Page 1

Harmony XB5R
EIO0000001177 03/2019
Harmony XB5R
ZBRN1/ZBRN2
User Manual
03/2019
EIO0000001177.04
www.schneider-electric.com
Page 2

The information provided in this documentation contains general descriptions and/or technical
characteristics of the performance of the products contained herein. This documentation is not
intended as a substitute for and is not to be used for determining suitability or reliability of these
products for specific user applications. It is the duty of any such user or integrator to perform the
appropriate and complete risk analysis, evaluation and testing of the products with respect to the
relevant specific application or use thereof. Neither Schneider Electric nor any of its affiliates or
subsidiaries shall be responsible or liable for misuse of the information contained herein. If you
have any suggestions for improvements or amendments or have found errors in this publication,
please notify us.
You agree not to reproduce, other than for your own personal, noncommercial use, all or part of
this document on any medium whatsoever without permission of Schneider Electric, given in
writing. You also agree not to establish any hypertext links to this document or its content.
Schneider Electric does not grant any right or license for the personal and noncommercial use of
the document or its content, except for a non-exclusive license to consult it on an "as is" basis, at
your own risk. All other rights are reserved.
All pertinent state, regional, and local safety regulations must be observed when installing and
using this product. For reasons of safety and to help ensure compliance with documented system
data, only the manufacturer should perform repairs to components.
When devices are used for applications with technical safety requirements, the relevant
instructions must be followed.
Failure to use Schneider Electric software or approved software with our hardware products may
result in injury, harm, or improper operating results.
Failure to observe this information can result in injury or equipment damage.
© 2019 Schneider Electric. All rights reserved.
2 EIO0000001177 03/2019
Page 3
Table of Contents
Safety Information. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
About the Book . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Chapter 1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Offer Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Chapter 2 Physical Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
2.1 Product Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Hardware Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.2 Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Mechanical Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Environmental Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Housing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.3 Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Electrical Specifications. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.4 Data Management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Compatibility Rules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Transmitter Types . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Monostable Input . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Set/Reset. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Chapter 3 ZBRN2 Modbus Serial Line Communication . . . . . . . . . 43
Communication on The Modbus Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Communication and Status Indicator. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Modbus Serial Line Wiring. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Modbus Settings and Supported Functions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Modbus Serial Line Cables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Chapter 4 ZBRN1 Ethernet Communication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Communication on The Ethernet Network. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Addressing Modes. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Communication and Status Indicator. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Modbus TCP Settings and Supported Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Ethernet Cable. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
11
18
18
20
21
28
30
32
33
33
36
37
38
40
41
44
47
48
50
52
56
60
62
64
65
EIO0000001177 03/2019 3
Page 4

Chapter 5 Modbus Registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
5.1 Harmony Hub Input Channels Registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Input Channels Registers. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Type 1 Input Channels Registers. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Type 5 Input Channels Registers. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Type 6 Input Channels Registers. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.2 Diagnostic Registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Module Diagnostics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Communication Diagnostics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Error Codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.3 Configuration Registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Module Configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Communication Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
68
69
71
72
73
76
77
86
88
91
92
97
Chapter 6 Radio . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
Radio Receiver. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
99
Chapter 7 User Interface. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
Principle . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Configuration Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SD Card Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
108
111
115
128
131
Chapter 8 DTM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 133
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
134
135
146
Chapter 9 SD Card . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 157
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
File Management and Diagnostics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
158
160
163
Chapter 10 First Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 169
First Start Up . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Pairing Procedures. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
170
172
174
Chapter 11 Architectures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 179
IT/OT Architecture . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
179
4 EIO0000001177 03/2019
Page 5

Safety Information
Important Information
NOTICE
Read these instructions carefully, and look at the equipment to become familiar with the device
before trying to install, operate, service, or maintain it. The following special messages may appear
throughout this documentation or on the equipment to warn of potential hazards or to call attention
to information that clarifies or simplifies a procedure.
EIO0000001177 03/2019 5
Page 6

PLEASE NOTE
Electrical equipment should be installed, operated, serviced, and maintained only by qualified
personnel. No responsibility is assumed by Schneider Electric for any consequences arising out of
the use of this material.
A qualified person is one who has skills and knowledge related to the construction and operation
of electrical equipment and its installation, and has received safety training to recognize and avoid
the hazards involved.
6 EIO0000001177 03/2019
Page 7

About the Book
At a Glance
Document Scope
This documentation is a reference for the wireless transmitters used with the ZBRN•
Harmony Hub.
The purpose of this document is to:
show you how to install and operate your Harmony Hub.
show you how to connect Harmony Hub with wireless transmitters, programmable logic
controllers (PLCs), and other devices.
help you become familiar with Harmony Hub features.
NOTE: Read and understand this document and all related documents
installing, operating, or maintaining your Harmony Hub.
The users must read through the entire document to understand all its features.
Validity Note
This documentation is valid for the ZBRN• Harmony Hub.
The technical characteristics of the devices described in the present document also appear online.
To access the information online:
Step Action
1 Go to the Schneider Electric home page
2 In the Search box type the reference of a product or the name of a product range.
3 If you entered a reference, go to the Product Datasheets search results and click on the
4 If more than one reference appears in the Products search results, click on the reference that
5 Depending on the size of your screen, you may need to scroll down to see the datasheet.
6 To save or print a datasheet as a .pdf file, click Download XXX product datasheet.
(see page 8)
www.schneider-electric.com
Do not include blank spaces in the reference or product range.
To get information on grouping similar modules, use asterisks (
reference that interests you.
If you entered the name of a product range, go to the Product Ranges search results and click
on the product range that interests you.
interests you.
.
*
).
before
The characteristics that are presented in the present document should be the same as those
characteristics that appear online. In line with our policy of constant improvement, we may revise
content over time to improve clarity and accuracy. If you see a difference between the document
and online information, use the online information as your reference.
EIO0000001177 03/2019 7
Page 8
Related Documents
Title of Documentation Reference Number
Harmony XB5R Wireless and Battery-less Pushbutton 960562 (Eng),
Harmony XB5R Expert Instruction Sheet EIO0000000812 (Eng),
Magelis Box iPC Modular and Display Optimized, Universal and
Performance (HMIBMI, HMIBMO, HMIBMP, HMIBMU, HMIDM) User Manual
ZBRN1 Instruction Sheet S1B87888
ZBRN2 Instruction Sheet S1B87941
ZBRCETH Instruction Sheet S1B88209
Packages Instruction Sheet S1A57199
Receivers Instruction Sheet S1A57202
Transmitter with Metal or Plastic Head and Cap Instruction Sheet S1A57198
Relay Antenna Instruction Sheet S1A57194
Handy Box Instruction Sheet S1A57210
960563 (Fre),
DIA5ED2110402EN (Eng),
DIA5ED2110402FR (Fre)
EIO0000000813 (Fre),
EIO0000000814 (Ger),
EIO0000000815 (Spa),
EIO0000000816 (Ita),
EIO0000000817 (Chs),
EIO0000000818 (Por)
EIO0000003374 (Eng),
EIO0000003375 (Fre),
EIO0000003376 (Ger),
EIO0000003377 (Spa),
EIO0000003378 (Ita),
EIO0000003379 (Chs),
You can download these technical publications and other technical information from our website
at https://www.schneider-electric.com/en/download
8 EIO0000001177 03/2019
Page 9

Product Related Information
HAZARD OF ELECTRIC SHOCK, EXPLOSION OR ARC FLASH
Disconnect all power from all equipment including connected devices prior to removing any
covers or doors, or installing or removing any accessories, hardware, cables, or wires except
under the specific conditions specified in the appropriate hardware guide for this equipment.
Always use a properly rated voltage sensing device to confirm the power off where and when
indicated.
Replace and secure all covers, accessories, hardware, cables, and wires and confirm that a
proper ground connection exists before applying power to the equipment.
Use only the specified voltage when operating this equipment and any associated products.
Failure to follow these instructions will result in death or serious injury.
UNINTENDED EQUIPMENT OPERATION
Only persons with expertise in the design and programming of control systems are allowed to
program, install, alter, and apply this product.
Follow all local and national safety codes and standards.
Failure to follow these instructions can result in death, serious injury, or equipment damage.
DANGER
WARNING
EIO0000001177 03/2019 9
Page 10

