Page 1

Page 2
Hard Disk Recorder
© 1998 Roland Corporation
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced in any form without the
written permission of ROLAND CORPORATION.
All trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
The cover illustration shows a Roland VS-880EX Digital Studio Workstation with
the optional Roland VS-CDR CD Recorder, two Roland MA-12 powered monitors,
and the VS-880EX TurboStart Video.
ZERO REW FF STOP
PLAY REC
Page 3

1
Just as word processors have revolutionized the writing process, digital
hard disk recorders (HDRs) are giving musicians unprecedented creative
freedom in the production of their music.
Imagine being able to...
...record as many tracks of a guitar solo as you
want without having to erase one take.
...listen to your song in many different
arrangements and choose the one that you or your
producer likes best.
...boldly experiment, knowing that your original
recordings are safe and mistakes can be ‘undone’.
...record, mix and add effects all in one digital unit.
This creative flexibility is what
Hard Disk Recording is all about.
This guide discusses the issues and power of Hard Disk Recording and
will help you to:
• Understand the basics of digital recording,
• Learn about different kinds of digital recorders,
• Understand how hard disk recording is different from
other types of digital recorders, and
• Understand the basics of how recording works on HDRs
and where your music “goes.”
You will see the incredible benefits of such features as: random access;
virtual tracks; and pointer based, non destructive editing.
You will also learn about integrating HDRs with effect processors and
MIDI devices, and how easy it is to understand and use HDR systems.
This second edition has even added the latest concepts and terms to keep
you up to date.
Most importantly, this guide will be your doorway to HDRs, showing you
how much control they can give you, empowering you to expand your
creativity and make your music sound its best.
An Introduction to Hard Disk Recording
Page 4
2
Every recording process converts audio to something.
Analog tape
Recording on analog tape converts
audio to constantly changing magnetic
fluctuations.
Although this process has been in use
for many years, it has some inherent
problems:
• Hiss on original tape and more in each copy
• Wow and flutter of tape media
• Degradation of tape over time
• Maintenance: regular cleaning and adjustment
• Linear access: to get from Introduction to the Ending, you must
go through all of your verses and choruses
Digital Recording
Just like music on an audio CD, digital
recording changes sound to numbers.
This process has some distinct advantages
over analog recording:
• No hiss, no wow, no flutter: virtually
no noise at all
• Copying with no degradation: you’re only copying
numbers
• Lots of processing options (reverb, delay, etc.) with no loss of
sound quality
• Some have random access locating: to get from the Introduction to the
Ending, just jump there instantly!
What IS Digital Recording?
HDR’s have extremely high quality audio
011101111
Page 5
3
There are several forms of digital recording:
• Digital Tape Recorders (such as Alesis ADAT®& Tascam DA-88®)
• MiniDisk Recorders
• Hard Disk Recorders
Digital Tape Recorders
Record digitally onto tape.
Advantages:
• Cheap media
Disadvantages:
• Linear access: to get from Introduction to the Ending, you must
go through all of your verses and choruses
• Destructive recording: lose the originals when you record over a track
• No UNDOS
• Impossible to copy from one section to another using one unit
• Limited editing without multiple units
• No virtual tracks
• Require you to buy external mixer and effects processors
Basically, they are very high quality “typewriters” (more on this later).
MiniDisk Based Systems
Record onto a data-type MiniDisk.
Advantages:
• Low cost
Disadvantages:
• Most are limited to 4 tracks
• Destructive recording without
multiple levels of undo
• Use analog mixers so there is
degradation when bouncing tracks
• No on board digital FX
• Track level copying or editing is either impossible or takes additional
time or disk space. See page 10 - 12 for more details.
• Can’t lock multiple units to increase the number of tracks
Different Forms of Digital Recording
Page 6
4
Hard Disk Recorders (HDRs)
Record digitally onto a Hard Disk. Recording to hard disk has many
advantages over the other types of digital recorders. For the remainder of
this booklet we will focus on HDRs. These recorders really open the doors
to your creativity.
Types of HDRs
There are two basic types of Hard Disk Recorders: Computer Based
Recorders, and Dedicated (Stand-alone) Hard Disk Recorders.
Computer Based Recorders
Advantages:
• Graphics
Disadvantages:
• Expensive
• Require advanced computer knowledge
• Usually require a powerful computer,
cards, cables, and external hardware
• Often less stable than dedicated units
• Not portable
Dedicated Hard Disk Recorders
Stand alone systems designed specifically
for audio recording and editing. Dedicated
HDRs range from units that are basically
recorders alone, to workstations (all-in-one
boxes with mixers with faders and knobs
and digital effects).
Advantages:
• Great dollar value
• Familiar layout and controls
• Easy to learn and use
• Extremely stable
• Portable
• Exceptional sound quality
• Multiple units can be easily sync’d to increase the number of tracks
Types of Hard Disk Recorders
8 Audio
Tracks
Sync
16 Mixed
Audio
Tracks
ZERO REW FF STOP
PLAY REC
Page 7

