Samsung SLS 2A00002100 User Manual

FCC ID : A3LSLS-2A00002100
ATTACHMENT E.
- USER MANUAL -
HCT CO., LTD.
SAN 136-1, AMI-RI, BUBAL-EUP, ICHEON-SI, KYOUNGKI-DO, 467-701, KOREA
TEL:+82 31 639 8517 FAX:+82 31 639 8525 www.hct.co.kr
Report No. : HCTR1003FR21 1/1

Ed. 00
MetroPCS
User Manual

COPYRIGHT
This manual is proprietary to SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd. and is protected by copyright.
No information contained herein may be copied, translated, transcribed or duplicated for any commercial
purposes or disclosed to the third party in any form without the prior written consent of SAMSUNG Electronics
Co., Ltd.
TRADEMARKS
Product names mentioned in this manual may be trademarks and/or registered trademarks of their respec tive
companies.
This manual should be read and used as a guideline for properly installing and operating the product.
This manual may be changed for the system improvement, standardization and other technical reasons without prior
notice.
If you need updated manuals or have an y questions concerning the contents of the manuals, contact our Document
Center at the following address or Web site:
Address: Document Center 3rd Floor Jeong-bo-tong-sin-dong. Dong-Suwon P.O. Box 105, 416, Maetan-3dong
Yeongtong-gu, Suwon-si, Gyeonggi-do, Korea 442-6 00
Homepage: http://www.samsungdocs.com
©2010 SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.

INTRODUCTION
Purpose
This document introduces evolved NodeB (eNB) system of the Samsung Electronics and
describes its architecture and functions.
Document Content and Organization
MetroPCS User Manual
This document consists of five Chapters, Abbreviation.
CHAPTER 1. Overview of LTE Network
y Introduction to LTE Network
y Interface between Systems
CHAPTER 2. Overview of LTE eNB
y Introduction to LTE eNB
y Main Functions
y Specifications
CHAPTER 3. System Architecture
y Hardware Structure
y Software Structure
CHAPTER 4. Message Flow
y Attach Procedure
y Service Request Procedure
y Detach Procedure
y Intra E-UTRAN Handover Procedure
y Network Synchronization Signal Flow
© SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd. I

INTRODUCTION
y Alarm and Reset Signal Flow
y Loading Flow
y Operation and Maintenance Signal Flow
CHAPTER 5. Additional Functions and Tools
Command Line Interface (CLI)
ABBREVIATION
Describes the acronyms used in this description.
Revision History
EDITION DATE OF ISSUE REMARKS
00 03. 2010. First Edition
II © SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd.

MetroPCS User Manual
TABLE OF CONTENTS
INTRODUCTION I
Purpose ..................................................................................................................................................I
Document Content and Organization.....................................................................................................I
Revision History.....................................................................................................................................II
CHAPTER 1. Overview of LTE Network 1-1
1.1 Introduction to LTE network................................................................................................. 1-1
1.2 Interface between Systems................................................................................................... 1-5
1.2.1 LTE Network Interface..........................................................................................................1-5
1.2.2 Inte rface pro tocol..................................................................................................................1-6
CHAPTER 2. Overview of LTE eNB 2-1
2.1 Introduction to LTE eNB........................................................................................................ 2-1
2.2 Main Functions ...................................................................................................................... 2-2
2.3 Specifications ........................................................................................................................ 2-4
CHAPTER 3. System Architecture 3-1
3.1 Hardware Structure................................................................................................................ 3-1
3.1.1 Digit al Unit (L9 DU)................................................................................................................3-2
3.1.2 Radio Unit.............................................................................................................................3-5
3.1.3 Cooling Archite cture..............................................................................................................3-8
3.1.4 Environmen t Sensors...........................................................................................................3-9
3.2 Software Structure............................................................................................................... 3-10
3.2.1 Operating Sy stem (OS )......................................................................................................3-10
3.2.2 Netw ork Processing Sof tw are (NP SW).............................................................................3-10
3.2.3 Device Driver (DD)..............................................................................................................3-11
3.2.4 Middlew are (MW) ................................................................................................................3-11
3.2.5 IP Rou ting Subsy stem ( IPRS)............................................................................................3-11
3.2.6 Call Pro cessing Sof tw are (CPS)........................................................................................3-11
3.2.7 Operation and Maintenance (OAM)...................................................................................3-13
© SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd. III

