SANYO LA4663 Datasheet
Monolithic Linear IC
Ordering number : ENN5905A
42800TN (OT)/70898RM (OT) No. 5905-1/10
SANYO Electric Co.,Ltd. Semiconductor Company
TOKYO OFFICE Tokyo Bldg., 1-10, 1 Chome, Ueno, Taito-ku, TOKYO, 110-8534 JAPAN
Two-Channel 16-W BTL General-Purpose
Audio Power Amplifier
LA4663
Overview
The LA4663 is a BTL 2-channel power amplifier IC that
was developed for ease of use in general audio
applications. In addition to providing improvements in a
wide range of electrical characteristics, the LA4663 aims
for improved listenability and an excellent costperformance ratio.
Applications
Radio/cassette players with built-in CD/MD players,
microcomponent stereo systems, active speakers,
electronic musical instruments, and other audio devices.
Features
• Wide operating supply voltage range (VCCop): 5.5 to
22 V (Certain conditions may apply.)
• High ripple rejection ratio: 60 dB (typical)
• Power: 16 W × 2 (VCC= 15 V/6Ω),
13 W × 2 (VCC= 12 V/4Ω), 6.5 W × 2 (VCC= 9 V/4Ω)
• Built-in signal muting circuit (AC muting) reduces the
number of external components and provides muting
with minimal switching noise.
• Startup circuit with a start time of 0.6 to 0.7 seconds.
The LA4663 provides distortion-free startup, since
output is only generated after the supply voltage reaches
the midpoint at power on.
(The startup time can be modified in end products by
using this circuit in conjunction with the muting circuit
described above.)
• Full complement of built-in protection circuits
(protection from shorting to ground, shorting to VCC,
load shorting, and overheating)
• High audio quality, minimal impulse noise
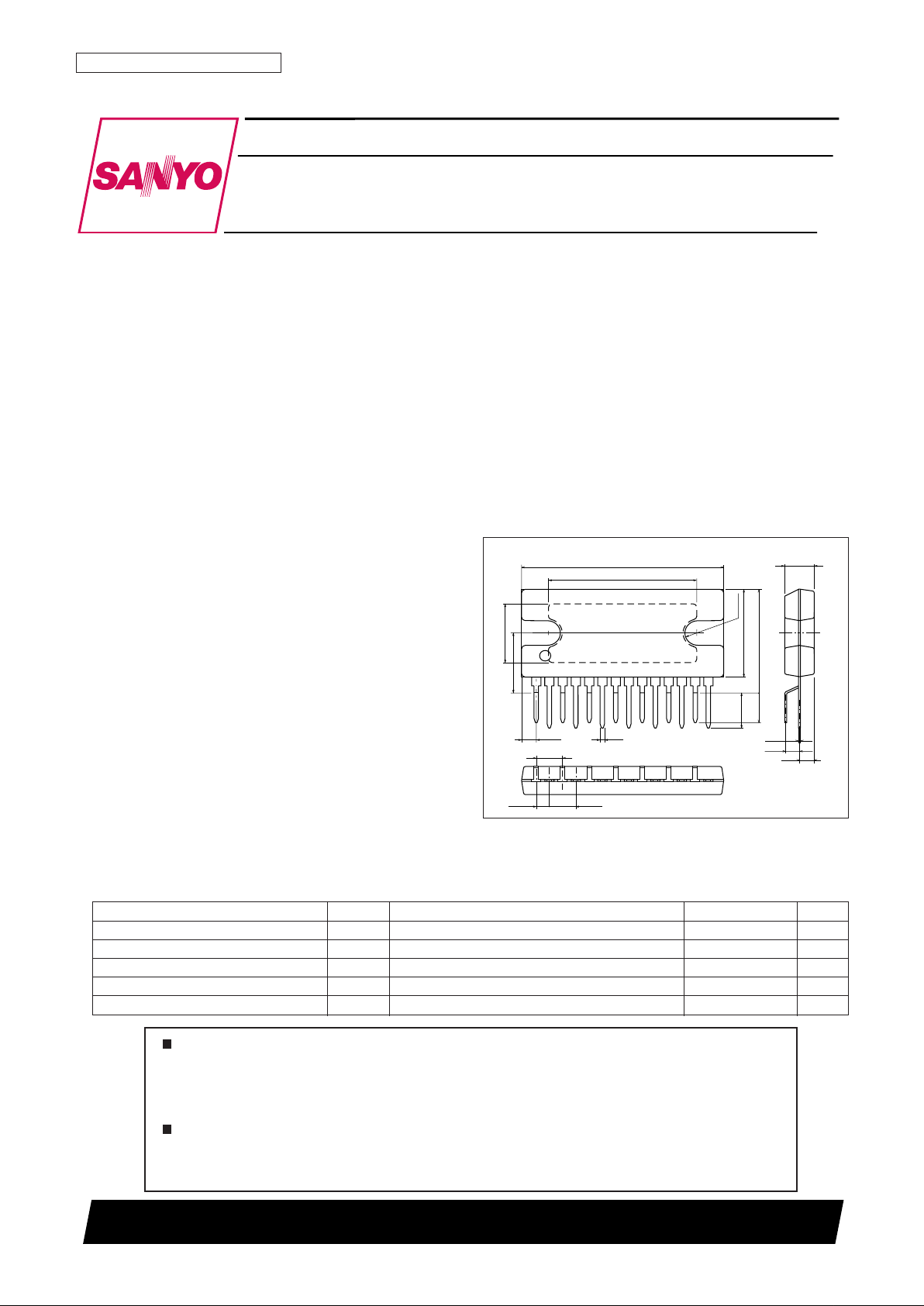
