Page 1
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
DATA SH EET
TDA837x family
2
I
C-bus controlled economy
PAL/NTSC and NTSC
TV-processors
Preliminary specification
File under Integrated Circuits, IC02
1997 Jul 01
Page 2
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
and NTSC TV-processors
FEATURES
Available in all ICs:
• Vision IF amplifier with high sensitivity and good figures
for differential phase and gain
• PLL demodulator for the IF signal
• Alignment-free sound demodulator
• Flexible source selection with a CVBS input for the
internal signal and Y/C or CVBS input for the external
signal
• Audio switch
• The output signal of the CVBS (Y/C) switch is externally
available
• Integrated chrominance trap and band-pass filters
(auto-calibrated)
• Luminance delay line integrated
• A symmetrical peaking circuit in the luminance channel
• Black stretching of non-standard CVBS or luminance
signals
• RGB control circuit with black current stabilization and
white point adjustment
• Linear RGB inputs and fast blanking
• Horizontal synchronization with two control loops and
alignment-free horizontal oscillator
• Slow start and slow stop of the horizontal drive pulses
• Vertical count-down circuit
• Vertical driver optimized for DC-coupled vertical output
stages
2
C-bus control of various functions
• I
• Low dissipation
• Small amount of peripheral components compared with
competition ICs.
TDA837x family
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The various versions of the TDA837x series are I
controlled single-chip TV processors which are intended to
be applied in PAL/NTSC (TDA8374 and TDA8375) and
NTSC (TDA8373 and TDA8377) television receivers.
All ICs are available in an SDIP56 package and some
versions are also available in a QFP64 package. The ICs
are pin compatible so that with one application board
NTSC and PAL/NTSC (or multistandard together with the
SECAM decoder TDA8395) receivers can be built.
Functionally this IC series is split in to 2 categories:
• Versions intended to be used in economy TV receivers
with all basic functions
• Versions with additional functions such as E-W
geometry control, horizontal and vertical zoom function
and YUV interface which are intended for TV receivers
with 110° picture tubes.
The various type numbers are given in Table 1.
The detailed differences between the various ICs are
given in Table 2.
2
C-bus
Table 1 TV receiver versions
TV RECEIVERS
ECONOMY MID/HIGH END ECONOMY MID/HIGH END
PAL only TDA8374B − TDA8374BH −
PAL/NTSC (SECAM) TDA8374 and TDA8374A TDA8375 and TDA8375A TDA8374AH TDA8375AH
NTSC TDA8373 TDA8377 and TDA8377A −−
1997 Jul 01 2
SDIP56 PACKAGE QFP64 PACKAGE
Page 3
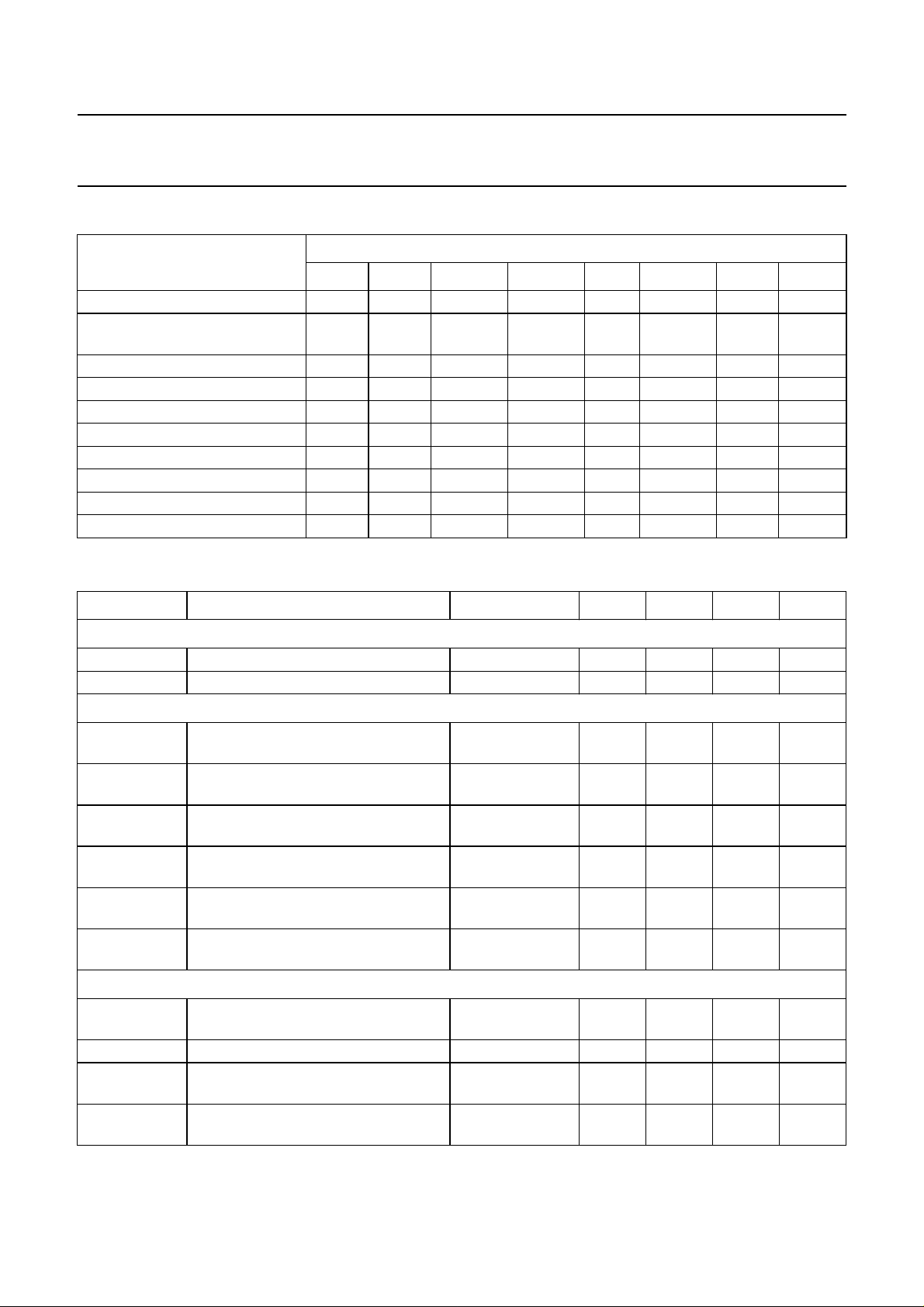
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
TDA837x family
and NTSC TV-processors
Table 2 Differences between the various ICs
CIRCUITS
8373 8374 8374A(H) 8374B(H) 8375 8375A(H) 8377 8377A
Multistandard IF − X −−XX −−
Automatic Volume Levelling
XX − −−− −−
(AVL)
PAL decoder − X X XXX −−
SECAM interface − X X XXX −−
NTSC decoder X X X X X X X X
Colour matrix PAL/NTSC (Japan) − X X XXX −−
Colour matrix NTSC (USA/Japan) X − − −−−XX
YUV interface −− − − XXXX
Horizontal geometry −− − − XXXX
Horizontal and vertical zoom −− − −XX XX
QUICK REFERENCE DATA
IC VERSION (TDA)
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Supplies
V
P
I
P
supply voltage − 8.0 − V
supply current − 110 − mA
Input voltages
V
48,49(rms)
video IF amplifiers sensitivity
− 70 −µV
(RMS value)
V
1(rms)
sound IF amplifiers sensitivity
− 1.0 − mV
(RMS value)
V
2(rms)
external audio input voltage
− 500 − mV
(RMS value)
V
11(p-p)
external CVBS/Y input voltage
− 1.0 − V
(peak-to-peak value)
V
10(p-p)
external chrominance input voltage
− 0.3 − V
(burst amplitude) (peak-to-peak value)
V
23-25(p-p)
RGB input voltage
− 0.7 − V
(peak-to-peak value)
Output signals
V
6(p-p)
IF video output voltage
− 2.5 − V
(peak-to-peak value)
I
54
V
oVSW
tuner AGC output current range 0 − 5mA
output signal level of video switch
− 1.0 − V
(peak-to-peak value)
V
30(p-p)
−(R − Y) output voltage
− 525 − mV
(peak-to-peak value)
1997 Jul 01 3
Page 4
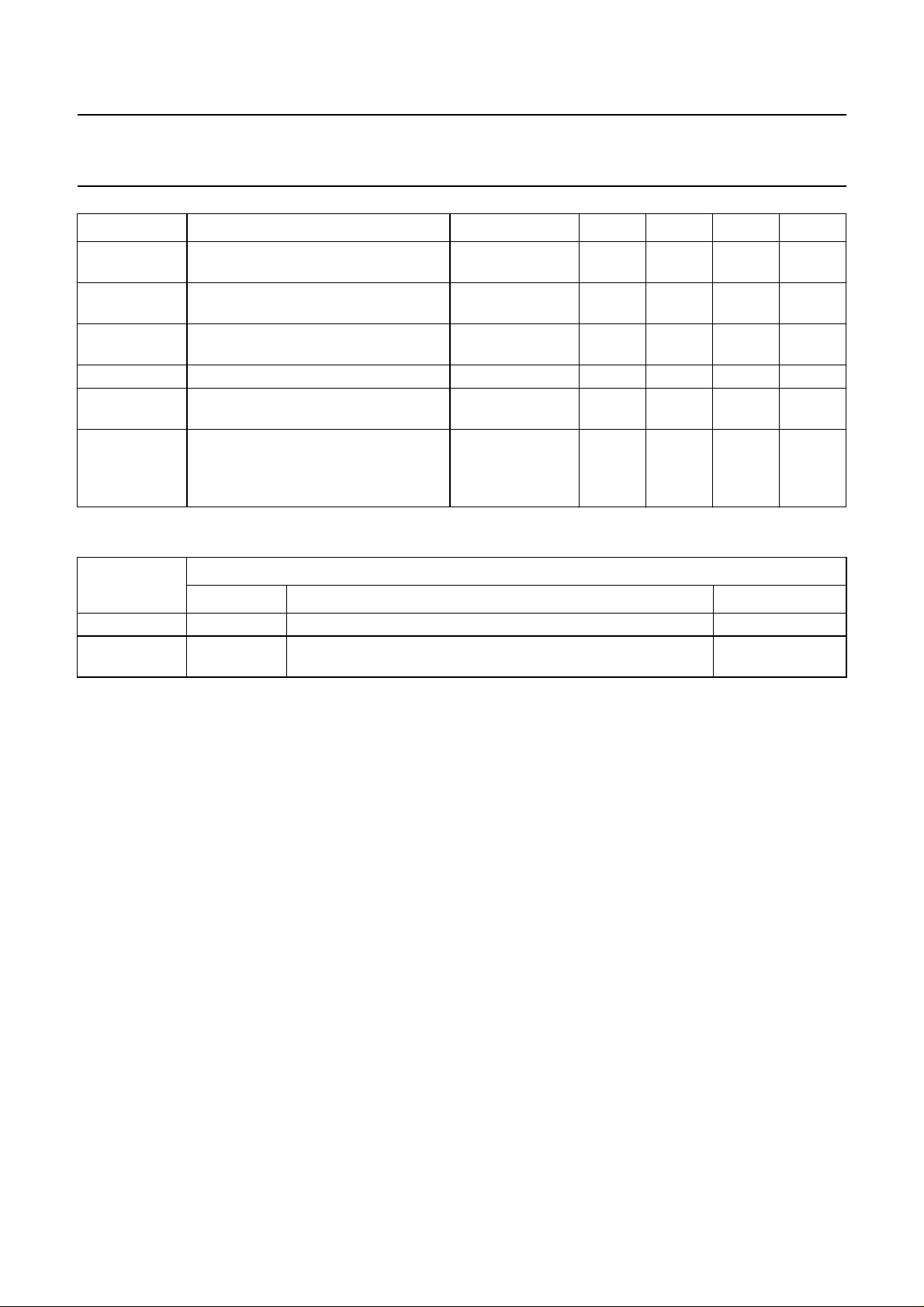
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
TDA837x family
and NTSC TV-processors
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
V
29(p-p)
V
28(p-p)
V
19-21(p-p)
I
40
I
46,47(p-p)
I
45(peak)
ORDERING INFORMATION
TYPE
NUMBER
TDA837xA SDIP56 plastic shrink dual in-line package; 56 leads (600 mil) SOT400-1
TDA837xH QFP64 plastic quad flat package; 64 leads (lead length 1.95 mm);
−(B − Y) output voltage
(peak-to-peak value)
luminance output voltage
(peak-to-peak value)
RGB output signal amplitudes
(peak-to-peak value)
horizontal output current − 10 − mA
vertical output current
(peak-to-peak value)
E-W output current (peak value) TDA8375A,
TDA8377A,
TDA8375 and
TDA8377
PACKAGE
NAME DESCRIPTION VERSION
body 14 × 20 × 2.7 mm; high stand-off height
− 675 − mV
− 1.4 − V
− 2.0 − V
− 1 − mA
− 1.2 − mA
SOT319-1
1997 Jul 01 4
Page 5

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
and NTSC TV-processors
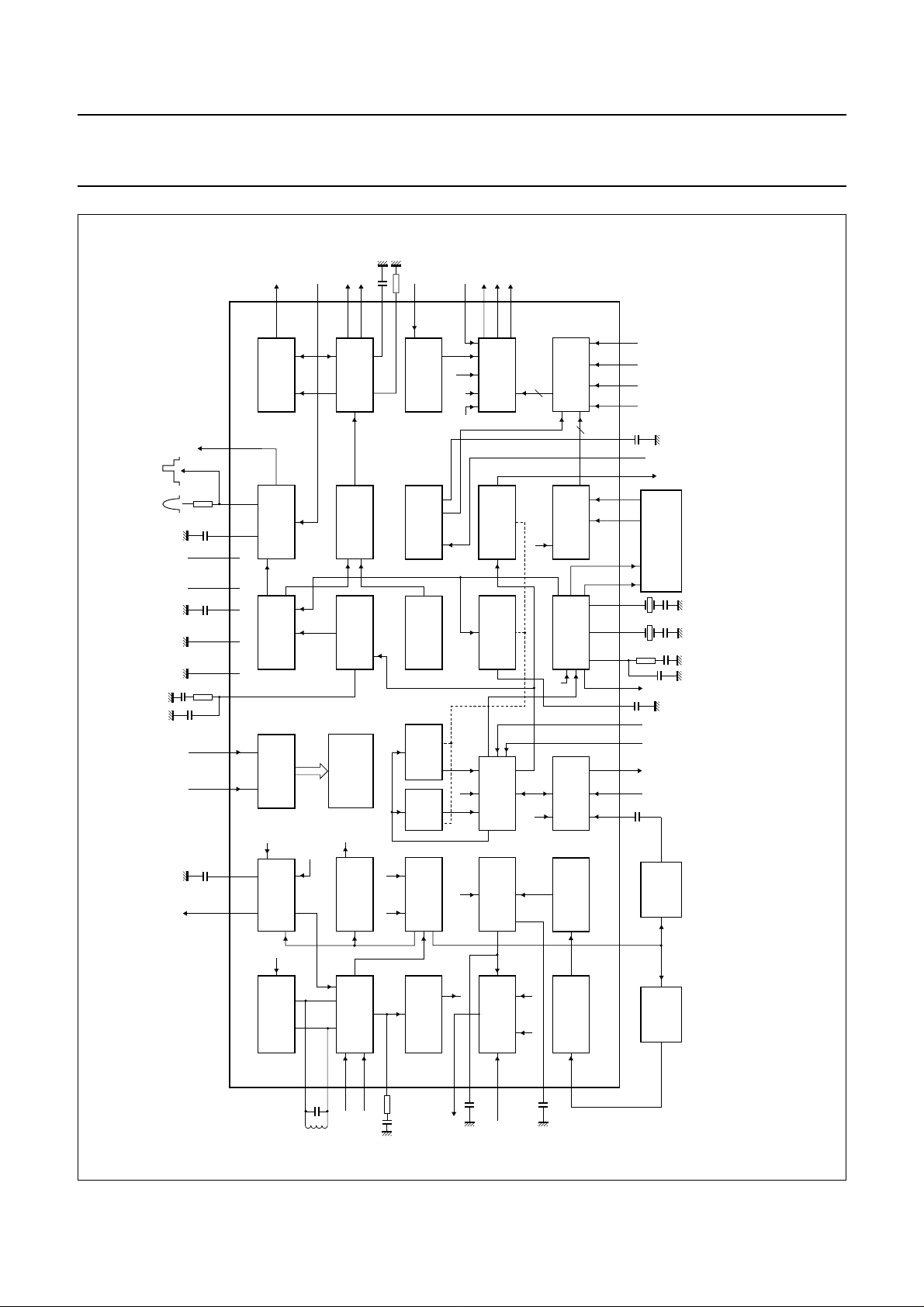
BLOCK DIAGRAM
18
52
51
46
50
40
OUTPUT
HORIZONTAL
2nd LOOP AND
+8 V
9 42 4154
44 12 37
AND
VCO
CONTROL
REF
47
VERTICAL
GEOMETRY
DIVIDER
VERTICAL
HORIZONTAL/
SYNC
SEPARATOR
AND 1st LOOP
TDA8373
BLACK
CURRENT
STABILIZER
BLACK
STRETCHER
SYNC
VERTICAL
SEPARATOR
22
CONTR
BRI
point
white
REF
20
19
21
AND
OUTPUT
RGB CONTROL
AND
DELAY
PEAKING
FILTER
TUNING
TDA837x family
MGK286
RGB INPUT
RGB MATRIX
AND SWITCH
3
AND
G - Y MATRIX
SAT CONTROL
B−Y
R−Y
NTSC
DECODER
24 25 26
2331
39
322930
3436336161110381713
3.6
MHz
3
SAT
ok, full pagewidth
VOL SW
SW
56
HUE
CVBS
SWITCH
PLL
DEMODULATOR
LIMITER
1
TRAP
SOUND
SOUND
BAND-PASS
Fig.1 Block diagram of bus-controlled economy NTSC TV-processor TDA8373.
43 14
8753
5
MUTE
BAND-PASS
TRAP
VIDEO
AND MUTE
AMPLIFIER
AFC
SW
MUTE
AFC
55245
15
SWITCH
CVBS Y/C
AND MUTE
PRE-AMPLIFIER
AVL AND
SWITCH AND
VOLUME CONTROL
C-BUS
2
I
TRANSCEIVER
point
tuner
take-over
AGC FOR IF
AND TUNER
ADJ
VCO
ADJUSTMENT
1 × 8 BITS
1 × 4 BITS
14 × 6 BITS
CONTROL DACs
IDENT
VIDEO
IDENTIFICATION
AND PLL
VIF AMPLIFIER
DEMODULATOR
49
48
4
3
1997 Jul 01 5
The TDA8373 is only supplied in an SDIP package.
Page 6

