Samsung HNC5527WX/XAA, ST54T8PCX/XAX Schematic

PROJECTION TV RECEIVER
Chassis : P55A(N) REV.1
Model: HCN5527WX/XAA
ST54T8PCX/XAX
PROJECTION TV RECEIVER CONTENTS
Precautions
Reference Information
Specifications
Alignment and Adjustments
Troubleshooting
Exploded View and Parts List
Electric Parts List
Block Diagrams
Wiring Diagram
Schematic Diagrams
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
1. Precautions
1-1 Safety Precautions
1. Be sure that all of the built-in protective
devices are replaced. Restore any missing
protective shields.
2. When reinstalling the chassis and its
assemblies, be sure to restore all protective
devices, including: nonmetallic control knobs
and compartment covers.
3. Make sure that there are no cabinet openings
through which people—particularly
children—might insert fingers and contact
dangerous voltages. Such openings include
the spacing between the picture tube and the
cabinet mask, excessively wide cabinet
ventilation slots, and improperly fitted back
covers.
If the measured resistance is less than 1.0
megohm or greater than 5.2 megohms, an
abnormality exists that must be corrected
before the unit is returned to the customer.
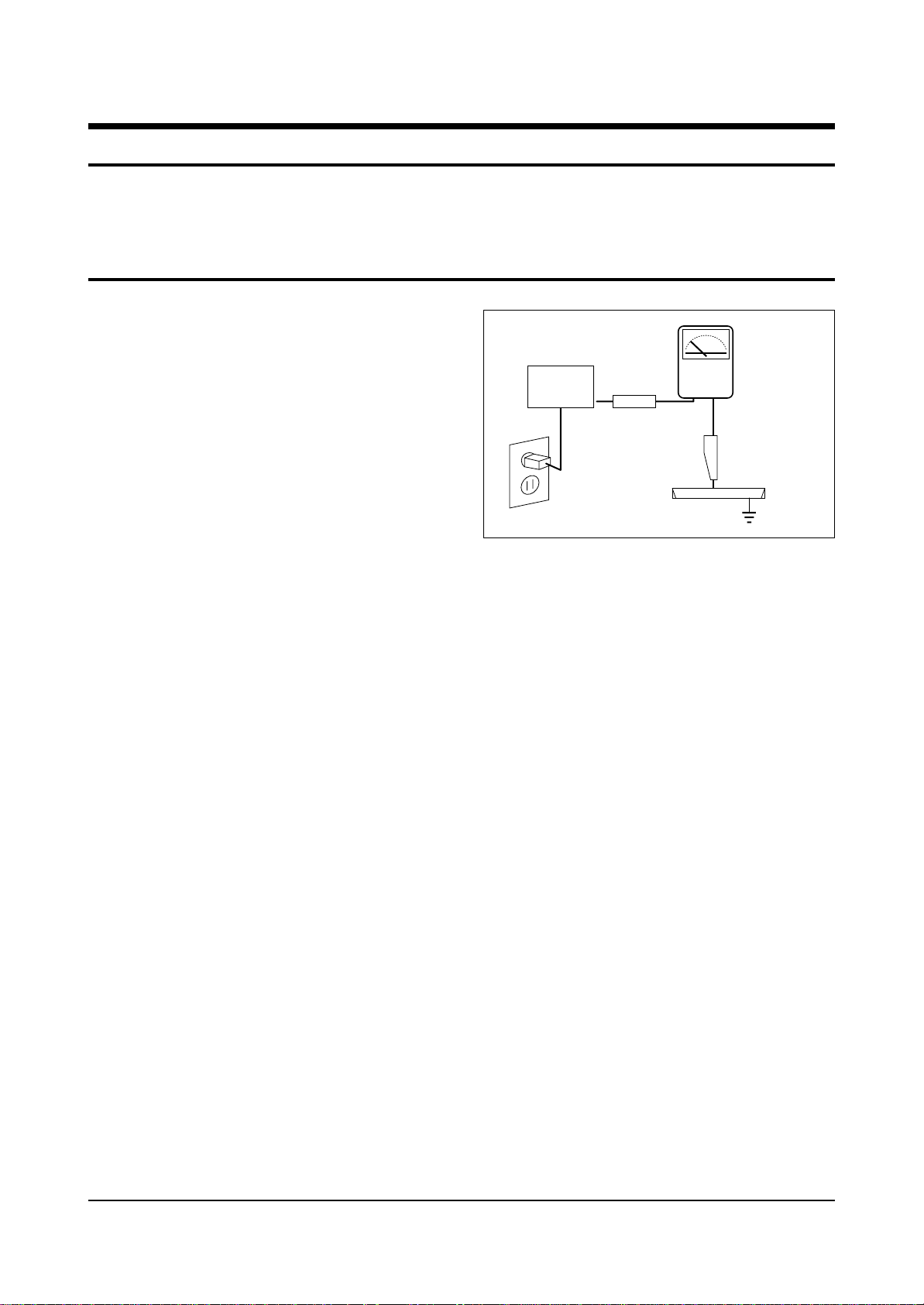
4. Leakage Current Hot Check (Figure 1-1):
Warning: Do not use an isolation
transformer during this test. Use a leakagecurrent tester or a metering system that
complies with American National Standards
Institute (ANIS C101.1, Leakage Current for
Appliances), and Underwriters Laboratories
(UL Publication UL1410, 59.7).
5. With the unit completely reassembled, plug
the AC line cord directly into the power
outlet. With the unit’s AC switch first in the
ON position and then OFF, measure the
current between a known earth ground (metal
water pipe, conduit, etc.) and all exposed
metal parts, including: antennas, handle
brackets, metal cabinets, screwheads and
control shafts. The current measured should
not exceed 0.5 milliamp. Reverse the powerplug prongs in the AC outlet and repeat the
test.
Fig. 1-1 AC Leakage Test
6. Antenna Cold Check:
With the unit’s AC plug disconnected from the
AC source, connect an electrical jumper across
the two AC prongs. Connect one lead of the
ohmmeter to an AC prong. Connect the other
lead to the coaxial connector.
7. X-ray Limits:
The picture tube is especially designed to prohibit X-ray emissions. To ensure continued
X-ray protection, replace the picture tube only
with one that is the same type as the original.
Carefully reinstall the picture tube shields and
mounting hardware; these also provide X-ray
protection.
8. High Voltage Limits:
High voltage must be measured each time servicing is done on the B+, horizontal deflection
or high voltage circuits. Correct operation of
the X-ray protection circuits must be
reconfirmed whenever they are serviced.
(X-ray protection circuits also may be called
“horizontal disable” or “hold-down”.)
Heed the high voltage limits. These include
the X–ray Protection Specifications Label, and
the Product Safety and X-ray Warning Note on
the service data schematic.
Precautions
Samsung Electronics 1-1
LEAKAGE
CURRENT
TESTER
DEVICE
UNDER
TEST
TEST ALL
EXPOSED METAL
SURFACES
2-WIRE CORD
ALSO TEST WITH
PLUG REVERSED
(USING AC ADAPTER
PLUG AS REQUIRED)
EARTH
GROUND
(READING SHOULD
NOT BE ABOVE
0.5mA)
Follow these safety, servicing and ESD precautions to prevent damage and protect against potential
hazards such as electrical shock and X-rays.

1-1 Safety Precautions (Continued)
9. High voltage is maintained within specified
limits by close-tolerance, safety-related
components and adjustments. If the high
voltage exceeds the specified limits, check
each of the special components.
10. Design Alteration Warning:
Never alter or add to the mechanical or
electrical design of this unit. Example: Do not
add auxiliary audio or video connectors. Such
alterations might create a safety hazard. Also,
any design changes or additions will void the
manufacturer’s warranty.
11. Hot Chassis Warning:
Some TV receiver chassis are electrically
connected directly to one conductor of the AC
power cord. If an isolation transformer is not
used, these units may be safely serviced only
if the AC power plug is inserted so that the
chassis is connected to the ground side of the
AC source.
To confirm that the AC power plug is inserted
correctly, do the following: Using an AC
voltmeter, measure the voltage between the
chassis and a known earth ground. If the
reading is greater than 1.0V, remove the AC
power plug, reverse its polarity and reinsert.
Re-measure the voltage between the chassis
and ground.
12. Some TV chassis are designed to operate with
85 volts AC between chassis and ground,
regardless of the AC plug polarity. These units
can be safely serviced only if an isolation
transformer inserted between the receiver and
the power source.
13. Some TV chassis have a secondary ground
system in addition to the main chassis ground.
This secondary ground system is not
isolated from the AC power line. The two
ground systems are electrically separated by
insulating material that must not be defeated
or altered.
14. Components, parts and wiring that appear to
have overheated or that are otherwise
damaged should be replaced with parts that
meet the original specifications. Always
determine the cause of damage or overheating, and correct any potential hazards.
15. Observe the original lead dress, especially
near the following areas: Antenna wiring,
sharp edges, and especially the AC and high
voltage power supplies. Always inspect for
pinched, out-of-place, or frayed wiring. Do
not change the spacing between components
and the printed circuit board. Check the AC
power cord for damage. Make sure that leads
and components do not touch thermally hot
parts.
16. Picture Tube Implosion Warning:
The picture tube in this receiver employs
“integral implosion” protection. To ensure
continued implosion protection, make sure
that the replacement picture tube is the same
as the original.
17. Do not remove, install or handle the picture
tube without first putting on shatterproof
goggles equipped with side shields. Never
handle the picture tube by its neck. Some
“in-line” picture tubes are equipped with a
permanently attached deflection yoke; do not
try to remove such “permanently attached”
yokes from the picture tube.
18. Product Safety Notice:
Some electrical and mechanical parts have
special safety-related characteristics which
might not be obvious from visual inspection.
These safety features and the protection they
give might be lost if the replacement component differs from the original—even if the
replacement is rated for higher voltage,
wattage, etc.
Components that are critical for safety are
indicated in the circuit diagram by shading,
( ) or ( ).
Use replacement components that have the
same ratings, especially for flame resistance
and dielectric strength specifications.
A replacement part that does not have the
same safety characteristics as the original
might create shock, fire or other hazards.
Precautions
1-2 Samsung Electronics

1-2 Servicing Precautions
1. Servicing precautions are printed on the
cabinet. Follow them.
2. Always unplug the unit’s AC power cord from
the AC power source before attempting to: (a)
Remove or reinstall any component or
assembly, (b) Disconnect an electrical plug or
connector, (c) Connect a test component in
parallel with an electrolytic capacitor.
3. Some components are raised above the printed
circuit board for safety. An insulation tube or
tape is sometimes used. The internal wiring is
sometimes clamped to prevent contact with
thermally hot components. Reinstall all such
elements to their original position.
4. After servicing, always check that the screws,
components and wiring have been correctly
reinstalled. Make sure that the portion around
the serviced part has not been damaged.
5. Check the insulation between the blades of the
AC plug and accessible conductive parts
(examples: metal panels, input terminals and
earphone jacks).
6. Insulation Checking Procedure: Disconnect the
power cord from the AC source and turn the
power switch ON. Connect an insulation
resistance meter (500V) to the blades of the AC
plug.
The insulation resistance between each blade
of the AC plug and accessible conductive parts
(see above) should be greater than 1 megohm.
7. Never defeat any of the B+ voltage interlocks.
Do not apply AC power to the unit (or any of
its assemblies) unless all solid-state heat sinks
are correctly installed.
8. Always connect a test instrument’s ground
lead to the instrument chassis ground before
connecting the positive lead; always remove
the instrument’s ground lead last.
9. When some parts inside the optical engine
(except lamp) are damaged, replace the whole
optical engine.
Precautions
Samsung Electronics 1-3
Warning 1 : First read the “Safety Precautions” section of this manual. If some unforeseen circumstance creates a
conflict between the servicing and safety precautions, always follow the safety precautions.
Warning 2 : An electrolytic capacitor installed with the wrong polarity might explode.
“CAUTION : Double-pole/neutral fusing”
1-3 Precautions for Electrostatically Sensitive Devices (ESDs)
1. Some semiconductor (“solid state”) devices
are easily damaged by static electricity. Such
components are called Electrostatically
Sensitive Devices (ESDs); examples include
integrated circuits and some field-effect
transistors. The following techniques will
reduce the occurrence of component damage
caused by static electricity.
