Page 1

November 2018
Form 8187 www.sencore.com | 1.605.978.4600 Revision 1.0
MRD 6000
4K UHD Receiver Decoder
User Manual
Page 2

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 2 (97)
Copyright
© 2018 Sencore, Inc. All rights reserved.
3200 Sencore Drive, Sioux Falls, SD USA
www.sencore.com
This publication contains confidential, proprietary, and trade secret information. No part of this document
may be copied, photocopied, reproduced, translated, or reduced to any machine-readable or electronic
format without prior written permission from Sencore. Information in this document is subject to change
without notice and Sencore Inc. assumes no responsibility or liability for any errors or inaccuracies.
Sencore, Sencore Inc, and the Sencore logo are trademarks or registered trademarks in the United States
and other countries. All other products or services mentioned in this document are identified by the
trademarks, service marks, or product names as designated by the companies who market those products.
Inquiries should be made directly to those companies. This document may also have links to third-party web
pages that are beyond the control of Sencore. The presence of such links does not imply that Sencore
endorses or recommends the content on those pages. Sencore acknowledges the use of third-party open
source software and licenses in some Sencore products. This freely available source code can be obtained
by contacting Sencore Inc.
About Sencore
Sencore is an engineering leader in the development of high-quality signal transmission solutions for the
broadcast, cable, satellite, IPTV, telecommunications, and professional audio/video markets. The
company’s world-class portfolio includes video delivery products, system monitoring and analysis solutions,
and test and measurement equipment, all designed to support system interoperability and backed by bestin-class customer support. Sencore meets the rapidly changing needs of modern media by ensuring the
efficient delivery of high-quality video from the source to the home. For more information, visit
www.sencore.com.
Page 3
MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 3 (97)
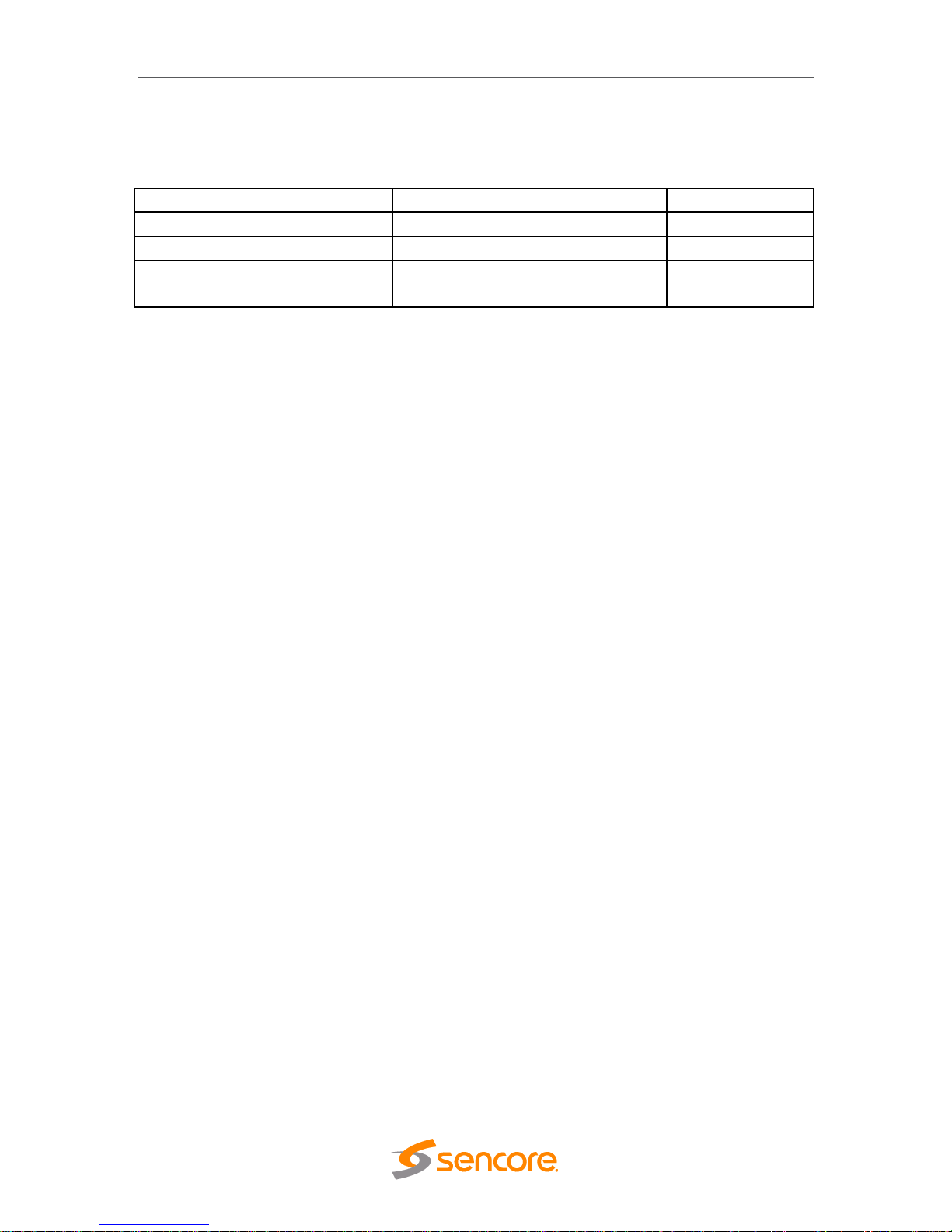
Revision History
Date
Version
Description
Author
11/06/2018
1.0
MRD 6000 Manual – First Draft
GAK
Page 4

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 4 (97)
Safety Instructions
• Read these instructions
• Keep these instructions
• Heed all warnings
• Follow all instructions
• Do not use this apparatus near water
• Clean only with dry cloth
• Do not block any ventilation openings. Install in accordance with the
manufacturer’s instructions
• Do not install near any heat sources such as radiators, heat registers, stoves, or
other apparatus (including amplifiers) that produce heat
• Do not defeat the safety purpose of the polarized or grounding-type plug. A
polarized plug has two blades with one wider than the other. A grounding type
plug has two blades and a third grounding prong. The wide blade or the third
prong is provided for your safety. If the provided plug does not fit into your outlet,
consult an electrician for replacement of the obsolete outlet.
• Protect the power cord from being walked on or pinched particularly at plugs,
convenience receptacles, and the point where they exit from the apparatus.
• Only use attachments/accessories specified by the manufacturer.
• Unplug this apparatus during lightning storms or when unused for long periods of
time.
• Refer all servicing to qualified service personnel. Servicing is required when the
apparatus has been damaged in any way, such as power-supply cord or plug is
damaged, liquid has been spilled or objects have fallen into the apparatus, the
apparatus has been exposed to rain or moisture, does not operate normally, or
has been dropped.
• Do not expose this apparatus to dripping or splashing and ensure that no objects
filled with liquids, such as vases, are placed on the apparatus.
• To completely disconnect this apparatus from the AC Mains, disconnect the
power supply cord plug from the AC receptacle.
• The mains plug of the power supply cord shall remain readily operable.
• Damage Requiring Service: Unplug this product from the wall outlet and refer
servicing to qualified service personnel under the following conditions:
o When the power-supply cord or plug is damaged.
o If liquid has been spilled, or objects have fallen into the product.
o If the product has been exposed to rain or water.
o If the product does not operate normally by following the operating
instructions. Adjust only those controls that are covered by the
operating instructions as an improper adjustment of the controls may
result in damage and will often require extensive work by a qualified
technician to restore the product to its normal operation.
o If the product has been dropped or damaged in any way.
o The product exhibits a distinct change in performance.
• Replacement Parts: When replacement parts are required, be sure the service
technician uses replacement parts specified by Sencore, or parts having the
same operating characteristics as the original parts. Unauthorized part
substitutions made may result in fire, electric shock or other hazards.
Page 5

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 5 (97)
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
There is always a danger present when using electronic equipment.
Unexpected high voltages can be present at unusual locations in defective
equipment and signal distribution systems. Become familiar with the equipment
that you are working with and observe the following safety precautions.
• Every precaution has been taken in the design of your MRD 6000 to ensure that
it is as safe as possible. However, safe operation depends on you the operator.
• Always be sure your equipment is in good working order. Ensure that all points
of connection are secure to the chassis and that protective covers are in place
and secured with fasteners.
• Never work alone when working in hazardous conditions. Always have another
person close by in case of an accident.
• Always refer to the manual for safe operation. If you have a question about the
application or operation call Sencore for assistance.
• WARNING – To reduce the risk of fire or electrical shock never allow your
equipment to be exposed to water, rain or high moisture environments. If
exposed to a liquid, remove power safely (at the breaker) and send your
equipment to be serviced by a qualified technician.
• To reduce the risk of shock the MRD 6000 must be connected to a mains socket
outlet with a protective earthing connection.
• For the MRD 6000 the mains plug is the main disconnect and should remain
readily accessible and operable at all times.
The MRD 6000 is equipped with an internal system battery. The MRD 6000
must be sent to Sencore service for replacement of this battery.
• When installing the MRD 6000 utilizing the DC power supply, the power supply
MUST be used in conjunction with an over-current protective device rated at 50
V, 5 A, type: Slow-blo, as part of battery-supply circuit.
• To reduce the risk of shock and damage to equipment, it is recommended that
the chassis grounding screw located on the rear of the MRD 6000 – be
connected to the installation’s rack, the vehicle’s chassis, the battery’s negative
terminal, and/or earth ground.
CAUTION – Danger of explosion if battery is incorrectly replaced. Replace only
with the same or equivalent type.
Page 6

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 6 (97)
FCC Class A Information
The MRD 6000 has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital
device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide
reasonable protection against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a
commercial environment. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio
frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may
cause harmful interference to radio communications. Operation of this equipment in a
residential area is likely to cause harmful interference in which case the user will be
required to correct the interference at his or her own expense.
Shielded cables must be used with this unit to ensure compliance with the Class A FCC
limits.
Warning: Changes or modifications to this unit not expressly approved by the
party responsible for compliance could void the user’s authority to operate the
equipment.
Dolby Digital Information
This product has been manufactured under license from Dolby Laboratories.
“Dolby Digital”, “AC-3”, and “Dolby Digital Plus” are licensed trademarks of Dolby
Laboratories.
Page 7

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 7 (97)
Package Contents
The following is a list of the items that are included along with the MRD 6000:
1. Declaration of Conformity
2. AC Power Cable
3. Quick Start Guide
Note: If any option cables were ordered with the MRD 6000, they will be included in the
box as well.
If any of these items were omitted from the packaging of the MRD 6000 please call 1800-SENCORE to obtain a replacement. Manuals for Sencore products can be
downloaded at www.sencore.com
1) Declaration of Conformity
2) AC Power Cable
3) Quick Start Guide
Page 8

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 8 (97)
Table of Contents
Section 1 Overview ........................................................................................... 10
1.1 Product Introduction ................................................................................................... 11
1.2 Front Panel Overview ................................................................................................ 11
1.3 Rear Panel Overview ................................................................................................. 12
1.4 Cooling ....................................................................................................................... 12
1.5 Rack Information ........................................................................................................ 12
Section 2 Installation ........................................................................................ 13
2.1 Rack Installation ........................................................................................................ 14
2.2 Power Connection ..................................................................................................... 14
2.3 AC Power Connection ............................................................................................... 14
2.4 Maintenance .............................................................................................................. 15
2.5 Network Setup via Front Panel .................................................................................. 15
Section 3 Operating the Front Panel ............................................................... 17
3.1 MRD 6000 Front Panel Overview .............................................................................. 18
Section 4 Operating the Web Interface ........................................................... 20
4.1 MRD 6000 Web Interface Overview .......................................................................... 21
4.1.1 Logging into the MRD 6000 Web Interface .......................................................... 21
4.1.2 Hiding Unused Inputs ..................................................................... 21
4.1.3 Buttons and Status Indicators ..................................................................... 21
4.1.4 Drag and Drop Menus ..................................................................... 22
4.2 Main Panel ................................................................................................................. 22
4.2.1 Configuring Active Inputs ..................................................................... 23
4.2.2 Configuring ASI Input ..................................................................... 25
4.2.3 Configuring MPEG/IP Input ..................................................................... 26
4.2.4 Configuring DVB-S/S2/S2X Input ..................................................................... 29
4.2.5 Configuring DVB-S/S2 Input ..................................................................... 31
4.2.6 Configuring 8VSB/QAM Input ..................................................................... 33
4.2.7 Configuring Turbo PSK Input (Currently Not Available) ....................................... 34
4.2.8 Configuring DVB-T2/C2/ISDB-T Input .................................................................. 34
4.2.9 Configuring DVB-CI Descrambling ..................................................................... 36
4.2.10 Configuring BISS Descrambling ..................................................................... 37
4.2.11 Configuring Service Selection ..................................................................... 40
4.2.12 Configuring Video Services ..................................................................... 43
4.2.13 Configuring Audio ..................................................................... 44
4.2.14 Configuring SDI Ports - SD & HD Interface ......................................................... 45
4.2.15 Configuring SDI Ports- UHD –4K Interface .......................................................... 46
4.2.16 Configuring SDI Audio Embedding ..................................................................... 48
4.2.17 Configuring Analog Audio Output ..................................................................... 49
4.2.18 Configuring Digital Audio Output ..................................................................... 49
4.2.19 PID Filter ..................................................................... 50
4.2.20 Configuring ASI Output ..................................................................... 51
4.2.21 Configuring the MPEG/IP Outputs ..................................................................... 52
4.2.22 Configuring the MPEG/IP MPE Outputs ............................................................... 54
4.2.23 Viewing PSIP Information ..................................................................... 56
4.3 Admin Panel .............................................................................................................. 57
4.3.1 Changing Unit Password ..................................................................... 58
4.3.2 Profiles ..................................................................... 58
4.3.3 General Settings ..................................................................... 59
4.3.4 Unit Network Configuration ..................................................................... 59
4.3.5 MPEG/IP Network Configuration ..................................................................... 61
Page 9

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 9 (97)
4.3.6 Licensing ..................................................................... 62
4.3.7 Date/Time ..................................................................... 63
4.3.8 Configuring SNMP ..................................................................... 64
4.3.9 Syslog ..................................................................... 65
4.3.10 In-Band Control ..................................................................... 66
4.3.11 Updating the MRD 6000 ..................................................................... 67
4.3.12 Reboot Unit ..................................................................... 68
4.3.13 Reset Defaults ..................................................................... 68
4.4 Reporting Panel ......................................................................................................... 69
4.4.1 Active Alarms ..................................................................... 69
4.4.2 Event Logs ..................................................................... 70
4.4.3 Configuring the Logs ..................................................................... 71
4.5 About Panel .................................................................................................................. 73
4.6 System Recovery .......................................................................................................... 73
Section 5 Appendices ....................................................................................... 74
Appendix A – Acronyms and Glossary .................................................... 75
Appendix B – Error and Event List ........................................................... 78
Appendix C - Specifications ..................................................................... 80
Appendix D – Pinouts for Analog Audio and Relay Connectors ........... 89
Appendix E – MRD 6000 Audio Explanation ........................................... 91
Appendix F – MRD 6000 Discrete Audio Configuration ......................... 94
Appendix G – Open Source Software ....................................................... 94
Appendix H – Warranty ............................................................................. 96
Appendix I – Support and Contact Information ..................................... 96
Page 10

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 10 (97)
Section 1 Overview
Introduction
This section includes the following topics:
1.1 Product Introduction ................................................................................................... 11
1.2 Front Panel Overview ................................................................................................ 11
1.3 Rear Panel Overview ................................................................................................. 12
1.4 Cooling ....................................................................................................................... 12
1.5 Rack Information ........................................................................................................ 12
Page 11

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 11 (97)
1.1 Product Introduction
The MRD 6000 4K/UHD receiver decoder continues Sencore’s long history of leadership
and innovation in professional receiver/decoders. It is built with the latest-generation
4K/UHD ASIC decoder technology delivering reliable, cost-effective monitoring, turnaround, signage, hospitality, and enterprise solutions.
The product boasts a full complement of cutting-edge features, including HEVC
decoding up to MP@HT and M10P@HT to L4.1 on streams to 40 Mbps for decoding
professional 4K and consumer UHD formats with 4:2:0 chroma 8 and 10 bit. It outputs
HDMI 2.0 and 4x3G-SDI of 4K/UHD to 4Kp60 and 2160p60 formats. It includes legacy
format decoding of MPEG 2 and H.264 up to HP@L4.2.
The MRD 6000 decodes and outputs 4K/UHD video with dual audio and includes core
features required in professional video delivery networks. Every MRD 6000 ships with a
full complement of basic inputs and outputs, including ASI input and output, SD/HD/SDI
outputs, and an HDMI digital video output. The HDMI output makes monitoring as easy
as finding the nearest standard consumer television or PC monitor.
The MRD6000 further features MPEG/IP I/O, DVB-S/S2/S2X satellite inputs, QAM/VSB
RF receiver, DVB-T/T2, C/C2, & ISDB-T inputs, BISS descrambling, and dual DVB-CI
CAM slot options. Its configurable feature set makes the MRD 6000 the ideal choice for
contribution reception or demanding distribution applications which require a future-proof
set of specifications.
The receiver maintains Sencore’s long tradition of ease of use, with a straight-forward
web interface accessible via all major browsers and complete control of the unit via the
front panel keypad, and is backed by Sencore’s best-in-class staff of ProCare support
engineers.
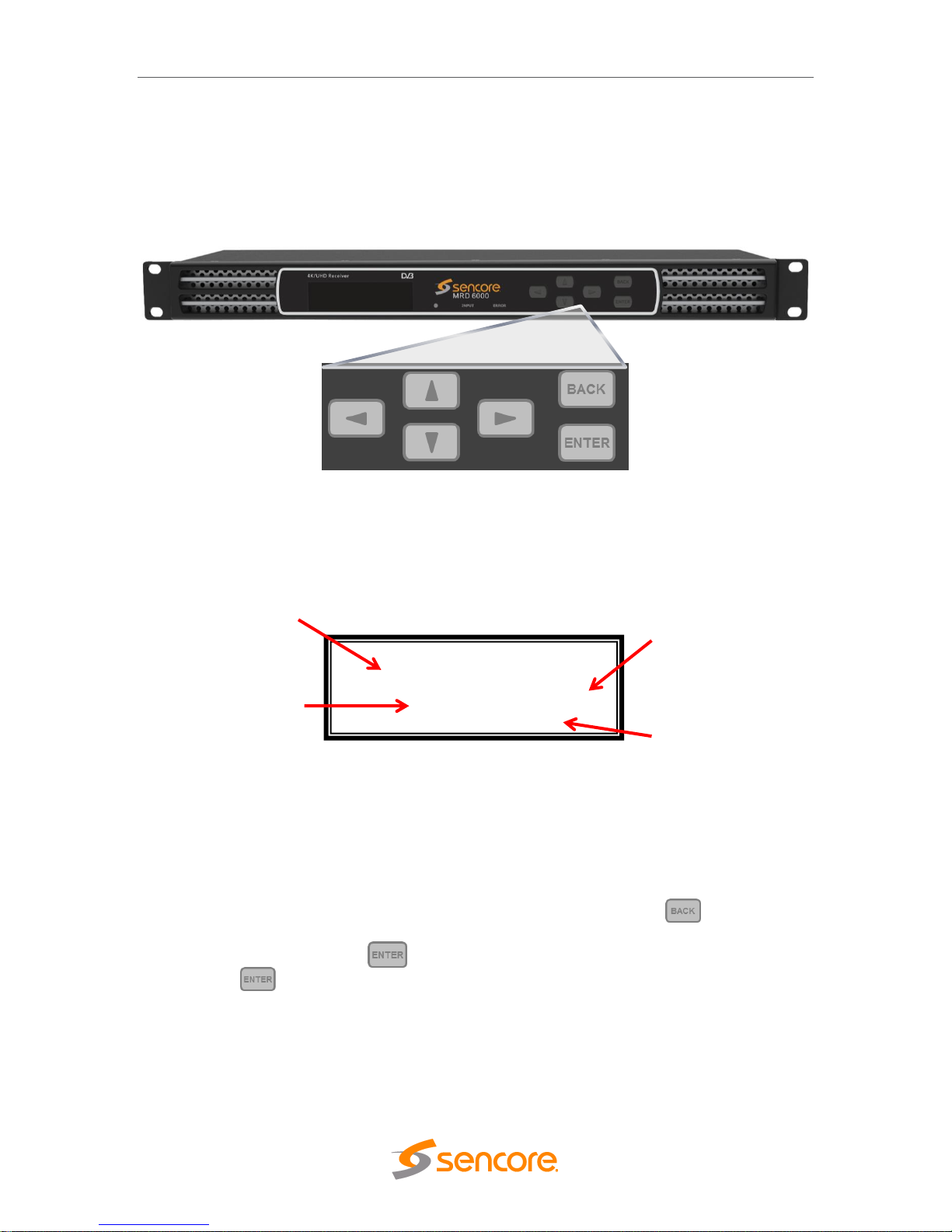
1.2 Front Panel Overview
The MRD 6000 can be controlled from the front panel using the LCD screen and buttons
that are shown below. A detailed description of using the front panel can found in
Section 0. All hardware listed below comes standard except for the DVB-CI slots which
are a factory installed option.
1. LCD screen: Shows menus for user status and unit control
2. Input Indicator: Light indicates input signal presence (green) or absent (red)
3. Error Indicator: Light indicates red when unit is in alarmed condition
4. Up, Down, Left, Right buttons: Provides navigation/entry within LCD screen
menus
5. Back and Enter Buttons: Provides navigation within LCD screen menus
1
2
435
Page 12

