SGS Thomson Microelectronics M29W004BT, M29W004BB90N6, M29W004BB70N1, M29W004BB55N1, M29W004BB Datasheet
...
1/20March 2000
M29W004BT
M29W004BB
4 Mbit (512Kb x8, Boot Block)
Low Voltage Single Supply Flash Memory
■ SINGLE 2.7 to 3.6V SU PPL Y VO LT AG E fo r
PROGRAM, ERAS E and READ O PER AT IONS
■ ACCESS TIME: 55ns
■ PROGRAMMING TIME
– 10µs by Byte typical
■ 11 MEMORY BLOCKS
– 1 Boot Block (Top or Bottom Location)
– 2 Parameter and 8 Main Blocks
■ PROGRAM/ERA SE CON T ROL LER
– Embedded Byte Program algorithm
– Embedded Multi-Block/Chip Erase algorithm
– Status Register Polling and Toggle Bits
– Ready/Busy Output Pin
■ ERASE SUSPEND and RESUME MODES
– Read and Program another Block during
Erase Suspend
■ TEMPORARY BLOCK UNPROTECTION
MODE
■ UNLOCK BYPASS PROGRAM COMMAND
– Faster Production/Batch Programming
■ LOW POWER CONSUMPTION
– Standby and Automatic Standby
■ 100,000 PROGRAM/ER ASE CYCL ES per
BLOCK
■ 20 YEARS DATA RETENTI ON
– Defectivity below 1 ppm/year
■ ELECTRONIC SIGNATURE
– Manufacturer Code: 20h
– Top Device Code M29W004BT: EAh
– Bottom Device Code M29W004BB: EBh
TSOP40 (N)
10 x 20mm
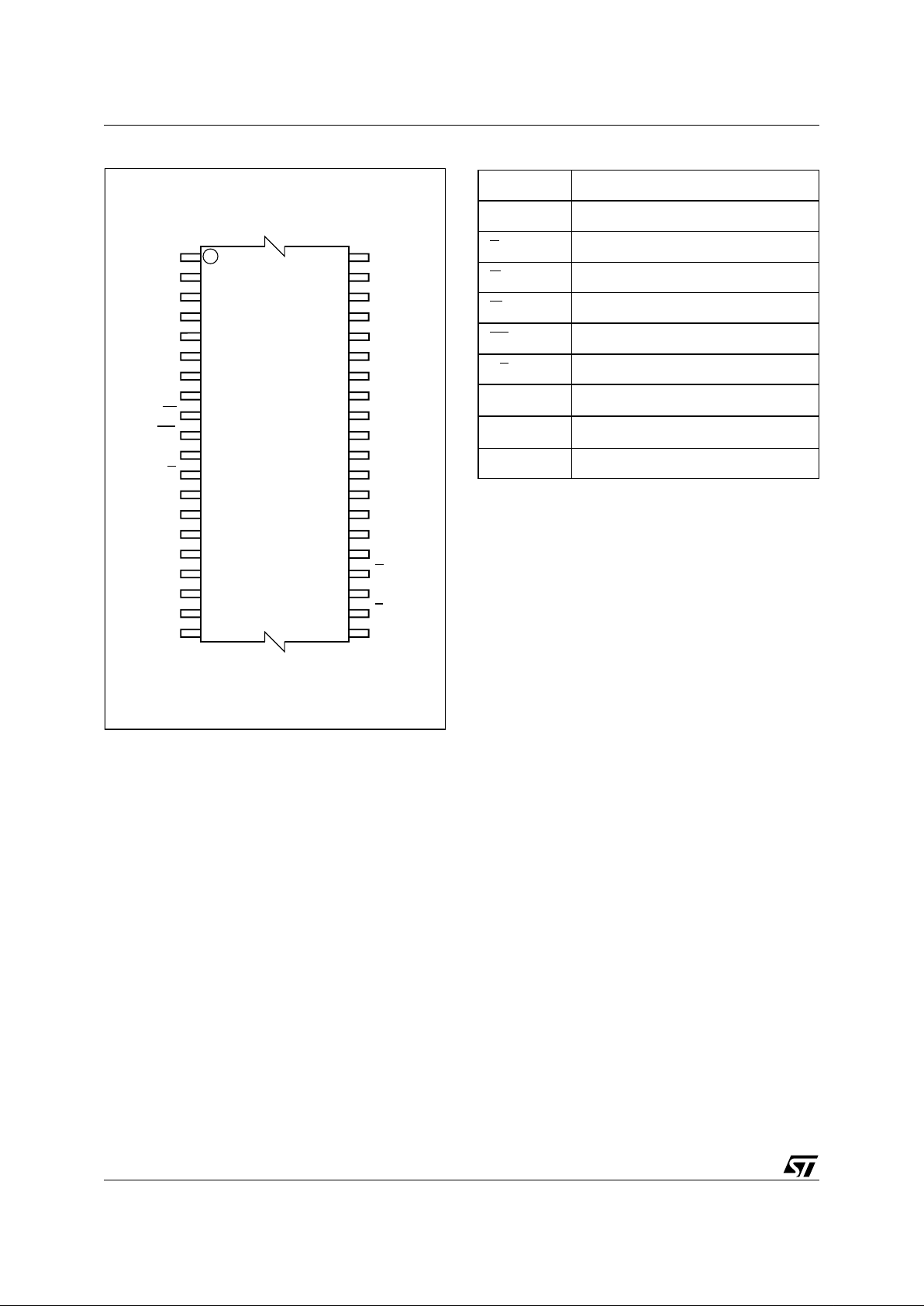
Figure 1. Logic Diagram
AI02954
19
A0-A18
W
DQ0-DQ7
V
CC
M29W004BT
M29W004BB
E
V
SS
8
G
RP
RB
M29W004BT, M29W004BB
2/20
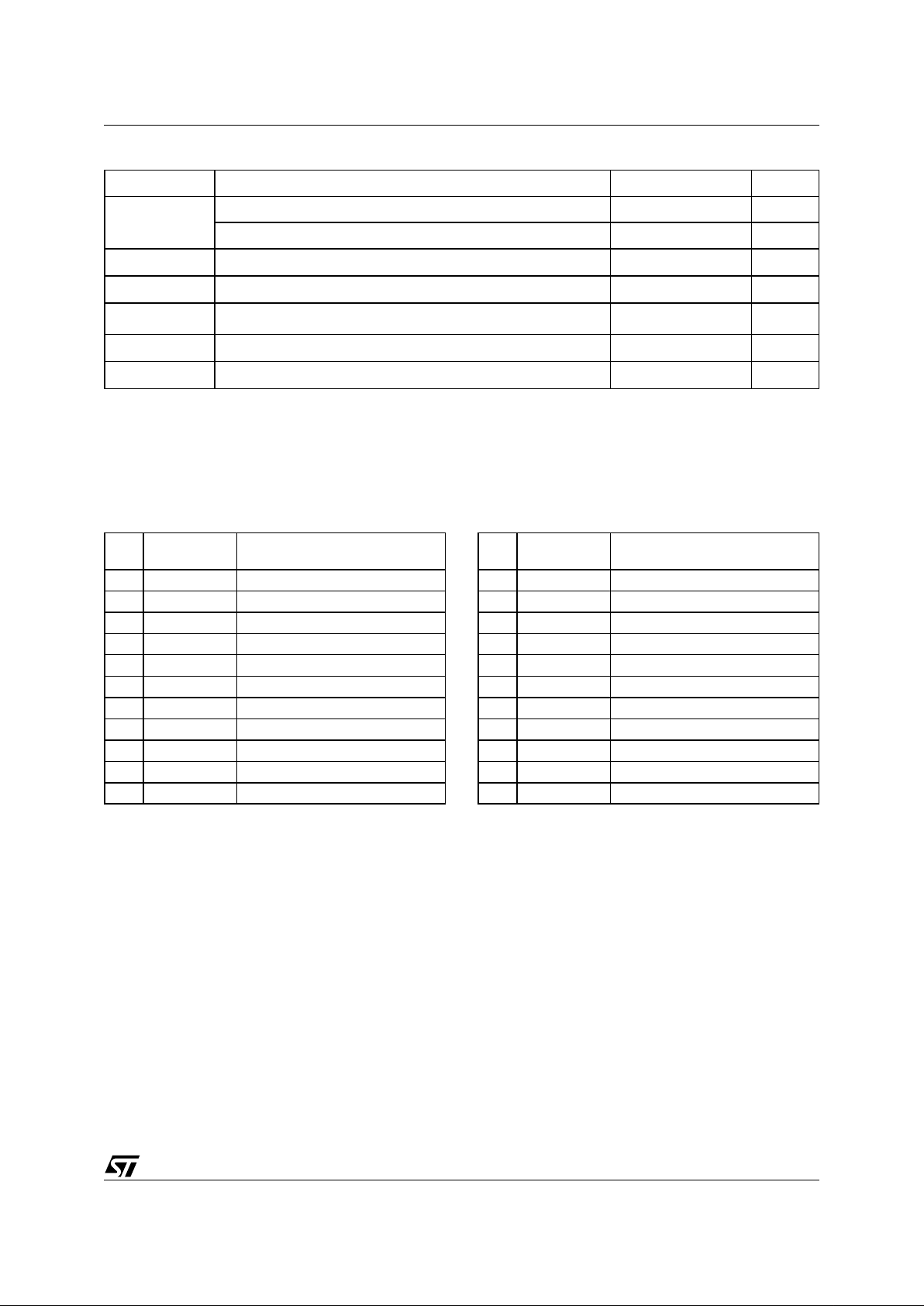
Figure 2. TSOP Connection s
V
SS
DQ1
DQ2A7
A1
E
A4
A3
A11
A17
A14
A15
DQ7
