Page 1
t
LED Drivers for LCD Backlights
1ch Boost up type
White LED Driver for large LCD
BD9486F
1.1 General Description
BD9486F is a high efficiency driver for white LEDs and is
designed for large LCDs. BD9486F has a boost DCDC
converter that employs an array of LEDs as the light
source.
BD9486F has some protect functions against fault
conditions, such as over-voltage protection (OVP), over
current limit protection of DCDC (OCP), LED OCP
protection, and Over boost protection (FBMAX).
Therefore it is available for the fail-safe design over a
wide range output voltage.
Features
DCDC converter with current mode
VOUT discharge function at shutdown
LED protection circuit (Over boost protection, LED
OCP protection)
Over-voltage protection (OVP) for the output voltage
Vout
Adjustable soft start
Adjustable oscillation frequency of DCDC
Wide range of analog dimming 0.2V to 3.0V
UVLO detection for the input voltage of the power
stage
Applications
TV, Computer Display, LCD Backlighting
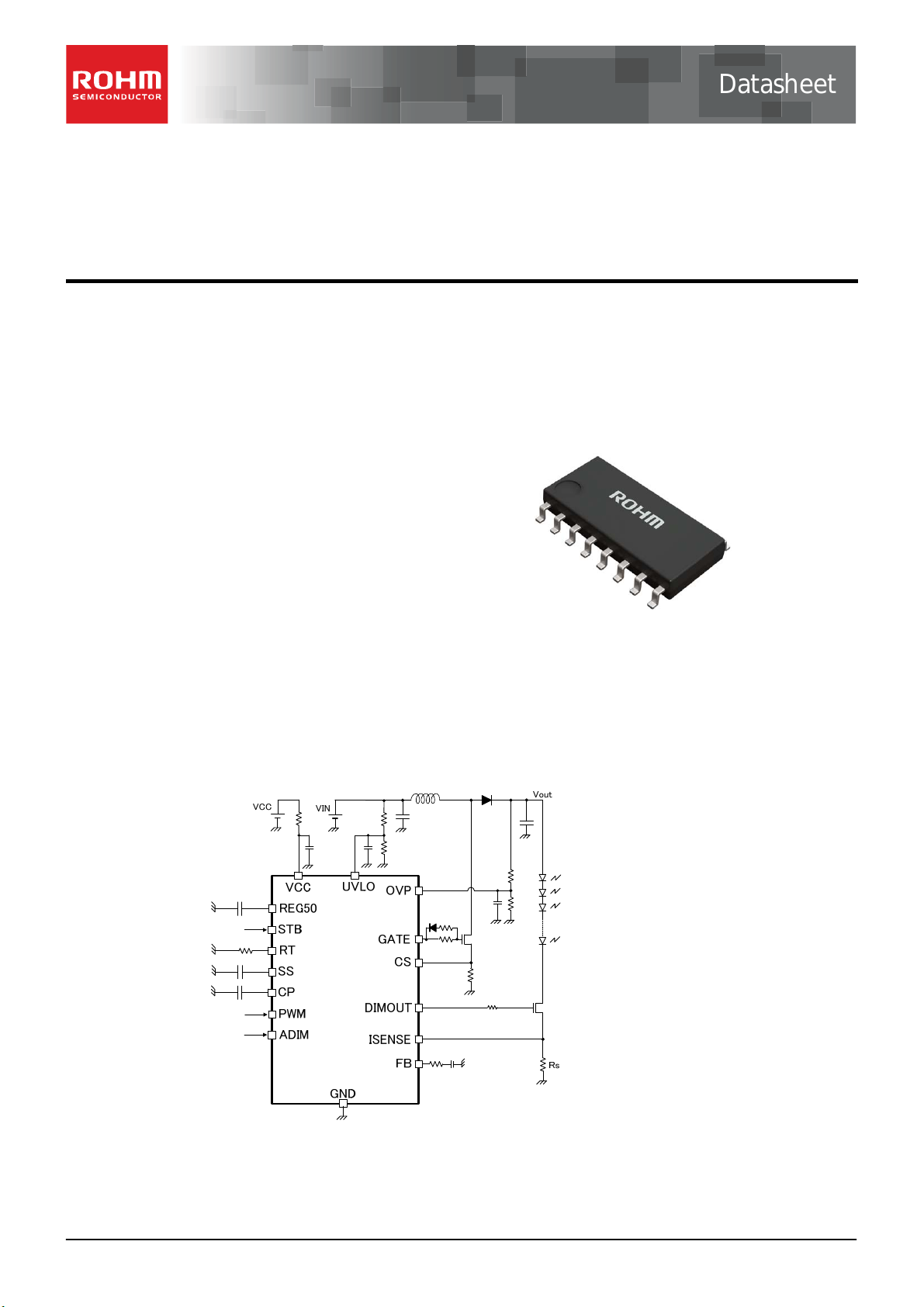
1.3 Typical Application Circuit(s)
Figure 2. Typical Application Circuit
Key Specifications
Operating power supply voltage range:9.0V to 18.0V
Oscillator frequency of DCDC: 150kHz (RT=100kΩ)
Operating Current: 2.6mA(Typ.)
Operating temperature range: -40°C to +85°C
1.2 Package(s) W(Typ) x D(Typ) x H(Max)
SOP16 10.00mm x 6.20mm x 1.71mm
Figure 1. SOP16
Datashee
Pin pitch 1.27mm
○Product structure:Silicon monolithic integrated circuit ○This product has not designed protection against radioactive rays
.
www.rohm.com
© 2013 ROHM Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
TSZ22111・14・001
1/34
TSZ02201-0F1F0C100240-1-2
15.Feb.2016 Rev.006
Page 2
Datasheet
BD9486F
Datasheet
●1.4 Absolute Maximum Ratings (Ta=25°C)
Parameter Symbol
Ratings Unit
Power Supply Voltage Vccmax 20 V
STB, OVP, UVLO, PWM, ADIM
Terminal Voltage
SS, RT, ISENSE, FB, CS, CP,
REG50 Terminal Voltage
DIMOUT, GATE Terminal
Voltage
Power Dissipation Pd 625
STB, OVP, UVLO,
PWM, ADIM
SS, RT, ISENSE, FB, CS,
CP, REG50
20 V
7 V
DIMOUT, GATE VCC V
(Note 1)
mW
Operating Temperature Range Topr -40 to +85 °C
Junction Temperature Tjmax 150 °C
Storage Temperature Range Tstg -55 to +150 °C
(Note 1) In the case of mounting 1 layer glass epoxy base-plate of 70mm×70mm×1.6mm, derate by 5.0mW/°C when operating above
Ta=25°C.