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
and NTSC TV-processors
18
52
51
46
50
+8 V
40
OUTPUT
HORIZONTAL
2nd LOOP AND
9 42 41
44 12 37
AND
VCO
CONTROL
REF
47
VERTICAL
GEOMETRY
DIVIDER
VERTICAL
HORIZONTAL/
SYNC
SEPARATOR
AND 1st LOOP
TDA8374
BLACK
CURRENT
STABILIZER
BLACK
STRETCHER
SYNC
VERTICAL
SEPARATOR
CONTR
white
22
BRI
point
REF
20
19
21
AND
OUTPUT
RGB CONTROL
AND
DELAY
PEAKING
FILTER
TUNING
TDA837x family
MGK287
RGB INPUT
RGB MATRIX
AND SWITCH
3
AND
G - Y MATRIX
SAT CONTROL
B−Y
R−Y
PAL/NTSC
DECODER
(51)
24 25 26
23
39
31
322930
TDA4665
34
3.6
MHz
35
4.4
MHz
36336161110381713
3
SAT
k, full pagewidth
43 14
87
53
54
C-BUS
2
I
TRANSCEIVER
point
tuner
take-over
AGC FOR IF
AND TUNER
ADJ
VCO
ADJUSTMENT
HUE
BAND-PASS
1 × 8 BITS
1 × 4 BITS
POL
CONTROL DACs
IDENT
14 × 6 BITS
VIDEO
IDENTIFICATION
MUTE
POL
VIDEO
TRAP
AND MUTE
AMPLIFIER
SW
MUTE
SWITCH
CVBS Y/C
SW
AND MUTE
PRE-AMPLIFIER
CVBS
SWITCH
PLL
DEMODULATOR
TRAP
SOUND
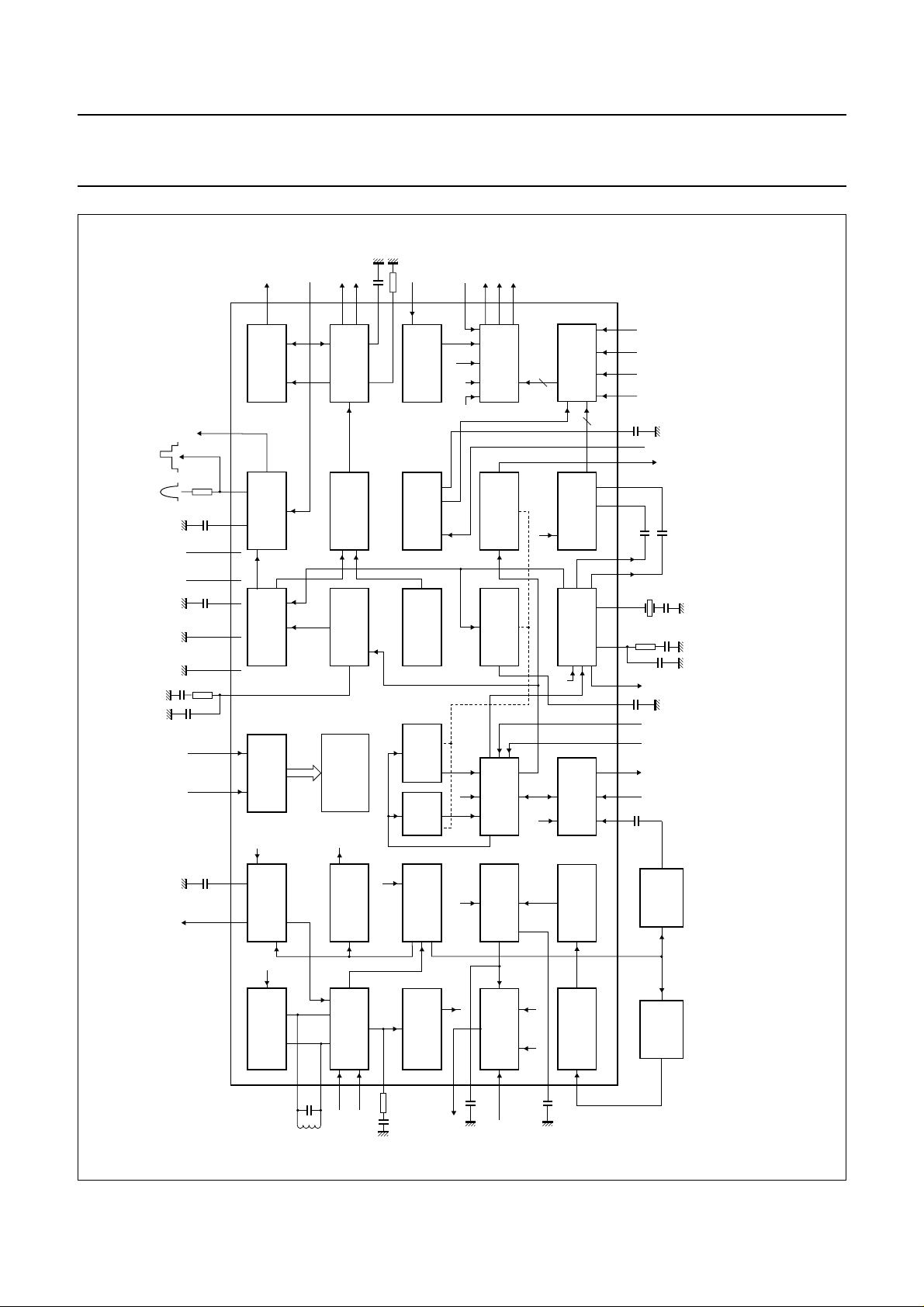
Fig.2 Block diagram of bus-controlled economy PAL/NTSC TV processor TDA8374.
AFC
AND PLL
VIF AMPLIFIER
DEMODULATOR
49
48
4
3
AFC
5
15
AVL AND
55245
VOL SW
SWITCH AND
VOLUME CONTROL
56
LIMITER
1
SOUND
BAND-PASS
1997 Jul 01 6
For most pins the QFP64 pinning is not indicated.
Page 7
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
and NTSC TV-processors
(5) 52
(63) 46
HORIZONTAL/
SYNC
1 × 8 BITS
CONTROL DACs
IDENT
VERTICAL
VIDEO
(4) 51
(64) 47
GEOMETRY
DIVIDER
VERTICAL
SEPARATOR
AND 1st LOOP
1 × 4 BITS
18 × 6 BITS
IDENTIFICATION
TDA8375
MUTE
POL
(30) 18
BLACK
BLACK
VERTICAL
VIDEO
CURRENT
STRETCHER
SYNC
BAND-PASS
TRAP
AMPLIFIER
ok, full pagewidth
(3) 50
(62) 45
E-W
GEOMETRY
40
(56)
41
(57)
42
(58)
OUTPUT
HORIZONTAL
2nd LOOP AND
37
(53)
12
+8 V
9
44
14
43
8
7
53
54
(22,23)
(19)
(60,61)
(25,26)
(59)
(18)
(17)
(6)
(7)
AND
VCO
CONTROL
C-BUS
2
I
TRANSCEIVER
point
tuner
take-over
AGC FOR IF
AND TUNER
ADJ
REF
POL
(34) 22
CONTR
STABILIZER
BRI
point
white
SEPARATOR
AND MUTE
AFC
(33) 21
REF
SW
MUTE
(32) 20
(31) 19
AND
OUTPUT
RGB CONTROL
CORING
DELAY PLUS
PEAKING PLUS
FILTER
TUNING
SWITCH
CVBS Y/C
AND MUTE
PRE-AMPLIFIER
TDA837x family
MGK288
(38)
26
(37)
25
(36)
RGB INPUT
AND SWITCH
3
AND
SAT CONTROL
R−Y
PAL/NTSC
DECODER
CVBS
SWITCH
PLL
DEMODULATOR
(35)
(55)
(39)
(40)
(47)
(48)
(45)
(46)
(50)
(51)
(52)
(49)
(28)
(21)
(20)
(54)
(29)
(24)
(16)
24
23
39
27
28
31
32
29
30
34
35
36
33
16
11
10
38
17
13
6
TDA4665
3.6
MHz
4.4
MHz
TRAP
SOUND
Fig.3 Block diagram of bus-controlled economy PAL/NTSC TV processor TDA8375.
3
RGB MATRIX
SAT
G - Y MATRIX
B−Y
HUE
SW
5 (15)
AFC
15 (27)
VCO
ADJUSTMENT
3 (13)
4 (14)
48 (1)
AND PLL
VIF AMPLIFIER
DEMODULATOR
49 (2)
1997 Jul 01 7
55 (8)
VOL SW
SWITCH AND
VOLUME CONTROL
2 (11)
56 (9)
LIMITER
1 (10)
SOUND
BAND-PASS
Page 8
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
and NTSC TV-processors
18
52
51
46
50
45
E-W
GEOMETRY
47
VERTICAL
GEOMETRY
BLACK
TDA8377
OUTPUT
HORIZONTAL
2nd LOOP AND
+8 V
9 42 41 40
44 12 37
AND
VCO
CONTROL
REF
DIVIDER
VERTICAL
HORIZONTAL/
SYNC
SEPARATOR
AND 1st LOOP
CURRENT
STABILIZER
BLACK
STRETCHER
SYNC
VERTICAL
SEPARATOR
22
CONTR
BRI
point
white
21
20
RGB CONTROL
DELAY PLUS
REF
19
AND
OUTPUT
CORING
PEAKING PLUS
FILTER
TUNING
TDA837x family
MGK289
RGB INPUT
RGB MATRIX
AND SWITCH
3
AND
G - Y MATRIX
SAT CONTROL
B−Y
R−Y
NTSC
DECODER
24 25 26
23
39
28 27
31
322930
3436336161110381713
3.6
MHz
3
SAT
ull pagewidth
43 14
87
53
54
C-BUS
2
I
TRANSCEIVER
point
tuner
take-over
AGC FOR IF
AND TUNER
ADJ
VCO
ADJUSTMENT
HUE
MUTE
BAND-PASS
TRAP
VIDEO
AND MUTE
AMPLIFIER
SW
MUTE
SWITCH
CVBS Y/C
SW
AND MUTE
PRE-AMPLIFIER
CVBS
PLL
SWITCH
DEMODULATOR
TRAP
SOUND
1 × 8 BITS
CONTROL DACs
IDENT
18 × 6 BITS
VIDEO
IDENTIFICATION
1 × 4 BITS
Fig.4 Block diagram of bus-controlled economy NTSC TV processor TDA8377.
AFC
AND PLL
VIF AMPLIFIER
DEMODULATOR
49
48
4
3
AFC
5
55215
VOL SW
SWITCH AND
VOLUME CONTROL
56
LIMITER
1
SOUND
BAND-PASS
1997 Jul 01 8
The TDA8377 is only supplied in an SDIP package.
Page 9

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
and NTSC TV-processors
PINNING
(2)
(1)
(1)
PIN
DESCRIPTION
2
C-bus)
2
C-bus)
39 luminance input
49 SECAM reference output
51 4.43 MHz crystal connection
SYMBOL
SDIP56 QFP64
SIF 1 10 sound IF input
AUDI 2 11 external audio input
VCO1 3 13 IF VCO 1 tuned circuit
VCO2 4 14 IF VCO 2 tuned circuit
PLL 5 15 PLL loop filter
IFVO 6 16 IF video output
SCL 7 17 serial clock input (I
SDA 8 18 serial data input/output (I
DEC
BG
9 19 band gap decoupling
CHROMA 10 20 chrominance input
CVBS/Y 11 21 CVBS/Y input
V
P1
CVBS
int
12 22 and 23 main supply voltage (+8 V)
13 24 internal CVBS input
GND1 14 25 and 26 ground
AUDO 15 27 audio output
DEC
CVBS
FT
ext
16 28 decoupling filter tuning
17 29 external CVBS input
BLKIN 18 30 black current input
BO 19 31 blue output
GO 20 32 green output
RO 21 33 red output
BCLIN 22 34 beam current input
RI 23 35 red input
GI 24 36 green input
BI 25 37 blue input
RGBIN 26 38 RGB insertion input
YIN 27
YOUT 28 40 luminance output
BYO 29 45 (B −Y) output
RYO 30 46 (R − Y) output
RYI 31 47 (R − Y) input
BYI 32 48 (B − Y) input
SEC
ref
33
XTAL1 34 50 3.58 MHz crystal connection
XTAL2 35
LFBP 36 52 loop filter burst phase detector
V
P2
37 53 horizontal oscillator supply voltage (+8 V)
CVBSO 38 54 CVBS output
TDA837x family
1997 Jul 01 9
Page 10
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
and NTSC TV-processors
(2)
PIN
DESCRIPTION
62 east-west drive output
SYMBOL
BLPH 39 55 black peak hold capacitor
HOUT 40 56 horizontal drive output
FBI/SCO 41 57 flyback input and sandcastle output
PH2 42 58 phase 2 filter/protection
PH1 43 59 phase 1 filter
GND2 44 60 and 61 ground 2
EWD 45
VDOB 46 63 vertical drive output B
VDOA 47 64 vertical drive output A
IFIN1 48 1 IF input 1
IFIN2 49 2 IF input 2
EHT/PRO 50 3 EHT/overvoltage protection input
VSAW 51 4 vertical sawtooth capacitor
I
ref
DEC
AGC
AGCOUT 54 7 tuner AGC output
AUDEEM 55 8 audio deemphasis
DEC 56 9 decoupling sound demodulator
i.c. − 12 internally connected
i.c. − 41 internally connected
i.c. − 42 internally connected
i.c. − 43 internally connected
i.c. − 44 internally connected
SDIP56 QFP64
52 5 reference current input
53 6 AGC decoupling capacitor
TDA837x family
Notes
1. In the TDA8373 and TDA8377 pin 35 (4.43 MHz crystal) is internally connected and pin 33 is just a subcarrier output
which can be used as a reference signal for comb filter ICs.
2. In the TDA8373 and TDA8374 the following pins are different (SDIP56): Pin 27: not connected; Pin 45: AVL
capacitor.
1997 Jul 01 10
Page 11
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
and NTSC TV-processors
handbook, halfpage
SIF
AUDI
VCO1
VCO2
PLL
IFVO
SCL
SDA
DEC
BG
CHROMA
CVBS/Y
V
P1
CVBS
GND1
AUDO
DEC
FT
CVBS
ext
BLKIN
BO
GO
RO
BCLIN
RGBIN
YIN
YOUT
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
int
14
TDA837x
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
RI
23
GI
24
BI
25
26
27
28
MGK284
56
55
54
53
52
51
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
DEC
AUDEEM
AGCOUT
DEC
AGC
I
ref
VSAW
EHT/PRO
IFIN2
IFIN1
VDOA
VDOB
EWD
GND2
PH1
PH2
FBI/SCO
HOUT
BLPH
CVBSO
V
P2
LFBP
XTAL2
XTAL1
SEC
ref
BYI
RYI
RYO
BYO
TDA837x family
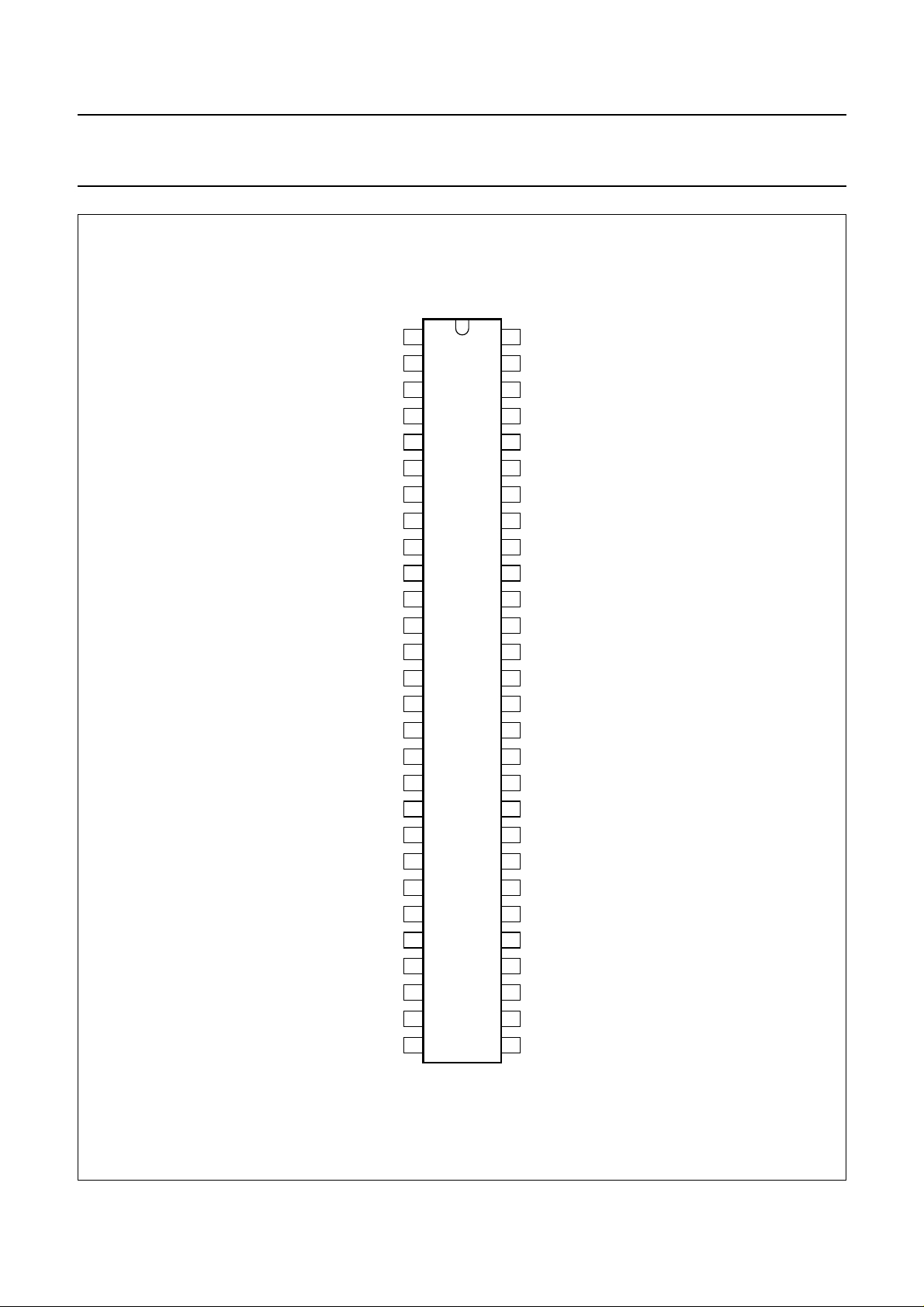
Fig.5 Pin configuration (SDIP56).
1997 Jul 01 11
Page 12
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
and NTSC TV-processors
handbook, full pagewidth
VDOA
VDOB
EWD
GND2
GND2
PH1
PH2
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
1
IFIN1
2
IFIN2
EHT/PRO
DEC
AGCOUT
AUDEEM
3
4
VSAW
5
I
ref
6
AGC
7
8
DEC
9
SIF
10
AUDI
11
i.c.
12
VCO1
13
VCO2
14
PLL
15
IFVO 33
16
TDA837xH
FBI/SCO
HOUT
57
56
BLPH
55
CVBSO
VP2LFBP
54
53
TDA837x family
ref
XTAL2
XTAL1
SEC
52
51
50
48
BYI
RYI
47
RYO
46
BYO
45
i.c.
44
i.c.
43
i.c.
42
i.c.
41
YOUT
40
YIN
39
RGBIN
38
BI
37
GI
36
RI
35
BCLIN
34
RO
17
SCL
18
SDA
19
BG
DEC
20
CHROMA
22
VP1V
CVBS/Y
23
24
int
P1
CVBS
21
Fig.6 Pin configuration (QFP64).
1997 Jul 01 12
25
GND1
26
GND1
27
AUDO
28
FT
DEC
29
ext
CVBS
30
BLKIN
31
BO
32
MGK285
GO 49
Page 13

