SGS Thomson Microelectronics M14C16, M14C04 Datasheet
M14C16
M14C04
Memory Card IC
16/4 Kbit Serial I²C Bus EEPROM
■ Two Wire I
2
C Serial Interface
Supports 400 kHz Protocol
■ Single Supply Voltage (2.5 V to 5.5 V)
■ Hardware Write Control
■ BYTE and PAGE WRITE (up to 16 Bytes)
■ BYTE, RANDOM and SEQUENTIAL READ
Modes
■ Self-Tim e d P ro g r amming Cycle
■ Automatic Address Incrementing
■ Enhanced ESD/Latch-Up Behaviour
■ 1 Million Erase/Write Cycles (minimum)
■ 40 Year Data Retention (minimum)
■ 5 ms Programming Time (typical)
DESCRIPTION
Each device is an electrically erasable program mable memory (EEPROM) fabricated with STMi-
croelectronics’s High Endurance, Single
Polysilicon, CMOS technology. This guarantees
an endurance typically well above one million
Erase/Write cycles, with a data retention of
40 years. The memory operates with a power supply as low as 2.5 V.
The M14C16 and M14C0 4 are each available in
wafer form (either sawn or unsawn) and in micromodule fo rm ( on film ) .
2
Each memory is com patible with t he I
C memor y
standard. This is a two wire serial interface that
2
2
Micromodule (D20)
Wafer
Figure 1. Logic Diagram
V
CC
2
2
Table 1. Signal Names
SDA Serial Data/Address Input/
Output
SCL Serial Clock
WC
V
CC
GND Ground
Write Control
Supply Voltage
SCL
SDA
M14xxxWC
GND
AI02217
1/13March 1999

M14C16, M14C04
Figure 2. D20 Contact Connections
V
CC
WC
SCL
GND
SDA
AI02168
uses a bi-directional data bus and serial clock. The
memory carries a built-in 7-bit unique Device Type
Identifier code (1010xxx, for the M14C16, and
101000x, for the M14C04, as shown in Table 3) in
accordance with the I
memory can be attached to each I
The memory behaves as a slave device in the I
2
C bus defini tion. Only one
2
C bus.
2
protocol, with all memory operations synchronized
by the serial clock. Read and write o perations are
initiated by a START condition, gene rated by the
bus master. The STA RT condition is followed by
the Device Select Code which is compos ed of a
stream of 7 bits (1010xxx, for the M14C16, and
101000x, for the M14C04, as shown in Table 3),
plus one read/write bit (R/W
) and is terminated by
an acknowledge bit.
When writing data to the memory, the mem ory in-
serts an acknowledge bit during the 9
th
bit time,
following the bus master’s 8-bit transmission.
When data is read by the bus master, the bus
master acknowledges the receipt of t he data b yte
in the same way. Data transfers are terminated by
a STOP condition after an Ack for WRITE, and after a NoACK for READ.
Power On Reset: V
Lock-Out Write Protect
CC
In order to prevent data corruption and inadvertent
write operations during power up, a Power On Reset (POR) circuit is included. The internal reset is
held active until the V
voltage has reached the
CC
POR threshold value, and all operations are disabled – the device will not respond to any command. In the same way, when V
drops from the
CC
operating voltage, below the POR threshold value,
all operations are disabled and the device will not
respond to any com ma nd. A s table a nd v alid V
must be applied before applying any logic signal.
