Datasheet M29W160BB90N1, M29W160BB70N1, M29W160BB, M29W160BT90N6, M29W160BT90N1 Datasheet (SGS Thomson Microelectronics)
...
1/25
PRELIMINARY DATA
February 2000
This is preliminary information on a new product now in development or undergoing evaluation. Details are subject to change without notice.
M29W160BT
M29W160BB
16 Mbit (2Mb x8 or 1Mb x16, Boot Block)
Low Voltage Single Supply Flash Memory
■ SINGLE 2.7 to 3.6V SUPPLY VOLTAGE for
PROGRAM, ERASE and READ OPERATIONS
■ ACCESS TIME: 70ns
■ PROGRAMMING TIME
–10µs per Byte/Word typical
■ 35 MEMORYBLOCKS
– 1 Boot Block (Top or Bottom Location)
– 2 Parameter and 32 Main Blocks
■ PROGRAM/ERASE CONTROLLER
– Embedded Byte/Word Program algorithm
– Embedded Multi-Block/Chip Erase algorithm
– Status Register Polling and Toggle Bits
– Ready/Busy Output Pin
■ ERASE SUSPEND and RESUME MODES
– Read and Program another Block during
Erase Suspend
■ UNLOCKBYPASS PROGRAM COMMAND
– FasterProduction/Batch Programming
■ TEMPORARY BLOCK UNPROTECTION
MODE
■ SECURITY MEMORY BLOCK
■ LOW POWER CONSUMPTION
– Standby and Automatic Standby
■ 100,000 PROGRAM/ERASE CYCLES per
BLOCK
■ 20 YEARS DATA RETENTION
– Defectivity below 1 ppm/year
■ ELECTRONIC SIGNATURE
– Manufacturer Code: 0020h
– Top Device Code M29W160BT: 22C4h
– Bottom Device Code M29W160BB: 2249h
44
1
TSOP48(N)
12 x 20mm
SO44 (M)
LFBGA48 (ZA)
8 x 6 solder balls
FBGA
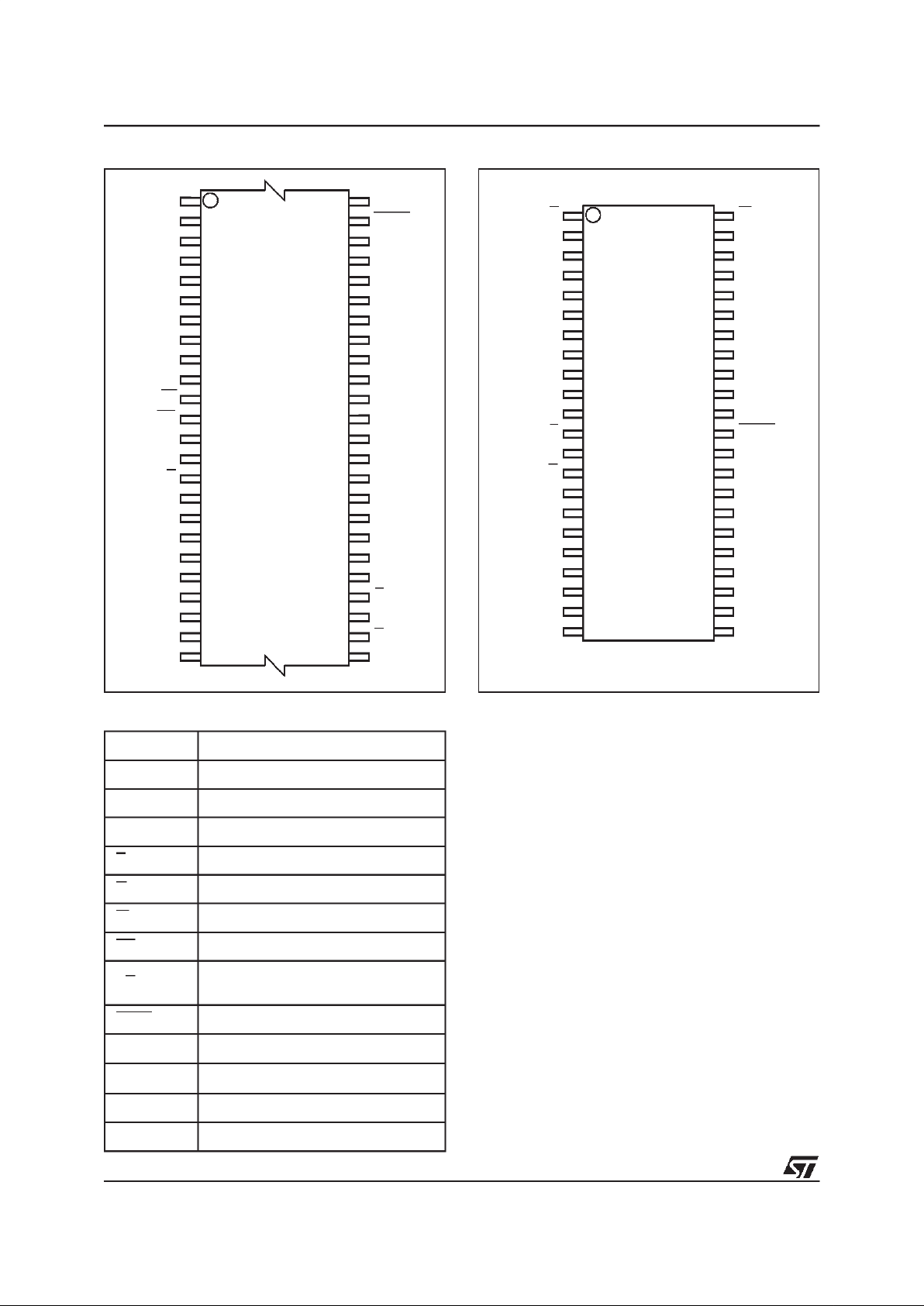
Figure 1. Logic Diagram
Note: RB not available on SO44 package.
AI00981
20
A0-A19
W
DQ0-DQ14
V
CC
M29W160BT
M29W160BB
E
V
SS
15
G
RP
DQ15A–1
BYTE
RB
M29W160BT, M29W160BB
2/25
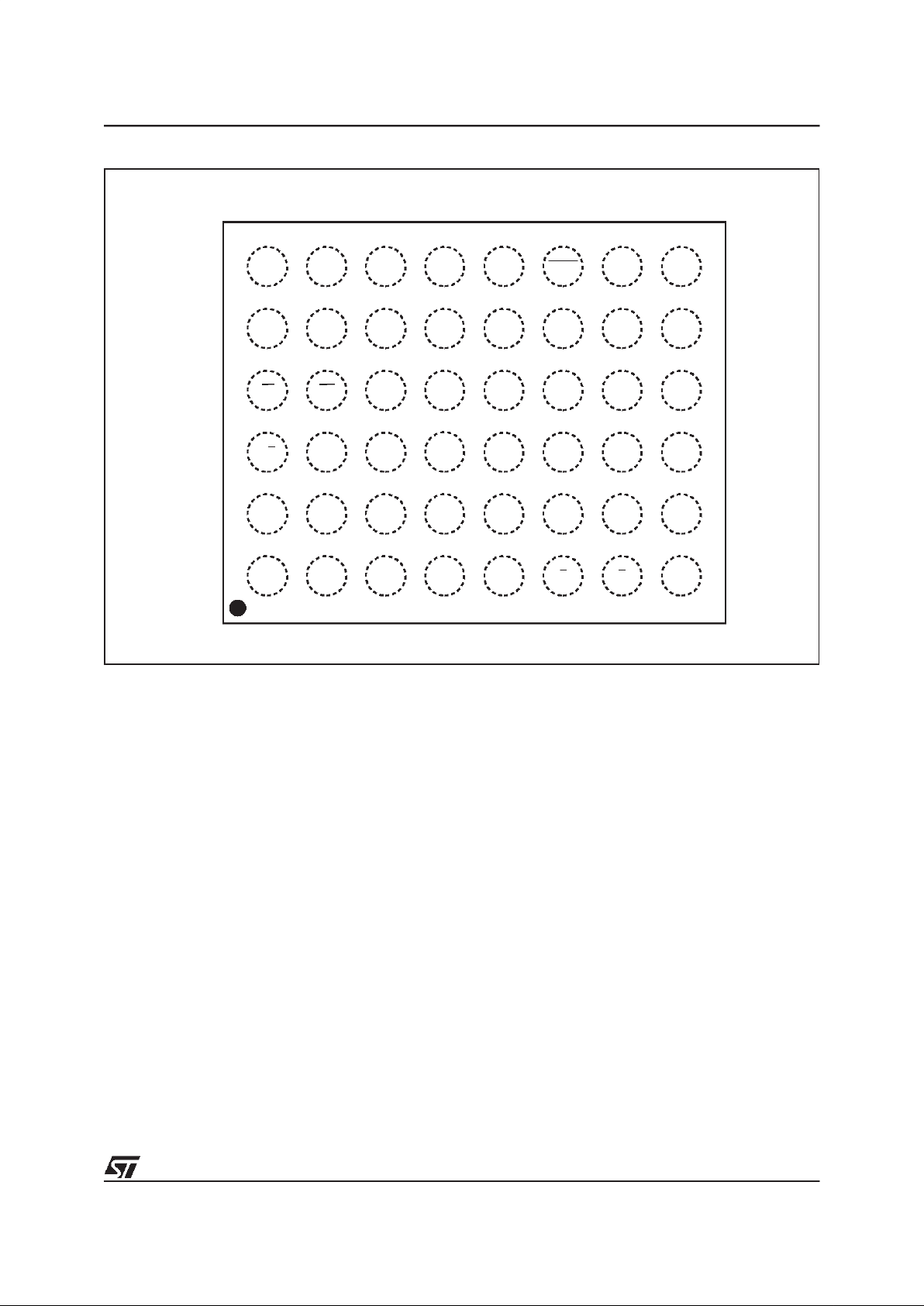
Figure 2. TSOP Connections
DQ3
DQ9
DQ2
A6
DQ0
W
A3
RB
DQ6
A8
A9
DQ13
A17
A10 DQ14
A2
DQ12
DQ10
DQ15A–1
V
CC
DQ4
DQ5
A7
DQ7
NC
NC
AI02994
M29W160BT
M29W160BB
12
1
13
24 25
36
37
48
DQ8
NC
A19
A1
A18
A4
A5
DQ1
DQ11
G
A12
A13
A16
A11
BYTE
A15
A14
V
SS
E
A0
RP
V
SS
Figure 3. SO Connections
G
DQ0
DQ8
A3
A0
E
V
SS
A2
A1
A13
V
SS
A14
A15
DQ7
A12
A16
BYTE
DQ15A–1
DQ5DQ2
DQ3
V
CC
DQ11
DQ4
DQ14
A9
A19
RP
A4
W
A7
AI00978
M29W160BT
M29W160BB
8
2
3
4
5
6
7
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
2322
20
19
18
17DQ1
DQ9
A6
A5
DQ6
DQ13
44
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
A11
A10
DQ10
21
DQ12
40
43
1
42
41
A17 A8
A18
Table 1. Signal Names
A0-A19 Address Inputs
DQ0-DQ7 Data Inputs/Outputs
DQ8-DQ14 Data Inputs/Outputs
DQ15A–1 Data Input/Output or Address Input
E Chip Enable
G Output Enable
W Write Enable
RP Reset/Block Temporary Unprotect
RB
Ready/Busy Output
(Not availableon SO44 package)
BYTE Byte/Word Organization Select
V
CC
Supply Voltage
V
SS
Ground
NC Not Connected Internally
DU Don’t Use as internally connected
3/25
M29W160BT, M29W160BB
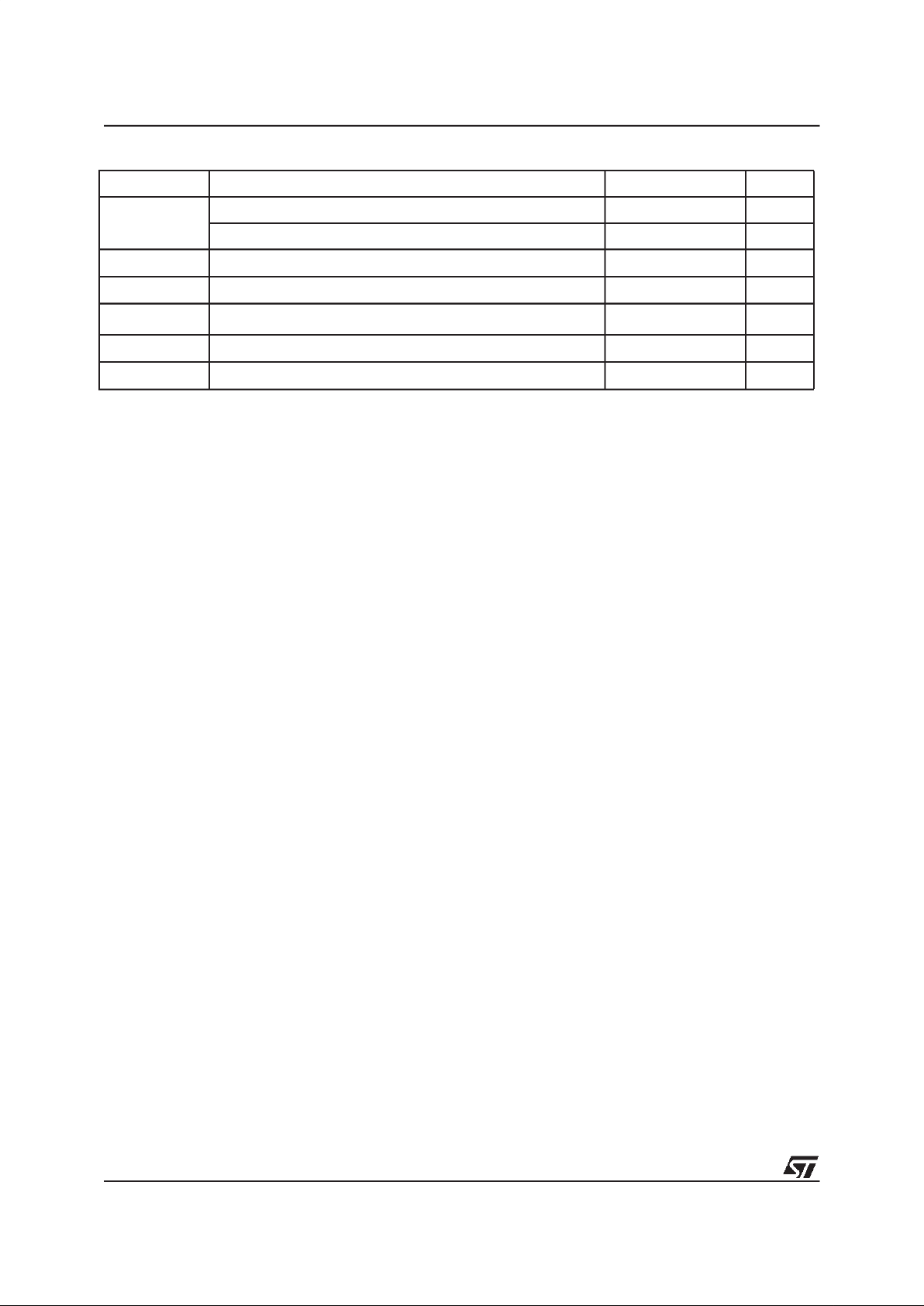
Figure 4. LFBGA Connections (Top view through package)
AI02985B
D
E
F
87654321
B
C
A
V
SS
DQ15
A–1
A15A14A12A13
DQ3DQ11DQ10A18DURB
DQ1DQ9DQ8DQ0A6A17A7
GEA0 A4A3
DQ2
DQ6DQ13DQ14A10A8A9
DQ4V
CC
DQ12DQ5A19DURPW
A11 DQ7
A1 A2 V
SS
A5
DU
A16
BYTE
M29W160BT, M29W160BB
4/25
SUMMARY DESCRIPTION
The M29W160B is a 16 Mbit (2Mb x8 or 1Mb x16)
non-volatile memory that can be read, erased and
reprogrammed. These operations can be performed using a single low voltage (2.7 to 3.6V)
supply. On power-up the memory defaults to its
Read mode where it can be read in the same way
as a ROM or EPROM.
The memory is divided into blocks that can be
erased independently so it is possible to preserve
valid data while old data is erased.Each block can
be protected independently to prevent accidental
Program or Erase commands from modifying the
memory. Program and Erase commands are written to the Command Interface of the memory. An
on-chip Program/Erase Controller simplifies the
process ofprogramming or erasing the memory by
taking care of all of the special operations that are
required to update the memory contents.
Table 2. Absolute Maximum Ratings
(1)
Note: 1. Except for the rating ”Operating Temperature Range”, stresses above those listed in the Table ”Absolute Maximum Ratings” may
cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only and operation of the device atthese or any other conditions
above those indicated in the Operating sections of this specification is not implied. Exposure to Absolute Maximum Rating conditions forextended periods may affect device reliability. Refer also tothe STMicroelectronics SURE Program and other relevant quality documents.
2. Minimum Voltage may undershoot to –2V during transition and for less than 20ns during transitions.
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
T
A
Ambient Operating Temperature (Temperature Range Option 1) 0 to 70 °C
Ambient Operating Temperature (Temperature Range Option 6) –40 to 85 °C
T
BIAS
Temperature Under Bias –50 to 125 °C
T
STG
Storage Temperature –65 to 150 °C
V
IO
(2)
Input or Output Voltage –0.6 to 4 V
V
CC
Supply Voltage –0.6 to 4 V
V
ID
Identification Voltage –0.6 to 13.5 V
The end of a program or erase operation can be
detected and any error conditions identified. The
command set required to control the memory is
consistent with JEDEC standards.
The blocks in the memory are asymmetrically arranged, seeTables 3 and 4, Block Addresses. The
first or last 64 Kbytes have been divided into four
additional blocks. The16 Kbyte Boot Block can be
used for small initialization code to start themicroprocessor, the two 8 Kbyte Parameter Blocks can
be used for parameter storage and the remaining
32K is a small Main Block where the application
may be stored.
Chip Enable, Output Enable andWrite Enable signals control the bus operation of the memory.
They allow simple connection to most microprocessors, often without additional logic.
The memory is offered in TSOP48 (12 x 20mm),
SO44 and LFBGA48 (0.8mm pitch) packagesand
it is supplied with all the bits erased (set to ’1’).
5/25
M29W160BT, M29W160BB
Table 3. Top Boot Block Addresses,
M29W160BT
#
Size
(Kby t es)
AddressRange
(x8)
Addres sRange
(x16)
34 16 1FC000h-1FFFFFh FE000h-FFFFFh
33 8 1FA000h-1FBFFFh FD000h-FDFFFh
32 8 1F8000h-1F9FFFh FC000h-FCFFFh
31 32 1F0000h-1F7FFFh F8000h-FBFFFh
30 64 1E0000h-1EFFFFh F0000h-F7FFFh
29 64 1D0000h-1DFFFFh E8000h-EFFFFh
28 64 1C0000h-1CFFFFh E0000h-E7FFFh
27 64 1B0000h-1BFFFFh D8000h-DFFFFh
26 64 1A0000h-1AFFFFh D0000h-D7FFFh
25 64 190000h-19FFFFh C8000h-CFFFFh
24 64 180000h-18FFFFh C0000h-C7FFFh
23 64 170000h-17FFFFh B8000h-BFFFFh
22 64 160000h-16FFFFh B0000h-B7FFFh
21 64 150000h-15FFFFh A8000h-AFFFFh
20 64 140000h-14FFFFh A0000h-A7FFFh
19 64 130000h-13FFFFh 98000h-9FFFFh
18 64 120000h-12FFFFh 90000h-97FFFh
17 64 110000h-11FFFFh 88000h-8FFFFh
16 64 100000h-10FFFFh 80000h-87FFFh
15 64 0F0000h-0FFFFFh 78000h-7FFFFh
14 64 0E0000h-0EFFFFh 70000h-77FFFh
13 64 0D0000h-0DFFFFh 68000h-6FFFFh
12 64 0C0000h-0CFFFFh 60000h-67FFFh
11 64 0B0000h-0BFFFFh 58000h-5FFFFh
10 64 0A0000h-0AFFFFh 50000h-57FFFh
9 64 090000h-09FFFFh 48000h-4FFFFh
8 64 080000h-08FFFFh 40000h-47FFFh
7 64 070000h-07FFFFh 38000h-3FFFFh
6 64 060000h-06FFFFh 30000h-37FFFh
5 64 050000h-05FFFFh 28000h-2FFFFh
4 64 040000h-04FFFFh 20000h-27FFFh
3 64 030000h-03FFFFh 18000h-1FFFFh
2 64 020000h-02FFFFh 10000h-17FFFh
1 64 010000h-01FFFFh 08000h-0FFFFh
0 64 000000h-00FFFFh 00000h-07FFFh
Table 4. Bottom Boot Block Addresses,
M29W160BB
#
Size
(Kbytes)
Address Range
(x8)
Address Range
(x16)
34 64 1F0000h-1FFFFFh F8000h-FFFFFh
33 64 1E0000h-1EFFFFh F0000h-F7FFFh
32 64 1D0000h-1DFFFFh E8000h-EFFFFh
31 64 1C0000h-1CFFFFh E0000h-E7FFFh
30 64 1B0000h-1BFFFFh D8000h-DFFFFh
29 64 1A0000h-1AFFFFh D0000h-D7FFFh
28 64 190000h-19FFFFh C8000h-CFFFFh
27 64 180000h-18FFFFh C0000h-C7FFFh
26 64 170000h-17FFFFh B8000h-BFFFFh
25 64 160000h-16FFFFh B0000h-B7FFFh
24 64 150000h-15FFFFh A8000h-AFFFFh
23 64 140000h-14FFFFh A0000h-A7FFFh
22 64 130000h-13FFFFh 98000h-9FFFFh
21 64 120000h-12FFFFh 90000h-97FFFh
20 64 110000h-11FFFFh 88000h-8FFFFh
19 64 100000h-10FFFFh 80000h-87FFFh
18 64 0F0000h-0FFFFFh 78000h-7FFFFh
17 64 0E0000h-0EFFFFh 70000h-77FFFh
16 64 0D0000h-0DFFFFh 68000h-6FFFFh
15 64 0C0000h-0CFFFFh 60000h-67FFFh
14 64 0B0000h-0BFFFFh 58000h-5FFFFh
13 64 0A0000h-0AFFFFh 50000h-57FFFh
12 64 090000h-09FFFFh 48000h-4FFFFh
11 64 080000h-08FFFFh 40000h-47FFFh
10 64 070000h-07FFFFh 38000h-3FFFFh
9 64 060000h-06FFFFh 30000h-37FFFh
8 64 050000h-05FFFFh 28000h-2FFFFh
7 64 040000h-04FFFFh 20000h-27FFFh
6 64 030000h-03FFFFh 18000h-1FFFFh
5 64 020000h-02FFFFh 10000h-17FFFh
4 64 010000h-01FFFFh 08000h-0FFFFh
3 32 008000h-00FFFFh 04000h-07FFFh
2 8 006000h-007FFFh 03000h-03FFFh
1 8 004000h-005FFFh 02000h-02FFFh
0 16 000000h-003FFFh 00000h-01FFFh
M29W160BT, M29W160BB
6/25
SIGNAL DESCRIPTIONS
See Figure 1, Logic Diagram, and Table 1, Signal
Names, fora brief overview ofthesignals connected to this device.
Address Inputs (A0-A19). The Address Inputs
select the cells in the memoryarray to access during Bus Read operations. During BusWrite operations they control the commands sent to the
Command Interface of the internal state machine.
Data Inputs/Outputs (DQ0-DQ7). The Data Inputs/Outputs outputthe datastored at the selected
address during a Bus Readoperation. DuringBus
Write operations they represent the commands
sent tothe Command Interface of theinternal state
machine.
Data Inputs/Outputs (DQ8-DQ14). The Data Inputs/Outputs outputthe datastored at the selected
address during a Bus Read operation when BYTE
is High, VIH. When BYTE is Low, VIL, these pins
are not used and arehigh impedance. During Bus
Write operations the Command Register does not
use these bits. When reading the Status Register
these bits should be ignored.
Data Input/Output or Address Input (DQ15A-1).
When BYTE is High, VIH, this pin behaves as a
Data Input/Output pin (as DQ8-DQ14). When
BYTE is Low, VIL, this pin behaves asan address
pin; DQ15A–1 Low willselect the LSB of the Word
on the other addresses, DQ15A–1 Highwill select
the MSB. Throughout the text consider references
to the Data Input/Output to include this pin when
BYTE is High and references to the Address Inputs to include this pin when BYTE is Low except
when stated explicitly otherwise.
Chip Enable (E). The Chip Enable, E, activates
the memory,allowing BusRead and Bus Writeoperations to be performed. When Chip Enable is
High, VIH, all other pins are ignored.
Output Enable (G). The Output Enable, G, controls the Bus Read operation of the memory.
Write Enable (W). The Write Enable, W, controls
the Bus Write operation of the memory’s Command Interface.
Reset/Block Temporary Unprotect (RP). The
Reset/Block Temporary Unprotect pin can be
used to apply a Hardware Resetto the memory or
to temporarily unprotect all Blocks that have been
protected.
A Hardware Reset is achieved by holding Reset/
Block Temporary Unprotect Low, VIL, for at least
t
PLPX
. After Reset/Block Temporary Unprotect
goes High, VIH, the memory will be ready for Bus
Read and Bus Write operations after t
PHEL
or
t
RHEL
, whicheveroccurs last. See the Ready/Busy
Output section, Table 18 and Figure 12, Reset/
Temporary Unprotect AC Characteristics for more
details.
Holding RP at VIDwill temporarily unprotect the
protected Blocks in the memory. Program and
Erase operations on all blocks will be possible.
The transition from VIHtoVIDmustbe slower than
t
PHPHH
.
Ready/Busy Output (RB). The Ready/Busy pin
is anopen-drain output that can be used to identify
when the memory array can be read. Ready/Busy
is high-impedance during Read mode, Auto Select
mode and Erase Suspend mode.
After a Hardware Reset, Bus Read and Bus Write
operations cannot begin until Ready/Busy becomes high-impedance. See Table 18 and Figure
12, Reset/Temporary Unprotect AC Characteristics.
During Program or Erase operations Ready/Busy
is Low, VOL. Ready/Busy will remain Low during
Read/Reset commands or Hardware Resets until
the memory is ready to enter Read mode.
The use ofan open-drain output allowsthe Ready/
Busy pins from several memories to be connected
to asingle pull-up resistor. A Low will then indicate
that one, or more, of the memories is busy.
Byte/Word Organization Select (BYTE). The
Byte/Word Organization Select pin is used to
switch between the 8-bit and 16-bit Bus modes of
the memory. When Byte/Word Organization Select isLow, VIL, the memory is in 8-bit mode, when
it is High, VIH, the memory is in 16-bit mode.
VCCSupply Voltage. The VCCSupply Voltage
supplies the power for all operations (Read, Program, Erase etc.).
The Command Interface is disabledwhen the V
CC
Supply Voltage is less than the Lockout Voltage,
V
LKO
. Thisprevents Bus Write operationsfrom accidentally damaging the data during power up,
power down and power surges. If the Program/
Erase Controller is programming orerasing during
this time thenthe operation aborts and the memory contents being altered will be invalid.
A 0.1µF capacitor should be connected between
the VCCSupply Voltage pin and the VSSGround
pin to decouplethe current surges from the power
supply. The PCB track widthsmust be sufficient to
carry the currents required during program and
erase operations, I
CC3
.
Vss Ground. The VSSGround is the reference
for all voltage measurements.
7/25
M29W160BT, M29W160BB
Table 5. Bus Operations, BYTE = V
IL
Note: X = VILor VIH.
Table 6. Bus Operations, BYTE = V
IH
Note: X = VILor VIH.
Operation E G W
Address Inputs
DQ15A–1, A0-A19
Data Inputs/Outputs
DQ14-DQ8 DQ7-DQ0
Bus Read
V
IL
V
IL
V
IH
Cell Address Hi-Z Data Output
Bus Write
V
IL
V
IH
V
IL
Command Address Hi-Z Data Input
Output Disable X
V
IH
V
IH
X Hi-Z Hi-Z
Standby
V
IH
X X X Hi-Z Hi-Z
Read Manufacturer
Code
V
IL
V
IL
V
IH
A0 = VIL,A1=VIL,A9=VID,
Others V
IL
or V
IH
Hi-Z 20h
Read Device Code
V
IL
V
IL
V
IH
A0 = VIH,A1=VIL,A9=VID,
Others V
IL
or V
IH
Hi-Z
C4h (M29W160BT)
49h (M29W160BB)
Operation E G W
Address Inputs
A0-A19
Data Inputs/Outputs
DQ15A–1, DQ14-DQ0
Bus Read
V
IL
V
IL
V
IH
Cell Address Data Output
Bus Write V
IL
V
IH
V
IL
Command Address Data Input
Output Disable X V
IH
V
IH
X Hi-Z
Standby
V
IH
X X X Hi-Z
Read Manufacturer
Code
V
IL
V
IL
V
IH
A0 = VIL,A1=VIL,A9=VID,
Others V
IL
or V
IH
0020h
Read Device Code
V
IL
V
IL
V
IH
A0 = VIH,A1=VIL,A9=VID,
Others V
IL
or V
IH
22C4h (M29W160BT)
2249h (M29W160BB)
BUS OPERATIONS
There are five standardbusoperations that control
the device. These are Bus Read, Bus Write, Output Disable, Standby and Automatic Standby. See
Tables 5 and 6, Bus Operations, for a summary.
Typically glitches of less than 5ns on Chip Enable
or WriteEnable areignored by the memory and do
not affect bus operations.
Bus Read. Bus Read operations read from the
memory cells, or specific registers in the Command Interface. A valid Bus Read operation involves setting the desiredaddress on the Address
Inputs, applying a Low signal, VIL, to Chip Enable
and Output Enable and keeping Write Enable
High, VIH. The Data Inputs/Outputs will output the
value, see Figure 9, Read Mode AC Waveforms,
and Table15, Read ACCharacteristics, for details
of when the output becomes valid.
Bus Write. Bus Write operations write to the
Command Interface. A valid Bus Write operation
begins by setting the desired address on the Address Inputs. The Address Inputs are latched by
the Command Interface onthe falling edgeof Chip
Enable or Write Enable, whichever occurs last.
The Data Inputs/Outputs are latched by the Command Interface on the rising edge of Chip Enable
or Write Enable,whichever occursfirst.OutputEnable must remain High, VIH, during the whole Bus
Write operation. See Figures 10 and 11, Write AC
Waveforms, and Tables 16 and 17, Write AC
Characteristics, for details of the timing requirements.