10 EIO0000001177 03/2019
Page 11
Harmony XB5R
Introduction
EIO0000001177 03/2019
Introduction
Chapter 1
Introduction
Offer Description
Overview
The Harmony XB5R offer using Harmony Hub allows more flexibility and simplicity in the
installation. Wireless transmitters technology reduces the wiring and the cost of installation.
Harmony Hub converts radio frequency inputs into various communication protocols and operates
as intermediate equipment between a transmitter and a PLC or industrial PCs (IT/OT box) that
support Modbus TCP protocols.
Harmony Hub can be used with transmitters such as XB4R and XB5R wireless and batteryless
pushbuttons, rope pull switch, mushroom head pushbuttons, emergency stop monitoring, wireless
and batteryless limit switches, temperature and energy sensors.
It has a wide range of industrial and building applications. For example, in packing lines, automatic
doors in logistic centers, manufacturing of vehicles in automotive industries, for bag filling in
cement industries, and for efficient use of power in office lighting.
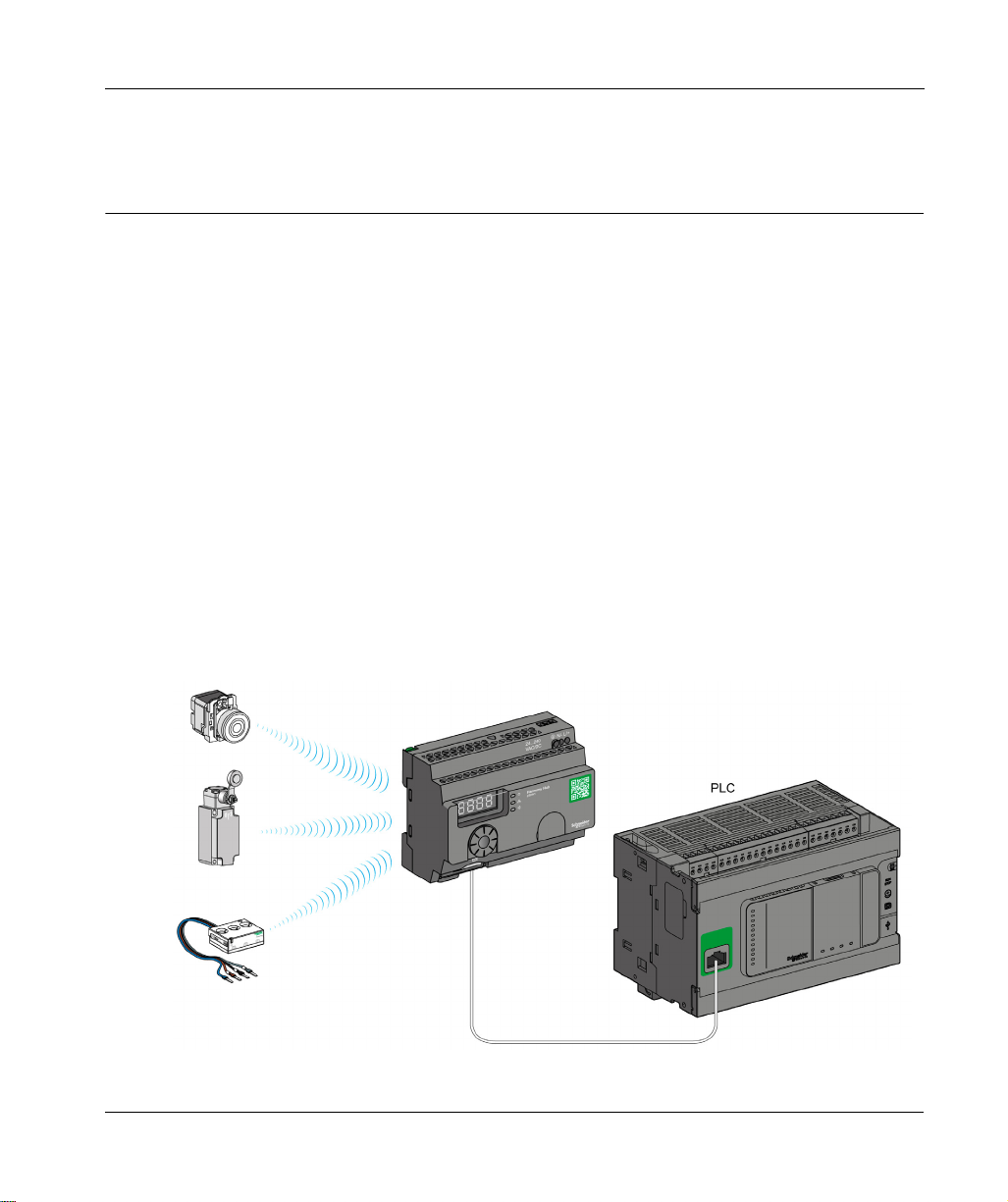
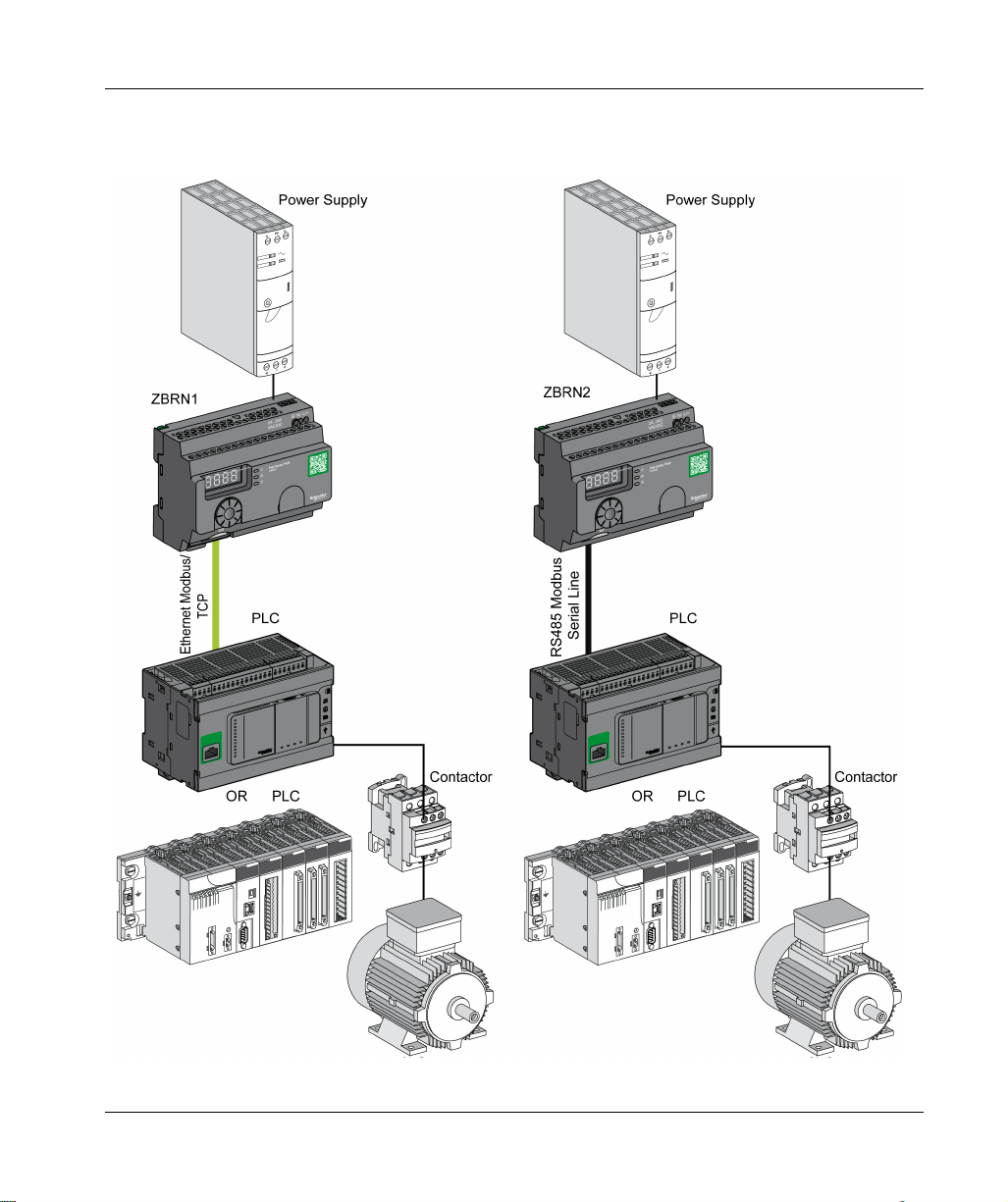
Basic Architecture with PLC
The following figure shows the transmission between three transmitters and a ZBRN1
Harmony Hub:
NOTE: You can associate 1 Harmony Hub with up to 60 transmitters. Each transmitter has a
unique ID (for example, 030079B1).
EIO0000001177 03/2019 11
Page 12
Introduction
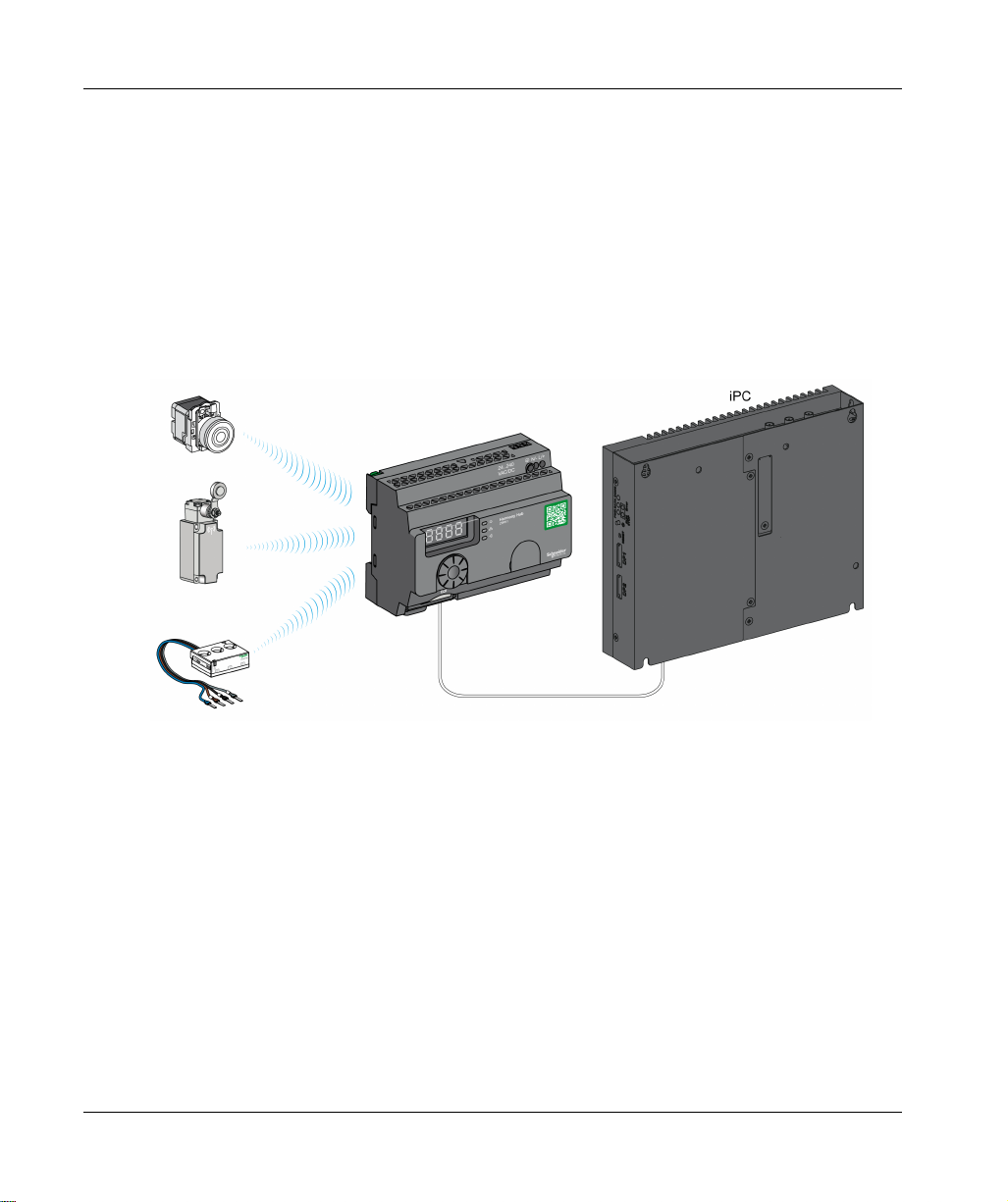
IT/OT Architecture
Harmony Hub provides network connectivity openness by operating as intermediate equipment
between the wireless devices and PLCs (Programmable Logic Controller) or all industrial PCs
(IT/OT box) that support Modbus TCP protocols.
Harmony Hub is providing an easy way to digitalize your production line to improve operation
efficiency (OEE) by using a non-intrusive wireless system easy to connect to your IT system.
Harmony Hub collect physical signals from an operator interface or secondary sensing to generate
computed data information for CMMS tools and operation management tools.
Data can be analyzed through our dedicated EcoStruxure platform through AVEVA Software,
Maintenace Advisor software, and Augmented Operator Advisor application.
12
For details, refer to IT/OT Architecture
(seepage179)
.
EIO0000001177 03/2019
Page 13

Compatible Transmitters
Harmony Hub is compatible with:
The Harmony battery-less and wireless pushbuttons offer based on radio technology
The Harmony battery-less and wireless rope pull switch
The OsiSense battery-less and wireless radio limit switches
Temperature sensors with battery
Energy sensors
The following figures show some examples of transmitters:
Example 1: pushbutton with a plastic head
Example 2: pushbutton with a metal head
Introduction
Example 3: pushbutton with a plastic head enclosed in a handy box
EIO0000001177 03/2019 13
Page 14
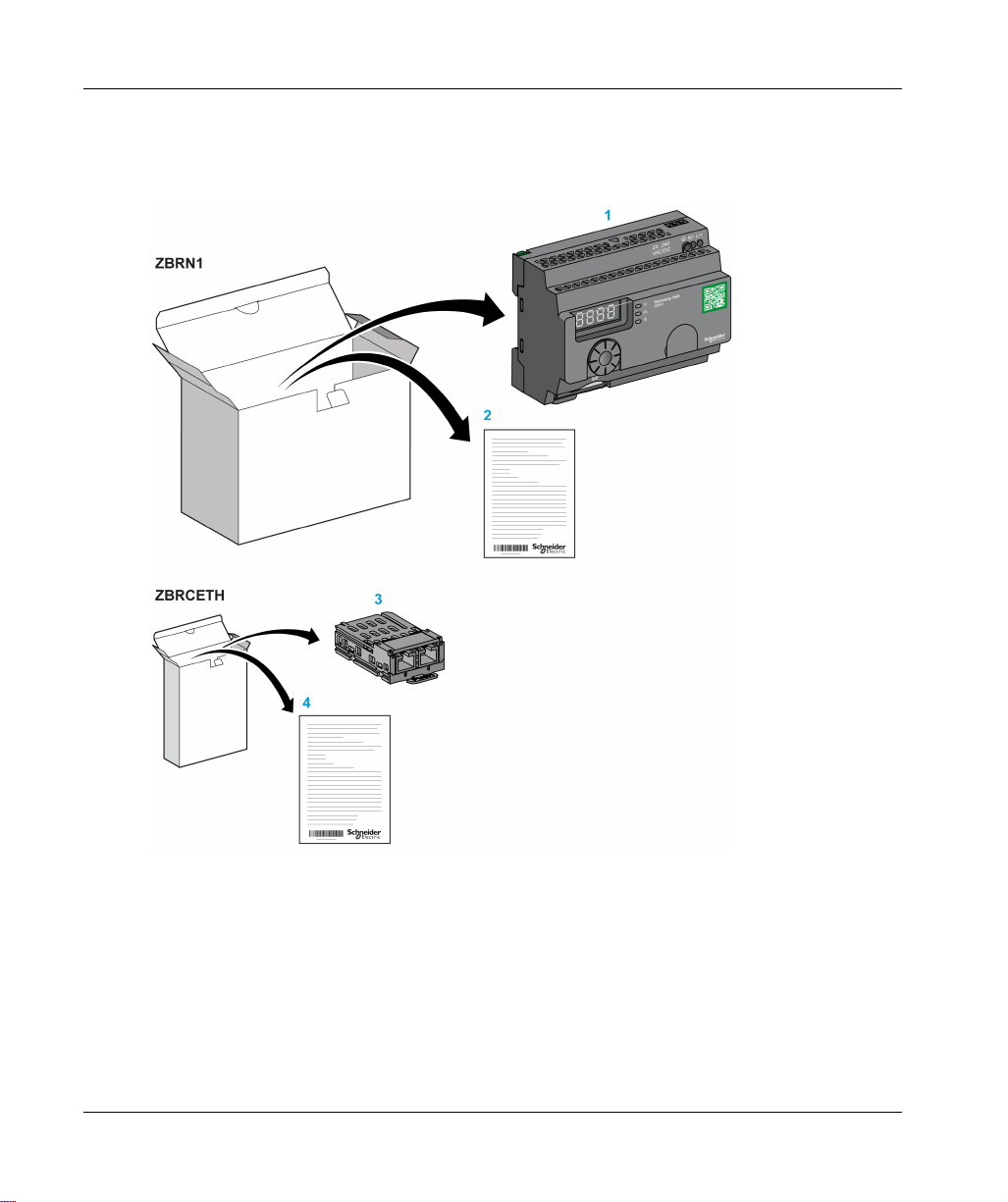
Introduction
Product References
ZBRN1: Standard Harmony Hub with Communication Module
14
1 Harmony Hub
2 Instruction Sheet (ZBRN1)
3 Modbus TCP Communication module
4 Instruction Sheet (ZBRCETH)
NOTE: ZBRN1 must be associated with a communication module, reference ZBRCETH (Ethernet
protocol).
EIO0000001177 03/2019
Page 15

ZBRN2: Harmony Hub for Modbus Serial Line Communication
1 Harmony Hub
2 Instruction Sheet
Introduction
Difference Between ZBRN1 and ZBRN2
ZBRN2 has an embedded communication port for a Modbus serial line, whereas ZBRN1 can
support different protocols using a communication module.
EIO0000001177 03/2019 15
Page 16