TABLE OF CONTENTS
CHAPTER 4. Message Flow 4-1
4.1 Attach Procedure....................................................................................................................4-1
4.2 Service Request Procedure...................................................................................................4-5
4.3 Detach Procedure...................................................................................................................4-9
4.4 Intra E-UTRAN Handover Procedure ..................................................................................4-12
4.5 Network Synchronization Signal Flow................................................................................4-18
4.6 Alarm and Reset Signal Flow..............................................................................................4-19
4.7 Loading Flow........................................................................................................................4-20
4.8 Operation and Maintenance Signal Flow............................................................................4-21
CHAPTER 5. Additional Functions and Tools 5-1
ABBREVIATION I
3 ..................................................................................................................................................I
A ~ E ..................................................................................................................................................I
F ~ L ................................................................................................................................................. II
M ~ S ................................................................................................................................................III
T ~ W ......................................................................................................................... .......................IV
IV © SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd.

MetroPCS User Manual/ED.00
LIST OF FIGURES
Figure 1.1 LTE Network Configuration ................................................................................... 1-1
Figure 1.2 LTE Network Interface........................................................................................... 1-5
Figure 1.3 User plane protocol stack between eNB and UE................................................... 1-6
Figure 1.4 Control plane protocol stack between eNB and UE ............................................... 1-7
Figure 1.5 User plane protocol stack between eNB and S-GW.............................................. 1-7
Figure 1.6 Control plane protocol stack between eNB and MME ........................................... 1-8
Figure 1.7 User plane protocol stack between eNBs.............................................................. 1-8
Figure 1.8 Control plane protocol stack between eNBs.......................................................... 1-9
Figure 1.9 Protocol stack between eNB and LSM.................................................................. 1-9
Figure 1.10 Protocol stack between eNB and LSS............................................................... 1-10
Figure 3.1 Rack Configuration of Macro Outdoor Cabinet...................................................... 3-1
Figure 3.2 Internal Configuration of Macro Outdoor Cabinet.................................................. 3-2
Figure 3.3 RF Configuration for Antenna Sharing................................................................... 3-7
Figure 3.4 Configuration of FANs........................................................................................... 3-8
Figure 3.5 Configuration of Environment Sensors.................................................................. 3-9
Figure 3.6 Software Structure............................................................................................... 3-10
Figure 3.7 OAM Block .......................................................................................................... 3-13
Figure 4.1 Attach procedure................................................................................................... 4-2
Figure 4.2 UE triggered Service Request procedure.............................................................. 4-6
Figure 4.3 Network triggered Service Request procedure...................................................... 4-8
Figure 4.4 UE initiated Detach procedure............................................................................... 4-9
Figure 4.5 MME initiated Detach procedure..........................................................................4-11
Figure 4.6 X2 based handover procedure............................................................................ 4-12
Figure 4.7 S1 based handover procedure............................................................................ 4-15
Figure 4.8 DU Synchronization Signal Flow......................................................................... 4-18
Figure 4.9 RU Synchronization Signal Flow......................................................................... 4-18
Figure 4.10 Alarm and Reset Signal Flow............................................................................ 4-19
Figure 4.11 Loading Flow ..................................................................................................... 4-20
Figure 4.12 Operation/Maintenance Signal Flow.................................................................. 4-21
Figure 5.1 Connecting to the CLI............................................................................................ 5-1
© SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd. V

TABLE OF CONTENTS
This page is intentionally left blank.
VI © SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd.

