLT-A057JBWZ Cont. box cover ass’y 1 AH
2- 2 DPLT-A059JBWZ Cont. box angle ass’y 1 AG
2- 3 LBNDKA109JBWZ Capacitor clamp 1 AC
2- 4 QACC-A260JBZZ Power supply cord 1 AS
2- 5 QW-VZC561JBE0 Lead wire 1 AD
2- 6 RC-HZA256JBE0 Fan motor capacitor 1 AM
2- 7 RC-HZA418JBZZ Running capacitor 1 AV
2- 8 TLABCB588JBRZ Wiring diagram 1 AB
2- 9 QSW-RA021JBE0 Selector switch 1 AS
2-10 RTHM-A190JBE0 Thermostat 1 BB
2-11 QW-VZD336JBE0 Lead wire 1 AG
2-12 QW-VZE252JBZZ Lead wire 1 AN
2-13 QW-IZA039JBZZ Comp. wiring 1 AS
2-14 LBND-A042JBE0 Wire fixing band 3 AC
CYCLE PARTS
3- 1 PCMPRA319JBEZ Compressor 1 BZ
3- 2 GLEG-A089JBE0 Compressor cushion 3 AR
3- 3 PPIPCF488JB1Z Discharge tube 1 AM
3- 4 PCON-A473JBEZ Condenser 1 BG
3- 5 PPIPCF491JB1Z Lead tube 1 AF
3- 6 DCPY-A258JBKZ Capillary tube ass’y 1 AR
3- 7 PEVA-A454JBEZ Evaporator 1 BD
3- 8 CPIP-A027JBKZ Suction tube ass’y 1 AR
3- 9 PSEL-B183JBE0 Terminal gasket 1 AC
3-10 RHOG-A177JBZZ Overload relay 1 AW
3-11 MSPR-A117JBE0 Protector spring 1 AE
3-12 PCOV-A382JBE0 Terminal cover 1 AE
3-13 PSEL-A691JBE0 Gasket washer 1 AF
3-14 PGUM-A113JBE0 Damper rubber 1 AH
3-15 LBND-A046JBEO Wire fixing band 1 AE
3-16 PSEL-C250JBEZ Evaporator insulator 1 AB
3-17 LBND-A042JBE0 Wire fixing band 1 AC
3-18 QW-VZD775JBZZ Overload relay wire 1 AD
20
Page 21

AF-05CML
REF. NO. PART NO. DESCRIPTION Q'TY CODE
ACCESSORY PARTS
4- 1 TINSEA299JBRZ Operation manual 1 AE
4- 2 LANGAA011JBFE Left closure frame 1 AH
4- 3 LANGAA012JBFE Right closure frame 1 AH
4- 4 PPLTPA016JBFB Closure 2 AK
4- 5 PSEL-A931JBE0 Window insulator 1 AH
4- 6 PSEL-A932JBE0 Window insulator 1 AE
4- 7 PSEL-C251JBEZ Window insulator 1 AC
4- 8 DX-BZA016JBK0 Screws kit 1 AW
4- 9 SSAKAA018YDE0 Bag 1AB
4-10 XCTSD40P10000 Tapping screw 6 AA
4-11 XMPSD40P25000 Wood screw 7 AA
4-12 LANGAA030JBTA Base pan angle 2 AD
4-13 SPADBA163JBEZ Card board 1 AC
4-14 SSAKHA009JBEZ Bag 1AC
4-15 CFZK-B935JBKZ Closure ass’y 1 AX
PACKING PARTS
5- 1 DPADBA004JBFZ Top pad ass’y 1 AH
5- 2 CPADBA046JBKZ Bottom pad ass’y 1 AN
5- 3 SPAKCB001JBEZ Packing case 1 AP
5- 4 SSAKHA245YDE0 Protect 1 AB
5- 5 SSAKAA053YDE0 Bag 1AB
SCREWS AND NUTS
6- 1 XTTSD40P20000 Tapping screw 4 AA
6- 2 XCTWJ40P16000 Tapping screw 2 AA
6- 3 XTTSD40P14000 Tapping screw 7 AA
6- 4 XTTSD40P12000 Tapping screw 13 AA
6- 5 XHTSD40P10000 Tap tight screw 6 AA
6- 6 XHTSD40P08000 Tap tight screw 5 AA
6- 7 XBPSD40P06J00 Machine screw 3 AB
6- 8 LX-BZA236JBE0 Special screw 1 AC
6- 9 LX-CZA038WRE0 Special screw 4 AA
6-10 LX-HZA001JBE0 Special screw 1 AB
6-11 LX-BZA140JBE0 Special screw 2 AB
6-12 LX-NZA074JBE0 Special nut 1 AB
6-13 LX-NZA103JBE0 Frange nut 1 AF
6-14 LX-NZA026JBE0 Special nut 3 AC
To have your order filled prompty and correctly, please furnish the following information.
1. MODEL NUMBER 2. REF. NO. 3. PART NO. 4. DESCRIPTION
HOW TO ORDER REPLACEMENT PARTS
21
Page 22

AF-05CML
12345
6
CABINET PARTS
A
6-4
4-12
1-11
1-32
4-9
1-10
4-10
4-11
6-4
4-3
6-1
4-7
4-5
6-1
4-6
6-10
4-4
6-5
4-2
6-11
1-4
6-4
1-9
6-14
1-3
6-9
1-2
6-11
1-8
5-3
4-13
4-14
B
4-15
C
4-8
4-1
6-5
A
B
6-9
C
D
E
F
6-2
G
1-22
1-12
1-21
1-13
1-19
1-17
1-20
1-33
1-18
1-26
1-16
1-31
1-24
1-25
6-4
6-3
6-3
1-14
1-7
1-15
5-1
2-4
5-5
6-8
6-4
6-3
1-30
5-2
5-4
1-29
6-4
D
E
F
G
1-28
1-27
6-2
H
123456
22
1-23
1-1
6-3
H
Page 23

AF-05CML
12345
6
CONTROL BOX PARTS
A
B
C
1-6
6-5
2-3
2-7
1-5
6-6
6-4
2-4
6-6
6-7
2-5
2-10
2-2
2-9
2-6
6-5
A
B
C
2-12
3-8
3-1
3-5
3-6
2-1
3-18
6-4
3-14
2-8
2-13
3-15
2-13
2-11
D
E
F
G
D
2-14
6-6
E
CYCLE PARTS
F
3-16
G
6-3
3-7
6-14
6-13
3-13
3-12
3-11
3-10
3-9
3-4
3-3
H
123456
6-5
3-17
H
6-14
3-2
23
Page 24

AF-05CML
COPYRIGHT © 2002 BY SHARP CORPORATION
ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.
No part of this publication may be reproduced,
stored in retrieval systems, or transmitted in any
form or by any means, electronic, mechanical,
photocopying, recording, or otherwise, without prior
written permission of the publisher.
24
’02 SHARP CORP. (3S0.85E) Printed in U.S.A.
 Loading...
Loading...