Package Dimensions
unit: mm
3113A-SIP14HZ
Specifications
Maximum Ratings at Ta = 25°C
Parameter Symbol Conditions Ratings Unit
Maximum supply voltage V
CC
max No signal 24 V
Maximum output current I
O
peak Per channel 3.5 A
Allowable power dissipation Pd max With an arbitrarily large heat sink 37.5 W
Operating temperature Topr –20 to +75 °C
Storage temperature Tstg –40 to +150 °C
27.0
20.0
R1.7
0.5
1.94
8.4
7.8
14.5max
14
1
0.4
11.8
5.2
4.6
1.6
2.2
4.0
1.78 3.56
3.56
[LA4663]
SANYO: SIP14HZ
Any and all SANYO products described or contained herein do not have specifications that can handle
applications that require extremely high levels of reliability, such as life-support systems, aircraft’s
control systems, or other applications whose failure can be reasonably expected to result in serious
physical and/or material damage. Consult with your SANYO representative nearest you before using
any SANYO products described or contained herein in such applications.
SANYO assumes no responsibility for equipment failures that result from using products at values that
exceed, even momentarily, rated values (such as maximum ratings, operating condition ranges, or other
parameters) listed in products specifications of any and all SANYO products described or contained
herein.
Operating Conditions *1at Ta = 25°C
Note *:1. When used with VCC, RL, and output level ranges such that Pd max for the heat sink actually used is not exceeded.
2. When both channels are operating with I
O
peak values that exceed 2 A per channel.
If the I
O
peak value does not exceed 2 A per channel, a range of 5.5 to 22 V is allowed for any allowable RL(for ranges where Pd max is not
exceeded).
