Seagate ST4000VX002,ST2000VX004,ST3000VX004,ST1000VX002 Product Manual

Product Manual
Seagate® SV35/Suveillance HDD
ST4000VX002
ST3000VX004
ST2000VX004
ST1000VX002
100759604
Rev. C
February 2015

Document Revision History
Revision Date Pages affected
Rev . A 10/01/2014 Initial release.
Rev. B 10/01/2014 fc, 2, 4-7 & 25.
Rev. C 02/27/2015 fc, bc, 15 & 18.
© 2015, Seagate Technology LLC All rights reserved.
Publication number: 100759604, Rev. C February 2015
Seagate, Seagate Technology and the Spiral logo are registered trademarks of Seagate Technology LLC in the United
States and/or other countries. Seagate SV35/Suveillance +SRS HDD and SeaTools are either trademarks or registered
trademarks of Seagate Technology LLC or one of its affiliated companies in the United States and/or other countries. All
other trademarks or registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
No part of this publication may be reproduced in any form without written permission of Seagate Technology LLC.
Call 877-PUB-TEK1(877-782-8351) to request permission.
When referring to drive capacity, one gigabyte, or GB, equals one billion bytes and one terabyte, or TB, equals one trillion
bytes. Your computer’s operating system may use a different standard of measurement and report a lower capacity. In
addition, some of the listed capacity is used for formatting and other functions, and thus will not be available for data
storage. Actual quantities will vary based on various factors, including file size, file format, features and application
software. Actual data rates may vary depending on operating environment and other factors. The export or re-export of
hardware or software containing encryption may be regulated by the U.S. Department of Commerce, Bureau of Industry
and Security (for more information, visit www.bis.doc.gov), and controlled for import and use outside of the U.S. Seagate
reserves the right to change, without notice, product offerings or specifications.

Contents
Seagate® Technology Support Services . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
1.0 Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
1.1 About the SATA interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
2.0 Drive Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
2.1 Specification summary tables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
2.2 Formatted capacity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
2.2.1 LBA mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
2.3 Default logical geometry . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
2.4 Recording and interface technology . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
2.5 Manufacturer Physical characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
2.6 Seek time. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
2.7 Start/stop times . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
2.8 Power specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
2.8.1 Power consumption . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
2.8.2 Conducted noise . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
2.8.3 Voltage tolerance. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
2.8.4 Power-management modes. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
2.9 Environmental specifications. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
2.9.1 Ambient temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
2.9.2 Temperature gradient. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
2.9.3 Humidity. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
2.9.4 Altitude. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
2.9.5 Shock. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
2.9.6 Non-operating vibration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
2.10 Acoustics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
2.10.1 Test for Prominent Discrete Tones (PDTs) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
2.11 Electromagnetic immunity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
2.12 MTBF and Warranty . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
2.13 Agency certification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
2.13.1 Safety certification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
2.13.2 Electromagnetic compatibility. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
2.13.3 FCC verification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
2.14 Environmental protection. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
2.14.1 European Union Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) Directive. . . . . 20
2.14.2 China Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) Directive . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
2.15 Corrosive environment. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
3.0 Configuring and Mounting the Drive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
3.1 Handling and static-discharge precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
3.2 Configuring the drive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
3.3 SATA cables and connectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
3.4 Drive mounting. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
4.0 SATA Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
4.1 Hot-Plug compatibility . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
4.2 SATA device plug connector pin definitions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
4.3 Supported ATA commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
4.3.1 Identify Device command. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
4.3.2 Set Features command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
4.3.3 S.M.A.R.T. commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Seagate SV35/Suveillance +SRS HDD Product Manual, Rev. C 2

Figures
Figure 1 Attaching SATA cabling. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Figure 2 Mounting dimensions (4 & 3-disk: 4TB, 3TB and 2TB models). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Figure 3 Mounting dimensions (1-Disk: 1TB model) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Seagate SV35/Suveillance +SRS HDD Product Manual, Rev. C 3

Seagate® Technology Support Services
For information regarding online support and services, visit:
Available services include:
http://www.seagate.com/about/contact-us/technical-support/
• Presales & Technical support
• Global Support Services telephone numbers & business hours
• Authorized Service Centers
For information regarding Warranty Support, visit:
For information regarding data recovery services, visit:
For Seagate OEM and Distribution partner portal, visit:
For Seagate reseller portal, visit:
http://www.seagate.com/partners/my-spp-dashboard/
http://www.seagate.com/support/warranty-and-replacements/
http://www.seagate.com/services-software/data-recovery-services/
http://www.seagate.com/partners
Seagate SV35/Suveillance +SRS HDD Product Manual, Rev. C 4
1.0 Introduction
This manual describes the functional, mechanical and interface specifications for the following:
Seagate SV35/Suveillance +SRS HDD model drives:
ST4000VX002
(Surveillance)
These drives provide the following key features:
• Enterprise-class reliability for 24×7 video surveillance applications
• Thermal monitoring and reporting for 24×7 operations
• Uncompromising reliability supports flexible surveillance design with case temperatures up to 70º C
• Performance-tuned for seamless video applications
• Built-in error recovery for non-stop video streaming
• Best-in-class acoustic performance means virtually silent operation
• High instantaneous (burst) data-transfer rates (up to 600MB per second).
