. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .. . . . .
Medalist Pro 2160
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .. . . . .
SCSI Interface Drive
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .. . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .. . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .. . . . .
Product Manual
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .. . . . .

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .. . . . .
Medalist Pro 2160 (ST52160N)
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .. . . . .
SCSI Interface Drive
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .. . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .. . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .. . . . .
Product Manual
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .. . . . .
© 1997 Seagate Technology, Inc. All rights reserved
Publication Number: 32650-001, Rev. B, July 1997
Seagate, Seagate Technology, the Seagate logo and Medalist are
registered trademarks of Seagate Technology, Inc. Other product nam es
are trademarks or registered trademarks of their owners.
Seagate reserves the right to change, without notic e, product offerings
or specifications. No part of this publication may be reproduced in any
form without written permission from Seagate Technology, Inc.
Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B iii
Contents
Introduct ion . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Specifications summary table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
1.0 Specifications summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
1.1 Formatted capacity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
1.2 Physical geometry . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
1.3 Functional specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
1.4 Physical dimensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
1.5 Seek ti me . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
1.6 Read look-ahead and caching . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
1.7 Start/stop command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
1.7.1 Power-up sequence . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
1.7.2 Power-down sequence . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
1.7.3 Auto-park . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
1.8 Power management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
1.8.1 Power consumption . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
1.8.2 Voltage tolerance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
1.8.3 Input noise . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
1.9 Environmental . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
1.9.1 Ambient temperature (HDA case) . . . . . . . . . . . 10
1.9.2 Temperature gradient . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
1.9.3 Altitude . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
1.9.4 Relative humidity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
1.10 Shock and vibration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
1.11 Acoustics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
1.12 Reliability . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
1.13 Agency listings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
1.14 Electromagnetic Compliance for the European Union . . . 13
1.15 FCC verification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13

iv Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B
2.0 Hardware and interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
2.1 SCSI-3 compatibility . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
2.2 Handling and static-discharge precautions . . . . . . . . . 17
2.3 Electrical interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
2.4 ST52160N interface connector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
2.4.1 ST52160N interface pin assignments . . . . . . . . . 21
2.5 Interface cable requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
2.5.1 Interface cable length for asynchronous operation . . . 22
2.5.2 Interface cable for Fast SCSI operation . . . . . . . . 22
2.5.3 Interface cable for UltraSCSI operation . . . . . . . . 22
2.6 Options jumper block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
2.6.1 SCSI address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
2.7 Active Termination . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
2.8 Parity enable option . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
2.8.1 Motor Start option . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
2.8.2 Remote LED connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
2.9 Daisy chaining . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
2.10 Hot-plugging . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
2.11 Mounting the drive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
3.0 Command set . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
3.1 Command descriptor block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
3.2 Status byte . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
3.3 Supported commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
3.4 Group 0 commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
3.4.1 Test Unit Ready command (00
3.4.2 Rezero Unit command (01
3.4.3 Request Sense command (03
3.4.4 Format Unit command (04
3.4.5 Reassign Blocks command (07
3.4.6 Read (6) command (08
3.4.7 Write (6) command (0A
) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
H
) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
H
) . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
H
) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
H
) . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
H
) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
H
) . . . . . . . . . . . 37
H
Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B v
3.4.8 Seek (6) command (0BH) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
3.4.9 Inquiry command (12
3.4.10 Mode Select (6) command (15
3.4.11 Reserve (6) command (16
3.4.12 Release (6) command (17
3.4.13 Mode Sense (6) command (1A
3.4.14 Start/Stop Unit command (1B
3.4.15 Receive Diagnostic Results command (1C
) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
H
) . . . . . . . . . . . 42
H
) . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
H
) . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
H
) . . . . . . . . . . . 47
H
) . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
H
) . . . . . 51
H
3.4.16 Supported Diagnostic Pages . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
3.4.17 Translate Address Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
3.4.18 Send Diagnostic command (1D
) . . . . . . . . . . . 55
H
3.5 Supported Diagnostics Page—Send Diagnostics . . . . . . 56
3.6 Translate Address Page—Send Diagnostic . . . . . . . . . 56
3.6.1 Read Capacity command (25
3.6.2 Read (10) command (28
3.6.3 Write (10) command (2A
3.6.4 Seek(10) command (2B
H
3.6.5 Write and Verify command (2E
3.6.6 Verify command (2F
) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
H
3.6.7 Read Defect Data command (37
3.6.8 Write Data Buffer command (3B
3.6.9 Read Data Buffer command (3C
3.6.10 Read Long command (3E
3.6.11 Write Long command (3F
) . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
H
) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
H
) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
H
) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
) . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
H
) . . . . . . . . . . . 62
H
) . . . . . . . . . . . 64
H
) . . . . . . . . . . . 66
H
) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
H
) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6 8
H
3.7 Group 2 Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
3.7.1 Reserve (10) command (56
3.7.2 Release (10) command (57
) . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
H
) . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
H
3.8 Group 3 and 4 commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
3.9 Group 5 and 6 commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
3.10 Group 7 commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71

vi Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B
Appendix A. Supported messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
A.1 Messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
A.2 Synchronous Data Transfer Request message (01
) . . . . 74
H
A.2.1 Wide Data Transfer Request Message . . . . . . . . . 75
Appendix B. Sense data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
B.1 Additional sense data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
B.2 Sense key . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7 9
B.3 Additional sense code and additional sense code qualifier . 80
Appendix C. Mode pages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
C.1 Read-Write Error Recovery page (01
C.2 Disconnect/Reconnect page (02
C.3 Format Device page (03
C.4 Rigid Disc Geometry page (04
C.5 Verify error recovery page (07
C.6 Caching page (08
H
) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
H
H
) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
H
) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
) . . . . . . . . . . . 84
H
) . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
H
) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9 0
C.6.1 Read look-ahead and caching . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
C.6.2 Write caching and write merging . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
C.6.3 Caching page description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
C.7 Control Mode page (0A
C.7.1 Unit Attention Parameters (00
) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
H
) . . . . . . . . . . . 100
H
Appendix D. Inquiry data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
D.1 Inquiry data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
D.2 Vital product data pages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
D.2.1 Unit Serial Number page (80
D.2.2 Implemented Operating Definition page (81
D.2.3 Firmware Numbers page (C0
D.2.4 Date Code page (C1
) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
H
D.2.5 Jumper Settings page (C2
) . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
H
) . . . . 107
H
) . . . . . . . . . . . 108
H
) . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
H
Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B vii
Figures
Figur e 1. Ty p ic a l startup cu r rent pro fi l e . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Figure 2. Single-ended transmitter and receiver . . . . . . . . . . .18
Figure 3. Connectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Figure 4. ST52160N jumper settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Figure 5. Standard Mounting dimensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B 1
Introduction
This manual describes the functional, mechanical and interface specifications for the Medalist
®
Pro 2160N hard disc drive. The Medalist Pro
2160N is referred to in this manual by its model number, ST52160N.
Seagate desktop products take a step into the future with the ST52160N.
The drive features MR heads and PRML recording technology and uses
an Ultra SCSI interface that supports a synchronous external transfer
rate of up to 20 Mbytes per second.
The ST52160N has other features that ensure fast data throughput. The
drive uses a 128-Kbyte buffer and an adaptable cache that aids the flow
of read and write data. Embedded servo technology allow the dri ve to
position the heads for data retrieval efficiently and accurately while
eliminating the periodic thermal recalibration that can interr upt during
data transfers. The drive also uses a 16-bit microprocessor and an
intelligent controller that provides data streaming: direct dat a transfers
between the drive and the host without microprocessor intervention. This
feature allows for a sustained data rate that f acilitates video playback
and other multimedia operations.
The drive conforms to the standard 3.5-inch footprint but has a 0.75-inch
(19-mm) height profile and a 5. 380- inc h-dept h pr ofile. The lower height
and shorter depth gives the designer or integrator more room for air
circulation, other peripherals or a smaller drive bay.
The SCSI commands the drive supports are listed in Section 3.3. on
page 30.

2 Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B
The following is a summary of the drive’s features:
Capacity
• 2.17 Gbytes, guaranteed
Features
• SCSI-3 SPI and SCAM Plug and Play compliant
• 8-bit Ultra SCSI
• Transfer rates up to 20 Mbytes per second
• 11-msec average seek time
• 5,379-RPM rotational speed
• 5.56 average latency
• 128-Kbyte buffer
• Rotational-position seek/sort
• On-the- fly EC C co rrect i on
• Embedded servo
• PRML channel
• MR heads
Acoustics
• 3.4-bel idle sound power level
• 27-dBA idle sound pressure level
Mini 3.5-inch form-factor
• 19-mm-height profile
• Fits standard 3.5-inch footprint
Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B 3
Specifications summary table
The following table serves as a quick reference for the ST52160N
performance specifications. These and other specifications are discussed in the Specifications summary section following the table.
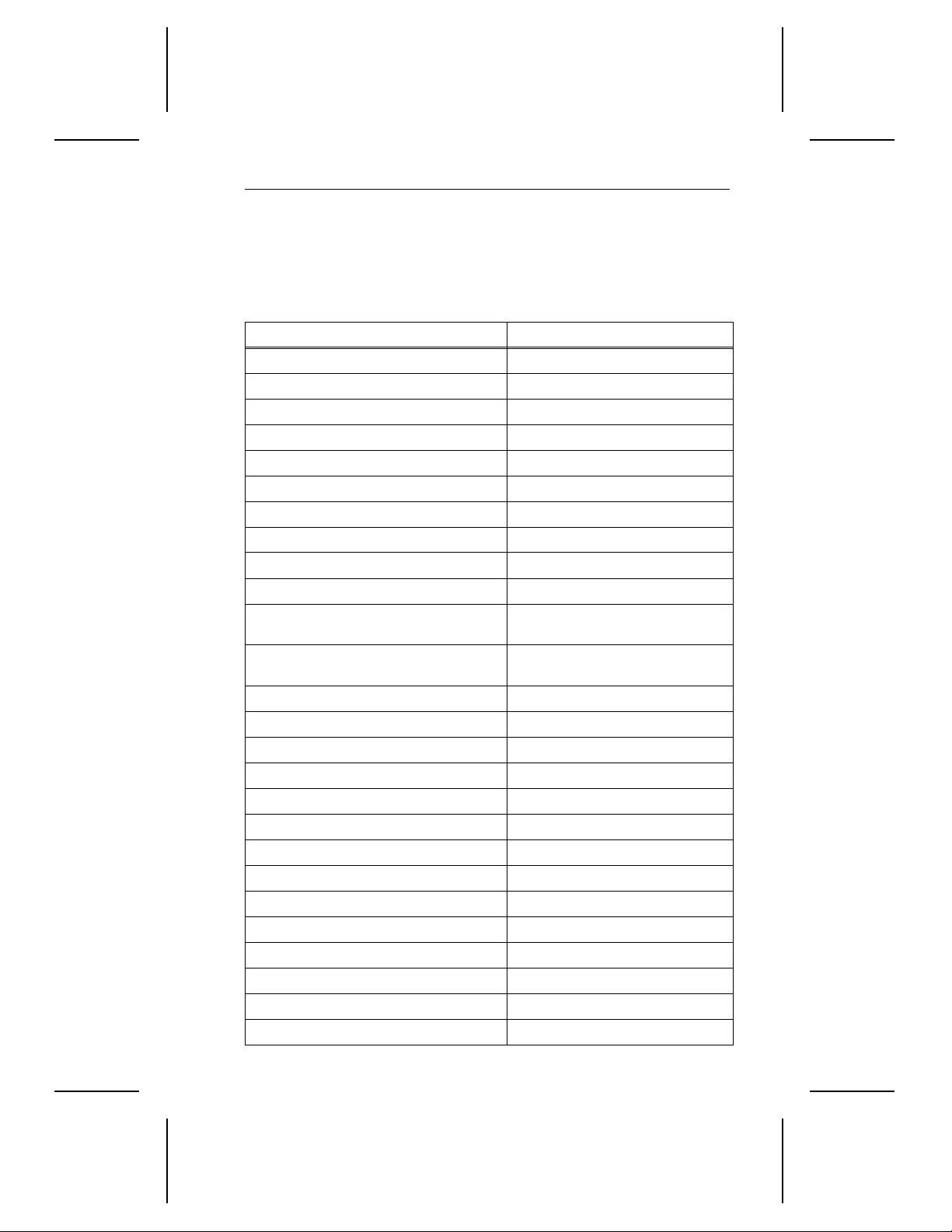
Drive specific at io n ST52160N
Guaranteed capacity (Gbytes, 10
Guaranteed sect or s 4,238,282
Bytes per sector 512
Sectors per tra ck ( aver age) 161
Physical cylinder s 6,536
Physical read/wr i te heads 4
Discs 2
Recording density (bits per inch, max) 122,369
Track density (tr acks per inch) 6,731
Spindle speed (RP M ) 5,397 ± 0.5%
Internal data-transfer rate
(Mbits per second max)
External transf er rat e
(Mbytes per sec ond, m ax)
Cache buffer (Kbytes) 128
Height, inche s max (mm) 0.748 (19.0)
Width, inches max (mm) 4.01 (101.8)
Depth, inches max (mm) 5.38 (136.6)
Typical weight, lb. (Kg) 1.0 (0.45)
Track-to-t ra ck seek time (msec , typical) 3.5
Average seek tim e (msec, typical) 11.0
Average seek tim e re ad ( m sec, t ypi cal) 12.0
Average seek tim e writ e ( m sec, t ypi cal) 13.0
Full-stroke seek tim e ( m sec, t ypical) 25.0
Average laten cy ( m sec) 5.56
Power-on to re ady ( sec , typi cal) 20
Spinup current: +12V (max) 1.9A
Seek power (typical) 8.2W
9
)2.17
56.3 to 99.6 MHz
10.0 asynchro nous
20.0 synchron ous
4 Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B
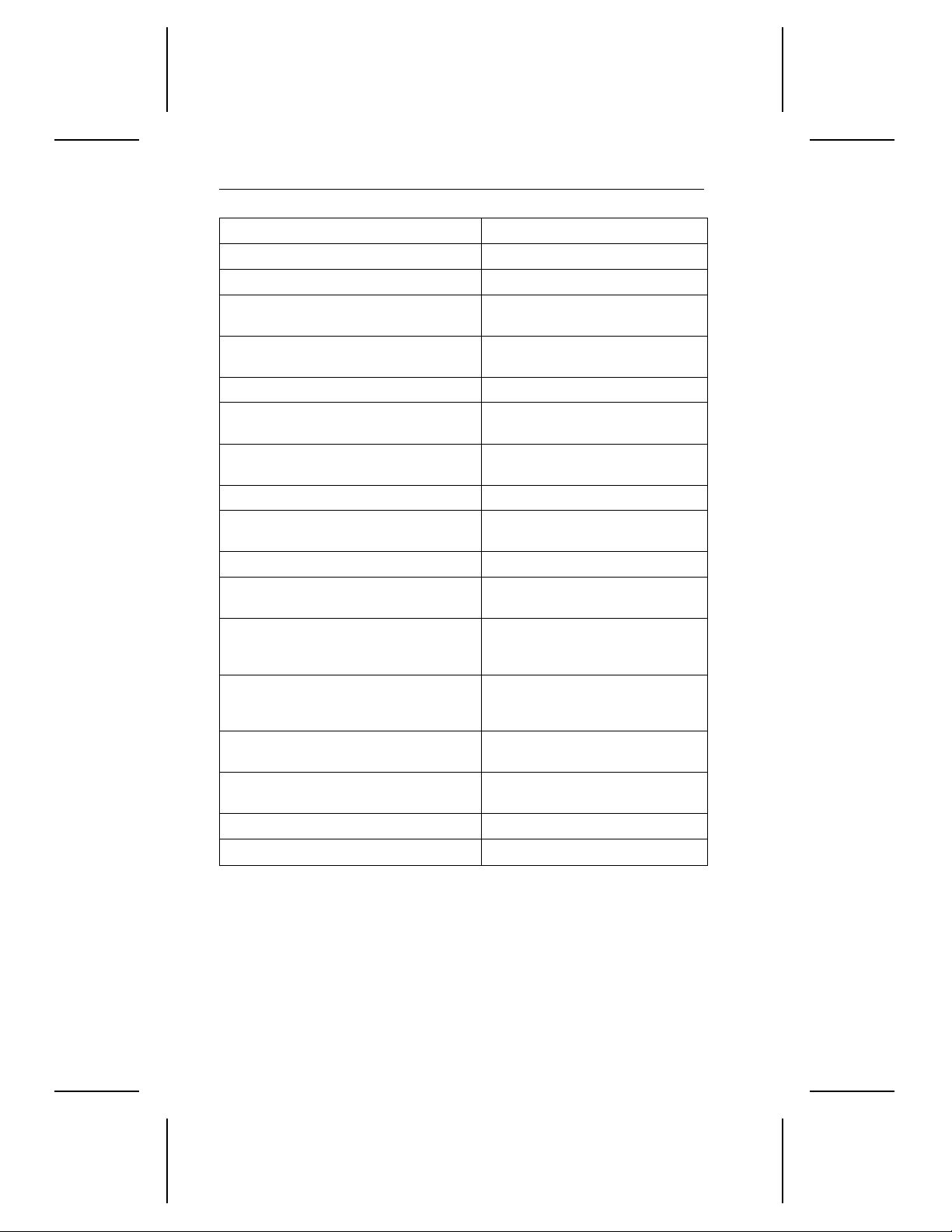
Drive specific at io n ST52160N
Read/Write po wer (typi ca l) 7.6W
Idle power (typical) 8.0W
Voltage tolerance (incl uding noise): +5V
Voltage tolerance (incl uding noise): +12V
Ambient temper at ur e, operat i ng ( C°) 5° to 55°C
Temperature gradient, operatin g
(°C per hou r m ax ) 20° C
Relative humidity,operating gradient
(max) 10% per hour
Relative humidity, operating 8% to 80%
Wet bulb temperature
operating (non cond ensi ng) 29.4°C
Altitude, opera ting –1,000 to 10,000 f t .
Shock, normal op er at ing
(Gs max for 11 msec) 2 Gs
Vibration, operating
(Gs max at 22–350 Hz without
nonrecoverable errors)
Vibration, nonoperating
(Gs max at 22–350 Hz with no physical
damage incurr ed)
Nonrecoverable read errors
(bits transferr ed)
Mean time between failures (MTBF)
(power-on hou rs )
Contact start -sto p cycl es 50,000
Service life (years) 5
± 5%
± 5%
0.75 Gs
0 to Peak
4 Gs
0 to Peak
1 per 10
500,000
13

Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B 5
1.0 Specifications summary
1.1 Formatt ed cap acit y
The capacities specified here do not include spare sectors and cylinders.
The media contains 2,000 spare blocks at the end of the volume.
1
Guaranteed capacity (Gbytes
Guaranteed sectors 4,238,282
1.2 Physical geometry
Discs 2
Read/write heads 4
Cylinders 6,536
Sectors per track (average) 161
1.3 Functional specifications
)2.17
Interface SCSI-3 SPI Compliant
PRML recording method Code (0,4,4)
External data-transfer rate
(Mbytes per sec, max)
Internal data-transfer rate
(Mbits per sec)
Bytes per sector 512
Data zones 19
2
Areal density (Mbits/ in
Track density (TPI) 6,731
Recording density (BPI, max) 122,369
1. One Gbyte equals 1,000,000,000 bytes.
) 823.7
10 asynchronous
20 synchronous
56.3–99.6 MHz

6 Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B
1.4 Physical dimensions
Height (max) 0.748 inches (19 mm)
Width (max) 4.01 inches (101.8 mm)
Depth (max) 5.38 inches (136.6 mm)
Weight (max) 1.0 lb. (0.45 Kg)
1.5 Seek time
All seek time measurements are taken under nominal conditions of
temperature and voltage with the drive mounted horizontally. In the
following table:
Track-to-track
•
seek time is the average of all possible s ingle-track
seeks in both directions.
•
Average/typical
seek time is a true statistical random average of at
least 5,000 measurements of seeks in both directions between random cylinders, less overhead.
•
Full-stroke
seek time is one-half the time needed to seek from logical
block address zero (LBA 0) to the maximum LBA and back to LBA 0.
Track-to-track
seek time typ
Average/typical
2
seek time
3
Full-stroke
seek time typ
4
Average
latency
3.5 msec typ 11.0 msec typ 25.0 msec typ 5.56 msec
4.5 msec max 12.0 msec read 27.0 msec max
13.0 msec write
Note.
Host overhead varies between systems and cannot be specified.
Drive internal overhead is measured by issuing a no-motion
seek. Drive overhead is typically less than 1.0 msec.
____________________
2. All possi ble one track seeks are divided into the time requir ed to pe rform these seeks.
Only the mechanism time is used; in terface overhead is excluded.
3. All possible seeks are divided into the time required to perform these seeks. Only the
mechanism time is used; interface overhead is excluded.
4. The average of 1,000 full-stroke seeks is used in this computation. Only the mechanism
time is used; interface overhead is e x cluded.
)
Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B 7
1.6 Read look-ahead and caching
The drive uses an algorithm that improves seek performance by storing
data in a buffer and processing it at a more convenient time. Three
methods are used: read l ook-ahead, read caching and write caching.
These are described in Appendix C.6 on page 94.
1.7 Start/stop command
If the motor-start option is disabled, the drive is ready within 20 seconds
after power is appli ed. If the motor -start option is enabl ed, the drive is
ready within 20 seconds after it receives the Motor Start command. If the
drive receives a command to spin down or power is removed, the driv e
stops within 15 seconds.
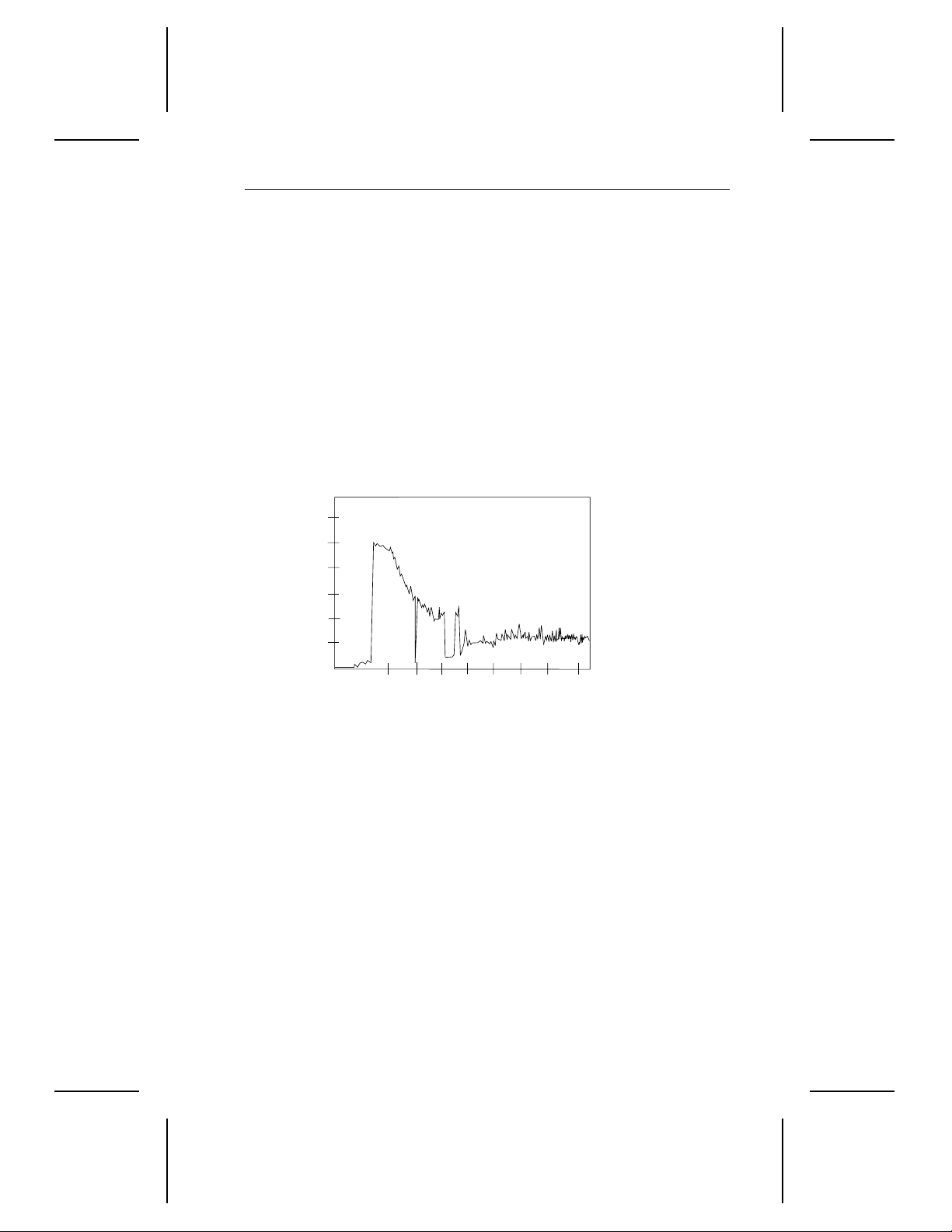
Current (mA)
2,100
1,900
1,700
1,500
1,300
1,100
0
0
24
8
6
Time (seconds
12
10
16
14
Figure 1. Typical startup curren t prof i le
1.7.1 Power-up sequence
The following typical power -up sequence is provided to assist you in
evaluating drive performance. This information does not constitute a
specification or a performance guarantee.
Power is applied to the disc drive.
1.
Depending on whether there is a jumper installed on pins 9 and 10 of
2.
the options jumper block (J5) shown in Figure 3 on page 19, either of
the following sequences occurs:
• If a jumper is not installed, the remote start option is not enabled, and
the drive begins to spin up as soon as power is applied.
• If a jumper is installed, the remote start option is enabled, and the drive
begins to spin up when the host sends a command for the motor to
start.

8 Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B
3. Within 250 msec after power is applied, the drive responds to the Test
Unit Ready, Request Sense, Mode Sense and Inquiry commands.
4. The drive begins to lock in speed-control circuits.
6. The actuator lock releases the actuator.
7. The spindle motor reaches operating speed in about 5 seconds. After
5 seconds, there are no speed variations.
8. The drive performs velocity-adjustment seeks.
9. The drive seeks track 0 and is then ready.
1.7.2 Power-down sequence
Caution. Do not move the drive until the motor has come to a complete
stop.
1. The power is turned off.
2. Within 15 seconds, the drive spindle stops rotating.
3. The read/write heads automatically move to the landing zone, which
is inside the maximum data cylinder.
4. The magnetic acuator lock mechanism locks the arm. This completes
the power-down sequence.
1.7.3 Auto-park
During power-down, the read/write heads automatically move to the
landing zone. The heads park inside the maximum data cylinder and the
magnetic actuator lock engages. When power is applied, the heads
recalibrate to track 0.
1.8 Power managemen t
The drive supports power-management modes that reduce its overall
power consumption. They automatically change from one mode to
another in response to interface activity. You do not need to change any
parameters or send any special commands to make the drive change
modes. The power-management modes are described as follows:
• Spinup. Spinup is def ined as the period during which t he spindl e is
coming up to operating speed. The power consumed in this mode is
equivalent to the average power during the first 10 seconds after the
drive begins to spin up.
Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B 9
• Seek. The servo electronics are active, and the heads are moving to
a specific location on the disc. The read/write electronics are powereddown. The power consumed in this mode is equivalent to the average
power measured while executing random seeks wit h a 2-revolution
(26.6 msec) dwell between seeks. T he drive enters this mode from
the Idle mode.
• Read/Write. The drive is reading or writing. All electronics are active
and the heads are on track.
• Idle. The motor is up to speed and the drive is in track-follow mode.
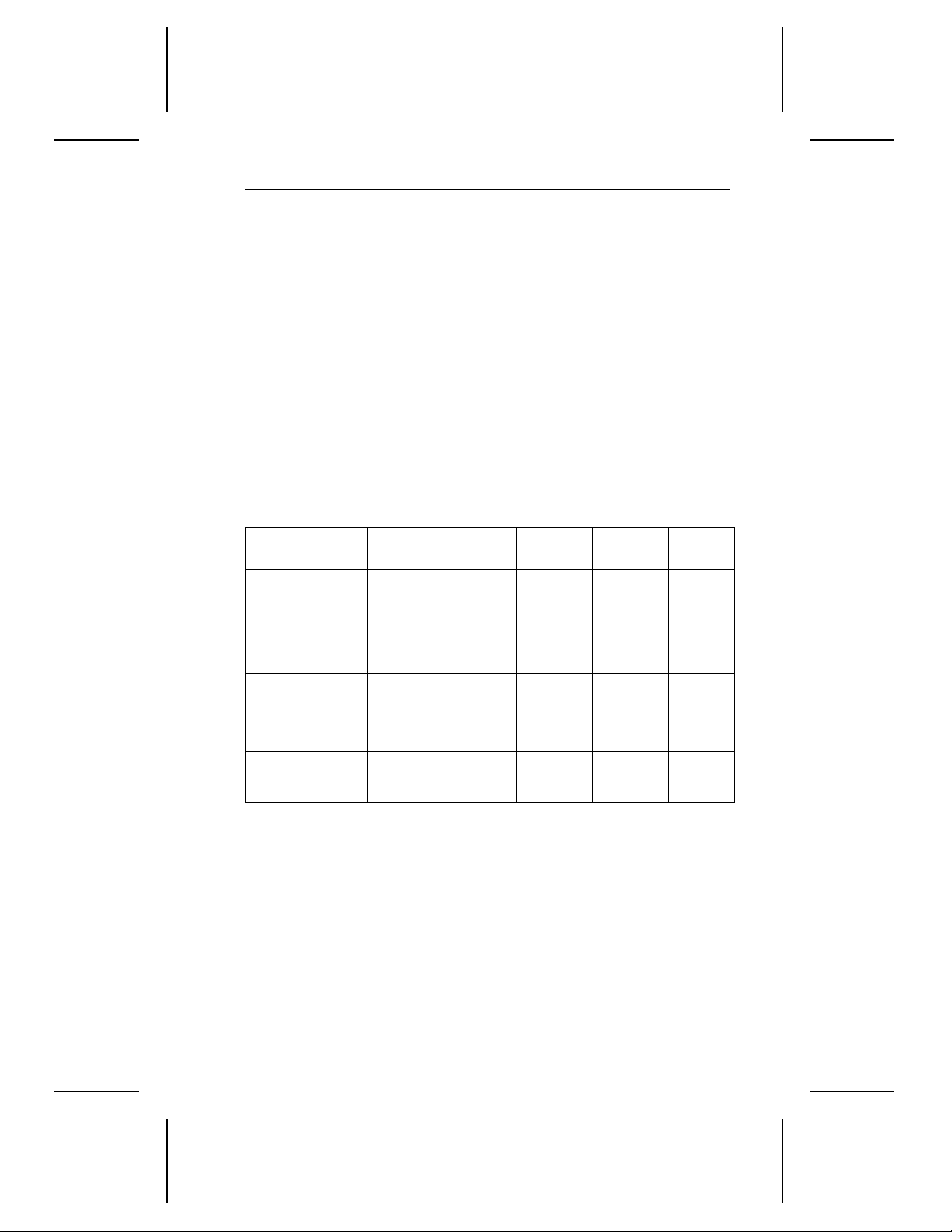
1.8.1 Power consumption
Values in the t able below were measured at the drive power connector
with an RMS DC ammeter. The terminating resistors are disabled, and
terminator power is supplied through the SCSI connector. All values are
measured 10 minutes after the drive spins up except as noted.
Spinup Seeking
Current at +12V
Amps peak 1.9 — — — —
RMS amps typ — 0.470 0.450 0.460 0.200
Watts typ — 5.640 5.400 5.520 2.400
Current at +5V
RMS amps typ — 0.500 0.500 0.480 0.480
Watts typ — 2.500 2.500 2.400 2.400
Power
Total watts typ — 8.2W 7.600W 8.0W 4.800W
Read/
Write
Idle Standby
1.8.2 Voltage tolerance
+5V +12V
Voltage tolerance
(including noise)
± 5% ± 5%

10 Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B
1.8.3 Input noise
+5V +12V
Voltage tolerance
(including noise)
Input noise frequency
(max)
Input noise
(max, peak-to-peak)
± 5% ± 5%
25 MHz 25 MHz
100 mV 240 mV
1.9 Environmental
This section specifies acceptable environmental conditions for the drive.
The operating specifications ass ume that the drive is powered up. The
nonoperating specifications assume that the drive is packaged as it was
shipped from the factory.
1.9.1 Ambient temperature (HDA case)
Operating 5°C to 55°C (41°F to 131°F)
Nonoperating –40°C to 70°C (–40°F to 158°F)
Note.
The system must provide sufficient airflow so that the
aluminum base surface temperature remains below 55°C.
1.9.2 Temperatur e grad ien t
Operating 20°C per hour (36°F per hour)
Nonoperating 30°C per hour (54°F per hour)
1.9.3 Altitude
Operating –1,000 ft. to 10,000 ft. (–305 m to 3,048 m)
Nonoperating –1,000 ft. to 40,000 ft. (–305 m to 12,192 m)
Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B 11
1.9.4 Relative humidity
Operating 8% to 80% noncondensing
Maximum wet bulb 29.4°C (84.9°F)
Operating gradient, max 10% per hour
Nonoperating 5% to 95% noncondensing
Maximum wet bulb 35°C (95.0° F)
1.10 Shock and vibration
All shock and vibration specifications assume that the inputs are measured
at the drive mounting screws. Shock measurements are based on an
11-msec, half sin e wave shoc k pulse, not to be repeated more than twic e
per second.
During normal operating shock and vi bration, there is no physical damage to the drive or performance degradation.
During abnormal operating shock and vibration, there is no physical
damage to the drive, although performance may be degraded during the
shock or vibration episode. When normal operating shock levels resume,
the drive meets its performance specifications.
During nonoperating shock and vibration, the read/write heads are
positioned in the shipping zone.
Normal
operating
Shock 2 Gs 10 Gs 75 Gs
5–22 Hz vibration 0. 020-i nch
displacement
22–350 Hz vibration 0.50 Gs 0.75 Gs 4.00 Gs
Abnormal
operating
0.030-inch
displacement
Nonoperating
0.160-inch
displacement

12 Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B
1.11 Acoustics
This table shows the overall A-weighted sound power and sound pressure levels for the drive. All measurements are generally consistent with
ISO document 7779. Acoustic measurements are taken under es sentially free-field conditions over a reflect ing plane. The drive is oriented
with the top cover up for all tests.
Overall A-weighted Value Idle Seek
Sound power, typ (bels) 3.4 4.0
Sound power, max (bels) 3.7 4.3
Sound pressure, typ (dBA)
Sound pressure, max (dBA) 30 33
27 30
1.12 Reliability
Read error rates are measured with automatic retries and data correction
with ECC enabled and all flaws reallocated. The mean t ime between
failures (MTBF) is measured at nominal power at sea level and an
ambient temperature of 35°C.
13
Nonrecoverable read errors 1 per 10
Seek errors 1 per 10
Contact stops and starts 50,000
MTBF 500,000 power-on hours
Service life 5 years
bits transferred
7
physical seeks
1.13 Agency listings
The drive is listed by agencies as follows:
• Recognized in accordance with UL 478 and UL 1950
• Certified to CSA C22.2 No. 220-M1986 and CSA C22.2 No. 950-
M1989
• Certified to VDE 0806/05.90 and EN 60950/1.88 as tested by VDE
Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B 13
1.14 Electromagnetic Compliance for the European
Union
This model has the CE Marking, signifying that it complies with the
European Union requirements of the Electromagnetic Compatibility Directive 89/336/EEC of 03 May 1989 as amended by Directive 92/31/EEC
of 28 April 1992 and Directive 93/68/EEC of 22 July 1993.
®
Seagate
above directives. The drive was tested in a representative system for
typical applications. The select ed system represents the most popular
characterist ics for test platforms.
The system configurations include:
• 486, Pentium, and PowerPC microprocessors
• 3.5-inch floppy disc drive
• Keyboard
• Monitor/display
Although the test system with this Seagate model complies to the
directives, we cannot guarantee that all systems will comply. The computer manufacturer or system integrator will confirm EMC compliance
and provide CE Marking for their product. The drive is not meant for
external uses (without properly designed enclosure, shielded I/O cable,
etc.), and a terminator should be used on all unused I/O ports.
uses an independent laboratory to confirm compli ance to the
1.15 FCC ver if icat io n
The ST52160N SCSI interface drive is intended t o be contained s olely
within a personal computer or similar enclosure (not attached to an
external device). As such, a drive is considered to be a subassembly
even when individually marketed to the customer. As a subassembly, no
Federal Communications Commission authorization, verification or certification of the device is required.
Seagate Technology, Inc. has tested the drive in an enclosure as
described above to ensure that the total assembly (enclosure, disc drive,
motherboard, power supply, etc.) does comply with the limits for a
Class B computing device, pursuant to Subpart J of Part 15 of the FCC
rules. Operation with noncertified assemblies is likely to result in interference to radio and television reception.

