Sennheiser HMEC 25-CA User Manual 2
Gebrauchsanleitung
Instructions for use
Notice d‘emploi
Istruzioni per l‘uso
Instrucciones para el uso
Gebruiksaanwijzing
HMEC 25-CA
P/N 025-230-125
HMEC 25-KA
P/N 025-230-115
™

Lärm - wo begegnet er uns nicht?
Ob am Arbeitsplatz, in der häuslichen Umgebung, in öffentlichen Verkehrsmitteln,
auf Flug-, Bahn- oder Busreisen - eigentlich begleitet er uns überall.
Die negativen Auswirkungen dieser Lärmbelästigungen sind durch Studien belegt
und auch jeder von uns wird sie schon gespürt haben:
왘 Nervosität
왘 Konzentrationsmangel
왘 Gereiztheit ...
sind nur die augenscheinlichen Auswirkungen auf den Organismus. Lärm wirkt
zudem auf das vegetative Nervensystem und kann zu Dauerschäden des Gehörs
führen.
Die Quellen des Lärms sind vielfältig und nur zu oft für den einzelnen nicht
abzustellen. Daher kann nur der persönliche Schutz an einem lärmerfüllten Ort
eine Lösung darstellen.
Gebrauchsanleitung ............................................................................................... 3
Instructions for use .............................................................................................. 11
Notice d´emploi .................................................................................................... 19
Istruzioni per l´uso ............................................................................................... 27
Instrucciones para el uso ..................................................................................... 35
Gebruiksaanwijzing .............................................................................................. 43
Mit dem System
NoiseGard
™
hat Sennheiser eine wirkungsvolle Lösung realisiert.
Das Funktionsprinzip und die Bedienung wird Ihnen in dieser Anleitung erläutert.
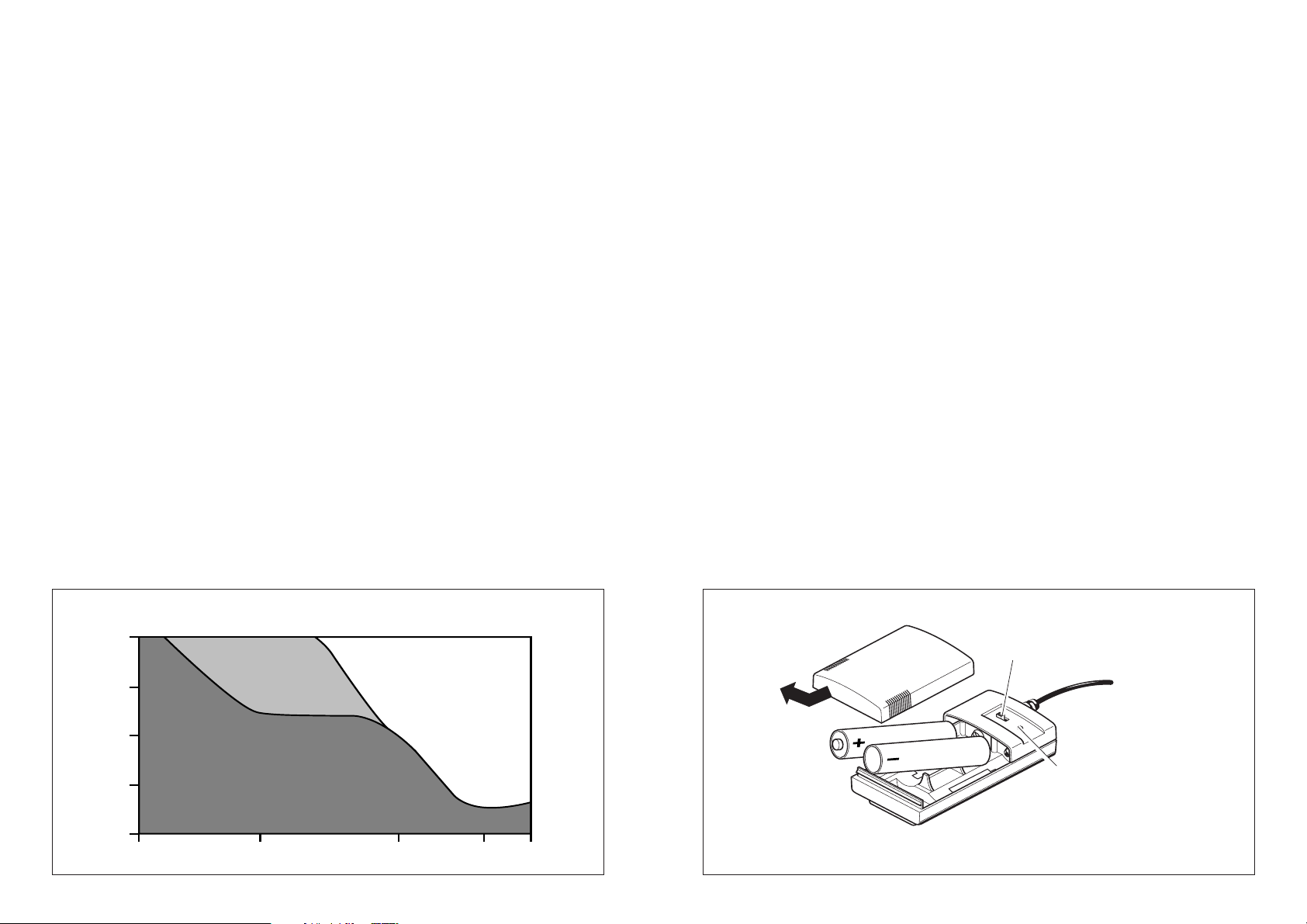
Schallpegel von Lärmquellen
140 dB Düsentriebwerk (25m Entfernung)
130 dB Flugzeugmotor
Laut
Leise
Die Maßeinheit für Schallpegel ist das Dezibel (dB). Eine Lärmdämpfung um 10 dB wird allgemein als Halbierung der Lautstärke empfunden, weitere 10 dB Dämpfung ergeben eine um 75%
reduzierte Lärmempfindung u.s.w.