A9
A16
G
NC
DQ5
DQ3
NC
V
CC
DQ4
DQ6
A8
W
RB
A18
NC
RP
AI02950
M29W004BT
M29W004BB
10
1
11
20 21
30
31
40
A0
A12
A13
NC
A10
A5
A6
V
CC
DQ0
V
SS
A2
Table 1. Signal Names
A0-A18 Address Inputs
DQ0-DQ7 Data Inputs/Outputs
E
Chip Enable
G
Output Enable
W
Write Enable
RP
Reset/Block Temporary Unprotect
RB
Ready/Busy Output
V
CC
Supply Voltage
V
SS
Ground
NC Not Connected Internally
be protected independently to prev ent accidental
Program or Erase commands from modifying the
memory. Program and Erase com m ands are wri tten to the Command Interface of t he memory. An
on-chip Program/Erase Controller simplifies the
process of programming or erasing the memory by
taking care of all of the special operations that are
required to update the memory contents. The end
of a program or erase op eration can be de tected
and any error conditions identified. The command
set required to control the memory is consistent
with JEDEC standards.
The blocks in the memory are asymmetrically arranged, see Tables 3 and 4, Block Addresses. The
first or last 64 Kbytes hav e been divide d into four
additional blocks. The 16 Kbyte Boot Block can be
used for small initialization code to start the microprocessor, the two 8 Kbyte Parameter Blocks can
be used for parameter storage and the rem aining
32 Kbyte is a small Main Block where the application may be stored.