• TGMR recording technology provides the drives with increased areal density.
• State-of-the-art cache and on-the-fly error-correction algorithms
• Native Command Queuing with command ordering to increase performance in demanding applications
• Full-track multiple-sector transfer capability without local processor intervention
• AcuTrac™ servo technology delivers dependable performance, even with hard drive track widths of only 75
nanometers.
• OptiCache™ technology boosts overall performance by as much as 45% over the previous generation.
• Quiet operation
• Compliant with RoHS requirements in China and Europe
• Diagnostic software performs a drive self-test that eliminates unnecessary drive returns.
• Support for S.M.A.R.T. drive monitoring and reporting
• Supports latching SATA cables and connectors
• Worldwide Name (WWN) capability uniquely identifies the drive.
• <1% AFR- designed for high write duty cycle across Seagate SV35/Suveillance +SRS HDD
• Streaming video optimization - consistent command completion times & ERC support across Seagate SV35/
Suveillance +SRS HDD
• ATA AV Command support - streaming video command support across Seagate SV35/Suveillance +SRS HDD
• Number of drives supported in surveillance environment:
Non RAID Application, sequential HDD usage model - Seagate SV35/Suveillance +SRS HDD
RAID Application - Seagate SV35/Suveillance +SRS HDD <=16 HDDs, SV35 <=4 HDDs
• Transient power on management - <=2A spin-up current across Seagate SV35/Suveillance +SRS HDD
• Rotational Vibration - mitigation of system level rotational vibration inside Seagate SV35/Suveillance +SRS
HDD
ST3000VX004
(SV35)
ST2000VX004
(SV35)
ST1000VX002
(SV35)
Seagate SV35/Suveillance +SRS HDD Product Manual, Rev. C 5
Introduction
1.1 About the SATA interface
The Serial ATA (SATA) interface provides several advantages over the traditional (parallel) ATA interface. The
primary advantages include:
• Easy installation and configuration with true plug-and-play connectivity. It is not necessary to set any jumpers
or other configuration options.
• Thinner and more flexible cabling for improved enclosure airflow and ease of installation.
• Scalability to higher performance levels.
In addition, SATA makes the transition from parallel ATA easy by providing legacy software support. SATA was
designed to allow users to install a SATA host adapter and SATA disk drive in the current system and expect all of
the existing applications to work as normal.
The SATA interface connects each disk drive in a point-to-point configuration with the SATA host adapter. There is
no master/slave relationship with SATA devices like there is with parallel ATA. If two drives are attached on one
SATA host adapter, the host operating system views the two devices as if they were both “masters” on two
separate ports. This essentially means both drives behave as if they are Device 0 (master) devices.
The host adapter may, optionally, emulate a master/slave environment to host software where two
Note
The SATA host adapter and drive share the function of emulating parallel ATA device behavior to provide
backward compatibility with existing host systems and software. The Command and Control Block registers, PIO
and DMA data transfers, resets, and interrupts are all emulated.