2. Immediately before handling any semicon
ductor components or assemblies, drain the
electrostatic charge from your body by
touching a known earth ground. Alternatively,
wear a discharging wrist-strap device. (Be
sure to remove it prior to applying power—
this is an electric shock precaution.)
3. After removing an ESD-equipped assembly,
place it on a conductive surface such as
aluminum foil to prevent accumulation of
electrostatic charge.
4. Do not use freon-propelled chemicals. These
can generate electrical charges that damage
ESDs.
5. Use only a grounded-tip soldering iron when
soldering or unsoldering ESDs.
6. Use only an anti-static solder removal device.
Many solder removal devices are not rated as
“anti-static”; these can accumulate sufficient
electrical charge to damage ESDs.
7. Do not remove a replacement ESD from its
protective package until you are ready to
install it. Most replacement ESDs are
packaged with leads that are electrically
shorted together by conductive foam,
aluminum foil or other conductive materials.
8. Immediately before removing the protective
material from the leads of a replacement ESD,
touch the protective material to the chassis or
circuit assembly into which the device will be
installed.
9. Minimize body motions when handling
unpackaged replacement ESDs. Motions such
as brushing clothes together, or lifting a foot
from a carpeted floor can generate enough
static electricity to damage an ESD.
Precautions
1-4 Samsung Electronics
CAUTION
These servicing instructions are for use by
qualified service personnel only.
To reduce the risk of electric shock do not
perform any servicing other than that contained
in the operating instructions unless you are
qualified to do so.
Reference Information
Samsung Electronics 2-1
2. Reference Information
2-1 Tables of Abbreviations and Acronyms
A
Ah
Å
dB
dBm
°C
°F
°K
F
G
GHz
g
H
Hz
h
ips
kWh
kg
kHz
kΩ
km
km/h
kV
kVA
kW
I
MHz
Ampere
Ampere-hour
Angstrom
Decibel
Decibel Referenced to One
Milliwatt
Degree Celsius
Degree Fahrenheit
degree Kelvin
Farad
Gauss
Gigahertz
Gram
Henry
Hertz
Hour
Inches Per Second
Kilowatt-hour
Kilogram
Kilohertz
Kilohm
Kilometer
Kilometer Per Hour
Kilovolt
Kilovolt-ampere
Kilowatt
Liter
Megahertz
MV
MW
MΩ
m
µA
µF
µH
µm
µs
µW
mA
mg
mH
mI
mm
ms
mV
nF
Ω
pF
Ib
rpm
rps
s
V
VA
W
Wh
Megavolt
Megawatt
Megohm
Meter
Microampere
Microfarad
Microhenry
Micrometer
Microsecond
Microwatt
Milliampere
Milligram
Millihenry
Milliliter
Millimeter
Millisecond
Millivolt
Nanofarad
Ohm
Picofarad
Pound
Revolutions Per Minute
Revolutions Per Second
Second (Time)
Volt
Volt-ampere
Watt
Watt-hour
Table 2-1 Abbreviations
Reference Information
2-2 Samsung Electronics
Table 2-2 Table of Acronyms
ABL
AC
ACC
AF
AFC
AFT
AGC
AM
ANSI
APC
APC
A/V
AVC
BAL
BPF
B-Y
CATV
CB
CCD
CCTV
Ch
CRT
CW
DC
DVM
EIA
ESD
ESD
FBP
FBT
FF
FM
FS
GND
G-Y
H
HF
HI-FI
IC
IC
IF
Automatic Brightness Limiter
Alternating Current
Automatic Chroma Control
Audio Frequency
Automatic Frequency Control
Automatic Fine Tuning
Automatic Gain Control
Amplitude Modulation
American National Standards Institute
Automatic Phase Control
Automatic Picture Control
Audio-Video
Automatic Volume Control
Balance
Bandpass Filter
Blue-Y
Community Antenna Television (Cable TV)
Citizens Band
Charge Coupled Device
Closed Circuit Television
Channel
Cathode Ray Tube
Continuous Wave
Direct Current
Digital Volt Meter
Electronics Industries Association
Electrostatic Discharge
Electrostatically Sensitive Device
Feedback Pulse
Flyback Transformer
Flip-Flop
Frequency Modulation
Fail Safe
Ground
Green-Y
High
High-Frequency
High Fidelity
Inductance-Capacitance
Integrated Circuit
Intermediate Frequency
I/O
L
L
LED
LF
MOSFET
MTS
NAB
NEC
NTSC
OSD
PCB
PLL
PWM
QIF
R
RC
RF
R-Y
SAP
SAW
SIF
SMPS
S/N
SW
TP
TTL
TV
UHF
UL
UV
VCD
VCO
VCXO
VHF
VIF
VR
VTR
VTVM
TR
Input/output
Left
Low
Light Emitting Diode
Low Frequency
Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor-Field-Effect-Tr
Multi-channel Television Sound
National Association of Broadcasters
National Electric Code
National Television Systems Committee
On Screen Display
Printed Circuit Board
Phase-Locked Loop
Pulse Width Modulation
Quadrature Intermediate Frequency
Right
Resistor & Capacitor
Radio Frequency
Red-Y
Second Audio Program
Surface Acoustic Wave(Filter)
Sound Intermediate Frequency
Switching Mode Power Supply
Signal/Noise
Switch
Test Point
Transistor Transistor Logic
Television
Ultra High Frequency
Underwriters Laboratories
Ultraviolet
Variable-Capacitance Diode
Voltage Controlled Oscillator
Voltage Controlled Crystal Oscillator
Very High Frequency
Video Intermediate Frequency
Variable Resistor
Video Tape Recorder
Vacuum Tube Voltmeter
Transistor
Reference Information
Samsung Electronics 2-3
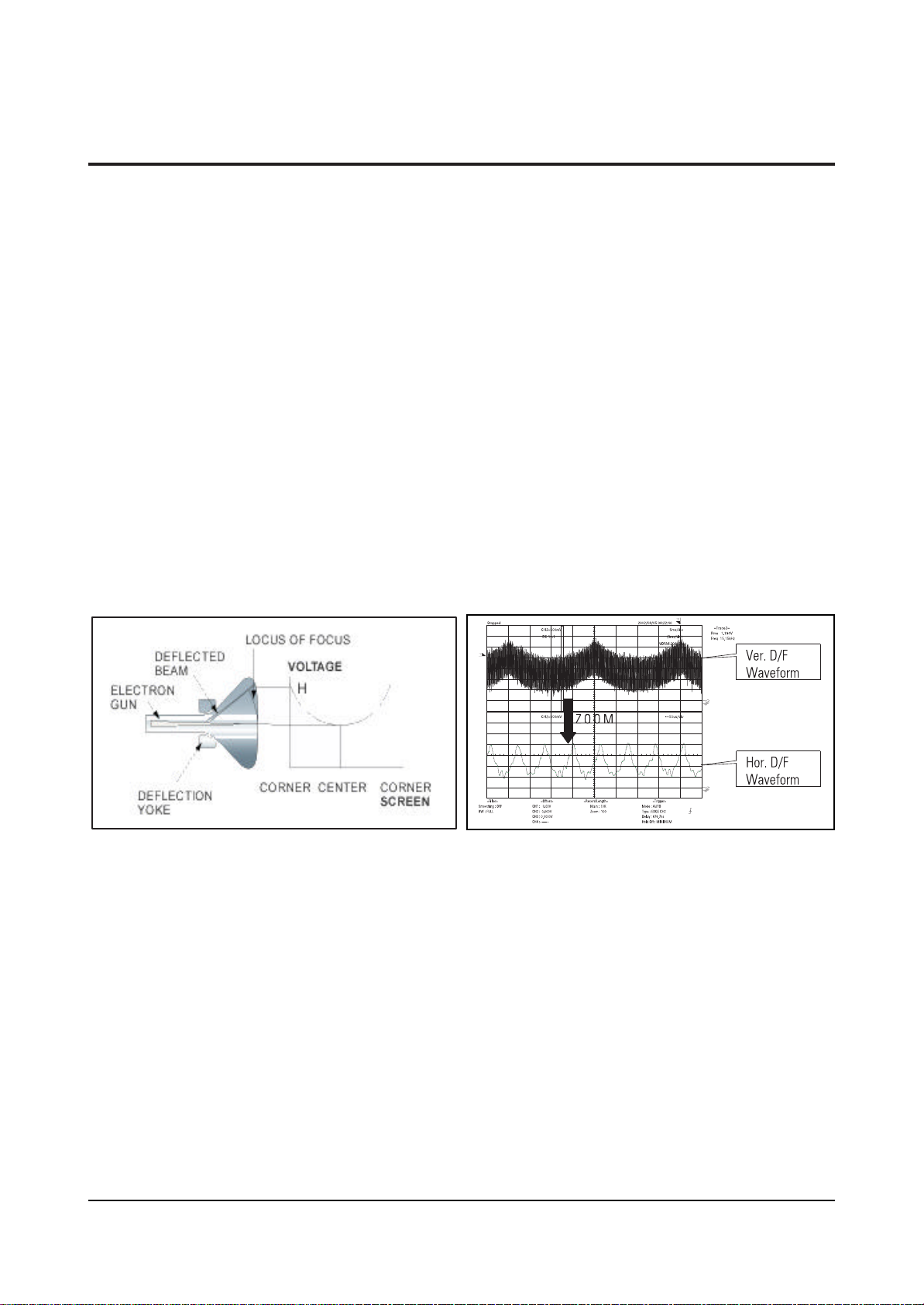
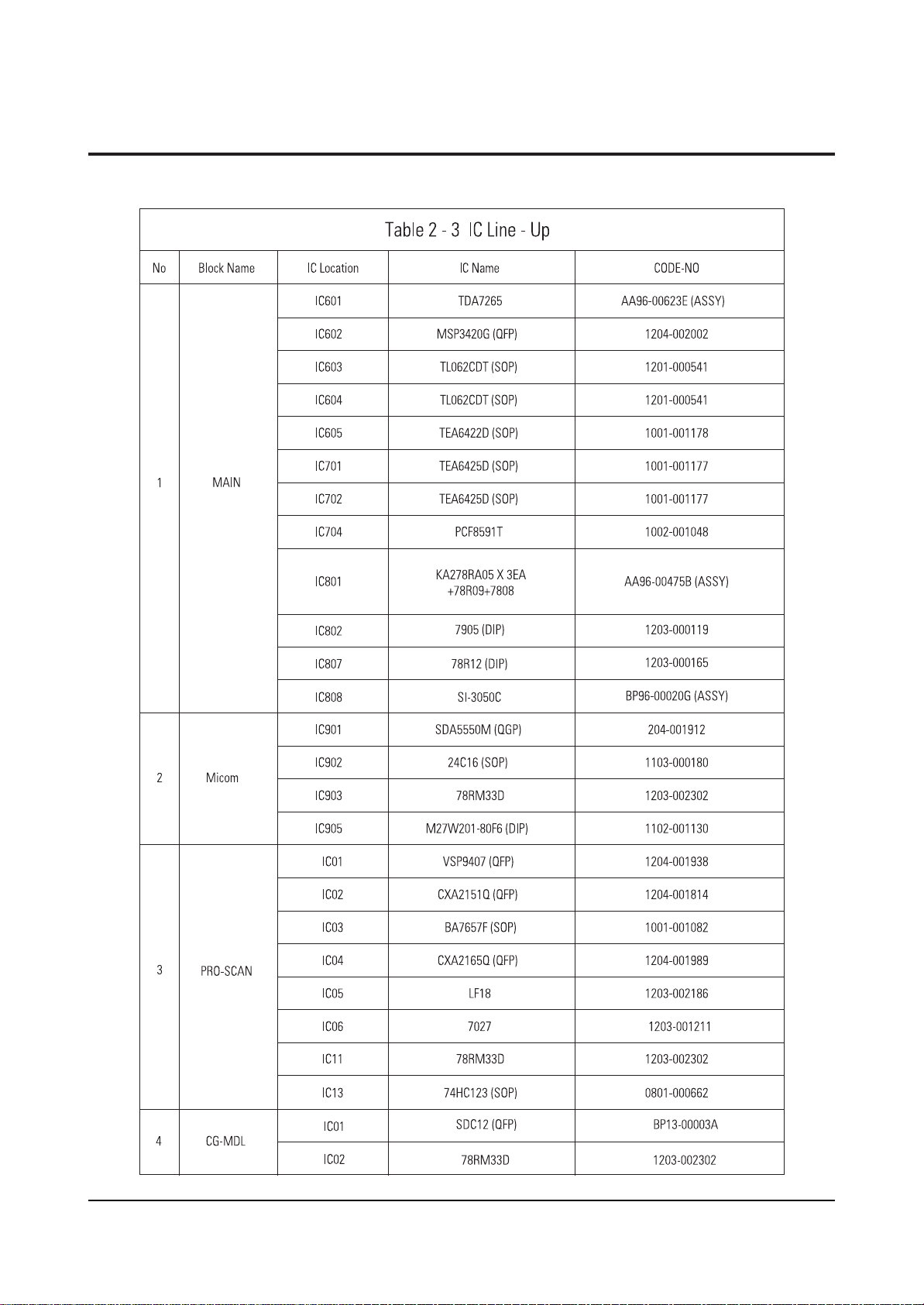
2-2 Description of Dynamic Focus
Most large-screen video display devices that are using CRT (including CDT) usually apply the Dynamic
Focus (hereinafter D/F) circuit.