120 dB Druckluftbohrer
110 dB Schmiedehammer, Betonwerk
100 dB Metalldruckgußmaschine
90 dB Metallwerkstatt
80 dB Traktor
70 dB Büro
60 dB Unterhaltung
50 dB Umweltlärm
40 dB Wohnraum
30 dB Bibliothek
20 dB Schlafzimmer
10 dB Wald, windstill
32
HMEC 25-CA / HMEC 25-KA
Eine Hör-/ Sprech-Garnitur faßt zwei Baugruppen, Kopfhörer und Mikrofon zu
einer Funktionseinheit zusammen. Überwiegender Einsatzbereich dieser Hör-/
Sprech-Garnituren HMEC 25-KA/-CA ist die Kommunikation im Flugzeugcockpit.
왘 Als Mikrofon wird ein hochwertiges dauerpolarisiertes Elektretmikofon
benutzt. Die notwendige Versorgungsspannung wird ( gemäß ARINC) über den
Anschlußstecker aus dem Bordnetz des Flugzeuges bezogen.
왘 Als Kopfhörer dienen Sennheiser
NoiseGard
™
-Systeme. Dies sind dynamische
Hörersysteme, bei denen, zusätzlich zur Wiedergabe eines Audiosignales, auf
elektronischem Weg tieffrequenter Störschall kompensiert wird. Die aktive
Lärmkompensation funktioniert nach dem physikalischen Prinzip, daß sich
Schall und "Antischall" (um 180° phasenverschoben) gegenseitig auslöschen.
Die
NoiseGard
™
-Kompensationselektronik im Kopfhörer benötigt eine
gesonderte eigene Stromversorgung, die das fest mit dem Kabel verbundene
Speiseteil (Siehe Abbildung rechts) liefert.
Einlegen der Batterien im Speiseteil
Die Kompensationselektronik
NoiseGard
™
wird durch eine Batteriebox im Kabel
der Hör-/ Sprech-Garnitur mit Strom versorgt. Legen Sie zwei Batterien in die
Batteriebox ein.
EIN- / Ausschalten
Der EIN/AUS-Schalter für die Stromversorgung der Kompensationselektronik
befindet sich an der Vorderseite der Batteriebox.
Kontroll-LED
Die LED auf der Batteriebox informiert Sie über den Batteriezustand:
왘 Leuchtet die LED grün, wird die Kompensationselektronik ausreichend mit
Strom versorgt.
Ungestörte Verständigung wird möglich, ohne die Lautstärke so laut einstellen
zu müssen, daß die Umweltgeräusche übertönt werden.
NoiseGard
™
erhöht den Komfort,
ist aber kein medizinischer Hörschutz !
Geräuschkompensation mit NoiseGard
™
Noise compensation HMEC 25
Reduction/dB
0
10
active
passive
20
30
40
20 100 1000 10000 20000
Frequency/Hz
왘 Leuchtet die LED rot, sind die Batterien fast erschöpft und müssen jetzt
getauscht werden. Noch ist NoiseGard
왘 Bleibt die LED nach dem Einschalten dunkel, sind die Batterien vollkommen
™
in Funktion.
erschöpft, die Hör-/ Sprech-Garnitur bleibt weiter einsatzbereit, aber ohne
Lärmkompensation.
Das Mikrofon ist durch die eigene Spannungsversorgung aus dem Bordnetz
des Flugzeuges unabhängig von den Batterien und bleibt immer in Funktion.
