NCV7425
LIN Transceiver with
Voltage Regulator and
Reset Pin
General Description
The NCV7425 is a fully featured local interconnect network (LIN)
transceiver designed to interface between a LIN protocol controller
and the physical bus.
The NCV7425 LIN device is a member of the in−vehicle
networking (IVN) transceiver family of ON Semiconductor that
integrates a LIN v2.1 physical transceiver and a low−drop voltage
regulator.
The LIN bus is designed to communicate low rate data from control
devices such as door locks, mirrors, car seats, and sunroofs at the
lowest possible cost. The bus is designed to eliminate as much wiring
as possible and is implemented using a single wire in each node. Each
node has a slave MCU−state machine that recognizes and translates
the instructions specific to that function. The main attraction of the
LIN bus is that all the functions are not time critical and usually relate
to passenger comfort.
Features
• LIN−Bus Transceiver
♦ LIN compliant to specification revision 2.1
(backward compatible to versions 2.0 and 1.3) and
J2602
♦ Bus Voltage ±45 V
♦ Transmission Rate up to 20 kBaud
♦ Integrated Slope Control for Improved EMI
Compatibility
• Modes
• Package
♦ SOIC−16 Wide Body Package with Exposed Pad
• Protection
♦ Thermal Shutdown
♦ Indefinite Short−Circuit Protection on Pins LIN and
WAKE Towards Supply and Ground
♦ Load Dump Protection (45 V)
♦ Bus Pins Protected Against Transients in an
Automotive Environment
♦ ESD Protection Level for LIN, INH, WAKE and
up to ±10 kV
V
BB
• Voltage Regulator
♦ Two Device Versions: Output Voltage 3.3 V or 5 V
For Loads up to 150 mA
♦ Undervoltage Detector with a Reset Output to the
Supplied Microcontroller
♦ INH Output for Auxiliary Purposes (switching of an
external pull−up or resistive divider towards battery,
control of an external voltage regulator etc.)
Quality
• NCV Prefix for Automotive and Other Applications
Requiring Unique Site and Control Change
Requirements; AEC−Q100 Qualified and PPAP
Capable
• These Devices are Pb−Free, Halogen Free/BFR Free
and are RoHS Compliant
Typical Applications
• Automotive
• Industrial Networks
www.onsemi.com
MARKING
DIAGRAM
16
SOIC−16 LEAD
WIDE BODY
16
1
See detailed ordering and shipping information in the
package dimensions section on page 19 of this data sheet.
♦ Normal Mode: LIN Communication in Either Low
EXPOSED PAD
CASE 751AG
x = 0 or 5
A = Assembly Location
WL = Wafer Lot
YY = Year
WW = Work Week
G = Pb−Free Package
ORDERING INFORMATION
NCV7425−x
AWLYYWWG
1
(up to 10 kBaud) or Normal Slope
♦ Sleep Mode: V
is Switched “off” and No
CC
Communication on LIN Bus
♦ Standby Mode: V
is Switched “on” but There is
CC
No Communication on LIN Bus
♦ Wake−up Bringing the Component From Sleep
Mode Into Standby Mode is Possible Either by LIN
Command or Digital Input Signal on WAKE Pin
Wake−up from LIN Bus can also be Detected and
Flagged When the Chip is Already in Standby Mode
© Semiconductor Components Industries, LLC, 2015
May, 2015 − Rev. 3
1 Publication Order Number:
NCV7425/D
NCV7425
Table 1. KEY TECHNICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Symbol Parameter Min Typ Max Unit
3.3 V VERSION
V
BB
V
BB
IBB_SLP Supply current in sleep mode 20
V
CC_OUT
(Note 2)
I
OUT_LIM
V
WAKE
V
INH
T
J_TSD
T
J
5 V VERSION
V
BB
V
BB
I
BB_SLP
V
CC_OUT
(Note 2)
I
OUT_LIM
V
WAKE
V
INH
T
J_TSD
T
J
1. The applied transients shall be in accordance with ISO 7637 part 1, test pulse 5. The device complies with functional class C;. The LIN
communication itself complies with functional class B. On regulator class A can be reached depending on the application and external
components
voltage must be properly stabilized by external capacitors: capacitor of min. 80 nF with ESR < 10 mW in parallel with a capacitor of min.
2. V
CC
8 mF, ESR < 1 W.