As CRT has non-spherical surface (perfect spherical surface = 1, non-spherical surface R>1), the distance
that the electron beam emitted from the electron gun reaches to the center of CRT is different from the one
that the electron beam reaches to the corners. (See Figure 1.)
Only the beam, which has the equal distance as the beam from the electron gun to the center of CRT
surface, can maintain the optimum focus.
By this reason, focus dagradation at corners occurs inevitably.
To recover this, the speed of the electron beam injected into the corners of CRT should increase and the
focus dagradation by the difference of distances can be compensated.
Increasing the voltage is used as a method of increasing the speed of the electron beam at the corners of
screen.
In this case, an ideal D/F voltage waveform is the form of parabola where the center of screen has low
voltage and the corners has the highest voltages.
The horizontal D/F waveform compensates the focus dagradation at left and right sides, but the vertical
D/F waveform does at top and bottom sides.
The horizontal D/F and vertical D/F waveforms are separately created and mix two signals to
compensate the focus of the whole screen.
And the vertical Dynamic Focus waveform is composed of the horizontal Dynamic Focus waveforms as
much as the number of scanning lines. (See Figure 2.)
Fig. 1 Dynamic Focus Diagram (Horizantal)
Fig. 2 H/V Dynamic Focus Waveform
Reference Information
2-4 Samsung Electronics
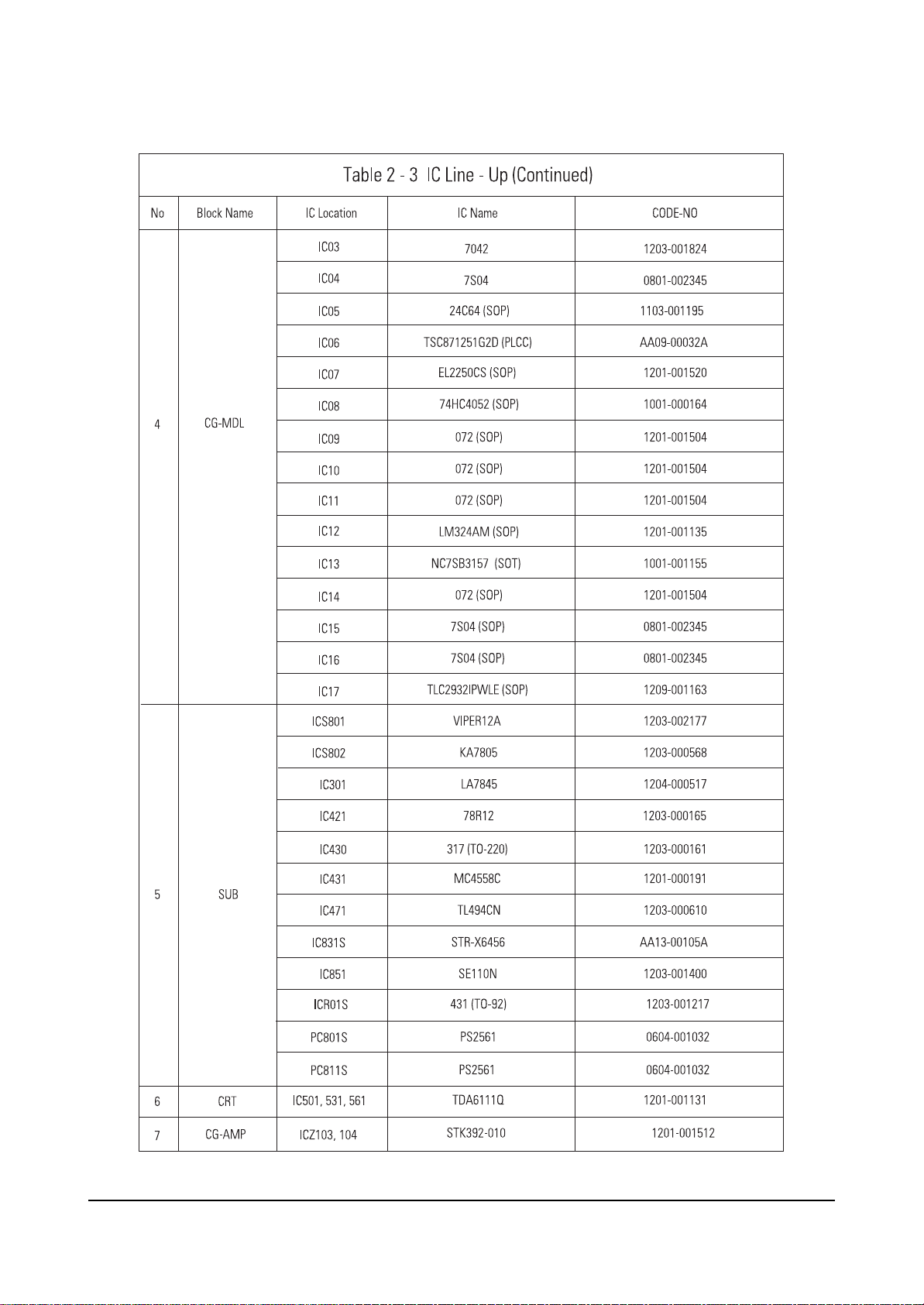
2-3 IC Line Up
2-3-1 Progressive
Reference Information
Samsung Electronics 2-5
Reference Information
2-6 Samsung Electronics
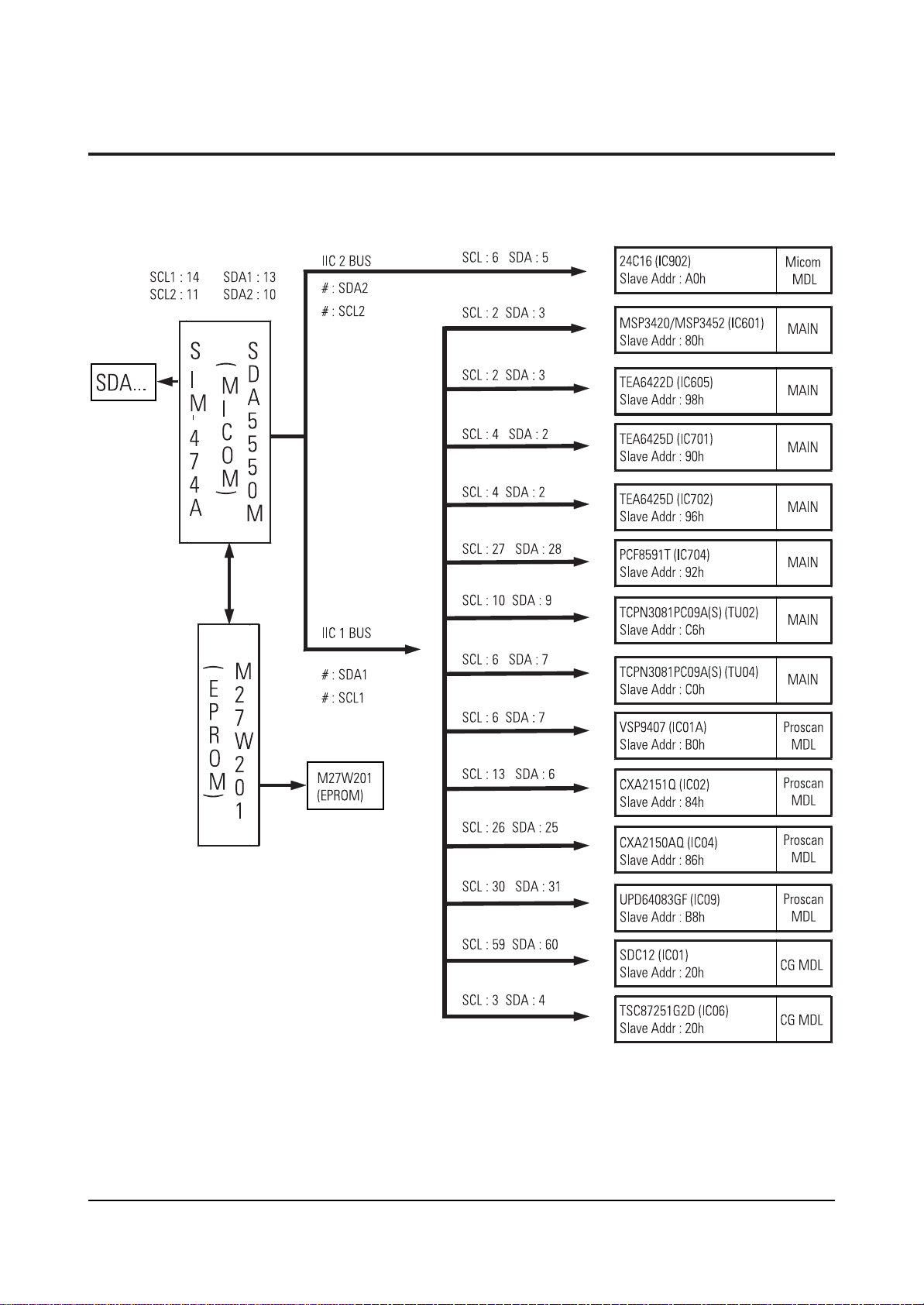
2-4 MICOM IIC BUS LINE -UP
Specifications
Samsung Electronics 3-1
3. Specifications
Broadcasting System
Scanning System
Tuning Range
Antenna Impedance
Intermediate Frequency
Sound Output
Rated Voltage
W/B Coordinates
High Voltage
FUSE
Power Consumption
Dimension
Weight
NTSC
Progressive Scanning
VHF : CH2 ~ CH13
75 ohm Unbalanced
Video : 45.75 MHz
Sound : 42.25 MHz
Chrominance Subcarrier : 42.17 MHz
STD : 10W
MAX : 15W
120V / 60 Hz
Hx : 266 Hy : 280 Y : 8.9
Lx : 268 Ly : 283 Y : 0.38
29KV
250V/6.3A
CODE NO : 3601-000300
240W
1002 X 450 X 1070mm
39.4 X 17.7 X 42.1 inch
49Kg 108lbs

MEMO
3-2 Samsung Electronics
Alignment and Adjustments
Samsung Electronics 4-1
4. Alignment and Adjustments
4-1 When entering the service mode:
