SAMSUNG ML6050XSA Service Manual
SERVICE
LASER PRINTER
ML-6050
QwikLaser 6050
LASER PRINTER CONTENTS
1. Precautions
2. Specifications
3. Reference Information
4. Disassembly and Reassembly
5. Troubleshooting
6. Exploded Views and Parts List
7. Electrical Parts List
8. Schematic Diagrams
MANUAL

©Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. Mar. 1999
Printed in Korea
P/N. JC68-00072A Rev.1.00
ELECTRONICS

Samsung Electronics 1-1
1. Precautions
1-1. Safety Precautions
Read each caution carefully:
1. Do not use this printer near water or when exposed
to inclement weather.
2. Do not place this printer on an unstable cart, stand
or table; the product may fall, causing serious damage to the product.
3. Slots and openings in the cabinet are provided for
ventilation. To ensure reliable operation and to protect the printer from everheating, do not block or
cover any of these openings. Do not place the printer in an enclosure unless the enclosure provides
adequate ventilation.
4. Never push objects of any kind into the printer
through the cabinet ventilation slots as they may
touch dangerous high voltage points, create short
circuits, cause a fire, or produce an electrical shock.
Never spill liquid of any kind on the printer.
5. Do not place the printer in a location where someone may trip on the cords.
6. Select a work surface that is large enough to hold
the printer.
7. Position the printer within six feet of the computer
and within five feet of an electrical outlet.
8. Operate this printer using the power source (110V,
220V, etc) indicated on the marking label. If you are
not sure of the type of power source available, consult your dealer or local power company.
9. If you need to use an extension power cord with
this printer, make sure that it uses a three-wire
grounded cord and that the total ampere ratings for
all of the products using the extension do not
exceed the extension cord ampere rating. Also,
make sure that the total of all products plugged
into the wall outlet does not exceed 15 amperes.
10. Do not allow anything to rest on the power cord
or data communications cable.
11. Unplug this printer from the wall outlet before
cleaning. Do not use liquid cleaners or aerosol
sprays. Use a damp cloth for cleaning.
12. Do not touch the surface of the photo-sensitive
drum as marks or scratches may impair print
quality.
13. Do not expose the drum unit to direct light for
prolonged periods.
14. Use only standard papers, OHP films, and
approved envelopes. Feed OHP films though the
manual feed slot only. See specifications for
approved papers and envelopes.
15. Other than replacing consumables such as paper
and toner, refer all questions to qualified service
personnel.
LASER STATEMENT (LASERTURVALLISUUS)
WARNING: NEVER OPERATE AND SERVICE THE PRINTER
WITH THE PROTECTIVE COVER REMOVED
FROM LASER/SCANNER ASSEMBLY. THE
REFLECTIVE BEAM, ALTHOUGH INVISIBLE, CAN
DAMAGE YOUR EYES.
Allonpituus 770-795nm
Teho 0.3mW±0.03mW
CAUTION
VORSICHT
ATTENTION
ATTENZIONE
PRECAUCION
INVISIBLE LASER RADIATION WHEN
THIS COVER OPEN. DO NOT OPEN
THIS COVER.
UNSICHTBARE LASERSTRAHLUNG,
WENN ABDECKUNG GEOFFNET.
NIGHT DEM STRAHLAUSSETZEN.
REYONNEMENT LASER INVISIBLE EN CAS D’OUVERTURE. EXPOSITION DANGERUSE AU FAISCEAU.
RADIAZIONE LASER INVISIBILE IN CASO DI
APERTURA. EVITARE L’ESPOSIZONE LA FASCIO.
REDIACION LASER INVISIBLE CUANDO SE
ABRE. EVITAR EXPONERSE AL RAYO.

Precautions
1-2
Samsung Electronics
1-2. Servicing Precautions
1. Before disassembly, pull the power plug from the AC
power connector.
2. To avoid spilling toner inside the machine, do not turn
the printer over or on its side before removing the
developer cartridge.
3. Faulty installation of DRAMs may cause permanent
damage to the Laser Printer.
4. Use only+5V power for video controller-related circuitry.
5. When replacing parts, use only the same type of part
as the original. Replacing components with a second
vendor ’s part may cause faulty operation.
6. Check the insulation between the blades of the AC
plug and accessible conductive parts (examples : metal
panels and input ports).
7. Insulation Checking Procedure:
Disconnect the power cord from the AC power source.
Connect an insulation resistance meter (500V) to the
blades of the AC plug.
The insulation resistance between each blade of the
AC plug and accessible conductive parts (see left)
should be greater than 1 megaohm.
8. Never defeat any of the B+ voltage interlocks. Do not
apply AC power to the unit (or any of its assemblies)
unless all solid-state heat sinks are correctly installed.
9. Always connect a test instrument’s ground lead to the
instrument chassis ground before connecting the positive lead; always remove the instrument’s ground lead
last.
Note: Requirements for AC power are described on the label affixed to the rear of the printer. Check the AC
voltage rating requirement before use.
1-3. ESD Precautions
1. Immediately before handling any semiconductor components assemblies, drain the electrostatic charge from
your body by touching a known earth ground.
Alternatively, wear a discharging wrist strap device.
(Be sure to remove the strap before applying power to
the unit under test to avoid potential shock.)
2. After removing ESD-equipped assembly, place it on a
conductive surface such as aluminum foil to prevent
accumulation of an electrostatic charge.
3. Do not use freon-propelled chemicals. These can generate electrical charges sufficient to damage ESDs.
4. Use only a ground-tip soldering iron when soldering
or desoldering ESDs.
5. Use only anti-static solder removal device. Some solder removal devices are not rated as “anti-static;”these
can accumulate sufficient electrical charge to damage
ESDs.
6. Do not remove a replacement ESD from its protective
package until you are ready to install it. Most replacement ESDs are package with leads that are electrically
shorted together by conductive foam, aluminum foil
or other conductive materials.
7. Immediately before removing the protective material
from the leads of a replacement ESD, touch the protective material to the chassis or circuit assembly into
which the device will be installed.
8. Minimize body motions when handling unpackaged
replacement ESDs. Motion such as your clothes brushing together, or lifting a foot from a carpeted floor can
generate enough static electricity to damage an ESC.
9. Handle ICs and EPROMs carefully to avoid bending a
pin.
10. Pay attention to the direction of parts when mount-
ing or inserting them on a PCB.
11. Components can be permanently damaged if heated
for longer than necessary while welding. All components are susceptible to heat damage.
Some semiconductor (“solid state”) devices are easily damaged from static electricity. Such components commonly are called Electrostatically Sensitive Devices (ESDs); examples include integrated circuits (ICs), LargeScale Integrated circuits (LSIs), some field-effect transistors, and semiconductor chip components. The following techniques will reduce the occurrence of component damage caused by static electricity:
CAUTION: Be sure the power is off to the
chassis or circuit board, and
observe all other safety precautions

Abbr Definition Abbr Definition
amps
ass’y
badac
bps
CBUSY
CCLK
clk
cm
CMSG
CON
DS
EBUSY
EMSG
Exitpap
GND
HLDA
hldar
HLDR
HOR
HSYNC
I/O
in
INT
INTA
INTR
lb.
LDON
lin
lock
Lready
ADC
ALE
ASCII
amperes
assembly
bad access
bits per second
Command busy
Command clock
clock
centimeter(s)
Command message
connector
Data Strobe
Engine Status busy
Engine Status message
Exit paper
ground
hold acknowledge
hold acknowledge received
hold request
horizontal
Horizontal sync
Input and Output
inch(es) or input
Interrupt
Interrupt Acknowledge
Interrupt Request
Pound(s)
laser Diode On
linearit
bus lock
LSU power ready
Analog to Digital Converter
Address-Latch Enable
American Standard Code for
Information Interchange
motor_pa
motor_pb
mpx
neg
od
OSC
OUT
pba
pcb
pix
Pmotor
pos
pot
ppm
PRINT
psync
pwr
Q_Lamp
qty
READY
sw
tach
thvea
Vcc
VDI
VDO
vert
Vp-p
VR
mm
LED
LSU
MHV
MPU
Motor phase A
Motor phase B
multiplex
negative
open drain
oscillator
output
printed board assembly
printed circuit board
picture
LSU motor on
positive or position
potential
print pages per minute
Print command
page synchronization
power
Quenching Lamp
quantity
Engine print ready
switch
tachometer
Transfer high voltage Enable
collector supply voltage (dc)
Video data from controller
Video data output
vertical
peak-to-peak voltage
variable resistor
millimeter(s)
Light Emitting Diode
Laser Scanner Unit
Main High Voltage
Micro Processor Unit
Samsung Electronics 3-1
3. Reference Information
3-1. Abbreviations and Acronyms
Tables 3-1-1 and 3-1-2 list abbreviations and acronyms which may be found in this service manual.
Abbreviations

Reference Information
3-2
Samsung Electronics
Abbr Definition Abbr Definition
BIOS
BPS
CMOS
CPU
DCU
DMA
DMAC
DOS
DPI
DRAM
DVM
EEPROM
ICU
Basic Input/Output System
Bits Per Second
Complementary Metal Oxide
Semiconductor
Central Processing Unit
Diagnostic Control Unit
Direct Memory Access or
Dynamic Memory Access
Direct Memory Access Controller
Disk Operating System
Dots Per Inch (resolution)
Dynamic Random Access Memory
Digital Voltmeter
Electronically Erasable
Programmable Read Only Memory
Image Control Unit
NC
PCB
PCU
PLCC
PPM
PQFP
PWM
QFP
RAM
ROM
SCC
SMPS
SOP
THV
TS
VCU
No Connection
Printed Circuit Board
Printed Control Unit
Plastic Leaded Chip Carrier
Page Per Minute
Plastic Quad Flat Package
Pulse Width Modulation
Quad Flat Package
Random Access Memory
Read Only Memory
Serial Communications Controller
Switching Mode Power Supply
Small Outline Package
Transfer High Voltage
Tri-State
Video Control Unit
3-2. Chip Replacement (SMD)
3-2-1. Precautions for Chip Replacement
1. Do not directly touch any portion of the part with
the soldering iron. ICs, especially TSOPs, are easily
damaged by heat.
2. Use care with the soldering iron tip and avoid
rapidly heating parts. Some parts can be damaged
by sudden heating. Preheat the part at about 100oC
for several minutes before installing it.
3. Use a soldering tip temperature of about 240oC.
For larger parts, use a slightly higher temperature
(about 280oC).
4. The thin (0.3mm) solder for miniature parts does
not contain adequate flux. Supplementary flux is
thus needed in most cases.