Introduction
16
EIO0000001177 03/2019
Page 17

Harmony XB5R
Physical Description
EIO0000001177 03/2019
Physical Description
Chapter 2
Physical Description
Purpose
This chapter provides an overview of the Harmony XB5R ZBRN1 and ZBRN2 hardware:
description, output connectors, installation, and power supply connections.
What Is in This Chapter?
This chapter contains the following sections:
Section Topic Page
2.1 Product Overview 18
2.2 Installation 20
2.3 Specifications 33
2.4 Data Management 36
EIO0000001177 03/2019 17
Page 18
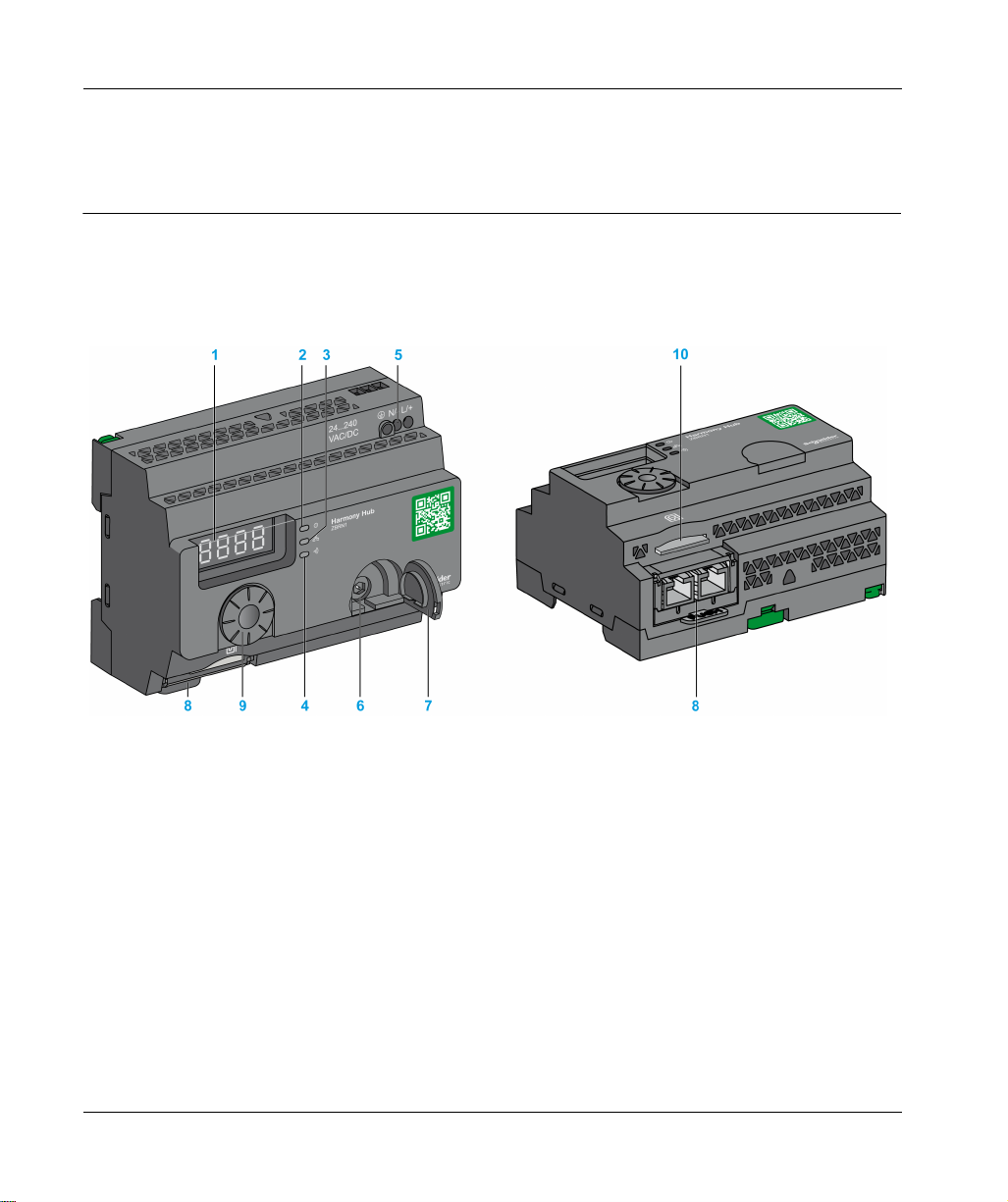
Physical Description
Product Overview
Section 2.1
Product Overview
Hardware Description
ZBRN1
18
1 Four 7-segments displays with 5 LEDs
2 Power LED
3 Communication LED
4 Radio signal strength LED
5 Power input terminal block
6 Connector for the optional external antenna
7 Protective plug for the connector for the optional external antenna
8 ZBRCETH Communication module inserted with 2 RJ45 Ethernet connectors
9 Jog dial
10 SD memory card slot
EIO0000001177 03/2019
Page 19
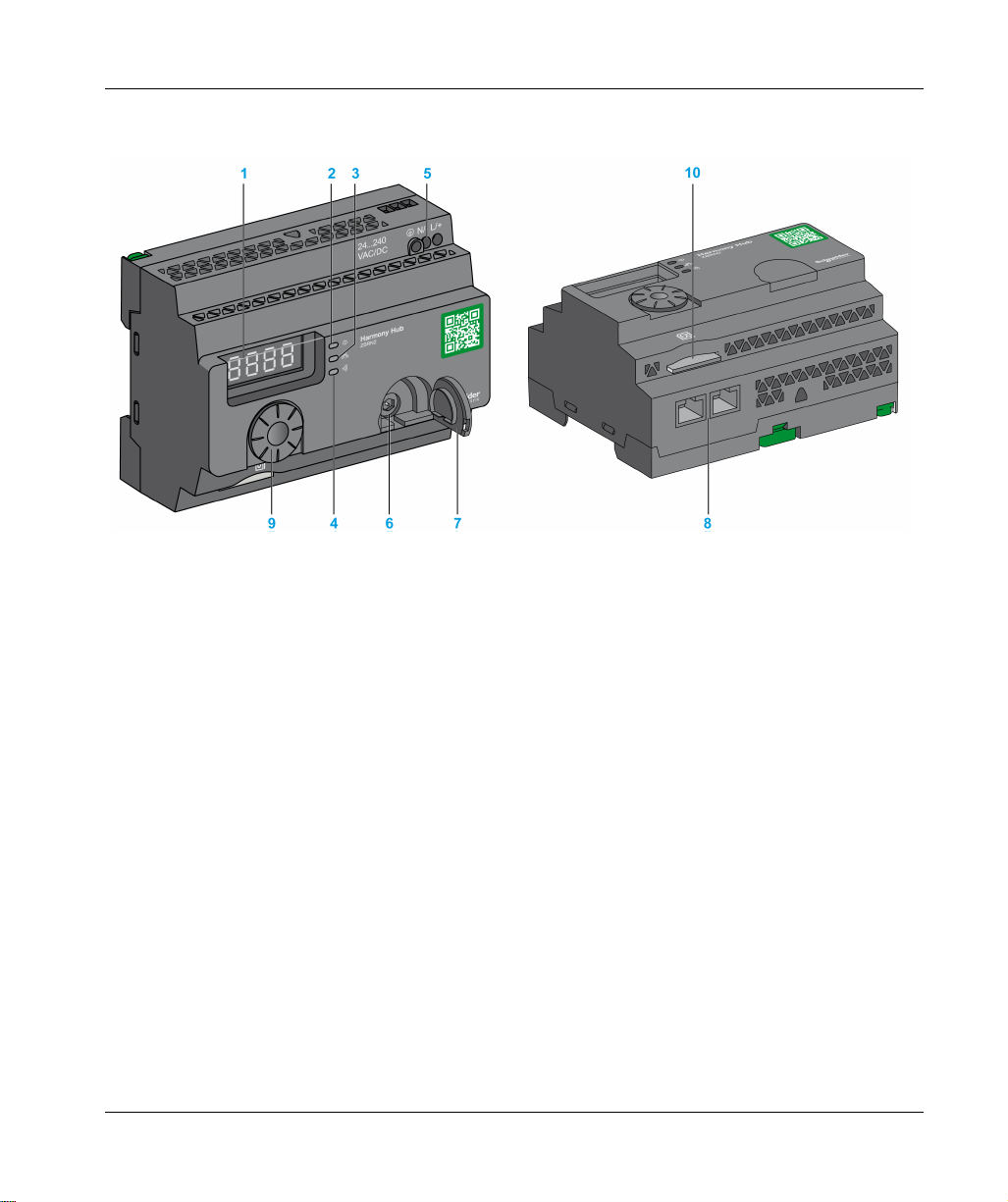
ZBRN2
Physical Description
1 Four 7-segments displays with 5 LEDs
2 Power LED
3 Communication LED
4 Radio signal strength LED
5 Power input terminal block
6 Connector for the optional external antenna
7 Protective plug for the connector for the optional external antenna
8 2 RS-485 Modbus serial line connectors
9 Jog dial
10 SD memory card slot
EIO0000001177 03/2019 19
Page 20

Physical Description
Installation
Section 2.2
Installation
What Is in This Section?
This section contains the following topics:
Installation Requirements 21
Mechanical Installation 28
Environmental Features 30
Housing 32
Topic Page
20
EIO0000001177 03/2019
Page 21

Installation Requirements
Before Starting
Read and understand this chapter before beginning the installation of your Harmony Hub.
HAZARD OF ELECTRIC SHOCK, EXPLOSION OR ARC FLASH
Disconnect all power from all equipment including connected devices prior to removing any
covers or doors, or installing or removing any accessories, hardware, cables, or wires except
under the specific conditions specified in the appropriate hardware guide for this equipment.
Always use a properly rated voltage sensing device to confirm the power off where and when
indicated.
Replace and secure all covers, accessories, hardware, cables, and wires and confirm that a
proper ground connection exists before applying power to the equipment.
Use only the specified voltage when operating this equipment and any associated products.
Failure to follow these instructions will result in death or serious injury.
Operating Environment
UNINTENDED EQUIPMENT OPERATION
Install and operate this equipment according to the environmental conditions described in the
operating limits.
Failure to follow these instructions can result in death, serious injury, or equipment damage.
Physical Description
DANGER
WARNING
EIO0000001177 03/2019 21
Page 22
Physical Description
Installation Considerations
UNINTENDED EQUIPMENT OPERATION
Use appropriate safety interlocks where personnel and/or equipment hazards exist.
Install and operate this equipment in an enclosure appropriately rated for its intended
environment.
Do not use this equipment in safety critical and hoisting machine functions due to:
No permanent communication
No acknowledge of the message from the receiver to the transmitters.
Do not disassemble, repair, or modify this equipment.
Do not connect any wiring to reserved, unused connections, or to connections designated as
not connected (N.C.).
Failure to follow these instructions can result in death, serious injury, or equipment damage.
WARNING
22
EIO0000001177 03/2019
Page 23
Architecture
The following figure shows the general principle of Harmony Hub architecture:
Physical Description
EIO0000001177 03/2019 23
Page 24