Nominal battery operating voltage 5 12 28 V
Load dump protection (Note 1) 45 V
mA
Regulated VCC output in normal mode, VCC load 0−100 mA 3.234 3.3 3.366
V
Regulated VCC output in normal mode, 100 mA < VCC load < 150 mA 3.201 3.3 3.399
VCC regulator current limitation 150 225 300 mA
Operating DC voltage on WAKE pin 0 V
BB
V
Maximum rating voltage on WAKE pin −45 45
Operating DC voltage on INH pin 0 V
BB
V
Junction thermal shutdown temperature 165 195 °C
Operating junction temperature −40 +150 °C
Nominal battery operating voltage 6 12 28 V
Load dump protection (Note 1) 45 V
Supply current in sleep mode 20
mA
Regulated VCC output in normal mode, VCC load 0−100 mA 4.90 5 5.10 V
Regulated VCC output in normal mode, 100 mA < VCC load < 150 mA 4.85 5 5.15 V
VCC regulator current limitation 150 225 300 mA
Operating DC voltage on WAKE pin 0 V
BB
V
Maximum rating voltage on WAKE pin −45 45
Operating DC voltage on INH pin 0 V
BB
V
Junction thermal shutdown temperature 165 195 °C
Operating junction temperature −40 +150 °C
Table 2. THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS
Symbol Parameter Conditions Value Unit
R
th(vj−a)_1
R
th(vj−a)_2
R
th(vj−a)_3
R
th(vj−a)_4
Thermal resistance junction−to−ambient on JEDEC 1S0P PCB Free Air 138 K/W
Thermal resistance junction−to−ambient on JEDEC 1S0P + 300 mm2 PCB Free Air 94 K/W
Thermal resistance junction−to−ambient on JEDEC 2S2P PCB Free Air 70 K/W
Thermal resistance junction−to−ambient on JEDEC 2S2P + 300 mm2 PCB Free Air 49 K/W
www.onsemi.com
2
NCV7425
WAKE
STB
EN
TxD
RxD
RSTN
V
CC
NCV7425
V−reg
V
CC
Control Logic
V
CC
V
CC
V
CC
Timeout
TEST
OTP_ZAP
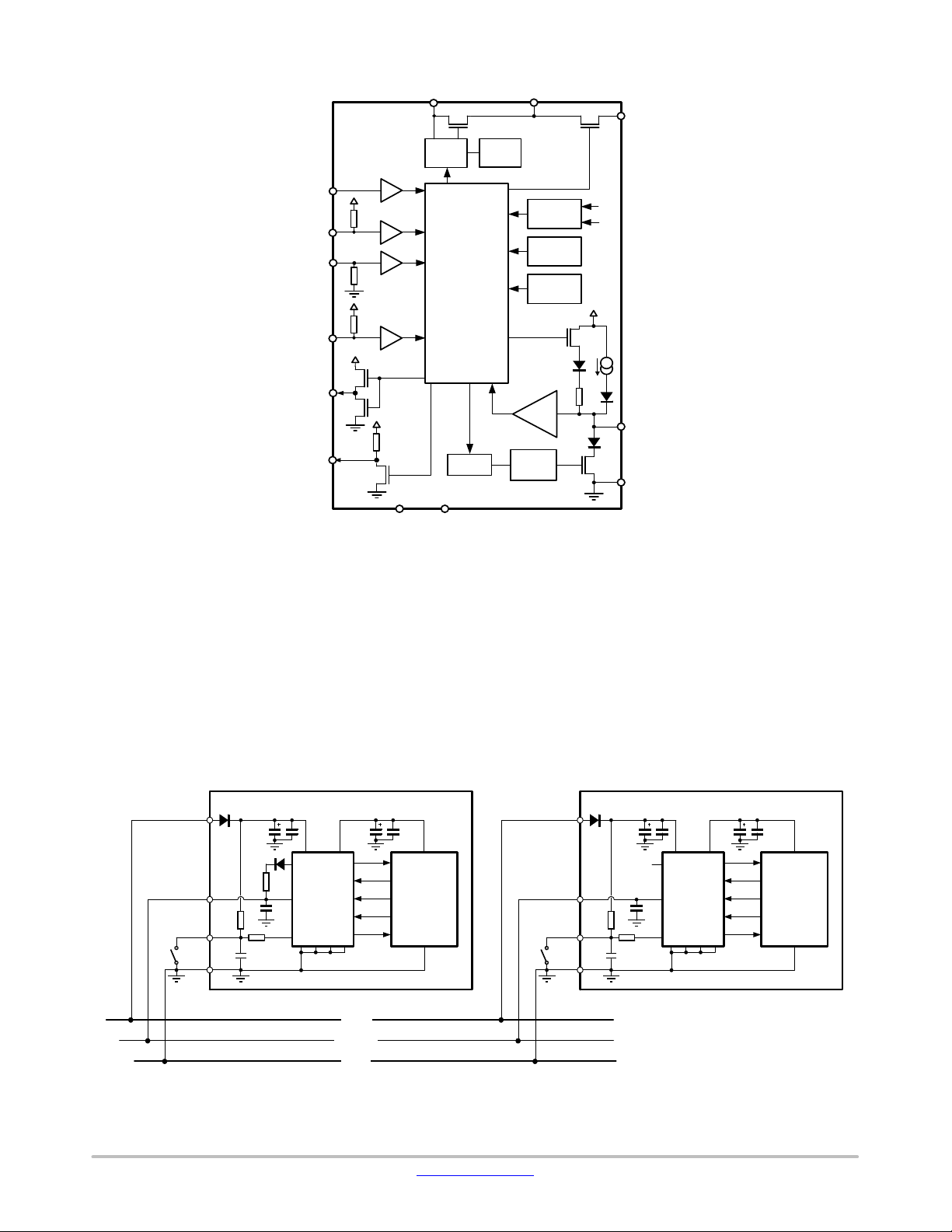