EIN/AUS
LED
54
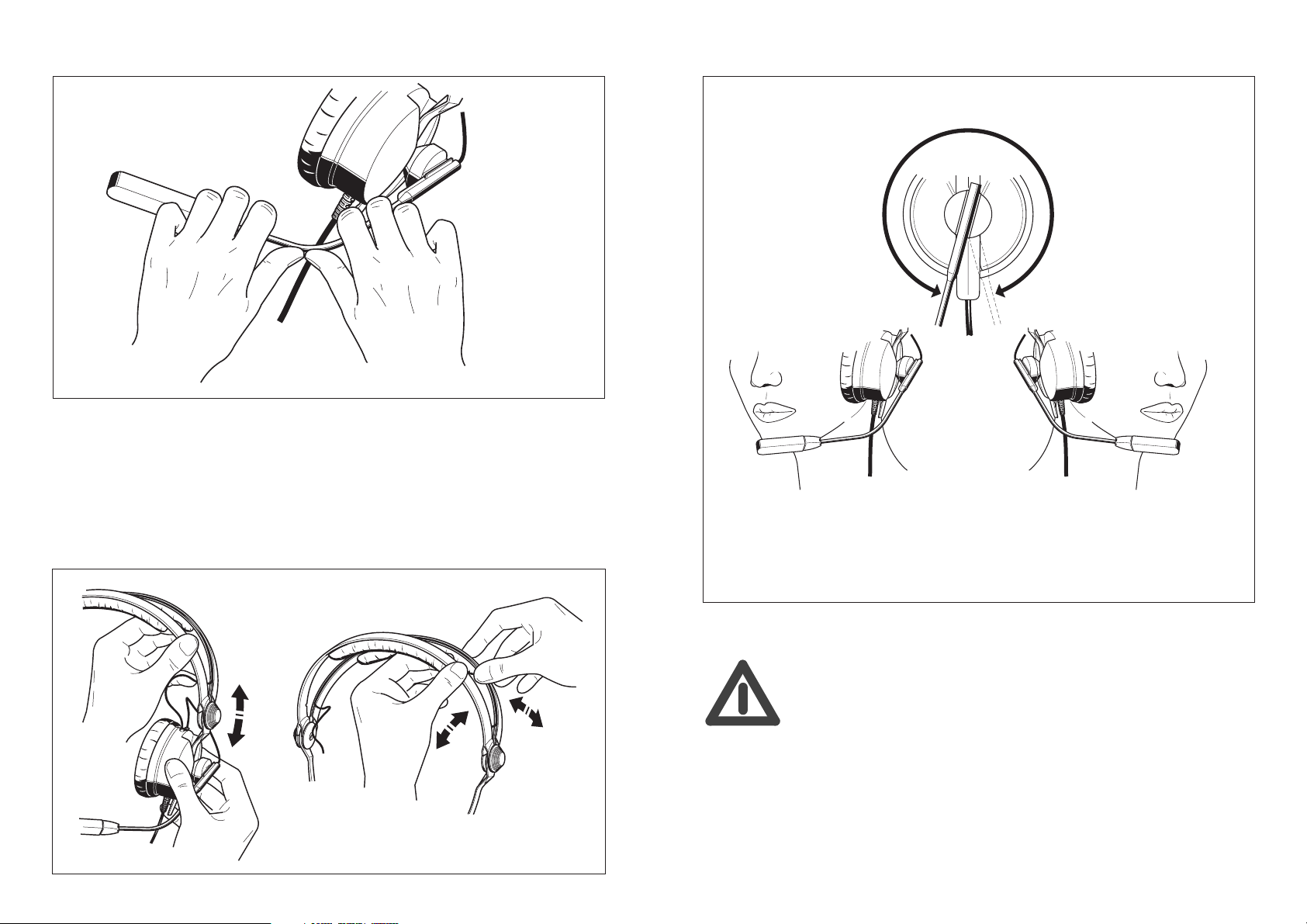
Mikrofonarm einstellen
Hinweis: Der Mikrofonarm kann durch Biegen individuell angepaßt werden.
Diese Einstellung sollte möglichst nicht ständig geändert werden, bei sehr häufigem
Hin- und Herbiegen kann der Arm brechen!
Kabel (rechts oder links)
350°
Kopfbügel einstellen
Kabel links
HINWEISE NoiseGard
Kabel rechts
™
dient der Geräuschverminde-
rung zur Erhöhung des Komforts.
NoiseGard™
ist kein medizinisches
Lärmschutzsystem!
NoiseGard™
ersetzt kein industrielles
Lärmschutzsystem zum Einsatz in
lärmerfüllter Umgebung!
Laut hören ? - NEIN !