Operating Characteristics at Ta = 25°C, VCC= 15 V, RL= 4 Ω, f = 1 kHz, Rg = 600 Ω
No. 5905-2/10
LA4663
Parameter Symbol Conditions
Ratings
Unit
min typ max
Quiescent current I
CCO
Rg = 0, RL= open 60 100 180 mA
Standby current Ist When standby is off and with no power supply capacitor 1 10 µA
Voltage gain V
G
VO= 0 dBm 38 40 42 dB
Total harmonic distortion THD P
O
= 1 W, Filter = FLAT 0.07 0.4 %
P
O
1 VCC= 15 V, THD = 10%, RL= 4 Ω 16 20 W
Output power P
O
2 VCC= 12 V, THD = 10%, RL= 4 Ω 13 W
P
O
3 VCC= 12 V, THD = 10%, RL= 6 Ω 10 W
Output offset voltage V
N
offset Rg = 0 –300 +300 mV
Output noise voltage V
NO
Rg = 0, BPF = 20 Hz to 20 kHz 0.2 0.5 mV
Ripple rejection ratio SVRR Rg = 0, V
R
= 0 dBm, fR= 100 Hz 50 60 dB
Channel separation CH sep Rg = 10 kΩ, V
O
= 0 dBm 50 60 dB
Input resistance Ri 14 20 26 kΩ
Standby pin applied voltage V
ST
Amplifier on (the pin 5 voltage) 2.5 10 V
Muting pin applied voltage V
M
Muting on (the pin 6 voltage) 1.5 3 V
Muting attenuation ATT
M
Muting on (VO= 1 V rms), BPF = 20 Hz to 20 kHz 70 80 dB
Parameter Symbol Conditions Ratings Unit
Recommended supply voltage V
CC
12, 15 V
Recommended load resistance range R
L
op 4 to 8 Ω
When R
L
= 8 Ω 5.5 to 21 V
Allowable operating supply voltage range *
2
VCCop
When R
L
= 6 Ω 5.5 to 20 V
When R
L
= 5 Ω 5.5 to 17 V
When R
L
= 4 Ω 5.5 to 15 V
0
10
15
13.9
20.8
10.4
3.1
5
30
20
25
40
35
80 160120100 140604020-20 0
2
3
2
3
5
7
10
100
2 3 5 7
1000
2 3 5 7
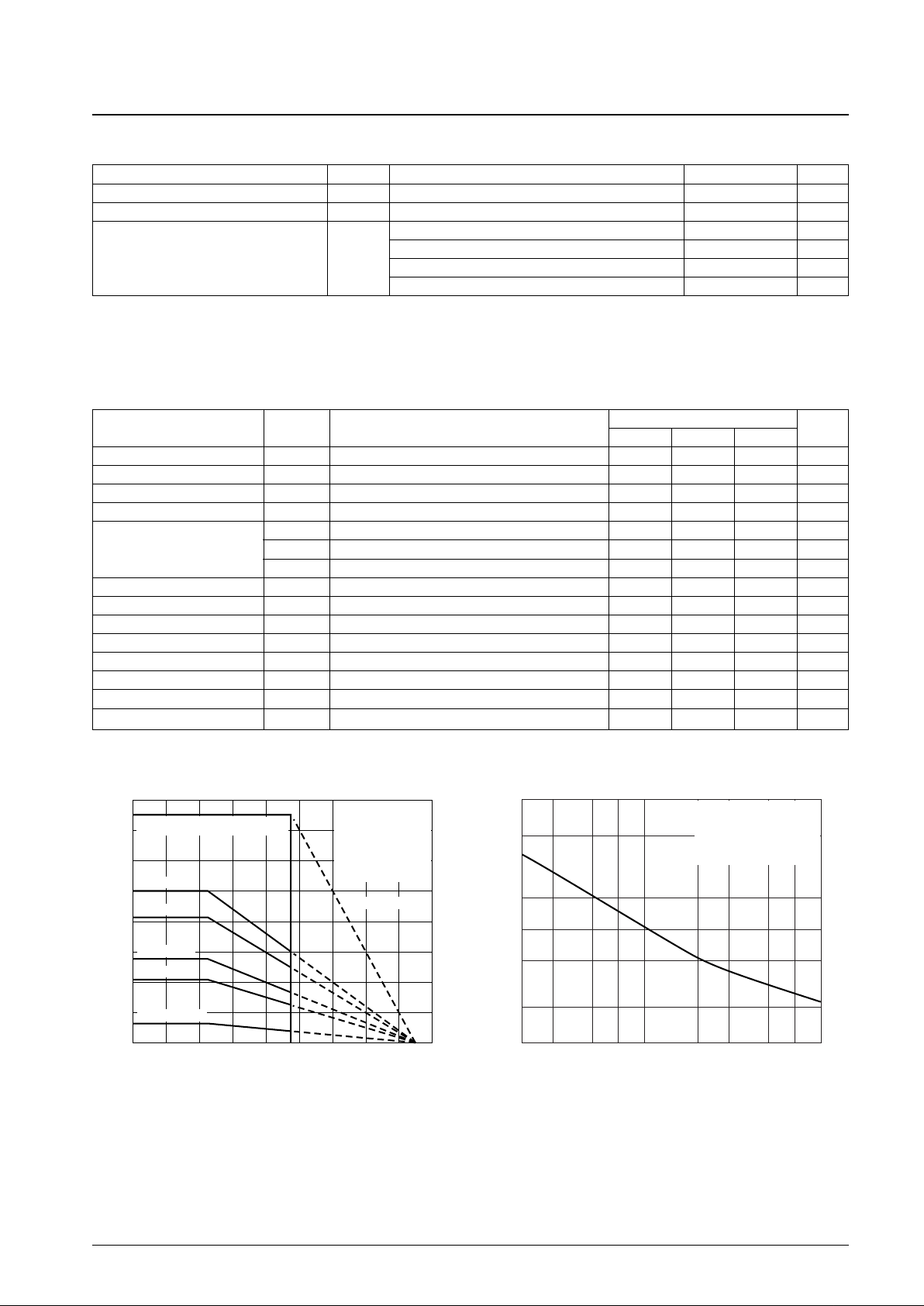
Pd max-Ta
θf=3°C/W
θjc=2°C/W
θf=4°C/W
θf=7°C/W
θf=10°C/W
No radiator fin
θf
-
S
f
Allowable power dissipation, Pd max — W
Ambient temperature, Ta — °C
With an arbitrarily large heat sink
With an Al heat sink
with mounting bolts
tightened down with
a torque of 39 N·cm
and silicone grease
applied.