●1.5 Operating Ratings
Parameter Symbol Range Unit
Power Supply Voltage VCC 9.0 to 18.0 V
DC/DC Oscillation Frequency fsw 50 to 800 kHz
Effective Range of ADIM Signal VADIM 0.2 to 3.0 V
PWM Input Frequency FPWM 90 to 2000 Hz
●1.6 External Components Recommended Range
Parameter Symbol Range Unit
REG50 Connection Capacitance C
0.5 to 10
REG50
SS Connection Capacitance CSS 0.001 to 2.2
(Note 2)
μF
(Note 2)
μF
RT Connection Resistance RRT 15 to 300 kΩ
GATE Drive Capacitance C
(Note 2) Please set connection capacitance above Min value of Recommended Range according to temperature characteristic
and DC bias characteristic.
to 1000 pF
GATE
●1.7 Pin Configuration ●1.8 Physical Dimension and Marking Diagram
BD9486F
Lot No.
Figure 3. Pin Configuration Figure4. Physical Dimension and Marking Diagram of SOP16
www.rohm.com
© 2013 ROHM Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
TSZ22111・15・001
2/34
TSZ02201-0F1F0C100240-1-2
15.Feb.2016 Rev.006
Page 3
Datasheet
BD9486F
●1.9 Electrical Characteristics (Unless otherwise specified, Ta=25°C,VCC=12V)
Parameter Symbol
【Total Current Consumption】
Circuit Current Icc - 2.6 5.2 mA
Circuit Current (standby) IST
【UVLO Block】
Operation Voltage(VCC) VUVLO_VCC 6.5 7.5 8.5 V VCC=SWEEP UP
Hysteresis Voltage(VCC)
UVLO Release Voltage VUVLO 2.88 3.00 3.12 V VUVLO=SWEEP UP
UVLO Hysteresis Voltage VUHYS 250 300 350 mV VUVLO=SWEEP DOWN
UVLO Pin Leak Current UVLO_LK -2 0 2 μA VUVLO=4.0V
【DC/DC Block】
ISENSE Threshold Voltage 1 VLED1 0.225 0.233 0.242 V VADIM=0.7V
ISENSE Threshold Voltage 2 VLED2 0.656 0.667 0.677 V VADIM=2.0V
ISENSE Threshold Voltage 3 VLED3 0.988 1.000 1.012 V VADIM=3.0V
ISENSE Clamp Voltage VLED4 0.989 1.015 1.040 V
Oscillation Frequency FCT 142.5 150 157.5 KHz RT=100kΩ
RT Short Protection Range RT_DET -0.3 -
RT Terminal Voltage VRT 1.6 2.0 2.4 V RT=100kΩ
RT Pin ON Resistance at OFF RRT_L - 2.0 4.0 kΩ At latch off
GATE Pin MAX DUTY Output MAX_DUTY 90 95 99 % RT=100kΩ
GATE Pin ON Resistance
(as source)
GATE Pin ON Resistance
(as sink)
SS Pin Source Current ISSSO -3.75 -3.0 -2.25 μA VSS=2.0V
SS Pin ON Resistance at OFF RSS_L - 3.0 5.0 kΩ
Soft Start Ended Voltage VSS_END 3.52 3.70 3.88 V SS=SWEEP UP
FB Source Current IFBSO -115 -100 -85 μA
FB Sink Current IFBSI 85 100 115 μA
OCP Detect Voltage VCS 360 400 440 mV CS=SWEEP UP
OCP Latch Off Detect Voltage VCS 0.85 1.00 1.15 V CS=SWEEP UP
【DC/DC Protection Block】
OVP Detect Voltage VOVP 2.88 3.00 3.12 V VOVP SWEEP UP
OVP Detect Hysteresis VOVP_HYS 150 200 250 mV VOVP SWEEP DOWN
OVP Pin Leak Current OVP_LK -2 0 2 μA VOVP=4.0V, VSTB=3.0V
VUHYS_VCC 150 300 600 mV VCC=SWEEP DOWN
RONSO 2.5 5.0 10.0 Ω
RONSI 2.0 4.0 8.0 Ω
Min. Typ. Max.
-
Limit
40 80 μA VSTB=0V
VRT
×90%
Unit Condition
VSTB=3.0V, PWM=3.0V,
GATE=L,IREG50=0mA
VADIM=3.3V
(at masked analog dimming)
V RT=SWEEP DOWN
VISENSE=0.2V, VADIM=3.0V,
VFB=1.0V
VISENSE=2.0V, VADIM=3.0V,
VFB=1.0V
Datasheet
www.rohm.com
© 2013 ROHM Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
TSZ22111・15・001
3/34
TSZ02201-0F1F0C100240-1-2
15.Feb.2016 Rev.006
Page 4
Datasheet
BD9486F
●1.9 Electrical Characteristics (Unless otherwise specified, Ta=25°C,VCC=12V)
Parameter Symbol
【LED Protection Block】
LED OCP Detect Voltage VLEDOCP 2.88 3.0 3.12 V VISENSE=SWEEP UP
Over Boost Detection Voltage VFBH 3.84 4.00 4.16 V VFB=SWEEP UP
【Dimming Block】
ADIM Pin Leak Current ILADIM -2 0 2 μA VADIM=2.0V
ISENSE Pin Leak Current IL_ISENSE -2 0 2 μA VISENSE=4.0V
DIMOUT Source ON
Resistance
DIMOUT Sink ON Resistance RONSI 4.0 8.0 16 Ω
【REG50 Block】
REG50 Output Voltage 1 REG50_1 4.95 5.00 5.05 V IO=0mA
REG50 Output Voltage 2 REG50_2 4.925 5.00 5.075 V IO=-5mA
REG50 Available Current | IREG50 | 5 - - mA
REG50_UVLO Detect Voltage REG50_TH 2.0 2.3 2.6 V
REG50 Discharge Current REG50_DIS 3.0 5.0 7.0 μA
【STB Block】
STB Pin HIGH Voltage STBH 2.0 - 18 V
STB Pin LOW Voltage STBL -0.3 - 0.8 V
STB Pull Down Resistance RSTB 600 1000 1400 kΩ VSTB=3.0V
【PWM Block】
PWM Pin HIGH Voltage PWM_H 1.5 - 18 V
PWM Pin LOW Voltage PWM_L -0.3 - 0.8 V
PWM Pin Pull Down Resistance RPWM 600 1000 1400 kΩ VPWM=3.0V
【FAIL Block 】
CP Detect Voltage VCP 2.85 3.0 3.15 V VCP=SWEEP UP
CP Charge Current ICP 2.7 3.0 3.3 μA
RONSO 5.0 10 20 Ω
Min. Typ. Max.