Mit einem Kopfhörer wird gern lauter als mit Lautsprechern gehört. Hohe
Lautstärke, die über längere Zeit auf Ihre Ohren einwirkt, kann zu dauerhaften
Hörschäden führen. Schützen Sie Ihr gesundes Gehör, Sennheiser-Kopfhörer
klingen auch bei niedriger Lautstärke besonders gut ...
76
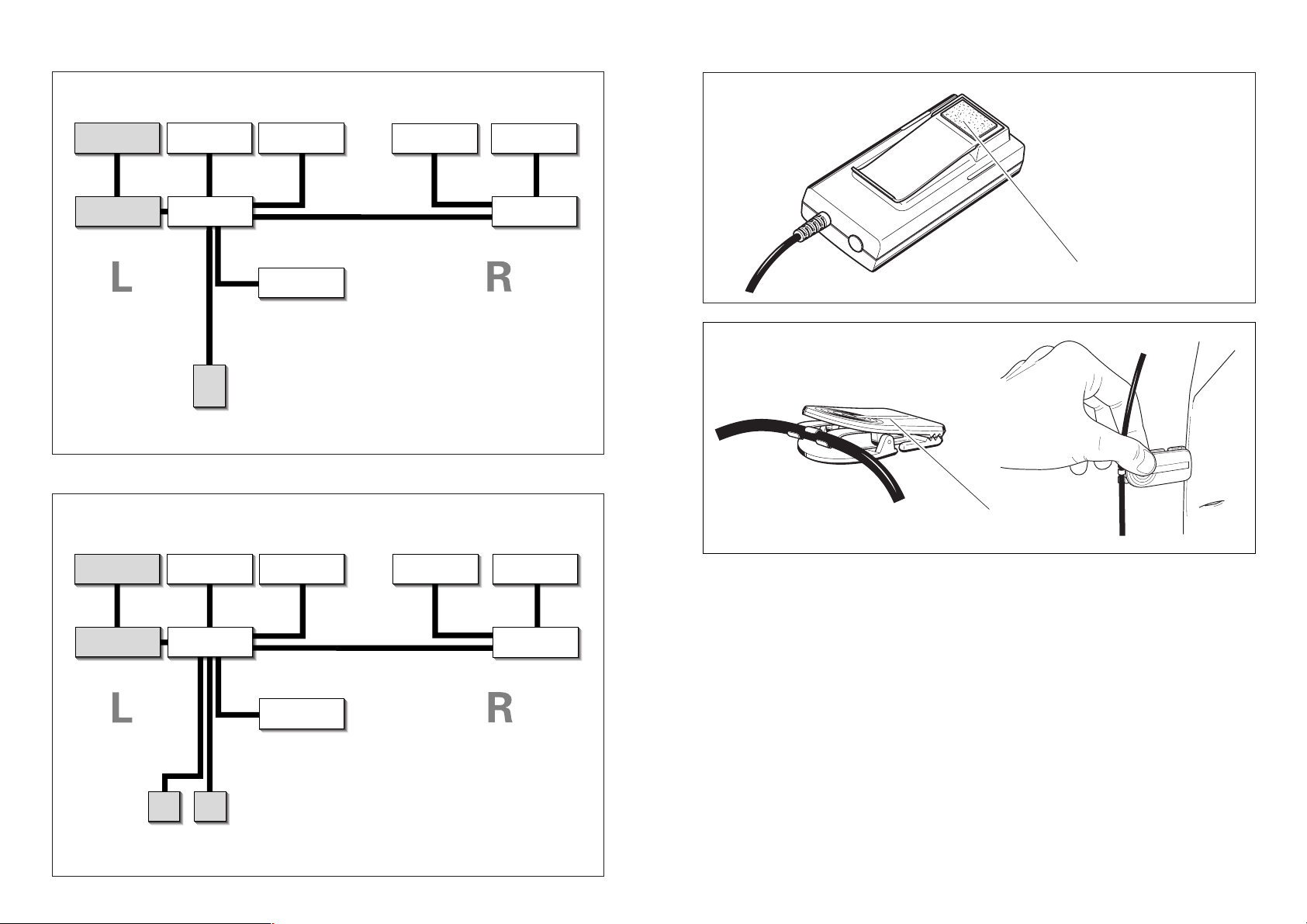
Blockschaltbild HMEC 25 CA
boom
microphone
microphone
amplifier
headphone
capsule (left)
compensation
circuit (left)
5-pin
XLR
plug
Blockschaltbild HMEC 25 KA
boom
microphone
headphone
capsule (left)
compensation
microphone (left)
battery
box
compensation
microphone (left)
compensation
microphone (right)
compensation
microphone (right)
headphone
capsule (right)
compensation
circuit (right)
headphone
capsule (right)
Klettband (selbstklebend)
MZQ 2002-1
Lieferumfang
microphone
amplifier
compensation
3-pin
plug
circuit (left)
3-pin
plug
battery
box
compensation
circuit (right)
