Page 1
X
General-purpose Operational Amplifiers / Comparators
NOW SERIES
Comparators
LM393MX,LM2903MX,LM339MX,LM2901MX
No.11094ECT06
●Description
The Universal Standard family LM393 / LM339 / LM2903 / LM2901 monolithic ICs integrate two / four independent
comparators on a single chip and feature high gain, low power consumption, and an o perating voltage range from 2[V] to
36[V] (single power supply).
NOW
SERIES
LM393 family
LM393MX
Dual
LM2903 family LM2901 family
LM2903MX
LM339 family
LM339MX
Quad
LM2901MX
●Features
1) Operating temperature range Commercial Grade
LM339/393 family: 0[℃] to +70[℃]
Extended Industrial Grade
LM2903/2901 family: -40[℃] to +85[℃]
2) Open collector output
3) Single / dual power supply compatible
4) Low supply current
0.8[mA] typ.(LM2901/339 family)
0.4[mA] typ.(LM2903/393 family)
5) Low input-bias current: 25[nA] typ.
16) Low input-offset current: 5[nA] typ.
7) Input common-mode voltage range, including ground
8) Differential input voltage range equal to maximum rated supply voltage
9) Low output saturation voltage
10) TTL,MOS,CMOS compatible output
●Pin Assignment
1
OUTPUT A
INVERTING
INPUT A
NON-INVERTING
INPUT A
1
2
+
-
3
+
-
GND
4
+
V
8
OUTPUT B
7
INVERTING
6
INPUT B
NON-INVERTING
5
INPUT B
OUTPUT2
OUTPUT1
INPUT1
INPUT1
INPUT2
INPUT2
2
+
3
V
- +
-
4
+
5
-
6
- +
+
7
- +
- +
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
OUTPUT3
OUTPUT4
GND
INPUT4
INPUT4
INPUT3
INPUT3
LM393MX LM339MX
LM2903M
S.O package14 S.O package8
LM2901MX
+
-
+
-
www.rohm.com
© 2011 ROHM Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
1/16
2011.06 - Rev.C
Page 2
LM393MX,LM2903MX,LM339MX,LM2901MX
Technical Note
●Absolute Maximum Ratings (Ta=25℃)
Parameter Symbol
Supply Voltage V+-GND +36 V
Input Differential Voltage Vid ±36 V
LM393 family LM339 family LM2903 family LM2901 family
Rating
Unit
Common-mode Input Voltage Vicm
Operating Temperature Range Topr 0 to +70
Storage Temperature Range Tstg
Maximum Junction Temperature Tjmax +150 ℃
-0.3 to +36
-40 to +85
-65 to +150
●Electric Characteristics
○LM393/339 Family(Unless otherwise specified, V+=+5[V])
Limits
Parameter Symbol
Input Offset Voltage (*1) VIO
Input Bias Voltage (*1) IIB
Input Offset Current (*1) IIO
Input Common-mode
Voltage Range
Supply Current ICC 25℃
Large Signal Voltage Gain AVD
Large Signal
Response Time
Response Time tRE 25℃ 1.5 -
Output Sink Current
Temperature
range
25℃ - 1 7 - 2 7
Full range - - 9 - - 15
25℃ - 25 250 - 25 250
Full range - - 400 - - 400
25℃ - 5 50 - 5 50
Full range - - 150 - - 150
VICR
tREL 25℃ - 300 - - 300 - ns
ISINK
25℃ 0 - V
Full range 0 - V+-2.0 - - V+-2.0
25℃
25℃
LM393 family LM339 family
Min. Typ. Max. Min. Typ. Max.
+
-1.5 - - V+-1.5
- 0.4 1 - 0.8 2.0
- 1 2.5 - 1.0 2.5 RL=∞,V+=36[V]
25 200
6 16
-
-
25 100
1.3 -
6 16
Unit Condition Fig.No
+
=5 to 30[V],VO=1.4[V],
V
RS=0[Ω]
mV
VCM=0[V] to V
IIN(+) or IIN(-)
nA
VCM=0[V]
nA IIN(+)-IIN(-),VCM=0[V] 88
+
=30[V] 88
V V
RL=∞,V
mA
+
=15[V],VO=1[V] to 11[V]
V
V/mV
-
-
RL≧15[kΩ]
VIN=TTL logic swing,
Vref=1.4[V]
VRL=5[V],RL=5.1[kΩ]
VRL=5[V],RL=5.1[kΩ]
μs
VIN=100[mVp-p]
overdrive=5[mV]
VIN(-)=1[V],VIN(+)=0[V]
mA
VO≦1.5[V]
+
=5[V]
+
-1.5[V]
V
℃
℃
88
88
89
88
89
89
89
Output Saturation Voltage VOL
Output Leakage Current IOH
Differential Input Vo ltage VID Full range - - 36 - - 36 V ALL VIN≧0[V] -
(*1) Absolute value
25℃ - 250 400 - 250 400
Full range - - 700 - - 700
25℃
Full range - - 1.0 μA
- 0.1 -
- 0.1 - nA
VIN(-)=1[V],VIN(+)=0[V]
mV
ISINK≦4[mA]
VIN(-)=0[V],VIN(+)=1[V],
VO=5[V]
www.rohm.com
© 2011 ROHM Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
2/16
2011.06 - Rev.C
89
89
Page 3
LM393MX,LM2903MX,LM339MX,LM2901MX
○LM2903/2901 family(Unless otherwise specified, V+=+5[V])
Limit
Parameter Symbol
Input Offset Voltage (*2) VIO
Input Bias Current (*2) IIB
Input Offset Current (*2) IIO
Input Common-mode
Voltage Range
Supply Current ICC
Voltage Gain AVD
Large Signal Response
Time
Response Time tRE 25℃ - 1.5 - - 1.3 - μs
Output Sink Current ISINK
Saturation Voltage VOL
Output Leakage Current Ileak
Temperature
range
25℃ - 2 7 - 2 7
Full range - 9 15 - 9 15
25℃ - 25 250 - 25 250
Full range - 200 500 - 200 500
25℃ - 5 50 - 5 50
Full range - 50 200 - 50 200
VICR
tREL 25℃ - 300 - - 300 - ns
25℃ - -
Full range - -
25℃
25℃
25℃
25℃ - 250 400
Full range - 400 700 - - 700
25℃ - 0.1 - - 0.1 - nA
Full range
LM2903 family LM2901 family
Min. Typ. Max. Min. Typ. Max.