Computer, OAand A/V systems are manufactured
using flux which can be cleaned by water. When
you replace the part or when troubleshooting, use
proper flux and solder which can be cleaned by
water.
Improper flux may cause the soldering area to corrode and may cause a fatal system error.
5. Use care not to damage the circuit pattern, especially when desoldering. Because of the many pins,
cleanliness of the pattern is extremely important
after removing an IC.
6. Use care to avoid solder bridges. Remove any
bridges that occur.
7. Position the part carefully. This also affects the soldering operation. Be very precise in positioning the
IC. Soldering opposite pins first holds the IC in
place and makes soldering the other pins easier.
8. Do not reuse removed parts.
9. Clock for solder joints, especially miniature parts
with small lead.
10. A defective trimming resistor cannot be adjusted
externally. Replace with an ordinary variable resistor.
11. Always inspect the work with a magnifying lens.
Check after installing cold solder joints, etc.

Reference Information
Samsung Electronics 3-3
3-2-2. Tools for Chip Replacement
The tools for chip replacement are as follows:
· Thin tip type soldering iron.
· Small flat-blade tip type soldering iron
· Special desoldering tip iron
· Air-blower Unit
· Flat Package Pick-up
· Flux that can be cleaned by water
· 0.3mm thin solder that can be cleaned by water
· Desoldering wire
· Tweezers
3-2-3. Chip Resistor and Chip Capacitors
TYPES
The types of chip resistors and chip capacitor are as
follows:
· Thick Film Chip Resistors
· Carbon Film Chip Resisters
· Metal Film Chip Resisters
· Chip Ceramic Capacitors
· Chip Trimming Resisters
REMOVING
1. Using Two soldering irons:
a. Use thin tip soldering irons
b. Use soldering tip temperature of about 280oC.
c. Simultaneously heat both ends of the part.
d. While heating, grasp the part with the tips of the
soldering irons and remove it.
e. Use desoldering wire to completely remove the
old solder from the part location on the board. A
clean pattern for installing the new part is very
INSTALLING
1. Clean the area where the new part is to be mounted.
2. Apply a water soluble flux.
3. Set part correctly into position and prevent is from
shifting.
4. Bring the soldering iron tip close to the part contact
without actually touching it. Melt thin (0.3mm) solder between the tip and part so that it flows into
the part contact.
5. Check work quality with a magnifying lens.
3-2-4. Chip Tantalum Capacitors and
Chip filters
TYPES
The types of chip tantalum capacitors and chip filters
are as follows:
· Chip Inductors
· Chip Tantalum Capacitors
· Chip Tantalum Electrolytic Capacitors
· Chip Aluminum Electrolytic Capacitors
· Chip Transformers
· Chip Filters
REMOVING
1. Using a special desoldering iron:
a. Select soldering tip according to part size.
b. Bring the tip into contact with the solder points.
c. When the solder melts, remove the part.
d. Remove the old solder with desoldering wire.
2. Using a special desoldering iron:
a. Use small flat-blade tips.
b. Heat both ends of the part simultaneously.
c. When the solder melts, grasp and remove the
part with the soldering iron tips.

Reference Information
3-4
Samsung Electronics
INSTALLING
1. Clean the area where the new part is to be mounted.
2. Apply a water soluble flux.
3. Set part correctly into position and prevent it from
shifting.
4. Use a sharp soldering iron tip. Bring the tip close to
the part contact without actually touching it. Melt
thin (0.3mm) solder between the tip and part so
that it flows into the part contact.
5. Check work quality with a magnifying lens.
3-2-5. Chip VRs, Chip Trimmer
Capacitors, Diode and Tr.
TYPES
The types of parts are as follows:
· Chip VRs
· Chip Trimmer Capacitors
· Diode
· Transistors
REMOVING
1. Using two soldering irons.
a. Use small-flat-blade tips.
b. Heat the leads of the part simultaneously.
c. When the solder melts, grasp and remove the
part with the soldering iron tips.
INSTALLING
1. Clean the area where the new part is to be mounted.
2. Apply a water soluble flux.
3. Set part correctly into position and prevent is from
shifting.
4. Use a sharp soldering iron tip. Bring close to the
part contact without actually touching it. Melt thin
(0.3mm) solder between the tip and part so that it
flows into the part contact.
3-2-6. Chip ICs
TYPES
The types of chip ICs are as follows:
1. SOP (Small Outline Package) IC
2. SSOP (Shrink Small Outline Package) IC
3. VSOP (Very Small Outline Package) IC
4. QFP (Quad Flat Package) IC
5. VQFP (Very Quad Flat Package) IC
6. PLCC (Plastic Leaded Chip Carrier) IC
7. TSOP (Thin Small Outline Package) IC
REMOVING
1. Using special desoldering iron:
a. Select the tip according to the size shape of the
IC.
b.“Tin” the tip with a small amount of the IC leads.
c. Set the tip squarely over the IC leads.
d. When the solder melts, carefully twist the iron.
e. Raise and remove the IC.
2. Using a shaped air-blower unit:
a. Select the correct nozzle.
b. Select the temperature and air-blow
(suggested : temperature : 7, air-blow:4)
c. Engage the IC removing tool.
d. Use the air-blow the preheat the IC for about 5
seconds, then heat with the nozzle until the IC
remove lifts the part from the board.
INSTALLING
1. Use desoldering wire to remove the previous solder
2. Clean the location.
3. Apply water soluble flux.
4. Position the IC and solder two pins at opposite
sides.
5. Use a sharp tipped soldering iron and carefully solder each pin. (After gaining experience, a thicker
tip can be used for better work efficiency)
6. Remove any solder bridges with desoldering wire.
Reference Information
Samsung Electronics 3-5
3-3. Recommended Test Equipment
Samsung recommends the following equipment when servicing the Laser Printer.
Digital Multimeter
Oscilloscope
High Voltage Probe
DCU (Diagnostic Control Unit)
A digital multimeter with attached LED or LCD 4-digit Panel
A digitizing oscilloscope which can measure more than 100MHz
A high voltage probe which can measure about less than 10KV
DCU can be supplied from Samsung which can easily shows the engine’s
error status
Table 3-4-1 Equipment List
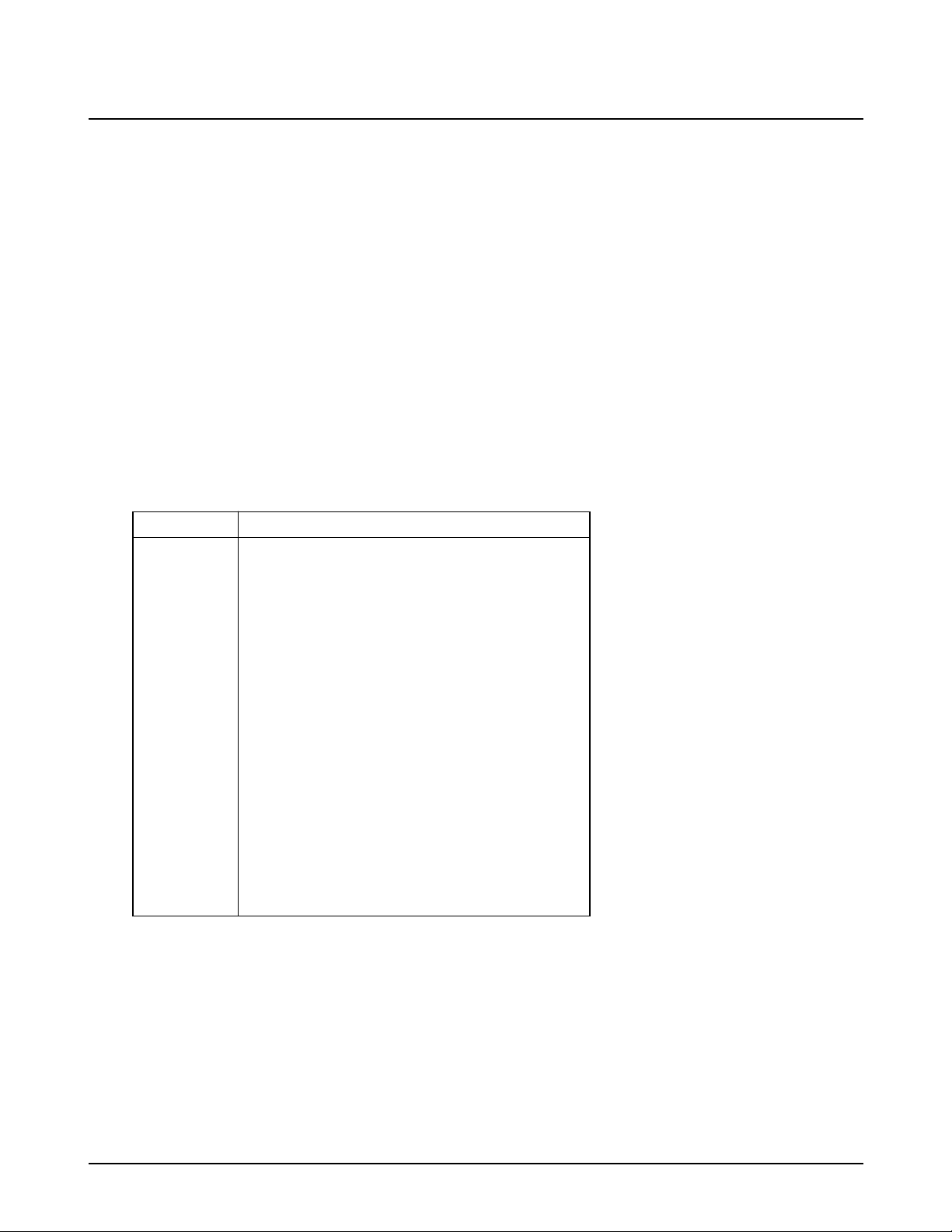
Figure 3-4-1 DCU
LBP DIAGNOSTIC CONTROL UNIT
DIAGNOSTIC MODE INDICATOR
04 DEV 300 DEV 350 DEV 350
05 LSU READY LSU MT & LD LSU MOTOR
07 PAPER EMPTY PAPER WIDTH NEW CRU
08 EXIT SENSOR FEED SENSOR
09 COVER OPEN
10 OVER HEATING PRINTING TEMP. READY TEMP.
ON
STATUS
SELF
TEST
DIAGNOSTIC
OFF
DIAGNOSTIC CODE
00 MAIN MOTOR OPERATING SYSTEM
01 MAIN HIGH VOLTAGE ON
02 TRANSFER HIGH VOLTAGE(-) ON
03 THV(+) REFERENCE ON
04 DEV/SUPPLY HIGH VOLTAGE/PTL ON
05 LSU OPERATING SYSTEM
06 PICKUP CLUTCH ON
07 PEMPTY/PWIDTH/NEW CRU TEST
08 FEED & EXIT SENSOR TEST
09 COVER OPEN SENSOR TEST
10 FUSER TEST
11 HOT BURN TEST
12 CLEANING MODE PRINT
13 THV(+) TRIGGER ALL HV & FAN ON
14 THV(+) REFERENCE ON
NORMAL STATUS CODE
61 WARM UP
00 READY(LEGAL)
01 READY(LETTER)
02 READY(A4)
03 READY(EXECUTIVE)
04 READY(B5)
20 PRINT START
30 FEED SENSOR ON
40 FEED SENSOR OFF
50 PAPER OUT
69 SLEEP MODE
ERROR STATUS CODE
60 OPEN FUSER ERROR
62 LOW TEMPERATURE ERROR
68 OVER HEATING ERROR
64 COVER OPEN ERROR
70 NO PAPER
71 PAPER JAM 0
72 PAPER JAM 1
73 PAPER JAM 2
95 LSU NOT READY
DIAGNOSTIC
MODE
TO ENTER DIAGNOSTIC MODE, PUSH THREE BUTTONS SIMULTANEOUSLY
AND TURN THE PRINTER POWER ON.