Physical Description
NOTE:
The previous figure is not exhaustive. It shows only the general principle of the architecture.
Refer to the specifications section
Harmony Hubs.
Refer to the user manual of your associated products for detailed wiring diagrams and
instructions.
Harmony Hub can be connected to any PLC supporting the network buses listed in this
document.
Connection Requirements
Power Supply Connection
24...240 Vac/Vdc
Network connection
RS-485 Modbus serial line network
Ethernet Modbus TCP network
(see page 33)
for detailed wiring diagram and instructions for
24
EIO0000001177 03/2019
Page 25
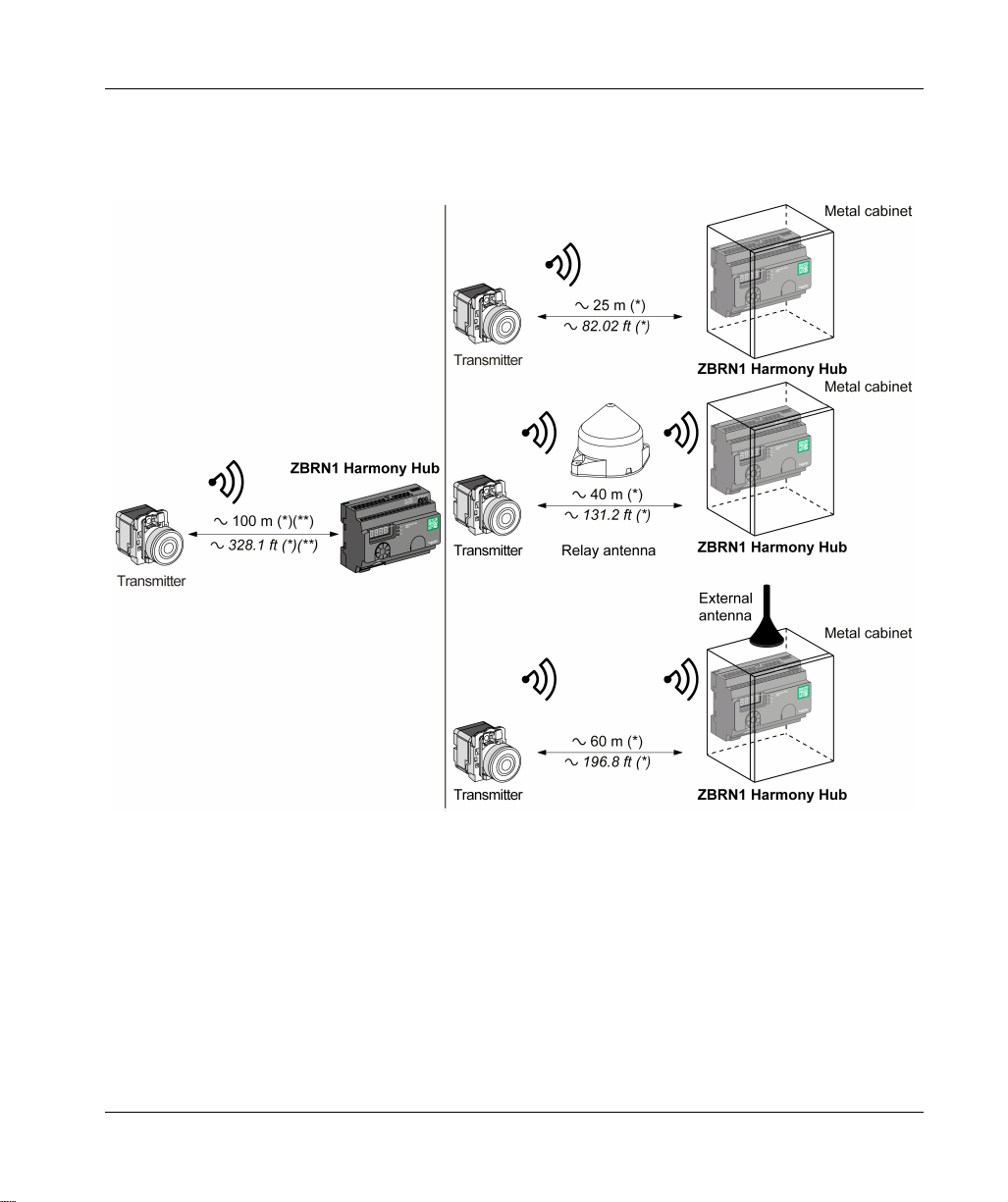
Maximum Distances
The following figure shows the maximum distance between the transmitters and the ZBRN1
Harmony Hubs:
Physical Description
(*) The application environment can modify the typical values.
(**) Free field (unobstructed and without electromagnetic perturbations).
EIO0000001177 03/2019 25
Page 26
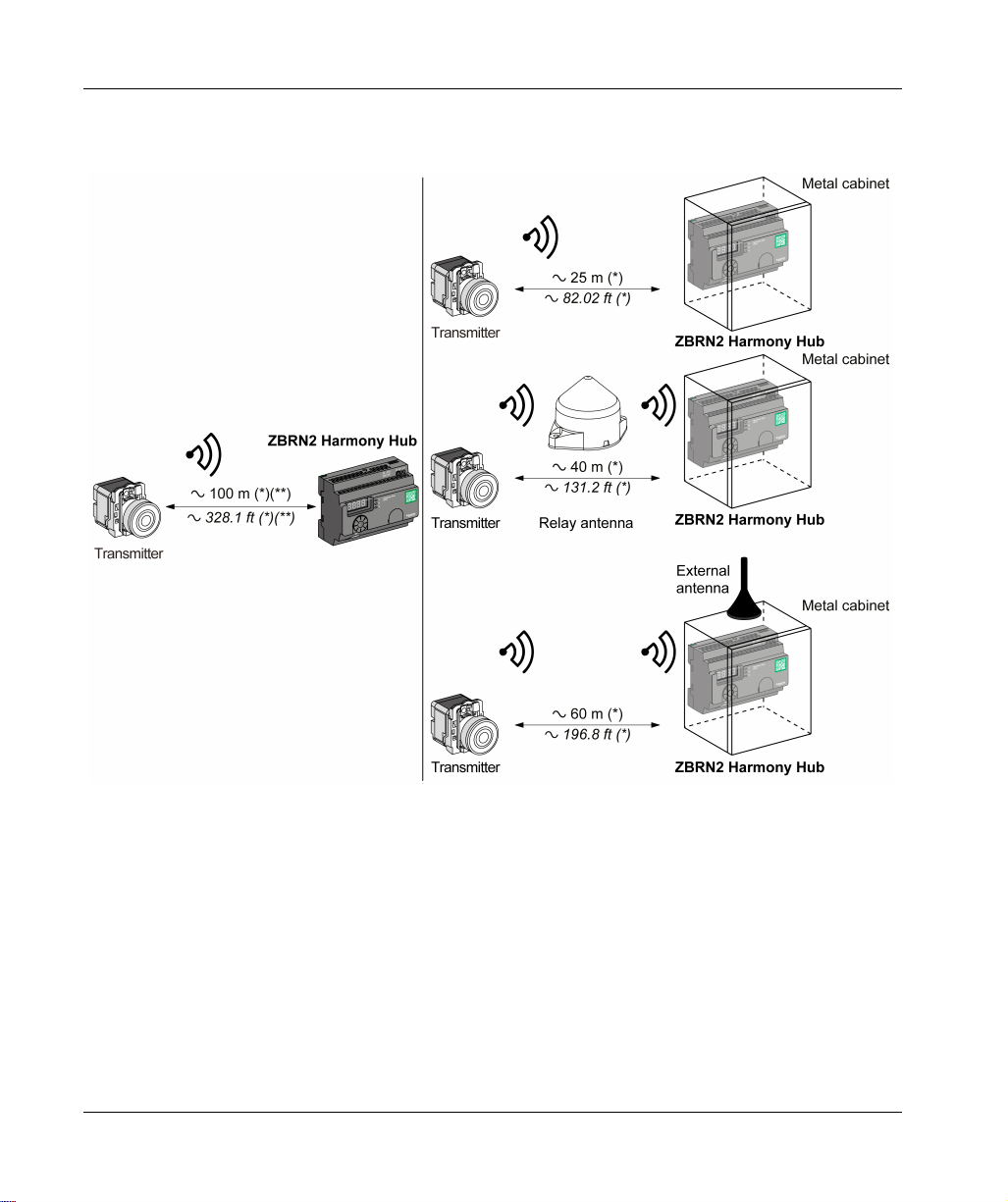
Physical Description
The following figure shows the maximum distance between the transmitters and the ZBRN2
Harmony Hubs:
26
(*) The application environment can modify the typical values.
(**) Free field (unobstructed and without electromagnetic perturbations).
EIO0000001177 03/2019
Page 27
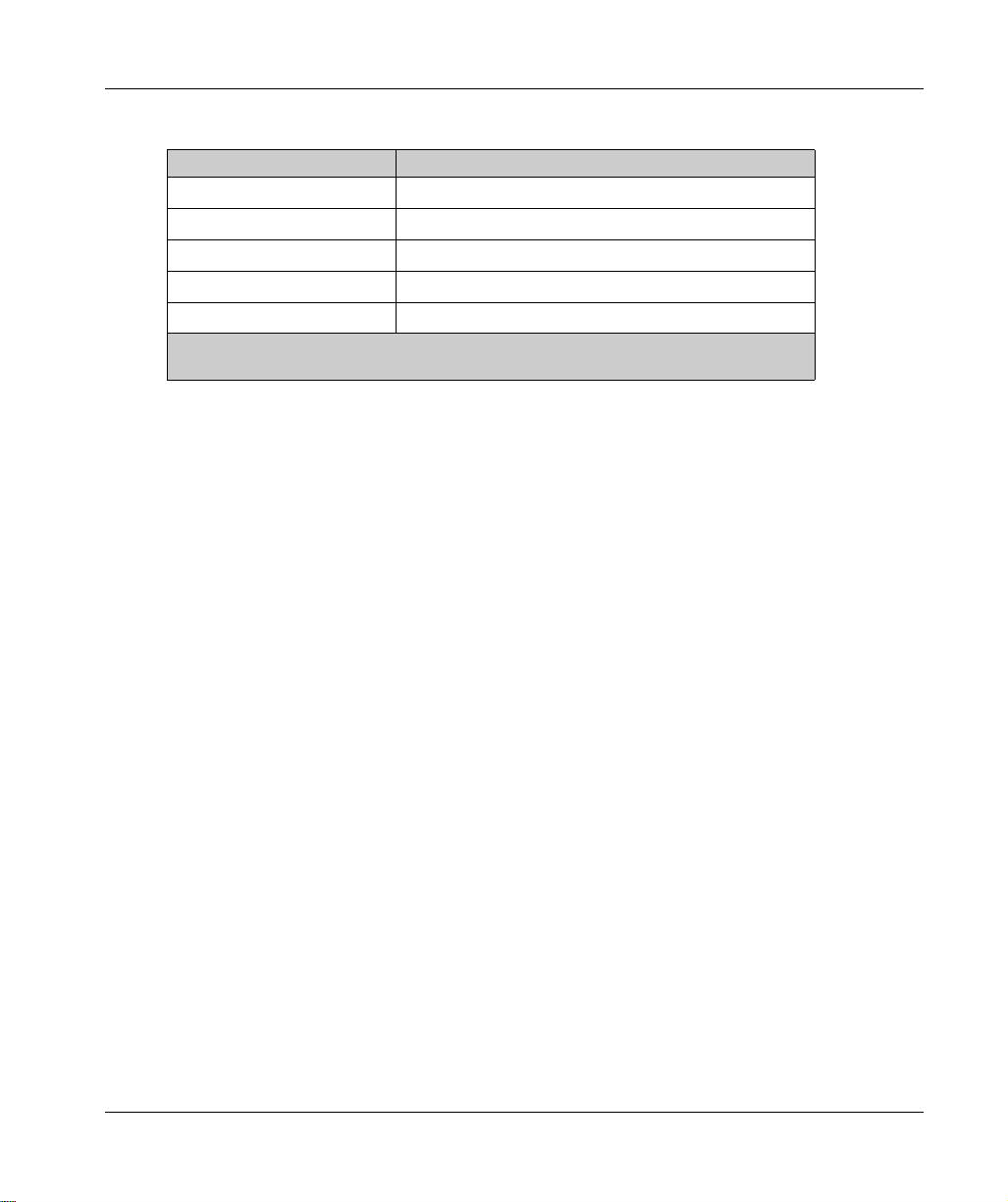
Physical Description
The level of signal attenuation depends on the material through which the signal passes:
Material Attenuation
Glass window
Plaster wall
Brick wall
Concrete wall
Metal structure
(*) Values for indication purpose only. Actual values depend on the thickness and nature of
the material.
10...20 %
30...45 %
60 %
70...80 %
60...100 %
(*)
(*)
(*)
(*)
(*)
NOTE: You can add ZBRA1 or ZBRA2 antenna or both to increase the range. The reception is
reduced if Harmony Hub is placed in a metal cabinet.
For further information on the use of ZBRA1 and ZBRA2 antennas, refer to the Radio chapter
(seepage99)
.
Impact of the radio performances in the environment:
For any environment, the radio performances are subjected to be instable due to perturbations
made by any kind of industrial machines, processes, or electronic devices.
As a consequence at any time, it is possible that the radio frames sent by a transmitter will not
be caught by the receiver during the perturbation.
With Harmony XB5R offer, only one radio frame is sent to the receiver, there is no permanent
radio communication. This reason prevents the use of Harmony XB5R offer for applications
where permanent reliability and/or permanent precisions are needed.
EIO0000001177 03/2019 27
Page 28

Physical Description
Mechanical Installation
Mounted on DIN Rail
Harmony Hub must be installed on DIN rails complying with EN/IEC 60715.
To install Harmony Hub, use a tool to press down the D lock for inserting the DIN rail.
The following figure shows the position of Harmony Hub on the DIN rail:
28
EIO0000001177 03/2019
Page 29

Mounted on a Grid or Plate
Harmony Hub can be installed on a grid or a plate.
The following steps explain how to install the module:
Step Action
1 Pull out the panel mounting hooks.
2 Mount Harmony Hub on the grid or plate using the screws as shown in the
following figure.
Physical Description
EIO0000001177 03/2019 29
Page 30
Physical Description
Environmental Features
Specifications
The following table shows the general environmental specifications:
Characteristics Specifications
Standards Conformity to
standards
Conformity to
standards
Conformity to
standards
Radio
certifications
Agencies
UL USA UL508, 17th edition
CSA Canada CSA C22.2, No. 142-M2000
C-Tick Australia –
GOST Russia –
ANATEL Brazil –
FCC USA –
SRRC China –
CCC China –
MIC Japan –
RSS Canada –
Ambient operating
temperature
Storage temperature –40...+70 °C (–40...+158 °F)
Relative humidity 95% RH at 55 °C (131 °F)
Degree of pollution 2 (IEC60664-1)
Degree of protection IP20
Shock resistance Half sine wave acceleration: 11 ms 30 gn (IEC 60068-2 27)
Resistance to vibration ±3.5 mm (±0.13 in.): 5...8.14 Hz
R&TTE 1999/5/EC, LVD 2006/95/EC, EMC2004/108/EC
EN/IEC 60947-1, EN/IEC 60947-5-1, EN/IEC60950-1, IEC61131-2, EN
300440-2, EN300489-3, EN300328, EN62311
UL 508 (USA), CSA C22-2 n° 14 (Canada), CCC (China), Gost (Russia)
FCC (USA), CSA, RSS (Canada), C-Tick (Australia), ANATEL (Brazil),
SRRC (China), MIC (Japan)
–25...+55 °C (–13...+131 °F)
1 gn: 8.14...150 Hz when mounted on a panel
2 gn: 8.45...150 Hz when mounted on a DIN rail (IEC 60068-2-6)
30
EIO0000001177 03/2019
Page 31

Characteristics Specifications
Altitude requirement Operation: 0...2000 m (6561.66 ft)
Storage: 0...3000 m (9842.49 ft)
Only used at altitude not exceeding 2000 m (6561.66 ft).
Only used in non-tropical climate regions.
Physical Description
EIO0000001177 03/2019 31
Page 32

Physical Description
Housing
Clearances and Mounting Position
(1) To enhance the signal reception, observe the above positioning.
(2) In a metal cabinet, the optimum place for Harmony Hub is on the top. This position avoids obstacles and
enhances the signal reception.
32
EIO0000001177 03/2019
Page 33

Specifications
Section 2.3
Specifications
Electrical Specifications
Power Supply Specifications
Harmony Hub complies with the following power requirements:
Electrical Features Description
Rated voltage 24...240 Vac 24...240 Vdc
Voltage range 21...264 Vac 21...264 Vdc
Rated frequency 50/60 Hz –
Frequency range 47...63 Hz –
Under voltage protection No No
Terminal blocks 3-pin terminal with a pitch of 7.62 mm (0.3 in.) on the output terminal block
Immunity to short interruptions
(Conforming to IEC 61000-4-
11)
Dielectric strength with others 3000 Vac / 4250 Vdc (input-output)
Short-circuit protection Yes (internal fuse 2 A, 250 V)
* PE = protective earth ground
Physical Description
AC Power Supply DC Power Supply
10 ms 10 ms
1500 Vac / 2150 Vdc (input-PE*)
EIO0000001177 03/2019 33
Page 34