CHAPTER 1. Overview of LTE
A
Network
1.1 Introduction to LTE network
3GPP Long Term Evolution (LTE) network is composed of E-UTRAN NodeB (eNB), LTE
System Manager (LSM) and Evolved Packet Core (EPC). LTE network is the subnet of
Packet Data Network (PDN) and enables User Equipments (UE) to interwork with IP
network.
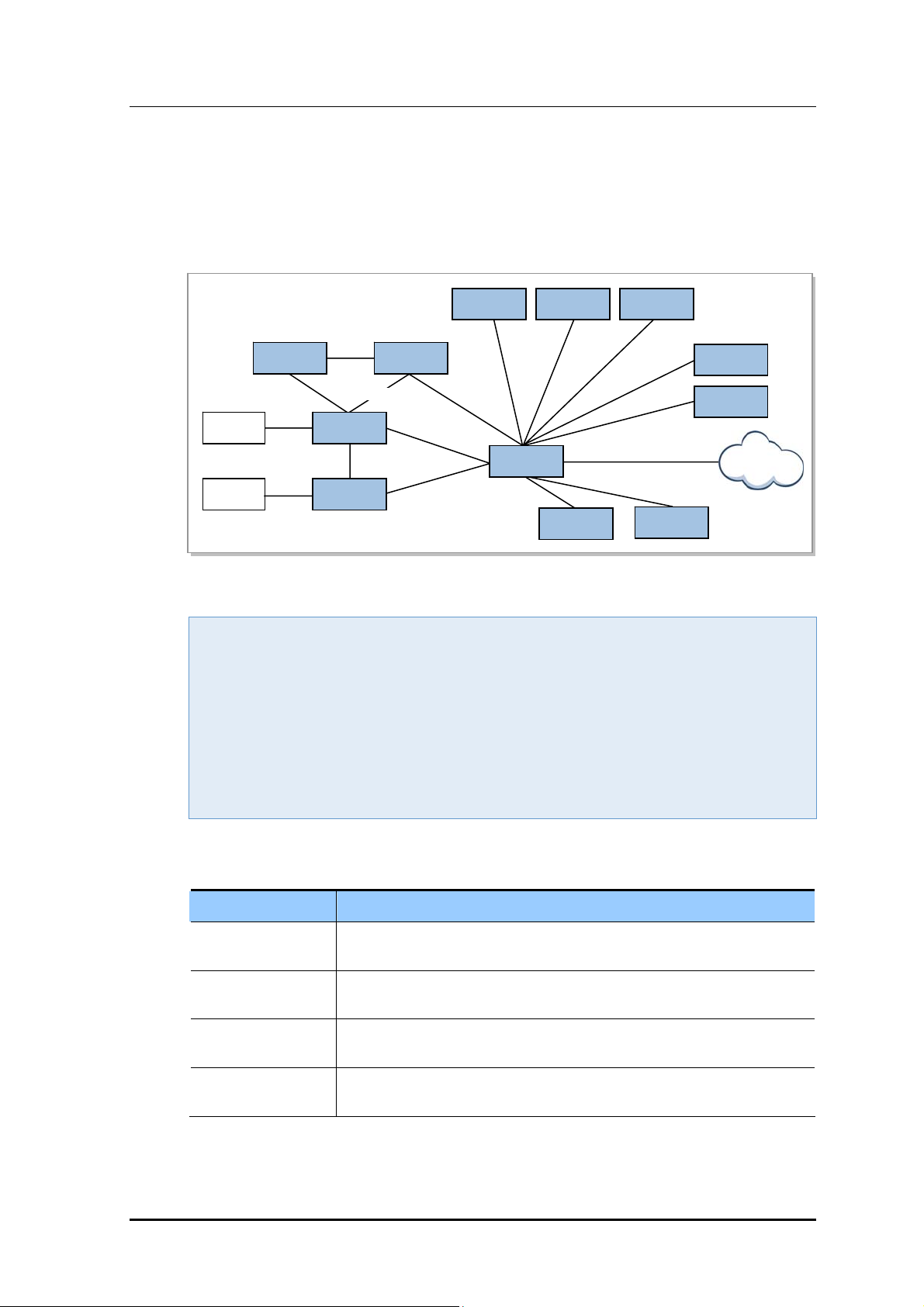
The following diagram shows the composition of 3GPP LTE network.
MetroPCS User Manual
Samsung Products
Other Products
LSM-R
(LTE eNB)
LTE eNB
CDM
Network
BSC/PCF
EMS (1x Core)
MME
EPC
Network
WSS
WGW
PSTN
PDSN
Packet Data
Network
S-GW
-
LSM-C (EPC)
Figure 1.1 LTE Network Configuration
© SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd. 1-1

