Page 1

1
HelloDevice Pro Series
User Guide
PS100/PS200/PS400
Version 1.0.5
2003-06-24
Page 2

2
User Guide for the HelloDevice Pro Series
Version 1.0.5
Firmware version 1.2.*
Printed in Korea
Copyright
Copyright 2002, Sena Technologies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Sena Technologies reserves the right to make changes and improvements to its product without
providing notice.
Trademark
HelloDevice™ is a trademark of Sena Technologies, Inc.
Windows® is a registered trademark of Microsoft Corporation.
Ethernet® is a registered trademark of XEROX Corporation.
Notice to Users
When a system failure may cause serious consequences, protecting life and property against such
consequences with a backup system or safety device is essential. The user agrees that protection
against consequences resulting from system failure is the user's responsibility.
This device is not approved for life-support or medical systems.
Changes or modifications to this device not explicitly approved by Sena Technologies will void the
user's authority to operate this device.
Technical Support
Sena Technologies, Inc.
210 Yangjae-dong, Seocho-gu
Seoul 137-130, Korea
Tel: (+82-2) 573-5422
Fax: (+82-2) 573-7710
E-Mail: support@sena.com
Website: http://www.sena.com
Page 3

3
Contents
1: Introduction 6
1.1 Overview................................................................................................................................ 6
1.2 Package Check List................................................................................................................ 7
1.3 Product Specification.............................................................................................................. 8
1.4 Terminologies and acronyms .................................................................................................. 9
2: Getting Started 11
2.1 Panel Layout ........................................................................................................................ 11
2.1.1 PS100 Panel Layout................................................................................................... 11
2.1.2 PS200 Panel Layout................................................................................................... 12
2.1.3 PS400 Panel Layout................................................................................................... 13
2.2 Connecting the Hardware ..................................................................................................... 15
2.2.1 Connecting the power................................................................................................. 15
2.2.2 Connecting to the network .......................................................................................... 15
2.2.3 Connecting to the device ............................................................................................16
2.3. Accessing Console Port....................................................................................................... 17
2.3.1 Using Serial console................................................................................................... 17
2.3.2 Using Remote console ............................................................................................... 19
3: IP Address Configuration 21
3.1 Static IP................................................................................................................................21
3.1.1 Overview.................................................................................................................... 21
3.1.2 IP address.................................................................................................................. 22
3.1.3 Subnet mask .............................................................................................................. 22
3.1.4 Default gateway ......................................................................................................... 22
3.1.4 Primary and Secondary DNS...................................................................................... 23
3.2 DHCP .................................................................................................................................. 23
3.2.1 Overview.................................................................................................................... 23
3.2.2 DHCP setting ............................................................................................................. 24
3.3 PPPoE................................................................................................................................. 25
3.3.1 Overview.................................................................................................................... 25
3.3.2 PPPoE setting............................................................................................................ 26
4: Serial Port Configuration 27
4.1 Host mode configuration....................................................................................................... 29
4.1.1 Overview.................................................................................................................... 29
4.1.2 TCP server mode operations ...................................................................................... 31
4.1.3 TCP client mode operations........................................................................................ 33
4.1.4 TCP server/client mode operations ............................................................................. 36
Page 4

4
4.1.5 UDP tunneling mode operations .................................................................................38
4.1.6 UDP server mode operations...................................................................................... 39
4.1.7 Modem emulation mode operations ............................................................................ 40
4.2 UART configuration.............................................................................................................. 42
4.2.1 Type........................................................................................................................... 43
4.2.2 Baud rate ................................................................................................................... 44
4.2.3 Data bits, Stop bits, Parity........................................................................................... 44
4.2.4 Flow control................................................................................................................ 45
4.2.5 DTR/DSR behavior..................................................................................................... 45
4.3 Cryptography configuration................................................................................................... 46
4.4 Options ................................................................................................................................ 47
4.4.1 Inactivity timeout.........................................................................................................47
4.4.2 Inter-character timeout ............................................................................................... 47
5: Advanced Options Configurations 49
5.1 Remote host access control .................................................................................................49
5.1.1 Configuration access.................................................................................................. 50
5.1.2 Serial Port access ...................................................................................................... 50
5.2 Manual DNS configuration.................................................................................................... 51
5.3 Locating server..................................................................................................................... 51
5.3.1 Overview.................................................................................................................... 51
5.3.2 Locating server configuration...................................................................................... 52
5.3.3 Locating server communication protocol..................................................................... 53
6: System Status and Log 54
6.1 Display system status........................................................................................................... 54
6.2 Display log data.................................................................................................................... 55
6.3 Automatic log delivery by email.............................................................................................55
7: System administration 57
7.1 User name and password..................................................................................................... 57
7.2 Date and time settings.......................................................................................................... 58
8: System tools 59
8.1 Factory default reset............................................................................................................. 59
8.2 Firmware upgrade ................................................................................................................ 59
8.3 Ping test............................................................................................................................... 61
8.4 Socket reset......................................................................................................................... 61
Appendix A: Connections 62
A.1 Ethernet Pin outs ................................................................................................................. 62
A.2 Serial Ports Pin Outs............................................................................................................ 62
A.3 Ethernet Wiring Diagram...................................................................................................... 63
Page 5

5
A.4 Serial Wiring Diagram .......................................................................................................... 63
Append ix B: Well-known port numbers 65
Appendix C: Troubleshooting 66
C.1 Power/LED status troubleshooting .......................................................................................66
C.2 Serial console troubleshooting .............................................................................................66
C.3 Remote console troubleshooting .......................................................................................... 66
C.4 IP address troubleshooting .................................................................................................. 67
C.5 DHCP troubleshooting ......................................................................................................... 67
C.6 TCP server operation troubleshooting .................................................................................. 67
C.7 Serial communication troubleshooting .................................................................................. 68
Page 6

6
1: Introduction
1.1 Overview
The HelloDevice Pro Series allows you to network-enable a variety of serial devices that were not
originally designed for networking. This capability brings the advantages of remote management and
data accessibility to thousands of serial devices over the network.
The PS100 is a versatile single-port serial-Ethernet communication device. The PS200 and PS400 are
two-port and four-port serial-Ethernet communication devices respectively expanding the capabilities
of the PS100. The HelloDevice Pro Series supports RS232, RS422 or RS485 on each serial port
allowing virtually any asynchronous serial device to be accessed over a network.
As for the Internet connectivity, the HelloDevice Pro Series supports open network protocols such as
TCP/IP, UDP and PPPoE (PPP-over-Ethernet) allowing serial devices to be accessed over DSL-
based broadband network or conventional LAN (Local Area Network) environment.
The HelloDevice Pro Series provides the full-featured management functions such as status monitor,
remote reset, error log monitor and firmware upgrade using Telnet and serial console port under the
password protection support. In addition, the HelloDevice Pro Series provides IP address filtering
function to protect unintentional data streams to be transmitted to the serial device, and static key
based 3DES data encryption to promise secure data communication.
The HelloDevice Pro Series was designed to accommodate the unique requirements of the Retail
POS, Security, Industrial automation and Medical marketplaces.
Parts of this manual assume the knowledge on concepts of the Internetworking protocols and serial
communications. If you are not familiar with these concepts, please refer to the standards or the
documentation on each subject.
Page 7

7
1.2 Package Check List
- HelloDevice Pro Series external box
- 110V or 230V Power supply adapter
- Serial data cable
- A hardcopy of Quick Start Guide
- CD-ROM including the HelloDevice-IDE, HelloDevice Manager and User Guide
Page 8
8
1.3 Product Specification
PS100 PS200 PS400
1-port
RS232/422/485
Male DB9
2-port
RS232/422/485
Male DB9
4-port
RS232/422/485
Male DB9
Serial speeds 1200bps to 115Kbps
Flow Control: None, Hardware RTS/CTS
Serial Interface
Signals:
RS232 Rx, Tx, RTS, CTS, DTR, DSR, GND
RS422 Rx+, Rx-, Tx+, TxRS485 Data+, Data-
10 Base-T Ethernet with RJ45 Ethernet connector Network Interfaces
Supports static and dynamic IP address
Protocols ARP, IP/ICMP, TCP, UDP, Telnet, DNS, SMTP, DHCP client, PPPoE
User ID & Password
Data encryption: 3DES
Security
IP address filtering
Telnet or serial console port or HelloDevice Manager
System log and statistics
Error log storage up to 100 messages
Automatic email delivery of error log
Full-featured system status display
Management
Firmware upgrade via serial console or telnet
Diagnostic LED Power
Ready
10 Base-T Link, Act
Serial Rx/Tx for each serial port
Supply voltage: 7.5 ~ 30 VDC Power
Supply current:
140mA (nom.)
Supply current:
140mA (nom.)
Supply current:
190mA (nom.)
Environmental Operating temperature: 0 ~ 55
o
C
Storage temperature: -4 ~ 66
o
C
Size:
112 mm L
82 mm W
25 mm H
(4.4 in x 3.2 in x 1.0 in)
Size:
135 mm L
80 mm W
25 mm H
(5.3 in x 3.1 in x 1.0 in)
Size:
230 mm L
153 mm W
30 mm H
(9 in x 6 in x 1.2 in)
Physical
properties
Weight: 290g Weight: 300g Weight: 920g
Approvals FCC(A), CE(A), MIC
Warranty 5-year limited warranty
Page 9

9
1.4 Termi no lo gie s an d a cr o n ym s
The Internetworking related terminologies used frequently in this manual are defined clearly to help
your better understanding of the HelloDevice Pro Series.
MAC address
On a local area network or other network, the MAC (Media Access Control) address is the computer's
unique hardware number. (On an Ethernet LAN, it's the same as your Ethernet address.)
It is a unique 12-digit hardware number, which is composed of 6-digit OUI (Organization Unique
Identifier) number and 6-digit hardware identifier number. The HelloDevice Pro Series has the MAC
address of 00-01-95-xx-xx-xx, which is labeled on the bottom side of the external box.
Host
A user’s computer connected to the network
In Internet protocol specifications, the term "host" means any computer that has full two-way access to
other computers on the Internet. A host has a specific "local or host number" that, together with the
network number, forms its unique IP address.
Session
A series of interactions between two communication end points that occur during the span of a single
connection
Typically, one end point requests a connection with another specified end point and if that end point
replies agreeing to the connection, the end points take turns exchanging commands and data ("talking
to each other"). The session begins when the connection is established at both ends and terminates
when the connection is ended.
Client/Server
Client/server describes the relationship between two computer programs in which one program, the
client, makes a service request from another program, the server, which fulfills the request.
A server is a computer program that provides services to other computer programs in the same or
other computers, whereas a client is the requesting program or user in a client/server relationship. For
example, the user of a Web browser is effectively making client requests for pages from servers all
over the Web. The browser itself is a client in its relationship with the computer that is getting and
returning the requested HTML file. The computer handling the request and sending back the HTML file
is a server.
Page 10
10
Table 1-1 Acronym Table
ISP Internet Service Provider
PC Personal Computer
NIC Network Interface Card
MAC Media Access Control
LAN Local Area Network
UTP Unshielded Twisted Pair
ADSL Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line
ARP Address Resolution Protocol
IP Internet Protocol
ICMP Internet Control Message Protocol
UDP User Datagram Protocol
TCP Transmission Control Protocol
DHCP Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
SMTP Simple Mail Transfer Protocol
FTP File Transfer Protocol
PPP Point-To-Point Protocol
PPPoE Point-To-Point Protocol over Ethernet
HTTP HyperText Transfer Protocol
DNS Domain Name Service
SNMP Simple Network Management Protocol
UART Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter
Bps Bits per second (baud rate)
DCE Data Communications Equipment
DTE Data Terminal Equipment
CTS Clear to Send
DSR Data Set Ready
DTR Data Terminal Ready
RTS Request To Send
Page 11

11
2: Getting Started
This chapter describes how to set up and configure the HelloDevice Pro Series in the first place.
- 2.1 Panel Layout explains the layout of the panel and LED indicators.
- 2.2 Connecting the Hardw are describes how to connect the power, the network, and the serial
device to the HelloDevice Pro Series.
- 2.3 Accessing Console Port describes how to access the console port using a serial console at a
local site or telnet console at a remote site.
Following items are pre-required to get started.
- One DC power adapter (included in the package).
- One serial data cable for configuration and for connecting the RS-232 serial device.
- One PC with Network Interface Card (hereafter, NIC) and/or one RS232 serial port.
- Terminal emulation program running on the PC
- One Ethernet cable
2.1 Panel Layout
2.1.1 PS100 Panel Layout
The PS100 has five LED indicator lamps for status display as shown in Figure 2-1. Two lamps on the
upper side indicate statuses of 10 Base-T Ethernet Link and Act. Next lamp indicates statuses of
receive and transmit of the serial port for data communication. Next two lamps indicate the system
running status and the system power-on status. Table 2-1 describes function of each LED indicator
lamp.
Page 12

12
Figure 2-1. The panel layout of the PS 100
Table 2-1. LED indicat or lam ps of the PS100
Lamps Function
LINK Turned on to Green if connected to 10 Base-T Ethernet network 10 Base-T
Rx/Tx Blink whenever there is any activities such as incoming or outgoing packets
through the PS100 Ethernet port
Serial port Rx/Tx Blink whenever there is any incoming or outgoing data stream through the
serial port of the PS100
Ready Turned on to GREEN if system is running. Status
Power Turned on to RED if power is supplied
2.1.2 PS200 Panel Layout
The front panel of the PS200, as shown below in Figure 2-2, has one power switch, one DB9 serial
port connector and eight LED indicator lamps for status display. The lamp on the left-hand side
indicates the status of the system power-on and system ready. Next two indicate statuses of 10 Base-
T Ethernet Link and Act. Four other lamps indicate statuses of receive and transmit of each serial port.
Table 2-2 describes function of each LED indicator lamp on the panel.
The rear panel of the PS200, also as shown below in Figure 2-2, has one power connector, one RJ45
Ethernet connector for 10 Base-T interface and four DB9 connectors for serial interface.
Page 13