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 12 (97)
1.3 Rear Panel Overview
The MRD 6000 comes standard with all of the hardware back panel features shown and
listed below except where noted as a factory installed option. Option cards are available
for the MRD 6000. Examples include a Quad Input DVB-S/S2/S2X card or dual port
MPEG/IP Input/Output card. ASI is a standard input and output on all MRD 6000 units.
The external genlock reference connection (3) is not currently an option for the MRD
6000 model.
1. RJ45 Management Network Port(s)
2. Relay Output Connector
3. Digital Audio Outputs
4. 15-Pin Analog Audio Connectos (See Appendix D)
5. Composite Video Output (BNC connector)
6. SDI Outputs (Five BNC provide Quad3G/3G/HD/SD-SDI)
7. Digital Video Output Connector (HDMI)
8. ASI Input and ASI Output Connectors
9. Option Card Slot #1 (factory installed)
10. Option Card Slot #2 (factory Installed)
11. Chassis ground
12. Unit Venting
1.4 Cooling
The MRD 6000 is cooled via forced induction through the front of the unit and
exhausted through the vents in the rear of the chassis. The MRD 6000 is equipped
with a temperature controlled status indicator. If the temperature inside the unit
exceeds 60°C the red “Error” text will illuminate on the front panel and a description
of the error will appear in the “Error List.”
1.5 Rack Information
The MRD 6000 is intended to be mounted in a standard 19” rack. It occupies 1RU of
rack space and the connections are all on the rear of the unit.
3
1
4
5
7
8
12
9
13
10
Page 13

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 13 (97)
Section 2 Installation
Introduction
This section includes the following topics:
2.1 Rack Installation ........................................................................................................ 14
2.2 Power Connection ..................................................................................................... 14
2.3 AC Power Connection ............................................................................................... 14
2.4 AC Dual Redundant Power Connection (optional) .................................................... 15
2.5 DC Power Connection ............................................................................................... 15
2.6 Maintenance .............................................................................................................. 15
2.7 Network Setup via Front Panel .................................................................................. 15
Page 14
MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 14 (97)
2.1 Rack Installation
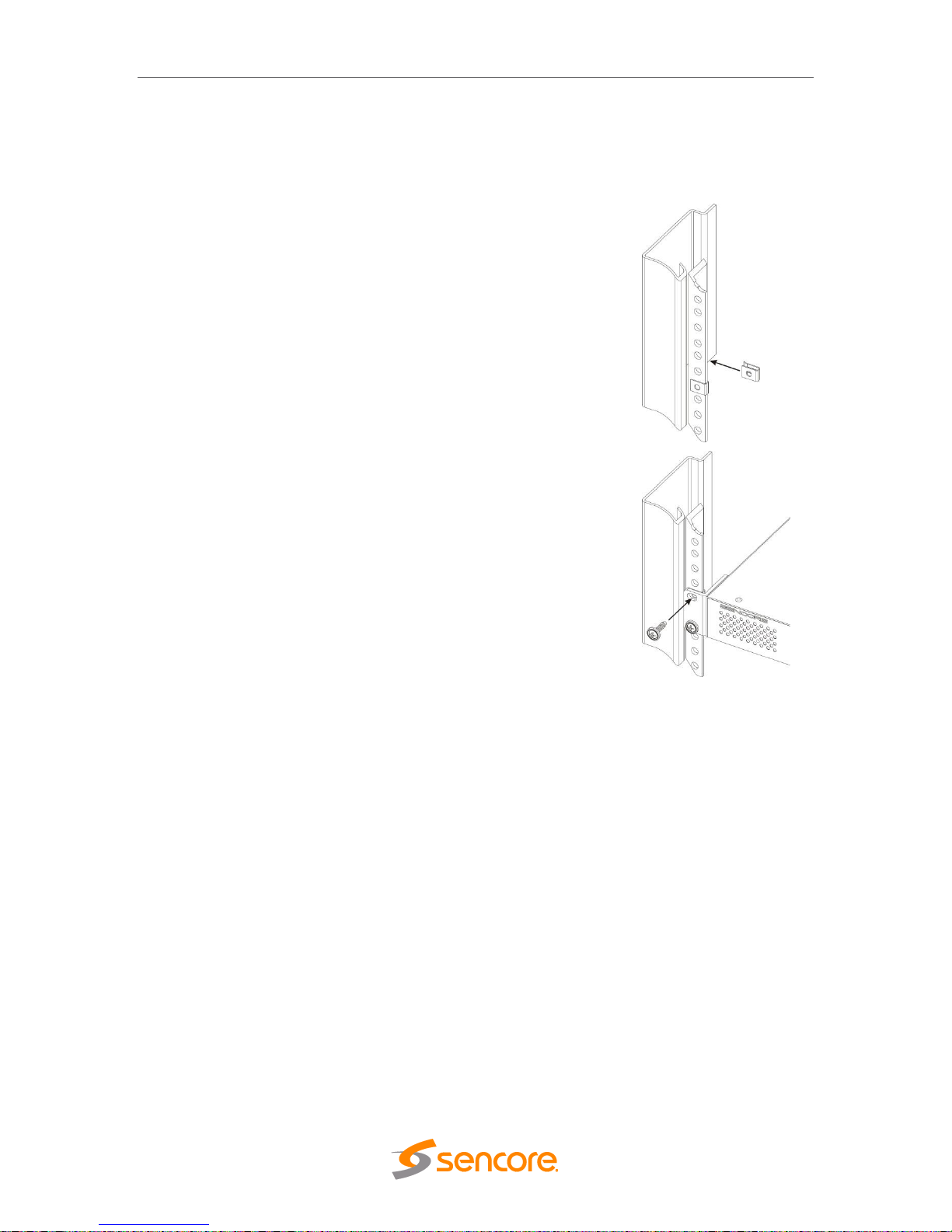
To install the MRD 6000 into a rack use the following steps:
1. Determine the desired position in the rack for the MRD
6000 making sure that the air intake on the front of the
unit and the exhausts on the sides of the unit will not be
obstructed.
2. Insert the rack mount clips into place over the mounting
holes in the rack.
3. Slide the MRD 6000 into position in the rack.
4. Secure the MRD 6000 to the rack by installing the four
supplied screws through the front mounting holes and
tightening.
5. If needed, secure a grounding wire use the grounding
location on the rear panel of the MRD 6000. See Section
1.3 for grounding location.
2.2 Power Connection
Using the proper power connections is vital to the safe operation of the MRD 6000.
Only use the supplied 3-prong power connector or one with equal specifications.
NEVER tamper with or remove the 3rd – prong grounding pin. This could cause
damage to the MRD 6000, personnel, or property.
2.3 AC Power Connection
The MRD 6000 is intended for use on either 120V or 240V systems. The power
supply will automatically detect the system it is connected to. To hook up the power
use the following steps:
1. Locate the AC power cord that was included with the MRD 6000.
2. Plug the female end of the power cord (end with no prongs) into the back of the
unit.
3. Locate a protected outlet (usually inside of the rack) to plug the male end of the
power cable into.
Page 15
MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 15 (97)
2.4 Maintenance
The MRD 6000 is a maintenance-free piece of equipment. There are no user
serviceable parts on the inside of the unit
2.5 Network Setup via Front Panel
The MRD 6000 can be setup on a network connection to allow remote management and
SNMP configuration. For these features to work, the network settings for the MRD 6000
must first be configured properly for the network it is connected to.
Static IP Address
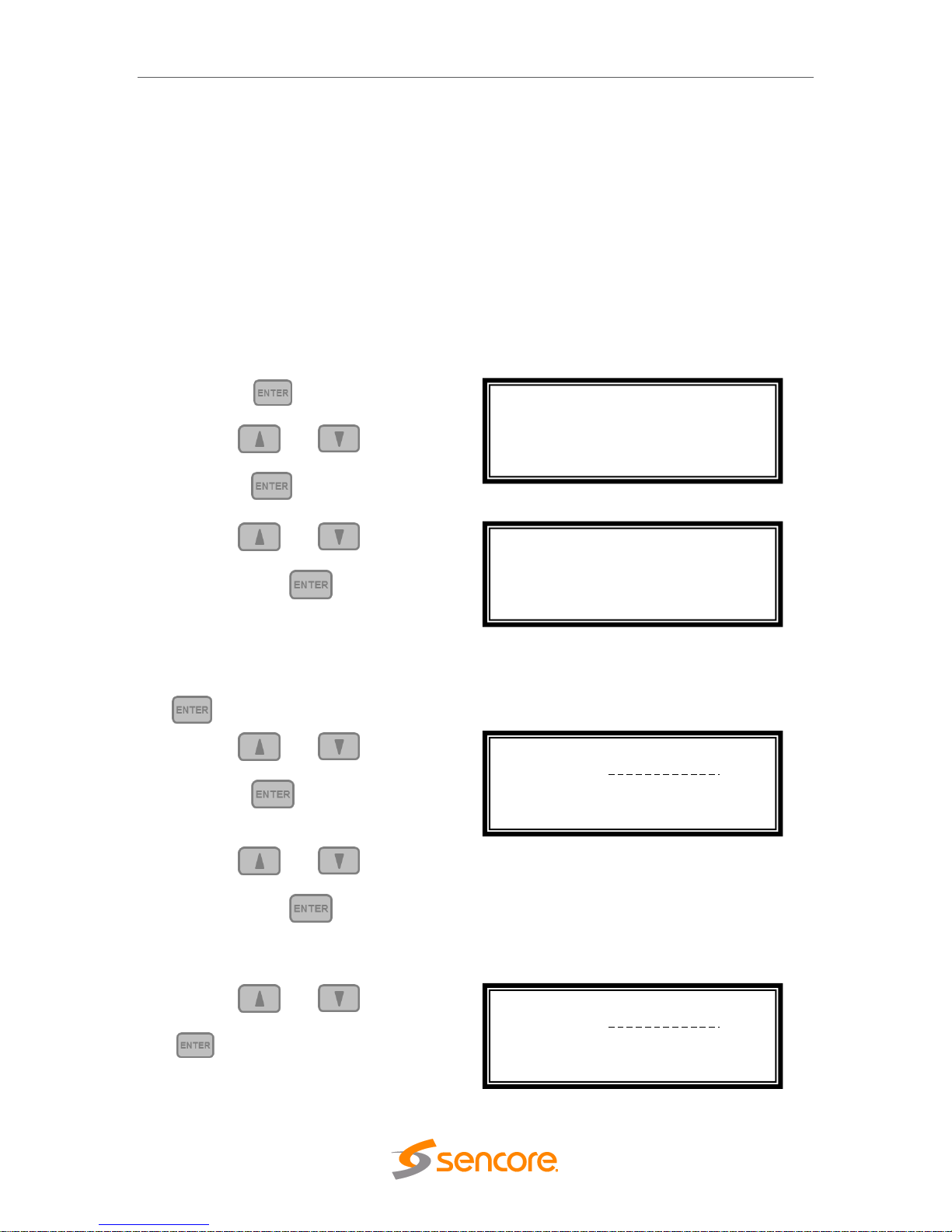
To setup the MRD 6000 with a static IP address, use the following steps:
1. Press the button.
2. Use the and buttons to
move the cursor to “Admin”, then
press the button.
3. Use the and buttons to
move the cursor to “Unit Networking”,
then press the button.
Note: The first menu displayed is status
menu. In order to begin making
changes to networking settings press
the button.
4. Use the and buttons to
move the cursor to “DHCP”, then
press the button.
5. Use the and buttons to
change the selection to “Disabled”
then press the button.
IP Address/Subnet Mask/Gateway
1. Use the and buttons to
move the cursor to “IP”, then press the
button.
Main Menu ↔↕
Baseband Outputs
Transport Stream Outputs
>Admin
Active Errors
Admin ↔↕
>Unit Networking
System Time
About System
Voltage Levels
Configure Network ↔↕
Host Name:
>DHCP: Disabled
Configure Network ↔↕
Host Name:
DHCP: Disabled
>IP: 0.0.0.0
Mask: 0.0.0.0
Page 16
MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 16 (97)
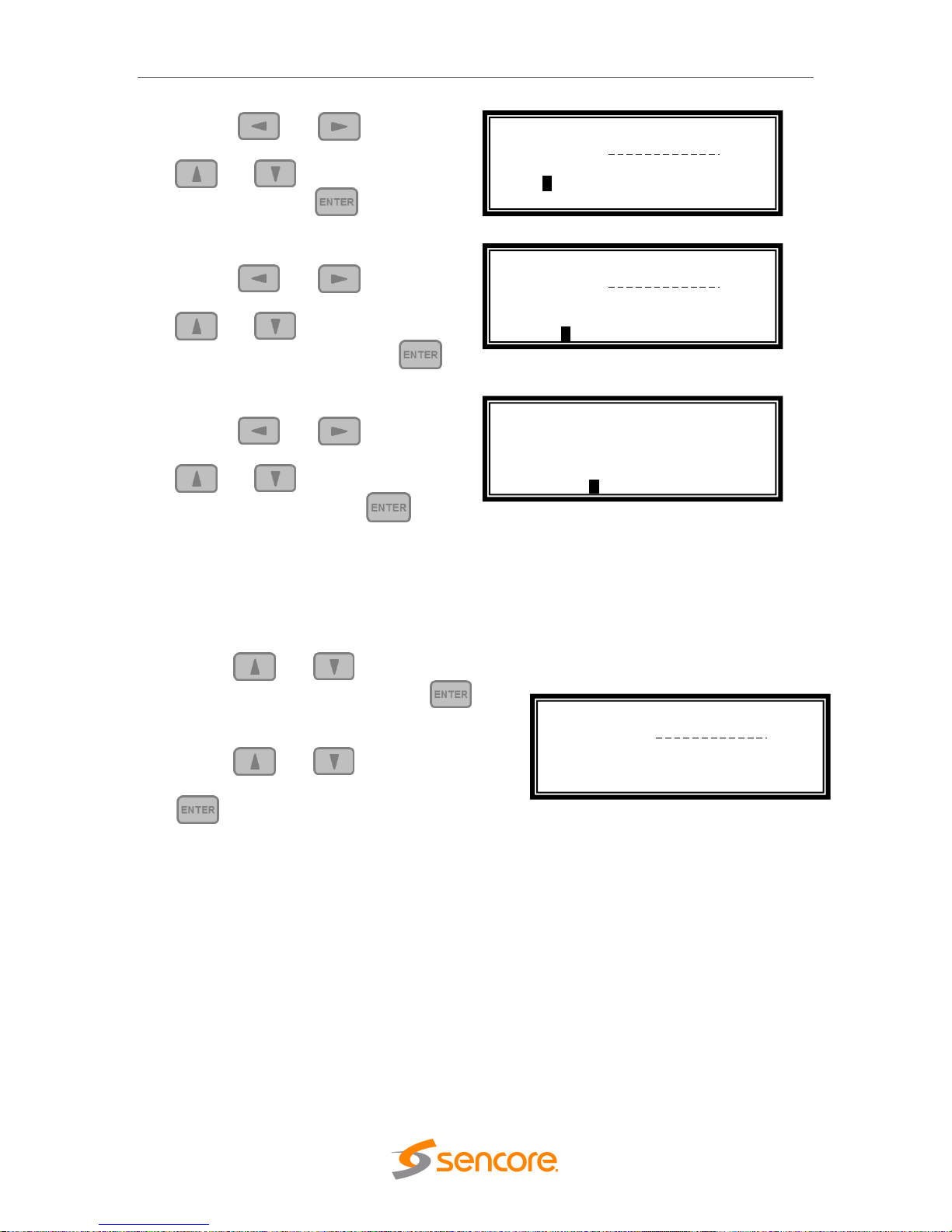
2. Use the and buttons to
select the column to edit and use the
and buttons to change the
IP, then press the button to
save the selection.
3. The cursor will now be on “Mask”.
4. Use the and buttons to
select the column to edit and use the
and buttons to change the
Subnet Mask, then press the
button to save the selection.
5. The cursor will now be on “Gateway”.
6. Use the and buttons to
select the column to edit and use the
and buttons to change the
Gateway, then press the button
to save the selection.
DHCP
The MRD 6000 can be configured to use DHCP to obtain an IP address/Subnet
Mask/Gateway.
1. Use the and buttons to move the
cursor to “DHCP:” then press the
button.
2. Use the and buttons to change
the selection to “Enabled” then press the
button to save the selection.
Note: It may take up to a minute for the MRD 6000 to obtain an IP address. During
this time the unit will display a “busy” message next to DHCP.
Configure Network ↔↕
Host Name:
DHCP: Disabled
>IP: 000.000.000.000
Mask: 0.0.0.0
Configure Network ↔↕
Host Name:
DHCP: Disabled
IP: 0.0.0.0
>Mask: 000.000.000.000
Configure Network ↔↕
DHCP: Disabled
IP: 0.0.0.0
Mask: 0.0.0.0
>Gateway: 000.000.000.000
Configure Network ↔↕
Host Name:
>DHCP: Enabled
Page 17