M29W160BT, M29W160BB
8/25
Output Disable. The Data Inputs/Outputs are in
the high impedance state when Output Enable is
High, VIH.
Standby. When Chip Enable is High, VIH, the
memory enters Standby mode and the Data Inputs/Outputs pins are placed in the high-impedance state. To reduce the Supply Current to the
Standby Supply Current, I
CC2
, ChipEnable should
be held within VCC± 0.2V. For the Standby current
level see Table 14, DC Characteristics.
During program or erase operations the memory
will continue to use the Program/Erase Supply
Current, I
CC3
, forProgram or Erase operations un-
til the operation completes.
AutomaticStandby. If CMOSlevels (VCC± 0.2V)
are usedto drive thebus and the busis inactivefor
150ns or more the memory enters Automatic
Standby where the internal Supply Current is reduced to the Standby Supply Current, I
CC2
. The
Data Inputs/Outputs will still output data if a Bus
Read operation is in progress.
Special Bus Operations
Additional bus operations can be performed to
read the Electronic Signature and also to apply
and remove Block Protection. These bus operations are intended for use by programming equipment and are not usually used in applications.
They require VIDto be applied to some pins.
Electronic Signature. The memory has two
codes, the manufacturer code and the device
code, that can be read to identify the memory.
These codes can be read by applying the signals
listed in Tables 5 and 6, Bus Operations.
BlockProtection andBlocks Unprotection. Each
block can be separately protected against accidental Program or Erase. Protected blocks can be
unprotected to allow data to be changed.
There are two methods available for protecting
and unprotecting the blocks, one for use on programming equipment and the other for in-system
use. For further information refer to Application
Note AN1122, Applying Protection and Unprotection to M29 Series Flash.
COMMAND INTERFACE
All Bus Write operations to the memory are interpreted by the Command Interface. Commands
consist of one or more sequential Bus Write operations. Failure to observe a valid sequence of Bus
Write operations will result in the memory returning to Read mode. The long command sequences
are imposed to maximize data security.
The address used for the commandschanges depending on whether the memory is in 16-bit or 8bit mode. See either Table 7, or 8, depending on
the configurationthat isbeing used, for a summary
of the commands.
Read/Reset Command. The Read/Reset command returns the memory to its Readmode where
it behaves like a ROM or EPROM, unless stated
otherwise (see Security Data command). It also
resets the errors in theStatus Register. Either one
or three Bus Writeoperations canbe used to issue
the Read/Reset command.
If the Read/Reset command is issued during a
Block Erase operation orfollowing a Programming
or Erase errorthen the memory will take upto 10µs
to abort. During the abort period no valid data can
be read from the memory. Issuing a Read/Reset
command during a Block Erase operation will
leave invalid data in the memory.
Auto Select Command. The Auto Select command is used to read the Manufacturer Code, the
Device Code and the Block Protection Status.
Three consecutive Bus Write operations are required to issue the Auto Select command. Once
the Auto Select command is issued the memory
remains in Auto Select mode until another command is issued.
From the Auto Select mode the Manufacturer
Code can be read using a Bus Read operation
with A0 = VILandA1 = VIL. The otheraddress bits
may be set to either VILor VIH. The Manufacturer
Code for STMicroelectronics is 0020h.
The Device Code can be read using a Bus Read
operation with A0 = VIHand A1 = VIL. The other
address bits may be set to either VILor VIH. The
Device Code for the M29W160BT is 22C4h and
for the M29W160BB is 2249h.
The Block Protection Status of each block can be
read using a Bus Read operation with A0 = VIL,
A1 = VIH, and A12-A19 specifying the address of
the block. The other address bits may be set toeither VILor VIH. If the addressed block is protected then 01h is output on Data Inputs/Outputs
DQ0-DQ7, otherwise 00h is output.
Program Command. The Program command
can be used to program a value to one address in
the memory array at a time. The command requires four Bus Write operations,the final write operation latches theaddress and data inthe internal
state machine and starts the Program/Erase Controller.
If the address falls in a protected block then the
Program command is ignored, the data remains
unchanged. The Status Register isnever readand
no error condition is given.
During the program operation the memory will ignore all commands. It is not possible to issue any
command to abort or pause the operation. Typical
program times are given in Table 10. Bus Read
operations during the program operation will output the Status Register on the Data Inputs/Outputs. See the section on the Status Register for
more details.

