SGS Thomson Microelectronics SM15T27A, SM15T27CA, SM15T30A, SM15T30CA, SM15T33A Datasheet
...
SM1 5T 6V8A / 220A
FEATURES
PEAKPULSEPOWER: 1500 W (10/1000µs)
BREAKDOWNVOLTAGERANGE :
From6.8 V to220 V
UNI AND BIDIRECTIONALTYPES
LOW CLAMPINGFACTOR
FASTRESPONSETIME
UL RECOGNIZED
DESCRIPTION
Transildiodes provide high overvoltageprotection
by clamping action. Their instantaneous
response to transient overvoltages makes them
particularly suited to protect voltage sensitive
devices such as MOS Technology and low
voltage supplied IC’s.
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUMRATINGS(T
amb
=25°C)
SM1 5T 6V8C A/22 0CA
TRANSIL
SMC
TM
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
P
PP
P Powerdissipationon infiniteheatsink T
I
FSM
T
stg
T
j
T
L
Note 1 : For a surge greater than the maximum values,the diode will fail in short-circuit.
Peak pulsepower dissipation (seenote1) Tjinitial= T
amb
Non repetitivesurge peak forward
currentforunidirectionaltypes
tp= 10ms
Tjinitial= T
amb
=50°C 6.5 W
amb
Storagetemperaturerange
Maximumjunction temperature
Maximumlead temperaturefor solderingduring10 s. 260 °C
1500 W
200 A
- 65 to +175
150
THERMAL RESISTANCES
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
R
R
th (j-l)
th (j-a)
Junctiontoleads 15 °C/W
Junctiontoambienton printedcircuiton recommendedpad
75 °C/W
layout
°C
°C
August 1999 Ed : 2A
1/5
SM15Txx
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
=25°C)
(T
amb
Symbol Parameter
V
RM
V
BR
V
CL
I
RM
I
PP
Stand-off voltage
Breakdown voltage
Clamping voltage
Leakage current @ VRM
Peak pulse current
αT Voltage temperature coefficient
V
F
Uni
directional
SM15T6V8A MDE
SM15T7V5A MDG
SM15T10A MDP
SM15T12A MDT
SM15T15A MDX
SM15T18A MEE
SM15T22A MEK
SM15T24A MEM
SM15T27A MEP
SM15T30A MER
SM15T33A MET
SM15T36A MEV
SM15T39A MEX
SM15T68A MFP
SM15T100A MFX
SM15T150A MGK
SM15T200A MGV
SM15T220A MGX
Forward Voltage drop
Types
Mar-
kingBidirectional
SM15T6V8CA BDE
SM15T7V5CA BDG
SM15T10CA NDP
SM15T12CA BDT
SM15T15CA BDX
SM15T18CA BEE
SM15T22CA BEK
SM15T24CA BEM
SM15T27CA BEP
SM15T30CA BER
SM15T33CA BET
SM15T36CA BEV
SM15T39CA BEX
SM15T68CA BFP
SM15T100CA BFX
SM15T150CA BGK
SM15T200CA BGV
SM15T220CA
Mar-
king
BGX 5 188 209 220 231 1 328 4.6 388 26 10.8 625
I
I
F
VV
CLVBR
I
I
RM
PP
V
F
V
I
RM@VRM
V
BR
@I
R
V
RM
VCL@IPPVCL@IPPαTC
max min nom max max max max typ
note2 10/1000µs 8/20µs note3 note4
µAVVVVmAVAVA10
1000
5.8 6.45 6.8 7.14 10 10.5 143 13.4 746 5.7 9500
500
6.4 7.13 7.5 7.88 10 11.3 132 14.5 690 6.1 8500
10
8.55 9.5 10 10.5 1 14.5 103 18.6 538 7.3 7000
5
10.2 11.4 12 12.6 1 16.7 90 21.7 461 7.8 6000
5
12.8 14.3 15 15.8 1 21.2 71 27.2 368 8.4 5000
5
15.3 17.1 18 18.9 1 25.2 59.5 32.5 308 8.8 4300
5
18.8 20.9 22 23.1 1 30.6 49 39.3 254 9.2 3700
5
20.5 22.8 24 25.2 1 33.2 45 42.8 234 9.4 3500
5
23.1 25.7 27 28.4 1 37.5 40 48.3 207 9.6 3200
5
25.6 28.5 30 31.5 1 41.5 36 53.5 187 9.7 2900
5
28.2 31.4 33 34.7 1 45.7 33 59.0 169 9.8 2700
5
30.8 34.2 36 37.8 1 49.9 30 64.3 156 9.9 2500
5
33.3 37.1 39 41.0 1 53.9 28 69.7 143 10.0 2400
5
58.1 64.6 68 71.4 1 92 16.3 121 83 10.4 1550
5
85.5 95.0 100 105 1 137 11 178 56 10.6 1150
5
128 143 150 158 1 207 7.2 265 38 10.8 850
5
171 190 200 210 1 274 5.5 353 28 10.8 675
-4
/°CpF
%I
PP
100
50
0
Note 2 : Pulse test:tp<50 ms.
