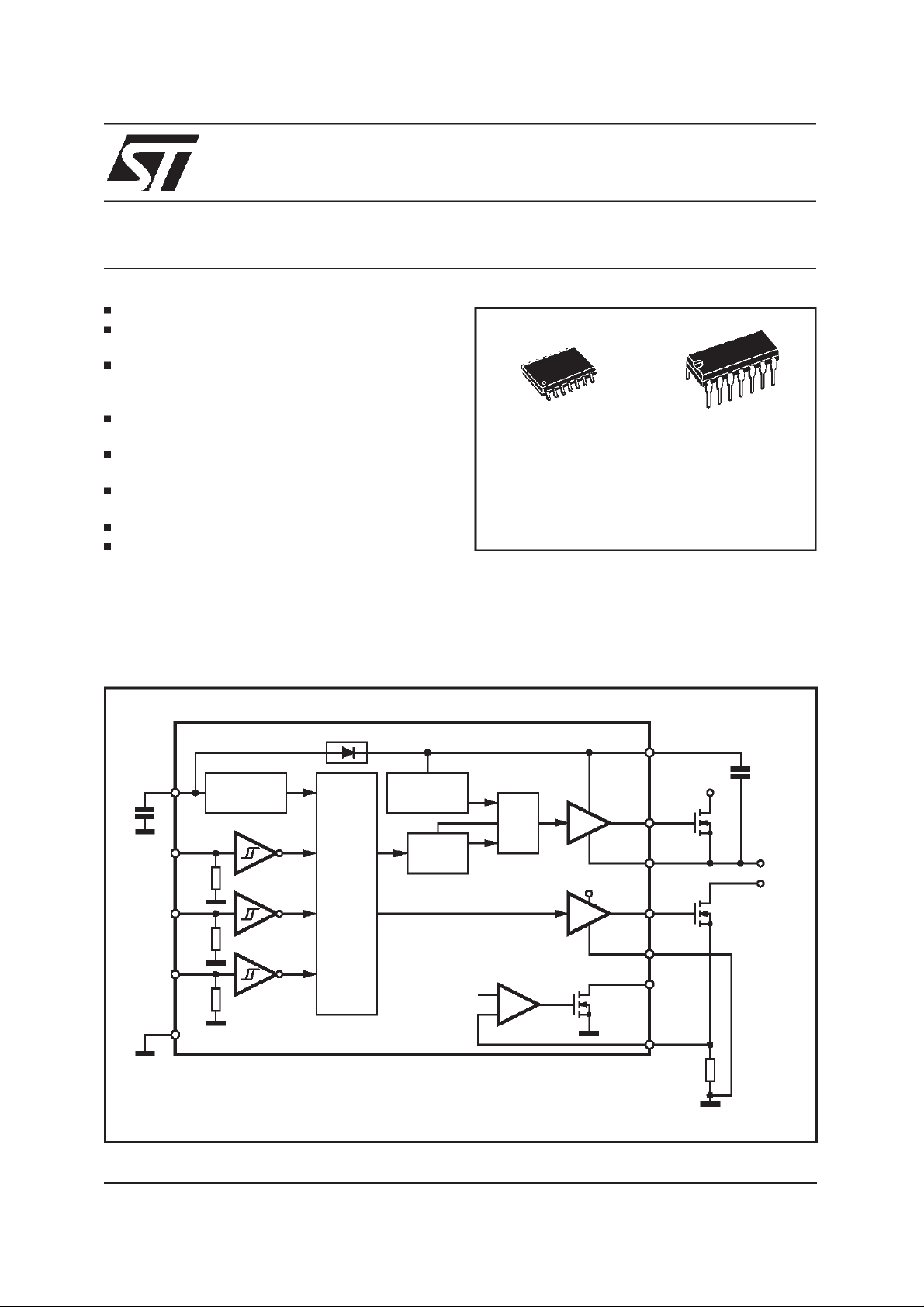
HIGH-VOLTAGE HIGH AND LOW SIDE DRIVER
HIGHVOLTAGERAIL UP TO 600V
dV/dt IMMUNITY +- 50 V/nsec iN FULL TEM-
PERATURERANGE
DRIVER CURRENTCAPABILITY:
400 mASOURCE,
650 mASINK
SWITCHING TIMES 50/30 nsec RISE/FALL
WITH 1nF LOAD
CMOS/TTL SCHMITT TRIGGER INPUTS
WITH HYSTERESISANDPULL DOWN
UNDER VOLTAGE LOCK OUT ON LOWER
AND UPPERDRIVING SECTION
INTEGRATEDBOOTSTRAPDIODE
OUTPUTSIN PHASEWITH INPUTS
DESCRIPTION
The L6386 is an high-voltage device, manufactured with theBCD ”OFF-LINE”technology. It has
a Driver structure that enables to drive inde-
L6386
SO14 DIP14
ORDERING NUMBERS:
L6386D L6386
pendent referenced Channel Power MOS or
IGBT. The Upper (Floating) Section is enabled to
work with voltage Rail up to 600V. The Logic Inputs are CMOS/TTL compatible for ease of interfacing with controlling devices.