Limit
Unit Condition
VREG50=SWEEP DOWN
VSTB=0V
STB=ON->OFF, REG50=4.0V,
PWM=L
Datasheet
www.rohm.com
© 2013 ROHM Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
TSZ22111・15・001
4/34
TSZ02201-0F1F0C100240-1-2
15.Feb.2016 Rev.006
Page 5
Datasheet
BD9486F
●2.1 Pin Function
No.
1 REG50 Out
2 STB In IC ON/OFF pin -0.3 to 20
3 OVP In Over voltage protection detection pin -0.3 to 20
4 UVLO In Under voltage lock out detection pin -0.3 to 20
5 SS Out Slow start setting pin -0.3 to 7
6 PWM In External PWM dimming signal input pin -0.3 to 20
7 CP Out Charge timer for abnormal state -0.3 to 7
8 ADIM In ADIM signal input pin -0.3 to 20
9 RT Out DC/DC switching frequency setting pin -0.3 to 7
10 FB Out Error amplifier output pin -0.3 to 7
11 ISENSE In LED current detection input pin -0.3 to 7
12 GND - -
13 DIMOUT Out Dimming signal output for NMOS -0.3 to VCC
14 GATE Out DC/DC switching output pin -0.3 to VCC
15 CS In
16 VCC In Power supply pin -0.3 to 20
Pin
Name
IN/OUT Function
5.0V output voltage pin and shutdown
timer pin
DC/DC output current detect pin,
OCP input pin
Rating [V]
-0.3 to 7
-0.3 to 7
Datasheet
www.rohm.com
© 2013 ROHM Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
TSZ22111・15・001
5/34
TSZ02201-0F1F0C100240-1-2
15.Feb.2016 Rev.006
Page 6
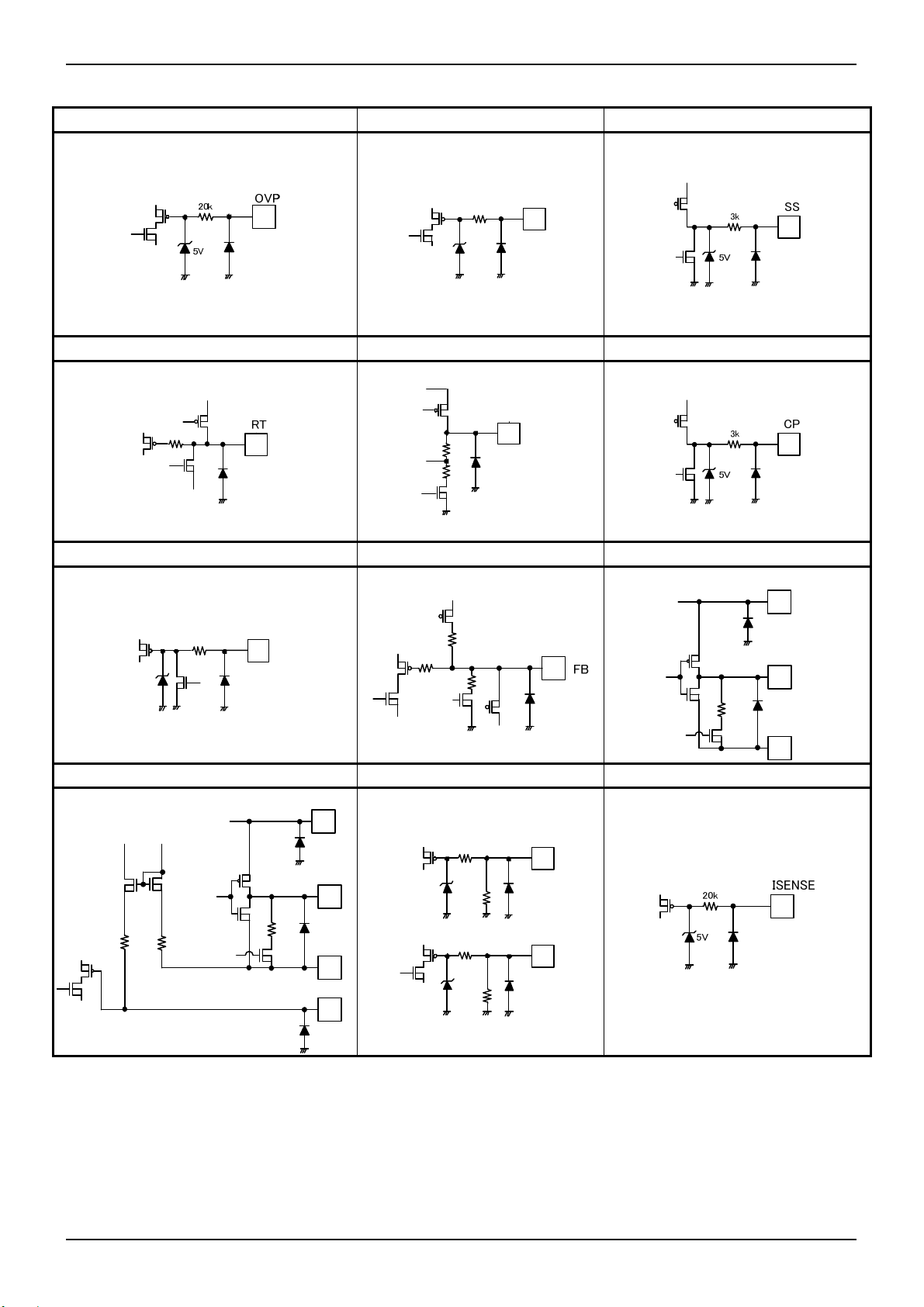
Datasheet
BD9486F
●2.2 Pin ESD Type
OVP UVLO SS
Datasheet
UVLO
REG50
RT
50k
5V
REG50 CP
ADIM FB DIMOUT / VCC
20k
5V
ADIM
VCC
DIMOUT
100k
VCC
GND
GATE / VCC / CS PWM / STB ISENSE
VCC
PWM
STB
VCC
100k
GATE
GND
100k
5V
1M
100k
CS
5V
1M
Figure 5. Pin ESD Type
www.rohm.com
© 2013 ROHM Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
TSZ22111・15・001
6/34
TSZ02201-0F1F0C100240-1-2
15.Feb.2016 Rev.006
Page 7
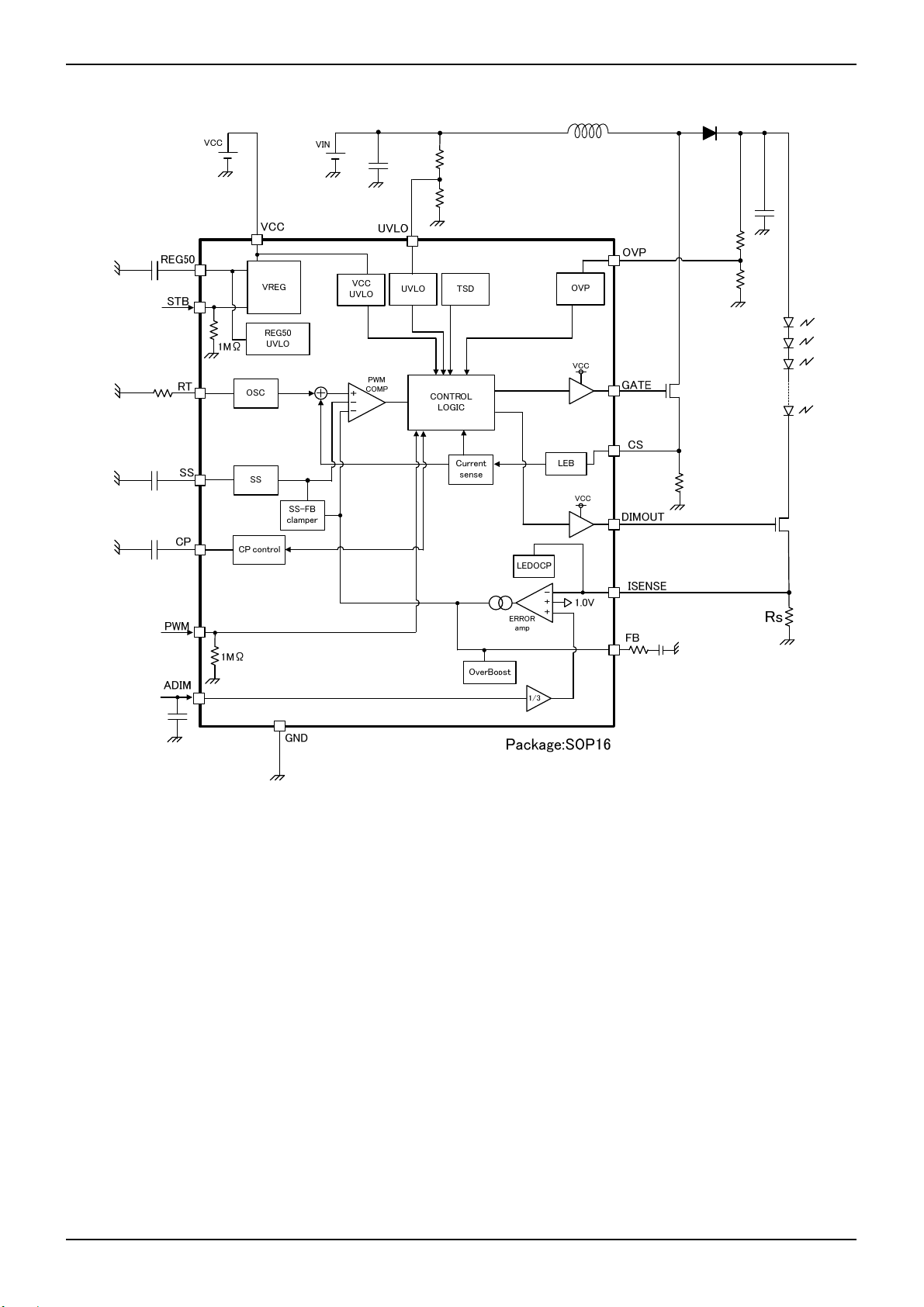
Datasheet
BD9486F
●2.3 Block Diagram
Datasheet
Figure 6. Block Diagram
www.rohm.com