1 HMEC 25-KA oder HMEC 25-CA
1 Schutz- und Transporttasche
1 Windschirm MZW 45 (Art.Nr. 75823)
1 Klettband (selbstklebend), Abb.
1 Klemmhalter MZQ 2002-1 (Art.Nr. 44740), Abb.
98

Technische Daten NoiseGard
™
HMEC 25-KA / -CA
The Problem of Noise
Kopfhörer
Wandlerprinzip dynamisch, geschlossen, ohraufliegend
Übertragungsbereich 16 Hz - 22 kHz
Impedanz aktiv/passive 200 Ohm (mono) 400 Ohm pro Seite (stereo)
Lautstärke aktiv und passiv gleich
Klirrfaktor < 1 %
Lärmdämpfung aktiv 15 dB
+ 3 dB im Bereich von 100 Hz - 2 kHz
Frequenzbereich der
aktiven Lärmdämpfung 50 - 600 Hz
Mikrofon incl. Vorverstärker
Wandlerprinzip Back-Elektret-Kondensatorkapsel,
geräuschkompensiert
Übertragungsbereich bei
einem Abstand von 2 cm 300 Hz - 5 kHz
zum Mundwinkel entsprechend DO-214
max. Schalldruckpegel 120 dB (Klirrfaktor 1 %)
Ausgangsspannung 400 mV ± 3 dB bei 114 dB aus 6 mm Abstand
(entsprechend DO-214)
Abschlußwiderstand 150 Ohm
Versorgungsspannung 8 - 16 V DC, ca 8 - 25 mA,
Beschaltung nach RTCA/DO 214
Allgemeine Daten
Kopfhörer-Andruckkraft ca 2,5 N
Gewicht ohne Kabel 170 g
Kabel einseitig, Länge gesamt: 1,8 m
Stecker HMEC25-KA: Stereo-Klinke 6,3 mm, mono beschaltet
PJ-068, 5,25 mm Mikrofon
HMEC25-CA: XLR-5
Stromversorgung 2 x 1,5 V Mignon (AA)
Alkali-Mangan Batterien (2700 mAh)
Betriebszeit ca. 20 h
Anzeige: Zweifarben-LED zur Batteriekontrolle
The negative effects of noise pollution have been proven by studies, and everybody
will have experienced them at some time or another:
왘 Nervousness
왘 Lack of concentration
왘 Irritability
And these are only the most obvious effects on the human body. Noise also affects
the autonomic nervous system and can lead to permanent hearing damage.
There are a multitude of noise sources, and the individual very often has no
influence over them. The only solution when being in a noisy place is protecting
oneself against ambient noise. These noise problems are particularly prevalent in
an aircraft cockpit where a pilot often has to have the communications headset so
loud as to risk permanent hearing damage.
With the
These operating instructions explain the NoiseGard
to use the
NoiseGard™ system, Sennheiser has come up with an effective solution.
NoiseGard
™
headset.
™
principle and show you how
Noise levels
140 dB Jet engine (at a distance of 25 m)
130 dB Aircraft engine (This is the treshold of pain)
loud
quiet
The unit of sound levels is the decibel (dB). A noise reduction of 10 dB is generally perceived as
a halving of the loudness, another 10 dB decrease halves the loudness yet again whitch corresponds to a loudness reduction of 75 %, and so on.
120 dB Pneumatic drill
110 dB Blacksmith's hammer, concrete works
100 dB Die-cast machine
90 dB Metal workshop
80 dB Tractor
70 dB Office
60 dB Conversation
50 dB Ambient noise
40 dB Living room
30 dB Library
20 dB Bedroom
10 dB Forest, no wind
1110
HMEC 25-KA / HMEC 25-CA
A headset is comprised of two units, a headphone and a microphone. The HMEC
25-KA/-CA headset is mostly used for communication in aircraft cockpits.
왘 The microphone is a high quality back-electret condenser microphone. As per
ARINC it receives its operating voltage via a connector from the aircraft´s
internal power supply.
왘 The headphone is a Sennheiser NoiseGard
™
system. This is a dynamic
headphone system which, in addition to reproducing the original audio signal,
electronically cancels the low frequencies of the ambient noise. This active
noise compensation operates on the principle that sound and ”anti-sound“ (in
phase opposition) cancel each other out. The
NoiseGard
™
compensation
circuitry in the headphone requires an extra power supply, so a battery compartment has been integrated into the headset cable (see illustration on the right).
Clearly intelligible communication is ensured, and the pilot no longer has to
turn the volume up to overcome ambient noise.
Inserting the batteries into the battery box
The
NoiseGard
™
compensation circuitry is powered via a battery pack integrated
into the headset cable. Insert two AA size batteries into the box as shown in the
digram below.
Switching the power supply on/off
The on/off switch for the power supply of the compensation circuitry is at the front
of the battery box.
