Page 1

SMD 989
DVB-S2 Satellite Modulator
User Manual
January 2018
Form 8011L www.sencore.com | 1.605.978.4600 Revision 3.2.2
Page 2

SMD 989– User Manual
Copyright
© 2011 Sencore, Inc. All rights reserved.
3200 Sencore Drive, Sioux Falls, SD USA
www.sencore.com
This publication contains confidential, proprietary, and trade secret information. No part of this document
may be copied, photocopied, reproduced, translated, or reduced to any machine-readable or electronic
format without prior written permission from Sencore. Information in this document is subject to change
without notice and Sencore Inc. assumes no responsibility or liability for any errors or inaccuracies.
Sencore, Sencore Inc, and the Sencore logo are trademarks or registered trademarks in the United States
and other countries. All other products or services mentioned in this document are identified by the
trademarks, service marks, or product names as designated by the companies who market those products.
Inquiries should be made directly to those companies. This document may also have links to third-party web
pages that are beyond the control of Sencore. The presence of such links does not imply that Sencore
endorses or recommends the content on those pages. Sencore acknowledges the use of third-party open
source software and licenses in some Sencore products. This freely available source code can be obtained
by contacting Sencore Inc.
About Sencore
Sencore is an engineering leader in the development of high-quality signal transmission solutions for the
broadcast, cable, satellite, IPTV, telecommunications, and professional audio/video markets. The
company’s world-class portfolio includes video delivery products, system monitoring and analysis solutions,
and test and measurement equipment, all designed to support system interoperability and backed by bestin-class customer support. Sencore meets the rapidly changing needs of modern media by ensuring the
efficient delivery of high-quality video from the source to the home. For more information, visit
www.sencore.com.
Page 2 (105)
Page 3
Revision History
Date
Version
Description
Author
08/09/2010
0.1
Initial Draft
RJH
11/12/2010
1.0
Product Release
RJH
11/24/2010
1.1
Minor Editing
JD
1/5/2011
1.2
Small Additions
RJH
5/2/2011
2.0
Updated for 2.0 Release
RJH
10/28/2011
2.1
Updates for 2.1 Release
RJH
01/17/2012
2.2
Update for 2.2.0 Release
GJL
05/01/2012
2.3
Update for 2.3.0 Release
GJL
01/16/2013
2.4
Update for 2.4.0 Release
GJL
06/07/2013
2.5
Update for 2.5.0 Release
GJL
12/20/2013
2.6
Update for 2.6.0 Release
GAK
7/1/2014
3.0
Update for 3.0.0 Release
GAK
5/20/2015
3.1
Update for 3.1.0 Release
GAK
1/21/2016
3.2
Update for 3.2.0 Release
GAK
1/08/2018
3.2.2
Edit for 3.2.2 Release
GAK
SMD 989– User Manual
Page 3 (105)
Page 4

Safety Instructions
Read these instructions
Keep these instructions
Heed all warnings
Follow all instructions
Do not use this apparatus near water
Clean only with dry cloth
Do not block any ventilation openings. Install in accordance with the
manufacturer’s instructions
Do not install near any heat sources such as radiators, heat registers, stoves, or
other apparatus (including amplifiers) that produce heat
Do not defeat the safety purpose of the polarized or grounding-type plug. A
polarized plug has two blades with one wider than the other. A grounding type
plug has two blades and a third grounding prong. The wide blade or the third
prong is provided for your safety. If the provided plug does not fit into your outlet,
consult an electrician for replacement of the obsolete outlet.
Protect the power cord from being walked on or pinched particularly at plugs,
convenience receptacles, and the point where they exit from the apparatus.
Only use attachments/accessories specified by the manufacturer.
Unplug this apparatus during lightning storms or when unused for long periods of
time.
Refer all servicing to qualified service personnel. Servicing is required when the
apparatus has been damaged in any way, such as power-supply cord or plug is
damaged, liquid has been spilled or objects have fallen into the apparatus, the
apparatus has been exposed to rain or moisture, does not operate normally, or
has been dropped.
Do not expose this apparatus to dripping or splashing and ensure that no objects
filled with liquids, such as vases, are placed on the apparatus.
To completely disconnect this apparatus from the AC Mains, disconnect the
power supply cord plug from the AC receptacle.
The mains plug of the power supply cord shall remain readily operable.
Damage Requiring Service: Unplug this product from the wall outlet and refer
servicing to qualified service personnel under the following conditions:
When the power-supply cord or plug is damaged.
If liquid has been spilled, or objects have fallen into the product.
If the product has been exposed to rain or water.
If the product does not operate normally by following the operating instructions.
Adjust only those controls that are covered by the operating instructions as an
improper adjustment of the controls may result in damage and will often require
extensive work by a qualified technician to restore the product to its normal
operation.
If the product has been dropped or damaged in any way.
The product exhibits a distinct change in performance.
Replacement Parts: When replacement parts are required, be sure the service
technician uses replacement parts specified by Sencore, or parts having the
same operating characteristics as the original parts. Unauthorized part
substitutions made may result in fire, electric shock or other hazards.
SMD 989– User Manual
Page 4 (105)
Page 5

SMD 989– User Manual
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
There is always a danger present when using electronic equipment.
Unexpected high voltages can be present at unusual locations in defective equipment
and signal distribution systems. Become familiar with the equipment that you are
working with and observe the following safety precautions.
Every precaution has been taken in the design of your Satellite Modulator to
insure that it is as safe as possible. However, safe operation depends on you the
operator.
Always be sure your equipment is in good working order. Ensure that all points
of connection are secure to the chassis, and that protective covers are in place
and secured with fasteners.
Never work alone when working in hazardous conditions. Always have another
person close by in case of an accident.
Always refer to the manual for safe operation. If you have a question about the
application or operation call Sencore for assistance.
WARNING – To reduce the risk of fire or electrical shock never allow your
equipment to be exposed to water, rain or high moisture environments. If
exposed to a liquid, remove power safely (at the breaker) and send your
equipment to be serviced by a qualified technician.
To reduce the risk of shock the SMD 989 must be connected to a mains socket
outlet with a protective earthing connection.
For the SMD 989 the mains plug is the main disconnect and should remain
readily accessible and operable at all times.
The SMD 989 is equipped with an internal system battery. The SMD must be
sent if to Sencore service for replacement
CAUTION – Danger of explosion if battery is incorrectly replaced. Replace only with
the same or equivalent type.
FCC Class A Information
The SMD 989 has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device,
pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection
against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This
equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used
in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications.
Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause harmful interference in which
case the user will be required to correct the interference at his or her own expense.
Shielded cables must be used with this unit to ensure compliance with the Class A FCC limits.
Warning: Changes or modifications to this unit not expressly approved by the party
responsible for compliance could void the user’s authority to operate the equipment.
Page 5 (105)
Page 6

SMD 989– User Manual
Content
Table of Figures ............................................................................................................................. 9
Introduction .................................................................................................................................. 11
Abbreviations............................................................................................................................. 12
Hardware Overview ..................................................................................................................... 13
SMD 989 Chassis and Controller .............................................................................................. 13
Alarm Contact Closure .......................................................................................................... 13
10 MHz Reference Input ....................................................................................................... 14
10 MHz Reference Output .................................................................................................... 14
Control Ethernet Connection................................................................................................. 14
SMD 910 Option (Single or Multistream/IF Output) .................................................................. 15
SMD 912(A) Option (Single Stream/IF Output) ......................................................................... 15
SMD 920 Option (L-Band Output) ............................................................................................. 16
SMD 940 Option (10MHz Reference on L-Band) ..................................................................... 17
SMD 942 Option (24VDC BUC Power & 10MHz on L-Band) ................................................... 17
SMD 944 Option (48VDC BUC Power & 10MHz on L-Band) ................................................... 17
SMD 952 Option (Dual Redundant AC Power Supply) ............................................................. 18
SMD 954 Option (Dual Redundant DC Power Supply) ............................................................ 18
Software Licensing Overview ..................................................................................................... 19
SMD 961 DVB-S Modulation ..................................................................................................... 19
SMD 962 Option (DVB-S2-S2X, QPSK & 8PSK Modulation) ................................................... 19
SMD 964 Option (DVB-S2-S2X,16, 32, 64APSK Modulation) .................................................. 19
SMD 965 Option (30 Msps) ....................................................................................................... 20
SMD 966 Option (45 Msps) ....................................................................................................... 20
SMD 970 Option (TS Analysis) ................................................................................................. 20
SMD 971 Option (BISS Scrambling) ......................................................................................... 20
SMD 968 Option (TurboPSK Advanced Modulation) ................................................................ 20
Installation .................................................................................................................................... 21
General Considerations ............................................................................................................ 21
Rack size............................................................................................................................... 21
Ventilation ............................................................................................................................. 21
Power Connection ................................................................................................................. 21
AC Power Connection ........................................................................................................... 21
AC Dual Redundant Power Connection (optional) ............................................................... 21
DC Dual Redundant Power Connection (optional) ............................................................... 21
Rack Installation ........................................................................................................................ 22
Controlling the SMD 989 Using the Web GUI ........................................................................... 23
ASI Inputs .................................................................................................................................. 24
IP Inputs (SMD 910) .................................................................................................................. 26
IP Inputs SMD 912(A)(A) .......................................................................................................... 29
Modulator Settings .................................................................................................................... 33
Configure Modulator – Modulation ........................................................................................ 34
Configure Modulator – Inputs ............................................................................................... 35
Configure Modulator – Modulation Parameters .................................................................... 36
Configure Modulator – Carrier ID .......................................................................................... 39
Configure Modulator – TS Analysis ...................................................................................... 41
Configure Modulator – S2 Multistream ................................................................................. 42
Configure Modulator - PRBS ................................................................................................ 43
Page 6 (105)
Page 7

SMD 989– User Manual
Configure Modulator - BISS .................................................................................................. 44
Configure Modulator – TurboPSK ......................................................................................... 45
Configure Modulator – DVB-S2X .......................................................................................... 48
Output Settings.......................................................................................................................... 52
IF Output ................................................................................................................................... 53
RF Output .................................................................................................................................. 53
Admin Tab ................................................................................................................................. 55
User Profiles ......................................................................................................................... 56
Setting Login Password ........................................................................................................ 56
Downloading SNMP MIBs..................................................................................................... 56
Diagnostics ........................................................................................................................... 57
Unit Software Updating ......................................................................................................... 57
Unit Software Rollback .......................................................................................................... 58
Unit License Update .............................................................................................................. 59
10 MHz Reference Clock ...................................................................................................... 59
SNMP Communities .............................................................................................................. 62
SNMP Trap Managers .......................................................................................................... 63
Alarms/Log Tab ......................................................................................................................... 64
Alarms/Logs Configure ......................................................................................................... 65
SNMP Trap Configurations ................................................................................................... 68
About Tab .................................................................................................................................. 70
Controlling the SMD 989 Using the Front Panel ....................................................................... 71
Front Panel Quick Actions Menu............................................................................................... 71
Front Panel Modulator Settings ................................................................................................. 72
Modulator Input Configuration .............................................................................................. 72
Modulator Configuration – Modulation Mode/Configuration ................................................. 73
Modulator Configuration – Modulator Parameters (Inputs) .................................................. 74
Modulator Configuration – Modulator Parameters ................................................................ 76
Modulator Configuration- BISS Configuration....................................................................... 78
Modulator Configuration- PRBS Configuration ..................................................................... 79
Modulator Configuration- Carrier ID Configuration ............................................................... 79
TS Analysis Configuration..................................................................................................... 81
Output Configuration ............................................................................................................. 83
Front Panel Admin Settings ...................................................................................................... 85
Network Settings ................................................................................................................... 85
Unit Time ............................................................................................................................... 87
Temperature ......................................................................................................................... 87
Front Panel Lock ................................................................................................................... 87
10 MHz Reference ................................................................................................................ 87
Front Panel Alarms/Logs ........................................................................................................... 88
Alarms ................................................................................................................................... 88
Conditions ............................................................................................................................. 90
Page 7 (105)
Page 8

SMD 989– User Manual
Events ................................................................................................................................... 92
SNMP Trap Configurations ................................................................................................... 93
Front Panel About ..................................................................................................................... 93
About Software ..................................................................................................................... 93
About Hardware .................................................................................................................... 93
Licenses ................................................................................................................................ 94
Appendix ...................................................................................................................................... 95
Specifications ............................................................................................................................ 95
Open Source Software ............................................................................................................ 102
Warranty .................................................................................................................................. 103
Support and Contact Information ............................................................................................ 104
Page 8 (105)
Page 9

SMD 989– User Manual
Table of Figures
Figure 1: Basic SMD 989 platform .......................................................................................................... 13
Figure 2: Contact closure alarm output connector ............................................................................... 13
Figure 3: Contact closure pin connection ............................................................................................. 14
Figure 4: SMD 910 single TS input with IF output ................................................................................. 15
Figure 5: SMD 912(A) single TS input with monitor and IF output ...................................................... 15
Figure 6: SMD 920 L-Band output - shown with SMD 910 .................................................................... 16
Figure 7: SMD 920 L-Band output - shown with SMD 912(A) ............................................................... 16
Figure 8: SMD 940..................................................................................................................................... 17
Figure 9: SMD 942 and SMD 944 ............................................................................................................. 17
Figure 10: SMD 952 Dual Redundant AC Power Supply ...................................................................... 18
Figure 11: SMD 954 Dual Redundant DC Power Supply ...................................................................... 18
Figure 12: SMD 963 option multistream TS input with IF output ......................................................... 19
Figure 13: Rack mounting ....................................................................................................................... 22
Figure 14: Logon screen .......................................................................................................................... 23
Figure 15: Bay 1 home screen ................................................................................................................. 23
Figure 16: Single ASI input ...................................................................................................................... 24
Figure 17 Input LIst - Shows Disabled inputs with Multistream License............................................ 24
Figure 18: ASI configuration ................................................................................................................... 25
Figure 19 Inputs on SMD 910 Modulator ................................................................................................ 26
Figure 20: Expanded IP status ................................................................................................................ 27
Figure 21 Configure IP Receive Menu .................................................................................................... 27
Figure 22 IP inputs on SMD912 ............................................................................................................... 29
Figure 23 IP Input Settings on SMD 912(A) modulator ......................................................................... 30
Figure 24 IP Input Details List with SMD 912(A) .................................................................................... 32
Figure 25 Single stream status ............................................................................................................... 33
Figure 26 Multistream status ................................................................................................................... 33
Figure 27 Configuration Modulator settings menu example ............................................................... 34
Figure 28 Modulation Mode selection - SMD910 (Left) and SMD912 (Right) ...................................... 34
Figure 29 Primary & backup input selection, failover selections ........................................................ 35
Figure 30: Single stream DVB-S2 Configuration shown ...................................................................... 36
Figure 31: Supported modulations & code rates for DVB-S/DSNG and DVB-S2 ............................... 37
Figure 32: Carrier ID – Global Unique ID ................................................................................................ 39
Figure 33: Carrier ID Configuration ........................................................................................................ 39
Figure 34 Configure TS Analysis ............................................................................................................ 41
Figure 35 SMD 963 multi-stream configuration ..................................................................................... 42
Figure 36: PRBS Pseudo Random Binary Sequence ............................................................................ 43
Figure 37 BISS Scrambling configuration ............................................................................................. 44
Figure 38 TurboPSK (Single) modulation selection.............................................................................. 45
Figure 39 Advanced Modulation Turbo PSK modes and code rates .................................................. 46
Figure 40: Reduced Latency Selections ................................................................................................ 47
Figure 41: Configure DVB-SX2 Modulation/FEC ................................................................................... 48
Figure 42: Modulation/FEC code rates DVB-SX2 .................................................................................. 49
Figure 43: Outputs section ...................................................................................................................... 52
Figure 44: IF settings ............................................................................................................................... 53
Figure 45: RF settings .............................................................................................................................. 54
Figure 46: RF settings with 10MHz option ............................................................................................. 54
Figure 47: Admin tab ................................................................................................................................ 55
Figure 48: Password/Unit update location ............................................................................................. 55
Figure 49: Profile Manager ...................................................................................................................... 56
Figure 50: Setting password ................................................................................................................... 56
Figure 51: MIBs ......................................................................................................................................... 57
Figure 52: Updating software .................................................................................................................. 57
Figure 53: Uploading file .......................................................................................................................... 57
Figure 54: Upload successful .................................................................................................................. 58
Page 9 (105)
Page 10

SMD 989– User Manual
Figure 55: Update confirmation .............................................................................................................. 58
Figure 56: Updating unit .......................................................................................................................... 58
Figure 57: Unit restarting ......................................................................................................................... 58
Figure 58: Software rollback ................................................................................................................... 59
Figure 59: Update License ....................................................................................................................... 59
Figure 60: Reference clock ...................................................................................................................... 59
Figure 61: Network configuration ........................................................................................................... 60
Figure 62: IP settings ............................................................................................................................... 60
Figure 63: Configure Clone Settings ...................................................................................................... 61
Figure 64: Bay License Configuration .................................................................................................... 61
Figure 65: Configure Bay Assignment ................................................................................................... 62
Figure 66: Date/Time configuration ........................................................................................................ 62
Figure 67: SNMP communities ................................................................................................................ 62
Figure 68: SNMP Managers ..................................................................................................................... 63
Figure 69: Alarms reporting view............................................................................................................ 64
Figure 70: Logs reporting view ............................................................................................................... 64
Figure 71: Logs Severity/Transition Indicators ..................................................................................... 64
Figure 72: Alarms View - Configure ........................................................................................................ 65
Figure 73: Alarm Configuration............................................................................................................... 65
Figure 74: Alarm Error Configuration ..................................................................................................... 65
Figure 75: Alarm descriptions ................................................................................................................. 66
Figure 76: Event Configuration ............................................................................................................... 67
Figure 77: Event descriptions ................................................................................................................. 67
Figure 78: SNMP trap view ...................................................................................................................... 68
Figure 79: SNMP manager configuration ............................................................................................... 68
Figure 80: SNMP trap descriptions ......................................................................................................... 69
Figure 81: About page .............................................................................................................................. 70
Figure 82: Alarm descriptions ................................................................................................................. 89
Figure 83: Relay event descriptions ....................................................................................................... 91
Figure 84: Event descriptions ................................................................................................................. 92
Page 10 (105)
Page 11

SMD 989– User Manual
Introduction
The SMD-989 is a versatile DVB-S/S2/S2X/TurboPSK modulator platform capable of one or two
channels of modulation per rack unit. The SMD-989 comes standard with IP and ASI inputs to
offer flexibility for future changes in network architecture or sourcing content from two different
interfaces. The SMD also supports advanced DVB-S2 features such as 16APSK and 32APSK
modulation as well as the carriage of multiple streams on a single RF carrier. It further supports
the advanced modulator coding scheme turbo PSK and S2X.
This manual describes how to install, configure, and operate the SMD 989 DVBS/S2/S2X/TurboPSK Modulator. It is written for professional operators of video distribution
systems and assumes a prerequisite level of technical knowledge.
The SMD 989 is controllable through the front panel interface, a supported web browser and/or
via SNMP which also provide alarms and traps that may be configured to alert users when errors
occur through automation systems.
Through the SMD 989 web interface, front panel, or SNMP the user can perform tasks such as
configuration, monitoring, and troubleshooting.
Supported WEB interface browsers include:
- Internet Explorer 7 & above
- Mozilla Firefox 3.5 & above
- Google Chrome
Please check to be sure your web browser is supported as above.
Page 11 (105)
Page 12

SMD 989– User Manual
Abbreviations
16 APSK – 16 Amplitude and Phase Shift Keying
32 APSK – 32 Amplitude and Phase Shift Keying
64 APSK -- 64 Amplitude and Phase Shift Keying
ASI – Asynchronous Serial Interface
BCH - Bose and Ray Chaudhuri code
BISS – Basic Interoperable Scrambling System
BNC – British Naval Connector
BPS – Bits per second
CAM – Conditional Access Module
CAT – Conditional Access Table
CI – Common Interface
CID – Carrier Identification
DHCP – Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
DVB – Digital Video Broadcasting
FCC – Federal Communications Commission
HD – High Definition
IF – Intermediate Frequency
I/O – Input/Output
IP – Internet Protocol
ISI – Intersymbol Interference
LED – Light Emitting Diode
MAC – Media Access Control
Mbps – 1,000,000 bits per second
MER – Modulation Error Ratio
MPEG – Refers to standards developed by the ISO/IEC JTC1/SC29
WG11 MPEG-2 – Refers to ISO/IEC standards 13818-1 (Systems), 13818-2
(Video), 13818-3 (Audio), 13818-4 (Conformance)
MPTS – Multiple Program Transport Stream
NTP – Network Time Protocol
PAT – Program Association Table
PCR – Program Clock Reference
PID – Packet Identifier
PMT – Program Map Table
QAM – Quadrature Amplitude Modulation
QPSK – Quadrature Phase Shift Keying
RF – Radio Frequency
RU – Rack Unit
RW – Read/Write
SD – Standard Definition
SI – Service Information
SNMP – Simple Network Management Protocol
SPTS – Single Program Transport Stream
TS – Transport Stream
Turbo PSK - Advanced Modulation Coding Phase Shift Keying
Page 12 (105)
Page 13