Physical Description
Power Supply Connections
You can connect the power supply to any common supply from 24...240 Vac/Vdc.
HAZARD OF ELECTRIC SHOCK, EXPLOSION OR ARC FLASH
Comply with the wiring diagram shown immediately after this message.
Failure to follow these instructions will result in death or serious injury.
DANGER
34
EIO0000001177 03/2019
Page 35

Physical Description
The following table shows the recommended wire sizes for the L/+ and N/- terminals:
The following table shows the recommended wire sizes for the PE terminal (protective earth
ground):
The following table shows the recommend torque for the 3 terminals:
WARNING
UNINTENDED EQUIPMENT OPERATION
For the protective earth ground (PE) wiring, use a cable not longer than 300 mm (11.8 in.).
Failure to follow these instructions can result in death, serious injury, or equipment damage.
The following table shows the input power consumption:
Reference Input Power
ZBRN1 9 W
ZBRN2 3.3 W
WARNING
UNINTENDED EQUIPMENT OPERATION
Supply this product with a power line protected by a circuit breaker rated 16 A maximum and
a ground fault circuit breaker.
A readily accessible disconnect device shall be incorporated external to the equipment.
Install this product in an electrical cabinet and lock the cabinet using a key.
Failure to follow these instructions can result in death, serious injury, or equipment damage.
EIO0000001177 03/2019 35
Page 36

Physical Description
Data Management
Section 2.4
Data Management
What Is in This Section?
This section contains the following topics:
Compatibility Rules 37
Transmitter Types 38
Monostable Input 40
Set/Reset 41
Topic Page
36
EIO0000001177 03/2019
Page 37

Compatibility Rules
Transmitter Compatibility
ZBRT2 transmitter is compatible with the following only:
ZBRR• receivers with firmware version 2.0 and higher
ZBRA1 relay antenna with firmware version 2.0 and higher
ZBRN• Harmony Hubs with firmware version higher than 1.2
Physical Description
EIO0000001177 03/2019 37
Page 38

Physical Description
Transmitter Types
ZBRT1 and ZBRTP Transmitters
The radio message is sent when the button is pressed, signaled by a click. If the button is held
down, the message is not transmitted continuously. The message is not sent when the button is
released.
To avoid any conflict of multiple transmission from different transmitters, a minimum of 10 ms is
required between each radio transmission.
38
ZBRT1 is used for applications where single pulse is required (for example, remote start of
machine and reset after machine fault detection).
EIO0000001177 03/2019
Page 39

ZBRT2 Transmitter
The radio message is sent when the button is pressed, signaled by a click. If the button is held
down, the message is not transmitted continuously.
A second radio message is sent when the button is released. This message is not transmitted
continuously. It is transmitted once, at the release of the pushbutton.
This transmitter is used only for the set/reset output mode.
Physical Description
EIO0000001177 03/2019 39
Page 40

Physical Description
Monostable Input
Principle
The battery-less transmitter is equipped with a dynamo generator that converts mechanical energy
(produced by pressing the pushbutton) into electrical energy. A radio-coded message with a
unique ID code is sent in single pulse form.
The radio signal is transmitted when the pushbutton is pressed. This action is indicated by a click
in the example shown below. If the button is held, the signal is not transmitted continuously. No
signal is sent when the button is released.
The corresponding input channel of Harmony Hub stays active, depending on the input holding
time range, from 100 ms...1 s.
The input holding time is set for all the input channels.
Example
The following figure shows an example of a monostable channel with the input holding time of
500 ms:
40
EIO0000001177 03/2019
Page 41

Set/Reset
Pushbutton Set/Reset
NOTE:
1. Release and push again to resynchronize
2. Push and release again to resynchronize
Physical Description
EIO0000001177 03/2019 41
Page 42

Physical Description
42
EIO0000001177 03/2019
Page 43

Harmony XB5R
Modbus Serial Line Communication
EIO0000001177 03/2019
ZBRN2 Modbus Serial Line Communication
Chapter 3
ZBRN2 Modbus Serial Line Communication
Purpose
This chapter provides an overview of the Modbus layout description, communication and status
indicator, line termination mode, settings, and the supported functions.
What Is in This Chapter?
This chapter contains the following topics:
Communication on The Modbus Network 44
Communication and Status Indicator 47
Modbus Serial Line Wiring 48
Modbus Settings and Supported Functions 50
Modbus Serial Line Cables 52
Topic Page
EIO0000001177 03/2019 43
Page 44

Modbus Serial Line Communication
Communication on The Modbus Network
Introduction
The Modbus protocol is a master/slave protocol. It allows a single master to request responses
from the slaves, or to act based on the request. The master can address individual slaves, or can
send a broadcast message to all slaves. The slaves return a message (response) to requests
addressed to them individually. The slaves do not return responses to broadcast requests from the
master.
RISK OF UNINTENDED EQUIPMENT OPERATION
Do not use more than one master on the Modbus network. Unintended I/O behavior can result if
more than one master is able to communicate on the network at the same time.
Depending on the I/O configuration, unintended equipment operation can result if more than one
master is in use.
Failure to follow these instructions can result in death, serious injury, or equipment damage.
Network Connection
WARNING
44
1 PLC as master
2 Modbus Advantys OTB network interface module
3 ZBRN2 Harmony Hub
4 ATV12 drive
5 Modbus serial line
EIO0000001177 03/2019
Page 45

Modbus Serial Ports
The following figure shows the serial line connectors in ZBRN2 :
1 Serial line connectors
ZBRN2 offers 1 Modbus serial line communication port equipped with 2 RJ45 plugs. It enables
wiring between the devices without using a hub.
The following table shows the specifications of ZBRN2 :
Features Specification
Function Modbus slave and Modbus RTU
Plug 2 RJ45 connectors
Isolated Yes
Maximum cable length 1000 m (3280.83 ft)
Polarization No
Supported baud rates Auto/1200/2400/4800/19200/38400/115200
Parity Even/Odd/No/Auto
Stop bit 1 bit (even and odd)
Modbus Serial Line Communication
2 bits (no parity)
EIO0000001177 03/2019 45
Page 46

Modbus Serial Line Communication
RJ45 Layout Description
Modbus serial port is an RS-485, 2-wire and common Modbus serial line using a RJ45 connector.
The following figure shows the layout of RJ45 connector:
RJ45 pin Signal Description
1 Unused –
2 Unused –
3 Unused –
4 D1 Transmission signal.
5 D0 Reception signal.
6 Unused Reserved.
7 Unused Reserved (5...24 Vdc).
8 Common Common of signal and supply.
46
EIO0000001177 03/2019
Page 47

Communication and Status Indicator
Modbus Communication and Status LED
1 Power LED
2 Communication LED
3 Radio signal strength LED
The yellow Modbus communication LED shows the following status:
On/flashing: Data is being exchanged (depends on the quantity of information).
Off: No data is being exchanged.
Modbus Serial Line Communication
EIO0000001177 03/2019 47
Page 48

Modbus Serial Line Communication
Modbus Serial Line Wiring
Network Connection
You can directly connect Harmony Hub to a PLC for a distance up to 20 m (65.62 ft) as shown in
the following figure:
UNINTENDED EQUIPMENT OPERATION
Use a Modbus serial line cable not longer than 20 m (65.62 ft).
Add a 120 ohm termination line when Harmony Hub is located at the end of the Modbus serial
line (reference VW3A8306RC).
Failure to follow these instructions can result in death, serious injury, or equipment damage.
WARNING
48
EIO0000001177 03/2019
Page 49

Using TWDXCAT3RJ
TWDXCAT3RJ is used for three connections, polarization, and line termination.
The following figure shows the connection of the device on the bus using TWDXCAT3RJ:
Using TWDXCAISO
TWDXCAISO is used for isolation and line termination.
The following figure shows the connection of the device on the bus using TWDXCAISO (even if
Harmony Hub is already isolated):
Modbus Serial Line Communication
For distances longer than 20 m (65.62 ft), verify that the other devices connected to the bus are
isolated. If other devices are not isolated, use the TWDXCAISO module.
EIO0000001177 03/2019 49
Page 50

Modbus Serial Line Communication
Modbus Settings and Supported Functions
Modbus Message Structure
The Modbus protocol uses 16-bit words (registers) divided into 2 bytes of 8 bits each. A Modbus
message starts with a header followed by a 1-byte address. A Modbus message uses a Modbus
function as its first byte.
The following table shows the full structure of a Modbus RTU message:
Address Modbus Messages CRC
Function Code Data
1 byte 1 byte n-byte field 2 bytes
List of Supported Commands
The following table shows the list of Modbus commands:
Modbus Function Code:
Dec Index (Hex)
01 (0001 H) – Read coils.
03 (0003 H) – Read holding registers.
06 (0006 H) – Write single register.
16 (0010 H) – Write n registers.
43 (002B H) 14 (000E H) Read device identification.
Sub-Function:
Modbus Encapsulated
Interface
Command
NOTE: Registers can be read or written only if the registers are adjacent.
Reading Coils (01):
This function code is used to read the content of one or more contiguous coil statuses in a slave.
Reading holding registers (03):
This function code is used to read the content of one or more adjacent registers in a slave.
Writing a register (06):
This function code is used to write the content of a register in a slave.
Writing n registers (16):
This function code is used to write the content of one or more contiguous registers in the slave.
Identification (43 Modbus Encapsulated Interface 14):
This function code is used to read the identification and other information relating to the physical
description of a slave.
50
EIO0000001177 03/2019
Page 51

List of Identification Registers
The following table lists the Modbus identification registers:
Identifier Register Name Value Data Type
0 (0000 H)
1 (0001 H)
2 (0002 H)
3 (0003 H)
4 (0004 H)
5 (0005 H)
VendorName
ProductCode
MajorMinorRevision
VendorUrl
ProductName
ModelName
Abort Code
Function Code Abort Code Description
03 H 02 H One of the registers does not exist.
03 H Incorrect register number
04 H Unavailable value
06 H 02 H The register does not exist.
04 H Invalid value or register in read only.
10 H 02 H The register does not exist.
03 H Incorrect register number
04 H Invalid value or register in read only.
2B H 01 H Modbus encapsulated interface different from 14
02 H Identifier does not exist.
03 H Identifier > 4 or = 0
Modbus Serial Line Communication
Schneider Electric ASCII string
ZBRN1: 052848
ZBRN2: 052849
1.0 for the first official version
http://www.schneider-electric.com
Harmony
ZBRN1
ZBRN2
EIO0000001177 03/2019 51
Page 52

Modbus Serial Line Communication
Modbus Serial Line Cables
Modbus Serial Line Cables for ZBRN2 Harmony Hub
The following figure shows the Modbus serial line cable with 2 RJ45 connectors to connect to any
device supporting the protocol:
Item Description Reference Length
1 Modbus serial line cable VW3A8306R03 0.3 m (0.9 ft)
VW3A8306R10 1 m (3.2 ft)
VW3A8306R30 3 m (9.8 ft)
52
EIO0000001177 03/2019
Page 53

Modbus Serial Line Communication
The following figure shows the Modbus serial line cable with 1 RJ45 connector and 1 mini DIN
connector to connect to a Twido PLC:
Item Description Reference Length
2 Modbus serial line cable for Twido PLC TWDXCARJ003 0.3 m (0.9 ft)
TWDXCARJ010 1 m (3.2 ft)
TWDXCARJ030 3 m (9.8 ft)
The following figure shows the Modbus serial line cable with 1 RJ45 connector and one USB
connector to connect to a PC:
Item Description Reference Length
3 Modbus serial line cable TCSMCNAM3M002P 2.5 m (8.2 ft)
EIO0000001177 03/2019 53
Page 54

Modbus Serial Line Communication
The following figures show USB to RS-485 converter and Modbus serial line cable to connect to a
PC:
Item Description Reference Length
4a USB to RS-485 converter TSXCUSB485 –
4b Modbus serial line cable VW3A8306R03 –
The following figures show USB to RS-485 converter and Modbus serial line cable to connect to a
Twido PLC.
54
Item Description Reference Length
5a USB to RS-485 converter TSXCUSB485 –
5b Modbus serial line cable for Twido PLC TWDXCARJP03P –
EIO0000001177 03/2019
Page 55

Harmony XB5R
Ethernet Communicati on
EIO0000001177 03/2019
ZBRN1 Ethernet Communication
Chapter 4
ZBRN1 Ethernet Communication
What Is in This Chapter?
This chapter contains the following topics:
Communication on The Ethernet Network 56
Addressing Modes 60
Communication and Status Indicator 62
Modbus TCP Settings and Supported Functions 64
Ethernet Cable 65
Topic Page
EIO0000001177 03/2019 55
Page 56

Ethernet Communication
Communication on The Ethernet Network
Introduction
Ethernet is a widely used, low-cost technology for local area networks. This technology is used to
exchange data between several devices connected together on a network.
Network Connection
56
1 Ethernet Advantys OTB network interface module
2 ZBRN1 Harmony Hub associated with ZBRCETH communication module
3 PLC
4 Ethernet
EIO0000001177 03/2019
Page 57

ZBRCETH Communication Module
ZBRCETH is a communication module that supports Ethernet Modbus TCP protocol.
The following procedure describes the insertion of the communication module:
Step Action
1 Disconnect all power from the ZBRN1 Harmony Hub.
2 Place the module in ZBRN1 Harmony Hub.
Ethernet Communication
1 ZBRN1 Harmony Hub
2 ZBRCETH communication module
3 Press firmly into place.
EIO0000001177 03/2019 57
Page 58

Ethernet Communication
The following procedure describes the removal of the communication module:
Step Action
1 Disconnect all power from the ZBRN1 Harmony Hub.
2 Push down the release tab.
3 Pull out the module.
58
ZBRCETH offers one Ethernet communication port equipped with two RJ45 plugs. It enables daisy
chain wiring between devices without using a switch.
EIO0000001177 03/2019
Page 59