13
(a) The front panel of the PS 200
(b) The rear panel of the PS200
Figure 2-2. The panel layout of the PS200
Table 2-2. LED indicat or lam ps of the PS200
Lamps Function
Power Turned on to RED if power is supplied System Status
LED
Ready Turned on to Green if system is running
Link Turned on to Green if connected to 10 Base-T Ethernet network Ethernet Status
LED
Act Blink whenever there is any activities such as incoming or outgoing packets
through the PS200 Ethernet port
Rx Blink whenever there is any incoming data stream through the specified
serial port of the PS200
Serial port 1~ 2
Status LED
Tx Blink whenever there is any outgoing data stream through the specified
serial port of the PS200
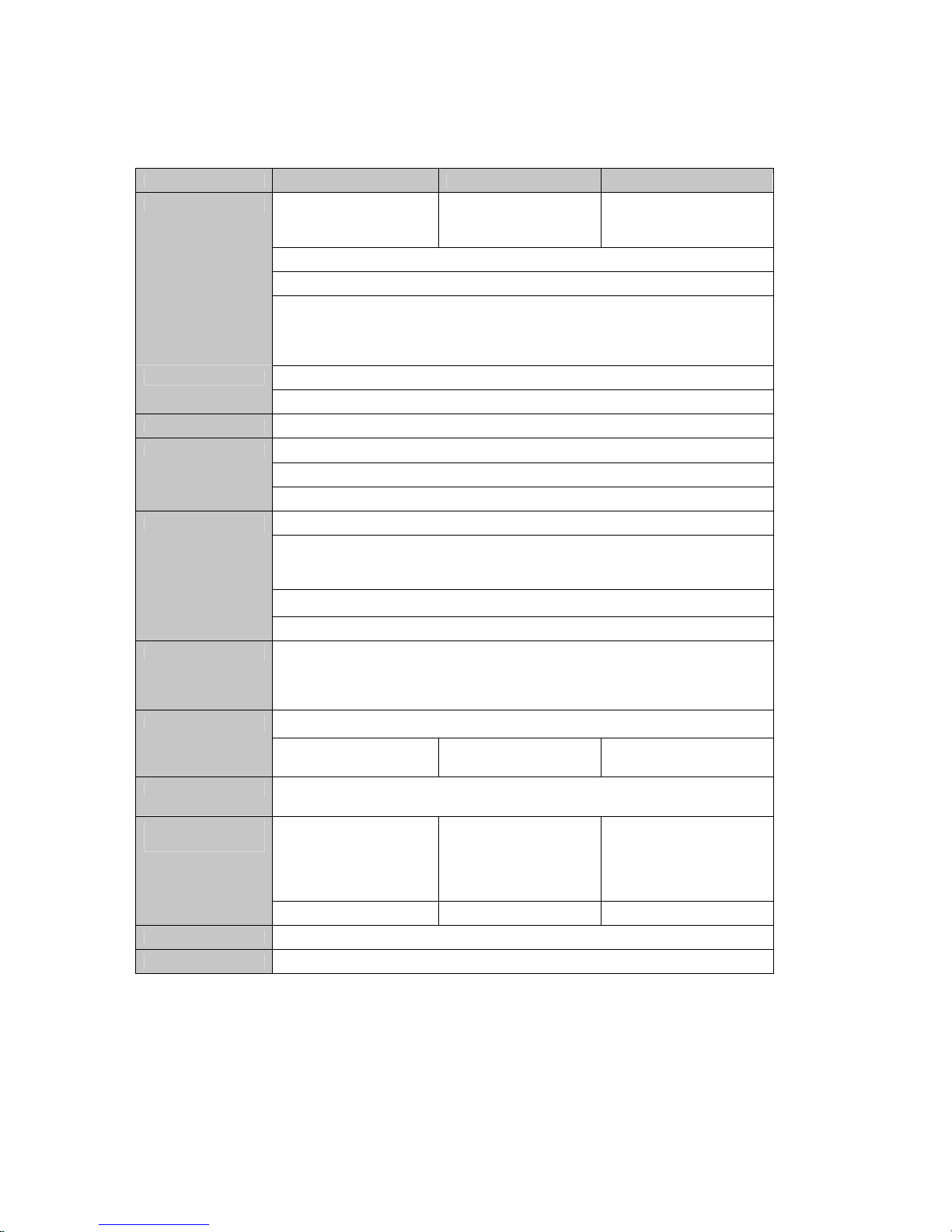
2.1.3 PS400 Panel Layout
The front panel of the PS400 has one power switch, one DB9 serial port connector and twelve LED
indicator lamps for status display. The lamp on the left-hand side indicates the status of the system
power-on and system ready. Next two lamps indicate statuses of 10 Base-T Ethernet Link and Act.
Eight other lamps indicate statuses of receive and transmit of each serial port. Table 2-3 describes
function of each LED indicator lamp on the panel.
The rear panel of the PS400 has one power connector, one RJ45 Ethernet connector for 10 Base-T
interface and four DB9 connectors for serial interface.
Page 14
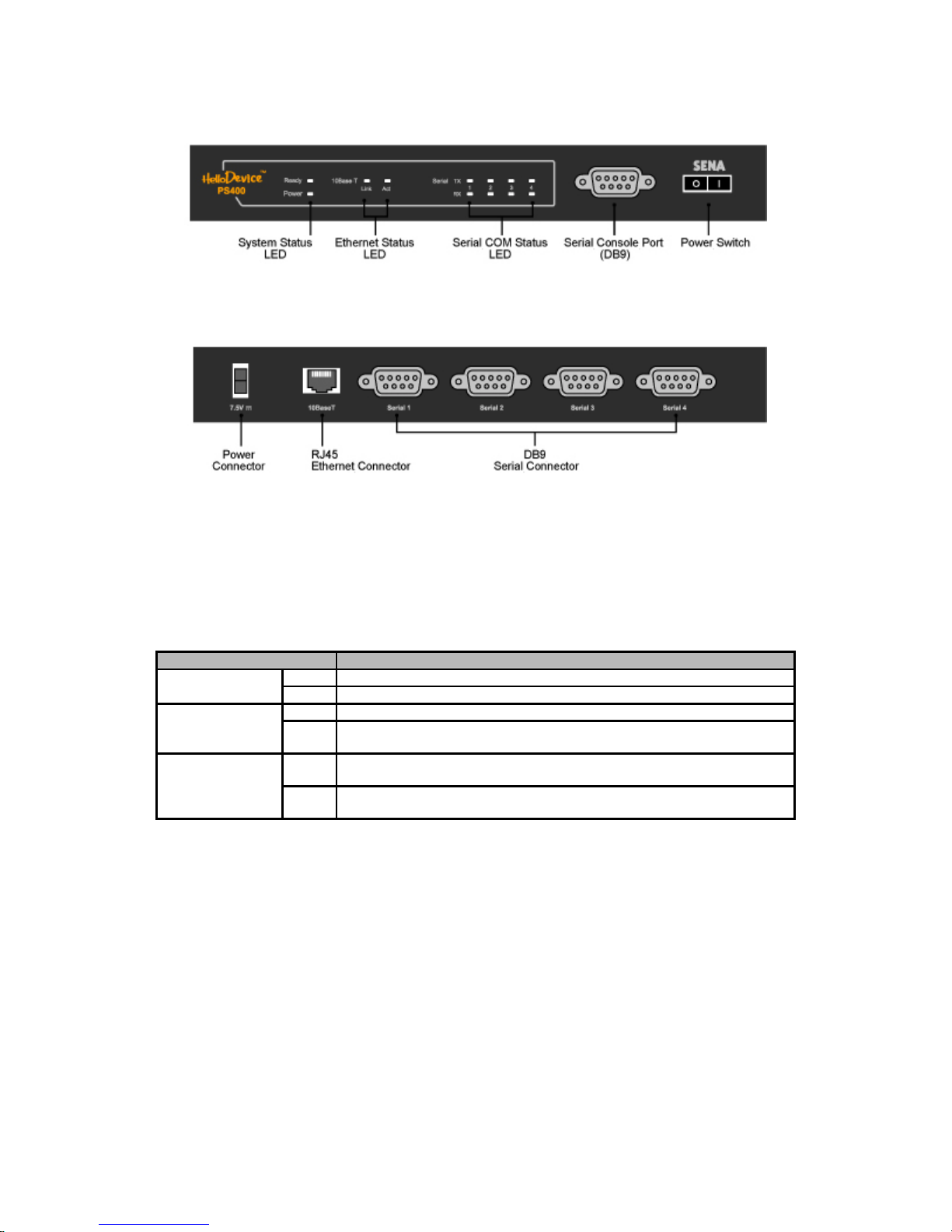
14
(a) The front panel of the PS 400
(b) The rear panel of the PS400
Figure 2-3. The panel layout of the PS400
Table 2-3. LED indicat or lam ps of the PS400
Lamps Function
Power Turned on to RED if power is supplied System Status
LED
Ready Turned on to Green if system is running
Link Turned on to Green if connected to 10 Base-T Ethernet network Ethernet Status
LED
Act Blink whenever there is any activities such as incoming or outgoing packets
through the PS400 Ethernet port
Rx Blink whenever there is any incoming data stream through the specified
serial port of the PS400
Serial port 1~ 4
Status LED
Tx Blink whenever there is any outgoing data stream through the specified
serial port of the PS400
Page 15
15
2.2 Connecting the Hardware
This section describes how to connect the HelloDevice Pro Series to serial devices for the first time
test.
- Connect the power to the HelloDevice Pro Series
- Connect the Ethernet cable between the HelloDevice Pro Series and Ethernet hub or switch
- Connect the serial data cable between the HelloDevice Pro Series and serial device(s)
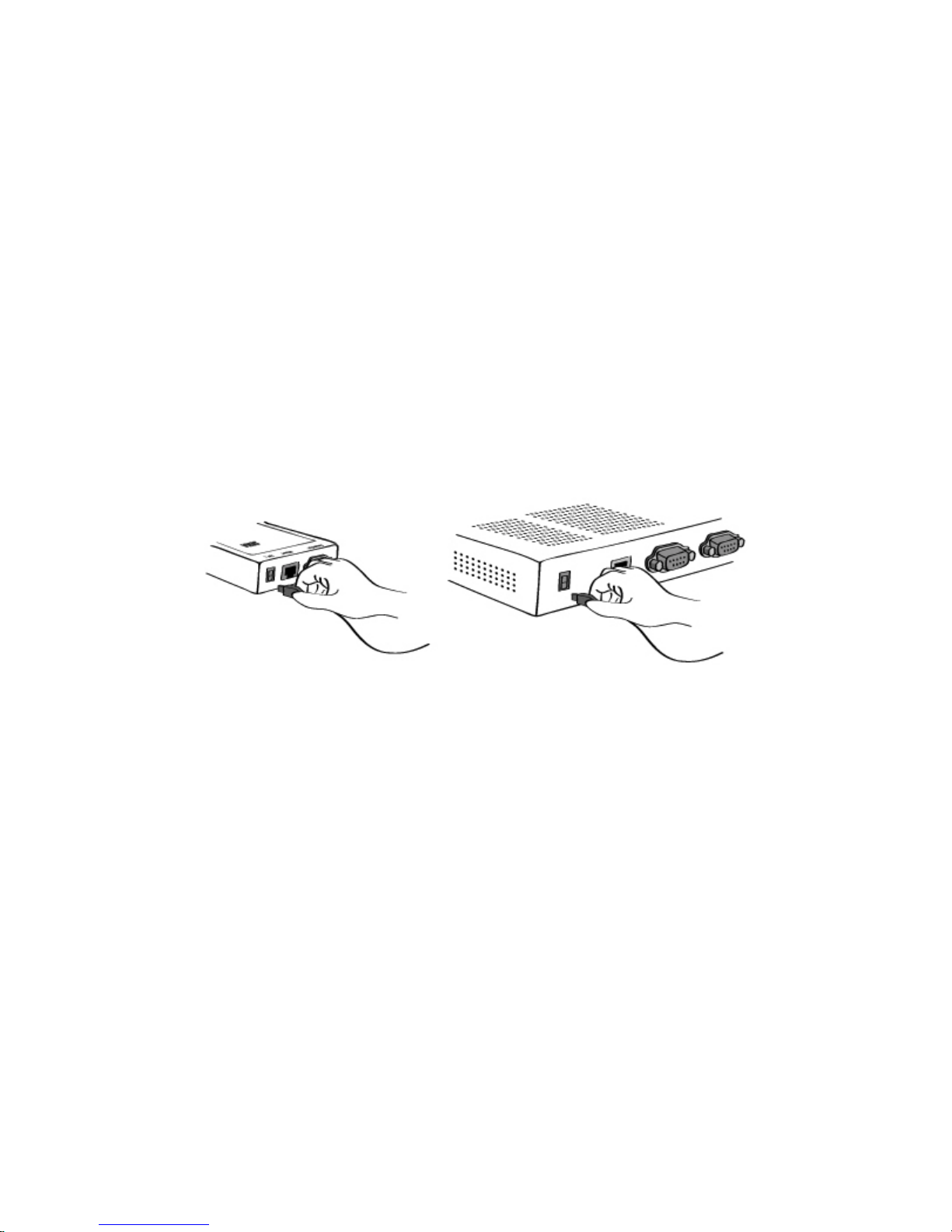
2.2.1 Connecting the power
Connect the power jack to the HelloDevice Pro Series power jack using DC power adapter included in
the package. If the power is properly supplied, the [Power] lamp will maintain solid red.
(a) Connecting the power to the PS100 (b) Connecting the power to t he PS200/ 400
Figure 2-4. Connect ing the power to the HelloDevice Pro Series
2.2.2 Connecting to the network
Connect the one end of the Ethernet cable to the HelloDevice Pro Series 10Base-T port and the other
to the Ethernet network. If the cable is properly hooked up, the HelloDevice Pro Series will have a
valid connection to the Ethernet network by indicating:
- [Link] lamp maintains solid green
- [Act] lamp continuously blinks to indicate the incoming/outgoing Ethernet packets
If any of the above does not happen, the HelloDevice Pro Series is not properly connected to the
Ethernet network.
Page 16