BLOCK DIAGRAM
V
CC
DETECTION
4
3
HIN
2
SD
1
LIN
SGND
7 6
UV
BOOTSTRAP DRIVER
LOGIC
UV
DETECTION
LEVEL
SHIFTER
VREF
R
R
S
-
+
LVG
DRIVER
DRIVER
V
CC
D97IN520D
HVG
14
13
12
Vboot
C
H.V.
HVG
OUT
LVG
9
PGND
8
DIAG
5
CIN
BOOT
TO LOAD
July 1999
1/10
L6386
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
Vout Output Voltage -3 toVboot - 18 V
Vcc Supply Voltage - 0.3 to +18 V
Vboot Floating Supply Voltage -1 to 618 V
Vhvg Upper Gate Output Voltage - 1 to Vboot V
Vlvg Lower Gate Output Voltage -0.3 toVcc +0.3 V
Vi Logic Input Voltage -0.3 toVcc +0.3 V
Vdiag Open Drain Forced Voltage -0.3 to Vcc +0.3 V
Vcin Comparator InputVoltage -0.3 toVcc +0.3 V
dVout/dt Allowed Output Slew Rate 50 V/ns
Ptot Total Power Dissipation (Tj = 85 °C) 750 mW
Tj Junction Temperature 150 °C
Ts Storage Temperature -50 to 150 °C
Note:
ESD immunity for pins 12, 13 and 14 is guaranteed up to900V (Human Body Model)
PIN CONNECTION
LIN
SD
HIN
V
DIAG
CIN
SGND
1
2
3
4
CC
5
6
7 PGND
D97IN521A
14
V
boot
13
HVG
12
OUT
11
N.C.
10
N.C.
9
LVG
8
THERMAL DATA
Symbol Parameter SO14 DIP14 Unit
R
th j-amb
Thermal ResistanceJunction to Ambient 165 100 °C/W
PIN DESCRIPTION
N. Name Type Function
1 LIN I Lower Driver Logic Input
2 SD (*) I Shut Down Logic Input
3 HIN I UpperDriver Logic Input
4 VCC I Low Voltage Supply
5 DIAG O Open Drain Diagnostic Output
6 CIN I Comparator Input
7 SGND Ground
8 PGND Power Ground
9 LVG (*) O LowSide Driver Output
10, 11 N.C. NotConnected
12 OUT O Upper Driver Floating Driver
13 HVG (*) O HighSide Driver Output
14 Vboot BootstrappedSupply Voltage
(*) The circuit guarantees 0.3V maximum on the pin (@ Isink = 10mA),with VCC >3V.This allows toomit the ”bleeder” resistor connected
betweenthegate and the source of the externalMOSFET normally used to hold the pin low; the gate driver assures low impedance also
in SD condition.