© 2013 ROHM Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
TSZ22111・15・001
7/34
TSZ02201-0F1F0C100240-1-2
15.Feb.2016 Rev.006
Page 8
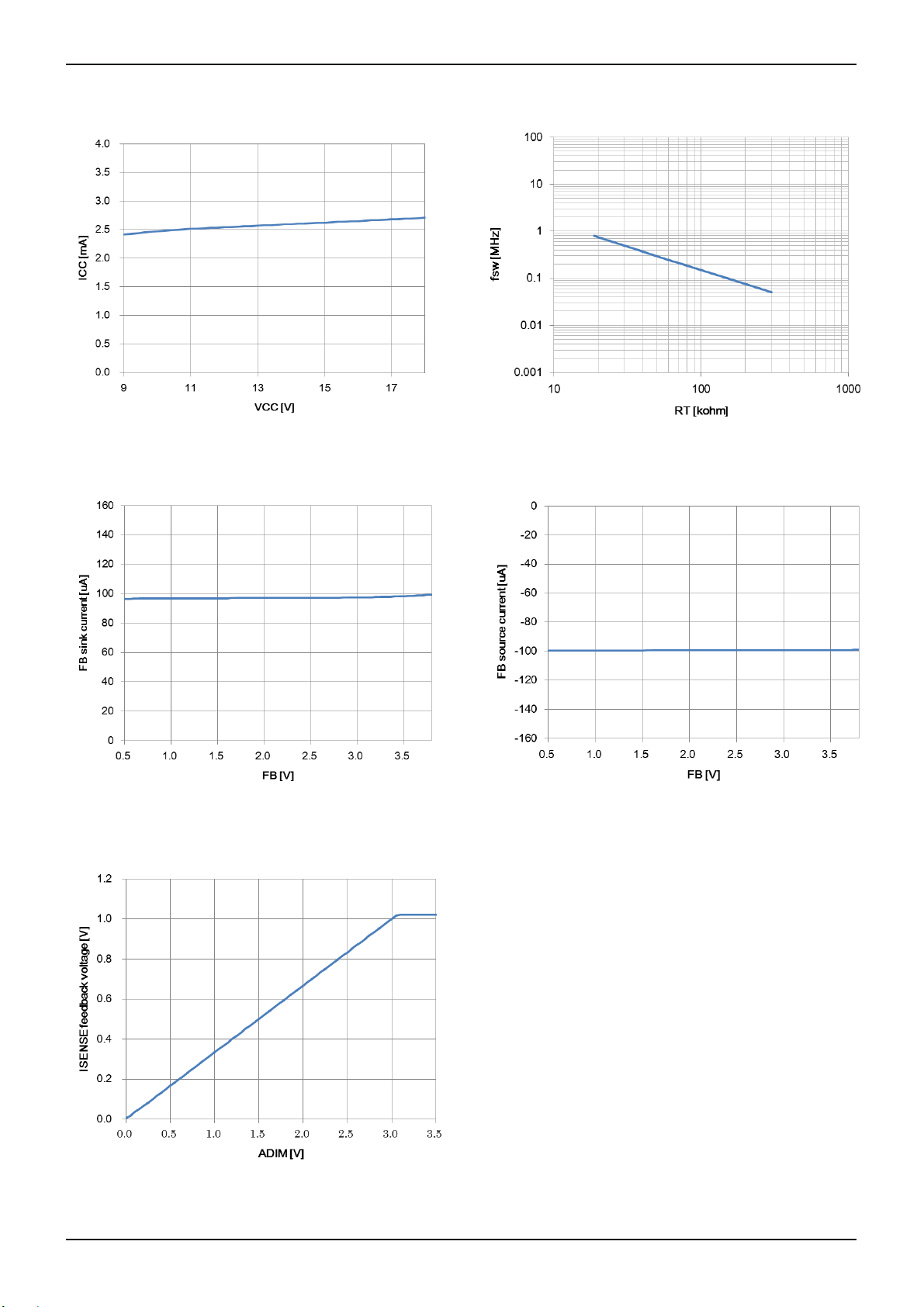
Datasheet
BD9486F
●2.4 Typical Performance Curves (Reference data)
Figure 7. Circuit current (active) Figure 8. Fsw vs RT characteristic
Datasheet
Figure 9. FB sink current vs FB voltage characteristic Figure 10. FB source current vs FB voltage characteristic
Figure 11. ISENSE feedback voltage vs ADIM voltage characteristic
www.rohm.com
© 2013 ROHM Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
TSZ22111・15・001
8/34
TSZ02201-0F1F0C100240-1-2
15.Feb.2016 Rev.006
Page 9
Datasheet
BD9486F
●2.5 Pin Description
○Pin 1: REG50
This is the 5.0V(typ.) output pin. Available current is 5mA (min).
And this terminal is also used as timer for discharging DCDC output capacitor.
Please refer to section“3.2.2 Shutdown Method and REG50 Capacitance Setting”, for detailed explanation.
○Pin 2: STB
This is the ON/OFF setting terminal of the IC. Input reset-signal to this terminal to reset IC from latch-off.
At startup, internal bias starts at high level, and then PWM DCDC boost starts after PWM rise edge inputs.
Note: IC status (IC ON/OFF) transits depending on the voltage inputted to STB terminal. Avoid the use of intermediate
level (from 0.8V to 2.0V).
In order to discharge output voltage while STB=L and REG50UVLO=H, DIMOUT can assert High, depending on PWM
logic. About discharge behavior at end, please refer to section “3.5.3 Timing Chart” or section “3.2.2 Shutdown Method
and REG50 Capacitance Setting”.
○Pin 3: OVP
The OVP terminal is the input for over-voltage protection. If OVP is more than 3.0V(typ), the over-voltage protection
(OVP) will work. At the moment of these detections, it sets GATE=L, DIMOUT=L and starts to count up the abnormal