Chip Enable, Output Enable and Write Enable signals control the bus operation of the memory.
They allow simple conne ction to most microprocessors, often without additional logic.
The memory is offered in a TSOP40 (10 x 20mm)
package and it is supplied with all the bits eras ed
(set to ’1’).
SUMMARY DESCRIPTION
The M29W004B is a 4 M bit (512Kb x8) n on-volatile memory that can be read, erased and reprogrammed. These operations can be performed
using a single low voltage (2.7 to 3.6V) supply. On
power-up the memory defaults to its Read mode
where it can be read in the same way as a ROM or
EPROM. The M29W004B is fully backward compatible with the M29W004.
The memory is divided into blocks that can be
erased independently so it is pos sible to pres erve
valid data while old data is erased. Each block can
3/20
M29W004BT, M29W004BB
Table 2. Absolute Maximum Ratings
(1)
Note: 1. Except for the ratin g " Operati ng Temperat ure Range" , stresses above th ose liste d i n t he Table " A bsolute M aximum Ratings" may
cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only and operation of the device at these or any other conditions
above those indi cated in the Operating sections of this s pecification is not impli ed. Exposure to A bsolute M aximum Rating conditions for extended per iods may aff ect device reliabilit y. Refer also to the STMicroel ectronics SURE Program an d other relevan t qual ity docum en ts .