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
and NTSC TV-processors
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
Vision IF amplifier
The IF amplifier contains 3 AC-coupled control stages with
a total gain control range which is higher than 66 dB.
The sensitivity of the circuit is comparable with that of
modern IF-ICs.
The video signal is demodulated by a PLL carrier
regenerator. This circuit contains a frequency detector and
a phase detector. During acquisition the frequency
detector will tune the VCO to the correct frequency.
The initial adjustment of the oscillator is realized via the
2
I
C-bus.
The switching, between SECAM L and L’, can also be
realized via the I2C-bus. After lock-in the phase detector
controls the VCO so that a stable phase relationship
between the VCO and the input signal is achieved.
The VCO operates at twice the IF frequency.
The reference signal for the demodulator is obtained by
using a frequency divider circuit.
The AFC output is obtained by using the VCO control
voltage of the PLL and can be read via the I2C-bus.
For fast search tuning systems the window of the AFC can
be increased by a factor of 3. The setting is realized with
the AFW bit.
Depending on the device type the AGC detector operates
on top-sync level (single standard versions) or on top-sync
and top-white level (multistandard versions).
The demodulation polarity is switched via the I2C-bus.
The AGC detector time constant capacitor is connected
externally. This is mainly because of the flexibility of the
application. The time constant of the AGC system during
positive modulation is rather long, this is to avoid visible
variations of the signal amplitude. To improve the speed of
the AGC system, a circuit has been included which detects
whether the AGC detector is activated every frame period.
When, during 3 frame periods, no action is detected the
speed of the system is increased. For signals without
peak-white information the system switches automatically
TDA837x family
to a gated black level AGC. Because a black level clamp
pulse is required for this method of operation the circuit will
only switch to black level AGC in the internal mode.
The circuits contain a second fast video identification
circuit which is independent of the synchronization
identification circuit. Consequently, search tuning is also
possible when the display section of the receiver is used
as a monitor. However, this identification circuit cannot be
made as sensitive as the slower sync identification circuit
(SL) and it is recommended to use both identification
outputs to obtain a reliable search system.
The identification output is applied to the tuning system via
2
the I
C-bus.
The input of the identification circuit is connected to pin 13,
the internal CVBS input (see Fig.1). This has the
advantage that the identification circuit can also be made
operative when a scrambled signal is received
[descrambler connected between the IF video output
(pin 6) and pin 13]. A second advantage is that the
identification circuit can be used when the IF amplifier is
not used (e.g. with built-in satellite tuners).
The video identification circuit can also be used to identify
the selected CBVS or Y/C signal. The switching between
the two modes can be realized with bit VIM.
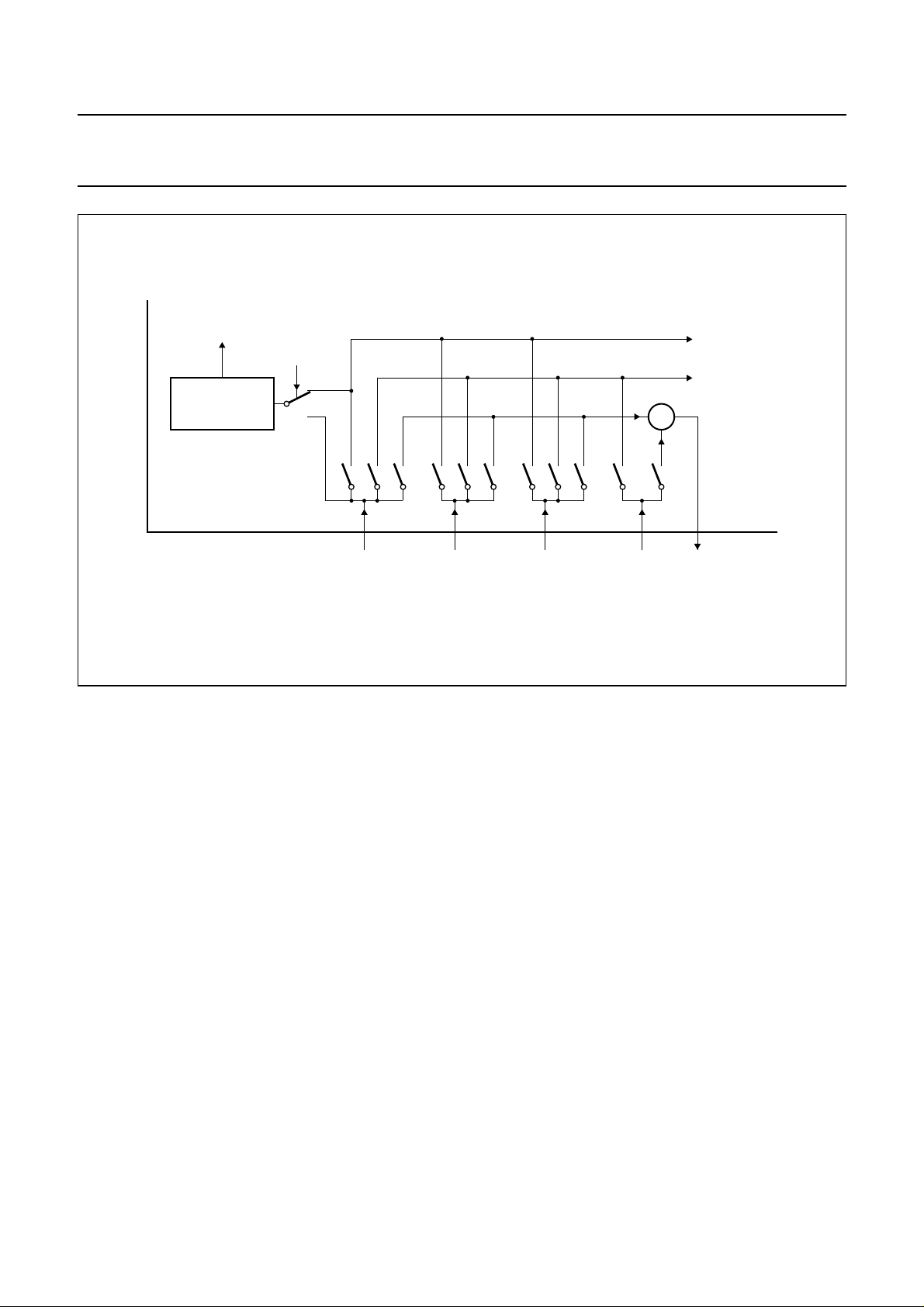
Video switches
The circuit has two CVBS inputs (CVBS
and a Y/C input. When the Y/C input is not required pin 11
can be used as the third CVBS input. The switch
configuration is illustrated in Fig.7. The selection of the
various sources is made via the I2C-bus.
The output signal of the CVBS switch is externally
available and can be used to drive the teletext decoder, the
SECAM add-on decoder and a comb filter.
In applications with comb filters a Y/C input is only possible
when additional switches are added. In applications
without comb filters the Y/C input signal can be switched
to the CVBS output.
and CVBS
int
ext
)
1997 Jul 01 13
Page 14
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
and NTSC TV-processors
handbook, full pagewidth
IDENT
VIM
VIDEO
IDENTIFICATION
S0
S0 S5
TDA837x
13
CVBS
int
CVBS
S1
S1 S6 S2
17
ext
11
CVBS/Y
S3 S7 S4
CHROMA CVBSO
TDA837x family
to luminance/
sync processing
to chrominance
processing
+
S8
10 38
MGK301
Fig.7 Configuration CVBS switch and interfacing of video identification.
Sound circuit
The sound band-pass and trap filters have to be
connected externally. The filtered intercarrier signal is fed
to a limiter circuit and is demodulated by a PLL
demodulator. This PLL circuit automatically tunes to the
incoming carrier signal, hence no adjustment is required.
The volume is controlled via the I2C-bus. The de-emphasis
capacitor has to be connected externally.
The non-controlled audio signal can be obtained from this
pin (pin 55) (via a buffer stage).
2
The FM demodulator can be muted via the I
C-bus. This
function can be used to switch-off the sound during a
channel change so that high output peaks are prevented
(also on the de-emphasis output).
The TDA8373 and TDA8374 contain an Automatic Volume
Levelling (AVL) circuit which automatically stabilizes the
audio output signal to a certain level which can be set by
the user via the volume control. This function prevents big
audio output fluctuations due to variations of the
modulation depth of the transmitter. The AVL function can
be activated via the I2C-bus.
Synchronization circuit
The sync separator is preceded by a controlled amplifier
which adjusts the sync pulse amplitude to a fixed level.
These pulses are fed to the slicing stage which operates at
50% of the amplitude.
The separated sync pulses are fed to the first phase
detector and to the coincidence detector. The coincidence
detector is used to detect whether the line oscillator is
synchronized and can also be used for transmitter
identification. The circuit can be made less sensitive by
using the STM bit. This mode can be used during search
tuning to ensure that the tuning system will not stop at very
weak input signals. The first PLL has a very high static
steepness so that the phase of the picture is independent
of the line frequency.
The line oscillator operates at twice the line frequency.
The oscillator capacitor is internal. Because of the spread
of internal components an automatic calibration circuit has
been added to the IC. The circuit compares the oscillator
frequency with that of the crystal oscillator in the colour
decoder.
1997 Jul 01 14
Page 15

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
and NTSC TV-processors
This results in a free-running frequency which deviates
less than 2% from the typical value. When the IC is
switched on the horizontal output signal is suppressed and
the oscillator is calibrated as soon as all subaddress bytes
have been sent. When the frequency of the oscillator is
correct the horizontal drive signal is switched on. To obtain
a smooth switching on and switching off behaviour of the
horizontal output stage the horizontal output frequency is
doubled during switch-on and switch-off (slow start/stop).
During that time the duty cycle of the output pulse has such
a value that maximum safety is obtained for the output
stage.
To protect the horizontal output transistor, the horizontal
drive is immediately switched off (via the slow stop
procedure) when a power-on reset is detected. The drive
signal is switched on again when the normal switch-on
procedure is followed, i.e. all subaddress bytes must be
sent and, after calibration, the horizontal drive signal will
be released again via the slow start procedure.
When the coincidence detector indicates an out-of-lock
situation the calibration procedure is repeated.
TDA837x family
For this reason this protection input can be used as ‘flash
protection’.
The drive pulses for the vertical sawtooth generator are
obtained from a vertical countdown circuit. This countdown
circuit has various windows depending on the incoming
signal (50 or 60 Hz and standard or non-standard).
The countdown circuit can be forced in various modes via
the I2C-bus. To obtain short switching times of the
countdown circuit during a channel change the divider can
be forced in the search window using the NCIN bit.
The vertical deflection can be set in the de-interlace mode
via the I2C-bus.
To avoid damage of the picture tube when the vertical
deflection fails, the guard output current of the TDA8350
and TDA8351 can be supplied to the beam current limiting
input. When a failure is detected the RGB outputs are
blanked and a bit is set (NDF) in the status byte of the
I2C-bus. When no vertical deflection output stage is
connected this guard circuit will also blank the output
signals. This can be overruled using the EVG bit.
The circuit has a second control loop to generate the drive
pulses for the horizontal driver stage. The horizontal
output is gated with the flyback pulse so that the horizontal
output transistor cannot be switched on during the flyback
time.
Adjustments can be made to the horizontal shift, vertical
shift, vertical slope, vertical amplitude and the S-correction
via the I2C-bus. In the TDA8375A, TDA8377A, TDA8375
and TDA8377 the E-W drive can also be adjusted via the
I2C-bus. The TDA8375 and TDA8377 have a flexible zoom
adjustment possibility for the vertical and horizontal
deflection. When the horizontal scan is reduced to display
4 : 3 pictures on a 16 : 9 picture tube an accurate video
blanking can be switched on to obtain well defined edges
on the screen. The geometry processor has a differential
output for the vertical drive signal and a single-ended
output for the E-W drive (TDA8375A, TDA8377A,
TDA8375 and TDA8377). Overvoltage conditions (X-ray
protection) can be detected via the EHT tracking pin.
When an overvoltage condition is detected the horizontal
output drive signal will be switched off via the slow stop
procedure. However, it is also possible that the drive is not
switched off and that just a protection indication is given in
the I2C-bus output byte. The choice is made via the input
bit PRD. The ICs have a second protection input on the
phase-2 filter capacitor pin. When this input is activated the
drive signal is switched off immediately (without slow stop)
and switched on again via the slow start procedure.
Chrominance and luminance processing
The circuit contains a chrominance band-pass and trap
circuit. The filters are realized by using gyrator circuits.
They are automatically calibrated by comparing the tuning
frequency with the crystal frequency of the decoder.
The luminance delay line and the delay for the peaking
circuit are also realized by using gyrator circuits.
The centre frequency of the chrominance band-pass filter
is 10% higher than the subcarrier frequency. This
compensates for the high frequency attenuation of the IF
saw filter. During SECAM reception the centre frequency
of the chrominance trap is reduced to obtain a better
suppression of the SECAM carrier frequencies. All ICs
have a black stretcher circuit which corrects the black level
for incoming video signals which have a deviation between
the black level and the blanking level (back porch).
The TDA8375A, TDA8377A, TDA8375 and TDA8377
have a defeatable coring function in the peaking circuit.
Some of the ICs have a YUV interface so that picture
improvement ICs such as the TDA9170 (contrast
improvement), TDA9177 (sharpness improvement) and
TDA4556 and TDA4566 (CTI) can be applied. When the
TDA4556 or TDA4566 is applied it is possible to increase
the gain of the luminance channel by using the GAI bit in
subaddress 03 so that the resulting RGB output signals
will not be affected.
1997 Jul 01 15
Page 16

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
and NTSC TV-processors
Colour decoder
Depending on the IC type the colour decoder can decode
NTSC signals (TDA8373 and TDA8377) or PAL/NTSC
signals (TDA8374 and TDA8375). The circuit contains an
alignment-free crystal oscillator, a killer circuit and two
colour difference demodulators. The 90° phase shift for the
reference signal is made internally.
The TDA8373 and TDA8377 contain an Automatic Colour
Limiting (ACL) circuit which prevents over saturation
occurring when signals with a high chroma-to-burst ratio
are received. This ACL function is also available in the
TDA8374 and TDA8375, however, it is only active during
the reception of NTSC signals.
The TDA8373 and TDA8377 have a switchable colour
difference matrix (via the I
reproduction can be adapted to the market requirements.
In the TDA8374 and TDA8375 the colour difference matrix
switches automatically between PAL and NTSC, however,
it is also possible to fix the matrix in the PAL standard.
The TDA8374 and TDA8375 can operate in conjunction
with the SECAM decoder TDA8395 so that an automatic
multistandard decoder can be realized. The subcarrier
reference output for the SECAM decoder can also be used
as a reference signal for a comb filter. Consequently, the
reference signal is continuously available when PAL or
NTSC signals are detected and only present during the
vertical retrace period when a SECAM signal is detected.
Which standard the TDA8374 and TDA8375 can decode
depends on the external crystals. The crystal to be
connected to pin 34 must have a frequency of 3.5 MHz
(NTSC-M, PAL-M or PAL-N). Pin 35 can handle crystals
with a frequency of 4.4 and 3.5 MHz. Because the crystal
frequency is used to tune the line oscillator, the value of
the crystal frequency must be communicated to the IC via
the I2C-bus. It is also possible to use the IC in the so called
‘3-norma’ mode for South America. In that event one
crystal must be connected to pin 35 and the other two to
pin 34. Switching between the 2 latter crystals must be
performed externally. Consequently, the search loop of the
decoder must be controlled by the microcontroller.
To prevent calibration problems of the horizontal oscillator
the external switching between the two crystals should be
performed when the oscillator is forced to pin 35.
2
C-bus) so that the colour
TDA837x family
For a reliable calibration of the horizontal oscillator it is
very important that the crystal indication bits (XA and XB)
are not corrupted. For this reason the crystal bits can be
read in the output bytes so that the software can check the
2
C-bus transmission.
I
RGB output circuit and black current stabilization
The colour difference signals are matrixed with the
luminance signal to obtain the RGB signals. Linear
amplifiers have been chosen for the RGB inputs so that the
circuit is suited for signals that are input from the SCART
connector. The insertion blanking can be switched on or off
using the IE1 bit. To ascertain whether the insertion pin
has a (continuous) HIGH level or not can be read via the
IN1 bit. The contrast and brightness control operate on
internal and external signals.
The output signal has an amplitude of approximately 2 V
(black-to-white) at nominal input signals and nominal
settings of the controls. To increase the flexibility of the IC
it is possible to add OSD and/or teletext signals directly at
the RGB outputs. This insertion mode is controlled via the
insertion input. The action to switch the RGB outputs to
black has some delay which must be compensated for
externally.
The black current stabilization is realized by using a
feedback from the video output amplifiers to the RGB
control circuit. The black current of the 3 guns of the
picture tube is internally measured and stabilized.
The black level control is active during 4 lines at the end of
the vertical blanking. The vertical blanking is adapted to
the incoming CVBS signal (50 or 60 Hz). When the flyback
time of the vertical output stage is longer than the 60 Hz
blanking time, or when additional lines need to be blanked
(e.g. for close captioning lines) the blanking can be
increased to the same value as that of the 50 Hz blanking.
This can be set using the LBM bit. The leakage current is
measured during the first line and, during the following
3 lines, the 3 guns are adjusted to the required level.
The maximum acceptable leakage current is ±100 µA.
The nominal value of the black current is 10 µA. The ratio
of the currents for the various guns automatically tracks
with the white point adjustment so that the background
colour is the same as the adjusted white point.
1997 Jul 01 16
Page 17

