SGS Thomson Microelectronics BYW29FP-200 Datasheet
®
HIGH EFFICIENCY FAST RECOVERY DIODES
MAIN PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS
BYW29/F/FP/G-200
I
F(AV)
V
RRM
8A
200 V
trr (max) 25 ns
V
(max) 0.85 V
F
FEATURES AND BENEFITS
Very Low Forward Losses
■
Negligible switching losses
■
High surge current capability
■
Insulated packages (ISOWATT220AC,
■
TO-220FPAC):
Insulation voltage: 2000 VDC
Typical insulation capacitance = 12 pF
DESCRIPTION
Single rectifier suited for Switch Mode Power
Supply and high frequency DC to DC converters.
Packaged in TO-220AC, ISOWATT220AC,
TO-220FPAC and D
2
PAK, this device is intended
for use in high frequency inverters, free wheeling
and polarity protection applications.
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
AK
K
A
NC
2
D
PAK
BYW29G-200
K
TO-220AC
BYW29-200
TO-220FPAC
BYW29FP-200
A
ISOWATT220AC
BYW29F-200
A
K
A
K
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
V
RRM
I
F(RMS)
I
F(AV)
Repetitive peak reverse voltage 200 V
RMS forward current 16 A
Average forward current
δ = 0.5
D2PAK /
TO-220AC
ISOWATT220AC
Tc =120°C 8 A
Tc = 100°C
TO-220FPAC
I
FSM
Surge non repetitive forward current
(All pins connected)
tp=10ms
sinusoidal
80 A
Tstg Storage and junction temperature range - 65 to + 150 °C
Tj Maximum operating junction temperature + 150
May 2002 - Ed: 4B
1/7
BYW29/F/FP/G-200
THERMAL RESISTANCE
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
Rth (j-c) Junction to case thermal resistance TO-220AC
2.8 °C/W
D2PAK
ISOWATT220AC 5
TO-220FPAC 5.5
STATIC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Symbol Parameter Test Conditions Min. Typ. Max. Unit
* Reverse leakage current VR=V
I
R
V
F**
Pulse test : * tp = 5 ms, duty cycle<2%
To evaluate the conduction losses use the following equation :