DOWN
UP
SHIFT STOP
ENTER
SEC CODE : ML+5000KC/XRX
Reference Information
3-6
Samsung Electronics
3-4. DCU Control
3-4-1. DCU Setup
1) Connect DCU to Controller Board Connector J6 (4 pins) or Engine Board CN2 (4pins).
2) To apply power, simultaneously press and hold down [DOWN], [SHIFT], and [STOP] keys. ‘78’ is displayed.
3) After 2-3 seconds, release the keys. ‘00’ is displayed.
4) Press [UP] or [SHIFT]+[DOWN] keys until the desired code number is displayed in the DCU display.
5) Press [ENTER] to begin operating.
6) Example : Select numbers ‘13’ and ‘14’ to adjust the electrophotography trigger voltage.
7) To end operation, press [SHIFT] and [STOP] keys.
3-4-2. DCU Diagnostic Mode
The DCU is used to diagnose the printer malfunction status.
00
01
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
MAIN MOTOR OPERATING SYSTEM
MAIN HIGH VOLTAGE ON
TRANSFER HIGH VOLTAGE(-) ON
THV(+) REFERENCE ON
DEV/SUPPLY HIGH VOLTAGE/PTL ON
LSU OPERATING SYSTEM
PICKUP CLUTCH ON
PEMPTY/PWIDTH/NEW CRU TEST
FEED & EXIT SENSOR TEST
COVER OPEN SENSOR TEST
FUSER TEST
HOT BURN TEST
CLEANING MODE PRINT
THV(+) TRIGGER ALL HV & FAN ON
THV(+) REFERENCE ON
Display Diagnostic Code Description

Reference Information
Samsung Electronics 3-7
3-4-3. DCU Error Status Code
DCU error code will indicate malfunction area of the machine.
60
62
68
64
70
71
72
73
95
OPEN FUSER ERROR
LOW TEMPERATURE ERROR
OVER HEATING ERROR
COVER OPEN ERROR
NO PAPER
PAPER JAM 0
PAPER JAM 1
PAPER JAM 2
LSU NOT READY
Display Diagnostic Code Description
3-4-4. Error Solution
60, 62, 68 1. Measure the resistance of the AC connector on the Fuser. Normal resistance is 2-4 ohmsfor
110V, 6-8 ohms for 220V.
2. Check if the fuser lamp works properly.
3. Measure the resistance at Q101 on the engine board. If abnormal, replace Q101, Q3, PC151, Q8.
70 1. Make sure that paper is loaded in the cassette.
2. Replace OP2 sensor (photo interrapter).
3. Check if the feed clutch works properly.
4. If abnormal, replace the feed clutch or Q4 on the engine board.
71 1. Make sure that paper is loaded in the cassette.
2. Check for pick-up unit. If it is heavily worn, replace it with new one.
3. Replace OP1 sensor.
72, 73 1. Make sure that the paper being used meets the specification.
2. Check if there is a paper jam in the fuser.
3. Replace OP1, OP3 on the engine board.
4. Check the fuser roller for any dirt. If dirty, clean the roller.
72, 73 1. Make sure that the paper being used meets the specification.
2. Check if there is a paper jam in the fuser.
3. Replace OP1, OP3 on the engine board.
4. Check the fuser roller for any dirt. If dirty, clean the roller.
95 1. Check for U205 on the engine board.
2. Replace LSU.
3. Measure the resistance at R62 and R8. If abnormal, replace them.
Display Solution

Reference Information
3-8
Samsung Electronics
Memo
MLE-6000
12PPM (A4 Size, 5% Character Pattern)
True 600 x 600 dpi
Laser Diode (LSU:Laser Scanner Unit)
Non-impact Electrophotography
Cassette & Manual, Option Feeder
*Size
(1) Standard : A4, Letter, Legal, B5, Executive, Folio
(2) Envelope : manual feed only
(3) Universal type
Length : 150 ~ 356 mm
Width : 90 ~ 216 mm
*Weigh : For Cassette, 60 ~ 90 g/m
2
For Manual, 60 ~ 120 g/m
2
*Recommended Paper
USA : X420, X4024, NEKOSA, BOISECASCADE
EC : REFLEX, ADAGIO
Transparancies : 3M(CG3300 or 3360)
Label : AVERY 53XX series
Face Down : 250 sheets, Face Up : 1 sheet
250 sheet tray
one option 250 sheet Drawer
70 seconds or less (23°C, 50%)
14 seconds or less (Fast Mode)
AC100~120V/ 220~240V(±15%), 50/60Hz (±3%)
300W Printing Avg/14W pring sleep
During Sleep : Max 28 W
Less than 30W during 1 hour when it turned on
C-UL, TUV, FCC, CDRH, CE, CB
Samsung Electronics 2-1
2. Specifications
Note: It is subject to change without notice.
Item
Engine
Print Speed
Resolution
Source of Light
Print Method
Feed Method
Paper Handling (input)
Paper Handing (output)
Feed Capacity
Warm-up time
First Print Time
Power Rating
Power Consumption
Power Saving
Consumption
Certification & Compliance
Specification & Description
Paper Type
Monarch
Com-10
Intl-DL
Intl C5
Paper size(mm2)
98.5 x 190.5
104.9 x 241.3
110 x 220
162 x 229
Specifications
2-2
Samsung Electronics
Stand by : Less than 36dB, Operating : Less than 49dB
Print Cartridge
150,000 sheets
Temperature : 10~30°C, Humidity : 20~80%RH
Temperature : 0~35°C, Humidity : 10~90%RH
Net : Max 11Kg, Gross : 12Kg
360 (W) x 368 (D) x 220 (H)mm
Life Span : 5,000 pages, 5% Pattern
Developing : Non-magnetic Contact Developing
Charging : Conductive Roller Charging
Density Adjustment : 3 step (Light, Medium, Dark)
Toner Supply Method : Exchanging the Developer
Toner Checking Sensor : None
Transfer System : Conductive Roller Transfer
Fusing System : Temperature & Pressure
Ozone Emission : Less than 0.1 PPM
PCL5e, PCLXL (compatible with HP LaserJet 5P)
1 bitmap
45 scalable (35 intelligent, 10 truetype)
ARM7 KS32C6100
Standard 4M byte (16M bit x 2)
Option SIMM Module ; 4, 8, 16, 32M byte
*Refer to Operator ’s Guide for instructions on SIMM installation.
2M byte (8M bit x 2 : Program) Flash Memory
512 bytes
Bidirectional Parallel Standard
- IEEE 1284 COMPATIBLE MODE
- IEEE 1284 NIBBLE MODE
- IEEE 1284 BYTE MODE
- IEEE 1284 ECP WITHOUT RLE
- IEEE 1284 ECP WITH RLE
Item
Acoustic Noise
Toner Supply
Expected Life Span
Operating Environment
Storage Environment
Weigh
External Dimension
Print Cartridge
Emulation
Font
CPU
RAM Memory
ROM
EEPROM
Interface
Specification & Description

Samsung Electronics 4-1
4. Disassembly and Reassembly
4-1. General Precautions on Disassembly
When you disassemble and reassemble components, you must use extreme caution. The close proximity of
cables to moving parts makes proper routing a must. If components are removed, any cables disturbed by the
procedure must be restored as close as possible to their original positions. Before removing any component
from the machine, note the cable routing that will be affected.
Whenever servicing the machine, you must perform as follows:
1. Remove the paper cassette(s), and the print cartridge. Do not expose the cartridge to direct room light or sun
light, and be careful not to scratch the drum surface.
2. Turn the power switch off.
3. Unplug all the cables from the printer.
4. Replace with only an authorized component.
5. Do not force to open or fasten a plastic material component.
6. Be careful no obstacles are included when you reassemble components.
7. When you reassemble components, be careful small size components are located in place.
8. If you turn the machine over to replace some parts, toner or paper particles may contaminate the LSU window. Protect the LSU window with clean paper.
Releasing Plastic Latches
Many of the parts are held in place with plastic latches. The
latches break easily; release them carefully. To remove such
parts, press the hook end of the latch away from the part to
which it is latched.

Disassembly and Reassembly
4-2
Samsung Electronics
4-2. Transfer Roller
1. Press the cover open switch and raise the printer
cover.
3. Pull the roller slightly to the right to release the left
end of the roller, then take it out.
2. Use a phillips screwdriver to release the right end
of the roller.