interval. If OVP detection continued to count four GATE clocks, IC reaches latch off. (Please refer to “3.5.5 Timing Chart”)
The OVP pin is high impedance, because the internal resistance is not connected to a certain bias.
Even if OVP function is not used, pin bias is still required because the open connection of this pin is not a fixed potential.
The setting example is separately described in the section ”3.2.7 OVP Setting”.
As PWM=L interval, IC operates to keep the OVP pin voltage therefore the output voltage. Please refer the section “TBD
the Retaining Function of The Output Voltage”.
○Pin 4: UVLO
Under Voltage Lock Out pin is the input voltage of the power stage. , IC starts the boost operation if UVLO is more than
3.0V(typ) and stops if lower than 2.7V(typ).
The UVLO pin is high impedance, because the internal resistance is not connected to a certain bias.
Even if UVLO function is not used, pin bias is still required because the open connection of this pin is not a fixed
potential.
The setting example is separately described in the section ”3.2.6 UVLO Setting”
○Pin 5: SS
This is the pin which sets the soft start interval of DC/DC converter. It performs the constant current charge of 3.0 μA to
external capacitance Css. The switching duty of GATE output will be limited during 0V to 3.7V of the SS voltage.
So the soft start interval Tss can be expressed as follows
Tss = 1.23*10
The logic of SS pin asserts low is defined as the latch-off state or PWM is not input high level after STB reset release.
When SS capacitance is under 1nF, take note if the in-rush current during startup is too large, or if over boost detection
(FBMAXI) mask timing is too short.
Please refer to soft start behavior in the section “3.5.4 Timing Chart ”.
○Pin 6: PWM
This is the PWM dimming signal input terminal. The high / low level of PWM pins are the following.