5
Let’s answer this question with an analogy:
What’s the big difference between a typewriter and a word processor?
When you write something on a piece
of paper with a typewriter, it’s there to
stay. If you want to change the order of
the words, add a paragraph in the
middle of the page, or correct a mistake,
you are out of luck. You have to start all
over again. This is similar to analog or
digital tape.
Word processors give you the creative
freedom to move paragraphs, copy sections,
insert new material, easily fix mistakes, or
save several versions of a document.
That’s one of the biggest differences
between hard disk recorders and linear
recording, either digital or analog tape.
HDRs enhance your creativity. They allow
you to re-organize your material, fix
mistakes and try different ideas to see how
they might sound.
Read on to find out about some of the great features HDRs give you,
including:
• Random Access
• Virtual Tracks
• Non destructive, pointer based editing
• Digital mixing
• Digital effects
• SMPTE, MIDI, and extensive syncing options
What’s the Big Deal About Hard Disk Recording?
HDRs allow you to try many ideas with your music.
Page 8
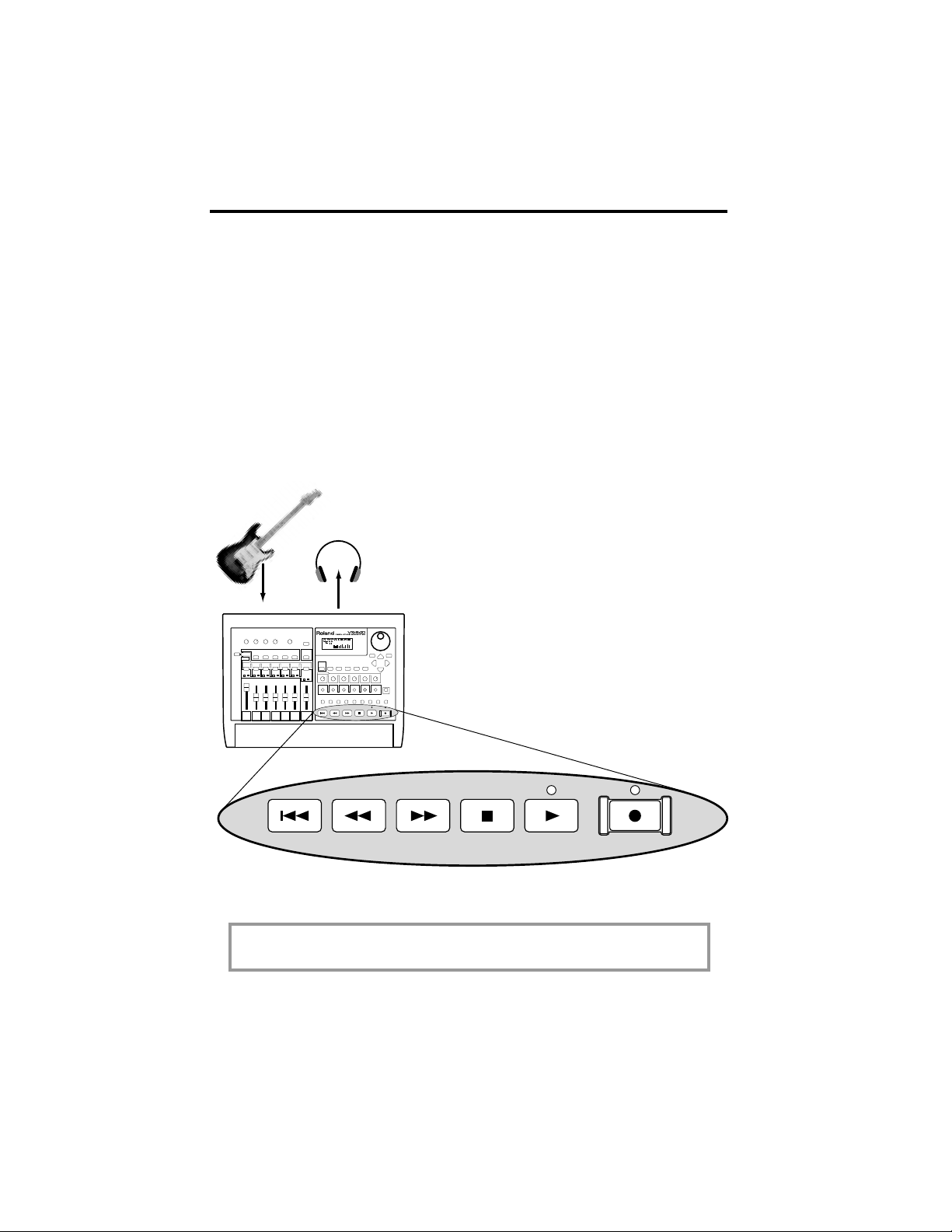
6
Dedicated HDRs with digital mixers are easier to use than any type of
tape recorder and mixer combination.
Just plug in and start recording, just as you would on an old fashioned
tape recorder.
You record right onto tracks just like a tape recorder. When you are
finished recording, you can listen to what you recorded and record more
material on other tracks.
This process is quite simple because the HDR takes care of all of the work
without you having to worry about it!
How Do I Record Music With an HDR?
Recording music with HDRs is very easy
STOP PLAY RECFFZERO REW
Page 9
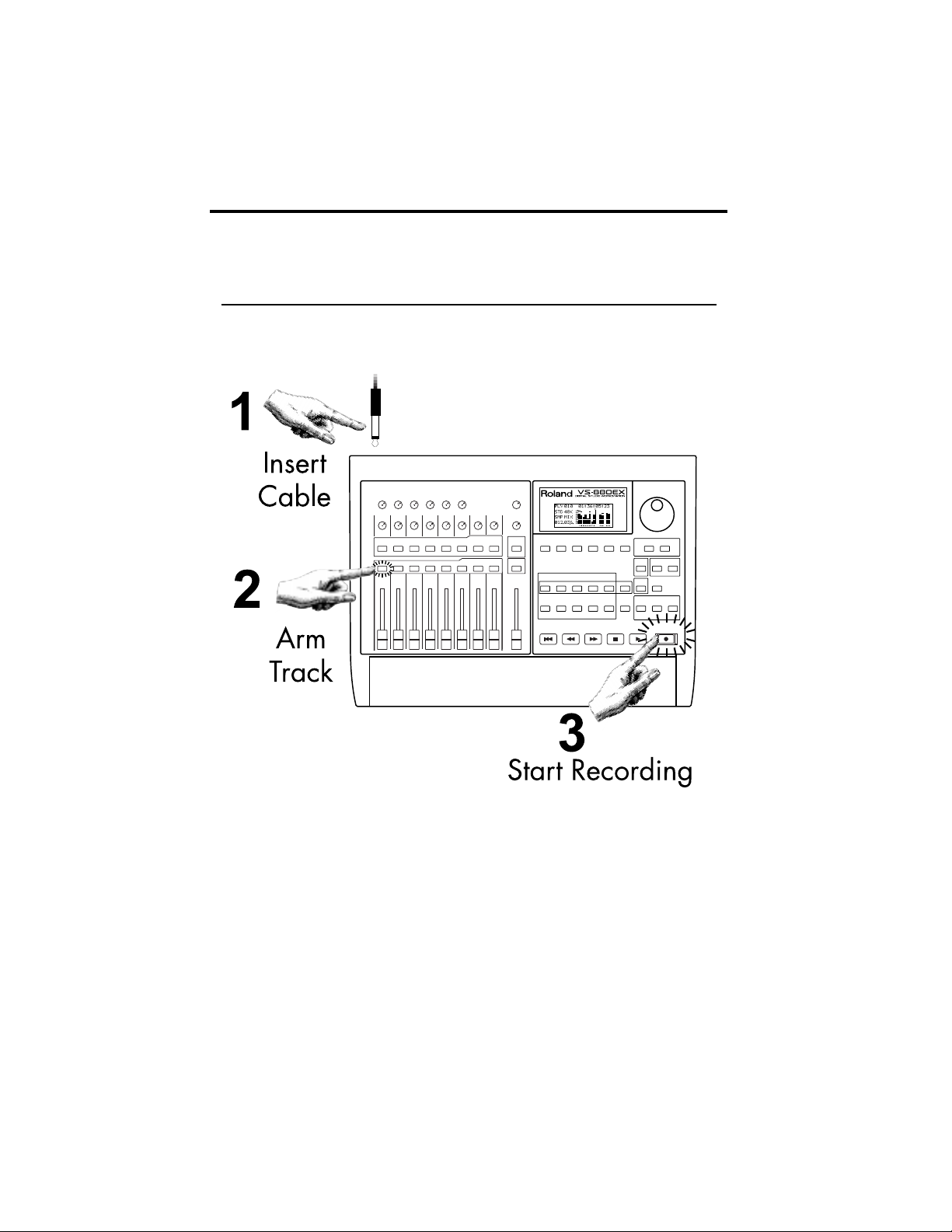
7
Recording is as easy as 1, 2, 3!
Recording to an HDR is similar to any tape recorder!
It is also easy to integrate HDRs with:
• Drum Machines (using MIDI)
• Keyboard sequencers
• Computer sequencers
• Video
• other forms of recorders, such as Digital Tape recorders
How Do I Record Music With an HDR?
ZERO REW FF STOP
PLAY REC
Page 10