Disassembly and Reassembly
Samsung Electronics 4-3
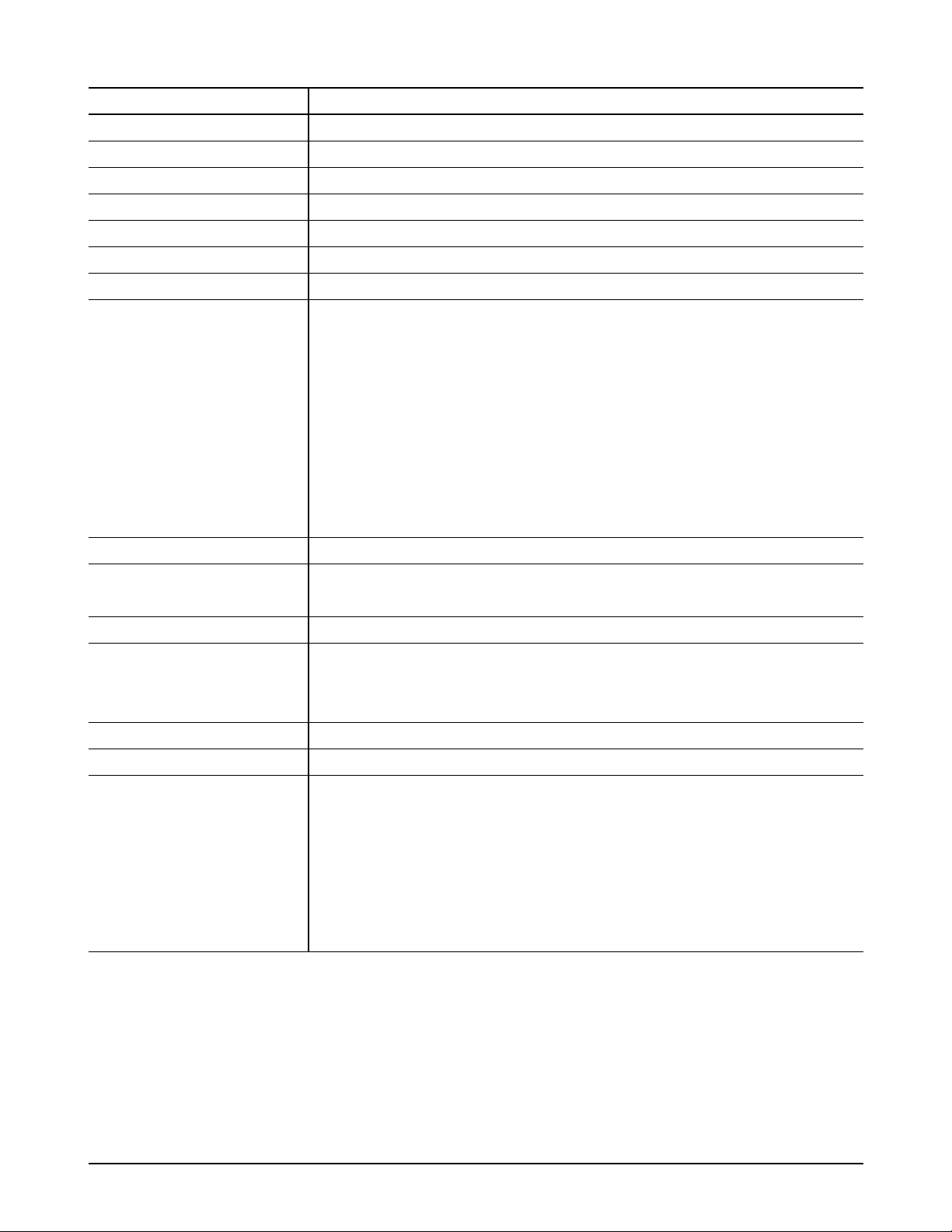
4-3. Controller Board
1. Remove the cover located at the right side of the
printer.
2. Remove one screw. Slide the shield cover in the
direction of OPEN arrow marked on the cover, then
remove the cover.
3. Unplug two connectors from the board.
4. Remove three screws securing the board and pull
the board out of the printer.
Disassembly and Reassembly
4-4
Samsung Electronics
4-4. Panel Board
1. Press the cover open switch and raise the printer
cover.
2. Remove the panel cap.
3. Unplug one connector from the panel board.
4. Remove three screws from the board, and remove
the board.
5. Remove the Window LED and button panel LED.

Disassembly and Reassembly
Samsung Electronics 4-5
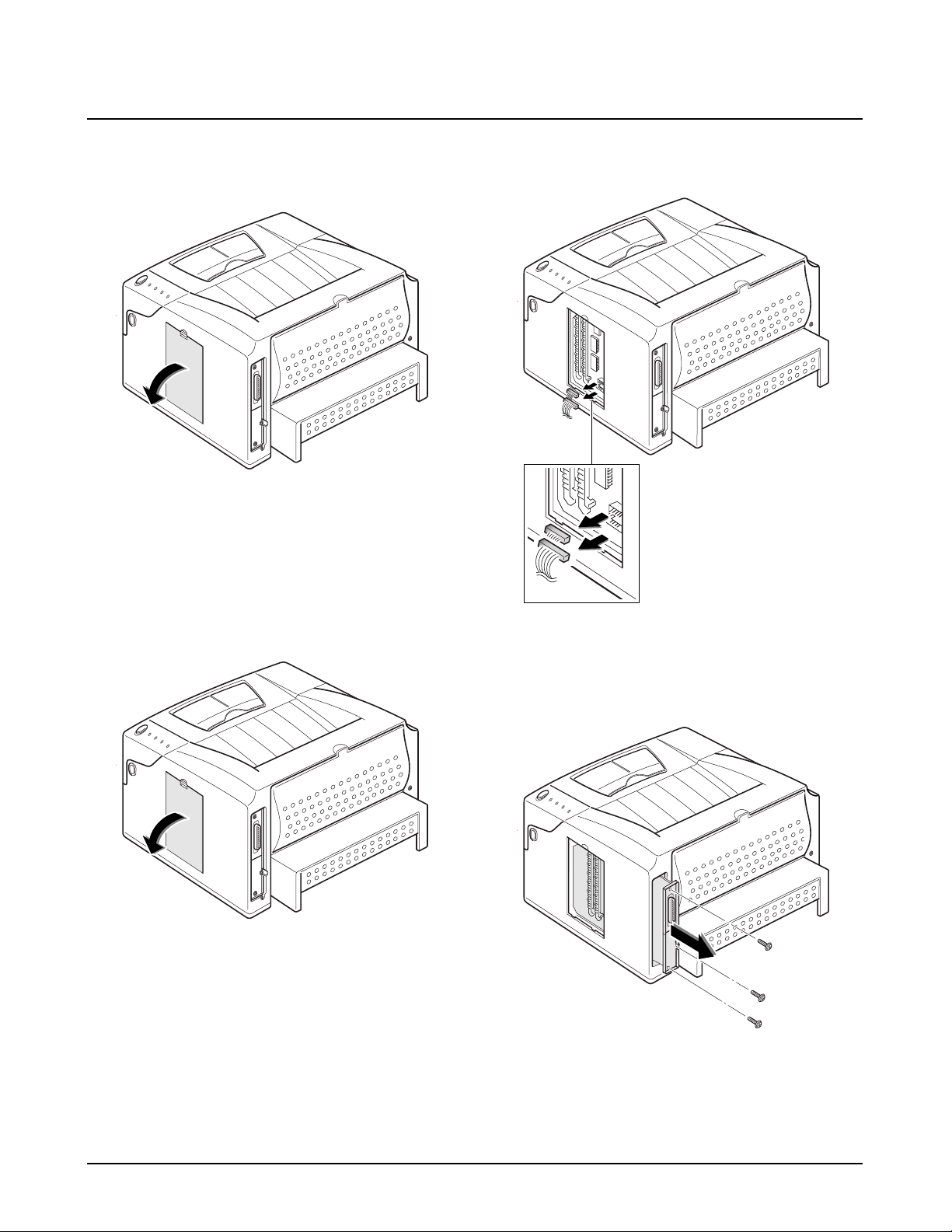
4-5. Pickup Assembly
1. Turn the printer over. Remove three screws from
the left base bracket, and take the bracket out.
2. Remove one ground screw.
3. Remove two screws securing the pickup assembly
and take the assembly out.
Push the solenoid if you
have difficulty to remove
the pickup assembly.
4. Check the pickup rubber wear. If the rubber is
heavily worn, replace it with a new one.
Squeeze this tab to
remove the rubber.