SMD 989– User Manual
CONTROL REF IN
ALARM
BAY 2
BAY 1
100-240VAC, 47-63Hz, 200W
Figure 1: Basic SMD 989 platform
Figure 2: Contact closure alarm output connector
ALARM
1
6
5
9
Hardware Overview
The SMD 989 consists of a chassis with two bays which can house individually configured
modulators. There are two different modulator options including the SMD 910 or SMD912(A).
These options are described in the next section of this manual. Each modulator option can be
configured to support either IF or L-band outputs. The modulators support all DVB-S/S2
modulation types from QPSK to 64 APSK. The SMD 910 modulator can be upgraded to support
multistream outputs with streams input to one of the four ASI ports or IP interface. The SMD912
modulator can be upgraded to support Turbo PSK advanced modulation. This section of the
manual describes the chassis and hardware options available.
SMD 989 Chassis and Controller
The Sencore SMD 989 satellite modulator platform can be configured in multiple hardware
configurations. The two bays with the controller located in the middle of the chassis as shown in
Figure 1.
The controller module hosts the graphical user interface along with the relays and 10 MHz input
reference. Looking at the rear of the chassis, the left slot is bay 1 and the right slot is bay 2.
Each bay is independently controlled and operated. Therefore each bay needs to be configured
separately in order to ensure the expected operation.
The SMD 989 platform offers eight modulation options. The modulation module is the SMD 910
which includes an MPEGoIP input via RJ45, four ASI inputs via BNC connectors, and an IF
output via a BNC connector. The SMD 910 option can be configured with an optional L-band
output module, the SMD 920 which includes and L-band output via an SMA connector. The other
licenses available are software licenses enabling features for bitrates, DVB-S2, and multistream.
Alarm Contact Closure
The Alarm contact closure output connector allows a user to configure two separate contacts that
can be used to drive external alarm indicators (sirens, flashlight etc.) or can be used to connect to
a redundancy switching system. The pinout in Figure 3 shows the relays in a de-energized state.
When the SMD 989 is on the relays energize. This allows the possibility to monitor the state of
the relays if the unit losses power the relays de-energize and a redundant unit can be activated.
Page 13 (105)
Page 14

SMD 989– User Manual
Pin 2: Relay
1 Common
Pin 4: Relay
2 Common
Pin 1: Relay 1
Normal Closed
Pin 3: Relay 1
Normal Open
Pin 6: Relay 2
Normal Closed
Pin 5: Relay 2
Normal Open
Figure 3: Contact closure pin connection
10 MHz Reference Input
The clock input (CLK IN) is used when a reference with enhanced stability is needed or when
several modulators need to be synchronized to the same clock source. The level should be 0
dBm nominally or within a range of -3 to +7 dbm.. The unit automatically senses and switches
between the internal or external reference based on presence detection. By default, the internal
clock reference is used. When an external clock input is sensed, the unit automatically locks to
the incoming reference.
10 MHz Reference Output
The clock output (CLK Out), not shown in figure 1, is used to provide a sample of the internal
reference clock when it is desired to synchronize other equipment to the modulator’s reference
clock or output. The output level is approximately 0 dbm. This output is subsequently and
automatically locked to a 10 MHz reference input when an input is applied to the 10 MHz
Reference Input.
Control Ethernet Connection
A standard RJ-45 connector provides connection to the SNMP and Web Interface of the SMD
989 platform. The connection is a 10/100 BaseT connection. A user can view the IP address of
the unit from the front panel or once known can access the web interface through any supported
web browser by typing the IP address of the unit. The control port is capable of both DHCP and
static IP addressing. By default the IP address of the SMD 989 is statically set to 10.0.0.60.
Supported Web Browsers include:
Internet Explorer 7 & above
Firefox 3.5 & above
Google Chrome
Page 14 (105)
Page 15

SMD 989– User Manual
Figure 5: SMD 912(A) single TS input with monitor and IF output
SMD 910 Option (Single or Multistream/IF Output)
The SMD 910 Module option offers single stream or S2 multistream modulation. A single stream
input is selected with one of the ASI and IP inputs to the modulator. There is one IP input port and
four ASI ports available by default and come standard. The user is allowed to select the desired
input in the front panel, web interface, and/or SNMP. Multistream permits multiple input selections
up to 6 streams via the ASI or IP inputs. The IF Out port provides the modulated IF output which
is 70 MHz by default but user selectable between 70 and 140 MHz.
Figure 4: SMD 910 single TS input with IF output
The SMD 910 option has three different types of I/O as shown in Figure 4.
- Data input (RJ45 10/100/1000 auto detect speed & status)
- ASI inputs (75 ohm BNC connectors x4)
- IF output (75 ohm BNC connector)
SMD 912(A) Option (Single Stream/IF Output)
The SMD 912 or SMD 912A Module option offers a single TS stream modulation. A single stream
input to the modulator is selected through either the ASI or IP inputs. There are two IP input ports
and two ASI input ports available by default and come standard. The user is allowed to select the
desired input in the front panel, web interface, and/or SNMP. The IF Out port provides the
modulated IF output which is user selectable between 70 and 140 MHz. The MON OUT (monitor
output) provides a fixed L-band test output at a frequency of 1100 MHz. The monitor output
simultaneously provides a second IF output which mirrors the selected IF output frequency with a
level that is – 20 dB in respect to the IF Out port level. The SMD 912 provides an IF output level
range from -30 to -5 dBm while the SMD 912A output range is -20 to +5 dBm.
The SDM 912(A) option has four different types of I/O as shown in Figure 5.
- Data inputs (RJ45 10/100/1000 auto detect speed & status x2)
- ASI inputs (75 ohm BNC connector x2)
- Monitor output (75 ohm BNC connector)
- IF output (75 ohm BNC connector)
Page 15 (105)
Page 16

SMD 989– User Manual
IF OUT
IF IN
1
2 3
4
DATA IN
L-BAND OUT
MON
PRI
ASI IN
SMD 920 Option (L-Band Output)
The SMD 920 module provides an L-Band output to either the SMD910 or SMD 912(A) modulator
boards. The SMD 920 must accompany either an SMD 910 or SMD 912(A) modulator board in
the SMD 989 platform. Inputs to the SMD 910 or SMD 912(A) are described on the previous page
of this manual. The SMD 920 module receives an IF input from the SMD 910 or SMD 912(A) and
upconverts it to an L-Band frequency output. A short jumper cable from the IF OUT to the IF IN
jacks is needed. The IF Input to the SMD 920 L-Band upconverter board is auto detected and
must be either a 70MHz or 140 MHz carrier. Therefore, the SMD 910 or SMD 912(A) must be set
to output either 70 or 140 MHz for use with the SMD 920. The L-band Output frequency is user
settable from 950 to 2150 MHz.
Figure 6: SMD 920 L-Band output - shown with SMD 910
The SMD 920 in combination with the SMD 910 modulator option has six different types of I/O as
shown in Figure 6.
Data input (RJ45 10/100/1000 auto detect speed & status)
ASI inputs (75 ohm BNC connector x4)
IF output (75 ohm BNC connector)
Upconverter IF input (75 ohm BNC Connector)
L-band primary output (50 ohm SMA connector)
L-band monitor output (50 ohm SMA connector -20 dBc from primary)
The SMD 920 in combination with the SMD 912(A) modulator option as 7 I/Os (Figure 7).
Figure 7: SMD 920 L-Band output - shown with SMD 912(A)
Data input (RJ45 10/100/1000 auto detect speed & status)
ASI inputs (75 ohm BNC connector x2)
Monitor output 1100MHz, -50 dBm (75 ohm BNC connector)
IF output (75 ohm BNC connector)
Upconverter IF input (75 ohm BNC Connector)
Page 16 (105)
Page 17

SMD 989– User Manual
L-band primary output (50 ohm SMA connector)
L-band monitor output (50 ohm SMA connector -20 dBc from primary)
SMD 940 Option (10MHz Reference on L-Band)
The SMD 940 Option, when used with options SMD 920, adds the capability to combine the LBand output with an internal 10MHz oven-controlled crystal oscillator or with an external 10MHz
reference. SMD 940 eliminates the need for an external diplexer. Option 940 is also adds the
capability to combine an external DC to the L-Band output when not used with options SMD 942
and SMD 944 described below. The L-BAND Pri output on the SMD 920 is connected to the
LOOP IN. The L-Band RF, 10MHz and DC are combined at the PRI OUT w/ 10MHz + DC
connector.
Figure 8: SMD 940
SMD 942 Option (24VDC BUC Power & 10MHz on L-Band)
The SMD 942 Option includes option SMD 940 with the additional capability to provide 24VDC
power along with 10MHz and L-Band modulated signal on the same connector. SMD 942
eliminates the need for an external DC supply and external diplexer. The L-BAND Pri output is
connected to the LOOP IN. The L-Band RF, 10MHz and DC are combined at the PRI OUT w/
10MHz + DC connector.
Figure 9: SMD 942 and SMD 944
SMD 944 Option (48VDC BUC Power & 10MHz on L-Band)
The SMD 944 Option includes option SMD 940 with the additional capability to provide 48VDC
power along with 10MHz and L-Band modulated signal on the same connector. SMD 944
eliminates the need for an external DC supply and external diplexer. The L-BAND Pri output is
connected to the LOOP IN. The L-Band RF, 10MHz and DC are combined at the PRI OUT w/
10MHz + DC connector.
Page 17 (105)
Page 18

SMD 989– User Manual
SMD 952 Option (Dual Redundant AC Power Supply)
The SMD 952 Option Dual Redundant AC Power Supply provides a redundant hot swappable
power supply for the unit. If either power supply fails the backup supply will be automatically
activated. A power supply failure event will result in an audible alarm notification along with Front
Panel and GUI Error notification. The audible alarm can be reset on by pressing the red button on
power supply module. The faulty supply can then be removed and replaced without the need to
power down the unit or remove the unit from the rack.
Figure 10: SMD 952 Dual Redundant AC Power Supply
SMD 954 Option (Dual Redundant DC Power Supply)
The SMD 952 Option Dual Redundant DC Power Supply provides a redundant hot swappable
power supply for the unit. If either power supply fails the backup supply will be automatically
activated. A power supply failure event will result in an audible alarm notification along with Front
Panel and GUI Error notification. The audible alarm can be reset on by pressing the red button on
power supply module. The faulty supply can then be removed and replaced without the need to
power down the unit or remove the unit from the rack.
Figure 11: SMD 954 Dual Redundant DC Power Supply
Page 18 (105)
Page 19

SMD 989– User Manual
IF OUT
IF IN
1
2 3
4
DATA IN
ASI IN
Figure 12: SMD 963 option multistream TS input with IF output
Software Licensing Overview
SMD 961 DVB-S Modulation
The SMD 961 option is a software license allowing the modulator board to modulate DVBS/DSNG using QPSK, 8PSK, or 16QAM. This option is enabled on all SMD 910 or SMD
912(A)(A) modules by default.
SMD 962 Option (DVB-S2-S2X, QPSK & 8PSK Modulation)
The SMD 962 option is a software license allowing the modulator SMD 910 or SMD 912(A) board
to modulate DVB-S and DVB-S2. This option includes the SMD 961 license which allows for
DVB-S/DSNG. The SMD 962 option includes QPSK and 8PSK for DVB-S2 and DVB-S2X to 15
Msps. This option can be licensed on the unit at any time without sending it back to the factory.
SMD 963 Option (DVB-S2 Multistream)
The SMD 963 option is a software license which enables multistream for CCM and VCM support
for the SMD 910 when used with DVB-S2. This option is not available when using the SMD
912(A)(A) modulator board. The 963 option supports up to a total of 6 TS streams sourced from
any of the ASI or IP inputs. The user is allowed to select the desired amount of inputs and type
from the front panel, web interface, and/or SNMP. This option can be licensed on an SMD989
unit with an SMD910 modulator at any time without sending it back to the factory. The SMD 970
TS Analysis option is not applicable with DVB-S2 Multistream signals.
The SMD 963 option has three different types of I/O as shown with SMD 910 board in Figure 12.
- Data input (RJ45 10/100/1000 auto detect speed & status)
- ASI inputs (75 ohm BNC connector)
- IF output (75 ohm BNC connector)
SMD 964 Option (DVB-S2-S2X,16, 32, 64APSK Modulation)
The SMD 964 option is a software license allowing the modulator SMD 910 or SMD 912(A) to
modulate DVB-S, DVB-S2 and DVB-S2X to 15 Msps. This option includes the SMD 961 and
SMD 962 licensed capabilities which allows for DVB-S, DVB-S2 and DVB-S2X at QPSK and
8PSK. The SMD 964 option further includes 16 APSK, 32 APSK, and,64APSK modulations for
DVB-S2 and DVB-S2X. This option can be licensed on the unit at any time without sending it
back to the factory.
Page 19 (105)
Page 20

SMD 989– User Manual
SMD 965 Option (30 Msps)
The SMD 965 option is a software license allowing the modulator SMD 910 board or SMD
912(A)(A) board to modulate at a symbol rate up to 30 Msps. The default symbol rate is 0.5 to 15
Msps and the SMD 965 option allows the modulator to extend the rate up to 30 Msps. This
option can be licensed on the unit at any time without sending it back to the factory.
SMD 966 Option (45 Msps)
The SMD 966 option is a software license allowing the modulator SMD 910 or SMD 912(A) board
to modulate at a symbol rate up to 45 Msps. The default symbol rate is 0.5 to 15 Msps and the
SMD 966 option allows the modulator to extend the rate up to 45 Msps. Since the SMD 966
allows up to 45 Msps it includes the SMD 965 license. This option can be licensed on the unit at
any time without sending it back to the factory.
SMD 970 Option (TS Analysis)
The SMD 970 option is a software license which adds TS analysis to the primary and secondary
(backup) inputs of the SMD 910 or SMD 912(A)(A) modulator. This option extends the input error
detection, of the primary and backup inputs following the TS 101 290 [4] guidelines. The TS
errors can be configured as a switch to backup trigger and as alarm indicators. This option can be
licensed on the unit at any time without sending it back to the factory.
SMD 971 Option (BISS Scrambling)
The SMD 971 option is a software license which enables support of Biss Scrambling in the SMD
910 or SMD 912(A) Modulator Module. BISS is a “Basic Interoperable Scrambling System” for
use on DVB signals which encrypts the entire transport stream using fixed session keys. SMD971 Supports Biss Mode 1 and BISS Mode E. BISS-E introduce encrypted session words and
allow centrally-managed conditional access. This option can be licensed on the unit at any time
without sending it back to the factory.
SMD 968 Option (TurboPSK Advanced Modulation)
The SMD 968 option is a software license which enables support of an advanced modulation and
coding technology in the SMD 912(A) modulator option. This option is not available on the SMD
910 modulator. This option enables the SMD 912(A) modulator to generate and an advanced
modulation and coding transmission developed by Broadcom. The transmission is commonly
referred to as 8PSK turbo code or simply “Turbo PSK.” This option when combined with SMD
965 increases the turbo output symbol rates from a limit of 15 Msps to 30 Msps. This option can
be licensed on a unit with SMD 912(A) modulator or dual modulators at any time without sending
it back to the factory.
Page 20 (105)
Page 21

SMD 989– User Manual
Installation
General Considerations
This section describes the installation procedure for the SMD 989.
Rack size
The chassis is designed to be installed in a standard 19-inch rack. The SMD 989 occupies 1RU
of rack space. All of the cable connections are located on the rear of the unit.
Ventilation
The SMD 989 is cooled via forced induction through the front of the unit and exhausted through
the vents in the rear. The SMD 989 is equipped with a temperature monitors to ensure operating
temperature is maintained.
Power Connection
Using the proper power connections is vital to the safe operation of the SMD 989. Only use the
supplied 3-prong power connector or one with equal specifications.
AC Power Connection
The SMD 989 is capable of either operating on 120V or 240V systems. The power supply will
automatically detect the system it is connected to. To hook up the power use the following steps:
1. Locate the AC power cord included with the SMD 989.
2. Plug the female end of the power cord (end with no prongs) into the back of the unit.
3. Locate a protected outlet (usually inside of the rack) to plug the male end of the power
cable into.
AC Dual Redundant Power Connection (optional)
The Dual Redundant option allows the SMD 989 to be powered by two separate AC supplies
either operating on 120V or 240V systems. The power supply will automatically detect the
system it is connected to. To hook up the power use the following steps:
1. Locate the AC power cords included with the SMD 989.
2. Plug the female end of the power cords (end with no prongs) into the back of the unit.
3. Locate a protected outlet (usually inside of the rack) to plug the male end of the power
cord into.
DC Dual Redundant Power Connection (optional)
The Dual Redundant option allows the SMD 989 to be powered by two separate DC supplies
operating on a -48VDC system. To hook up the power use the following steps:
1. Connect the negative 48VDC to the terminal labeled -48V.
2. Connect ground to the terminal labeled 0V
Page 21 (105)
Page 22
SMD 989– User Manual
Figure 13: Rack mounting
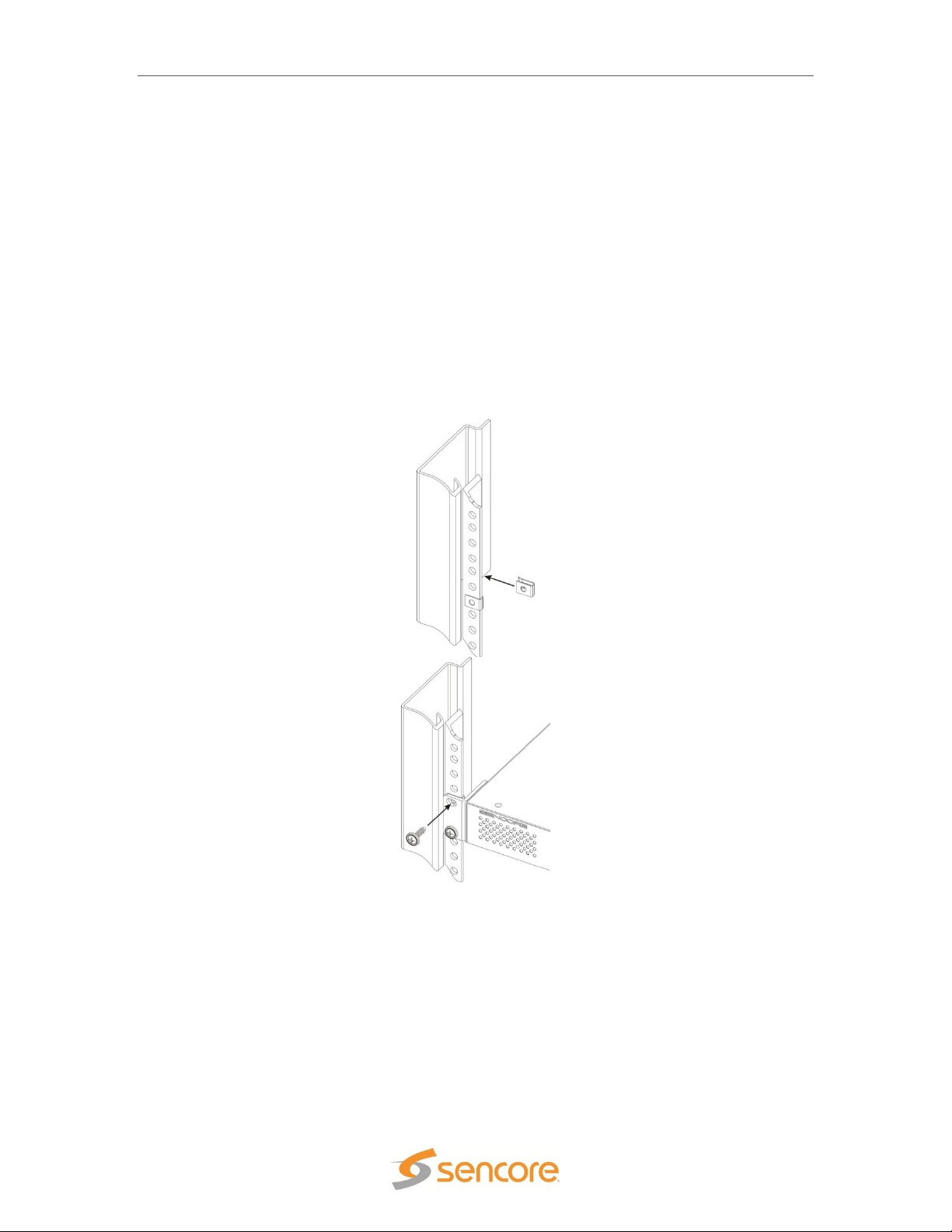
Rack Installation
To install the SMD 989 into a rack use the following steps:
1. Determine the desired position in the rack for the SMD making sure that the air intake on
the front of the unit and the exhausts on the rear of the unit will not be obstructed.
2. Insert the rack mount clips into place over the mounting holes in the rack.
3. Slide the SMD into position in the rack.
4. Secure the SMD to the rack by installing the four screws through the front mounting holes
and tightening.
WARNING: To prevent injury, the apparatus must be securely attached to the floor/wall in
accordance with the installation instructions.
Page 22 (105)
Page 23