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 17 (97)
Section 3 Operating the Front
Panel
Introduction
This section includes the following topics:
3.1 MRD 6000 Front Panel Overview .............................................................................. 18
Page 18
MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 18 (97)
3.1 MRD 6000 Front Panel Overview
The MRD 6000 front panel allows the user to configure all settings that are present in the
web interface using the buttons located on the front of the unit. The screen below is the
idle screen of the MRD 6000. This idle screen allows the user to view the incoming
bitrate of the active input, which input is set to active, the management IP address of the
unit and the service currently set to decode.
1. Bitrate of incoming stream displayed in Mbps.
2. Current active input.
3. IP address of management port.
4. Current decoded service.
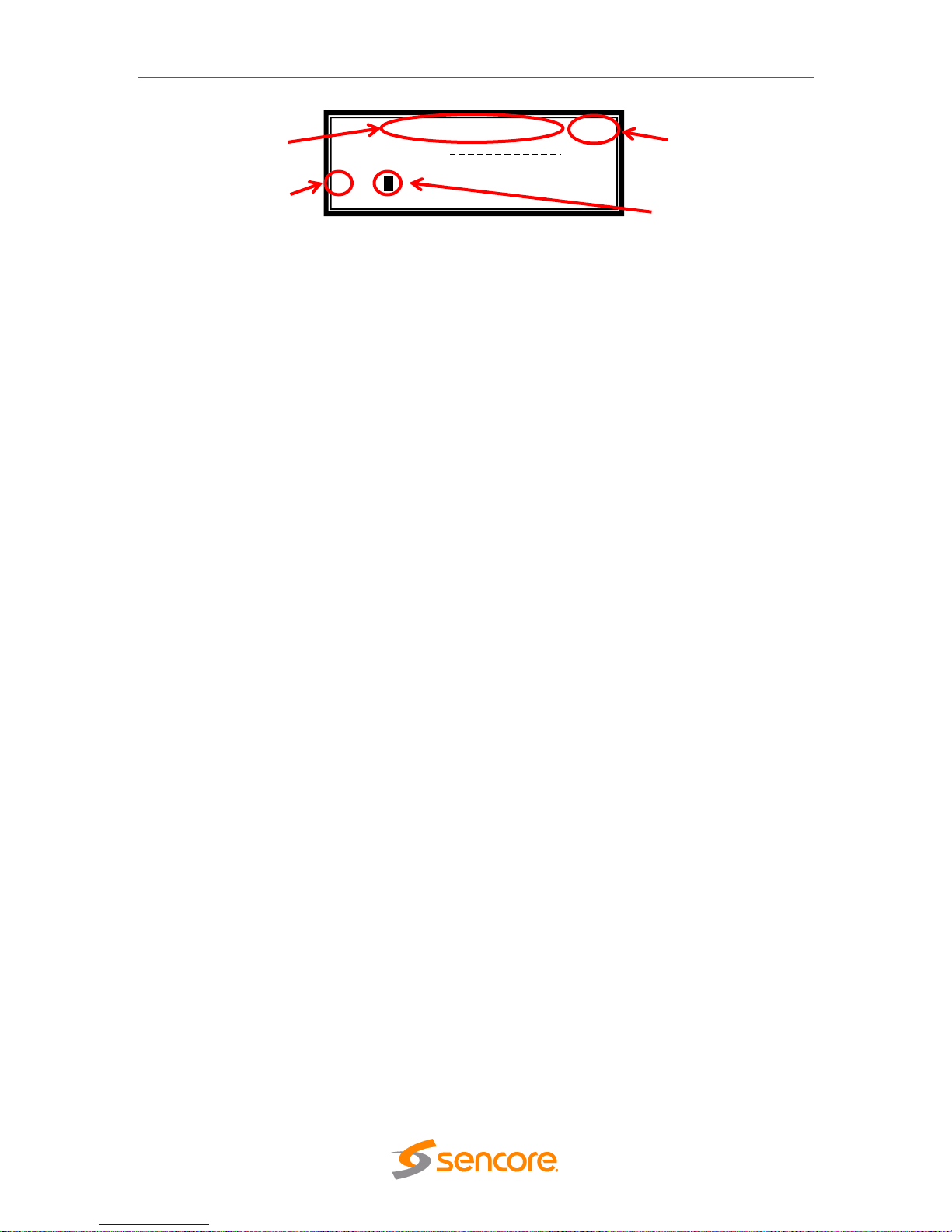
The following figure shows a typical screen on the front panel. Several important
features have been circled and noted below. These features are common to all screens
and assist when navigating, viewing and editing unit information. The button allows
the user to return to the home screen, cancel settings and go back a menu. In order to
edit a selected parameter the button must be pressed. Once a parameter has been
changed the button must be pressed again before the change takes effect on the
unit.
↔↕
Bitrate: 68.502 Mbps
Input: MPEG/IP 2 Stream 1
IP: 10.0.7.106
Service: NBA TV HD
1
2
3
4
Page 19
MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 19 (97)
1. Screen title.
2. Icons indicate which control buttons are currently valid for entry.
3. Cursor shows which line is active.
4. When editing, active character or item is highlighted.
Configure Network ↔↕
Host Name:
DHCP: Disabled
>IP: 000.000.000.000
Mask: 0.0.0.0
4
3
1
2
Page 20

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 20 (97)
Section 4 Operating the Web
Interface
Introduction
This section includes the following topics:
4.1 MRD 6000 Web Interface Overview .......................................................................... 21
4.2 Main Panel ................................................................................................................. 22
4.3 Admin Panel .............................................................................................................. 57
4.4 Reporting Panel ......................................................................................................... 69
4.5 About Panel ............................................................................................................... 73
Page 21
MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 21 (97)
4.1 MRD 6000 Web Interface Overview
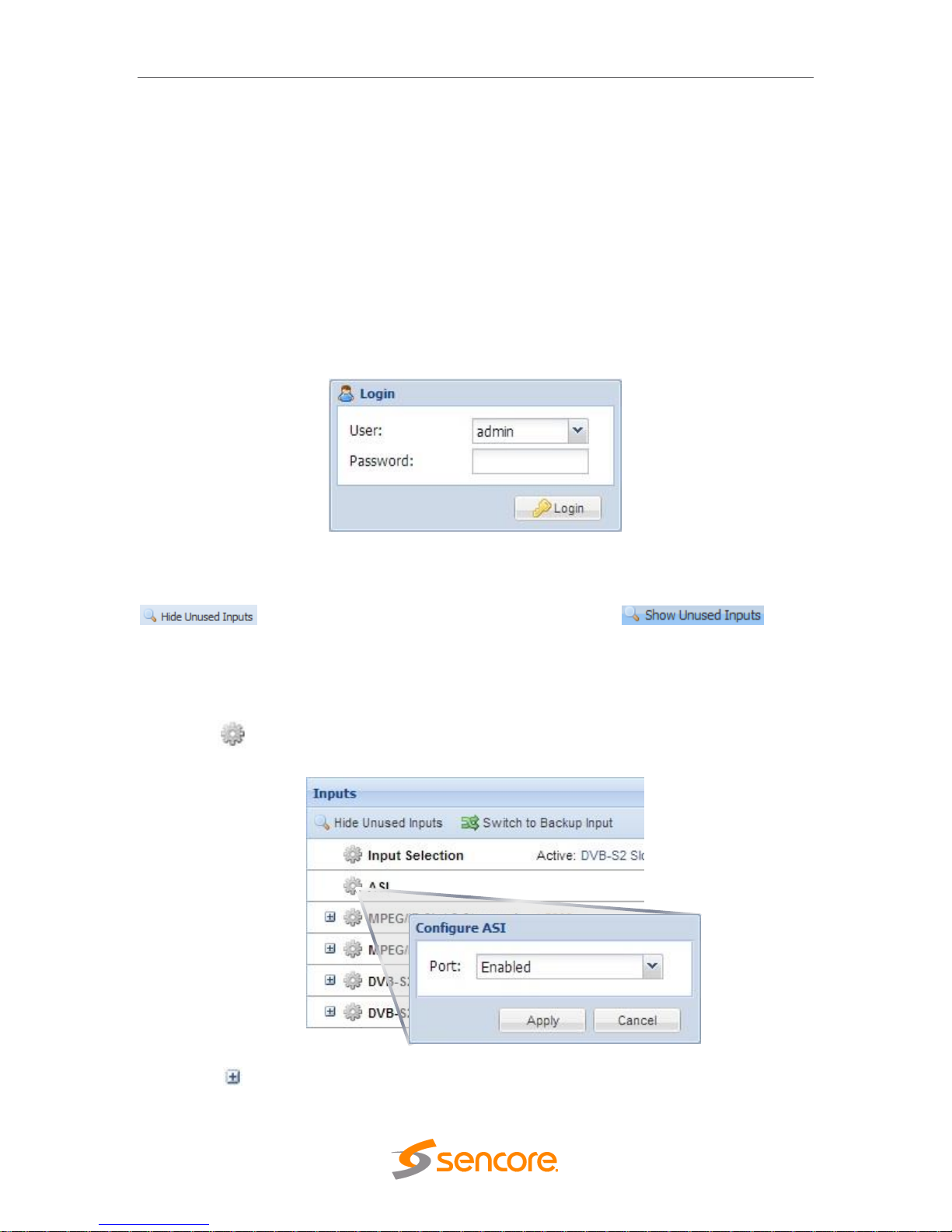
4.1.1 Logging into the MRD 6000 Web Interface
To open the MRD 6000 web interface use one of the following supported browsers and
navigate to the unit’s IP address:
• Internet Explorer 7 & above
• Firefox 3.5 & above
• Google Chrome
The user will need to login to the web interface. By default the admin user account is
available without a password. Press the login button in order to login to the web
interface.
4.1.2 Hiding Unused Inputs
The MRD 6000 web interface allows the user to hide inactive inputs using the
button or show all available inputs by click the
button. Only the inputs configured as the Primary Input and Backup Input (see Section
4.2.1) will be displayed when unused inputs are hidden.
4.1.3 Buttons and Status Indicators
When the icon is shown user configuration is available. Clicking this button will open
menus where settings can be changed by the user.
When the icon is shown additional status information can be viewed. Clicking this
button expands the menu to display the additional status information. All text in status
Page 22
MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 22 (97)
menus shown in ORANGE are user configurable settings. Text shown in BLUE is not
user configurable and is strictly a status or value. To minimize the status windows again
click the icon.
Status in the MRD 6000 web interface is shown with LED status indicators:
Green LED
Status is good. No errors are present and function is operating
normally.
Red LED
Status indicates function is affected by active error. To view the
errors navigate to Alarms panel to view Active Errors.
Grey LED
Status is inactive. Function is currently disabled or unavailable.
4.1.4 Drag and Drop Menus
Certain menus in the MRD 6000 allow the user to drag and drop items to auto populate
fields. Conditional Access and Service Selection menus are some examples of menus
that drag and drop can be used. In the example below a service in the transport stream
view on the right hand side of the window is selected and dragged over to auto populate
the PIDs in the service selection section.
4.2 Main Panel
The Main panel of the MRD 6000 web interface is used to configure the unit to decode,
de-encapsulate and demodulate. When configuring the MRD 6000 the user begins at the
top of the menu and works down. The inputs are configured, then descrambling (if
present), then service or PIDs are selected for decode, then outputs are configured.
Pictured below is a fully populated unit with all options licensed.
Page 23

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 23 (97)
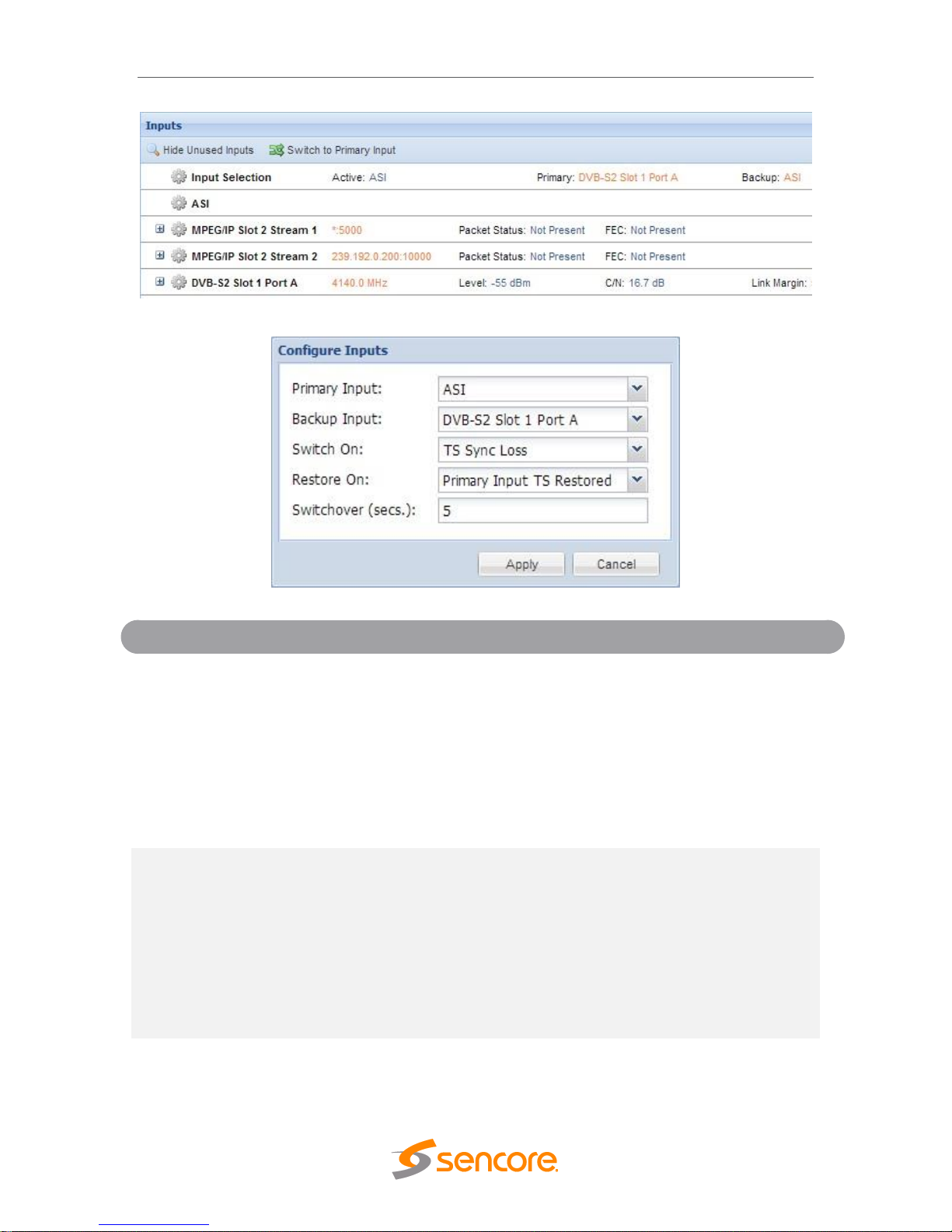
4.2.1 Configuring Active Inputs
This menu allows the user to configure a primary and backup input. In case there is an
input failover the MRD 6000 is capable of detecting the failed state and switching to a
secondary backup input in order to provide a continuous output. Which input is primary
and backup, how the inputs switchover and restore and switchover timing is all user
configurable. The user can force the MRD 6000 to switch between the Primary and
Backup Inputs by clicking the button. To change the active input and
failover settings click the icon next to Input Selection:
Page 24
MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 24 (97)
Active Input Indicator
Active Input and Failover Configuration Menu
Setting
Range
Description
Primary Input
ASI
MPEG/IP Slot X Stream X
DVB-S2 Slot X Port X
DVB-S2X Slot X Stream X
8VSB/QAM Slot X
DVB-T2/C2/ISDB-T Slot X
None
Used for both normal operation and input
failover settings. During normal operation this
input will be the active input.
Backup Input
ASI
MPEG/IP Slot X Stream X
DVB-S2 Slot X Port X
DVB-S2X Slot X Stream X
8VSB/QAM Slot X
DVB-T2/C2/ISDB-T Slot X
None
During failover operation this input will
become the active input. The catalyst for
what causes the unit to switch to this input is
configured in the following setting.
Switch On
Manual Only
TS Sync Loss
Manual Only: the unit will not switch inputs
automatically. The user must manually
switch inputs.
Page 25

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 25 (97)
Decode Failure
TS Sync Loss: the MRD 6000 will switch
from the primary to the backup input if the
primary stream loses synchronization for the
duration of the Switchover Interval.
Decode Failure: the unit will switch to the
backup input when it encounters decoding
errors on the primary input.
Restore On
Manual Only
Primary Input TS Restored
Backup Input TS Sync Loss
Decode Failure
Manual Only: the unit will not restore to the
primary input automatically. The user must
manually switch inputs.
Primary Input TS Restored: the MRD 6000
restores to primary when the Primary input
regains transport stream synchronization.
Backup Input TS Sync Loss: the unit will
switch from backup to primary when the
backup stream loses synchronization for the
duration of the Switchover interval.
Decode Failure: the unit restores to the
Primary Input when the Backup Input
experiences a decoding error.
Switchover
1-20 seconds
The time in seconds which Switch On or
Restore On value must remain in the
configured state before the MRD 6000
switches between the Primary Input and
Backup Input or vice versa.
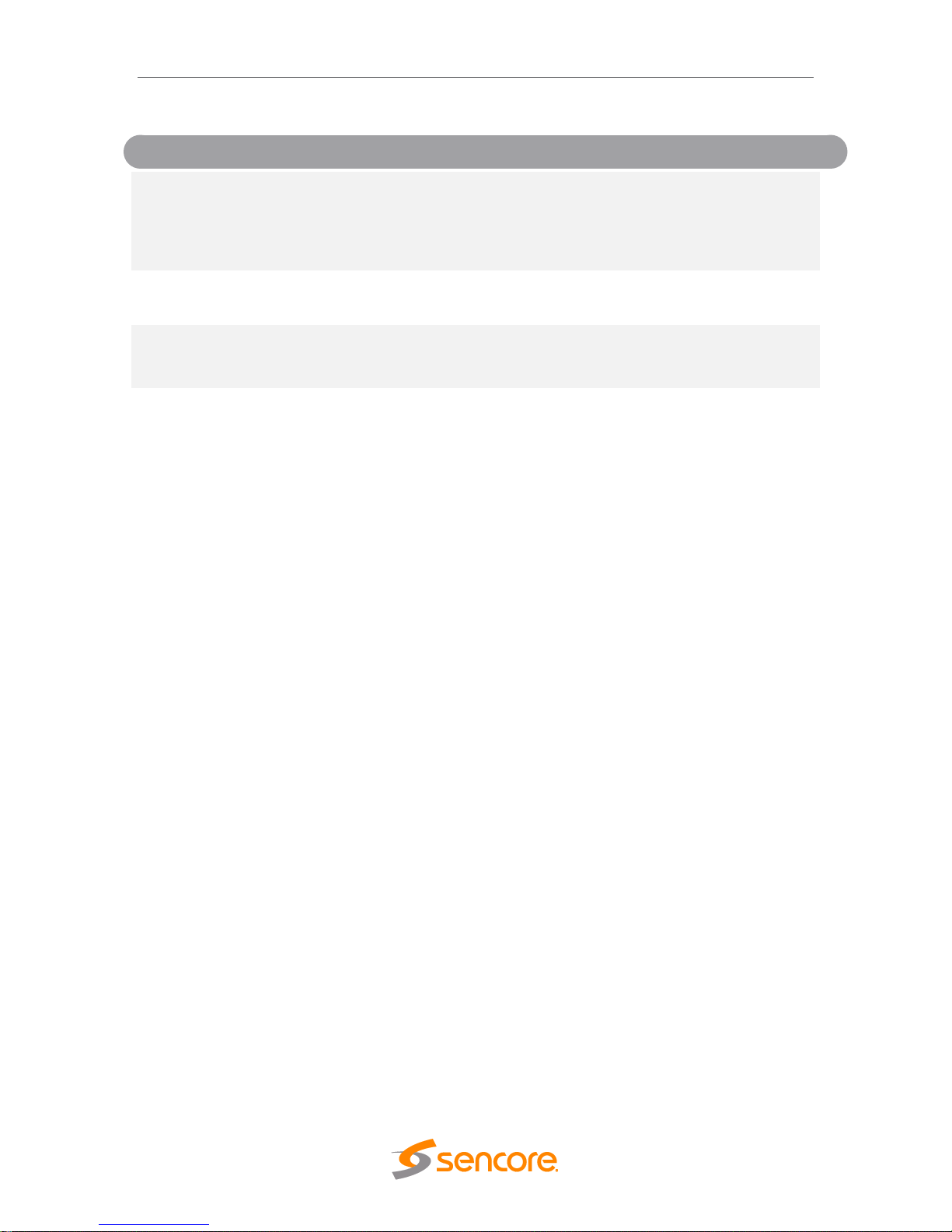
4.2.2 Configuring ASI Input
This menu allows the user to either Enable or Disable the ASI Input on the MRD 6000.
The ASI ports can be configured as either an input or output. ASI inputs can be
configured to enable or disable the null stripped feature. ASI outputs can be configured
to pass the selected TS input directly unmodified to the output or apply PID filtering to
the output.
Page 26
MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 26 (97)
Setting
Range
Description
Direction
Input
Output
Configrue the ASI port to either an input or
an output. Applies only to main board
revision J or later. Main board version can be
located on the about tab under the Options
section.
Port
Enabled
Disabled
This setting allows the user to enable or
disable the ASI Input to the MRD 6000.
Null Stripped
Disabled
Enabled
Enabling Null Stripped allows the MRD 6000
to receive streams that do not contain null
packets. (i.e. VBR Transport Streams)
4.2.3 Configuring MPEG/IP Input
If the MPEG/IP Input card was selected as a factory installed option, the following menus
and options will be available for configuration. This menu allows the user to configure the
MPEG/IP inputs. Each MPEG/IP card has two ports that can be set to receive and/or
transmit. This menu is for setting up the reception of MPEG/IP unicast or multicast
transport streams. The menu for Stream 1 and 2 have the same settings. IGMPv2 is
used to join/leave multicast streams by default if no IGMP Filter addresses are entered.
If IGMP Filter Mode addresses are specified then IGMPv3 is used.
Page 27