9/25
M29W160BT, M29W160BB
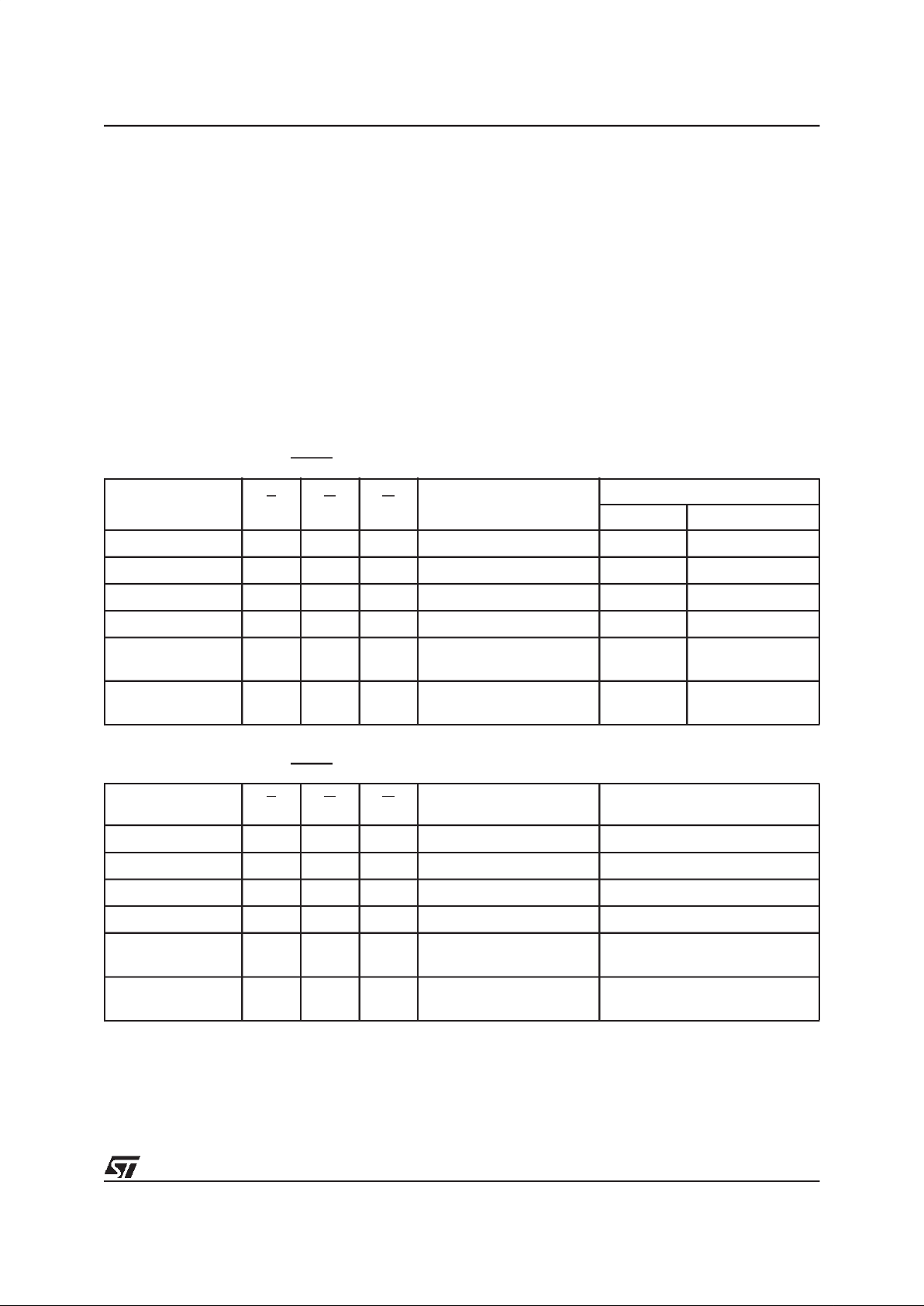
Table 7. Commands, 16-bit mode, BYTE = V
IH
Table 8. Commands, 8-bit mode, BYTE = V
IL
Note: X Don’t Care, PA Program Address, PD Program Data, BA Any address in the Block.
All values in the table are in hexadecimal.
The Command Interface only uses A–1, A0-A10 and DQ0-DQ7 to verify the commands; A11-A19, DQ8-DQ14 and DQ15 are Don’t Care.
DQ15A–1 is A–1 when BYTE is V
IL
or DQ15 when BYTE is VIH.
Read/Reset. After a Read/Reset command, read the memory as normal until another command is issued.
Auto Select. After an Auto Select command, readManufacturer ID, Device ID or Block Protection Status.
Program, Unlock Bypass Program, Chip Erase, BlockErase. After these commands read the Status Register until the Program/Erase
Controller completes and the memory returns to Read Mode. Add additional Blocks during Block Erase Command with additional Bus Write
Operations until Timeout Bit isset.
Unlock Bypass. After the Unlock Bypass command issue Unlock Bypass Program or Unlock Bypass Reset commands.
Unlock Bypass Reset. After the Unlock Bypass Reset command read the memory asnormal until another command is issued.
Erase Suspend. After the EraseSuspend command readnon-erasing memory blocks as normal, issue AutoSelect and Program commands
on non-erasing blocks as normal.
Erase Resume. After the Erase Resume command the suspended Erase operation resumes, read the Status Register until the Program/
Erase Controller completes and the memory returns to Read Mode.
Security Data. After the Security Data command read the Security Memory Block. Use an address outside the Security Memory Block when
issuing the command.
Command
Length
Bus Write Operations
1st 2nd 3rd 4th 5th 6th
Addr Data Addr Data Addr Data Addr Data Addr Data Addr Data
Read/Reset
1X F0
3 555 AA 2AA 55 X F0
Auto Select 3 555 AA 2AA 55 555 90
Program 4 555 AA 2AA 55 555 A0 PA PD
Unlock Bypass 3 555 AA 2AA 55 555 20
Unlock Bypass
Program
2X A0PAPD
Unlock Bypass Reset 2 X 90 X 00
Chip Erase 6 555 AA 2AA 55 555 80 555 AA 2AA 55 555 10
Block Erase 6+ 555 AA 2AA 55 555 80 555 AA 2AA 55 BA 30
Erase Suspend 1 X B0
Erase Resume 1 X 30
Security Data 1 X B8
Command
Length
Bus Write Operations
1st 2nd 3rd 4th 5th 6th
Addr Data Addr Data Addr Data Addr Data Addr Data Addr Data
Read/Reset
1X F0
3 AAA AA 555 55 X F0
Auto Select 3 AAA AA 555 55 AAA 90
Program 4 AAA AA 555 55 AAA A0 PA PD
Unlock Bypass 3 AAA AA 555 55 AAA 20
Unlock Bypass
Program
2X A0PAPD
Unlock Bypass Reset 2 X 90 X 00
Chip Erase 6 AAA AA 555 55 AAA 80 AAA AA 555 55 AAA 10
Block Erase 6+ AAA AA 555 55 AAA 80 AAA AA 555 55 BA 30
Erase Suspend 1 X B0
Erase Resume 1 X 30
Security Data 1 X B8