Pilot light
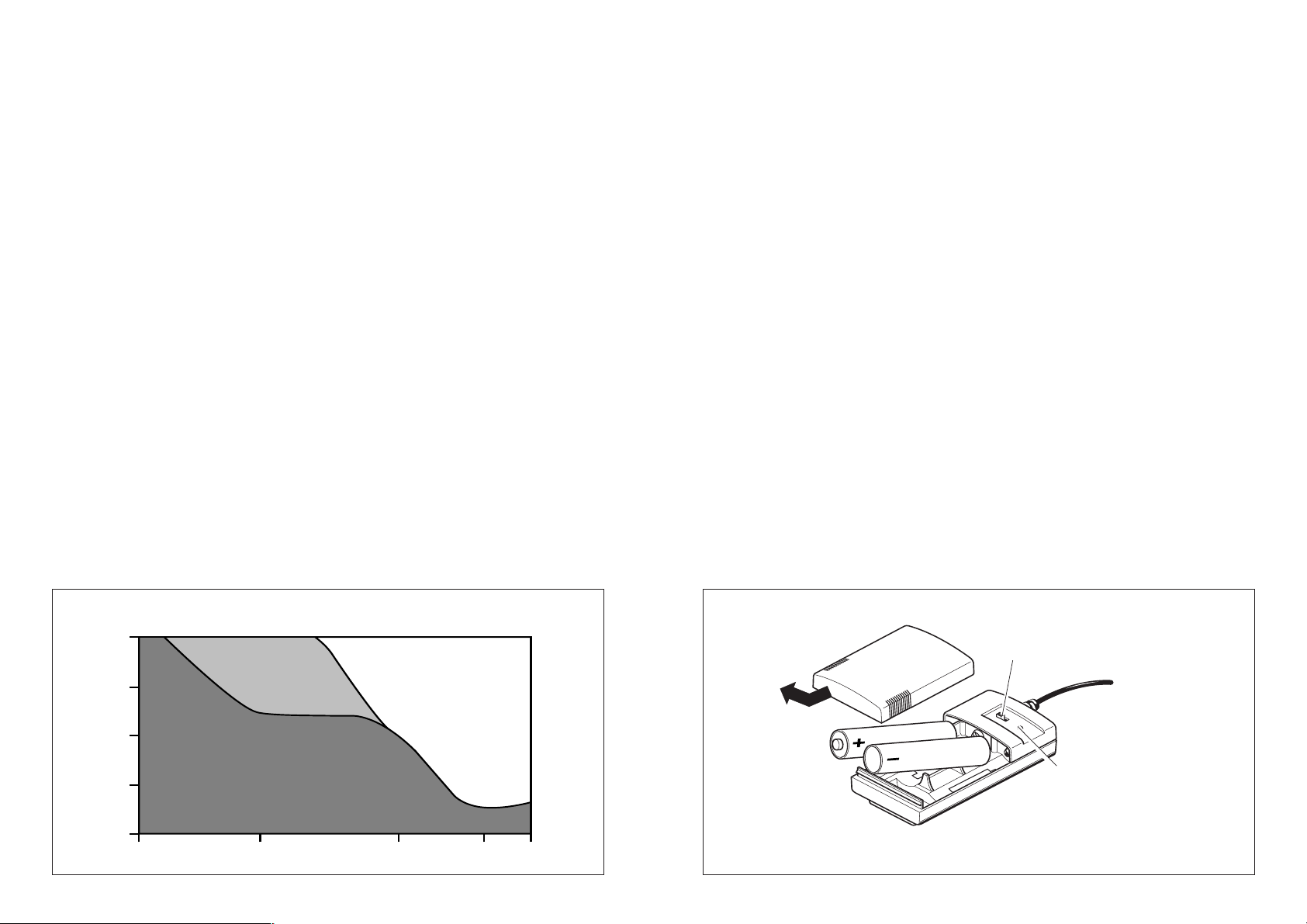
An LED on the battery box indicates the battery status:
왘 When the LED lights up green, the power supply for the compensation
circuitry is sufficient.
NoiseGard
™
increases your comfort,
but it is not a medical hearing protection!
Active noise compensation with NoiseGard
Noise compensation HMEC 25
Reduction/dB
0
10
20
30
40
20 100 1000 10000 20000
active
™
passive
Frequency/Hz
왘 When the LED is red, the batteries are almost flat and should be changed
immediately. The
왘 If the LED does not light up at all when the power supply is switched on, the
NoiseGard
™
system is still operational.
batteries are completely flat. The headset is still operational but without the
noise compensation.
The microphone is powered by the aircraft‘s internal power supply. Thus, it
is independent of the batteries and always remains operational.