CHAPTER 1. Overview of LTE Network
Evolved UTRAN Node-B (eNB)
The eNB is located between the UE and EPC. It processes packet calls by connecting to the
UE wirelessly according to the LTE Air standard. The eNB performs functionalities such as
transmission and receipt of wireless signals, modulation and demodulation of packet traffic
signals, packet scheduling for efficient utilization of wireless resources, Hybrid Automatic
Repeat Request (HARQ)/ARQ processing, Packet Data Convergence Protocol (PDCP) for
packet header compression, and wireless resources control. Moreover, it performs handover
interoperating with the EPC.
Evolved Packet Core (EPC)
The EPC succeeds to the 3GPP Release 7 packet-switched core network and consists of
Mobility Management Entity (MME), Serving GW (S-GW), and PDN GW (P-GW).
The MME performs MS mobility management and session management, Mobile Station
(MS) authentication, and HO control. The MME also processes the control plane through
interoperation between eNB and MME, UE and MME, Serving General Packet Radio
Service (GPRS) Support Node (SGSN) and MME, MME and MME, MME and SGW,
MME, Home Subscriber Server (HSS) and Equipment Identity Register (EIR). The SGW/P-GW processes the user plane.
It processes routing and forwarding the user data between the UE and the PDN network.
The P-GW performs the gateway function to the PDN network, interoperation with non3GPP network, and address allocation for the UE.
Mobility Management Entity (MME)
The MME processes the control functions for the control plane, such as call connection
control and mobility management, tracking area list management, bearer and session
management by processing NAS signaling with the MS and S1 Application Protocol (S1AP) signaling with the eNB.
The control functions for the control plane that the MME processes are given below.
y Non Access Stratum (NAS) signaling
y NAS signaling security
y Inter Core Network (CN) node signaling for mobility between 3GPP access networks
y UE Reachability in ECM-IDLE state (including control and execution of paging
retransmission)
y Tracking Area list management
y PDN GW and Serving GW selection
y MME selection for handovers with MME change
y SGSN selection for handovers to 2G or 3G/3GPP access networks
y Roaming (S6a towards home HSS)
y Authentication
y Bearer management functions including dedicated bearer establishment
y Lawful Interception
1-2 © SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd.

MetroPCS User Manual/ED.00
Serving Gateway (S-GW)
The S-GW performs the mobility anchor function within the LTE system and between LTE
and 3GPP access system, and processes transmission of downlink/uplink packet data.
The S-GW supports GPRS Tunneling Protocol (GTP) and Proxy Mobile IP (PMIP)
protocols for signaling processing with MME, P-GW, and SGSN.
PDN Gateway (P-GW)
The P-GW allocates an IP address to UE and, for mobility between the LTE system and
non-3GPP access system, provides the anchor function and the packet filtering function for
each subscriber. In addition, it handles accounting and bearer policy in accordance with the
policy interoperating with the Policy Charging & Rule Function (PCRF), and provides the
accounting function, the transmission rate management and change functions that depend
on the service level.
LTE System Manager (LSM)
The LSM provides the interface for the operator, and the software management,
configuration management, performance management, and error management functions so
that s/he can operate and maintain eNB/EPC. The LTE System Manager-Core (LSM-C)
performs the operating management function for EPC (MME, S-GW, P-GW). The LTE
System Manager-Radio (LSM-R) performs the operating management function for eNB,
and also the SON server (LTE SON server, LSS) function.
Home Subscriber Server (HSS)
The HSS is a database management system that stores and manages the parameters and
location information for all registered mobile subscribers. The HSS manages key data such
as the mobile subscriber’s access capability, basic services and supplementary services, and
provides a routing function to the subscribed receivers.
Policy Charging & Rule Function (PCRF)
The PCRF creates policy rules to dynamically apply the QoS and accounting policies
differentiated by service flow, or creates the policy rules that can be applied commonly to
multiple service flows. Since the IP edge contains the Policy and Charging Enforcement
Function (PCEF), it can apply the policy rules transmitted from PCRF to each service flow.
Authorization, Authentication and Accounting (AAA)
The AAA is a system providing authentication and authorization functions to the packet
data service subscribers. The AAA server also provides a billing function based on service
usage.
Charging Gateway Functionality (CGF)
The accounting data generated from the PCEF is stored in the CGF and is provided for
each subscriber.
© SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd. 1-3

