Page 1

GEBRAUCHSANLEITUNG
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
NOTICE D‘EMPLOI
ISTRUZIONI PER L‘USO
INSTRUCCIONES PARA EL USO
GEBRUIKSAANWIJZING
HMEC 25-6A
025-230-765
HMEC 25-KAP-2
025-230-715
“
Page 2

Gebrauchsanleitung ............................................................................................... 3
Instructions for use .............................................................................................. 11
Notice d´emploi .................................................................................................... 19
Istruzioni per l´uso ............................................................................................... 27
Instrucciones para el uso ..................................................................................... 35
Gebruiksaanwijzing .............................................................................................. 43
Lärm - wo begegnet er uns nicht?
Ob am Arbeitsplatz, in der häuslichen Umgebung, in öffentlichen Verkehrsmitteln,
auf Flug-, Bahn- oder Busreisen - eigentlich begleitet er uns überall.
Die negativen Auswirkungen dieser Lärmbelästigungen sind durch Studien belegt
und auch jeder von uns wird sie schon gespürt haben:
왘 Nervosität
왘 Konzentrationsmangel
왘 Gereiztheit ...
sind nur die augenscheinlichen Auswirkungen auf den Organismus. Lärm wirkt
zudem auf das vegetative Nervensystem und kann zu Dauerschäden des Gehörs
führen.
Die Quellen des Lärms sind vielfältig und häufig für den einzelnen nicht abzustellen.
Daher kann nur der persönliche Schutz an einem lärmerfüllten Ort eine Lösung
darstellen.
Mit dem System NoiseGard™ hat Sennheiser eine wirkungsvolle Lösung realisiert.
Das Funktionsprinzip und die Bedienung wird Ihnen in dieser Anleitung erläutert.
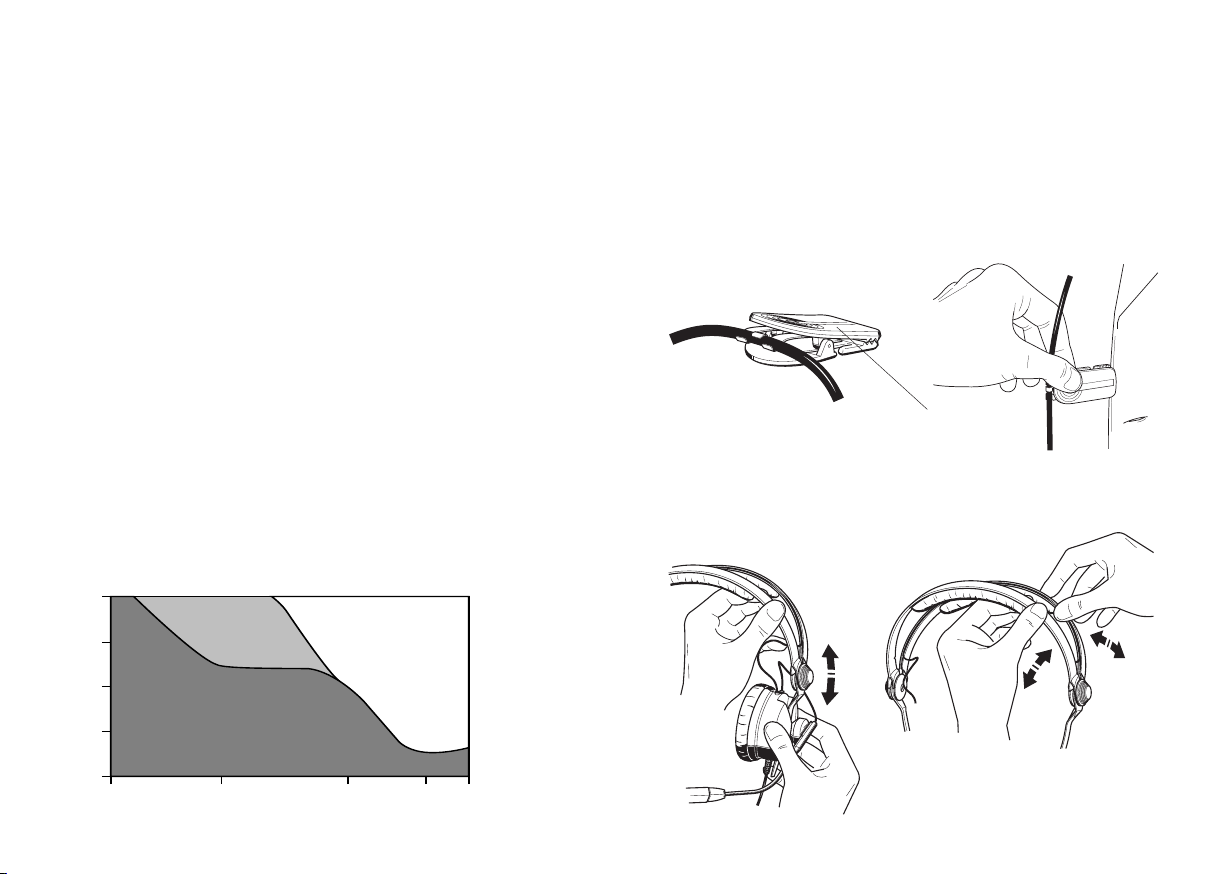
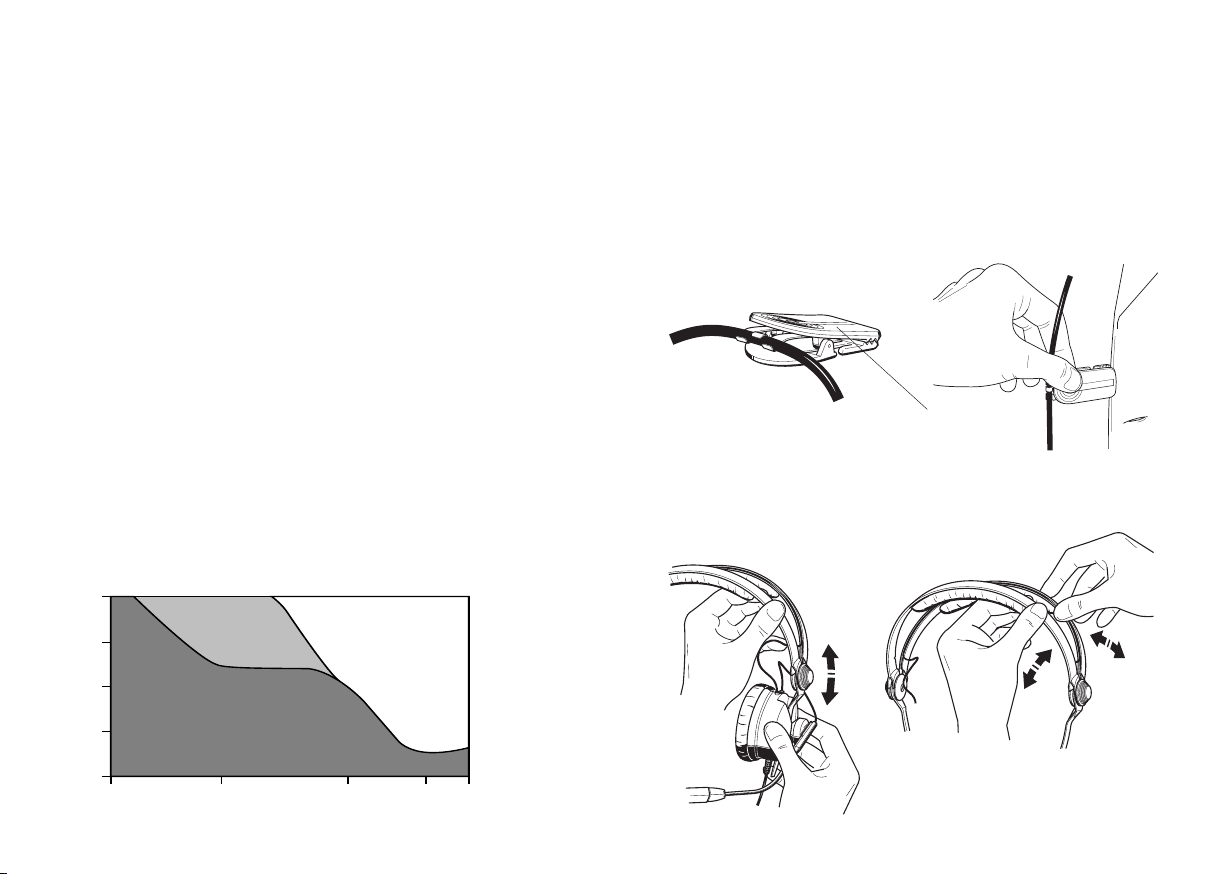
Schallpegel von Lärmquellen
140 dB Düsentriebwerk (25m Entfernung)
Laut
Leise
Die Maßeinheit für Schallpegel ist das Dezibel (dB). Eine Lärmdämpfung um 10 dB wird allgemein als Halbierung der Lautstärke empfunden, weitere 10 dB Dämpfung ergeben eine um 75%
reduzierte Lärmempfindung u.s.w.
130 dB Flugzeugmotor
120 dB Druckluftbohrer
110 dB Schmiedehammer, Betonwerk
100 dB Metalldruckgußmaschine
90 dB Metallwerkstatt
80 dB Traktor
70 dB Büro
60 dB Unterhaltung
50 dB Umweltlärm
40 dB Wohnraum
30 dB Bibliothek
20 dB Schlafzimmer
10 dB Wald, windstill
32
Page 3
HMEC 25-6A / HMEC 25-KAP-2
Eine Hör-/ Sprech-Garnitur faßt zwei Baugruppen, Kopfhörer und Mikrofon zu
einer Funktionseinheit zusammen. Überwiegender Einsatzbereich dieser Hör-/
Sprech-Garnituren HMEC 25-6A/-KAP-2 ist die Kommunikation im Flugzeugcockpit.
왘 Als Mikrofon wird ein hochwertiges dauerpolarisiertes Elektretmikofon
benutzt. Die notwendige Versorgungsspannung wird ( gemäß ARINC) über den
Anschlußstecker aus dem Bordnetz des Flugzeuges bezogen.
왘 Als Kopfhörer dienen Sennheiser NoiseGard™-Systeme. Dies sind dynamische
Hörersysteme, bei denen, zusätzlich zur Wiedergabe eines Audiosignales, auf
elektronischem Weg tieffrequenter Störschall kompensiert wird. Die aktive
Lärmkompensation funktioniert nach dem physikalischen Prinzip, daß sich
Schall und "Antischall" (um 180° phasenverschoben) gegenseitig auslöschen.
Die NoiseGard™-Kompensationselektronik im Kopfhörer benötigt eine