Al heat sink, t = 1.5 mm
With mounting bolts
tightened down with a
torque of 39 N·cm and
silicone grease applied.
Heat sink area, Sf— cm
2
Heat sink thermal resistance, θ
f
— °C/W

Usage Notes
1. Maximum ratings
If the device is operated in the vicinity of the maximum ratings, it is possible for small changes in the operating
conditions to result in the maximum ratings being exceeded. Since this can result in destruction of the device,
applications should be designed with adequate margins in the supply voltage and other parameters so that the maximum
ratings are never exceeded during device operation.
2. Protection circuits
While the LA4663 includes a full complement of built-in protection circuits, care is required in the usage. In particular,
be careful not to short any pairs of device pins together.
[Notes on the shorting (power, ground, and load shorting) protection circuit]
• This protection circuit operates whenever a power short (a short between the output and VCC), a ground short (a short
between the output and ground), or a load short (shorting between the + and – outputs) is detected. Although there are
cases where the protection circuit may not operate if the supply voltage is under 9 V, the thermal protection circuit will
protect the device in this range.
• The protection circuit continues to operate during the interval that the abnormal short continues, and automatically
recovers when the error state is resolved. However, under certain usage conditions, there are situations where the
protection circuit may lock and remain locked even after the problem has been resolved. In these cases, the circuit can
be reset by switching to standby mode or turning off the power temporarily.
• If the output is shorted to VCCwith the IC in the standby state and furthermore, a VCCof 20 V or higher applied, an
offset will be created between the + and – outputs. If a load is connected in this state, a current will flow in that load,
and the IC may be destroyed. Applications should assure that this does not occur.
• In the following situations, the operation of the protection circuit may result in a sound switching phenomenon at high
output levels. This may be a problem, depending on the details of the end product circuit itself, and must be verified in
an actual system.
• At low load resistances RL(high loads) and at high VCCvoltages, and with both channels operating at IOpeak levels of
over 2 A per channel. (This phenomenon is more likely to occur the higher the chip temperature.)
For systems operating under the most sever conditions (high temperatures and high outputs), specific operating
conditions such that the above phenomenon does no occur are listed in the “Allowable operating supply voltage range
(VCCop)” item in the Operating Conditions section of the specifications. (Refer to the VCCop ranges for different R
L
values.)
[Thermal protection circuit]
• A thermal protection circuit is provided to prevent damage to or destruction of the IC itself when the IC generates
abnormally high temperatures. This means that gradual attenuation is applied to the output signals by the thermal
protection circuit if the IC junction temperature (Tj) rises above about 160°C due to insufficient heat sinking or other
problems.
3. Notes on printed circuit boards
• When designing the printed circuit board pattern, keep the input lines separated from both the VCC lines and the
output lines. This is to prevent increased distortion and oscillation.
• When high output levels are used, make power-ground lines as wide as possible and as short as possible to prevent the
PWR GND pins potential from increasing with respect to pre-ground. (From the standpoint of IC stability, ideally, the
ground pin potential should be the lowest potential in the system. This is to prevent trouble caused by several types of
induced parasitic devices due to increases in the GND pin potential due to the structure of the IC.)
No. 5905-3/10
LA4663
 Loading...
Loading...