16
(a) Connecting a network cable to the PS100 (b) Connecting a netw or k cable to the PS200/400
Figure 2-5. Connect ing a network cable to the HelloDevice Pr o S er i es
2.2.3 Connecting to the device
Connect the serial data cable between the HelloDevice Pro Series and the serial device. If necessary,
supply the power to the serial device attached to the HelloDevice Pro Series.
(a) Connecting a serial devic e to the PS100
(b) Connecting a serial devic e to the PS200/400
Figure 2-6. Connect ing a s er ial dev ice to the HelloDevice Pro Series
Page 17

17
2.3. Acces si ng C o ns ole Port
There are two ways to access console port of the HelloDevice Pro Series depending on whether the
user is located at a local site or a remote site.
- Serial console:
Local users can connect directly to the serial console port of the HelloDevice Pro Series using
serial console cable (null-modem cable).
- Remote console:
Remote users can make a telnet connection to the remote console port (port 23) of the
HelloDevice Pro Series via TCP/IP network.
Both methods require the user to log into the HelloDevice Pro Series in order to continue.
2.3.1 Using Serial console
1) Connect the one end of the serial console cable to the console port on the HelloDevice Pro
Series.
(a) Connecting a serial console cable to the PS100 (b) Connecting a serial console cable to the PS200
(c) Connecting a serial c ons ole c able to the PS400
Figure 2-7. Connect ing a s er ial c onsole cable to the PS200
Page 18

18
2) Connect the other end of the cable to the serial port of user’s computer.
3) Run a terminal emulator program such as HyperTerminal. Set up the serial configuration
parameters of the terminal emulation program as follows:
9600 Baud rate, Data bits 8, Pari t y Non e, S top bit s 1, Hardware f lo w co nt rol (RTS/CTS)
4) Press [ENTER] key.
5) Type the user name and password to log into the HelloDevice Pro Series. A factory default
setting of the user name and password are both admin.
lo gi n : ad min
Password : *****
6) If the user logged into the HelloDevice Pro Series successfully, the main menu screen will
appear on the computer.
From the main menu screen, shown below in Figure 2-8, users can select the menu item for the
configuration of the HelloDevice Pro Series parameters by typing the menu number and pressing
[ENTER] key. In the submenu screen, users can configure the required parameters guided by online
comments. All the parameters are stored into the non-volatile memory space of the HelloDevice Pro
Series, and it will not be stored until users select menu 7.Save changes. When users are finished
with the configuration, the system needs to be rebooted by selecting the menu 9.Exit and reboot.
All the configuration changes will be effective after the reboot.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------ We lc om e to PS-400 co nf ig uration pa ge
Curren t time : 2002 /05/04 14:13:25
Serial No. : PS20 0-020200028 MAC Address : 00-01-95-04-13-80
F/W REV. : V1.2.12 UP time : 0 Days 02:26:00
IP mode : DHCP IP Address : 192.168.0 .152
------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Console#1 (Serial) : Connected
Console#2 (Telnet) : Available (NULL)
Console#3 (Telnet) : Available (NULL)
Console#4 (Telnet) : Available (NULL)
------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Select menu
1. IP Configurat ion
2. Serial port configuration
3. System Status & log
4. Syste m administ ration
5. Advan ced options
6. Syste m tools
7. Save changes
8. Exi t wi thout rebo ot
9. Exi t an d reboot
<ESC> Back , <ENTER> Refresh
----->
Figure 2-8. The main menu screen (PS400)
Page 19

19
2.3.2 Using Remote console
The IP address of the HelloDevice Pro Series must be known before users can access the remote
console port (See IP Address Configuration in chapter 3 for details). Remote console access
function is optional, and can be disabled in the remote access option on the menu (See Remote Host
Access Control in section 5.1 for details). This is useful when system administrator does not want
others to modify the existing configuration. The HelloDevice Pro Series supports Telnet protocol for
remote consoles and the port number for the remote consoles is 23, which is a TCP port number
assigned for Telnet.
Up to three remote console sessions can be established simultaneously using telnet. When they are
established, the first console session has a right to change the parameter values while others have a
right to read parameter values only. If the serial console is established, all of the remote telnet
consoles do not have a right to update the parameter values.
1) Run a telnet program or a program that supports telnet functions such as TeraTerm-Pro or
HyperTerminal. The target IP address and the port number should be those of the
HelloDevice Pro Series. If required, specify the port number as 23. Type the following
command in the command line interface of your computer.
telnet 192.168.1.254
Or run a telnet program with parameters as follows.
Figure 2-9 Telnet pr ogr am set up example
2) The user has to log into the HelloDevice Pro Series. Type the user name and password. A
factory default setting of the user name and password are both admin.
Page 20

20
We lc om e to PS-400 Co nf ig uration
Console#1 (Serial) : Not Connected
Console#2 (Telnet) : Available (NULL)
Console#3 (Telnet) : Available (NULL)
Console#4 (Telnet) : Establishe d (192.168.0.16)
lo gi n : ad min
Password : *****
Figure 2-10. Users ’ logging into the HelloDevice Pro Series (PS400)
3) If the user logged into the HelloDevice Pro Series successfully, the same main menu screen
as the one of serial console will be displayed. The user can select the menu by typing the
menu number and then pressing [ENTER] key. In the corresponding menu screen, the user
can configure the required parameters.
4) If serial console or the other remote consoles are connected already, the new console will be
established as read-only mode. Figure 2-11 shows the screen display of a read-only mode
console.
We lc om e to PS-400 Co nf ig uration
Console#1 (Serial) : Not Connected
Console#2 (Telnet) : Available (NULL)
Console#3 (Telnet) : Establishe d (192.168.0.16) : Read-only
Console#4 (Telnet) : Establishe d (192.168.0.16)
This Console(#3) is Read-Only
lo gi n : ad min
Password : *****
------------------------------------------------------------------------------ We lc om e to PS-400 co nf ig uration pa ge
Curren t time : 2002 /05/04 14:19:47
Serial No. : PS200-020200028 MAC Address : 00-01-95-04-13-80
F/W REV. : V1.2.12 UP time : 0 Days 02:32:22
IP mode : DHCP IP Address : 192.168.0 .152
------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Console#1 (Serial) : Not Connected
Console#2 (Telnet) : Available (NULL)
Console#3 (Telnet) : Establishe d (192.168.0.16) : Read-only
Console#4 (Telnet) : Establishe d (192.168.0.16)
This Console(#3) is Read-Only
------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Select menu
1. IP Configurat ion
2. Serial port configuration
3. System Status & log
4. Syste m administ ration
5. Advan ced options
6. Syste m tools
7. Save changes
8. Exi t wi thout rebo ot
9. Exi t an d reboot
<ESC> Back , <ENTER> Refresh
----->
Figure 2-11. Scr een dis play of a r ead- only m ode c ons ole (PS400)
Page 21

21
3: IP Address Configuration
A valid IP address of the HelloDevice Pro Series needs to be assigned before it starts to work in the
user's network environment. A network system administrator may provide the user with this IP
address setting information for the network. The IP address must be unique within the network.
Otherwise, the HelloDevice Pro Series will not have a valid connection to the network.
Users can choose the desired IP mode out of the three IP operating modes, i.e., Static IP, DHCP, and
PPPoE, on the IP Configuration Screen of console interface. The factory default IP mode is DHCP
mode. Table 3-1 shows the parameter items for IP Configuration menu.
Table 3-1. Hierarchic al v iew of the IP Configuration menu item s
IP mode
IP address
Subnet mask
Default gateway
Static IP
Primary DNS/ Secondary DNS
DHCP IP mode
IP mode PPPoE
PPPoE User name/ Password
3.1 Static IP
3.1.1 Overview
In the Static IP mode, users have to manually specify all the parameters such as IP addresses of the
HelloDevice Pro Series, the gateway computer and the domain name server computers, and the
network subnet mask. The HelloDevice Pro Series tries to locate such information whenever it boots
up.
The user interface for St a tic IP configuratio n is shown below in Figure 3-1. Users can select menu by
typing the menu number and then pressing [ENTER] key.
---------------------------------------------------IP config ur at io n
---------------------------------------------------Select me nu :
1. IP mo de: static IP
2. IP addre ss : 19 2. 168.1.1
3. Sub net mask: 255.255.255.0
4. Defaul t ga te wa y: 192.168 .1 .2 54
5. Primar y DN S: 210 .106.255 .1 88
6. Second ar y DN S: 210.106.2 55 .1 89
<ESC > Back, <ENTER> Refresh
--->
Figure 3-1. Static IP c onfiguration screen
Page 22

22
3.1.2 IP address
In the Static IP mode, the IP address is an identification number assigned to a computer as a
permanent address on the network. Computers use IP addresses to identify and talk to each other on
the network. Choose the proper IP address which is unique and valid on the network environment.
---> 2
Ente r IP address: 192.168.1.100[ENTE R]
Figure 3-2. Setting the IP address in Static IP mode
Note:
The IP address in the form of 192.168.1.x is private in a sense that they are not assigned by an ISP.
Application of the HelloDevice Pro Series may require sending data back and forth over a public
network, such as the Internet. In this case, it is required to assign a valid public IP address. The public
IP address is generally purchased or leased from a local ISP.
3.1.3 Subnet mask
A subnet represents all the network hosts at one geographic location, in one building, or on the same
local area network. When there is any outgoing packet over the network, the HelloDevice Pro Series
will check whether the desired TCP/IP host specified in the packet is on the local network segment
with the help of the subnet mask. If the address is proven to be on the same network segment as the
HelloDevice Pro Series, the connection is established directly from the HelloDevice Pro Series.
Otherwise, the connection is established through the given default gateway.
---> 3
Enter sub ne t ma sk : 255.255. 25 5. 0[ENTER]
Figure 3-3. Setting the subnet mask in Static IP mode
3.1.4 Default gateway
A gateway is a network point that acts as an entrance to another network. Usually, the computers that
control traffic within the network or at the local Internet service provider are gateway nodes. The
HelloDevice Pro Series needs to know the IP address of the default gateway computer in order to
Page 23

23
communicate with the hosts outside the local network environment. For correct information on the
gateway IP address, please refer to the network administrator.
---> 4
Enter default gateway: 192.168.1.1[ENTER]
Figure 3-4. Setting the default gateway in Static IP m ode
3.1.4 Primary and Secondary DNS
When users want to visit certain website, the computer asks a Domain Name System (DNS) server for
the correct IP address of the web site, and the computer uses the answer to connect to the web server.
DNS is the way that Internet domain names are identified and translated into IP addresses. Domain
name is the form of alphanumeric name such as sena.com and it is usually easier to remember. A
DNS server is a host that can translate such text-based domain names into the numeric IP addresses
for TCP/IP connection.
In order to use this DNS feature of the HelloDevice Pro Series, users need to set the IP address of this
DNS server to be able to access the host with the domain name. The HelloDevice Pro Series provides
the way to configure IP addresses of DNS servers, i.e. Primary DNS server, Secondary DNS server.
A secondary DNS server is specified for use when the primary DNS server is unavailable.
---> 5 (or 6)
Enter primary (or secondary) DNS server: 211.112.43.133[ENTER]
Figure 3-5. Setting the DNS servers in Static IP mode
3.2 DHCP
3.2.1 Overview
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is a communications protocol that lets network
administrators manage and automate the assignment of IP addresses centrally in an organization's
network. DHCP lets a network administrator supervise and distribute IP addresses from a central point
and automatically send a new IP address when a computer is plugged into a different place in the
network.
As described in the section 3.1, the IP address must be entered manually at each computer in Static
IP mode and, if computers move to another location in another part of the network, a new IP address
must be entered. Meanwhile, all the parameters including the IP address, subnet mask, gateway, DNS
Page 24