○Pin 7: CP
Timer pin for counting the abnormal state of the over boost protection (FBMAX). If the abnormal state is detected, the CP
pin starts charging the external capacitance by 3μA. As the CP voltage reaches 3.0V, IC will be latched off. (GATE=L,
DIMOUT=L).
Please refer to section“3.2.8 Interval Until Latch Off Setting”, for detailed explanation.
○Pin 8: ADIM
This is the input pin for analog dimming signal. The ISENSE feedback point is set as 1/3 of this pin bias. If more than 3.0V
is input, ISENSE feedback voltage is clamped to limit to flow LED large current. In this condition, the input current is
caused. Please refer to <ISENSE> terminal explanation.
6
*Css Css: the external capacitance of the SS pin.
State PWM input voltage
PWM=H PWM=1.5V to 18.0V
PWM=L
PWM=‐0.3V to 0.8V
Datasheet
www.rohm.com
© 2013 ROHM Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
TSZ22111・15・001
9/34
TSZ02201-0F1F0C100240-1-2
15.Feb.2016 Rev.006
Page 10
Datasheet
BD9486F
Datasheet
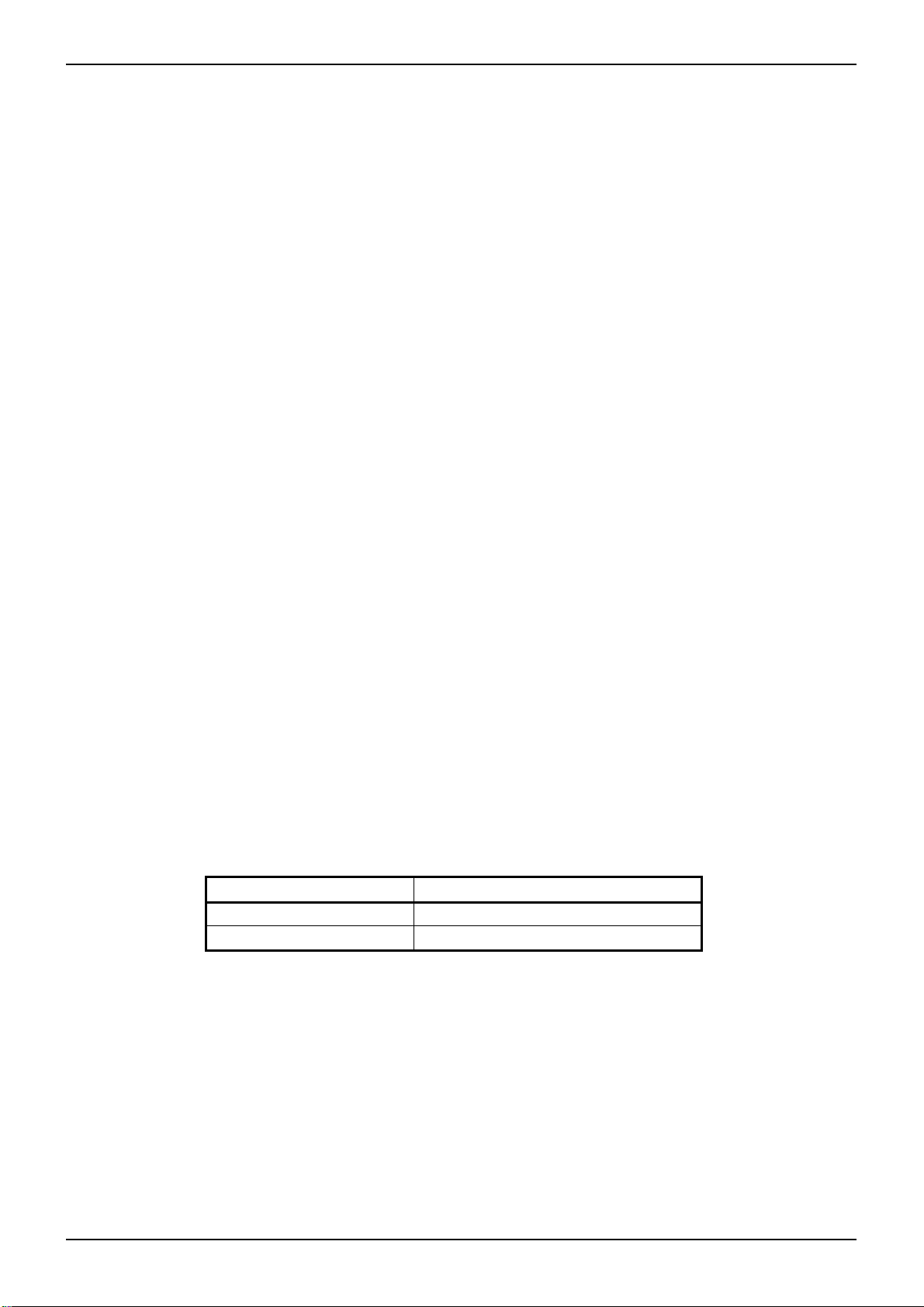
○Pin 9: RT
This is the DC/DC switching frequency setting pin. DCDC frequency is decided
by connected resistor.
○The relationship between the frequency and RT resistance value (ideal)
R
RT
15000
SW
]k[
]kHz[f
The oscillation setting ranges from 50kHz to 800kHz.
The setting example is separately described in the section ”3.2.5 DCDC
Oscillation Frequency Setting”
Figure 12. RT terminal circuit example
The fail logic indicating the abnormal state can be obtained by using the right
circuit example. The gate capacitor is limited to 200pF. We recommend
RE1C001VN for M1.The RT pin output the 2.0V(typ.) in the normal state and
drops to 0V in the latch off state. When REG50 reaches to 0V,there is a point
that FAIL output voltage is unstable, if this is a problem, please add C1 capacitor.
Please refer to section “2.7 Behavior List of the Protect Functions” or “3.5 Timing
Chart”.
○Pin 10: FB
CH1:
STB
CH2:
REG50
CH3:
FAIL
This is the output terminal of error amplifier.
FB pin rises with the same slope as the SS pin during the soft-start period.
After soft -start completion (SS>3.7V), it operates as follows.
When PWM=H, it detects ISENSE terminal voltage and outputs error signal compared to analog dimming signal (ADIM).