14 Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B
Radio and television interference. This equipment generates and uses
radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in strict accordance
with the manufacturer’s instructions, may cause interference to radio and
television reception.
This equipment is designed to provide reasonable protection against
such interference in a residential installation. However, there is no
guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this
equipment does cause inter ferenc e to radio or television, which can be
determined by turning the equipment on and off, you are encouraged to
try one or more of the following corrective measures:
• Reorient the receiving antenna.
• Move the device to one side or the other of the radio or TV.
• Move the device farther away from the radio or TV.
• Plug the equipment into a di fferent outlet so that the receiver and
computer are on different branch outlets.
If necessary, you should consult your dealer or an experienced radio/television technician for additional s uggestions. You may find helpful the
following booklet prepared by the Federal Communications Commission:
How to Identify and Resolve Radio-Television Interference Problems.
This booklet is available from the Superintendent of Documents, US
Government Printing Office, Washington, DC 20402. Refer to publication
number 004-000-00345-4.
Note. This di gital apparatus does not exceed the Clas s B limits for
radio noise emissions from computer equipment as set out in the
radio interference regulations of the Canadian Depart ment of
communications.
Le présent appareil numérique n′émet pas de bruits radioél ectriques dépassant les limites applicables aux appar eils numériques de Classe B prescrites dans le règlement sur le brouillage
radioélectrique édicté par le Ministère des Communications du
Canada.
Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B 15
Sicherheitsanleitung
Das Gerrät ist ein Einbaugerät, das für eine maximale Umgebung-
1.
stemperatur von 55°C vorgesehen ist.
Zur Befestigung des Laufwerks werden 4 Schrauben 6-32 UNC-2A
2.
benötigt. Bei seitlicher Befestigung darf die maximale Länge der
Schrauben im Chassis nicht mehr als 5,08 mm und bei Bef estigung
an der Unterseite nicht mehr als 5,08 mm betragen.
Als Versorgungsspannugen werden benötigt:
3.
+5V æ 5% 0.55A
+12V æ 5% 0.35A (1,9A fur ca. 10 Sek. fur ± 10%)
Die Versorgungsspannung muss SELV entsprechen.
4.
Alle Arbeiten an der Festplat te dürfen nur von ausgebildet em Serv-
5.
icepersonal durchgeführt werden. Bitte entfernen Sie nicht die Aufschriftenschilder des Laufwerkes.
Der Einbau des Laufwerkes muss den Anforderungen gemäss DIN
6.
IEC 950 VDE 0805/05.90 entsprechen.

16 Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B
Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B 17
2.0 Hardware and interface
The ST52160N uses an Ultra SCSI interface that consis ts of an 8-bit
bidirectional data bus. The interface supports multiple initiators, disconnect and reconnect, self-configuring host software and logical block
addressing.
The Ultra SCSI interface uses a singled-ended driver/receiver configuration that uses asynchronous or synchronous communication protocols.
The ST52160N supports asynchronous transfer rates up to 10 Mbytes
per second and synchronous transfer rates up to 20.0 Mbytes per
second.
2.1 SCSI-3 compatibility
The drive interface is described in the Seagate SCSI-2 /SCSI-3 Interface
Manual, publication number 77738479. The drive complies with the
mandatory subset of the ANSI SCSI-2 Interface. The Fast SCSI-3
interface is based on the ANSI Small Computer System Interface-2
(SCSI-2), document number ANSI X3.131-1994.
2.2 Handling and static-discharge precautions
The drive has static-sensitive devices. Avoid damaging the drive and
these devices by obser ving the f ollowing standard handl ing and stati cdischarge precautions:
• Keep the drive in its static-shielded bag until you are ready to complete
the installation. Do not attach any cables to the drive while it is in its
static-shielded bag.
• Before handling the drive, put on a grounded wris t strap, or ground
yourself frequently by touching the metal chassis of a computer that
is plugged into a grounded outlet. Wear a grounded wrist strap
throughout the entire installation procedure.
Wool and synthetic clothes, carpets, plastics and Styrofoam contributes to electrostatic buildup. Static discharge may damage sensitive
components in your drive and computer.
• Handle the drive by its edges or frame only.
• The drive is extremely fragile—handle it with care. Do not press down
on the drive’s top cover.
• Always rest the drive on a padded, antistatic surface until you mount
it in the host system.
• Do not touch the connector pins or the printed circuit board.
18 Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B
• Do not remove the factory-installed labels from the drive or cover them
with additional labels. If you do, you void the warranty. Some factoryinstalled labels contain information needed to service the drive. Others
are used to seal out dirt and contamination.
2.3 Electrical interface
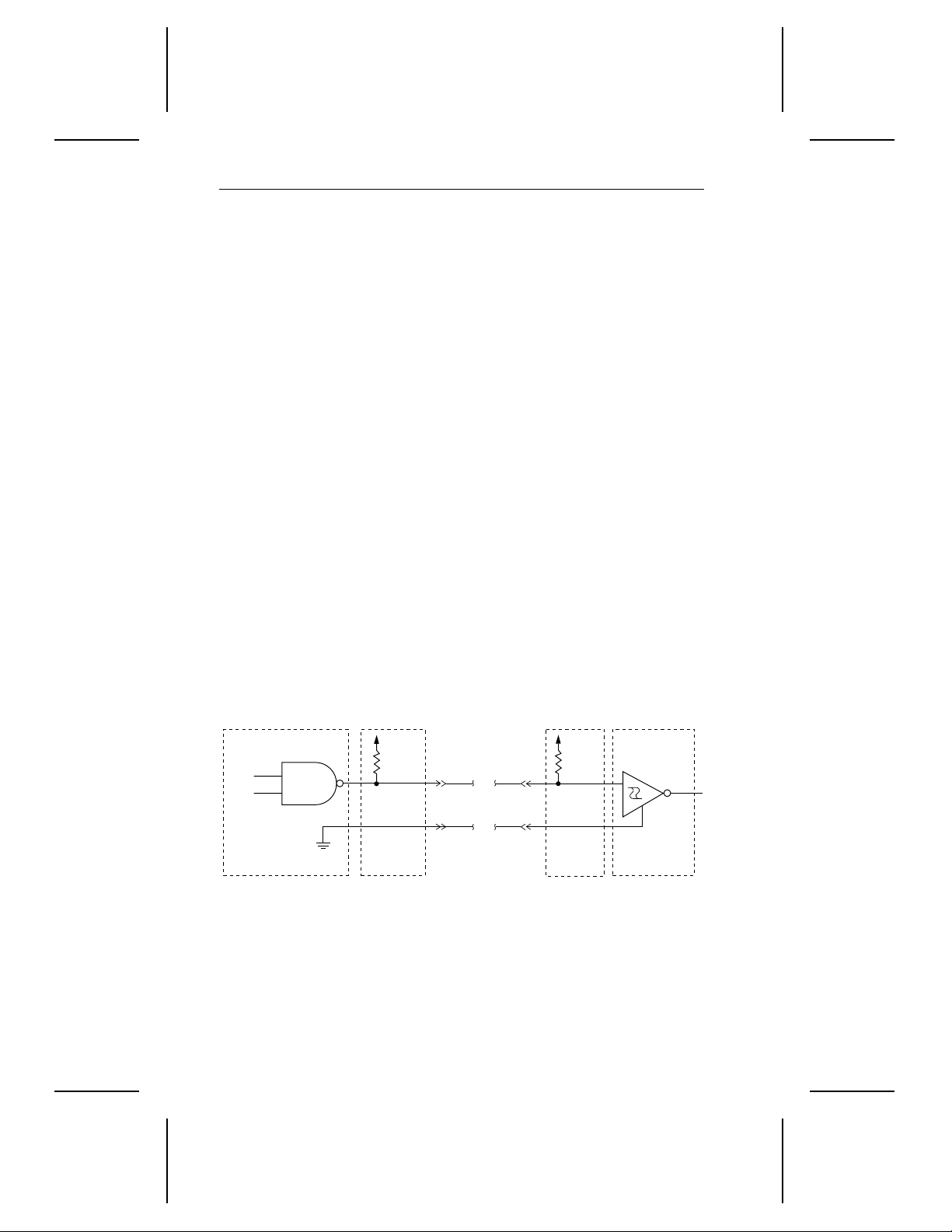
The ST52160N is designed t o use single-ended int erface signals, s ingle-ended drivers and receivers, and active terminator circuitry. Figure 2
shows a single-ended transmitter and r ec eiv er without the active terminator circuitry.
•
Transmitter characteristics.
The drive uses an ANSI SCSI-compatible, open-collector, single-ended driver. This driver is capable of
sinking a current of 48 mA with a low-level output voltage of 0.4 volts.
•
Receiver characteristics.
The drive uses an ANSI SCSI single-
ended receiver with hysteresis gate or equivalent as a line receiver.
The loss in the cable is defined as the difference between the voltages
of the input and output signals, as shown below:
Logic level Driver output (x) Receiver input (x)
Asserted (1)
Negated (0)
Line driver
(transmitter or transceiver)
ANSI SCSI
compatible circuit
≤
x ≤ 0.4V 0.0V ≤ x ≤ 0.8V
0.0V
≤
2.5V
x ≤ 5.25V 2.0V ≤ x ≤ 5.25V
+2.85V
110
ohms
Flat cable pair
+2.85V
110
ohms
Line receiver
ANSI SCSI
compatible
circuit
Figure 2. Single-ended transmitter and receiver
Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B 19
ST52160N
Options Jumper
Block (J5)
50-Pin Interface
connector
Pin 1
Standard
power connector
4
3
2
1
Circuit board
+5V
+
5V return
+12V return
+12V
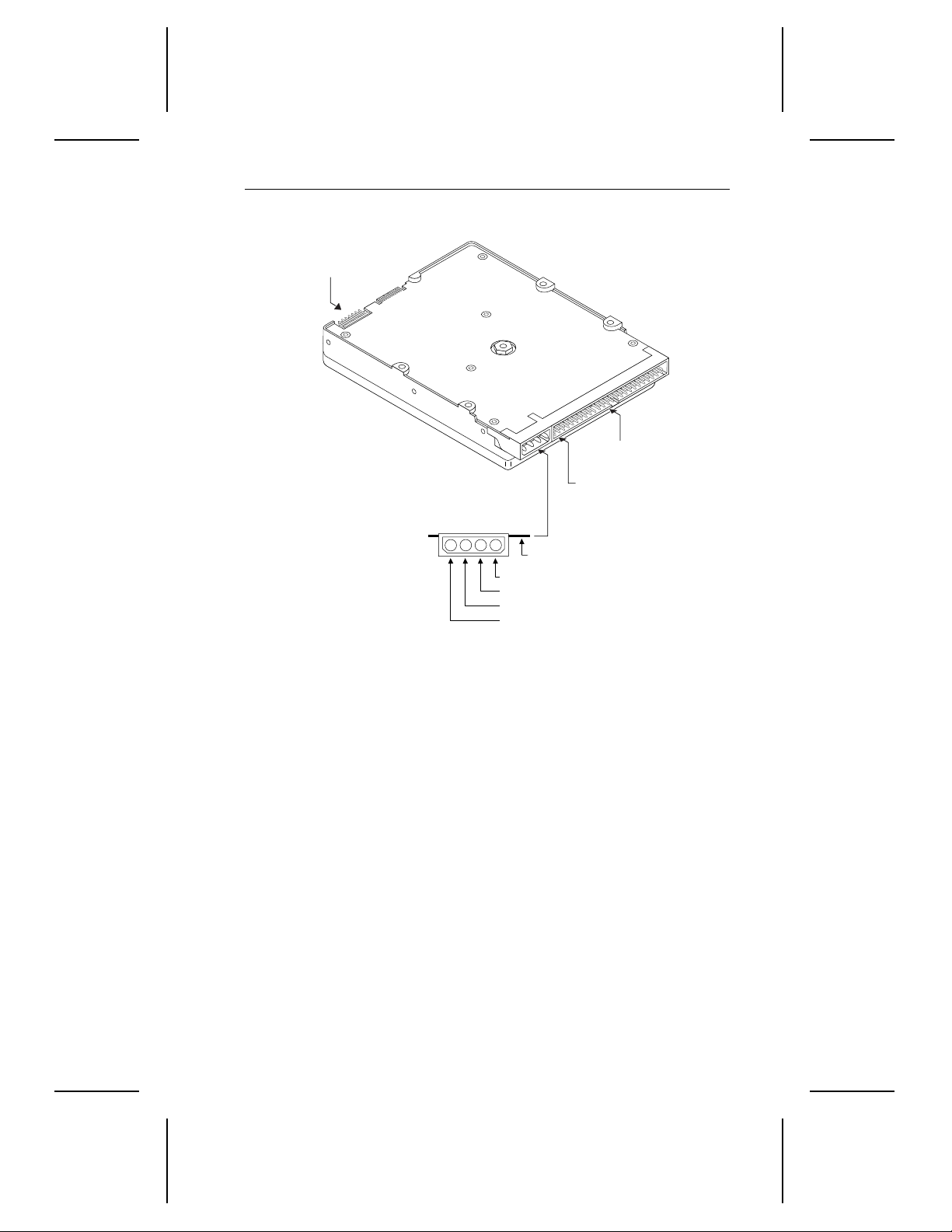
Figure 3. Connectors

20 Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B
2.4 ST52160N int erface connector
The ST52160N uses a standard 50- pin, nonshiel ded, keyed connector
and a standard 4-pin power connector. The interface connector consists
of two rows of 25 male contacts 0.100 inches apart. Pin 1 on the
connector is shown in Figure 3 on page 19. Recommended mating
connectors and their part numbers are listed below.
Part numbers for mating 3M connectors that are compatible with the
drives are listed below. These connectors do not have a center key and
are available with or without strain relief.
Without strain relief
No center key
Closed end
(for cable ends)
Open end
(for daisy chain)
Part numbers for mating Molex connectors compatible with the drives
are listed below. These connectors have a center key.
Closed end
(for cable ends)
Open end
(for daisy chain)
Below are part numbers for strain reliefs that can be used with the M olex
connectors.
Molex strain relief,
preferred version
in Europe
Molex strain relief,
preferred version
in Japan
3M
3425-7000
3M
3425-6000
Molex
39-51-2504
Molex
39-51-2501
Molex 90170-0050
Molex 15-25-1503
With strain relief
No center key
3M
3425-7050
3M
3425-6050

Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B 21
2.4.1 ST52160N interface pin assignments
The table below shows the pin as signment for the ST52160N 50-pin
interface connector. A minus sign (−) indicates an active-low signal.
Signal name
–DB(0) 2 1
–DB(1) 4 3
–DB(2) 6 5
–DB(3) 8 7
–DB(4) 10 9
–DB(5) 12 11
–DB(6) 14 13
–DB(7) 16 15
–DB(P) 18 17
Ground 19–22 —
Reserved 23–25 —
Terminator power 26 —
Reserved 27–28 —
Ground 29–30 —
–ATN 32 31
Ground 33–34 —
–BSY 36 35
–ACK 38 37
–RST 40 39
–MSG 42 41
–SEL 44 43
–C/D 46 45
–REQ 48 47
–I/O 50 49
Signal
pin number
Ground
pin number
Caution.
Do not connect pin 25 to ground. If you plug in the connector
upside down, the terminator power on pin 26 is shorted to
ground. This may damage the drive.

22 Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B
2.5 Interface cab le requi re ment s
A characteristic impedance of 100 ohms + 10% is recommended f or the
unshielded flat or twisted-pair interface cable. However, most available
cables have a somewhat lower characteristic i mpedance. To minimize
discontinuities and signal reflections, do not use cables of different
impedances on the same bus. If shielded and unshielded cables are
mixed within the same bus, the effect of impedance mismatch must be
carefully considered. This is es pecially important for maintaining adequate margins for Ultra SCSI trans fer r ates. Ultra SCSI implementation
may require adjustments to cable lengt h, the number of loads and the
transfer rates to achieve satisfactory system operation.
Part Manufacturer
Flat Cable 3M-3365-50
Twisted Pair Spectra Twist-N-Flat 455-248-50
2.5.1 Interface cable length for asynchronous
operation
The SCSI interface cable must meet the following requirements for
normal operation:
• The cable length cannot be longer than 6.0 meters.
• Cable stubs cannot be more than 0.1 meter long and must be
separated by at least 0.3 meter.
2.5.2 Interface cable for Fast SCSI operation
When using Fast SCSI synchronous data-transfer rates, the SCSI interface cable must meet the following additional requirements:
• The cable length cannot be longer than 3.0 meters.
• The cable should not attenuate a 5-MHz signal more than 0.095 dB
per meter.
• The DC resistance at 20°C must not exceed 0.230 ohms per meter.
• A shielded, twisted-pair cable should not have a propagation delay
delta greater than 20 nsec per meter.
2.5.3 Interface cable fo r Ultr a SCS I op er ati on
• The cable cannot be longer than 3.0 meters when using up to 4
devices.

Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B 23
• The maximum cable length when using 5 to 8 devices cannot be longer
than 1.5 meters.
• Cable stubs cannot be more than 0.1 meter long and must be
separated by at least 0.3 meter.
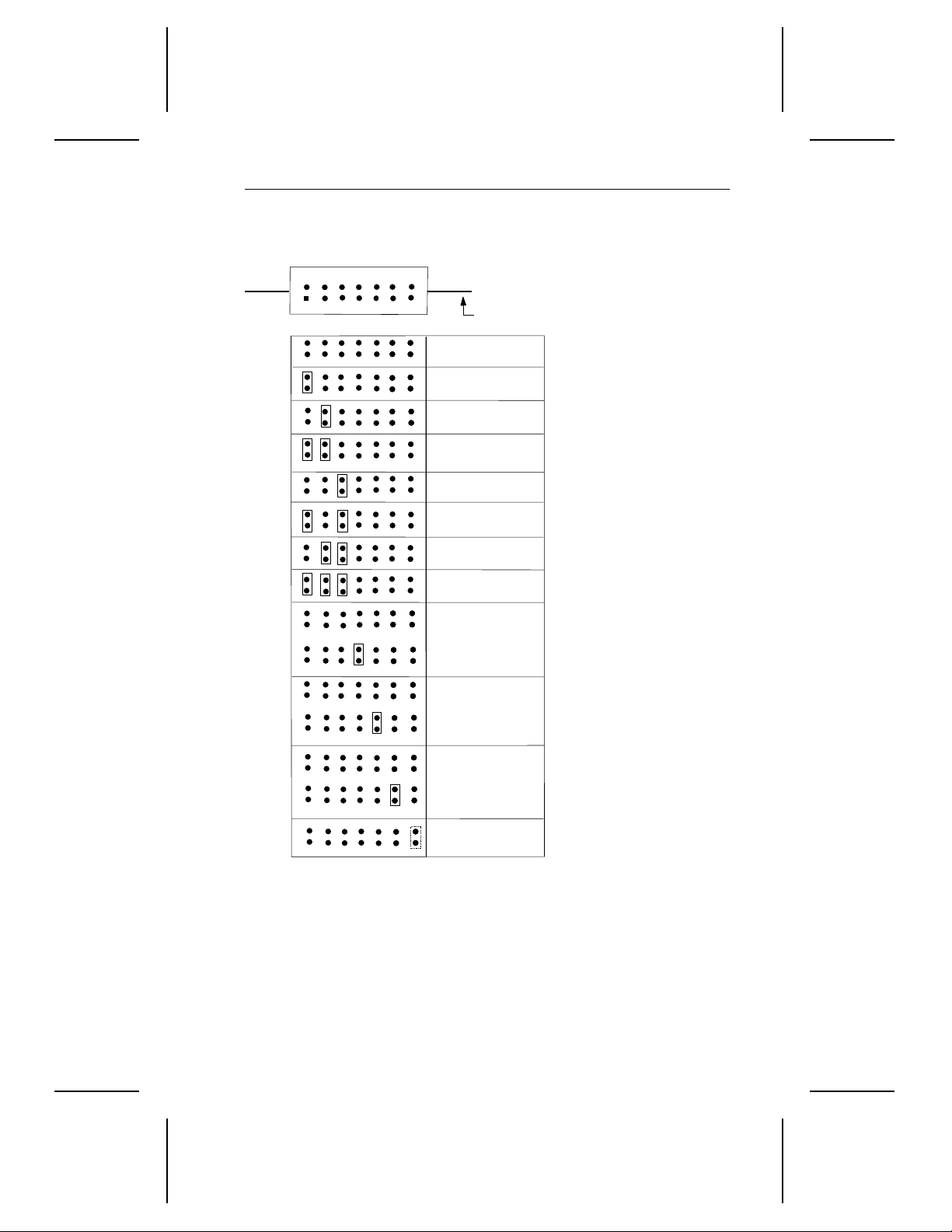
2.6 Options jumper block
The ST52160N options jumper block allows you to:
• Set the SCSI ID address.
• Enable or disable active termination.
• Enable parity.
• Activate the motor start/stop option.
• Attach a remote LED.
These functions are represented on the drive’s options jumper block (J5).
Figure 4 on page 25 shows you how to configure the jumpers.
The options jumper block accepts 2-mm jumpers. If you need additional
jumpers, use the jumpers listed below or equivalent.
Manufacturer Part number
Seagate 13211-001
Du Pont 89133- 001
Methode 8618-202-70
2.6.1 SCSI address
The SCSI ID address is set using pins 1 and 2, 3 and 4, and 5 and 6 on
the options jumper block (J5). The drive is shipped wit h no jumpers on
the SCSI addresses. This makes the default SCSI ID 0. To configure the
drive for a different address, consult the c hart in Figure 4 on page 25.
Refer to your host adapter manual for the preferred addressing scheme.

24 Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B
2.7 Active Termi nation
Active termination is configured on the ST52160N using pins 11 and 12
on the J5 options jumper block. Active termination is enabled when there
is no jumper on pins 11 and 12. Active termination is disabled when a
jumper is placed on pins 11 and 12. The drive provides termination power
to the drive’s terminator chips and to the S CSI bus. No other option is
available.
2.8 Parity enable option
Parity is enabled on the ST52160N when a jumper is installed on pins 7
and 8 of the options jumper block (J5). The drive is shipped with parity
enabled.
2.8.1 Motor Start option
The Motor Start option c auses the drive to wait for a Start/ Stop Unit
command from the host before starting or stopping the spindle motor.
Motor Start is enabled on the ST52160N when a jumper is installed on
pins 9 and 10 of the options jumper block (J5).
2.8.2 Remote LED connection
Pins 13 and 14, located on the options jumper block, are reserved for a
remote LED. Pin 13 is ground. The options jumper block accepts 2-mm
connectors. You may need to replace t he c ur r ent LED cable connector
with a 2-mm connector. If you ar e plac ing the drive in an array configuration, we recommend the LiteOn (part number LTL-3231A) LED or
equivalent.
2.9 Daisy chaining
You can connect the ST52160N in a daisy-chain configuration with a
maximum of eight SCSI devices (host included) that have single-ended
drivers and receivers. E ac h S CS I device must be set to a unique SCSI
ID number. SCSI ID 7 is usually used by the host adapter.
Devices at both ends of the SCSI bus must be terminated; intermediate
devices should not be terminated. All electrical signals are common
between all SCSI devices.
Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B 25
ST52160N Options jumper block (J5)
2346 10
1
5
9
7
1213148
11
SCSI ID 0
SCSI ID 1
SCSI ID 2
SCSI ID 3
SCSI ID 4
SCSI ID 5
SCSI ID 6
SCSI ID 7
SCSI Parity
Disabled
SCSI Parity
Enabled
Remote Start
Disabled
Remote Start
Enabled
SCSI Terminator
Enabled
SCSI Terminator
Disabled
Remote LED
Connection
Drive oriented with
circuit board side down
Notes.
Pins 13 and 14 are used
for a remote LED connection.
Pin 13 is for cathode and
Pin 14 is for anode.
Figure 4. ST52160N j um per set tings

26 Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B
2.10 Hot-plugging
Hot-plugging allows you t o connect and di sconnect the I/ O and power
cables for each SCSI device in a daisy chain without powering down the
system. When hot-plugging, the following conditions must be met:
• All I/O transactions are complete before you install or remove a drive.
• The terminators at either end of the SCSI bus are in place.
• The drive you are disconnecting or connecting is not the device that
supplies terminator power or terminator resistance to the bus.
To avoid damage to the head/disc assembly, the spindle motor must be
completely stopped and the heads must be parked before you remove
the drive from the system. You can stop the spindle and park the heads
as follows:
• If the drive is not configured to use the remote start/stop feature,
disconnect the DC power cable from the drive DC power connector
and wait 30 seconds.
• If the drive is configured to use the remote start/stop feature, issue the
Start/Stop Unit command and wait 30 seconds.
2.11 Mounting the drive
The drive fits the standard 3.5-inch form-factor but has a 0.75-inch height
profile and a 5.38-inch depth profile. Y ou can mount it securely in the
computer using either the bottom or s ide mounting holes, as described
below. Position the drive so that you do not strain or crimp the cables.
Refer to Figure 5 on page 27 for the mounting dimensions.
Bottom mo untin g ho les.
four available bottom mounting holes. Do not insert the screws more than
0.20 inches (6 turns) into the drive frame.
Side mount ing ho les .
the six available side mounting holes. Use two mounting holes on each
side of the drive. Do not insert the screws more than 0.20 inches (6 turns)
into the drive frame.
Caution
• Use only mounting screws of the correct size and length.
• Lightly tighten the mounting screws—do not apply more than 6 inch-lb
. To prevent damage to the drive:
of torque.
Insert 6-32 UNC-2A mounting screws in the
Insert 6-32 UNC-2A mounting screws in four of

Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B 27
In the following figure, all dimensions are in inch es a nd m illimeters (mm).
Six 6-32 NC-2B threaded hole
Max screw insertion depth: 0.20 inches
0.748 max
(19.000)
2.362 ± 0.010
(59.995. ± 0.254)
0.240 ± 0.020 (6.096
4.000 ± 0.010 (101.60
1.985 ± 0.020
(50.419 ± 0.508)
Four 6-32 NC-2B threaded hole
Max screw insertion depth: 0.20 inches
± 0.508)
± 0.254)
5.380 max (136.165)
1.750 ± 0.010
(44.450 ± 0.254)
0.250 ± 0.010
(6.350 ± 0.254)
1.120 (28.448)
1.625 ± 0.020
(41.275 ± 0.508)
4.010 max (101.854)
3.750 ± 0.010 (95.250 ± 0.254)
1.145 (29.083)
0.175 (4.445)
0.188
0.238
(6.045)
(4.775)
Figure 5. Standard Mounting dimensions
Pin 1Pin 1

28 Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B

Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B 29
3.0 Command set
The drive supports a subset of the Group 0, Group 1 and Group 2
standard SCSI commands. The commands are described in this section.
3.1 Command descriptor block
The initiator makes a request to the drive by sending a command
descriptor block (CDB) to the drive. Each CDB has the following common
characterist ics:
• Byte 0 always contains the operation code.
• The three most significant bits (bits 7–5) of byte 1 contain the logical
unit number (LUN). This field is ignored if an Identify Message is sent.
• The last byte is always zero.
3.2 Status byte
The drive terminates each command by sending the status byte (shown
below) to the initiator during the status phase before the command
complete message.
Bytes
76543210
Reserved
00 0
status byte
Good status.
Check condition status.
tion or an abnormal condition. In response, the initiator may issue
a Request Sense command to determine the nature of the condition.
Busy status.
from an initiator. The initiator retries the command later. The drive
returns a busy status if 1) the initiator has not sent the disconnect
message and tries to queue a command or 2) the initiator rejects
the disconnect message and the queue is not empty.
can be any of the following:
The drive has s uccessfully completed a com mand.
The drive is busy and is unable to accept a command
The
00
H
02
H
08
H
0
Bits
Status byte code
The drive detected an error, an excep-
Rsvd

30 Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B
18HReservation conflict status.
A SCSI device t ried to ac cess the
drive, but was unable to because the drive was already reserved
by another SCSI device.
Queue full status.
28
H
The drive received a command but rejected it
because the queue was full. The drive only uses this status if
tagged command queuing is implemented.
3.3 Supported commands
The drive supports the commands listed below.
Group 0 commands Op eration code
Test Unit Ready 00
Rezero Unit 01
Request Sense 03
Format Unit 04
Reassign Blocks 07
Read (6) 08
Write (6) 0A
Seek (6) 0B
Inquiry 12
Mode Select (6) 15
Reserve (6) 16
Release (6) 17
Mode Sense (6) 1A
Start/Stop Unit 1B
Receive Diagnostic Results 1C
Send Diagnostic 1D
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
Group 1 commands Operation code
Read Capacity 25
Read (10) 28
Write (10) 2A
Seek (10) 2B
Write and Verify 2E
H
H
H
H
H

Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B 31
Group 1 commands Operation code
Verify 2F
Read Defect Data 37
Write Data Buffer 3B
Read Data Buffer 3C
Read Long 3E
Write Long 3F
H
H
H
H
H
H
Group 2 commands
Reserve (10) 56
Release (10) 57
H
H
3.4 Group 0 commands
3.4.1 Test Unit Ready command (00H)
The Test Unit Ready command verifies that the drive is ready; it is not a
request for a self-test. If the drive can accept an appropriate media
access command without encountering an error, it returns a good status.
Bytes
Bits
76543210
000000000
1 LUN 00000
200000000
300000000
400000000
500000000

32 Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B
3.4.2 Rezero Unit command (01H)
The Rezero Unit command retracts the read/write heads to the cylinder
that contains logical block zero.
Bytes
76543210
000000001
1 LUN 00000
200000000
300000000
400000000
500000000
Bits
3.4.3 Request Sense comm an d (03H)
The Request Sense command requests the drive to transfer sense data
to the initiator in the additional sense data format. The additional sense
format is described in Appendix B on page 77.
The sense data applies to the previous command on which a check
condition status was returned. This sense data is saved for the initiator
until:
• The initiator uses the Request Sense command to request the sense
data, or
• Another command is received from the initiator that issued t he original
command that caused the check condition status.
If any of the following f atal errors occur during a Reques t Sense command, the drive sends a check condition status, and the sense data m ay
be invalid.
• The drive receives a nonzero reserved bit in the CDB.
• An unrecovered parity error occurs on the data bus.
• A malfunction prevents return of sense data.
If any other error occurs during the Request Sense command, the drive
returns sense data with a good status.

Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B 33
Bytes
000000011
1 LUN 00000
200000000
300000000
4 Allocation length
500000000
Byte 4 The
76543210
allocation length
the initiator has allocated for returned sense data. The drive
returns the number of bytes specified by the allocation length up
to 22 bytes. If the allocation length is set to zero, no sense data
is returned.
This is not an error.
specifies the maximum number of bytes
Bits
3.4.4 Format Unit command (04H)
The Format Unit command assures that the media is formatted so that
all of the addressable data blocks can be accessed. In addition, the media
can be certified and control structures can be created for the management of the media and defects.
If the specified logical unit is reserved, the Format Unit command is
rejected with a reservation conflict status. Ext ent reservations are not
supported. See Section 3. 4.11 on page 45 f or more information about
reservations.
The initiator can specify (or not specify) sectors to be reallocated during
the formatting process.
Bytes
0 00000100
1 LUN
2 00000000
3–4 Interleave
5 00000000
Byte 1 The
76543210
format data
bit,
and the
tion 3.4.4.2. on page 34.
(Fmt Data) bit, the
Defect list format
Bits
Fmt
Data
Cmp
lst
Defect list format
complete list
field are described i n Sec-
(Cmp l st)

34 Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B
Bytes 3–4 The
interleave
value. However, the drive always formats the disc with an
interleave of 1:1.
field is not supported. It can contain any
3.4.4.1 Defect lists
When the Format Unit command is issued, media defect information can
be gathered from several sources. Four of these sources—primary
defect list, certification defect list, data defect list and grown defect
list—are defect lists written to the drive. They are defined below. Assignments in Byte 1 of the defect list header—described in Section 3.4.4.3
on page 36, determine the use of the defect list during formatting. The
Reassign Blocks and Read Defect Data commands also use these lists.
• The
• The
• The
• The
primary defect list (PList)
to the disc when the drive is manufactured. These defects are permanent and cannot be changed.
certification defect list (CList)
sectors that the drive reads during the Format Unit command certification. The CList is inc orporat ed into the GList before the end of t he
Format Unit command.
data defect list (DList)
the drive during a data-out phase of the current Form at Unit command.
The drive sends the DList in the last bytes of the data-out phase
(described in Section 3.4.4.3 on page 36) and may add it to the GList.
grown defect list (GList)
or the target detects that does not include defects from the PList. The
GList includes: defects that the format operation detects during media
certification, the DList, defec ts previously identified wit h a Reassign
Blocks command and defects previously detected by the target that
were automatically reallocated.
is a list of media defects that are written
is a temporary list of unrecoverable
is a list of sectors the initiator supplies to
is a list of defects that the initiator supplies
3.4.4.2 Format Unit parameters
For each format listed in the following table, except the default format,
the initiator sends a defect list header. This header is described in Section
3.4.4.3. The physical sector format is desc ribed in Section 3.4.4.4. on
page 37. The block format and bytes-from-index format are not supported.

Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B 35
Byte 1 of CDB
Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2–Bit 0
Fmt
Cmp
Data
00XXX
01XXX
100XX
1 0 100
1 0 101
1011X
110XX
1 1 100
1 1 101
1111X
Lst
Defect List
Format
Description
Default format
send the defect list header or DList to
the drive. The drive reallocates all
sectors in the PList and GList.
Format option with the PList only
initiator does not send the defect list
header or DList to the drive. The drive
reallocates all sectors in the PList and
erases the GList.
Extended format.
defect list header but no DList. All
sectors in the PList and GList are
reallocated.
The drive does not support
bytes-from-index format.
. The initiator does not
. The
The initiator sends a
Format option with the GList and DList.
The initiator sends the defect list
header, which may be followed by a
DList in physical sector format. The
drive adds the DList to the existing
GList. All sectors in the PList and GList
are reallocated.
Reserved
Format option without GList or DList
The drive erases any previous GList.
The initiator sends a defect list header
but no DList. All sectors in the PList are
reallocated.
The drive does not support
bytes-from-index format.
Format option with DList only.
erases any previous GList. The initiator
sends the defect list header, which may
be followed by a DList in physical sector
format. The DList becomes the new
GList. All sectors in the PList and GList
are reallocated.
.
The drive
Reserved

36 Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B
3.4.4.3 Defect list header and defect list
The defect list, shown below, contains a 4-byte header, followed by one
or more defect descriptors. Byte 1 of the defect list header determines
whether the P and C defects are reallocated.
Bytes
000000000
1 FOV DPRY DCRT STPF 0 0 0 0
2–3 Defect list length
4–
Byte 1
Bytes 2–3
76543210
n
If the FOV bit is 1, the DPRY, DCRT and STPF bits are
interpreted. If the FOV bit is 0, the DPRY, DCRT and STPF
bits must be zeros.
If the DPRY bit is 0, the def ects des cribed in the PList are
reallocated during formatting. The drive sends a check
condition status if it cannot find the PList. If DPRY is 1, the
PList is maintained but the sectors are not reallocated.
If the DCRT bit is 1, the drive does not verify the data written
during the format. Therefore, no CList for this format is
created or reallocated. If the DCRT is 0, the drive verifies
the data written during the format, creates a CList and
reallocates sectors that were unrecoverable.
If the STPF bit is 1, the drive stops formatting if it encounters
an error while accessing either the P or G defect list. If the
STPF
bit is 0, the drive continues formatting even though it
has encountered an error while accessing either the P or G
defect list.
The
defect list length
that follows the header. For each sector to be reallocated,
the defect list contains one defect descript or that contains
8 bytes in either the bytes-from-index format or the physical
sector format. A length of zero indicates that no DList
follows; this is not an error.
Bits
Defect descriptor
is the length, in bytes, of the defect list
Bytes 4–
n
The defect descriptors are described in Sections 3.4.4.4. on
page 37. A length of zero indicates that no DList follows;
this is not an error.

Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B 37
3.4.4.4 Defect descriptor—physical sector format
Defects are specified in t he physical sector format when t he defect l ist
format field is 101
tion 3.4.4. on page 33.
Each defect descriptor for the physical sector format specifies a sectorsize defect location that is composed of the cylinder number of the defect,
the head number of the defect and the defect sector number. The defect
descriptors must be in ascending order.
See Byte 1 of the Format Unit command in Sec-
B.
A defect sector number of FFFFFFFF
(which means reassign the entire
H
track) is illegal.
The information in the following table is for each defect.
Bytes
76543210
Bits
0–2 Cyli nder number of defect
3 Head number of defect
4–7 Defect sector number
3.4.5 Reassign Blocks command (07H)
When the drive receives the Reassign Blocks command, it reassigns
defective logical blocks to available spare sectors.
ARRE and AWRE may perform automatic reassignments inde-
Note.
pendently of this command.
After sending the Reassign Blocks command, the initiator transfers a
defect list that contains the logical block addresses to be reassigned. The
drive reassigns the logical blocks. The data contained in the logical
blocks may not be preserved.
The drive can repeatedly assign a logical block to multiple physical
addresses until there are no more spare locations available on the disc.
If the drive does not have enough spare sectors to reas sign all of the
defective logical blocks, the command terminates with a check condition
status, and the sense key is set to media error. The logical block address
of the first logical block not reassigned is returned in the information bytes
of the sense data.

38 Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B
Bytes
76543210
000000111
1 LUN 00000
200000000
300000000
400000000
500000000
Bits
3.4.5.1 Reassign Blocks defect list
The Reassign Blocks defect list contains a 4-byte header followed by one
or more defect descriptors. The length of each defect descriptor is 4
bytes.
Bytes
0 00000000
1 00000000
2–3 Defect list length
n
4–
76543210
Defect descriptors
Bits
Byte 2–3 The
the defect descriptors that follow. The defect li st length is
equal to four times the number of defects.
Bytes 4–
n
The
address of the defect. The defect descriptors must be in
ascending order.
defect list length
defect descriptor
specifies the total length, in bytes, of
contains the 4-byte logical block

Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B 39
3.4.6 Read (6) command (08H)
When the drive receives the Read command, it transfers data to the
initiator.
The Read-Write Error Recovery page (01
handles errors during a Read command. The Read-Write Error Recovery
page is discussed in Appendix C.1 on page 84.
If there is a reservation access conflict, this command terminates with a
reservation conflict status and no data is read. For more information
about the reservation conflict status, see Section 3.2. on page 29.
In systems that support disconnection, the drive disconnects when a valid
Read command is received, unless the data is available in the cache
buffer. The buffer-full ratio byte of the Disconnect/Reconnect page
determines when the drive reconnects. (The Disconnect/Reconnect
page is discussed in Section C.2. on page 86). The drive may disconnect,
if allowed, whenever there is less than one block in the buffer.
Because the drive uses read look-ahead functions, it may read more
data into the buffer than specified by the transfer length in the CDB.
Note.
Bytes
The Read (6) command cannot access all logical blocks on the
drive. The Read (10) command must be used to access all logical
blocks.
76543210
000001000
1 LUN Logical block address (MSB)
2 Logical block address
3 Logical block address (LSB)
4 Transfer length
500000000
) determines how the drive
H
Bits
Bytes 1–3
Byte 4
logical block address
The
the read begins.
transfer length
The
logical blocks of data to be transferred. A transfer length
of 0 indicates that 256 logical blocks will be transferred. Any
other value indicates the number of logical blocks transferred.
specifies the logical block where
specifies the number of contiguous

40 Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B
3.4.7 W rite (6) command (0AH)
When the drive receives the Write command, it writes the initiator’s data
to the disc.
The Read-Write Error Recovery page (01
handles bad sectors during a Write command. T he Read-Write Error
Recovery page is discussed in Appendix C.1 on page 84. If the system
supports disconnection, the dr ive can disconnect and reconnect while
executing this command. The drive disconnects when either an internal
error-recovery procedure is required or the drive’s internal data buffer is
full. The buffer-empty ratio in the Disconnect/Reconnect page determines when the drive reconnects. Section C.2 on page 86 documents
the Disconnect/Reconnect page.
If there is a reservation access conflict, this command terminates with a
reservation conflict status and no data is written. For more information
about the reservation conflict status, see Section 3.2. on page 29.
The Write (6) command cannot access all logical blocks on the
Note.
drive. The Write (10) command must be used to access all
logical blocks.
Bytes
000001010
1 LUN Logical block address (MSB)
2 Logical block address
76543210
) determines how the drive
H
Bits
3 Logical block address (LSB)
4 Transfer Length
500000000
Bytes 1–3
Byte 4
The
blocks of data to be transferred. A transfer length of zero
indicates that 256 logical blocks are to be transferred. Any other
value indicates the number of logical blocks to be transferred.
logical block address
The
the write operation begins.
transfer length
specifies the number of contiguous logic al
specifies the logical block where

Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B 41
3.4.8 Seek (6) command (0BH)
When the drive receives the Seek command, it seeks to the track of the
specified logical block address. This command is not necessary because
all commands that access the disc contain implied seeks. In systems that
support disconnection, the drive disconnects when it receives a valid
Seek command.
The Seek (6) command cannot access all logical blocks on the
Note.
drive. The Seek (10) command must be used to access all logical
blocks.
Bytes
000001011
1 LUN Logical block address (MSB)
2 Logical block address
3 Logical block address (LSB)
400000000
500000000
Bytes 1–3
76543210
logical block address
The
which the head seeks.
Bits
specifies the logical block to
3.4.9 Inquiry comma nd (12H)
When the drive receives the Inquiry command, it sends the inquiry data
to the initiator. When the requested inquiry data cannot be returned, a
check condition status is reported.
If an Inquiry command is received from an initiator with a pending
unit-attention condition (before the drive reports a check condition
status), the drive performs the Inquiry command and the Unit Attention
condition is not cleared.
The initiator should allocate 36
returned to the initiator is summarized in Appendix D on page 103.
bytes for inquiry data. The inquiry data
H

42 Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B
Bytes
000010010
1 LUN Reserved EVPD
2
300000000
4 Allocation length, in bytes
500000000
Byte 1 If the
Byte 2 The
Byte 4 The
76543210
00000000
enable vital product data (EVPD
returns the standard inquiry data. If the EVPD bit is one, the drive
returns the optional vital product data specified in byte 2.
page code
information the drive returns. If EVPD is zero, this field must be
zero.
allocation length
has allocated for returned inquiry data. The drive returns the
number of bytes specified by the allocation length up to a
maximum of 148 bytes. If the allocation length is zero, no data
is returned.
at least 36
inquiry data.
field specifies which page of the vit al product
specifies the number of bytes the initiator
This is not an error.
to allow the initiator to receive all of the standard
H
Bits
Page code
) bit is zero, the drive
The allocation length should be
3.4.10 Mode Select (6) command (15H)
The Mode Select command allows the initiator to change parameters
stored in the mode pages. The mode pages are described in Appendix C.
on page 83. The drive stores four copies of each mode page:
• Current values copy. This copy contains the parameter values the
drive uses to control its operation. After a power-on reset, hard reset
or bus device reset, the current values are equal to the saved values
if the saved values can be retrieved, or to the default values if the
saved values cannot be retrieved.
• Changeable values copy. This copy does not actually contain any
parameters. Instead, it contains a map of each mode page, indicating
which parameters are changeable by the initiator. If a bit contains a 1,
the corresponding value in the mode page is changeable. If a bit
contains a 0, the corresponding value in the mode page is not
changeable. The changeability values for each bit of each mode page
and the default values are listed in Appendix C.

Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B 43
• Default values copy. This copy contains the parameter values the
drive used as its current values when it was manufactured. The drive
defaults to these values after a reset condit ion, unless valid saved
values are available. The default values are listed in A ppendix C on
page 83.
• Saved values copy. T he saved values are the values the drive stores.
If the parameter is changeable, these values can be set using a Mode
Select command. If the parameter is not changeable, the default
values are always used.
The drive has one set of mode parameters for all of the initiators on the
SCSI bus. If the initiator that issued the Mode Select command changes
a parameter that applies to other initiators , t he dri ve generates a sense
key of Unit At tention with an addi tional sense key of m ode parameters
changed (2A
/01) for all the other initiators. The sense keys and addi-
H
tional sense codes are discussed in Appendix B on page 77.
Before sending the Mode Select command, the initiator should send a
Mode Sense command requesting that the driv e r eturn the changeable
values for all pages. The initiator uses this information to determine which
pages are supported, the proper length for the pages and which parameters in the pages can be changed for that logical unit. Also, before sending
each Mode Select command, the initiator should send a Mode Sense
command to request the current values.
When the drive receives the Mode Select command, it updates the
savable parameters with the current values included in the Mode Select
command. After the drive saves the parameters, it reports a good status.
The drive verifies all Mode Select data.
If the drive detects invalid parameter data during the Mode Select
command, it sends a sense key of
code of
Bytes
invalid field in parameter list,
76543210
illegal request
and no parameters are changed
Bits
with an additional sense
000010101
1 LUN PF = 1 0 0 0 SP
200000000
300000000
4 Parameter list length
500000000
.

44 Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B
Byte 1 The
page format (PF)
bit is always one. This means that the data
sent by the initiator after the mode select header and block
descriptors complies with the page format.
When the
save pages (SP)
bit is 1, the drive saves the savable
pages in nonvolatile memory.
When the
save pages (SP)
bit is 0, the drive s av es the current
pages in RAM only, which means that the parameters are lost
when the drive is powered down.
Byte 4 The
parameter list length
specifies the length, in bytes, of the
header and mode page tran sferr ed to the drive . A para meter list
length of 0 means that no data is transferre d. To calculate the
parameter list length for any given mode page, add the parameter
list header (4 bytes), the block descriptor (if any, 8 bytes), the 2-byte
mode page header an d the length of eac h mode page. For the
length of the mode pages, refer to Appendix C on page 83.
3.4.10.1 Mode Select parameter list
The Mode Select parameter list contains a 4-byte header, followed by a
1-block descriptor (if any), followed by the Mode Select parameter pages.
Each block descriptor specifies the media characteristics for all or part
of a logical unit. The rest of the Mode Select parameters are grouped by
function and organized into mode pages. The mode pages are described
in Appendix C on page 83.
Bytes
76543210
Bits
Parameter list header
0 (default) Reserved (00
H
1 (default) Medium type (00
2 (default) Reserved (00
H
3 (default) Block descriptor length (00
(Optional) Block descriptor data
4 (default) Density code (00
5–7 Number of blocks
8 (default) Reserved (00
H
9–11 Block length
Parameter information
12–
n
Mode pages
)
)
H
)
or 08H)
H
)
H
)

Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B 45
Byte 1 The
Byte 3 If the
Byte 4 The
Bytes 5–7 The
Bytes 9–11 T he
Note. Bytes 4–11 will be provided if the initiator requests the Block
Descriptor.
medium type
drive is a direct-access device.
block descriptor length
is sent to the drive. If the
no block descriptor is sent to the drive.
density code
number of blocks
which is listed in Section 1.1 on page 5. The number of
blocks can be reduced to a value less than maximum by
entering the required number of bloc k s i n bytes 5, 6 and 7
of the block descriptor data and then performing a Mode
Select command.
block length
field is always 00H, which means that the
is 8 bytes, a block descriptor
block descriptor length
is always 00H and cannot be changed.
is equal to the guaranteed sectors,
is always 0200H and cannot be changed.
is 0 bytes,
3.4.11 Reserve (6) command (16H)
When the initiator issues a Reserve command, it requests that the drive
be reserved for exclusive use by the initiator until the reservation is:
• Superseded by another Reserve command from the initiator that
made the reservation. An initiator that has already reserved the drive
can modify the reservation by issuing another Reserve command.
When the drive receives the superseding Reserve command, the
previous reservation is canceled.
• Released by a Release command from the same initiator. See the
Release command in Section 3.4.12 on page 46.
• Released by a bus device reset message from any initiator.
• Released by a hard reset.
After the drive honors the reservation from one initiator, it accepts
Inquiry, Request Sense and Reserve and Release commands from other
initiators; the drive rejects all other commands with a reservation conflict
status.

46 Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B
Bytes
000010110
1 LUN 3rd pty 3rd party device ID Extent
2 Ignored
3 Ignored
4 Ignored
500000000
Byte 1 If the
Byte 2–4 The field is ignored. The drive does not support extent
76543210
3rd pty
the 3rd pty bit i s 1, the initiat or reserves the drive f or another
initiator. The SCSI ID of the third-party initiator is specified in the
3rd party device ID
reservations.
bit is 0, the init iator reserves the drive f or itself . If
field.
Bits
3.4.12 Release (6) command (17H)
When an initiator that had reserved the dri ve using the Reserve command issues the Release command, i t cancels the reservation. If the
drive is not currently r eserved or is reserv ed by another initiator and it
receives a Release command, the drive returns a good status and
maintains the reservation.
Bytes
000010111
1 LUN 3rd pty 3rd party device ID Extent
2 Ignored
3 Ignored
4 Ignored
500000000
Byte 1 If the
Byte 2–4 The field is ignored. The drive does not support extent
76543210
3rd pty
bit is 0, the initiator releases its own reservation. If
the 3rd pty bit is 1, the initiator releases the drive for another
initiator. An initiator can only release a third-party reservation
that it made. The SCSI ID of the third-party initiator is specified
in the
3rd party device ID
reservations.
Bits
field.

Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B 47
3.4.13 Mode Sense (6) command (1AH)
When the initiator sends this command to the drive, it returns mode-page
parameters to the initiator. This command is used in conjunction with the
Mode Select command.
Bytes
000011010
1 LUN 0 DBD 0 0 0
2 PC Page code
300000000
4 Allocation length
500000000
Byte 1
Byte 2
76543210
A disable block descriptor (DBD) bit of 0 indicates that the target
may return 0 or mor e block descriptors in the returned Mode
Sense data. This is at the target’s discretion. A DBD bit of 1
specifies that the target will not return any block descriptors in
the returned Mode Sense data.
The page control (PC) field determines the content of Mode
Parameter bytes. Regardless of the value of the PC, the bl ock
descriptor always contains the current values.
PC bit 7 PC bit 6 Effect
0 0 Return current values.
0 1 Return changeable values.
1 0 Return default values.
11
Bits
Return saved values.
Byte 4
page code
The
The page codes are listed in Section 3.4.13.1 on page 54.
allocation length
The
initiator has allocated for returned Mode Sense data. An allocation length of 0 means that no Mode Sense data is to be
transferred. This condition is not considered an error. Any other
value represents the number of bytes to be transferred. For a
description of the allocation length, see Section 3.4.13.1.
is the designator that is unique to each page.
specifies the number of bytes that the

48 Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B
3.4.13.1 Page code and allocation length
The Mode Sense command descriptor block contains a page code
(byte 2, bits 5–0) and an allocation length (byte 4). These parameters
are described in the following table for SCSI-3 devices. You can transfer
mode pages to the initiator either of two ways:
• Transfer all mode pages at once by using page code 3F
H
, or
• Transfer one mode page at a time by using the page codes and any
number greater than or equal to the allocation length of the mode
page.
Page
code
Allocation
length
Mode Sense data returned
4 bytes of Mode Sense header
8 bytes of block descriptor
01
H
18
2 bytes of mode-page header
H
10 bytes of Read/Write Error Recovery
parameters
4 bytes of Mode Sense header
02
H
1C
8 bytes of block descriptor
H
2 bytes of mode-page header
14 bytes of Disconnect/Reconnect parameters
4 bytes of Mode Sense header
03
H
24
8 bytes of block descriptor
H
2 bytes of mode-page header
22 bytes of Format Device parameters
4 bytes of Mode Sense header
04
H
24
8 bytes of block descriptor
H
2 bytes of mode-page header
22 bytes of Rigid Disc Geometry parameters
4 bytes of Mode Sense header
8 bytes of block descriptor
07
H
18
2 bytes of mode-page header
H
10 bytes of Verify Error Recovery Page
parameters
4 bytes of Mode Sense header
08
H
20H
8 bytes of block descriptor
2 bytes of mode-page header
18 bytes of Caching parameters
4 bytes of Mode Sense header
0A
H
18
8 bytes of block descriptor
H
2 bytes of mode-page header
10 bytes of Control Mode page parameters
Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B 49
Page
code
Allocation
length
Mode Sense data returned
4 bytes of Mode Sense header
00
H
10H
8 bytes of block descriptor
2 bytes of mode-page header
2 bytes of Unit Attention Page parameters
3.4.13.2 Mode Sense data
The Mode Sense parameter list contains a 4-byte header followed by an
8-byte block descriptor (if any), followed by the mode pages. The header
and block descriptor are shown below. The mode pages are described
in Appendix C on page 83.
Bytes
76543210
0 Mode Sense data length
1 (default) Medium type (00
2 WP=0 Reserved
3 (default) Block descriptor length (08
(Optional) Block descriptor
4 (default) Density code (00
5–7 Number of blocks
8 (default) Reserved (00
9–11 Block length
12–
n
Bits
Mode p a ge s
Mode pages
)
H
)
H
)
H
)
H
Byte 0 The
bytes minus 1 of the Mode Sense data to be transferred
to the initiator.
Byte 1 The
Byte 2 The
media is write-enabled.
Byte 3 The
block descriptor. This value does not include the page
headers and mode pages that follow the block descriptor,
if any.
Byte 4 The
Mode Sense data length
medium type
WP (write protect)
block descriptor length
density code
is always 0.
bit is always 0, which means the
is the number of bytes in the
is not supported.
specifies the number of