Disassembly and Reassembly
4-6
Samsung Electronics
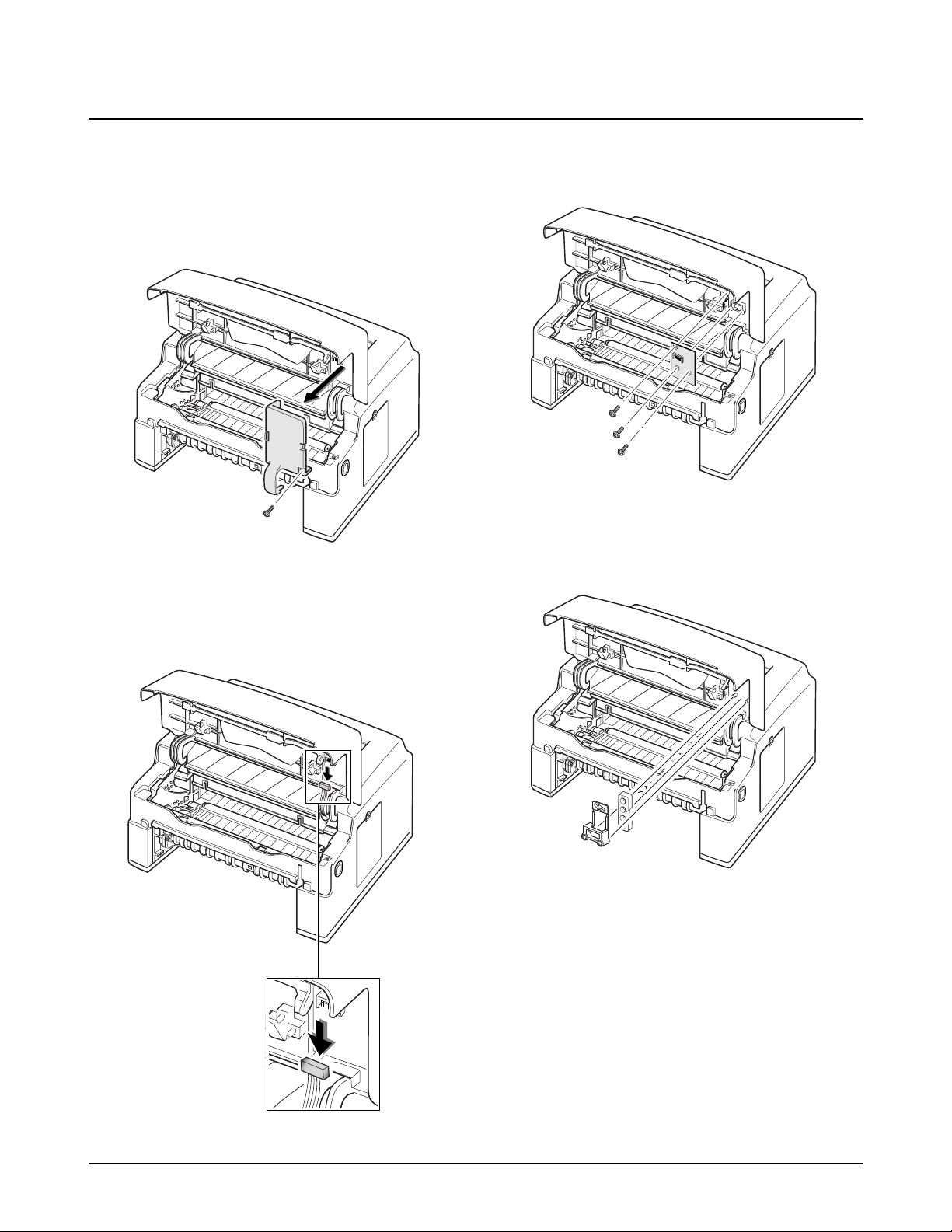
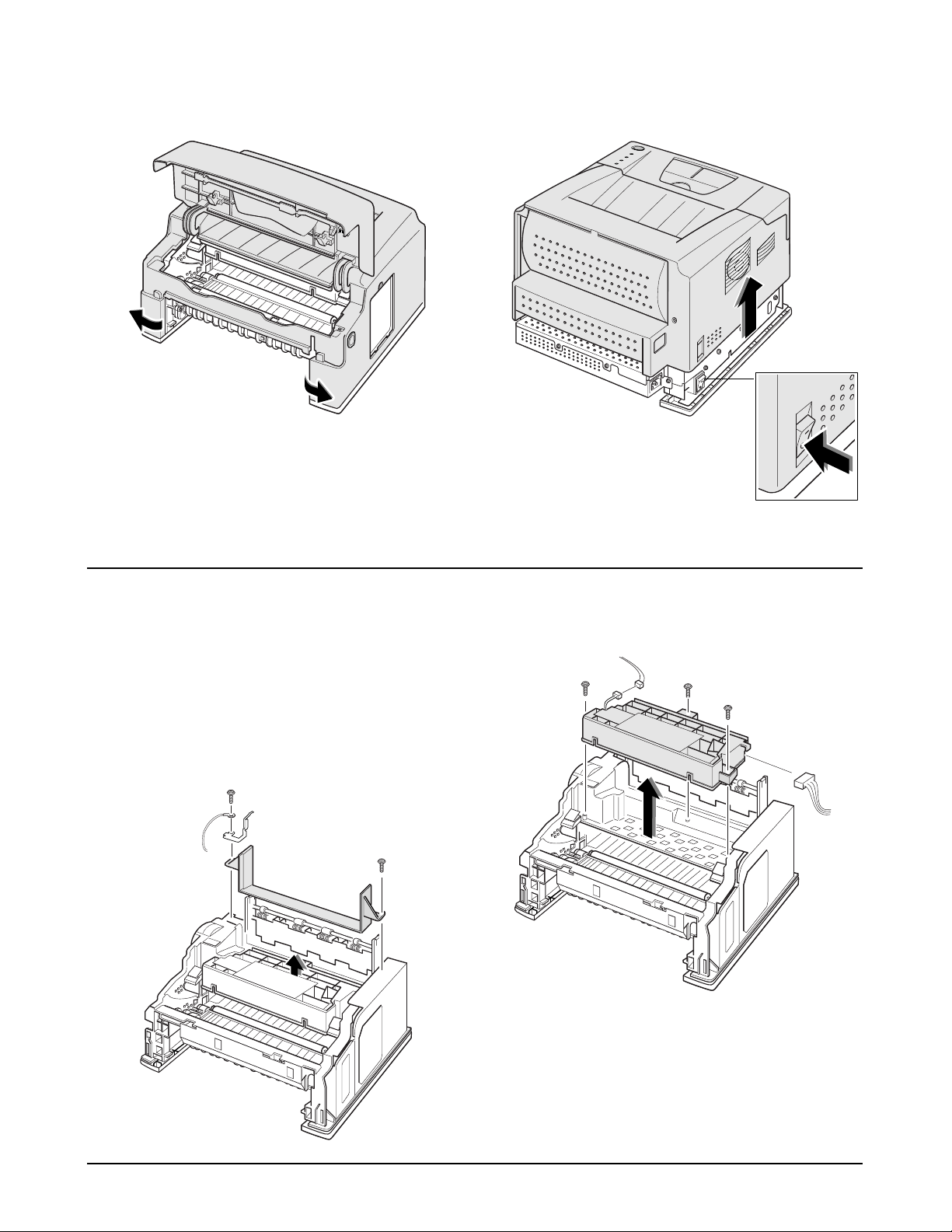
4-6. Main Cover
1. Before you remove the cover, you should remove:
-Controller Board (see page 4-3)
2. Remove two screws at the back of the printer.
3. Open the printer cover, and remove two screws.
4. Remove the panel cap inside the operator panel.
5. Unplug one connector from the panel board.
Disassembly and Reassembly
Samsung Electronics 4-7
6. Unlatch the front ends of the cover. 7. Slide the main cover upward, out of printer.
Note that the power switch is
properly released from the cover.
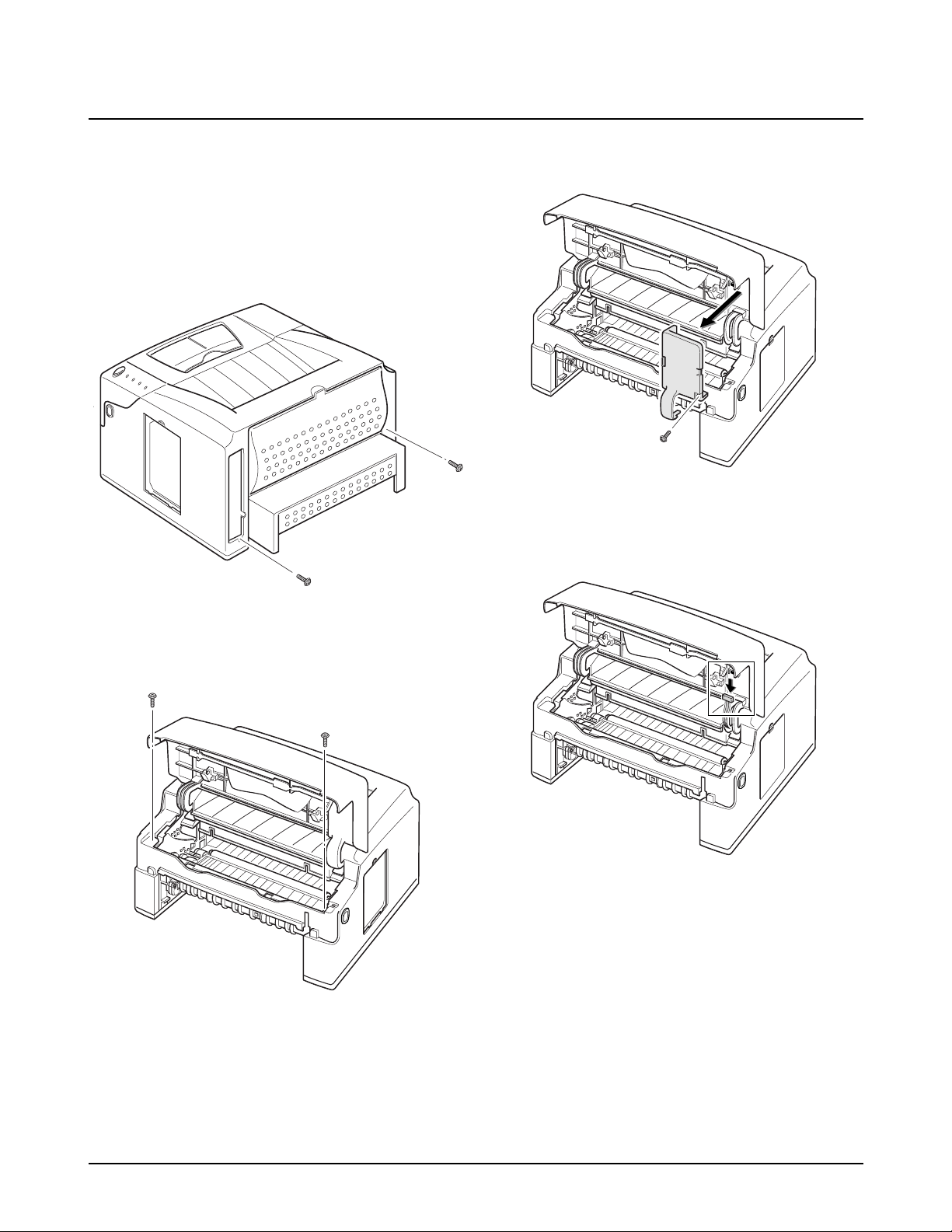
4-7. LSU
1. Before you remove the LSU, you should remove:
-Controller Board (see page 4-3)
-Main Cover (see page 4-6)
2. Remove two screws securing the fuser cover, and
remove the fuser cover.
3. Remove three screws, and remove the LSU. Then
unplug two connectors from the LSU.

Disassembly and Reassembly
4-8
Samsung Electronics
4-8. Exit Assembly
1. Before you remove the exit assembly, you should
remove:
-Controller Board (see page 4-3)
-Main Cover (see page 4-6)
-Fuser Cover (see page 4-10)
2. Remove three screws, and remove the bracket.
3. Remove two screws, unlatch the exit tray and take
it out.
4. If you want to remove the roller shaft, unlatch both
ends of the shaft and take it out.
5. If you want to remove the exit rollers, sqeeze the
bottom of roller and take it out.