gesonderte eigene Stromversorgung, die das fest mit dem Kabel verbundene
Speiseteil (Siehe Abbildung S. 6) liefert.
Ungestörte Verständigung wird möglich, ohne die Lautstärke so laut einstellen
zu müssen, daß die Umweltgeräusche übertönt werden.
NoiseGard
ist aber kein medizinischer Hörschutz !
™
erhöht den Komfort,
Lieferumfang
1 HMEC 25-6A oder HMEC 25-KAP-2
1 Schutz- und Transporttasche
1 Windschirm MZW 45 (Art.Nr. 75823)
1 Klemmhalter MZQ 2002-1 (Art.Nr. 44740), s. Abb.
MZQ 2002-1
Geräuschkompensation mit NoiseGard
™
Noise compensation HMEC 25
Reduction/dB
0
10
20
30
40
20 100 1000 10000 20000
active
passive
Kopfbügel einstellen
Frequency/Hz
54
Page 4
Kabel (rechts oder links)
HMEC 25-6A HMEC 25-KAP-2
NoiseGard™ ein- und ausschalten
Ist die aktive Lärmkompensation NoiseGard™ ausgeschaltet, können Sie das
Headset wie ein ganz gewöhnliches Headset einsetzen.
Schalten Sie das NoiseGard™-System ein, indem Sie den ON/OFF-Schalter in die
Position ‚ON’ schieben.
Mono-/Stereo-Umschaltung
Üblicherweise empfangen Sie Ihre Tonquelle in Mono und können den Mono-/
Stereo-Umschalter in der Position ‚Mono’ belassen. Schalten Sie an einem StereoIntercom-System den Kopfhörer auf ‚Stereo’ um.
350°
Kabel links
Hinweise
왘 NoiseGard™ dient der Geräuschverminde-
rung zur Erhöhung des Komforts.
왘 NoiseGard™ ist kein medizinisches
Lärmschutzsystem!
왘 NoiseGard™ ersetzt kein industrielles
Lärmschutzsystem zum Einsatz in
lärmerfüllter Umgebung!
Laut hören ? - Nein !
Mit einem Kopfhörer wird gern lauter als mit Lautsprechern gehört. Hohe
Lautstärke, die über längere Zeit auf Ihre Ohren einwirkt, kann zu dauerhaften
Hörschäden führen. Schützen Sie Ihr gesundes Gehör, Sennheiser-Kopfhörer
klingen auch bei niedriger Lautstärke besonders gut ...
Kabel rechts
76
Page 5
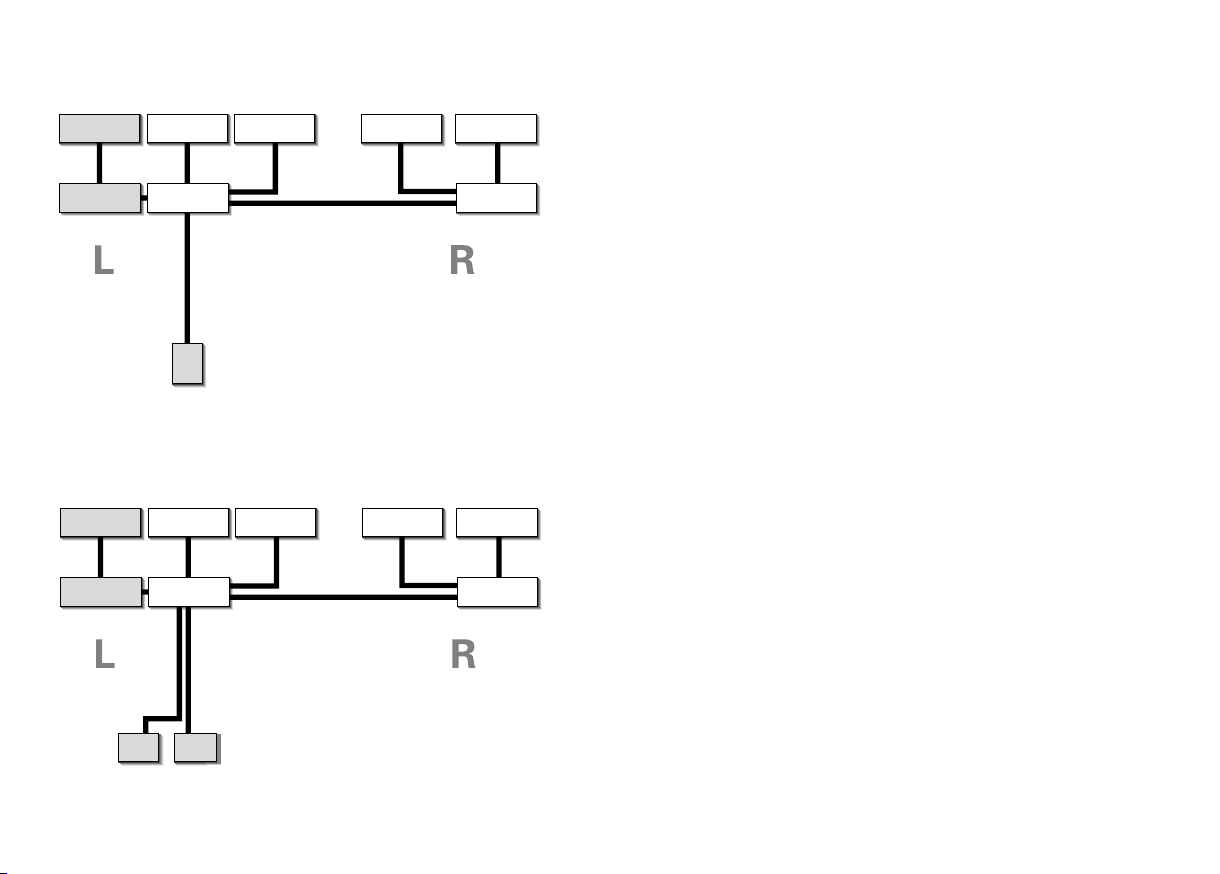
Blockschaltbild HMEC 25-6A
boom
microphone
microphone
amplifier
headphone
capsule (left)
compensation
circuit (left)
compensation
microphone (left)
compensation
microphone (right)
headphone
capsule (right)
compensation
circuit (right)
Technische Daten NoiseGard
™
HMEC 25-6A / HMEC 25 KAP-2
Kopfhörer
Wandlerprinzip dynamisch, geschlossen, ohraufliegend
Übertragungsbereich 16 Hz - 22 kHz
Impedanz aktiv/passive 200 / 180 Ohm (mono)
400 / 360 Ohm pro System (stereo)
Lautstärke aktiv und passiv gleich
Klirrfaktor < 1 %
Lärmdämpfung aktiv 15 dB ± 3 dB im Bereich von 100 Hz - 2 kHz
Frequenzbereich der
aktiven Lärmdämpfung 50 - 600 Hz
6-pin
Redel
plug
Blockschaltbild HMEC 25-KAP-2
boom
microphone
microphone
amplifier
PJ 068
plug
headphone
capsule (left)
compensation
circuit (left)
6,35 mm
plug
compensation
microphone (left)
compensation
microphone (right)
headphone
capsule (right)
compensation
circuit (right)
Mikrofon inkl. Vorverstärker
Wandlerprinzip Back-Elektret-Kondensatorkapsel,
geräuschkompensiert
Übertragungsbereich 300 Hz - 5 kHz
entsprechend RTCA/DO-214
max. Schalldruckpegel 120 dB
Ausgangsspannung 400 mV ± 3 dB bei 114 dB aus 6 mm Abstand
(entsprechend RTCA/DO-214)
Abschlußwiderstand 150 Ohm
Versorgungsspannung typ. 16 V DC, ca 8 - 25 mA,
Beschaltung nach RTCA/DO 214
Allgemeine Daten
Kopfhörer-Andruckkraft ca 2,5 N
Gewicht ohne Kabel 170 g
Kabel einseitig, Länge gesamt: 1,8 m
Stecker HMEC 25-6A: 6-PIN Redel
HMEC 25-KAP-2: PJ 068 (Mikrofon)
6,35mm Klinkenstecker (Hörer)
NoiseGard™-Speisung 12 - 35 V DC
Stromaufnahme typ 18 mA
98
Page 6