+
V
+
V
- 0.4 1 - 0.8 2
- 1 2.5 - 1 2.5 RL=∞,V+=36[V]
25 100
6 16
- -
-1.5
-2.0
-
-
1
- -
- -
25 100
6 16
-
250 400
- -
+
V
-1.5
+
V
-2.0
-
-
1 μA
Technical Note
Unit Condition
+
=30[V],VO=1.4[V],
V
RS=0[Ω]
mV
VCM=0[V] to V
IIN(+) or IIN(-)
nA
VCM=0[V]
nA IIN(+)-IIN(-),VCM=0[V] 88
+
=30[V] 88
V V
RL=∞,V
mA
+
=15[V],VO=1[V] to
V
11[V],
V/mV
RL≧15[kΩ]
VIN=TTL logic swing,
Vref=1.4[V]
VRL=5[V],RL=5.1[kΩ]
VRL=5[V],RL=5.1[kΩ]
VIN=100[mVp-p],
overdrive=5[mV]
VIN(-)=1[V],VIN(+)=0[V]
mA
VO≦1.5[V]
VIN(-)=1[V],VIN(+)=0[V]
mV
ISINK≦4[mA]
VIN(-)=0[V],VIN(+)=1[V],
VO=5[V]
VIN(-)=0[V],VIN(+)=1[V],
VO=30[V]
+
=5[V]
+
-1.5[V]
Fig.N
o.
88
88
89
88
89
89
89
89
89
Differential Input Vo ltage VID Full range - - 36 - - 36 V ALL VIN≧0[V] -
(*2) Absolute value
www.rohm.com
© 2011 ROHM Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
3/16
2011.06 - Rev.C
Page 4
LM393MX,LM2903MX,LM339MX,LM2901MX
y
y
y
y
y
y
y
y
y
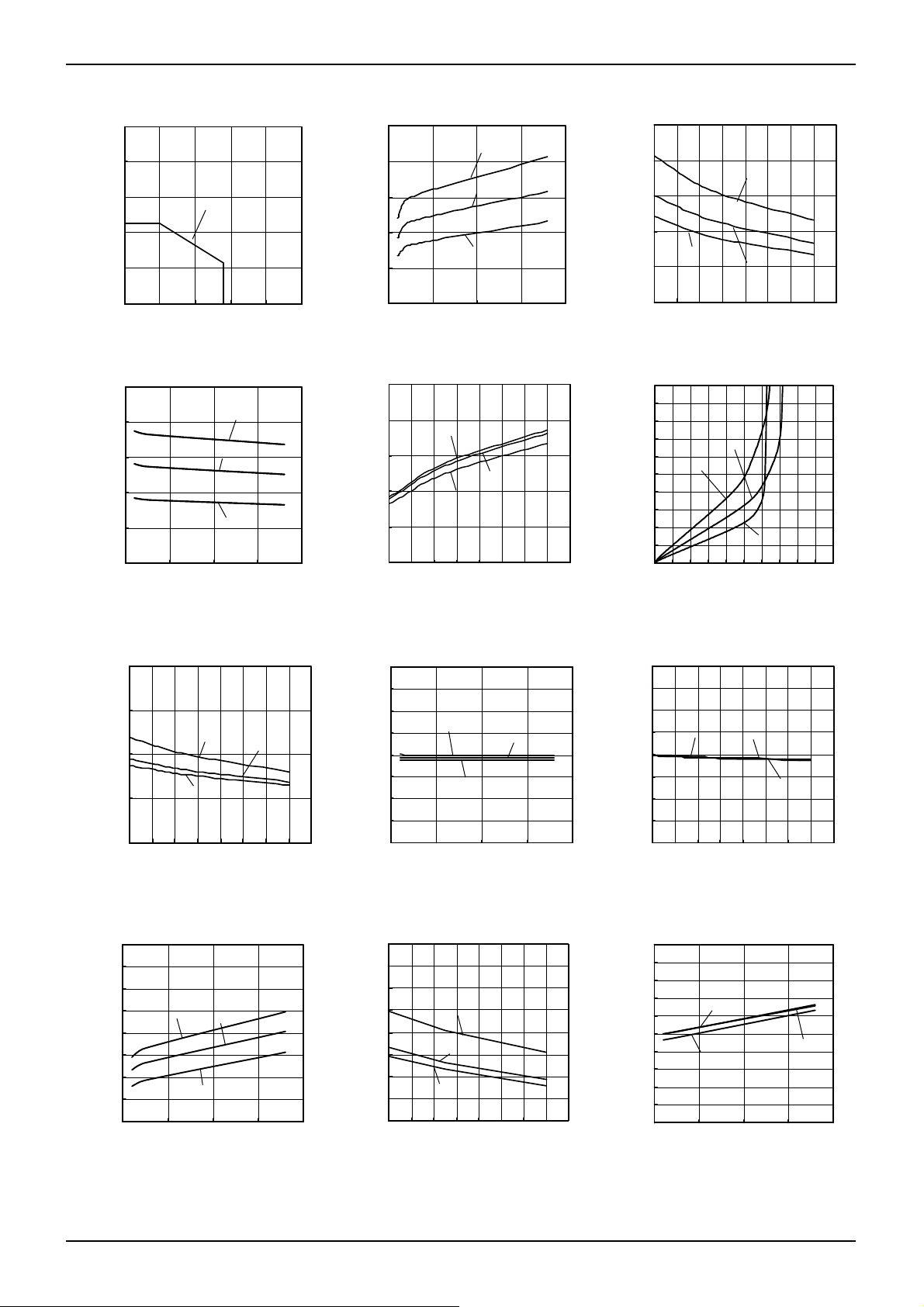
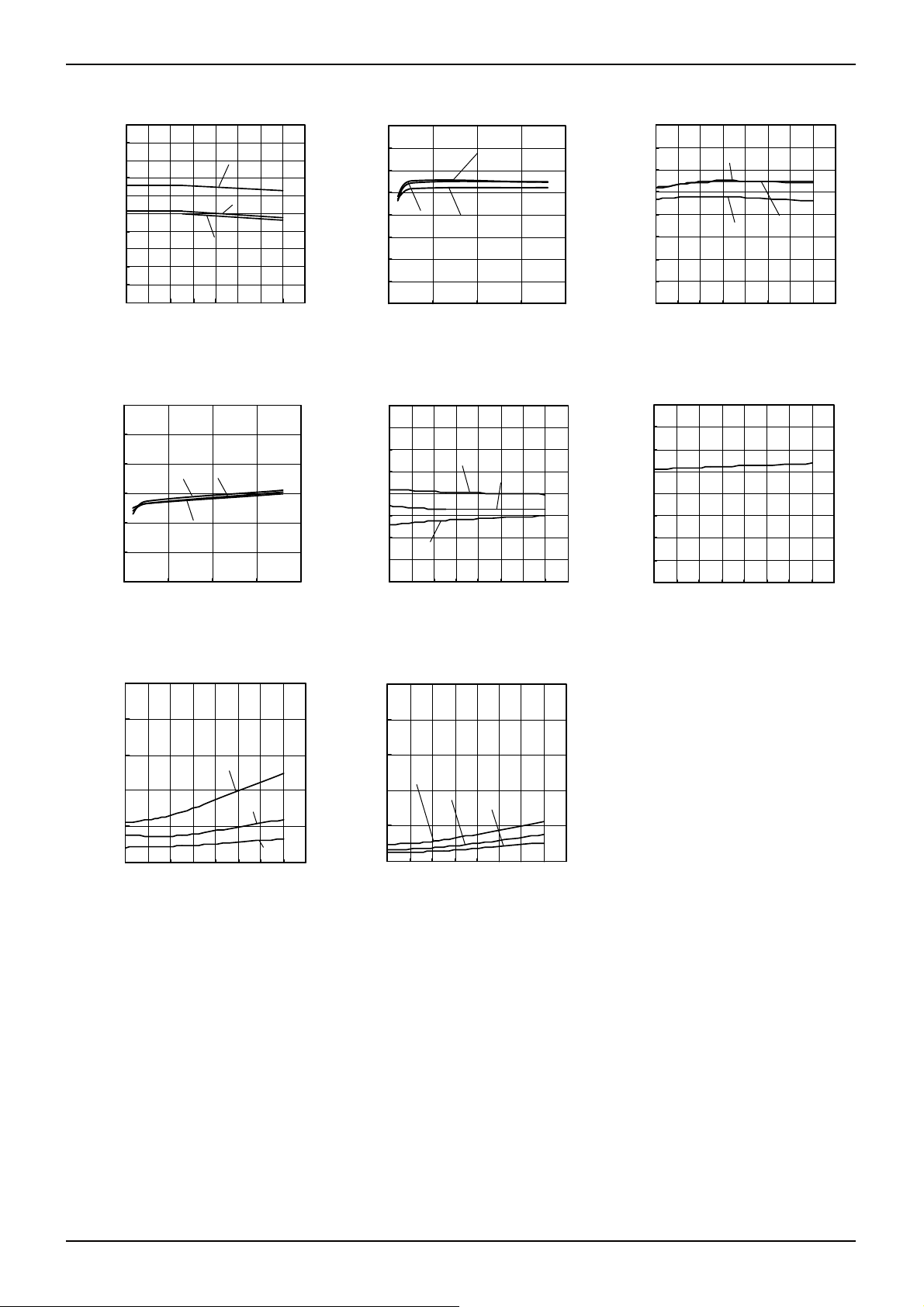
●Reference Data LM393 family
1000
800
LM 393 family
1
.
0.8
600
LM393MX
0.6
400
200
POWER DISSIPATION [mW] .
0
0 255075100125
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE [℃] .
70
Fig.1 Fig.2 Fig. 3
Derating Curve
500
400
300
LM 393 famil
70℃
25℃
0.4
SUPPLY CURRENT [mA]
0.2
0
0 10203040
SUPPLY VOLTAGE [V]
Supply Current – Supply Voltage
500
400
300
2V
200
100
OUTPUT SATURATION VOLTAGE [mV]
0
010203040
SUPPLY VOLTAGE [V]
Output Saturation Voltage
– Supply Voltage
40
0℃
Fig.4 Fig. 5 Fig. 6
(IOL=4[mA])
LM 393 famil
30
36V
20
10
OUTPUT SINK CURRENT [mA]
0
0 1020304050607080
2V
AM BIE NT T EMP ERAT UR E [℃]
5V
Fig. 7 Fig. 8 Fig. 9
Output Sink Current – Ambient Temperature
160
140
120
100
80
60
40
INPUT BIAS CURRENT [nA]
20
0
010203040
Input Bias Current – Supply Voltage
(*)The data above is ability value of sample, it is not guaranteed. LM393family: 0[℃]~+70[℃]
(VOUT=1.5[V])
LM 393 famil
0℃
25℃
70℃
SUPPLY VOLTAGE [V]
Fig. 10 Fig. 11 Fig. 12
200
100
OUTPUT SATURATION VOLTAGE [mV]
0
0 1020304050607080
36V
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE [℃]