50 Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B
Bytes 5–7 The
Byte 8 Reserved
Bytes 9–11 The
number of blocks
blocks available to the user.
block length
in each logical block described by the block descriptor.
field contains the t otal number of
specifies the number of bytes contained
3.4.14 Start/Stop Unit command (1BH)
When the drive receives t he Start/Stop Uni t command, the drive either
spins up or spins down, depending on the setting of the start bit in byte 4.
If the host adapter supports disconnection, the drive disconnects when
it receives the Start/Stop Unit command and reconnects when it is up to
speed and ready.
Bytes
0 00011011
1 LUN = 0 0 0 0 0 Immed
2 00000000
3 00000000
4 0000000Start
5 00000000
76543210
Bits
Byte 1 If the
the command is completed. If the Immed bit is 1, the drive returns
the status when it receives the command.
Byte 4 If the
spins down.
immediate (Immed)
start
bit is 1, the drive spins up. If the
bit is 0, the drive returns the status after
start
bit is 0, the drive

Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B 51
3.4.15 Receive Diagnostic Results command (1CH)
When the drive receives the Receive Diagnostics command after powerup or after a Send Diagnostic command of PF=0, it sends eight diagnostic
data bytes to the initiator. The drive supports the optional Page format
wherein the initiator sends additional pages after a Send Diagnostic
command. These additional pages hav e a page code that specifies to
the drive the format of the data to be returned after it receives a Receive
Diagnostic Results command.
Bytes
76543210
Bits
0 00011100
1 LUN = 0 00000
2 00000000
3–4 Allocation length
5 00000000
Bytes 3–4
allocation length
The
specifies the number of bytes the
initiator has allocated for returned diagnostic result data. An
allocation length of 0 means that no diagnostic data is
transferred;
this is not an error.
The drive sends the lesser
of the allocation l ength or the bytes available, whichever
number is less.
3.4.15.1 Diagnostic data format
Bytes
76543210
0–1 (default) Additional length (0006
2–5 FRU code
6 Diagnostic error code
7 Vendor-unique error code
Bits
)
H
Byte 0–1
Bytes 2–5
additional length
The
value indicates t he number of additional bytes included in the diagnostic data list . A value of
0000
means that there are no additional bytes. A value of
H
0006
means that no product-unique bytes are available.
H
field replaceable unit (FRU)
If the
FRU information. If the FRU code is 01
code is 00H, there is no
, replace the drive.
H
Other values are drive-unique.

52 Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B
Byte 6 The
Byte 7 The
diagnostic error code
is not supported.
vendor-unique error codes
are listed in Section 3.4.15.2.
3.4.15.2 Diagnostic error codes
The following diagnostic error codes are reported in byte 7 of the
diagnostic data format in Section 3.4.15.1.
Error code Description
01
02
09
44
80
81
H
H
H
H
H
H
Sequencer test error
Microprocessor RAM diagnostic error
Fatal hardware error during drive diagnostics
EEPROM test error
Buffer controller diagnostic error
Buffer RAM diagnostic error
3.4.16 Supported Diagnostic Pages
The following table lists all of the diagnostic pages that supports the drive.
If the Send Diagnostics command requests the Supported Diagnostics
Page list (PF=1), the drive returns data in the format shown in the table
below after it receives the Receive Diagnostics Results command.
Bytes
76543210
0 Page Code (00
Bits
)
H
1 Reserved
2–3 P age Length (
n – 3) (1)
4
:
Supported Page List (2)
n
Notes::
1. The page length field specifies the length in bytes of the
supported page list.
2. The supported page lists contains a list of all diagnostic page
codes implemented by the drive in ascending order beginning with page code 00
and 40
H.
. The drive supports only pages 00
H
H

Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B 53
3.4.17 Translate Address Page
The translate address page allows the initiator to translate a logical block
address into a physical sector address or a physical sector address into
a logical block address. The address to be translated is passed to the
target during the data-out phase. This phase is associated with the Send
Diagnostics command and the results are returned to t he initiator during
the data-in phase following the Receive Diagnostic command. The
translated address is returned in the Translate Address Page as shown
in the following tables.
Bytes
76543210
0 Page Code (40
Bits
H
) (1)
1 Reserved
2–3
Page Length
(000A) (2)
4 Reserved Supplied Format (3)
5
6
13
RAREA
(4)
:
ALTSEC
(5)
ALTTK
(6)
Rsrvd
Translated Format (7)
Translated Address (8)
(if available)
Notes:
The translate address page contains a 4-byte page header
1.
that specifies the page code and length followed by 2 bytes,
which describe the supplied format followed by the translated address.
The page length field cont ains the number of parameters that
2.
follow.
The Supplied Format field contains the value from the Send
3.
Diagnostic command supplied format field.
. A reserved area (RAREA) bit of 1 indicates that all or part of
4
the translated address falls within a reserved area of the
media (such as speed tolerance gap, alternate sector and
vendor-reserved area). If the entire translated address falls
within a reserved area, the target may not return a translated
address. A RAREA bit of zero indicates that no part of the
translated address falls within a reserved area of the media.

54 Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B
5. An alternate sector (ALTSEC) bit of 1 indicates that the translated address is physically located in an alternate sector of
the media. If the drive cannot determine whether all or part
of the translated address is located in an alternate sector, it
will set this bit to zero. An ALTSEC bit of zero indicates that
no part of the translated address is located in an alternate
sector of the medium or that the drive is unable to determine
this information.
6. An alternate track (ALTTRK) bit of 1 indicates that part or all
of the translated address is located on an alternate track. An
ALTTRK bit of zero indicates that no part of the translated
address is located on an alternate track of the medium.
7. The Translated Format field contains the value from the Send
Diagnostic command translate format field).The values are
000 (Logical block format) or 101 (Physical sector address
format).
8. The Translated Address field contains the address supplied
by the initiator in the Send Diagnostic command. This field
will be in the format specified in the translate format field.
The supported formats are shown in the following tables.
Address Field Logical Block Address Format
Bytes
0–3 Logical Block Address
400000000
500000000
600000000
700000000
Bytes
0–2 Cy linder Number
3 Head Number
4–7 Sector Number
76543210
Address Field Physical Sector Format
76543210
Bits
Bits

Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B 55
3.4.18 Send Diagnostic command (1DH)
Bytes
0 00011101
1 LUN = 0 PF 0
2 00000000
3–4 Parameter list length
5 00000000
Byte 1
76543210
If the PF (Page Format) bit is set to 0 and the
is set to 1, the drive performs the buffer RAM diagnostics,
which is the default self- test. If the default self-test is requested, the parameter list length is 0 and no data is
transferred. If the self-test pass es successfully, the command terminates with a good status. If the self-test fails, the
command terminates with a check condition status and the
sense key is hardware error.
If the PF bit i s set to 1, SelfTest bit is 0,
(DevOfL) and
diagnostic page is sent as the parameter list. The supported
pages are the
late Address
bytes for page 00
The DevOfL bit is not supported and must be 0 if
bit =1.
unit off line
Supported Pages
(40H) page. The parameter length is 4 (04H)
and 14 (0EH) bytes for page 40H.
H
Bits
Self
Test
Dev
OfL
device off line
(UnitOfL) are ignored and a
(00H) page and the
Unit
OfL
SelfTest
Trans-
SelfTest
bit
Bytes 3–4
The UnitOfL bit is not supported and must be 0 if
bit =1.
parameter list length
The
must be 0 if
SelfTest
bit =1.
SelfTest

56 Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B
3.5 Support ed Diag no st ics Page—S en d Diag no stics
This page contains instructions for the drive to make available the list of
all supported diagnostic pages to be returned by a subsequent Receive
Diagnostics Results command. The definition of this page includes only
not
the first 4 bytes. If the page length is
zero, the drive terminates the
Send Diagnostics command with a Chec k Condi tion status. The Sense
Key is set to Illegal Request with an additional sense code of Invalid Field
Parameter List.
Supported Diagnostic Pages Page
Bytes
76543210
0 Page Code (00
Bits
)
H
1 Reserved
2–3 Page Length (Must Be Zero)
3.6 Translate Address Page—Send Diagnostic
The translate address page allows the initiator to translate a logical block
address into a physical sector address or a physical sector address into
a logical block address. The address to be translated is passed to the
drive with the Send Diagnostics command, and the results are returned
to the initiator during the data-in phase following the Receive Diagnostic
command. The format of the translate address page—Send Diagnostic,
is shown in the following table. The translated address is returned in the
translate address page returned after the Recei ve Diagnostic Results
Command.
Bytes
76543210
0 Page Code (40
Bits
) (1)
H
1 Reserved
2–3
4
Reserved
Page Length
(000A
)
H
Supplied Format (1)
5 Reserved Translated Format (7)
6
:
Address To Translate (3)
13

Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B 57
Notes:
1. The Supplied Format field specifies the form at of the address
to translate field. The valid values for this field are 000 for
logical block address format or 101 for physical sector address
format. If the drive does not support the requested format, it
terminates the Send Diagnostic command with a Check Condition status. The sense key is set t o Illegal Request and an
additional sense code is set to Invali d Field in t he Parameter
List.
2. The Translate F ormat field specifies t he format to which the
initiator wants the address to be translat ed. The valid values
for this field are 000 for logical block address format or 101 f or
physical sector address format. The Translate Format field
must be different than the Supplied Format field. If the drive
does not support the requested format, it terminates the command with a Check Condition status. The sense key is set to
Illegal Request and an additional sense code is set to Invalid
Field in Parameter List.
3. The Address to Translate field contains a single addr ess that
the initiator is r equesting the driv e to t ranslate. The f ormat of
this field is defined by the Supplied Format field.
For systems that support disconnection, the drive disconnects
while executing this command.
3.6.1 Read Capacity command (25H)
The initiator uses the Read Capacity command to determine the capacity
of the drive. When the drive r eceives the Read Capacity command, it
sends the initiator read capacity data, which is described in Section
3.6.1.1. on page 58.
Bytes
0 0010010 1
1 LUN 0000 0
2–5 Logical block address
6 0000000 0
7 0000000 0
8 0000000PMI
9 0000000 0
7654321 0
Bits

58 Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B
Bytes 2–5 The logical block address specified in the CDB cannot be
greater than the logical block address reported by the drive
in the read capacity data else check condition.
Byte 8 If the
partial medium indicator (PMI)
block address in the CDB is also zero. The read capacity
data that the drive returns contains the logical block address
and block length of the last logical block of the drive.
If the PMI bit is 1, the drive returns the read capacity data,
which contains the l ogical bl ock address and bl ock l ength
of the last logical block address, after which a substantial
delay (approximately 1 msec) in data transfer occurs. This
logical block address must be greater than or equal to the
logical block address specified in the CDB. This reported
logical block address is a track (head) boundary.
bit is zero, the logical
3.6.1.1 Read Capacity data
The Read Capacity data is shown below.
Bytes
0–3 Logical block address
4–7 B loc k length (00000200
Bytes 0–3 The logical block addr ess is determined by the PMI bit in
7654321 0
the CDB of the Read Capacity command. The PMI bit is
described in Section 3.6.1. on page 57.
Bits
)
H
Bytes 4–7 The block length is always 512.
3.6.2 Read (10) command (28H)
When the drive receives the Read (10) command, it transfers data to the
initiator. This command is the same as the Read (6) command discussed
in Section 3.4.6 on page 39 except that in the CDB for the Read (10)
command, a 4-byte logical block address and a 2-byte transfer length
can be specified.
If there is a reservation access conflict, this command terminates with a
reservation conflict status and no data is read. For more information
about the reservation conflict status, see Section 3.2 on page 29.

Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B 59
Bytes
0 00101000
1 LUN DPO FUA 0 0 0
2–5 Logical block address
6 00000000
7–8 Transfer length
9 00000000
Byte 1 If the
Bytes 2–5 The
Bytes 7–8 The
76543210
disable page out (DPO)
the drive receives during this command has the lowest
priority for being retained in the cache. If the DPO is 0, the
cached data has the highest priority for being retai ned in
the cache.
If the
forced unit access (FUA)
the disc to get the data requested by the initiator, even if the
data is available in the cache. If the F UA bit is 0, the drive
can get the data from the cache or the disc.
logical block address
the read operation begins.
transfer length
logical blocks of data to be transferred. A transfer length of
0 means that no logical blocks are to be transferred. This
condition is not considered an error.
Bits
bit is 1, the cached data that
bit is 1, the drive must access
specifies the logical block where
specifies the number of contiguous
3.6.3 Write (10) command (2AH)
When the drive receives the Write (10) command, the drive writes the
data from the initiator to the disc. This command is the same as the Write
(6) command, except that the CDB for this command contains a 4-by te
logical block address and a 2-byte transfer length. For more information
about the Write (6) command, see Section 3.4.7 on page 40.
If there is a reservation access conflict, this command terminates with a
reservation conflict status and no data is written. For more information
about the reservation conflict status, see Section 3.2. on page 29.

60 Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B
Bytes
0 00101010
1 LUN DPO FUA 0 0 0
2–5 Logical block address
6 00000000
7–8 Transfer length
9 00000000
Byte 1 If the
Bytes 2–5 The
Bytes 7–8 The
76543210
disable page out (DPO)
the drive receives during this command has the lowest
priority for being retained in the cache. If the DPO is 0, the
cached data has the highest priority for being retai ned in
the cache.
If the
forced unit access (FUA)
the disc to write the dat a sent by the initiator, even if the
data can be stored in the cache. If the FUA bit is 0, the drive
can write the data to the cache or the disc.
logical block address
the write operation begins.
transfer length
logical blocks of data to be transferred. A transfer length of
0 means that no logical blocks are to be transferred; this is
not an error.
Bits
bit is 1, the cached data that
bit is 1, the drive must access
specifies the logical block where
specifies the number of contiguous
3.6.4 Seek (10) command (2BH)
The Seek (10) command requests that the drive seek to the specified
logical block address. This command is the same as the Seek (6)
command, except that the CDB includes a 4-byte logical block address.
The Seek (6) command is described in Section 3.4.8. on page 41.

Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B 61
Bytes
000101011
1 LUN 00000
2–5 Logical block address
600000000
700000000
800000000
900000000
76543210
Bits
3.6.5 Write and Verify command (2EH)
When the drive receives the Write and Verify command, it writes the data
sent by the initiator to the media and then verifies that the data is correctly
written.
If the host adapter supports dis connection, t he drive dis connects while
it is executing this command.
Bytes
000101110
1 LUN 0 0 0 BytChk 0
2–5 Logical block address
600000000
7–8 Transfer length
900000000
76543210
Bits
Byte 1 If the
media after a write by checking the ECC syndromes. If the
BytChk bit is one, t he dr iv e v er ifies the media after a wri te
by performing a byte-by-byte comparison of the data stored.
Bytes 2–5 The
where the drive begins writing and verifying the data.
Bytes 7–8 The
transfer length
logical blocks to be transferred. I f the transfer length is 0,
the initiator does not transf er any data and the drive does
not write or verify any data. This condition is not considered
an error.
byte check (BytChk)
logical block address
field specifies the number of contiguous
bit is 0, the drive verifies the
field specif ies the logical block

62 Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B
3.6.6 Verify command (2FH)
When the drive receives the Verify command, it verifies the data on the
disc. If the host adapter supports disconnection, the drive disconnects
while it is executing this command.
Bytes
000101111
1 LUN 0 0 0
2–5 Logical block address
600000000
7–8 Verification Length
900000000
Byte 1
Bytes 2–5
Bytes 7–8
76543210
byte check (BytChk)
If the
media by checking the ECC syndromes. If the BytChk bit is
1, the drive verifies the media by performing a byte-by-byte
comparison of the data sent from the initiator.
The
logical block address
where the drive begins verifying the data.
verification length
The
ous logical blocks to be verified. If the verification length is
0, the drive does not verify any logical block s, although an
implied seek is still performed. This condition is not considered an error.
Bits
Byt
Chk
bit is 0, the drive verifies the
field specif ies the logical block
field specifies the number of contigu-
0
3.6.7 Read Defect Data command (37H)
When the drive receiv es this command, it reads the defect data and
transfers the defect data to the initiator.
This command can be used in conjunction with t he Format Unit command. Read Defect Data reads the defect lists off the buffer memory and
resends the lists as defect data but does not change the lists.
The Read Defect Data command can be used to access two types of
defect lists: the
These lists are described in Section 3.4.4.1. on page 34.
primary defect list (PList)
and the
grown defect list (GList)
.

Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B 63
Bytes
76543210
Bits
000110111
1 LUN 00000
2000PListGListDefect list format
300000000
400000000
500000000
600000000
7–8 Allocation length
900000000
PList
Byte 2 If the
bit is 1, the drive sends the primary defect list. If
the PList bit is 0, the drive does not send the primary defect
list.
If the
GList
bit is 1, the drive sends the grown defect list. If
the GList bit is 0, the drive does not send the grown defect
list.
If both the PList and GList bits are zero, t he drive returns
the defect list header only.
If the defect list format field contains 101
the drive returns
B,
the defect data in the physical sector f ormat. If the defect
list format field contains 000
or 100B, the drive returns the
B
defect data in the default format, which is the physical sector
format, and generates a check condition status.
Bytes 7–8 The allocation length specifies the number of bytes the
initiator has all ocated for the returned defect data;
not an error.
An allocation length of 0 indicates that no
this is
defect data is transferred. The data-in phase ends when the
allocation length bytes have been transferr ed or when all
available defect data has been transf erred to the initiator,
whichever is less.