24
servers will be automatically configured when the IP address is assigned in DHCP mode. DHCP uses
the concept of a "lease" or amount of time for which a given IP address will be valid for a computer. All
the parameters required to assign an IP address are configured on DHCP server side, and each
DHCP client computer receives this information when the IP address is provided at its boot-up.
To obtain an IP address, the HelloDevice Pro Series sends a corresponding DHCP request as a
broadcast over the network after each reset. The reply generated by the DHCP server contains the IP
address as well as the subnet mask, gateway address, DNS servers and the lease time. The
HelloDevice Pro Series immediately places this information in its non-volatile memory. If the operating
time reaches the lease time, the HelloDevice Pro Series will request the DHCP server for renewal of
its lease time. If the DHCP server approves extending the lease, the HelloDevice Pro Series can
continue to work with the current IP address. Otherwise, the HelloDevice Pro Series will start the
procedure to request a new IP address to the DHCP server.
Note:
In DHCP mode, all the network-related parameters for the HelloDevice Pro Series are supposed to be
configured automatically. In case that automatic configuration of DNS server fails, it can be configured
manually in Manual DNS Configuration menu. (See Manual DNS Conf ig urat ion in section 5.3 for
further information).
A DHCP sever assigns IP addresses dynamically from an IP address pool, which is managed by the
network administrator. This means DHCP client, i.e. the HelloDevice Pro Series, receives a different
IP address each time it boots up. To prevent the case that users do not know the IP address of the
HelloDevice Pro Series in such environments, its IP address should be reserved on the DHCP server
side. In order to reserve the IP address in the DHCP network, the administrator needs the MAC
address of the HelloDevice Pro Series found on the label sticker at the bottom of the HelloDevice Pro
Series:
MAC=00:01:95:04:0c:a1
3.2.2 DHCP setting
---------------------------------------------------IP config ur at io n
---------------------------------------------------Select me nu :
IP mode: DH CP
<ESC > Back, <ENTER> Refresh
---> 1
Select mode (1 = Static IP, 2 = DHCP, 3 = PPPoE)
---> 2
Figure 3-6. Setting DHCP m ode
Page 25

25
3.3 PPPoE
3.3.1 Overview
PPPoE (PPP over Ethernet) is a specification for connecting multiple computer users on an Ethernet
local area network to a remote site through common customer premises equipment, which is the
telephone company's term for a modem and similar devices. PPPoE can be used to have an office or
building-full of users share ADSL, cable modem, or wireless connection to the Internet. Usually, it is
used in broadband Internet access such as ADSL.
To make the HelloDevice Pro Series work in PPPoE mode, users should have a PPPoE account and
the equipments for PPPoE access such as an ADSL modem. Since the HelloDevice Pro Series
provides the PPPoE protocol, it can access the remote host on the Internet over ADSL connection. It
is required to set up the user name and password of the PPPoE account for the HelloDevice Pro
Series.
If the IP mode is set to PPPoE, The HelloDevice Pro Series negotiates the PPPoE connection with
PPPoE server whenever it boots up. During the negotiation, it receives the information required for
Internet connection such as IP address, gateway, subnet mask and DNS servers. If the connection is
established, the HelloDevice Pro Series tries to maintain the connection as long as possible. If the
disconnection is detected, the HelloDevice Pro Series will attempt to make a new PPPoE connection
by requesting the new connection.
(a) Installation of the PS100 with ADSL connecti on
(b) Installation of the PS200/400 with ADSL connection
Figure 3-7. Installation of the HelloDevice Pr o S er ies w ith A DS L c onnec tion
Page 26

26
3.3.2 PPPoE setting
To make the HelloDevice Pro Series work in PPPoE mode, users need to configure the PPPoE
username and password for their ADSL account.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- IP configuration
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- Select menu
1. IP mode : PPPoE
2. Change PPPoE username : whoever
3. Cha ng e PPPoE user pas sw ord : pppoep wd
<ESC> Back , <ENTER> Refresh
-----> 2
En te r us er name : pppo eu se r
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- IP configuration
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- Select menu
1. IP mode : PPPoE
2. Change PPPoE username : pppoeuser
3. Cha ng e PPPoE user pas sw ord : pppoep wd
<ESC> Back , <ENTER> Refresh
-----> 3
Enter password : pppoepassword
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- IP configuration
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- Select menu
1. IP mode : PPPoE
2. Change PPPoE username : pppoeuser
3. Cha ng e PPPoE user pas sw ord : pppoep as sword
<ESC> Back , <ENTER> Refresh
----->
Figure 3-8. Set up usernam e and password for PPPoE account
Page 27

27
4: Serial Port Configuration
Serial port configuration screen can be reached through menu 2 in the main menu screen. Serial port
configuration menu contains four groups of the parameters such as Host mode configuration, UART
configuration, Cryptography configuration and additional options for serial data communication. Users
need to set up all those parameters for each serial port considering the serial device that will be
hooked up to the serial port.
- Host mode: Host mode related parameters for each serial port
- UART: Serial communication parameters such as baud rate, parity, data bits, stop bits, etc.
- Cryptography: Encryption related parameters for data communication
- Options: Timer related parameters for data communication
The following picture shows the initial screen of Serial Port configuration menu of the PS400. With the
PS100, only port#1 settings menu will be shown, while with the PS200, port#1 and port#2 settings
menu will be shown.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- Serial configuration
--------------------------------------------------------------------------Port# Mode Po rt Dest ination Ty pe Sett ings Flow
1 TC P s 6000 N/A RS232 9600-N-8-1 RTS/CTS
2 TC P s 6001 N/A RS232 9600-N-8-1 RTS/CTS
3 TC P s 6002 N/A RS232 9600-N-8-1 RTS/CTS
4 TC P s 6003 N/A RS232 9600-N-8-1 RTS/CTS
Select me nu
1. port# 1 settings
2. port# 2 settings
3. port# 3 settings
4. port# 4 settings
<ESC> Back , <ENTER> Refresh
----->
Figure 4-1. Initial sc r een for serial port configur ation (PS400)
If users select the desired serial port number, the following screen of four menu groups for the
selected serial port will be displayed. Table 4-1 shows a hierarchical view of all the menu items of
serial port configuration.
Page 28

28
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- Serial configuration --> port #1
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- Select menu
1. Host mode configuration
2. UART Configur ation
3. Crypt ography Configur ation
4. Option
<ESC> Back , <ENTER> Refresh
----->
Figure 4-2. Initial sc r een for each serial port configuration
Table 4-1. Hierarchic al v iew of the Serial Port Configuration m enu items
Host Mode
TCP Server
Local Port
Host Mode
Destination IP/Port
Enable/Disable
TCP Client
Cyclic
Connection
Interval
Host Mode
Local Port
Destination IP/Port
Enable/Disable
TCP Server/Client
Cyclic
Connection
Interval
Host Mode
Local Port
UDP Tunneling
Destination IP/Port
Host Mode
UDP Server
Local Port
Host mode
Modem Emulation Host Mode
Type
Baud rate
1200/2400/4800/9600
19200/38400/57600/115200
Data bits 7/8
Parity None/Even/Odd
Stop bits 1/2
Flow control None, Hardware (RTS/CTS)
Always HIGH
Always LOW
DTR behavior
Show TCP connection
None
Open/Close TCP connection
RS232
DSR behavior
Accept TCP connection only by HIGH
RS485 echo TYPE, Baud rate, Data bits, Parity, Stop bits
RS485 non-echo TYPE, Baud rate, Data bits, Parity, Stop bits
UART
RS422 TYPE, Baud rate, Data bits, Parity, Stop bits
None Method
Method
Cryptography
3DES
Key string
Inactivity timeout
Options
Inter-character timeout
Page 29

29
4.1 Host mode configuration
4.1.1 Overview
Host mode represents the operating session mode of the HelloDevice Pro Series. Several host modes
are available for the data communication between serial devices and remote hosts. Since TCP is
connection-oriented protocol, server, client, server/client modes are provided. Other than those TCP
based modes, UDP mode is provided for connectionless communication. Modem emulation mode
supports several basic AT commands for TCP session control so that users can change the host mode
on-line from the serial device by using AT commands. Table 4-2 shows the brief description of the host
modes.
Table 4-2. The HelloDevic e P r o S er ies T CP/IP s es s ion modes
Mode Description
TCP server Select this mode, when users want the HelloDevice Pro Series to operate as a TCP server.
The HelloDevice Pro Series stands by until there is any TCP connection request. If TCP
connection is not already established at that time, the HelloDevice Pro Series accepts the
request and the session is established. In the established state, it transmits the data through
the corresponding serial port if there is any data from the remote host. Since the HelloDevice
Pro Series supports only one TCP session per serial port, the additional TCP connection
request will be rejected if already established
. This mode is useful when users want to send
data to the serial device at any time they want.
TCP client Select this mode, when users want the HelloDevice Pro Series to operate as a TCP client.
When the serial device sends data or pre-defined timer is expired, the HelloDevice Pro Series
tries to establ ish a TCP connection to a remote server through its TCP port. If a TCP session is
established between them, the HelloDevice Pro Series will send data to the server. If there’s
any data from the server during the session, it will also send the data through the serial port.
However, if the HelloDevice Pro Series failed to connect to the remote server, the data from
the serial port will be discarded. This is useful when the serial device initiates sending data
such as data gathering application.
TCP
server/client
If you are not sure which mode to choose, select this mode since it will be applied in most
applications. In this mode, the HelloDevice Pro Series operates as TCP server AND client. If
the connection is not established, it will accept all incoming connection and connect to the
remote host if there are any data from the serial device. Otherwise, it will send data back and
forth. In summary, the HelloDevice Pro Series will work as if it is virtually connected to the
remote host.
UDP
tunneling
The UDP tunneling mode operation is similar to that of TCP server/client mode except that it is
based on UDP protocol and only one pre-defined remote host is able to communicate with the
HelloDevice Pro Series.
UDP server While UDP tunneling mode allows only one remote host for UDP communications, UDP server
mode allows any remote host to access the HelloDevice Pro Series. In this mode, the
HelloDevice Pro Series gets the information on the remote host from the latest incoming
datagram information.
Modem
emulation
Select this mode when the serial device already supports modem AT commands or users
want to perform the session control by using AT commands. Only TCP session is supported.
Page 30

30
A factory default host mode is TCP Server, and users can select the mode by using the menu,
Serial Port Configuration–host mode Configuration–Host mode.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- serial configuration -->port# 1 --> TCP/IP
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- Select menu
1. Host mode : TCP Server
2. Local port : 6000
<ESC> Back , <ENTER> Refresh
-----> 1
Select host mode
1 = TCP Se rver, 2 = TCP Cl ie nt, 3 = TCP Serve r / Cl ie nt
4 = UDP Server / Client, 5 = modem emulation
----->
Figure 4-3. Set up Host Mode
For easier understanding of TCP modes, a simplified State Tran sition Diagram is often used. And
too help users understand the diagram, the TCP state of the HelloDevice Pro Series is briefly
described as follows.
- Listen
It represents “a waiting for a connection request from any remote host”. It is a default start-up
mode when it is set as TCP server mode. This state is valid only in TCP server mode operation.
- Closed
It means “No connection state at all”. If the data transfer is completed, the state is changed to this
state if one of the host requests disconnection request. If it is in TCP server mode, the state is
automatically changed to [Listen] mode. It is a default start-up mode when it is set as TCP client
mode or TCP server/client mode.
- Sync-Received
In TCP server mode, the state will be changed from [Listen] to [Sync-Received], if any remote
host sends connection request. If the HelloDevice Pro Series accepts the request, the state will be
changed into [Established]. This state is not valid in TCP client mode.
- Sync-Sent
If the HelloDevice Pro Series sends a connection request to a remote host, the state is changed
from [Closed] to [Sync-Sent]. This state is maintained until the remote host accepts the
connection request. This state is valid only in TCP client mode.
- Established
It represents “an open connection”. If one of the hosts accepts a connection request from the
other host, the connection is opened and state is changed into [Established].
Page 31

31
- Data
When it is in [Established] state, data from a host will be transferred to the other one. For easier
understanding of the TCP session operation, we called the state as [Data] state when actual data
transfer is performed. Actually, the [Data] mode is a part of [Established] state as is described in
the RFC 793 [Transmission Control Protocol]. This is a normal state for the data transfer phase of
the connection.
4.1.2 TCP server mode operations
The HelloDevice Pro Series works as a TCP server, and the default TCP state is [Listen] in this mode.
The HelloDevice Pro Series supports only one TCP socket connection per one serial port. If a
connection is currently established, the additional connection requests will be rejected. The remote
host will be either Ethernet-Serial communication devices acting as a TCP client or a socket program
acting as a TCP client running on users’ PC.
1) Typical State Transition
[Listen] --> [Sync-Received] --> [Established] --> [Data] --> [Closed] --> [Listen]
At start-up, an initial TCP state is [Listen]. If there is any incoming TCP connection request, the state
will be changed into [Sync-Received], then [Established], which means a session is opened. For a
while, data will be transferred between the hosts. This is the [Data] state. The session will be
disconnected due to the request of one of them, which is [Closed] state. And then, the state is
automatically changed to its original state, [Listen].
2) Operations
Serial data transfer
When a session has been established, the HelloDevice Pro Series reads the data from the serial
port buffer till internal serial buffer is full or inter-character time interval reaches the time specified
as inter-char acter tim eout value. Then, it transfers the data to the IP address (or domain name) of
the remote host (See Options in section 4.4 for more details on inter-character tim eout). If there’s
no remote host connected to the HelloDevice Pro Series, all the incoming data from the serial port
are discarded.
Session disconnection
The connected session will be disconnected when the remote host sends disconnection request
or when no data transfer activity is found through the serial port for a certain amount of time,
which is “Inactivity tim eout” (See Options in section 4.4 for details on Inactivit y timeout).
Page 32