It detects over boost (FBMAX) over FB=4.0V(typ). After the SS completion, if FB>4.0V and PWM=H continues 4clk GATE,
the CP charge starts. After that, only the FB>4.0V is monitored, if CP charge continues to the CP=3.0V, IC will be latched
off. (Please refer to section “3.5.6 Timing Chart”.)
The loop compensation setting is described in section "3.4 Loop Compensation".
○Pin 11: ISENSE
This is the input terminal for the current detection. Error amplifier compares the
lower one among 1/3 of the voltage terminal ADIM analog dimming and 1.0V(typ).
And it detects abnormal LED overcurrent at ISENSE=3.0V(typ) over. If GATE
terminal continues during four CLKs (equivalent to 40μs at fosc = 100kHz), it
becomes latch-off. (Please refer to section “3.5.7 Timing Chart”.)
1.015V
1.0V
Gain=1/3
Error amp Vth[V]
67mV
0.2
0
3.0
3.3
ADIM[V]
Figure 13. Relationship of the feedback voltage and ADIM Figure 14. ISENSE terminal circuit example
○Pin 12: GND
This is the GND pin of the IC.
www.rohm.com
© 2013 ROHM Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
TSZ22111・15・001
10/34
TSZ02201-0F1F0C100240-1-2
15.Feb.2016 Rev.006
Page 11
Datasheet
BD9486F
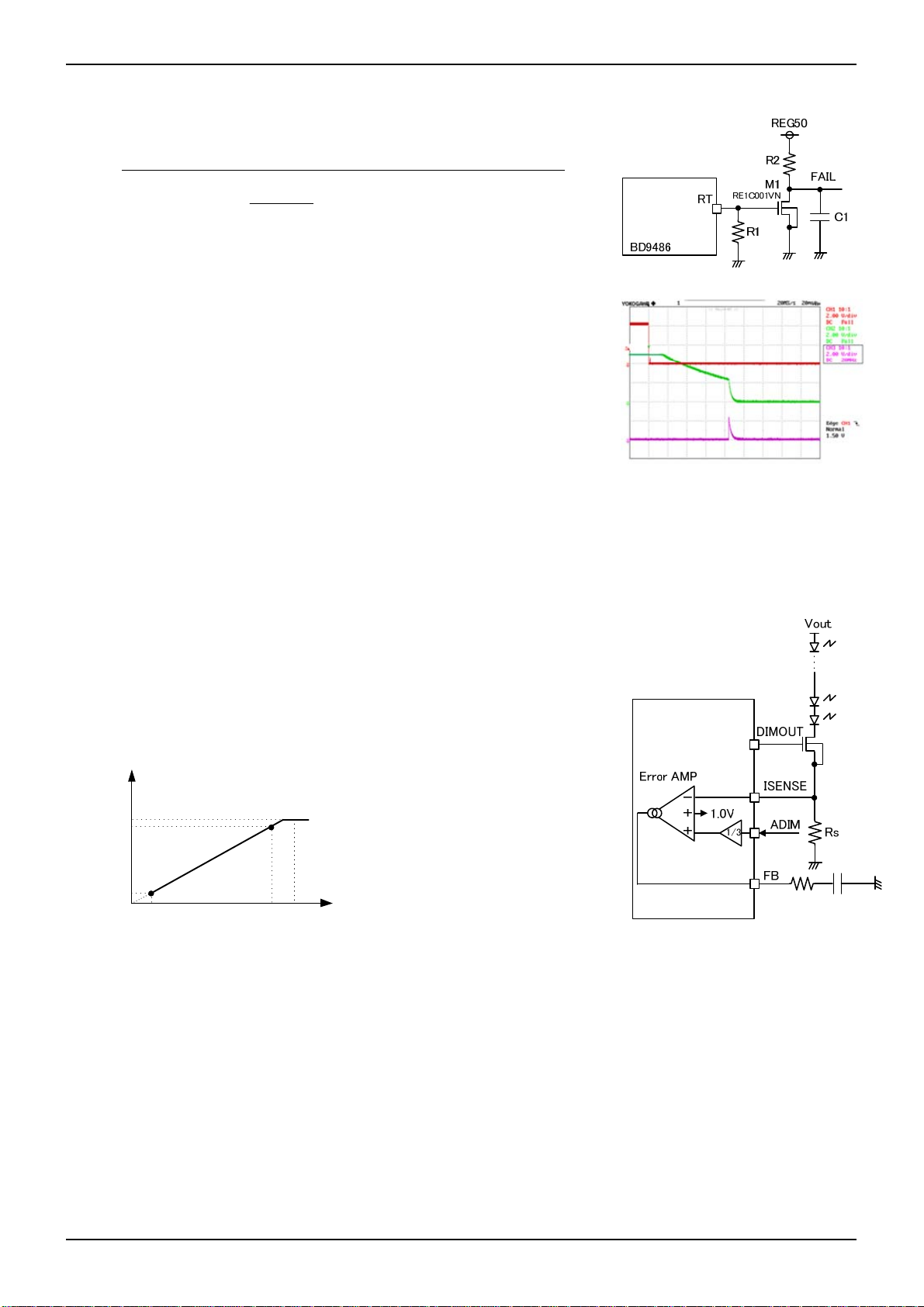
○Pin 13: DIMOUT
This is the output pin for external dimming NMOS. The table below shows the rough output
logic of each operation state, and the output H level is VCC. Please refer to “3.5 Timing Chart”
for detailed explanations, because DIMOUT logic has an exceptional behavior. Please insert
the resistor R
PWM turns from low to high.
○Pin 14: GATE
This is the output terminal for driving the gate of the boost MOSFET. The high level is VCC. Frequency can be set by the
resistor connected to RT. Refer to <RT> pin description for the frequency setting.
○Pin 15: CS
The CS pin has two functions.
1. DC / DC current mode Feedback terminal
The inductor current is converted to the CS pin voltage by the sense resistor
R
This voltage compared to the voltage set by error amplifier controls the
CS.
output pulse.
2. Inductor current limit (OCP) terminal
The CS terminal also has an over current protection (OCP). If the voltage is
more than 0.4V(typ.), the switching operation will be stopped compulsorily. And
the next boost pulse will be restarted to normal frequency.
In addition, the CS voltage is more than 1.0V(typ.) during four GATE clocks, IC
will be latch off. As above OCP operation, if the current continues to flow
nevertheless GATE=L because of the destruction of the boost MOS, IC will
stops the operation completely.