SMD 989– User Manual
Figure 15: Bay 1 home screen
Figure 14: Logon screen
Controlling the SMD 989 Using the Web GUI
From any supported web browser (IE 7 or above, Firefox 3.5, Google Chrome) that is connected
to the same network as the SMD 989, type the IP address of the unit to access the web interface.
By default the IP address of the unit is set to static at 10.0.0.60. The SMD 989 is also capable of
DHCP addressing and accessing via host name. Refer to Controlling the SMD 989 Using the
Front Panel for initial IP settings.
Upon correctly connecting to the unit, a dialog box similar to Figure 14 appears asking the user to
login. By default the password is left blank. Once logged on, the password can be set in the
“Admin” tab.
When logged in a page similar to that shown in Figure 15 appears. Depending on the options of
modules/features installed, page variations will be seen and are normal.
The main screen for each bay is displayed in a left-to-right fashion. Inputs are shown on the left,
processing in the middle section and outputs are shown on the right. The user is capable of
configuring all parameters of the modulator from this page by clicking on the (cog) icon
which represents a settings configuration.
Page 23 (105)
Page 24

SMD 989– User Manual
Figure 16: Single ASI input
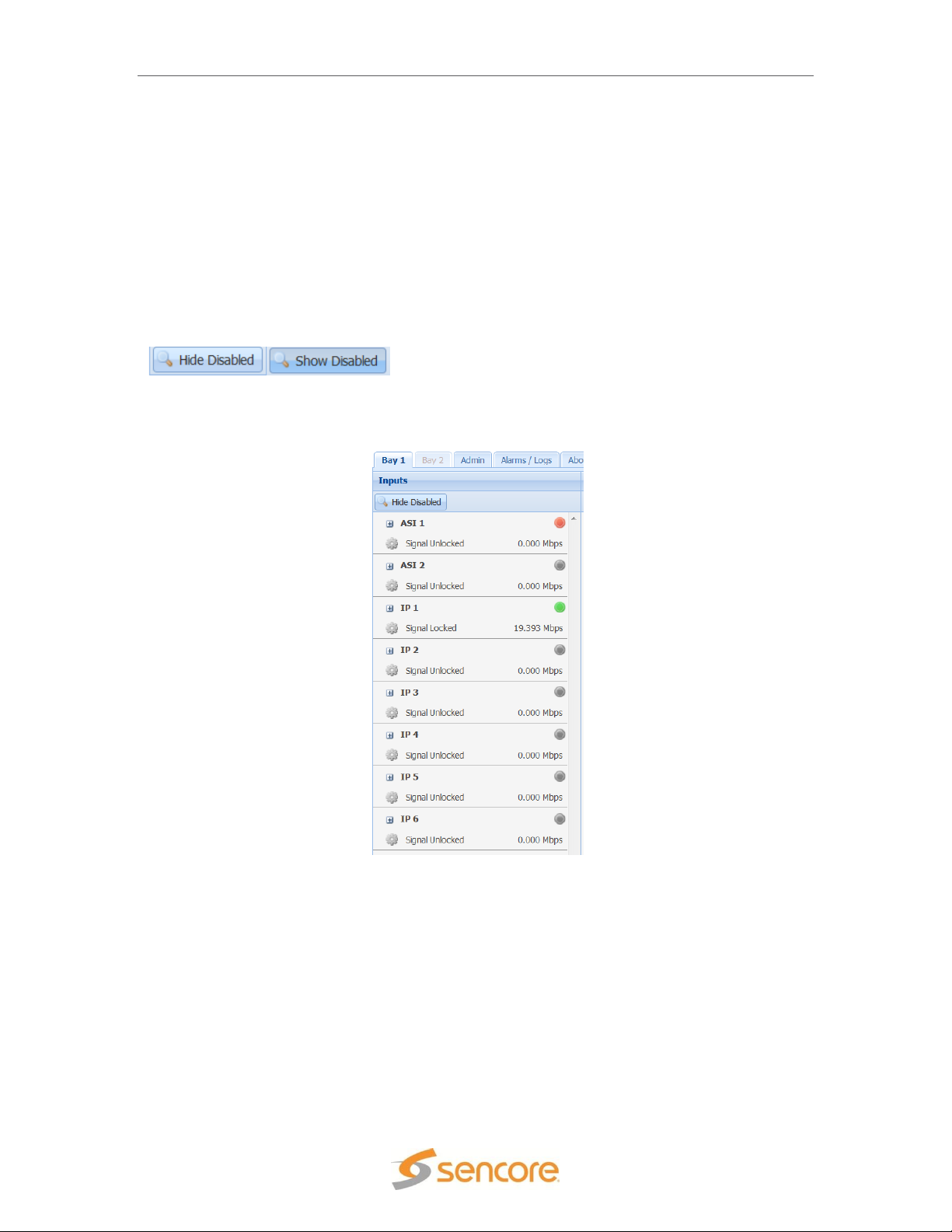
ASI Inputs
The ASI inputs to the modulator are shown on the left column of the home screen for each bay.
The available inputs are listed in sections or rows. Each input has either an enabled or disabled
status. To see all the possible inputs, click on the Show Disabled tab. To see only the enabled
inputs, click on the Hide Disabled tab. Depending on the unit licensing the inputs that are enabled
by default and listed may be different.
The inputs available on the SMD 910 modulator include (4) ASI inputs and (6) IP inputs. These
will be shown when the Show Disabled icon is selected. The inputs available on the SMD 912(A)
modulator includes (2) ASI inputs and 6 IP inputs in both IP port 1 and IP port 2.
Clicking on the “ ” sign by each ASI port allows the advanced details to be shown for the port.
ASI details include only a packet size indication.
By default ASI input port 1 is enabled, but by clicking on the settings tab for each ASI input the
port may be enabled. To configure an ASI port, click on the Icon. In the Configuration ASI
Port menu, as shown in Figure 18, the input can be enabled or disabled. Each input port allows
the user to set a local Alias for each port. This is a friendly name that can be used to name the
input for easy reference in the future.
Page 24 (105)
Figure 17 Input List - Shows Disabled inputs with Multistream License
Page 25

SMD 989– User Manual
Green LED
Status is good. No errors are present and
function is operating normally.
Red LED
Status indicates input is active but with
active error(s). View errors in the
Alarms/Logs menu
Grey LED
Input is inactive and/or alarms are inactive
Figure 18: ASI configuration
Each input port listing or section contains an active input bitrate indication on the right side of the
section. When the input is enabled and an active transport stream is present on that input, the
bitrate counter indicates the incoming bitrate in Mbps.
Each input port listing contains a status indicator light near the right side of the listing. If the port
is enabled and no sync is detected, an error will be indicated by a red light. Errors can be user
enabled/disabled if desired. Please see the Alarm/Logs Section for details. The chart below
describes the status indicator lights.
Page 25 (105)
Page 26

SMD 989– User Manual
Green LED
Status is good. No errors are present and
function is operating normally.
Red LED
Status indicates input is active but with
active error(s). View errors in the
Alarms/Logs menu
Grey LED
Input is inactive and/or alarms are inactive
IP Inputs (SMD 910)
The IP inputs to the SMD 910 modulator are shown on the left column of the home screen for
each bay. The available IP inputs are listed in rows under the ASI inputs. Each IP input has
either an enabled or disabled status. To see all the possible IP inputs, click on the Show Disabled
tab. To see only the enabled inputs, click on the Hide Disabled tab. Depending on the unit
licensing the IP inputs that are enabled by default and listed may be different.
The IP inputs available on the SMD 910 modulator include (6) IP inputs via IP port 1. These
inputs are shown when the Show Disabled icon is selected as shown in Figure 19.
Each IP input port listing or section contains an active input bitrate indication on the right side of
the section. When the input is enabled and an active transport stream is present on that input, the
bitrate counter indicates the incoming bitrate in Mbps.
Each IP input port listing contains a status indicator light near the right side of the listing. If the
port is enabled and no sync is detected, an error will be indicated by a red light. Errors can be
user enabled/disabled if desired. Please see the Alarm/Logs Section for details. The chart below
describes the status indicator lights.
Page 26 (105)
Figure 19 Inputs on SMD 910 Modulator
Page 27

SMD 989– User Manual
Figure 20: Expanded IP status
Each input has a listing of advanced details providing information regarding the settings and
status of the input. Clicking on the “ ” sign by each IP port allows the advanced details to be
shown as presented in Figure 20. Click on the down arrow to close the advanced details list
menu. The advanced details list includes routing, port, input buffer, protocol, packet, and IGMP
filter information which reflects the current settings of the IP input port.
Each input can be configured within a configuration menu. Figure 21 represents the IP settings
(SMD 910) for an individual IP source, by default all IP inputs Input ports are enabled by clicking
on the settings tab for each IP input and enabling the port, moving the port into the Enabled List.
This allows for customizing the view for quick reference. The input can be returned to the
disabled section or list by disabling the port in the settings tab.
Page 27 (105)
Figure 21 Configure IP Receive Menu
Page 28

SMD 989– User Manual
Receive
Enabled
Disabled
This setting allows the user to enable or
disable the IP input stream for primary or
backup use or input to the modulator
Alias
Permits entry of friendly name or description
Routing Mode
Multicast
Unicast
Multicast setting allows the unit to receive
multicast streams. Multicast streams
originate from the IP range 224.0.0.0 –
239.255.255.255. Unicast allows the unit to
receive unicast streams. Unicast streams
originate directly from a source device.
Destination IP
224.0.0.0 –
239.255.255.255
This setting is only available when receiving
a multicast stream. This address is the IP
address the source device is sending to.
Destination Port
0 – 65535
This is the UDP port the source device is
sending to. This is the only setting required to
receive a unicast stream.
Input Buffer Size
(KB)
10 – 600 KB
This setting determines how much data is
received before the SMD 989 starts
decoding. Increasing this value will allow the
SMD 989 to receive streams on networks
with high network jitter. Increasing this value
also increases the latency of the SMD 989.
IGMP Filter Mode
Exclude
Include
Used on networks supporting IGMPv3. If this
setting is set to Exclude any streams
originating from the user defined IP
addresses will be rejected. If this setting is
set to Include any streams originating from
the user defined IP addresses will be
received.
The following chart provides a list of the selections in the IP input configuration menu and a
description of setting.
Note: IGMPv2 is used to join/leave multicast streams by default if no IGMP Filter addresses are
entered. If IGMP Filter Mode addresses are specified then IGMPv3 is used.
Page 28 (105)
Page 29
SMD 989– User Manual
IP Inputs SMD 912(A)
The SMD 912(A) or SMD 912(A) provides two physical IP input ports compared to one port on
the SMD 910. It further provides RTP/FEC receive capabilities along with configuration of the
input buffer by delay time. The IP inputs are also monitored for FEC status information and errors.
This section provides details of IP input settings and monitoring details when using the SMD
912(A) modulator.
The IP inputs to the SMD 912(A) modulator are shown on the left column of the home screen for
each bay. The available IP inputs are listed in rows under the ASI inputs. Each IP input has
either an enabled or disabled status. To see all the possible IP inputs, click on the Show Disabled
tab. To see only the enabled inputs, click on the Hide Disabled tab. Depending on the unit
licensing the IP inputs that are enabled by default and listed may be different.
The IP inputs available on the SMD 912(A) modulator include (6) IP inputs. These six inputs may
be sourced from either IP port 1 or IP port 2. These six possible inputs are shown when the Show
Disabled icon is selected as shown in figure 22.
Figure 22 IP inputs on SMD912
The modulator setup provides a user selection of a primary and backup input routed to the
modulator. This is explained in the next section of this manual. The primary and backup inputs
are selected from the list of inputs on the left side of the home menu. For normal operation the
primary and backup inputs must be selected from listed inputs that are enabled and actively
receiving an input transport stream. The DVB-S/DSNG single-stream, DVB-S2 CCM singlestream, DVB S2X single-stream or TurboPSK modulation modes default the primary input to ASI
1.
Each IP input port listing or section contains an active input bitrate indication on the right side of
the section. When the input is enabled and an active transport stream is present on that input, the
bitrate counter indicates the incoming bitrate in Mbps.
Page 29 (105)
Page 30

SMD 989– User Manual
Green LED
Status is good. No errors are present and
function is operating normally.
Red LED
Status indicates input is active but with
active error(s). View errors in the
Alarms/Logs menu
Grey LED
Input is inactive and/or alarms are inactive
Each IP input port listing contains a status indicator light near the right side of the listing. If the
port is enabled and no sync is detected, an error will be indicated by a red light. Errors can be
user enabled/disabled if desired. Please see the Alarm/Logs Section for details. The chart below
describes the status indicator lights.
Each input can be configured within its own configuration menu. . Figure 23 represents the IP
settings (SMD 912(A)) for an individual IP source. This section provides a description of the
settings in the input’s Configure IP Receive menu.
The Receive Enable/Disable field is used to make the input active or inactive. When enabled or
active the SMD 989 begins to monitor the input status with the alarms and logging. By default
most input ports are disabled, but by clicking on the settings tab for an IP input and selecting
enable the port is moved into the Enabled list. This allows for customizing the view of the inputs in
the home menu. The input can be returned to the disabled status by disabling the input.
Figure 23 IP Input Settings on SMD 912(A) modulator
The Configure IP Receive menu permits user definition of the receive characteristics of that input.
The following chart provides a list of the selections along with a description of the settings for
each field.
Each input allows the user to set a local alias or friendly name for easy reference. The general IP
settings section allows a user to enter the unicast/multicast address along with destination port.
Page 30 (105)
Page 31

SMD 989– User Manual
Alias
Permits entry of friendly name or description
Receive
Enabled
Disabled
This setting allows the user to enable or
disable these input stream settings.
Physical
Connector
Port 1
Port 2
The physical connector on the MPEG/IP card
that will be used to receive the input.
Routing Mode
Multicast
Unicast
Multicast setting allows the unit to receive
multicast streams. Multicast streams
originate from the IP range 224.0.0.0 –
239.255.255.255. Unicast allows the unit to
receive unicast streams. Unicast streams
originate directly from a source device.
Destination IP
224.0.0.0 –
239.255.255.255
This setting is only available when receiving
a multicast stream. This address is the IP
address the source device is sending to.
Destination Port
0 – 65535
This is the UDP port the source device is
sending to. This is the only setting required to
receive a unicast stream.
FEC
Enabled
Disabled
Enabling FEC (Forward Error Correction)
tells the SMD 989 to look at Destination Port
+2 and Destination Port +4 for a SMPTE
2022 FEC Matrix.
RTP SSRC
Enabled
Disabled
Enabling RTP SSRC allows the SMD989 to
filter the input by the user defined value. Only
streams containing the user defined value
will be received by the SMD989.
SSRC Filter Value
0 – 4294967295
The Filter Value the SMD 989 checks for
before receiving a stream with RTP SSRC.
Buffer Mode
Size (KB)
Delay (ms)
Allows option to set buffer mode to Size in
KB or Delay ms
Buffer Size (KB)
10 – 4000 KB
This setting determines how much data is
received before the SMD 989 starts
decoding. Increasing this value will allow the
SDM 989 is receive streams on networks
with high network jitter. Increasing this value
also increases the latency of the SMD 989.
Buffer Delay (ms)
1 – 4000 ms
The buffer delay setting allows the buffer size
to be set by delay time. The Buffer delay time
will be determined by the input data rate.
IGMP Filter Mode
Exclude
Include
Used on networks supporting IGMPv3. If this
setting is set to Exclude any streams
originating from the user defined IP
addresses will be rejected. If this setting is
set to Include any streams originating from
the user defined IP addresses will be
received.
With the SMD 912(A) the input buffer size is settable at a range from 1 to 4,000 KB. The larger
the buffer size, the more latency will be created in the system. The tradeoff is a potential for IP
jitter and dropped packets. It further permits setting an input buffer delay of 1 to 4000 mS.
The advanced settings allow source specific multicasting using IGMP v3 joins. The filter can be
set to exclude or include. IGMP addresses can be added and removed by clicking the
Page 31 (105)
Page 32

SMD 989– User Manual
appropriate heading in the table. There can be up to 64 addresses entered with the highest
address taking priority over the addresses below it. IGMPv2 is used to join/leave multicast
streams by default if no IGMP Filter addresses are entered. If IGMP Filter Mode addresses are
specified then IGMPv3 is used.
Each input has a listing of advanced details providing information regarding the settings and
status of the input. Clicking on the “ ” sign by each IP port allows the advanced details to be
shown as presented in Figure 24. Click on the down arrow to close the advanced details list
menu.
Figure 24 IP Input Details List with SMD 912(A)
The advanced details list includes configuration, status, and counter section. The Config section
provides physical port, routing, input buffer, RTP SSRC information, FEC status, and the IGMP
filter mode. The Status section provides buffer setting, protocol, and FEC data. The Counter
section provides active packet error detection and counts.
Page 32 (105)
Page 33

SMD 989– User Manual
Figure 26 Multistream status
Modulator Settings
The section overviews the processing or modulator as shown in the middle of the individual bay
home screen. Depending on the enabled licenses, the status might look slightly different as
shown in Figure 25 and Figure 26.
Figure 25 Single stream status
Page 33 (105)
Page 34

SMD 989– User Manual
Configure Modulator – Modulation
To configure the modulator click on the “Configure Modulator Options” icon
at the top of the middle “Modulators” section.
Figure 27 is a representation of the menu with settings for single stream (single DVB-S2 CCM
mode) modulation. Within the Configure Modulation Options menus five tabs may be shown at
the top of the menu. These may be selected to configure settings for the modulator.
Inputs: Provide configuration of the Primary and Backup input feed to the modulator
Modulation: Provides configuration of the modulator transmission
BISS: Provides configuration of the BISS encryption to the modulator transmission
PRBS: Provides Psuedo Random Binary Sequence bit error rate test signal
Carrier ID: Provides configuration of the Carrier ID of the modulator transmission
The following manual sections provide details of the modulator configuration settings available for
single stream, multistream and turboPSK modulation.
located
Figure 27 Configuration Modulator settings menu example
The Modulation Mode field at the top of the Configure Modulator menu provides an important
selection of the type of output transmission the modulator will generate. Click on the dropdown
arrow to produce a list of available modulation modes. The modes listed will vary depending on
the system modulator and licensing. Click on a listing to select.
Figure 28 Modulation Mode selection - SMD910 (Left) and SMD912(A) (Right)
Page 34 (105)
Page 35