The SATA host adapter contains a set of registers that shadow the contents of the traditional device registers,
referred to as the Shadow Register Block. All SATA devices behave like Device 0 devices. For additional
information about how SATA emulates parallel ATA, refer to the “Serial ATA International Organization: Serial ATA
Revision 3.0.” The specification can be downloaded from
devices on separate SATA ports are represented to host software as a Device 0 (master) and Device
1 (slave) accessed at the same set of host bus addresses. A host adapter that emulates a master/
slave environment manages two sets of shadow registers. This is not a typical SATA environment.
www.sata-io.org.
Seagate SV35/Suveillance +SRS HDD Product Manual, Rev. C 6
2.0 Drive Specifications
Unless otherwise noted, all specifications are measured under ambient conditions, at 25°C, and nominal power.
For convenience, the phrases the drive and this drive are used throughout this manual to indicate the following
drive models:
ST4000VX002
(Surveillance)
ST3000VX004
(SV35)
ST2000VX004
(SV35)
ST1000VX002
(SV35)
2.1 Specification summary tables
The specifications listed in Table 1 are for quick reference. For details on specification measurement or definition,
refer to the appropriate section of this manual.
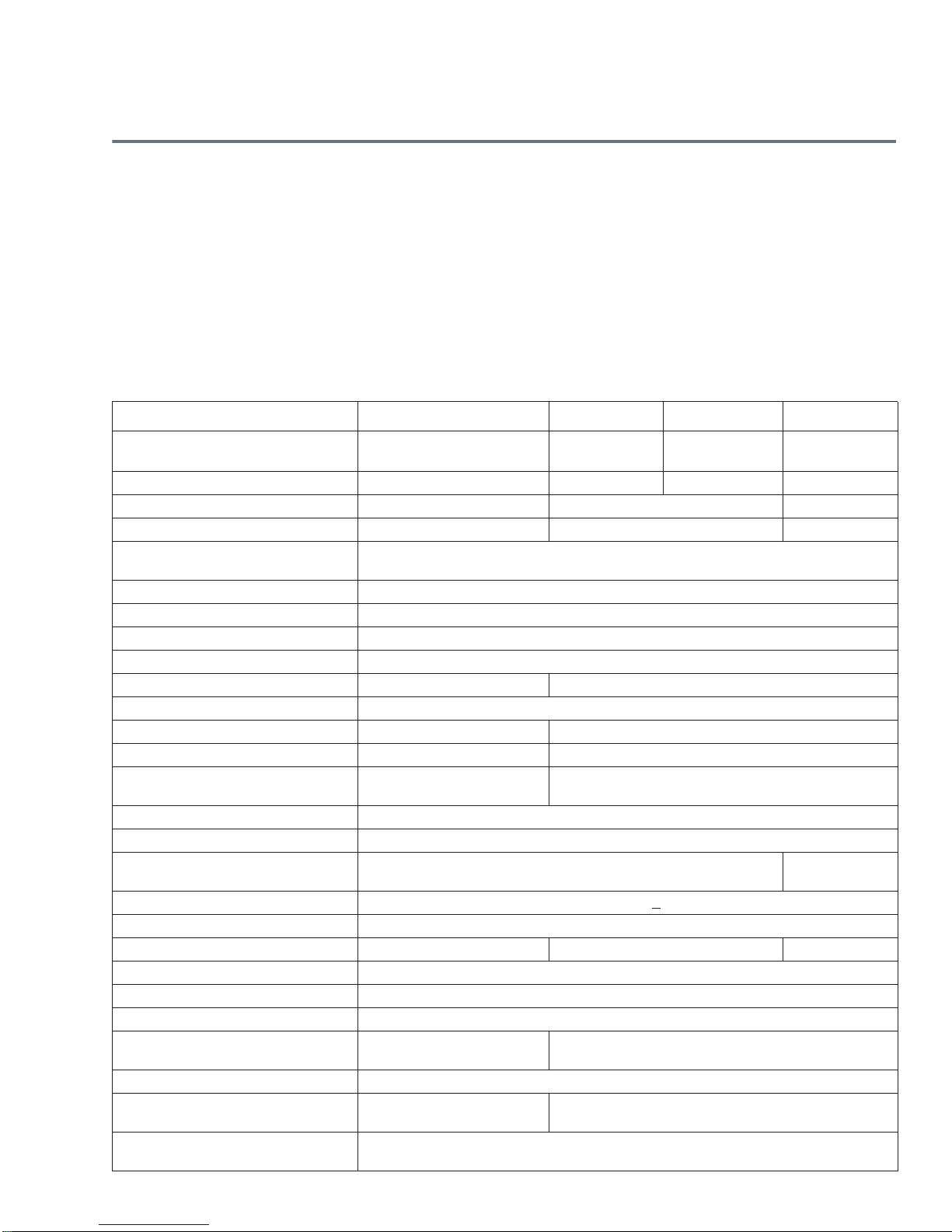
Table 1 Drive specifications summary for Seagate SV35/Suveillance +SRS HDD models
Drive Specification ST4000VX002 ST3000VX004 ST2000VX004 ST1000VX002
Formatted capacity