2. Mini m um Voltage ma y undershoot to –2V duri ng transit i on and for less t han 20ns duri ng transit io ns.
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
T
A
Ambient Operating Temperature (Temperature Range Option 1) 0 to 70 °C
Ambient Operating Temperature (Temperature Range Option 6) –40 to 85 °C
T
BIAS
Temperature Under Bias –50 to 125 °C
T
STG
Storage Temperature –65 to 150 °C
V
IO
(2)
Input or Output Voltage –0.6 to 4 V
V
CC
Supply Voltage –0.6 to 4 V
V
ID
Identification Voltage –0.6 to 13.5 V
Table 3. Top Boot Block Addresses
M29W004BT
#
Size
(Kbytes)
Address Range
10 16 7C000h-7FFFFh
9 8 7A000h-7BFFFh
8 8 78000h-79FFFh
7 32 70000h-77FFFh
6 64 60000h-6FFFFh
5 64 50000h-5FFFFh
4 64 40000h-4FFFFh
3 64 30000h-3FFFFh
2 64 20000h-2FFFFh
1 64 10000h-1FFFFh
0 64 00000h-0FFFFh
Table 4. Bottom Boot Block Addresses
M29W004BB
#
Size
(Kbytes)
Address Range
10 64 70000h-7FFFFh
9 64 60000h-6FFFFh
8 64 50000h-5FFFFh
7 64 40000h-4FFFFh
6 64 30000h-3FFFFh
5 64 20000h-2FFFFh
4 64 10000h-1FFFFh
3 32 08000h-0FFFFh
2 8 06000h-07FFFh
1 8 04000h-05FFFh
0 16 00000h-03FFFh

M29W004BT, M29W004BB
4/20
SIGNAL DESCRIPTIONS
See Figure 1, Logic Diagram, and Table 1, Sign al
Names, for a brief overview of the signals connected to this device.
Address Inputs (A0-A18). The Address Inputs
select the cells i n the memory array to a ccess during Bus Read operations. During Bus Write operations they control the commands sent to the
Command Interface of the internal state machine.
Data Inputs/Outputs (DQ0-DQ7). The Data Inputs/Outputs output the data stored at the selected
address during a Bus Read operation. During Bus
Write operations they represent the commands
sent to the Command Interface of the internal state
machine.
Chip Enable (E
). The Chip Enable, E, activates
the memory, allowing Bus Read and Bus Write operations to be performed. When Chip Enable is
High, V
IH
, all other pins are ignored.
Output Enable (G
). The Output Enable, G, con-
trols the Bus Read operation of the memory.
Write Enable (W
). The Write Enable, W, controls
the Bus Write operation of the memory’s Command Interf a c e .
Reset/Block Temporary Unprotect (RP
). The Re-
set/Block Temporary Unprotect pin can be used to
apply a Hardware Reset to the memory or to temporarily unprotect all Blocks that have been protected.
A Hardware Reset is achieved by holding Reset/
Block Temporary Unprotect Low, V
IL
, for at least
t
PLPX
. After Reset/Block Temporary Unprotect
goes High, V
IH
, the memory will be ready for Bus
Read and Bus Write operations after t
PHEL
or
t
RHEL
, whichever occurs last. See the Ready/Busy
Output section, Table 15 and Figure 10, Reset/
Temporary Unprotect AC Characteristics for more
details.
Holding RP
at VID will temporarily unprotect the
protected Blocks in the memory. Program and
Erase operations on all blocks will be possible.
The transition from V
IH
to VID must be slower than
t
PHPHH
.
Ready/Busy Output (RB
). The Ready/Busy pin
is an open-drain output that can be used to identify
when the memory array can be read. Ready/Busy
is high-impedance during Read mode, Auto Select
mode and Erase Suspend mode.
After a Hardware Reset, Bus Read and Bus Write
operations cannot begin until Ready/Busy becomes high-impedance. See Tabl e 15 and Figure
10, Reset/Temporary Unprotect AC Ch aracteristics.
During Program or Erase operations Ready/Busy
is Low, V
OL
. Ready/Busy will remain Low during
Read/Reset commands or Hardw are Resets until
the memory is ready to enter Read mode.
The use of an open-drain output allows the Ready/
Busy pins from several memories to be connected
to a single pull-up resistor. A Low will then indicate
that one, or more, of the memories is busy.
V
CC
Supply Voltage. The VCC Supply Voltage
supplies the power for all operations (Read, Program, Erase etc.).