SMD 989– User Manual
Configure Modulator – Inputs
The Input tab provides selection of the Primary Input and the option to enable a Backup Input to
the modulator. A backup input may be selected in the event of a primary input fault. The selected
Primary or the Backup Input is routed to the main modulator input. The selected Primary and
Backup Inputs must be enabled and active inputs. (See the previous section of this manual)
Switching Manually from Primary Input To Backup Input:
You can switch manually between the Primary Input and Backup input with the icon located at the
top of the middle modulator section. Click on the icon. This icon changes
to a Switch to Primary Input icon when the Backup Input is active.
There are several options for defining failover conditions in which the input to the modulator
switches from the Primary Input to the Backup input. There are also options for defining
conditions in which the input returns from the Backup Input to the Primary Input.
- Failover to Backup can be set to On Primary TS Sync Loss, On Primary TS
Analysis Failure or Manual Only. TS Sync Loss mode allows the SMD 989 to switch
to backup if the primary input transport sync is lost. In TS Analysis mode failover is
based on transport stream errors or sync loss. This allows the SMD 989 to switch to
a backup source when there are errors in the transport stream even if it does not lose
sync. (TS Analysis Failover/Restore switching requires SMD 970 TS Analysis Option)
If TS Sync Loss Failover is selected. Restore to Primary can be set to Manual Only,
On Primary TS Sync Restored, or On Backup TS Sync Loss. The switchover
Interval(s) can be set from 1 to 20 seconds.
If TS Analysis Failover (option) is selected, Restore to Primary options are Manual
Only on Primary TS Analysis Restored or On Backup TS Analysis Failure. Failover
conditions can be enabled/disabled and Switch After interval can be set from 1 to 30
seconds.
IMPORTANT NOTE: When selecting TS Analysis Failover for Primary or Backup inputs, the
TS Analysis feature must be enabled or active for the respective primary and/or backup.
See section Configure Modulator – TS Analysis on page 41.
Figure 29 Primary & Backup Input, Failover and Restore
Page 35 (105)
Page 36

SMD 989– User Manual
Configure Modulator – Modulation Parameters
The Modulation tab provides setup settings of the modulation parameters. First, choose the
Modulation/FEC code to use and then select how you wish to set the output symbol rate. You
may enter the desired output symbol rate or input bit rate or have the internal calculator
recommend a setting. The following section describes entry of these parameters.
The Enter Rate By field provides the user a choice of how to setup the output Symbol Rate or
Max Bitrate entry fields. The values in these fields are mathematically related depending on the
modulation mode, modulation type, and FEC settings. The SDM 989 contains an internal symbol
rate or max. input bitrate calculator to assist.
Enter Rate By
- Output Symbol Rate
- Input Bitrate
Description: Output Symbol Rate mode allows the entry of the desired output symbol rate. The
SMD 989 calculates the maximum input bit rate and lists it in the Max. Bitrate field.
Description: Input Bit Rate mode allows the entry of a known input bit rate. The SMD 989 then
calculates the needed symbol rate and lists it in the Symbol Rate field.
With output Symbol Rate you enter the desired output symbol rate. It must be mathematically
proper based upon the input bit rate measured by the system. When a higher than needed
symbol rate is entered, the modulator inserts null packets to achieve the rate. When entering a
lower than needed symbol rate the SMD 989 removes nulls, if they exist, from the stream.
With Input Bitrate, the SMD 989 uses the entered bitrate along with the modulation settings to
calculate the needed symbol rate. If it is known that the input transport stream contains a
significant amount of null packets it is possible to enter a bitrate that is lower than the actual input
transport stream bitrate. In this case the SMD 989 will remove existing nulls.
Important Note: When entering a bitrate lower than the input bitrate or a symbol rate below
the minimum, there must be enough nulls in the input transport stream to be removed to
allow the lower bitrate or symbol rate or errors in the transmission transport stream result.
The SMD 989 contains a symbol rate or input bit rate calculator to assist with these selections. By
clicking the icon, the recommended symbol rate will be inserted into the Symbol Rate field
or maximum input bitrate inserted in the Bitrate field.
Page 36 (105)
Figure 30: Single stream DVB-S2 Configuration
Page 37

SMD 989– User Manual
DVB-S/DSNG
DVB-S2
Code
R12ate
QPSK
8PSK
16QAM
QPSK
8PSK
16APSK
32APSK
¼
√
1/3
√
2/5
√
½
√
√
3/5
√ √
2/3
√ √ √ √
√
¾
√ √ √ √ √ √
4/5
√ √
√
5/6
√ √ √ √ √ √
7/8
√ √
8/9
√ √ √ √ √
9/10
√ √ √ √
Modulation/FEC: The modulations and supported code rates are shown in Figure 31. The
supported modes are selectable in the drop down list in the Modulation/FEC field. The listings will
depend on unit licensing and the selected mode in the Modulation Mode field at the top of the
menu.
Figure 31: Supported modulations & code rates for DVB-S/DSNG and DVB-S2
The remaining settings include (Bold indicates default):
Pilot Insertion (Only available in DVB-S2 Modes)
- Enable
- Disable
Description: When enabled, every 16 slots of 90 symbols the modulator will insert 36
non-modulated symbols to aid in receiver synchronization. The use of a pilot allows the
receiver to maintain carrier recovery, even when the user data payload cannot be
decoded.
Frame Size (Only available in DVB-S2 Modes)
- Normal (64,800 bits)
- Short (16,200 bits)
Description: Short frames introduce more overhead but give a shorter encapsulation
delay. Short frames are 4 time shorter than normal frames.
Spectral Inversion
Page 37 (105)
- Normal
- Inverted
Page 38

SMD 989– User Manual
Description: Determines whether the spectrum is inverted or normal.
Note: When the SMD 920 L-Band option is installed, the default spectral inversion is
inverted as the upconverter will invert. Setting the output to Inverted will give a normal
output from the upconverter. This is shown in the RF Output status for Spectral Inversion.
Alpha Filter Rolloff
- 0.35
- 0.25
- 0.20
- 0.15
- 0.10
- 0.05
Description: The filter rolloff is known as the Alpha coefficient (α). The smaller the α, the
less bandwidth will be required on the satellite.
Rate Adaptation (Only available in DVB-S2 single mode)
- Disable
- Enable
Description: When set to enable a rate adaption is applied to the DVB-S2.mode. When
disabled the rate adaptation is not active. Rate adaptation forces the modulator to add or
remove null packets and re-stamp PCRs in order to match TS bitrate to the modulation
payload rate. Disabling rate adaptation is desirable where the input TS must be
preserved through the transmission chain. In such use cases, it is expected that the input
TS bitrate is fairly consistent and the payload mismatch can be resolved by occasionally
inserting a dummy frame instead.
PL Scramble Code (Physical Layer Scrambling is only available in DVB-S2 or DVB-S2X
single modes)
Description: This is used to specify a randomized scrambling sequence applied to each
PL frame and initiated at the end of each PL header. Scrambling randomizes band
energy dispersion and allows for a “signature” when may provide association to a satellite
operator or satellite. The complex code relates to an “n” value defined by an entry of 0 to
262 141.
PRBS Enable/Disable A pseudo random binary sequence test signal is available for
testing. When Enabled the PRBS replaces the normal input modulation feeding the
modulator. Select Disabled for normal output applications. See the PRBS section of this
manual for added information.
PRBS: (Only available in DVB-S2 Modes)
- Enable
- Disable
Page 38 (105)
Page 39

SMD 989– User Manual
Configure Modulator – Carrier ID
Carrier ID – DVB CID Global Unique ID: The SDM 989 can optionally provide a carrier added to
the transmission that contains a unique identifier value (DVB CID Global Unique ID). The
identifier value may be used to trace and quickly resolve a satellite interference event to a
transmitting source. The Global Unique Identifier is a fixed value for the equipment manufacturer
and is not editable by the user. It may be derived from a 48 bit MAC address or a 48 bit Space
Data Association modulator identifier.
Figure 32: Carrier ID – Global Unique ID
Configure Carrier ID provides a CID control field and an information field. The CID control
provides a means to enable or disable the CID transmission. Optionally an Informational Field
may be populated with latitude, longitude, phone and message data.
Transmission: Provides an enable or disable selection for the CID transmission.
- Enabled
- Disabled
Description: When enabled, a CID transmission is generated and added to the output. When
disable no CID output including the Global Unique ID and Information fields are output.
Page 39 (105)
Figure 33: Carrier ID Configuration
Page 40

SMD 989– User Manual
Latitude: Provide entry of a latitude pure decimal value to the CID information field.
- Value Entry
- Enabled/Disabled
Description: When enabled, the entered latitude value is added to the Information Field of the CID
transmission. Enter values 0 to 90 with up to 3 decimal places. Enter positive values for northern
hemisphere and negative values for the southern hemisphere. When disabled, the latitude value
is not transmitted in the CID.
Longitude: Provides entry of a longitude decimal value to the CID information field.
- Value Entry
- Enabled/Disabled
Description: When enabled, the entered longitude value is added to the Information Field of the
CID. Enter values 0 to 180 with up to 4 decimal places. Enter positive values for eastern
hemisphere and negative values for the western hemisphere. Wen disabled, the longitude value
is not transmitted in the CID.
Telephone: Provides an entry of a contact phone number with an extension number to the CID
Information Field.
- Value Entry
- Enabled/Disabled
Description: When enabled, the entered phone number is added to the Information Field of the
CID. You may enter up to 18 digits or a total of 17 digits if an extension number is entered in the
ext. field. When disabled, the telephone number is not transmitted in the CID.
User Data: Provides an entry of up to 24 characters for including a message in the CID
Information Field.
- Text Entry Field:
- Enabled/Disabled
Description: When enabled, the user data or entered characters are added into the CID
Information Field. Up to 24 characters may be entered and transmitted as user data. When
disabled, the user data is not transmitted in the CID.
Note: When a CID carrier is enabled and added to the transmission it is known to slightly
degrade the MER performance of the satellite IF/RF transmission. Details of this are explained in
the ETSI TS 103129 Annex B.2. standard.
Page 40 (105)
Page 41

SMD 989– User Manual
Configure Modulator – TS Analysis
Configure TS Analysis (SMD 970 option) The Configure TS Analysis allows the setup of TS
Analysis. TS Analysis errors are as defined by TR 101 290 [4]. The TS Analysis may be used for
failover input switching, error logging, alarms, SNMP traps, and/or relay switching.
TS Analysis
- Enabled
- Disabled
Errors – Threshold
- Sync Loss: an error will be indicated when sync has been lost for at least 1 second.
- Sync Byte: Corruption: an error will be indicated when the number of errors/second
entered has been exceeded. Can be set from 1 to 999 errors/second.
- PAT Error: an error will be indicated when the PAT is not present for a period
exceeding the time entered (in ms) Can be set from 100ms to 10000ms. Default is
500ms.
- Continuity Count Error: an error will be indicated when the number of detected
Continuity Count Error per second exceeds the value entered. Can be set from1 to
999 errors per second. Default is 1 error per second.
- PMT Error: an error will be indicated when the PMT is not present for a period
exceeding the time entered (in ms). Can be set from 100ms to 10000ms. Default is
500ms.
- ES PID Error: an error will be indicated when an Elementary Stream (ES) is not
present for a period exceeding the time entered (in ms). Can be set from 100ms to
10000ms. Default is 500ms. The modulator will automatically detect up to 400
elementary stream PIDs on both the primary and backup transport streams.
- Null Packet Ratio: an error is indicated when the ratio of the number of null packets
in comparison to the normal video packets every second exceeds the maximum or
minimum ratio entered.
Exclude PID Entering a PID value here will remove the PID entered from all TS Analysis
functions. This eliminates logging or errors associated with the PIDs listed.
Page 41 (105)
Figure 34 Configure TS Analysis
Page 42

SMD 989– User Manual
Configure Modulator – S2 Multistream
Configuration for DVB-S2 Multistream Modulation is similar to single stream settings with the
ability to add 6 streams to the modulation as shown in Figure 35 below.
Figure 35 SMD 963 multi-stream configuration
Multi-stream is supported in DVB-S2 CCM and VCM modes using the SMD910 modulator. Multistream DVB-S2 CCM limits the modulation type and FEC to the same for all the streams. Multistream DVB-S2 VCM as shown in Figure 35 allows a modulation type and FEC to be set for each
stream in the modulation.
Each input can be set to the desired incoming stream. If the input set to “OFF” the stream is not
configured to be used in the modulation. If the Input is set to something other than OFF and no
stream is present, an error indicating that input is missing is generated.
For each stream an Input Stream Identifier (ISI) is needed. This value is used by receivers to
select the appropriate stream out of the multi-stream modulation.
Note: When in the Multi-stream Modulation mode, the input backup and TS Analysis features are
not available.
Page 42 (105)
Page 43

SMD 989– User Manual
Figure 36: PRBS Pseudo Random Binary Sequence
Configure Modulator - PRBS
The PRBS tab provides selection of the available PRBS (Pseudo Random Binary Sequence) test
signal available for use with either the SMD 910 or SMD 912(A) modulators.
PRBS (Pseudo Random Binary Sequence): The PRBS feature provides a digital test signal
with known properties used for BERT (bit error rate testing) of satellite equipment or transmission
paths. Test signals used are a binary PN (Pseudo-Noise) signal known as a PN-23 or Inverted
PN-23.
PN23 Normal: A normal version of the Pseudo-Noise PN-23 test signal
PN 23 Inverted: An inverted version of the Pseudo-Noise PN-23 test signal
For BERT tests, the PRBS setting may be set to Enabled. When Enabled, the normal input signal
to the modulator is removed and replaced with the selected PN-23 or Inv PN-23 signal.
IMPORTANT: For normal or non-testing applications in which the input is to be used to
modulate the satellite IF or L-Band carrier output, the PRBS test signal must be set to
DISABLED.
Page 43 (105)
Page 44

SMD 989– User Manual
Configure Modulator - BISS
Configure BISS Scrambling (SMD 971 Option) The BISS Scrambling is configured by selecting
the BISS tab in the Configuration Modulator window. When BISS Scrambling is enabled the entire
transport stream will be scrambled. A CA_descriptor will be added to the PMT and CAT table will
be created if one does not exist. If a CAT table does exist it will be altered.
Scrambling:
Enabled/Disabled: When set to Enabled the BISS encryption feature becomes active and is
ready for the entry of either the Mode 1 or Mode E session word/ID. When Disabled no BISS
encryption is added to the stream.
.
Figure 37 BISS Scrambling configuration
BISS Mode 1: Permits entry of an encrypted twelve (12) character hex session word.
BISS Mode E: Permits entry of an encrypted sixteen (16) character hex session word along with
a 14 character hex Injected ID. In BISS Mode E the session word is encrypted and cannot be
viewed from the front panel or any remote interface.
Page 44 (105)
Page 45

SMD 989– User Manual
Configure Modulator – TurboPSK
Configure TurboPSK modulation (SMD 968 Option) The SMD 912(A) modulator is capable of
outputting an advanced modulation scheme known as Turbo PSK. This output is only available
when the SMD 968 option is added to a modulator platform which includes an SMD 912(A)
modulator board(s).
To configure the modulator click on the “Configure Modulator
Options” button located at the top of the middle section. The
Configure Modulator menu provides selection of the Modulation Mode. Click the dropdown arrow
and select TurboPSK (Single).
Figure 38 TurboPSK (Single) modulation selection
The Modulation tab provides setup settings of the modulation parameters. First, choose the
Modulation/FEC code to use and then enter the desired output symbol rate or input bit rate. The
following section describe the Turbo PSK parameters.
The Enter Rate By field provides the user a choice of how to setup the output Symbol Rate entry
fields. The values in these fields are mathematically related. The SDM 989 contains an internal
symbol rate calculator to assist.
Enter Rate By
- Output Symbol Rate
- Input Bitrate
Description: Output Symbol Rate mode allows the entry of the actual output symbol rate desired.
With Input Bitrate by entering the bitrate of the input transport stream the SMD 989 uses this
bitrate along with the Modulation/FEC settings to calculate the modulation symbol rate. If it is
known that the input transport stream contains a significant amount of null packets it is possible to
enter a bitrate that is lower than the actual input transport stream bitrate. In this case the SMD
989 will remove the nulls.
Note: When entering a bitrate lower than the input bitrate there must be enough nulls in the input
transport stream to be removed to allow the lower bitrate. Entering a bitrate that is too low will
result in transport stream errors.
Page 45 (105)
Page 46

SMD 989– User Manual
Code Rate
QPSK
8PSK
16 QAM
½ X
2/3 X X
¾ X X X 3/4 (2.05)
X 3/4 2.10 4/5
X
5/6 X X
7/8 X
8/9 X
By clicking the icon, the recommended symbol rate will be inserted into the symbol rate.
Turbo PSK modulation includes many modulation types and FEC code combinations. Figure 39
shows code rates available for the Turbo PSK modulation mode and a representation of the
settings for TurboPSK single mode modulation in the dropdown menu.
Figure 39 Advanced Modulation Turbo PSK
modes and code rates
The remaining settings include (Bold indicates
default):
Spectral Inversion
- Normal
- Inverted
Description: Determines whether the spectrum is inverted or normal.
Note: When the SMD 920 L-Band option is installed, the default spectral inversion is
inverted as the upconverter will invert. Setting the output to Inverted will give a normal
output from the upconverter. This is shown in the RF Output status for Spectral Inversion.
Alpha Filter Rolloff
- 0.35
- 0.25
- 0.20
- 0.15
- 0.10
- 0.05
Description: The filter rolloff is known as the Alpha coefficient (α). The smaller the α, the
less bandwidth will be required on the satellite.
Advanced Turbo Modulation Settings
The TurboPSK modulation mode provides several advanced features which may be enabled or
selected for use. The Advanced section provides settings for Sync Byte Deletion, Reduced
Latency, and PRBS.
Page 46 (105)
Page 47

SMD 989– User Manual
Figure 40: Reduced Latency Selections
Sync Byte Deletion: The Sync Byte Deletion advanced feature permits removal of the incoming
MPEG stream sync bytes from reaching the modulator. so as to not output symbols containing
the sync byte information. This enables a savings in bandwidth of 1 byte every 188 bytes as
modulator output symbols containing sync byte data are removed.
The Sync Byte Deletion setting can be disabled or enabled. When set to Enabled, the modulator
blocks the incoming Sync Byte. When Enabled the receive demodulator must reinsert it. When
Disabled the modulator receives the full transport stream including the Sync Bytes.
Reduced Latency:
The advanced section contains several reduced latency modes which may be applied to the
TurboPSK modulation. The reduced latency modes of the TurboPSK modulation provides several
levels of latency that can be applied. The reduced latency modes are only applicable to special
low symbol rate data satellite applications using the TurboPSK modulation.
Reduced Latency Selections
- Disabled: (Default) No latency reduction - with additional input buffering
- Normal: Introduces slight latency without additional input buffering
- Reduced 1: Adds latency reduction to the Normal mode
- Reduced 2: Adds latency reduction to the Reduced 1 mode
- Reduced 3: Adds latency reduction to the Reduced 2 mode
- Minimum: Adds latency reduction to the Reduced 3 mode
PRBS (Pseudo Random Binary Sequence): The PRBS feature provides a digital test
signal with known properties used for BERT (bit error rate testing) of satellite equipment
or transmission paths. Test signals used are a binary PN (Pseudo-Noise) signal known
as a PN-23 or Inverted PN-23. The test signal is selected within the PRBS tab/menu.
For BERT tests, the PRBS setting may be set to Enabled. When Enabled, the normal
input signal to the modulator is removed and replaced with the PN-23 or Inv PN-23
signal.
IMPORTANT: For normal or non-testing applications in which the input is to be
used to modulate the satellite IF or L-Band carrier output, the PRBS test signal
must be set to DISABLED.
Page 47 (105)
Page 48

SMD 989– User Manual
Configure Modulator – DVB-S2X
Configure DVB-S2X modulation. The SMD 912(A) and SMD 910 modulators are capable of
outputting an extended modulation scheme for DVB-S2 known as DVB-S2X. This output is active
and follows licensing as described earlier in this manual.
To configure the modulator click on the “Configure Modulator
Options” button located at the top of the middle section. The
Configure Modulator menu provides selection of the Modulation Mode. Click the dropdown arrow
and select DVB-S2X(Single).
Figure 41: Configure DVB-SX2 Modulation/FEC
The Modulation tab provides setup settings of the modulation parameters. First, choose the
Modulation/FEC code to use and then select how you wish to set the output symbol rate. You
may enter the desired output symbol rate or input bit rate or have the internal calculator
recommend a setting. The following section describes entry of these parameters.
The Enter Rate By field provides the user a choice of how to setup the output Symbol Rate or
Max Bitrate entry fields. The values in these fields are mathematically related depending on the
modulation mode, modulation type, and FEC settings. The SDM 989 contains an internal symbol
rate or max. input bitrate calculator to assist.
Enter Rate By
- Output Symbol Rate
- Input Bitrate
Description: Output Symbol Rate mode allows the entry of the desired output symbol rate. The
SMD 989 calculates the maximum input bit rate and lists it in the Max. Bitrate field.
Description: Input Bit Rate mode allows the entry of a known input bit rate. The SMD 989 then
calculates the needed symbol rate and lists it in the Symbol Rate field.
With output Symbol Rate you enter the desired output symbol rate. It must be mathematically
proper based upon the input bit rate measured by the system. When a higher than needed
symbol rate is entered, the modulator inserts null packets to achieve the rate. When entering a
lower than needed symbol rate the SMD 989 removes nulls, if they exist, from the stream.
Page 48 (105)
Page 49

