ROHM BH9595FP-Y Datasheet
1
Mulimedia ICs
SCSI active terminator
BH9595FP-Y / BH9596FP-Y
These SCSI active terminators, developed as a substitute for conventional discrete terminators, maintain good consistency between VM level (2.85V) and GND level (0V) and between VM level and VDD level, and have extremely
low power consumption, dropping to a maximum of 90 milliwatts at standby (compared to the maximum of 990 milliwatts used by conventional resistance terminators). These SCSI active terminators electrically control SCSI lines,
connecting and disengaging the terminating resistor by electrically controlling the enable pin. (The enable pin is
enabled at the HIGH level and switched to the High-Z state by the LOW level in the BH9595 and by the HIGH level in
the BH9596, completely disconnecting the SCSI line from the SCSI terminator.)
These SCSI active terminators allow for the configuration of flexible, energy-saving SCSI networks, and are ideal for
notebook computers, hard disk drives and a wide range of other products with SCSI capabilities.
•
Applications
Compact disk drives, optical disk drives, CD-ROM drives, tape drives, personal computers (including laptop
computers and notebook computers), workstations,
mainframes, laser printers, plotters
•
Features
1) Internal 2.85V power supply and push-pull opera-
tion, for good consistency at all signal levels.
2) Enable pin for terminator enabling and disconnect-
ing, facilitating SCSI network construction.
3) Low power consumption, ideal for energy-saving
systems.
Power consumption during standby : 90mW (compared to 990mW for conventional resistor terminators)Power consumption at 25% duty : 614mW
(compared to 1,360mW for convention resistor terminators)Significant reductions in power consumption are possible.
4) Wide operating range.