The Command Interface is disabled when the V
CC
Supply Voltage is less than the L ockout Voltage,
V
LKO
. This prevents Bus Write operations from accidentally damaging the data during power up,
power down and power surges. If the Program/
Erase Controller is programming or erasing during
this time then the operation aborts and the memory contents being altered will be invalid.
A 0.1µF capacitor should be connected between
the V
CC
Supply Voltage pin and the VSS Ground
pin to decouple the current surges from the power
supply. The PCB track widths must be sufficient to
carry the currents required during program and
erase operations, I
CC3
.
V
SS
Ground. The VSS Ground is the reference for
all voltage measurements.
5/20
M29W004BT, M29W004BB
Table 5. Bus Operations
Note: X = VIL or VIH.
Operation E G W Address Inputs
Data
Inputs/Outp uts
Bus Read
V
IL
V
IL
V
IH
Cell Address Data Output
Bus Write
V
IL
V
IH
V
IL
Command Address Data Input
Output Disable
XV
IH
V
IH
X Hi-Z
Standby
V
IH
X X X Hi-Z
Read Manufacturer
Code
V
IL
V
IL
V
IH
A0 = VIL, A1 = VIL, A9 = VID,
Others V
IL
or V
IH
20h
Read Device Code
V
IL
V
IL
V
IH
A0 = VIH, A1 = VIL, A9 = VID,
Others V
IL
or V
IH
EAh (M29W004BT)
EBh (M29W004BB)
BUS OPERATIONS
There are five standard bus operations that control
the device. These are Bus Read, Bus Wri te, Output Disable, Standby and Automatic Standby. See
Table 5, Bus Operations, for a summary. Typically
glitches of less than 5ns on Chip Enabl e o r Write
Enable are ignored by t he mem ory and do not a ffect bus operations.
Bus Read. Bus Read operations read from the
memory cells, or specific registers in the Command Interface. A valid Bus Read operation involves setting the desired address on the Address
Inputs, applying a Low sig nal, V
IL
, to Chip Enable
and Output Enable and keeping Write Enable
High, V
IH
. The Data Inputs/Outputs will output the
value, see Figure 7, Rea d Mode AC Wav eforms,
and Table 12, Read AC Characteristics, for details
of when the output becomes valid.
Bus Write. Bus Write operations write to the
Command Interface. A valid Bus Write operation
begins by setting the desire d address on t he Address Inputs. The Address Inputs are latched by
the Command Interface on the falling edge of Chip
Enable or Write Enable, whichever occurs last.
The Data Inputs/Outputs a re latched by the Command Interface on the rising edge of Chip Enable
or Write Enable, whichever occurs first. Output Enable must remain High, V
IH
, during the whole Bus
Write operation. See Figures 8 and 9, Write AC
Waveforms, and Tables 13 and 14, Write AC
Characteristics, for details of the timing requirements.
Output Disa bl e . The Data Inputs/Outputs are in
the high impedance s tate when Output Enable is
High, V
IH
.
Standby. When Chip Enable is High, V
IH
, the
memory enters Standby mode and the Data Inputs/Outputs pins are placed in the high-imped-
ance state. To reduce the S upply Current to the
Standby Supply Current, I
CC2
, Chip Enable should
be held within V
CC
± 0.2V. For the Standby current
level see Table 11, DC Characteristics.
During program or erase operations the memory
will continue to use the Program/Erase Supply
Current, I
CC3
, for Program or Erase operations un-
til the operation completes.
Automatic Standby. If CMOS levels (V
CC
± 0.2V)
are used to drive the bus and the bus is inactive for
150ns or more the memory enters Automatic
Standby where the internal Supply Current is reduced to the Standby Supply Current, I
CC2
. The
Data Inputs/Outputs will still output data if a Bus
Read operation is in progress.
Special Bus Operations
Additional bus operations can be performed to
read the Electronic Signature and also to apply
and remove Block Protec tion. These bus operations are intended for use by programming equipment and are not usually used in applications.
They require V
ID
to be applied to some pins.
Electronic Signature. The memory has two
codes, the manufacturer code and the device
code, that can be read to identify the memory.
These codes can be read by applying t he signals
listed in Table 5, Bus Operations.
Block Protectio n and Blocks Unprotection. Each
block can be separately protected against accidental Program or Erase. Protected blocks can be
unprotected to allow data to be changed.