The Problem of Noise
The negative effects of noise pollution have been proven by studies, and everybody
will have experienced them at some time or another:
왘 Nervousness
왘 Lack of concentration
왘 Irritability
And these are only the most obvious effects on the human body. Noise also affects
the autonomic nervous system and can lead to permanent hearing damage.
There are a multitude of noise sources, and the individual very often has no
influence over them. The only solution when being in a noisy place is protecting
oneself against ambient noise. These noise problems are particularly prevalent in
an aircraft cockpit where a pilot often has to have the communications headset so
loud as to risk permanent hearing damage.
With the NoiseGard
These operating instructions explain the NoiseGard
to use the NoiseGard™ headset.
Noise levels
loud
quiet
The unit of sound levels is the decibel (dB). A noise reduction of 10 dB is generally perceived as
a halving of the loudness, another 10 dB decrease halves the loudness yet again whitch corresponds to a loudness reduction of 75 %, and so on.
™
system, Sennheiser has come up with an effective solution.
140 dB Jet engine (at a distance of 25 m)
130 dB Aircraft engine (This is the treshold of pain)
120 dB Pneumatic drill
110 dB Blacksmith's hammer, concrete works
100 dB Die-cast machine
90 dB Metal workshop
80 dB Tractor
70 dB Office
60 dB Conversation
50 dB Ambient noise
40 dB Living room
30 dB Library
20 dB Bedroom
10 dB Forest, no wind
™
principle and show you how
1110
Page 7
HMEC 25-6A / HMEC 25-KAP-2
A headset is comprised of two units, a headphone and a microphone. The HMEC
25-6A/-KAP-2 headset is mostly used for communication in aircraft cockpits.
왘 The microphone is a high quality back-electret condenser microphone. As per
ARINC it receives its operating voltage via a connector from the aircraft´s
internal power supply.
왘 The headphone is a Sennheiser NoiseGard
headphone system which, in addition to reproducing the original audio signal,
electronically cancels the low frequencies of the ambient noise. This active
noise compensation operates on the principle that sound and ”anti-sound“ (in
phase opposition) cancel each other out. The NoiseGard™ compensation
circuitry in the headphone requires an extra power supply, so a battery compartment has been integrated into the headset cable (see illustration p. 14).
Clearly intelligible communication is ensured, and the pilot no longer has to
turn the volume up to overcome ambient noise.
NoiseGard
™
increases your comfort,
but it is not a medical hearing protection!
Active noise compensation with NoiseGard
Noise compensation HMEC 25
Reduction/dB
0
™
system. This is a dynamic
™
Supply schedule
1 HMEC 25-6A or HMEC 25-KAP-2
1 Carrying case
1 wind-shield MZW 45 (Art.No 75823)
1 MZQ 2002-1 clip (Art.No 44740), s. fig.
MZQ 2002-1
Adjusting the headband
10
20
30
40
20 100 1000 10000 20000
active
passive
Frequency/Hz
1312
Page 8
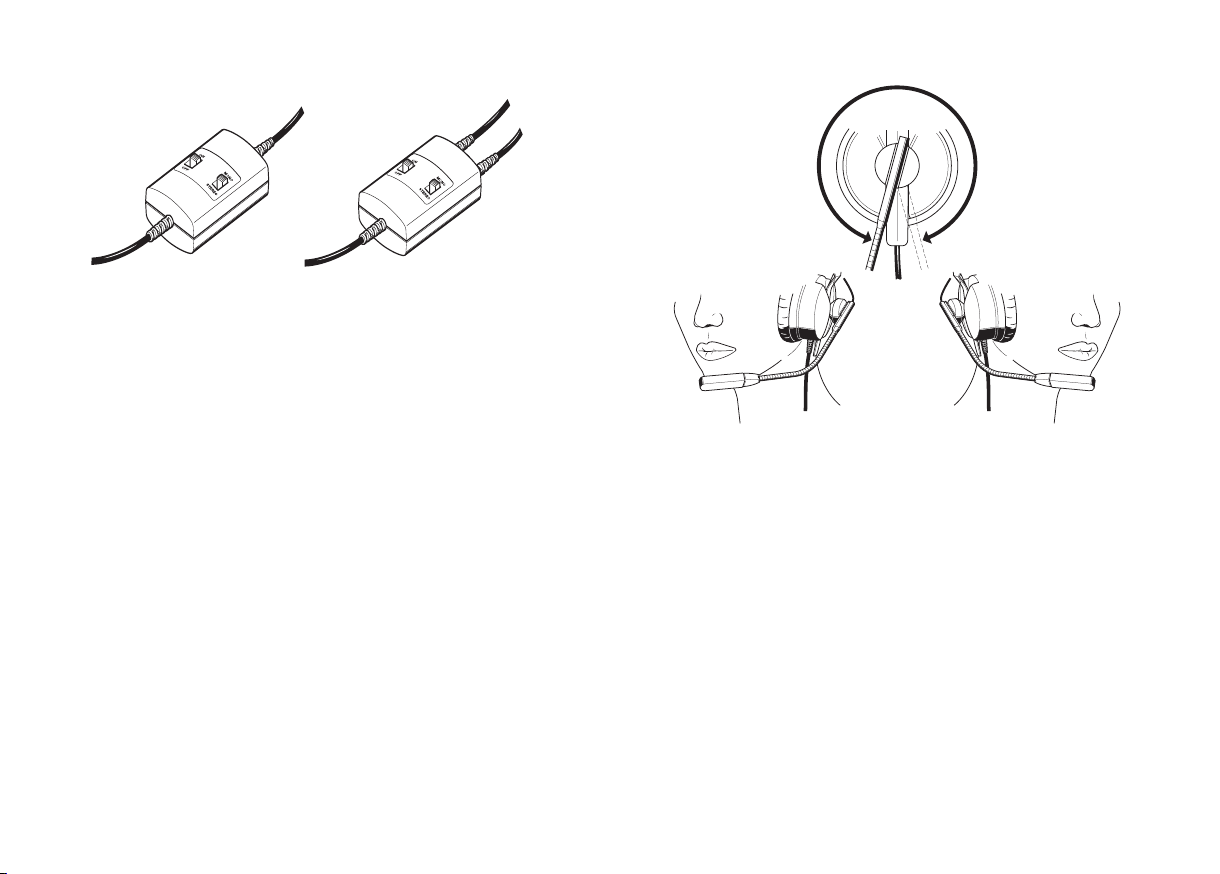
Cable (Worn on left or right side)
HMEC 25-6A HMEC 25-KAP-2
Turning NoiseGard™ ON/OFF
With the NoiseGard™ active noise compensation turned off, the headset can be
used as a conventional headset.
Turn on the NoiseGard™ active noise compensation by setting the ON/OFF switch
to ON.
Mono/Stereo selection
In general, you’ll receive a mono sound source so that the Mono/Stereo switch can
remain set to ‘Mono’. When using a stereo intercom system, set the Mono/Stereo
switch to ‘Stereo’.
350°
Cable on the left
Note:
왘 NoiseGard™ reduces noise and increases comfort.
왘 NoiseGard™ is not a medical noise protection system!
왘 NoiseGard™ cannot replace an industrial ear defender system for use in noisy
environments!
Volume up? - No !
When people use headphones, they tend to choose a higher volume than with
loudspeakers. Listening with high volume levels for a longer time can lead to
permanent hearing defects. Because the NoiseGard™ circuitry is reducing the
ambient noise, the headphones can be set at a correspondingly lower level leading
to more comfortable hearing conditions so protecting your hearing.
Cable on the right
1514
Page 9