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 27 (97)
General and Advanced options for IP input
Setting
Range
Description
Receive
Enabled
Disabled
This setting allows the user to enable or
disable these input stream settings.
Physical
Connector
Port 1
Port 2
The physical connector on the MPEG/IP card
that will be used to receive the input.
Mode
Multicast
Unicast
Multicast setting allows the unit to receive
multicast streams. Multicast streams
originate from the IP range 224.0.0.0 –
239.255.255.255. Unicast allows the unit to
receive unicast streams. Unicast streams
originate directly from a source device.
Destination IP
224.0.0.0 –
239.255.255.255
This setting is only available when receiving
a multicast stream. This address is the IP
address the source device is sending to.
Destination Port
0 - 65535
This is the UDP port the source device is
sending to. This is the only setting required to
receive a unicast stream.
FEC
Enabled
Enabling FEC (Forward Error Correction)
tells the MRD 6000 to look at Destination
Page 28
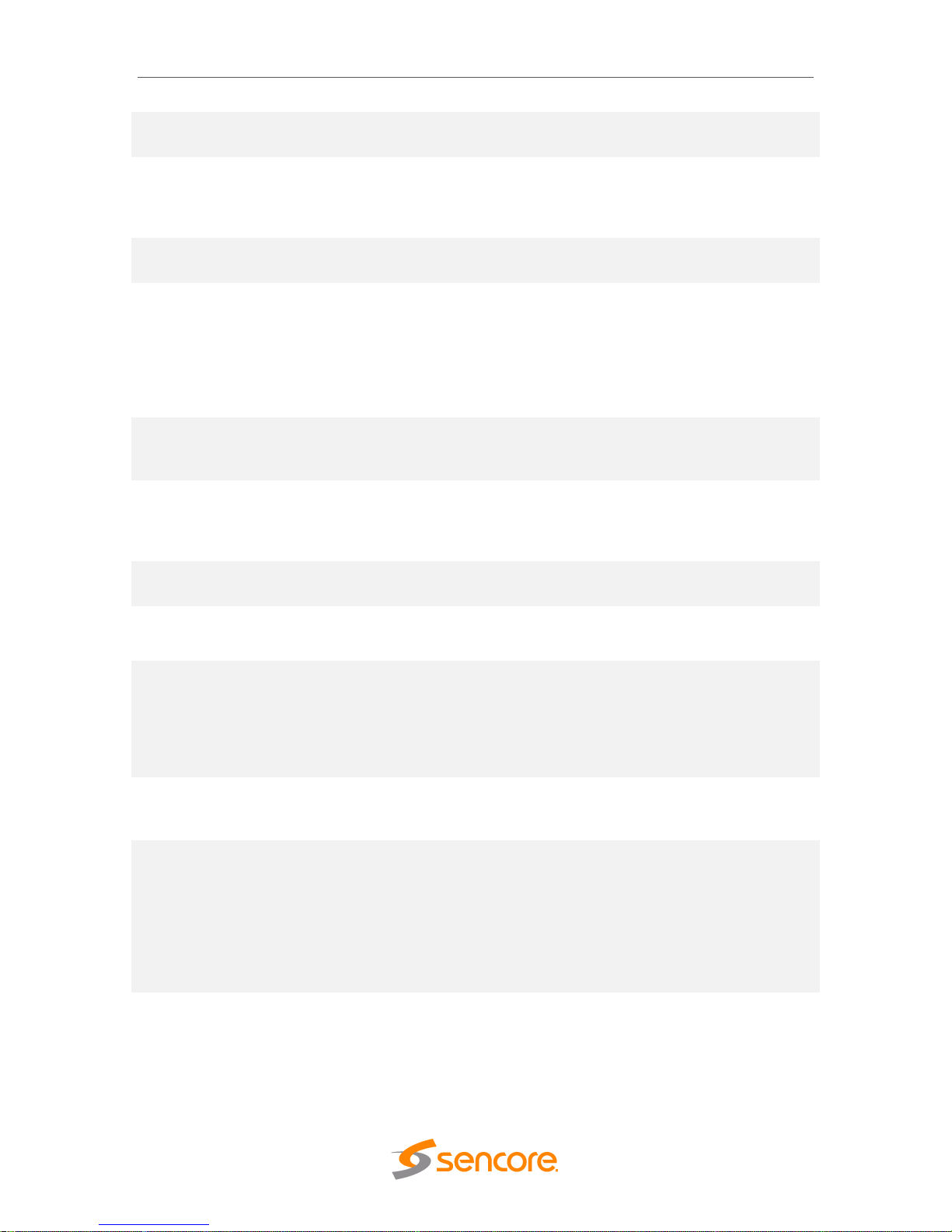
MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 28 (97)
Disabled
Port +2 and Destination Port +4 for a SMPTE
2022 FEC Matrix.
Internal Source
Filter
Enabled
Disabled
Enabling Source filtering disables IGMP V3
filtering and allows a user to whitelist a single
IP address for a given multicast and block all
other source IP’s
Internal Source
Filter IP
0.0.0.0 – 255.255.255.255
Source IP for whitelist. All other source IP
addresses are blocked
IGMP Filter Mode
Exclude
Include
Used on networks supporting IGMPv3. If this
setting is set to Exclude any streams
originating from the user defined IP
addresses will be rejected. If this setting is
set to Include any streams originating from
the user defined IP addresses will be
received.
Null Stripped
Enabled
Disabled
Enabling Null Stripped allows the MRD 6000
to receive streams that do not contain null
packets. (i.e. VBR TS Streams)
RTP SSRC
Enabled
Disabled
Enabling RTP SSRC allows the MRD 6000 to
filter the input by the user defined value. Only
streams containing the user defined value
will be received by the MRD 6000.
SSRC Filter Value
0 - 4294967295
The Filter Value the MRD 6000 checks for
before receiving a stream with RTP SSRC.
Buffer Mode
Size (KB)
Delay (ms)
Allows option to set buffer mode to Size in
KB or Delay ms
Buffer Size (KB)
1 – 4000 KB
This setting determines how much data is
received before the MRD 6000 starts
decoding. Increasing this value will allow the
MRD 6000 is receive streams on networks
with high network jitter. Increasing this value
also increases the latency of the MRD 6000.
Buffer Delay (ms)
1 – 4000 ms
The buffer delay setting allows the buffer size
to be set by delay time. The Buffer delay time
will be determined by the input data rate.
Statistics Reset
Mode
Manual
Auto
Statistics can be viewed by hitting the +
symbol next to the MPEG/IP option card on
the main window. Selecting Auto will reset
the statistics on a chosen interval. When the
reset occurs, statistical information for that
period will be logged. Selecting Manual will
only clear the statistics by hitting the refresh
button.
Reset Interval
(min)
5-65535
Interval in which the Auto option will reset
and log the statistics displayed on the main
window
Page 29

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 29 (97)
IP statistics menu
4.2.4 Configuring DVB-S/S2/S2X Input
If the DVB-S/S2/S2X input card was selected as a factory installed option, the following
menus and options will be available for configuration. This menu allows the user to
configure the DVB-S/S2/S2X inputs. The input card is equipped with dual demodulators
and four ports (labeled A, B, C and D). This configuration allows the card to receive two
signals simultaneously for fast switching between primary and backup inputs. The menu
for both demodulators have the same settings. The input card will automatically detect
modulation and symbol rate during signal acquisition. LNB Power configuration for this
input card is done in the Admin tab.
Setting
Range
Description
Receive
Enabled
Disabled
This setting allows the user to enable or
disable this input stream.
Physcial
Port A
This setting allows the user to select which
Page 30
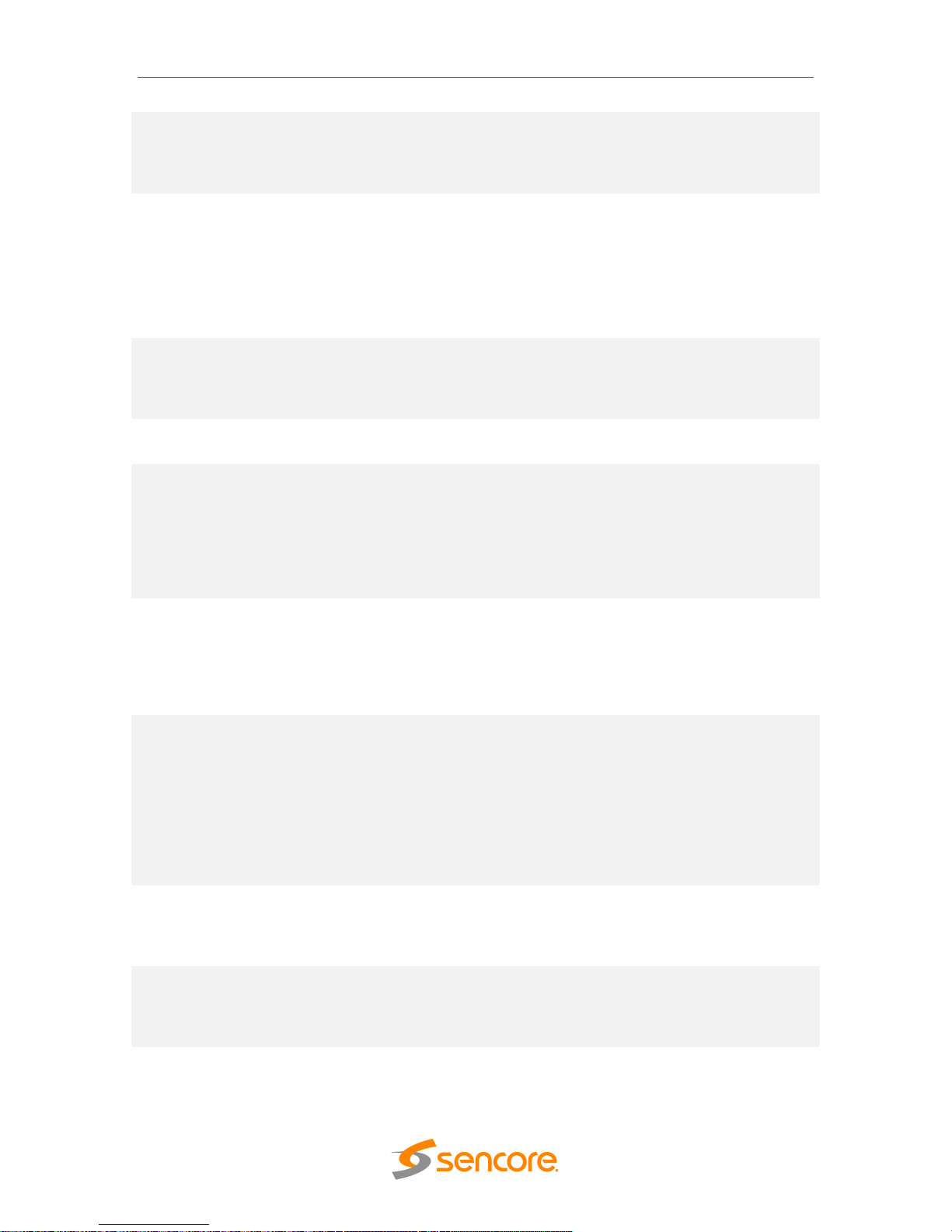
MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 30 (97)
Connector
Port B
Port C
Port D
physical RF connector will be used to receive
the stream.
Satellite
Frequency
C-Band: 4GHz – 8GHz
Ku Band: 11.2Ghz –
14.5Ghz
L-Band: 950MHz –
2150MHz
Dependent on LO Offset
If LO Offset is set to 0 then L-Band frequency
is entered into the Satellite Frequency dialog
box. If LO Offset to set to a pre-defined
option then enter C-band or Ku-Band
frequency.
Symbol Rate
Mode
Auto
Manual
This setting allows user to select if the
satellite tuner automatically searches and
determines the received signal symbol rate
or if it is entered manually in the space below
Symbol Rate
(Msps)
0.5 to 60
If Symbol Rate Mode is set to Manual then
enter the satellite receive signal symbol rate
Manual Search
Range
Enabled
Disabled
This setting determines the satellite receiver
automatic fine tuning (AFT) search range.
Disabled by default – permits the receiver to
auto tune or AFT range (+/- 20 MHz).
Enabled allows the user to enter a manual
range limiting or expanding the AFT search
range
Search Range
(MHz)
.5 – 70 MHz
If the Manual Search Range is set to Enabled
then enter a MHz value for an AFT search
range. The entered value includes a positive
and negative search total range. For
example: 10 MHz enables a +/- 5 MHz
search range.
LO Offset
5150
9750
10600
10750
11250
The offset in MHz that the local oscillator is
operating. Set to the LO frequency when you
want to enter the Satellite transponder
frequency in the Satellite Frequency field. Set
to 0.0 when you want to enter the L-Band
frequency in the Satellite Frequency field.
Note that this setting and the Satellite
Frequency setting determine the L-Band
frequency input to the receiver.
PL Scrambling
Code
0 – 262141
The MRD has the ability to receive satellite
signals scrambled using PL Scrambling. In
order to receive the stream, enter the value
of the incoming signals PL Scrambling code.
ISI
Enter input stream
identifier (ISI)
Enter unique ID of the stream you want to
receive within the DVB-S2/S2X satellite
multi-stream (Advanced MRD 60916 licensed
feature)
Page 31

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 31 (97)
4.2.5 Configuring DVB-S/S2 Input
If the DVB-S/S2 Input card was selected as a factory installed option, the following
menus and options will be available for configuration. This menu allows the user to
configure the DVB-S/S2 inputs. Each DVB-S/S2 input card has four ports (labeled A, B,
C and D) which only one port can be active at a time. This menu is for setting up the
reception of DVB-S/S2 satellite signals. The menu for Port A, B, C and D have the same
settings.
Setting
Range
Description
Port
Enabled
Disabled
This setting allows the user to enable or
disable this reception port.
Mode
DVB-S
DVB-S2
Auto
This setting allows the user to choose
between DVB-S or DVB-S2 modulation
schemes. Setting to Auto will have the unit
automatically detect whether the input is
DVB-S or DVB-S2.
Satellite
Frequency
C-Band: 4GHz – 8GHz
Ku Band: 11.2Ghz –
14.5Ghz
L-Band: 950MHz –
2150MHz
Dependent on LO Offset
If LO Offset is set to 0 then L-Band frequency
is entered into the Satellite Frequency dialog
box. If LO Offset to set to a pre-defined
option then enter C-band or Ku-Band
frequency.
Page 32

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 32 (97)
Wide Search
Enable
Disable
When Enabled the search range may be
extended depending on the symbol rate. See
appendix C for more information.
LO Offset
5150
9750
10600
10750
11250
The offset in MHz that the local oscillator is
operating.
Symbol Rate
Mode
Manual
Auto
The Manual option allows the user to choose
the symbol rate. The Auto option
automatically detects the incoming symbol
rate.
Note: Acquisition time may be longer in auto
mode, especially when the symbol rate is
below 1MSps or above 55MSps.
Symbol Rate
0 - 60
The symbol rate of incoming satellite signal
in MSps. Accurate to one decimal place
(kSps). Used when Symbol Rate Mode is set
to Manual.
PLS Code
0 – 262141
The MRD 6000 has the ability to receive
satellite signals scrambled using PL
Scrambling. In order to receive the stream,
enter the value of the incoming signals PL
Scrambling code.
LNB Power
Off
13 VDC
14 VDC
18 VDC
19 VDC
The MRD 6000 has the ability to provide the
necessary voltage to power an LNB. Select
the correct voltage to supply to the LNB.
22kHz Tone
Enabled
Disabled
Enabling or disabling the 22khz tone allows
the MRD 6000 to trigger the LNB to switch
polarities.
Multistream State
Enabled
Disabled
The MRD 6000 has the ability to receive
multistream satellite signals. If the signal is
multistream capable, enable this setting. This
option is only available in DVB-S2 Mode.
NOTE: This is a licensed feature.
ISI
0-255
This setting is the ISI (Input Stream Identifier)
the MRD 6000 uses to filter multistream
input. This option is only available if
Multistream is licensed and enabled.
Page 33

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 33 (97)
4.2.6 Configuring 8VSB/QAM Input
If the 8VSB/QAM Input card was selected as a factory installed option, the following
menus and options will be available for configuration. This menu allows the user to
configure the 8VSB/QAM input. This menu is for setting up the reception of 8VSB off air
signals or QAM cable signals.
Setting
Range
Description
Receive
Enabled
Disabled
This setting allows the user to enable or
disable this reception port.
Mode
8VSB
64-QAMB
256-QAMB
This setting allows the user to choose
between 8VSB or QAM modulation schemes.
Channel Plan
Off Air
FCC Cable
HRC Cable
IRC Cable
If 8 VSB is the selected Mode, the only
available option is Off Air. If either 64-QAMB
or 256-QAMB is the selected Mode, this
setting allows the user to choose which
Cable scheme is used.
Channel
Off Air: 2-69
FCC, HRC, or IRC Cable:
2-158
This setting is for the desired channel to be
received.
Low RF Level
(dBmV)
-34 - +40
This is the Low RF Level threshold when the
Low Level Alarm will be triggered in dBmV
Low MER (dB)
0 – 40
This is the Low MER threshold when the Low
MER Alarm will be triggered in dB.
Page 34

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 34 (97)
4.2.7 Configuring Turbo PSK Input (Currently Not Available)
Reception of aTurbo PSK satellite signal requires a special input receiver card option
which is not currently available for the MRD 6000. Please contact Sencore for an
alternative model receiver/decoder for this application.
4.2.8 Configuring DVB-T2/C2/ISDB-T Input
If the DVB-T2/C2/ISDB-T Input card was selected as a factory installed option, the
following menus and options will be available for configuration. This menu allows the
user to configure a DVB-T/T2/C/C2 or ISDB-T input.
Setting
Range
Description
Recieve
Enabled
Disabled
This setting allows the user to enable or
disable this reception port.
Mode
DVB-T
DVB-T2
DVB-C
DVB-C2
ISDB-T
This setting allows the user to choose
between DVB-T/T2/C/C2 or ISDB-T
modulation schemes.
Channel Plan
Australia
Eur-Asia-Afr
This setting allows the user to select which
channel plan they would like to use. Channel
Plan options are tied to which modulation
Page 35

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 35 (97)
Ireland
New Zealand
Taiwan
South Africa
South America
United Kingdom
European Cable
Japan
Philippines
mode is selected.
Channel
Select a channel from the channels available
in the dropdown. The list of available
channels will be based on which channel
plan is selected
Frequency (MHz)
42-1002
Selecting a channel from the channel
dropdown will populate this field
automatically based on the user selected
channel. A user can manually select a
frequency if desired
Bandwidth
1.7 MHz
5 MHz
6 MHz
7 MHz
8 MHz
Selecting a channel from the channel
dropdown will populate this field
automatically based on the user selected
channel plan. A user can mannualy select
channel bandwidth if desired.
PLP ID
Unique PLP ID used to select a particular
stream within the DVB-T2 or DVB-C2 input
signal
Profile
Auto
Base
Lite
Select the DVB-T2 profile to use
Low RF Level
(dBmV)
-34 - +40
This is the Low RF Level threshold when the
Low Level Alarm will be triggered in dBmV
Low MER (dB)
0 - 40
This is the Low MER threshold when the Low
MER Alarm will be triggered in dB.
Page 36

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 36 (97)
4.2.9 Configuring DVB-CI Descrambling
This section will describe how to configure DVB-CI descrambling in the MRD 6000. First,
the user will need to configure the CAM slots and descrambling mode. Once this is
complete the user can configure which services or PIDs to descramble.
4.2.9.1 Configuring DVB-CI Slots
This menu allows the user configure the DVB-CI slots in the MRD 6000. The MRD 6000
has two DVB-CI slots, a top and bottom, where CAM Modules can be inserted. Both
slots are individually configurable using the Bottom Slot and Top Slot tabs. CAM
Modules can be reset manually using the button. The button opens the
MMI (Man Machine Interface) for the CAM in the respective slot. MMI support is
dependent on what is supported by the CAM
.
Setting
Range
Description
Mode
Descramble Decoded PIDs
Descramble Selected PIDs
Descramble Selected Services
Decoded PIDs sets the MRD to descramble
only the PIDs of the service that is currently
set to decode. If the PIDs change in the
incoming stream the MRD will adapt to these
changes, provided that Service Selection is
set to “Service Lock” (Refer to Section
4.2.11). Selected PIDs sets the MRD to
descramble PIDs set in the Descramble
Services window (Refer to Section 4.2.9.2).
If the PIDs change in the incoming stream
the MRD will not adapt to these changes and
will not be able to descramble. Selected
Services sets the MRD to descramble
Services set in the Descramble Services
window Refer to Section 4.2.9.2). If the
Services change in the incoming stream the
MRD will not be able to descramble.
Top Slot
Bottom Slot
Enabled
Disabled
This setting allows the user to enable or
disable the DVB-CI slot.
Page 37