M29W160BT, M29W160BB
10/25
After the program operation has completed the
memory will return to the Read mode, unless an
error has occurred. When an error occurs the
memory will continue to output the Status Register. A Read/Reset command mustbe issued to reset the error condition and return to Read mode.
Note that the Program command cannotchange a
bit set at ’0’ back to ’1’. One of the Erase Commands must beused to set all the bits ina block or
in the whole memory from ’0’ to ’1’.
Unlock Bypass Command. The Unlock Bypass
command is used in conjunction with the Unlock
Bypass Program command toprogram the memory. When the access time to the device is long (as
with some EPROM programmers) considerable
time saving can be made by using these commands. Three Bus Write operations are required
to issue the Unlock Bypass command.
Once the Unlock Bypass command has been issued the memory will only accept the Unlock Bypass Program command and the Unlock Bypass
Reset command. The memory can be read as if in
Read mode.
Unlock Bypass Program Command. The Un-
lock Bypass Program command can be used to
program one address in memory at a time. The
command requires two Bus Write operations, the
final write operation latches the address and data
in the internal state machine and starts the Program/Erase Controller.
The Program operation using the Unlock Bypass
Program commandbehaves identically to theProgram operation using the Program command. A
protected block cannot be programmed; the operation cannot be aborted and theStatus Register is
read. Errors must be reset using the Read/Reset
command, which leaves the device in Unlock Bypass Mode.See the Programcommand for details
on the behavior.
Unlock Bypass Reset Command. The Unlock
Bypass Reset command can be used to return to
Read/Reset mode from Unlock Bypass Mode.
Two BusWrite operations are required to issuethe
Unlock Bypass Reset command.
Chip Erase Command. The Chip Erase command canbeused to erase the entire chip. SixBus
Write operations are required to issue the Chip
Erase Command and start the Program/Erase
Controller.
If any blocks are protected then these are ignored
and all the other blocks are erased. If all of the
blocks are protected the ChipErase operation appears tostart but will terminate withinabout 100µs,
leaving the data unchanged. No error condition is
given when protected blocks are ignored.
During the erase operationthe memory will ignore
all commands. It is not possible to issue any com-
mand to abort the operation. Typical chip erase
times are given in Table 10. All Bus Read operations during the Chip Erase operation will output
the Status Register on the Data Inputs/Outputs.
See the section on the Status Register for more
details.
After the Chip Erase operation has completed the
memory will return to the Read Mode, unless an
error has occurred. When an error occurs the
memory will continue to output the Status Register. A Read/Reset commandmust be issued to reset the error condition and return to Read Mode.
TheChip Erase Command setsall of the bits in unprotected blocks of the memory to ’1’. All previous
data is lost.
Block Erase Command. The Block Erase command can be used to erase a list of one or more
blocks. Six Bus Write operations are required to
select the first block in the list. Each additional
block in the list can be selected by repeating the
sixth Bus Write operation using the address of the
additional block. The Block Erase operation starts
the Program/Erase Controller about 50µs after the
last BusWrite operation. Once the Program/Erase
Controller starts it is not possible to select any
more blocks.Each additional block must therefore
be selectedwithin 50µsof the lastblock. The50µs
timer restarts when an additionalblock isselected.
The Status Register can be read after the sixth
Bus Write operation. See the Status Register for
details on how to identify if the Program/Erase
Controller has started the Block Erase operation.
If any selected blocksare protected thenthese are
ignored and all the other selected blocks are
erased. If all of the selected blocks are protected
the Block Erase operation appears to start but will
terminate within about 100µs, leaving thedata unchanged.No error condition is givenwhen protected blocks are ignored.
During the Block Erase operation the memory will
ignore all commands except the Erase Suspend
and Read/Reset commands. Typical block erase
times are given in Table 10. All Bus Read operations during the Block Erase operation will output
the Status Register on the Data Inputs/Outputs.
See the section on the Status Register for more
details.
After the Block Erase operation has completedthe
memory will return to the Read Mode, unless an
error has occurred. When an error occurs the
memory will continue to output the Status Register. A Read/Reset commandmust be issued to reset the error condition and return to Read mode.
The Block Erase Command sets all of the bits in
the unprotected selected blocks to ’1’. All previous
data in the selected blocks is lost.