ON/OFF
LED
1312
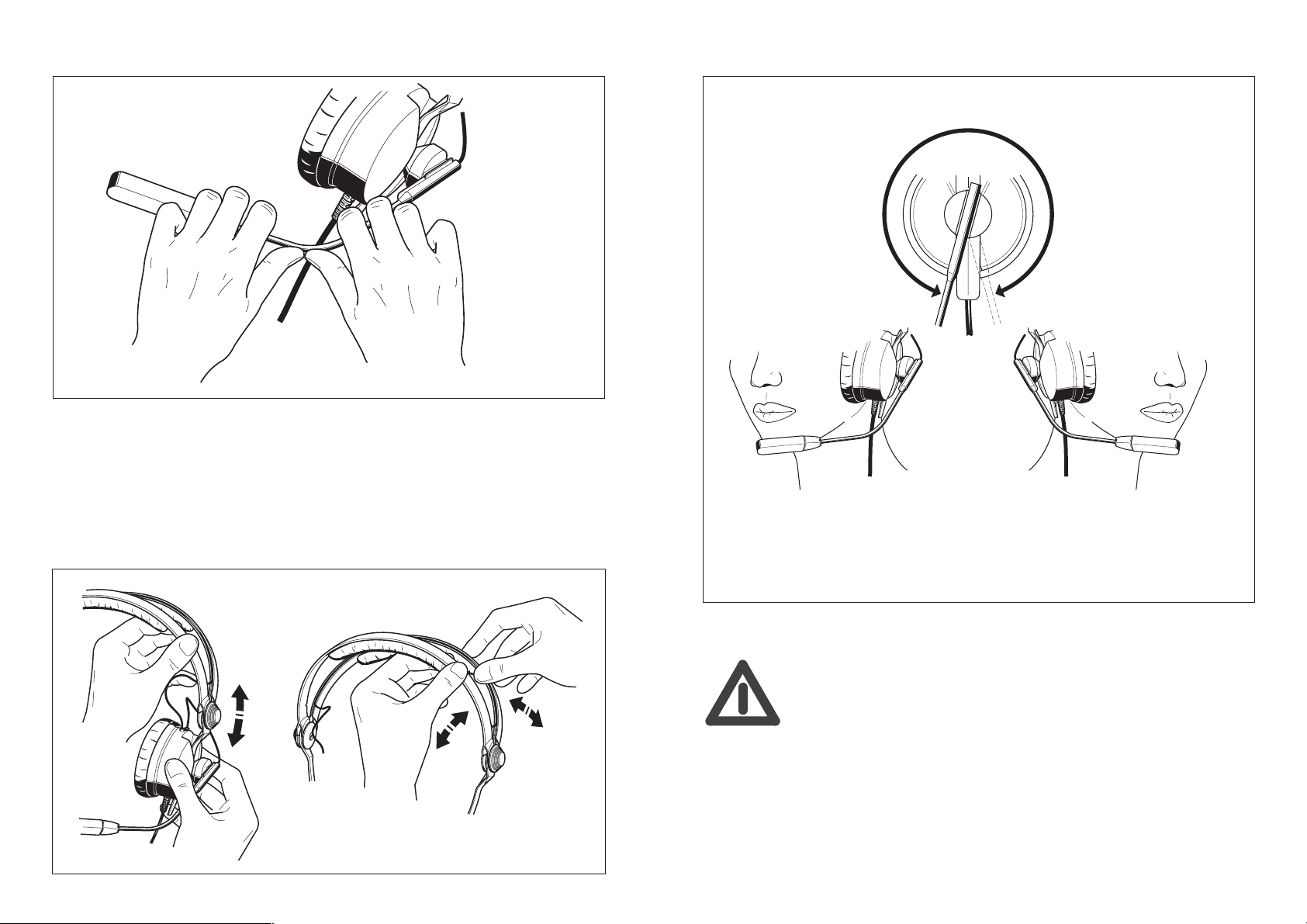
Adjusting the microphone boom
N.B.: The microphone boom is adjusted for an individual user. However, care
should be taken when doing this. Once set, the boom should not be re-adjusted.
If it is continually flexed it is liable to break.
Cable (worn on the right or left side)
350°
Adjusting the headband
N.B.:
Cable on the left
NoiseGard™
NoiseGard™
Cable on the right
reduces noise and increases comfort.
is not a medical noise protection
system!
NoiseGard™
cannot replace an industrial ear
defender system for use in noisy environments!
Volume up? - NO !
When people use headphones, they tend to choose a higher volume than with
loudspeakers. Listening with high volume levels for a longer time can lead to
permanent hearing defects. Because the
NoiseGard
™
circuitry is reducing the
ambient noise, the headphones can be set at a correspondingly lower level leading
to more comfortable hearing conditions so protecting your hearing.
