Transistors ! !!!!!! !!DTA123JUB
z
z
z
z
z
z
z
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
-100mA / -50V Digital transistors
(with built-in resistors)
DTA123JUB
Applications
Inverter, Interface, Driver
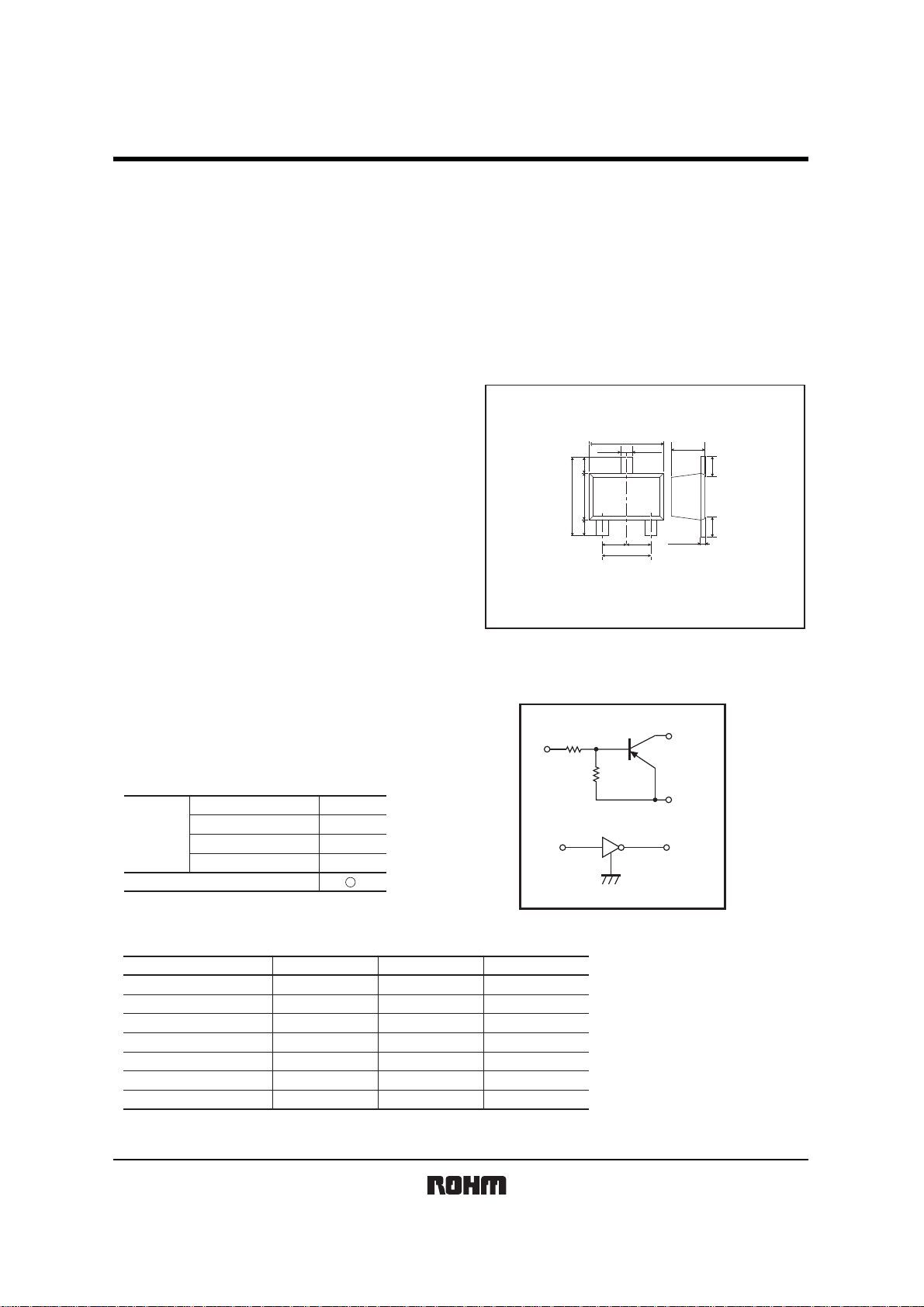
Dimensions (Unit : mm)
UMT3F
z
Features
1) Built-in bias resistors enable the configuration of
an inverter circuit without connecting external
input resistors (see equivalent circuit).