11/25
M29W160BT, M29W160BB
Erase Suspend Command. The Erase Suspend
Command may be used to temporarily suspend a
Block Erase operation and return the memory to
Read mode. The command requires one Bus
Write operation.
The Program/Erase Controller will suspend within
15µs of the Erase Suspend Command being issued. Once the Program/Erase Controller has
stopped the memorywill be set to Read mode and
the Erasewill be suspended. Ifthe Erase Suspend
command is issued during the period when the
memory is waiting for an additional block (before
the Program/Erase Controller starts) then the
Erase is suspendedimmediately and will start immediately when the Erase Resume Command is
issued. It will not be possible to select any further
blocks for erasure after the Erase Resume.
During Erase Suspend it is possible to Read and
Program cells in blocks that are not being erased;
both Read and Program operations behave as
normal on these blocks. Reading from blocks that
are being erased will output the Status Register. It
is also possible to enter the Auto Select mode: the
memory willbehave asin the Auto Selectmode on
all blocksuntil a Read/Reset commandreturns the
memory to Erase Suspend mode.
Erase Resume Command. The Erase Resume
command must be used to restart the Program/
Erase Controller from Erase Suspend. An erase
can be suspended and resumed more than once.
Security Data Command. The Security Data
command can be used toread the Security Memory Block. The Security Memory Block is a block of
256 words that is usually undefined. Volume customers can request that a unique security code is
pre-programmed by ST into each part. One Bus
Write operation is required to issue the Security
Data command. Oncethe SecurityData command
is issued Bus Read operations read from the Security Memory Block instead of the memory array,
until another command is issued.
After issuing the Security Data command from
Auto Select modea Read/Reset command will return to Auto Select mode. An invalid command will
return to Read mode.
Valid addresses forthe Security Memory Blockare
given in Table 9, Security Memory Block Addresses. Although the address for the Security Data
command is Don’t Care, it is necessary to choose
an address outside theSecurity Memory Block for
correct operation.
Table 9. Security Memory Block Addresses
Size
(words)
Address Range
(x8)
Address Range
(x16)
256 000000h-0001FFh 000000h-0000FFh
Table 10. Program, Erase Times and Program, Erase Endurance Cycles
(TA= 0 to 70°C or –40 to 85°C)
Note: 1. TA=25°C, VCC= 3.3V.
Parameter Min
Typ
(1)
Typical after
100k W/E Cycles
(1)
Max Unit
Chip Erase (All bits in the memory set to ‘0’) 10 10 sec
Chip Erase 22 22 120 sec
Block Erase (64 Kbytes) 0.8 0.8 6 sec
Program (Byte or Word) 10 10 200 µs
Chip Program (Byte by Byte) 22 22 120 sec
Chip Program (Word by Word) 11 11 60 sec
Program/Erase Cycles (per Block) 100,000 cycles