8
Just as a tape recorder stores your music on tape, a hard disk recorder
stores your recordings on a hard drive. The hard drive can be inside your
HDR, or your HDR may be connected to an external Hard Drive with a
SCSI connector.
The great part: the HDR takes care of the details for you. You really don’t
have to think about it any more than you would with an old style tape
recorder.
Where Does the Audio Go in Hard Disk Recording?
HDRs record audio onto a hard disk.
ZERO REW FF STOP
PLAY REC
Page 11

9
A large hard disk can hold many songs. Just as a tape gets full, a hard
disk also gets full. What do I do then?
Some hard disk recorders have removable media built-in. When you
want to start a new song, you just pop out the removable cartridge and
put in a new one. The cartridges are very inexpensive and as easy to find
and buy as tape.
On other systems, to store your songs and free up space for new
recordings, all you need to do is “backup” your recordings onto some
form of removable media. Removable media types include Zip drives,
Audio DAT, Magneto Optical drives, and even CD-R (Recordable CD).
You can backup songs onto media for future use, or to free up disk space
for more recordings.
HDR’s can backup a LOT more than audio!
This type of digital backup has some distinct advantages. Unlike analog
tape, which only stores your recorded takes, some HDRs can also store all
of your mixer settings, effects settings, virtual tracks, edits, different
versions of your song, and even all of your Undos! This gets you going
very quickly and accurately when you want to work on the song again.
What Do I Do When the Disk Gets Full?
It’s easy
and economical
to back up a
Hard Disk Recorder
to removable
media.
Backing up an HDR to removable media stores lots
more information than an analog or digital tape.
Backup
to SCSI
Removable
Media
Re-load
from SCSI
Removable
Media
ZERO
REW FF STOP
PLAY REC
Page 12

10
Pointer based editing is the key difference between any tape based system
(either analog or digital) and Hard Disk Recorders.
Once you have recorded something onto your hard disk, you never
“touch” that material again. It stays there, ready for a command from the
HDR to play part or all of it.
For example, if you record a vocal on tape, and then decide to erase part,
you are erasing your original recorded material. It is gone forever!
If you record a vocal on a pointer based hard disk recorder and erase part
of it, you aren’t erasing the original material, you are just telling the HDR
to play only part of the original recording. You never actually erase the
original material! You can use an UNDO to get back to the original
recording if you decide that you like the original better.
Likewise, if you want to copy a drum part you recorded, you don’t need
to record that part again as you would have to on a tape based system. All
you are doing is instructing the HDR to play the same material over and
over at different points in your song, using “pointers” to the original
material. This is commonly referred to as “pointer based editing.”
What Is Pointer Based Editing?
Copying a
drum part
using pointers
does not
actually
require
re-recording
the material.
WARNING - make sure your HDR is pointer based
or these advantages do not apply
!
Hard Disk
Page 13

11
What are the advantages of “pointer based editing?”
First of all, in most HDRs, you can Undo any erase, cut, or copy anytime.
Remember, the original is still there! You never lose your ability to go
back and change something if you decide you need to.
Secondly, copying is instantaneous because you aren’t actually copying
the original material, you are just adding a “pointer” to tell the HDR to
play it again. You can use copy to make different arrangements of your
song, and it doesn’t use any room on your hard disk!
Let’s say you record a guitar part on a track. Then you punch in a new
section and you realize you made the punch too early. With an HDR, you
can always go back to the original recording. Try that with tape!
You can erase, cut, or move anything anywhere without destroying your
valuable recordings. If you don’t like it, just ‘Undo’ it.
This all means that you can try any old idea that you like, and compare it
with the original to decide which you like best. This is a huge advantage
for your creativity.
This is what Hard Disk Recording is all about!
Pointer Based Editing
Pointer based editing allows you to quickly try your
ideas without the fear of making a mistake.
Guitar
Solo
Guitar
Solo
PunchInGuitar
Solo
Original Version
Punch In
Guitar
Solo
Undo to Original Version
Page 14

12
Song Arrange
Some Hard Disk Recorders can even edit for you. This function is called
Song Arrange. It steps you through the process of re-arranging your
song, automatically making a copy with the new sections for you.
You could specify a shorter Intro, two Choruses after the first verse, a
repeat of the Intro before the Bridge, then a doubled ending. You can
even add other parts to this new version and compare it to the original.
Song Arrange does the edits automatically, instantly, without taking up
any disk space!
Summary of Pointer Based Editing
Pointer Based Editing has many advantages. It allows you to Undo an
edit such as an Erase or punch-in. Looping a drum part or copying a
vocal is virtually instant on most pointer based HDRs. Pointer based
editing even allows you to experiment with different versions of a song,
all virtually instant and without taking up any additional disk space.
To help clarify the difference between HDRs, MiniDisk recorders, and
digital tape recorders; let’s examine what you would need to do to loop a
drum part on each of these types of recorders.
Looping a Drum Part on Digital Tape: You would need two tape
recorders, one for the source and one for the copies. You would also have
to synchronize them and figure out exactly where to punch in each copy.
This process is destructive re-writing of the original, and would be very
time consuming.
Looping a Drum Part on a MiniDisk: Most MiniDisk 4 tracks don’t allow
track level editing, so the process would be the same as described in the
digital tape example. Otherwise, it would require destructive re-writing
of each copy to disk, taking time and disk space.
Pointer Based Editing
Pointer Based Editing
lets you experiment quickly and easily
without worry!
Page 15