Figure 1. Block Diagram
Band−
gap
V
shutdown
Receiver
Slope
Control
BB
POR
Thermal
Osc
PD20090609.1
INH
V
BB
V
CC
V
BB
LIN
GND
TYPICAL APPLICATION
Application Information
The EMC immunity of the Master−mode device can be
further enhanced by adding a capacitor between the LIN
output and ground. The optimum value of this capacitor is
determined by the length and capacitance of the LIN bus, the
number and capacitance of Slave devices, the pull−up
resistance of all devices (Master and Slave), and the required
time constant of the system, respectively.
VBAT
WAKE
GND
10uF 100nF
V
BB
INH
LIN
10nF
LIN
1nF 1kW
WAKE
10uF
V
CC V
RxD
TxD
EN
NCV7425
STB
RSTN
TESTOTP_ZAP
GND
KL30
LIN−BUS
KL31
100nF
Master Node
CC
Micro
controller
GND
V
voltage must be properly stabilized by external
CC
capacitors: capacitor of min. 80 nF (ESR < 10 mW) in
parallel with a capacitor of min. 8 mF (ESR < 1 W).
The 10 mF capacitor on the battery is optional and serves
as reservoir capacitor to deal with battery supply
micro−cuts.
VBAT
WAKE
LIN
GND
10nF
10uF 100nF10uF 100nF
V
BBVCC
RxD
INH
TxD
GND
EN
STB
RSTN
TESTOTP_ZAP
LIN
220pF
WAKE
Slave Node
V
Micro
controller
PD20090609.2
CC
GND
Figure 2. Application Diagram
www.onsemi.com
3
NCV7425
V
LIN
GND
GND
WAKE
INH
OTP_SUP
n.c.
1
BB
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
NCV7425
V
16
CC
15
RxD
TxD
14
RSTN
13
STB
12
EN
11
TEST
10
n.c.
9
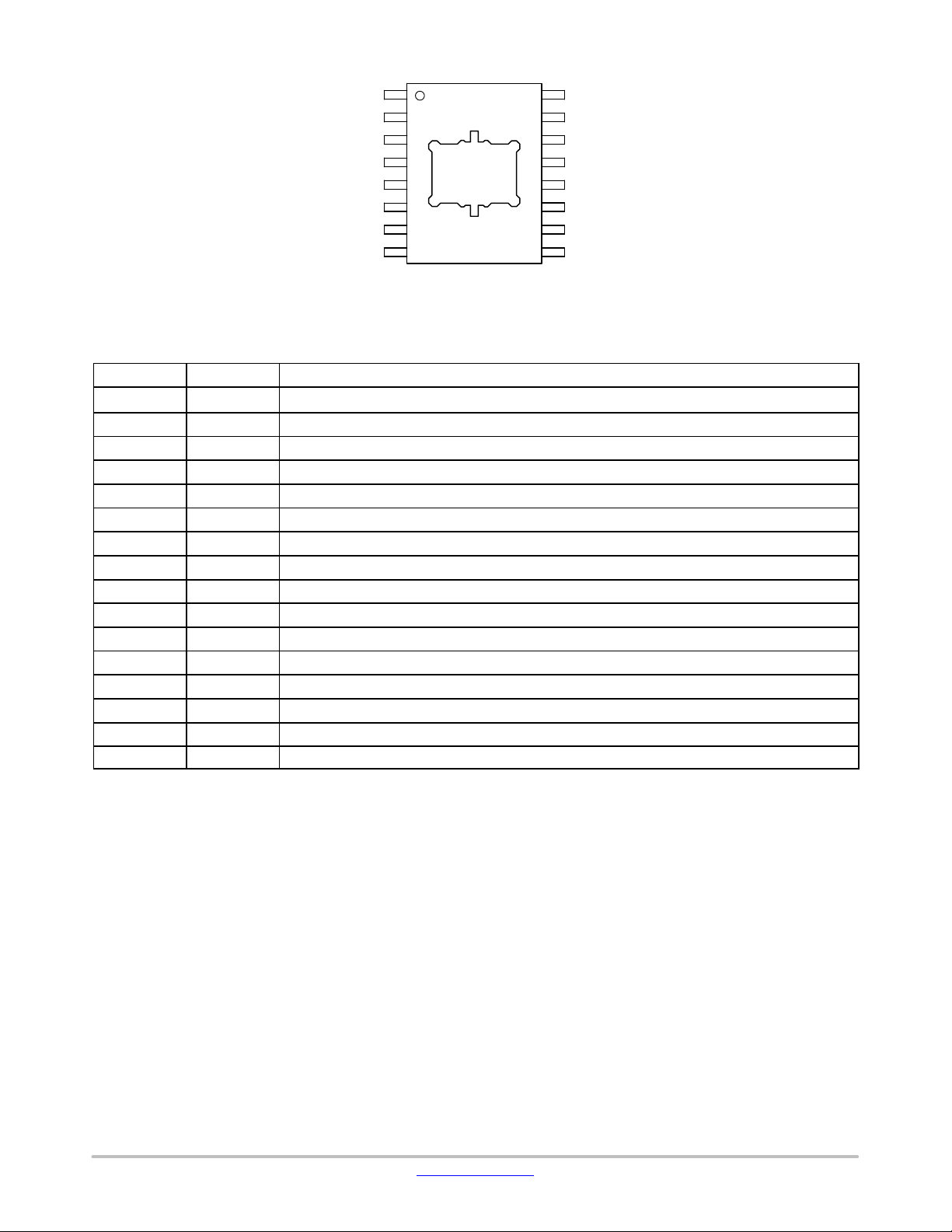
Figure 3. Pin Assignment
Table 3. PIN FUNCTION DESCRIPTION
Pin Number Pin Name Description
1 V
BB
2 LIN LIN bus output/input
3 GND Ground
4 GND Ground
5 WAKE High voltage digital input pin to switch the part from sleep− to standby mode