M29W160BT, M29W160BB
12/25
STATUS REGISTER
Bus Read operations from any address always
read the Status Register during Program and
Erase operations. It isalso read during Erase Suspend whenanaddress within a block beingerased
is accessed.
The bits in the Status Register are summarized in
Table 11, Status Register Bits.
Data Polling Bit (DQ7). The Data Polling Bit can
be used to identify whether the Program/Erase
Controller has successfully completed its operation or if it has responded to an Erase Suspend.
The Data Polling Bit is output on DQ7 when the
Status Register is read.
During Program operations the Data Polling Bit
outputs the complement of the bit being programmed to DQ7. After successful completion of
the Program operation the memory returns to
Read modeand BusRead operationsfrom theaddress just programmed output DQ7, not its complement.
During Erase operations the Data Polling Bit outputs ’0’, the complement of the erased state of
DQ7. After successfulcompletion of the Erase operation the memory returns to Read Mode.
In Erase Suspend mode the Data Polling Bit will
output a ’1’ during a Bus Read operation within a
block being erased. The Data Polling Bit will
change from a ’0’ to a ’1’ when the Program/Erase
Controller has suspended the Erase operation.
Figure 5, Data Polling Flowchart, gives an example of how touse the Data Polling Bit. A Valid Address is the address being programmed or an
address within the block being erased.
Toggle Bit (DQ6). The Toggle Bit can be used to
identify whetherthe Program/Erase Controllerhas
successfully completed its operation or if ithas responded to an Erase Suspend. The Toggle Bit is
output on DQ6 when the Status Register is read.
During Program and Erase operations the Toggle
Bit changes from ’0’ to ’1’ to ’0’, etc., with successive Bus Read operations at any address. After
successful completion of the operation thememory returns to Read mode.
During Erase Suspend mode the Toggle Bit will
output whenaddressing a cellwithin a block being
erased. The Toggle Bit will stoptoggling when the
Program/Erase Controller has suspended the
Erase operation.
Figure 6, Data Toggle Flowchart, gives an example of how to use the Data Toggle Bit.
Error Bit (DQ5). The Error Bit can be used to
identify errors detected by the Program/Erase
Controller. The Error Bit is set to ’1’ when a Program, BlockErase or Chip Erase operationfails to
write the correct data to the memory. If the Error
Bit is set a Read/Reset command must be issued
before other commands are issued. The Error bit
is output onDQ5 when theStatus Registeris read.
Note thatthe Program command cannotchange a
bit setat ’0’back to ’1’ andattempting to dosomay
or may not set DQ5at ‘1’. In both cases, a successive BusRead operationwill showthe bit is still ‘0’.
One of the Erase commands must be used to set
all the bits in a block or in the whole memory from
’0’ to ’1’.
Table 11. Status Register Bits
Note: Unspecified data bits should be ignored.
Operation Address DQ7 DQ6 DQ5 DQ3 DQ2
RB
Program Any Address DQ7 Toggle 0 – – 0
Program During Erase
Suspend
Any Address DQ7 Toggle 0 – – 0
Program Error Any Address DQ7 Toggle 1 – – 0
Chip Erase Any Address 0 Toggle 0 1 Toggle 0
Block Erase before
timeout
Erasing Block 0 Toggle 0 0 Toggle 0
Non-Erasing Block 0 Toggle 0 0 No Toggle 0
Block Erase
Erasing Block 0 Toggle 0 1 Toggle 0
Non-Erasing Block 0 Toggle 0 1 No Toggle 0
Erase Suspend
Erasing Block 1 No Toggle 0 – Toggle 1
Non-Erasing Block Data read as normal 1
Erase Error
Good Block Address 0 Toggle 1 1 No Toggle 0
Faulty Block Address 0 Toggle 1 1 Toggle 0