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 37 (97)
4.2.9.2 Configuring Service Descrambling
This menu allows the user to select the services the MRD 6000 will descramble using
the CAM Modules and Smart Cards inserted into the DVB-CI slots. See Section 4.2.9.1
to configure these slots. These options are applicable only if the Mode in the DVB-CI
settings is set to Selected PIDs or Selected Services (Refer to Section 4.2.9.1). The drag
and drop method can be used to drag services from the right column to the left column.
The drop down menu next to each selected service allows the user to choose either the
bottom or top slot to descramble the service. If in Selected PIDs mode, PIDs to
descramble can be added manually by clicking button. If in Selected Services
mode, Services to descramble can be added manually by clicking the
button. The icons next to each service indicate whether the service is scrambled or not
scrambled. Scrambled services will show the icon next to them while services that are
not scrambled will show the icon. Clicking the button forces the MRD 6000
to rescan the transport stream for changes.
DVB-CI Service Descrambling Menu
4.2.10 Configuring BISS Descrambling
This section will describe how to configure BISS descrambling in the MRD 6000. There
are two types of BISS descrambling.
In “Descramble All PIDs” or “Descramble Decoded PIDs” mode, the user simply
configures a BISS key set and selects it from the drop down.
For streams with multiple, per-service keys the user must first configure the key sets,
and then assign them to services.
Page 38

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 38 (97)
4.2.10.1 Configuring BISS Keys
This menu allows the user to configure BISS descrambling. 12 unique BISS keys can be
entered. If the BISS mode is set to Mode E a icon will appear next to Mode E
Injected ID. This icon allows the user to unlock and modify the Injected ID.
BISS Menu
Setting
Range
Description
Operation Mode
Disabled
Descramble Decoded
PIDs
Descramble Selected
Services
Descramble All PIDs
Descramble Decoded PID’s will descramble
the pids that are currently assigned to be
decoded by the MRD 6000.
Descramble Selected Services will allow the
user to select service(s) to be descrambled
on the Selected Services tab.
Descramble All PIDs will apply the selected
key to the entire transport stream.
Selected Key
Key 1-12
Select a key to configure.
Alias
16 characters
Set an Alias for the selected key.
Mode
Mode 1
This setting sets the Mode of the BISS key
that has scrambled the transport stream.
Page 39

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 39 (97)
Mode E
Mode 1 Session Word
N/A
If Mode 1 is selected the user enters the
BISS session word here.
Mode E Session Word
N/A
If Mode E is selected the user enters the
BISS session word here.
Mode E Injected ID
N/A
If Mode E is selected the user enters the
BISS injected ID here.
4.2.10.2 Configuring Per-Service Descrambling
This menu allows the user to select the services the MRD 6000 will descramble using
the BISS keys configured in Section 4.2.10.1. These options are applicable only if
Operation Mode in the BISS settings is set to Descramble Selected Services (Refer to
Section 4.2.10.1). The drag and drop method can be used to drag services from the right
column to the left column. The BISS key to descramble services can be selected using
the drop down menu next to each service. Services can be added manually by clicking
button. Clicking the button forces the MRD 6000 to rescan the
transport stream for changes.
BISS Service Descrambling Menu
Page 40

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 40 (97)
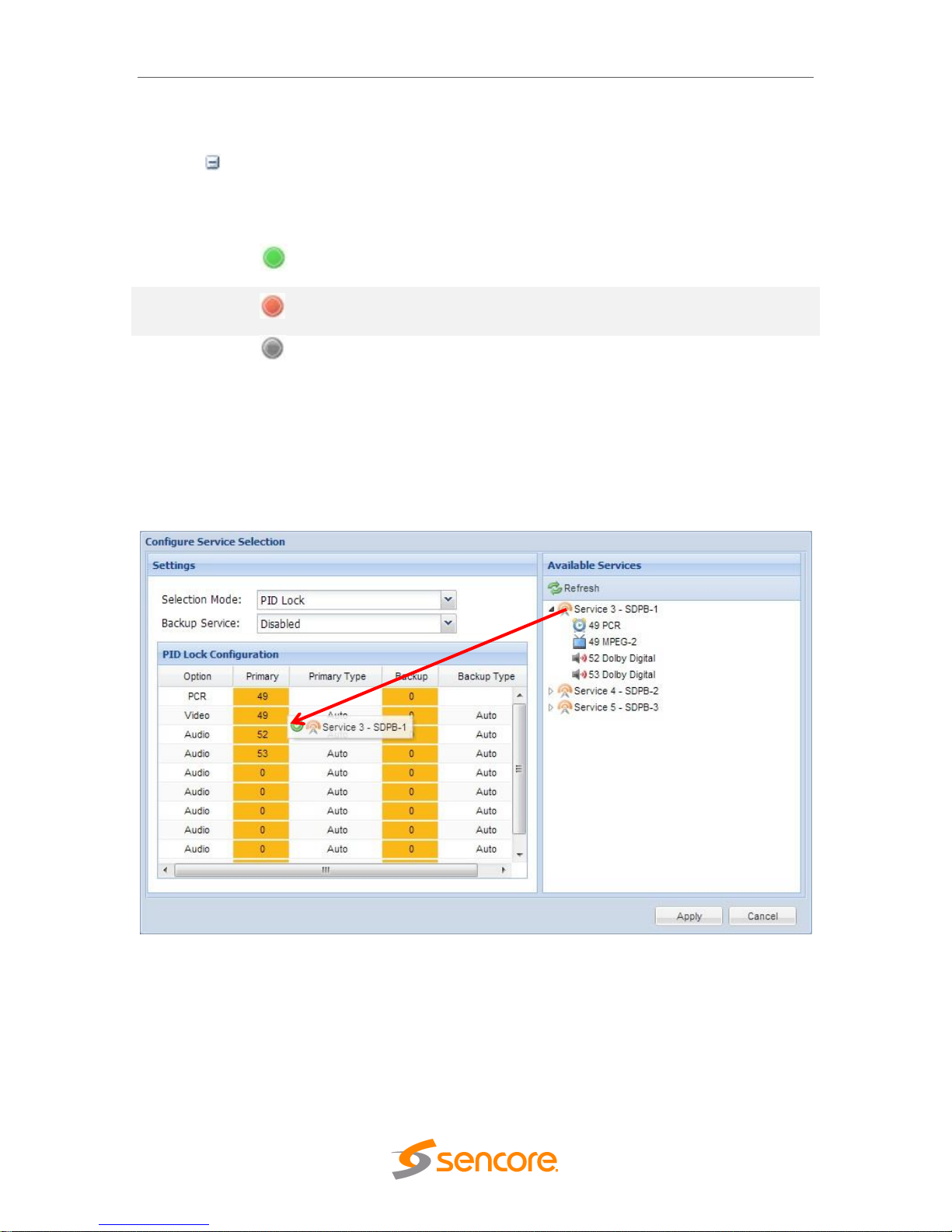
4.2.11 Configuring Service Selection
This menu allows the user to configure the PIDs or Service the MRD 6000 decodes.
Depending on the Selection Mode that is selected, the menu changes to reflect the
applicable settings.
Service Lock
In Service Lock mode the MRD is set to decode a specified service number or service
name. If the PIDs within the service change at any time, the MRD continues to decode
the service. The drag and drop method can be used to populate the Service Name or
Service Number dialog boxes.
Service Lock Selection Menu
Setting
Range
Description
Selection Mode
Service Lock
PID Lock
Auto Seek
Setting to Service Lock sets the unit to
decode any PIDs associated with a service
number or service name. Setting to PID Lock
sets the unit to decode only the PIDs
specified in the PID Lock Configuration
matrix. Auto Seek mode will tune the unit to
the first service listed in the PAT if a transport
stream is present.
On Backup
Use Primary Service
Use Backup Service
Sets the service the MRD 6000 will tune to in
case of an input failover. If Use Primary
Service is selected the MRD 6000 will tune to
the service name specified in the Primary
section. If Use Backup Service is selected
the service name specified in the Backup
section will be tuned. How the MRD 6000
Page 41

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 41 (97)
fails over inputs is configured in Section
4.2.1
Lock Mode
Service Name
Service Number
If set to Service Name the MRD will decode
only services matching the name specified
(SDT in DVB or TVCT in ATSC tables must
be present in this mode). If set to Service
Number the MRD will decode only services
matching the number specified.
Note: S302M Audio Type is auto detected by the MRD 6000
PID Lock Mode
In PID Lock mode the MRD decodes only the PIDs specified by the user in the PID Lock
Configuration matrix. The drag and drop method can be used to auto-populate the cells
in the matrix. Stream types can be manually defined under the Primary Type and
Backup Type columns. Individual cells under Primary and Backup columns can be
selected and PIDs can be typed in manually.
PID Lock Selection Menu
Setting
Range
Description
On Backup
Use Primary PIDs
Use Backup PIDs
Sets the PIDs the MRD 6000 will tune to in
case of an input failover. If Use Primary PIDs
is selected the MRD 6000 will tune to the
PIDs specified in the Primary PID column. If
Use Backup PIDs is selected the service
name specified in the Backup PID column
will be tuned. How the MRD 6000 fails over
inputs is configured in Section 4.2.1.
Page 42

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 42 (97)
Auto Seek Mode
In Auto Seek mode the MRD decodes the first service listed in the PAT. All PIDs in this
service are automatically selected for decoding. No other configurations are available in
this mode. This mode is recommended to verify the MRD is receiving a valid signal and
is able to decode. This mode is not recommended for a professional environment as
changes in the PAT’s listings and order of listings can unexpectedly cause changes the
service being decoded.
Auto Seek Menu
Page 43

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 43 (97)
4.2.12 Configuring Video Services
The menu allows the user to configure the SDI, Digital Video (HDMI), and Composite
output formats of the MRD 6000. Please note that the composite video output is only
active if the output video format is SD (720x480i, 720x576i). For all other selected
formats, there is no output from the composite video BNC jack. The video format
selected determines which of the SDI output jacks is actively outputting.
Setting
Range
Description
Format Mode
Auto
Manual
Setting to Auto the MRD 6000 will output
video to match the incoming native video
format. Setting to Manual the user can define
the video format the MRD 6000 will output.
Manual Format
Refer to Appendix C
for supported
formats.
This setting is the video format the MRD
6000 will output.
Page 44

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 44 (97)
4.2.13 Configuring Audio
This menu allows the user to configure the audio downmix settings of the decoder. Two
audio presets are available: Transmission and Monitor. These presets can be applied by
clicking the button. The menus for Audio 1 through Audio 4 all contain the same
settings. Note: The number of audio services decoded by the MRD 6000 and listed may
vary with licensing.
Setting
Range
Description
Operational Mode
Line Mode
RF Mode
Custom 1
Custom 0
Refer to Appendix E for explanation.
Processing Mode
Downmix
Discrete
Refer to Appendix E for explanation.
Refer to Appendix F for explanation
Dynamic Range
Enabled
Disabled
Refer to Appendix E for explanation.
Downmix
Lo/Ro (Stereo)
Lt/Rt (Dolby Surround)
Lt/Rt (Auto)
Dual Mono
Dual Left
Dual Right
When the audio is downmixed in the MRD
6000 two audio channels are created. The
channels can be configured using the
settings available in the drop down menu.
(Refer to Appendix E)
Format Mode
Consumer
Professional
This option selects the PCM or Dolby Digital
format mode. (Refer to Appendix E)
Page 45

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 45 (97)
4.2.14 Configuring SDI Ports - SD & HD Interface
The following menus allow the user to configure the SDI video output from ports 1A & 1B
when either an SD or HD, non UHD/4K format, is selected for output. See section 4.2.12
for information on output format selection. For SD-SDI or HD-SDI formats a single link
connection is used as per SMPTE 259 or SMPTE 292.
SD or HD
Setting
Range
Description
Video Loss Mode
Disable SDI
Display Raster
Setting to Disable SDI squelches the SDI
output of the MRD in case of an error state.
Setting to Display Raster the MRD will
display the raster color selected in Section
4.2.12. This Feature is not yet available.
When outputting common SD-SDI or HD-SDI formats port 1A provides the main output.
Port 1B provides a second simultaneous output identical to the Port 1A output.
Port 1A: Main Output for all SD and HD-SDI formats
Port 1B: Provides Secondary or Simultaneous Output mirroring port 1A’s output
Page 46

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 46 (97)
4.2.15 Configuring SDI Ports- UHD –4K Interface
The UHD selection tab provides a menu which provides configuration of the UHD/4K
outputs. The Video Loss Mode sets the output to either be disabled (no output) or to
output a black raster when an error condition exists which prevents a normal decoded
output. The Output Mapping selection configures the quad 3G SDI outputs to carry a 4K
format to a compatible quad SDI 3G input device/monitor.
UHD
Setting
Range
Description
Video Loss
Mode
Disable SDI
Display Raster
Setting to Disable SDI squelches the SDI output of
the MRD in case of an error state. Setting to Display
Raster the MRD will display the raster color selected
in Section 4.2.12. This Feature is not yet
available.
UHD/SDI
Output
Maping
Two Sample
Interleave
Square Division
Setting to Two Sample Interleve configures the SDI
output for quad 3G SDI format in which each of 4
stream outputs carries ¼ pixels and the picture
resolution. Setting to Square Division configures a
quad SG SDI output format in which each of 4
streams carries a quarter section of the picture in full
resolution. Quad 3G SDI Formats conform to
SMPTE 425-3 and SMPTE 425-5
Quad 3G- SDI requires 4 SDI output port/connections. Ports 1A, 2, 3, and 4 on the MRD
6000 provide the respectable outputs for the 4K formats when selected. See section
4.2.12 on configuring the SDI output format.
SDI Link connections 1A,2,3,4 from the MRD 6000 must appropriately match the quad
SDI inputs of the receive/monitor device so the 4K image can be properly
processed/rendered. The following section provides a brief explaination of the two
methods commonly used to interface a 4K SDI signal over four 3G-SDI link connections.
Page 47

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 47 (97)
Two Sample Interleave
SMPTE 425-3 and SMPTE 425 define new image mapping structures which provide a
means to interface 4K over an SDI interface. Interfacing 4K SDI up to 60 fps requires
using four 3G-SDI links. Two methods of carrying 4K via 4 link connections include
1.Two Sample Interleave
2. Four Quadrant Division (Square Division).
In each of these methods ¼ of the picture image is carried by each of the four link
connections. A brief explanation of each follows.
Two Sample Interleave breaks the image into interleaved samples of the entire picture.
A line interleaving system has one line with alternating pixels 1 and 2, whle the next line
has alternating pixels 3 and 4 as illustrated. 3G-SDI link 1 carries the #1 pixels, while link
2 carrires the #2 pixels, link 3 the #3 pixels and link 4 the #4 pixels. In this manner each
of the 3G-SDI links carries pixels in ½ the scan lines and ½ the pixels in each line of the
(1080p resolution) image or frame.
Square Division or Four Quadrants Division
The Square Division method, also referenced as Four Quadrant Division, divides the
picture equally in quarter sections as illustrated. Each section is ¼ of the 4k image or
1080p. SDI link 1 carries the upper left image pixels, link 2 carries the upper right pixels,
link 3 carries the lower left pixels, and link 4 carries the lower right pixels. The SDI
receive device assembles the pixels from the 4 links to recreate the image.
Simultaneous HD-SDI output in 4K Mode
The MRD 6000 provides a simultaneous HD-SDI output when you have selected and
are outputting a UHD/4K format using Two Sample Interleave. For any of the available
UHD/4K formats, SDI output ports labeled 1A, 2, 3, and 4 are used to provide the
Page 48

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 48 (97)
UHD/4K SDI output via four 3G-SDI link connections. When outputting the Two Sample
Interleave mode 4K SDI, port 1A contains ¼ of the image pixels. Port 1B is internally
configured by the MRD 6000 to always output a mirror image of the signal on port 1A.
Therefore, for all UHD/4K formatted signals with Two Sample Interleave, the Port 1B
output is an HD 1080 formatted signal at the 4K frame rate selected. For example, if the
MRD 6000 is decoding/outputting a 3180x2160p50 stream, SDI port 1B is outputting a
1080p50 HD-SDI signal.
4.2.16 Configuring SDI Audio Embedding
This menu allows the user to configure SDI embedded audio settings. The MRD 6000
comes standard with the ability to decode two audio services. With additional licensing
the MRD 6000 can handle up to four unique audio services. When licensed for four
audio services, the user will have four audio pairs available to embed audio in the SDI.
These two SDI groups provide inclusion of four audio pairs, with two pairs to each group.
All audio pairs share the same options.
SDI Embedded Audio Configuration Menu
Setting
Range
Description
Group 1-4
Pair 1-2
Off
Audio 1-4 PCM
Audio 1-4 Pass-through
Assigning a PCM audio to a Group Pair will embed
the decoded or downmixed two channel audio using
the settings defined in Section 4.2.13. Assigning
Pass-Through to a Group Pair will embed
unprocessed compressed audio in the SDI VANC.
Selecting Off disables the Group Pair completely.
Page 49

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 49 (97)
4.2.17 Configuring Analog Audio Output
This menu allows the user to configure the analog output outputs of the MRD 6000. Two
analog audio outputs are available. The dBu level of the outputs can be adjusted for
each of the four audio outputs. For the Analog Output connector pin out refer to
Appendix D.
4.2.18 Configuring Digital Audio Output
This menu allows the user to configure the digital audio outputs of the MRD 6000. The
number of outputs available directly correlates with the number of audio services the unit
is licensed to support. Up to four digital audio outputs are available .
Setting
Range
Description
Analog
Output 1-2
Off
Audio 1-2
Assign Audio 1-2 to an analog audio output for
output. Select Off to disable the analog output
completely.
Level
-10 to 4
Level of the analog audio output in dBu.
Page 50

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 50 (97)
Setting
Range
Description
Digital Output
1-8
Off
Audio 1-4 PCM
Audio 1-4 Pass-through
Assigning a PCM audio to a digital output will output
the decoded or downmixed two channel audio using
the settings defined in Section 0. Assigning Pass-
Through to a digital output will output unprocessed
compressed audio. Selecting Off disables the digital
output completely.
4.2.19 PID Filter
If the PID/Service Filter license is enabled, the following menus and options will be
available for configuration. PID filtering will allow the user to create a new output TS by
selecting and dragging one or more services/PIDs from the incoming transport stream
into the Selected Services/Pids box or use the currently decoded stream. The user can
also configure a TS bitrate for each PID filtered stream and select different table
inclusion options.
Page 51

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 51 (97)
Setting
Range
Description
Select PID Filter
PID filter 1-10
Select which PID filter to configure
TS Bitrate (Mbps)
.25 to 160
Configure the TS Bitrate for the PID filter stream
selected
Table Processing
Mode
PSI (MPEG)
Adjusted tables: PAT, PMT
Passed tables: CAT, NIT
Discarded tables: all remaining
Table Processing
Mode
SI (DVB)
Adjusted tables: PAT, PMT,SDT
Passed tables: CAT, NIT, EIT, RST, TDT, TOT
Discarded tables: TSDT, BAT
Selection Mode
Use Selected
Services/PIDs
Use Decoded Service
Use Selected Services/PIDs will allow the user to
select which services are in the new TS. Use
Decoded Service will only include the service that
is currently selected for decoding by the MRD 6000
4.2.20 Configuring ASI Output
This menu allows the user to configure the ASI output of the MRD 6000. When enabled
this output acts as an active loop output of the active input. For example, if the DVBS/S2 input card is the current active input the ASI output port will output a demodulated
signal of the satellite input.
Page 52

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 52 (97)
Setting
Range
Description
Port
Enabled
Disabled
Enable or disable the ASI output port.
Source
Unmodified Input
Descrambled
Descrambled and
Processed
Pid Filter 1-10
Unmodified Input will pass the incoming TS to the
output without applying any BISS or DVB-CI
decryption
Descrambled (or Descrambled and Processed) will
output the TS with any applied BISS or DVB-CI
decryption.
PID Filter will output the TS from the PID filter menu
option.
4.2.21 Configuring the MPEG/IP Outputs
This menu allows the user to configure the MPEG/IP outputs. Each MPEG/IP card has
two ports that can be set to receive and/or transmit. This menu is for setting up the
transmission of MPEG/IP unicast or multicast transport streams. The menu for Stream 1
and 2 have the same settings.The menu for Streams 3 through 10 will contain the same
options as Transmit 1 and Transmit 2 with one exception: Forward Error Correction is
only available (if licensed) on Transmit 1 and 2.
Page 53