Note 3 : ∆VBR=αT*(T
Note 4 : VR= 0 V, F = 1 MHz.For bidirectional types,
capacitancevalue is dividedby 2.
10 s
PULSE WAVEFORM10/1000 s
1000 s
- 25)*VBR(25°C).
amb
2/5
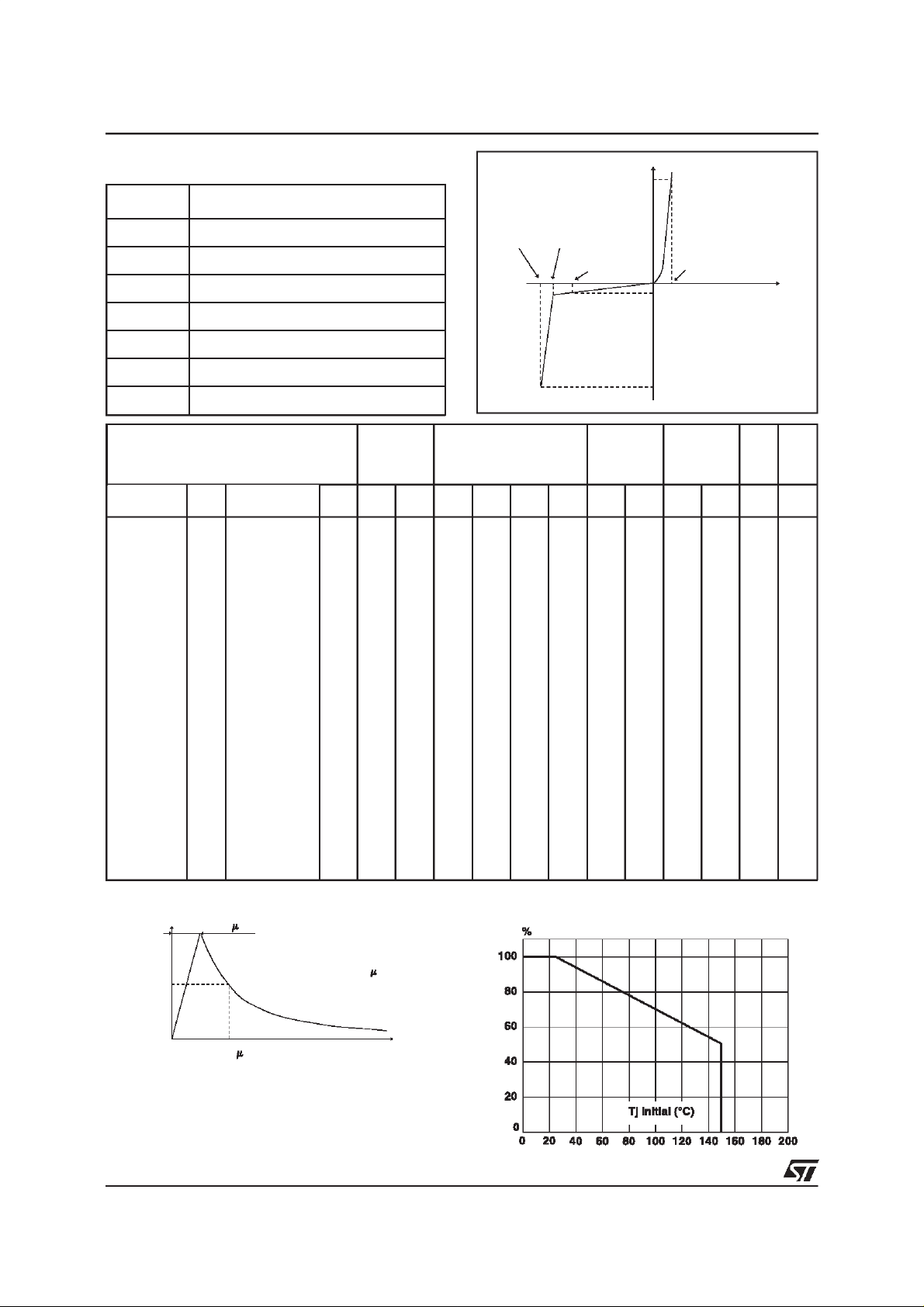
Fig. 1: Peak pulse powerdissipation versus initial
junctiontemperature(printed circuit board).
t
 Loading...
Loading...