CHAPTER 1. Overview of LTE Network
Online Charging System (OCS)
When a subscriber for whom online information is required makes a call, the PCEF sends
and receives his accounting information in interoperation with the OCS.
Domain Name Service (DNS)
The DNS manages mapping between domain names and IP addresses. When an MS
requests, it notifies the IP address of the requested domain.
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
The DHCP server is an auxiliary device for providing packet services. It manages and
assigns IP addresses.
1-4 © SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd.
MetroPCS User Manual/ED.00
1.2 Interface between Systems
1.2.1 LTE Network Interface
The figure below shows LTE network interface.
PCRF OCS CGF
LSS LSM
SNMP/FTP/SOAP
UE
UE
Uu
Uu
FTP/
SOAP
SNMP/FTP/SOAP
eNB
X2
eNB
S1
S1
Gx Gy Gz
TL1/FTP
EPC
socket
DHCP
AAA
S6b
HSS
S6a
SGi
DNS
Figure 1.2 LTE Network Interface
AAA: Authentication, Authorization and Accounting CGF: Charging Gateway Function
DHCP: Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol DNS: Domain Name System
eNB: E-UTRAN NodeB LSM: LTE System Manager
EPC: Evolved Packet Core HSS: Home Subscriber Server
OCS: Online Charging System PCRF: Policy and Charging Rule Function
PDN: Packet Data Network UE: User Equipment
FTP: File Transfer Protocol SOAP: Simple Object Access Protocol
SNMP: Simple Network Management Protocol TL1: Transaction Language 1
LSM
PDN
The interfaces between LTE system co mponents are depicted below.
Interfaces Interface Specifications
UE/eNB - Physical Interface: LTE PHY OFDMA/SC-FDMA
- Interface protocol: LTE Uu Interface
eNB/EPC - Physical Interface: FE/GE
- Interface protocol: LTE S1 Interface (S1-MME, S1-U)
eNB/eNB - Physical Interface: FE/GE
- Interface protocol: LTE X2 Interface
eNB/LSM - Physical Interface: FE/GE
- Interface protocol: SNMP/FTP/SOAP
© SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd. 1-5

CHAPTER 1. Overview of LTE Network
Interfaces Interface Specifications
EPC/LSM - Physical Interface: FE/GE
- Interface protocol: TL1/FTP
eNB/LSS - Physical Interface: FE/GE
- Interface protocol: SNMP/FTP
LSS/LSM - Physical Interface: FE/GE
- Interface protocol: RMI/SOAP
EPC/PCRF - Physical Interface: FE/GE
- Interface protocol: Gx Interface
(Continued)
EPC/DHCP
Server
- Physical Interface: FE/GE
- Interface protocol: socket communication
1.2.2 Interface protocol
These are interface protocols between components.
Interface between eNB and UE
This shows the user plane protocol stack for interface between eNB and UE.
PDCP
RLC
MAC
PHY
UE
PDCP
RLC
MAC
PHY
eNB
Figure 1.3 User plane protocol stack between eNB and UE
The user plane protocol stack between eNB and UE is used for transmission of the IP
packet, consisted of packet data convergence protocol (PDCP) sublayer, Radio Link
Control (RLC) sublayer, Medium Access Control (MAC) sublayer and physical layer.
1-6 © SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd.