Output Saturation Voltage
– Ambient Temperature
(IOL=4[mA])
8
6
4
2
0
-2
-4
INPUT OFFSET VOLTAGE [mV]
-6
-8
0 10203040
0℃
70℃
SUPPLY VOLTAGE [V]
Input Offset Voltage – Supply Voltage
160
140
120
100
80
60
40
INPUT BIAS CURRENT [nA] .
20
0
01020304050607080
36V
5V
2V
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE [℃]
Input Bias Current – Ambient Temperature
70℃
0℃
25℃
Technical Note
LM 393 famil
1
0.8
0.6
0.4
SUPPLY CURRENT [mA]
2V
0.2
0
0 1020304050607080
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE [℃]
Supply Current – Ambient Temperature
LM 393 famil
5V
2.0
1.8
1.6
1.4
1.2
1.0
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
LOW LEVEL OUTPUT VOLTAGE [V]
0.0
0 2 4 6 8 101214161820
25℃
70℃
OUTPUT SINK CURRENT [mA]
Low Level Output Voltage
– Output Sink Current
(VCC=5[V])
2V
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE [℃]
25℃
LM 393 famil
8
6
4
2
0
-2
-4
INPUT OFFSET VO LTAG E [m V]
-6
-8
0 1020304050607080
Input Offset Voltage – Ambient Temperature
LM 393 family
50
40
30
20
10
0
-10
-20
-30
INPUT OFFSET CURRENT [ nA ]
-40
-50
0 10203040
0℃
70℃
SUPPLY VOLTAGE [V]
Input Offset Current – Supply Voltage
LM 393 family
36V
5V
LM 393 famil
0℃
LM 393 famil
5V
36V
LM 393 famil
25℃
www.rohm.com
© 2011 ROHM Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
4/16
2011.06 - Rev.C
Page 5
LM393MX,LM2903MX,LM339MX,LM2901MX
y
y
y
y
y
Technical Note
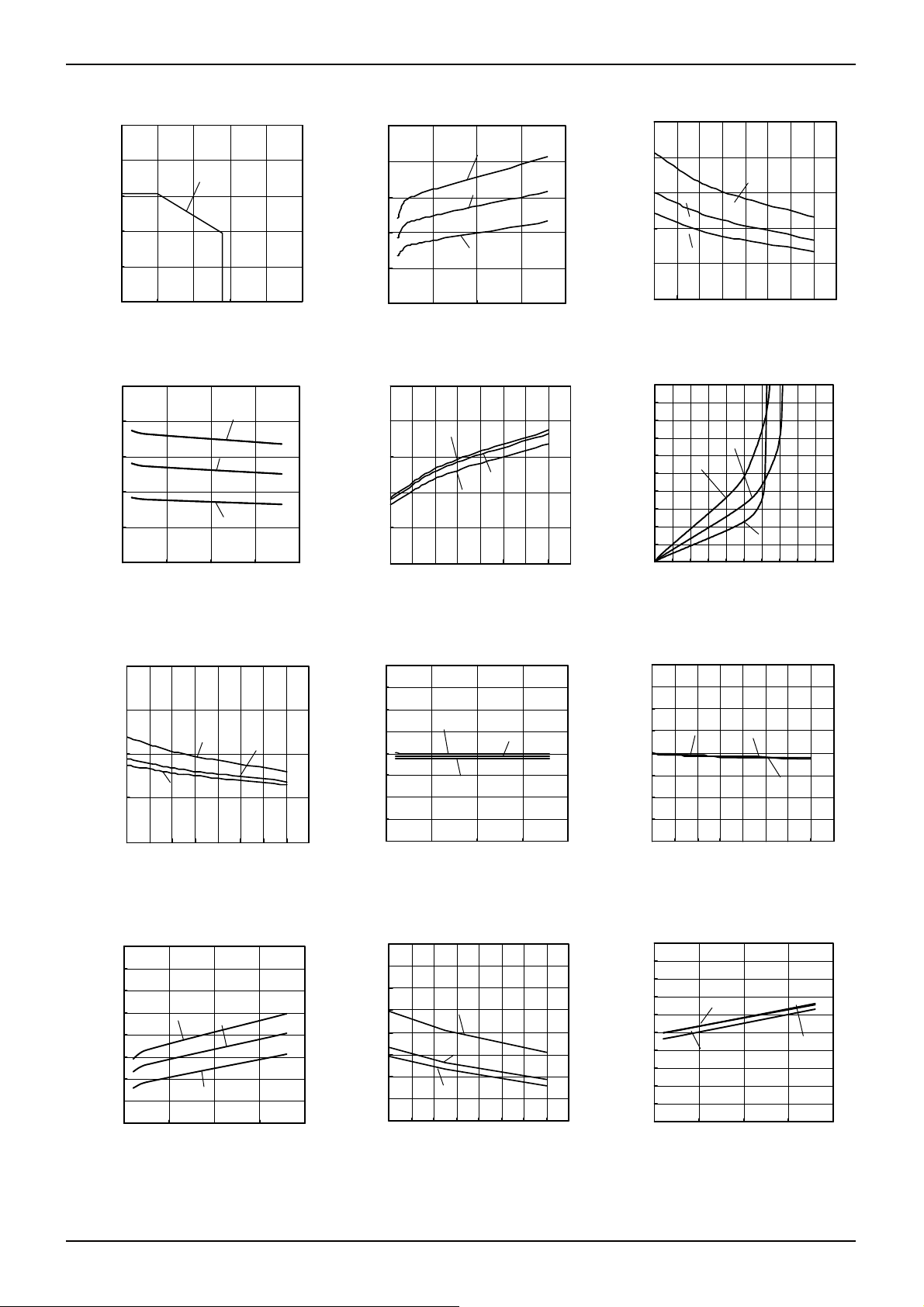
●Reference Data LM393 family
36V
5V
2V
25℃
5mV overdrive
20mV overdrive
100mV overdrive
LM 393 famil
LM 393 family
LM 393 famil
140
130
120
110
100
LARGE SIGNAL VOLTAGE GAIN [dB] .
70℃
0℃
90
80
70
60
010203040
SUPPLY VOLTAGE [V]
Large Signal Voltage Gain
– Supply Voltage
140
130
120
110
100
90
80
70
POWER SUPPLY REJECTION RATIO [dB]
60
0 102030405060 70 80
36V
2V
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE [°C]
Common Mode Rejection Ratio
– Ambient Temperature
5
] .
s
4
3
5mV overdrive
2
1
RESPONSE TIME (HIGH to LOW) [μ
0
0 1020 304050607080
20mV overdrive
100mV overdrive