13
Unlike a tape based system, HDRs don’t make you fast forward through
all the verses and choruses to get from the beginning to the end. Just
jump there instantly.
Random Access is FAST!
You can immediately jump to a specific bar and beat, or time location in
your song. In fact, some HDRs allow you to have hundreds of markers
so you can jump to any location, instantly.
This is another way that HDRs help your creative process - speed. You
don’t have to wait to rewind to try a new solo when your creative juices
are really flowing. You can jump instantly to the second chorus to see
how it compares to the first. You can instantly jump from one version of
your song to another, to see how it sounds with 2 choruses after the
second verse instead of the one you originally recorded. The possibilities
are endless.
What Is Random Access?
Using a Random access system
means not having to wait for rewinding –
you can keep your creative processes flowing.
TAPE
Page 16

14
Using Pointer Based Editing in a Random Access System allows you to
quickly and easily try different versions of your song.
Try different arrangements of your song:
#1. Copy your whole song
#2. Change the order of verses, number of
choruses, choice of solo and vocal, etc.
#3. Use markers to quickly jump from section to
section to compare the two versions of your
song.
If your HDR has a digital mixer with FX and automation, you can even
compare mixes of your song in this same way.
Random Access
Random Access and Pointer Based Editing
can help you make better music.
Marker1Marker2Marker3Marker4Marker5Marker6Marker7Marker8Marker9Marker
Song Version 1
Drums
M. Voc.
Gtr. #1
Bass
>
>
>
>
Intro Vs.1 Ch.1 Ch.2 SoloIntro Vs.1 Ch.1 Vs.2 Solo
>
>
>
>
>
>
>
>
>
>
Sax #1>
Drums
F. Voc.
Ac. Gtr.
Bass
Song Version 2
10
>
>
>
>
>
>
Gtr. #1
>
>
>
>
>
>
>
OD Gtr.
>
Page 17

15
In the “old days” most albums were recorded in studios with expensive
tape recorders with lots of tracks. Often the artist needed many tracks in
order to have several different versions of the lead vocal, or the guitar
solo. Or, maybe they wanted to have several background vocals on
different tracks, so they could mix them later. They needed so many
tracks because they didn’t want to throw away any of their recorded
takes!
The Virtual Tracks that some HDRs have give you this same ability to
keep all of your takes for later comparison, editing, or re-mixing.
Here’s how Virtual Tracks work:
Picture several piles of filing cards. Each pile has one card on top, with
several others underneath. By shuffling the cards, you can bring any
individual card to the top at any time. Virtual Tracks work in the same
manner. Each track has one main or top virtual track. That is the track you
hear.
You can bring any track to the top anytime you want. In fact, you can
even make a new virtual track that contains pieces of the other virtual
tracks or even mixes of the other tracks. These Virtual Tracks or layers are
just different storage locations for your recordings.
What Are Virtual Tracks?
You can keep many takes of a guitar solo
on the same track using virtual tracks.
Page 18

16
How can you use Virtual Tracks to help you make music?
Recording a guitar solo:
On different Virtual Tracks of one track, you can record several solos. You
don’t have to erase previous takes or lose other tracks. You keep your
creativity flowing, then later decide which solo (or parts of solos) you
want to use.
Recording background vocals:
Record several tracks of background vocals. Mix or bounce them together
to one track for playback. You can now re-use these tracks for other
instruments and still re-mix the original vocal parts later if you need to.
They’re still safely stored on virtual tracks.
Recording a dry guitar and a processed guitar at the same time:
Record a guitar with all of your effect pedals. At the same time, record the
guitar without effects on a different track. Keep the “dry” guitar on a
different virtual track in case you later decide to try a different effect on
the guitar.
Virtual Tracks can make your music sound better.
“Best of” version
copied from other virtual tracks
Virtual Tracks
Page 19

17
Some HDRs have built-in digital effects. These effects allow you to
process your sound without leaving the digital domain. Some even have
effects such as Roland’s COSM guitar preamp and microphone modeling.
Just plug in a guitar or mic and choose from a selection of amp and
microphone sounds at any point during recording, editing, or mixing.
Remember, you lose quality every time you move in and out of the digital
domain. Also, if your HDR doesn’t have internal effects, you will need to
buy additional effects processors.
Advantages of internal digital effects:
• Maintain the highest sound quality by keeping everything in the
digital domain
• Customize different effects types and levels for every track
• Experiment with different effects without changing or
losing your original recordings
• Keep the dry, uneffected track for use at any time
• Automation
• No cables to worry about
You can have a truly portable studio, with on-board processing to make a
vocal or guitar part sound great, without having to lug around extra gear.
This diagram shows how Virtual Tracks and internal digital effects
work together to get the most out of your music!
Digital Effects
Keeping your whole song digital
can make it sound much better.
Tracks
Virtual
1
Dry Vocal
2
Vocal > Comp/De-esser/Para EQ/Rev:Lg Hall
3
Voice > Comp/Para EQ/Rev:Sm Hall
4
Voice > Para EQ
etc.
etc.
Track 1
Tracks
Virtual
Dry Guitar
1
Guitar > COSM Preamp
2
Guitar > Gtr Multi-Effect
3
etc.
4
etc.
Track 2
(etc.)
Page 20