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
TDA837x family
and NTSC TV-processors
The input impedance of the black current measuring pin is
14 kΩ. To prevent the voltage on this pin exceeding the
supply voltage during scan an internal protection diode
has been included.
When the TV receiver is switched on the black current
stabilization circuit is not active, the RGB outputs are
blanked and the beam current limiting input pin is
short-circuited. Only during the measuring lines will the
outputs supply a voltage of 4.2 V to the video output stage
2
C-bus specification
I
Table 3 Slave address (8A)
A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0 R/W
1000101I/O
The slave address is identical for all types. The
subaddresses of the various types are slightly different.
The list of subaddresses for each type is given in
Tables 4, 6, 8 and 10.
TART-UP PROCEDURE
S
to ascertain whether the picture tube is warming up. As
soon as the current supplied to the measuring input
exceeds a value of 190 µA the stabilization circuit will be
activated. After a waiting time of approximately 0.8 s the
blanking and beam current limiting input pins are released.
The remaining switch-on behaviour of the picture is
determined by the external time constant of the beam
current limiting network.
on when the oscillator is calibrated. Each time before the
data in the IC is refreshed, the status bytes must be read.
If POR = 1, then the procedure given above must be
carried out to restart the IC. When this procedure is not
followed the horizontal frequency in the TDA8374 and
TDA8375 may be incorrect after power-up or a power dip.
Read the status bytes until POR = 0 and send all
subaddress bytes. The horizontal output signal is switched
1997 Jul 01 17
Page 18
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
TDA837x family
and NTSC TV-processors
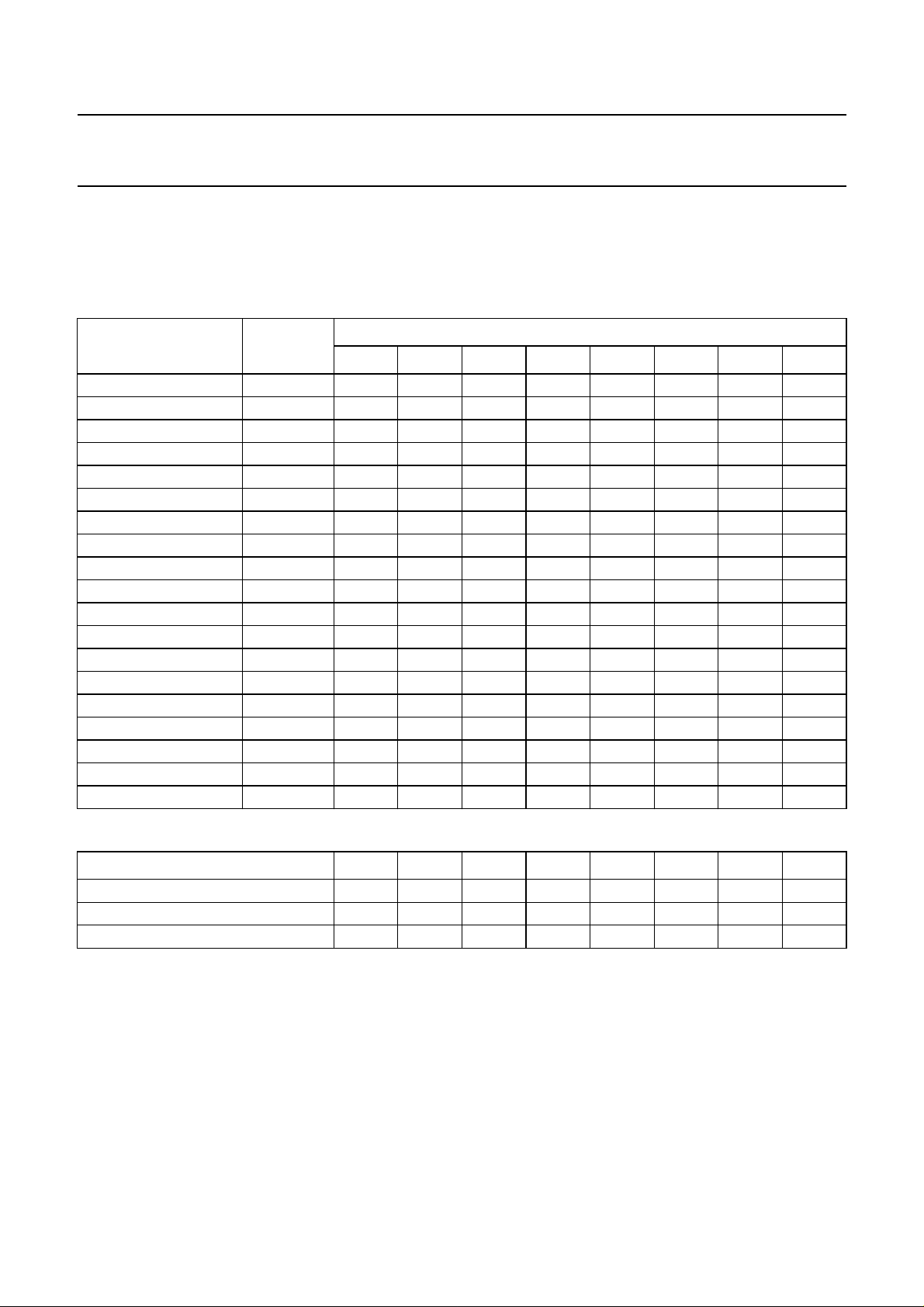
TDA8373
Valid subaddresses: 00 to 16 (subaddresses 04 to 07 are not used), subaddress FE is reserved for test purposes.
Auto-increment mode available for subaddresses.
Table 4 Inputs
FUNCTION
Control 0 00 INA INB INC 0 FOA FOB 0 0
Control 1 01 0 0 DL STB POC 0 1 1
Hue 02 AVL AKB A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Horizontal Shift (HS) 03 VIM GAI A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Vertical Slope (VS) 08 NCIN STM A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Vertical Amplitude (VA) 09 VID LBM A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
S-Correction (SC) 0A 0 EVG A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Vertical shift (VSH) 0B SBL PRD A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
White point R 0C 0 0 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
White point G 0D 0 0 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
White point B 0E MAT 0 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Peaking 0F 0000A3A2A1A0
Brightness 10 RBL 0 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Saturation 11 IE1 0 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Contrast 12 AFW IFS A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
AGC takeover 13 0 VSW A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Volume control 14 SM FAV A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Adjustment IF-PLL 15 L’FA A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Spare 16 00000000
SUB
ADDRESS
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
DATA BYTE
Table 5 Output status bytes (note 1)
OUTPUT ADDRESS D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
00 POR X X SL XPR CD2 CD1 CD0
01 NDF IN1 X IFI AFA AFB SXA SXB
02 X X X IVW X ID2 ID1 ID0
Note
1. X = don’t care.
1997 Jul 01 18
Page 19
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
TDA837x family
and NTSC TV-processors
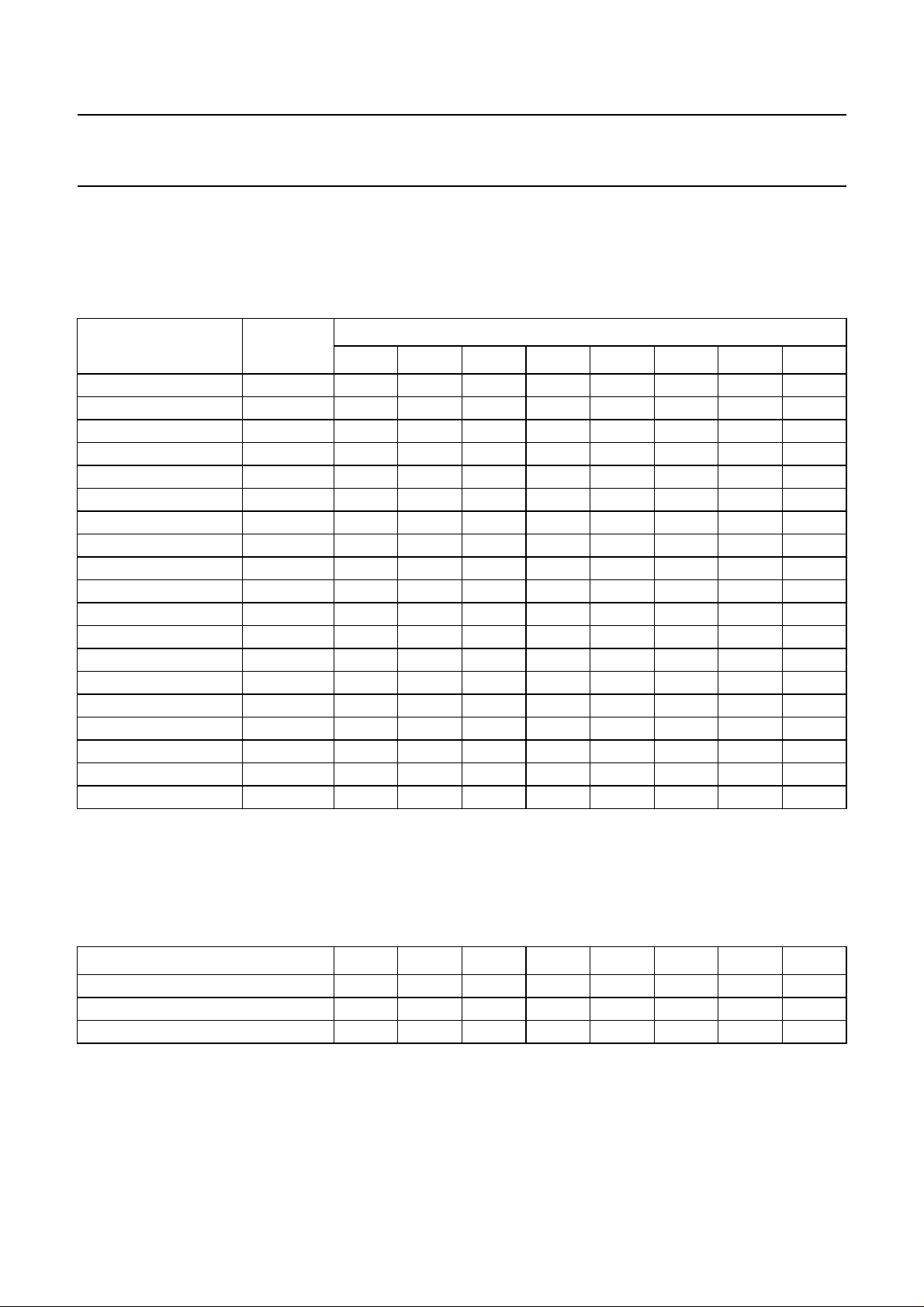
TDA8374, TDA8374AH and TDA8374BH
Valid subaddresses: 00 to 16 (subaddresses 04 to 07 are not used), subaddress FE is reserved for test purposes.
Auto-increment mode available for subaddresses.
Table 6 Inputs (notes 1 and 2)
FUNCTION
Control 0 00 INA INB INC 0 FOA FOB XA XB
Control 1 01 FORF FORS DL STB POC CM2 CM1 CM0
Hue 02 AVL AKB A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Horizontal Shift (HS) 03 VIM GAI A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Vertical Slope (VS) 08 NCIN STM A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Vertical Amplitude (VA) 09 VID LBM A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
S-Correction (SC) 0A 0 EVG A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Vertical shift (VSH) 0B SBL PRD A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
White point R 0C 0 0 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
White point G 0D 0 0 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
White point B 0E MAT 0 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Peaking 0F 0000A3A2A1A0
Brightness 10 RBL 0 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Saturation 11 IE1 0 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Contrast 12 AFW IFS A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
AGC takeover 13 MOD VSW A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Volume control 14 SM FAV A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Adjustment IF-PLL 15 L’FA A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Spare 16 00000000
SUB
ADDRESS
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
DATA BYTE
Notes
1. The AVL and MOD bit are not available in the TDA8374A.
2. In the TDA8374B the AVL and MOD bit is also missing and the CM0 to CM2 and CD0 to CD2 bits have less
possibilities because this IC can only decode PAL or PAL/SECAM signals (when the TDA8395 is applied).
Table 7 Output status bytes (note 1)
OUTPUT ADDRESS D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
00 POR FSI X SL XPR CD2 CD1 CD0
01 NDF IN1 X IFI AFA AFB SXA SXB
02 X X X IVW X ID2 ID1 ID0
Note
1. X = don’t care.
1997 Jul 01 19
Page 20

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
TDA837x family
and NTSC TV-processors
TDA8375 and TDA8375AH
Valid subaddresses: 00 to 16, subaddress FE is reserved for test purposes. Auto-increment mode available for
subaddresses.
Table 8 Inputs
FUNCTION
Control 0 00 INA INB INC 0 FOA FOB XA XB
Control 1 01 FORF FORS DL STB POC CM2 CM1 CM0
Hue 02 HBL AKB A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Horizontal Shift (HS) 03 VIM GAI A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
E-W width (EW) 04 0 0 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
E-W Parabola/Width (PW) 05 0 0 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
E-W Corner Parabola (CP) 06 0 0 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
E-W trapezium (TC) 07 0 0 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Vertical Slope (VS) 08 NCIN STM A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Vertical Amplitude (VA) 09 VID LBM A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
S-Correction (SC) 0A HCO EVG A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Vertical shift (VSH) 0B SBL PRD A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
White point R 0C 0 0 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
White point G 0D 0 0 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
White point B 0E MAT 0 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Peaking 0F 0000A3A2A1A0
Brightness 10 RBL COR A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Saturation 11 IE1 0 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Contrast 12 AFW IFS A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
AGC takeover 13 MOD VSW A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Volume control 14 SM FAV A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Adjustment IF-PLL 15 L’FA A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Vertical zoom (VX)
(1)
SUB
ADDRESS
16 0 0 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
DATA BYTE
Note
1. The vertical zoom byte and the HBL bit are active only in the TDA8375.
Table 9 Output status bytes (note 1)
OUTPUT ADDRESS D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
00 POR FSI X SL XPR CD2 CD1 CD0
01 NDF IN1 X IFI AFA AFB SXA SXB
02 X X X IVW X ID2 ID1 ID0
Note
1. X = don’t care.
1997 Jul 01 20
Page 21

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
TDA837x family
and NTSC TV-processors
TDA8377 and TDA8377A
Valid subaddresses: 00 to 16, subaddress FE is reserved for test purposes. Auto-increment mode available for
subaddresses.
Table 10 Inputs
FUNCTION
Control 0 00 INA INB INC 0 FOA FOB 0 1
Control 1 01 0 0 DL STB POC 0 1 1
Hue 02 HBL AKB A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Horizontal Shift (HS) 03 VIM GAI A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
E-W width (EW) 04 0 0 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
E-W Parabola/Width (PW) 05 0 0 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
E-W Corner Parabola (CP) 06 0 0 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
E-W trapezium (TC) 07 0 0 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Vertical Slope (VS) 08 NCIN STM A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Vertical Amplitude (VA) 09 VID 0 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
S-Correction (SC) 0A HCO EVG A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Vertical shift (VSH) 0B SBL PRD A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
White point R 0C 0 0 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
White point G 0D 0 0 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
White point B 0E MAT 0 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Peaking 0F 0000A3A2A1A0
Brightness 10 RBL COR A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Saturation 11 IE1 0 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Contrast 12 AFW IFS A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
AGC takeover 13 0 VSW A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Volume control 14 SM FAV A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Adjustment IF-PLL 15 L’FA A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Vertical zoom (VX)
(1)
SUB
ADDRESS
16 0 0 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
DATA BYTE
Note
1. The vertical zoom byte and the HBL bit are active only in the TDA8377.
Table 11 Output status bytes (note 1)
OUTPUT ADDRESS D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
00 POR X X SL XPR CD2 CD1 CD0
01 NDF IN1 X IFI AFA AFB SXA SXB
02 X X X IVW X ID2 ID1 ID0
Note
1. X = don’t care.
1997 Jul 01 21
Page 22
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
TDA837x family
and NTSC TV-processors
INPUT CONTROL BITS
Table 12 Source select
INA INB INC
0 0 0 internal CVBS plus audio internal CVBS
0 0 1 external CVBS plus audio external CVBS
0 1 0 Y/C plus external audio Y/C (Y plus C)
0 1 1 CVBS3 plus external audio CVBS3
1 0 0 Y/C plus internal audio internal CVBS
1 1 0 Y/C plus external audio external CVBS
Table 13 Phase 1 (ϕ-1) time constant
FOA FOB MODE
0 0 normal
0 1 slow and gated
1 0 slow/fast and gated
1 1 fast
SELECTED SIGNALS
(DECODER AND AUDIO)
SWITCH OUTPUT
Table 14 Crystal indication
XA XB CRYSTAL
0 0 two 3.6 MHz crystals
0 1 one 3.6 MHz crystal (pin 34)
1 0 one 4.4 MHz crystal (pin 35)
1 1 3.6 MHz and 4.4 MHz crystals (pins 34 and 35)
Table 15 Forced field frequency TDA8374 and TDA8375
FORF FORS FIELD FREQUENCY
0 0 auto (60 Hz when line not synchronized)
0 1 60 Hz; note 1
1 0 keep last detected field frequency
1 1 auto (50 Hz when line not synchronized)
Note
1. When switched to this mode while locked to a 50 Hz signal, the divider will only switch to forced 60 Hz when an
out-of-sync is detected in the horizontal PLL.
1997 Jul 01 22
Page 23

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
and NTSC TV-processors
Table 16 Interlace
DL STATUS
0 interlace
1 de-interlace
Table 17 Standby
STB MODE
0 standby
1 normal
Table 18 Synchronization mode
POC MODE
0 synchronization active
1 synchronization not active
Table 19 Colour decoder mode
CM2 CM1 CM0 DECODER MODE
0 0 0 not forced, own intelligence, two
crystals
0 0 1 forced crystal pin 34
(PAL/NTSC)
0 1 0 forced crystal pin 34 (PAL)
0 1 1 forced crystal pin 34 (NTSC)
1 0 0 forced crystal pin 35
(PAL/NTSC)
1 0 1 forced crystal pin 35 (PAL)
1 1 0 forced crystal pin 35 (NTSC)
1 1 1 forced SECAM crystal pin 35
Table 20 Automatic volume levelling
(TDA8373 and TDA8374)
AVL LEVEL
0 automatic volume levelling not active
1 automatic volume levelling active
Table 21 RGB blanking mode (TDA8375 and TDA8377)
HBL MODE
0 normal blanking with horizontal blanking
pulse
1 wider blanking to obtain well defined edges
TDA837x family
Table 22 Black current stabilization
AKB STABILIZATION
0 black-current stabilization on
1 black-current stabilization off
Table 23 Video identification mode
VIM VIDEO IDENT MODE
0 video identification coupled to the internal
CVBS input (pin 13)
1 video identification coupled to the selected
CVBS input
Table 24 Gain of luminance channel
GAI GAIN
0 normal gain of luminance channel
[V
= 1.0 V (b-w)]
27
1 high gain of luminance channel
[V
= 0.45 V (p-p)]
27
Table 25 Vertical divider mode
NCIN VERTICAL DIVIDER MODE
0 normal operation of the vertical divider
1 vertical divider switched to search window
Table 26 Search tuning mode
STM SEARCH TUNING MODE
0 normal operation
1 reduced sensitivity of the coincidence
detector (bit SL)
Table 27 Video identification mode
VID VIDEO IDENT MODE
0 video identification switches phase 1 loop on
and off
1 video identification not active
Table 28 Long blanking mode (TDA8374 and TDA8375)
LBM BLANKING MODE
0 blanking adapted to standard (50 or 60 Hz)
1 fixed blanking in accordance with 50 Hz
standard
1997 Jul 01 23
Page 24

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
and NTSC TV-processors
Table 29 EHT tracking mode (TDA8375 and TDA8377)
HCO TRACKING MODE
0 EHT tracking only on vertical
1 EHT tracking on vertical and E-W
Table 30 Enable vertical guard (RGB blanking)
EVG VERTICAL GUARD MODE
0 vertical guard not active
1 vertical guard active
Table 31 Service blanking
SBL SERVICE BLANKING MODE
0 service blanking off
1 service blanking on
Table 32 Overvoltage input mode
PRD OVERVOLTAGE MODE
0 overvoltage detection mode
1 overvoltage protection mode
Table 33 PAL/NTSC or NTSC matrix
(TDA8374 and TDA8375)
TDA837x family
Table 36 Noise coring peaking
(TDA8375 and TDA8377))
COR MODE
0 noise coring off
1 noise coring on
Table 37 Enable fast blanking
IE1 FAST BLANKING
0 fast blanking not active
1 fast blanking active
Table 38 AFC window
AFW AFC WINDOW
0 normal window
1 enlarged window
Table 39 IF sensitivity
IFS IF SENSITIVITY
0 normal sensitivity
1 reduced sensitivity
Table 40 Modulation standard (TDA8374 and TDA8375)
MAT MATRIX
0 matrix adapted to standard
(NTSC = Japanese)
1 PAL matrix
Table 34 PAL/NTSC or NTSC matrix
(TDA8373 and TDA8377)
MAT MATRIX
0 Japanese matrix
1 USA matrix
Table 35 RGB blanking
RBL MODE
0 blanking not active
1 blanking active
MOD MODULATION
0 negative modulation
1 positive modulation
Table 41 Video mute
VSW STATE
0 normal operation
1 IF video signal switched off
Table 42 Sound mute
SM STATE
0 normal operation
1 sound muted
1997 Jul 01 24
Page 25

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
and NTSC TV-processors
Table 43 Fixed audio volume
FAV STATE
0 normal volume control
1 audio output level fixed
Table 44 Demodulator frequency adjustment
L’FA STATE
0 normal IF frequency
1 frequency shift for L’ standard
UTPUT CONTROL BITS
O
Table 45 Power-on-reset
POR MODE
0 normal mode
1 power-down mode
TDA837x family
Table 50 Output vertical guard
NDF VERTICAL OUTPUT STAGE
0 vertical output stage OK
1 failure in vertical output stage
Table 51 Indication RGB insertion
IN1 RGB INSERTION
0 no insertion
1 insertion
Table 52 Output video identification
IFI VIDEO SIGNAL
0 no video signal identified
1 video signal identified
Table 53 AFC output
Table 46 Field frequency (TDA8374 and TDA8375)
FSI FREQUENCY
050Hz
160Hz
Table 47 Phase 1 lock indication
SL INDICATION
0 not locked
1 locked
Table 48 X-ray protection
XPR OVERVOLTAGE
0 no overvoltage detected
1 overvoltage detected
Table 49 Colour decoder mode (TDA8374 and TDA8375)
CD2 CD1 CD0 STANDARD
0 0 0 no colour standard identified
0 0 1 NTSC with crystal at pin 34
0 1 0 PAL with crystal at pin 35
0 1 1 SECAM
1 0 0 NTSC with crystal at pin 35
1 0 1 PAL with crystal at pin 34
1 1 0 spare
1 1 1 spare
AFA AFB CONDITION
0 0 outside window; too low
0 1 outside window; too high
1 0 inside window; below reference
1 1 inside window; above reference
Table 54 Crystal indication
SXA SXB CRYSTAL
0 0 two 3.6 MHz crystals
0 1 one 3.6 MHz crystal
1 0 one 4.4 MHz crystal
1 1 3.6 MHz and 4.4 MHz crystals
Table 55 Condition vertical divider
IVW VIDEO SIGNAL
0 no standard video signal detected
1 standard video signal detected
(525 or 625 lines)
1997 Jul 01 25
Page 26