SIGNAL DESCRIPTION
Serial Clock (SCL)
The SCL input pin is used to synchronize a ll data
in and out of the memory. A pull up resistor can be
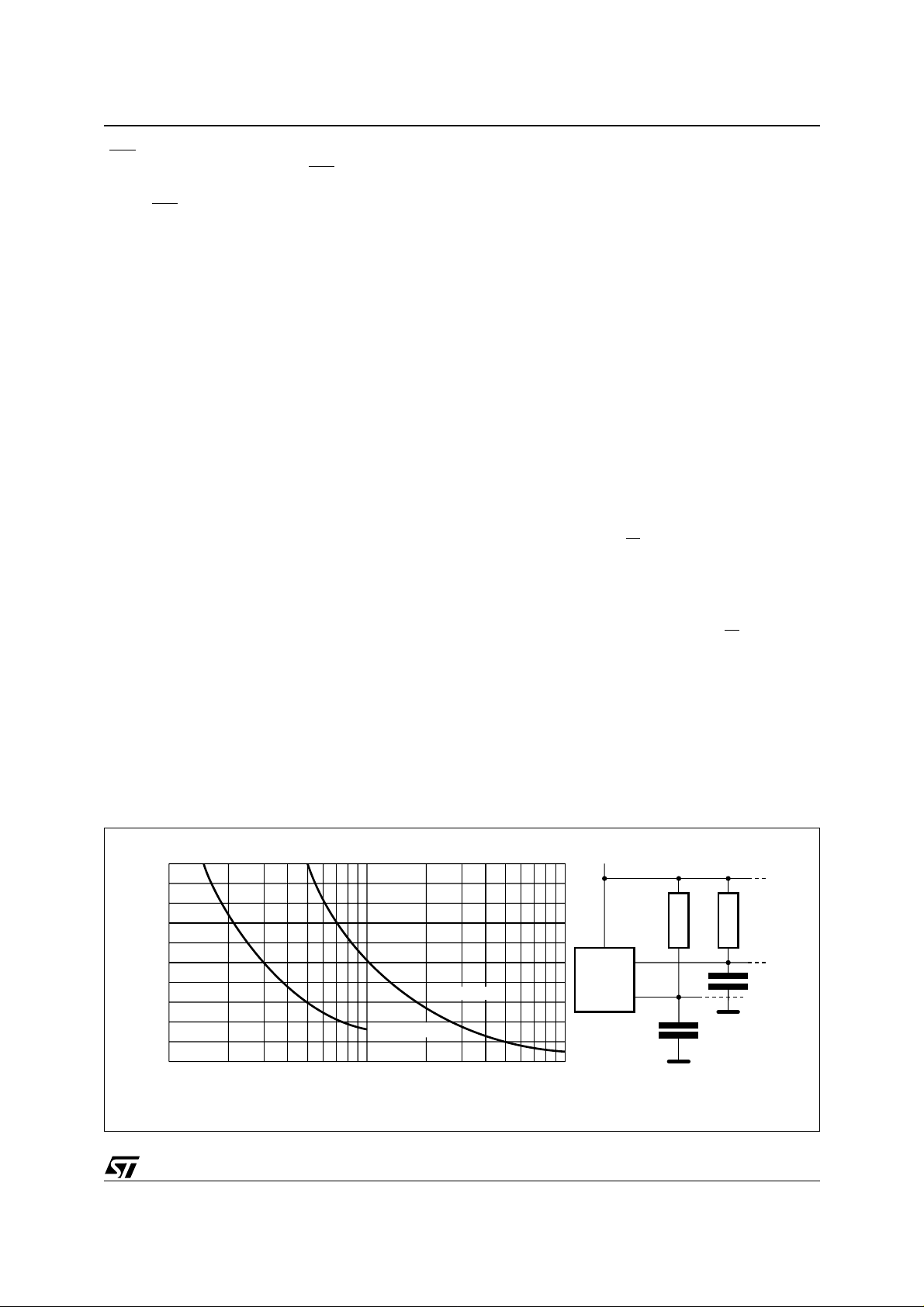
connected from the SCL line to VCC. (Figure 3 indicates how the value of the pull-up resistor can be
calculated).
C
Serial Data (SDA)
The SDA pin is bi-directional, and is used to transfer data in or out of the memory. It is an open drain
output that may be wire-OR’ed with other open
drain or open collector signals on the bus. A pull
up resistor must be connected from the SDA bus
to V
. (Figure 3 indicates how the value of the
CC
pull-up resistor can be calculated).
Write Control (WC
)
The hardware Write Control contact (WC
for protecting the entire contents o f the memory
from inadvertent erase/write. The Write Control
signal is used to enable (WC
=VIL) or disable
CC
) is useful
Table 2. Absolute Maximum Ratings
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
T
A
T
STG
V
IO
V
CC
V
ESD
Note: 1. Exc ept for the rating “Operating Temperature Range”, stresses above those l i sted in the Table “Absolute M aximum Ratings” m ay
2/13
cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and operation of the device at these or any other conditions
above those indi cated in t he Opera t in g sections of thi s specifi cation i s not imp l i ed. Exposu re to Ab solute Maxi m um Rati ng condi tions for extended periods may affect device reliability. Refer also to the ST SURE Program and other relevant quality documents.