18
Digital Mixing
ZERO REW FF STOP
PLAY REC
There are many advantages to HDRs with built-in digital mixers.
• You keep everything in the digital domain. You don’t lose fidelity when
bouncing or mixing tracks
• Digital mixers with automation, snap shots, and scenes give you more
control over your mix
• Dedicated digital faders and knobs make mixing faster and easier
• Built-in digital mixers adds portability to your HDR system
If your HDR does not contain a mixer, you’ll need to purchase a console
specifically designed for recording.
An integrated HDR and digital mixer often allows you to:
• Compare different mixer settings instantly (level, pan, etc.)
• Restore all effect and mixer settings when you re-load a song!
• Craft intricate mixes
• Recall the levels and effects for bounced tracks to re-mix them
• Even automate your mix
Internal digital mixing allows you to make make an audio CD directly
from some Hard Disk Recorders! This gives you complete control over
your entire musical project.
EZ Routing
Some HDRs with integrated digital mixers include onboard assistance with
the process of Recording, Bouncing & Mixing. The HDR makes mixer and
routing settings automatically after you answer simple on-screen questions.
Save time by storing your custom mixer
and effect settings with each song.
Page 21

19
Many people use MIDI to record keyboards or drum machines. Most
HDRs make it easy to work with MIDI.
HDRs with digital mixers typically have additional inputs for keyboards,
sound modules, or an outboard mixer. These inputs can be mixed with
your recorded tracks for the final digital mix.
Some even allow you to create a tempo map of bars and beats to match
your song. This makes your editing more musical and creates MIDI Clock
to keep your drum machine or keyboard sequencer in sync with your
HDR.
MIDI Machine Control and MIDI Time Code are also ways that most
HDRs synchronize with your sequencer.
If your HDR has a digital mixer that can be controlled via MIDI, then
your computer sequencer can be used to automate and control your mix.
Some HDRs even have the ability to automate the mix without the need
to purchase an external MIDI sequencer.
These capabilities allow you to easily integrate an HDR into your MIDI
environment.
What About MIDI?
from Keyboard Workstation
Analog Audio
ZERO
REW FF STOP
MIDI Connections
with a Sequencer within
a Keyboard Workstation
PLAY REC
Page 22

Having all of your audio and FX in the digital domain has huge
advantages, as we have seen. One of the great new technologies available
using digital FX is modeling. Modeling technology takes a known source
and "models" the sound characteristics of one or more usually very
expensive sound processors or devices.
The three most powerful modeling technologies available today are
COSM* guitar amplifier modeling, COSM microphone modeling, and
COSM speaker modeling.
Guitar modeling simulates the sound of very expensive guitar pre-amps,
amplifiers and speaker systems using as an input a standard electric
guitar.
Microphone modeling simulates the response of some very expensive
large and small diaphragm condenser mics using as an input very
inexpensive dynamic microphones.
Speaker modeling creates the listening experience you would have using
a variety of expensive studio monitors or even TV speaker or a boom box
from the same, inexpensive digital powered reference monitors**. Using
just this one set of speakers you can hear how your mix would sound in a
variety of listening environments. This is a great way to improve your
mixing skills and make your music sound its best in a variety of settings.
* COSM stands for Composite Object Sound Modeling, a proprietary
technology from Roland Corporation. COSM is used to model a wide
variety of expensive microphones, guitar amplifiers, and monitor
speakers.
**COSM speaker modeling uses the COSM modeling software in the
VS-880EX or VS-1680 with the the Roland DS-90 Digital Powered
Reference Monitors to model a wide variety of speaker systems.
20
Modeling
Page 23

21
How Does Modeling Work??
Let’s take a closer look at speaker modeling to understand how this
revolutionary technology works. First of all, you need a "source" speaker
system designed to work with the modeling. All of the sound
reproduction characteristics of that speaker system is studied by the
engineers and mapped out. Next, the same characteristics of the speakers
being modeled are studied and also charted out. Then advanced DSP
technology is used to adjust the output characteristics of the source
speaker system to exactly match the output qualities and characteristics of
the speakers being modeled.
The bottom line is that you can listen to your mixes as they would sound
on a wide variety of very expensive and also some inexpensive, lower
fidelity but very common speaker systems. Using Speaker Modeling,
you can check your mixes and make sure they will sound great in many
different listening environments just as they do in very expensive studios
all over the world!
Modeling technology lets you save lots of money
and still make world class music.
Page 24

22
Time Compression
Some HDRs include the option of Time Compression. Since the
information on an HDR is stored as numbers (binary info just like a
computer), it’s possible to process these numbers several ways.
One way is to change the length
of something without changing
the pitch.
OR, fix the pitch without changing the length.
So now you can fix that flat vocal note, or slow down a rushed drum
fill in an otherwise perfect take!
SCSI (Small Computer System Interface)
A SCSI connection allows your HDR to connect to extra storage (hard
drives) for more recording space. It also makes it easy to backup and
store your songs for later use to SCSI removable media like Zip and
magneto optical drives.
A SCSI buss may allow you to interface directly with a computer for
audio file integration with a sequencer. In some cases SCSI will allow
you to record a CD directly from your dedicated Hard Disk Recorder,
or even to backup song information including all Virtual Tracks, all
mixer settings including EQ, effects, scenes and automation, and all
editing and UNDO levels.
Other Advantages of Hard Disk Recorders
Page 25