64 Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B
3.6.7.1 Defect list header
The defect data always begins with a 4-byte header, followed by an
8-byte descriptor for each defect. The defect list header format is
described below.
Bytes
000000000
1 0 0 0 PList GList Defect list format
2–3 Defec t List Length
Byte 1
Bytes 2–3
76543210
PList
If the
defect list. If the PList bit is 0, the defect data does not
contain the primary defect list.
If the
defect list. If the GList bit is 0, the defect data does not
contain the grown defect list.
The
page 68.
The defect list length always specifies the length of the
defect data in bytes, even if the all ocation length (in the
CDB) is not lar ge enough to accommodate all t he defect
descriptors. If the PList and GList bits are 0, no defect
descriptor bytes are sent to t he initiator and t he defect list
length is 0.
bit is 1, the defect data cont ains the primary
GList
bit is 1, the defect data contains the grown
defect list format
Bits
field is described in Section 3.6.7. on
3.6.8 Write Data Buffer command (3BH)
The Write Data Buffer command supports s everal different features. It
can be used with the Read Data Buffer command to diagnose problems
in the drive’s data buffer memory and to test the integrity of the SCSI bus.
You can also use the Write Data Buffer command to download microcode
to the buffer and to save it in flash memory.
This command treats the buffer as a single segment, regardl ess
Note.
of the number of segments specified in Caching page 08
ing page 08
is described in Section C.6.3. on page 96.)
H
. (Cach-
H

Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B 65
Bytes
76543210
Bits
000111011
1 LUN 0 0 Mode
2 Buffer ID (00
)
H
3–5 Buffer offset
6–8 Parameter list length
900000000
Byte 1 If the
mode
bits contain 000B, the initiator transfers data to
the drive buffer with a 4-byte header that contains all zeros.
This mode is called
If the
mode
bits contain 010B, the initiator transfers data to
write combined header and data
.
the drive buffer without the header. This mode is called
data
.
mode
If the
bits contain 101B, the initiator downloads microcode to the drive buffer, and the drive saves the microcode
in flash memory. The drive uses the new mic r ocode for all
future operations. This mode is called
and save
.
download microcode
After the microcode has been successfully downloaded, the
drive generates a unit attention condition of
been downloaded
for all initiators except the one that issued
microcode has
the current Write Data Buffer command.
write
All other settings for the mode bits are reserved.
Byte 2 This field is ignored if the mode bits are 101
Byte 3–5 The
buffer offset
is added to the starting address of the
buffer to determine the destination of the first data byte. The
bytes that follow are placed in sequential addresses. If the
sum of the buffer offset and the transfer length exceeds the
buffer size reported by the Read Data Buffer command (see
Section 3.6.9), the drive generates a check condition status
and the initiator does not transfer any data. This field is
ignored if the mode bits are 101
Bytes 6–8 The
parameter list length
field specifies the maximum num-
.
B
ber of bytes the initiator transfers. If the initiat or transfers
the 4-byte header, the transfer length includes the header.
If the transfer length is zero, no data is transferred to the
drive buffer; this is not considered an error. The field is
ignored if the mode bits are 101
.
B
.
B

66 Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B
3.6.9 Read Data Buffer command (3CH)
The Read Data Buffer command supports several different features. The
Read Data Buffer command can be used along with the Write Data Buffer
command to diagnose problems i n the drive’ s data buffer memory and
to test the integrity of the SCSI bus.
Note.
Bytes
This command treats the buffer as a single segment, regardless of
the number of segments specified in mode page (08
(08
), the Caching page, is described in Section C.6. on page 94).
H
). (Mode page
H
Bits
76543210
000111100
1 LUN 0 0 Mode
2 Buffer ID (00
)
H
3–5 Buffer offset
6–8 Allocation length
900000000
Byte 1
If the mode bits contain 000
the initiator reads data from
B,
the drive buffer. The data is preceded by a 4-byte header.
This mode is called
read combined header and data.
If the mode bits contain 010B, the initiator reads data from the
drive buffer without a header. This mode is called
If the
mode
bits contain 011
a maximum of 4 bytes of
B,
read data.
READ BUFFER descriptor information is returned. The
drive returns the descriptor information for the buffer specified by the buffer ID.
If there is no buffer associated with the specified buffer ID,
the drive returns all zeros in the READ BUFFER descriptor.
The buffer offset is reserved in this mode. The allocation
length should be set to four or gr eater. The drive transfers
the lesser of the allocation length or 4 bytes of READ
BUFFER descriptor.
READ BUFFER Descriptor
Bytes
76543210
Bits
0 Offset Boundary
1–3 (MSB) Buffer Capacity (LSB)

Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B 67
The offset boundary field returns the boundary alignment
within the selected buffer for subsequent WRITE BUFFER
and READ BUFFER commands. The value contained in the
offset boundary field shall be interpreted as a power of two.
Buffer Of fse t Boundary
Offset Boundary 20 Offset Boundary Buffer Offsets
52
5
= 32 32-byte boundaries
0 is the only
FF
H
Not Applicable
supported buffer
offset
The buffer capacity field r eturns the size of the selected
buffer in bytes.
mode
All other settings for the
bits are reserved.
Byte 2 The
Byte 3–5 The
buffe r ID
is not supported and must always be 0.
buffer offset
is added to the starting address of the
buffer to determine the source of the first data byte. The
bytes that follow are read from sequential addresses. If the
sum of the buffer offset and the transfer length exceeds the
available length reported in the Read Buffer header (see
Section 3.6.9.1), the drive transfers all the data contained
in the buffer.
Bytes 6–8 The
allocation length
field specifies the maximum number
of bytes read by the initiator. If the 4-byte header is transferred, the transfer length includes the header. If the transfer
length is 0, no data is read;
this is not an error.
3.6.9.1 Read Buffer Header
The following table shows the structure of the 4-byte Read Buffer Header.
Bytes
76543210
00
1–3 Buffer capacity
Bytes 1–3 The
buffer capacity
buffer. Byte 1 is MSB; byte 3 is LSB.
Bits
field specifies the size of the drive
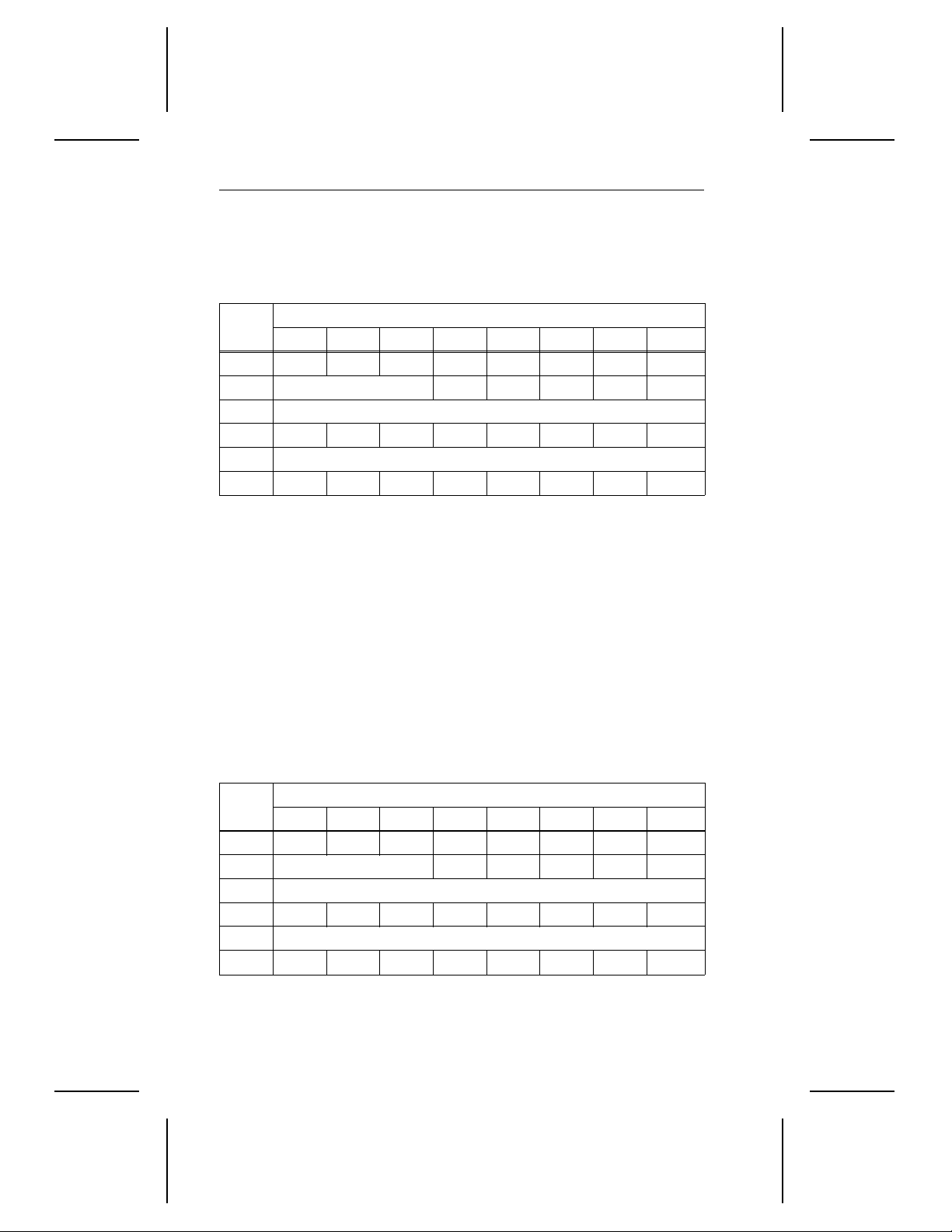
68 Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B
3.6.10 Read Long command (3EH)
When the drive receives the Read Long command, it transfer s data to
the initiator.
Bytes
000111110
1 LUN 00000
2–5 Logical block address
600000000
7–8 Byte transfer length
900000000
Bytes 2–5
Bytes 7–8
76543210
logical block address
The
begins reading data.
byte transfer length
The
transferred to the initiator. The drive transfers the logical
block size plus twenty. If the byt e transfer length is 0, the
drive does not transfer any data to the initiator. This condition is not considered an error. Other wise, transfer length
must be 532 (214
H
Bits
specifies the LBA where the drive
specifies the number of bytes
) bytes.
3.6.11 Write Long command (3FH)
When the drive receives the Write Long command, it writes one logical
block of data and twenty bytes of error correction code (ECC) to the disc.
During this command, the drive does not perform any ECC verification.
Bytes
000111111
1 LUN 00000
2–5 Logical block address
600000000
7–8 Byte transfer length
900000000
Bytes 2–5
76543210
logical block address
The
begins writing data.
Bits
specifies the LBA where the drive

Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B 69
Bytes 7–8 The
byte transfer length
specifies the number of bytes the
initiator transfers to the drive.
If the transfer length does not equal the sum of the logical
block size plus twenty, the command is terminat ed with a
check condition status.
If the byte transfer length is zero, the initiator does not
transfer any data to the drive; thi s condition is not considered an error. Otherwise, the transfer length must be 532
(214
) bytes.
H
3.7 Group 2 Commands
3.7.1 Reserve (10) command (56H)
The Reserve (10) command is used to reserve a logical unit. The 3rd
party reservation allows logical units to be reserved for another specified
SCSI device.
3rd
Party
(2)
Bits
)
H
Reserved Extent
(3)
Bytes
76543210
0 Operation Code (56
1 Logical Unit Number
(1)
2 Ignored (4)
3 3rd Party Device ID not supported
4 Reserved
5 Reserved
6 Reserved
7–8 Ignored (4)
9 Control Byte (5)
Notes:
1. The Logical Unit Number must be 0.
2. If bit 4 is 0, byte 2 must also be 0. If bit 4 is 1, byte 2 identifies
the SCSI bus ID of the device for which the drive is reserved.
3. Extent is not supported.
4. The field is ignored. The drive does not support extent reser-
vations.

70 Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B
5. Normally all zeros. Control Byte can be supported as a special factory-installed option.
3.7.2 Release (10) command (57H)
The Release (10) command is used t o release a previously reserved
logical unit. It is not an error for an initiator to attempt to release a
reservation that is not currently valid. In this case, the drive returns a
GOOD status without altering any other reservation.
3rd
Party
(2)
Bits
)
H
Reserved
Bytes
76543210
0 Operation Code (57
Logical Unit Number
1
(1)
2 Ignored (4)
3 3rd Party Device ID (2)
4 Reserved
5 Reserved
6
7–8
Reserved
Ignored (4)
9 Control Byte (5)
Notes:
1. The Logical Unit Number must be zero.
2. If bit 4 is 0, bits 3, 2, and 1 are 0. If bit 4 is 1, bits 3, 2 and
identify the SCSI bus ID of the device that reserves the drive.
Extent
(3)
3. Extent is not supported
4. The field is ignored. The drive does not support extent reser-
vations.
5. Normally all zeros. Control Byte can be supported as a spe-
cial factory-installed option.

Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B 71
3.8 Group 3 and 4 command s
Group 3 commands are reserved. Group 4 commands are 16-byte
commands. Group 4 commands are not supported. If the drive receives
one of these commands, it returns a check condition status.
Caution.
Do not use Group 3 and 4 commands. If you do, you may
destroy data on the disc.
3.9 Group 5 and 6 command s
Group 5 and 6 commands are 12-byte commands. Group 5 commands are
not implemented. If the drive receives a Group 5 command, it returns a check
condition status. Group 6 commands are reserved for Seagate use.
Caution.
Do not use Group 6 commands. If you do, you m ay destroy
data on the disc.
3.10 Group 7 commands
Group 7 commands are 10-byte commands. These commands are not
implemented. If the dr iv e r ec eiv es one of these commands, it returns a
check condition status.

72 Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B

Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B 73
Appendix A. Supported messages
A.1 Messages
The implemented 1- and 2-byte messages are listed below.
Must
Code Message name Direction
Abort O Yes
06
H
0D
Abort tag O Yes
H
0C
Bus device reset O Yes
H
0E
Clear queue O Yes
H
00
Command complete I —
H
04
Disconnect
H
80
Identify I/O No
H
05
Initiator detected error O Yes
H
09
Message parity error O Yes
H
07
Message reject I/O Yes
H
08
No operation
H
21
Head of queue tag
H
22
Ordered queue tag
H
20
Simple queue tag
H
23
Ignore Wide Residue
H
02
Save data pointer I —
H
5
5
5
5
I—
OYes
ONo
ONo
ONo
I—
negate ATN
before last
ACK?
_____________________
5. These are 2-byte messages.

74 Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B
A.2 Synchronou s Data Tr an sfe r Requ est mess age
(01H)
The synchronous Data Transfer Request message is an extended message.
Depending on the value contained in the SSM bit (contained in byte 2 of
the Operating page in Appendix D.2.2. on page 107), the drive or the
initiator can negotiate for synchronous data transfer after a reset. If any
problem precludes the successful exchange of synchronous Data Transfer Request messages, the initiator and drive default to asynchronous
data transfers. Also, reception of a Wide Data Transfer Request message
sets the drive to the default asynchronous transfers.
This exchange of messages establishes the minimum transfer period and
the maximum allowed REQ/ACK offset.
Bytes
Byte 0
Byte 1
Byte 2
Byte 3
Byte 4
Bits
7 6 543210
0 E x tended message (01
1 Extended message length (03
2 Identifier code (01
)
H
)
H
)
H
3 Minimum transfer period divided by 4
4 REQ/ACK offset
This byte identifies the message as an extended message.
This byte reports the length of the message.
This byte identifies the message as a synchronous data-transfer
request message.
The value contained i n this byte is speci fied in nsec. It is equal
to the minimum period in which the device can receive data, in
units of 4 nsec. In byte 3, the minimum value supported by the
drive is 0C
, which is equivalent to a transfer period of 48 nsec,
H
or a maximum external transfer rate of 20 Mbytes per second. A
value of 19
is equivalent to a transfer period of 100 nsec, or a
H
maximum external transfer rate of 10 Mbytes per second. A
value of 32
is equivalent to a transfer period of 200 nsec, or a
H
maximum external transfer rate of 5 Mbytes per second.
REQ/ACK offset
The
is the maximum number of REQ pulses
that may be outstanding before its corresponding ACK pulse is
received at the target. A REQ/ACK offset of zero indicates
asynchronous mode. The drive supports a maximum REQ/ACK
offset of 0F
.
H

Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B 75
A.2.1 Wide Data Transfe r Requ est Messa ge
Bytes
0 Extended message (01
1 Extended message length (02
2 W ide Data Transfer Request code (03
76 54321 0
)
H
)
H
)
H
3 Transfer Width Exponent
The originating SCSI device (the SCSI device that sends the first pair of
WDTR messages) sets its transfer value to the maximum data path i t
chooses to accommodate.
If the responding SCSI device can also accommodate this transfer width,
it returns the same value in its WDTR message. If it requires a smaller
transfer width, it substitut es a smal ler value in its WDTR message. The
successful completion of an exchange of WDTR messages impli es an
agreement as follows:
Bits
Responding Device
WDTR Respons e
Implied Agreement
Each device transmits and
receives data with a transfer
Nonzero transfer width
width equal to the
responding SCSI devices’
transfer width
Transfer width equal to zero
MESSAGE REJECT message
8-bit data transfer
8-bit data transfer

76 Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B

Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B 77
Appendix B. Sense data
This appendix contains the descriptions for sense data returned by the
Request Sense command. For more information on the Request Sense
command, see the
, publication number 77738479-F.
sion 2
B.1 Additional sense data
When the initiator issues a Reques t Sens e c ommand, the drive returns
the following additional sense data.
Seagate SCSI-2/3 Interface Manual Volume 2; Ver-
Bytes
0 Valid
1 Segment number (00
2 0 0 ILI 0 Sense key
3–6 Information bytes
7 Additional sense length
8–11 Command specific data
12 A dditional sense code
13 Additional sense code qualifier
14 FRU code
15 SKSV Sense-key specific
16–17 Sense-key specific
18–21 Physical Location
Byte 0
76543210
111000X
valid
If the
valid. If the valid bit is 0, the information bytes are not valid.
If
error code
command that is currently pending. If
of 71
command for which a good status has already been returned.
bit is 1, the information bytes (bytes 3 through 6) are
contains a value of 70H, the error occurred on the
, the error occurred during the execution of a previous
H
Bits
Error code
H
error code
)
contains a value
Byte 1
segment number
The
is always 0.