(512 bytes/sector)*
Guaranteed sectors 7,814,037,168 5,860,533,168 3,907,029,168 1,953,525,168
Heads 8 6 2
Disks 4 3 1
Bytes per sector (4K physical
emulated at 512-byte sectors)
Default sectors per track 63
Default read/write heads 16
Default cylinders 16,383
Recording density (max) 1807kFCI
Track density (avg) 340 ktracks/in 352 ktracks/in
Areal density (avg) 625Gb/in
Internal data transfer rate (max) 1813Mb/s 2147Mb/s
Average data rate, read/write (MB/s) 146MB/s 156MB/s
Maximum sustained data rate,
OD read (MB/s)
I/O data-transfer rate (max) 600MB/s
Cache buffer 64MB
Height (max) 26.1mm / 1.028 in
Width (max) 101.6mm /4.0 in (
Length (max) 146.99mm / 5.787 in
Weight (typical) 610g /1.345 lb 626g /1.38 lb 415g/0.915lb
Average latency 4.16ms
Power-on to ready (max) <17.0s
Standby to ready (max) <17.0s
Average seek, read (typical)
Average seek, write (typical)
Startup current (typical) 12V (peak) 2.0A
Voltage tolerance (including noise)
Ambient temperature
(drive case temperature)
4000GB
(4TB)
180MB/s 210MB/s
<12.0ms typical
<12.0ms typical
5V: ±5%
12V: ±10%
3000GB
(3TB)
4096
0° to 70°C (operating)
–40° to 70°C (non-operating)
2000GB
2
+ 0.010 in)
<8.5ms typical
<9.5ms typical
5V: ±5%
12V: +10% / -7.5%
(2TB)
1000GB
(1TB)
20.20mm /
0.795 in
Seagate SV35/Suveillance +SRS HDD Product Manual, Rev. C 7
Drive Specifications
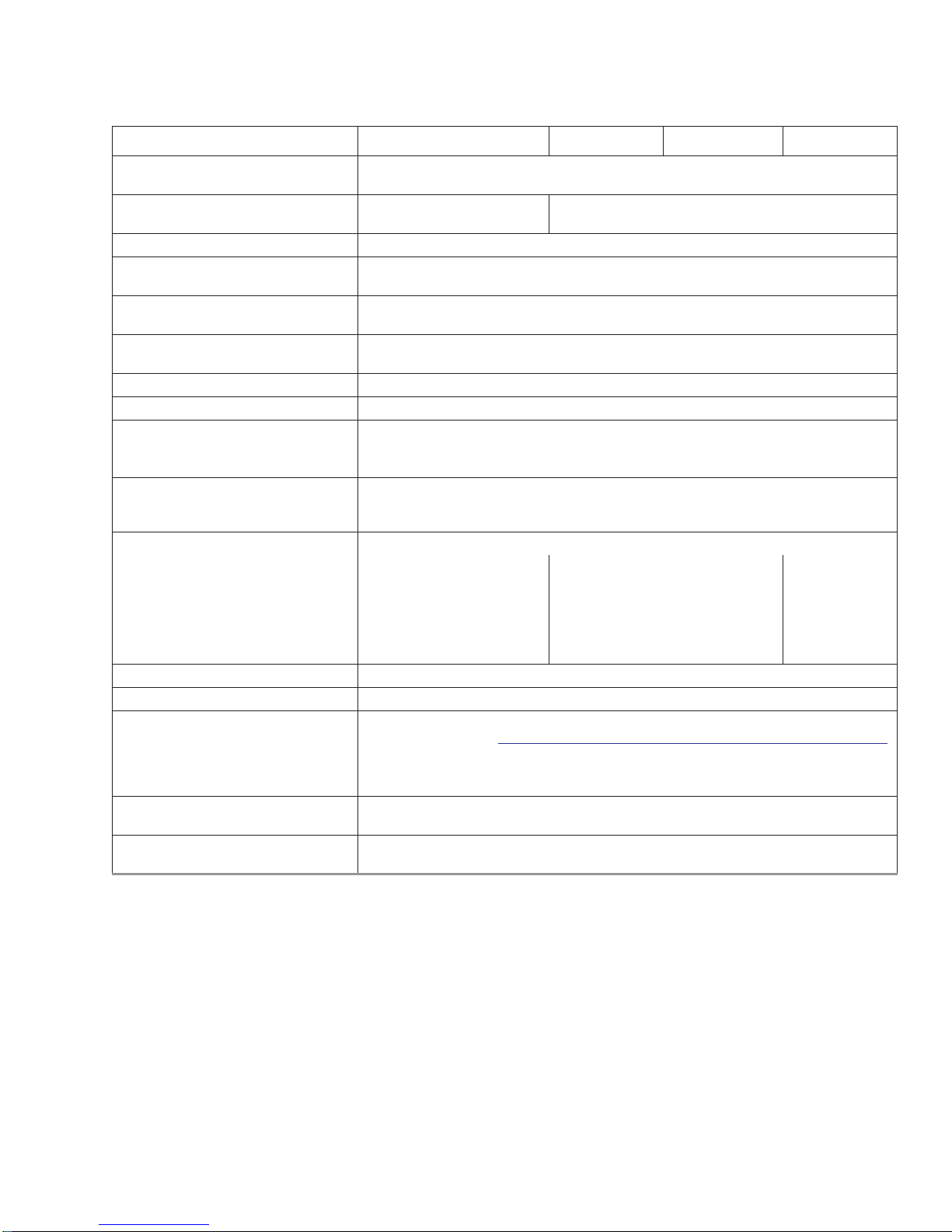
Table 1 Drive specifications summary for Seagate SV35/Suveillance +SRS HDD models (continued)