23
Comparison Chart
NoNoNoNoNoNoNoNoNoNoNoNoNoNoNoNoNo
No
NoNoNo
No
Limited
No
No
Limited
NoNoNo
No
Limited
No
Very Limited
No
NoNoNoNoNo
No
Yes
NoNoNoNoNo
No
No
NoNoNoNoNoNoNoNoNoNoNoNoNoNoNoNoNo
Digital Tape MiniDisk Analog Tape
128
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
VS-880EXVS-840EX
64
Roland VS Family of
Hard Disk Recorders
YES
NO
YES
NO
YES
YES
YES
NO
YES
YES
999
YES
YES
YES
999
NO
YES
Optional
No
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
OUT
F e a t u r e
Yes
YES
As Master
Virtual Tracks, and Undo’s
NoNoNoNoNo
YES
YES
NO
YES
YES/YES
NO
YES
YES/NO
(3rd party software)
NO
YES
C o m p a r i s o n
Non Destructive Pointer Based Editing
EZ Routing
Song Arrange
PC & Macintosh file transfers
Microphone Modeling / Speaker Modeling
Direct CD Mastering & Backup
Sync multiple units for 16/24/or 32 tracks
Backing up stores mixer settings, effects,
Instant, random access locating
Digital inputs and outputs
Undo’s
SCSI Buss for external drives and backup
Onboard Digital EQ
Time Compression
Note Level Pitch Correction
Easy Multiple Versions of the Same Material
Waveform Editing
Non-destructive Track & Phrase Level Editing
Non Destructive Punch In and Out
Snapshot Mixer Automation
Dynamic Mixer Automation
Onboard Digital Stereo Effects
Onboard Digital Mixing
64 Virtual Tracks
Page 26

24
Summary
Hard Disk Recording offers extensive advantages over other recorders.
How many people who have gotten familiar with the flexibility of a word
processor would ever go back to using a typewriter? HDRs give you this
same kind of power with your music.
HDRs have the ability to:
• use Virtual Tracks to record and edit many different solos on one track
• keep background vocal takes in case you want to re-mix them later
• have access to the quality and control of built in digital effects
• record and edit without fear of losing your valuable material
due to many levels of Undo
• be able to try many different arrangements of your song
• use mixer automation
• record an entire song, mix, & effects in digital domain
• master a CD directly from your HDR
• jump from Intro to the last chorus instantly without having to wait
for fast forward (or rewind)
• synchronize easily with MIDI, video, and other recorders
• connect multiple units together in sync for more tracks
All of these advantages truly will help you make better sounding music,
whether its a demo of your songs, a sound track for a film, or a finished
CD made digitally right from your HDR.
Enhancing your creativity is what Hard Disk Recorders are all about.
The Roland VS-880EX
The Roland VS-880EX includes all of the great HDR features and
advantages we have been discussing.
• 128 Virtual Tracks
• 999 levels of Undo
• Fully automated 16 channel
digital mixer
• Two built-in stereo digital effects
processors with: COSM mic,
amp, and speaker modeling; 3-D
effects; reverbs; delays; graphic
and parametric EQ’s; compressors; limiters; guitar effects; etc.
• 1,000 markers
• 32 bands of digital EQ
• Waveform editing
• Integration with computer based
systems
• Portability
• SCSI port for expansion
• Extensive syncing methods
• Digital In & Out
• ‘TurboStart’ video included
Page 27

25
The Roland VS-840EX
The Roland VS-840EX is less expensive than the VS-880EX, but still
packs powerful features, plus a few of its own.
• 64 Virtual Tracks
• 999 Levels of Undo
• Built-in Zip drive for fast and easy song storage
• 12 Channel Digital Mixer with Scene Memories
• Built-in Stereo Effect Processor with COSM guitar amp modeling,
reverbs, delays, RSS 3-D effects, parametric EQs, compressors,
limiters, guitar effects, bass simulator, and more
• Tuner
• 1000 Markers
• EZ Routing and Quick Record
• Song Arrange
• Waveform Editing
• 24 bands of Digital EQ
• Digital Output (Optical and Coaxial)
• Bar and Beat Tempo Maps and Display
• Dedicated guitar input
• Portability
The Roland VS-1680
For even more power, the Roland VS-1680 includes:
• 16 Channels of Track Playback
• Internal 16 Track to 2 Track bouncing
• 8 Tracks of simultaneous recording
• 256 Virtual Tracks
• 26 Channels of Fully Automated digital mixing
• 4 onboard digital stereo FX processors (with optional FX boards)
• Crossfading and advanced editing capability
• SCSI support for computer integration and direct CD burning
• COSM microphone, guitar amplifier, and speaker modeling
• and much more.
Page 28