MetroPCS User Manual/ED.00
This shows the control plane protocol stack for interface between eNB and UE.
RRC RRC
PDCP
RLC
MAC
PHY
UE
Figure 1.4 Control plane protocol st ac k betwee n eNB a nd UE
PDCP
RLC
MAC
PHY
eNB
The control plane protocol stack between eNB and UE is used for transmission the control
signal, consisted of Radio Resource Control (RRC), PDCP sublayer, RLC sublayer, MAC
sublayer and physical layer.
Interface between eNB and S-GW
This shows the user plane protocol stack for interface between eNB and Serving Gateway
(S-GW).
User Plane
PDUs
GTP-U GTP-U
UDP
IP
L2
L1
eNB
Figure 1.5 User plane protocol stack between eNB and S-GW
User Plane
PDUs
UDP
IP
L2
L1
S-GW
The user plane protocol stack between eNB and S-GW is used for transmission of Protocol
Data Unit (PDU)s of user plane, consisted of GPRS Tunneling Protocol - User (GTP-U),
User Datagram Protocol (UDP), IP, L2 data link layer and L1 physical layer.
© SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd. 1-7

CHAPTER 1. Overview of LTE Network
Interface between eNB and MME
This shows the control plane protocol stack for interface between eNB Mobility
Management Entity (MME).
S1-AP S1-AP
SCTP SCTP
IP
L2
L1
eNB
IP
L2
L1
MME
Figure 1.6 Control plane protocol st ac k betwee n eNB a nd MM E
The control plane protocol stack between eNB and MME is used for the signaling
transmission for S1 interface, consisted of Stream Control Transmission Protocol (SCTP),
IP, L2 data link layer and L1 physical layer.
Interface between eNB and eNB
This shows the user plane protocol stack for interface between eNBs.
User Plane
PDUs
User Plane
PDUs
GTP-U GTP-U
UDP
IP
L2
L1
eNB
UDP
IP
L2
L1
eNB
Figure 1.7 User plane protocol stack between eNBs
1-8 © SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd.

MetroPCS User Manual/ED.00
The user plane protocol stack between eNBs is used to transmit the user plane PDUs
between eNBs, consisted of GTP-U, UDP, IP, L2 data link layer and L1 physical layer.
This shows the control plane protocol stack for interface between eNBs.
X2-AP X2-AP
SCTP SCTP
IP
L2
L1
eNB
IP
L2
L1
eNB
Figure 1.8 Control plane protocol st ac k betwee n eNBs
The control plane protocol stack between eNBs is used for transmission of control signal
between eNBs, consisted of SCTP, IP, L2 data link layer and L1 physical lay er.
Interface between eNB and LSM
This shows the protocol stack for interface between eNB and LSM.
SOAP
HTTP
FTP/
SFTP
SNMP
SOAP
HTTP
FTP/
SFTP
SNMP
TCP
IP
L2
L1
eNB
UDP
TCP
IP
L2
L1
LSM
UDP
Figure 1.9 Protocol stack between eNB and LSM
© SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd. 1-9

CHAPTER 1. Overview of LTE Network
The protocol stack between eNB and LTE System Manager (LSM) is used for transmission
of Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP), File Transfer Protocol (FTP), Secure FTP
(SFTP) and Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) using Hypertext Transfer
Protocol (HTTP), consisted of TCP/UDP, IP, L2 data link layer and L1 physical layer.
Interface between eNB and LSS
This shows the protocol stack for interface between eNB and LSS (LTE SON Server).
SOAP
HTTP
TCP
FTP/
SFTP
IP
L2
L1
eNB
SNMP
UDP
SOAP
HTTP
TCP
FTP/
SFTP
SNMP
UDP
IP
L2
L1
LSM
Figure 1.10 Protocol stack between eNB and LSS
The protocol stack between eNB and LSS is used for transmission of SOAP, FTP, secure
FTP and SNMP using HTTP, consisted of TCP/UDP, IP, L2 data link layer and L1 physical
layer.
1-10 © SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd.