1. Turn on the TV, and then select “STANDARD”on the picture adjustment mode.
2. Turn off the TV (STAND-BY).
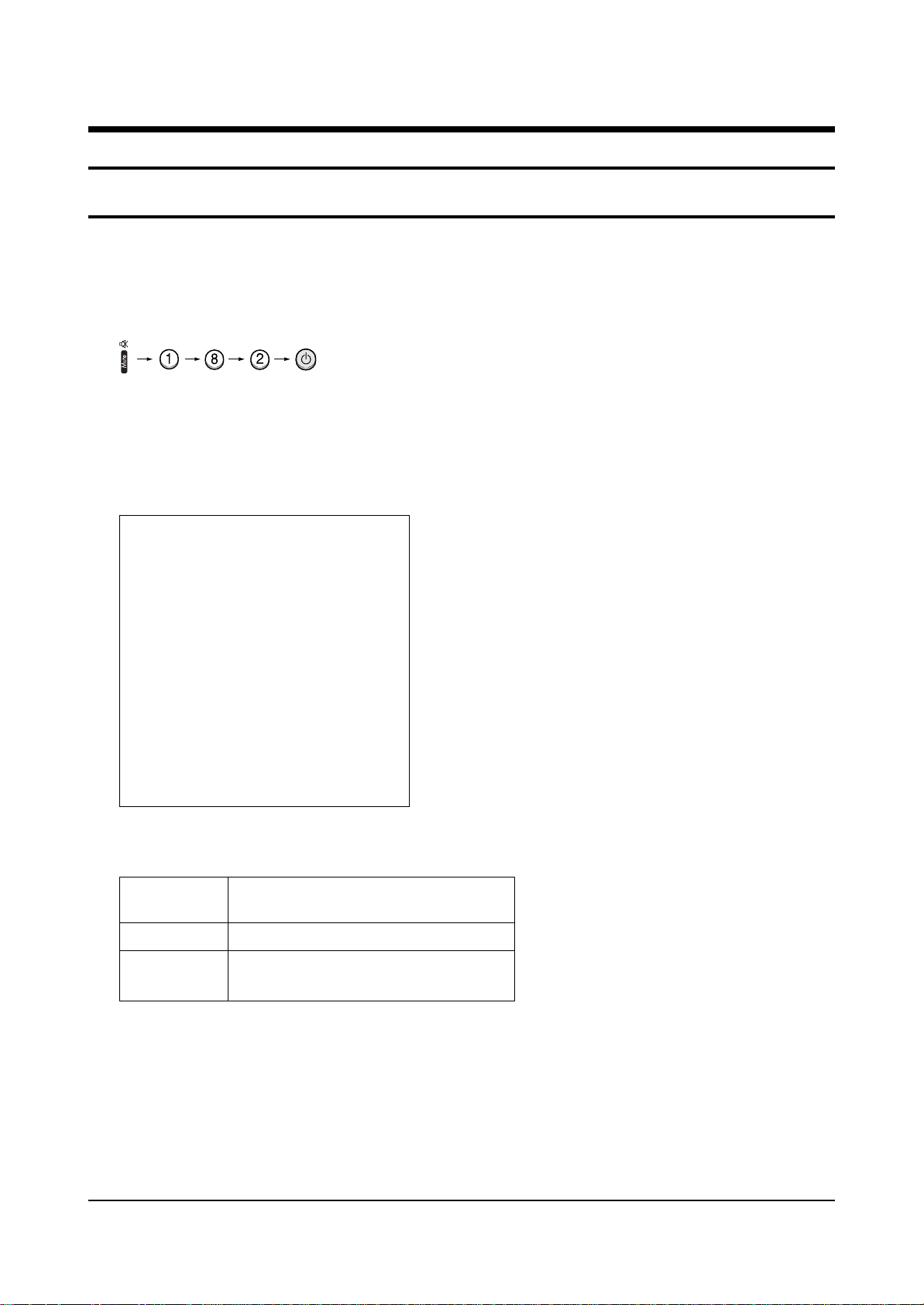
3. Enter the service mode by pressing the remote control keys in the following sequence :
Note : If necessary, re-do steps 1~3.
Initial display when the service mode is switched.
SERVICE / Sim-474A
DEFLECTION
480P OFFSET
1080i OFFSET
CONVERGENCE OFFSET
VIDEO ADJUST 1
VIDEO ADJUST 2
VIDEO ADJUST 3
VIDEO ADJUST 4
OPTION (E3h 98h 0ch)
RESET / 02-05-03
1. When a RF signal is received
MAIN MENU MENU DISPLAY
CH UP/DOWN Select item by moving cursor
VOL UP/DOWN Decrease or increase the adjustment values
3. Service Mode Control Keys
< PRECAUTIONS >
1. When EEPROM IC (IC902) is replaced, first connect the power cord and wait for about 4~5 seconds.
2. After replacing EEPROM IC (IC902), enter the Service mode. Next, enter the standard data or the
previous EEPROM IC data before replacement. And then check and adjust any items related to
Geometric, Picture, Option.
Alignment and Adjustments
4-2 Samsung Electronics
4-2-1 Defection
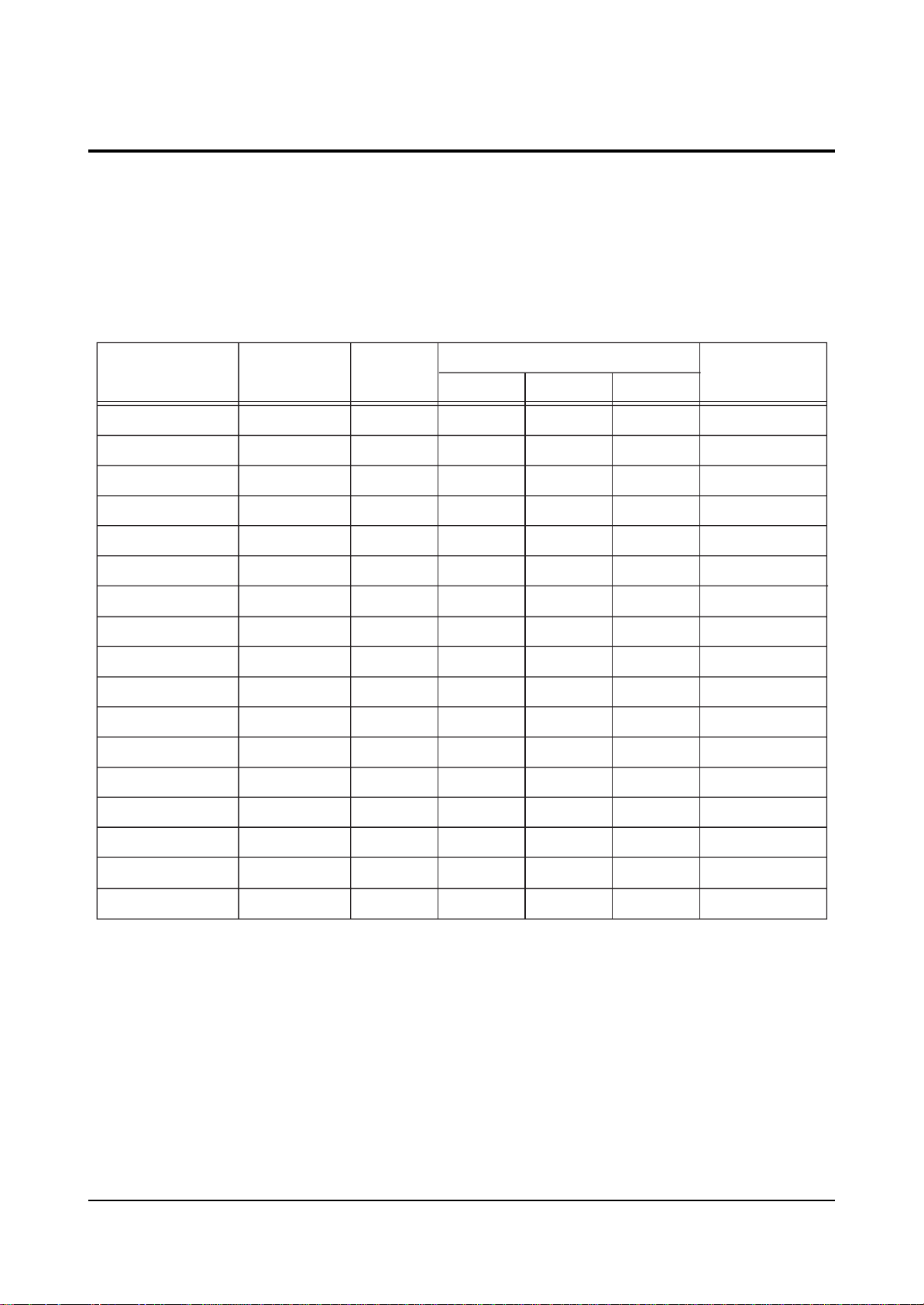
4-2 Factory Data
☞ DVI connection item is corresponded to DVI application model.
ITEM INITIAL DATA
V Amp
V Shift
H EW
H Shift
V Linearity
Upper Linearity
Lower Linearity
VSC
H Parabola
Upper Corner
Lower Corner
H Trapezium
Bow
Range
0 ~ 63
32
32
6 fix
7
8
3
10
32
32
32
32
0 ~ 63
0 ~ 63
0 ~ 63
0 ~ 15
0 ~ 15
0 ~ 15
0 ~ 15
0 ~ 63
0 ~ 63
0 ~ 63
0 ~ 63
0 ~ 63
EEP-ROM Copy Data
RF
31
29
31
31
7
0
0
7
31
31
31
31
31
480P
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
1080i
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Remark
variable
variable
fix
fix
fix
fix
fix
fix
fix
fix
fix
fix
Angel
V Position
CXA Left Blk
CXA Right Blk
32
32
35
35
0 ~ 63
0 ~ 63
0 ~ 63
0 ~ 63
31
31
35
35
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
fix
fix
fix
fix
Alignment and Adjustments
Samsung Electronics 4-3
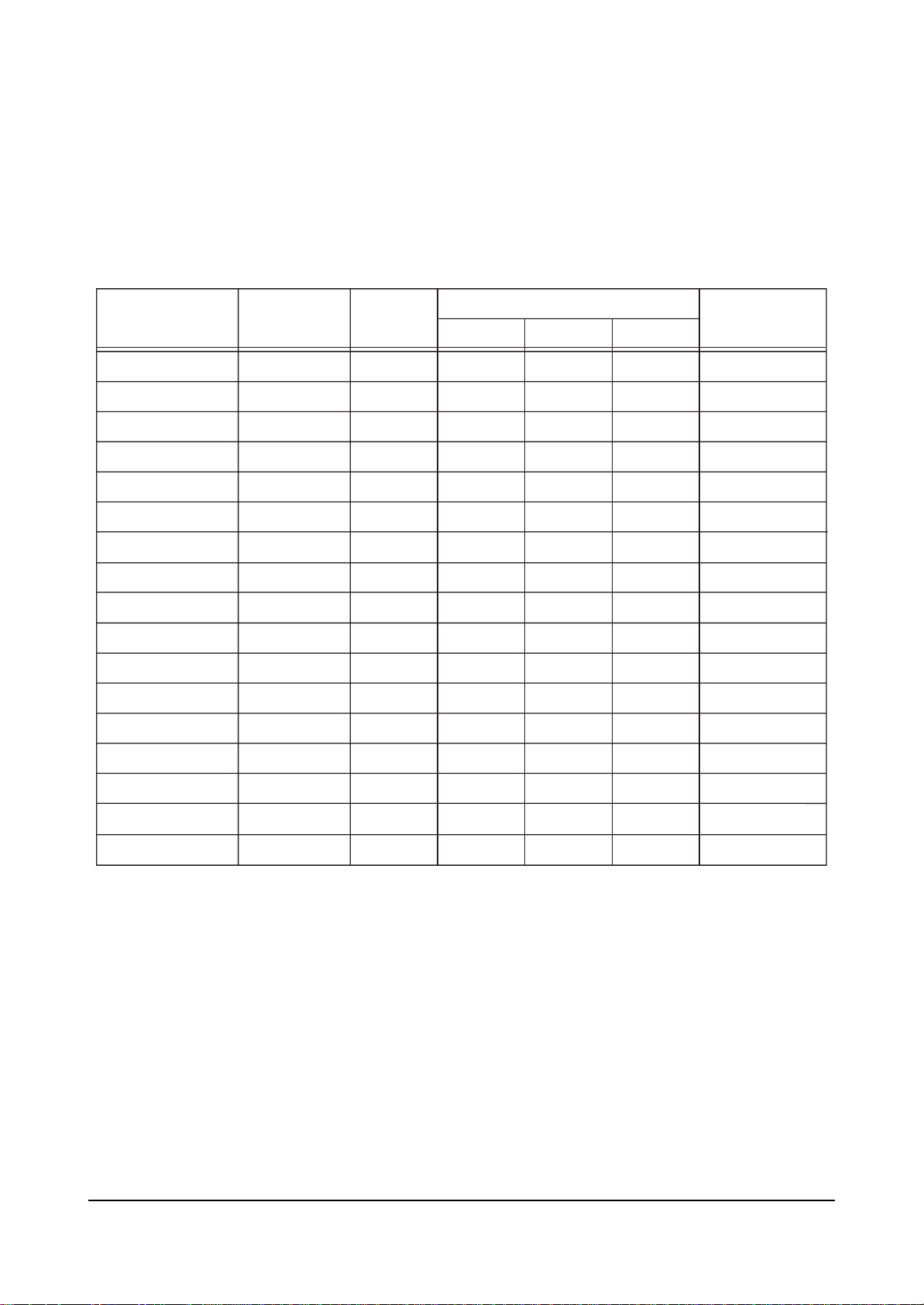
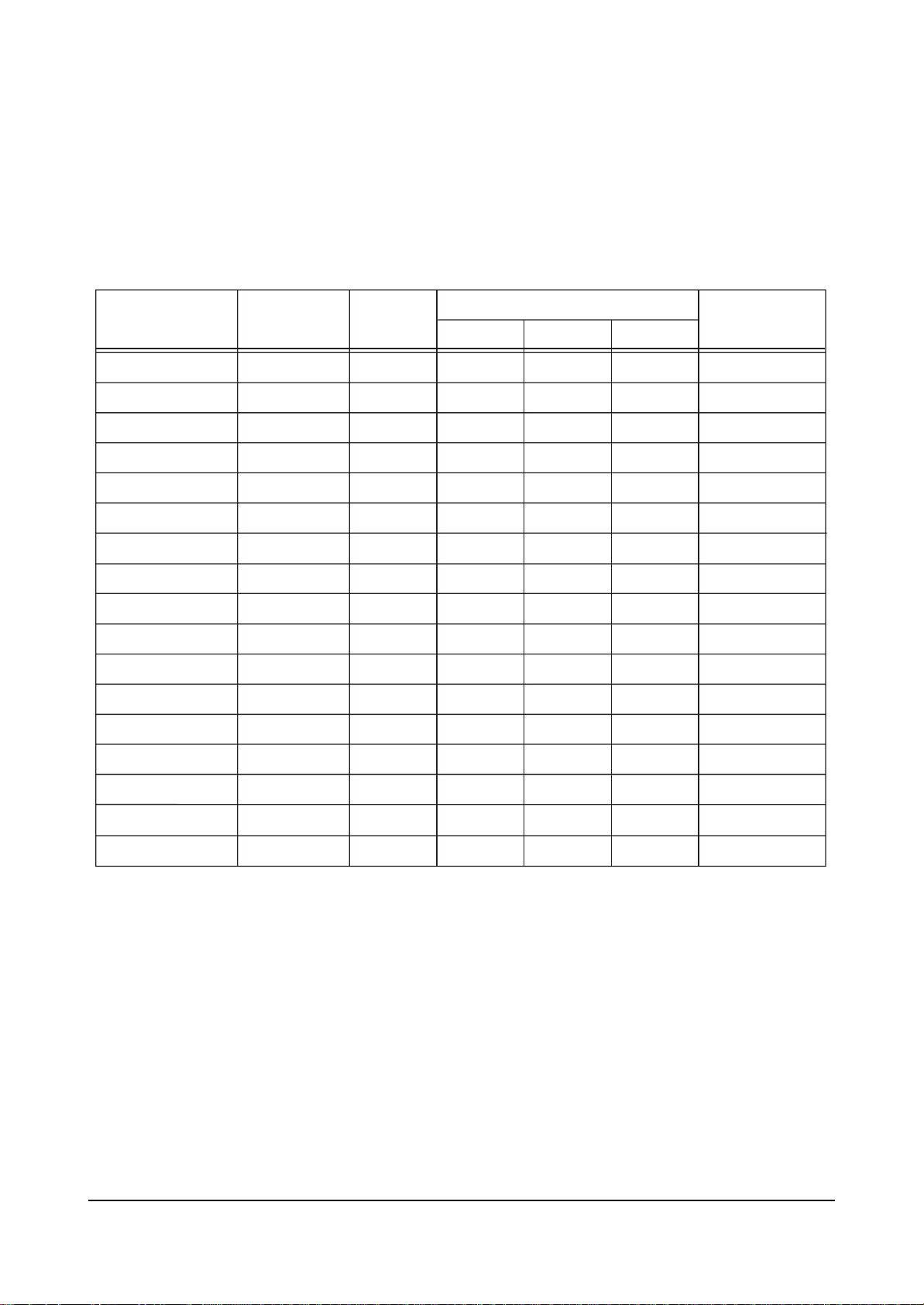
4-2-2 480P Offset
ITEM INITIAL DATA
V Amp
V Shift
H EW
H Shift
V Linearity
Upper Linearity
Lower Linearity
VSC
H Parabola
Upper Corner
Lower Corner
H Trapezium
Bow
Range
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
-63 ~ 63
-63 ~ 63
-63 ~ 63
-63 ~ 63
-15~ 15
-15~ 15
-15~ 15
-15~ 15
-63 ~ 63
-63 ~ 63
-63 ~ 63
-63 ~ 63
-63 ~ 63
EEP-ROM Copy Data
RF 480P
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1080i
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Remark
variable
variable
variable
variable
fix
fix
fix
fix
fix
fix
fix
fix
fix
Angel
V Position
CXA Left Blk
CXA Right Blk
0
0
-63 ~ 63
-63 ~ 63
-63 ~ 63
-63 ~ 63
-
-
-
-
0
0
28
36
-
-
-
-
fix
fix
fix
fix
Alignment and Adjustments
4-4 Samsung Electronics
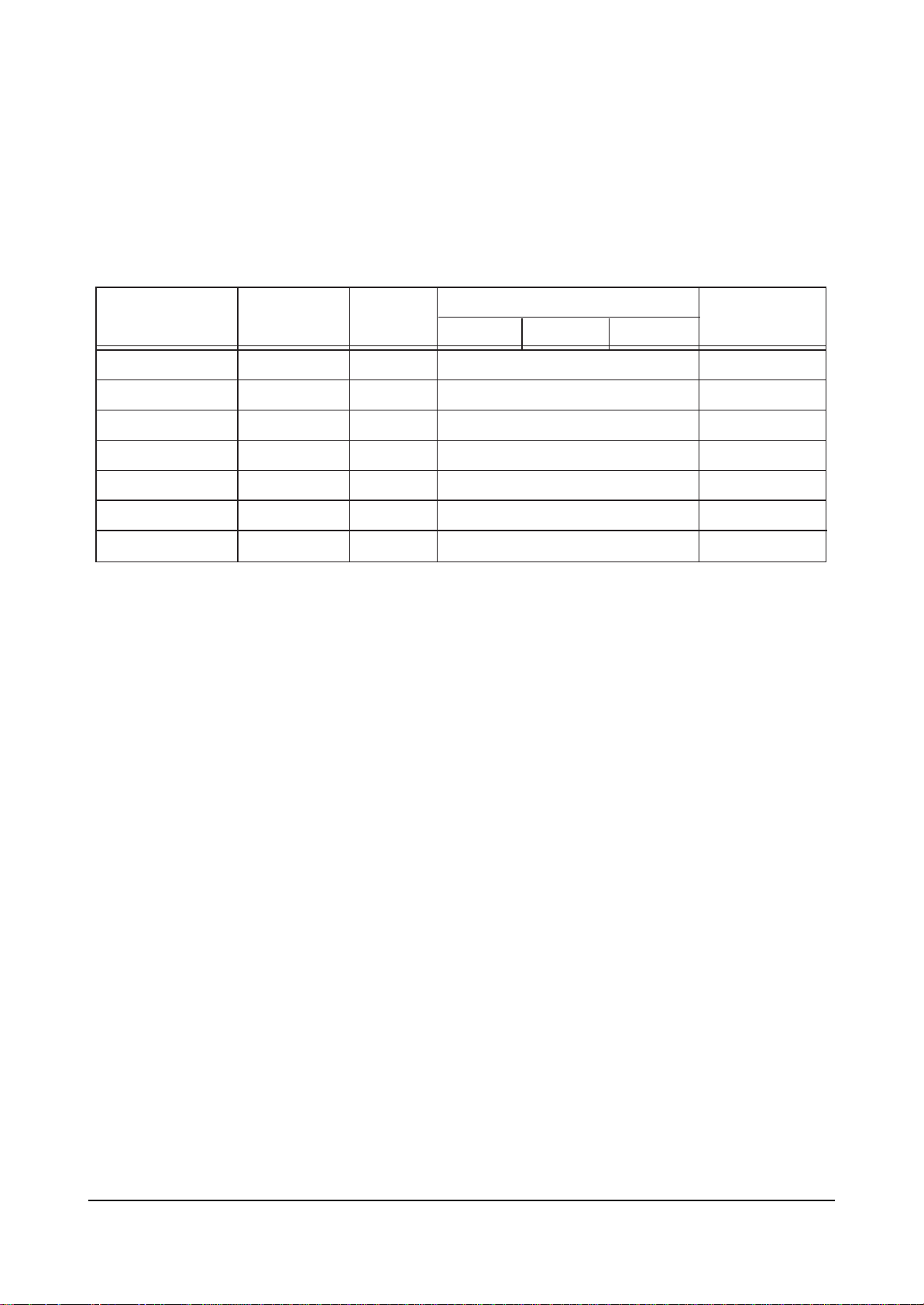
4-2-3 1080i Offset
ITEM INITIAL DATA
V Amp 0
V Shift 0
H EW 0
H Shift 0
V Linearity 0
Upper Linearity 0
Lower Linearity 0
VSC 0
H Parabola 0
Upper Corner 0
Lower Corner 0
H Trapezium 0
Bow 0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
Range
-63 ~ 63
-63 ~ 63
-63 ~ 63
-63 ~ 63
-15~ 15
-15~ 15
-15~ 15
-15~ 15
-63 ~ 63
-63 ~ 63
-63 ~ 63
-63 ~ 63
-63 ~ 63
EEP-ROM Copy Data
RF 480P
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
1080i
Remark
variable
variable
variable
fix
Angel 0
V Position 0
0
0
CXA Left Blk
CXA Right Blk
-63 ~ 63
-63 ~ 63
-63 ~ 63
-63 ~ 63
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
63
20
Alignment and Adjustments
Samsung Electronics 4-5
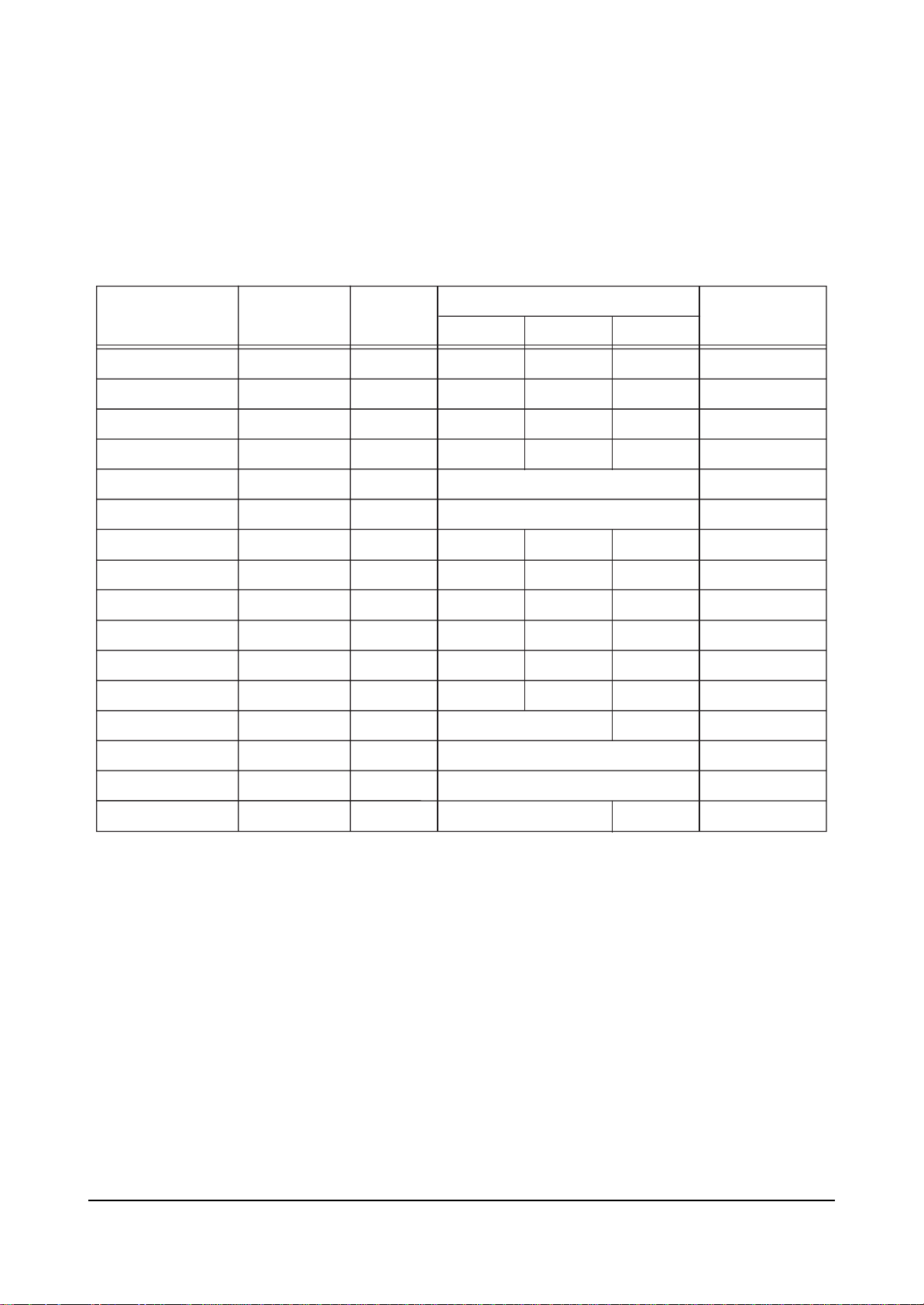
4-2-4 CONVERGRNCE OFFSET
ITEM INITIAL DATA
Offset Enable
V Amp
V Shift
H EW