78 Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B
Byte 2 If the
incorrect length indicator (ILI)
bit is zero, the requested block of data from the previous command did not
match the logical block length of the data on the disc. If
the ILI bit is 1, the requested block of data from the
previous command matched the logical block length of the
data on the disc.
The
sense key
indicates one of nine general error cate-
gories. These error categories are listed in Section B.2.
Bytes 3–6 When the
valid
bit is 1, the
information bytes
logical block address of the current logical block as sociated with the sense key. For example, if the sense key is
media error, the information bytes contain the logical
block address of the offending block.
Byte 7 The
additional sense length
0E
additional bytes. If the alloc ation length of the com-
H
is limited to a maximum of
mand descriptor block is too sm all to accom modat e all of
the additional sense bytes, the additional sense length is
not adjusted to reflect the truncation.
Bytes 8–11 These bytes contain command-specific data.
Bytes 12–13 The
additional sense code
qualifier
provide additional details about errors. See Sec-
and
additional sense code
tion B.3. on page 80.
Byte 14 The
field replaceable unit (FRU) code
is used by field
service personnel only.
contain the
Bytes 15–17 The SHSV bit and sense-key specific bytes.
Bytes 18–19 Physical cylinder
Byte 20 Physical head
Byte 21 Sector
Note. The Physical Location bytes contain the offending cylinder, head
and sector if the valid bit is 1.

Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B 79
B.2 Sense key
The sense keys in the lower-order bits of byte 2 of the sense data returned
by the Request Sense command are described i n the following table.
You can find a more detailed description of the error by checking the
additional sense code and the additional sense code qualifier in Section B.3 on page 80.
Sense
key
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
B
E
Description
No Sense.
H
In the case of a successful command, no specific
sense key information needs to be reported for the drive.
Recovered error.
H
The drive completed the last command
successfully with some recovery action. When many
recovered errors occur during one command, the drive
determines which error to report.
Not ready.
H
The addressed logical unit cannot be accessed.
Operator intervention may be required to correct this
condition.
Medium error.
H
The command was terminated with a
nonrecoverable error condition, possibly caused by a flaw in
the media or an error in the recorded data.
Hardware error.
H
The drive detected a nonrecoverable
hardware failure while performing the command or during a
self-test. This includes, for example, SCSI interface parity
errors, controller failures and device failures.
Illegal r e que s t.
H
This indicates an illegal parameter in the
CDB or in the additional parameters supplied as data for
some commands (for example, the Format Unit command,
the Mode Sense command and others). If the drive detects
an invalid parameter in the CDB, it terminates the command
without altering the media. If the drive detects an invalid
parameter in the additional parameters supplied as data, the
drive may have already altered the media.
Unit attention.
H
Seagate SCSI-2 Interface Manual
The drive may have been reset. See the
for more details about the
Unit Attention condition.
Aborted command.
H
The drive aborted the command. The
initiator may be able to recover by retrying.
Miscompare.
H
The source data did not match the data read
from the media.

80 Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B
B.3 Additional sense code and additional sense code
qualifier
The additional sense code and additional sense code qualifiers returned
in byte 12 and byte 13, respectively, of the Sense Data Format of the
Request Sense command are listed in the following table.
Error code (hex)
DescriptionByte 12 Byte 13
00 00 No additional information is supplied.
01 00 There is no index/sector signal.
02 00 There is no seek complete signal.
03 00 A write fault occurred.
04 00 Drive not ready; no additional information
04 01
04 02 Drive not ready; waiting for initialization
04 03 Drive not ready; human intervention required
04 04 Drive not ready; format in process
09 00 Track following error
11 00 An unrecovered read error occurred.
11 01
11 02
11 04
14 00 No sector found
15 00 A seek positioning error occurred.
16 00 Data synchronization mark error.
17 01
18 00 Data recovered with ECC
18 01 The data was recovered with ECC and retries.
18 02
19 00
Drive not ready; in Spinup mode
Read retries exhausted
Error too long to correct
Unrecoverable read error; Autoreallocation
failed
The data was recovered with retries.
The data was recovered and ARRE was
performed.
There is an error in the defect list.
19 01
Defect list not available

Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B 81
Error code (hex)
DescriptionByte 12 Byte 13
19 02
Error in PList
19 03
1A 00
1C 00
1C 01
1C 02
1D 00
20 00
21 00
24 00
25 00
26 00
26 01
26 02
26 03
Error in GList
A parameter overrun occurred.
The defect list could not be found.
The primary defect list could not be found.
GList not found
A miscompare occurred during a verify
operation.
The drive received an invalid command
operation code.
The logical block address was not within the
acceptable range.
The drive received a CDB that contains an
invalid bit.
The drive received an invalid LUN.
The drive received an invalid field in the
Parameter List.
CDB with unsupported parameter
CDB with invalid parameter
CDB with unsupported threshold parameter
29 00
2A 00
2A 01
2A 02
2F 00
31 00
32 00 No spare defect locations available.
39 00 Saved pages not found
3F 01
A power-on reset or a bus device reset
occurred.
Parameter changed by another initiator
The Mode Select parameters were changed
by another initiator.
Log parameters changed
Commands cleared by another initiator
Medium format corrupted
The firmware/microcode was changed.

82 Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B
Error code (hex)
DescriptionByte 12 Byte 13
40 00 Target operating conditions have changed.
40 01 Buffer parity error detected
40 93 Error in write to flash
43 00
A message error occurred.
44 00
47 00
48 00
49 00
4E 00
An internal controller error occurred.
A SCSI bus parity error occurred.
The initiator detected an error.
The initiator receives an invalid message from
the drive.
The drive attempted to perform overlapped
commands.

Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B 83
Appendix C. Mode pages
Mode pages are groups of parameters that the drive stores. These
parameters can be read using the Mode Sense command and changed
using the Mode Select command. These commands are described in
Sections 3.4.10 and 3.4.13. on pages 42 and 47.
This appendix contains the default parameters and the directly changeable parameters for the mode pages. The current parameters and the
saved parameters are not shown.
The default values contained in this appendix may differ from the
Note.
default values actually contained in your drive. To determine the
default values, use the Mode Sense command.
Contains
directly
Page
Mode page
code Bytes
Read-Write Error Recovery
page 01
Disconnect/Reconnect page
02
Format Device page 03
Rigid Disc Geometry page 04
Verify error recovery page 07
Caching page (SCSI-3) 08
Control Mode page 0A
Unit Attention Page 00
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
12 Yes
16 Yes
24 No
24 No
12 Yes
20 Yes
12 Yes
4Yes
changeable
parameters
For all mode pages:
• If the changeable value is 0, the initiator
If the changeable value is 1, the initiator
cannot
change the bit directly.
can
change the bit directly.
For example, in the mode page header, the changeable value for the
page code bits is 0, which means that the page code cannot be
changed; the changeable value of the PS bit is 1, which means that
the PS bit can be changed.
• During the Mode Sense command, the PS (parameter savable) bit
is 1, which means the mode page is saved on the disc. During the
Mode Select command, you must set the PS bit to 0.
• An “X” means that the value of the bit cannot be specified. For
example, the default value of bit 0 of byte 1 of page 00
(the Operating
H
page) cannot be specified because the bit can be either 1 or 0.

84 Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B
All mode pages contain a 2-byte header that contains the page code and
the page length for that particular page. The header is shown below.
Bytes
Bits
7 6 543210
0 PS Page code
changeable 1 0 0 0 0000
1 Page length
changeable 00
Byte 0 During the Mode Sense command, the
H
PS
(parameter savable)
bit is 1, which means the mode page is saved on the disc. During
the Mode Select command, you must set the PS bit to 0.
The
Byte 1 The
page code
page length
is the unique code that identifies the page.
is the length, in bytes, of the page.
C.1 Read-Write Error Recovery page (01H)
The Read-Write Error Recovery page is shown below. This table summarizes the function, the default value and the changeability of each bit.
Bytes
7 6 543210
0 PS (1) Page code (01
1 Page length (0A
2 AWRE ARRE TB RC EER PER DTE DCR
default 0 0 0 0 1000
changeable 1 1 1 1 1111
3 (default) Read retry count (20
changeable FF
4 (default) Correction span (40H)
changeable 00
5 (default) Head offset count (00H)
changeable 00
6 (default) Data strobe offset count (00H)
changeable 00
Bits
)
H
)
H
)
H
H
H
H
H
continued

Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B 85
continued fro m pre vious page
Bytes
Bits
7 6 543210
7 (default) Reserv ed (00
changeable 00
)
H
H
8 (default) Write retry count (20H)
changeable FF
H
9 (default) Reserv ed (00H)
changeable 00
H
10–11 (default) Recovery time limit (FFFFH)
changeable 0000
Byte 2 When the
automatic write reallocation enabled (AWRE)
H
the drive automati cally reallocat es bad blocks detected while
writing to the disc. When the AWRE bit is 0, the drive does not
perform automatic reallocation; instead, the drive reports a
check condition status with a sense key of media error.
Note. The AWRE bit does not apply during the Format com-
mand.
When the
automatic read reallocation enabled (ARRE)
the drive automati cally reallocat es bad blocks detected while
reading from the disc . When the A RRE bi t is 0, the dr ive does
not automatically reallocate bad blocks. Instead, a check condition status is reported with a sense key of media error.
bit is 1,
bit is 1,
The
transfer block (TB)
When the
read continuous (RC)
bit is not supported.
bit is 1, the drive sends all data
without making any corrections. This function supersedes other
bits in this byte. When the RC bit is 0, the correction is performed
according to the other bits in this byte.
When the
enable early recovery (EER)
bit is 1, the drive applies
on-the-fly T>1 ECC correction as soon as possible, before it
attempts other retry mechanisms, and without reporting successful corrections to the host as a recovered error. Seek error
retries and message system errors are not aff ected by this bit.
When this bit is set, the DCR bit must be 0. When the EER bit is
0, the drive applies ECC c orrection before other retry mechanisms but does not perform T>1 corrections on-the-fly; any
successful correction is reported to the host as a recovered error.

86 Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B
The
post error (PER)
The
disable transfer on error (DTE)
The
disable correction (DCR)
bit is not supported.
bit is not supported.
bit is not supported.
Byte 3 The
read retry count
field is the maximum number of
times the drive attempts its recovery algorithms. The read
retry count field has a range of 0 through 20
Byte 4 The
correction span
is the size of the largest read data
.
H
error, in bits, on which ECC correction is attempted. The
drive can correct up to 64 bits. Longer errors are reported
as nonrecoverable.
Byte 5 The
head offset count
is not implemented. Head offsets
are performed as part of the drive’s retry algorithms.
Byte 6 The
data strobe offset count
is not implemented.
Byte 7 Reserved
Byte 8 The
write retry count
field contains the maximum number
of times the drive attempts its recovery algorithms. The
write retry count field has a range of 0 through 20
H.
Byte 9 Reserved
Bytes 10–11 The
recovery time limit
field always has a value of FFFFH,
which means that the recovery time is unlimited.
C.2 Disconnect/Reconnect page (02H)
The Disconnect/Reconnect page is shown below. This table summarizes
the function, the default value and the changeability of each bit.
Bytes
Bits
7 6543210
0 PS (1) Page code (02
1 Page length (0E
2 (default) Buffer full ratio (99
changeable FF
H
3 (default) Buffer empty ratio (99H)
changeable FF
H
4–5 (default) Bus inactivity limit (0000
changeable 0000
continued
H
)
H
)
H
)
H
)
H

Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B 87
continued fro m pre vious page
6–7 (default) Disconnect time limit (0000H)
changeable 0000
H
8–9 (default) Connect time limit (0000H)
changeable 0000
H
10–11 (default) Reserved (0000H)
changeable 0000
H
12–15 (default) Reserved (00000000H)
changeable 00000000
H
Byte 2 The
how full the drive’s buffer is before reconnecting. The drive
rounds up to the nearest whole logical block. This parameter is the numerator of a fraction that has 256 as its
denominator.
Byte 3 The
mands, how empty the drive’s buffer is before reconnecting to fetch more data. The drive r ounds up to the nearest
whole logical block. This parameter is the numerator of a
fraction that has 256 as its denominator.
Bytes 4–5 The
µsec increments, that the drive can assert the Busy signal
without handshakes unti l it disconnects. The drive can
round down to its nearest capable val ue. I f t he bus i nactivity limit is 0000
for 1 msec without handshakes.
Bytes 6–7 The
time, in 100-µsec increments, that the drive remains
disconnected until it attempts to reconnect. A value of 0
indicates that the drive is allowed to reconnect immediately.
Bytes 8–9 The
in 100-µsec increments, that the drive should remain
connected until it attempts to disconnect. The drive may
round to its nearest capable value. A value of 0 means
that the drive c an remain connected indefinitely until it
tries to disconnect.
buffer full ratio
field indicates, on Read commands,
buffer empty ratio
bus inactivity lim it
field indicates the time, in 100-
, the drive maintains the BSY– signal
H
disconnect time limit
connect time limit
field indicates the maximum time,
field indicates, on Write com-
field indicates the minimum
Bytes 10–11 Reserved
Bytes 12–15 Reserved

88 Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B
C.3 Format Device page (03H)
The Format Device page is shown below. This table summarizes the
function, the default value and the changeability of each bit.
Bytes
Bits
76543210
0 PS (1) Page code (03
1 Page length (16
2–3 (default) T racks per zone (0000
changeable 0000
H
)
H
)
H
H)
4–5 (default) Alternate sectors per zone (07D0H)
changeable 0000
6–7 (default) Alternate tracks per zone (0000
changeable 0000
H
)
H
H
8–9 (default) Alternate tracks per volume (0000H)
changeable 0000
H
10–11 (default) Sectors per track (00A1H)
changeable 0000
H
12–13 (default) Data bytes per physical sector (0200H)
changeable 0000
H
14–15 (default) Interleave (0001H)
changeable 0000
H
16–17 (default) Track skew factor (00024H)
changeable 0000
H
18–19 (default) Cylinder skew factor (0034H)
changeable 0000
20 SSEC HSEC RMB SURF
default 0100
H
Reserved
changeable 00000000
21–23 (default) Reserved (000000
changeable 000000
)
H
H

Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B 89
Bytes 2–3 The
drive allocates to each defect-management zone. Spare
sectors or tracks are placed at the end of each defectmanagement zone. If each zone is treated as containing one
track, the valid value for tracks per zone is 1. If each zone is
treated as containi ng one cylind er, the val id val ue is equa l
to the number of read/write heads. The drive supports only
one zone for the entire drive.
Bytes 4–5 The
of spare sectors to be reserved at the end of each defectmanagement zone. The drive defaults to 7D0
spare blocks at the end of the volume.
Bytes 6–7 The
of spare tracks the drive reserves at the end of each
defect-management zone. A value of 0 indicates that no
spare tracks are reserved at the end of each zone for
defect management.
Bytes 8–9 The
of spare tracks to be reserved at the end of the drive for
defect management. A value of 0 indicates that no spare
tracks are reserved at the end of each zone for def ect
management.
Bytes 10–11 The
cal sectors the drive allocates per track. The drive reports
the average number of physical sectors per track because
the number of sectors per track varies between the outer
and inner tracks.
tracks per zone
field indicates the number of tracks the
alternate sectors per zone
alternate tracks per zon
alternate tracks per volume
sectors per track
field indicates the number of physi-
field indicates the number
(2000)
H
e field indicates the number
field indicates the number
Bytes 12–13 The
data bytes per physical sector
field indicates the
number of data bytes allocated per physical sector.
Bytes 14–15 The
interleave
field is the interleave value sent to the drive
during the last Format Unit c ommand. This field is valid
only for Mode Sense commands. The drive ignores this
field during Mode Select commands. The interleave is
always 1:1.
Bytes 16–17 The
track skew factor
6
field indicates the number of
physical sectors on the media between the last logical
block of one track and the first logic al block of the next
sequential track of the same cylinder. The actual track
skew factor that the drive uses is different for every zone.
6. The skew is in units of servo bursts, which are not visible through the interface.
The values shown is the skew approximated to the nearest sector.

90 Medalist Pro 2160N Product Manual, Rev. B
The default value is 0024H, which is the track skew factor
for the first zone.
Bytes 18–19 The
cylinder skew factor6
physical sectors between the last logical block of one
cylinder and the first logical block of the next cylinder. The
actual cylinder skew factor that the drive uses depends
on the zone. The default value is 0034
cylinder skew factor for the first zone.
Byte 20 The
drive type
The
soft sectoring (SSEC)
reported as not changeable. Although it can be set to
satisfy system requirements, it does not affect drive performance.
The
hard sectoring (HSEC)
reported as not changeable. Although it can be set to
satisfy system requirements, it does not affect drive performance.
The
removable media (RMB)
cating that the drive does not support removable media.
This same bit is also returned in the Inquiry parameters.
The
surface map (SURF)
drive allocates successive logical blocks to all sectors
within a cylinder before allocating logical blocks to the
next cylinder.
Bytes 21–23 Reserved
field indicates the number of
, which is the
H
field bits are defined as follows:
bit is set to 1. This bit is
bit is set to 0. This bit is
bit is always set to 0, indi-
bit is set to 0, indicating that the
C.4 Rigid Disc Geometry page (04H)
The Rigid Disc Geometry page is shown below. This table summarizes
the function, the default value and the changeability of each bit.
Bytes
7 6543210
0 PS (1) Page code (04
1 Page length (16
2–4 Number of cylinders (1988
changeable 000000
5 Number of heads (04H)
continued
Bits
)
H
)
H
)
H
H
 Loading...
Loading...