2) The bias resistors consist of thin-film resistors
with complete isolation to allow negative biasing
of the input. They also have the advantage of
almost completely eliminating parasitic effects.
3) Only the on/off conditions need to be set for
operation, making the device design easy.
Structure
PNP silicon epitaxial planar transistor type
(Resistor built-in)
z
Packaging specifications
UMT3F
TL
3000
Part No.
DTA123JUB
Package
Packaging type Taping
Code
Basic ordering unit (pieces)
(1) IN
(2) GND
(3) OUT
Equivalent circuit
IN
IN
2.0
0.32
(3)
0.4250.425
2.1
1.25
(1) (2)
0.65 0.65
1.3
Abbreviated symbol : 132
R
1
R
2
0.9
0.530.53
0.13
Each lead has same dimensions
OUT
GND(+)
OUT
GND(+)
z
Absolute maximum ratings (Ta=25qC)
Parameter Symbol
Supply voltage
Input voltage
Collector current
Output current
Power dissipation
Junction temperature
Range of storage temperature
Characteristics of built-in transistor
∗1
∗2
Each terminal mounted on a recommended land
V
V
I
C(max.)
I
P
Tj
Tstg
CC
IN
O
R1=2.2kΩ, R2=47kΩ
UnitLimits
−50
∗1
∗2
D
−12 to +5
−100
−100
200
150
−55 to +150
V
V
mA
mA
mW
°C
°C
1/2
Transistors ! !!!!!! !!DTA123JUB
z
z
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
Electrical characteristics (Ta=25qC)
Parameter Symbol
V
Input voltage
Output voltage
Input current
Output current
DC current gain
Transition frequency
Input resistance
Resistance ratio