6 INH Inhibit output
7 OTP_SUP Supply for programming of trimming bits at factory testing, needs to be grounded in the application
8 n.c. not connected
9 n.c. not connected
10 TEST Digital input for factory testing, needs to be grounded in the application
11 EN Enable input for mode control
12 STB Standby mode control input
13 RSTN Reset output; open−drain output with an on−chip pull−up resistor
14 TxD Transmit data input, Low in dominant state
15 RxD Receive data output; Low in dominant state; push−pull output
16 V
CC
Battery supply input
Voltage regulator output
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
Overall Functional Description
LIN is a serial communication protocol that efficiently
supports the control of mechatronic nodes in distributed
automotive applications. The domain is class−A multiplex
buses with a single master node and a set of slave nodes.
NCV7425 is designed as a master or slave node for the
LIN communication interface with an integrated 3.3 V or
5 V voltage regulator having a current capability up to
150 mA for supplying any external components
(microcontroller, CAN node, etc.).
NCV7425 contains the LIN transmitter, LIN receiver,
voltage regulator, power−on−reset (POR) circuits and
thermal shutdown (TSD). The LIN transmitter is optimized
for the maximum specified transmission speed of 20 kBaud
www.onsemi.com
with EMC performance due to reduced slew rate of the LIN
output.
The junction temperature is monitored via a thermal
shutdown circuit that switches the LIN transmitter and
voltage regulator off when temperature exceeds the TSD
trigger level.