V Amp 1080i
V Shift 1080i
H EW 1080i
Range
0 variable
15
0
15
15
0
15
0 ~ 1
-63 ~ 63
-63 ~ 63
-63 ~ 63
-63 ~ 63
-63 ~ 63
-63 ~ 63
EEP-ROM Copy Data
RF 480P
0
15
0
15
15
0
15
Remark
1080i
variable
variable
variable
variable
variable
variable
Alignment and Adjustments
4-6 Samsung Electronics
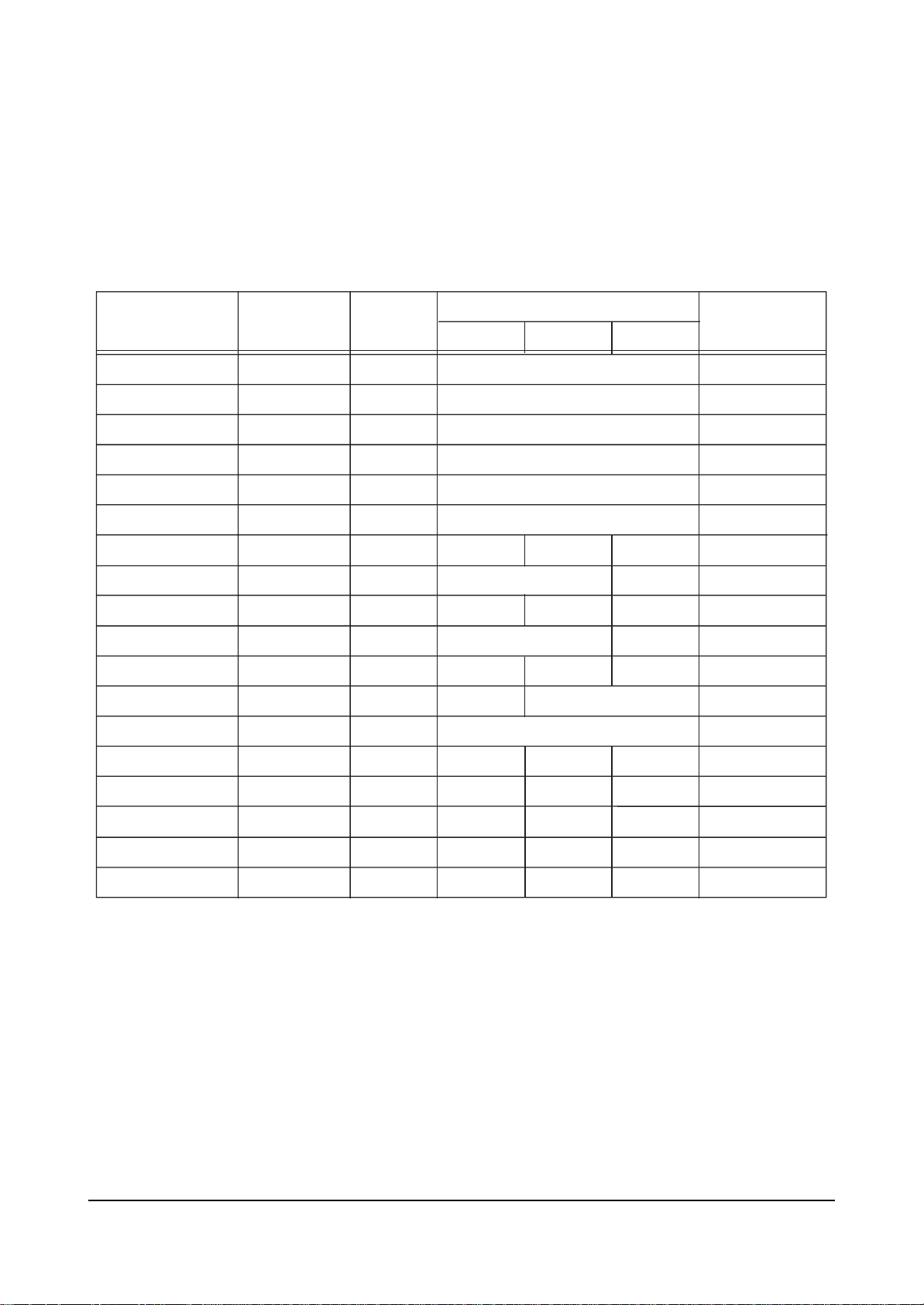
4-2-5 VIDEO ADJUST 1
ITEM INITIAL DATA
R Cutoff 20
G Cutoff 20
B Cutoff 20
Color On/Off 1
CR offset 32 fix
CB offset 32
R Driver 31
G Driver 31
B Driver 31
Sub Bright 15
Sub Contrast 7
Sub Color 20
SubTint 7
Range
0 ~ 63
0 ~ 63
0 ~ 63
0 ~ 1
0 ~ 15
0 ~ 15
0 ~ 15
0 ~ 15
0 ~ 63
0 ~ 63
0 ~ 15
0 ~ 23
0 ~ 13
EEP-ROM Copy Data
RF-Copy
31
31
31
W/B
Control Value
20
20
20
1
32
32
20
20
20
31
31
31
15
7
20
8(AV/SV/DVD/480P)
1080i
31
31
31
20
20
20
10
Remark
variable
variable
fix
fix
variable
fix
variable
variable
variable
fix
CTI Level 1
CDL AXIS 2
LTI Level 0
0 ~ 3
0 ~ 3
0 ~ 3
1 (RF/AV/SV/DVD/480P/1080i)
2
1(RF/AV/SV/DVD/480P)
fix
fix
2
fix
Alignment and Adjustments
Samsung Electronics 4-7
4-2-6 VIDEO ADJUST 2
ITEM INITIAL DATA
ABL Mode 3
Gamma 2
DPIC Level 3
DC Trans 3
ABL TH 15
VM Level 2
VM Coring 0
VM f0 0
VM Limit 0
VM Delay 0
SHP CD 1
SHP f0 0
SHP f1 & P/O 11
Range
0 ~ 3
0 ~ 3
0 ~ 3
0 ~ 3
0 ~ 15
0 ~ 3
0 ~ 3
0 ~ 3
0 ~ 3
0 ~ 3
0 ~ 3
0 ~ 1
0 ~ 15
EEP-ROM Copy Data
RF 480P
3
1
3
1
15
2
0
2 (RF/AV/SV/DVD/480P)
0
0 (RF/AV/DVD)
1 (480P)
1
0
1 (AV/SV/DVD/Comp2)
13 1 (RF/AV/SVHS/DVD/Comp2)
1080i
1
Remark
fix
fix
fix
fix
fix
fix
fix
fix
fix
fix
AKB Time 13
Y/C Delay 30
PIP Y/C Delay 30
BAND PASS F 1
HIGH PASS F 3
0 ~ 31
0 ~ 31
0 ~ 31
0 ~ 7
0 ~ 7
16
30
30
1
3
Alignment and Adjustments
4-8 Samsung Electronics
4-2-7 VIDEO ADJUST 3
ITEM INITIAL DATA
VSU 2
Melody Volume 4
H Comp 0
V Comp 0
Pin Comp 0
AFC Comp 0
Sync Comp 0
NR Off Value 5
V-Mute(x100ns)
Range
0 ~ 15
0 ~ 20
0 ~ 15
0 ~ 15
0 ~ 15
0 ~ 7
0 ~ 1
0 ~ 9
8
0 ~ 10
EEP-ROM Copy Data
RF 480P
2
4
0
0
0
0
0
5
8
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Remark
1080i
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Alignment and Adjustments
Samsung Electronics 4-9
4-2-8 VIDEO ADJUST 4
ITEM INITIAL DATA
System RF 1
System_VSD_480P 1
System_1080i 2
Shp_Fo_VSD_480P 1
HPF_VSD 3
BPF_VSD 1
Chrm_bdwth_RF 28
Chrm_bdwth_Video 28
Chrm_bdwth_Svideo 30
Chrm_bdwth_DVD 28
IF_Comp_RF 2
IF_Comp_Video 4
IF_Comp_Svideo 5
Range
0 ~ 3
0 ~ 3
0 ~ 3
0 ~ 1
0 ~ 7
0 ~ 7
0 ~ 63
0 ~ 63
0 ~ 63
0 ~ 63
0 ~ 7
0 ~ 7
0 ~ 7
EEP-ROM Copy Data
RF 480P
1
1
1
3
1
3 (AVS/SV/DVD)
1 (AVS/SV/DVD)
28
28
30
28
2
4
5
1080i
2
Remark
fix
fix
fix
fix
fix
fix
fix
fix
fix
IF_Comp_DVD 4
VM_Delay_480P 1
0 ~ 7
0 ~ 3
4
1
fix
fix
Alignment and Adjustments
4-10 Samsung Electronics
4-2-9 OPTION
ITEM INITIAL DATA
CRT WIDE
PIP ON
3D-Comb Filter OFF
Blue Screen
OFF
BBE Effect
Auto power On
System CT
Virtual Dolby
OFF
ACS
V chip (CT,CTA)
V chop Area USA
Sub Woofer
OFF
No Sync Mute
DVI
AGC
Tubo Effect
Burst Screen
DW Multi
OFF
OFF
OFF
Large
Letter Box
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
Range
WIDE ↔ 4:3
ON ↔ OFF
ON ↔ OFF
ON ↔ OFF
ON ↔ OFF
ON ↔ OFF
CT (EN+SP+ER)→CT-A(E+SP+F)
ON ↔ OFF
ON ↔ OFF
ON ↔ OFF
USA
ON ↔ OFF
ON ↔ OFF
ON ↔ OFF
ON ↔ OFF
ON ↔ OFF
ON ↔ OFF
Large ↔ Double
ON ↔ OFF
HCM4216W,HCM4215W,
HCL4715WB,HCM4715W
(PCL5415RB,PCM5415R)
HCM5525WB,PTH5598W
WIDE(4:3)
ON
OFF
ON
ON
ON
CT
OFF
ON
ON
USA
OFF
ON
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
Large
ON
HCM422W,HCM473WB
(PCL545RB,PCM545R)
HCM553WB
WIDE(4:3)
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
CT
OFF
ON
ON
USA
OFF
ON
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
Double
ON
Alignment and Adjustments
Samsung Electronics 4-11