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 53 (97)
Setting
Range
Description
Transmit
Enabled
Disabled
Enable or disable the MPEG/IP transmit group.
Source
Unmodified Input
Descrambled
Descrambled and
Processed
Pid Filter 1-10
Unmodified Input will pass the incoming TS to the
output without applying any BISS or DVB-CI
decryption.
Descrambled (or Descrambled and Processed) will
output the TS with any applied BISS or DVB-CI
decryption.
PID Filter will output the TS from the PID filter
menu option.
Physical
Connector
Port 1
Port 2
The physical connector on the MPEG/IP card that
will be used to transmit the output.
Destination IP
Multicast - 224.0.0.0 -
239.255.255.255
When sending to a unicast address the destination
IP address must match the receiving device’s IP
address. When sending a multicast the address
must be sent within the multicast IP range.
Destination Port
0 - 65535
When sending to a unicast address, the destination
port must match the receiving device’s port. When
sending a multicast, any port within the accepted
Page 54

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 54 (97)
range can be used, but it is good practice to always
choose a port >1030 and an even number
Source Port
0 - 65535
This is the port used by the MRD 6000 to transmit
the MPEG/IP stream.
TS Packets Per IP
Packet
1-7
The number of TS packets that are contained with
a single IP packet. Default is 7. Lowering this value
below default increases network overheard.
Differentiated
Services
Default
Assured Forwarding
1-1 to 4-3
Expedited
Forwarding
Define the quality of service (QoS) classification the
packets carry when transmitted.
Encapsulation
UDP
RTP
Sets the Encapsulation to UDP or RTP.
FEC
Off
Columns
Colums/Rows
Sets the FEC Type or disables FEC.
FEC Columns
1-20 (Columns)
4-20 (Columns/Rows)
Defines the number of Columns used to construct
the FEC Matrix. (Columns * Rows must be ≤ 100.)
FEC Rows
4-20
Defines the number of Rows used to construct the
FEC Matrix. (Columns * Rows must be ≤ 100.)
4.2.22 Configuring the MPEG/IP MPE Outputs
This menu allows the user to configure the MPEG/IP Multi-Protocol Encapsulation
(MPE) outputs. Each MPE Output allows the user to select an MPE data PID from the
transport stream to be output.
Page 55

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 55 (97)
Setting
Range
Description
Transmit
Enabled
Disabled
Enable or disable transmission of de-encapsulated
MPE data.
Physical
Connector
Port 1
Port 2
The physical connector on the MPEG/IP card that
will be used to transmit the MPE data.
PID Selected MPE PID from the transport stream to use
for MPE output
MAC Filter State
Enabled
Disabled
Enable or Disable the filtering of output data based
on a MAC address in the selected MPE PID
MAC Address
00:00:00:00:00:00
FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF
Filtered MAC address that will be transmitted in the
MPE output. All data with other MAC addresses in
the selected MPE PID will be discarded
Page 56

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 56 (97)
4.2.23 Viewing PSIP Information
To view the PSIP information for the applied TS, select the View PSI Tables button
located on the right hand side of the Inputs section. This will open a new window that
displays all of the PSIP information for the applied TS. The tables displayed will include
PAT, PMT and CAT and tables associated with the stream type (DVB,ATSC). SDT
tables will be displayed for DVB streams and MGT,TVCT,EIT, ETT, STT tables will be
displayed for ATSC streams.
Clicking the Refresh button in the upper left corner will update the tables displayed.
Page 57

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 57 (97)
4.3 Admin Panel
To access the Admin Control Panel, click on the tab. This menu allows the
user to control many aspects of the MRD 6000.
Page 58

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 58 (97)
4.3.1 Changing Unit Password
The MRD 6000 can be assigned an access password and the current access password
can be changed. In order to make changes to passwords, click the
button. A window will appear to enter the current password and new password.
4.3.2 Profiles
The MRD 6000 has the ability to save all configured settings to multiple profiles. Profiles
can be saved locally, renamed and saved to external storage to be used on other MRD
6000s. Profiles can be used to quickly and easily change the configuration of an MRD
6000 to suit different inputs and decoding requirements.
Action
Button
Description
Add New Profile
Adds a new profile from current settings. User must
name profile before creation is complete.
Upload Profile
Allows the user to browse to external storage or
workstation to upload profile to MRD 6000.
Apply Profile
Select a profile from the drop down menu and click
this button. The MRD 6000 will apply all settings
contained in the profile selected.
Page 59

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 59 (97)
Rename Profile
Select a profile from the drop down menu and click
this button. The user will be prompted for a new
name for the profile.
Delete Profile
Select a profile from the drop down menu and click
this button. The user will be prompted to confirm
deletion of the profile.
Download Profile
Select a profile from the drop down menu and click
this button. The user will be prompted to select a
directory to download the profile.
4.3.3 General Settings
The MRD 6000 can be assigned an alias which is displayed in the upper right hand
corner of the web interface. The alias can help define which MRD 6000 the operator is
currently logged into. The BISS-E Injected ID for BISS Mode E can also be protected
from being accidently changed. Setting the Protect BISS-E Injected ID to Yes will force
the user to unlock the dialog box in the BISS Descrambling configuration menu before
allowing any changes to be made. The edit the Unit Alias or protect the BISS-E Injected I
D click on the button. The PID Display mode changes how PID
values are displayed in the web interface. The values can either be displayed in decimal
or HEX values. The ASI Out/Video Sync Function is for special applications purposes.
This should remain set to ASI Out.
4.3.4 Unit Network Configuration
The management port of the MRD 6000 can be configured from the web interface. To
make changes to the management port click, the button under the Unit Network
Configuration section. Domain name servers can be configured on the MRD clicking the
Page 60

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 60 (97)
button. IP address and web address entries are accepted as
Nameserver addresses.
If the MRD 6000 contains a 58127 option card the unit can be configured to have an
optional 2nd control port.
NOTE: Exercise extreme caution when performing changes to this menu as
network communication can be lost with the MRD 6000.
Setting
Range
Description
Mode
DHCP
Static
Setting to DHCP will allow the network assign an IP
address automatically to the MRD 6000 (if
supported). Setting to Static allows the user to
manually define all TCP/IP settings for the
management port.
Hostname
Valid characters:
A through Z
0 through 9
- (hyphen)
This setting allows the user to define an optional
unit Hostname.
IP
Four decimal octets:
XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX
This option is only available if Static Mode is set.
This is the IP address assigned to the management
port.
Page 61

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 61 (97)
Subnet Mask
255.0.0.0 –
255.255.255.254
This option is only available if Static Mode is set.
This is the Subnet Mask assigned to the
management port.
Gateway
Four decimal octets:
XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX
This option is only available if Static Mode is set.
This is the Gateway address assigned to the
management port.
The 2nd management port of the MRD 6000 can be configured from the web interface.
To make changes to which port is the 2nd management port click, the configure control
ports button under the Unit Network Configuration section.
4.3.5 MPEG/IP Network Configuration
The MPEG/IP card is used to receive MPEG over IP transport streams. The MPEG/IP
card supported unicast, multicast, UDP and RTP. The ports of the MPEG/IP card on the
MRD 6000 can be configured from the web interface. To configure the Default Gateway
and ICMP Response settings click the button.
Setting
Range
Description
Default Gateway
Port 1
Port 2
Setting to Port 1 uses the gateway address of port
1 as the default gateway. Setting to Port 2 uses the
gateway address of port 2 as the default gateway.
ICMP Response
Enabled
Disabled
Setting to enabled allows the MRD 6000 to respond
to ICMP requests (ping). If disabled the MRD 6000
will not respond to these requests.
To configure the TCP/IP settings of the MPEG/IP ports click the button under the
MPEG/IP Network Configuration section next to the corresponding port. The settings for
both ports are the same.
Page 62

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 62 (97)
Setting
Range
Description
IP Address
1.0.0.0 - 126.0.0.0
128.0.0.0 -
191.255.0.0
192.0.1.0 -
223.255.255.0
This setting is the TCP/IP address assigned to the
port.
Subnet Mask
255.0.0.0 –
255.255.255.254
This setting is the subnet mask assigned to the
port.
Gateway
1.0.0.0 - 126.0.0.0
128.0.0.0 -
191.255.0.0
192.0.1.0 -
223.255.255.0
This setting is the gateway address assigned to the
port.
Link Speed
Auto
1000Mbps/Full
1000Mbps/Half
100Mbps/Full
100Mbps/Half
10Mbps/Full
10Mbps/Half
Setting Link Speed to Auto allows the MRD 6000 to
determine the link speed of the network. If this is
not possible or the user wants to define a link
speed select one of the other values available.
4.3.6 Licensing
Certain features of the MRD 6000 require licenses in order to be functional. The
interface displays all licenses available as well as the following status:
• License Locked or Unlocked
• License is Supported or Unsupported by the installed hardware
If licenses need to be applied to the MRD 6000 click button. The menu
below will appear where the user can copy and paste the provided license key from
Page 63

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 63 (97)
Sencore. The currently applied license key can be viewed by clicking the
button.
4.3.7 Date/Time
The MRD 6000 can be set to synchronize with an NTP server or a manual data and time
can be defined by the user. Click the button to configure the date
and time. These values are used to timestamp entries in the Alarm and Event logs under
the Reporting tab.
Setting
Range
Description
Update Mode
NTP
Manual
Setting to NTP uses the local network’s NTP server
to synchronize date and time. Manual allows the
user to define a date and time.
NTP Server
Four decimal octets:
XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX
Domain Name
This is the IP Address or Domain Name of the local
NTP Server on the network. This setting is only
available if Update Mode is set to NTP.
Date
MM/DD/YYYY
This setting is the user defined date. A calendar
widget can be used to select the data by clicking
the button. This setting is only available if
Update Mode is set to Manual.
Time
00:00:00 – 24:00:00
This setting is the user defined time. The time is
based on a 24 hour clock. This setting is only
Page 64

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 64 (97)
available if the Update Mode is set to Manual.
4.3.8 Configuring SNMP
4.3.8.1 SNMP Communities
SNMP Communities define whether users have read-only or read-write SNMP rights.
These two communities are given unique names. The default names for these
communities are:
• Read –Only Community: public
• Read- Write Community: private
To modify the names of these communities click on the button.
4.3.8.2 SNMP Trap Managers
The SNMP trap managers are recipients of SNMP traps sent from the MRD 6000. The
following menu allows the user to configure the recipient’s IP addresses. To add and
remove recipients of the SNMP traps click the button.
Action
Button
Description
Page 65

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 65 (97)
Add Manager
Clicking this button prompts the user for the IP
address of the SNMP trap manager.
Delete All
Clicking this button prompts the user to confirm the
deletion of all SNMP trap manager IP addresses. If
the user confirms deletion all SNMP trap manager
IP addresses will be removed.
Delete Single Entry
Highlight a single SNMP trap manager IP address
and click this button to delete the entry. A prompt
will appear confirming the deletion of IP address.
4.3.8.3 Download SNMP MIB Files
The MRD 6000 stores the SNMP MIB files for the currently installed version of software
on the unit. These files can be downloaded directly from the MRD 6000 by clicking on
the button. The screen below will appear where the files can be downloaded
and saved off of the unit.
4.3.9 Syslog
The MRD 6000 can be configured to send error and event logs formatted in the syslog
protocol to a remote user specified Syslog server.
Page 66

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 66 (97)
Action
Range
Description
State
Enabled
Disabled
Enable or Disable sending messages to Syslog
server.
Network Protocol
UDP
TCP
Select which network protocol used to transmit to
the Syslog server
IP Address
Four decimal octets:
XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX
IP of the Syslog server. 0.0.0.0 and
255.255.255.255 are not permitted
Port
0 - 65535
Destination port of the Syslog server
4.3.10 In-Band Control
The In-Band Control is used to change settings and receive updates from data within a
PID in the incoming TS, as injected by the Sencore CMD 4000 In-band Control Server.
The following menu allows the user to configure the In-Band Control settings. To
configure the In-Band Control settings click the button.
Action
Range
Description
State
Enabled
Disabled
Enable or Disable the In-Band Control.
PID
1-8190
Sets the unit to look for commands on the PID that
is set.
Group
None
1-128
This setting assigns the unit to a corresponding
Group or No Group.
Page 67

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 67 (97)
4.3.11 Updating the MRD 6000
4.3.11.1 Applying Software Updates
Updates to the MRD 6000 are performed through the web interface. A software update
file is provided by Sencore and then uploaded to the unit. Once uploaded, the software
update is applied to the unit. To upload software updates to the unit click on the
button. The current version and uploaded version is displayed in the
Software Versions section. The MRD 6000 will reboot after a software update is
complete.
Action
Button
Description
Upload Software
Update
To upload software updates to the MRD 6000 click
this button. The user will be prompted to navigate
to an update file. The file will then upload to the
MRD 6000. When complete the MRD 6000 with
prompt the user to either apply the update or
cancel
Delete the
Uploaded Software
Clicking this button prompts the user to confirm the
deletion of the software update from the MRD
6000. This will also clear the Uploaded Version
status of the Software Versions section.
Update Software to
Uploaded Version
Clicking the button starts the software update
process. The MRD 6000 will prompt the user to
confirm the update. Click Yes to continue or No to
cancel.
4.3.11.2 Rollback Software Updates
The MRD 6000 is capable of reverting back to a previous version of software using the
Rollback feature. The MRD 6000 maintains two separate software images; one is the
most current version of software with all current settings and the other is the previous
Page 68

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 68 (97)
version of software with all settings. To perform a rollback, click the button
and then click the tab. The MRD 6000 will reboot after the rollback process is
complete.
Action
Button
Description
Rollback Software
Clicking this button starts the Rollback process.
The MRD 6000 will prompt the user to confirm the
rollback or click cancel to stop the process.
4.3.12 Reboot Unit
The MRD 6000 can be rebooted from the web interface. In order to perform a reboot
click the button. The MRD 6000 will prompt the user to confirm the reboot.
Once the reboot is complete the login screen will appear allowing the web interface to be
logged into.
4.3.13 Reset Defaults
The MRD 6000 settings can be reset to factory defaults. All settings will be returned to
the factory defaults except the network management ports TCP/IP settings. All event
logs will be cleared. To reset all settings to default click the button. The
MRD 6000 will prompt the user to confirm the reset.
Page 69

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 69 (97)
4.4 Reporting Panel
The tab in the MRD 6000 contains logs for active alarms currently affecting
the unit and an event log. The active alarms are updated periodically in order to reflect
the real-time state of the unit. Once an error is cleared it will be cleared from the active
alarms window. The event log can be used to view alarm and event history. Both the
active alarm and event logs can be configured to hide or change the behavior of alarms
and events.
4.4.1 Active Alarms
Clicking on the button displays the Active Alarms menu. This list displays all
of the active alarms currently affecting the unit. There are four columns in the log that
display different types of information.
Title
Description
Page 70

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 70 (97)
State
This column displays the nature of the alarm. The icon means the log
entry is informational and is not an error. The icon means the log
entry is an active alarm.
Name
This column displays the description of the error. The function that is
experiencing an error condition is described here.
Location
This column displays the hardware or function that is experiencing the
active error.
Last Changed
This column displays the data and time the error was raised. This data
and time correlates with the Date and Time settings configured in
Section 4.3.7.
4.4.2 Event Logs
Clicking on the button displays the Event Log menu. This list displays all of
the events and alarms that have affected the unit. The MRD 6000 stores up to four days’
worth of logs. If the unit is rebooted or powered off and on the event logs are cleared.
The logs can be cleared manually by clicking the button. The logs can be
downloaded as a .tsv file and saved to an external location by clicking the
button. There are five columns in the log that display different types of information.
Page 71

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 71 (97)
Title
Description
Severity
This column displays the nature of the alarm. The icon means the log
entry is informational and is not an error. The icon means the log
entry is an active alarm.
Timestamp
This column displays the data and time the error was raised or cleared.
This data and time correlates with the Date and Time settings configured
in Section 4.3.7.
Transition
This column displays when an alarm transition from a bad to good state.
When an error is raised the icon is displayed. When an error is
cleared the icon is displayed. When an event takes place the icon
is displayed.
Message
This column displays the description of the error or event. The function
or hardware that experienced the event or error is described here.
Location
This column displays the hardware or function that experienced the
alarm or event.
4.4.3 Configuring the Logs
The MRD 6000 allows the user to configure alarms and events. Events and alarms can
be hidden, set to send SNMP traps or close a relay when active. In order to configure
these options click the button while in the section of the
tab. The tab allows the user to configure the alarms reported by
the MRD 6000. The tab allows the user to configure the events reported by the
MRD 6000. Each column and its function are described below. A user configured time
offset can also be applied to allow viewing the logs in a local time zone.
Page 72

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 72 (97)
`Title
Description
Name
This column displays the name of the error or condition. This is
informational data: no options can be set here.
Location
This column displays the hardware or function that the alarm or event
applies to. This is informational data; no options can be set here.
Log
Checking the box in this column creates an entry in the event log in the
case this error or event is raised. If this box is unchecked this error or
event will be hidden and not logged if raised.
Log Severity
This column is only available in the tab This option allows the
user to set the severity of the error to Info or Error. If Info is selected in
the drop down box the icon will displayed in the event log. If Error is
selected the icon will be displayed in the event log.
Alarm
This column is only available in the tab This option allows the
user to enable or disable this alarm in the Active Alarms log. If checked
the alarm will be displayed in the Active Alarms log if raised. If this box is
unchecked this error will be hidden.
SNMP Trap
This column allows the user to send an SNMP Trap if this alarm is
raised. If this box is checked an SNMP Trap is sent when this alarm is
raised. If this box is unchecked an SNMP is not sent.
Relay
This column allows the user to set a Relay closure if this alarm is raised.
If this box is checked a Relay will be closed. If this box is unchecked a
Relay will not be closed. See D for pinout
.
Relay #
This column allows the user to select which of the three relays available
on the MRD 6000 will be closed when the alarm is raised.
Relay Duration
This column is only available in the tab. This option allows the
user to define the length of time in milliseconds the relay will be closed
after the event is logged. This setting can be configured from 100-1000
milliseconds.
Page 73

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 73 (97)
4.5 About Panel
Under the tab, is useful information about the unit software, serial number and
licensing. There are no user definable parameters in the About panel. The Panel
includes information about the unit software version currently installed, the unit serial
and/or ID number, which licenses are installed, and how to contact Sencore. Information
regarding third party software is available by clicking on the dropdown menu box.
4.6 System Recovery
The MRD 6000 has the ability to recover from a complete system software corruption.
The system recovery allows a user to start the platform into a prompt where a software
update will allow the system to be installed in the event all other images will not work.
To use the system recovery, push and hold two front panel pushbuttons (any 2 buttons)
when power is applied to the unit. Hold the buttons for at least 20 seconds and then
release.
The unit will boot into a recovery mode indicated by the front panel display and indicate
a unit management IP address. The user can press the “Enter” button on the front panel
to configure the IP address if necessary. A web browser can then be used to connect to
the system and apply an update to the unit.
Page 74

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 74 (97)
Section 5 Appendices
Introduction
This section includes the following appendices:
Appendix A – Acronyms and Glossary .................................................... 75
Appendix B – Error and Event List ........................................................... 78
Appendix C – Specifications ..................................................................... 80
Appendix D – Pinouts for Analog Audio and Relay Connectors ........... 89
Appendix E – MRD 6000 Audio Explanation ........................................... 91
Appendix F – MRD 6000 Discrete Audio Configuration ......................... 94
Appendix G – Open Source Software ....................................................... 94
Appendix H – Warranty ............................................................................. 96
Appendix I – Support and Contact Information ..................................... 96
Page 75