32
IP address filtering
The HelloDevice Pro Series will not accept the incoming connection request from the remote
hosts which are not in the host list (See Remote Host Access Control in section 5.1 for details).
Figure 4-4 shows the State Transition Diagram of the session operations in TCP server mode.
Closed
Established
Listen
Data
Incoming TCP connection request
Inactivity time-out
Incoming TCP
disconnection request
Incoming data via serial port
Incoming data
from remote host
Sync-Recvd
Accept Reject
Figure 4-4. State Trans ition Diagram of TCP server mode
3) Parameters
Local port
This is the TCP port number through which remote host can connect a TCP session, and, send
and receive data. Incoming connection request to the ports other than Local Port will be rejected.
The HelloDevice Pro Series does not restrict the number to a specific range, but it is strongly
recommended not to use the well-known ports for certain application (See Appendix D. Well-
known Port Numbers). To change the port number, select menu 2 on the TCP Server mode
configuration screen.
Page 33

33
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- serial configuration -->port# 1 --> TCP/IP
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- Select menu
1. Host mode : TCP Server
2. Local port : 6000
<ESC> Back , <ENTER> Refresh
-----> 2
En te r lo cal port num be r : 60 01
Figure 4-5. Changing Local T CP P ort number
4.1.3 TCP client mode operations
The HelloDevice Pro Series works as a TCP client, and the default TCP state is [Closed] in this mode.
The remote host will be either Ethernet-Serial communication devices acting as a TCP server or a
socket program acting as a TCP server running on users’ PC.
1) Typical State Transition
[Closed] --> [Sync-Sent] --> [Established] --> [Data] --> [Closed]
At start-up, an initial TCP state is [Closed]. If there is any incoming data through the serial port, the
HelloDevice Pro Series will try to connect to a user-defined remote host. Then, the state will be
changed to [Sync-Sent], which means the connection request is being sent. If the remote host accepts
the request, the state will be changed into [Established], which means a session has been opened.
For a while, data will be transferred between the hosts. This is [Data] state. The session will be
disconnected due to the request of one of them, which is its original state, [Closed].
2) Operations
Serial data transfer
Whenever the serial device sends data through the serial port of the HelloDevice Pro Series, data
will be accumulated to the serial port buffer of the HelloDevice Pro Series. If the internal serial port
buffer is full or inter-character time interval reaches to the time specified as inter-character timeout
value, it tries to connect to the user-defined IP address (or domain name) of the remote host, if
TCP session is not established yet (See Options in section 4.4 for details on inter-character
timeout). If the HelloDevice Pro Series succeeds in connecting to the remote host, the data in the
serial port buffer will be transferred to the host. Otherwise, all the data stored in the buffer will be
cleared.
Session disconnection
The connected session will be disconnected when the remote host sends disconnection request
Page 34

34
or when no data transfer activity is found through the serial port for certain amount of time, which
is “Inactivity timeout” (See Options in section 4.4 for details on Inactivity timeout). All the data
remained in the serial port buffer will be cleared when it is disconnected.
Connection request from remote host
All the incoming TCP connection requests will be rejected in TCP client mode.
Cyclic Connection
It Cyclic Connection function is enabled, the HelloDevice Pro Series will make an attempt to
connect to the user-defined remote host at certain interval even if there’s no incoming serial data
from the device. If the remote host prepares certain data, it will be transferred to the serial device
via its serial port after the connection is established. Eventually, users can monitor the serial
device periodically by making the remote host send the serial command to the HelloDevice Pro
Series whenever it is connected to the remote host. This option is useful when users need to
gather the device information periodically even if the serial device does not send its data
periodically. Figure 4-6 shows the State Transition Diagram of the session operations in TCP client
mode.
Established
Closed
Data
Incoming data via
serial port
Inactivity time-out
TCP connection request rejected
Or
internal TCP timer is expired
TCP connection request accepted
Sync-Sent
Incoming data via
serial port
Incoming data
from remote host
Incoming TCP
disconnection request
Cyclic connection
interval time-out
Figure 4-6. State Trans ition Diagram of TCP client mode
Page 35

35
3) Parameters
Remote IP address (or domain name) and Remote Port
This is the information on the remote host to which the HelloDevice Pro Series will try to connect
in TCP client mode. The IP address (or domain name) should be specified together with the TCP
port number. To specify the information on the remote host, select menu 2 on the TCP Client
mode configuration screen. The format of remote host information is as follows.
[IP address (or domain name)]:[TCP Port number]
e.g.)
211.116.20.197:1221 : IP address 211.116.20.197, Port 1221
ser.sena.com:6001 : domain name ser.sena.com, Port 6001
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- serial configuration -->port# 1 --> TCP/IP
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- Select menu
1. Host mode : TCP Client
2. Destination IP & port : 192.168.1. 120:6010
3. Cyclic connection : Disable
<ESC> Back , <ENTER> Refresh
-----> 2
En te r de stinatio n IP and port (ex: 192 .1 68.1.1:70 01 )
-----> 192.168.1.200:6001
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- serial configuration -->port# 1 --> TCP/IP
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- Select menu
1. Host mode : TCP Client
2. Destination IP & port : 192.168.1. 200:6001
3. Cyclic connection : Disable
<ESC> Back , <ENTER> Refresh
----->
Figure 4-7. Set up remote host information
Cyclic connection interval
This is the time interval at which the HelloDevice Pro Series will try to connect to the remote host
regardless of the existence of incoming data from the serial port. If the interval is specified with a
valid value other than 0, the function is enabled. The time interval will be the specified value by
the unit of minute. To specify the interval, select menu 3 on the TCP Client mode configuration
screen.
Page 36

36
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- serial configuration -->port# 1 --> TCP/IP
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- Select menu
1. Host mode : TCP Client
2. Destination IP & port : 192.168.1. 200:6001
3. Cyclic connection : Disable
<ESC> Back , <ENTER> Refresh
-----> 3
Enter cyclic connection interval in minute(0=disable) : 10
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- serial configuration -->port# 1 --> TCP/IP
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- Select menu
1. Host mode : TCP Client
2. Destination IP & port : 192.168.1. 200:6001
3. Cyclic connection : 10 Min
<ESC> Back , <ENTER> Refresh
----->
Figure 4-8. Set up Cyclic Connec tion interval
4.1.4 TCP server/client mode operations
The HelloDevice Pro Series works as either TCP server or client according to the situation. This will be
the typical mode for most applications, since it will transfer the data either from serial port or from TCP
port. The default TCP state is [Listen] which is the same as that of TCP server mode.
1) Typical State Transition
[Listen] --> [Sync-Received] --> [Established] --> [Data] --> [Closed] --> [Listen]
Or
[Listen] --> [Sync-Sent] --> [Established] --> [Data] --> [Closed] --> [Listen]
The initial state is [Listen]. If there are data coming from the serial port, it will connect to the remote
host as a TCP client. If there is incoming connection request from the remote host, it will accept the
connection as a TCP server, and then transfer data through the serial port. Thus, users can assume
that the HelloDevice Pro Series is always connected to the specified remote host.
2) Operations
The only difference from TCP server mode is that the HelloDevice Pro Series will try to connect and
send serial data to the remote host even if the TCP session is not established. The difference from
TCP client mode is that it will accept incoming connection request from remote host if the session is
not established. The detailed operation principles are the same as that of TCP server and TCP client
Page 37

37
mode. See section 4.1.2 and 4.1.3 for more details on each session mode.
Established
Inactivity time-out
TCP connection request rejected
Or internal TCP time-out
TCP connection request accepted
Sync-Sent
Incoming data via serial port
Incoming data
from remote host
In-coming TCP Close request
Listen
Incoming TCP connection request
Incoming data via serial port
Sync-Recvd
Reject
Accept
Closed
Data
Figure 4-9. State Trans ition Diagram of TCP server/ c lient mode
3) Parameters
Local Port
See section 4.1.2 for details
Remote IP address (or domain name) and Remote Port
See section 4.1.3 for details
Cyclic connection interval
See section 4.1.3 for details
Page 38

38
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- serial configuration -->port# 1 --> TCP/IP
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- Select menu
1. Host mode : TCP Server & client
2. Local port : 6000
3. Destination IP & port : 192.168.1. 200:6001
4. Cyclic connection : 10 Min
<ESC> Back , <ENTER> Refresh
----->
Figure 4-10. Set up parameters for TCP server/client mode
4.1.5 UDP tunneling mode operations
The UDP tunneling mode operation is similar to that of TCP server/client mode except that it is based
on UDP protocol and only one pre-defined remote host is able to communicate with the HelloDevice
Pro Series. Users do not have to configure the parameter of inactivity timeout, since UDP is a
connectionless protocol.
1) Operations
If a remote host sends a UDP datagram to the UDP Local port of the HelloDevice Pro Series, it checks
if the IP address of the host is the same as the pre-defined Destination IP address. If the IP addresses
are the same, the HelloDevice Pro Series transfers the data through the serial port. Otherwise, the
HelloDevice Pro Series discards the incoming UDP datagram.
If there is any incoming data from the serial port, the HelloDevice Pro Series transfers the data to the
remote host defined as Destination IP & Port. Although the remote port is not open, the HelloDevice
Pro Series does not transfer the data again.
2) Parameters
Local port
The concept is the same as that of TCP communication. See TCP Server mode operat ions in
the section 4.1.2 for details.
Remote IP address (or domain name) and Remote Port
The concept is the same as that of TCP communication. See TCP Client mode operations in the
section 4.1.3 for details.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- serial configuration -->port# 1 --> TCP/IP
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- Select menu
1. Host mode : UDP tunneling
2. Local port : 6000
Page 39

39
3. Destination IP & port : 192.168.1. 200:6001
<ESC> Back , <ENTER> Refresh
----->
Figure 4-11. Set up parameters for UDP tunneling mode
4.1.6 UDP server mode operations
While UDP tunneling mode allows only one remote host for UDP communications, UDP server mode
allows any remote host to access the HelloDevice Pro Series. In this mode, the HelloDevice Pro
Series gets the information on the remote host from the latest incoming datagram information and
keeps this information for inactivity timeout management, which is configured in Serial
Configuration - Options menu (see 4.4.1 for detail).
1) Operations
In UDP server mode, a remote host should initiate UDP data communication. If there is any incoming
UDP datagram to the HelloDevice Pro Series, it will make a virtual connection with the remote host for
inactivity timeout duration. Before the inactivity timeout value expires, the HelloDevice Pro Series
transfers the UDP data to the serial port, and send back the data from the serial port to the latest
remote host who sent the UDP datagram. Virtual connection timeout will be reset to inactiv ity tim eout
value whenever there is any data transfer between remote host and the serial device. If other remote
hosts send UDP datagrams while a virtual connection is established, the UDP datagram will be
discarded. If there is no data transfer during inactiv ity timeout, the virtual connection will be closed and
other remote hosts can access the HelloDevice Pro Series from then on.
2) Parameters
Local port
The concept is the same as that of TCP communication. See TCP Server mode operat ions in
the section 4.1.2 for details.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- serial configuration -->port# 1 --> TCP/IP
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- Select menu
1. Host mode : UDP server
2. Local port : 6000
<E SC > Ba ck, <ENTER > Re fr esh
----->
Figure 4-12. Set up parameters for UDP server mode
Page 40

40
4.1.7 Modem emulation mode operations
In modem emulation mode, the serial port process acts as if it is a modem attached to the serial
device. It accepts AT modem commands and answers to them, as modems would do. It also handles
the modem signals correctly. Modem emulation mode is useful in the following cases.
- There already exists a modem attached to the users’ serial device.
If users’ serial device already has a modem for phone-line connection, it can be just replaced by
the HelloDevice Pro Series for Ethernet connection. What users need to do is to use an IP
address (or domain name) instead of phone number as a parameter of ATA/ATDT commands.
- It is required to send serial data to the multiple remote hosts.
If the serial device should send data to the multiple hosts, modem emulation mode is required.
For example, the first data from the serial device can be sent to the first data acquisition server
and the second to the second server. What user device has to do is to change the IP address (or
domain name) parameter whenever the device sends ATD(T) XXX command.
By using the modem emulation mode of the HelloDevice Pro Series, users can have their serial device
connected to the Ethernet network easily, which is cheaper than using phone line modem. Table 4-3 is
a summarized AT command table which is supported by the HelloDevice Pro Series. Table 4-4 is a
summarized AT commands response numeric codes. Figure 4-12 shows the typical case of the serial
port command flow when ATDA command is used to connect to the Ethernet network.
Table 4-3. AT commands suppor ted in the Pro Series
Command Internal Operation
Response
1
(Verbose Code)
+++ Return to command input mode OK
A/ Repeat last command
AT? Check status of TCP connection
If connected,
OK[CR][LF]
If disconnected,
NO CARRIER [CR][LF]
ATD(T)[remote IP]:[remote
port]
Set TCP mode as TCP client mode. And then, try to connect to
the specified remote host.
e.g. atdt192.168.1.9:1002:
Connect to IP address, 192.168.1.9, port 1002
If successful,
CONNECT [CR][LF]
If failure in connection,
NO CARRIER [CR][LF]
If other errors,
ERROR [CR][LF]
AT or ATZ Initialize TCP socket and serial port
ATA[Local port number]
Set TCP mode as TCP server mode. And then, set TCP state
as [Listen].
If successful,
OK [CR][LF]
1
If Echo mode is enabled, the command will be sent back first. And then, c orresponding r esponse will be sent. If disabled, only
respons e will be sent.
Page 41