P=0.65xI
Forward voltage drop IF=5A Tj= 125°C 0.85 V
** tp = 380 µs, duty cycle<2%
+ 0.040 I
F(AV)
F2(RMS)
RRM
=10A Tj= 125°C 1.05
I
F
=10A Tj=25°C 1.15
I
F
Tj= 25°C 10 µA
= 100°C 0.6 mA
T
j
RECOVERY CHARACTERISTICS
Symbol Parameter Test Conditions Min. Typ. Max. Unit
t
rr
Reverse recovery
time
Tj= 25°C IF= 0.5A
Irr = 0.25 A IR=1A
=25°CI
T
j
=1A
F
25 ns
35
dIF/dt = -50A/µsVR=30V
t
fr
Forward recovery
time
Tj=25°CI
=1A
F
dIF/dt = 100A/µs
15
VFR= 1.1xVFmax
V
FP
Peak forward
voltage
Tj=25°CIF=1A
dIF/dt = 100A/µs
2
ns
V
2/7
BYW29/F/FP/G-200
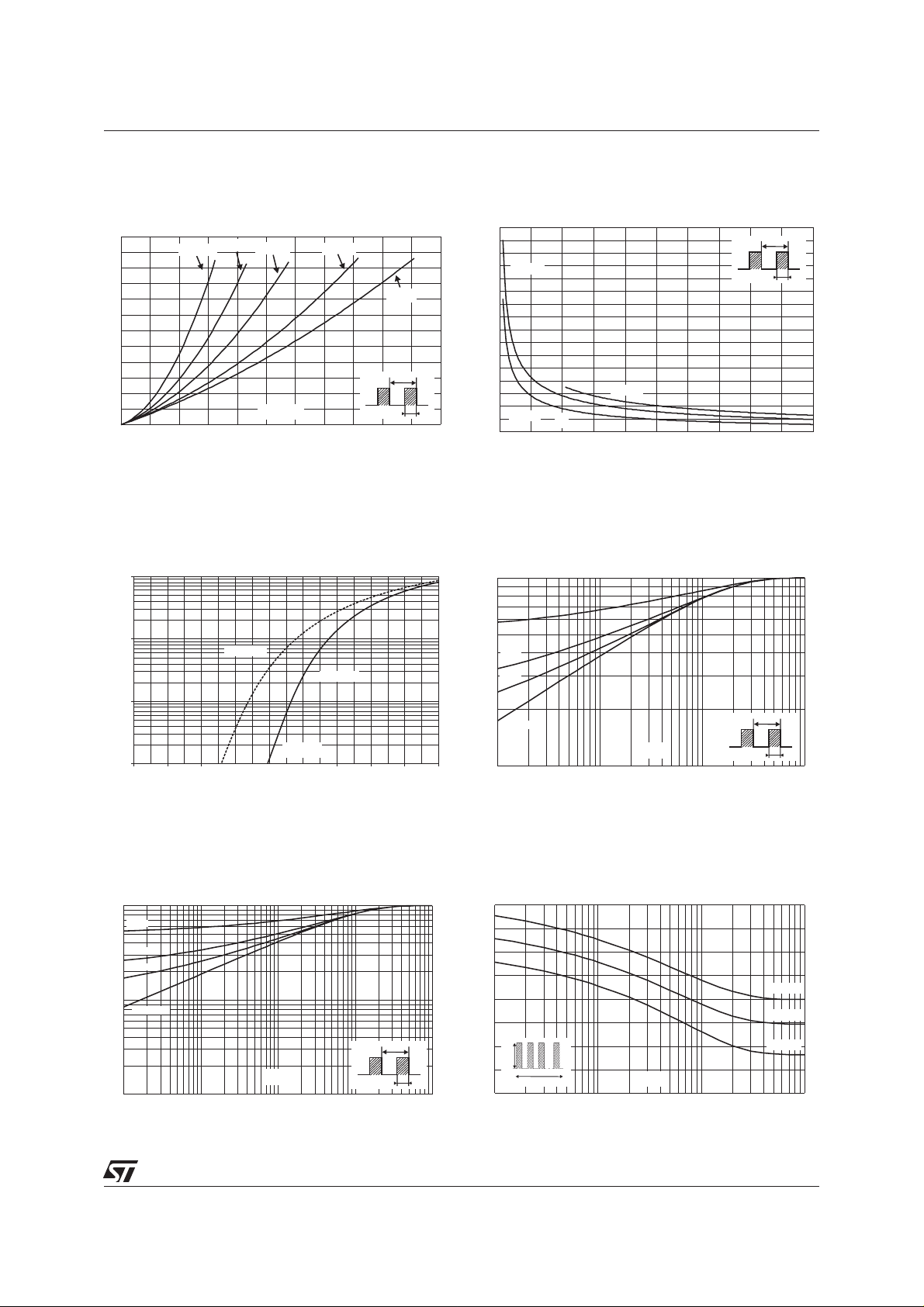
Fig.1 : Average forward power dissipation versus
average forward current.
PF(av)(W)
12
10
8
6
4
2
0
01234567891011
δ = 0.05
δ = 0.1
δ = 0.2
IF(av)(A)
δ = 0.5
δ
=tp/T
δ = 1
T
tp
Fig.3 : Forward voltage drop versus forward current (maximum values).
IFM(A)
100.0
Fig.2 : Peak current versus form factor.
IM(A)
160
140
P = 10W
120
100
80
60
40
20
P= 5W
0
0.0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1.0
δ
P = 15W
T
IM
δ
=tp/T
tp
Fig.4-1 : Relative variation of thermal impedance
junctiontocaseversus pulse duration (TO-220AC,
2
PAK).
D
Zth(j-c)/Rth(j-c)
1.0
δ = 0.5
10.0
1.0
Tj=125°C
Tj=25°C
VFM(V)
0.1
0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8
Fig.4-2 :Relative variation of thermal impedance
junction to case versus pulse duration
(TO-220FPAC, ISOWATT220AC).
Zth(j-c)/Rth(j-c)
1.0
δ = 0.5
δ = 0.2
δ = 0.1
0.1
Single pulse
T
tp(s)
0.0
1.E-03 1.E-02 1.E-01 1.E+00 1.E+01
δ
=tp/T
tp
δ = 0.2
δ = 0.1
δ
=tp/T
T
2
PAK).
Tc=120°C
tp
Tc=25°C
Tc=75°C
Single pulse
tp(s)
0.1
1.E-03 1.E-02 1.E-01 1.E+00
Fig.5-1 :Nonrepetitive surge peakforwardcurrent
versus overload duration (TO-220AC, D
IM(A)
80
70
60
50
40
30
20
IM
10
0
1.E-03 1.E-02 1.E-01 1.E+00
δ=0.5
t
t(s)
3/7
 Loading...
Loading...