Disassembly and Reassembly
Samsung Electronics 4-9
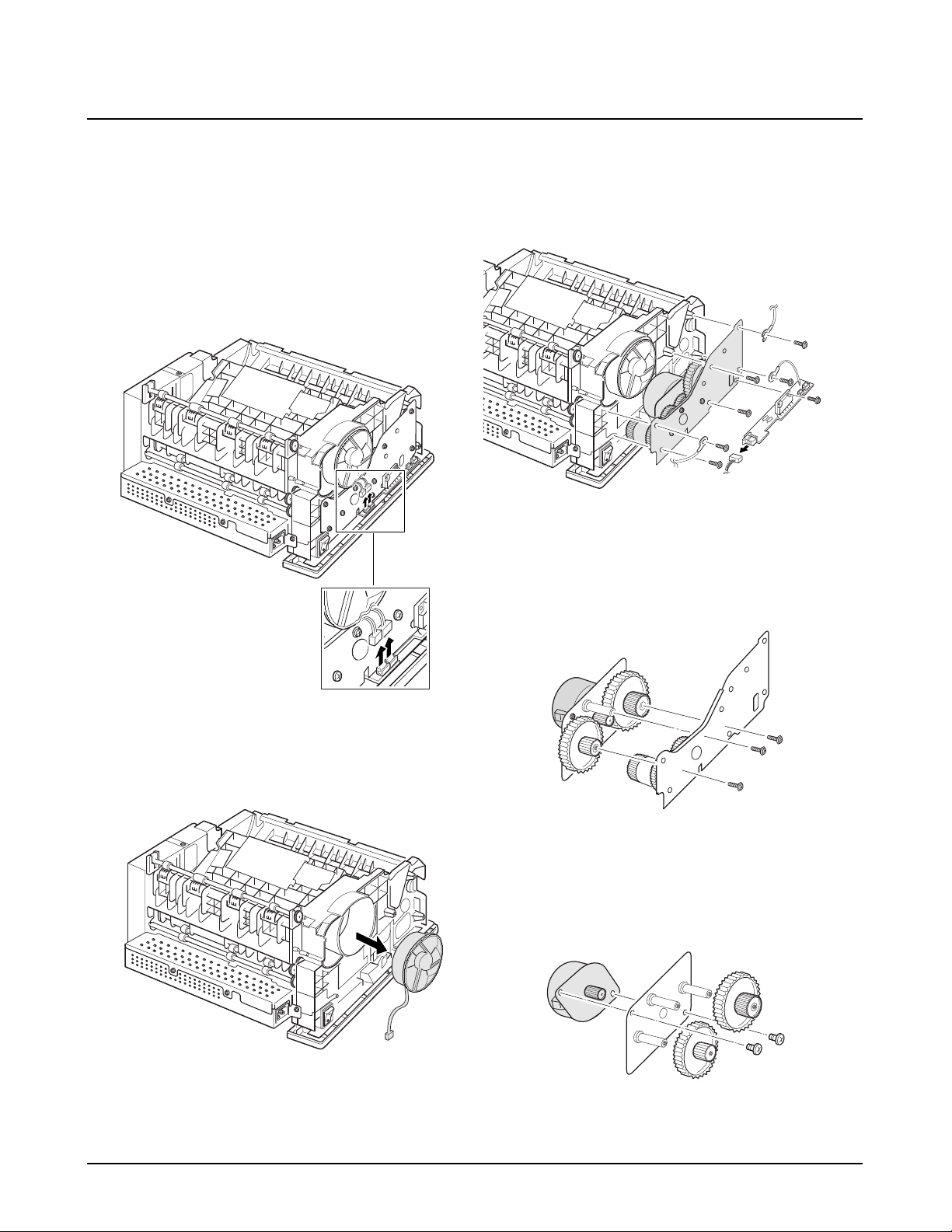
4-9. Drive Assembly and Fan
1. Before you remove the drive assembly or fan, you
should remove:
-Controller Board (see page 4-3)
-Main Cover (see page 4-6)
2. Unplug two connectors.
3. If you want to replace the fan, take the fan out.
4. Remove seven screws securing the drive assembly
from the gear bracket, and remove the drive assembly and motor drive board. Unplug one connector
from the board.
5. If you want to remove the motor from the drive
assembly, remove three gold screws securing the
motor assembly to the gear bracket.
6. Remove the motor assembly. Remove two screws
securing the motor to the motor bracket, then take
the motor out.
Disassembly and Reassembly
4-10
Samsung Electronics
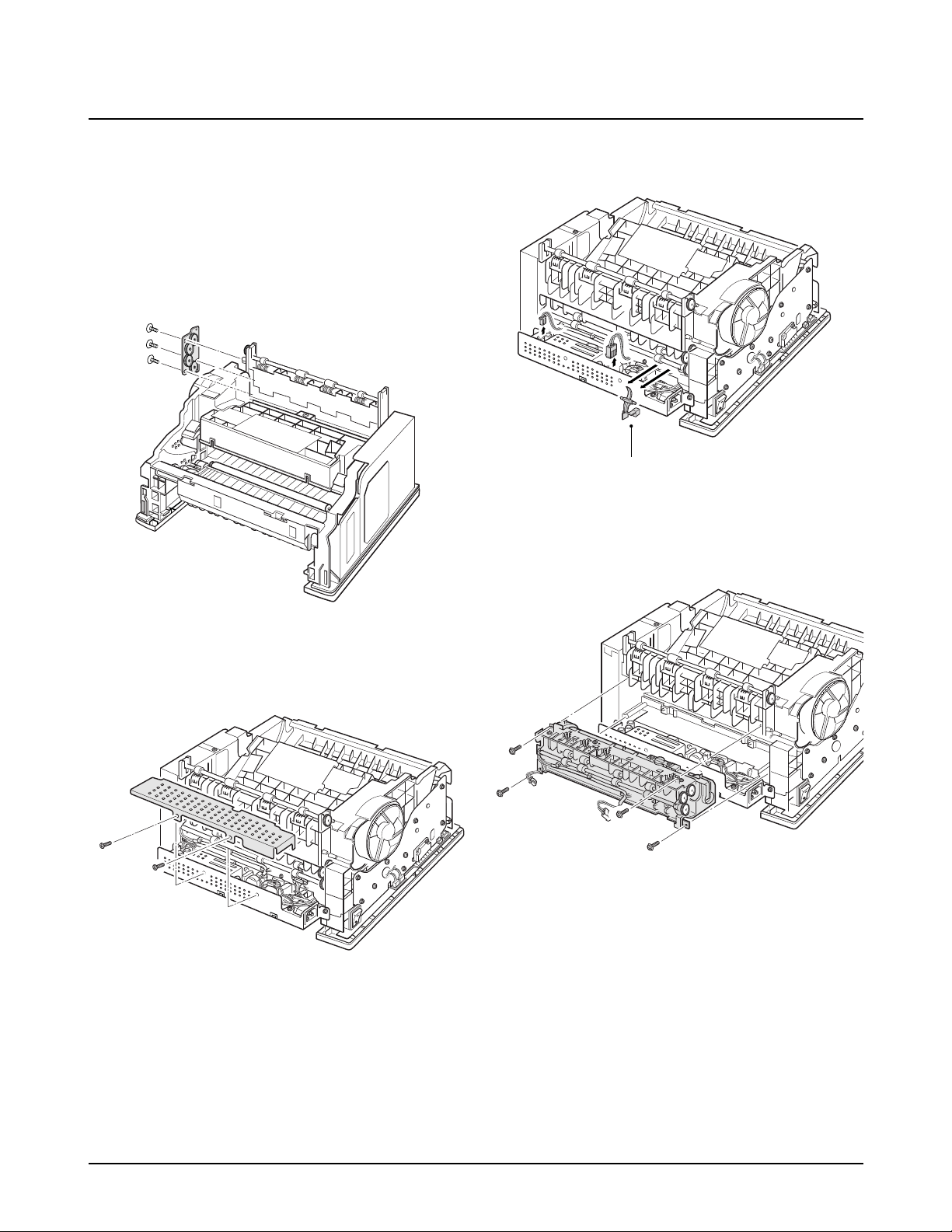
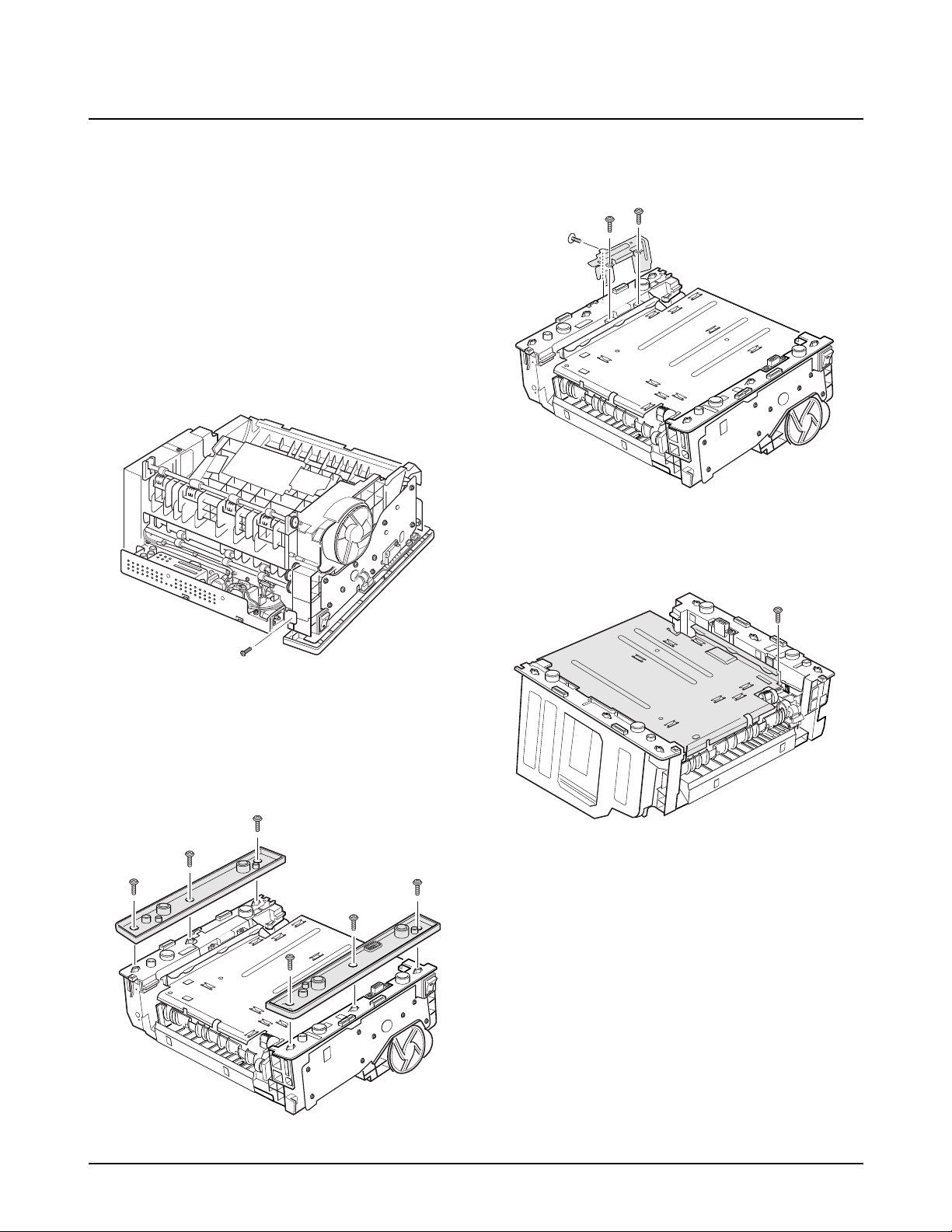
4-10. Fuser
1. Before you remove the fuser, you should remove:
-Controller Board (see page 4-3)
-Main Cover (see page 4-6)