The following table shows the specifications of the communication module:
Feature Specifications
Plug Two RJ45 connectors
Driver
Type of cable Shielded
Topology Daisy chain
Automatic polarity correction Yes
RJ45 Layout Description
ZBRCETH communication module has two RJ45 connectors for Ethernet connectivity as shown in
the following figure:
Ethernet Communication
10/100 MB/s
Auto negotiation
Half/Full duplex
The following table shows the pin details of the RJ45 connector:
RJ45 pins Signal Description
1 TX+ Transmission signal
2 TX- Transmission signal
3 RX+ Reception signal
4 Unused –
5 Unused –
6 RX- Reception signal
7 Unused –
8 Unused –
EIO0000001177 03/2019 59
Page 60

Ethernet Communication
Addressing Modes
Address Assignment
Assign the IP address to Harmony Hub using one of the following methods:
By a DHCP (dynamic host control protocol) server.
By a BOOTP (bootstrap protocol) server (BOOTP zone).
Using the IP address stored in the flash memory.
NOTE: If Harmony Hub detects a duplicate address, it does not start until a unique address is
assigned to the transmitter.
Address Assignment by a DHCP Server
The IP address assigned by a DHCP server is stored in a table of DHCP server.
Step Action Comments
1 Select DHCP mode from the Ethernet
menu using the jog dial on
Harmony Hub.
2 Select the DHCP value between 0–159
using the jog dial.
3 Wait 10 s. When the display stops flashing after
For further information, refer to the IP
setting menu
This action defines the device name.
10 s, Harmony Hub triggers a request
for an IP address.
(see page 124)
.
Address Assignment by BOOTP Server
The BOOTP server contains a MAC address table for the device connected to network with its IP
address. The following steps explain how to assign the address to Harmony Hub from the BOOTP
server:
Step Action Comments
1 Select the BOOTP mode from the
Ethernet menu using the jog dial on
Harmony Hub.
2 Wait 10 s. When the display stops flashing after
60
For further information, refer to the IP
setting menu
10 s, Harmony Hub triggers a request
for an IP address.
(see page 124)
.
EIO0000001177 03/2019
Page 61

Assignment of Stored IP Addresses
Harmony Hub uses the IP address stored in its flash memory. The following steps explain how to
assign the address to Harmony Hub from the flash memory:
Step Action Comments
1 Select the Static IP mode from the
Ethernet menu using the jog dial on
Harmony Hub.
2 Wait 10 s. When the display stops flashing after
Modbus Unit ID Parameter
Use the PLC with the following UIDs to access the device communication details:
Use UID 247 to access the Ethernet diagnostics information ( ZBRCETH communication
module server).
Use UID 248 or 255 to access the Modbus TCP registers, such as input registers and holding
time (ZBRN1 Harmony Hub server).
Ethernet Communication
Harmony Hub uses the IP address
stored in the flash memory. For further
information, refer to the IP setting
menu
(see page 124)
10 s, Harmony Hub triggers a request
for an IP address.
.
EIO0000001177 03/2019 61
Page 62

Ethernet Communication
Communication and Status Indicator
Status LED on The ZBRN1 Harmony Hub
1 Power LED
2 Communication LED
3 Radio signal strength LED
The yellow Ethernet communication LED shows the following status:
On/flashing: Data is being exchanged (depends on the quantity of information).
Off: No data is being exchanged.
62
EIO0000001177 03/2019
Page 63

Ethernet Communication
Status LED on The ZBRCETH Communication Module
The following table shows the Ethernet Modbus TCP LED status:
Item Name LED State Description Module State
1 Link/Activity port 1 Solid green Ethernet link is present at
100 Mbit/s.
Flashing green Ethernet link is present with
Ethernet traffic at
100 Mbit/s.
Solid yellow Ethernet link is present at
10 Mbit/s.
Flashing yellow Ethernet link is present with
Ethernet traffic at 10 Mbit/s.
2 Module status Green On. The module is turned on.
Off. The module is off.
3 Network status Red Harmony Hub is being
turned on.
Solid green The network is operating
normally.
4 flashes A duplicate IP condition
exists.
5 flashes The module is attempting to
get an IP configuration from
BootP server.
6 flashes The operation is normal with
default IP addressing
settings.
4 Link/Activity port 2 Solid green Ethernet link is present at
100 Mbit/s.
Flashing green Ethernet link is present with
Ethernet traffic at
100 Mbit/s.
Solid yellow Ethernet link is present at
10 Mbit/s.
Flashing yellow Ethernet link is present with
Ethernet traffic at 10 Mbit/s.
The module is detecting an
Ethernet link.
The module is detecting Ethernet
traffic.
The module is detecting an
Ethernet link.
The module is detecting Ethernet
traffic.
The module is being turned on.
The module is operating normally.
The module is offline.
The module is sending
BOOTP/DHCP requests to a
BootP server and awaiting a reply.
The BootP request timed out. The
module applies the default IP
address (85.16.x.y).
The module is detecting an
Ethernet link.
The module is detecting Ethernet
traffic.
The module is detecting an
Ethernet link.
The module is detecting Ethernet
traffic.
EIO0000001177 03/2019 63
Page 64

Ethernet Communication
Modbus TCP Settings and Supported Functions
For further information on Modbus TCP settings, refer to the Modbus Settings and Supported
Functions
(seepage50)
.
64
EIO0000001177 03/2019
Page 65

Ethernet Cable
Ethernet Cable for ZBRN1 Harmony Hub
The following figure shows the Ethernet cable used to connect to the terminal equipment:
Item Description Reference Length
1 Ethernet cable (2 x RJ45
connectors, one at each
end)
Ethernet Communication
490NTW00002U 2 m (6.6 ft)
490NTW00005U 5 m (16.4 ft)
490NTW00012U 12 m (39.4 ft)
EIO0000001177 03/2019 65
Page 66

Ethernet Communication
66
EIO0000001177 03/2019
Page 67

Harmony XB5R
Modbus Registers
EIO0000001177 03/2019
Modbus Registers
Chapter 5
Modbus Registers
Introduction
All the following addresses are indicated according to the IEC %MW standard format.
For access to Modbus registers, add 1 to each address.
UNINTENDED EQUIPMENT OPERATION
Do not write or read the register addresses which are not mentioned in this document.
Failure to follow these instructions can result in death, serious injury, or equipment damage.
All the registers used are 16 bits.
What Is in This Chapter?
This chapter contains the following sections:
Section Topic Page
5.1 Harmony Hub Input Channels Registers 68
5.2 Diagnostic Registers 76
5.3 Configuration Registers 91
WARNING
EIO0000001177 03/2019 67
Page 68

Modbus Registers
Harmony Hub Input Ch annels Registers
Section 5.1
Harmony Hub Input Channels Registers
What Is in This Section?
This section contains the following topics:
Input Channels Registers 69
Type 1 Input Channels Registers 71
Type 5 Input Channels Registers 72
Type 6 Input Channels Registers 73
Topic Page
68
EIO0000001177 03/2019
Page 69

Input Channels Registers
Input Channels
The following table presents the input channel registers:
Modbus Registers
Register
Address
Name Access
(1)
Type
Input
Channel
Channel
Status
0000 Input register 1 R 0...15 0: Off
1: On
0001 Input register 2 R 16...31 0: Off
1: On
0002 Input register 3 R 32...47 0: Off
1: On
0003 Input register 4 R 48...59 0: Off
1: On
0004
Reserved - - - …
0009
0010
…
Input Channel 0
data
R 0 - Stores the data of input channel 0.
0042
0043
…
Input Channel
1…58 data
R 1...58 - Stores the data of input channels from 1
1956
1957
…
1989
1990
Input
Channel 59
data
Reserved - - - -
R 59 - Stores the data of input channel 59.
…
1999
1 R: Read only.
2 Only for pushbuttons and limit switches.
Description
Stores the status (0 or 1) of input
channels from 0 to 15
(2)
.
Stores the status (0 or 1) of input
channels from 16 to 31
(2)
.
Stores the status (0 or 1) of input
channels from 32 to 47
(2)
.
Stores the status (0 or 1) of input
channels from 48 to 59
(2)
.
to 58.
EIO0000001177 03/2019 69
Page 70

Modbus Registers
Input Registers
Input registers 1…4 are reserved to type 1 and some type 6 transmitters. Each bit represents an
input of Harmony Hub. When a message is received, the status bit is updated to 1 for the duration
of the holding time.
Input register 1:
A 16-bit register stores the status of channels from 0...15. One bit is assigned for one input channel
to store the input status as 0 or 1.
Input register 2:
A 16-bit register stores the status of channels from 16...31. One bit is assigned for one input
channel to store the input status as 0 or 1.
Input register 3:
A 16-bit register stores the status of channels from 32... 47. One bit is assigned for one input
channel to store the input status as 0 or 1.
Input register 4:
A 16-bit register to store the status of channels from 48...59. One bit is assigned for one input
channel to store the input status as 0 or 1.
NOTE: Out of the 16 bits of the register, 12 bits are used to store the status of the input channel.
Input Channel Data Registers
The input channel data table (0010…1989) is composed with 60 sub-sections for the 60 inputs.
Each sub-section is 33 registers long.
For the input channel N (0…59):
First input data register address (N) = 33 * N + 10
The content of each input channel data registers depends on the transmitter type:
Type 1 input channel registers for push buttons and limit switches.
Type 5 input channel registers for thermal monitoring sensors.
Type 6 input channel registers for generic ZigBee and power tag sensors.
(seepage71)
(see page 72)
(see page 73)
70
EIO0000001177 03/2019
Page 71

Type 1 Input Channels Registers
Type 1 Input Channels Data
The following table presents the type 1 transmitter data mapping:
Modbus Registers
Offset
Register
Name Access
Type
Channel Status Description
+0 Device type R Bit 0…Bit 7: Type of transmitter
0: none
1…6: type number
Bit 8…Bit 15: Reserved
+1 Time out
RSSI
R Bit 0…Bit 7: Timeout flag:
True: FF H (time out expired)
False: 00 H
Bit 8…Bit 15: RSSI:
(-127…127 dBm)
-128: Invalid value
+2 Time stamp R Two registers to store the double word
+3
value.
+2: Stores the most significant word.
+3: Stores the least significant word.
FFFF FFFF H: Invalid value
00FF 0000 H: Rollback value
+4…32 Reserved - - -
R: Read only.
Stores the type of transmitter
associated to the input channel.
Stores the time-out flag and the
radio reception power value.
Stores the details of the time stamp
(μs/320).
EIO0000001177 03/2019 71
Page 72

Modbus Registers
Type 5 Input Channels Registers
Type 5 Input Channels Data
The following table presents the type 5 transmitter data:
Offset
Register
Name Access
Type
Channel Status Description
+0 Device type R Bit 0…Bit 7: Type of transmitter
0: none
1…6: type number
Bit 8…Bit 15: Reserved
+1 Time out
RSSI
R Bit 0…Bit 7: Timeout flag:
True: FF H (time out expired)
False: 00 H
Bit 8…Bit 15: RSSI:
(-127…127 dBm)
-128: Invalid value
+2 Time stamp R Two registers to store the double word
+3
value.
+2: Stores the most significant word.
+3: Stores the least significant word.
FFFF FFFF H: Invalid value
00FF 0000 H: Rollback value
+4 Battery
voltage
R Bit 0…Bit 7: Battery voltage
FF H: Invalid value
Bit 8…Bit 15: Reserved
+5 Reserved - - -
+6 Temperature R
8000 H: Invalid value Stores the measured temperature
+7…32 Reserved - - -
R: Read only.
Stores the type of transmitter
associated to the input channel.
Stores the time-out flag and the
radio reception power value.
Stores the details of the time stamp
(μs/320).
Stores the internal battery voltage
(0.01 mV).
(0.01 °C).
72
EIO0000001177 03/2019
Page 73

Type 6 Input Channels Registers
Type 6 Input Channels Data
The following table presents the type 6 generic I/O transmitter data:
Modbus Registers
Offset
Register
+0 Device type R Bit 0…Bit 7: Type of transmitter
Name Access
Type
Channel Status Description
Stores the type of transmitter
0: none
1…6: type number
associated to the input channel.
Bit 8…Bit 15: Reserved
+1 Time out
RSSI
R Bit 0…Bit 7: Timeout flag:
True: FF H (time out expired)
False: 00 H
Stores the time-out flag and the
radio reception power value.
Bit 8…Bit 15: RSSI:
(-127…127 dBm)
-128: Invalid value
+2 Time stamp R Two registers to store the double word
+3
value.
+2: Stores the most significant word.
Stores the details of the time stamp
(μs/320).
+3: Stores the least significant word.
FFFF FFFF H: Invalid value
00FF 0000 H: Rollback value
+4 Battery
voltage
R Bit 0…Bit 7: Battery voltage
FF H: Invalid value
Stores the internal battery voltage
(0.01 mV).
Bit 8…Bit 15: Reserved
+5 Internal
Temperature
+6 Temperature R
R
-200…200 °C
8000 H: Invalid value
8000 H: Invalid value Stores the measured temperature
Stores the internal temperature
(°C).
(0.01 °C).
+7 Energy R Four registers to store the energy value.
+8
+9
+7: Stores the most significant word.
+10: Stores the least significant word.
FFFF FFFF FFFF FFFF H: Invalid value
Stores the energy (without unit).
+10
+11 Unit R - Stores the unit of measure.
+12 Power A R
8000 H: Invalid value Stores the measured power
phase A (W).
+13 Power B R
8000 H: Invalid value Stores the measured power
phase B (W).
R: Read only.
EIO0000001177 03/2019 73
Page 74