HMEC 25-6A block diagram
Technical data NoiseGard
™
HMEC 25-6A / -KAP-2
boom
microphone
microphone
amplifier
headphone
capsule (left)
compensation
circuit (left)
6-pin
Redel
plug
compensation
microphone (left)
HMEC 25-KAP-2 block diagram
boom
microphone
microphone
amplifier
PJ 068
plug
headphone
capsule (left)
compensation
circuit (left)
6,35 mm
plug
microphone (left)
compensation
compensation
microphone (right)
compensation
microphone (right)
headphone
capsule (right)
compensation
circuit (right)
headphone
capsule (right)
compensation
circuit (right)
Headphone
Transducer principle dynamic, open, supra-aural
Frequency response 16 Hz - 22 kHz
Impedance active/passive 200 / 180 Ω (mono)
400 / 360 Ω per side (stereo)
same volume for active and passive
THD < 1 %
Compensation active 15 dB ± 3 dB between 100 Hz and 2 kHz
Frequency response of
the active compensation 50 - 600 Hz
Microphone incl. preamplifier
Transducer principle Noise-compensated back-electret condenser
microphone capsule
Frequency response 300 Hz - 5 kHz (as per RTCA/DO-214)
Max. sound pressure level 120 dB
Output voltage 400 mV ± 3 dB at 114 dB
and a distance of 6 mm
(as per RTCA/DO-214)
Terminating impedance 150 Ω
Operating voltage typ. 16 V DC, approx. 8 - 25 mA,
connections as per RTCA/DO 214
General data
Contact pressure approx. 2.5 N
Weight without cable 170 g
Cable single-sided, total length 1.8 m
Connectors HMEC 25-6A: 6-PIN Redel
HMEC 25-KAP-2: headphone: 6.35 mm (1/4") jack plug
microphone: PJ-068, 5.25 mm
Power supply NoiseGard™- 12 - 35 V DC
Current consumption typ. 18 mA
1716
Page 10

Le bruit - il est partout !
Que ce soit sur le lieu de travail, à la maison, dans les transport publics, en avion,
en train ou en car - il y a toujours du bruit.
De nombreuses études ont démontré les effets négatifs de cette pollution par le
bruit - et tout le monde les connaît:
왘 nervosité
왘 manque de concentration
왘 irritabilité...
- et ce sont seulement les effets les plus évidents. Le bruit attaque aussi le système
neurovégétatif et peut entraîner une détérioration définitive de l´ouïe.
Les sources du bruit sont multiples, et la plupart du temps on n´est pas maître de
le faire cesser. La seule solution dans un environnement bruyant est donc de se
protéger individuellement. C´est surtout vrai pour les pilotes. Dans les cockpits, le
bruit est un très grand problème, et souvent, le pilote doit ajuster l´ensemble
casque/micro si fort qu´il risque d´endommager son ouïe de façon permanente.
Avec le système NoiseGard™, Sennheiser a créé une solution très efficace. Son
principe de fonctionnement et son emploi sont décrits dans ce guide.
Quelques niveaux sonores
140 dB Moteur à réaction (à 25 m)
haut
bas
L´unité de mesure du niveau sonore est le décibel (dB). Une atténuation sonore de 10 dB est en
général perçue comme une réduction du bruit de 50 % ; si l´on atté nue encore ce volume de 10
dB, la réduction sonore perçue du bruit est 75 %, et ainsi de suite.
130 dB Moteur d´avion
120 dB Perceuse pneumatique
110 dB Marteau de forge, usine de béton
100 dB Machine à mouler sous pression
90 dB Usinage des métaux
80 dB Tracteur
70 dB Bureau
60 dB Conversation
50 dB Bruit ambiant
40 dB Salle de séjour
30 dB Bibliothèque
20 dB Chambre à coucher
10 dB Forêt, calme
1918
Page 11