MetroPCS User Manual
CHAPTER 2. Overview of LTE eNB
2.1 Introduction to LTE eNB
The 3GPP LTE represents a major advance in cellular technology. LTE is designed to meet
needs for high-speed data and media transport as well as high-capacity voice support.
The LTE encompasses high-speed data, multimedia unicast and multimedia broadcast
services. The LTE PHY is a highly efficient means of conveying both data and control
information between an enhanced eNB and mobile UE.
LTE has been set aggressive performance requirements that rely on physical layer
technologies. These include Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) and
Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO) data transmission. In addition, the LTE PHY uses
Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA) on the downlink and Single
Carrier - Frequency Division Multiple Access (SC-FDMA) on the uplink.
LTE eNB is controlled by EPC and connects LTE calls to UE.
The LTE eNB interfaces with UE via a wireless channel observing the 3GPP LTE standard
and provides high-speed data service and multimedia service in wireless broadband.
The LTE eNB provides the following functions: modulation/demodulation of packet traffic
signal, scheduling and radio bandwidth allocation to manage air resources efficiently and
ensure Quality of Service (QoS), connection control and set/hold/disconnect the packet call
connection, handover control and EPC interface and system operation management
function.
© SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd. 2-1

CHAPTER 2. Overview of LTE eNB
2.2 Main Functions
The major characteristics of the LTE system are listed below.
OFDMA Downlink Transmission
OFDMA is employed as the multiplexing scheme in the LTE downlink.
OFDMA is used to transmit data to several users simultaneously by using the sub-carrier
allocated to each user and transmit data by allocating one or more sub-carriers to a specific
subscriber according to the channel status and the transmission rate requested by a user.
In addition, since it can select the sub-carriers with excellent features for each subscriber
and allocate them to the subscribers when some subscribers divide and use the whole subcarrier, it can raise the data throughput by distributing the resources efficiently.
SC-FDMA Uplink Transmission
In the uplink, SC-FDMA is selected to efficiently meet Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio
Access (E-UTRA) performance requirements. SC-FDMA has a low power amplifier derating (Cubic Metric/PAPR) requirement, thereby conserving battery life or extending
range.
Downlink MIMO
For the LTE downlink, a 2 × 2 configuration for MIMO is assumed as baseline
configuration, i.e., 2 transmit antennas at the base station and 2 receive antennas at the
terminal side. Configurations with 4 antennas are also considered.
It has to be differentiated between spatial multiplexing and transmit diversity, and it
depends on the channel condition which scheme to select. Spatial multiplexing allows
transmitting different streams of data simultaneously on the same downlink resource block
(s). These data stream can belong to one single user (single user MIMO/SU-MIMO) or to
different users (multi user MIMO/MU-MIMO). While SU-MIMO increases the data rate of
one user, MU-MIMO allows increasing the overall capacity.
Uplink MIMO
Uplink MIMO schemes for LTE will differ from downlink MIMO schemes to take into
account UE complexity issues. For the uplink, MU-MIMO can be used. Multiple UEs may
transmit simultaneously on the same resource block.
This is also referred to as Spatial Domain Multiple Access (SDMA).
The scheme requires only one transmit antenna at UE side which is a big advantage.
2-2 © SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd.

MetroPCS User Manual/ED.00
Power Control
The LTE carries out the power control function for the uplink signal received from multiple
UEs and then set the power intensity of the uplink signal to a specific level.
The LTE transmits the power correction command to each UE and then makes the UE
power intensity be the level required when the UE transmits the modulated uplink signal in
a specific Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM) modulation method.
LTE eNB is mainly composed of digital unit and radio unit to perform the advance
technologies.
The main functions of digital unit are as follows.
y Subscriber data traffic processing
y Call processing, resource allocation and OAM
y GTP, PDCP, OAM, RRC, RRM processing
y Reception of the GPS signal and creation and supply of the clock
y Fault diagnosis and alarm collection and control
y Fast Ethernet/Gigabit Ethernet interface to backhaul
y RLC, MAC/PHY processing
y OFDMA/SC-FDMA channel processing
The main functions of radio unit are as follows.
y Upconversion/downconversion of frequency
y High-power amplification of RF transmission signal
y Suppression of out-of-band spurious wave emitted from RF Rx/Tx signal
y Gain control of RF Rx/Tx signal
y Rx/Tx RF signal from/to an antenna
y Low noise amplification of band-pass filtered RF Rx signal
© SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd. 2-3
 Loading...
Loading...