SMD 989– User Manual
DVB-S2X
Code Rate
QPSK
8PSK
16APSK
32APSK
64APSK
¼
√ √
3/5
√ √
2/3
√ √
¾
√ √ √
√
4/5
√ √ √ √
5/6
√ √ √ √ √
7/8
7/9
√ √ √
8/9
√ √ √
√
9/10
√ √ √
√
11/15
√ √
13/18
√
23/36
√ √
25/36
√
26/45
√
28/45
√
32/45
√
77/90
√
½-L
√
2/3-L
√ √
3/5-L
√
5/9-L
√ √
8/15-L
√
32/45-L
√
26/45-L
√
With Input Bitrate, the SMD 989 uses the entered bitrate along with the modulation settings to
calculate the needed symbol rate. If it is known that the input transport stream contains a
significant amount of null packets it is possible to enter a bitrate that is lower than the actual input
transport stream bitrate. In this case the SMD 989 will remove existing nulls.
Important Note: When entering a bitrate lower than the input bitrate or a symbol rate below the
minimum, there must be enough nulls in the input transport stream to be removed to allow the
lower bitrate or symbol rate or errors in the transmission transport stream result.
The SMD 989 contains a symbol rate or input bit rate calculator to assist with these selections. By
clicking the icon, the recommended symbol rate will be inserted into the Symbol Rate field or
maximum input bitrate inserted in the Bitrate field.
Figure 42: Modulation/FEC code rates DVB-S2X
Page 49 (105)
Page 50

SMD 989– User Manual
Modulation/FEC: The modulations and supported code rates are shown in Figure 42. The
supported modes are selectable in the drop down list in the Modulation/FEC field.
The remaining settings include (Bold indicates default):
Pilot Insertion (Only available in DVB-S2 and DVB-S2X Modes)
- Enable
- Disable
Description: When enabled, every 16 slots of 90 symbols the modulator will insert 36
non-modulated symbols to aid in receiver synchronization. The use of a pilot allows the
receiver to maintain carrier recovery, even when the user data payload cannot be
decoded.
Frame Size (Only available in DVB-S2 and DVB-S2X Modes)
- Normal (64,800 bits)
- Short (16,200 bits)
Description: Short frames introduce more overhead but give a shorter encapsulation
delay. Short frames are 4 time shorter than normal frames.
Spectral Inversion
- Normal
- Inverted
Description: Determines whether the spectrum is inverted or normal.
Note: When the SMD 920 L-Band option is installed, the default spectral inversion is
inverted as the upconverter will invert. Setting the output to Inverted will give a normal
output from the upconverter. This is shown in the RF Output status for Spectral Inversion.
Alpha Filter Rolloff
- 0.35
- 0.25
- 0.20
- 0.15
- 0.10
- 0.05
Description: The filter rolloff is known as the Alpha coefficient (α). The smaller the α, the
less bandwidth will be required on the satellite.
Rate Adaptation (Only available in DVB-S2 and DVB-S2X single modes)
- Disable
- Enable
Page 50 (105)
Page 51

SMD 989– User Manual
Description: When set to enable a rate adaption is applied to the DVB-S2X.mode. When
disabled the rate adaptation is not active. Rate adaptation forces the modulator to add or
remove null packets and re-stamp PCRs in order to match TS bitrate to the modulation
payload rate. Disabling rate adaptation is desirable where the input TS must be
preserved through the transmission chain. In such use cases, it is expected that the input
TS bitrate is fairly consistent and the payload mismatch can be resolved by occasionally
inserting a dummy frame instead.
PL Scramble Code (Physical Layer Scrambling is available in DVB-S2X single mode)
Description: This is used to specify a randomized scrambling sequence applied to each
PL frame and initiated at the end of each PL header. Scrambling randomizes band
energy dispersion and allows for a “signature” when may provide association to a satellite
operator or satellite. The complex code relates to an “n” value defined by an entry of 0 to
262 141.
PRBS Enable/Disable A pseudo random binary sequence test signal is available for
testing. When Enabled the PRBS replaces the normal input modulation feeding the
modulator. Select Disabled for normal output applications.
The PRBS feature provides a digital test signal with known properties used for BERT (bit
error rate testing) of satellite equipment or transmission paths. Test signals used are a
binary PN (Pseudo-Noise) signal known as a PN-23 or Inverted PN-23. The test signal is
selected in the PRBS tab.
IMPORTANT: For normal or non-testing applications in which the input is to be
used to modulate the satellite IF or L-Band carrier output, the PRBS test signal
must be set to DISABLED.
Page 51 (105)
Page 52

SMD 989– User Manual
Figure 43: Outputs section
Output Settings
This section focuses around the IF and optional RF (SMD 920 option) settings found on the right
column of the individual bay home screen.
All SMD 989 modulations will have an IF output area indicating an active or muted output,
frequency range from 57 up to 145 MHz, output level and tilt level. If the SMD 920 L-Band option
is available it will indicate the RF settings for the module as shown in Figure 43.
There are three quick access buttons at the top of the Outputs section. These buttons provide
easy access to common functions or functions that may need to be accessed quickly.
- Mute: By clicking the mute button the IF/RF outputs will be muted. When the output is
muted the icon will change to “Unmute”
- Modulating: Clicking the Modulating quick access icon will stop modulated output and
go to a carrier wave (CW). When in CW mode the Modulating icon will change to a
CW image and read “CW Only”
- RF Level (dBm): This allows the RF output level to be adjusted by either entering the
value, from -30dBm to 5dBm, or by using the up and down arrows.
Page 52 (105)
Page 53

SMD 989– User Manual
Figure 44: IF settings
IF Output
Clicking on “Configure IF Options” will produce a dialog box as shown in Figure 44.
The output can be set as active or mute.
The IF output frequency is selectable between 57 & 140 MHz in 1 Hz increments. When used
with the option SMD 920 RF Upconverter set the IF frequency to 70MHz or 140MHz and the level
to -10dBm.
The level for the IF Output is adjustable between -30 to -5 dBm for the SMD 910 and SMD 912.
The SMD 912A output level is from -20 to +5dBm. When feeding the SMD 920 option
upconverter the IF output level is optimal at -10 dBm for any of the modulator models.
The tilt adjustment allows a user to adjust the overall slope of the output spectrum. The range is
selectable from -3 to +3 dB.
RF Output
If the RF L-Band SMD 920 option is installed in the SMD 989
bay, an RF Output section is shown. The header selections
provide quick selection for Mute, Modulating, and RF Level.
Click on the field to activate. When mute is active no output
satellite carrier is output. When the Modulating field is clicked
the output modulation is removed and a carrier only is
transmitted. By clicking the up or down arrows the output RF
level can be increased or decreased incrementally.
By clicking on the “Configure RF Options,” cog a dialog box
appears showing RF output selections as shown in Figure 45.
The output can be set as active or mute. This may also be
toggled by clicking on the Mute field in the Outputs header.
When mute is active no output satellite carrier is output.
The output frequency is settable at a range of 950 to 2150 MHz, When LO Offset is 0MHz.
The LO Offset (MHz) can be entered to allow the desired Satellite Frequency (MHz) to be
entered. The SMD 989 will output the proper frequency to achieve the correct satellite frequency
when combined with the external Upconverter LO (Local Oscillator). This eliminates the need to
determine what the output frequency of the SMD 989 should be to achieve the desired satellite
frequency. In the example settings below the output of the SMD 989 will be the same.
The output level is settable at a range of -30 to 5 dBm. This level may also be incremented to a
higher or lower level using the up/down arrows in the RF Level (dBm) header section.
Page 53 (105)
Page 54

SMD 989– User Manual
Figure 45: RF settings
Figure 46: RF settings with 10MHz option
If the RF L-Band SMD 920 option is installed along with 10 MHz BUC Power SMD 94X option the
ability to configure the RF output as well as the ability to enable or disable the 10MHz Ref. Clock
and the BUC Power is also shown. By clicking on the “Configure RF Options,” a dialog box will
appear as shown in Figure 46. Enabling the 10 MHz Ref. Clock or BUC Power will diplex them
with the L-Band PRI RF output looped to the optional SMD 94X LOOP IN.
The parameters shown in blue in the RF Output section indicate the status of that parameter and
cannot be edited in the RF Output configuration window. These statuses are:
- RF Frequency: This is determined by the calculation of the Satellite Frequency and
the L.O. Offset frequency.
- IF Input Level: This indicates OK if the IF input is at the proper level. The Level
indication can be “Low”, “OK” or “High.” If this does not show OK as the status, check
that the IF output is set to -10dBm. If the level indicates LOW or HIGH you may
increase or decrease the IF Level slightly to return the IF Input Level to OK status.
This provides the optimum spectral output performance of the RF upconverter.
- Oscillator Status: Indicates if the 10MHz reference is locked to the incoming IF.
- Output Status: Indicates Present when the output is active, or Missing if the output
is muted.
- Spectral Inversion: This reflects what the RF output will be after the RF
upconverter. This indication changes depending on the Spectral Inversion setting in
the Configure Modulation Options. If the Spectral Inversion is set to Normal in the
modulation configuration, the RF Output will be inverted. If the Spectral Inversion is
set to Inverted in the modulation configuration, the RF Output will be normal.
Page 54 (105)
Page 55

SMD 989– User Manual
Figure 47: Admin tab
Figure 48: Password/Unit update location
Admin Tab
The Admin tab located after the two bays in the web interface allow system specific settings to be
set or modified.
Located directly under the admin control panel are the options for saving/loading profiles,
changing the password, downloading the SNMP MIBs, downloading the diagnostic file, unit
software updating, and license changes.
Page 55 (105)
Page 56

SMD 989– User Manual
Figure 50: Setting password
User Profiles
The “Profiles” button opens a dialog box as shown in Figure 49. The user can create a new
profile based on the configuration of the complete system. The profile can be saved locally and
downloaded to a remote location for backup. The profile can also be uploaded and restored for
systems that have the same configuration.
Figure 49: Profile Manager
Note: The configuration of the unit must be the same from system to system to allow the profile to
load. If a profile is loaded onto a different channel platform, the profile will not load.
Setting Login Password
Once a user has clicked on the “Change Password” button located at the top of the admin tab a
dialog box will appear as shown in Figure 50.
The user will need to type the new password and confirm the password to change it from the
previous password.
Downloading SNMP MIBs
Clicking on the “Download SNMP MIBs” button located at the top of the Admin Tab will open a
dialog box as shown in Figure 51.
A new window will appear with the ability to download each MIB.
Page 56 (105)
Page 57

SMD 989– User Manual
Figure 52: Updating software
Figure 53: Uploading file
Figure 51: MIBs
Diagnostics
The “Diagnostics” button will generate a text file for troubleshooting by Sencore support. This file
included the configuration of the system, a log history, and current licensing of the SMD 989 to
provide a complete understanding of the system. The file will be saved to the computer browsing
to the SMD 989.
Unit Software Updating
To update the unit’s software click on the “Update Unit” button located at the top of the admin
tab. This will open a dialog box as shown in Figure 52. .
The first step is to select the update file to update by clicking on the Upload button and browsing
to the location of the file. Locate the file and click open, the file will automatically upload. Once
upload is complete a dialog box will confirm successful upload or indicate an error while verifying
the file’s contents.
Once uploaded successfully, the uploaded version will appear on the Update Unit dialog screen.
Page 57 (105)
Page 58

SMD 989– User Manual
Figure 54: Upload successful
To complete update click on the update button and the unit will commence with the update
process indicating when update is complete.
Figure 55: Update confirmation
Figure 56: Updating unit
Once update is complete the system will be restarted. The user will be prompted to log back into
the web interface once the unit is updated and operational.
Figure 57: Unit restarting
Unit Software Rollback
The SMD 989 offers the ability to roll back to the previous version of software that was installed
on the unit. The roll back feature will restore the unit back to the previous state before the latest
update was performed.
Page 58 (105)
Page 59

SMD 989– User Manual
Figure 58: Software rollback
Figure 60: Reference clock
The rollback option is located in the “Update Unit” dialog box under the rollback tab as shown in
Figure 58.
Unit License Update
The SMD 989 offers the ability to license certain features for the individual options installed into
the chassis. The Update License button allows these licenses to be installed.
Upon receiving the new license code from Sencore, copy and paste the new license code into the
box that appears when clicking on the “Update License” button.
Figure 59: Update License
10 MHz Reference Clock
In the admin tab under system information, the 10 MHz reference is shown. This can either be
internal or external. The reference location is autosensing meaning if an external reference is
detected it will automatically switch. If no external clock is sensed, the controller will use the
internal 10 MHz clock for the modulation reference.
An error can be enabled to alert the user if the external reference is lost. To enable this error
monitoring please refer to the Reporting tab section, the error is disabled/turned-off by default.
Page 59 (105)
Page 60

SMD 989– User Manual
Figure 61: Network configuration
Figure 62: IP settings
Network Configuration
In the middle of the admin tab is the IP address configuration for the physical ports. The “Unit
Network Configuration” shows the management port’s settings. The current status is shown,
but can be modified by clicking on the cog located on the left of the status.
Clicking on the configure cog a dialog box will appear similar to Figure 62. For the modulator
configuration, only IP, subnet, and gateway are allowed to be set. The management port
supports DHCP and static IP addressing.
If set to DHCP the user can enter a hostname to easily access the SMD 989 by the name rather
than the IP address given by DHCP. When the mode is set to static, the user has to set the IP,
subnet, and gateway addresses.
Page 60 (105)
Page 61

SMD 989– User Manual
Figure 63: Configure Clone Settings
Modulator Clone Settings Configuration:
The Modulator Clone function allows the modulation settings on this SMD 989 to be configured
the same as another SMD 989 connected on the same network. When enabled entering the IP
address of the remote unit to be cloned and the Public SNMP Community name the modulation
settings will be configured the same as the remote SMD 989 modulator. The settings that will
apply are listed.
- Modulation Mode
- Symbol Rate
- Modulation FEC Setting
- Pilot Insertion
- Frame Size
- Spectral Inversion
- Alpha Filter Rolloff
- Clean Carrier CW
- IF Output Frequency
- IF Output Level
- IF Output Tilt
- RF Output Frequency
- L.O. Offset
- RF Output Level
License Configuration
The user has the ability to view and change licensing to any of the options available within the
SMD989 platform. A list of possible and enabled licenses are shown.
Figure 64: Bay License Configuration
If one license is enabled and both SMD 989 bays have hardware present, the license can be
transferred between the bays by clicking on the “Configure Bay Assignment” button. A dialog box
will appear allowing the license to be enabled on a certain bay. If both bays are license the dialog
box will simply display both bays.
Page 61 (105)
Page 62

SMD 989– User Manual
Figure 66: Date/Time configuration
Figure 67: SNMP communities
Figure 65: Configure Bay Assignment
Date/Time
The user has the ability to set the local time for the SMD 989 platform. The time can be
configured using an NTP server by entering the address to synchronize the time and date or it
can be entered manually as shown in Figure 66.
SNMP Communities
The communities for the SNMP management can be changed from the default of “public” for
read-only communities and “private” for read-write communities.
Page 62 (105)
Page 63

SMD 989– User Manual
SNMP Trap Managers
The managers for the SNMP management can be entered or removed by clicking on “Configure
SNMP Managers”
Figure 68: SNMP Managers
Page 63 (105)
Page 64

SMD 989– User Manual
Figure 69: Alarms reporting view
Figure 70: Logs reporting view
Alarms/Log Tab
The Alarms/Log tab holds all of the status and alarm indications for the SMD 989 platform. The
Alarms/Log tab has two views Alarms and Logs.
The Alarms view shows the current active alarms.
The Logs View shows a history of Alarms and Events. Clicking Refresh will update the log
listings in the browser. Clicking Clear in the top menu bar will remove all logged alarms and
events. To download and save a history of the Logs click Download and a TSV file will be
downloaded from the SMD 989. The TSV file can be imported to a spreadsheet or text document.
The Logs Severity/Transition Indicators at the bottom of the Alarms/Logs menu provides a
reference to the severity icons listed by each log entry. It further provides a transition event or
error condition change indicators. Error logs are either informative (Info) or are unit or signal error
conditions. Transition entries indicate changes between error conditions and indicate if the log
entry went to good or went bad.
Figure 71: Logs Severity/Transition Indicators
Page 64 (105)
Page 65

SMD 989– User Manual
Figure 73: Alarm Configuration
Figure 72: Alarms View - Configure
Figure 74: Alarm Error Configuration
Alarms/Logs Configure
The “Configure” button opens a configuration screen as shown in Figure 73.
The Configure Report Information window will open. In the Conditions tab, click the + icon to
expand the alarm configuration options in the Conditions tab. The Selection Options popup menu
allows easier configuration of the selected alarm error condition.
The Error drop down menu is shown in Figure 74. Each condition can be configured as an error
or information situation under log severity. The Alarm Relay can also be assigned and set for
Relay 1 or Relay 2. When the Relay is enabled the error will trip the respective Relay at the Alarm
Contact Closure connector. Note: To see or select relay 1 and relay 2 click on the relay field to
enable a dropdown arrow.
Page 65 (105)
Page 66

SMD 989– User Manual
Name
Description of Trap
10MHz Ext. Ref Clock Error
Indicates the unit’s external reference source has
changed between either internal or external.
12V Supply Error
Unable to detect 12V from Power Supply
3V Supply Error
Unable to detect 3V from Power Supply
5V Supply Error
Unable to detect 5V from Power Supply
ASI TS Sync Error
No ASI Sync with TS Input
ASI Bitrate Error
ASI Input Bit Rate Error
Backup Input Active
Unit switched to backup Input
Fan Speed Below Lower Limit
A fan failure has been detected
FEC Reception Error
Error in FEC detected
IF Output Mute Error
Indicates the IF output is muted
IP Loss Error
Indicates MPEG/IP Data loss
MPEG/IP Bitrate Error
Indicates IP Bit Rate Error
MPEG/IP NIC Link Error
Indicates the MPEG/IP Data Link is broken
MPEG/IP TS Sync Error
Indicates MPEG/IP Data interface cannot sync
with the TS
RTP Reception Error
RTP reception errors indicated
Output Buffer Error
Data underflow/overflow in buffer, rate adaption
issue where TS packets are discarded
TS Continuity Count Error
TS Analysis – CC Error indicated in TS Header
TS ES PID Error
TS Analysis – PID error in ES
TS PAT Error
TS Analysis – PAT CC error
TS PMT Error
TS Analysis – PMT CC error
TS Sync Byte Error
TS Analysis – TS sync byte
TS Sync Loss Error
TS Analysis – Sync Loss
Temperature Error
Internal temp. is outside range of 0 to 45 Celsius
Upconverter IF Input Freq. Error
Not within auto-lock range of 70 or 140 MHz
Upconverter IF Input Level Error
Indicates IF input is not within the acceptable level
range for the upconverter
Upconverter Mute Error
Indicates the RF upconverter is muted
Upconverter Oscillator Error
Indicates a loss of oscillator or communication
Upconverter Output Error
Indicates loss of RF upconverter output or system
communications
Error handling voltage and temp limits that will trigger an alarm if exceeded:
3 Volt Controller Supply
Page 66 (105)
Figure 75: Alarm descriptions
Page 67