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 75 (97)
Appendix A – Acronyms and Glossary
8VSB: Vestigial sideband modulation with 8 discrete amplitude levels.
16VSB: Vestigial sideband modulation with 16 discrete amplitude levels.
AAC: Advanced Audio Coding
AC-3: Also known as Dolby Digital
AES: Audio Engineering Society
AFD: Auto Format Descriptor
ASI: Asynchronous Serial Interface
ATSC: Advanced Television Systems Committee
AV: Audio Video
Bit Rate: The rate at which the compressed bit stream is delivered from the channel to
the input of a decoder.
BNC: British Naval Connector
BPS: Bits per second.
CAM: Conditional Access Module
CAT: Conditional Access Table
CAT6: Category 6 – Cable standard for gigabit Ethernet
CC: Closed Caption
CI: Common Interface
CoP: Code of Practice
CRC: Cyclic Redundancy Check
CVCT: Cable Virtual Channel Table
dB: Decibel
DDPlus: Dolby Digital Plus
DHCP: Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
DPI: Digital Program Insertion
DTVCC: Digital Television Closed Captioning
DVB: Digital Video Broadcasting
EBU: European Broadcasting Union
EIA: Electronic Industries Alliance
EIT: Event Information Table
EPG: Electronic Program Guide
ETM: Extended Text Message
ETT: Extended Text Table
Event: An event is defined as a collection of elementary streams with a common time
base, an associated start time, and an associated end time.
FCC: Federal Communications Commission
FEC: Forward Error Correction
Field: For an interlaced video signal, a “field” is the assembly of alternate lines of a
frame. Therefore, an interlaced frame is composed of two fields, a top field and a
bottom field.
Frame: A frame contains lines of spatial information of a video signal. For progressive
video, these lines contain samples starting from one time instant and continuing
through successive lines to the bottom of the frame. For interlaced video a frame
consists of two fields, a top field and a bottom field. One of these fields will
commence one field later than the other.
HANC: Horizontal Ancillary
HD: High Definition
High level: A range of allowed picture parameters defined by the MPEG-2 video coding
specification which corresponds to high definition television.
Page 76

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 76 (97)
I/O: Input/Output
IP: Internet Protocol
Kbps: 1000 bit per second
LED: Light Emitting Diode
LNB: Low-Noise Block
MAC: Medium Access Control
Main level: A range of allowed picture parameters defined by the MPEG-2 video coding
specification with maximum resolution equivalent to ITU-R Recommendation 601.
Main profile: A subset of the syntax of the MPEG-2 video coding specification that is
expected to be supported over a large range of applications.
Mbps: 1,000,000 bits per second.
MER: Modulation Error Ratio
MGT: Master Guide Table
MIB: Management Information Base
MP@HL: Main profile at high level.
MP@ML: Main profile at main level.
MPEG: Refers to standards developed by the ISO/IEC JTC1/SC29 WG11, Moving
Picture Experts Group. MPEG may also refer to the Group.
MPEG-2: Refers to ISO/IEC standards 13818-1 (Systems), 13818-2 (Video), 13818-3
(Audio), 13818-4
MPTS: Multiprogram Transport Stream
MRD: Modular Receiver Decoder
NTP: Networking Time Protocol
NTSC: National Television System Committee
OSD: On Screen Display
PAL: Phase-Alternating Line
PAT: Program Association Table
PCM: Pulse-Code Modulation
PCR: Program Clock Reference
PCM: Pulse-code Modulation
PID: Packet Identifier. A unique integer value used to associate elementary streams of a
program in a single or multi-program transport stream.
PMT: Program Map Table
Profile: A defined subset of the syntax specified in the MPEG-2 video coding
specification
Program specific information (PSI): PSI consists of normative data which is
necessary for the demultiplexing of transport streams and the successful
regeneration of programs.
Program: A program is a collection of program elements. Program elements may be
elementary streams. Program elements need not have any defined time base; those
that do have a common time base and are intended for synchronized presentation.
PTS: Presentation Time Stamp
QAM: Quadrature Amplitude Modulation
QPSK: Quadrature Phase-Shift Keying
RDS: Receiver Decoder System
RF: Radio Frequency
RGBHV: Red, Green, Blue, Horizontal, Vertical
RO: Read Only
RPM: Revolutions Per Minute
RRT: Rating Region Table
RS-232: Recommended Standard. A standard for serial binary data interconnection.
Page 77

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 77 (97)
RU: Rack Unit
RW: Read/Write
SD: Standard Definition
SDI: Serial Digital Interface
SFP: Small Form-Factor Pluggable
SI: System Information
SMPTE: Society of Motion Pictures and Television Engineers
SNMP: Simple Network Management Protocol
SPTS: Single Program Transport Stream
SSRC: Synchronization Source
STD input buffer: A first-in, first-out buffer at the input of a system target decoder for
storage of compressed data from elementary streams before decoding.
STD: System Target Decoder. A hypothetical reference model of a decoding process
used to describe the semantics of the Digital Television Standard multiplexed bit
stream.
STT: System Time Table
TS: Transport Stream
TVCT: Terrestrial Virtual Channel Table
UTC: Coordinated Universal Time
VANC: Vertical Ancillary
VBI: Video Blanking Interval
VCT: Virtual Channel Table. Used in reference to either TVCT or CVCT.
XLR: Cannon “X” series connector, with a Latch, and Rubber around the contacts.
YPbPr: Component Red, Green, Blue
Page 78

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 78 (97)
Appendix B – Error and Event List
Error
Description
12V Supply Error
Voltage on 12V rail has exceeded safe operational range.
3.3V Supply Error
Voltage on 3.3V rail has exceeded safe operational range.
5V Supply Error
Voltage on 5V rail has exceeded safe operational range.
Audio Not Decoding
Audio is corrupted in incoming stream or format is not supported.
Auto Video Format Error
MRD 6000 is unable to determine the native incoming video in
order to format output.
BISS Conflicting PIDs
PIDs selected to be descrambled by one BISS key are already
assigned to be descrambled by another BISS key.
BISS Service Not Found
Service that BISS key is assigned to descramble is not present in
the incoming stream.
Backup Input Active
Condition
Primary input is currently in a failed condition and the MRD 6000
has failed over to the Backup input.
Bitrate Exceeded Error
Total incoming transport stream bitrate has exceeded 213 Mbps.
CAM Descramble Fail
CAM Module is not descrambling selected pids or services
CAM Not Present
DVB-CI Descrambling is enabled but CAM Module is not
installed.
CAM PID Not Found
PID selected to be descrambled by the CAM is not present in the
incoming stream.
ES Type Mismatch
Elementary stream type does not match the stream type defined
by the user.
FEC Reception Error
Packets in incoming IP stream cannot be repaired with forward
error correction.
Fan Speed Below Lower
Limit
Cooling fan in the MRD 6000 has failed.
IP Loss Error
No IP packets have been received by the MPEG/IP card for two
seconds.
ISI Not Found
ISI value defined by the user is not found in the incoming
multistream signal.
Input Video Unsupported
Native format of incoming video is not a supported video format.
LNB Power Error
LNB Power is enabled but the MRD 6000 is detecting power is
being provided by another source, there is excessive current
drain or an overvoltage has occurred.
Link Loss Error
Physical IP link is not present on the MPEG/IP card.
Loss of Carrier Lock
Receiver carrier lock source is lost.
Low Level
8VSB/QAM RF Level is below the user settable threshold
Low Mer
8VSB/QAM MER is below the user settable threshold
Multistream Mode Input
Mismatch
Multistream Mode is enabled and input signal is not multistream
capable or Multistream Mode is disabled and input signal is
multistream capable.
Page 79

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 79 (97)
No Services Detected
Service Lock service selection mode is enabled but no services
are present in the active input transport stream.
Pid Filter Overflow Error
Configured PID Filter TS rate is too low.
Pid Filter Selection Not
Present
Selected Service or PID is not present for inclusion in the output
PID filter TS.
RTP Reception Error
Uncorrectable out of order or duplicate packets are present in
incoming IP stream.
ES Sync Error Condition
One of the in-use elementary streams is not synchronized to the
PCR
Selected Audio PID Not
Present
PID Locked mode is set as service selection mode and audio PID
defined by user is not present in the incoming stream.
Selected PCR PID Not
Present
PID Locked mode is set as service selection mode and PCR PID
defined by user is not present in the incoming stream.
Selected Video PID Not
Present
PID Locked mode is set as service selection mode and video PID
defined by user is not present in the incoming stream.
Service Not Found
Service Lock service selection mode is enabled but service
defined by user is not present in the incoming stream.
Temperature Error
The MRD 6000 has detected the internal temperature is 60
degrees Celsius or above.
Transport Error Indicator
The MRD 6000 has detected that the transport stream error
indicator is present on the active input.
Transport Stream Not
Present
The MRD 6000 has detected that the transport stream from the
active input is no longer present.
TS Sync Loss
Transport stream sync for IP stream is not detected.
Unicast Receiver Not
Found Error
The MRD 6000 cannot discover the destination for the unicast IP
stream within 10 seconds after the initial ARP is sent.
Unlicensed Modulation
Input stream on active input is either 16APSK or 32APSK and the
modulations are no licensed on the MRD 6000.
Unlicensed
VCM/Multistream
Input stream on the active input contains a multistream signal
and the MRD 6000 is not licensed for multistream.
Video Not Decoding
The configured service or video PID to be decoded is not being
successfully decoded by the MRD 6000.
Page 80

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 80 (97)
Appendix C - Specifications
MRD 6000 – Base Unit
Includes –
Display, keypad, embedded controller, chassis/case,
power supply/line cord
System –
Display Type:
LCD
Display Configuration:
240 pixels by 64 pixels
Keypad:
Snap-dome Membrane
Front Panel Lockout:
Password control, up to 8 alpha-numeric characters (no
punctuations or spaces allows)
Configurations Allows:
Single video decoder with up to two option cards
Rear Panel:
Fixed inputs and outputs with two option card slots.
Option cards not field upgradeable.
Remote Operation/Update Interface –
Type:
Ethernet, 10/100
Rear Panels indicators:
Link (Green LED), Activity (Amber LED)
Connector:
RJ45
Front Panel Indicators –
Error LED:
Red indicates error is occurring
Off indicates no errors detected
INPUT LED:
Green indicates valid input is present
Off indicates no valid input
Monitor and Control Interfaces –
Web server GUI:
HTTP via web browsing for control & monitoring
Front Panel:
Control & monitoring
SNMP:
Control & monitoring
Operating Altitudes
0 to 10000 feet
AC Power –
Operating Voltage:
100-240VAC
PSU Max Power:
150W
Current Draw:
Base Unit with no option cards –
38-40W
MPEG/IP option card with active input –
2-3W (additional)
DVB-S/S2 option card with active input and LNB load of
19V @ 500mA –
8-9W (additional)
DVB-CI Module option with 2 CAM Modules installed –
2-3W (additional)
8VSB/QAM option card with active input –
2-3W (additional)
Max Power Draw:
70-72W
Frequency:
48-63Hz
Connector:
IEC C14
Line Cord:
Detachable, 3-prong
Base Unit with active ASI input –
54-55W
Page 81

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 81 (97)
Video Decoding Features
General –
TS Data Rate:
.25-200 Mb/s
Video Decoder –
Video Profiles and Levels:
Base Unit –
MPEG-2: to MP@HL,
H.264: to HP@L4.2
HEVC : to MP@HT up to L4.1, M10P@HT up to L4.1
Video Bit Rate:
MPEG-2 1-100Mb/s (dependent on profile)
H.264 CABAC Entropy coded 1 - 80Mb/s
CAVLC Entropy coded 1 - 100Mb/s
HEVC .25 – 40 Mbps
Video Formats:
Base Unit –
1080i x 1920 (16x9) @ 25, 29.97 and 30Hz
1080p x 1920 (16x9) @ 23.97, 24, 25, 29.97 and 30Hz
1080p x 1920 (16x9) @ 50, 59.94 and 60Hz
720p x 1280 (16x9) @ 50, 59.94, and 60Hz
576i x 720 (4x3 or 16x9) @ 25Hz
576i x 704 (4x3 or 16x9) @ 25hz
576i x 544 (4x3 or 16x9) @ 25hz
480i x 720 (4x3 or 16x9) @ 29.97Hz
4K/UHD Video Formats
Licensed formats (MRD 60730)
4096p x 2160 (16x9) 50, 59.94, and 60 Hz
4096p x 2160 (16x9) 23.98, 24, 25, 29.97, and 30 Hz
3840p x 2160 (16x9) 50, 59.94, and 60 Hz
3840p x 2160 (16x9) 23.98, 24, 25, 29.97, and 30 Hz
SDI (Serial Digital Interface) Video
Out –
SDI Standards:
Base Unit –
SD-SDI ANSI/SMPTE 259M
HD-SDI ANSI/SMPTE 292M
3G-SDI Level A ANSI/SMPTE 424M
Quad 3G-SDI SMPTE 425-3, SMPTE 425-5
Modes: Two Sample Interleave, Square Division
Connector:
75Ω Female BNC (4x) (Ports: 1A, 2, 3, 4)
Return Loss:
≥15 dB, 5Mhz to 1.5GHz
≥10 dB, 1.5 GHz to 3.0GHz
Drive Level:
800 mVpp ±10%
Data Bit Rate:
3G-SDI – 3.0 Gb/s
HD-SDI – 1.5 Gb/s
SD-SDI – 270Mb/s
Display Modes:
HD – Pillarbars, Cropped, Anamorphic
SD – Letterbox, Cropped, Anamorphic
Simultaneous SDI (Serial Digital
Interface) Video Out –
SDI Standards:
Mirrored 1x simultaneous output (Port 1 = Port 1B), Note:
When outputting 4K format (Two Sample Interleave) the
Simultaneous Output is a 1080p format of the 4K mode
Connector:
75Ω Female BNC
Page 82

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 82 (97)
Return Loss:
≥15 dB, 5Mhz to 1.5GHz
Drive Level:
800 mVpp ±10%
Data Bit Rate:
SD-SDI – 270Mb/s
Display Modes:
16x9 – Pillarbox, Center-Cut, Anamorphic
4x3 – Letterbox, Center-Cut, Anamorphic
Composite Video Out –
Video Format Standards:
SMPTE 170M-2004, NTSC, PAL-B/G/I/D/M/N
Connector:
Return Loss:
One 75 Ω ±10% Female BNC (CVBS)
>25dB, 0 to 6.00 MHz
Frequency Response:
Drive Level:
Chroma/Luma Delay:
Field Time Distortion:
Line Time Distortion:
Short Time Distortion:
Differential Gain:
Differential Phase:
Signal to Noise Ratio:
K factor
± 0.7dB From 0 to 4.00MHz
140 IRE (1.0Vpp), ±2 IRE
±26 ns Max
< 2% (± 3 IRE)
< 1% (± 1 IRE)
< 2% (± 3 IRE)
< 4%
< 1.5° degrees
≥55dB luminance weighted
< 2.5%
Digital Video Out –
Digital Video Standard:
SDA-HDMI-OM-E Rev A
Connector:
HDMI-type Female Type-A
Audio Decoding Features
Number of Audio Services:
Base Unit –
2 Audio Services
4 Audio Service Decode License (MRD 66840) Adds –
2 Audio Services (4 total)
Audio Codecs Supported:
Dolby Digital (AC-3) & Plus (EAC-3) AAC-LC, HE-AAC,
& HE-AACv2
MPEG1L2 & MPEG2L2
Linear PCM & Dolby E (Pass-through)
Output Formats:
Digital Pass-through
PCM (Decoded Discrete channels for 5.1 sources or
Downmixed for 5.1 Sources)
Analog (Decoded Discrete channels for 5.1 sources or
Downmixed for 5.1 Sources)
Audio Output Features
AES Outputs –
4x 75Ω BNC AES3/EBU Unbalanced
Analog Outputs –
Output Type:
Balanced, 1 channel pairs (+/-, L/R)
Connector:
1x High density 15-pin D-sub, male
Impedence:
<100Ω Nominal Output Impedance
Max Output Level:
+24dBu @ 0dBFs
Adjustable down to +10dBu by 0.5dB steps.
Conditions For Measurements
≥600Ω Load Impedance
Page 83

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 83 (97)
–20dBFS encoded TS source
Output level is adjusted to +4 dBu @ -20 dBFS
THD+N:
Dynamic Range:
< 0.015% from 20 Hz to 20khz @ +24dBu
104 dB
Signal to Noise
80 dB
Crosstalk:
< -80dB from 20Hz to 20kHz
Frequency Response:
±0.5dB 20Hz to 20kHz,
Optional Breakout Cables:
4x XLR Breakout Cable (MRD_AUD_OPT_XLR)
4x BNC Breakout Cable (MRD_AUD_OPT_BNC)
1x Terminal Block (MRD_AUD_OPT_TERM)
SDI Embedded Audio Output
Standards:
Density:
Sampling Frequency:
SMPTE 272M (for SD-SDI)
SMPTE 299 (for HD-SDI)
8 Audio Pairs
48 kHz
Ancillary Data Support
SDI VANC Data Types:
AFD (SMPTE 2016)
Closed Captions (CEA-708)
OP-47 (SMPTE RDD-08)
SMPTE RDD-11
TVG2X, AMOL-48/96 (SCTE-127)
Teletext/WSS/VPS (SMPTE-2031)
Time Code (SMPTE 12M-2)
SMPTE2038
Source ID
SCTE104 (SMPTE 2010)
VII (SMPTE RP-186)
SDI HANC Data Types:
Time Code (SMPTE 12M-2)
VBI Waveforms (SDI/Composite):
Synchronization with video :
Line 21 Captions (CEA-608)
TVG2X, AMOL-48/96 (SCTE-127)
Teletext (EN300706)
WSS (EN300294)
VPS (EN300231))
Timecode in VBI (SMPTE 12M-1)
Frame Accurate
ASI Input and Output Features
General –
Connector:
2x BNC, Female
Impedance:
75Ω
Return Loss:
≥15dB, 3.5 to 270 MHz
ASI Serial TS Input / Output –
Number of ASI Inputs:
1
Number of ASI Outputs:
1 (non loop-through)
Standard:
EN50083-9 (V2:3/98) DVB ASI
Data Bit Rate:
270 Mb/s
Maximum TS Rate:
200 Mb/s
Minimum TS Rate:
250 Kb/s
Packet Sizes
Input:188 and 204 bytes
Output: 188 bytes
Modes Supported:
Burst, Byte
Page 84

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 84 (97)
DVB-CI Descrambling Module Option
CAM Decryption –
General –
Compatibility Standard:
DVB-CI EN 50221
Number of CAM Slots:
2
Auto CAM insertion/removal
detection:
Yes
CAM Usage:
Selectable, Enable/Disable
CAM Name Display:
Yes
Multicrypt Support:
Yes
Decryption Selection –
Elementary Stream types:
Video (MPEG2 & H264), Audio
Selection Modes:
Base Unit –
Decoded Elementary Streams
Multi-Service Descrambling License (MRD 58991) Adds
–
Individually selectable elementary streams
Maximum TS bitrate
DVB-CI – 100Mb/s
CAS Supported –
All major CA vendors supported
BISS Descrambling Option
Compatibility Standard:
DVB-CSA
Supported Modes:
Base Unit – None
BISS Descrambling License (MRD58921) Adds –
Mode 1, Mode E, Injected ID
No limitation to number of services descrambled per key
Multi-BISS descrambling using up to 12 keys
Maximum TS bitrate:
200 Mb/s
IP Input/Output Module Option
General –
Connector:
2x 10/100/1000 auto negotiate Base-T RJ-45 Ethernet
Ports
Receive –
Input Format:
UDP, RTP and RTP with extension headers
Multicast and Unicast
CBR, VBR, Null Stripped
Receiver Capability:
2 simultaneous MPEG over IP transport streams
FEC Receive:
Pro MPEG CoP3 SMPTE2022
Range: L*D≤100
1≤L≤20
4≤D≤20
Annex B
Multicast Filtering:
Filters based on IP address
Buffer size:
1 - 4000 KB, or 1 – 4000ms, user configurable
Bitrate Range:
.25 – 200 Mb/s
Packets/IP Frame:
1-7 MPEG Packets/IP Frame
IGMP Compatibility:
Version 2 and 3
Page 85