Modbus Registers
Offset
Register
Name Access
Type
Channel Status Description
+14 Power C R 8000 H: Invalid value Stores the measured power
phase C (W).
+15 Current A R
FFFF H: Invalid value Stores the measured current
phase A (A *100).
+16 Current B R
FFFF H: Invalid value Stores the measured current
phase B (A *100).
+17 Current C R
FFFF H: Invalid value Stores the measured current
phase C (A *100).
+18 Voltage A R FFFF H: Invalid value Stores the measured voltage phase
A (V *100).
+19 Voltage B R
FFFF H: Invalid value Stores the measured voltage
phase B (V *100).
+20 Voltage C R
FFFF H: Invalid value Stores the measured voltage
phase C (V *100).
+21 CO2 R Two registers to store the double word
+22
value.
+21: Stores the most significant word.
Stores the measured CO2 level
(0.01 %).
+22: Stores the least significant word.
7FC0 0000 H: Invalid value
+23 CO R Two registers to store the double word
+24
value.
+23: Stores the most significant word.
Stores the measured CO level
(0.01 %).
+24: Stores the least significant word.
7FC0 0000 H: Invalid value
+25 Illuminance R
FFFF H: Invalid value Stores the measured illuminance
(10,000*Log(Lux)+1).
+26 Pressure R
FFFF H: Invalid value Stores the measured pressure
(10*kPa).
+27 Flow R
+28 Humidity R
+29 Occupancy R Bit 0…Bit 7: Occupancy
FFFF H: Invalid value Stores the measured flow
0…10,000
FFFF H: Invalid value
3
(100*m
/h).
Stores the measured humidity
(100*%).
Stores the status occupancy
FF H: Invalid value
(without unit).
Bit 8…Bit 15: Reserved
+30 State On/Off R Bit 0…Bit 7: State On/Off
FF H: Invalid value
Stores the state On/Off (without
unit).
Bit 8…Bit 15: Reserved
R: Read only.
74
EIO0000001177 03/2019
Page 75

Modbus Registers
Offset
Register
Name Access
Type
Channel Status Description
+31 Level state R Bit 0…Bit 7: Level state
FF H: Invalid value
Bit 8…Bit 15: Reserved
+32 Door lock
state
R Bit 0…Bit 7: Door lock state
FF H: Invalid value
Bit 8…Bit 15: Reserved
R: Read only.
Stores the level state (without unit).
Stores the door lock state (without
unit).
EIO0000001177 03/2019 75
Page 76

Modbus Registers
Diagnostic Registers
Section 5.2
Diagnostic Registers
What Is in This Section?
This section contains the following topics:
Module Diagnostics 77
Communication Diagnostics 86
Error Codes 88
Topic Page
76
EIO0000001177 03/2019
Page 77

Module Diagnostics
Product Information
The following table presents the product information registers:
Modbus Registers
Register
Address
4000 Device name R 1: ZBRN1
4001 Firmware version R Example for 0121: V01.21 Stores the firmware version.
4002 Communication
4003 Configuration R Bit 0: The device is being configured
4004 Detected error R For more details, refer to Harmony Hub
4005 Communication
4006 Configuration file
4007 Client ID R Bit 0…Bit 3
R: Read only.
RW: Read and write.
Name Access
Type
R Bit 0: ZBRN2 (Modbus serial line)
protocol
R Bit 0: ZBRN2 (Modbus serial line)
status
R Example for 0121: V01.21
version
Status Description
Stores the device name.
2: ZBRN2
Stores the communication
Bit 1: ZBRN1 (Ethernet)
through the user interface.
Bit 1: The device is being configured
through the SD card interface.
Bit 2: The device is being configured
through the Modbus interface.
error codes
Bit 1: ZBRN1 (Ethernet)
FFFF H: No file used
0: None
1…15: Client ID
(seepage88)
.
protocol used by
Harmony Hub.
Stores the configuration
status of the device.
Stores the code of the
detected error.
Stores the communication
protocol used by
Harmony Hub.
Stores the configuration file
version.
Stores the client ID.
EIO0000001177 03/2019 77
Page 78

Modbus Registers
Register
Address
Name Access
Type
Status Description
4008 Action status R Bit 0…Bit 7: Action status
0: Action successful
1: Action not successful
2: Invalid parameter
Bit 8…Bit 15: Action code
0: None
1: Off-line association
2: On-line association
3: Remove device
4: Clear all devices
5: Start teach
5: Stop teach
15: Start remote configuration
16: Stop remote configuration
17: Get device
22: Update the radio connection
24: Start tech all
240: Jump test
4009 Input R Bit 0…Bit 7: Current input for action Get
Device
R: Read only.
RW: Read and write.
Stores the Modbus action and
the related status.
-
78
EIO0000001177 03/2019
Page 79

Binding List Information
The following table presents the binding list information registers:
Modbus Registers
Register
Address
4010 Number of max
Name Access
Type
R - Stores the maximal quantity
binding
Status Description
of sensors on the binding list.
4011 Bound quantity R - Stores the number of inputs
occupied (with associated offline and associated on-line
sensors)
4012 Paired quantity R - Stores the number of inputs
associated on-line
4013 No paired
quantity
4014 Number of max
Device types
4015 Device type
enable
R - Stores the number of inputs
associated off-line
R - Stores the number of
transmitter types supported
R Bit field
Bit 0: Type 0 (free)
Bit x: Type x
Stores the flags to show the
supported transmitter types.
R: Read only.
RW: Read and write.
EIO0000001177 03/2019 79
Page 80

Modbus Registers
Radio Communication Information
The following table presents the radio communication information registers:
Register
Address
4016 Radio
4017 R Bit 0…Bit 7: zz
4018 Radio
4019 R
4020 Radio
4021 R
4022 Radio
4023 R
4024 Radio channel R 11...26: The radio channel with frequency
4025 Emitted radio
4026 Radio
R: Read only.
RW: Read and write.
Name Access
Type
R Bit 0…Bit 7: xx Stores the ZigBee stack
connection
firmware version
R Two registers to store the double word
connection Packets received
counter
R Two registers to store the double word
connection - Bad
packets received
counter
R Two registers to store the double word
connection Packets sent
counter
R -22…4: Signal strength in dBm
signal strength
R 0: OFF
connection state
Status Description
Bit 8…Bit 15: yy
value.
4018: Stores the most significant word.
4019: Stores the least significant word.
The value is incremented each time
Harmony Hub receives a packet from an
associated transmitter.
value.
4020: Stores the most significant word.
4021: Stores the least significant word.
The value is incremented each time
Harmony Hub receives a bad packet from
an associated transmitter.
value.
4022: Stores the most significant word.
4023: Stores the least significant word.
The value is incremented each time
Harmony Hub sends a packet to an
associated transmitter.
2.405 GHz (channel 11...26 IEEE
802.15.4).
-127: Starting or OFF
-128: Error detected.
20: HOLD
21: INIT
22: SCAN
23: RUN
24: Commissioning
FE H: Starting
FF H: Error detected.
version: Vxx.yy.zz
Stores the number of packets
received by radio connection.
Stores the number of bad
packets received by radio
connection.
Stores the number of packets
sent by radio connection.
Stores the details of the radio
channel.
Stores the details of the signal
strength for emission.
Stores the details of the radio
connection state.
80
EIO0000001177 03/2019
Page 81

Modbus Registers
Register
Address
4027 Radio device
Name Access
Type
R 0: None (off)
type
Status Description
1: Green power
2: ZigBee green power concentrator
3: ZigBee green power router
4: Controller under upgrade
24: Commissioning
FE H: Starting
FF H: Error detected.
4028 Radio Pan ID R 0001 H…FFFE H
0000 H: Off, starting or error detected
4029 Radio short
address
R 0000 H…FFFC H
FFFD H: Off,or error detected
FFFE H: Starting
4030 Radio IEEE
4031
address
4032
R Four registers to store the IEEE address.
4030: Stores the most significant word.
4033: Stores the least significant word.
4033
4034 Radio
connection -
R The value is incremented each time
Harmony Hub radio connection restarts.
Boot counter
4035
Reserved - - …
4039
R: Read only.
RW: Read and write.
Stores the current radio
device type.
Stores the radio Pan ID.
Stores the radio short
address.
Stores the radio IEEE
address.
Stores the number of radio
connection restarts.
EIO0000001177 03/2019 81
Page 82

Modbus Registers
Modbus Serial Line Communication Information
The following table presents the Modbus serial line communication information registers:
Register
Address
4040 Modbus boot
4041
…
4049
4050 Modbus error
4051
…
4089
4090 Modbus system
4091
4092
4093
4094
…
4099
R: Read only.
RW: Read and write.
Name Access
counter
Reserved - - -
counter
Reserved - - -
clock
Reserved - - -
Status Description
Type
R The value is incremented each time
Harmony Hub Modbus controller restarts.
R The value is incremented each time
Harmony Hub Modbus controller detects an
error.
R Four registers to store the Modbus system
clock.
4090: Stores the most significant word.
4093: Stores the least significant word.
Stores the number of Modbus
controller restarts.
Stores the number of Modbus
detected errors.
Stores the Modbus system
clock (ms).
82
EIO0000001177 03/2019
Page 83

Input Channel Transmitter Information
The following table presents the input channel 0 transmitter information registers:
Modbus Registers
Register
Address
4100 Green power -
4101
4102 Green power -
4103
4104 Green power -
4105 R
4106 Green power -
4107 R
4108 Green power -
4109 R
4110 Green power -
R: Read only.
RW: Read and write.
Name Access
Input 0
Frame counter
Input 0
Time stamp
Input 0
Packets received
counter
Input 0
Bad packets
received counter
Input 0
Lost packets
received counter
Input 0
Radio link
strength
Status Description
Type
R Two registers to store the double word
value.
4100: Stores the most significant word.
4101: Stores the least significant word.
The value is incremented each time
Harmony Hub input 0 receives a frame from
an associated transmitter.
R Two registers to store the double word
value.
4102: Stores the most significant word.
4103: Stores the least significant word.
The value is updated each time
Harmony Hub input 0 receives a frame from
an associated transmitter.
R Two registers to store the double word
value.
4104: Stores the most significant word.
4105: Stores the least significant word.
The value is incremented each time
Harmony Hub receives a packet from an
associated transmitter.
R Two registers to store the double word
value.
4106: Stores the most significant word.
4107: Stores the least significant word.
The value is incremented each time
Harmony Hub receives a bad packet from
an associated transmitter.
R Two registers to store the double word
value.
4108: Stores the most significant word.
4109: Stores the least significant word.
The value is incremented each time
Harmony Hub detects a lost packet from an
associated transmitter.
R Bit 0…Bit 7: LQI (0…255)
Bit 8…Bit 15: Radio reception power (128…127 dBm)
Stores the number of the
Green power - input 0 frame
counter.
Stores the details of the
Green power - input 0 time
stamp (μs/320).
Stores the number of the
Green power - input 0 packets
received since last restart.
Stores the number of the
Green power - input 0 bad
packets received since last
restart.
Stores the number of the
Green power - input 0 lost
packets since last restart.
Stores the radio signal
strength of the Green power
input 0
EIO0000001177 03/2019 83
Page 84

Modbus Registers
Register
Name Access
Address
4111 Green power -
Input 0
Teach status
Status Description
Type
R Bit 0…Bit 7: Detected error code
00: No error detected
01: Commissioning unsupported
02: Commissioning Error Transmitter
Type
03: Commissioning Error Manufacturer
ID
04: Commissioning Error Manufacturer
Product ID
05: Commissioning Error Security
06: Commissioning Error Transmitter
Capacity
07: Commissioning Error Cluster List
08: Data Command ID filter
09: No data
10: Data unsupported Command ID
11: Data Error parse Length
Manufacturer ID
12: Data Error parse Length Cluster ID
13: Data Error parse Length Attribute Id
14: Data Error parse Length data
15: Data unsupported data Type
17: Data Mismatch data Type
18: Data Parse Error
16: Data Error Search Attribute
19: Data Error
20: Process E3 invalid unit attribute
21: Process E3 invalid value attribute
22: Process E3 Error
23: process ZCL Invalid Metering Value
24: process ZCL Invalid Electrical
measurement Current value
25: process ZCL Invalid Electrical
measurement Voltage value
26: process ZCL Invalid Electrical
measurement Power value
27: Process Error
Stores the teach status for the
Green power input 0.
R: Read only.
RW: Read and write.
84
Bit 8…Bit 15: Teach status)
1: Sensor is selected for a teach action
EIO0000001177 03/2019
Page 85

Modbus Registers
Register
Address
4112
Name Access
Status Description
Type
- - - Reserved
…
4113
4114 Green power -
Input 0
R Bit 0…Bit 7: Type 2 sensor timeout
Bit 8…Bit 15: Type 2 clamp type
Type 2 sensor
details
R: Read only.
RW: Read and write.
NOTE: For the input channel N (0…59): Register address (N) = 14 * N + 4100
Stores the clamp type and
timeout.
EIO0000001177 03/2019 85
Page 86

Modbus Registers
Communication Diagnostics
Modbus Serial Line Communication Diagnostics
The following table presents the Modbus serial line communication diagnostics registers:
Register
Address
5000 Actual baud rate R 1: 1200 bps
5001 Actual frame
5002 Number of
5003 R
5004 Number of bad
5005 R
5006 Number of
5007 R
5008 Number of bad
5009 R
5010
…
5999
R: Read only.
Name Access
Type
R 1: The frame format sent is 8 data bits, even
setting
R Two registers to store the double word
packages
received
R Two registers to store the double word
packages
received
R Two registers to store the double word
packages sent
R Two registers to store the double word
packages sent
- - - Reserved
Status Description
2: 2400 bps
3: 4800 bps
4: 9600 bps
5: 19,200 bps
6: 38,400 bps
7: 115,200 bps
parity, and 1 stop bit.
2: The frame format sent is 8 data bits, odd
parity, and 1 stop bit.
3: The frame format sent is 8 data bits, no
parity, and 2 stop bits.
value.
5002: Stores the most significant word.
5003: Stores the least significant word.
value.
5004: Stores the most significant word.
5005: Stores the least significant word.
value.
5006: Stores the most significant word.
5007: Stores the least significant word.
value.
5008: Stores the most significant word.
5009: Stores the least significant word.
Stores the baud rate at
which the data is sent.
Stores the data frame
format received by
Harmony Hub.
Stores the number of
packages received by
Harmony Hub.
Stores the number of bad
packages received by
Harmony Hub.
Stores the number of
packages sent by the
transmitters.
Stores the number of bad
packages sent by the
transmitters.
86
EIO0000001177 03/2019
Page 87