SMD 989– User Manual
Name
Description of Event
10MHz Ext. Ref Clock Change
Indicates the external reference clock was not present
Date/Time Change
The unit’s date/time has been changed
NTP Update
The unit’s date/time was updated by the NTP server
Software Update Failed
The software update did NOT complete successfully
Software Update Succeeded
The software update completed successfully
Unit Booted
The unit has been started
Unit Shutdown
The unit was shutdown
Figure 76: Event Configuration
sensor3VMinLimit.0 - 3.10 VDC
sensor3VMaxLimit.0 - 3.50 VDC
5 Volt Controller Supply
sensor5VMinLimit.0 - 4.70 VDC
sensor5VMaxLimit.0 - 5.30 VDC
12 Volt Controller Supply
sensor12VMinLimit.0 - 11.28 VDC
sensor12VMaxLimit.0 - 12.72 VDC
Unit Temperature
sensorTempMinLimit.0 - 0 C
sensorTempMaxLimit.0 - 45.00 C
The Events tab allows the setup of Events reporting and actions. Events are notable status
changes in the SMD 989. Click the + icon to expand the event configuration options. The
Selection Options popup menu allows easier configuration of the selected event. Refer to Figure
77. Event Descriptions.
Page 67 (105)
Figure 77: Event descriptions
Page 68

SMD 989– User Manual
Figure 78: SNMP trap view
Figure 79: SNMP manager configuration
SNMP Trap Configurations
The SNMP trap configurations can be viewed under the reporting tab by clicking the
“Configurations” at the top-left of the report control panel. All conditions can be
enabled/disabled from sending SNMP Traps. The current status is shown under configuration.
To enable/disable the SNMP events click on the “Configure” button located on the right side of
the screen.
The SNMP trap manager IP addresses can be added under the admin tab and the events that
trigger traps to be sent are enabled/disabled under configure settings.
Page 68 (105)
Page 69

SMD 989– User Manual
Name
Description of Trap
10MHz Ext. Ref Clock Error
Indicates the unit’s external reference source has
changed between either internal or external.
12V Supply Error
Unable to detect 12V from Power Supply
3V Supply Error
Unable to detect 3V from Power Supply
5V Supply Error
Unable to detect 5V from Power Supply
ASI TS Sync Error
No ASI Sync with TS Input
ASI Bitrate Error
ASI Input Bit Rate Error
Backup Input Active
Unit switched to backup Input
Fan Speed Below Lower Limit
A fan failure has been detected
FEC Reception Error
Error in FEC detected
IF Output Mute Error
Indicates the IF output is muted
Input Bit Rate Exceeded
The incoming bitrate exceeds the symbol rate and
modulation configuration.
IP Loss Error
Indicates MPEG/IP Data loss
MPEG/IP Bitrate Error
Indicates IP Bit Rate Error
MPEG/IP NIC Link Error
Indicates the MPEG/IP Data Link is broken
MPEG/IP TS Sync Error
Indicates MPEG/IP Data interface cannot sync
with the TS
RTP Reception Error
RTP reception errors indicated
Output Buffer Error
Data underflow/overflow in buffer, rate adaption
issue where TS packets are discarded
TS Continuity Count Error
TS Analysis – CC Error indicated in TS Header
TS ES PID Error
TS Analysis – PID error in ES
TS PAT Error
TS Analysis – PAT CC error
TS PMT Error
TS Analysis – PMT CC error
TS Sync Byte Error
TS Analysis – TS sync byte
TS Sync Loss Error
TS Analysis – Sync Loss
Temperature Error
Internal temp. is outside range of 0 to 45 Celsius
Upconverter IF Input Freq. Error
Not within auto-lock range of 70 or 140 MHz
Upconverter IF Input Level Error
Indicates IF input is not within the acceptable level
range for the upconverter
Upconverter Mute Error
Indicates the RF upconverter is muted
Upconverter Oscillator Error
Indicates a loss of oscillator or communication
Upconverter Output Error
Indicates loss of RF upconverter output or system
communications
Page 69 (105)
Figure 80: SNMP trap descriptions
Page 70

SMD 989– User Manual
Figure 81: About page
About Tab
The about tab provides the software and hardware details and versions for the equipment found
within the SMD 989 platform. It further provides licensing information although added information
on licensing may be found in the ADMIN tab. This information will be referenced when talking to
technical support. The contact information is also provided for reaching technical support.
Page 70 (105)
Page 71

SMD 989– User Manual
>BAY 1: MODULATOR CONFIG
ADMIN
ALARM/LOGS
Bay1:Modulator Bay2:Modulat ↔↕
40.000 MSps 20.000 MSps
4Streams S2CCM 4Streams S2VCM
RF:1450.00 MHz RF:2150.00 MHz
>MUTE ALL
CLEAN CARRIER ONLY: DISABLED
Once the SMD 989 is finished loading, depending on the
number of bays populated, a screen similar to the ones
on the right will appear. An SMD 989 with two
modulators is indicated by Bay 1 and Bay 2.
Press the Up or Down arrow key and, the main menu
will be displayed as shown to the right.
The user can select from the following:
- Modulator settings for the particular bay
- Administrator settings for network, time, and
lockout settings
- Alarm/Logs for alarms, logs, and SNMP trap
information
- About for system software/firmware versions
Front Panel Quick Actions Menu
From the first or opening menu, press the Left or Right
arrow key and, the Quick Actions menu (Left arrow =
Bay 1, Right arrow = Bay 2) will be displayed as shown
to the right. The Quick Actions menu allows quick
access to the following settings:
- Mute: mutes the RF & IF outputs
- Clear Carrier Only: in Disabled mode the
output is modulated. Enabled the output is
in Clean Carrier mode. (CW only)
- RF Level allows setting the output from -
30.0 to + 5.0 dBm.
- (Levels change immediately on output upon
incrementing the level values in the
respective digits via the front panel display)
Controlling the SMD 989 Using the Front Panel
This section of the user manual covers the menus and operation of the SMD 989 platform using the
front panel for control. All functionality of the front panel is also capable through the Web User
Interface.
4 Errors
MAIN MENU ↕
ABOUT
BAY 1: QUICK ACTIONS ↕
RF LEVEL: -20.0 dBm
Page 71 (105)
Page 72

SMD 989– User Manual
>INPUT CONFIGURATION
MODULATION CONFIGURATION
TS ANALYSIS CONFIGURATION
OUTPUT CONFIGURATION
>ASI 1: ALIAS NAME
ASI 2: TEST
ASI 3: NOT USED
IP 1: LIVE INPUT
IP 2: BACKUP INPUT
>PORT: ENABLED
ALIAS: ALIAS NAME
SYNC: SYNCHRONIZED
PACKET SIZE: 188-BYTE
BITRATE: 19.392 MBPS
>RECEIVE: ENABLED
ALIAS: LIVE INPUT
ROUTING: MULTICAST
ADDRESS: 237.0.0.10
DESTINATION PORT: 1234
>TS PACKETS / IP PACKETS: 7
SYNC: SYNCHRONIZED
BIT RATE: 10.486 MBPS
BUFFER: 1000 KB
DISPLAY DELAY:84 MS
Select the modulator settings from the main menu,
the user will be able to set input, modulation, and
output parameters for the given bay the modulator is
installed.
Once input configuration is selected, all available
inputs ASI and IP will be shown.
ASI Settings and status include:
- Enabling/Disabling the port
- Entering an alias that can be used to
name the input for easy reference in the
future
- Synchronization status
- Packet size
- Bitrate (Mbps)
IP Settings and status include:
- Enabling/Disable the port
- Entering an alias that can be used to
name the input for easy reference in the
future
- Routing: Destination IP address
- Destination port
- TS Packets per IP packet
- Synchronization status
- Bitrate (Mbps)
- IP input buffer (100 KB – 4 MB)
- IP IGMP versioning
- Transport Protocol
- Packet Counters (SMD 912(A))
- FEC Row/Column Info (SMD 912(A))
Front Panel Modulator Settings
BAY 1: MODULATOR CONFIG ↕
Modulator Input Configuration
BAY 1: INPUT CONFIGURATION ↕
Selecting any of the specific ASI or IP ports, the individual settings can be modified.
Page 72 (105)
INPUT STATUS: BAY 1: ASI 1 ↕
INPUT STATUS: BAY 1: IP 1 ↕
INPUT STATUS: BAY 1: IP 1 ↕
Page 73

SMD 989– User Manual
GLOBAL SETTINGS
>SYMBOL RATE: 20.014553 MSPS
MINIMUM: 16.45536 MSPS
FRAME SIZE: NORMAL
SPECTRAL INVERSION: NORMAL
GLOBAL SETTINGS
FRAME SIZE: NORMAL
SPECTRAL INVERSION: NORMAL
ALPHA FILTER ROLLOFF: 0.35
>CARRIER WAVE: DISABLED
MODULATION: BAY 1: STREAM 1
>INPUT: ASI1 UNIT ALIAS
MODULATOIN/FEC: 8PSK 2/3
PILOT INSERTION: ENABLED
ISI: 002
MODULATION PARAMETERS
>MODULATION MODE: S2 MULTI-CCM
BISS CONFIGURATION
PRBS CONFIGURATION
CARRIER ID CONFIGURATION
>GLOBAL SETTINGS
STREAM 1: ASI1 ALIAS NAME
STREAM 2: ASI2 TEST
STREAM 3: IP1 LIVE
STREAM 4: IP2 BACKUP
INPUT CONFIGURATION
>MODULATION CONFIGURATON
TS ANALYSIS CONFIGURATION
OUTPUT CONFIGURATION
This screen is the global settings when in DVB-S2
multistream (VCM) mode.
This screen is the multistream (VCM) individual
stream settings
When in a CCM/VCM multistream mode a new menu
is presented to the user under modulation
parameters. This new menu allows the user to set
global and individual stream settings.
Note: If multistream DVB-S2 VCM is selected,
Modulation, FEC, and Pilot Insertion will be set for
each individual stream. If multistream DVB-S2 CCM
is selected, the modulation and FEC will be located
under the modulator parameters.
Modulator Configuration – Modulation Mode/Configuration
The Modulator Configuration menus are found under the
Bay 1 and Bay 2 listings in the Main Menu. The
Modulator Configuration menu has several menus which
configure the modulator. The menus vary with hardware
and licensing options. The modulation mode is selected
in the Modulation Mode field. Depending on the options
installed, the modulation mode might be limited to only
CCM (single). The modulation parameters change
depending on the type of modulation mode selected.
Modulation Mode
o DVB-S/DSNG
o S2 Multi –CCM (SMD 910)
o S2 Multi-VCM (SMD 910)
o S2 Single –CCM
o S2X Single-CCM
o TurboPSK
BAY 1: MODULATOR CONFIG ↕
BAY 1: MODULATION MODE ↕
BAY 1: MODULATOR PARAMETER ↕
↕
↕
Page 73 (105)
↕
Page 74

SMD 989– User Manual
>MODULATION PARAMETERS
MODULATION MODE: S2 MULTI-CCM
BISS CONFIGURATION
PRBS CONFIGURATION
CARRIER ID CONFIGURATION
INPUT CONFIGURATION
>MODULATION CONFIGURATON
TS ANALYSIS CONFIGURATION
OUTPUT CONFIGURATION
>PRIMARY INPUT: ASI1
BACKUP INPUT: IP1
ACTIVE INPUT: ASI1 (PRIMARY)
SWITCH TO BACKUP INPUT
>CONFIGURE FAILOVER
ENTER RATE BY: SYMBOL RATE
SYMBOL RATE: 38.000000 MSPS
Mbps
>MODULATION FEC: 8PSK 5/6
PILOT INSERTION: DISABLED
FRAME SIZE: NORMAL
SPECTRAL INVERSION: INVERTED
>ALPHA FILTER ROLLOFF: 0.35
CLEAN CARRIER ONLY: DISABLED
RATE ADAPTATION: ENABLED
PRBS: DISABLED
Modulator Configuration – Modulator Parameters (Inputs)
The Modulation Parameters menu provides configuration
of the parameters of the modulator. It includes the
following line listings in the front panel menus. Listings
differ depending on the modulation mode selected.
BAY 1: MODULATOR CONFIG ↕
Modulation Parameters
- Primary Input
- Backup Input
- Active Input
- Switch to Primary/Secondary Input
- Configure Failover
- Enter Rate By
- Symbol Rate
- Max Bitate
- Modulation/FEC
- Pilot Insertion
- Frame Size
- Spectral Inversion
- Alpha Filter rollfoff
- Clean Carrier Only
- Rate Adaption
- PL Scrambling Code
- PRBS
BAY 1: MODULATION MODE ↕
BAY 1: MODULATION CONFIG ↕
BAY 1: MODULATOR MODULATION ↕
MAX BITRATE: 49.4564248
BAY 1: MODULATOR MODULATION ↕
Primary Input: Selects the input signal that is routed to the
modulator. User may select from any input available on the
SMD910 or SMD912.
Backup Input: Selects an input to serve as a backup input
should the primary input meet failover conditions or a user
desires to switch manually to a backup input. User may
select from any input available on the SMD910 or
SMD912.
Note: When selecting inputs to the modulator be sure that
the inputs selected are enabled in the Input Configuration Menu and properly configured.
Active Input: This field indicates the currently active or selected input.
Primary Input; Indicates the Primary Input is active and being routed to the modulator.
Backup Input: Indicates the Backup Input is active and being routed to the modulator
Switch to Backup/Primary Input: This field permits manual switching to the primary or backup
input from the currently active input.
Page 74 (105)
BAY 1: MODULATOR MODULATION ↕
PL SCRAMBLING CODE: 000000
Page 75

SMD 989– User Manual
FAILOVER: PRIMAY TS ERROR
RESTORE: BACKUP TS ERROR
>APPLY CHANGES
>FAILOVER CONDITIONS
BAY 1: MODULATOR MODULATION
SWITCH TO BACKUP INPUT
>CONFIGURE FAILOVER
ENTER RATE BY: SYMBOL RATE
SYMBOL RATE: 38.000000 MSPS
+1.1 SYNC LOSS ERROR
05 SEC
>+1.2 SYNC BYTE ERROR
05 SEC
+1.3A PAT ERROR
05 SEC
+1.4 CONTINUITY COUNT ERROR
05 SEC
+1.5A PMT ERROR
05 SEC
+1.6 ES PID ERROR
05 SEC
+NULL PACKET ERROR
05 SEC
Modulator Configuration – Modulator Parameters (Failover)
Failover: This field provides options to enable a Backup Input in the event of a Primary Input
fault. Failover and Restore selection must to applied, after changes select the Apply Changes
field and press the ENTER front panel key.
Failover to backup options include:
Primary Sync Loss
Primary TS Error
MAX BITRATE: 49.4564248 Mbps
Manual Only
TS Sync Loss mode allows the SMD 989 to switch to
backup if the primary input transport sync is lost. In
BAY 1: FAILOVER CONFIG ↕
the TS Analysis mode failover is based on transport
stream errors or sync loss. This allows the SMD 989
to switch to a backup source when there are errors in
the transport stream even if it does not lose sync.
Restore: This field defines the conditions which direct the modulator to return or switch back to
the primary input.
Restore to primary options include:
Primary TS Sync Restored
BAY 1: FAILOVER CONDITIONS↕
Backup TS Sync Loss
Primary TS Error
Manual Only
Primary TS Analysis Restored
BAY 1: FAILOVER CONFIG ↕
Backup TS Analysis Failure
The restore to primary options depend on the Failover
setting. If failover to backu is TS Sync Loss, restore
can be set to Primary TS Sync Restored, or On
Backup TS Sync Loss. The switchover Interval(s) can
BAY 1: FAILOVER CONFIG ↕
be set from 1 to 20 seconds. If switch to Backup is set
to Manual, Restore to Primary can only be set to
Manual.
If TS Analysis Failure (option) is selected, Restore
options are Manual Only on Primary TS Analysis
Restored or On Backup TS Analysis Failure.
Failover conditions can be enabled/disabled and Switch After interval can be set from 1 to 30
seconds.The switch after intervals for each of the TS analysis categories defines a wait time or
delay before the modulator switches to the backup or switches from backup to primary when TS
analysis errors are detected. If the TS Errors are corrected within this time the switch is not
implemented and the TS analysis resumes.
IMPORTANT NOTES: 1. When selecting TS Analysis Failover for Primary or Backup inputs,
the TS Analysis feature must be enabled or active for the respective primary and/or
backup. See the TS Analysis Configuration menu.
3. You cannot use the TS Analysis for failover when you are setup to output VCM or
CCM Multistream with the SMD910 modulator.
Page 75 (105)
Page 76

SMD 989– User Manual
CONFIGURE FAILOVER
>ENTER RATE BY: SYMBOL RATE
SYMBOL RATE: 38.000000 MSPS
Mbps
>MODULATION FEC: 8PSK 5/6
PILOT INSERTION: DISABLED
FRAME SIZE: NORMAL
SPECTRAL INVERSION: INVERTED
Modulator Configuration – Modulator Parameters
The Enter Rate field provides the user a choice of how to setup the modulator’s output Symbol
Rate or Max Bitrate entry fields. The values in these fields are mathematically related depending
on the modulation mode, modulation type, and FEC settings. The SDM 989 contains an internal
symbol rate or max. input bitrate calculator to assist.
It is recommended that you first select the
modulation/FEC code you wish to use.
BAY 1: MODULATOR MODULATION ↕
Enter Rate By
MAX BITRATE: 49.4564248
- Output Symbol Rate
- Input Bitrate
Description: Output Symbol Rate mode allows the entry of the desired output symbol rate. The
SMD 989 calculates the maximum input bit rate and lists it in the Max. Bitrate field.
Description: Input Bit Rate mode allows the entry of a known input bit rate. The SMD 989 then
calculates the needed symbol rate and lists it in the Symbol Rate field.
With output Symbol Rate you enter the desired output symbol rate. It must be mathematically
proper based upon the input bit rate measured by the system. When a higher than needed
symbol rate is entered, the modulator inserts null packets to achieve the rate. When entering a
lower than needed symbol rate the SMD 989 removes nulls, if they exist, from the stream.
With Input Bitrate, the SMD 989 uses the entered bitrate along with the modulation settings to
calculate the needed symbol rate. If it is known that the input transport stream contains a
significant amount of null packets it is possible to enter a bitrate that is lower than the actual input
transport stream bitrate. In this case the SMD 989 will remove existing nulls. Note: There must
be enough nulls in the input transport stream to be removed to allow the lower bitrate or
symbol rate or errors in the transmission transport stream result.
Modulation/FEC: This field selects the modulator’s output modulation type and FEC code for the
selected modulation mode on page 73.
Pilot Insertion (Enabled/Disabled) (Available in
DVB-S2, DVB-S2X Modes)
Description: When enabled, every 16 slots of 90
symbols the modulator will insert 36 non-modulated
symbols to aid in receiver synchronization.
Frame Size (Available in DVB-S2 and DVB-S2X Modes)
- Normal (64,800 bits)
- Short (16,200 bits)
Description: Short frames introduce more overhead but give a shorter encapsulation delay. Short
frames are 4 time shorter than normal frames.
Spectral Inversion: This field sets the spectrum to inverted or normal.
- Normal
- Inverted
Page 76 (105)
BAY 1: MODULATOR MODULATION ↕
Page 77

SMD 989– User Manual
>ALPHA FILTER ROLLOFF: 0.35
CLEAN CARRIER ONLY: DISABLED
RATE ADAPTATION: ENABLED
PRBS: DISABLED
Note: When the SMD 920 L-Band option is installed, the default spectral inversion is inverted as
the upconverter is set to invert. Setting the output to Inverted will give a normal output from the
upconverter. This is shown in the RF Output status for Spectral Inversion.
Alpha Filter Rolloff
- 0.35
- 0.25
BAY 1: MODULATOR MODULATION ↕
- 0.20
- 0.15
PL SCRAMBLING CODE: 000000
- 0.10
- 0.05
Description: The filter rolloff is known as the Alpha coefficient (α). The smaller the α, the less
bandwidth will be required on the satellite. Rolloff in DVB-S limited to 0.35, 0.25 and 0.20.
Clean Carrier Only (Disabled/Enabled)
Description: When set to Enabled the modulator outputs only a cw carrier for testing purposes.
Rate Adaptation (Disabled/Enabled) Only available in DVB-S2 or DVB-S2X single mode)
Description: When enabled a rate adaption is applied. When disabled the rate adaptatiois not
active. Rate adaptation adds or removes null packets and re-stamps PCRs in order to match TS
bitrate to the modulation payload rate.
PL Scrambling Code (6 digit value entry)
Description: This is used to specify a randomized scrambling sequence applied to each
PL frame and initiated at the end of each PL header. Scrambling randomizes band energy
dispersion and allows for a “signature” when may provide association to a satellite operator or
satellite. The complex code relates to an “n” value defined by an entry of 0 to 262 141.
PRBS (Enabled/Disabled)
Description: When Enabled the PRBS replaces the normal input modulation feeding the
modulator with a PN23 normal or inverted BERT test signal. Select Disabled for normal output
applications.
IMPORTANT: For normal or non-testing applications in which the input is to be used to
modulate the satellite IF or L-Band carrier output, the PRBS test signal must be set to
DISABLED.
Page 77 (105)
Page 78