∗ Characteristics of built-in transistor
z
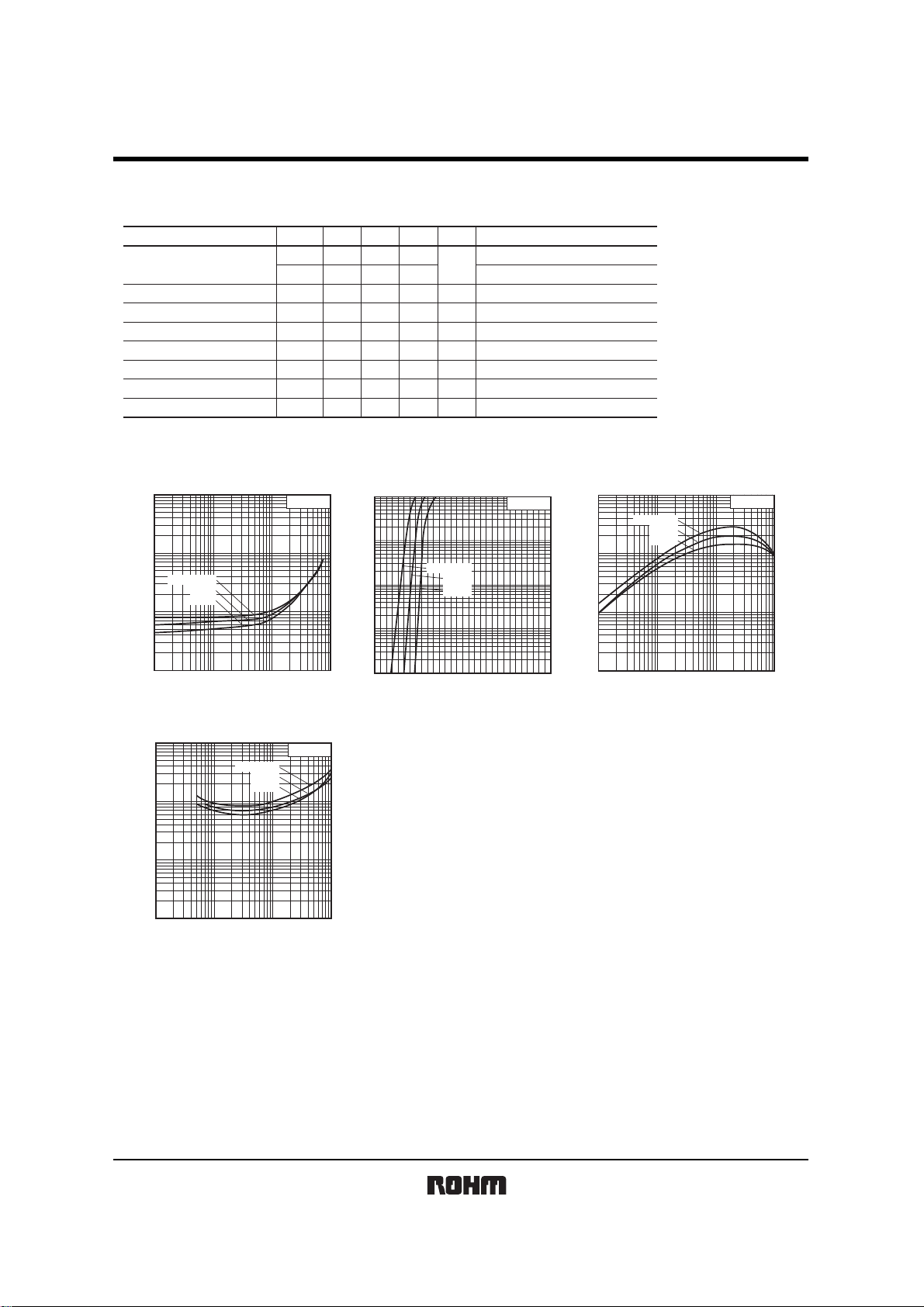
Electrical characteristic curves
−100
−50
−20
(V)
I(on)
−10
−5
Ta=−40°C
100°C
−
500μ
100μ
−
200μ
OUTPUT CURRENT : I
25°C
−
1m
−
2m
−
−2
−1
−500m
INPUT VOLTAGE : V
−200m
−100m
−
I(off)
V
I(on)
V
O(on)
I
I
I
O(off)
G
I
f
T
R
1
R2/R
1
VO=−0.3V
−
20m
5m
−
10m
−
50m
O
(A)
Fig.1 Input voltage vs. output current
(ON characteristics)
−1
−500m
−200m
(V)
O(on)
−100m
−50m
−20m
−10m
−5m
OUTPUT VOLTAGE : V
−2m
−1m
−100μ
−1m
−200μ
OUTPUT CURRENT : I
Ta=100°C
−2m −20m−500μ−5m −50m
25°C
−40°C
−10m
lO/lI=20
O
(A)
Fig.4 Output voltage vs. output current
−
−100m
Typ. Max. Unit Conditions
Min.
−
−1.1
−
−
−
80
−
1.54
17
−10m
−5m
−2m
(A)
−1m
−500μ
−200μ
−100μ
−50μ
−20μ
−10μ
OUTPUT CURRENT : Io
100m
−0.5
−
−
−
−300
−100
−3.6
−
−500
−
−
−
−
250
2.2
21
−5μ
−2μ
−1μ
0
−
MHz
2.86
26
Ta=100°C
−40°C
0.5−1.0−1.5−2.0−2.5
INPUT VOLTAGE : V
V
V
V
mV
I
V
mA
nA
V
−
V
V
kΩ
−−
25°C
Fig.2 Output current vs. input voltage
(OFF characteristics)
CC
=−5V, IO=−100μA
O
=−0.3V, IO=−5mA
O
=−5mA, II=−0.25mA
I
=−5V
CC
=−50V, VI=0V
O
=−5V, IO=−10mA
CE
=−10V, IE=5mA, f=100MHz∗
−
VCC=−5V
−
3.0
I(off)
(V)
1k
500
I
200
100
50
20
10
5
DC CURRENT GAIN : G
2
1
−100μ−1m −10m −100m
Ta=100°C
25°C
−40°
C
−200μ−2m −20m−500μ−5m −50m
OUTPUT CURRENT : I
VO=−
O
(A)
Fig.3 DC current gain vs. output
current
5V
2/2
 Loading...
Loading...