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE [°C]
Response Time (High to Low)
–Ambient Temperature
(VCC=5[V],VRL=5[V],RL=5.1[kΩ])
50
40
30
20
10
0
-10
-20
-30
INPUT O FFSET CU RRENT [ nA ]
-40
-50
0 1020 304050 607080
AMBIE NT TEMPERA TURE [℃]
Fig. 13 Fig. 14 Fig. 15
Input Offset Current
– Ambient Temperature
160
140
120
.
100
80
60
COMMON MODE REJ E CT I O N RA T I O [ d B]
40
010203040
0℃
70℃
SUPPLY VOLTAGE [V]
Fig. 16 Fig. 17 Fig. 18
Common Mode Rejection Ratio
– Supply Voltage
5
4
3
2
1
RESPONSE TIME (LOW to HIGH ) [μs] . .
0
01020304050607080
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE [°C]
Fig. 19 Fig. 20
Response Time (Low to High)
– Ambient Temperature
(VCC=5[V],VRL=5[V],RL=5.1[kΩ])
25℃
LM 393 famil
LM 393 famil
5V
LM 393 famil
140
130
120
110
100
90
80
70
LARGE SIGNAL VOLTAGE GAIN [dB] .
60
01020304050607080
36V
2V
AMBIE NT TEMPER ATURE [°C ]
Large Signal Voltage Gain
– Ambient Temperature
140
130
120
110
100
90
80
70
POWER SUPPLY REJECTION RATIO [dB] .
60
0 1020304050607080
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE [°C]
Power Supply Rejection Ratio
– Ambient Temperature
LM 393 family
5V
LM 393 family
(*)The data above is ability value of sample, it is not guaranteed. LM393family:0[℃]~+70[℃]
(*)上記のデータはサンプルの実力値であり、保証するものではありません。BA10393F:-40[℃]~+85[℃]
www.rohm.com
© 2011 ROHM Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
5/16
2011.06 - Rev.C
Page 6
LM393MX,LM2903MX,LM339MX,LM2901MX
y
y
y
y
y
y
y
y
y
●Reference Data LM339 family
25℃
25℃
70
0℃
70℃
LM 339 famil
LM 339 famil
LM 339 family
5V
LM 339 family
1
.
0.8
0.6
0.4
SUPPLY CURRENT [mA]
0.2
0
0 10203040
0℃
25℃
70℃
SUPPLY VOLTAGE [V]
Supply Current – Supply Voltage
500
400
300
200
100
OUTPUT SATURATION VOLTAGE [mV]
0
01020304050607080
2V
36V
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE [℃]
Output Saturation Voltage
– Ambient Temperature
(IOL=4[mA])
8
6
4
2
0
-2
-4
INPUT OFFSET VOLTAGE [mV]
-6
-8
0 10203040
0℃
70℃
SUPPLY VOLTAGE [V]
Input Offset Voltage – Supply Voltage
160
140
120
100
80
60
40
INPUT BIAS CURRENT [nA] .