SMD 989– User Manual
MODULATION PARAMETERS
MODULATION MODE: S2 SINGLE-CCM
>BISS CONGIGURATION
PRBS CONFIGURATION
CARRIER ID CONFIGURATION
BISS CONFIGURATION
SCRAMBLING: ENABLED
>BISS MODE: MODE 1
SESSION WORD: ************
SPECTRAL INVERSION
>ALPHA FILTER ROLLOFF: 0.3
SYNC BYTE DELETION: ENABLED
REDUCED LATENCY: DISABLED
Sync Byte Deletion: (Enabled/Disabled)
Description: This selection permits removal of the incoming MPEG stream sync bytes from
reaching the modulator. This saves a bandwidth of 1 byte every 188 bytes. When set to Enabled,
the modulator blocks the incoming Sync Byte. When Enabled the receive demodulator must
reinsert it. When Disabled the modulator receives the full transport stream including the Sync
Bytes.
Reduced Latency: (Only in Turbo PSK mode)
Reduced Latency Selections
BAY 1: MODULATOR MODULATION ↕
- Disabled: (Default) No latency reduction -
with additional input buffering
- Normal: Introduces slight latency without
additional input buffering
- Reduced 1: Adds latency reduction to the Normal mode
- Reduced 2: Adds latency reduction to the Reduced 1 mode
- Reduced 3: Adds latency reduction to the Reduced 2 mode
- Minimum: Adds latency reduction to the Reduced 3 mode
Description: The reduced latency modes of the TurboPSK modulation provides several levels of
latency that can be applied. The reduced latency modes are only applicable to special low symbol
rate data satellite applications using the TurboPSK modulation.
Modulator Configuration- BISS Configuration
Configure BISS Scrambling (SMD 971 Option) The BISS
Scrambling is configured by selecting the BISS tab in the
Configuration Modulator window. When BISS Scrambling is
enabled the entire transport stream will be scrambled. A
CA_descriptor will be added to the PMT and CAT tablle if
one does not exist. If a CAT table does exist it will be
altered.
Scrambling: Set to Enable to scramble the Transport Stream. When disabled the transport
stream is not encrypted and therefore does not require a BISS key at the receiver.
BAY 1: MODULATOR CONFIGURAT ↕
Enable/Disabled (Disabled is Default)
BISS Mode 1: Allows the entry of an unencrypted twelve
(12) character hex session word.
BISS Mode E: Allows the entry of an encrypted sixteen (16)
character hex session word along with a 14 character hex
and cannot be viewed from the front panel or any remote
interface.
Session Word: Provides the entry field to specify the BISS mode 1 or mode e encryption key.
↕
Page 78 (105)
Page 79

SMD 989– User Manual
GLOBAL UNIQUE ID
2E:00:06:4D:FF:FF:00:1F:67
TRANSMISSION: ENBABLED
TRANSMISSION LATITUDE: ENABLED
MODULATION PARAMETERS
MODULATION MODE: S2 MULTI-CCM
BISS CONFIGURATION
PRBS CONFIGURATION
>CARRIER ID CONFIGURATION
PRBS MODE: PN23 (NORMAL)
MODULATION PARAMETERS
MODULATION MODE: S2 SINGLE-CCM
>BISS CONGIGURATION
PRBS CONFIGURATION
CARRIER ID CONFIGURATION
Modulator Configuration- PRBS Configuration
Configure PRBS (PRBS Pseudo Random Binary
Sequence) Configuration menu. This menu provides
selection of the available PRBS test signal available for use
with either the SMD910 or SMD912 modulators. The PRBS
feature provides a digital test signal with known properties
used for BERT (bit error rate testing) of satellite equipment
or transmission paths. Test signals used are a binary PN
(Pseudo-Noise) signal known as a PN-23 or Inverted PN-23.
PN23 Normal: A normal version of the Pseudo-
Noise PN-23 test signal
PN 23 Inverted: An inverted version of the Pseudo-
Noise PN-23 test signal
When Enabled, the normal input signal to the modulator is
removed and replaced with the selected PN-23 or Inv PN-23
signal. The PRBS signal is enabled in the Modulation Configuration menu.
BAY 1: MODULATOR CONFIGURAT ↕
BAY 1: PRBS CONFIGURAT ↕
Modulator Configuration- Carrier ID Configuration
The Carrier ID Configuration settings permit viewing of the Global Unique ID and permit entry and
enabling of the latitude, longitude, telephone and user
data to the CID information fields. Select the CARRIER ID
CONFIGUATION in the MODULATOR CONFIGURATION
menu.
Global Unique ID:
A CID carrier may be added to the modulaotor
transmission that contains a unique identifier value. The
Global Unique Identifier is a fixed value for the equipment manufacturer and is not editable by the
user. It may be derived from a 48 bit MAC address or a 48 bit Space Data Association modulator
identifier.
Transmission: Provides an enable or disable selection
for the CID transmission.
- Enabled
- Disabled
Description: When enabled, a CID transmission is
generated and added to the output. When disable
no CID output including the Global Unique ID and
Information fields are output
BAY 1: MODULATOR CONFIGURAT ↕
CARRIER ID CONFIGURATION ↕
Latitude: Provide entry of a latitude pure decimal value to the CID information field.
- Enable/Disabled
Page 79 (105)
Page 80

SMD 989– User Manual
CARRIER ID CONFIGURATION
LATITUDE: +44.5550
>TRANSMIT LONGITUDE: ENABLE
LONGITUDE:-109.9998
TRANSMIT TELEPHONE: ENABLE
TRANSMIT TELEPHONE: ENABLED
>TEL: +659884334433
TRANSMIT USER DATA: ENABLED
USER: UPLINK KCCC 1 SD
- Entered Value
Description: When enabled, the entered latitude value is added to the Information Field of the CID
transmission. Enter values 0 to 90 with up to 3 decimal places. Enter positive values for northern
hemisphere and negative values for the southern hemisphere. When disabled, the latitude value
is not transmitted in the CID.
Longitude: Provides entry of a longitude decimal value
to the CID information field.
↕
- Enable/Disable
- Entered Value
Description: When enabled, the entered longitude value
is added to the Information Field of the CID. Enter values 0 to 180 with up to 4 decimal places.
Enter positive values for eastern hemisphere and negative values for the western hemisphere.
Wen disabled, the longitude value is not transmitted in the CID.
Telephone: Provides an entry of a contact phone
number with an extension number to the CID
CARRIER ID CONFIGURATION ↕
Information Field.
- Enable/Disable
- Entered Value
Description: When enabled, the entered phone number is added to the Information Field of the
CID. You may enter up to 18 digits or a total of 17 digits if an extension number is entered in the
ext. field. When disabled, the telephone number is not transmitted in the CID.
User Data: Provides an entry of up to 24 characters for including a message in the CID
Information Field.
- Enable/Disabled
- Text Entry Field
Description: When enabled, the user data or entered characters are added into the CID
Information Field. Up to 24 characters may be entered and transmitted as user data. When
disabled, the user data is not transmitted in the CID.
Note: When a CID carrier is enabled and added to the transmission or modulated RF output of
the SMD 989 it slightly degrades the MER performance of the RF transmission.
Entering CID Values: The latitude, longitude, telephone and user data Carrier ID Configuration
fields are all fields which permit user data selection/entry. Press the UP or DOWN arrow front
panel pushbutton to position the arrow in front of the selection row in the menu. Press the front
panel ENTER button to enter. A field is highlighted as the selected digit or character. Press the
UP or DOWN front panel buttons to increment through available values or characters in that field.
Press the LEFT or RIGHT arrow buttons to move to the next field and repeat until the desire
value is entered.
Page 80 (105)
Page 81

SMD 989– User Manual
BAY 1: TS ANALYSIS CONFIGURAT
>TS ANALYSIS ON PRIMARY
TS ANALYSIS ON SECONDARY
BAY 1: TS ANALYSIS ON PRIMARY
PRIMARY TS ANALYSIS: ENABLED
>TS ERROR CONFIGURATION
PID FILTER
<< NO TS ERRORS >>
BAY 1: TS ERRORS
1.3
BAY 1: PID FILTER
> ADD Pid
REMOVE Pid
900
BAY 1: MODULATOR CONFIG
INPUT CONFIGURATION
MODULATION CONFIGURATION
>TS ANALYSIS CONFIGURATION
OUTPUT CONFIGURATION
TS Analysis Configuration
Configure TS Analysis (SMD 970 option) The Configure
TS Analysis allows the setup of TS Analysis. TS Analysis
errors are as defined by TR 101 290 [4].
TS Analysis
- Enabled
- Disabled
When set to Enabled the TS Analysis feature becomes active and analyzes the incoming primary
and/or secondary stream. Errors are detected based upon
the threshold criteria defined in the TS Error Configuration
menu. Detected errors may be used as alarms, logged
errors, SNMP traps, or triggers to switch inputs or an
external relay.
PID Filter
The Pid Filter provides selection of individual Pids within
the incoming transport stream in which you do not want
the TS Analysis to actively analyze. This eliminates
unwanted TS Analysis error logs or alarms on Pids known
to contain conditions not compliant with TR 101 290
criteria.
- Add
- Remove
Description: To add a Pid select the Add or Remove row
and press ENTER. Use Up and Down arrows to increment
1200
each digit to the desire Pid value. Use the Left and Right
arrow keys to move to different digit fields. Press the
ENTER key to accept the value. To remove select the
Remove row and press Enter. Use Up and Down arrow
keys to place the marker in front of Pid value to be deleted. Press the Enter key to delete.
TS Analysis Errors/Thresholds
Errors – Threshold
- Sync Loss (1.1): an error will be indicated when sync has been lost for at least 1
second.
- Sync Byte (1.2): Corruption: an error will be indicated when the number of
errors/second entered has been exceeded. Can be set from 1 to 999 errors/second.
- PAT Error (1.3): an error will be indicated when the PAT is not present for a period
exceeding the time entered (in ms) Can be
set from 100ms to 10000ms. Default is
500ms.
- Continuity Count Error (1.4): an error will be
indicated when the number of detected
Continuity Count Error per second exceeds
1.1) SYNC LOSS
1.2) SYNC BYTE CORRUPTION
> THRESHOLD: .001 ERORRS/SEC
a) PAT ERRROR
Page 81 (105)
Page 82

BAY 1: TS ERRORS
THRESHOLD: 00500 ms
BAY 1: TS ERRORS
THRESHOLD: 20%
the value entered. Can be set from1 to 999 errors per second. Default is 1 error per
second.
- PMT Error (1.5a): an error will be indicated when the PMT is not present for a period
exceeding the time entered (in ms). Can be
set from 100ms to 10000ms. Default is
500ms.
- ES PID Error (1.6): an error will be indicated
when an Elementary Stream (ES) is not
present for a period exceeding the time
entered (in ms). Can be set from 100ms to
10000ms. Default is 500ms. The modulator will automatically detect up to 400
elementary stream PIDs on both the primary
and backup transport streams.
- Null Packet Ratio: an error is indicated when
the ratio of the number of null packets in
comparison to the normal video packets
every second exceeds the value entered.
SMD 989– User Manual
1.4) CONTINUITY COUNT ERROR
THRESHOLD: .001 ERRORS/SEC
1.5a) PMT ERROR
1.6) ES PID ERROR
THRESHOLD: 00500 ms
NULL PACKET ERROR
Page 82 (105)
Page 83

BAY 1: IF OUTPUT
>OUTPUT: ACTIVE
FREQUENCY: 70 MHZ
LEVEL: -10 DBM
TILT: +0.0 DB
BAY 1: OUTPUT STATUS: RF
>OUTPUT: ACTIVE
SAT FREQUENCY: 00950.000 MHZ
LO OFFSET: 00000.000 MHZ
RF FREQUENCY: 00950.000 MHZ
10 MHZ REF. CLOCK : ENABLED
BUC POWER : ENABLED
+ BAY 1: OUTPUT CONFIGURATION
↕
>IF OUTPUT
RF OUTPUT
BAY 1: MODULATOR CONFIG
INPUT CONFIGURATION
MODULATION CONFIGURATION
TS ANALYSIS CONFIGURATION
> OUTPUT CONFIGURATION
Output Configuration
The IF output settings include:
The output can be set as active or mute.
When muted there is no modulator output.
The output frequency is selectable between
57 & 145 MHz (SMD910). Set to 70 MHz to
feed the SMD 920 L-Band upconverter.
The level for the IF output is adjustable
between -30 to -5 dBm. The SMD 920’s
optimum input level default is -10 dBm.
The tilt adjustment allows a user to adjust the
overall slope of the output spectrum. The
range is selectable from -3 to +3 dB
If the RF L-Band SMD 920 option is installed in the
SMD 989 bay, the ability to configure the RF output is
shown.
The output can be set to active or mute.
When muted there is no modulator output.
The output frequency is settable at an L-band
frequency of 950 to 2150 MHz if the LO
Offset is set to 0 MHz.
To enter a satellite frequency, first enter the
Satellite Frequency followed by the entry of
the block upconverter frequency – press
Enter. If the difference is not in the L-band
The Modulator Configuration menu contains an
output configuration selection. When selected it leads
to settings for the IF output and RF output. This
section overviews the IF Output and RF Output
menus.
SMD 989– User Manual
Page 83 (105)
↕
Page 84

SMD 989– User Manual
BAY 1: RF OUTPUT
>LEVEL: -10.0 DBM
IF INPUT STATUS: OK
OUTPUT STATUS: PRESENT
OSCILLATOR STATUS: LOCKED
SPECTRUM INVERTED: NORMAL
range an error is indicated.
The output RF level is settable at a range of 30 to +5 dBm.
The input status from the IF output is given in
high, medium or low depending on the level
of input detected. The ideal input is -10 dbm.
Output status is an indication that a signal
level is present on the output for confidence
monitoring. An alarm can be enabled to alert
you if output status is lost.
The oscillator status is an indication the
oscillator is locked for confidence monitoring.
An alarm can be enabled to alert if the
oscillator status becomes unlocked.
If duplexing options are installed a menu selection to
enable/disable the 10 MHz clock and/or
enable/disable the BUC power is shown.
- Spectral Inversion: Normal/Inverted.
This reflects what the RF output will be
after the RF upconverter. This will
change depending on the Spectral
Inversion setting in the Configure
Modulation Options. If the Spectral
Inversion is set to Normal in the
modulation configuration, the RF Output
will be inverted. If the Spectral Inversion
is set to Inverted in the modulation
configuration, the RF Output will be
shown as normal.
↕
Page 84 (105)
Page 85

SMD 989– User Manual
ADMIN SETTINGS
>NETWORKING
TIME
TEMPERATURE
PROFILES
NETWORKING SELECT
>UNIT NETWORK
MPEG/IP BAY 1 PORT 1
MPEG/IP BAY 1 PORT 2
CONFIGURE MPEG/IP BAY 1
MPEG/IP BAY 2 PORT 1
UNIT NETWORK STATUS
>IP ADDRESS: 10.0.15.6
SUBNET MASK: 255.255.0.0
GATEWAY: 10.0.1.3
HOSTNAME: DETG_SMD
MAC: 00.00.00.00.00.00
ADMIN SETTINGS
>SETTINGS CLONE
GENERAL SETTINGS
FEFERENCE CLOCK
LOCK FRONT PANEL
The admin settings allow system specific settings to
be set, viewed, and modified.
Networking: Provides information and entry of
network connections for management and MPEG-IP
ports on the SMD 910 SMD 912(A) cards.
Time: Provide a menu to set and manage the unit
date and time.
Temperature: Indicates the units internal
temperature.
Profiles: Provides creation or recall of stored unit
profiles to unit memory.
Settings Clone: Enable/Disable cloning of settings
between bays of the modulator.
Reference Clock: Internal or External, Indicates if
10MHz reference clock is generated internally or
locked automatically to an input 10 MHz ref.
General Settings: Enable/Disable setting which
mutes the modulator when configurations changes
are made. Default is disabled.
Lock Front Panel: Provides password management
of front panel keys
To view or edit the networking settings select either
the control unit network or the correct bay for IP data
network settings.
The unit network menu provides status for current IP
address. If DHCP is enabled, the current IP address
is shown. If static is enabled, press enter to manually
change the IP address, subnet mask, and gateway.
The hostname allows a user to remotely connect to
the SMD 989 platform with a web browser by simply
typing the hostname and not the IP address into the
address bar. This is helpful when used on DHCP
networks.
Front Panel Admin Settings
↕
↕
Network Settings
Page 85 (105)
↕
↕
Page 86

SMD 989– User Manual
BAY 1: MODULATOR NETWORKING
>IP ADDRESS: 10.0.0.61
SUBNET MASK: 255.255.255.0
GATEWAY: 10.0.0.1
MAC: 00.00.00.00.00.00
LINK STATUS: HALF DUPLEX
The each modulator comes standard with an IP input
for data reception. The physical settings are settable
by selecting the bay the modulator is located.
↕
Page 86 (105)
Page 87

TIME
>TIME: 2010/8/12 03:27:48
SOURCE: NTP SERVER
ADDRESS: 10.0.1.23
TIME
TIME: 2010/8/12 03:27:48
SOURCE: MANUAL
>SET DATE: 2010/8/12
SET TIME: 03:27:48
TEMPERATURE
UNIT TEMP: 26.39C
FRONT PANEL LOCK
>PASSWORD: _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
Unit Time
The time and date for the unit can be set manually or
synchronized with an NTP server. The date and time
are used for storing the correct time for alarms and
logs for accurate representation of when the
occurrence took place.
The current temperature for the unit can be viewed in
both Centigrade and Fahrenheit.
The front panel can be locked to prevent any
accidental changes from being made. A password is
prompted before the front panel can be locked. Once
locked, the same password is needed to unlock the
front panel.
Temperature
SMD 989– User Manual
↕
↕
↕
79.50F
Front Panel Lock
10 MHz Reference
The 10 MHz reference clock is automatic presence sensing. If an external clock is present and
the system is capable of locking, it will automatically use the external reference. If no external
presence is detected, the internal clock is used. Disabled by default, the external reference clock
alarm can alert a user if the external reference is lost.
Page 87 (105)
↕
Page 88

ALARMS/LOGS
>ACTIVE ALARMS (1)
CONDITION CONFIGURATION
EVENT LOGS (142)
EVENT CONFIGURATION
ACTIVE ALARMS
>ASI TS SYNC ERROR – LOC: BAY 1,
Front Panel Alarms/Logs
The Alarms/Logs section of the front panel holds all
of status and alarm indications for the SMD 989
platform. The alarms, logs, SNMP, and relays are
separated by individual menus and configurable to
the exact settings a user desires to monitor.
Alarms
To view active alarms, select and press enter to view the
alarms that are currently generated for the enabled
alarms in the SMD 989. Use the right/left errors to view
complete error details.
Page 88 (105)
SMD 989– User Manual
↕
↔
Page 89

SMD 989– User Manual
Name
Description of Trap
10MHz Ext. Ref Clock Error
Indicates the unit’s external reference source has
changed between either internal or external.
12V Supply Error
Unable to detect 12V from Power Supply
3V Supply Error
Unable to detect 3V from Power Supply
5V Supply Error
Unable to detect 5V from Power Supply
ASI TS Sync Error
No ASI Sync with TS Input
ASI Bitrate Error
ASI Input Bit Rate Error
Backup Input Active
Unit switched to backup Input
Fan Speed Below Lower Limit
A fan failure has been detected
FEC Reception Error
Error in FEC detected
IF Output Mute Error
Indicates the IF output is muted
IP Loss Error
Indicates MPEG/IP Data loss
MPEG/IP Bitrate Error
Indicates IP Bit Rate Error
MPEG/IP NIC Link Error
Indicates the MPEG/IP Data Link is broken
MPEG/IP TS Sync Error
Indicates MPEG/IP Data interface cannot sync
with the TS
RTP Reception Error
RTP reception errors indicated
Output Buffer Error
Data underflow/overflow in buffer, rate adaption
issue where TS packets are discarded
TS Continuity Count Error
TS Analysis – CC Error indicated in TS Header
TS ES PID Error
TS Analysis – PID error in ES
TS PAT Error
TS Analysis – PAT CC error
TS PMT Error
TS Analysis – PMT CC error
TS Sync Byte Error
TS Analysis – TS sync byte
TS Sync Loss Error
TS Analysis – Sync Loss
Temperature Error
Internal temp. is outside range of 0 to 45 Celsius
Upconverter IF Input Freq. Error
Not within auto-lock range of 70 or 140 MHz
Upconverter IF Input Level Error
Indicates IF input is not within the acceptable level
range for the upconverter
Upconverter Mute Error
Indicates the RF upconverter is muted
Upconverter Oscillator Error
Indicates a loss of oscillator or communication
Upconverter Output Error
Indicates loss of RF upconverter output or system
communications
Error handling voltage and temp limits that will trigger an alarm if exceeded:
3 Volt Controller Supply
Page 89 (105)
Figure 82: Alarm descriptions
Page 90