13/25
M29W160BT, M29W160BB
Figure 5. Data Polling Flowchart
READ DQ5 &
DQ7
at VALID ADDRESS
START
READ
DQ7
at VALID ADDRESS
FAIL PASS
AI03598
DQ7
=
DATA
YES
NO
YES
NO
DQ5
=1
DQ7
=
DATA
YES
NO
Figure 6. Data Toggle Flowchart
READ DQ6
START
READ
DQ6
TWICE
FAIL PASS
AI01370B
DQ6
=
TOGGLE
NO
NO
YES
YES
DQ5
=1
NO
YES
DQ6
=
TOGGLE
READ
DQ5 & DQ6
Erase Timer Bit (DQ3). The Erase Timer Bit can
be used to identify the start of Program/Erase
Controller operation during a Block Erase command. Once the Program/Erase Controller starts
erasing the EraseTimer Bit is set to ’1’. Beforethe
Program/Erase Controller starts the Erase Timer
Bit is set to ’0’ and additional blocks to be erased
may be written to the Command Interface. The
Erase Timer Bit is output on DQ3 when the Status
Register is read.
Alternative Toggle Bit (DQ2). The Alternative
Toggle Bit can be used to monitor the Program/
Erase controller during Erase operations. The Alternative Toggle Bit is output on DQ2 when the
Status Register is read.
During ChipErase andBlock Eraseoperations the
Toggle Bit changes from ’0’ to ’1’ to ’0’, etc., with
successive Bus Read operations from addresses
within theblocksbeing erased.Once the operation
completes the memory returns to Read mode.
During Erase Suspend the Alternative Toggle Bit
changes from ’0’ to ’1’ to ’0’, etc. with successive
Bus Read operations from addresses within the
blocks being erased. Bus Read operations to addresses within blocks not being erased will output
the memory cell data as if in Read mode.
After an Erase operation that causes the Error Bit
to be setthe Alternative Toggle Bit can be used to
identify which block or blocks have caused the error. The Alternative Toggle Bit changes from ’0’ to
’1’ to ’0’, etc. with successive Bus Read Operations from addresses within blocks that have not
erased correctly. The Alternative Toggle Bit does
not change ifthe addressed block haserased correctly.

M29W160BT, M29W160BB
14/25
Figure 7. AC Testing Input Output Waveform
AI01417
3V
0V
1.5V
Figure 8. AC Testing Load Circuit
AI02762
0.8V
OUT
CL= 30pF or 100pF
CLincludes JIG capacitance
3.3kΩ
1N914
DEVICE
UNDER
TEST
Table 13. Capacitance
(TA=25°C, f = 1 MHz)
Note: Sampled only, not 100% tested.
Symbol Parameter Test Condition Min Max Unit
C
IN
Input Capacitance
V
IN
=0V
6pF
C
OUT
Output Capacitance V
OUT
=0V 12 pF
Table 12. AC Measurement Conditions
Parameter
M29W160B
70 90 120
V
CC
Supply Voltage
3.0 to 3.6V 2.7 to 3.6V 2.7 to 3.6V
Load Capacitance (C
L
) 30pF 30pF 100pF
Input Rise and Fall Times ≤ 10ns ≤ 10ns ≤ 10ns
Input Pulse Voltages 0 to 3V 0 to 3V 0 to 3V
Input and Output Timing Ref. Voltages 1.5V 1.5V 1.5V

15/25
M29W160BT, M29W160BB
Table 14. DC Characteristics
(TA= 0 to 70°C or –40 to 85°C)
Note: 1. Sampled only,not 100% tested.
2. T
A
=25°C, VCC= 3.3V.
Symbol Parameter Test Condition Min
Typ
(2)
Max Unit
I
LI
Input Leakage Current
0V ≤ V
IN
≤ V
CC
±1
µA
I
LO
Output Leakage Current 0V ≤ V
OUT
≤ V
CC
±1
µA
I
CC1
Supply Current (Read)
E=V
IL
,G=VIH,
f = 6MHz
510mA
I
CC2
Supply Current (Standby)
E=V
CC
± 0.2V,
RP = V
CC
± 0.2V
35 100
µA
I
CC3
(1)
Supply Current (Program/Erase)
Program/Erase
Controller active
20 mA
V
IL
Input Low Voltage –0.5 0.8 V
V
IH
Input High Voltage
0.7V
CC
VCC+ 0.3
V
V
OL
Output Low Voltage
I
OL
= 1.8mA
0.45 V
V
OH
Output High Voltage IOH= –100µA
V
CC
–0.4
V
V
ID
Identification Voltage 11.5 12.5 V
I
ID
Identification Current
A9 = V
ID
100 µA
V
LKO
(1)
Program/Erase Lockout Supply
Voltage
1.8 2.3 V

M29W160BT, M29W160BB
16/25
Figure 9. Read Mode AC Waveforms
AI02922
tAVAV
tAVQV tAXQX
tELQX tEHQZ
tGLQV
tGLQX tGHQX
VALID
A0-A19/
A–1
G
DQ0-DQ7/
DQ8-DQ15
E
tELQV tEHQX
tGHQZ
VALID
tBHQV
tELBL/tELBH tBLQZ
BYTE
Table 15. Read AC Characteristics
(TA= 0 to 70°C or –40 to 85°C)
Note: 1. Sampled only,not 100% tested.
Symbol Alt Parameter Test Condition
M29W160B
Unit
70 90 120
t
AVAV
t
RC
Address Validto Next Address Valid
E=V
IL
,
G=V
IL
Min 70 90 120 ns
t
AVQV
t
ACC
Address Valid to Output Valid
E=V
IL
,
G=V
IL
Max 70 90 120 ns
t
ELQX
(1)
t
LZ
Chip Enable Low to Output
Transition
G=V
IL
Min 0 0 0 ns
t
ELQV
t
CE
Chip Enable Low to Output Valid
G=V
IL
Max 70 90 120 ns
t
GLQX
(1)
t
OLZ
Output Enable Low to Output
Transition
E=V
IL
Min 0 0 0 ns
t
GLQV
t
OE
Output Enable Low to Output Valid
E=V
IL
Max 30 35 50 ns
t
EHQZ
(1)
t
HZ
Chip Enable High to Output Hi-Z
G=V
IL
Max 25 30 30 ns
t
GHQZ
(1)
t
DF
Output Enable High to Output Hi-Z
E=V
IL
Max 25 30 30 ns
t
EHQX
t
GHQX
t
AXQX
t
OH
Chip Enable, Output Enable or
Address Transition to Output
Transition
Min 0 0 0 ns
t
ELBL
t
ELBH
t
ELFL
t
ELFH
Chip Enable to BYTE Low or High Max 5 5 5 ns
t
BLQZ
t
FLQZ
BYTE Low to Output Hi-Z Max 25 30 30 ns
t
BHQV
t
FHQV
BYTE High to Output Valid Max 30 40 40 ns

17/25
M29W160BT, M29W160BB
Figure 10. Write AC Waveforms, Write Enable Controlled
AI02923
E
G
W
A0-A19/
A–1
DQ0-DQ7/
DQ8-DQ15
VALID
VALID
V
CC
tVCHEL
tWHEH
tWHWL
tELWL
tAVWL
tWHGL
tWLAX
tWHDX
tAVAV
tDVWH
tWLWHtGHWL
RB
tWHRL
Table 16. Write AC Characteristics, Write Enable Controlled
(TA= 0 to 70°C or –40 to 85°C)
Note: 1. Sampled only,not 100% tested.
Symbol Alt Parameter
M29W160B
Unit
70 90 120
t
AVAV
t
WC
Address Valid toNext Address Valid Min 70 90 120 ns
t
ELWL
t
CS
Chip Enable Low to Write Enable Low Min 0 0 0 ns
t
WLWH
t
WP
Write Enable Low to Write Enable High Min 45 50 50 ns
t
DVWH
t
DS
Input Valid to Write Enable High Min 45 50 50 ns
t
WHDX
t
DH
Write Enable High to Input Transition Min 0 0 0 ns
t
WHEH
t
CH
Write Enable High to Chip Enable High Min 0 0 0 ns
t
WHWL
t
WPH
Write Enable High to Write Enable Low Min 30 30 30 ns
t
AVWL
t
AS
Address Valid toWrite Enable Low Min 0 0 0 ns
t
WLAX
t
AH
Write Enable Low to Address Transition Min 45 50 50 ns
t
GHWL
Output Enable High to Write Enable Low Min 0 0 0 ns
t
WHGL
t
OEH
Write Enable High to Output Enable Low Min 0 0 0 ns
t
WHRL
(1)
t
BUSY
Program/Erase Valid to RB Low Max 30 35 50 ns
t
VCHEL
t
VCS
VCCHigh to Chip Enable Low
Min 50 50 50 µs