2. Remove three screws, and remove the bracket.
3. Remove two screws from the SMPS bracket.
4. Remove the exit actuator. Unplug two connectors.
Exit Actuator
5. Remove four screws, and remove the fuser assembly.
Disassembly and Reassembly
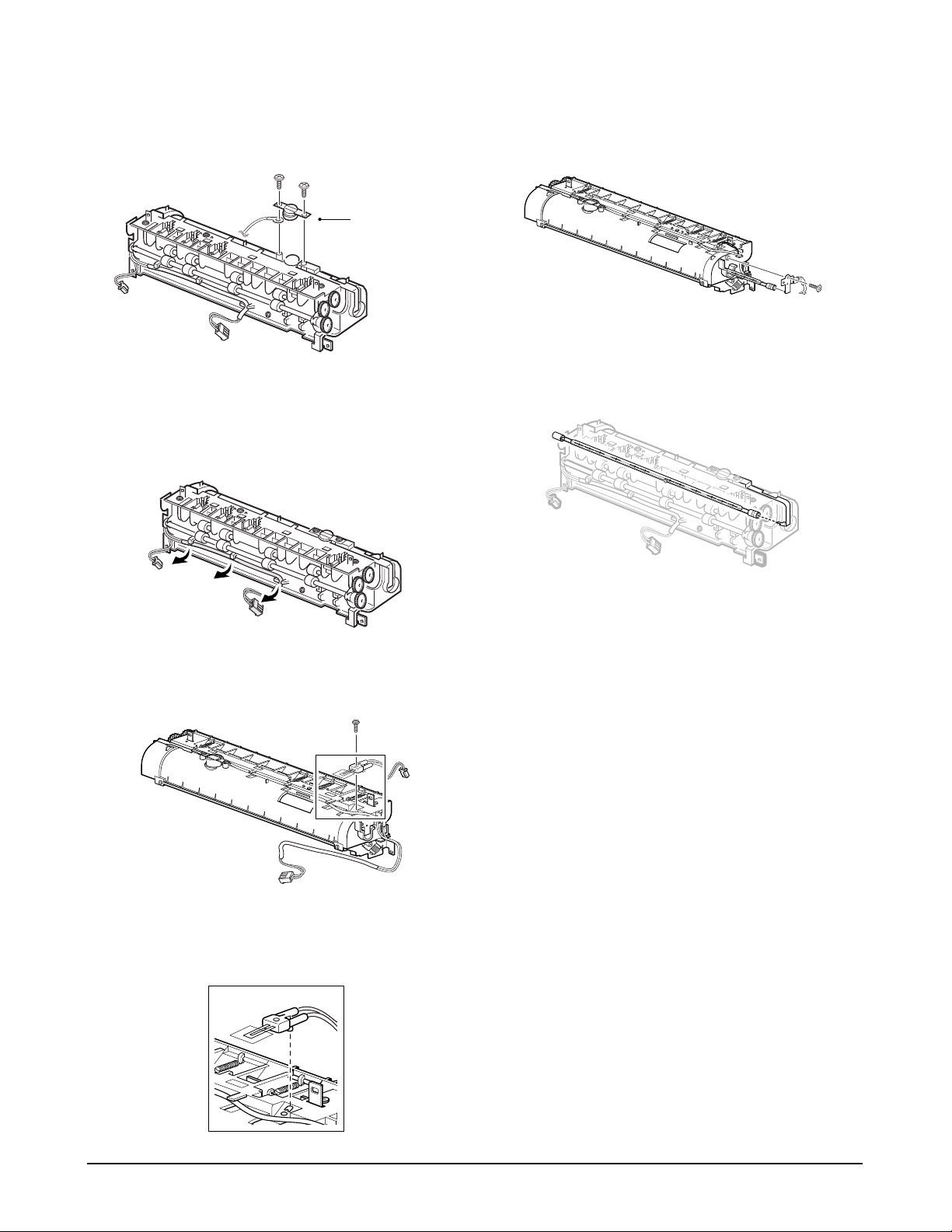
Samsung Electronics 4-11
To remove the thermostat from the fuser assembly :
Remove two screws, and take the thermostat out.
Thermostat
To remove the thermistor from the fuser assembly :
1. Release the wire from the three holders.
2. Remove one screw, then take the thermistor out.
Note: When you reassemble the thermistor, make sure
that it puts in place.
To remove the halogen lamp from the fuser assembly :
Remove one screw.
Note: When you reassemble the halogen lamp, make
sure that it is inserted into the slot properly.
Disassembly and Reassembly
4-12
Samsung Electronics
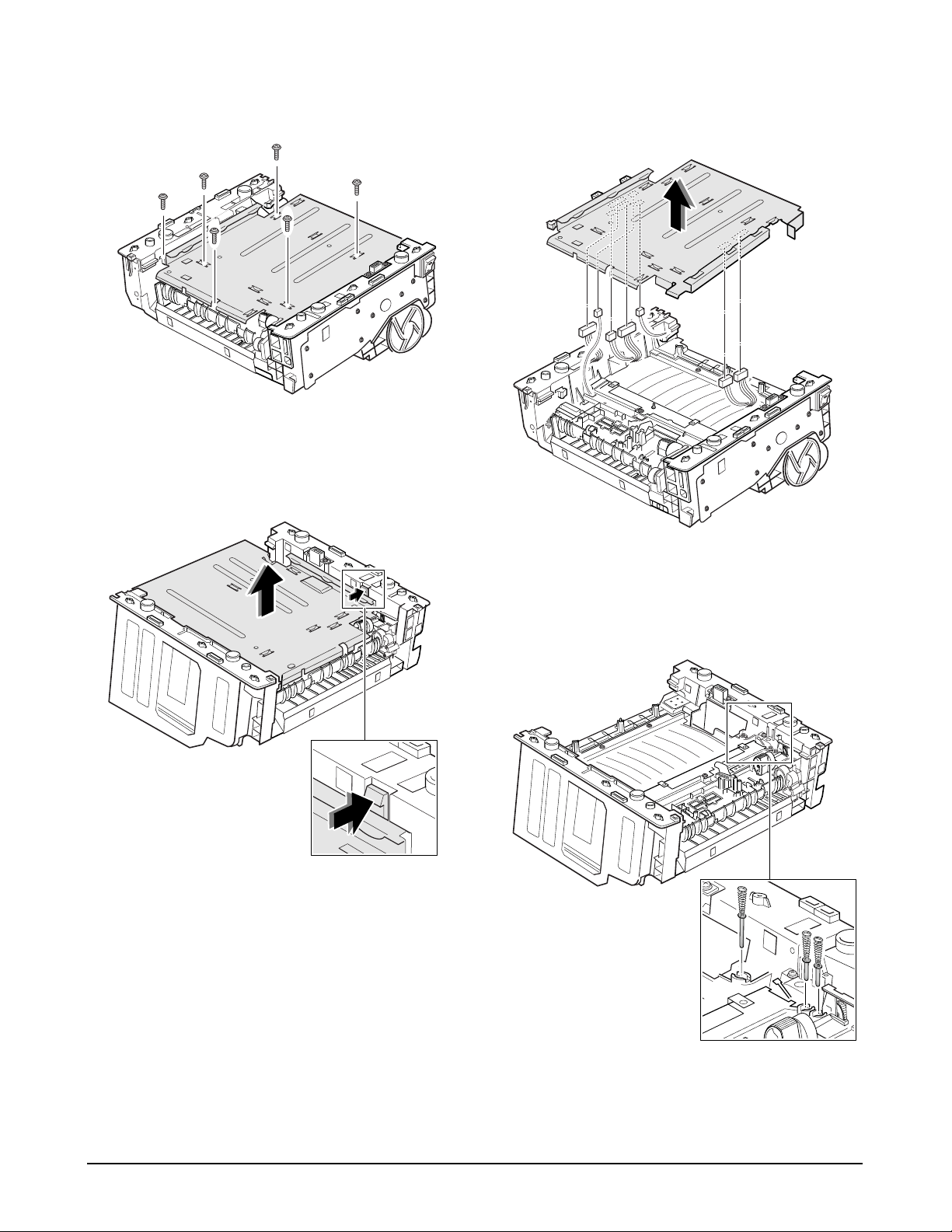
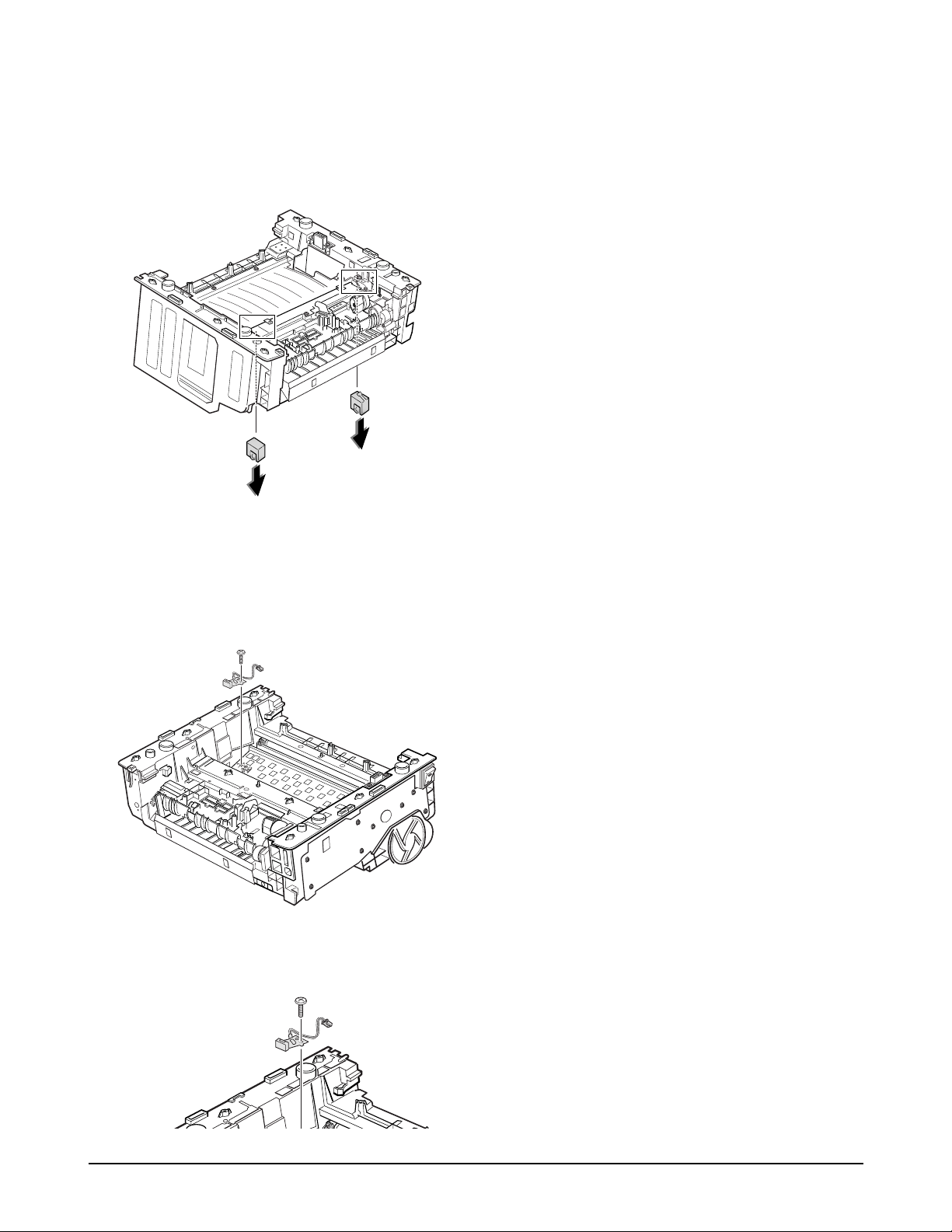
4-11. Engine Board and Miscellaneous
1. Before you remove the engine board, you should
remove:
-Controller Board (see page 4-3)
-Main Cover (see page 4-6)
3. Remove one screw from the engine board.
4. Turn the printer over. Remove six screws from the
left and the right base brackets, and take them out.