There are two methods available for protecting
and unprotecting the blocks, one for use on programming equipment and the other for in-system
use. For further information refer to Application
Note AN1122, Applying P rotection and Unp rotection to M29 Series Flash.

M29W004BT, M29W004BB
6/20
COMMAND INTERFACE
All Bus Write operations t o the me mory are in terpreted by the Command Interface. Commands
consist of one or more sequential Bus Write operations. Failure to observe a valid sequence of Bus
Write operations will result in the memory returning to Read mode. The long command sequences
are imposed to maximize data security.
The commands are summarized in Table 6, Commands. Refer to Table 6 in conjunction with the
text descriptions below.
Read/Reset Command. The Read/Reset command returns the memory to its Read mode where
it behaves like a ROM or EPROM. It also resets
the errors in the Status Register. Either one or
three Bus Write operations can be u sed to issue
the Read/Reset command.
If the Read/Reset command is issued during a
Block Erase operation or following a Programming
or Erase error then the memory will take up to 10
µs
to abort. During the abort period no valid data can
be read from the mem ory. Issuing a Read/Reset
command during a Block Erase operation will
leave invalid data in the memory.
Auto Select Command. The Auto Select command is used to read the Man ufacturer Code, the
Device Code and the Block Protection Status.
Three consecutive Bus Write operations are required to issue the Auto Select command. Once
the Auto Select comma nd is issued the memory
remains in Auto Select mode unt il another command is issued.
From the Auto Select mode the Manufacturer
Code can be read using a Bus Read operation
with A0 = V
IL
and A1 = VIL. The other address bits
may be set to either V
IL
or VIH. The Manufa cturer
Code for STMicroelectronics is 20h.
The Device Code can be read using a B us Read
operation with A0 = V
IH
and A1 = VIL. The other
address bits may be set to e ither V
IL
or VIH. The
Device Code for the M29W004BT is EAh and the
M29W004BB is EBh .
The Block Protecti on St at us of e ac h bl ock can be
read using a Bus Rea d operation with A0 = V
IL
,
A1 = V
IH
, and A13-A18 specifying the add ress of
the block. The other address bits may be set to either V
IL
or VIH. If the addressed block is protected
then 01h is output on the Data Inputs/Outputs, otherwise 00h is output.
Program Command. The Program command
can be used to program a value to one address in
the memory array at a time. The command requires four Bus Write operations, the final write op-
eration latches the address and data in the internal
state machine and starts the Program/Erase Controller.
If the address falls in a pro tected block then the
Program command is ignored, the data remains
unchanged. The Status Register is never read and
no error condition is given.
During the program operat ion the memo ry will ignore all commands. I t is n ot poss ible t o iss ue any
command to abort or pause the operation. Typical
program times are given in Table 7. Bus Read operations during the program o peration will output
the Status Register on the Data Inputs/Outputs.
See the section on the S tatus Register for more
details.
After the program operation has completed the
memory will return to the Read mode, unle ss an
error has occurred. When an error occurs the
memory will continue to output the Status Register. A Read/Reset command must be issued to reset the error condition and return to Read mode.
Note that the Program command cannot change a
bit set at ’0’ bac k to ’1’. One of the E rase Commands must be used to set all the bits in a block or
in the whole memory from ’0’ to ’1’.
Unlock Bypass Command. The Unlock Bypass
command is used in conjunction with the Unlock
Bypass Program command to program the memory. When the access time to the device is long (as
with some EPROM programmers) considerable
time saving can be made by using these commands. Three Bus Write operations are requ ired
to issue the Unlock Bypass command.
Once the Unlock Bypas s command has bee n issued the memory will only accept the Unloc k Bypass Program command and the Unlock Bypass
Reset command. The memory can be read as if in
Read mode.
Unlock Bypass Program Command. The Unlock Bypass Prog ram comma nd can be used to
program one address in memory at a time. The
command requires two B us Write operations, the
final write operation latches the address and data
in the internal stat e machine and starts th e Program/Erase Controller.
The Program operation using the Unlock Bypass
Program command behaves identically to the Program operation using the Program command. A
protected block cannot be programmed; the operation cannot be aborted and the Status Register is
read. Errors must be reset using the Read/Re set
command, which l eaves the d evice in Unlo ck Bypass Mode. See the Program command for details
on the behavior.
 Loading...
Loading...