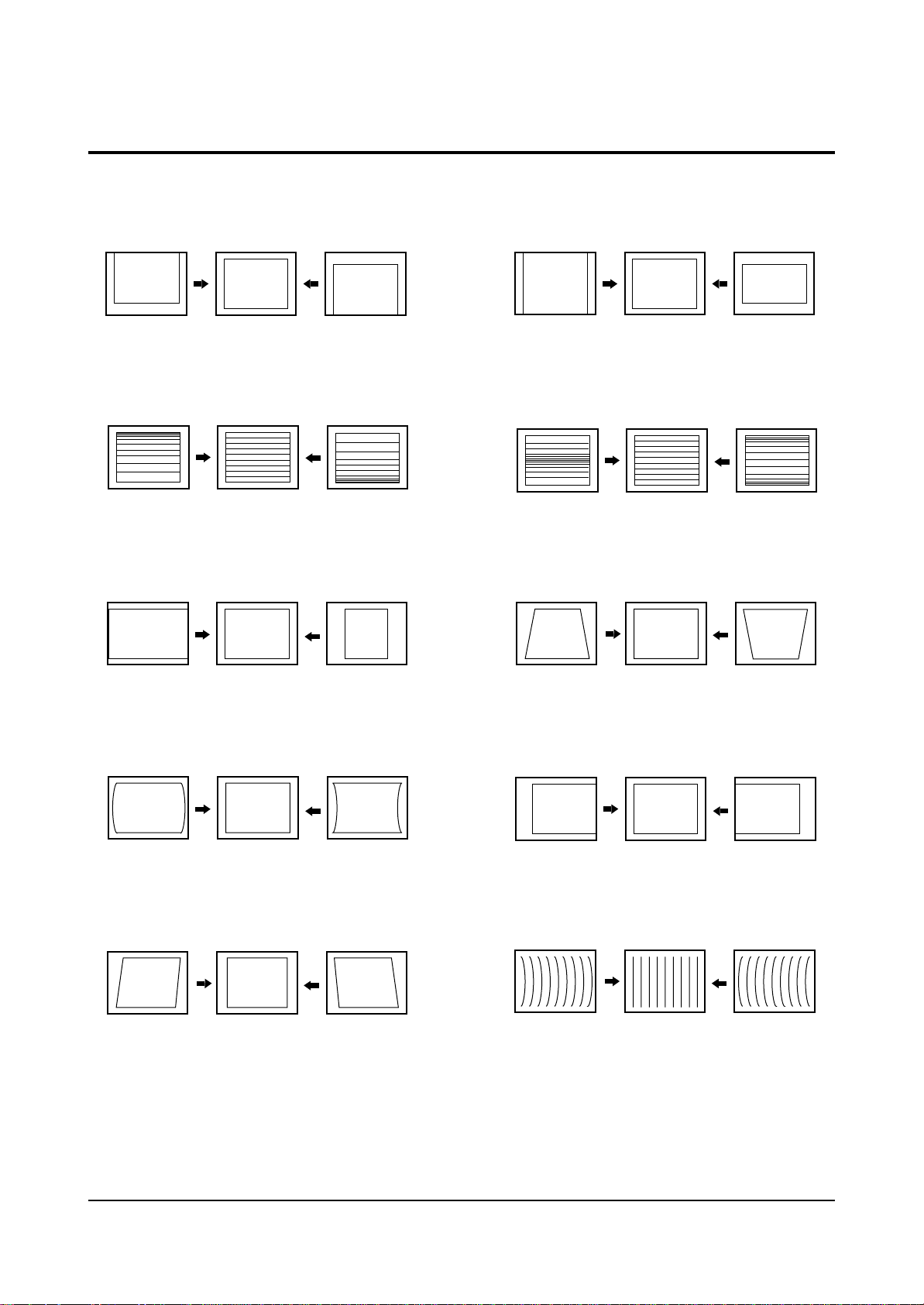
4-3 Screen Change (When adjusting I2C Bus Geometric items)
1 V SHIFT
2 V LINEARITY
3 H SIZE
6 V SIZE
7 V - S - CORRECTION
8
PIN PHASE
4
PIN AMP
5 V ANGLE
9 H SHIFT
10 V BOW
Alignment and Adjustments
4-12 Samsung Electronics
4-4 Other Adjustments
4-4-1 Screen Adjustment
1. Warm up the TV for at least 30 minutes.
2. Select the “ STANDARD” Video mode.
3. Turn to the Video Mode (No Signal) using a
remote-control.
4. Connect an oscilloscope to RK,GK,BK.
5. Adjust the VR (VR501, VR531, VR561) screen
so that RK, GK, BK pulse is 20Vp-p each.
(Turn the R,G,B VR screen fully
counterclockwise in the area of each flyback
line.)
4-4-2 White Balance Adjustment
1. Select the “STANDARD” video mode.
2. Input 100% white pattern.
3. In the stand-by mode, press the remote-control
keys in the following sequence:
4. Warm up the TV for at least 30 minutes.
5. Input a 10-step signal.
6. R-cut off, B-cut off, and G-cut off by pressing
the Volume keys.
7. Adjust the low light with viewing the dark
side of the screen.
8. Select R-drive, G-drive, and B-drive by
pressing the Volume keys.
9. Adjust the high light with viewing the light
side of the screen.
10. If necessary, redo adjustments 6~9.
11. Press the Menu key to exit.
4-4-3 Sub-Brightness Adjustment
1. Input a sub-brightness adjustment signal.
(TOSHIBA PATTERN)
2. In the stand-by mode, press the remote-control
keys in the following sequence :
3. Select SBT by pressing the Volume keys.
4. Adjust so that the 63 step on the right side of
the screen is not seen (Use the Volume
keys).
5. Press the Menu key to exit.
4-4-4 High Voltage (29KV) Check
PRECAUTION
1. Input a lion head pattern.
2. Select “STANDARD” video mode.
3. Warm up the TV for at least 10 minutes.
4. Use a 1000:1 probe.
ADJUSTMENT
1. Connect the (+) terminal of the 1000:1 probe to
the high voltage distributor and the (-)
terminal to GND (located on the deflection
board).
2. Adjust RR471S (located on the deflection
board) so that the digital meter indicates
DC 29V ± 0.1V.
4-4-5 F.S. (Fail Safe) Adjustment
Note : The finished product has a well-mounted
VR (RR402S).
If necessary, do the F.S. adjustments in the
following sequence.
1. Use a digital multimeter.
2. Connect the digital multimeter to the JIG pin
(DZ482S) terminals
3. Adjust VR (RR402S) so that the voltage
becomes 2.25V.
4. After the adjustments are complete, be sure to
mount VR (RR402S) correctly.
Alignment and Adjustments
Samsung Electronics 4-13
4-4-6 F.S. (Fail Safe) Circuit Check
Note : The F.S. Circuit check must be performed
after servicing.
1. Turn on the TV.
2. Select the “STANDARD” video mode.
3. Short F/S Test point (located on the SUB PCB).
Then, both sound and picture disappear.
(Note: Even if the shorted terminals are
removed, both sound and
picture do not appear. This proves the F.S.
circuit is working. )
4. To restore both sound and picture, turn off the
TV and reset it after about 30 seconds.
4-4-7 Static Focus Adjustment
PRECAUTION
1. Select the “STANDARD” video mode.
2. Input a crosshatch pattern.
3. Cover the lenses that are not being adjusted.
4. Connect a convergence jig and read data.
5. Adjust the lens for best focus.
(See Fig, 4-1)
STATIC FOCUS (CONTINUED)
Vary the focus pack VR (Red, Blue) on the
front cabinet. Adjust the TV for best possible
focus around the center of the crosshatch
pattern, without losing overall screen balance.
Figure Crosshatch Pattern
Examine these points together.
4-4-8 Lens Focus Adjustment
PRECAUTIONS
1. Do this adjustment after the static focus
adjustment and the tilt adjustment.