HMEC 25-6A / HMEC 25-KAP-2
L´ensemble casque/micro HMEC 25-6A/-KAP-2 est avant tout conçu pour la
communication dans les cockpits d´avion.
왘 Comme microphone, on a choisi un microphone autopolarisé haut de gamme.
La tension d´alimentation est prise - selon ARINC - sur le circuit de bord.
왘 Le casque emploie le système NoiseGard
plus de reproduire le signal audio, compense électroniquement les bruits
basses fréquences. La compensation active du bruit fonctionne sur le principe
selon lequel son et «antison» (déphasé de 180°) s´annulent réciproquement.
Pour cette compensation NoiseGard™, l´électronique dans le casque nécessite une
alimentation séparée qui est integrée dans le cable (voir illustration p. 22).
La communication devient parfaitement intelligible , et il ne faut plus pousser
le volume pour couvrir le bruit ambiant.
™
. C´est un système dynamique qui, en
Contenu
1 HMEC 25-6A ou HMEC 25-KAP-2
1 Sacoche
1 bonnette anti-vent MZW 45 (Art.No 75823)
1 fixation à pince MZQ 2002-1, fig.
NoiseGard
™
augmente le confort, mais
ce n´est pas une protection médicale pour l´ouïe !
Compensation du bruit avec NoiseGard
™
Noise compensation HMEC 25
Reduction/dB
0
10
20
30
40
20 100 1000 10000 20000
active
passive
MZQ 2002-1
Comment ajuster l´arceau du casque
Frequency/Hz
2120
Page 12

Câble (à gauche ou à droite)
HMEC 25-6A HMEC 25-KAP-2
Commutation Marche/Arrêt du NoiseGard
Avec le système de compensation de bruit NoiseGard™ hors fonction, le casque
micro peut être utilisé comme un modèle conventionnel.
Pour mettre en marche le système NoiseGard™, placez le commutateur ON/OFF
sur ON.
™
Commutation Mono/Stéréo
En général, vous recevez un son mono. Le commutateur Mono/Stéréo doit alors
être placé sur ‘Mono’. Lors de l’utilisation d’un système intercom stéréo, placez le
commutateur Mono/Stéréo sur ‘Stéréo’.
350°
Câble à gauche
Nota
왘 NoiseGard™ sert à réduire le bruit et à augmenter
le confort.
왘 NoiseGard™ n´est pas une protection médicale pour l´ouïe!
왘 NoiseGard™ ne peut pas remplacer un système
industriel de protection contre le bruit qu´il faut utiliser dans un environnement
bruyant!
Pousser le volume ? - Non !
Avec un casque, on préfère d´écouter plus fort qu´avec les haut-parleurs. Des volumes
forts pendant un temps prolongé peuvent entraîner une détérioration définitive de
l´ouïe. Comme l´électronique NoiseGard™ réduit le bruit ambiant, le casque peut être
ajusté à un niveau plus bas. L´écoute devient plus confortable et votre ouïe sera protégée.
Câble à droite
2322
Page 13

Schema fonctionel HMEC 25-6A
Caractéristiques techniques NoiseGard
™
HMEC 25-6A / -KAP-2
boom
microphone
microphone
amplifier
headphone
capsule (left)
compensation
circuit (left)
6-pin
Redel
plug
compensation
microphone (left)
Schema fonctionel HMEC 25-KAP-2
boom
microphone
microphone
amplifier
PJ 068
plug
headphone
capsule (left)
compensation
circuit (left)
6,35 mm
plug
compensation
microphone (left)
compensation
microphone (right)
compensation
microphone (right)
headphone
capsule (right)
compensation
circuit (right)
headphone
capsule (right)
compensation
circuit (right)
Casque
Principe transducteur dynamique, ouvert, supra-aural
Bande passante 16 Hz - 22 kHz
Impédance active/passive 200 / 180 Ω (mono)
400 / 360 Ω par système (stéréo)
Volume active et passive identique
Distorsion harmonique < 1 %
Atténuation active 15 dB ± 3 dB de 100 Hz à 2 kHz
Bande passante de la compensation 50 - 600 Hz
Microphone, préamplificateur inclus
Principe transducteur Capsule à électret (autopolarisée) à
compensation de bruit
Bande passante 300 Hz - 5 kHz, selon RTCA/DO-214
Niveau de pression acoustique max. 120 dB
Tension de sortie 400 mV ± 3 dB à 114 dB à 6 mm
de distance (selon RTCA/DO-214)
Impédance de charge 150 Ω
Tension d´alimentation typ. 16 V CC, approx. 8 - 25 mA,
connexions selon RTCA/DO 214
Caractéristiques générales
Pression exercée par les écouteurs approx. 2,5 N
Poids sans câble 170 g
Câble unilatéral, longueur totale 1,8 m
Connecteur HMEC 25-6A: connecteur Redel à 6 broches
HMEC 25-KAP-2: jack 6,35 mm (casque)
PJ-068, 5,25 mm (microphone)
Alimentation NoiseGard™ 12 - 35 V CC
Consommation typ. 18 mA
2524
Page 14

Rumore - dove non lo incontriamo?
Sia sul posto di lavoro che nell'ambiente domestico, nei mezzi di trasporto pubblici,
nei viaggi in aereoplano, in ferrovia o in pullman - esso ci accompagna dovunque.
Gli effetti negativi di questi rumori fastidiosi sono comprovati da studi effettuati e
anche ciascuno di noi li avrà già provati.
왘 nervosismo
왘 mancanza di concentrazione
왘 irritabilità...
sono solo gli effetti più appariscenti sull'organismo. Il rumore agisce inoltre sul
sistema neurovegetativo e può provocare danni permanenti all'udito.
Le fonti di rumore sono molteplici e troppo spesso non eliminabili per il singolo
individuo. Per questo motivo solo la protezione personale in un luogo rumoroso
può rappresentare una soluzione.
Con il sistema NoiseGard
™
la Sennheiser ha realizzato una soluzione efficace. Il
principio di funzionamento e l'impiego Vi vengono spiegati in queste istruzioni.
Livello di pressione acustica delle sorgenti sonore
140 dB Motore a reazione (distanza 25 m)
Rumoroso
silenzioso
L'unità di misura per il livello di pressione acustica è il decibel (dB). Un'attenuazione del rumore
di 10 dB viene generalmente percepita come un dimezzamento del volume, un'attenuazione di
altri 10 dB fornisce una percezione sonora ridotta del 75% ecc.
130 dB Motore di aeroplane
120 dB Martello pneumatico
110 dB Martello fucinatura, betoniera
100 dB Macchina per pressofusione di metalli
90 dB Officina metalmeccacica
80 dB Trattore
70 dB Ufficio
60 dB Conversazione
50 dB Rumore ambientale
40 dB Soggiorno
30 dB Biblioteca
20 dB Camera da letto
10 dB Bosco, senza vento
2726
Page 15