2/10
L6386
RECOMMENDED OPERATINGCONDITIONS
Symbol Pin Parameter Test Condition Min. Typ. Max. Unit
Vout 12 Output Voltage Note1 580 V
Vboot-
Vout
fsw Switching Frequency HVG,LVGloadCL= 1nF 400 kHz
Vcc 4 Supply Voltage 17 V
T
Note 1:
ELECTRICALCHARACTERISTICS
AC Operation(Vcc = 15V; Tj = 25°C)
Symbol Pin Parameter Test Condition Min. Typ. Max. Unit
ton 1.3
toff High/Low SideDriver Turn-Off
tsd 2 vs
tr 13,9 Rise Time CL = 1000pF 50 ns
tf 13,9 Fall Time CL = 1000pF 30 ns
DC Operation(Vcc = 15V; Tj = 25°C)
14 Floating Supply Voltage Note1 17 V
j
if the condition Vboot - Vout < 18V is guaranteed,Vout can range from -3 to580V.
Junction Temperature -45 125 °C
High/Low SideDriver Turn-On
Propagation Delay
vs 9,
13
Vout = 0V 110 150 ns
Vout = 0V 105 150 ns
Propagation Delay
Shut Down to High/Low Side
9,13
Propagation Delay
Vout = 0V 105 150 ns
Symbol Pin Parameter Test Condition Min. Typ. Max. Unit
Low Supply Voltage Section
Vcc 4 Supply Voltage 17 V
Vccth1 Vcc UV Turn On Threshold 11.5 12 12.5 V
Vccth2 Vcc UV Turn Off Threshold 9.5 10 10.5 V
Vcchys Vcc UV Hysteresis 2 V
Iqccu UndervoltageQuiescentSupplyCurrent Vcc ≤ 11V 200 µA
Iqcc Quiescent Current Vcc = 15V 250 320 µA
Bootstrapped Supply Section
Vboot 14 Bootstrapped Supply Voltage 17 V
Vbth1 Vboot UV TurnOn Threshold 10.7 11.9 12.9 V
Vbth2 Vboot UV TurnOff Threshold 8.8 9.9 10.7 V
Vbhys Vboot UV Hysteresis 2 V
Iqboot Vboot QuiescentCurrent Vout = Vboot 200
Ilk Leakage Current Vout = Vboot = 600V 10 µA
Rdson Bootstrap Driver on Resistance (*) Vcc≥12.5V;Vin = 0V 125
Driving Buffers Section
Iso 9, 13 High/Low SideDriver Short Circuit
VIN = Vih (tp < 10µs) 300 400 mA
Source Current
Isi High/Low SideDriver Short Circuit
500 650 mA
Sink Current
Logic Inputs
Vil 1,2,3 Low Level Logic Threshold Voltage 1.5 V
Vih High LevelLogic Threshold Voltage 3.6 V
Iih High LevelLogic Input Current VIN = 15V 50 70
Iil Low LevelLogic Input Current VIN = 0V 1 µA
−(V
(*)
R
where I
is tested in thefollowing way: R
DSON
ispin 8 current whenV
1
(V
=
DSON
I
CBOOT=VCBOOT1,I2
CC−VCBOOT1)
1(VCC,VCBOOT1
whenV
CBOOT=VCBOOT2
− V
CC
)−I2(VCC,V
CBOOT2
CBOOT2
.
)
)
A
µ
Ω
A
µ
3/10

L6386
DC OPERATION(continued)
Symbol Pin Parameter Test Condition Min. Typ. Max. Unit
Sense Comparator
Vio Input OffsetVoltage -10 10 mV
Iio 6 Input Bias Current Vcin ≥ 0.5 0.2 µA
Vol 2 Open Drain Low Level Output
Voltage, Iod = -2.5mA
Vref Comparator Reference voltage 0.460 0.5 0.540 V
Figure 1. TimingWaveforms
HIN
LIN
SD
HOUT
LOUT
0.8 V
V
REF
V
CIN
DIAG
Note: SD active condition is latched until next negative IN edge.
Figure 2. TypicalRise and Fall Times vs.