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
TDA837x family
and NTSC TV-processors
Table 56 IC version indication
ID2 ID1 ID0 STANDARD
0 0 0 TDA8373
0 0 1 TDA8377
0 1 0 TDA8374B
0 1 1 TDA8374A
1 0 0 TDA8374
1 0 1 TDA8377A
1 1 0 TDA8375A
1 1 1 TDA8375
LIMITING VALUES
In accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 134).
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. MAX. UNIT
V
P
T
stg
T
amb
T
sld
T
j
V
es
supply voltage − 9.0 V
storage temperature −25 +150 °C
operating ambient temperature 0 70 °C
soldering temperature for 5 s − 260 °C
operating junction temperature − 150 °C
electrostatic handling HBM; all pins; notes 1 and 2 −2000 +2000 V
MM; all pins; notes 1 and 3 −200 +200 V
Notes
1. All pins are protected against ESD by means of internal clamping diodes.
2. Human Body Model (HBM): R = 1.5 kΩ; C = 100 pF.
3. Machine Model (MM): R = 0 Ω; C = 200 pF.
QUALITY SPECIFICATION
In accordance with
Handbook”
. The handbook can be ordered using the code 9397 750 00192.
“SNW-FQ-611E”
. The number of the quality specification can be found in the
Latch-up
• I
• I
≥ 100 mA or ≥1.5V
trigger
≤−100 mA or ≤−0.5V
trigger
P(max)
P(max)
.
“Quality Reference
1997 Jul 01 26
Page 27

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
TDA837x family
and NTSC TV-processors
CHARACTERISTICS
V
=8V; T
P
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Supplies
AIN SUPPLY (PIN 12)
M
V
P1
I
P1
P
tot
HORIZONTAL OSCILLATOR SUPPLY (PIN 37)
V
P2
I
P2
IF circuit
V
ISION IF AMPLIFIER INPUTS (PINS 48 AND 49)
V
i(rms)
R
i
C
i
∆G
v
V
i(max)(rms)
PLL DEMODULATOR (PLL FILTER ON PIN 5); note 3
f
PLL
f
cr(PLL)
t
acq(PLL)
∆f
VCO(T)
f
tune(VCO)
∆f
DAC
f
shift(L’)
=25°C; the pin numbers given refer to the SDIP56 package; unless otherwise specified.
amb
supply voltage 7.2 8.0 8.8 V
supply current − 110 − mA
total power dissipation − 900 − mW
supply voltage 7.2 8.0 8.8 V
supply current − 6 − mA
input sensitivity (RMS value) note 1
f
= 38.90 MHz − 70 100 µV
i
f
= 45.75 MHz − 70 100 µV
i
= 58.75 MHz − 70 100 µV
f
i
input resistance (differential) note 2 − 2 − kΩ
input capacitance (differential) note 2 − 3 − pF
voltage gain control range 64 −−dB
maximum input signal
100 150 − mV
(RMS value)
PLL frequency range 32 − 60 MHz
PLL catching range − 2 − MHz
PLL acquisition time −−20 ms
VCO frequency variation with
note 4 − tbf − kHz/K
temperature
VCO tuning range via the I2C-bus − 2.5 − MHz
frequency variation per step of
− 20 − kHz
the DAC (A0 to A6)
frequency shift with the L’ FA bit − 5.5 − MHz
1997 Jul 01 27
Page 28

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
TDA837x family
and NTSC TV-processors
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
VIDEO AMPLIFIER OUTPUT (PIN 6); note 5
V
o
zero signal output level negative modulation;
note 6
positive modulation; note 6 − 2.0 − V
V
V
6(ts)
6(w)
top sync level negative modulation 1.9 2.0 2.1 V
white level positive modulation when
available
∆V
6
difference in amplitude between
negative and positive
modulation
Z
o
I
bias
video output impedance − 50 −Ω
internal bias current of NPN
emitter follower output transistor
I
source(max)
B bandwidth of demodulated
maximum source current −−5mA
at −3dB 6 9 − MHz
output signal
G
diff
ϕ
diff
NL
vid
V
clamp
N
th(clamp)
differential gain note 7 − 25%
differential phase notes 4 and 7 −−5 deg
video non-linearity note 8 −−5%
white spot clamp level − 5.3 − V
noise inverter threshold clamp
note 9 − 1.7 − V
level
N
ins
noise inverter insertion level note 9 − 2.6 − V
δ intermodulation notes 4 and 10
blue V
yellow V
= 0.92 or 1.1 MHz 60 66 − dB
o
V
= 2.66 or 3.3 MHz 60 66 − dB
o
= 0.92 or 1.1 MHz 56 62 − dB
o
= 2.66 or 3.3 MHz 60 66 − dB
V
o
S/N signal-to-noise ratio notes 4 and 11
V
=10mV 52 60 − dB
i
at end of control range 52 61 − dB
V
V
6(rc)
6(2H)
residual carrier signal note 4 − 5.5 − mV
residual 2nd harmonic of carrier
note 4 − 2.5 − mV
signal
− 4.7 − V
− 4.5 − V
− 015%
1.0 −−mA
1997 Jul 01 28
Page 29

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
TDA837x family
and NTSC TV-processors
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
IF AND TUNER AGC; note 12
Timing of IF-AGC with a 2.2µF capacitor (pin 53)
modulated video interference 30% AM for 1 to 100 mV;
t
res(IFinc)
response time to an IF input
signal amplitude increase of
52 dB
t
res(IFdec)
response to an IF input signal
amplitude decrease of 52 dB
I
53
allowed leakage current of the
AGC capacitor
Tuner take-over adjustment (via I2C-bus)
V
i(min)(rms)
minimum starting level for tuner
take-over (RMS value)
V
i(max)(rms)
maximum starting level for tuner
take-over (RMS value)
Tuner control output (pin 54)
V
oAGC(max)
maximum tuner AGC output
voltage
V
o(sat)
I
oAGC(max)
output saturation voltage minimum tuner gain;
maximum tuner AGC output
swing
I
LI(RF)
∆V
i
leakage current RF AGC −−1µA
input signal variation for a
control current variation of 1 mA
AFC OUTPUT (VIA I2C-BUS); note 13
RES
w
sen
w
senL
AFC
AFC resolution − 2 − bits
window sensitivity 65 80 100 kHz
window sensitivity in large
window mode
VIDEO IDENTIFICATION OUTPUT (VIA I2C-BUS)
t
d
delay time of identification after
the AGC has stabilized on a
new transmitter
0 to 200 Hz (system B/G)
positive (when available)
and negative modulation
negative modulation − 50 − ms
positive modulation (when
available)
negative modulation −−10 µA
positive modulation (when
available)
maximum tuner gain;
note 2
I54=2mA
−−10 %
− 2 − ms
− 100 − ms
−−200 nA
− 0.4 0.8 mV
40 80 − mV
−−V
+1 V
P
−−300 mV
5 −−mA
0.5 2 4 dB
195 240 300 kHz
−−10 ms
1997 Jul 01 29
Page 30

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
TDA837x family
and NTSC TV-processors
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Sound circuit
DEMODULATOR PART
V
i(crPLL)(rms)
f
cr(PLL)
R
i
C
i
AMR AM rejection V
E-EMPHASIS
D
V
o(rms)
R
o
V
O
AUDIO ATTENUATOR CIRCUIT
V
o(rms)
V
oAVL(rms)
V
oFAV(rms)
R
o
V
O
THD total harmonic distortion note 17 −−0.5 %
PSRR power supply ripple rejection note 4 − tbf − dB
S/N
int
S/N
ext
T
dep(out)
CR control range tbf 80 tbf dB
VC
step
OSS suppression of output signal
V
shift
EXTERNAL AUDIO INPUT
V
i(rms)
R
i
input limiting voltage for PLL
− 12mV
catching range (RMS value)
PLL catching range note 14 4.2 − 6.8 MHz
input resistance note 2 − 8.5 − kΩ
input capacitance note 2 −−5pF
= 50 mV (RMS); note 15 60 66 − dB
i
output signal amplitude
note 14 − 500 − mV
(RMS value)
output resistance − 15 − kΩ
DC output voltage − 3 − V
controlled output signal
at −6 dB; note 14 500 700 900 mV
amplitude (RMS value)
output signal level when AVL is
note 16 300 400 500 mV
activated (RMS value)
output signal level when FAV is
note 14 − 500 − mV
activated (RMS value)
output resistance − 500 −Ω
DC output voltage − 3.3 − V
FAV = 1; note 18 −−tbf %
internal signal-to-noise ratio notes 4 and 19 − 60 − dB
external signal-to-noise ratio notes 4 and 19 − 80 − dB
temperature dependancy of
notes 4 and 20 −−tbf dB
output level
step size volume control − 1.5 − dB
control curve see Fig.8
− 80 − dB
when the mute is active
DC shift of the output level when
− 10 50 mV
the mute is activated
input signal amplitude
− 500 1500 mV
(RMS value)
input resistance − 25 − kΩ
1997 Jul 01 30
Page 31

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
TDA837x family
and NTSC TV-processors
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
G
v(in-out)
α
ct
AUTOMATIC VOLUME LEVELLING CIRCUIT (TDA8373 AND TDA8374 ONLY; CAPACITOR CONNECTED TO PIN 45)
G
max
G
min
I
att
I
dec
V
ctrl(max)
V
ctrl(min)
CVBS, Y/C, RGB, CD inputs and luminance input and output
CVBS
AND Y/C SWITCH (PINS 11, 13, 17 AND 38)
V
11(p-p)
I
17
SS
CVBS
V
10(p-p)
V
38(p-p)
Z
o
V
sync
RGB INPUTS (PINS 23, 24 AND 25)
V
23-25(p-p)
V
23-25(p-p)
∆V
o
I
23-25
∆t
d
FAST BLANKING (PIN 26)
V
i
V
26(max)
voltage gain between input and
maximum volume − 12 − dB
output
crosstalk between audio signals 60 −−
gain maximum boost; note 16 − 6 − dB
gain minimum boost −−14 − dB
attack charge current − 1 − mA
decay discharge current − 200 − nA
control voltage maximum boost − 1 − V
control voltage minimum boost − 5 − V
CVBS or Y input voltage
note 21 − 1.0 1.4 V
(peak-to-peak value)
CVBS input current − 4 −µA
suppression of non-selected
notes 4 and 22 50 −−dB
CVBS input signal
chrominance input voltage
notes 2 and 23 − 0.3 0.45 V
(burst amplitude) (peak-to-peak
value)
output signal amplitude
− 1.0 − V
(peak-to-peak value)
output impedance −−250 Ω
top sync level − 2.5 − V
input signal amplitude for an
note 24 − 0.7 0.8 V
output signal of 2 V
(black-to-white) (peak-to-peak
value)
input signal amplitude before
note 4 1.0 −−V
clipping occurs (peak-to-peak
value)
difference between black level
−−20 mV
of internal and external signals
at the outputs
input currents note 2 − 0.1 1 µA
delay difference for the three
note 4 − 0 − ns
channels
input voltage no data insertion −−0.3 V
data insertion 0.9 −−V
maximum input pulse insertion −−3.0 V
1997 Jul 01 31
Page 32

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
TDA837x family
and NTSC TV-processors
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
∆t
d(blank,RGB)
t
sw
I
26
SS
int
SS
ext
V
i
t
d(blank-RGB)
COLOUR DIFFERENCE INPUT SIGNALS (PINS 31 AND 32)
V
31(p-p)
V
32(p-p)
I
31,32
LUMINANCE INPUTS AND OUTPUTS (PINS 27 AND 28); note 25
V
27,28
delay difference of blanking and
note 4 −−50 ns
RGB signals
switching speed of blanking
− 10 − ns
circuit
input current −−0.2 mA
suppression of internal RGB
signals
suppression of external RGB
signals
insertion; fi= 0 to 5 MHz;
notes 4 and 22
no insertion;
fi= 0 to 5 MHz;
− 55 − dB
− 55 − dB
notes 4 and 22
input voltage to insert black level
4 −−V
at the RGB outputs to facilitate
‘On Screen Display’ signals
being applied to the outputs
delay between blanking input
−−80 ns
and RGB outputs
input signal amplitude (R − Y)
note 2 − 1.05 − V
(peak-to-peak value)
input signal amplitude (B − Y)
note 2 − 1.35 − V
(peak-to-peak value)
input current for both inputs note 2 − 0.1 1.0 µA
output signal amplitude
− 1 − V
(black-to-white)
Chrominance filters
C
HROMINANCE TRAP CIRCUIT; note 26
f
trap
trap frequency − f
osc
− MHz
QF trap quality factor note 27 − 2 −
CSR colour subcarrier rejection 20 −−dB
f
trap(SECAM)
trap frequency during SECAM reception − 4.3 − MHz
CHROMINANCE BAND-PASS CIRCUIT
f
c
Q
bp
centre frequency − 1.1f
osc
band-pass quality factor − 3 −
− MHz
Luminance processing
Y
DELAY LINE
t
d(Y)
B
del(int)
delay time note 4 − 480 − ns
bandwidth of internal delay line note 4 8 −−MHz
PEAKING CONTROL; note 28
t
W
width of preshoot or overshoot at 50% of pulse; note 8 − 160 − ns
1997 Jul 01 32
Page 33

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
TDA837x family
and NTSC TV-processors
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
S
c(th)
OS overshoot at maximum peaking positive − 45 − %
neg/pos ratio of negative and positive
N
OISE CORING STAGE
S coring range − 15 − IRE
BLACK LEVEL STRETCHER; note 29
BL
shift(max)
BL
shift
Horizontal and vertical synchronization and drive circuits
peaking signal compression
− 50 − IRE
threshold
negative − 80 − %
− 1.8 −
overshoots
peaking control curve 16 steps see Fig.9
maximum black level shift 15 21 27 IRE
level shift at 100% of peak white −1 0 +1 IRE
at 50% of peak white −1 − +3 IRE
at 15% of peak white 6 8 10 IRE
S
YNC VIDEO INPUT (PINS 11, 13 AND 17)
V
11,13,17
SL
HS
SL
VS
sync pulse amplitude note 2 50 300 350 mV
slicing level for horizontal sync note 30 − 50 − %
slicing level for vertical sync note 30 − 30 − %
HORIZONTAL OSCILLATOR
f
∆f
fr
fr
free running frequency − 15625 − Hz
spread on free running
−−±2%
frequency
∆f/∆V
P
frequency variation with respect
VP= 8.0 V ±10%; note 4 − 0.2 0.5 %
to the supply voltage
∆f
(max)(T)
maximum frequency variation
T
= 0 to 70 °C; note 4 −−80 Hz
amb
with temperature
FIRST CONTROL LOOP (FILTER CONNECTED TO PIN 43); note 31
f
hr(PLL)
f
cr(PLL)
S/N signal-to-noise ratio of the video
holding range PLL −±0.9 ±1.2 kHz
catching range PLL note 4 ±0.6 ±0.9 − kHz
− 20 − dB
input signal at which the time
constant is switched
HYS hysteresis at the switching point − 1 − dB
S
ECOND CONTROL LOOP (CAPACITOR CONNECTED TO PIN 42)
∆ϕ
t
cr
/∆ϕ
i
o
control sensitivity − 150 −µs/µs
control range from start of
11 12 −µs
horizontal output to flyback at
nominal shift position
t
shift
horizontal shift range 63 steps ±2 −−µs
1997 Jul 01 33
Page 34

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
TDA837x family
and NTSC TV-processors
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
∆ϕ control sensitivity for dynamic
phase compensation
V
prot
voltage to switch-on the flash
note 32 6 −−V
protection
I
i(prot)
input current during protection −−1mA
HORIZONTAL OUTPUT (PIN 40); note 33
V
OL
I
o(max)
LOW level output voltage Io=10mA −−0.3 V
maximum allowed output
current
V
o(max)
maximum allowed output
voltage
δ duty factor note 4 − 50 − %
V
= HIGH − 75 − %
o
f
sw
frequency during switch-on and
switch-off
t
sw
switch-on time − 50 − ms
maximum RGB drive − 100 − ms
minimum RGB drive − 50 − ms
FLYBACK PULSE INPUT AND SANDCASTLE OUTPUT (PIN 41)
I
i(fb)
required input current during the
note 4 100 − 300 µA
flyback pulse
V
41
output voltage during burst key 4.8 5.3 5.8 V
during blanking 1.8 2.0 2.2 V
V
i(clamp)
clamped input voltage during
flyback
t
W
pulse width burst key pulse 3.3 3.5 3.7 µs
vertical blanking; note 34 − 14 − lines
t
d(bk-sync)
delay of start of burst key to start
of sync
VERTICAL OSCILLATOR; TDA8373 AND TDA8377 OPERATING AT 60 HZ; note 35
f
f
fr
lock
free running frequency − 50/60 − Hz
frequency locking range 45 − 64.5 Hz
divider value not locked − 625/525 − lines
LR locking range 488 − 722 lines/
V
ERTICAL RAMP GENERATOR (PINS 51 AND 52)
V
51(p-p)
I
dch
I
ch
sawtooth amplitude
(peak-to-peak value)
discharge current − 1 − mA
charge current set by external
VS = 1FH;
C=100nF;R=39kΩ
note 36 − 19 −µA
resistor
V
slope
vertical slope control range (63 steps) −20 − +20 %
− 5.3 −µs/V
10 −−mA
−−V
− 2f
H
P
− Hz
V
2.6 3.0 3.4 V
5.2 5.4 5.6 µs
frame
− 3.5 − V
1997 Jul 01 34
Page 35

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
TDA837x family
and NTSC TV-processors
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
∆I
ch
V
rampL
VERTICAL DRIVE OUTPUTS (PINS 46 AND 47)
I
o(dif)(p-p)
I
CM
V
46,47
EHT TRACKING/OVERVOLTAGE PROTECTION (PIN 50)
∆V
50
m
scan
v
sen
EW
sen
I
eq
V
50
DE-INTERLACE
ff
d
E-W WIDTH (TDA8375A, TDA8377A, TDA8375 AND TDA8377); note 37
CR control range 63 steps 100 − 65 %
I
eq
V
oEW
I
oEW
E-W PARABOLA/WIDTH (TDA8375A, TDA8377A, TDA8375 AND TDA8377)
CR control range 63 steps 0 − 22 %
I
eq
E-W CORNER/PARABOLA (TDA8375A, TDA8377A, TDA8375 AND TDA8377)
CR control range 63 steps −43 − 0%
I
eq
E-W TRAPEZIUM (TDA8375A, TDA8377A, TDA8375 AND TDA8377)
CR control range 63 steps −5 − +5 %
I
eq
VERTICAL AMPLITUDE
CR control range 63 steps; SC = 00H 80 − 120 %
I
eq(dif)(p-p)
VERTICAL SHIFT
CR control range 63 steps −5 − +5 %
I
eq(dif)
charge current increase f = 60 Hz − 20 − %
LOW voltage level of ramp in
− 2.07 − V
the normal or expand mode
differential output current
VA = 1FH − 0.95 − mA
(peak-to-peak value)
common mode current − 400 −µA
output voltage range 0 − 4.0 V
input voltage range 1.2 − 2.8 V
scan modulation range −5 − +5 %
vertical sensitivity − 6.3 − %/V
E-W sensitivity when switched on −−6.3 − %/V
E-W equivalent output current +100 −−100 µA
overvoltage detection level note 32 − 3.9 − V
first field delay − 0.5H −
equivalent E-W output current 0 − 700 µA
E-W output voltage range 1.0 − 8.0 V
E-W output current range 0 − 1200 µA
equivalent E-W output current E-W = 3FH 0 − 440 µA
equivalent E-W output current PW = 3FH; E-W = 3FH −190 − 0 µA
equivalent E-W output current −100 − +100 µA
equivalent differential vertical
SC = 00H 760 − 1140 µA
drive output current
(peak-to-peak value)
equivalent differential vertical
−50 − +50 µA
drive output current
1997 Jul 01 35
Page 36