HMEC 25-6A / HMEC 25-KAP-2
Una cuffia riunisce due gruppi costruttivi, l'auricolare e il microfono, in una unità
funzionale. Il prevalente campo di impiego di queste cuffie HMEC 25-6A/KAP-2
è la comunicazione nella cabina dei piloti di aereoplani.
왘 Come microfono viene utilizzato un microfono a elettrete a polarizzazione
continua di alta qualità. La tensione di alimentazione necessaria viene fornita
(in conformità a ARINC) dalla rete di bordo del velivolo attraverso la spina
di collegamento.
왘 Come cuffia vengono impiegati i sistemi Sennheiser NoiseGard
sistemi di cuffie dinamici, nei quali, oltre alla riproduzione di un segnale audio,
il rumore a bassa frequenza viene compensato per via elettronica. La
compensazione attiva del rumore funziona in base al principio fisico che il
rumore e l'"antirumore" (con uno spostamento di fase di 180˚) si cancellano
a vicenda. L'elettronica di compensazione NoiseGard
™
un'alimentazione elettrica propria, che viene fornita dall'alimentatore (vedi
figura p. 30) collegata con comando fisso al cavo.
La comprensione senza disturbo diventa possibile senza dover regolare il
volume al punto da coprire i rumori dell'ambiente.
NoiseGard™ aumenta il confort,
non è tuttavia una protezione medica dell'udito!
™
. Questi sono
nella cuffia necessita di
Volume fornitura:
1 HMEC 25-6A oppure HMEC 25-KAP-2
1 tasca di protezione e di trasporto
1 cuffia antivento MZW 45 (Art.No. 75823)
1 supporto di fissaggio MZQ 2002-1 (Art.No 44740), fig.
MZQ 2002-1
Compensazione del rumore con NoiseGard
™
Noise compensation HMEC 25
Reduction/dB
0
10
20
30
40
20 100 1000 10000 20000
active
passive
Regolazione della staffa per la testa
Frequency/Hz
2928
Page 16

Cavo (a destra o a sinistra)
HMEC 25-6A HMEC 25-KAP-2
Conexión y desconexión del NoiseGard
Cuando la compensación activa de ruidos NoiseGard™ está desconectada puede
emplear Vd. el Headset tal como un casco auricular común y corriente.
Para conectar el sistema NoiseGard™ ponga el interruptor ON/OFF en la posición
‘ON’.
™
Conmutación monofónico/estereofónico
Generalmente recibe Vd. la fuente de sonido en operación monofónica y puede
dejar el conmutador monofónico/estereofónico en la posición ‘Mono’. En un
sistema Intercom estereofónico conmute el auricular a ‘Stereo’.
350°
Cavo a sinistra
Awertenze
왘 NoiseGard™ serve a ridurre il rumore per aumentare il confort.
왘 NoiseGard™ non è un sistema medico di protezione contro il rumore!
왘 NoiseGard™ non sostituisce nessun sistema di protezione industriale contro il
rumore, da impiegare in un ambiente rumoroso!
Ascoltare ad alto volume? - No!
Con una cuffia si ascolta volentieri ad un volume più alto che non con gli
autoparlanti. Un volume alto, che agisce sulle Vostre orecchie per un tempo
prolungato, può provocare danni permanenti all'udito. Proteggete il Vostro udito
sano, le cuffie Sennheiser hanno un bel suono anche a basso volume...
Cavo a destra
3130
Page 17

Schema a blocchi HMEC 25-6A
Dati tecnici NoiseGard™ HMEC 25-6A/-KAP-2
boom
microphone
microphone
amplifier
headphone
capsule (left)
compensation
circuit (left)
6-pin
Redel
plug
compensation
microphone (left)
Schema a blocchi HMEC 25-KAP-2
boom
microphone
microphone
amplifier
PJ 068
plug
headphone
capsule (left)
compensation
circuit (left)
6,35 mm
plug
compensation
microphone (left)
compensation
microphone (right)
compensation
microphone (right)
headphone
capsule (right)
compensation
circuit (right)
headphone
capsule (right)
compensation
circuit (right)
Cuffia
Principio convertitore dinamico, chiuso, sopraurale
Banda di trasmissione 16 Hz - 22 kHz
Impedenz attiva/passiva: 200 / 180 ohm (mono)
400 / 360 ohm per ogni lato (stereo)
Volume attivo e passivo uguale
Fattore di distorsione < 1 %
Smorzamento rumore 15 dB ± 3 dB nel campo di 100 Hz - 2 kHz
Risposta armonica dello
smorzamento rumore attivo 50 - 600 Hz
Microfono incl. preamplificatore
Principio convertitore Capsula condensatore controelettrodo
elettrite, con compensazione del rumore
Banda di trasmissione 300 Hz - 5 kHz
in conformità a RTCA/DO-214
dall’angolo della bocca
Max livello pressione sonora 120 dB
Tensione di uscita 400 mV ± 3 dB a 114 dB distanza 6 mm
(in conformità a RTCA/DO-214)
Resistenza terminale 150 Ω
Tensione di alimentazione tip. 16 V DC, ca 8 - 25 mA,
cablaggio secondo RTCA/DO-214
Dati generali
Forza pressione cuffia ca. 2,5 N
Peso senza cavo 170 g
Cavo su un lato, lunghezza totale: 1,8 m
Spina HMEC 25-6A: 6-PIN Redel
HMEC 25-KAP-2: 6,35 mm jack plug cuffia
PJ-068, 5,25 mm microfono
Alimentazione NoiseGard™ 12 - 35 V DC
Assorbimento corrente tip. 18 mA
3332
Page 18

El ruido - ¿Dónde podemos aislarnos de él?
Bien sea en el puesto de trabajo, en la vivienda, en los medios de transporte público,
en los viajes en avión, en tren o en bus: en todas partes hay ruido.
Los efectos negativos de las molestias que causa el ruido han sido documentados
por medio de estudios. Y, también, cada uno de nosotros los habrá sentido.
왘 La nerviosidad,
왘 la falta de concentración,
왘 y la irritabilidad ...,
son tan sólo los efectos aparentes causados en el organismo. El ruido, sin embargo,
influye además en el sistema nervioso vegetativo y puede ocasionar daños
permanentes de la capacidad auditiva.
Los orígenes del ruido son múltiples y, con frecuencia, imposibles de suprimir. Por
eso, en un lugar ruidoso, únicamente la protección personal constituye una
solución adecuada.
Con el sistema NoiseGard
funcionamiento y manejo se explican en estas instrucciones.
Nivel de sonoridad de las fuentes de ruidos
Alto
Bajo
El decibelio (dB) es la unidad de medida para expresar la intensidad de los sonidos. En general, una
atenuación de ruidos de 10 dB se percibe como una disminución de un 50% de la intensidad del
sonido; una amortiguación adicional de 10 dB disminuye la percepción de ruidos en un 75%, etc.
™
Sennheiser ha logrado una solución efectiva. Su
140 dB Mecanismo de accionamiento a reacción (25 m de distancia)
130 dB Motor de avión
120 dB Taladro neumático
110 dB Martello de forja, fábrica de hormigón
100 dB Máquina de fundición a presión (de metales)
90 dB Taller metalúrgico
80 dB Tractor
70 dB Oficina
60 dB Recreación
50 dB Ruido medioambiental
40 dB Vivienda
30 dB Biblioteca
20 dB Dormitorio
10 dB Bosque, sin viento
3534
Page 19