Modbus TCP Communication Diagnostics
The following table presents the Modbus TCP communication diagnostics registers:
Modbus Registers
Register
Address
5000 IP address R Two registers to store the four bytes value.
5001
5002 IP mask R Two registers to store the four bytes value.
5003
5004 IP gateway R Two registers to store the four bytes value.
5005
5006 MAC address R Three registers to store the MAC address. Stores the MAC address
5007
5008
5009
…
5018
5019 Number of
5020 R
5021 Number of bad
5022 R
5023 Number of
5024 R
5025 Number of bad
5026 R
5027
…
5999
R: Read only.
Name Access
Type
- - - Reserved
R Two registers to store the double word
packages
received
R Two registers to store the double word
packages
received
R Two registers to store the double word
packages sent
R Two registers to store the double word
packages sent
- - - Reserved
Status Description
Stores the IP address used.
0.0.0.0 … 255.255.255.255
Stores the IP mask used.
0.0.0.0 … 255.255.255.255
0.0.0.0 … 255.255.255.255
value.
5019: Stores the most significant word.
5020: Stores the least significant word.
value.
5021: Stores the most significant word.
5022: Stores the least significant word.
value.
5023: Stores the most significant word.
5024: Stores the least significant word.
value.
5025: Stores the most significant word.
5026: Stores the least significant word.
Stores the IP gateway used.
used.
Stores the number of
packages received by
Harmony Hub.
Stores the number of bad
packages received by
Harmony Hub.
Stores the number of
packages sent by
Harmony Hub.
Stores the number of bad
packages sent by the
transmitters.
EIO0000001177 03/2019 87
Page 88

Modbus Registers
Error Codes
Harmony Hub Error Codes
The following table presents Harmony Hub error codes:
Error Code Detected Error Range Description
00 General No error detected
01 Target not supported
02 Invalid version of Industrial configuration
03 Industrial configuration not found
04 Invalid Industrial configuration
05 Assert Error
10 SD memory card
11 The SD card is write protected
12 Not enough space available in the SD card
13 Invalid parameter
14 Invalid network configuration file
15 Invalid device configuration file
16 More than one network configuration file in the net folder
17 More than one device configuration file in the device folder
18 No network configuration file in the net folder
19 No device configuration file in the device folder
20 Green Power COM_FCS_ERROR
21 Invalid Status Code in response
22 Process Timeout
23 Request Invalid
24 Request Execution Timeout
25 Invalid parameter
26 Decode Message Error
27 Module Invalid Capacity
28 Incompatible Version
29 Start/Stop Process
2A Error during start Process
2B Error during run Process
2C Error during upgrade Process
2D Undefined message
For more details on
the SD card files, refer
to File management
and diagnostics
(see page 163)
The SD card cannot be accessed
.
88
EIO0000001177 03/2019
Page 89

Error Code Detected Error Range Description
30 Ethernet Duplicate IP address
31 Invalid IP address
32 Communication module detected error
33 Communication module not supported
34 Communication module not detected
40 Data Error while processing device data
41 Error while processing device commissioning
50 Watchdog Harmony Hub Reset
51 Other Reset
60 Backup Invalid configuration slot 1
61 Invalid configuration slot 2
62 Invalid configuration slot 1 and slot 2
63 Initialization configuration slot 1
64 Initialization configuration slot 2
65 Store configuration slot 1
66 Store configuration slot 2
67 Store 2 configuration slot 1
68 Store 2 configuration slot 2
70 Modbus Modbus Invalid configuration
80 Action Trace Action Process
Modbus Registers
EIO0000001177 03/2019 89
Page 90

Modbus Registers
Transmitter Error Codes
The following table presents the transmitter error codes:
Error Code Detected Error Range Description
00 General No error detected
10 Commissioning Commissioning unsupported
11 Commissioning Error Device Type
12 Commissioning Error Manufacturer ID
13 Commissioning Error Manufacturer Product ID
14 Commissioning Error Security
15 Commissioning Error Device Capacity
16 Commissioning Error Cluster List
20 Data Data Command ID filter
21 No data
22 Data unsupported Command ID
23 Data Error parse Length Manufacturer ID
24 Data Error parse Length Cluster ID
25 Data Error parse Length Attribute Id
26 Data Error parse Length data,
27 Data unsupported data Type,
28 Data Error Search Attribute
29 Data Mismatch data Type
2A Data Parse Error
2B Data Error
30…37 Process E3 Reserved
40 Process ZCL Process ZCL Invalid Metering Value 1
41 Process ZCL Invalid Metering Value 2
42 Process ZCL Invalid Metering Value 3
43 Process ZCL Invalid Metering Value 4
44 Process ZCL Invalid Electrical measurement Current value 1
45 Process ZCL Invalid Electrical measurement Current value 2
46 Process ZCL Invalid Electrical measurement Voltage value 1
47 Process ZCL Invalid Electrical measurement Voltage value 2
48 Process ZCL Invalid Electrical measurement Power value 1
49 Process ZCL Invalid Electrical measurement Power value 2
50 Process Process Error
90
EIO0000001177 03/2019
Page 91

Configuration Registers
Section 5.3
Configuration Registers
What Is in This Section?
This section contains the following topics:
Module Configuration 92
Communication Configuration 97
Modbus Registers
Topic Page
EIO0000001177 03/2019 91
Page 92

Modbus Registers
Module Configuration
Channel Configuration
The following table presents the channel configuration for all inputs registers:
Register
Address
6000 Radio
6001 Radio
6002 Radio
6003 Emitted
6004
…
6009
6010 Table
6011
…
6019
6020 Holding time RW – 0: 100 ms
6021
…
6099
RW: Read and write.
Name Access
Type
RW – 0: None (off)
communicati
on mode
RW – 11...26: The radio channel
channel
RW – 0001 H…FFFF H Stores the radio Pan ID.
Pan ID
RW – -22…4: Signal strength in
radio signal
strength
Reserved – – – –
RW – 0: One UID per Harmony Hub
selection
Reserved – – – –
Reserved – – – –
Input
Channel
Channel Status Description
1: Green power
2: ZigBee green power
concentrator
3: ZigBee green power router
with frequency 2.405 GHz
(channel 11...26 IEEE
802.15.4).
dBm
1…4: One UID per sensor
1: 200 ms
2: 300 ms
3: 400 ms
4: 500 ms
5: 1 s
Stores the radio communication
mode.
Stores the radio channel.
Stores the details of the signal
strength for emission.
Stores the table selection.
Stores the holding time for all
the input channels.
92
Holding time:
A 16-bit register stores the holding time of the input channels.
EIO0000001177 03/2019
Page 93

Teaching List
The following table presents the teaching list registers:
Modbus Registers
Register
Address
6100
…
Name Access
Type
Input
Channel
Channel Status Description
Teaching list RW 0…59 Bit 0 to 2:
0: The channel is
6159
1…6: The type 1…6
Bits3 to 13 are not used.
Bit 14: Pairing status
0: Sensor associated
1: Sensor associated
Bit 15: Address type length
0: Address Type Source Id
1: Address Type IEEE on
6160
Reserved – – – –
…
6199
RW: Read and write.
Teaching list:
A 16-bit register stores the details of the transmitters used.
Stores the details of the
transmitter used.
disabled.
transmitter is used.
online.
offline.
on 4 bytes.
8 bytes.
EIO0000001177 03/2019 93
Page 94

Modbus Registers
Input Parameters 1…2
The following table presents the input parameters registers 1…2:
Register
Address
6200
…
6259
6260
…
6299
6300
…
6359
6360
…
6399
RW: Read and write.
Name Access
Input
parameter 1
list
Reserved – – – –
Input
parameter 2
list
Reserved – – – –
Input
Type
RW 0…59 Holding time. Stores the input parameter 1 list.
RW 0…59 – Stores the input parameter 2 list.
Channel
Channel Status Description
94
EIO0000001177 03/2019
Page 95

MAC Addresses
The following table presents the MAC addresses registers:
Modbus Registers
Register
Address
6400
…
6519
6520
…
6639
6640
…
6699
RW: Read and write.
Name Access
Transmitter
ID/MAC
addresses
Transmitter
ID/MAC
extended
addresses
Reserved – – – –
Input
Type
RW 0…59 srcID4: First byte of the MAC
RW 0…59 srcID0: First byte of the MAC
Channel
Channel Status Description
address.
srcID5: Second byte of the
MAC address.
srcID6: Third byte of the MAC
address.
srcID7: Fourth byte of the
MAC address.
address.
srcID1: Second byte of the
MAC address.
srcID2: Third byte of the MAC
address.
srcID3: Fourth byte of the
MAC address.
Stores the MAC addresses of the
transmitters.
Two registers are used to store MAC
address of one transmitter.
Example:
Transmitter ID (written on the
transmitter label) = 030079B1.
Registers 6410–6411, input channel
5.
6410: stores 0300 (2 bytes of the
transmitter ID).
6411: stores 79B1 (2 bytes of the
transmitter ID).
Stores the MAC extended
addresses of the transmitters.
Two registers are used to store
extended MAC address of one
transmitter.
Example:
Transmitter ID (written on the
transmitter label) = 030079B1.
Registers 6530–5331, input channel
5.
6530: stores 0300 (2 bytes of the
transmitter ID).
6531: stores 79B1 (2 bytes of the
transmitter ID).
Transmitter/MAC addresses:
Two registers of 16 bits store the MAC address of the transmitters.
The first byte of the MAC address is stored in 8 bits of register 1.
The second byte of the MAC address is stored in 8 bits of register 1.
The third byte of the MAC address is stored in 8 bits of register 2.
The fourth byte of the MAC address is stored in 8 bits of register 2.
EIO0000001177 03/2019 95
Page 96

Modbus Registers
Input Parameters 3…5
The following table presents the input parameters registers 3…5:
Register
Address
6700
…
6759
6760
…
6799
6800
…
6859
6860
…
6899
6900
…
6959
6960
…
6999
RW: Read and write.
Name Access
Input
parameter 3
list
Reserved – – – –
Input
parameter 4
list
Reserved – – – –
Input
parameter 5
list
Reserved – – – –
Input
Type
RW 0…59 – Stores the input parameter 3 list.
RW 0…59 – Stores the input parameter 4 list.
RW 0…59 – Stores the input parameter 5 list.
Channel
Channel Status Description
96
EIO0000001177 03/2019
Page 97

Communication Configuration
Modbus Serial Line Communication Configuration
Modbus Registers
Register
Address
7000 Baud rate RW 1: 1200 bps
7001 Frame setting RW 0: Automatic detection
7002 Slave ID RW 1…247 Stores the Modbus slave ID
7003 Auto detection RW 0: Auto detection mode is disabled.
7004
…
7999
RW: Read and write.
Name Access
Type
- - - Reserved
Status Description
Stores the baud rate at
2: 2400 bps
3: 4800 bps
4: 9600 bps
5: 19,200 bps
6: 38,400 bps
7: 115,200 bps
2: The frame format sent is 8 data bits, odd
parity, and 1 stop bit.
3: The frame format sent is 8 data bits, no
parity, and 2 stop bits.
1: Auto detection mode is enabled.
which the data is sent.
Stores the data frame
format received by
Harmony Hub.
of Harmony Hub.
Stores the auto detection
mode.
EIO0000001177 03/2019 97
Page 98

Modbus Registers
Modbus TCP Communication Configuration
Register
Address
7000 IP address RW Two registers to store the four bytes value.
7001
7002 IP mask RW Two registers to store the four bytes value.
7003
7004 IP gateway RW Two registers to store the four bytes value.
7005
7006 IP mode RW 0: DHCP
Name Access
Type
Status Description
Stores the IP address.
0.0.0.0 … 255.255.255.255
Stores the IP mask.
0.0.0.0 … 255.255.255.255
Stores the IP gateway.
0.0.0.0 … 255.255.255.255
Stores the IP mode.
1: BOOTP
2: Stored.
3: Default.
7007 IP name RW 0…255 Stores the IP name.
7008
- - - Reserved
…
7999
RW: Read and write.
98
EIO0000001177 03/2019
Page 99

Harmony XB5R
Radio
EIO0000001177 03/2019
Radio
Chapter 6
Radio
Radio Receiver
Introduction
Harmony Hub is equipped with a radio receiver. It receives radio frames from wireless transmitters.
Radio Receiver Specifications
The following table shows the specifications of the radio receiver:
Characteristics Specifications
Frequency 2.405 GHz (channel 11 IEEE 802.15.4)
Maximum distance 100 m (328.08 ft) (when Harmony Hub is in free field)
For more details, refer to Maximum Distances
EIO0000001177 03/2019 99
(see page 25)
.
Page 100

Radio
ZBRA2 External Antenna
The ZBRA2 external antenna is an accessory, which you have to order separately. You can
connect it to Harmony Hub to improve the signal reception.
To install the ZBRA2 external antenna, open the protective plug and connect the antenna as shown
in the following figure:
1 Protective plug
2 Radio connector
100
NOTE: Only the ZBRA2 external antenna can be connected to the radio connector.
The following table shows the specifications of ZBRA2 antenna:
Parameters Specifications
Bandwidth 83...100 MHz
Frequency 2400...2483 MHz
Gain >3 dBi
Impedance 50 ohms
Polarization Vertical
RF connector Radial R 300113100
Cable length 2 m (6.56 ft)
EIO0000001177 03/2019
 Loading...
Loading...