2. Remove the SMPS bracket as described in ‘4-10
Fuser ’ and unplug four connectors.
5. Remove three screws securing the ICU ground, and
remove the ICU ground.
6. Remove one ground screw.
Disassembly and Reassembly
Samsung Electronics 4-13
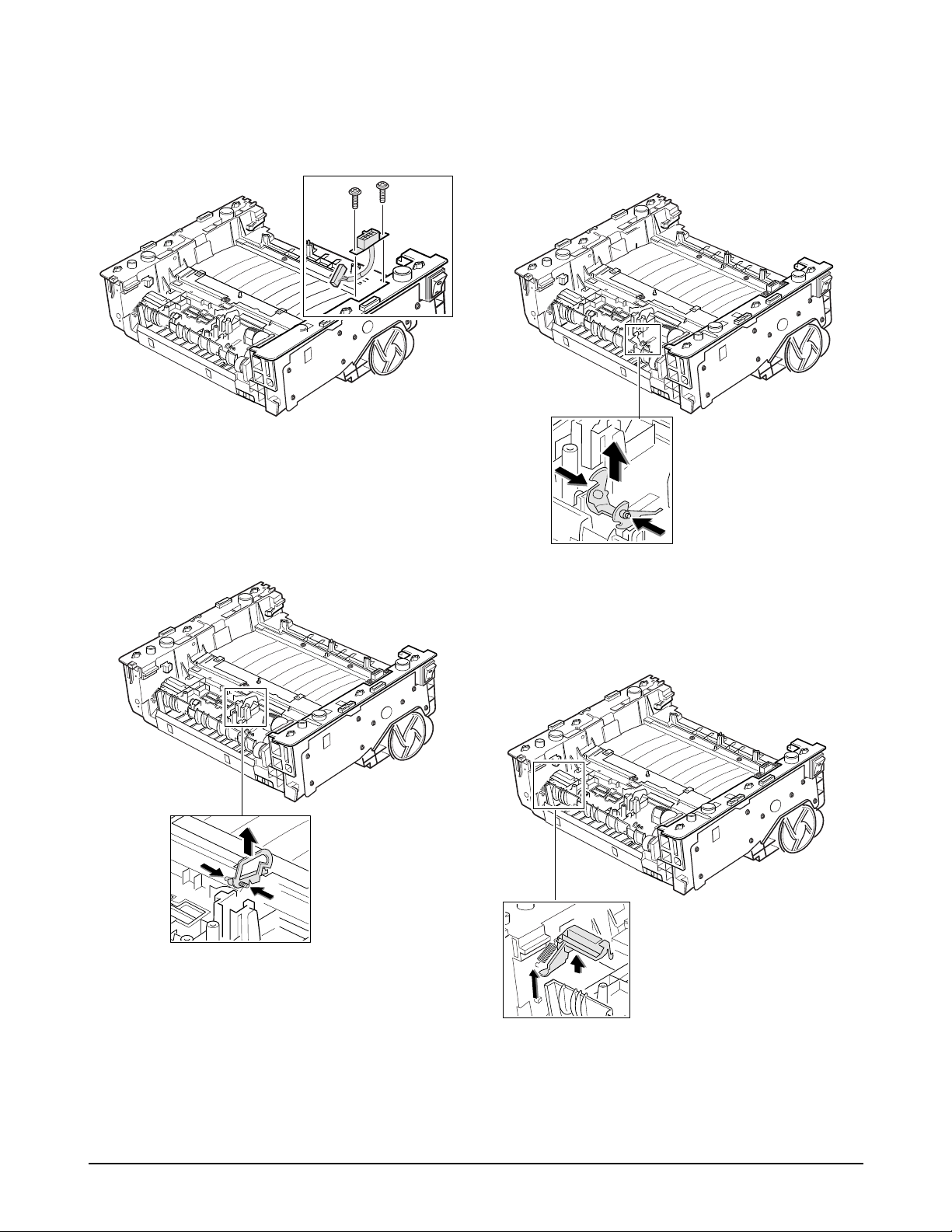
7. Remove six screws securing the PCU shield. 9. Unplug all connectors from the PCU shield, and
remove the shield.
8. While you push the stopper to release the PCU
shield, take the PCU shield out of the printer.
To replace HV terminals :
Remove the terminals.
Note: When you replace with new ones, be careful
that they are inserted in place.
Stopper
HV terminals
Disassembly and Reassembly
4-14
Samsung Electronics
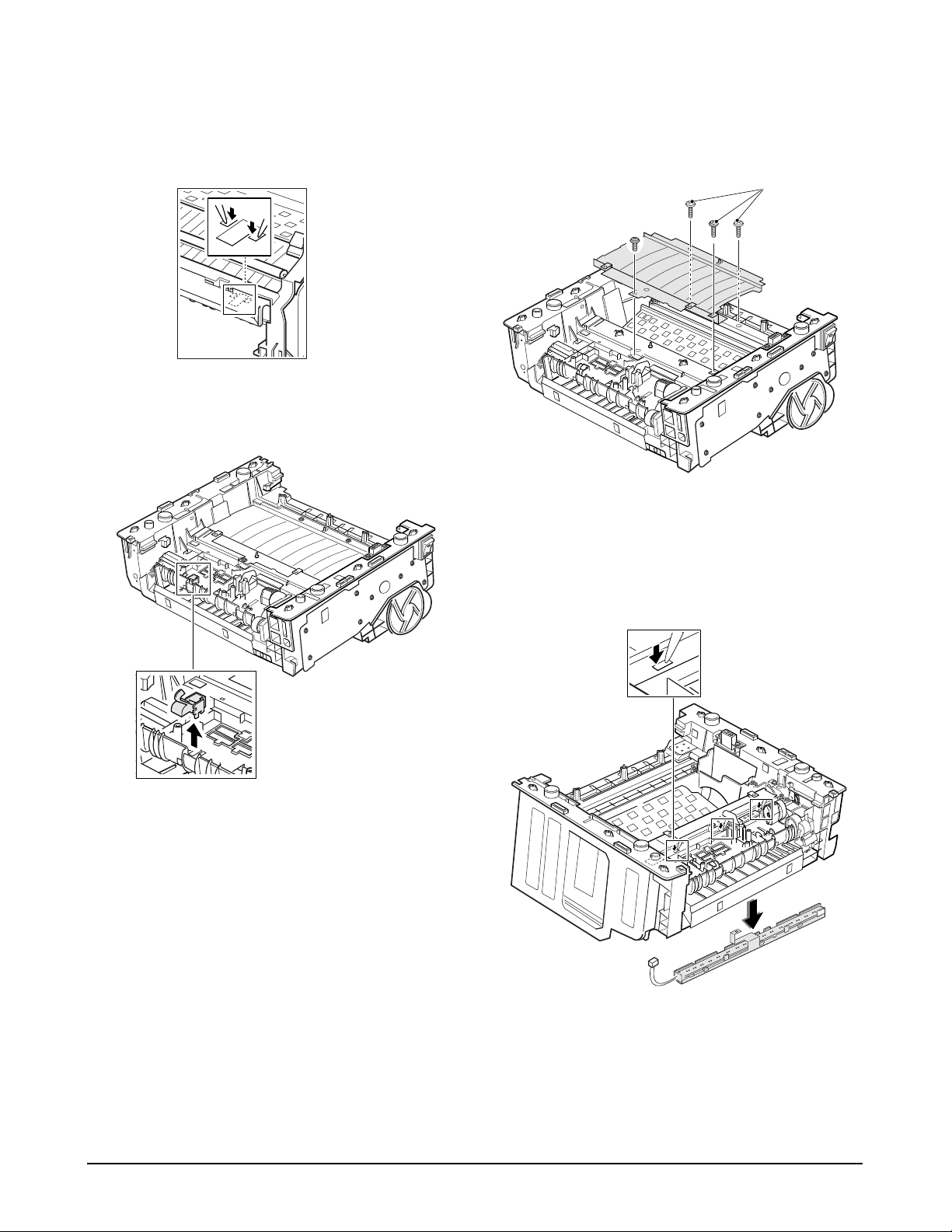
To replace the SCF connector :
Remove two screws and take it out.
To replace the paper empty sensor :
Take the sensor out while you push the both ends of
the sensor inward.
To replace the pickup sensor :
Take the sensor out while you push the both ends of
the sensor.
To replace the cover open sensor :
Remove the spring and take it out.
Paper empty sennsor
Disassembly and Reassembly
Samsung Electronics 4-15
To replace the actuator :
1. Turn the mechanism back and push down the
points as shown to unlatch the actuator.
2. Turn the unit over, and remove the actuator.
To remove the transfer guide :
Remove four screws and take the guide out.
M3 x 8
To replace the PTL module :
Release the three tabs latching the sensor using a
phillips screwdriver, then push the sensor down.
Disassembly and Reassembly
4-16
Samsung Electronics
To replace the transfer roller bushings
(left and right) :
Release each tab latching the left and right holder,
then push the holder down.
To replace the thermistor assembly :
Remove one screw, and remove the thermistor
assembly.
Note: When you reassemble the thermistor assembly,
make sure that it puts in place.
 Loading...
Loading...