TERM power : 4.0 ~ 5.5V (Transient : 6.0V)
5) Thin, microminiature design, ideal for space-saving
applications.
Package body size : 13.6 × 5.4 × 1.9mm
6) Active termination of 18-line SCSI.
7) Internal thermal shutdown circuit.
8) Compatibility with SCSI-I and SCSI-II.
2
Mulimedia ICs BH9595FP-Y / BH9596FP-Y
•
Absolute maximum ratings (Ta = 25°C)
Power supply voltage
DC Output current
∗
1
DC Output current
∗
2
Input voltage
Power dissipation
∗
3
Operating temperature
Storage temperature
∗
2 Sink Current (from SCSI Line to Module) / Line
∗
1 Drain Current (from Module to SCSI Line) / Line
∗
3 When mounted to a 90 × 50 × 1.6 mm glass epoxy board
Parameter Symbol Limits Unit
V
DD1 V
I
SLD – 30 mA
I
SLS 35 mA
Vi V
1.45 W
Topr °C
Tstg °C
Pd
– 0.6 ~ (V
DD1
+ 0.6)
– 0.3 ~ + 7.0
0 ~ + 75
– 55 ~ + 125
•
Recommended operating conditions (Ta = 25°C)
Power supply voltage
Input voltage
Input voltage
SCSI Line voltage
∗
Transient 6V
Parameter Symbol Min. Typ. Max. Unit
V
DD1 4.0 4.5 5.5
∗
V
V
IH VDD1 – 0.6 — VDD1 + 0.6 V
V
IL – 0.3 — 0.8 V
V
SLX – 0.3 — VDD1 + 0.3 V
•
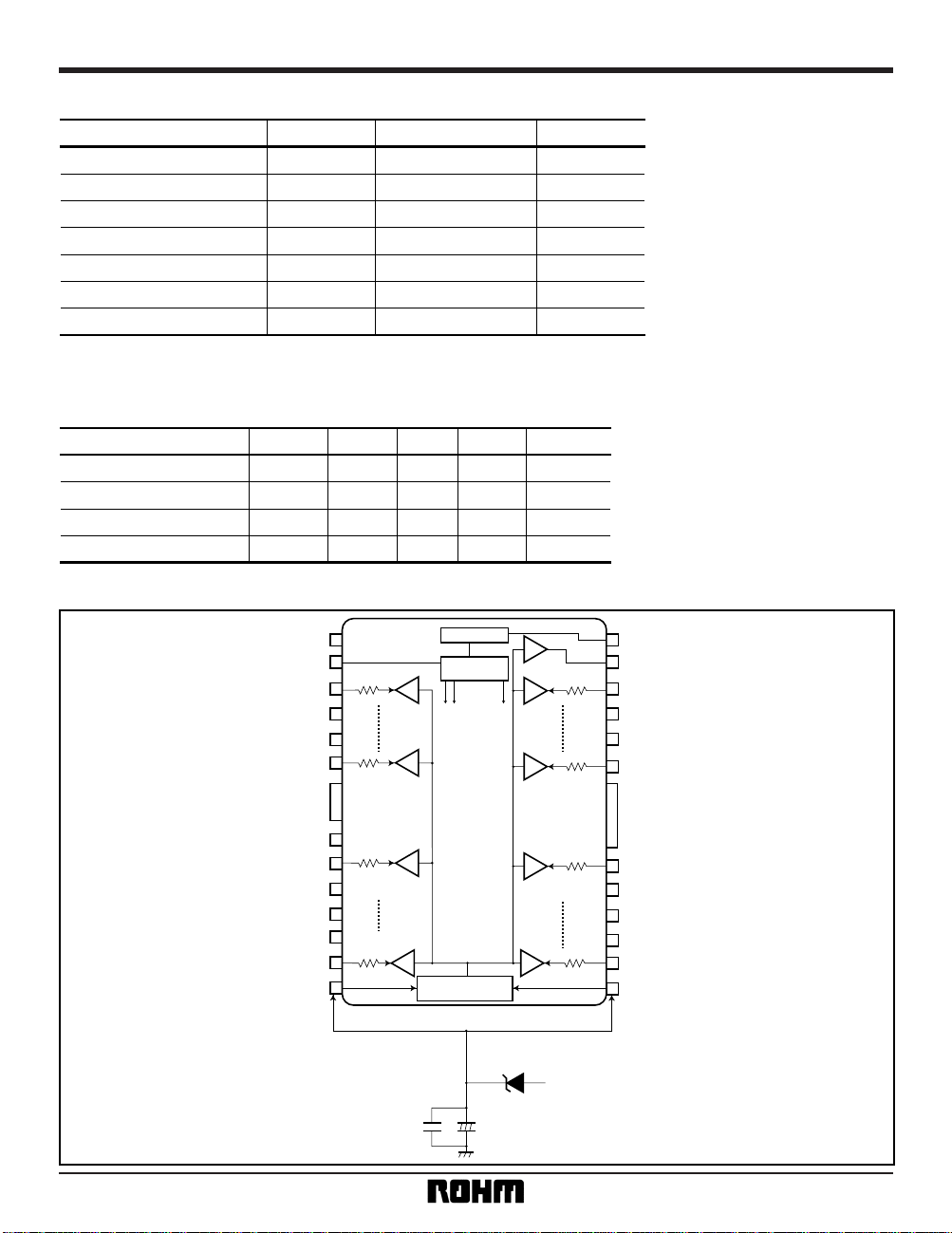
Block diagram
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
110Ω
Resistors
(PUSH - PULL)
(PUSH - PULL)
(PUSH - PULL)
POW
POW
POW
POW
POW
(PUSH - PULL)
(PUSH - PULL)
POW
POW
POW
(PUSH - PULL)
POW
to SW
2.85V SUPPLY
TSD
MODE
CONTROL
2.85V GENERATER
VDD1
SCSI LINE 6
SCSI LINE 7
SCSI LINE 8
SCSI LINE 9
SCSI LINE 10
GND
SCSI LINE 11
SCSI LINE 12
SCSI LINE 15
SCSI LINE 16
SCSI LINE 17
SCSI LINE 18
SCSI LINE 1
SCSI LINE 2
SCSI LINE 3
SCSI LINE 4
SCSI LINE 5
V
DD1
GND
GND
SCSI LINE 13
SCSI LINE 14
VM
TSD
Not to be used
(N.C.)
“H”: ENABLE
“L”: DISCONNECT
EN
(TRMPWR)
Schottky barrier diodes
SYSTEM POWER
5.0V
2.2
µ
0.1µ
+
–
∗
“L”: ENABLE
“H”: DISCONNECT
∗
For BH9596
BH9595FP-Y
 Loading...
Loading...