41
ATEn
E, E0: Disable echo
E1: Enable echo
ATHn
H, H0, H1: Disconnect current TCP connection
All the data will be cleared
ATOn O, O0: Turn to data mode
ATQn
Q, Q0: Response display on (default)
Q1: Response display off
ATVn
V, V0: Response = <numeric code> [CR][LF]
V1 (default): Response = <verbose code> [CR][LF]
AT&D n
D, D0: ignore DTR(PC) signal
D2(default): disconnect TCP session
AT&Fn F, F0, F1: Restore default modem settings
AT&Kn
K, K0: No flow control
K3: RTS/CTS flow control (default)
K4: Xon/Xoff (if supported)
AT&Sn
S, S0: DSR(PC) always high
S1: DSR(PC) shows TCP connection
If failure,
ERROR [CR][LF]
ATIn
I, I0 : display “Sena Technologies, Inc.”
I3 : display model number
Others : display “OK”
AT\Tn
Set inactivity timer to n minutes
\T, \T0: inactivity timer disabled (default)
OK [CR][LF]
AT\Tsn
Set inactivity timer to n seconds
\Ts, \Ts0: inactivity timer disabled (default)
OK [CR][LF]
ATBn , ATCn, ATLn , ATMn ,
ATNn , ATP, AT T, ATYn,
AT%Cn, AT % En, AT & B n ,
AT&G n, AT&I n, AT&Q n ,
AT&V, AT } Mn, AT \ An,
AT\Bn, AT\Nn
None OK [CR][LF]
ATS? , ATSn=x, AT & C n ,
AT&W n, AT&Zn=x
None ERROR [CR][LF]
ATFn None
If n=1
OK [CR][LF]
If others,
ERROR [CR][LF]
ATW n, ATXn No ne
If n=0
OK [CR][LF]
If others,
ERROR [CR][LF]
Table 4-4. AT commands Response Code
Verbose Code
(After “ATV1” command executed)
Numeric Code
(After “ATV0” command executed)
Description
OK 0 Command executed
CONNECT 1 Modem connected to line
RING 2 A ring signal has been detected
NO CARRIER 3 Modem lost carrier signal
ERROR 4 Invalid command
Page 42

42
HelloDevice
Pro Series
Serial
Device
AT Z
AT Z
OK
AT DT
CONNECT
DATA….
DATA….
AT DT
+++
AT H
AT H
Command mode
OK
TCP mode
Command mode
TCP connection
Request
TCP connection
Established.
DATA….
DATA….
TCP
disconnection
NO CARRIER
Request TCP
disconnection
Figure 4-13. Typical cas e of command/data flow of modem emulat ion m ode
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- serial configuration -->port# 1 --> TCP/IP
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- Select menu
1. Host mode : Modem emulation
<ESC> Back , <ENTER> Refresh
----->
Figure 4-14. Set Modem Emulation mode
4.2 UART configuration
To attach the serial device to the HelloDevice Pro Series serial port, its serial port operation should
match exactly to that of the serial device. UART parameters are required to match this serial
communication operation. To change the UART parameters, users need to go to Serial port
Page 43

43
configuration-UART configuration menu screen.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- Serial configuration --> port#1 ---> UART
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- Select menu
1. Typ e : RS 232
2. Baud rate : 9600
3. Data bits : 8
4. par it y : None
5. Stop Bits : 1
6. Flo w co ntrol : Hard wa re
7. DTR behavior : Always High
8. DSR behavior : None
<ESC> Back , <ENTER> Refresh
----->
Figure 4-15. UART conf igur ation menu screen
4.2.1 Ty pe
First of all, the HelloDevice Pro Series and the serial device must agree on the serial communication
type, which is one of RS232, RS422, RS485 echo mode or RS485 non-echo mode. The HelloDevice
Pro Series serial ports are configured for RS232 communication as a factory default, but they can also
be configured for RS422 and RS485 communication. To change the serial communication type, set up
the mode in the Type menu. See Appendix B for serial port connections due to the Type setup.
The HelloDevice Pro Series supports two types of RS485 communication – echo mode and non-echo
mode, which are both two-wire mode. In RS485 echo mode, all data sent to the serial port are
received back from the serial port automatically and compared with the data sent for the data integrity
while there is no action of receiving-back in non-echo mode.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- Serial configuration --> port#1 ---> UART
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- Select menu
1. Typ e : RS 232
2. Baud rate : 9600
3. Data bits : 8
4. par it y : None
5. Stop Bits : 1
6. Flo w co ntrol : Hard wa re
7. DTR behavior : Always High
8. DSR behavior : None
<ESC> Back , <ENTER> Refresh
-----> 1
Select serial type
1 = RS232, 2 = RS485 Echo, 3 = RS485 NonEcho, 4 = RS422
----->
Page 44

44
Figure 4-16. Set up Serial c ommunication type
4.2.2 Baud rate
The valid baud rate for the HelloDevice Pro Series is as follows.
1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 14400, 19200, 38400, 57600 and 115200
The baud rate can be changed by selecting the menu of Serial port configuration-UART
configuration–Baud rate.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- Serial configuration --> port#1 ---> UART
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- Select menu
1. Typ e : RS 232
2. Baud rate : 9600
3. Data bits : 8
4. par it y : None
5. Stop Bits : 1
6. Flo w co ntrol : Hard wa re
7. DTR behavior : Always High
8. DSR behavior : None
<ESC> Back , <ENTER> Refresh
-----> 2
Select baud rate
1 = 1200, 2 = 2400, 3 = 4800, 4 = 9600
5 = 19200, 6 = 38400, 7 = 57600, 8 = 115200
----->
Figure 4-17. Set up the baud r ate
4.2.3 Data bits, Stop bits, Parity
The factory default setting of the data bits, stop bits and parity are 8, 1 and None. They can be
changed using the menu 3, 4 and 5.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- Serial configuration --> port#1 ---> UART
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- Select menu
1. Typ e : RS 232
2. Baud rate : 9600
3. Data bits : 8
4. par it y : None
5. Stop Bits : 1
6. Flo w co ntrol : Hard wa re
7. DTR behavior : Always High
8. DSR behavior : None
<ESC> Back , <ENTER> Refresh
-----> 3 (o r 4 or 5)
Se le ct data bits (1 = 7 bi ts , 2 = 8 bi ts) :
(Or
Select pa ri ty (1 = No ne, 2 = Even, 3 = od d) :
Sele ct stop bits (1 = 1 bit , 2 = 2 bits) :
Page 45

45
)
Figure 4-18. Set up the data bits, stop bits, parity
4.2.4 Flow control
The factory default setting of the flow control is None. Only hardware flow control using RTS/CTS is
supported by the HelloDevice Pro Series. Hardware flow control method controls data communication
flow by sending signals back and forth between two connected devices.
Note:
Flow control is supported only in RS232 mode. RS422 and RS485 mode do not support any kind of
flow control method in hardware or software.
It can be configured using the menu 6.Flow control.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- Serial configuration --> port#1 ---> UART
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- Select menu
1. Typ e : RS 232
2. Baud rate : 9600
3. Data bits : 8
4. par it y : None
5. Stop Bits : 1
6. Flo w co ntrol : Hard wa re
7. DTR behavior : Always High
8. DSR behavior : None
<ESC> Back , <ENTER> Refresh
-----> 6
Select flow control (1 = None, 2 = Hardwa re) :
Figure 4-19. Set up the flow control
4.2.5 DTR/DSR behavior
The purpose of the DTR/DSR pin is to emulate modem signal control or to control TCP connection
state by using serial port signal. The DTR is a write-only output signal, whereas the DSR is a read-only
input signal in the HelloDevice Pro Series side.
The DTR output behavior can be set to one of three types: always high, always low or show TCP
connection. If the DTR behavior is set to show TCP connection, the state of the DTR pin will be
maintained high if the TCP connection is established.
The DSR input behavior can be set to one of three types: none, open/close T CP connection or allow
TCP connection only by high. Open/close TCP connection is valid only if the host mode is a TCP client
or equivalent. If the DSR behavior is set to open/close TCP connection, the high state of the DSR pin
will make the HelloDevice Pro Series send a connection request to the specified destination host,
Page 46

46
whereas the low state close a connection. Allow TCP connection only by HIGH is valid only if host
mode is TCP server or equivalent. If this option is set, the incoming TCP connection request will be
accepted only when the DSR signal is high state.
-----> 7
Select DTR output behavior
1 = Always HIGH
2 = Always LOW
3 = Show TCP connection (HIGH while connected)
--->
Figure 4-20. Set up the DTR out put behavior
-----> 8
Select behavior on DSR input
1 = None
2 = Allo w TCP connec ti on only by HIG H
(TC P server or correspo nding mode only)
3 = Open/close TCP connect ion
(Open = HIGH, Close = LOW, TCP client or corresponding mode only)
----->
Figure 4-21. Set up the DS R output behav ior
4.3 Cryptography configuration
The HelloDevice Pro Series supports encrypted sessions for only TCP modes including modem
emulation mode (not UDP mode). By setting the cryptography method as 3DES, the HelloDevice Pro
Series can communicate with other HelloDevice Pro Series in encrypted sessions. If you need your
PC to communicate with HelloDevice Pro Series using encryption, please contact Sena technical
support.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- Serial configuration --> port#1 ---> Cryptography
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- Select menu
1. Cryptography method : None
<ESC> Back , <ENTER> Refresh
-----> 1
Se le ct cryptogra ph y me thod (1 = None , 2 = 3D ES) : 2
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- Serial configuration --> port#1 ---> Cryptography
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- Select menu
1. Cryptography method : 3DES
2. Key string : Encryption
<ESC> Back , <ENTER> Refresh
-----> 2
En te r ar bitrary ke y st ri ng (maximu m 31 chars)
-----> Anykeystring
Page 47

47
Figure 4-22. Set up the cry ptography method and cryptography key s tring
4.4 Options
4.4.1 Inactivity timeout
The purpose of this parameter is to maintain the TCP connection state as Closed or Listen in TCP
host modes or to close UDP virtual connection in UDP server mode unless there is any data transfer
between the serial device and the HelloDevice Pro Series. If there is no incoming or outgoing data
through the serial port during the specified inactiv ity timeout interval, the existing TCP connection or
virtual UDP connection will be closed automatically.
If the value of inact ivity timeout is set to 0 and the host mode is set to one of the TCP modes, the
current TCP connection is maintained unless there’s no connection close request. Although inactivity
timeout is disabled, the HelloDevice Pro Series will check the connection status between the
HelloDevice Pro Series and the remote host by sending “keep alive” packets periodically. If the remote
host does not answer the packets, it is regarded that the connection is down unintentionally. Then, the
HelloDevice Pro Series will force to close the existing TCP connection.
If the value of inac tiv ity timeout is set to 0 and the host mode is set to UDP server mode, virtual UDP
connection with the first remote host that sends UDP packet to the HelloDevice Pro Series will be
maintained forever till device is rebooted.
Note:
At least, this value should be set larger than that of inter-char acter timeout. To prevent the unintended
loss of data due to the session disconnection, it is highly recommended that this value is set large
enough so that the intended data transfer is completed.
4.4.2 Inter-character timeout
This parameter defines the interval that the HelloDevice Pro Series fetches the overall serial data from
its internal buffer. If there is incoming data through the serial port, the HelloDevice Pro Series stores
data into the internal buffer. The HelloDevice Pro Series transfers data stored in the buffer via TCP/IP,
only if the internal buffer is full or if the inter-character time interval reaches to the time specified as
inter-charact er timeout.
Optimal inter-character timeout would be different according to your application but at least it must be
larger than one character interval within specified baud rate. For example, assume that the serial port
is set to 1200 bps, 8 Data bits, 1 stop bit, and no parity. In this case, the total number of bits to send a
character is 10 bits and the time required to transfer one character is
Page 48

48
10 (bits) / 1200 (bits/s) * 1000 (ms/s) = 8.3 ms.
Therefore, you have to set inter-character timeout to be larger than 8.3 ms. The inter-character
timeout is specified in milliseconds and must be larger than 10 ms.
If users want to send the series of characters into a packet, serial device attached to the HelloDevice
Pro Series should send characters without time delay larger than inter-character timeout between
characters and the total length of data must be smaller than or equal to the HelloDevice Pro Series
internal buffer size. The buffer size of HelloDevice Pro Series is 600 bytes per a port.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- Serial configuration --> port#1 ---> option
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- Select menu
1. Ina ct ivity time ou t : 10 0 sec
2. Inter-character timeout : 1 ms
<ESC> Back , <ENTER> Refresh
-----> 1
Enter inactivity timeout value to disconnect TCP connection in seconds
( 1 - 3600)Sec , 0 = unlimited
-----> 300
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- Serial configuration --> port#1 ---> option
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- Select menu
1. Ina ct ivity time ou t : 30 0 sec
2. Inter-character timeout : 1 ms
<ESC> Back , <ENTER> Refresh
-----> 2
En te r In ter-char ac te r timeout in mil lisecond s (1 - 10 00 0) : 100
Figure 4-23. Set up the options of inactivity tim eout and Inter - c har ac ter timeout
Page 49

49
5: Advanced Options Configurations
With advanced options, you can configure remote host access control, locating server configuration
and manual DNS server settings. Table 5-1 shows the hierarchical view of advanced options.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- Advanc ed options
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- Select menu
1. Remote host access control
2. Man ua l DNS config ur at ion for DHCP & PPP oE
3. Locating server configuratio n
<ESC> Back , <ENTER> Refresh
----->
Figure 5-1. Main menu scr een of the Advanced Options
Table 5-1. Hierarchical view of the advanced options menu item s
Telnet configuration enable/disable
Allowed remote hosts for configuration
Remote Host access control
Allowed remote hosts for port#n
Enable/Disable
Primary DNS
Manual DNS for DHCP & PPPoE
Secondary DNS
Mode Enable
Server IP/Port
Locating server Configuration
Disable Mode
5.1 Remote host access control
The HelloDevice Pro Series has an IP address based filtering method to control the access to the
telnet or the serial port of the HelloDevice Pro Series from the remote hosts to prevent unauthorized
access. You can allow one of the following cases by setting the parameter.
- Only one host of specific IP address can access the HelloDevice Pro Series
- Hosts on the specific subnet can access the HelloDevice Pro Series
- Any host can access the HelloDevice Pro Series
Page 50