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
TDA837x family
and NTSC TV-processors
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
S-CORRECTION
CR control range 63 steps 0 − 30 %
VERTICAL EXPAND (ZOOM) MODE (TDA8375 AND TDA8377); note 38
Output current variation compared with nominal scan
∆I
o
I
o(lim)
Colour demodulation part
C
HROMINANCE AMPLIFIER
CR
ACC
∆V
ACC
th
on
hys
off
ACL
CIRCUIT; note 40
R
EFERENCE PART
vertical expand factor 0.75 1.38 A
output current limiting and RGB
1.08 A
blanking
ACC control range note 39 26 −−dB
change in amplitude of the
−−2dB
output signals over the ACC
range
threshold colour killer ON −30 −−dB
hysteresis colour killer OFF at strong signal conditions;
− +3 − dB
S/N ≥ 40 dB; note 4
at noisy input signals;
− +1 − dB
note 4
chrominance burst ratio at which
− 3.0 −
the ACL starts to operate
Phase-locked loop; note
f
cr
frequency catching range ±360 ±600 − Hz
∆ϕ phase shift for a ±400 Hz
41
note 4 −−2 deg
deviation of the oscillator
frequency
Oscillator
TC
osc
temperature coefficient of the
note 4 − 2.0 2.5 Hz/K
oscillator frequency
∆f
osc
oscillator frequency deviation
VP=8V±10%; note 4 −−250 Hz
with respect to the supply
R
neg(min)
C
L(max)
minimum negative resistance −−1kΩ
maximum load capacitance −−15 pF
HUE CONTROL
CR
hue
hue control range 63 steps ±35 ±40 − deg
hue control curve see Fig.10
1997 Jul 01 36
Page 37

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
TDA837x family
and NTSC TV-processors
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
∆hue hue variation for ±10% V
P
∆hue(T) hue variation with temperature T
DEMODULATORS (PINS 29 AND 30)
V
30(p-p)
(R − Y) output signal amplitude
(peak-to-peak value)
V
29(p-p)
(B − Y) output signal amplitude
(peak-to-peak value)
G gain ratio between both
demodulators G
G
(R − Y)
(B − Y)
and
∆V spread of signal amplitude ratio
PAL/NTSC
Z
o
output impedance between
(R − Y) and (B − Y)
B bandwidth of demodulators −3 dB; note 43 − 650 − kHz
V
29,30(p-p)
residual carrier output
(peak-to-peak value)
V
30(p-p)
H/2 ripple at (R − Y) output
(peak-to-peak value)
∆V
o(T)
change of output signal
amplitude with temperature
∆V
o/VP
change of output signal
amplitude with supply voltage
E
ϕ
phase error in the demodulated
signals
COLOUR DIFFERENCE MATRICES (IN CONTROL CIRCUIT) TDA8374 AND TDA8375
note 4 − 0 − deg
= 0 to 70 °C; note 4 − 0 − deg
amb
TDA8374 and TDA8375;
− 0.525 − V
note 42
TDA8374 and TDA8375;
− 0.675 − V
note 42
1.60 1.78 1.96
TDA8374 and TDA8375;
−1 − +1 dB
note 4
note 2 − 500 −Ω
fc; (R − Y) output 5 mV
f
; (B − Y) output −−5mV
c
2f
; (R − Y) output 5 mV
c
2f
; (B − Y) output −−5mV
c
−−25 mV
note 4 − 0.1 − %/K
note 4 −−±0.1 dB
note 4 −−±5 deg
PAL or (SECAM when TDA8395 is applied); (R−Y) and (B−Y) not affected
(G − Y)/
(R − Y)
(G − Y)/
(B − Y)
ratio of demodulated signals −−0.51
±10%
ratio of demodulated signals −−0.19
±25%
NTSC mode; the colour-difference matrix results in the following signals (nominal hue setting)
(B − Y) (B − Y) signal 2.03/0° 2.03U
R
(R − Y) (R − Y) signal 1.59/95°−0.14UR+ 1.58V
(G − Y) (G − Y) signal 0.61/240°−0.31UR− 0.53V
1997 Jul 01 37
−
−
R
R
Page 38

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
TDA837x family
and NTSC TV-processors
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
COLOUR DIFFERENCE MATRICES (IN CONTROL CIRCUIT) TDA8373 AND TDA8377
MAT = 0; the colour-difference matrix results in the following signals (nominal hue setting)
(B − Y) (B − Y) signal 2.03/0° 2.03U
(R − Y) (R − Y) signal 1.59/95°−0.14UR+ 1.58V
(G − Y) (G − Y) signal 0.61/240°−0.31UR− 0.53V
MAT = 1; the colour-difference matrix results in the following signals (nominal hue setting)
(B − Y) (B − Y) signal 1.14/−10° 1.12UR− 0.20V
(R − Y) (R − Y) signal 1.14/100°−0.20UR+ 1.12V
(G − Y) (G − Y) signal 0.30/235°−0.17UR− 0.25V
REFERENCE SIGNAL OUTPUT (PIN 33); note 44
f
ref
V
33(p-p)
reference frequency − 3.58 or
output signal amplitude
(peak-to-peak value)
COMMUNICATION WITH THE TDA8395 (TDA8374 AND TDA8375 ONLY)
V
o
output level PAL/NTSC identified − 1.5 − V
no PAL/NTSC identified;
SECAM (by TDA8395)
identified
I
31
required current to stop
PAL/NTSC identification circuit
during SECAM
R
R
R
R
R
R
− MHz
4.43
0.2 0.25 0.3 V
− 5.0 − V
150 −−µA
Control part
S
ATURATION CONTROL; note 24 (SEE Fig.11)
CR
sat
saturation control range 63 steps 52 −−dB
CONTRAST CONTROL; note 24 (SEE Fig.12)
CR
con
contrast control range 63 steps − 15 − dB
tracking between the three
channels over a control range of
10 dB
RIGHTNESS CONTROL (SEE Fig.13)
B
CR
bri
brightness control range 63 steps −±0.7 − V
RGB OUTPUT SIGNALS (PINS 19 TO 21)
V
19-21(p-p)
output signal amplitude at
nominal luminance input signal,
nominal contrast and white point
adjustment (peak-to-peak value)
V
o(max)(p-p)
output signal at maximum white
point setting (peak-to-peak
value)
−−0.5 dB
note 24 1.8 2.1 2.4 V
− 3.0 − V
1997 Jul 01 38
Page 39

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
TDA837x family
and NTSC TV-processors
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
V
BW(max)(p-p)
V
WP(max)(p-p)
V
red(p-p)
∆V
blank
t
W(blank)
I
bias
I
o
Z
o
CR
bl
V
bl
V
o(4L)
∆bl(T) variation of black level with
∆bl relative variation in black level
S/N signal-to-noise ratio of the
V
r(p-p)
maximum signal amplitude
note 45 − 2.6 − V
(black-to-white)
maximum signal amplitude at
− 3.6 − V
maximum white point setting
(peak-to-peak value)
output signal amplitude for the
tbf 2.1 tbf V
‘red’ channel at nominal settings
for contrast and saturation
control and no luminance signal
to the input (R − Y, PAL)
(peak-to-peak value)
difference between blanking
0.7 0.8 0.9 V
level measuring pulse
width of the video blanking pulse
when the HBL bit is active
TDA8375, TDA8377,
TDA8375A and
14.4 14.7 15.0 µs
TDA8377A; note 46
internal bias current of NPN
− 1.5 − mA
emitter follower output transistor
available output current − 5 − mA
output impedance − 150 −Ω
control range of the black
current stabilization
at Vbl= 2.5 V and nominal
brightness and white-point
−−±1V
adjustment (with respect to
the measuring pulse)
black level shift with picture
note 4 −−20 mV
content
output voltage of the 4-L pulse
− 4.2 − V
after switch-on
note 4 − 1.0 − mV/K
temperature
note 4
between the three channels
during variations of
supply voltage (±10%) nominal controls −−20 mV
saturation (50 dB) nominal contrast −−20 mV
contrast (15 dB) nominal saturation −−20 mV
brightness (±0.5 V) nominal controls −−20 mV
temperature (range 40 °C) −−20 mV
RGB input; note 47 60 −−dB
output signals
residual voltage at the RGB
outputs (peak-to-peak value)
CVBS input; note 47 50 −−dB
at f
at 2f
osc
plus higher
osc
−−15 mV
−−15 mV
harmonics in RGB outputs
1997 Jul 01 39
Page 40

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
TDA837x family
and NTSC TV-processors
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
B bandwidth of output signals RGB input at −3dB 8 −−MHz
CVBS input at −3 dB;
f
= 3.6 MHz
osc
CVBS input at −3 dB;
f
= 4.44 MHz
osc
S-VHS input; at −3dB 5 −−MHz
W
HITE-POINT ADJUSTMENT
I2C-bus setting for nominal gain HEX code − 20H −
G
inc(max)
G
dec(max)
maximum increase of the gain HEX code 3FH 40 50 60 %
maximum decrease of the gain HEX code 00H 35 45 55 %
BLACK CURRENT STABILIZATION (PIN 18); note 48
I
bias
bias current for the picture tube
nominal white point setting − 10 −µA
cathode
I
L
I
scan(max)
Z
i
acceptable leakage current −±100 −µA
maximum current during scan − 0.3 − mA
input impedance − 15 − kΩ
BEAM CURRENT LIMITING/VERTICAL GUARD INPUT (PIN 22); note 49
V
CR
contrast reduction starting
voltage
V
difCR
voltage difference for full
contrast reduction
V
BR
brightness reduction starting
voltage
V
difBR
voltage difference for full
brightness reduction
V
bias
Z
int
V
det
I
i(min)
internal bias voltage − 3.3 − V
internal impedance − 40 − kΩ
detection level for vertical guard − 3.65 − V
minimum input current to
activate the guard circuit
I
i(max)
maximum allowable input
current
− 2.8 − MHz
− 3.5 − MHz
− 3.1 − V
− 2 − V
− 1.6 − V
− 1 − V
− 100 −µA
− 1 − mA
Notes
1. On set AGC.
2. This parameter is not tested during production and is just given as application information for the designer of the
television receiver.
3. Loop bandwidth BL= 60 kHz (natural frequency fn= 15 kHz; damping factor d = 2; calculated with sync level as FPLL
input signal level). LC-VCO circuit: Q0≥ 60, C
= 12 pF, C
ext
=20pF.
int
4. This parameter is not tested during production but is guaranteed by the design and qualified by means of matrix
batches which are made in the pilot production period.
5. Measured at 10 mV (RMS) top sync input signal.
6. So called projected zero point, i.e. with switched demodulator.
1997 Jul 01 40
Page 41

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
TDA837x family
and NTSC TV-processors
7. Measured in accordance with the test line given in Fig.14. For the differential phase test the peak white setting is
reduced to 87%.
a) The differential gain is expressed as a percentage of the difference in peak amplitudes between the largest and
smallest value relative to the subcarrier amplitude at blanking level.
b) The phase difference is defined as the difference in degrees between the largest and smallest phase angle.
8. This figure is valid for the complete video signal amplitude (peak white-to-black), see Fig.15.
9. The noise inverter is only active in the ‘strong signal mode’ (no noise detected in the incoming signal).
10. The test set-up and input conditions are given in Fig.16. The figures are measured with an input signal of
10 mV (RMS).
V
11. Measured with a source impedance of 75 Ω, where:
12. The AGC response time is also dependent on the acquisition time of the PLL demodulator. The values given are valid
when the PLL is in lock.
13. The AFC control voltage is obtained from the control voltage of the VCO of the PLL demodulator. The tuning
information is supplied to the tuning system via the I2C-bus. Two bits are reserved for this function. The AFC value
is valid only when the SL bit = 1.
14. Vi= 100 mV (RMS), FM: 1 kHz, ∆f=±50 kHz.
15. Vi= 50 mV (RMS), f = 4.5 to 5.5 MHz; FM: 70 Hz, ±50 kHz deviation; AM: 1 kHz, 30% modulation.
16. The Automatic Volume Levelling (AVL) circuit automatically stabilizes the audio output signal to a certain level which
can be set by means of the volume control. This AVL function prevents big audio output fluctuations due to variation
of the modulation depth of the transmitter. The AVL can be switched on and off via the I
For the TDA8373 the AVL is active over an input voltage range (measured at the de-emphasis output) between
75 and 750 mV (RMS). For the TDA8374 this input level is dependent on the crystals which are connected to the
colour decoder. When only 3.5 MHz crystals are connected (indicated via the XA/XB bits) the active input level is
identical to that of the TDA8373. When a 4.4 MHz crystal is connected the input signal range is increased to
150 to 1500 mV (RMS), this to cope with the larger FM swing of European transmitters.
The AVL control curve for the 2 standards is given in Fig.29 and Fig.30. The control range of +6 to −14 dB is valid
for input signals with 50% of the maximum frequency deviation.
17. Vi= 100 mV (RMS), f = 5.5 MHz; FM: 1 kHz, ±17.5 kHz deviation, 15 kHz bandwidth; audio attenuator at −6 dB.
18. Vi= 100 mV (RMS), f = 4.5 to 5.5 MHz, FM: 1 kHz, ±100 kHz deviation.
19. Unweighted RMS value, Vi= 100 mV (RMS), FM: 1 kHz, ±50 kHz deviation, volume control: −6 dB.
20. Audio attenuator at −20 dB; temperature range = 10 to 50 °C.
21. Signal with negative-going sync. Amplitude includes sync pulse amplitude.
22. This parameter is measured at nominal settings of the various controls.
23. Indicated as a signal for a colour bar with 75% saturation (chroma-to-burst ratio = 2.2 : 1).
24. Nominal contrast is specified with the DAC in position 20H. Nominal saturation as maximum −10 dB. At nominal
settings of brightness and white point the black level at the outputs is 300 mV lower than the level of the black current
measuring pulses.
25. The luminance output and input of the TDA8375A, TDA8377A, TDA8375 and TDA8377 can be connected directly.
When additional picture improvement ICs (such as the TDA9170) are applied the inputs of these ICs must be
AC-coupled because of the black level clamp requirement. The output of the picture improvement ICs can be directly
coupled to the luminance input as long as the DC level of the signal has a value between 1 and 7 V.
To be able to apply CTI ICs such as the TDA4565 and TDA4566 the gain of the luminance channel can be increased
via the setting of the GAI bit in the I2C-bus subaddress 03.
S/N = 20 log
--------------------------------------------------------V
m rms()
O(b-w)
B=5MHz()
2
C-bus.
1997 Jul 01 41
Page 42

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
TDA837x family
and NTSC TV-processors
26. When the colour decoder is forced to a fixed subcarrier frequency (via the XA/XB or the CM bits) the chroma trap is
always switched on, also when no colour signal is identified. When 2 crystals are active the chroma trap is switched
off when no colour signal is identified.
27. The −3 dB bandwidth of the circuit can be calculated using the following equation:
1
f
f
=
3dB–
28. Valid for a signal amplitude on the Y input of 0.7 V (black-to-white) (100 IRE) with a rise time (10% to 90%) of 70 ns
and the video switch in the Y/C mode. During production the peaking function is not tested by measuring the
overshoots but by measuring the frequency response of the Y output.
29. For video signals with a black level which deviates from the back porch blanking level the signal is ‘stretched’ to the
blanking level. The amount of correction depends on the IRE value of the signal (see Fig.17). The black level is
detected by means of an external capacitor. The black level stretcher can be made inoperative by connecting the pin
to ground. The values given are valid only when the luminance input signal has an amplitude of 1 V (p-p).
30. The slicing level is independent of sync pulse amplitude. The given percentage is the distance between the slicing
level and the black level (back porch). When the amplitude of the sync pulse exceeds the value of 350 mV the sync
separator will slice the sync pulse at a level of 175 mV above top sync. The maximum sync pulse amplitude is
4 V (p-p).
31. To obtain a good performance for both weak signal and VCR playback the time constant of the first control loop is
switched depending on the input signal condition and the condition of the bus. Therefore the circuit contains a noise
detector and the time constant is switched to ‘slow’ when too much noise is present in the signal. In the ‘fast’ mode,
during the vertical retrace time, the phase detector current is increased by 50% so that phase errors due to the head
switching of the VCR are corrected as soon as possible. Switching between the two modes can be made
automatically or overruled by the bus (see Tables 4, 6, 8 and 10).
The circuit contains a video identification circuit which is independent of first loop. This identification circuit can be
used to close or open the first control loop when a video signal is present or not on the input. This ensures a stable
On-Screen-Display (OSD) when just noise is present at the input. The coupling of the video identification circuit with
the first loop can be overruled via the I
circuit is only active for ‘internal’ CVBS signals.
To prevent the horizontal synchronization being disturbed by anti-copy guard signals, such as Macrovision, the
phase detector is gated during the vertical retrace period so that pulses during scan have no effect on the output
voltage. The width of the gate pulse is approximately 22 µs. Furthermore the phase detector is gated during the lower
part of the picture (pulse width = 12 µs) to prevent disturbances due to overmodulated subtitles. The latter gating is
active only with standard signals (number of lines per frame 625 or 525). During weak signal conditions (noise
detector active) the gating is active during the complete scan period and the width of the gate pulse is reduced to
5.7 µs so that the effect of the noise is reduced to a minimum. The output current of the phase detector in the various
conditions are given in Table 57.
32. The ICs have 2 protection inputs.
The protection at pin 42 is intended to be used as ‘flash’ protection. When this protection is activated the horizontal
drive is switched off immediately and then switched on again via the slow start procedure.
The protection on pin 50 is intended for overvoltage (X-ray) protection. When this protection is activated the
horizontal drive can be switched off directly (via the slow stop procedure). It is also possible to continue the horizontal
drive and to set the protection bit (XPR) in the output bytes of the I2C-bus. The choice between the 2 modes of
operation is made with the PRD bit.
1
–
osc
--------
2Q
2
C-bus. The coupling between the phase 1 detector and the videoidentification
1997 Jul 01 42
Page 43

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
TDA837x family
and NTSC TV-processors
33. During switch-on the horizontal output starts with twice the frequency and with a duty cycle of 75% (Vo= HIGH). After
approximately 50 ms the frequency is changed to the normal value. Because of the high frequency the peak currents
in the horizontal output transistor are limited. Also during switch-off the frequency is switched to twice the value and
the RGB drive is set to maximum so that the EHT capacitor is discharged. This switching to maximum drive occurs
only when RBL = 0, for RBL = 1 the drive voltage remains minimum during switch-off. After approximately 100 ms
the RGB drive is set to minimum and 50 ms later the horizontal drive is switched off.
The horizontal output is gated with the flyback pulse so that the horizontal output transistor cannot be switched on
during the flyback time.
34. The vertical blanking pulse in the RGB outputs has a width of 26 or 21 lines (50 or 60 Hz system). The width of the
vertical sync pulse in the sandcastle pulse has a width of 14 lines. This to prevent a phase distortion on top of the
picture due to timing modulation of the incoming flyback pulse.
35. The timing pulses for the vertical ramp generator are obtained from the horizontal oscillator via a divider circuit. This
divider circuit has 3 modes of operation. A brief explanation is given below. For the TDA8373 and TDA8377 only the
60 Hz figures are valid.
a) Search mode ‘large window’:
This mode is switched on when the circuit is not synchronized or when a non-standard signal (number of lines
per frame in the 50 Hz mode is between 311 and 314 and in the 60 Hz mode between 261 and 264) is received.
In the search mode the divider can be triggered between line 244 and line 361 (approximately 45 to 64.5 Hz).
b) Standard mode ‘narrow window’:
This mode is switched on when more than 15 succeeding vertical sync pulses are detected in the narrow window.
When the circuit is in the standard mode and a vertical sync pulse is missing the retrace of the vertical ramp
generator is started at the end of the window. Consequently, the disturbance of the picture is very small.
The circuit will switch back to the search window when, for 6 successive vertical periods, no sync pulses are found
within the window.
c) Standard TV-norm (divider ratio 525 (60 Hz) or 625 (50 Hz):
When the system is switched to the narrow window it is checked whether the incoming vertical sync pulses are
in accordance with the TV-norm. When 15 standard TV-norm pulses are counted the divider system is switched
to the standard divider ratio mode. In this mode the divider is always reset at the standard value even if the vertical
sync pulse is missing.
When 3 vertical sync pulses are missed the system switches back to the narrow window and when also in this
window no sync pulses are found (condition 3 missing pulses) the system switches over to the search window.
The vertical divider needs some waiting time during channel-switching of the tuner. When a fast reaction of the
divider is required during channel-switching the system can be forced to the search window by means of the NCIN bit
in subaddress 08.
36. Conditions: frequency is 60 Hz; normal mode; VS = 1F.
37. The output range percentages mentioned for E-W control parameters are based on the assumption that 400 µA
variation in E-W output current is equivalent to 20% variation in picture width. Because of the horizontal and vertical
zoom feature in the TDA8375 and TDA8377 (see also note 38) the E-W width control range is increased compared
with previous ICs such as the TDA8366. The increased E-W width control is also available in the TDA8375A and
TDA8377A although these devices do not have the vertical zoom feature.
38. The TDA8375 and TDA8377 have a zoom adjustment possibility for the vertical and horizontal deflection. For this
reason an extra DAC has been added in the vertical amplitude control which controls the vertical scan amplitude
between 0.75 and 1.38 of the nominal scan. At an amplitude of 1.08 of the nominal scan the output current is limited
and the blanking of the RGB outputs is activated (see Fig.28). In addition to the variation of the vertical amplitude the
vertical slope control range is also increased. This gives the possibility to vary the position of the bottom part of the
picture independent from the upper part. The nominal scan height must be adjusted at a position of 19H of the vertical
‘zoom’ DAC
1997 Jul 01 43
Page 44