20
0
01020304050607080
36V
5V
2V
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE [℃]
Input Bias Current – Ambient Temperature
1000
800
600
400
200
POWER DISSIPATION [mW] .
0
0 25 50 75 100 125
500
LM339MX
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE [℃] .
Fig.21 Fig.22 Fig. 23
Derating Curve
400
300
200
100
OUTPUT SATURATION VOLTAGE [mV]
0
0 10203040
SUPPLY VOLTAGE [V]
Fig.24 Fig. 25 Fig. 26
Output Saturation Voltage
– Supply Voltage
(IOL=4[mA])
40
30
20
10
OUTPUT SINK CURRENT [mA]
0
0 1020304050607080
Output Sink Current – Ambient Temperature
160
140
120
100
80
60
40
INPUT BIAS CURRENT [nA]
20
0
010203040
Input Bias Current – Supply Voltage
(*)The data above is ability value of sample, it is not guaranteed. LM339family:0[℃]~+70[℃]
36V
2V
AM BIE NT T EMP ERAT UR E [℃]
Fig. 27 Fig. 28 Fig. 29
(VOUT=1.5[V])
0℃
70℃
SUPPLY VOLTAGE [V]
Fig. 30 Fig. 31 Fig. 32
5V
25℃
LM 339 famil
LM 339 famil
LM 339 famil
LM 339 famil
Technical Note
1
0.8
0.6
5V
0.4
SUPPLY CURRENT [mA]
0.2
0
2V
0 1020304050607080
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE [℃]
Supply Current – Ambient Temperature
2.0
1.8
1.6
1.4
1.2
1.0
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
LOW LEVEL OUTPUT VOLTAGE [V]
0.0
0 2 4 6 8 101214161820
25℃
70℃
OUTPUT SINK CURRENT [mA]
Low Level Output Voltage
– Output Sink Current
(VCC=5[V])
8
6
4
2
0
-2
-4
INPUT OFFSET VO LTAG E [m V]
-6
-8
2V
0 10203040 506070 80
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE [℃]
Input Offset Voltage – Ambient Temperature
50
40
30
20
10
0
-10
-20
-30
INPUT OFFSET CURRENT [nA]
-40
-50
010203040
0℃
70℃
SUPPLY VOLTAGE [V]
Input Offset Current – Supply Voltage
LM 339 family
36V
LM 339 famil
0℃
LM 339 famil
5V
36V
LM 339 famil
25℃
www.rohm.com
© 2011 ROHM Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
6/16
2011.06 - Rev.C
Page 7

LM393MX,LM2903MX,LM339MX,LM2901MX
y
y
y
y
Technical Note
●Reference Data LM339 family
50
40
30
20
10
0
-10
-20
-30
INPUT O FFSET CU RRENT [n A ]
-40
-50
0 1020 304050 607080
AMBIE NT TEMPERA TURE [
Fig. 33 Fig. 34 Fig. 35
Input Offset Current
– Ambient Temperature
160
140
120
.
100
80
60
COMMON MODE REJE CT ION RATIO[dB]
40
010203040
0℃ 25℃
70℃
SUPPLY VOLTAGE [V]
Fig. 36 Fig. 37 Fig. 38
Common Mode Rejection Ratio
– Supply Voltage
5
4
3
2
1
RESPONSE TIME (LOW to HIGH) [μs] . .
0
0 1020304050607080
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE [°C]
Fig. 39 Fig. 40
Response Time (Low to High)
– Ambient Temperature
(VCC=5[V],VRL=5[V],RL=5.1[kΩ])
LM 339 famil
36V
5V
2V
LM 339 family
5mV overdrive
20mV overdrive
100mV overdrive
]
℃
LM 339 famil
140
130
120
110
100
LARGE SIGNAL VOLTAGE GAIN [dB] .
70℃
90
80
70
60
010203040
0℃
SUPPLY VOLTAGE [V]
Large Signal Voltage Gain
– Supply Voltage
140
130
120
110
100
90
80
70
POWER SUPPLY REJECTION RATIO [dB]
60
0 102030405060 70 80
36V
2V
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE [°C]
Common Mode Rejection Ratio
– Ambient Temperature
5
] .
s
4
3
5mV overdrive
2
1
RESPONSE TIME (HIGH to LOW) [μ
0
0 1020 304050607080
20mV overdrive
100mV overdrive
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE [°C]
Response Time (High to Low)
–Ambient Temperature
(VCC=5[V],VRL=5[V],RL=5.1[kΩ])
25℃
5V
LM 339 family
LM 339 famil
LM 339 famil
140
130
120
110
100
90
80
70
LARGE SIGNAL VO LTAGE GAIN [dB] .
60
01020304050607080
36V
2V
AMBIE NT TEMPER ATURE [°C ]
Large Signal Voltage Gain
– Ambient Temperature
140
130
120
110
100
90
80
70
POWER SUPPLY REJECTION RATIO [dB] .