1514
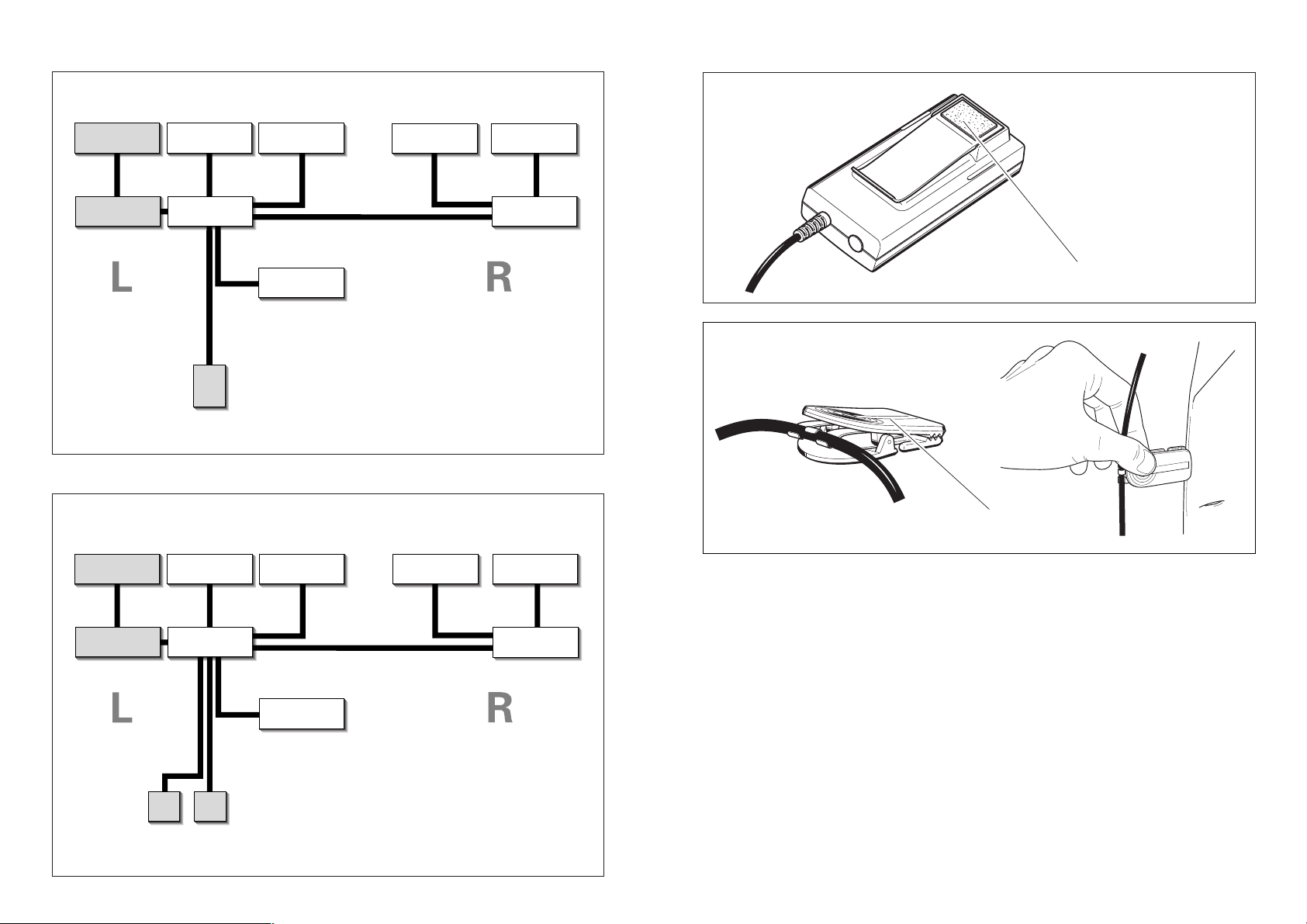
HMEC 25-CA Block Diagram
boom
microphone
microphone
amplifier
headphone
capsule (left)
compensation
circuit (left)
5-pin
XLR
plug
HMEC 25-KA Block Diagram
boom
microphone
microphone
amplifier
headphone
capsule (left)
compensation
circuit (left)
compensation
microphone (left)
battery
box
compensation
microphone (left)
compensation
microphone (right)
compensation
microphone (right)
headphone
capsule (right)
compensation
circuit (right)
headphone
capsule (right)
compensation
circuit (right)
self-adhesive piece of velcro
MZQ 2002-1
Supply schedule 1 HMEC 25-KA or HMEC 25-CA
1 Carrying case
1 wind-shield MZW 45 (Art.No 75823)
1 self-adhesive piece of velcro, fig.
1 MZQ 2002-1 clip (Art.No 44740), fig.
3-pin
plug
3-pin
plug
battery
box
1716
 Loading...
Loading...