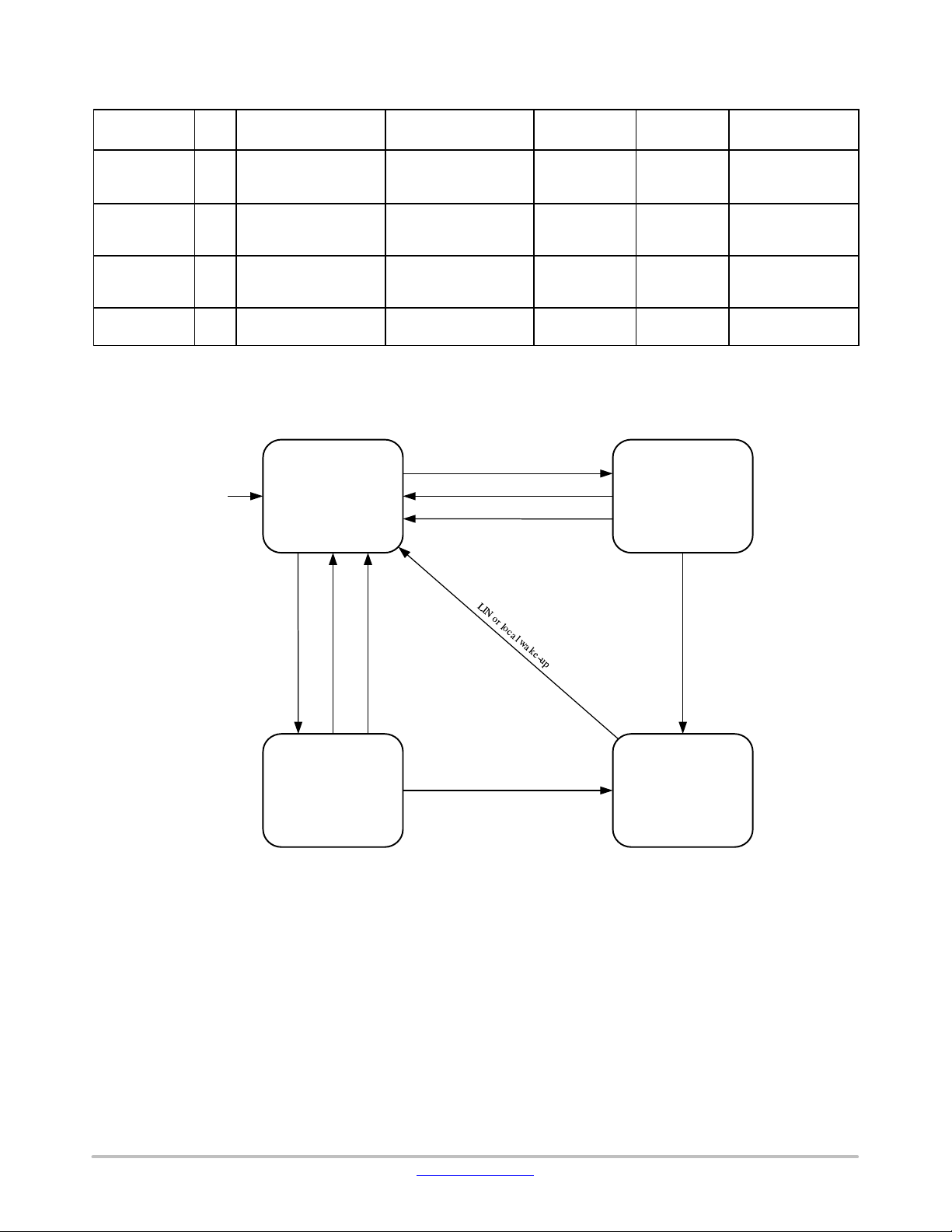
NCV7425 has four operating states (normal mode, low
slope mode, standby mode, and sleep mode) that are
determined by the input signals EN, WAKE, STB, and TxD.
Operating States
NCV7425 provides four operating states, two modes for
normal operation with communication, one standby without
communication and one low power mode with very low
current consumption − see Figure 4 and Table 4.
4
NCV7425
Table 4. MODE SELECTION
LIN
Mode V
Normal −
Slope (Note 3)
CC
ON Low = Dominant State
High = Recessive State
RxD INH
High if STB = High
during state transition;
Floating otherwise
Normal − Low
Slope (Note 4)
ON Low = Dominant State
High = Recessive State
High if STB = High
during state transition;
Floating otherwise
Standby
(Note 5)
ON Low after LIN
wake−up, High
Floating OFF OFF Controlled by V
otherwise (Note 6)
Sleep OFF Clamped to V
(Note 6)
CC
Floating OFF OFF Low
3. The normal slope mode is entered when pin EN goes High while TxD is in High state during EN transition.
4. The low slope mode is entered when pin EN goes High while TxD is in Low state during EN transition. LIN transmitter gets on only after TxD
returns to High after the state transition.
5. The standby mode is entered automatically after power−up.
6. In standby and Sleep mode, the High state is achieved by internal pull−up resistor to V
Transceiver
30 kW on LIN
RSTN
Normal Slope ON High
Low Slope ON High
undervoltage
monitor
.