60
0 1020304050607080
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE [°C]
Power Supply Rejection Ratio
– Ambient Temperature
LM 339 family
5V
LM 339 family
(*)The data above is ability value of sample, it is not guaranteed. LM339family:0[℃]~+70[℃]
www.rohm.com
© 2011 ROHM Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
7/16
2011.06 - Rev.C
Page 8

LM393MX,LM2903MX,LM339MX,LM2901MX
●Reference Data LM2903 family
800
600
400
LM 2903 family
-40℃
200
POWE R D ISSIP A TION P d [ m W]
0
0 25 50 75 100
AM B IEN T TEM P ER A TU RE [℃ ]
Fig. 41 Fig. 42 Fig. 43
85
Derating Curve
LM 2903 family
Supply Current – Supply Voltage
85℃
85℃
2V
25℃
-40℃
36V
Fig. 44 Fig. 45 Fig. 46
Output Saturation Voltage
– Supply Voltage
(IOL=4[mA])
LM 2903 family
Output Saturation Voltage
– Ambient Temperature
(IOL=4[mA])
5V
36V
-40℃
2V
25℃
85℃
Fig. 47 Fig. 48 Fig. 49
Output Sink Current – Ambient
Temperature
(VOUT=1.5[V])
LM 2903 family
Input Offset Voltage – Supply Voltage
-40℃
25℃
36V
85℃
5V
2V
Fig. 50 Fig. 51 Fig. 52
Input Bias Current – Supply Voltage
Input Bias Current – Ambient Temperature
(*)The data above is ability value of sample, it is not guaranteed.LM2903family:-40[℃]~+85[℃]
Technical Note
LM 2903 family
25℃
Supply Current – Ambient Temperature
LM 2903 family LM 2903 family
5V
LM 2903 family
Input Offset Voltage – Ambient Temperature
LM 2903 family
Input Offset Current – Supply Voltage
36V
5V
2V
85℃
Low Level Output Voltage
– Output Sink Current
(VCC=5[V])
2V
5V 36V
-40℃
25℃
LM 2903 family
25℃
-40℃
LM 2903 family
LM 2903 family
85℃
www.rohm.com
© 2011 ROHM Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
8/16
2011.06 - Rev.C
Page 9

LM393MX,LM2903MX,LM339MX,LM2901MX
Technical Note
●Reference Data LM2903 family
15V
LM 2903 family
5V
2V
5V
36V
LM 2903 family
25℃
85℃
-40℃
LM 2903 family
36V
Input Offset Current – Ambient Temperature
Fig. 53 Fig. 54 Fig. 55
85℃
-40℃
LM 2903 family
25℃
Large Signal Voltage Gain
– Supply Voltage
LM 2903 family
36V
5V
2V
Large Signal Voltage Gain
– Ambient Temperature
25℃
-40℃
LM 2903 family
85℃
Fig. 56 Fig. 57 Fig. 58
Common Mode Rejection Ratio
– Supply Voltage
LM 2903 family
Common Mode Rejection Ratio
– Ambient Temperature
LM 2903 family
Input Offset Voltage – Input Voltage
(VCC=5V)
LM 2903 family
85℃
25℃
-40℃
5mV overdrive
20mV overdrive
100mV
overdrive
Fig. 59 Fig. 60 Fig. 61
Power Supply Rejection Ratio
– Ambient Temperature
LM 2903 family
Response Time (Low to High)
– Over Drive Voltage
(VCC=5[V],VRL=5[V],RL=5.1[kΩ])
LM 2903 family
Response Time (Low to High)
– Ambient Temperature
(VCC=5[V],VRL=5[V],RL=5.1[kΩ])
85℃
25℃
-40℃
5mV overdrive
100mV overdrive
20mV overdrive
(*)The data above is ability value of sample, it is not guaranteed. LM2903family:-40[℃]~+85[℃]
Fig. 62 Fig. 63
Response Time (High to Low)
– Over Drive Voltage
Response Time (High to Low)
– Ambient Temperature
www.rohm.com
© 2011 ROHM Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
9/16
2011.06 - Rev.C
Page 10

LM393MX,LM2903MX,LM339MX,LM2901MX
Technical Note
●Reference Data LM2901 family
1000
800
600
LM 2901 family
400
200
POWE R D ISSIP A TION P d [ m W]
0
0 25 50 75 100
AM B IENT TEMP ER A TUR E [℃]
Fig. 64 Fig. 65 Fig. 66
Derating Curve
LM 2901 family
85℃
25℃
-40℃
Fig. 67 Fig. 68 Fig. 69
Output Saturation Voltage
– Supply Voltage
(IOL=4[mA])
LM 2901 family
5V
36V
2V
Fig. 70 Fig. 71 Fig. 72
Output Sink Current – Ambient
Temperature
(VOUT=1.5[V])
LM 2901 family
-40℃
25℃
85℃
Fig. 73 Fig. 74 Fig. 75
Input Bias Current – Supply Voltage
(*)The data above is ability value of sample, it is not guaranteed.LM2903family:-40[℃]~+85[℃]
5V
LM 2901 family
2V
LM 2901 family
-40℃
25℃
85℃
85
36V
Supply Current – Supply Voltage
LM 2901family LM 2901family
Supply Current – Ambient Temperature
5V
2V
36V
Output Saturation Voltage
– Ambient Temperature
(IOL=4[mA])
LM 2901 family
-40℃
25℃
85℃
Input Offset Voltage – Supply Voltage
LM 2901 family
36V
5V
2V
Input Bias Current – Ambient Temperature
85℃
Low Level Output Voltage
– Output Sink Current
(VCC=5[V])
2V
5V 36V
Input Offset Voltage – Ambient Temperature
-40℃
Input Offset Current – Supply Voltage
25℃
-40℃
LM 2901 family
LM 2901 family
25℃
85℃
www.rohm.com
© 2011 ROHM Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
10/16
2011.06 - Rev.C
Page 11

LM393MX,LM2903MX,LM339MX,LM2901MX
Technical Note
●Reference Data LM2901 family
15V
LM 2901 family
5V
2V
5V
36V
LM 2901 family
25℃
85℃
-40℃
LM 2901 family
36V
Input Offset Current – Ambient Temperature
Fig. 76 Fig. 77 Fig. 78
85℃
-40℃
LM 2901 family
25℃
Large Signal Voltage Gain
– Supply Voltage
LM 2901 family
36V
5V
2V
Large Signal Voltage Gain
– Ambient Temperature
25℃
-40℃
LM 2901 family
85℃
Fig. 79 Fig. 80 Fig. 81
Common Mode Rejection Ratio
– Supply Voltage
LM 2901 family
Common Mode Rejection Ratio
– Ambient Temperature
LM 2901 family
Input Offset Voltage – Input Voltage
(VCC=5V)
LM 2901 family
85℃
25℃
-40℃
5mV overdrive
20mV overdrive
100mV
overdrive
Fig. 82 Fig. 83 Fig. 84
Power Supply Rejection Ratio
– Ambient Temperature
LM 2901 family
Response Time (Low to High)
– Over Drive Voltage
(VCC=5[V],VRL=5[V],RL=5.1[kΩ])
LM 2901 family
Response Time (Low to High)
– Ambient Temperature
(VCC=5[V],VRL=5[V],RL=5.1[kΩ])
85℃
25℃
-40℃
5mV overdrive
100mV overdrive
20mV overdrive
(*)The data above is ability value of sample, it is not guaranteed. LM2903family:-40[℃]~+85[℃]
Fig. 85 Fig. 86
Response Time (High to Low)
– Over Drive Voltage
Response Time (High to Low)
– Ambient Temperature
www.rohm.com
© 2011 ROHM Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
11/16
2011.06 - Rev.C
Page 12

LM393MX,LM2903MX,LM339MX,LM2901MX
/
R
●Circuit Diagram
Technical Note
+
V
+
INPUT
-
INPUT
Fig.87 Circuit Diagram (each Comparator)
●Measurement circuit 1 NULL Method measurement condition V
Parameter VF S1 S2 S3
Input Offset Voltage VF1 ON ON ON 5 to 30 0
Input Offset Current VF2 OFF OFF ON 5 0
Input Bias Current
Voltage Gain
VF3 OFF ON
VF4 ON OFF 5 0
VF5
ON ON ON
VF6 15 0
ON
LM393/LM339 family LM2903/LM2901 family
V + GND EK VICR V + GND EK VICR
0 5 to 30 0
0 5 0
0 5 0
0 5 0
0 15 0
0 15 0
5 0
15 0
-1.4
-1.4
-1.4
-1.4
-1.4
-11.4
Calculation-
-
+
,GND,EK,VICR unit:[V]
-1.4
-1.4
-1.4
-1.4
-1.4
-11.4
OUTPUT
GND
Calculation
0 1
0 2
0
0
0
0
3
4
1.Input offset voltage (VIO)
Vio
VF1
/RsRf1+
2.Input offset current (IIO)
Iio
VF1VF2 -
Rs)Rf(1+Ri
3.Input bias current (IIb)
Ib
VF3VF4 -
4.Voltage gain (AVD)
AV
10×
Log20×
www.rohm.com
© 2011 ROHM Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
[V]
[A]
/Rf(1+Ri2×
/ Rs)
VF6 - VF5
[A]
0.1[μF]
Rf
S1
RS=50[Ω]
VIC
RS=50[Ω]
/Rs)Rf(1+
[dB]
Ri=10[kΩ]
Ri=10[kΩ]
50[kΩ]
S2
Fig.88 Measurement Circuit1 (each Comparator)
V
DUT
GND
+
50[kΩ]
S3
RL
VRL
12/16
RK
EK
500[kΩ]0.1[μF]
500[kΩ]
RK
1000[pF]
+15[V]
NULL
-15[V]
VF
V
2011.06 - Rev.C
Page 13

LM393MX,LM2903MX,LM339MX,LM2901MX
●Measurement Circuit 2: Switch Condition
Technical Note
SW No.