HMEC 25-6A / HMEC 25-KAP-2
El juego de intercomunicación reúne dos módulos, es decir el auricular y el
micrófono, es una sóla unidad funcional. Estos juegos de intercomunicación
HMEC 25-KA/-CA se emplean sobre todo para efectos de comunicación en
cabinas de aviones.
왘 Como micrófono se emplea un micrófono electreto de alta calidad, polarizado
permanentemente. La tensión de abastecimiento necesaria (según ARINC) se
toma de la red de a bordo del avión, a través del enchufe de conexión.
왘 Como auriculares se emplean los sistemas NoiseGard
son sistemas de auriculares dinámicos en los cuales, además de la reproducción
de una señal de video, se compensa por medios electrónicos el sonido
perturbador de baja frecuencia. La compensación de ruido activa funciona
según el principio físico según el cual, la sonoridad y la "antisonoridad" se
anulan recíprocamente (mediante la oposición de fase en 180˚).
왘 La eléctronica de compensación NoiseGard
™
existente en el auricular requiere su
propia alimentación de corriente, que es proporcionada por el bloque de alimentación, unido firmemente al cable del auricular (ver la ilustración p. 38).
De tal forma se logra una comunicación sin perturbaciones, sin tener que
regular el sonido a un volumen tan alto como para poder suprimir los ruidos
medioambientales.
NoiseGard™ aumenta el confort
aunque no es un sistema médico de protección auditiva
Compensacion de ruidos con NoiseGard
™
Noise compensation HMEC 25
Reduction/dB
0
™
de Sennheiser. Estos
Volumen del suministro:
1 HMEC 25-6A ó HMEC 25-KAP-2
1 bolsa protectora
1 caperuza antivento MZW 45 (Art.No. 75823)
1 clip MZQ 2002-1 (Art. No. 44740), fig.
MZQ 2002-1
Ajuste de los aros del auricular
10
20
30
40
20 100 1000 10000 20000
active
passive
Frequency/Hz
3736
Page 20

Cable (a la derecha/a la izquierda)
HMEC 25-6A HMEC 25-KAP-2
Accensione e spegnimento del NoiseGard™
Quando la compensazione attiva del rumore NoiseGard™ è spenta, potete utilizzare
la cuffia microfonica come una cuffia microfonica tradizionale.
Accendete la compensazione del rumore NoiseGard™ portando l’interruttore ON/
OFF nella posizione “ON”.
Commutazione Mono-/Stereo
Normalmente ricevete la Vostra fonte acustica in forma mono e potete lasciare il
commutatore Mono-/Stereo nella posizione “Mono”. Commutate la cuffia su
“stereo” quando utilizzate un sistema Intercom stereo.
350°
Cable a la izquierda
Advertencias
왘 NoiseGard
왘 NoiseGard
왘 NoiseGard
™
sirve para disminuir los ruidos, a la vez que se aumenta el confort.
™
no es un sistema médico para protección contra los ruidos.
™
no es un sistema industrialde protección contra ruidos para uso en
ambientes muy ruidosos.
¿Oir a alto volumen? - ¡No!
Generalmente, quien usa un auricular se inclina a aumentar el volumen por encima del que
se obtiene en los altavoces. Sin embargo, el efecto del nivel de sonido a todo volumen y
durante largo tiempo puede ocasionar daños permanentes de la audición. Proteja su oído el sonido de los auriculares Sennheiser es siempre sobresaliente, incluso a bajo volumen ...
Cable a la derecha
3938
Page 21

Diagrama de bloques HMEC 25-6A
boom
microphone
microphone
amplifier
headphone
capsule (left)
compensation
circuit (left)
compensation
microphone (left)
compensation
microphone (right)
headphone
capsule (right)
compensation
circuit (right)
Datos técnicos NoiseGard™ HMEC 25-6A/ -KAP-2
Auricular
Principio transductor dinámico, cerrado, supraaural
Gama de transmisión 16 Hz - 22 kHz
Impedancia activa/pasiva: 200 / 180 ohmios (mono),
400 / 360 ohmios/lado (estéreo)
Volumen igual, activo o pasivo
Factor de distorsión < 1%
Atenuación de ruidos 15 dB ± 3 dB en la gama de 100 Hz - 2 kHz
Respuesta de frecuencia de la
atenuación activa de ruidos 50 - 600 Hz
6-pin
Redel
plug
Diagrama de bloques HMEC 25-KAP-2
boom
microphone
microphone
amplifier
PJ 068
plug
headphone
capsule (left)
compensation
circuit (left)
6,35 mm
plug
compensation
microphone (left)
compensation
microphone (right)
headphone
capsule (right)
compensation
circuit (right)
Micrófono incl. preamplificador
Principio transductor Cápsula electreto,
con compensación de ruidos
Gama de transmisión 300 Hz - 5 kHz
según RTCA/DO-214
Máx. presión sonora 120 dB
Tensión de salida 400 mV ± 3 dB a 114 dB, a una distancia
de 6 mm (según RTCA/DO-214)
Resistencia de enlace 150 Ω
Tensión de alimentación tip. 16 V CC, aprox. 8 - 25 mA,
clase de circuito según RTCA/DO-214
Datos generales
Fuerza de apriete del auricular aprox. 2,5 N
Peso sin cable 170 g
Cable de un lado, largo total: 1,8 m
Enchufe HMEC 25-6A: enchufe Redel de 6 polos
HMEC 25-KAP-2: jack 6,35 mm (auricular)
PJ-068, 5,25 mm (micrófono)
NoiseGard™ Alimentación 12 - 35 V CC
Consumo de corriente tip. 18 mA
4140
Page 22

Lawaai - waar vinden wij het niet?
Op het werk, in de huiselijke omgeving, in openbare vervoermiddelen, bij
vlieg-, trein- of busreizen - bijna overal worden wij door lawaai begeleid.
De negatieve invloed van deze geluidsoverlast is door studies bewezen en wij zullen
het zelf ook allemaal wel al gemerkt hebben:
왘 Nervositeit
왘 gebrek aan concentratie
왘 geprikkelde stemming
zijn slechts de duidelijk zichtbare uitwerkingen op het organisme. Lawaai heeft
bovendien een negatieve werking op het vegetatieve zenuwstelsel en kan blijvende
schade van het gehoor tot gevolg hebben.
De bronnen van het lawaai zijn veelvoudig en vaak door het individu niet te
onderscheiden. Daarom kan alleen de persoonlijke bescherming een oplossing
bieden op plaatsen met geluidsoverlast.
In het systeem NoiseGard
Het principe van de functie en de bediening willen wij u in deze gebruiksaanwijzing
toelichten.
Geluidsniveau van lawaaibronnen
Luid
zacht
De maateenheid voor het geluidsniveau is de Decibel (dB). Een demping van het lawaai met 10
dB wordt als halvering van de geluidsterkte waargenomen, nog eens 10 dB vermindering
betekent een subjectief waargenomen reductie van 75% van het lawaai enz.
™
heeft Sennheiser een werkzame oplossing gerealiseerd.
140 dB Straalaandrijving (25 m afstand)
130 dB Vliegtuigmotor
120 dB Persluchtboormachine
110 dB Smidhamer, betonfabriek
100 dB Metaaldrukgietmachine
90 dB Metaalwerkplaats
80 dB Tractor
70 dB Kantoor
60 dB Gesprek
50 dB Omgevingslawaai
40 dB Woonruimte
30 dB Bibliotheek
20 dB Slaapkamer
10 dB Bos, windstil
4342
Page 23