CC
CC
VBB power−up
Standby mode
−
VCC: on
−LIN TRX: off
−INH: floating
−LIN term.: current source
−RxD pin: High/Low
−RSTN pin:
V
CC_UV
undervoltage
CC
ENchanges 0−>1 while TxD=0
V
EN changes 1−>0 while STB=1
Normal mode
(low slope )
: on
V
−
CC
−LIN TRX: on
−INH: High/floating
−LIN term.: 30kW
−RxD pin: LIN data
−RSTN pin: High
EN changes 0−>1while TxD=1
EN changes 1−>0 while STB=1
VCC undervoltage
EN changes 1−>0 while STB=0
Figure 4. State Diagram
Normal mode
(normal slope )
V
: on
−
CC
−LIN TRX: on
−INH: High/floating
−LIN term.: 30kW
−RxD pin: LIN data
−RSTN pin: High
EN changes 1−>0 while STB=0
Sleep mode
−
VCC: off
−LIN TRX: off
−INH: floating
−LIN term.: current source
−RxD pin:
−RSTN pin: Low
at V
CC
PD20090610.01
Normal Slope Mode
In normal slope mode the transceiver can transmit and
receive data via LIN bus with speed up to 20 kBaud. The
transmit data stream of the LIN protocol is present on the
TxD pin and converted by the transmitter into a LIN bus
signal with controlled slew rate to minimize EMC emission.
The receiver consists of the comparator that has a threshold
with hysteresis in respect to the supply voltage and an input
filter to remove bus noise. The LIN output is pulled High via
an internal 30 kW pull−up resistor. For master applications
it is needed to put an external 1 kW resistor with a serial
diode between LIN and V
(or INH) − see Figure 2. The
BB
www.onsemi.com
mode selection is done by EN=High when TxD pin is High.
If STB pin is High during the standby−to−normal slope
mode transition, INH pin is pulled High. Otherwise, it stays
floating.
Low Slope Mode
In low slope mode the slew rate of the signal on the LIN
bus is reduced (rising and falling edges of the LIN bus signal
are longer). This further reduces the EMC emission. As a
consequence the maximum speed on the LIN bus is reduced
up to 10 kBaud. This mode is suited for applications where
the communication speed is not critical. The mode selection
5
NCV7425
is done by EN=High when TxD pin is Low. In order not to
transmit immediately a dominant state on the bus (because
TxD = Low), the LIN transmitter is enabled only after TxD
returns to High. If STB pin is High during the
standby−to−low slope mode transition, INH pin is pulled
High. Otherwise, it stays floating.
Standby Mode
The standby mode is always entered after power−up of the
NCV7425. It can also be entered from normal mode when
the EN pin is Low and the standby pin is High. From sleep
mode it can be entered after a local wake−up or LIN
wake−up. In standby mode the V
voltage regulator for
CC
supplying external components (e.g. a microcontroller)
stays active. Also the LIN receiver stays active to be able to
detect a remote wake−up via bus. The LIN transmitter is
disabled and the slave internal termination resistor of 30 kW
between LIN and V
is disconnected in order to minimize
BB
current consumption. Only a pull−up current source
between V
and LIN is active.
BB
Wake
V
BB
Detection of Local Wake−Up
50% V
BB
Sleep Mode
The Sleep Mode provides extremely low current
consumption. This mode is entered when both EN and STB
pins are Low coming from normal mode. The internal
termination resistor of 30 kW between LIN and VBB is
disconnected and also the V
regulator is switched off to
CC
minimize current consumption.
Wake−up
NCV7425 has two possibilities to wake−up from sleep or
standby mode (see Figure 4):
Local wake−up: enables the transition from sleep mode to
standby mode
Remote wake−up via LIN: enables the transition from
sleep to standby mode and can be also detected when already
in standby mode.