CONDITION SELECT
>FAN ERROR - UNIT
3V SUPPLY ERROR - UNIT
5V SUPPLY ERROR - UNIT
12V SUPPLY ERROR – UNIT
ASI TS SYNC ERROR – BAY 1
FAN ERROR
>LOGGING: ENABLED
SNMP TRAP: DISABLED
RELAY: RELAY 1
RELAY ACTIVATION: DISABLED
ALARM NOTIFICATION: ENABLED
sensor3VMinLimit.0 - 3.10 VDC
Each condition can be user configurable to be an
error, logged, SNMP trap, and alarm relay triggered
event.
sensor3VMaxLimit.0 - 3.50 VDC
5 Volt Controller Supply
sensor5VMinLimit.0 - 4.70 VDC
sensor5VMaxLimit.0 - 5.30 VDC
12 Volt Controller Supply
sensor12VMinLimit.0 - 11.28 VDC
sensor12VMaxLimit.0 - 12.72 VDC
Unit Temperature
sensorTempMinLimit.0 - 0 C
sensorTempMaxLimit.0 - 45.00 C
Conditions
SMD 989– User Manual
↕
↕
Page 90 (105)
Page 91

SMD 989– User Manual
Name
Description of Trap
10MHz Ext. Ref Clock Error
Indicates the unit’s external reference source has
changed between either internal or external.
12V Supply Error
Unable to detect 12V from Power Supply
3V Supply Error
Unable to detect 3V from Power Supply
5V Supply Error
Unable to detect 5V from Power Supply
ASI TS Sync Error
No ASI Sync with TS Input
ASI Bitrate Error
ASI Input Bit Rate Error
Backup Input Active
Unit switched to backup Input
Fan Speed Below Lower Limit
A fan failure has been detected
FEC Reception Error
Error in FEC detected
IF Output Mute Error
Indicates the IF output is muted
IP Loss Error
Indicates MPEG/IP Data loss
MPEG/IP Bitrate Error
Indicates IP Bit Rate Error
MPEG/IP NIC Link Error
Indicates the MPEG/IP Data Link is broken
MPEG/IP TS Sync Error
Indicates MPEG/IP Data interface cannot sync
with the TS
RTP Reception Error
RTP reception errors indicated
Output Buffer Error
Data underflow/overflow in buffer, rate adaption
issue where TS packets are discarded
TS Continuity Count Error
TS Analysis – CC Error indicated in TS Header
TS ES PID Error
TS Analysis – PID error in ES
TS PAT Error
TS Analysis – PAT CC error
TS PMT Error
TS Analysis – PMT CC error
TS Sync Byte Error
TS Analysis – TS sync byte
TS Sync Loss Error
TS Analysis – Sync Loss
Temperature Error
Internal temp. is outside range of 0 to 45 Celsius
Upconverter IF Input Freq. Error
Not within auto-lock range of 70 or 140 MHz
Upconverter IF Input Level Error
Indicates IF input is not within the acceptable level
range for the upconverter
Upconverter Mute Error
Indicates the RF upconverter is muted
Upconverter Oscillator Error
Indicates a loss of oscillator or communication
Upconverter Output Error
Indicates loss of RF upconverter output or system
communications
Page 91 (105)
Figure 83: Relay event descriptions
Page 92

EVENT SELECT
>DATE/TIME CHANGE – UNIT
UNIT BOTUP – UNIT
UNIT SHUTDOWN – UNIT
10 MHZ REFERENCE CHANGE – UNIT
NTP UPDATE - UNIT
DATE/TIME CHANGE
>LOGGING: ENABLED
SNMP TRAP: DISABLED
RELAY: RELAY 1
RELAY ACTIVATION: DISABLED
REALY DURATION: 0100 MS
EVENT LOGS
>130 2010/08/25 UNIT BOOTED
129 2010/08/25 IF OUTPUT: NOTM
128 2010/08/25 IF OUTPUT: MUTED
127 2010/08/25 ASI TS: ABSENT
Events
Each possible event is configurable to be enabled or
disabled if the user does not want it to be logged. An
alarm can be disabled and a SNMP trap can still be
enabled to be generated for an event.
Name
Description of Event
10MHz Ext. Ref Clock Change
Indicates the external reference clock was not present
Date/Time Change
The unit’s date/time has been changed
NTP Update
The unit’s date/time was updated by the NTP server
Software update failed
The unit failed to update the software
Software update succeeded
The unit successfully completed a software update
Unit Bootup
The unit has been loaded
Unit Shutdown
The unit was shutdown
ASI TS Sync Error
No ASI Sync with TS Input has been detected
SMD 989– User Manual
↕
↕
↔↕
Figure 84: Event descriptions
Page 92 (105)
Page 93

SMD 989– User Manual
ABOUT
>SOFTWARE
HARDWARE
LICENSES
UNIT SERIAL: 1234567
SOFTWARE VERSIONS
PRODUCT: SMD 989
VERSION: 3.1.0
HARDWARE SELECT
>SYSTEM CONTROLLER
L-BAND UPCONVERTER
DVB-S2 MODULATOR
L-BAND UPCONVERTER
DVB-S/S2 MODULATOR
SNMP COMMUNITIES
>RO COMMUNITY: PUBLIC_ _ _ _ _ _
RW COMMUNITY: PRIVATE_ _ _ _ _
SNMP TRAP MANAGER
>ADD IP
REMOVE IP
10.0.2.45
192.168.1.45
The system’s SNMP communities can be
configured by selecting SNMP Trap Menu from
the reporting options. In the SNMP trap
communities, IP addresses can be added and
the events that trigger traps to be sent are
enabled/disabled under the conditions
configuration.
The “About screen” provides information for
software, hardware and licensing installed in the
SMD 989 platform. This information is needed when
talking to technical support.
Sample Software Versions
Sample About Hardware
SNMP Trap Configurations
Front Panel About
↕
↕
About Software
About Hardware
↕
↕
↕
MODULATOR WITH DUAL GIG
Page 93 (105)
Page 94

SMD 989– User Manual
DVB-S2 MODULATOR
LOCATION: BAY 1
MODEL: SMD 910
ASSEMBLY: 2
PI: 1 REV: D
REVISION: F
L-BAND UPCONVERTER
LOCATION: BAY 1
MODEL: SMD 920
ASSEMBLY: 2
NAME: 1143
PI: 0
LICENSE SELECT
>961 – DVB-S/DSNG MODULATION
962 – DVB-S2 MODULATION
963 – DVB=S2 MULTI-STREAM MODUL
964 – DVB-S2 16 AND 32 APSK
965 – 30 MBPS MAX SYMBOL RATE
Sample About Modulator
Sample About Upconverter
↕
↕
Licenses
Sample License
↕
Page 94 (105)
Page 95

SMD 989– User Manual
Specifications are subject to change without notice.
Appendix
Specifications
SMD 989 Base Unit Includes: Display, keypad, embedded controller,
Chassis/case, Power Supply/line cord
System –
Display Type: Organic LED
Display Configuration: 256 pixels by 64 pixels
Keypad: Snap-dome Membrane
Front Panel Lockout: Password control, up to 10 alpha-numeric
characters (no punctuations or spaces allowed)
Configurations Allowed: Single Bay
Dual Bays
Rear panel: 2 independent bays
Remote Operation/Update Interface –
Type: Ethernet, 10/100
Rear panel indicators: Link (Green LED), Activity (Amber LED)
Connector: RJ45
Front Panel Indicators –
Input LED: Green indicates valid input on selected input,
Off indicates no valid signal on the selected input
Error LED: Red indicates error is occurring
OFF indicates no errors detected
10 MHz Reference Input –
Connector: (1) BNC, female
Impedance: 50 ohms
Min Level: -3 dBm
Max Level: 7 dBm
Detection: Autosensing
Return Loss: >15 dB
Monitor and Control Interfaces –
Web server GUI HTTP via web browser for Control & Monitoring
Front Panel Yes Control & Monitoring
SNMP Yes Control & Monitoring
Contact Closure Interface –
Type: (2) Electrical contact closure alarm contacts
Connector: Connector 9-pin sub-D Female
Alarms supported: User configurable to any alarm in system
Page 95 (105)
Page 96

SMD 989– User Manual
Specifications are subject to change without notice.
AC Power –
Operating Voltage: 95-135 VAC or 180-265 VAC
Current Draw/Power: 200 Watts
Frequency: 47-63Hz
Line Cord: Detachable, 3-prong
General –
RoHS Compliant: Yes
Operating Temperature: 0 to 45 degrees C
Operating Humidity: <95% Non-Condensing
Cooling: Forced air, front intake, rear exhaust
Temperature monitor: Fan failure, internal temperature sensor
Size: Height = 1RU (13/4”), Width = 19”, Depth = 19”
19 in. rack mountable, removable ears
Rack clips and screws included
Weight: ~9.5 lbs. (base unit)
~12.75 lbs. (Fully Loaded)
Pollution Degree: 2
Installation Category: II
Grounding Post: On chassis
Grounding Thread Size: 8/32”
SMD 952 Dual Redundant AC Power Supply – Option
Operating Voltage: 95-135 VAC or 180-265 VAC
Current Draw: 275 Watts
Frequency: 47-63Hz
Line Cord: Detachable, 3-prong
Redundancy Dual Hot Swappable Load Sharing
SMD 954 Dual Redundant DC Power Supply – Option
Operating Voltage: -40 to -72VDC, Normal -48VDC
Current Draw: 250 Watts
Frequency: 0Hz
Connection: Screw Terminal, -48VDC and 0VDC
Redundancy Dual Hot Swappable Load Sharing
SMD 910 Single Stream Modulator
General –
RoHS Compliant: Yes
ASI Serial TS Input –
Connector: (4) BNC, female
Impedance: 75 ohms
Standard: ETSI EN 50083-9 DVB ASI
Data Bit Rate: 270 Mbps
Packet Size: 188 or 204 byte support
Transmission Mode: Burst and packet mode support
Min TS Rate Supported: 0.5 Mbps
Max TS Rate Supported: 160 Mbps
Page 96 (105)
Page 97

SMD 989– User Manual
Specifications are subject to change without notice.
IP TS Input –
Connector: (1) – 10/100/1000 Auto-negotiating Base-T
RJ-45 Ethernet Port
Input format: UDP, RTP, and RTP with extension headers
Multicast and Unicast
Bitrate Range: 0.5 – 160 Mbps
Packets/IP Frame 1-7 MPEG Packets/IP Frame
IGMP Compatibility: Version 2 and 3
Min TS Rate Supported: 0.5 Mbps
Max TS Rate Supported: 160 Mbps
Network Jitter Buffer: 100 KB to 4MB
IF-band Output –
Connector: (1) BNC, female
Impedance: 75 ohms
Min Level: -30 dBm
Max Level: -5 dBm
Level Adjustability: 1 dB increments
Frequency: 70 MHz Default (Selectable 57-145 MHz)
Frequency Stability: +/-5x10
-8
over operational temp range
Return Loss: >20 dB
Tilt Adjustment: +/- 3.0 dB in 0.1 dB steps
SMD 912 or SMD912A Single Stream Modulators
General –
RoHS Compliant: Yes
ASI Serial TS Input –
Connector: (2) BNC, female
Impedance: 75 ohms
Standard: ETSI EN 50083-9 DVB ASI
Data Bit Rate: 270 Mbps
Packet Size: 188 or 204 byte support
Transmission Mode: Burst and packet mode support
Min TS Rate Supported: .5 Mbps
Max TS Rate Supported: 213 Mbps
IP TS Input –
Connector: (2) – 10/100/1000 Auto-negotiating Base-T
RJ-45 Ethernet Ports
Input format: UDP, RTP, and RTP with extension headers
Multicast and Unicast
Bitrate Range: 0.5 – 213 Mbps
Packets/IP Frame 1-7 MPEG Packets/IP Frame
IGMP Compatibility: Version 2 and 3
Min TS Rate Supported: 0.5 Mbps
Max TS Rate Supported: 213 Mbps per stream
Network Jitter Buffer: 1 KB to 4MB
Buffer Size: 1-4000 KB, or 1-4000ms delay, user configured
Analysis: Duplicate, Lost, Corrected, Un-corrected, Out-of order packet counters
FEC Status: Row/Column Mode, Rows, Columns
Page 97 (105)
Page 98

SMD 989– User Manual
IF-band Output –
Connector: (1) BNC, female
Impedance: 75 ohms
Min Level: SMD 912: -30 dBm,
SMD 912A: -20 dBm
Max Level: SMD 912: -5 dBm,
SDM912A: +5 dBm
Level Adjustability: 1 dB increments
Frequency: 70 MHz Default (Selectable 60-140 MHz)
Frequency Accuracy: +/-0.6 ppm + +/-0.25 ppm/yr.
Return Loss: >20 dB (37MHz – 180 MHz)
Tilt Adjustment: +/- 3.0 dB in 0.1 dB steps
Spurious Outputs: -58 dBc or greater @ -10dBm
RF Monitor Test Output
Connector: (1) BNC, female
Impedance: 75 ohms
Outputs RF/IF: 1100 MHz RF & Secondary IF
RF Frequency: 1100 MHz
RF Level: -50 dBm +/- 5 db
Secondary IF Frequency: Same as Primary IF Freq.
Secondary IF Level: -20 dB of Primary IF Output
SMD 961 DVB-S/DSNG Modulation
Supported modulation schemes and FEC:
DVB-S+*
QPSK 1/2, 2/3, 3/4, 5/6, 7/8
8PSK 2/3, 5/6, 8/9
16QAM 3/4, 7/8
Min Symbol Rate: 0.5 MSps
Max Symbol Rate: Up to 45 MSps with SMD 966 License
Roll-off Factor: 20%, 25%, 35%
Spurious Performance -50 dBc @ -10 dBm
PRBS PN23, Inverted PN23
SMD 962 DVB-S2/DVB-S2X Modulation
Supported modulation schemes and FEC (SMD910, SMD912 or SMD912A):
DVB-S2
QPSK 1/4, 1/3, 2/5, 1/2, 3/5, 2/3, 3/4, 4/5, 5/6, 8/9, 9/10
8PSK 3/5, 2/3, 3/4, 5/6, 8/9, 9/10
(9/10 is Normal FECFRAME only)
DVB-S2X
QPSK 1/4, 1/3, 2/5, 1/2, 3/5, 2/3, 3/4, 4/5, 5/6, 8/9,
QPSK 9/10, 13/45, 9/20, 11/20 (Normal FECFRAME only)
QPSK 4/15, 7/15, 8/15, 11/45 14/45, 32/45 (Short FECFRAME)
8PSK 3/5, 2/3, 3/4, 5/6, 8/9,
8PSK 9/10, 23/56, 25/36, 13/18 (Normal FECFRAME only)
8PSK 7/15, 8/15, 26/45, 32/45 (Short FECFRAME only)
8PSK-L 5/9, 26/45 (Normal FECFRAME only)
Min Symbol Rate: 0.5 MSps
Max Symbol Rate: Up to 45 MSps with SMD 966 License
Frame length: Short (16,200 bits) or Normal (64,800 bits)
Roll-off Factor: 05%, 10%, 15%, 20%, 25%, 35%
Spurious Performance -50 dBc @ -10 dBm
Page 98 (105)
Page 99

SMD 989– User Manual
SMD 963 Multistream DVB-S2 Option
In Addition to SMD 910 Specifications
ASI Serial TS Input –
Connector: (4 Total) BNC, female
Impedance: 75 ohms
Standard: ETSI EN 50083-9 DVB ASI
Data Bit Rate: 270 Mbps
Packet Size: 188 or 204 byte support
Transmission Mode: Burst and packet mode support
Min TS Rate Supported: 0.5 Mbps
Max TS Rate Supported: 160 Mbps
IP Serial TS Input –
Connector: (1) – 10/100/1000 Auto-negotiating Base-T
RJ-45 Ethernet Port
Input format: UDP, RTP, and RTP with extension headers
Multicast and Unicast
Number of Streams: Up to 6 streams for multistream
Bitrate Range: 0.5 – 160 Mbps
Packets/IP Frame 1-7 MPEG Packets/IP Frame
IGMP Compatibility: Version 2 and 3
Min TS Rate Supported: 0.5 Mbps
Max TS Rate Supported: 160 Mbps
Network Jitter Buffer: 100 KB to 4MB
Multistream –
Modes: DVB-S2 Single Stream CCM
DVB-S2 Multistream CCM
DVB-S2 Multistream VCM
TS Supported: Up to 6 any combination of ASI and IP
SMD 964 DVB-S2/DVB-S2X Modulation
Supported modulation schemes and FEC (SMD 910 or SMD 912(A))
DVB-S2
QPSK Includes all formats of SMD 962
8PSK Includes all formats of SMD 962
16APSK 2/3, 3/4, 4/5, 5/6, 8/9, 9/10
32APSK 3/4, 4/5, 5/6, 8/9, 9/10
*9/10 is not supported in Short Frame Mode
DVB-S2X
QPSK Includes all formats of SMD 962
8PSK Includes all formats of SDM 962
16APSK 2/3, 3/4 , 4/5, 5/6, 8/9, 9/10, 26/45,3/5,
32APSK 3/4 , 4/5, 5/6, 8/9, 32/45, (2/3 Short FECFRAME)
32APSK 9/10, 11/15, 7/9, (Normal FECFRAME only)
32 APSK-L 32/45 Normal FECFRAME only
64 APSK 11/15, 7/9, 4/5, 5/6, (Normal FECFRAME only)
64APSK-L 32/45 (Normal FECFRAME only)
Min Symbol Rate: 0.5 MSps
Max Symbol Rate: Up to 45 MSps with SMD 966 License
Frame length: Short (16,200 bits) or Normal (64,800 bits)
Roll-off Factor: 20%, 25%, 35%
Page 99 (105)
Page 100

SMD 989– User Manual
Spurious Performance -50 dBc @ -10 dBm
SMD 968 TurboPSK Modulation (SMD 912(A) Only)
Supported modulation schemes and FEC:
QPSK 1/2, 2/3, 3/4, 5/6, 7/8
8PSK 2/3, 3/4, 4/5, 5/6, 8/9
16QAM 3/4
Note: Turbo PSK mode ¾ 2.05 = “3/4”, ¾ 2.10 = “4/5”
Min Symbol Rate: 0.5 MSps
Max Symbol Rate: Up to 30 MSps with SMD 966 License
Frame length: Short (16,200 bits) or Long (64,800 bits)
Alpha Filter Roll-off Factor: 05%, 10%, 15%, 20%, 25%, 35%
Spurious Performance -58 dBc @ -10 dB
Modulator Latency: Normal, Reduced 1, 2 or 3, Minimum
Sync Byte Delete Removes input sync byte
SMD 970 TS Analysis and Null Packet Error Detection (SMD 910 or SMD 912(A))
TS Analysis TR101290 P1 Error Detect/Adjustable Thresholds
TS Analysis Inputs Dual Analysis – Primary and Backup Inputs
TS Analysis Thresholds User definable thresholds
Null Packet Ratio Null Packets/Total packets avg. over 1 sec
(Expressed as percentage)
Null Packet Error Threshold Range User Entry 1-99% (Default 20%)
Null Packet Error Null Packet Ratio exceeds threshold
Accuracy 1%
SMD 971 BISS Scrambling Option (SMD 910 or SMD 912(A))
Scrambling Entire Transport Stream. A CA_descriptor is
added the PMT of each scrambled service a
CAT is created or edited.
Mode 1 12 character unencrypted hex Session word
Mode E 16 Character encrypted hex Session word and
14 character injected Identifier (ID)
PRBS (Pseudo Random Binary Sequence)
Signal Types: PN23, Inverted PN23
Page 100 (105)
 Loading...
Loading...