Drive Specification ST4000VX002 ST3000VX004 ST2000VX004 ST1000VX002
Temperature gradient
Relative humidity
5% to 90% (operating)
5% to 95% (non-operating)
20°C per hour max (operating)
30°C per hour max (non operating)
5% to 95% (operating)
5% to 95% (non-operating)
Relative humidity gradient (max) 30% per hour
Wet bulb temperature (max)
Altitude, operating
Altitude, non-operating
(below mean sea level, max)
37.7°C max (operating)
40.0°C max (non-operating)
–304.8m to 3048m
(–1000 ft to 10,000+ ft)
–304.8m to 12,192m
(–1000 ft to 40,000+ ft)
Operational Shock (max) 80 Gs at 2ms
Non-Operational Shock (max) 300 Gs at 2ms
2Hz to 22Hz: 0.25 Gs (Limited displacement)
Vibration, operating
22Hz to 350Hz: 0.50 Gs
350Hz to 500Hz: 0.25 Gs
5Hz to 22Hz: 3.0 Gs
Vibration, non-operating
22Hz to 350Hz: 3.0 Gs
350Hz to 500Hz: 3.0 Gs
Drive acoustics, sound power
Idle**
Seek
2.3 bels (typical)
2.4 bels (max)
2.5 bels (typical)
2.6 bels (max)
Non-recoverable read errors 1 per 10
2.4 bels (typical)
2.6 bels (max)
2.6 bels (typical)
2.7 bels (max)
14
bits read
Annualized Failure Rate (AFR) <1%
To determine the warranty for a specific drive, use a web browser to access the
http://www.seagate.com/support/warranty-and-replacements/
Warranty
following web page:
From this page, click on the "Check to see if the drive is under Warranty" link. Users
will be asked to provide the drive serial number, model number (or part number) and
country of purchase. The system will display the warranty information for the drive.