M29W160BT, M29W160BB
18/25
Table 17. Write AC Characteristics, Chip Enable Controlled
(TA= 0 to 70°C or –40 to 85°C)
Note: 1. Sampled only,not 100% tested.
Symbol Alt Parameter
M29W160B
Unit
70 90 120
t
AVAV
t
WC
Address Valid toNext Address Valid Min 70 90 120 ns
t
WLEL
t
WS
Write Enable Low to Chip Enable Low Min 0 0 0 ns
t
ELEH
t
CPH
Chip Enable High to Chip EnableHigh Min 45 50 50 ns
t
DVEH
t
DS
Input Valid to Chip Enable High Min 45 50 50 ns
t
EHDX
t
DH
Chip Enable High to Input Transition Min 0 0 0 ns
t
EHWH
t
WH
Chip Enable High to Write Enable High Min 0 0 0 ns
t
EHEL
t
CP
Chip Enable Low to Chip Enable Low Min 30 30 30 ns
t
AVEL
t
AS
Address Valid toChip Enable Low Min 0 0 0 ns
t
ELAX
t
AH
Chip Enable Low to Address Transition Min 45 50 50 ns
t
GHEL
Output Enable High Chip Enable Low Min 0 0 0 ns
t
EHGL
t
OEH
Chip Enable High to Output Enable Low Min 0 0 0 ns
t
EHRL
(1)
t
BUSY
Program/Erase Valid to RB Low Max 30 35 50 ns
t
VCHWL
t
VCS
VCCHigh to Write Enable Low
Min 50 50 50 µs
Figure 11. Write AC Waveforms, Chip Enable Controlled
AI02924
E
G
W
A0-A19/
A–1
DQ0-DQ7/
DQ8-DQ15
VALID
VALID
V
CC
tVCHWL
tEHWH
tEHEL
tWLEL
tAVEL
tEHGL
tELAX
tEHDX
tAVAV
tDVEH
tELEHtGHEL
RB
tEHRL

19/25
M29W160BT, M29W160BB
Table 18. Reset/Block Temporary Unprotect AC Characteristics
(TA= 0 to 70°C or –40 to 85°C)
Note: 1. Sampled only,not 100% tested.
Symbol Alt Parameter
M29W160B
Unit
70 90 120
t
PHWL
(1)
t
PHEL
t
PHGL
(1)
t
RH
RP High to Write Enable Low,Chip Enable
Low, Output Enable Low
Min 50 50 50 ns
t
RHWL
(1)
t
RHEL
(1)
t
RHGL
(1)
t
RB
RB High to Write Enable Low,Chip Enable
Low, Output Enable Low
Min 0 0 0 ns
t
PLPX
t
RP
RP Pulse Width Min 500 500 500 ns
t
PLYH
(1)
t
READY
RP Low to Read Mode Max 10 10 10 µs
t
PHPHH
(1)
t
VIDR
RP Rise Timeto V
ID
Min 500 500 500 ns
Figure 12. Reset/Block Temporary Unprotect AC Waveforms
AI02931
RB
W,
RP
tPLPX
tPHWL, tPHEL, tPHGL
tPLYH
tPHPHH
E, G
tRHWL, tRHEL, tRHGL

M29W160BT, M29W160BB
20/25
Table 19. OrderingInformation Scheme
Note: The last two characters of the ordering code may be replaced by a letter code for preprogrammed
parts, otherwise devices are shipped from the factory with the memorycontent bits erased to ’1’.
For a list of available options (Speed, Package, etc...) or for further information on any aspect of this device, please contact the ST Sales Office nearest to you.
Example: M29W160BB 90 N 1 T
Device Type
M29
Operating Voltage
W=V
CC
= 2.7 to 3.6V
Device Function
160B = 16 Mbit (2Mb x8 or 1Mb x16), Boot Block
Array Matrix
T = Top Boot
B = Bottom Boot
Speed
70 = 70 ns
90 = 90 ns
120 = 120 ns
Package
N = TSOP48: 12 x 20 mm
M = SO44
ZA = LFBGA48: 0.80mm pitch
Temperature Range
1=0to70°C
6=–40to85°C
Option
T = Tape & Reel Packing

21/25
M29W160BT, M29W160BB
Table 20. Revision History
Date Revision Details
July 1999 First Issue
10/08/99
FBGA Connections change (Table 1, Figure 4)
Chip Erase Max. specification added (Table10)
Block Erase Max. specification added (Table10)
Program Max. specification added (Table 10)
Chip Program Max. specification added (Table 10)
I
CC1,ICC2
Typ.specification added (Table14)
I
CC2
TestCondition change (Table14)
I
CC2
Max. specification change (Table 14)
t
WLWH
, 90ns speed, change (Table16)
t
DVWH
, 70 and 90ns speed, change (Table16)
t
WLAX
, 90ns speed, change (Table16)
t
ELEH
, 90ns speed, change (Table17)
t
DVEH
, 70 and 90ns speed, change (Table17)
t
ELAX
, 90ns speed, change (Table17.)
10/27/99 Device Code in Auto Select Program, corrected
02/09/00
Security Data Command change (Table7, 8)
Status Register bit DQ5 clarification
Data Polling Flowchart diagram change (Figure 5)
Data ToggleFlowchart diagram change (Figure 6)
LFBGA Package Mechanical Data change (Table23)
LFBGA Package Outline drawing change (Figure 15)

M29W160BT, M29W160BB
22/25
Table 21. TSOP48 - 48 lead Plastic Thin Small Outline, 12 x 20mm, Package Mechanical Data
Symbol
mm inches
Typ Min Max Typ Min Max
A 1.20 0.0472
A1 0.05 0.15 0.0020 0.0059
A2 0.95 1.05 0.0374 0.0413
B 0.17 0.27 0.0067 0.0106
C 0.10 0.21 0.0039 0.0083
D 19.80 20.20 0.7795 0.7953
D1 18.30 18.50 0.7205 0.7283
E 11.90 12.10 0.4685 0.4764
e 0.50 – – 0.0197 – –
L 0.50 0.70 0.0197 0.0276
α 0° 5° 0° 5°
N48 48
CP 0.10 0.0039
Figure 13. TSOP48 - 48 lead Plastic Thin Small Outline, 12 x 20mm, Package Outline
Drawing is not to scale.
TSOP-a
D1
E
1N
CP
B
e
A2
A
N/2
D
DIE
C
LA1 α

23/25
M29W160BT, M29W160BB
Figure 14. SO44 - 44 lead Plastic Small Outline, 525 mils body width, Package Outline
Drawing is not to scale.
SO-b
E
N
CP
B
e
A2
D
C
LA1 α
H
A
1
Table 22. SO44 - 44 lead Plastic Small Outline, 525 mils body width, Package Mechanical Data
Symbol
mm inches
Typ Min Max Typ Min Max
A 2.42 2.62 0.0953 0.1031
A1 0.22 0.23 0.0087 0.0091
A2 2.25 2.35 0.0886 0.0925
B 0.50 0.0197
C 0.10 0.25 0.0039 0.0098
D 28.10 28.30 1.1063 1.1142
E 13.20 13.40 0.5197 0.5276
e 1.27 – – 0.0500 – –
H 15.90 16.10 0.6260 0.6339
L 0.80 – – 0.0315 – –
α 3° ––3°––
N44 44
CP 0.10 0.0039

M29W160BT, M29W160BB
24/25
Table 23. LFBGA48 - 8 x 6 balls, 0.80mm pitch, Package Mechanical Data
Symbol
mm inch
Typ Min Max Typ Min Max
A 1.350 0.0531
A1 0.300 0.200 0.350 0.0118 0.0079 0.0138
A2 0.750 1.000 0.0295 0.0394
b 0.300 0.550 0.0118 0.0217
D 9.000 8.800 9.200 0.3543 0.3465 0.3622
D1 5.600 – – 0.2205 – –
ddd 0.150 0.0059
e 0.800 – – 0.0315 – –
E 8.000 7.800 8.200 0.3150 0.3071 0.3228
E1 4.000 – – 0.1575 – –
FD 1.700 – – 0.0669 – –
FE 2.000 – – 0.0787 – –
SD 0.400 – – 0.0157 – –
SE 0.400 – – 0.0157 – –
Figure 15. LFBGA48 - 8 x 6 balls, 0.80 mm pitch, Bottom View Package Outline
Drawing is not to scale.
E1E
D1
D
eb
A2
A1
A
BGA-Z00
ddd
FD
FE
SD
SE

25/25
M29W160BT, M29W160BB
Information furnished is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, STMicroelectronics assumes no responsibility for the consequences
of useofsuch information nor for any infringement ofpatents orother rights of third partieswhich may result from itsuse. Nolicense is granted
by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of STMicroelectronics. Specifications mentioned in this publication are subject
to change without notice. This publication supersedes and replaces allinformation previously supplied. STMicroelectronics products are not
authorized for use as critical components in lifesupport devices or systems without express written approval of STMicroelectronics.
The ST logo is registered trademark of STMicroelectronics
2000 STMicroelectronics - All Rights Reserved
All othernames are the property of their respective owners.
STMicroelectronics GROUP OF COMPANIES
Australia - Brazil - China - Finland - France - Germany - Hong Kong - India - Italy - Japan - Malaysia -Malta - Morocco -
Singapore - Spain - Sweden - Switzerland - United Kingdom - U.S.A.
http://www.st.com
 Loading...
Loading...