2. Select the “STANDARD” video mode.
(Contrast:100, Brightness:50)
3. Input a crosshatch pattern.
ADJUSTMENT
1. Loosen the lens screws.
2. Cover the two lenses that are not being
adjusted.
3. Adjust the lens, observing the color aberration
vertically and horizontally within 3 blocks of
the center of the crosshatch pattern.
4. When the lens is turned clockwise, the color
aberration will change as follows:
Lens Color Aberration Change
R Orange - Crimson
G Blue - Red
B Purple - Green
5. Green lens adjustment:
Set the lens at the point where Blue just
changes to Red. If the color aberration is
irregular throughout the picture screen, adjust
the lens to show Red color aberration
(approximately 1~3 mm area) within a 3-block
grid around the horizontal center-line. If the
color aberration is irregular, adjust the lens as
shown in the diagram below. (Accurate
alignment of Green is important for overall
color quality.)
6. Red lens adjustment
Set the Red lens at the point where Orange
becomes Crimson.
7. Blue lens adjustment
Set the Blue lens at the point where Purple
becomes Green.
P
L1
L2
RED ABERRATION
BLUE ABERRATION
L1, L2 < P
_
Fig. 4-1 Crosshatch Pattern.
Fig. 4-2 Color Aberration
Examine these points together
Alignment and Adjustments
4-14 Samsung Electronics
1. Select the “STANDARD” video mode.
2. Warm up the set at least for 10 minutes.
3. Enter the Convergence mode by pressing the remote control buttons in the following sequence
:
4. Set the Beam Alignment Adjustment CY to Zero magnetic field area.
5. Check the squarewave at the point where the focus is misaligned (Use an audio oscillator).
6. Press the button on the remote control, and a vibrating dot-pattern appears.
7. Adjust the Focus-pack VR for defocusing.
8. Mute the other patterns (R/B) other than G-PATTERN.
(Use / buttons on the remote control.)
9. Adjust the 2, 4 polarities of VM-COIL as shown in figure below.
10. Adjust the G-Focus until any light around the core disappears.
11. Adjust G-Focus so that the surrounding flash can disappear from the spot.
12. After G-Focus adjustments are complete, adjust R-Focus as above procedures.
13. The B-CRT adjustments can be omitted because the variance of beam focus is small.
(Only Vm-coil is mounted.)
14. Adjust the Focus-pack VR for fine focusing.
15. Press the button on the remote control, and the mode changes to the Convergence Adjustment
mode.
16. Press the button on the remote control to return to normal viewing.
4-5 Beam alignment Adjustments
(Creation of CPM Zero Magnet)
(Creation of the 2-pole/4-pole zero magnets)
G-FOCUS
(Varying G-Focus Pack)
G-FOCUS
(When VM 2-Pole Adjustment is completed)
CORE
CORE
Varying the 2-pole of VM
Varying the 4-pole of VM
(Positioning the Core in the Center)
(Adjust until the light around
the core becomes a circle)
Alignment and Adjustments
Samsung Electronics 4-15
4-6 Hige Voltage Part
4-6-1 PWM REG Circuit
For the existing high voltage REG circuit (input
voltage variation type), a dynamic REG response
is not provided. So it is difficult for both beam
linearity and uniformity in screen size to be
maintained on the screen with rapidly changing
beams.
A PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) type of high
voltage, however, provides the maintenance of
beam linearity and uniformity in screen size via a
quick response to beam change by performing
sync lock every 1H line, and detecting beam
fluctuation at 1H line, and then controlling the IC
current of high voltage output circuit.
1. High Voltage Fluctuation Detect (DC Detect)
FBT pin 11 detects DC high voltage fluctuation.