HMEC 25-6A / HMEC 25-KAP-2
Een luister-/spreekgarnituur vat twee bouwgroepen, hoofdtelefoon en microfoon tot
een functie-eenheid samen. Het belangrijkste toepassingsgebied van deze luister-/
spreek-garnituren HMEC 25-6A/-KAP-2 is de communicatie in de cockpit van een
vliegtuig.
왘 Als microfoon wordt een hoogwaardige continu gepolariseerde
elektretmicrofoon toegepast. De noodzakelijke voeding wordt (overeenkomstig
ARINC) via de aansluitstekker uit het boordnet van het vliegtuig opgenomen.
왘 Als hoofdtelefoon dienen Sennheiser NoiseGard
luistersystemen waarbij naast de weergave van een audiosignaal op elektronische
wijze storend lawaai met een diepe frequente wordt gecompenseerd. Deze
actieve lawaaicompensatie functioneert volgens het natuurkundige principe dat
geluid en antigeluid (180˚ in fase verschoven) zich tegen elkaar opheffen. De
NoiseGard™ compensatie elektronika in de hoofdtelefoon heeft een eigen
stroomverzorging nodig. Deze wordt geleverd door het netvoedingsgedeelte
dat vast verbonden is met de kabel van de hoofdtelefoon (zie afbeelding p. 46).
Het wordt mogelijk om ongestoord van muziek te genieten zonder het volume
zo luid te moeten instellen dat de geluiden van het milieu overspeeld worden.
NoiseGard
™
verhoogt het comfort
is echter geen medische gehoorbescherming!
™
systemen. Dit zijn dynamische
Leveringspakket:
1 HMEC 25-6A of HMEC 25-KAP-2
1 Beschermings- en transporttasje
1 windbeschermingskorfie MZW 45 (Art.No. 75823)
1 klemhouder MZQ 2002-1 (Art.No 44740), afb.
MZQ 2002-1
Geluidscompensatie met NoiseGard
™
Noise compensation HMEC 25
Reduction/dB
0
10
20
30
40
20 100 1000 10000 20000
active
passive
Hoofdbeugel instellen
Frequency/Hz
4544
Page 24

Kabel (rechts of links)
HMEC 25-6A HMEC 25-KAP-2
Het aan- en uitzetten van de NoiseGard
™
Wanneer het lawaaibestrijdingssysteem NoiseGard™ uitstaat, beschikt u over een
gewone headset.
U zet de NoiseGard™ aan door de ON/OFF-schakelaar op ON te zetten.
Het selecteren van mono of stereo
De meeste communicatiesystemen zenden een monosignaal uit. Normaal gesproken
kunt u de mono/stereo-schakelaar dan ook op ‘mono’ laten staan. Zet de schakelaar
op ‘stereo’ wanneer u de headset bij een stereo-communicatiesysteem gebruikt.
350°
Kabel links
Opmerkingen
왘 NoiseGard
™
dient ter reductie van het lawaai om
zodoende het comfort te verhogen.
왘 NoiseGard
™
is geen medisch
lawaaibeschermingssysteem!
왘 NoiseGard
™
vervangt geen industrieel
lawaaibeschermingssysteem voor de toepassing
in een omgeving met geluidsoverlast
Luid luisteren ? - Neen !
Met een hoofdtelefoon wordt vaak luider geluisterd als via luidsprekers. Een hoog
volume dat gedurende een lage tijd op uw oren inwerkt kan tot permanente
beschdigigen van het gehoor voeren. Bescherm uw gezonde gehoor, Sennheiserhoofdtelefoons klinken ook bij een laag volume bijzonder goed ...
Kabel rechts
4746
Page 25

Blokschakelschema HMEC 25-6A
Technische gegevens NoiseGard™ HMEC 25-6A / -KAP-2
boom
microphone
microphone
amplifier
headphone
capsule (left)
compensation
circuit (left)
6-pin
Redel
plug
compensation
microphone (left)
Blokschakelschema HMEC 25-KAP-2
boom
microphone
microphone
amplifier
PJ 068
plug
headphone
capsule (left)
compensation
circuit (left)
6,35 mm
plug
compensation
microphone (left)
compensation
microphone (right)
compensation
microphone (right)
headphone
capsule (right)
compensation
circuit (right)
headphone
capsule (right)
compensation
circuit (right)
Koptelefoon
Omzetprincipe dynamisch, gesloten, op het oor liggend
Overdrachtsbereik 16 Hz - 22 kHz
Impedantie actief/passief: 200 / 180 ohm (mono)
400 / 360 ohm per systeem (stereo)
Volume actief en passief gelijk
Vervormingsfactor < 1%
Lawaaidemping actief 15 dB ± 3 dB in het bereik van 100 Hz - 2 kHz
Frequentiegebied
van de actieve lawaaidemping 50 - 600 Hz
Microfoon incl. voorversterker
Omzetprincipe Back-Elektret-condensatorkapsel
met lawaaicompensatie
Overdrachtsgebied 300 Hz - 5 kHz
conform RTCA/DO-214
Max. geluidsniveau 120 dB
Uitgangsspanning 400 mV ± 3 dB bij 114 dB
vanuit 6 mm afstand
(conform RTCA/DO-214)
Aansluitweerstand 150 Ω
Voedingsspanning typ. 16 V DC, ca. 8 - 25 mA,
geschakeld conform RTCA/DO-214
Algemene gegevens
Aandrukkracht hoofdtelefoon ca. 2,5 N
Gewicht zonder kabel 170 g
Kabel enkelzijdig, totale lengte 1,8 m
Stekker HMEC 25-6A: 6-PIN Redel
HMEC 25-KAP-2: PJ-068 (microfoon)
6,35 mm jack connector (hoofdtelefoon)
NoiseGard™ voeding 12 - 35 V DC
Stroomopname typ. 18 mA
4948
Page 26

Konformitätserklärung
Sennheiser electronic GmbH & Co. KG erklären, daß dieses Gerät die anwendbaren CE-Normen und Vorschriften erfüllt.
Approval
Sennheiser electronic GmbH & Co. KG declare that this device is in compliance with the applicable CE standards and regulations.
Certification
Sennheiser electronic GmbH & Co. déclarons que cet appareil est en conformité avec les normes CE.
Certificazione
Sennheiser electronic GmbH & Co. KG dichiara che questo apparecchio
risponde alle normative e alle prescrizioni CE applicabili.
Autorizacion
Sennheiser electronic GmbH & Co. KG declara que este aparato cumple las
normas y directrices de la CE aplicables.
Vergunning
Sennheiser electronic GmbH & Co. KG verklaren, dat dit toestel voldoet aan
de toepasselijke CE-normen en voorschriften.
Aktuelle Informationen zu Sennheiser-Produkten erhalten Sie auch im Internet
unter „http://www.sennheiser.com“.
Up to date information on Sennheiser products can also be found on the Internet
at “http://www.sennheiser.com”.
Vous trouverez également toutes les informations actuelles relatives aux produits
Sennheiser sur Internet, sous “http://www.sennheiser.com“.
Informazioni attuali sulla gamma di prodotti Sennheiser sono disponibili anche in
Internet al sito „http://www.sennheiser.com“.
También en Internet, bajo „http://www.sennheiser.com“ obtendrá Vd.
informaciones actuales sobre los productos Sennheiser.
Actuele informatie met betrekking tot Sennheiser producten vindt u ook op
Internet onder “http://www.sennheiser.com“.
Page 27

Änderungen vorbehalten
Subject to alterations
Modificaciones reservadas
Sous réserve de modification
Con riserva di modifiche
Wijzigingen voorbehouden
Sennheiser electronic GmbH & Co. KG Telefon: 05130/600-0
D-30900 Wedemark Telefax: 05130/600-300
Printed in Germany Publ. 05/02 86071 / A01
 Loading...
Loading...