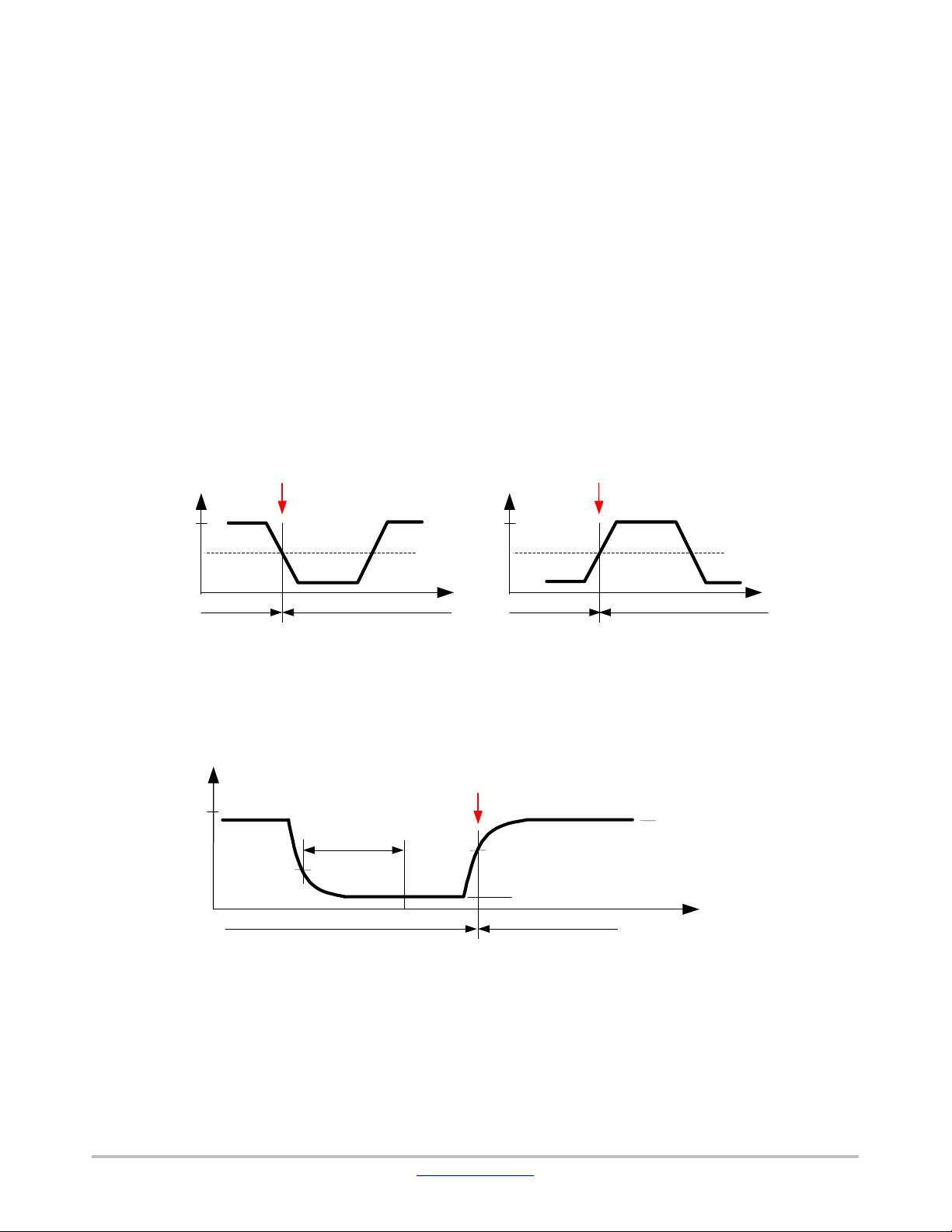
A local wake−up is only detected in sleep mode if a
transition from Low to High or from High to Low is seen on
the WAKE pin.
Detection of Local Wake−Up
50% VBB typ.
typ.
Wake
V
BB
Sleep Mode Standby Mode
Figure 5. Local Wake−Up Signal
A remote wake−up is only detected if a combination of (1)
a falling edge at the LIN pin (transition from recessive to
dominant) is followed by (2) a dominant level maintained
LIN
Detection of Remote Wake−Up
V
BB
t
WAKE
40% V
BB
Sleep Mode
Figure 6. Remote Wake−Up Behavior
The wake−up source is distinguished by pin RxD in the
standby mode:
RxD remains High after power−up or local wake−up.
RxD is kept Low until normal mode is entered after a
remote wake−up (LIN)
t
Sleep Mode Standby Mode
for a time period > t
WAKE
PC20060427.3
and (3) again a rising edge at pin
t
LIN (transition from dominant to recessive) happens.