50
5.1.1 Configuration access
The HelloDevice Pro Series remote console access feature can be enabled or disabled by selecting
submenu 1.Remote configuration by Telnet. Factory default setting of this feature is
“Enabled”. If the remote configuration feature is enabled, you can specify a host or hosts allowed to
access the HelloDevice Pro Series for configuration by selecting submenu 2.Allowed remote
hosts for configuration. When you select this menu, you have to enter the IP address or
subnet to be allowed to access the HelloDevice Pro Series in the format of “subnet or IP
address/subnet mask”. If you want to allow only a specific host to access the HelloDevice Pro Series
for configuration, enter “IP address/255.255.255.255” such as 192.168.1.100/255.255.255.255. If you
want to allow any hosts on the specified subnet, enter “subnet/subnet mask” such as
“192.168.1.0/255.255.255.0”. If you want to allow any host, enter “0.0.0.0/0.0.0.0”. Please refer to
Table 5-2 for more details. Default setting of allowable remote hosts for configuration is “Any”.
Table 5-2 Input examples of allowed remote hosts
Allowable Hosts Input format
Any host 0.0.0.0/0.0.0.0
192.168.1.120 192.168.1.120/255.255.255.255
192.168.1.1 ~ 192.168.1.254 192.168.1.0/255.255.255.0
192.168.0.1 ~ 192.168.255.254 192.168.0.0/255.255.0.0
192.168.1.1 ~ 192.168.1.126 192.168.1.0/255.255.255.128
192.168.1.129 ~ 192.168.1.254 192.168.1.128/255.255.255.128
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- Advanced options -> Remote host access control
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- Select menu
1. Rem ot e configur at io n by telnet : En ab le
2. All ow ed remote ho st s fo r configur at ion : Any
3. Allowed remote hosts for Port#1 : Any
4. Allowed remote hosts for Port#2 : Any
5. Allowed remote hosts for Port#3 : Any
6. Allowed remote hosts for Port#4 : Any
<ESC> Back , <ENTER> Refresh
----->
Figure 5-2. Set up the par am eter s for telnet remote configuration acc es s
5.1.2 Serial Port access
Similar to remote configuration access control, the remote host for each serial port could be also
filtered based on IP address. You can use this option by selecting submenu 3~6. Refer to table 5-2 for
more details for the input format.
Page 51

51
-----> 2 (o r 3, 4, 5, 6)
Enter IP ad dr es s or network of ho st s al lowed to acce ss
Form at) IP-address/s ubnet-ma sk
Ex1) 192.168.1.0/255.255.255.0 to allow hosts of 192.168.1.*
Ex2) 192.168.1.99/255.255.255.255 to allow hosts of 192.168.1.99
Ex3) 0.0.0.0 / 0.0.0.0 t o allow any remot e host
-----> 192.168.0.0/255.255.0.0
Figure 5-3. Set up the serial por t access option
5.2 Manual DNS configuration
If DHCP servers or PPPoE servers do not provide DNS server configuration or if users want to use
different DNS servers from automatically provided ones, users can configure DNS servers manually.
Factory default setting of manual DNS server configuration is “Disabled”
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- Advanced options -> Manual DNS conf iguration
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- Select menu
1. Man ua l DNS config ur at ion for DHCP & PPP oE : Disable
<ESC> Back , <ENTER> Refresh
-----> 1
Do you want to configure DNS manually for DHCP & PPPoE? (y/n) : y
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- Advanced options -> Manual DNS conf iguration
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- Select menu
1. Man ua l DNS config ur at ion for DHCP & PPP oE : Enable
2. Primary DNS : 211.172.129.198
3. Secondary DNS : 211.172.129.19 9
<ESC> Back , <ENTER> Refresh
-----> 2
En te r Pr imary DNS IP add re ss : 211.116 .2 6.193
Figure 5-4. Manual DNS c onfiguration
5.3 Locating server
5.3.1 Overview
If users want the HelloDevice Pro Series to work as a server (TCP or UDP), the host acting as a client
has to know the IP address of the HelloDevice Pro Series. However, under the dynamic IP address
environment such as DHCP or PPPoE, arbitrary IP address is assigned to the PS200, which means
special consideration is required to access the current IP address of it. To tackle this problem, the
Page 52

52
HelloDevice Pro Series can be configured to send its IP address information whenever it is assigned a
new IP address or periodically to a specific server called locating server. You can operate a specific
host as your locating server or you can use your client host as a locating server simultaneously.
No special library or toolkit to implement locating server is provided. You have to implement your
program by yourself using the protocol provided below or contact us.
5.3.2 Locating server configuration
Locating server configuration screen is shown in Figure 5-5. You have to configure locating server IP
address, locating server UDP port number and connection time interval as well as to use locating
server feature or not. Initially locating server feature is configured as “Disabled”.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- Advanced options -> Locating server
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- Select menu
1. Use locating server : Disable
<ESC> Back , <ENTER> Refresh
-----> 1
Do you want to put your information to locating server ? (y/n): y
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- Advanced options -> Locating server
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- Select menu
1. Use locating server : Enable
2. Locating server connection tim e interval: 1 Min
3. Loc at ing server IP ad dr ess and port : 192 .168.1.21 1 : 99 99
<ESC> Back , <ENTER> Refresh
-----> 2
Enter locating server connection time interval in minutes (1 ~ 3600)
-----> 10
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- Advanced options -> Locating server
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- Select menu
1. Use locating server : Enable
2. Locating server connection tim e interval: 10 Min
3. Loc at ing server IP ad dr ess and port : 192 .168.1.21 1 : 99 99
<ESC> Back , <ENTER> Refresh
-----> 3
Enter locating server IP address and port (EX: 211.116.26.213:9999)
-----> 211.116.26.213:9999
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- Advanced options -> Locating server
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- Select menu
1. Use locating server : Enable
2. Locating server connection tim e interval: 10 Min
3. Locating server IP address and port : 211.116.26.213 : 9999
<ESC> Back , <ENTER> Refresh
----->
Figure 5-5. Locat ing s er v er configuration
Page 53

53
5.3.3 Locating server communication protocol
When the HelloDevice Pro Series sends its IP address information to the locating server, data format
will be as follows:
Description Magic Cookie Data(0) Data(1) … Data(n)
Bytes 4 Variable Variable Variable
Value F1-AA-AA-BC
Data(n) format
Description Data ID Length Data
Bytes 1 1 Variable
Value 1~6 Variable Variable
Data ID
ID Description Length
1 Device name var
2 Model name var
3 Serial number var
4 MAC address 6
5 IP address 4
6 Local ports* 2 or 4 or 8
Note:
Local ports: Each 2 byte data represent current local port setting of the corresponding serial port. Local ports data
length of PS100 should be 2 bytes, while 4 bytes and 8 bytes for PS200 and PS400 respectively. Configured
local TCP (or UDP) port numbers for each serial port are filled with network-order bytes, (i.e. higher bytes first). If
the host mode of a serial port is set to client mode, the local port number is regarded as 0.
Example of the PS100:
If port number = 6001 (1771h), Local ports data = 17h, 71h
If host mode is TCP client, Local port data = 0h, 0h
Example of the PS400:
Port1 = 6001 (1771h), Port2 = 6002 (1772h), Port3 = TCP client, Port4 = 6003(1773h)
Local ports data = 17h, 71h, 17h, 72h, 00h, 00h, 17h, 73h
Page 54

54
6: System Status and Log
The HelloDevice Pro Series provides system status display and log data display for management.
System status includes Ethernet status and status of each serial port. In addition, the HelloDevice Pro
Series can be configured to deliver log data automatically by email to a specific recipient. Users can
use or configure these features by selecting menu 3.System status & log in the main menu
screen.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- System status
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- Select menu
1. Display system status
2. Display log
3. Reset incoming/outgoing stat istics
4. Clear log
5. Send log by Email : Disable
<ESC> Back , <ENTER> Refresh
----->
Figure 6-1 System status menu
6.1 Display system status
Users can view current system status by selecting submenu 1.Display system status. System
status includes Ethernet status, serial port status and incoming/outgoing data statistics. Users can
reset Incoming/outgoing statistics by selecting submenu 3.Reset incoming/outgoing
statistics.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- System status
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- Select menu
1. Display system status
2. Display log
3. Reset incoming/outgoing stat istics
4. Clear log
5. Send log by Email : Disable
<ESC> Back , <ENTER> Refresh
-----> 1
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- System informati on
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- Model No.: PS200 Seri al No.: PS200-020 20001
Page 55

55
F/W REV. : V1.00 MA C Address : 00-01- 95-04-04 -33
Cur Status : Running Cu rrent time : 2038/ 05/10 04:34:10
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- IP information
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- IP Mode : Static IP Expiration : N/A
IP Address : 192.168.2.100 Subnetmask : 255.255.0.0
Gatewa y : 192.168. 1.1 R eceive/Tr ansmit errors : N/A
Primar y DNS : 211.172.129. 198 Secon dary DNS : 211.172.1 29.199
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- Port #0 informat ion
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- Connec tion Mode : Modem Emul Local port : 6000
Destin ation : 192.168.1. 120:6010 Host allowed : 0.0.0.0/0 .0.0.0
Incoming bytes : 268492 Outgoing bytes : 285121
UART : 9600-N-8-1-Hardware Encryption : 3DES
Inacti vity timeout : 300 sec Inter-cha racter timeout : 100 ms
...
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- Port #3 informat ion
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- Connec tion Mode : TCP Server Local port : 6003
Destin ation : 192.168.1. 120:6013 Host allowed : 0.0.0.0/0 .0.0.0
Incomi ng bytes : 0 Outgo ing bytes : 0
UART : 9600-N-8-1-Hardware Encryption : None
Inacti vity timeout : 100 sec Inter-cha racter timeout : 1 ms
End of Status
Press Enter
Figure 6-2. System st atus display (PS400)
6.2 Display log data
Users can see the system log by selecting submenu 2.Display log. Users can also clear current
log data by selecting submenu 4.Clear log.
2002-02-10 04:41:32 > ### No valid log table. Initialize logs ###
2002-02-10 04:41:44 > ### Boot up System Start ###
2002-02-10 04:41:44 > ### Start with Static IP by 192.168.2.100 ###
End of Log
Press Enter
Figure 6-3. System log display
6.3 Automatic log de li very by email
The HelloDevice Pro Series can be configured to send log data automatically if the number of log
messages unsent reaches the pre-defined number. Users can enable this feature by selecting
submenu 5.Send log by email. If this feature is enabled, you have to configure email related
Page 56

56
information such as number of logs to be sent, SMTP server, log recipient’s mail address and device
mail address.
The device mail address specifies sender’s mail address for the log delivery email. Almost every
SMTP servers check sender’s mail address with host domain name’s validity only. Consequently, for
the device mail address, you can use arbitrary username with registered hostname such as
arbitrary_user@yahoo.com or anybody@sena.com.
-----> 5
Select email log send option ( 1 = Enable , 2 = Disable) : 1
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- System status
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- Select menu
1. Display system status
2. Display log
3. Reset incoming/outgoing stat istics
4. Clear log
5. Send log by Email : Enable
6. Number of log message to send a mail(1 - 100) : 5
7. SMTP server : smtp.yourcompany .com
8. PS-400 mail address : PS200@your company.com
9. Log recipient's mail address : admin@yourcompany.com
<ESC> Back , <ENTER> Refresh
----->
Figure 6-4 Email log send configuration
Page 57

57
7: System administration
Users can configure system administration parameters by selecting menu 4.System
administration in the main menu screen. In this menu, users can configure administrator
username, password, current date and time information.
7.1 User name and password
Users can change the administrator’s username and password as they want. The maximum character
length for the both is 31. The default settings of username and password are both “admin”.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- User Administrator
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- Select menu
1. Administrator username : admin
2. Administrator password : *****
3. Device name : PS200 Device
4. Dat e : 20 02/02/10
5. Tim e : 04 :45:38
<ESC> Back , <ENTER> Refresh
-----> 1
En te r cu rrent pass wo rd : *****
En te r Ne w Username : roo t
>> > Ad mi nistrato r us er name chang ed successfu lly !
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- User Administrator
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- Select menu
1. Administrator username : root
2. Administrator password : *****
3. Device name : PS200 Device
4. Dat e : 20 02/02/10
5. Tim e : 04 :45:52
<ESC> Back , <ENTER> Refresh
-----> 2
En te r cu rrent pass wo rd : *****
En te r Ne w password : *** *
Re ty pe password : ** **
>>> Password changed successful ly!
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- User Administrator
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- Select menu
1. Administrator username : root
2. Administrator password : ****
3. Device name : PS200 Device
4. Dat e : 20 02/02/10
5. Tim e : 04 :45:58
<ESC> Back , <ENTER> Refresh
----->
Figure 7-1. Adminis trator username and passwor d c onfiguration
Page 58