2. MIL -STD-883C, 3015.7 (1 00 pF , 1500 Ω)
3. EIA J I C-121 (Condition C) (200 pF, 0 Ω)
Ambient Operating Temperature 0 to 70 °C
Storage Temperature
Input or Output range -0.6 to 6.5 V
Supply Voltage -0.3 to 6.5 V
Electrostatic Discharge Voltage (Human Body model)
Electrostatic Discharge Voltage (Machine model)
1
Wafer form
Module form
2
3
-65 to 150
-40 to 120
4000 V
400 V
°C
M14C16, M14C04
(WC=VIH) write instructions to the entire memory
area. When unconnected, the WC
ly read as V
When WC
and write operations are allowed.
IL
=1, Device Select and Address bytes
input is internal-
are acknowledged, Data bytes are not acknowledged.
Please see the Application Note
AN404
for a more
detailed description of the Write Control feature.
DEVICE OPERATION
2
The memory device supports the I
C protocol, as
summarized in Figure 4. Any device that sends
data on to the bus is defined to be a transmitte r,
and any device that reads the data to be a receiver. The device that controls the data transfer is
known as the mas ter, and the other a s the slave.
A data transfer can only be initiated by the master,
which will also provide the serial clock for synchronization. The memory device is always a slave device in all communication.
Start Condition
START is identified by a high t o low transition of
the SDA line while the clock, SCL, is s tab le in t he
high state. A START condition must precede any
data transfer comman d. Th e m em ory devi ce continuously monitors (except during a program ming
cycle) the SDA and SCL lines for a START condition, and will not respond unless one is given.
Stop Condition
STOP is identified by a low to high transition of the
SDA line while the clock SCL is stable in the high
state. A STOP condition terminates com munication between the memory device and the bus master. A STOP condition at the end of a Read
command, after (and only after) a NoAC K, forces
the memory device into its standby state. A STOP
condition at the end of a Write command triggers
the interna l EEPRO M write cycle.
Acknowledge Bit (ACK)
An acknowledge signal is used to indicate a successful data transfer. The bus transmitter, either
master or slave, will release the SDA bus after
sending 8 bits of data. During t he 9
th
clock pulse
period the receiver pulls the SDA bus low to acknowledge the receipt of the 8 data bits.
Data Input
During data input, the memory device samples the
SDA bus signal on the rising edge of the clock,
SCL. For correct device operation, the SDA signal
must be stable during the clock low-to-high transi-
only
tion, and the data must change
when the SCL
line is low.
Memory Addressing
To start communication betwee n the bus master
and the slave memory, the master must initiate a
START condition. Following this, the master sends
8 bits to the SDA bus line (with the most significant
bit first). These bits represent the Device Select
Code (7 bits) and a RW
bit.
The seven most s ignificant bits of the Device Select Code are the Device Type Identifier, according
to the I
2
C bus definition. For the mem ory device,
the seven bits are fixed as shown in Table 3.
th
The 8
bit is the read or write bit (RW). This bit is
set to ‘1’ for read and ‘0’ for write operations. If a
match occurs on the Device Select Code, the corresponding memory gives an acknowledgment on
the SDA bus during the 9
th
bit time. If the memory
does not match the Device Select code, it will deselect itself from the bus, and go into stand-by
mode.
Figure 3. Maximum R
20
16
12
8
Maximum RP value (kΩ)
4
0
10 1000
Value versus Bus Capacitance (C
L
fc = 100kHz
fc = 400kHz
100
C
(pF)
BUS
) for an I2C Bus
BUS
V
MASTER
CC
SDA
SCL
R
R
C
BUS
L
C
BUS
AI01665
3/13
L

M14C16, M14C04
Figure 4. I
2
C Bus Protocol
SCL
SDA
CONDITION
SCL
SDA
START
CONDITION
SCL
START
1 23 789
MSB
1 23 789
SDA
INPUT
SDA
CHANGE
STOP
CONDITION
ACK
SDA
Write Operations
Following a START con dition the ma ster sends a
Device Select code with the RW
shown in Table 4. The memory acknowledges it
and waits for a byte address, which provides access to the memory area. After receipt of the address, the memory again responds with an
MSB ACK
in the memory may be inhibited if input pin WC
taken high.
bit set to ’0’, as
Any write command with WC
time from the START condition until the end of the
address) will not modify the memory content and
will NOT be acknowledged on data bytes, as
shown in Figure 5.
STOP
CONDITION
AI00792
is
=1 (during a period of
acknowledge and waits for t he data byte. Writing
Table 3. Device Select Code
b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
M14C16 Select 1010A10A9A8RW
M14C04 Select 101000A8RW
Note: 1. A10, A9 and A8 correspond to th e m ost signifi cant bits of the memory array address word.
1
Device Code Chip Enable RW
4/13
 Loading...
Loading...