26
Glossary
Analog Audio Storage: Constantly changing voltages stored on magnetic
tape.
Arming tracks
: Selecting a track to record on. Also called "Record Ready".
Audio DAT: Audio recorder that stores 2 tracks of material on magnetic
tape in digital format. Often used for pre mastering storage and usually
has stereo digital inputs.
Automated Mix
: Storage of fader movement, panpots, and all mixing
controls to allow very precise control over the final mix.
Back up
: To archive or save a second version of the material you have
recorded and edited to some form of removable media. This frees up
space for new songs. The fastest back up is via the SCSI port to
removable media. Other forms include digital back up to Audio DAT.
Bouncing T
racks: Combining several tracks to a mono or stereo track.
Used to free up tracks for more recording. Usually the original tracks
are then recorded over, erasing the original recordings. With Virtual
Tracks, the original tracks can be saved for re-mixing later, if needed.
Computer based r
ecorder: Digital Audio Recording that uses a computer
for control. This method usually requires software, audio cards,
external sync boxes, and audio interfaces.
Digital
Audio Storage: Audio is converted to binary numbers and stored
on hard drives, or tape.
EZ
Routing: A fast & easy way to set up Recording, Bouncing & Mixing.
Makes mixer and routing settings after you answer on-screen questions.
HDR
: Hard Disk Recorder. A Digital Recorder that stores audio on a hard
disk.
Har
d Disk: Mechanism used to store digital information for computers
and HDRs.
Hiss
: The background noise common to all analog recorders. This is more
noticeable in smaller tape formats such as cassettes and is additively
increased during any copying process such as track bouncing.
MIDI
: Musical Instrument Digital Interface. A language allowing note
information and control information to be communicated from
keyboards to sound modules and to be recorded on MIDI sequencers.
MIDI Clock
: Timing information derived from Tempo Maps used to
synchronize MIDI sequencers and other devices.
MMC
: MIDI Machine Control. Transport commands such as Play, Stop,
and Locate that are used to control one audio or MIDI device from
another.
MTC
: MIDI Time Code. A representation of real time in Hours: Minutes:
Seconds: Frames: Subframes communicated via MIDI and used for
synchronizing audio or MIDI recording devices.
MiniDisk Recor
ders: Record audio onto data type MiniDisks. Usually
combined with analog mixers, they can only play back up to 4 tracks.
Page 29

27
Glossary
Non destructive editing: Editing that doesn’t change, erase or delete the
original material, just changes a playlist of play and stop pointers.
Random
Access: The ability to instantly jump to any event in time.
Pitch Corr
ection: A digital algorithm that changes the pitch of a phrase of
audio without changing its length.
Pointer Based Editing
: Feature of HDRs that make them non destructive
and capable of many levels of undo. Editing doesn’t re-record or erase
the original material, which remains unchanged for future use.
Removable Media Drives
: Zip, Magneto Optical, CD-R (Recordable CD), or
other drive that stores data on removable disks or cartridges. They allow
you to back up your songs, or load previously recorded material. They are
almost always SCSI devices.
Restor
e: Loading material that has been archived on removable media or
other digital back-up to your hard drive for more editing or recording.
SCSI
: Small Computer Systems Interface. A high speed standard used to
transfer digital information from a computer or HDR to another storage
device such as an external Hard Drive or removable media.
SMPTE
: A representation of real time in Hours: Minutes: Seconds: Frames:
Subframes format that can be recorded to an audio track or to video,
used for synchronizing audio, video or MIDI recording devices.
Snap Shot
: Storage of all mixer settings at one instant in time.
Song
Arrange: Automatic way to make a copy of a song with a new
arrangement. User specifies sections and their order, then the HDR auto
matically makes a new copy without using any additional disk space.
Magneto Optical (MO) drive
: SCSI based removable media that stores
digital information using lasers and a polymer substrate. Very reliable
storage, but not as fast to read or write as magnetic hard drives.
SubMix
: Often MIDI generated audio is mixed to stereo and routed as a
separate, or “sub”, mix to the digital mixer of an HDR. The total mix is
then output digitally to DAT for mastering. This allows the HDR
recorded material to remain in the digital domain.
T
empo Maps: Referencing recordings by Bars and Beats for easy editing.
Tempo maps can be created before or after a recording has been made.
T
ime Compression: A digital algorithm that changes the length of a phrase of
material without changing its pitch. Used for matching or changing tempos.
Undo
: The ability to instantly restore a system to a previous state after an
edit or recording. Multiple levels of undo allow a user to try several
edits without the risk of losing their original material.
V
irtual Tracks: Storage areas for more recordings "underneath" the main
track. Virtual tracks allow recording many different solos or versions
on the same track, without throwing away material. Later the material
can be edited together to produce a "best of", or different version. Stays
with the song when it is saved or backed up.
Page 30

®ÂØÒňÎ
®
Roland Corporation U.S., 7200 Dominion Circle, Los Angeles, CA 90040-3696
 Loading...
Loading...