58
7.2 Date and time settings
The HelloDevice Pro Series has current date and time information, which is backed up by internal
battery power. Users can change current date and time by selecting submenu 3 or 4.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- User Administrator
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- Select menu
1. Administrator username : root
2. Administrator password : ****
3. Device name : PS200 Device
4. Dat e : 20 38/05/10
5. Tim e : 04 :48:03
<ESC> Back , <ENTER> Refresh
-----> 4
En te r Cu rrent Date (y yy y/mm/dd) : 200 2/3/14
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- User Administrator
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- Select menu
1. Administrator username : root
2. Administrator password : ****
3. Device name : PS200 Device
4. Dat e : 20 02/03/14
5. Tim e : 04 :48:15
<ESC> Back , <ENTER> Refresh
-----> 5
En te r Cu rrent Time (h h: mm:ss) : 18: 00 :00
Figure 7-2. Date and time conf igur ation
Page 59

59
8: System tools
The HelloDevice Pro Series provides administrative functions by console such as factory default
settings restore, firmware upgrade and ping test. These functions can be found in 6. System tools in
the main menu.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------ System tools
------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Select menu
1. Rel oa d factory de fa ul t settings
2. Rel oa d factory de fa ul t settings exc ept IP settin g
3. Firmw are upgrade
4. Ping Test
5. Socke t reset
<ESC> Back , <ENTER> Refresh
----->
Figure 8-1 System tools m enu
8.1 Factory default res et
Users can restore factory default settings by selecting submenu 1.Reload factory default
settings or by pushing hardware factory default reset switch of the HelloDevice Pro Series. If users
want to keep IP configuration after reload of factory settings, select submenu 2.Reload factory
default settings except IP settings.
8.2 Firmwar e up grad e
Firmware of the HelloDevice Pro Series can be upgraded both by serial console or remote console.
The latest firmware can be obtained from our web site: http://www.sena.com/support/downloads/. For
firmware upgrade, your terminal emulation program must support Zmodem transfer protocol. After
firmware upgrade, previous settings will be reset to factory default settings except IP configuration
settings.
Please follow the instructions below for firmware upgrade:
1) Obtain the latest firmware.
2) Connect your terminal emulation program using serial console or telnet. If you use serial console of
the HelloDevice Pro Series, please remember the setting of the terminal emulation program as follows.
9600 Baud rate, Dat a bits 8, Parity None, Stop bits 1, Hardware f low control (RTS/CTS)
Page 60

60
3) Select firmware upgrade menu.
4) Follow the step as guided by online messages.
-----> 3
Ar e yo u su re to start fi rm wa re upgrade ? (y/ n) : y
Pr ep ar ing for firm wa re upgrade. Wa it a moment...
Transfer firmware by zmodem using your terminal application.
**B01ff000005b157
Figure 8-2. Firmwar e upgr ade dis play
Figure 8-3 Transfer binary file by Zmodem (HyperTer m inal)
5) If firmware is upgraded successfully, the HelloDevice Pro Series will reboot automatically.
6) If the firmware upgrade fails, the HelloDevice Pro Series will display messages as follows, and it will
preserve the firmware of current version.
-----> 3
Ar e yo u su re to start fi rm wa re upgrade ? (y/ n) : y
Pr ep ar ing for firm wa re upgrade. Wa it a moment...
Transfer firmware by zmodem using your terminal application.
**B01ff000005b157
**B01ff000005b157
**B01ff000005b157
**B01ff000005b157
**B01ff000005b157
Firmware upgrade failure. Recov ering the previous firmware...
Recovering completed. Device will reboot in a moment...
Figure 8-4. Firmware upgrade failure message
Page 61

61
8.3 Ping test
You can test your network configuration by sending ICMP echo messages (ping) to remote hosts in
4.Ping Test menu. Figure 8-5 shows how to use ping test function to check network connection.
-----> 4
Enter IP Address or Hostname to ping : 192.168.1.1
to 192.168.1.1 pining 4times..
Receive time = 1 ms Sequence num = 0
Receive time = 1 ms Sequence num = 1
Receive time = 1 ms Sequence num = 2
Receive time = 1 ms Sequence num = 3
Figure 8-5 Ping test sc reen
8.4 Socket reset
You can reset the network socket for the corresponding serial port in 5.Socket Reset menu. Figure
8-6 shows how to reset sockets and serial ports manually.
-----> 5
Select a serial port to reset:
1 = po rt #1 : Listen (600 0)
2 = po rt #2 : Listen (600 1)
3 = po rt #3 : Listen (600 2)
4 = po rt #4 : Listen (600 3)
-----> 1
Ar e yo u su re to reset? (y/ n) : y
Socket Initialized !
Figure 8-6 Socket reset screen
Page 62

62
Appendix A: Connections
A.1 Ethernet Pin outs
The HelloDevice Pro Series uses standard Ethernet connector, which is a shielded connector
compliant with AT&T258 specifications. Table A-1 shows the pin assignment and the wire color.
Figure A-1 Pin layout of the RJ45 connec tor
Table A-1. Pin assignment of t he RJ 45 connector
Pin Description Color
1 Tx+ White with orange
2 Tx- Orange
3 Rx+ White with green
4 NC Blue
5 NC White with blue
6 Rx- Green
7 NC White with brown
8 NC Brown
A.2 Serial Ports Pin Outs
The pin assignment of the HelloDevice Pro Series DB9 connector is summarized in Table A-2. Each
pin has a function according to the serial communication type configuration.
6 7 8 9
1 2 3 4 5
Figure A-2 Pin layout of the DB-9 c onnector
Table A-2. Pin assignment of t he DB -9 connector
Pin RS232 RS422 RS485
1 - Tx- Data2 Rx - 3 Tx Rx- 4 DTR Rx+ 5 GND - 6 DSR - 7 RTS - 8 CTS - 9 - Tx+ Data+
Page 63

63
A.3 Ethe rnet Wiring Diagram
Rx+(1)
Rx-(2)
Tx+(3)
Tx-(6)
HelloDevice
Remote Host
Rx+(1)
Rx-(2)
Tx+(3)
Tx-(6)
Figure A-3 Ethernet dir ect connection using cross ov er ethernet cable
Rx+(1)
Rx-(2)
Tx+(3)
Tx-(6)
HelloDevice
Hub
Rx+(1)
Rx-(2)
Tx+(3)
Tx-(6)
Remote Host
Rx+(1)
Rx-(2)
Tx+(3)
Tx-(6)
Rx+(1)
Rx-(2)
Tx+(3)
Tx-(6)
Figure A-4 Ethernet c onnec tion using straight thr ough Ether net cable
A.4 Serial Wiring Diagram
Tx(3)
Rx(2)
RTS(7)
CTS(8)
DTR(4)
DSR(6)
GND(5)
Rx
Tx
CTS
RTS
DSR
DTR
GND
HelloDevice
Serial Device
RS232
Figure A-5 RS232 wiring diagram
Page 64

64
HelloDevice
Device
N
N=max 31
Device
1
Data-(1)
Data+(9)
120 Ω
…
Data- Data+
Data- Data+
Device
N-1
120 Ω
Data-
Data+
RS485
Figure A-6 RS485 wiring diagram
Device
N-1
Device
N
N=max31
Tx-(1)
Tx+(9)
120 Ω
…
120 Ω
Rx-
Rx+
Rx-(3)
Rx+(4)
120 Ω 120 Ω
Tx-
Tx+
RS422
Device
1
Rx-Rx+ Tx-Tx+
Rx-Rx+ Tx-Tx+
HelloDevice
Figure A-7 RS422 wiring diagram
Page 65

65
Appendix B: Well-known port numbers
The port numbers are divided into three ranges: the Well Known Ports, the Registered Ports, and the
Dynamic and/or Private Ports. The Well Known Ports are those from 0 through 1023. The Registered
Ports are those from 1024 through 49151. The Dynamic and/or Private Ports are those from 49152
through 65535.
The Well Known Ports are assigned by the IANA, and on most systems, can only be used by system
processes or by programs executed by privileged users. Table B-1 shows famous port numbers
among the well-known port numbers. For more details, please visit IANA website:
http://www.iana.org/assignments/port-numbers
Table B-1 Well-known por t numbers
Port number Protocol TCP/UDP
21 FTP (File Transfer Protocol) TCP
22 SSH (Secure SHell) TCP
23 Telnet TCP
25 SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) TCP
37 Time TCP, UDP
39 RLP (Resource Location Protocol) UDP
49 TACACS, TACACS+ UDP
53 DNS UDP
67 BOOTP server UDP
68 BOOTP client UDP
69 TFTP UDP
70 Gopher TCP
79 Finger TCP
80 HTTP TCP
110 POP3 TCP
119 NNTP (Network News Transfer Protocol) TCP
161/162 SNMP UDP
Page 66

66
Appendix C: Troubleshooting
C.1 Power/LED status troubleshooting
Problem Cause Action
Power LED does
not light up
Power cabl e is not
connected
Check power connection
Ethernet cable is not
connected
Check Ethernet cable connection Link LED does not
light up
Invalid Ethernet cable is
used
There are two types of Ethernet cables: Straight-through cable
and crossover cable. If you are using an Ethernet hub, use
straight-through cable. If direct connection between the
HelloDevice Pro Series and remote host is used, use crossover
cable instead.
ACT LED does not
blink
Invalid IP configuration Check IP configuration parameters
C.2 Serial console troubleshooting
Problem Cause Action
Invalid serial cable Be sure to use a serial console cable (null-modem cable) for
serial console
Serial console is not
connected
Invalid serial port
configuration of terminal
emulation program
Check serial port configuration of termi nal emulation program:
9600 bps, 8 Data bits, No parity, 1 stop bit, Hardware flow
control
Serial console is
halted for few
seconds periodically
IP mode is DHCP or
PPPoE, but IP is not
assigned
If IP mode is set to DHCP or PPPoE but IP is not actually
assigned because of DHCP server or PPPoE server failure,
serial console is halted for few seconds at every 20 seconds.
Change IP mode to the static IP mode
Cannot login to
console
Invalid username and/or
password
Use valid username and password. If username and/or
password are lost, perform factory default reset using factory
reset switch. Factory default value of username and password
are both admin
C.3 Remote console troubleshooting
Problem Cause Action
The HelloDevice Pro
Series is not assigned
valid IP address
Use serial console to assign valid IP address to the HelloDevice
Pro Series
Cannot connect to
the HelloDevice Pro
Series using telnet
The HelloDevice Pro
Series is configured to
reject IP address of the
PC
Change the remote host access control parameter using serial
console to all ow the IP address of the PC
Page 67

67
Maximum number of
remote consoles
already established
Retry after one of the other remote consoles i s finished.
Cannot login to
console
Invalid username and/or
password
Use valid username and password. If username and/or
password are lost, perform factory default reset using factory
reset switch. Factory default value of username and password
are both admin
C.4 IP address tr o ubl eshootin g
Problem Cause Action
Use serial console to find IP address Cannot find IP
address of the
HelloDevice Pro
Series
Use HelloDeviceManager program to probe the HelloDevice
Pro Series on the network
The HelloDevice Pro
Series is not assigned
valid IP address
Use serial console to assign valid IP address to the
HelloDevice Pro Series
HelloDeviceManager
cannot probe the
HelloDevice Pro
Series
HelloDeviceManager
and the HelloDevice Pro
Series are not on the
same subnet
Run HelloDeviceManager on the PC that is on the same subnet
with the HelloDevice Pro Series
C.5 DHCP troubleshooting
Problem Cause Action
Cannot lease IP
address
DHCP server is not
working
Check if DHCP server is working correctly
IP address of the
HelloDevice Pro
Series is changed
DHCP server does not
extend lease time
Check if DHCP server is working correctly
C.6 TCP ser ver op er at i o n tr ou bl es ho oting
Problem Cause Action
IP configuration of
remote host is invalid
Check if IP configuration of the remote host is valid
Host mode of the
HelloDevice Pro Series
serial port is not TCP
server
Change the host mode of the HelloDevice Pro Series serial port
to TCP server or TCP server/client
IP address of the
HelloDevice Pro Series
or TCP/UDP port
number is wrong
Specify valid IP address and TCP/UDP port number of the
HelloDevice Pro Series
Cannot connect to
the HelloDevice Pro
Series
DSR option is set but
DSR input is not high
Disable DSR option or make DSR input of the HelloDevice Pro
Series high
Page 68

68
The HelloDevice Pro
Series is configured to
reject IP address of the
PC
Change the remote host access control parameter using serial
or remote console to allow the IP address of the PC
TCP connection with
the other host is
established already
Close established TCP connection or connect later
C.7 Serial communication troubleshooting
Problem Cause Action
Serial data are not
transferred by
TCP/IP immediately
Too large inter-character
timeout
Set inter-character timeout with smaller value
Cannot
communicate with
the HelloDevice Pro
Series
Invalid serial port
configuration
Check if serial port configuration of the HelloDevice Pro Series
are the same with that of the serial device
Only serial port#2
of PS400 is not
working (PS400
only)
Serial console is used Serial port#2 of the PS400 is used commonly for both data port
and serial console port. While serial console is used, data
transfer through serial port#2 is disabled. Close serial console to
use serial port#2 for data transfer.
Invalid data
transferred
Invalid serial port
configuration
Check if serial port configuration is correct.
Invalid serial port
configuration
Check if serial port is set to RS485 Echo or RS485 Non-echo
mode.
RS485 mode is not
working
Terminator resistor is not
attached
The HelloDevice Pro Series has no terminator resistor inside for
RS485 communication. Please attach a 120 Ω resistor between
Data+ and Data- pins.
Invalid serial port
configuration
Check if serial port is set to RS422 mode. RS422 mode is not
working
Terminator resistor is not
attached
The HelloDevice Pro Series has no terminator resistor inside for
RS422 communication. Please attach 120 Ω resistors between
Tx+, Tx- and between Rx+, Rx- pins.
 Loading...
Loading...