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
TDA837x family
and NTSC TV-processors
39. At a chrominance input voltage of 660 mV (p-p) [colour bar with 75% saturation i.e. burst signal amplitude
300 mV (p-p)] the dynamic range of the ACC is +6 and −20 dB.
40. The ACL function is available in the NTSC devices and is active in the PAL/NTSC devices when NTSC signals are
received. The ACL circuit reduces the gain of the chroma amplifier for input signals with a chroma-to-burst ratio which
exceeds a value of 3.0.
41. All frequency variations are referenced to 3.58 or 4.43 MHz carrier frequency. All oscillator specifications are
measured with the Philips crystal series 9922 520 with a series capacitor of 18 pF. The oscillator circuit is rather
insensitive to the spurious responses of the crystal. As long as the resonance resistance of the 3rd overtone is higher
than that of the fundamental frequency the oscillator will operate at the correct frequency. Typical parameters for the
above mentioned crystals are as follows:
a) Load resonance frequency f0= 4.433619 or 3.579545 MHz (CL= 20 pF).
b) Motional capacitance C
c) Parallel capacitance C
The minimum detuning range can only be specified if both the IC and the crystal tolerances are known and the figures
given are therefore valid for the specified crystal series. In this figure tolerances of the crystal with respect to nominal
frequency, motional capacitance and ageing have been taken into account and have been counted for gaussian
addition. Whenever different typical crystal parameters are used the following equation might be helpful for
calculating the impact on the detuning capabilities:
The detuning range divided by
The resulting detuning range should be corrected for temperature shift and supply deviation of both the IC and the
crystal. The actual series capacitance in the application should be C
on and off chip. For 3-norma applications with 2 crystals connected to one pin the maximum parasitic capacitance of
the crystal pin should not exceed 15 pF.
42. The (R − Y) and (B −Y) signals are demodulated with a phase difference of the reference carrier of 90° and a gain
BY–()
ratio .
------------------- RY–()
1.78=
The output signal amplitudes of the TDA8373 and TDA8377A have twice the value. This is necessary to compensate
for the gain of the baseband delay line (TDA4665). The matrixing to the required signals is realized in the control part.
43. This parameter indicates the bandwidth of the complete chrominance circuit including the chrominance band-pass
filter. The bandwidth of the low-pass filter of the demodulator is approximately 1 MHz.
44. The sub-carrier output signal can be used as reference signal of external comb filter ICs (all ICs) and as a reference
signal for the SECAM decoder TDA8395 (only TDA8374 and TDA8375). In the latter types the output signal is
continuously available when PAL or NTSC signals are detected. When the system identifies a SECAM signal the
reference signal is only present in the vertical retrace period. This to prevent interference between the reference
signal and the SECAM input signal. For comb filter applications the DC load on this pin should be limited to 50 µA to
avoid problems with SECAM identification.
45. At nominal setting of the gain control. When this amplitude is exceeded the signal will be clipped.
46. When the reproduction of 4 : 3 pictures on a 16 : 9 picture tube is realized by means of a reduction of the horizontal
scan amplitude, the edges of the picture may be slightly disturbed. This effect can be prevented by adding additional
blanking to the RGB signals. This blanking pulse is derived from the horizontal oscillator and is directly related to the
incoming video signal (independent of the flyback pulse). The additional blanking overlaps the normal blanking signal
with approximately 1 µs on both sides. This blanking is activated with the HBL bit (only in the TDA8375 and
TDA8377).
47. Signal-to-noise ratio (S/N) is specified as a peak-to-peak signal with respect to RMS noise (bandwidth 5 MHz).
= 20.6 fF (4.43 MHz crystal) or 14.7 fF (3.58 MHz crystal).
mot
= 5 pF for both crystals.
par
C
mot
-------------------------------
1
+
C
par
----------C
L
2
= 18 pF to account for parasitic capacitances
L
1997 Jul 01 44
Page 45

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
TDA837x family
and NTSC TV-processors
48. This is a current input. The indicated value of the nominal bias current is obtained at the nominal setting of the gain
(white point) control. The actual value of the bias current depends on the gain control setting of each channel. As a
result the ‘black current’ of each gun is adapted to the white point setting so that the background colour will follow
the white point adjustment.
49. The beam current limiting and the vertical guard function have been combined on this pin. The beam current limiting
function is active during the vertical scan period.
Table 57 Output current of the phase detector in the various conditions
2
I
C-BUS COMMANDS IC CONDITIONS ϕ-1 CURRENT/MODE
VID POC FOA FOB IDENT COIN NOISE SCAN V-RETR GATING MODE
− 0 0 0 yes yes no 180 270 yes
− 0 0 0 yes yes yes 30 30 yes auto
− 0 0 0 yes no − 180 270 no auto
− 0 0 1 yes yes − 30 30 yes slow
− 0 0 1 yes no − 180 270 no slow
− 0 1 0 yes yes no 180 270 yes fast
− 0 1 0 yes yes yes 30 30 yes slow
−−11−−−180 270 no fast
00−−no −−6 6 no OSD
− 1 −−−−−−−−off
(1)
auto
Note
1. During vertical retrace the width is 22 µs and during the lower part of the picture 12 µs. In the other conditions the
width is 5.7 µs and the gating is continuous.
handbook, halfpage
0
(dB)
−20
−40
−60
−80
−100
MGK290
0
10
20 30 40
DAC (HEX)
handbook, halfpage
40
(%)
30
20
10
0
Positive overshoot.
0
4
8C10F
DAC (HEX)
MGK291
Fig.8 Volume control curve.
1997 Jul 01 45
Fig.9 Peaking control curve.
Page 46

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
and NTSC TV-processors
handbook, halfpage
(deg)
40
20
0
−20
−40
0
10
20 30 40
DAC (HEX)
MGK292
handbook, halfpage
300
(%)
250
200
150
100
50
0
TDA837x family
MGK293
0
10
20 30 40
DAC (HEX)
handbook, halfpage
100
(%)
80
60
40
20
0
Fig.10 Hue control curve.
010
20 30 40
DAC (HEX)
MGK294
handbook, halfpage
0.7
(V)
0.35
0
−0.35
−0.7
Fig.11 Saturation control curve.
0
10
20 30 40
DAC (HEX)
MGK295
Fig.12 Contrast control curve.
1997 Jul 01 46
Relative variation with respect to the measuring pulse.
Fig.13 Brightness control curve.
Page 47

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
and NTSC TV-processors
MBC212
16 %
for negative modulation
100% = 10% rest carrier
TDA837x family
100%
92%
30%
handbook, full pagewidth
MBC211
Fig.14 Video output signal.
100%
86%
72%
58%
44%
30%
µs
646056524844403632221210 26
Fig.15 Test signal waveform.
1997 Jul 01 47
Page 48

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
and NTSC TV-processors
handbook, full pagewidth
13.2 dB
30 dB
SC CC PC
3.2 dB
BLUE
13.2 dB
30 dB
SC CC PC
YELLOW
TDA837x family
10 dB
MBC213
PC
SC Σ
CC
Input signal conditions: SC = Sound Carrier; CC = Colour Carrier; PC = Picture Carrier.
All amplitudes with respect to top sync level.
at 3.58 or 4.4 MHz
V
Value at 0.92 or 1.1 MHz 20 log
Value at 2.66 or 3.3 MHz 20 log
=
O
-----------------------------------------------------------V
at 0.92 or 1.1 MHz
O
at 3.58 or 4.4 MHz
V
O
-----------------------------------------------------------at 2.66 or 3.3 MHz
V
O
ATTENUATOR
3.6 dB+=
TEST
CIRCUIT
SPECTRUM
ANALYZER
gain setting
adjusted for blue
MBC210
Fig.16 Test set-up intermodulation.
1997 Jul 01 48
Page 49

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
and NTSC TV-processors
100
handbook, halfpage
out
(IRE)
80
60
40
20
B
0
B
A
A
−20
A-A = maximum black level shift; B-B = level shift at 15% of peak white.
Fig.17 Input/output relationship of the black level stretcher.
40 80 10060200
TDA837x family
MGK297
in (IRE)
TEST AND APPLICATION INFORMATION
handbook, full pagewidth
from
tuner
SAW
FILTER
TRAP
4316 11
58
59
24
29
21
20
54 50 51 39 47 48 57
4.4
MHz
BAND-
PASS
10 27 17 18
TDA837x
46 45
3.5
MHz
TDA8395
35 36 37 38
TDA4665
33
32
31
30
34
62
63
64
56
MGK302
Fig.18 Simplified application diagram.
1997 Jul 01 49
Page 50

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
TDA837x family
and NTSC TV-processors
East-West output stage
In order to obtain correct tracking of the vertical and horizontal EHT correction, the E-W output stage should be
dimensioned as illustrated in Fig.19.
Resistor Rew determines the gain of the E-W output stage. Resistor Rc determines the reference current for both the
vertical sawtooth generator and the geometry processor. The preferred value of Rc is 39 kΩ which results in a reference
current of 100 µA (V
The value of R
ew
Example: With V
handbook, full pagewidth
= 3.9 V).
ref
must be:
= 3.9 V; Rc=39kΩ and V
ref
R
ew
R
×=
c
V
scan
---------------------- 18 V
×
scan
ref
= 120 V then Rew≈ 68 kΩ.
V
supply
R
39 kΩ
(2%)
TDA8375
TDA8377
52 51
V
ref
c
45
C
saw
100 nF
(5%)
E-W drive
R
ew
E-W
OUTPUT
STAGE
HORIZONTAL
DEFLECTION
STAGE
DIODE
MODULATOR
V
V
MGK300
scan
EW
Fig.19 East-West output stage.
Control ranges of geometry control parameters
Typical case curves; R
=39kΩ, C
c
SAW
= 100 nF.
Figures 20 to 23 are valid for all types. Figures 24 to 27 are valid for TDA8375 and TDA8377.
1997 Jul 01 50
Page 51

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
and NTSC TV-processors
time
MGH366
t
600
handbook, halfpage
I
vert
(µA)
400
200
0
−200
−400
−600
0
1
/2 t
500
handbook, halfpage
I
vert
(µA)
300
100
−100
−300
−500
−700
0
TDA837x family
MGH367
1
/2 t
time
t
VA = 0, 31H and 63H; VSH = 31H; SC = 0.
Fig.20 Control range of vertical amplitude.
600
handbook, halfpage
I
vert
(µA)
400
200
0
−200
−400
−600
0
1
/2 t
time
MGH368
VS = 0, 31H and 63H; VA = 31H; VHS = 31H; SC = 0.
Fig.21 Control range of vertical slope.
time
MGH369
t
600
handbook, halfpage
I
vert
(µA)
400
200
0
−200
−400
t
−600
0
1
/2 t
VSH = 0, 31H and 63H; VA = 31H; SC = 0.
Fig.22 Control range of vertical shift.
1997 Jul 01 51
SC = 0, 31H and 63H; VA = 31H; VHS = 31H.
Picture height does not change with S-correction for
nominal vertical amplitude (VA = 31).
Fig.23 Control range of S-correction.
Page 52

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
and NTSC TV-processors
time
MBK039
t
1200
handbook, halfpage
I
ew
(µA)
1000
800
600
400
200
0
0
1
/2 t
900
handbook, halfpage
I
ew
(µA)
800
700
600
500
400
300
0t
TDA837x family
MBK040
1
/2 t
time
EW = 0, 31H and 63H; PW = 31H; CP = 31H.
Fig.24 Control range of E-W width.
900
handbook, halfpage
I
ew
(µA)
800
700
600
500
400
300
0t
1
/2 t
time
MBK041
PW = 0, 31H and 63H; EW = 31H; CP = 31H.
Fig.25 Control range of E-W parabola/width ratio.
700
handbook, halfpage
I
ew
(µA)
600
500
400
300
0t
1
/2 t
MBK042
time
CP = 0, 31H and 63H; EW = 31H; PW = 63H.
Fig.26 Control range of E-W corner/parabola ratio.
1997 Jul 01 52
TC = 0, 31H and 63H; EW = 31H; PW = 31H; CP = 0.
Fig.27 Control range of E-W trapezium correction.
Page 53

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
and NTSC TV-processors
Adjustment of geometry control parameters
The deflection processor of the TDA8373 and TDA8374
offers 5 control parameters for picture alignment:
• Vertical picture alignment
– S-correction
– vertical amplitude
– vertical slope
– vertical shift
– Horizontal shift alignment.
The TDA8375, TDA8377, TDA8375A and TDA8377A offer
in addition the following functions for horizontal alignment:
• E-W width
• E-W parabola/width
• E-W corner/parabola
• E-W trapezium correction.
It is important to notice that the ICs are designed for use
with a DC-coupled vertical deflection stage. This is the
reason why a vertical linearity alignment is not necessary
(and, therefore, not available).
For a particular combination of picture tube type and
vertical output stage and E-W output stage, it is
determined which are the required values for the settings
of S-correction. These parameters can be preset via the
2
C-bus and do not need any additional adjustment.
I
The remainder of the parameters are preset with the
mid-value of their control range (i.e. 1FH), or with the
values obtained by previous TV set adjustments.
The vertical shift control is intended for compensation of
off-sets in the external vertical output stage or in the
picture tube. It can be shown that without compensation
these off-sets will result in a certain linearity error,
especially with picture tubes that need large S-correction.
The total linearity error is in 1st order approximation
proportional to the value of the off-set and to the square of
the S-correction needed. The necessity to use the vertical
TDA837x family
shift alignment depends on the expected off-sets in vertical
output stage and picture tube, on the required value of the
S-correction and on the demands upon vertical linearity.
For adjustment of the vertical shift and vertical slope
independent of each other, a special service blanking
mode can be entered by setting the SBL bit HIGH. In this
mode the RGB outputs are blanked during the second half
of the picture. There are 2 different methods for alignment
of the picture in vertical direction. Both methods make use
of the service blanking mode.
The first method is recommended for picture tubes that
have a marking for the middle of the screen. With the
vertical shift control the last line of the visible picture is
positioned exactly in the middle of the screen. After this
adjustment the vertical shift should not be changed.
The top of the picture is placed by adjusting the vertical
amplitude and the bottom by adjusting the vertical slope.
The second method is recommended for picture tubes that
have no marking for the middle of the screen. For this
method a video signal is required in which the middle of the
picture is indicated (e.g. the white line in the circle test
pattern). With the vertical slope control the beginning of the
blanking is positioned exactly on the middle of the picture.
Then the top and bottom of the picture are placed
symmetrically with respect to the middle of the screen by
adjustment of the vertical amplitude and vertical shift. After
this adjustment the vertical shift has the correct setting and
should not be changed.
If the vertical shift alignment is not required VSH should be
set to its mid-value (i.e. VSH = 1FH). The top of the picture
is then placed by adjusting the vertical amplitude and the
bottom by adjusting the vertical slope. After the vertical
picture alignment the picture is positioned in the horizontal
direction by adjusting the horizontal shift.
To obtain the full range of the vertical zoom function with
the TDA8375 and TDA8377 the adjustment of the vertical
geometry should be carried out at a nominal setting of the
zoom DAC at position 19H.
1997 Jul 01 53
Page 54

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
and NTSC TV-processors
handbook, full pagewidth
vertical
position
(%)
−10
−20
−30
−40
−50
−60
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
0
75%
top
picture
100%
bottom
picture
138%
1/2 t
TDA837x family
MGK296
t
time
blanking for exponential 138%
Fig.28 Sawtooth waveform and blanking pulse of the TDA8375 and TDA8377.
4
10
handbook, halfpage
audio
output
(mV) (RMS)
3
10
2
10
10 10
6 dB
AVL on
AVL off
25 kHz (norm)
C
BA
2
D
de-emphasis (mV) (RMS)
14 dB
10
MGK298
3
4
10
See Table 58.
Fig.29 AVL characteristics of the TDA8373 and TDA8374 for 3.5 MHz standard.
1997 Jul 01 54
Page 55

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
and NTSC TV-processors
4
10
handbook, halfpage
audio
output
(mV) (RMS)
3
10
2
10
10 10
6 dB
AVL on
AVL off
50 kHz (norm)
C
BA ED
2
de-emphasis (mV) (RMS)
14 dB
3
10
MGK299
TDA837x family
4
10
See Table 59.
Fig.30 AVL characteristics of the TDA8374 for 4.4 MHz standard.
Table 58 Explanation to Fig.29
A B C D DESCRIPTION
50 100 250 500 de-emphasis pin 55 [mV (RMS)]
5 10 25 50 FM swing (kHz)
50 100 250 500 AVL input [mV (RMS)]
100 200 500 1000 external input [mV (RMS)]
Table 59 Explanation to Fig.30
A B C D DESCRIPTION
100 200 250 1000 de-emphasis pin 55 [mV (RMS)]
10 20 25 100 FM swing (kHz)
50 100 125 500 AVL input [mV (RMS)]
100 200 250 1000 external input [mV (RMS)]
1997 Jul 01 55
Page 56

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
and NTSC TV-processors
INTERNAL PIN CONFIGURATION
TSTCON
1
2.2 kΩ300 Ω
Fig.31 Pin 1.
sound limiter
plus demodulator
10 pF
15
pF
15
kΩ
3 4
MGK303
kΩ
15
+
2
100 Ω
++
TDA837x family
sound switch
plus amplifier
25
kΩ
Fig.32 Pin 2.
4 V
MGK304
+
6
kΩ
++
200
Ω
+
6
kΩ
Fig.33 Pins 3, 4 and 5.
6
MGK306
5
MGK305
5 V
300 Ω
7
MGK343
Fig.34 Pin 6.
1997 Jul 01 56
Fig.35 Pin 7.
Page 57

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
and NTSC TV-processors
5 V
8
30 Ω
300 Ω
MGK307
Fig.36 Pin 8.
TDA837x family
++
9
MGK308
Fig.37 Pin 9.
TSTCON
10
300 Ω
+
100
kΩ
10 pF
100
kΩ
DECODER
Fig.38 Pin 10.
12, 37
+
TXT
PIP
analog supply
MGK344
30 kΩ
V
MGK309
+
11, 13, 17
ref
100 Ω
decoder
luma
decoder
chroma
sync
switch
output
DUMMY
CLAMP
switch control
MGK310
Fig.39 Pins 11, 13 and 17.
+
14
GND1
MGK333
Fig.40 Pins 12 and 37.
1997 Jul 01 57
Fig.41 Pin 14.
Page 58