SW
1
SW
2
SW
3
SW
4
SW
5
SW
6
Supply Current ― OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF
Output Sink Current VOL=1.5[V] OFF ON ON OFF ON ON OFF
Saturation Voltage IOL=4[mA] OFF ON ON OFF OFF OFF ON
Output Leakage Current VOH=36[V] OFF ON ON OFF OFF OFF ON
Response Time
RL=5.1[kΩ]
VRL=5[V]
ON OFF ON ON OFF ON OFF
+
V
5[V]
A
-
SW1 SW2
SW3 SW7
VIN-
VIN+ VRL
GND
+
0[V]
SW4 SW5
RL
SW6
A
V
VOL/VOH
SW
7
+100[mV]
0[V]
VUOT
5[V]
0[V]
VIN
Fig.89 Measurement Circuit 2 (each Comparator)
Input waveform
over drive
Output waveform
2.5[V]
Tr e LH
VIN
0[V]
+100[mV]
VUOT
5[V]
0[V]
Tr e LH
Fig.90 Response Time
Input waveform
over drive
Output waveform
2.5[V]
www.rohm.com
© 2011 ROHM Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
13/16
2011.06 - Rev.C
Page 14

LM393MX,LM2903MX,LM339MX,LM2901MX
●Description of electrical characterist ics
Described below are descriptions of the relevant electrical terms.
Please note that item names, symbols, and their meanings may differ from those on another manufacturer’s documents.
1. Absolute maximum ratings
The absolute maximum ratings are values that should never be exceeded, since d oing so may result in deterioration of
electrical characteristics or damage to the part itself as well as peripheral components.
1.1 Power supply voltage (V
Expresses the maximum voltage that can be supplied between the positive and negative power supply terminals without
causing deterioration of the electrical characteristics or destruction of the internal circuitry.
1.2 Differential input voltage (VID)
Indicates the maximum voltage that can be supplied between the non-inverting and inverting terminals without damaging
the IC.
1.3 Input common-mode voltage range (VICR)
Signifies the maximum voltage that can be supplied to non-inverting and inverting terminals without causing deterioration
of the electrical characteristics or damage to the IC itself. Normal operation is not guaranteed within the input
common-mode voltage range of the maximum ratings – use within the input common-mode voltage range of the electric
characteristics instead.
1.4 Operating temperature range and storage temperature range (Topr,Tstg)
The operating temperature range indicates the temperature range within which the IC can operate. The higher the
ambient temperature, the lower the power consumption of the IC. The storage temperature range denotes the range of
temperatures the IC can be stored under without causing excessive deterioration of the e lectrical ch aracteristics.
1.5 Power dissipation (Pd)
Indicates the power that can be consumed by a particular mounted board at ambient temperature (25°C). For packaged
products, Pd is determined by maximum junction temperature and the thermal resistance.
2. Electrical characteristics
2.1 Input offset voltage (VIO)
Signifies the voltage difference between the non-inverting and inverting terminals. It can be thought of as the input
voltage difference required for setting the output voltage to 0V.
2.2 Input offset current (IIO)
Indicates the difference of the input bias current between the non-inverting and inverting terminals.
2.3 Input bias current (IIB)
Denotes the current that flows into or out of the input terminal, it is defined by the average of the input bias current at the
non-inverting terminal and the input bias current at the inverting terminal.
2.4 Input common-mode voltage range (VICR)
Indicates the input voltage range under which the IC operates normally.
2.5 Large signal voltage gain (AVD)
The amplifying rate (gain) of the output voltage against the voltage difference between the non-inverting an d inverting
terminals, it is (normally) the amplifying rate (gain) with respect to DC voltage.
AVD = (output voltage fluctuation) / (input offset fluctuation)
2.6 Circuit current (ICC)
Indicates the current of the IC itself that flows under specific conditions and during no-load steady state.
2.7 Output sink current (IOL)
Denotes the maximum current that can be output under specific output conditions.
2.8 Output saturation voltage low level output voltage (VOL)
Signifies the voltage range that can be output under specific output conditions.
2.9 Output leakage current (ILeak)
Indicates the current that flows into the IC under specific input and output conditions.
2.10 Response time (tre)
The interval between the application of input and output conditions.
2.11 Common-mode rejection ratio (CMRR)
Denotes the ratio of fluctuation of the input offset voltage when the in-phase input voltage is changed (DC fluctuation).
CMRR = (change of input common-mode voltage) / (input offset fluctuation)
2.12 Power supply rejection ratio (PSRR)
Signifies the ratio of fluctuation of the input offset voltage when the supply voltage is changed (DC fluctuation).
PSRR = (change in power supply voltage) / (input offset fluctuation)
+
/GND)
Technical Note
www.rohm.com
© 2011 ROHM Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
14/16
2011.06 - Rev.C
Page 15

LM393MX,LM2903MX,LM339MX,LM2901MX
●Derating Curves
800
600
400
200
POWE R D ISSIP A TION P d [ m W]
0
0 25 50 75 100
Power Dissipation Power Dissipation
LM393MX
LM2903MX
70
85 85
AM B IENT TEMP ER A TUR E [℃ ]
LM393MX, LM2903MX
Package Pd[W] θja [℃/W] Package Pd[W] θja [℃/W]
SO package8 (*8)
450 3.6 SO package14 610 4.9
θja = (Tj-Ta)/Pd[℃/W]
Fig.102 Derating Curves
●Notes for use
1) Unused circuits
When there are unused circuits it is recommended that they be connected as in Fig. 103,
setting the non-inverting input terminal to a potential within the in-phase input voltage
range (VICR).