The detected DC high voltage value is input to
PWM IC471 pin1 through R473, VR471, R471,
and then it is input to a differential AMP circuit
that differentiates the gap after comparing with
the reference voltage input to pin2.
2. High Voltage Fluctuation Detect (AC Detect)
To check AC high voltage fluctuation, the
output from FBT is detected by using a
capacitor inside the high voltage distributor. The
detection of AC high voltage fluctuation,
a detection of dynamic beam current change is
required in order to keep beam linearity and
uniformity in size.
Regarding the capacitor, a capacity of less than
3000P should be applied to a PWM type. (The
existing type needs a capacity of about 6000P.)
AC detect circuit eliminates unnecessary high
frequency by using C476, D472. Also, AC gain is
limited to + / - 0.7V (D472). This AC gain is
combined with the detection value of DC high
voltage fluctuation by using C478.
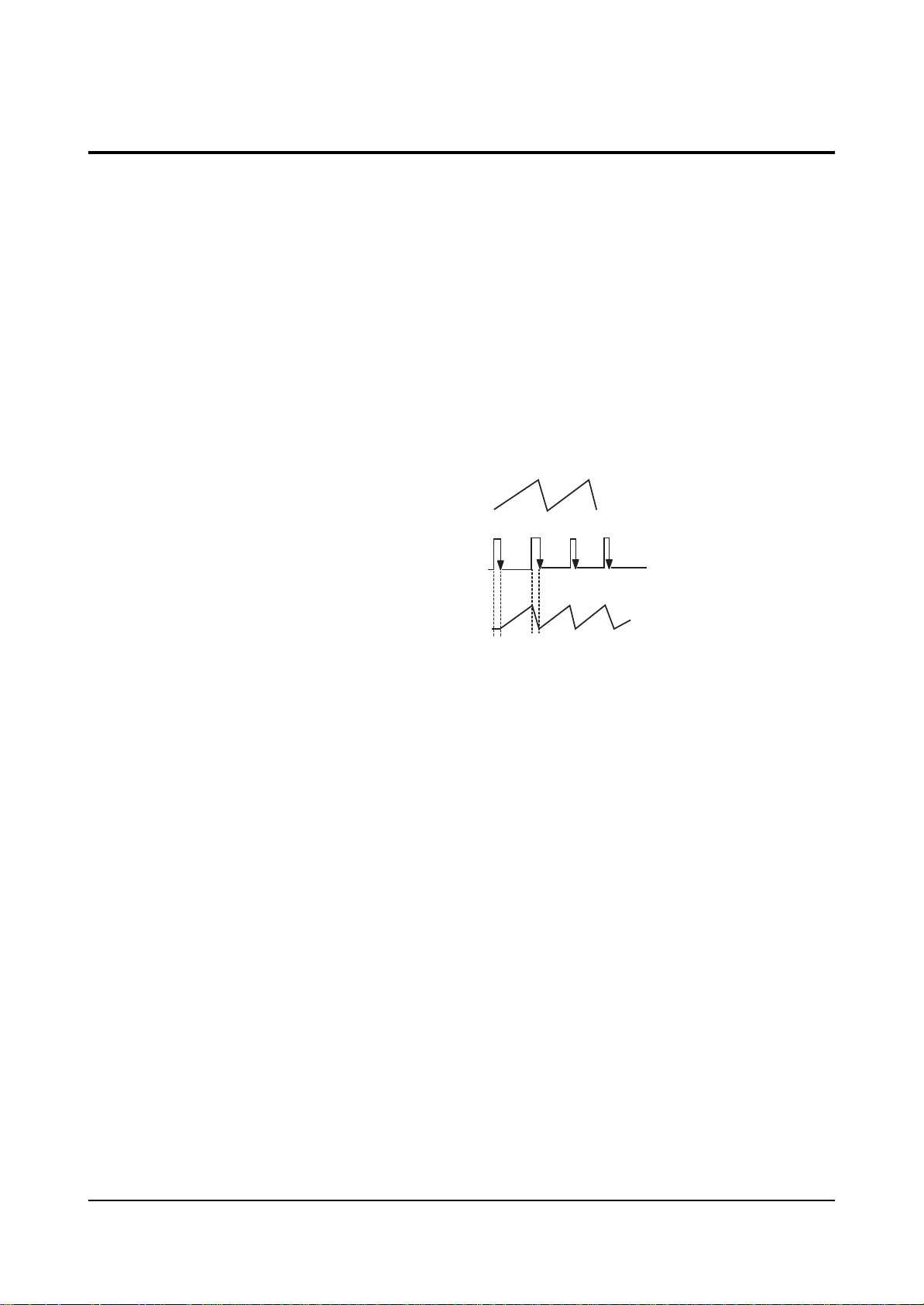
3. PWM IC OSC Sync Lock
A PWM type IC needs sync lock for PWM pulse
and horizontal scan line.
The standard time constant of OSC circuit is
determined by C487, R475 (PWM IC pins 5 and 6).
And the standard OSC frequency is about 27
kHz . The horizontal frequency of scan line is
31.5kHz(NT), 3375kHz(DTV), 15.75kHz(Interface),
so sync lock for this horizontal frequency should
be performed using sync lock circuit. The sync
lock circuit consists of Q481(Tr KSC815-Y),
D479, D478, and C492. The input AFC signal is
connected to PWM IC pin 5 through D479 so
that it can be negative Trig.
4. Dead Time (HV Protect)
Dead Time (PWM IN pin4) consists of C481,
delays high voltage for a certain time to soft
start in power on, a x-ray protection circuit.
The voltage of Dead Time is detected by FBT
pin7 and through DC Feedback. The normal
voltage of Dead Time is +27V. When high
voltage increases, however, detected voltage is
in proportion to high voltage. Then, the detected
voltage is applied to ICR01S(TL431).
If the voltage is over 2.5V (normal:about 2.25V),
TL431 turns ON, the base port of QR401S
becomes low, and then an emitter current flows.
At this time, a high voltage protection point is
set. When QR401S turns ON, high voltage is
applied to PWM IC pin4 and then muted.
OSC : 27KHz
AFC Waveform : 31.5KHz(NT)
Locked OSC Waveform : 31.5KHz
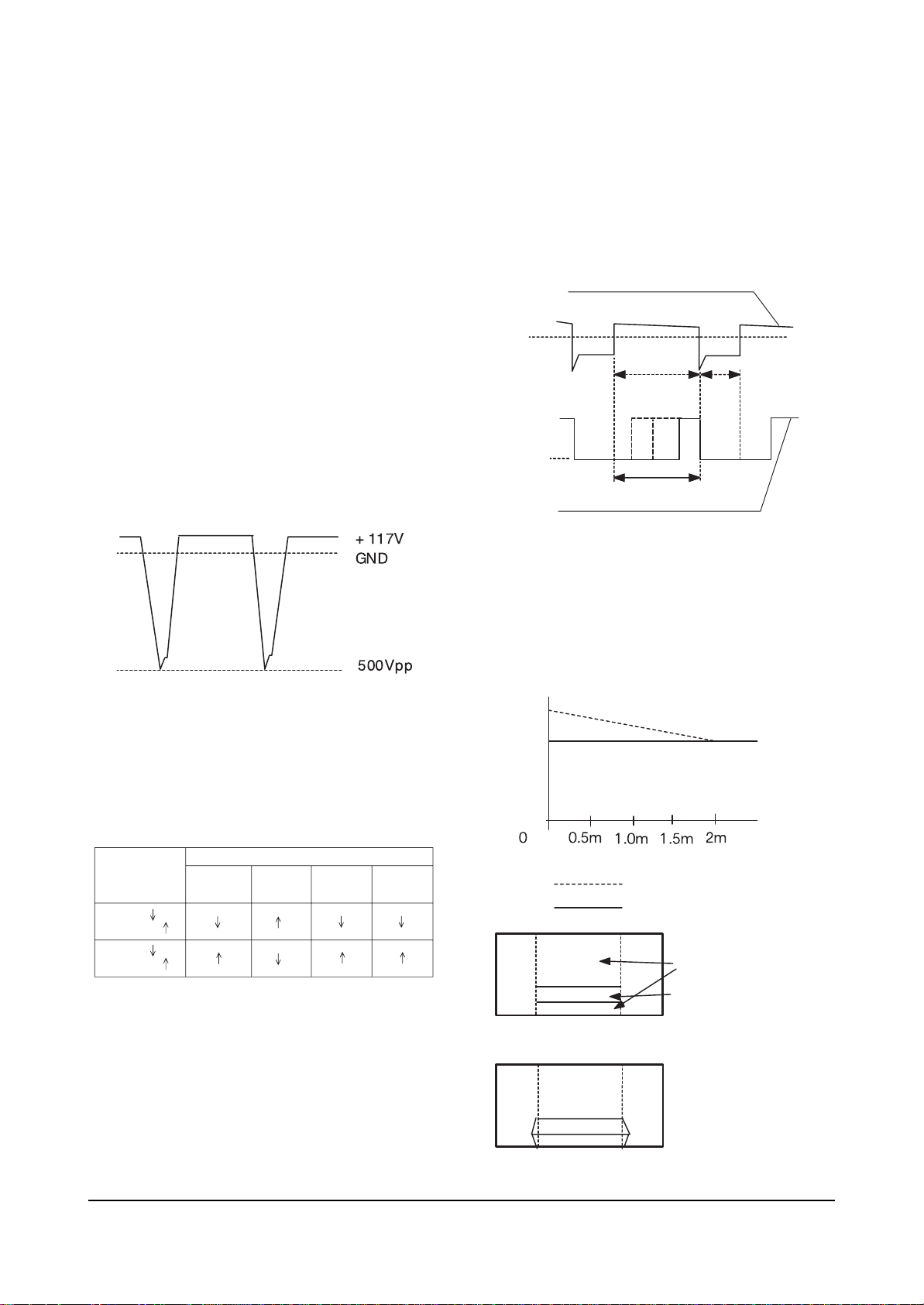
Alignment and Adjustments
4-16 Samsung Electronics
5. Output Circuit
The voltages, which are detected form an error
detection circuit of PWM IC (Differential AMP)
and Dead Time, each is applied to PWM
conparator . Due to these detection coltages, Q1,
Q2 (Output TR) parallel operate. Q482 (External
TR), however, functions as a buffer; natches
inpedance between the output port of PWM IC
and the final output TR(IRFS640). The PWM
pulse (applied to the final output FET (IRFS640
GATE) varies the IC current of high voltage
TR(Q473) by adjusting the load impedance of
starage Trans (T431). Due to this variation of
current, the gain for Q473 emitter pulse changes
T444(FBT)makes this emitter pulse became high
voltage. Such change keeps both dynamic and
static changes fixed. The output waveform of
high valtage TR emitter is as shown in the figure
below.
6. Paraneters according to beam
To maintain the set high voltage value (31kV),
parmaters such as +Ve (DC), Vcp High Voltage
change (See the table below).
7. Response Waveform
To reduce unstable high voltage fluctuation, the
existing high voltage type REG circuit controls
dynamic fluctuation by using C-block capacitor.
But, it can't detect actual dynamic fluctuation.
Also, its velocity of response to static fluctuation
is late because +B power supply changes per
about 1V. A PWM modulation type REG detects
static, dynamic high voltage fluctuation for only
Ton Time (when the current of the output TR
collector flows) each 1H, and modulates the
width of PWM pulse. So, this PWM type has
better improvement in the characteristic of high
voltage REG as compared to the existing type.
8. Application Effects
1) Improvement of horizontal size fluctuation
2) Linearity improved
3) Embodiment of X-ray protection circuit
The figures below show characteristics when a
PWM high voltage REG circuit is applied.
Beam
(High voltage )
Factor of high
voltage change
Beam
(High voltage )
Width of FET
Gate Pulse
+ Ve (DC)
Vcp
High
Voltage
Parameters
High Voltage Drive Base Current
PWM Input Waveform of FET GATE
GND
GND
PWM Variation tange
Ton Toff
Beam
High Voltage
High Voltage OFF
High Voltage REG ON
BLACK
WHITE
When a Toshiba Pattern
is recrived, the screen is
displayed as shown in
figute side
Existing type
PWM type
 Loading...
Loading...