Load Capacitance
time
(nsec)
250
200
150
100
50
D99IN1054
Tr
Tf
D97IN522A
Figure 3. QuiescentCurrent vs. Supply
Voltage
Iq
(µA)
4
10
3
10
2
10
D99IN1057
0
0 1 2 3 4 5 C (nF)
For both high and low side buffers @25°C Tamb
4/10
10
0 2 4 6 8 10121416VS(V)

L6386
BOOTSTRAPDRIVER
A bootstrap circuitryis needed to supply the high
voltage section. This function is normally accomplished by a high voltage fast recovery diode (fig.
4a). In the L6386 a patented integrated structure
replaces the external diode. It is realized by a
high voltage DMOS, driven synchronously with
the low side driver (LVG), with in series a diode,
as shownin fig. 4b
An internal charge pump (fig. 4b) provides the
DMOS driving voltage .
The diode connected in series to the DMOS has
been added to avoid undesirable turn on of it.
CBOOT selection and charging
To choose the proper C
BOOT
:
value the external
MOS can be seen as an equivalent capacitor.
This capacitor C
is related to the MOS total
EXT
gate charge :
Q
gate
=
C
EXT
V
gate
The ratio betweenthecapacitorsC
EXT
andC
BOOT
is proportionalto the cyclicalvoltage loss .
It has to be:
C
>>>C
BOOT
EXT
supply 1µCtoC
. This charge on a 1µFca-
EXT
pacitormeans a voltagedrop of 1V.
The internal bootstrap driver gives great advantages: the external fast recovery diode can be
avoided (it usually has great leakage current).
This structure can work only if V
OUT
is close to
GND (or lower) and in the meanwhile the LVG is
on. The charging time (T
charge
) of the C
BOOT
the time in whichboth conditions are fulfilledand
it has to be long enough to chargethe capacitor.
The bootstrap driver introduces a voltage drop
due to the DMOS R
(typical value: 125
DSON
Ohm). At low frequency this drop can be neglected. Anyway increasing the frequency it
must be taken in to account.
The following equation is useful to compute the
drop on the bootstrap DMOS:
Q
= I
V
drop
chargeRdson
where Q
power MOS, R
is the gate charge of the external
gate
is the on resistance of the
dson
bootstrap DMOS, and T
→V
charge
drop
gate
=
T
charge
R
dson
is the chargingtime
of the bootstrapcapacitor.
For example: using a power MOS with a total
gate charge of 30nC the drop on the bootstrap
DMOSis about1V, if the T
charge
is 5µs. In fact:
is
e.g.: if Q
3nF. With C
is 30nC and V
gate
BOOT
is 10V, C
gate
EXT
= 100nF the drop would be
300mV.
If HVG has to be supplied for a long time, the
C
selectionhas to take into account also the
BOOT
leakage losses.
e.g.: HVG steady state consumptionis lower than
200µA, so if HVG T
is 5ms, C
ON
BOOT
has to
Figure 4. Bootstrap Driver.
D
BOOT
V
S
HVG
LVG
ab
V
V
BOOT
OUT
H.V.
C
BOOT
TO LOAD
is
V
age drop on C
V
has to be taken into account when the volt-
drop
drop
30nC
=
BOOT
⋅
125Ω~0.8V
5µs
is calculated: if this drop is
too high, or the circuit topology doesn’t allow a
sufficient charging time, an external diode can be
used.
V
V
S
HVG
LVG
BOOT
H.V.
V
OUT
C
BOOT
TO LOAD
D99IN1056
5/10

L6386
Figure 5. Turn On Time vs. Temperature
250
@ Vcc = 15V
200
150
Typ.
100
Ton(ns)
50
0
-45 -25 0 25 50 75 100 125
Tj (°C)
Figure 6. Turn Off Time vs. Temperature
250
@ Vcc= 15V
200
150
Typ.
100
Toff(ns)
50
0
-45 -25 0 25 50 75 100 125
Tj (°C)
Figure 8. V
UV TurnOn Thresholdvs.
BOOT
Temperature
15
14
13
Typ.
12
11
10
Vbth1 (V)
9
8
7
-45 -25 0 25 50 75 100 125
Tj (°C)
Figure 9. V
UV TurnOff Thresholdvs.