2) Input terminal voltage
Applying GND + 36V to the input terminal is possible without causing deterioration of
the electrical characteristics or destruction, irrespective of the supply voltage. However,
this does not ensure normal circuit operation. Please note that the circuit operates
normally only when the input voltage is within the common mode input voltage range of
the electric characteristics.
3) Power supply (single / dual)
The op-amp operates when the specified voltage supplied is between V
op-amp can be used as a dual supply op-amp as well.
4) Power dissipation Pd
Using the unit in excess of the rated power dissipation may cause deterioration in electrical characteristics due to a rise
in chip temperature, including reduced current capability. Therefore, please take into consideration the power
dissipation (Pd) under actual operating conditions and apply a sufficient margin in thermal design. Refer to the thermal
derating curves for more information.
5) Short-circuit between pins and erroneous mounting
Incorrect mounting may damage the IC. In addition, the pres ence of foreign particles between the outputs, the output
and the power supply, or the output and GND may result in IC destruction.
6) Terminal short-circuits
When the output and V+ terminals are shorted, excessive output current may flow, resulting in undue heat generation
and, subsequently, destruction.
7) Operation in a strong electromagnetic field
Operation in a strong electromagnetic field may cause malfunctions.
8) Radiation
This IC is not designed to withstand radiation.
9) IC handing
Applying mechanical stress to the IC by deflecting or bending the board may cause fluctuations in the electrical
characteristics due to piezoelectric (piezo) effects.
10) Board inspection
Connecting a capacitor to a pin with low impedance may stress the IC. Therefore, discharging the capacitor after every
process is recommended. In addition, when attaching and detaching the jig during the inspection p hase, ensure that
the power is turned OFF before inspection and removal. Furthermore, please take measures against ESD in the
assembly process as well as during transportation and storage.
1000
800
600
400
200
POWE R D ISSIP A TION P d [ m W]
Technical Note
NOW SERIES LM2903/2901/393/339 family
LM2901MX
LM339MX
0
0 25 50 75 100
AM B IEN T TEM P ER A TU RE [℃]
LM339MX, LM2901MX
+
and GND. Therefore, the single supply
70
θja = (Tj-Ta)/Pd[℃/W]
V
-
+
GND
Fig.103
+
www.rohm.com
© 2011 ROHM Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
15/16
2011.06 - Rev.C
Page 16

LM393MX,LM2903MX,LM339MX,LM2901MX
●Ordering part number
Technical Note
L M 3 3 9
Family name
LM393
LM339
LM2901
M
Package
M : S.O package
LM2903
S.O package8
4.9±0.2
(MAX 5.25 include BURR)
5678
+6°
4°
−4°
<Tape and Reel information>
6.0±0.3
3.9±0.2
234
1
0.545
S
1.375±0.1
0.175
1.27
0.42±0.1
0.1
S
0.45Min.
0.2±0.1
(Unit : mm)(Unit : mm)
Quantity
Direction
of feed
X
Packaging and forming specification
X: Embossed tape and reel
Embossed carrier tapeTape
2500pcs
The direction is the 1pin of product is at the upper left when you hold
()
reel on the left hand and you pull out the tape on the right hand
Direction of feed
Reel
1pin
Order quantity needs to be multiple of the minimum quantity.
∗
S.O package14
(Max 9.0 include BURR)
3.9± 0.1
6.0± 0.2
0.515
1.65MAX
1.27
1.375± 0.075
0.175± 0.075
8.65± 0.1
1PIN MARK
0.42
+0.05
−0.04
0.08
814
71
0.08 S
+6°
<Tape and Reel information>
4°
−4°
Quantity
Direction
1.05±0.2
0.65±0.15
+0.05
0.22
−0.03
S
M
(Unit : mm)
(Unit : mm)
of feed
Embossed carrier tapeTape
2500pcs
The direction is the 1pin of product is at the upper left when you hold
()
reel on the left hand and you pull out the tape on the right hand
Direction of feed
Reel
1pin
Order quantity needs to be multiple of the minimum quantity.
∗
www.rohm.com
© 2011 ROHM Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
16/16
2011.06 - Rev.C
Page 17

Notes
No copying or reproduction of this document, in part or in whole, is permitted without the
consent of ROHM Co.,Ltd.
The content specied herein is subject to change for improvement without notice.
The content specied herein is for the purpose of introducing ROHM's products (hereinafter
"Products"). If you wish to use any such Product, please be sure to refer to the specications,
which can be obtained from ROHM upon request.
Examples of application circuits, circuit constants and any other information contained herein
illustrate the standard usage and operations of the Products. The peripheral conditions must
be taken into account when designing circuits for mass production.
Great care was taken in ensuring the accuracy of the information specied in this document.
However, should you incur any damage arising from any inaccuracy or misprint of such
information, ROHM shall bear no responsibility for such damage.
The technical information specied herein is intended only to show the typical functions of and
examples of application circuits for the Products. ROHM does not grant you, explicitly or
implicitly, any license to use or exercise intellectual property or other rights held by ROHM and
other parties. ROHM shall bear no responsibility whatsoever for any dispute arising from the
use of such technical information.
The Products specied in this document are intended to be used with general-use electronic
equipment or devices (such as audio visual equipment, ofce-automation equipment, communication devices, electronic appliances and amusement devices).
The Products specied in this document are not designed to be radiation tolerant.
While ROHM always makes effor ts to enhance the quality and reliability of its Products, a
Product may fail or malfunction for a variety of reasons.
Please be sure to implement in your equipment using the Products safety measures to guard
against the possibility of physical injur y, re or any other damage caused in the event of the
failure of any Product, such as derating, redundancy, re control and fail-safe designs. ROHM
shall bear no responsibility whatsoever for your use of any Product outside of the prescribed
scope or not in accordance with the instruction manual.
The Products are not designed or manufactured to be used with any equipment, device or
system which requires an extremely high level of reliability the failure or malfunction of which
may result in a direct threat to human life or create a risk of human injury (such as a medical
instrument, transportation equipment, aerospace machinery, nuclear-reactor controller, fuelcontroller or other safety device). ROHM shall bear no responsibility in any way for use of any
of the Products for the above special purposes. If a Product is intended to be used for any
such special purpose, please contact a ROHM sales representative before purchasing.
If you intend to export or ship overseas any Product or technology specied herein that may
be controlled under the Foreign Exchange and the Foreign Trade Law, you will be required to
obtain a license or permit under the Law.
Notice
www.rohm.com
© 2011 ROHM Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
Thank you for your accessing to ROHM product informations.
More detail product informations and catalogs are available, please contact us.
ROHM Customer Support System
http://www.rohm.com/contact/
R1120
A
 Loading...
Loading...