LIN recessive level
60% V
BB
LIN dominant level
Standby Mode
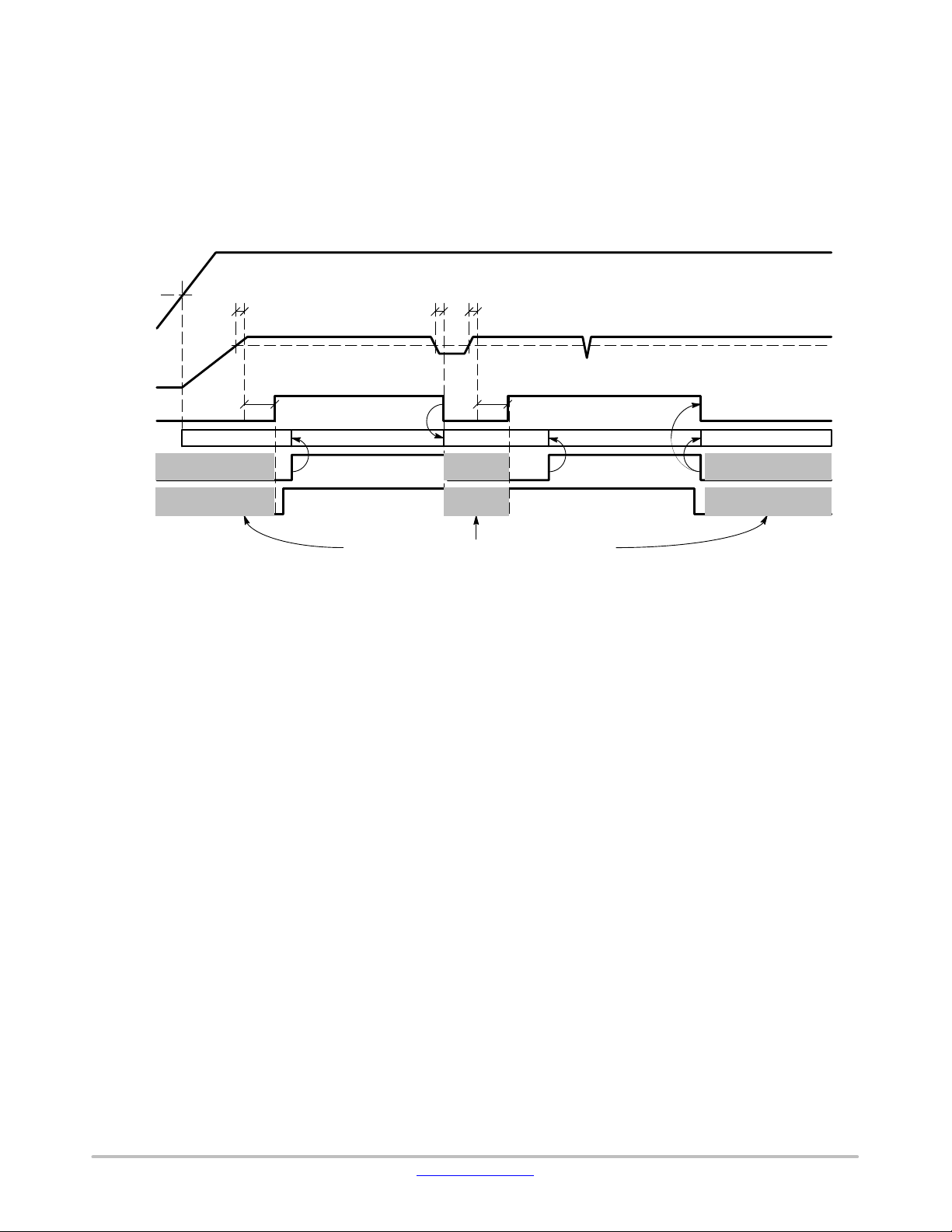
VCC Undervoltage Detection and RSTN Pin
t
PC20060427.2
In standby, normal and low slope modes, the V
regulator is monitored. Whenever the regulator output falls
below V
CC_UV_THR
voltage) for longer than V
level (typically 90% of the nominal
CC_UV_deb
(typically 5 ms), an
CC
www.onsemi.com
6
NCV7425
undervoltage is detected. Output pin RSTN is pulled to Low
level to indicate the undervoltage condition to the external
load (a microcontroller). At the same time, the device enters
automatically the standby mode. As soon as the regulator
output returns above the undervoltage level, the RSTN Low
level is extended by typically 6ms and only then released to
High level in order to ensure microcontroller initialization
under correct supply conditions.
POR
VBB
VCC
RSTN
EN
STB
H_VBB
V
CC_UV_THR
CC_UV_deb
V
RSTN
CC_UV_debVCC_UV_deb
V
ext
STB and EN levels discarded when RSTN=Low
In the sleep mode, RSTN pin is kept Low regardless the
V
level − it means that RSTN becomes Low immediately
CC
at sleep mode entry even if the V
capacitor is still charged.
CC
In all situations where RSTN pin is kept Low, the digital
inputs to NCV7425 are discarded by the internal control
logic and have no effect on its behavior.
The RSTN pin function is illustrated in Figure 7.
< V
CC_UV_deb
ext
RSTN
Standby mode Normal mode Sleep modeNormal modeStandby mode
FB20130807.01
Figure 7. RSTN Pin Behavior
www.onsemi.com
7
 Loading...
Loading...