Load/Unload cycles
(25°C, 50% rel. humidity)
Supports Hotplug operation per the
Serial ATA Revision 3.0 specification
300,000
Ye s
2.2 bels
(typical)
2.3 bels (max)
2.3 bels
(typical)
2.4 bels (max)
*One GB equals one billion bytes and 1TB equals one trillion bytes when referring to hard drive capacity. Accessible capacity may vary depending
on operating environment and formatting.
* *During periods of drive idle, some offline activity may occur according to the S.M.A.R.T. specification, which may increase acoustic and power to operational levels.
*** All specifications above are based on native configurations.
Seagate SV35/Suveillance +SRS HDD Product Manual, Rev. C 8

Drive Specifications
2.2 Formatted capacity
Model Formatted capacity* Guaranteed sectors Bytes per sector
ST4000VX002 4000GB 7,814,037,168
ST3000VX004 3000GB 5,860,533,168
4K
ST2000VX004 2000GB 3,907,029,168
ST1000VX002 1000GB 1,953,525,168
*One GB equals one billion bytes and 1TB equals one trillion bytes when referring to hard drive capacity. Accessible capacity may vary depending
on operating environment and formatting.
2.2.1 LBA mode
When addressing these drives in LBA mode, all blocks (sectors) are consecutively numbered from 0 to n–1, where
n is the number of guaranteed sectors as defined above.
See Section 4.3.1, "Identify Device command" (words 60-61 and 100-103) for additional information about 48-bit
addressing support of drives with capacities over 137GB.
2.3 Default logical geometry
• Cylinders: 16,383
• Read/write heads: 16
• Sectors per track: 63
LBA mode
When addressing these drives in LBA mode, all blocks (sectors) are consecutively numbered from 0 to n–1, where
n is the number of guaranteed sectors as defined above.
2.4 Recording and interface technology
4-disk models 3 & 1-disk models
Interface SATA
Recording method TGMR
Recording density (kFCI) 1807
Track density (ktracks/inch avg) 340 352
Areal density (Gb/in2 avg) 625
Internal data transfer rate (Mb/s max) 1813 2147
Maximum sustained data transfer rate, OD read (MB/s) 180 210
Average data rate, read/write (MB/s) 146 156
I/O data-transfer rate (MB/s max) 600
Seagate SV35/Suveillance +SRS HDD Product Manual, Rev. C 9

Drive Specifications
2.5 Manufacturer Physical characteristics
Maximum height (4TB, 3TB & 2TB models) 26.10mm / 1.028 in
(1TB model) 20.20mm / 0.795 in
Maximum width 101.6mm / 4.0 in (± 0.010 in)
Maximum length 146.99mm / 5.787 in
Typical weight
ST4000VX002 610g / 1.345 lb
ST3000VX004 & ST2000VX004 626g / 1.38 lb
ST1000VX002 415g / 0.915 lb
Cache buffer 64MB (64,768kb)
2.6 Seek time
Seek measurements are taken with nominal power at 25°C ambient temperature. All times are measured using
drive diagnostics. The specifications in the table below are defined as follows:
• Track-to-track seek time is an average of all possible single-track seeks in both directions.
• Average seek time is a true statistical random average of at least 5000 measurements of seeks between
random tracks, less overhead.
Typical seek times (ms) Read Write
Track-to-track 1.0 1.2
Average 8.5 9.5
Average latency 4.16
These drives are designed to consistently meet the seek times represented in this manual. Physical seeks,
Note
regardless of mode (such as track-to-track and average), are expected to meet the noted values. However,
due to the manner in which these drives are formatted, benchmark tests that include command overhead or
measure logical seeks may produce results that vary from these specifications.
2.7 Start/stop times
4-disk models 3-disk models 1-disk models
Power-on to ready
(in seconds)
Standby to ready
(in seconds)
Ready to spindle stop
(in seconds)
Time-to-ready may be longer than normal if the drive power is removed without going through normal OS
powerdown procedures.
15 (typical)
17 (max)
15 (typical)
17 (max)
8.5 (typical)
10 (max)
8.5 (typical)
10 (max)
10 (typical)
11 (max)
Seagate SV35/Suveillance +SRS HDD Product Manual, Rev. C 10
 Loading...
Loading...