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
and NTSC TV-processors
+
2 kΩ
300 Ω
V/I
V
ref
+
15
MGK312
10 pF
= 4 V
MGK314
18
sound
amplifier
+
100 µA
Fig.42 Pin 15.
14 kΩ
200
µA
I
L
10
µA
TDA837x family
−100 µA/ +100 µA
+
16
300 Ω
50 kΩ
10 pF
Fig.43 Pin 16.
+
+
100 Ω
2 mA
filter
tuning
MGK313
19, 20, 21
MGK315
Fig.44 Pin 18.
vertical
guard
+
22
1 kΩ
200 µA
4 V
40
kΩ
peak white
limiting
Fig.46 Pin 22.
1997 Jul 01 58
+
contrast
control
Fig.45 Pins 19, 20 and 21.
V
ref1
+
V
ref2
brightness
control
MGK316
Page 59

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
and NTSC TV-processors
+
6 V
6 V
+
Fig.47 Pins 23, 24 and 25.
+
+
+
50 µA
0.2 µA
+
300 Ω
MGK317
23, 24, 25
+
+
50
pF
10 Ω
27
MGK319
TDA837x family
+
insertion
+
500 Ω
blanking
10 Ω
+
4 V
MGK318
+
28
MGK320
+
26
300 Ω
Fig.48 Pin 26.
500 µA
Fig.49 Pin 27.
+
+
+
100 Ω
29, 30
MGK321
Fig.51 Pins 29 and 30.
1997 Jul 01 59
31, 32
Fig.50 Pin 28.
++
100 Ω
2.5 V
MGK322
Fig.52 Pins 31 and 32.
Page 60

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
and NTSC TV-processors
++
30 Ω
250 µA
2.7 V
Fig.53 Pin 33.
+
33
MGK323
34, 35
+
pin 34: crystal = 3.58 MHz; R = 1 kΩ
MGK324
pin 35: crystal = 4.43 MHz; R = 1 kΩ
Fig.54 Pins 34 and 35.
TDA837x family
+
R
3.7 V
R
+
36
100 Ω
3.8 V
MGK325
Fig.55 Pin 36.
39
+
TSTCON
100 Ω
38
Fig.56 Pin 38.
+
+
400 Ω
+
600
µA
MGK326
+
30 Ω
40
MGK327
Fig.57 Pin 39.
1997 Jul 01 60
protection
Fig.58 Pin 40.
MGK328
Page 61

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
and NTSC TV-processors
burstkey
+
41
30 Ω
V blank
Fig.59 Pin 41.
5.3 V
2.9 V
2 µA
burstkey
+
+
MGK329
TDA837x family
J
3 V
4 V
+
300 Ω
42
3.3 V
+
flash
level
Fig.60 Pin 42.
4.7 V
+
5.3 V
MGK330
+
300 Ω300 Ω
43
dF
HOSC
+
J
4 V
MGK331
(NC plus POR)
Fig.61 Pin 43.
1997 Jul 01 61
Page 62

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
and NTSC TV-processors
44
GND2, connected to substrate
MGK311
Fig.62 Pin 44.
+
46, 47
TDA837x family
+
45
600 Ω
MGK332
Fig.63 Pin 45.
1 kΩ
1 kΩ
++
to
IF amplifier
+
48
49
100 Ω
2.4 pF
+
100 Ω
MGK334
MGK335
Fig.64 Pins 46 and 47.
Fig.65 Pins 48 and 49.
+
+
J
+
MGK337
Fig.67 Pin 51.
XPR
J
3.9 V
MGK336
51
+
50
300 Ω
2 V
J
Fig.66 Pin 50.
1997 Jul 01 62
Page 63

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
and NTSC TV-processors
+
52
Fig.68 Pin 52.
+
1.5
mA
AGC det
53
TDA837x family
I
ref
V
ref
MGK338
+
+
LSPEED
NEGMOD
TSTCON
54
MGK340
gating
50
µA
500
nA
Fig.69 Pin 53.
600
µA
demodulator
sound
++
20 kΩ
clamp
MGK339
55
sound switch
plus amplifier
3 V
MGK341
Fig.70 Pin 54.
1997 Jul 01 63
Fig.71 Pin 55.
Page 64

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
and NTSC TV-processors
+
56
−50/50 µA
Fig.72 Pin 56.
100 µA
DC
stabilisation
MGK342
TDA837x family
1997 Jul 01 64
Page 65

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
and NTSC TV-processors
PACKAGE OUTLINES
QFP64: plastic quad flat package;
64 leads (lead length 1.95 mm); body 14 x 20 x 2.7 mm; high stand-off height
c
y
X
51 33
52
32
Z
A
E
TDA837x family
SOT319-1
pin 1 index
64
1
w M
b
0.25
p
0.50
0.35
D
H
D
D
0.25
20.1
0.13
19.9
e
DIMENSIONS (mm are the original dimensions)
mm
A
max.
3.3
0.36
0.10
2.87
2.57
UNIT A1A2A3bpcE
Note
1. Plastic or metal protrusions of 0.25 mm maximum per side are not included.
Z
D
0 5 10 mm
(1)
(1) (1)(1)
14.1
13.9
20
19
scale
eH
H
24.2
1
23.6
B
D
e
H
E
w M
b
p
v M
A
v M
B
LLpQZywv θ
E
18.2
17.6
1.0
0.6
A
2
A
E
1.43
1.23
A
1
detail X
0.2 0.10.21.95
Q
(A )
3
θ
L
p
L
Z
E
D
1.2
0.8
o
7
o
0
1.2
0.8
OUTLINE
VERSION
SOT319-1
IEC JEDEC EIAJ
REFERENCES
1997 Jul 01 65
EUROPEAN
PROJECTION
ISSUE DATE
92-11-17
95-02-04
Page 66

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
and NTSC TV-processors
SDIP56: plastic shrink dual in-line package; 56 leads (600 mil)
D
seating plane
L
Z
56
e
b
TDA837x family
SOT400-1
M
E
A
2
A
A
1
w M
b
1
29
c
(e )
M
1
H
pin 1 index
1
0 5 10 mm
scale
DIMENSIONS (mm are the original dimensions)
UNIT b
mm
Note
1. Plastic or metal protrusions of 0.25 mm maximum per side are not included.
max.
5.08
OUTLINE
VERSION
SOT400-1
A
A
A
12
min.
max.
0.51
4.0
IEC JEDEC EIAJ
1.3
0.8
b
1
0.53
0.40
REFERENCES
0.32
0.23
cEe M
(1) (1)
D
52.4
51.6
14.0
13.6
E
28
(1)
Z
1
L
M
E
3.2
15.80
2.8
15.24
EUROPEAN
PROJECTION
17.15
15.90
e
w
H
0.181.778 15.24
ISSUE DATE
95-12-06
max.
2.3
1997 Jul 01 66
Page 67

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
and NTSC TV-processors
SOLDERING
Introduction
There is no soldering method that is ideal for all IC
packages. Wave soldering is often preferred when
through-hole and surface mounted components are mixed
on one printed-circuit board. However, wave soldering is
not always suitable for surface mounted ICs, or for
printed-circuits with high population densities. In these
situations reflow soldering is often used.
This text gives a very brief insight to a complex technology.
A more in-depth account of soldering ICs can be found in
our
“IC Package Databook”
SDIP
SOLDERING BY DIPPING OR BY WA VE
The maximum permissible temperature of the solder is
260 °C; solder at this temperature must not be in contact
with the joint for more than 5 seconds. The total contact
time of successive solder waves must not exceed
5 seconds.
The device may be mounted up to the seating plane, but
the temperature of the plastic body must not exceed the
specified maximum storage temperature (T
printed-circuit board has been pre-heated, forced cooling
may be necessary immediately after soldering to keep the
temperature within the permissible limit.
R
EPAIRING SOLDERED JOINTS
Apply a low voltage soldering iron (less than 24 V) to the
lead(s) of the package, below the seating plane or not
more than 2 mm above it. If the temperature of the
soldering iron bit is less than 300 °C it may remain in
contact for up to 10 seconds. If the bit temperature is
between 300 and 400 °C, contact may be up to 5 seconds.
QFP
REFLOW SOLDERING
Reflow soldering techniques are suitable for all QFP
packages.
The choice of heating method may be influenced by larger
plastic QFP packages (44 leads, or more). If infrared or
vapour phase heating is used and the large packages are
not absolutely dry (less than 0.1% moisture content by
weight), vaporization of the small amount of moisture in
them can cause cracking of the plastic body. For more
information, refer to the Drypack chapter in our
Reference Handbook”
(order code 9398 652 90011).
). If the
stg max
“Quality
(order code 9397 750 00192).
TDA837x family
Reflow soldering requires solder paste (a suspension of
fine solder particles, flux and binding agent) to be applied
to the printed-circuit board by screen printing, stencilling or
pressure-syringe dispensing before package placement.
Several techniques exist for reflowing; for example,
thermal conduction by heated belt. Dwell times vary from
50 to 300 seconds depending on heating method. Typical
reflow temperatures range from 215 to 250 °C.
Preheating is necessary to dry the paste and evaporate
the binding agent. Preheat for 45 minutes at 45 °C.
WAVE SOLDERING
Wave soldering is not recommended for QFP packages.
This is because of the likelihood of solder bridging due to
closely-spaced leads and the possibility of incomplete
solder penetration in multi-lead devices.
If wave soldering cannot be avoided, the following
conditions must be observed:
• A double-wave (a turbulent wave with high upward
pressure followed by a smooth laminar wave)
soldering technique should be used.
• The footprint must be at an angle of 45° to the board
direction and must incorporate solder thieves
downstream and at the side corners.
Even with these conditions, do not consider wave
soldering the following packages: QFP52 (SOT379-1),
QFP100 (SOT317-1), QFP100 (SOT317-2),
QFP100 (SOT382-1) or QFP160 (SOT322-1).
During placement and before soldering, the package must
be fixed with a droplet of adhesive. The adhesive can be
applied by screen printing, pin transfer or syringe
dispensing. The package can be soldered after the
adhesive is cured. Maximum permissible solder
temperature is 260 °C, and maximum duration of package
immersion in solder is 10 seconds, if cooled to less than
150 °C within 6 seconds. Typical dwell time is 4 seconds
at 250 °C.
A mildly-activated flux will eliminate the need for removal
of corrosive residues in most applications.
R
EPAIRING SOLDERED JOINTS
Fix the component by first soldering two diagonallyopposite end leads. Use only a low voltage soldering iron
(less than 24 V) applied to the flat part of the lead. Contact
time must be limited to 10 seconds at up to 300 °C. When
using a dedicated tool, all other leads can be soldered in
one operation within 2 to 5 seconds between
270 and 320 °C.
1997 Jul 01 67
Page 68

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
TDA837x family
and NTSC TV-processors
DEFINITIONS
Data sheet status
Objective specification This data sheet contains target or goal specifications for product development.
Preliminary specification This data sheet contains preliminary data; supplementary data may be published later.
Product specification This data sheet contains final product specifications.
Short-form specification The data in this specification is extracted from a full data sheet with the same type
number and title. For detailed information see the relevant data sheet or data handbook.
Limiting values
Limiting values given are in accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 134). Stress above one or
more of the limiting values may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only and operation
of the device at these or at any other conditions above those given in the Characteristics sections of the specification
is not implied. Exposure to limiting values for extended periods may affect device reliability.
Application information
Where application information is given, it is advisory and does not form part of the specification.
LIFE SUPPORT APPLICATIONS
These products are not designed for use in life support appliances, devices, or systems where malfunction of these
products can reasonably be expected to result in personal injury. Philips customers using or selling these products for
use in such applications do so at their own risk and agree to fully indemnify Philips for any damages resulting from such
improper use or sale.
2
PURCHASE OF PHILIPS I
C COMPONENTS
Purchase of Philips I
components in the I2C system provided the system conforms to the I2C specification defined by
Philips. This specification can be ordered using the code 9398 393 40011.
2
C components conveys a license under the Philips’ I2C patent to use the
1997 Jul 01 68
Page 69

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
and NTSC TV-processors
NOTES
TDA837x family
1997 Jul 01 69
Page 70

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
and NTSC TV-processors
NOTES
TDA837x family
1997 Jul 01 70
Page 71

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled economy PAL/NTSC
and NTSC TV-processors
NOTES
TDA837x family
1997 Jul 01 71
Page 72

Philips Semiconductors – a worldwide company
Argentina: see South America
Australia: 34 Waterloo Road, NORTH RYDE, NSW 2113,
Tel. +61 2 9805 4455, Fax. +61 2 9805 4466
Austria: Computerstr. 6, A-1101 WIEN, P.O. Box 213,
Tel. +43 1 60 101, Fax. +43 1 60 101 1210
Belarus: Hotel Minsk Business Center, Bld. 3, r. 1211, Volodarski Str. 6,
220050 MINSK, Tel. +375 172 200 733, Fax. +375 172 200 773
Belgium: see The Netherlands
Brazil: see South America
Bulgaria: Philips Bulgaria Ltd., Energoproject, 15th floor,
51 James Bourchier Blvd., 1407 SOFIA,
Tel. +359 2 689 211, Fax. +359 2 689 102
Canada: PHILIPS SEMICONDUCTORS/COMPONENTS,
Tel. +1 800 234 7381
China/Hong Kong: 501 Hong Kong Industrial Technology Centre,
72 Tat Chee Avenue, Kowloon Tong, HONG KONG,
Tel. +852 2319 7888, Fax. +852 2319 7700
Colombia: see South America
Czech Republic: see Austria
Denmark: Prags Boulevard 80, PB 1919, DK-2300 COPENHAGEN S,
Tel. +45 32 88 2636, Fax. +45 31 57 0044
Finland: Sinikalliontie 3, FIN-02630 ESPOO,
Tel. +358 9 615800, Fax. +358 9 61580920
France: 4 Rue du Port-aux-Vins, BP317, 92156 SURESNES Cedex,
Tel. +33 1 40 99 6161, Fax. +33 1 40 99 6427
Germany: Hammerbrookstraße 69, D-20097 HAMBURG,
Tel. +49 40 23 53 60, Fax. +49 40 23 536 300
Greece: No. 15, 25th March Street, GR 17778 TAVROS/ATHENS,
Tel. +30 1 4894 339/239, Fax. +30 1 4814 240
Hungary: see Austria
India: Philips INDIA Ltd, Shivsagar Estate, A Block, Dr. Annie Besant Rd.
Worli, MUMBAI 400 018, Tel. +91 22 4938 541, Fax. +91 22 4938 722
Indonesia: see Singapore
Ireland: Newstead, Clonskeagh, DUBLIN 14,
Tel. +353 1 7640 000, Fax. +353 1 7640 200
Israel: RAPAC Electronics, 7 Kehilat Saloniki St, PO Box 18053,
TEL AVIV 61180, Tel. +972 3 645 0444, Fax. +972 3 649 1007
Italy: PHILIPS SEMICONDUCTORS, Piazza IV Novembre 3,
20124 MILANO, Tel. +39 2 6752 2531, Fax. +39 2 6752 2557
Japan: Philips Bldg 13-37, Kohnan 2-chome, Minato-ku, TOKYO 108,
Tel. +81 3 3740 5130, Fax. +81 3 3740 5077
Korea: Philips House, 260-199 Itaewon-dong, Yongsan-ku, SEOUL,
Tel. +82 2 709 1412, Fax. +82 2 709 1415
Malaysia: No. 76 Jalan Universiti, 46200 PETALING JAYA, SELANGOR,
Tel. +60 3 750 5214, Fax. +60 3 757 4880
Mexico: 5900 Gateway East, Suite 200, EL PASO, TEXAS 79905,
Tel. +9-5 800 234 7381
Middle East: see Italy
Netherlands: Postbus 90050, 5600 PB EINDHOVEN, Bldg. VB,
Tel. +31 40 27 82785, Fax. +31 40 27 88399
New Zealand: 2 Wagener Place, C.P.O. Box 1041, AUCKLAND,
Tel. +64 9 849 4160, Fax. +64 9 849 7811
Norway: Box 1, Manglerud 0612, OSLO,
Tel. +47 22 74 8000, Fax. +47 22 74 8341
Philippines: Philips Semiconductors Philippines Inc.,
106 Valero St. Salcedo Village, P.O. Box 2108 MCC, MAKATI,
Metro MANILA, Tel. +63 2 816 6380, Fax. +63 2 817 3474
Poland: Ul. Lukiska 10, PL 04-123 WARSZAWA,
Tel. +48 22 612 2831, Fax. +48 22 612 2327
Portugal: see Spain
Romania: see Italy
Russia: Philips Russia, Ul. Usatcheva 35A, 119048 MOSCOW,
Tel. +7 095 755 6918, Fax. +7 095 755 6919
Singapore: Lorong 1, Toa Payoh, SINGAPORE 1231,
Tel. +65 350 2538, Fax. +65 251 6500
Slovakia: see Austria
Slovenia: see Italy
South Africa: S.A. PHILIPS Pty Ltd., 195-215 Main Road Martindale,
2092 JOHANNESBURG, P.O. Box 7430 Johannesburg 2000,
Tel. +27 11 470 5911, Fax. +27 11 470 5494
South America: Rua do Rocio 220, 5th floor, Suite 51,
04552-903 São Paulo, SÃO PAULO - SP, Brazil,
Tel. +55 11 821 2333, Fax. +55 11 829 1849
Spain: Balmes 22, 08007 BARCELONA,
Tel. +34 3 301 6312, Fax. +34 3 301 4107
Sweden: Kottbygatan 7, Akalla, S-16485 STOCKHOLM,
Tel. +46 8 632 2000, Fax. +46 8 632 2745
Switzerland: Allmendstrasse 140, CH-8027 ZÜRICH,
Tel. +41 1 488 2686, Fax. +41 1 481 7730
Taiwan: Philips Semiconductors, 6F, No. 96, Chien Kuo N. Rd., Sec. 1,
TAIPEI, Taiwan Tel. +886 2 2134 2865, Fax. +886 2 2134 2874
Thailand: PHILIPS ELECTRONICS (THAILAND) Ltd.,
209/2 Sanpavuth-Bangna Road Prakanong, BANGKOK 10260,
Tel. +66 2 745 4090, Fax. +66 2 398 0793
Turkey: Talatpasa Cad. No. 5, 80640 GÜLTEPE/ISTANBUL,
Tel. +90 212 279 2770, Fax. +90 212 282 6707
Ukraine: PHILIPS UKRAINE, 4 Patrice Lumumba str., Building B, Floor 7,
252042 KIEV, Tel. +380 44 264 2776, Fax. +380 44 268 0461
United Kingdom: Philips Semiconductors Ltd., 276 Bath Road, Hayes,
MIDDLESEX UB3 5BX, Tel. +44 181 730 5000, Fax. +44 181 754 8421
United States: 811 East Arques Avenue, SUNNYVALE, CA 94088-3409,
Tel. +1 800 234 7381
Uruguay: see South America
Vietnam: see Singapore
Yugoslavia: PHILIPS, Trg N. Pasica 5/v, 11000 BEOGRAD,
Tel. +381 11 625 344, Fax.+381 11 635 777
For all other countries apply to: Philips Semiconductors, Marketing & Sales Communications,
Building BE-p, P.O. Box 218, 5600 MD EINDHOVEN, The Netherlands, Fax. +31 40 27 24825
© Philips Electronics N.V. 1997 SCA54
All rights are reserved. Reproduction in whole or in part is prohibited without the prior written consent of the copyright owner.
The information presented in this document does not form part of any quotation or contract, is believed to be accurate and reliable and may be changed
without notice. No liability will be accepted by the publisher for any consequence of its use. Publication thereof does not convey nor imply any license
under patent- or other industrial or intellectual property rights.
Internet: http://www.semiconductors.philips.com
Printed in The Netherlands 547047/1200/01/pp72 Date of release: 1997 Jul 01 Document order number: 9397 750 01808
Page 73

This datasheet has been download from:
www.datasheetcatalog.com
Datasheets for electronics components.
 Loading...
Loading...