BOOT
@ Vcc = 15V
Temperature
15
14
13
12
11
Typ.
10
Vbth2 (V)
9
8
7
-45 -25 0 25 50 75 100 125
Tj (°C)
@ Vcc = 15V
Figure 7. Shutdown Time vs. Temperature
250
@ Vcc = 15V
200
150
Typ.
100
tsd (ns0
50
0
-45-250 255075100125
Tj (°C)
6/10
Figure 10. V
3
UV Hysteresis
BOOT
@ Vcc = 15V
2.5
Typ.
2
Vbhys (V)
1.5
1
-45 -25 0 25 50 75 100 125
Tj (°C)

L6386
Figure 11. Vcc UV Turn On Thresholdvs. Tem-
perature
15
14
13
Typ.
12
Vccth1(V)
11
10
9
-45 -25 0 25 50 75 100 125
Tj (°C)
Figure 12. Vcc UV Turn Off Thresholdvs.
Temperature
12
11
Figure 14. Output SourceCurrent vs. Tem-
perature
1000
@ Vcc = 15V
800
600
Typ.
400
current (mA)
200
0
-45 -25 0 25 50 75 100 125
Tj(°C)
Figure 15. Output SinkCurrent vs. Tempera-
ture
1000
@ Vcc =15V
800
Typ.
10
Typ.
9
Vccth2(V)
8
7
-45 -25 0 25 50 75 100 125
Tj (°C)
Figure 13. Vcc UV Hysteresisvs. Tempera-
ture
3
2.5
Typ.
2
Vcchys (V)
1.5
600
400
current (mA)
200
0
-45 -25 0 25 50 75 100 125
Tj (°C)
1
-45 -25 0 25 50 75 100 125
Tj (°C)
7/10

L6386
DIM.
MIN. TYP. MAX. MIN. TYP. MAX.
a1 0.51 0.020
B 1.39 1.65 0.055 0.065
b 0.5 0.020
b1 0.25 0.010
D 20 0.787
E 8.5 0.335
e 2.54 0.100
e3 15.24 0.600
F 7.1 0.280
I 5.1 0.201
L 3.3 0.130
Z 1.27 2.54 0.050 0.100
mm inch
OUTLINE AND
MECHANICAL DATA
DIP14
8/10

L6386
DIM.
MIN.. TYP. MAX.. MIN.. TYP.. MAX..
A 1.75 0.069
a1 0.1 0.25 0.004 0.009
a2 1.6 0.063
b 0.35 0.46 0.014 0.018
b1 0.19 0.25 0.007 0.010
C 0.5 0.020
c1 45°(typ.)
D (1) 8.55 8.75 0.336 0.344
E 5.8 6.2 0.228 0.244
e 1.27 0.050
e3 7.62 0.300
F (1) 3.8 4 0.150 0.157
G 4.6 5.3 0.181 0.209
L 0.4 1.27 0.016 0.050
M 0.68 0.027
S8°
(1) D and F donot include mold flash or protrusions. Mold flash or
potrusions shall not exceed 0.15mm (.006inch).
mm inch
(max. )
OUTLINE AND
MECHANICAL DATA
SO14
9/10

L6386
Information furnished is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, STMicroelectronics assumes no responsibility for the consequences
of use of such information nor for any infringement of patents or other rights of third parties which may result from its use. No license is
granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of STMicroelectronics. Specification mentioned in this publication are
subject to change without notice. This publication supersedes and replaces all information previously supplied. STMicroelectronics products
are not authorized for use as critical components in life support devices or systems without express written approval of STMicroelectronics.
The ST logo is a registeredtrademark of STMicroelectronics
1999 STMicroelectronics – Printed in Italy – All Rights Reserved
STMicroelectronics GROUP OFCOMPANIES
Australia - Brazil - China- Finland - France - Germany - Hong Kong - India - Italy - Japan - Malaysia - Malta - Morocco -
Singapore - Spain - Sweden - Switzerland - UnitedKingdom - U.S.A.
http://www.st.com
10/10
 Loading...
Loading...