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 85 (97)
Transmit –
Output Format:
UDP and RTP
Bitrate Range:
.25 – 200 Mb/s
Packets/IP Frame:
1-7 MPEG Packets/IP Frame
Number of Outputs:
2 Mirrored TS – Unicast and/or Multicast
IP FEC Output (MRD58925) Adds –
FEC:
Columns, Columns/Rows
FEC Transmit:
Pro MPEG CoP3 SMPTE2022
Range: L*D≤100
1≤L≤20
4≤D≤20
DVB-S/S2/S2X Input Module Option
General –
Frequency Range:
950 MHz – 2150 MHz
Number of inputs:
4 (A, B, C and D)
Connector:
F-81 Type, Female (4)
Impedance:
75 Ohms
Return Loss:
>9 dB
Separation:
>50 dB adjacent, >60 dB non-adjacent
RF frequency:
950 MHz to 2150 MHz in 100 kHz steps
Tuning:
Difference between Satellite frequency and LO
frequency
Satellite frequency:
950 – 14500 MHz
LO frequency:
0 – 12000 MHz, with presets of 0, 5150, 9750,
10600, 10750 and 11250 MHz
Packet size:
188 bytes
Tuning Step Size:
125 kHz, maximum
Nyquist root filter roll-off factors:
.05, .10, .15, .20, .25, .35
RF Input Level:
-65 dBm to -25 dBm
Input RF Spectrum:
Normal/Inverted Auto Detect
PL Scrambling Codes supported:
0-262,141
Image Rejection:
>30dB
Noise Figure:
Max TS Bitrate:
<15dB, maximum
160 Mb/s
LNB Power and 22 kHz Tone –
LNB Power
Off/13/14/18/19VDC @ >450mA
LNB voltage regulation:
± 4%
22 kHz Tone:
Off/On @ 650 mV (± 250 mV) peak-peak
DVB-S –
Standard:
EN 300 421
FEC Code:
Conv. + Reed-Solomon
Modulation:
QPSK
Modulation/Coding supported:
CCM
Code rates:
1/2, 2/3, 3/4, 5/6, 7/8
QPSK Symbol rate:
0.5-60 MSym/s
DVB-S2 –
Standard:
EN 302 307
Decoding type:
LDPC and BCH
Modulation:
QPSK, 8PSK
Modulation/Coding supported:
CCM
FEC Framing Type
Short frame size (16200), Normal frame size (64800)
Supported rates:
QPSK: 1/4, 1/3, 2/5, 1/2, 3/5, 2/3, 3/4, 4/5, 5/6, 8/9,
9/10
Page 86

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 86 (97)
8PSK: 3/5, 2/3, 3/4, 5/6, 8/9, 9/10
Symbol rate:
0.5-60 MSym/s
Pilot:
On/Off Auto Detect
DVB-S2 Advanced (MRD 58916) Adds –
Modulation:
16APSK, 32APSK
Modulation/Coding:
VCM
Supported Rates:
16APSK: 2/3, 3/4, 4/5, 5/6, 8/9, 9/10
32APSK: 3/4, 4/5, 5/6, 8/9, 9/10
Symbol Rate:
0.5-60 MSym/s
Multistream reception:
Single ISI (stream specified)
ISSY:
Supported
DVB-S/S2 Input Module Option
General –
Frequency Range:
950 MHz – 2150 MHz
Number of inputs:
4 (A, B, C and D)
Connector:
F-81 Type, Female (4)
Impedance:
75 Ohms
Return Loss:
>9 dB
Separation:
>50 dB adjacent, >60 dB non-adjacent
RF frequency:
950 MHz to 2150 MHz in 100 kHz steps
Tuning:
Difference between Satellite frequency and LO
frequency
Satellite frequency:
950 – 14500 MHz
LO frequency:
0 – 12000 MHz, with presets of 0, 5150, 9750,
10600, 10750 and 11250 MHz
Packet size:
188 bytes
Tuning Step Size:
125 kHz, maximum
Nyquist root filter roll-off factors:
.05, .10, .15, .20, .25, .35
RF Input Level:
-65 dBm to -25 dBm
AFC Tuning Range:
± .5 MHz in Standard and Wide mode (with SR .5
≤ 1 MSps)
± 1 MHz in Standard and Wide mode (with SR 1 ≤
2 MSps)
± 1.5 MHz in Standard and Wide mode (with SR 2
≤ 3 MSps)
± 2 MHz in Standard and Wide mode (with SR 3 ≤
4 MSps)
± 2.5 MHz in Standard and Wide mode (with SR 4
≤ 5 MSps)
± 3 MHz in Standard mode (with SR ≥ 5 MSps)
± 4 MHz in Wide mode (with SR 5 ≤ 6 MSps)
± 5 MHz in Wide mode (with SR ≥ 6 MSps)
Standard / Wide modes user selectable
Input RF Spectrum:
Normal/Inverted Auto Detect
PL Scrambling Codes supported:
0-262,141
Image Rejection:
>30dB
Noise Figure:
<15dB, maximum
Page 87

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 87 (97)
Max TS Bitrate:
160 Mb/s
LNB Power and 22 kHz Tone –
LNB Power
Off/13/14/18/19VDC @ >450mA
LNB voltage regulation:
± 4%
22 kHz Tone:
Off/On @ 650 mV (± 250 mV) peak-peak
DVB-S –
Standard:
EN 300 421
FEC Code:
Conv. + Reed-Solomon
Modulation:
QPSK
Modulation/Coding supported:
CCM
Code rates:
1/2, 2/3, 3/4, 5/6, 7/8
QPSK Symbol rate:
0.5-60 MSym/s
DVB-S2 –
Standard:
EN 302 307
Decoding type:
LDPC and BCH
Modulation:
QPSK, 8PSK
Modulation/Coding supported:
CCM
FEC Framing Type
Short frame size (16200), Normal frame size (64800)
Supported rates:
QPSK: 1/4, 1/3, 2/5, 1/2, 3/5, 2/3, 3/4, 4/5, 5/6, 8/9,
9/10
8PSK: 3/5, 2/3, 3/4, 5/6, 8/9, 9/10
Symbol rate:
0.5-60 MSym/s
Pilot:
On/Off Auto Detect
DVB-S2 Advanced (MRD 58916) Adds –
Modulation:
16APSK, 32APSK
Modulation/Coding:
VCM
Supported Rates:
16APSK: 2/3, 3/4, 4/5, 5/6, 8/9, 9/10
32APSK: 3/4, 4/5, 5/6, 8/9, 9/10
Symbol Rate:
0.5-60 MSym/s
Multistream reception:
Single ISI (stream specified)
ISSY:
Supported
8VSB/QAM Input Module Option
General –
Frequency Range:
50 MHz – 1000 MHz
VHF/UHF (Ch2 – Ch69)
CATV (Ch2 – Ch158)
Channel Plans:
Off Air, FCC, IRC, HRC
Number of inputs:
1
Connector:
F-Type, Female
Impedance:
75 Ohms
Sensitivity:
-34dBmV to + 40dBmV (A74 Compliant)
Modulation:
8VSB, QAM-B
MER:
Range: 0dB to 40dB
Accuracy: +/- 2dB
Low Limit Alarm: User Defined Entry
RF Level:
Range: -34dBmV to +40dBmV
Accuracy: +/- 5dBmV
Low Limit Alarm: User Defined Entry
QAM – Standard:
ITU Annex B/SCTE DVS-031
QAM Mode:
64 and 256
De-interleaver:
I=1-128, J=128/1
Nyquist Roll Off (Alpha):
12%, 18%
8VSB –
Page 88

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 88 (97)
Standard:
ATSC A/53E
Decoding Levels:
8
Nyquist Roll Off (Alpha):
11.5%
DVB-T2/C2/ISDB-T Input Module Option
General –
Frequency Range:
42 MHz – 1002 MHz
Number of inputs:
1
Connector:
F-Type, Female
Impedance:
75 Ohms
Sensitivity:
-34dBmV to + 40dBmV (A74 Compliant)
Modulation:
QPSK, 16QAM, 32QAM, 64QAM, 128QAM,
256QAM, 1024QAM, 4096QAM
MER:
Range: 0dB to 40dB
Accuracy: +/- 2dB
Low Limit Flag: User Defined
RF Level:
Range: -34dBmV to +40dBmV
Accuracy: +/- 5dBmV
Low Limit Flag: User Defined
Page 89

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 89 (97)
Appendix D – Pinouts for Analog Audio and Relay Connectors
(DB-15) ANALOG AUDIO 1-2
PIN
CHANNEL
FUNCTION
1
Channel 1
Left +
2
Channel 1
Right +
3
Channel 2
Left +
4
Channel 2
Right +
5
--
--
6
Channel 1
Left -
7
Channel 1
Right -
8
Channel 2
Left -
9
Channel 2
Right -
10
--
--
11
--
Ground
12
--
Ground
13
--
Ground
14
--
Ground
15
--
Ground
(DB-15) ANALOG AUDIO 3-4
PIN
CHANNEL
FUNCTION
1
Channel 3
Left +
2
Channel 3
Right +
3
Channel 4
Left +
4
Channel 4
Right +
5
--
--
6
Channel 3
Left -
7
Channel 3
Right -
8
Channel 4
Left -
9
Channel 4
Right -
10
--
--
11
--
Ground
12
--
Ground
13
--
Ground
14
--
Ground
15
--
Ground
AUD 1-2
RELAY
AUD 3-4
Page 90

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 90 (97)
(DB-9) RELAY PINOUT
PIN
RELAY
FUNCTION
1
Relay 1
Normally Open
2
Relay 1
Normally Closed
3
Relay 2
Common
4
Relay 3
Normally Open
5
Relay 3
Normally Closed
6
Relay 1
Common
7
Relay 2
Normally Open
8
Relay 2
Normally Closed
9
Relay 3
Common
DB-9 Connector
(Female) Pin #’s
DB-15 Connector
(Male) Pin #’s
Note: Relay functions shown represent the MRD in a powered-on
state with no active alarms.
Page 91

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 91 (97)
Appendix E – MRD 6000 Audio Explanation
Downmix Audio Setup
There are two primary modes of audio down mix operation for the MRD 6000
receiver/decoders. These settings only affect the signal if the digital output is set to
PCM. It will also affect those embedded audio channels that are set to a PCM down
mix. There are no gain changes or decoding if the digital or embedded outputs are set
to Pass-through. The preset modes are Monitor (the default setting) and Transmission.
The first preset, Transmission, allows no changes by the customer. Transmission is
intended to provide a limited dynamic range signal to drive a set top box or a transmitter.
The Transmission mode does respond to dialog normalization data. It provides a gain
boost of 11 dB and has compression to prevent the signal from overdriving a modulator.
The 11dB gain boost is applied to the analog outputs, AES digital outputs set to PCM,
and any embedded outputs set to PCM. It will not affect the gain of digital outputs or
embedded outputs set to Pass-Through. It is intended to provide a similar audio level as
a broadcast TV station signal through an RF modulator. The down mix includes the
center and surrounds channels if they are present, and is represented as Lt/Rt. (left total,
right total)
The second preset is Monitor. It has moderate processing, no gain boost and its down
mix involves left and right channels only (Lo/Ro). The mode setting is Line as the default,
but may be changed to RF, Custom 0 or Custom 1. In Line mode, the Dolby Dialog
Normalization data is followed along with moderate processing. The default down mix
setting for Monitor is Lo/Ro. The down mix may be changed to Lt/Rt or Lt/Rt/auto. Lt/Rt
auto follows the embedded data in the stream if the producer has a preferred down mix.
It will switch automatically between Lo/Ro and Lt/Rt depending on the data in the
stream. If no mode is specified, the down mix will be Lt/Rt. In addition, the Dual Mono
modes of operation may be selected. They will only have an effect if the stream is
encoded as Dual Mono. Dual Left or Dual Right applies that signal to both left and right
channels of the digital service, left and right channels of the analog outputs, and left and
right channels of any embedded stream set to PCM. Selecting RF as the compression
setting will add 11 dB of gain and the same processing as the Transmission mode to the
analog outputs, AES digital outputs set to PCM, and any embedded outputs set to PCM.
There is an additional selection at the bottom of the Dolby setup pull-down menu. This
allows selection between Professional Mode and Consumer Mode. In Professional
Mode the built-in latency value is 32 msec for all formats. In Consumer Mode, this
latency varies depending on the format. If you wish to monitor using a consumer
receiver, you should choose Consumer Mode. The output sampling rate will always be
48 kHz, even in consumer. The Consumer/Pro identification bit will be set to Consumer.
Normal operation in the air chain will use the Professional setting. This setting affects
both Dolby Digital (AC-3) and Dolby Digital Plus.
If you want to run with no processing, choose Custom 1, Lo/Ro, and Dynamic Range
disabled. This will still allow gain changes called for in the Dolby metadata via DialNorm settings in the stream.
Page 92

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 92 (97)
Audio Output Settings
The digital audio services may be set to PCM (AES) or Pass-through (AES data) as an
output. This applies to all available sources. The PCM setting will decode and
automatically down mix an AC-3 or Dolby Digital Plus stream to two channels of AES
audio. Pass-through simply passes thru the Dolby AC-3 data in an AES stream to be
decoded by an external decoder such as the Dolby 568. Be aware the Dolby DP-568 is
a professional decoder and always has a decoding latency of 32 msec. The older Dolby
DP-564 has both professional and consumer modes of operation. If it identifies the
Pro/Consumer ID bit as Professional, the latency will always be 32 msec. If it identifies
the Pro/Consumer bit as Consumer, the latency will vary according to the format. Check
the DP-564 manual for the actual latency values for Consumer mode. The analog
channels can be assigned to any of the digital sources. The analog gain may be
adjusted for the desired level. The gain setting does not affect the level of either the
embedded audio or the digital services. A setting of +4 dBu provides an output of +4
dBu for a digital signal level of -20 dBFS. To check the audio output level, place the
audio setup in Custom1 mode, down mix set to Lo/Ro, and the Dynamic Range
disabled. This will remove any signal processing in the down mix. Set the digital service
output being measured to PCM. A test stream of -20dBFS will output from the digital
services as -20dBFS. If the analog channels are set to a gain setting of +4 dBu, the
output should be +4 dBu plus or minus 0.5 dBu. The analog output level can be set in
increments of 0.5 dBu from -10 dBu to +4 dBu referenced to a -20 dBFS digital input
level. When you are setting the output levels it is suggested that an AC-3 stereo tone
(2.0) be used as the source. Do not use a Dolby AC-3 5.1 tone source as your test
signal. The five channels will down mix to a different level structure than a stereo signal
depending on the down mix setting.
Downmix Reference Table
The following table is applicable for MPEG Audio (Mono and Stereo), Dolby Digital
(Mono, Stereo and 5.1), Dolby Digital Plus (Mono, Stereo and 5.1) and AAC (Mono,
Stereo and 5.1).
Incoming audio PID -->
Downmix Option
--> Output effect
Stereo
Lo/Ro
OUT = IN
Stereo
Lt/Rt (DS)
OUT = IN
Stereo
Lt/Rt (Auto)
OUT = IN
Stereo
Dual mono
OUT = IN
Stereo
Dual left
OUT L = OUT R = IN L
Stereo
Dual right
OUT L = OUT R = IN R
Mono
Lo/Ro
OUT L = OUT R = IN
Mono
Lt/Rt (DS)
OUT L = OUT R = IN
Mono
Lt/Rt (Auto)
OUT L = OUT R = IN
Mono
Dual mono
OUT L = OUT R = IN
Page 93

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 93 (97)
Mono
Dual left
OUT L = OUT R = IN
Mono
Dual right
OUT L = OUT R = IN
5.1
Lo/Ro
OUT L = L + C + Ls
OUT R = R + C + Rs
(per ATSC A52)
5.1
Lt/Rt (DS)
OUT L = L + C – Ls - Rs
OUT R = R + C + Ls +Rs
(per ATSC A52)
5.1
Lt/Rt (Auto)
Lo/Ro or Lt/Rt depending
on dolby metadata
5.1
Dual mono
OUT L = front left
OUT R = front right
5.1
Dual left
OUT L = OUT R = IN Lo
5.1
Dual right
OUT L = OUT R = IN Ro
Page 94

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 94 (97)
Appendix F – MRD 6000 Discrete Audio Configuration
The MRD 6000 currently does not offer a Discrete Audio mix option or license. This
option is available on other Sencore receiver/decoders models and differs from a normal
downmix in tht is simply decodes selected audio channels rather than mixing multiple
channels into 2 channels. Its primary use is for passing individual audio channels, such
as in Dolby 5.1, to separate audio components and/or outputs. If you require this feature
please contact Sencore for an alternative solution.
Appendix G – Open Source Software
The MRD 6000 includes:
Package
Version
License
Copyright
AT32 UC3B Software
Framework
1.7.0
BSD
2009, Atmel Corporation
BaseX4JIT
4.0
GPL Version 3, 29 June
2007
2007-2009, Active Group,
Inc
BusyBox
1.20.1
GPL Version 2, June 1991
Erik Anderson, et. al.
Cgicc
3.2.9
LGPL Version 29, June
2007
Stephen F. Booth
dfu-programmer
0.5.2
GPL Version 2, June 1991
Weston Schmidt
Dropbear
2012.55
MIT-like
2002-2008 Matt Johnston,
et. al (see license)
E2fsprogs
1.41.9
GPL Version 2, June 1991
Theodore Ts’o
ethtool
2.6.34
GPL Version 2, June 1991
David Miller, et. al.
FamFamFam Silk Icons
013
Creative Commons
Attribution 2.5
Mark James
FastDB
3.71
MIT-like
Konstantin Knizhnik
FCGI
2.4.6
FastCGI
Open Market, Inc
Iproute2
3.4.0
GPL Version 2, June 1991
Stephen Hemminger,
Alexey Kuznetsov
Libusb
0.1.12
GPL Version 2.1, Feb 1999
Johannes Erdfelt, Thomas
Sailer, Brad Hards
Lighttpd
1.4.23
BSD
2004, Jan Kneschke
Linux
2.6.30
GPL Version 2, June 1991
Linus Torvalds, et. Al.
Log4cpp
1.0
GPL Version 2.1 Feb 1999
Bastiann Bakker
Monit
5.1.1
GPL Version 3, 29 June 07
2010 Tildeslash Ltd.
Net-SNMP
5.7.1
BSD
1989, 1991, 1992 by
Carnegie Mellon Univsty.
NTP
4.2.4p7
NTP License
1992-2009 David L. Mills
Page 95

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 95 (97)
OpenSSL
1.0.1c
BSD-Like
1998-2008 The OpenSSL
Project, 1995-1998
OProfile
0.9.7
GPL Version 2, June 1991
John Levon, Philippe Elie,
et. al
PCRE
8.00
BSD
1997-2009 University of
Cambridge, 2007-2008
POPT
1.14
MIT
1998 Red Hat Software
qDecoder
12.0.2
BSD
200-2012 Seungyoung
Kim
Socket-CAN
1171
BSD-like, GPL Version 2,
June 1991
2002-2007 Volkswagen
Group Electronic
Research
Spawn-FCGI
1.6.3
BSD
Jan Kneschke, Stefan
Bahler
TCLAP
1.2.0
MIT
2003 Michael E Smoot
U-Boot
2009.11.1
GPL Version 2, June 1991
Wolfgane Denk, et. al.
USB-Utils
0.86
GPL Version 2, June 1991
Thomas Sailer, Johannes
Erdfelt, David Brownell,
Zlib
1.2.3
Zlib/libpng License
1995-2005 Jean-loup
Gailly and Mark Adler
Page 96

MRD 6000 – User Manual
Page 96 (97)
Appendix H – Warranty
Sencore One-Year Warranty
Sencore warrants this instrument against defects from any cause, except acts of God
and abusive use, for a period of 1 (one) year from date of purchase. During this
warranty period, Sencore will correct any covered defects without charge for parts, labor,
or recalibration.
Appendix I – Support and Contact Information
Returning Products for Service or Calibration
The MRD 6000 is a delicate piece of equipment and needs to be serviced and repaired
by Sencore. Periodically it is necessary to return a product for repair or calibration. In
order to expedite this process please carefully read the instructions below.
RMA Number
Before any product can be returned for service or calibration, an RMA number must be
obtained. In order to obtain a RMA number, use the following steps:
1. Contact the Sencore service department by going online to www.sencore.com
and select Support.
2. Select Service and Repair from the options given.
3. Fill in the following required information:
a. First & Last Name
b. Company
c. Email
d. Phone Number
e. Ship and Bill to Address
f. Unit Model and Serial Numbers
4. A RMA number will be emailed you shortly after completing the form with return
instructions.
Shipping the Product
Once an RMA number has been issued, the unit needs to be packaged and shipped
back to Sencore. It’s best to use the original box and packaging for the product but if
this not available, check with the customer service representative for the proper
packaging instructions.
Note: DO NOT return any power cables or accessories unless instructed to do so by
the customer service representative
Page 97

Sencore Inc.
3200 Sencore Drive
Sioux Falls, SD 57107 USA
www.sencore.com
Copyright © 2018 Sencore Inc. 1.605.978.4600
 Loading...
Loading...