Both of the above functions are enabled after 300ns (typ) when GATE pin
asserts high, because the Leading Edge Blanking function (LEB) is included
into this IC to prevent the effect of noise.
Please refer to section “3.3.1 OCP Setting / Calculation Method for the Current Rating of DCDC Parts”, for detailed
explanation.
If the capacitance Cs in the right figure is increased to a micro order, please be careful that the limited value of NMOS
drain current Id is more than the simple calculation. Because the current Id flows not only through Rcs but also through
Cs, as the CS pin voltage moves according to Id.
○Pin 16: VCC
This is the power supply pin of the IC. Input range is from 9V to 18V.
The operation starts at more than 7.5V(typ) and shuts down at less than 7.2V(typ)
between the dimming MOS gate to improve the over shoot of LED current, as
DIM
Status DIMOUT output
Normal Same logic to PWM
Abnormal GND Level
Figure 15. DIMOUT terminal circuit example
Figure 16. CS terminal circuit example
Datasheet
www.rohm.com
© 2013 ROHM Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
TSZ22111・15・001
11/34
TSZ02201-0F1F0C100240-1-2
15.Feb.2016 Rev.006
Page 12
Datasheet
BD9486F
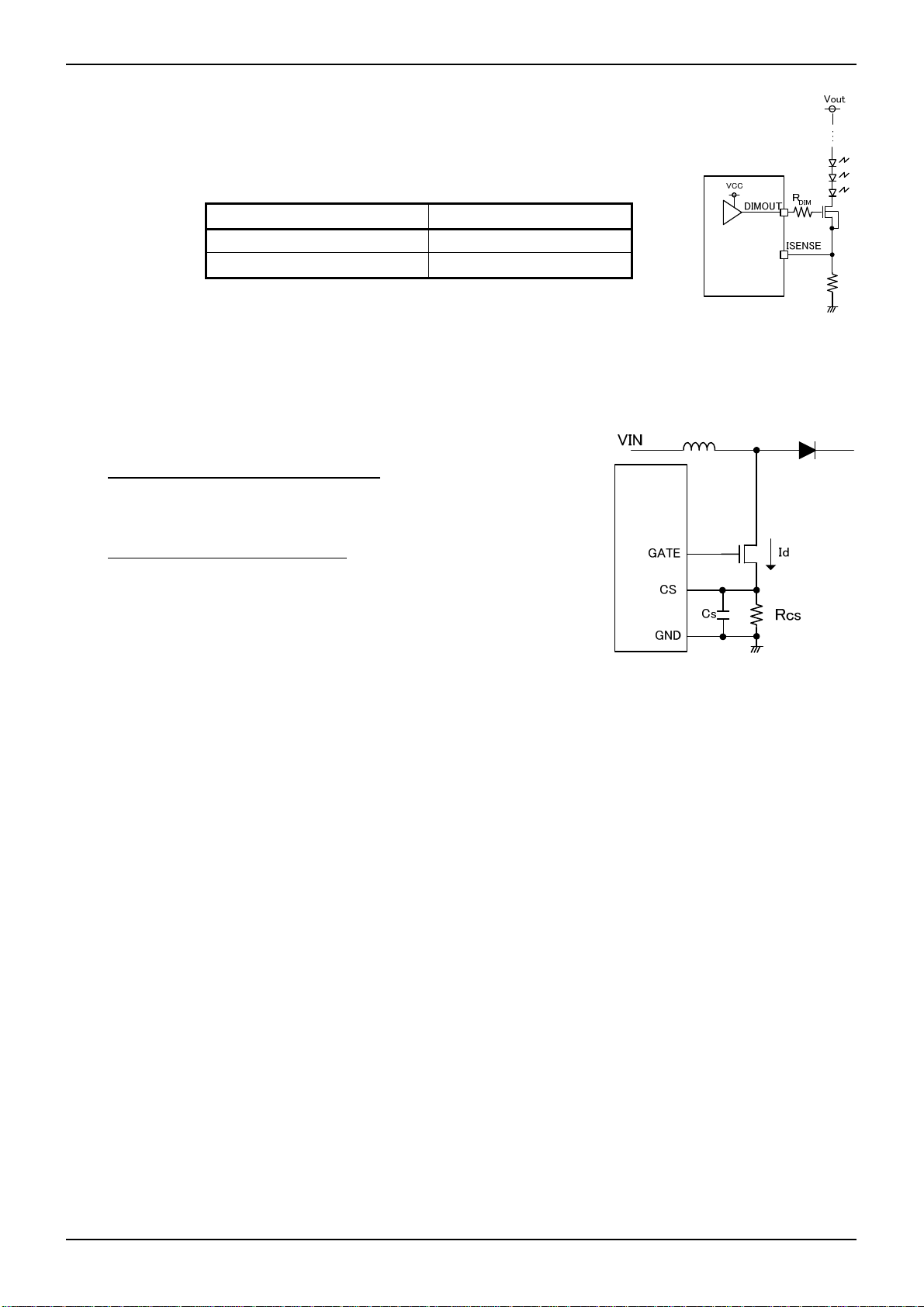
●2.6 Detection Condition List of the Protect Functions (TYP Condition)
Protect Function
FBMAX FB FB > 4.0V H(4clk) SS>3.7V FB < 4.0V CP charge Latch off
LED OCP ISENSE ISENSE > 3.0V - - ISENSE < 3.0V 4clk Latch off
Detection
Pin
Detection
Condition
Detect Condition
PWM
SS
Release
Condition
Timer
Operation
Datasheet
Protection Type
RT GND SHORT RT RT<VRT×90% - -
UVLO UVLO UVLO<2.7V - - UVLO>3.0V NO Restart by release
REG50UVLO REG50 REG50<2.3V - - REG50>2.6V NO Restart by release
VCC UVLO VCC VCC<7.2V - - VCC>7.5V NO Restart by release
OVP OVP OVP>3.0V - - OVP<2.8V 4clk Latch off
OCP CS CS>0.4V - - - NO Pulse by Pulse
OCP LATCH CS CS>1.0V - - CS<1.0V 4clk Latch off
Release
RT=GND
NO Restart by release
To reset the latch type protection, please set STB logic to ‘L’ once. Otherwise the detection of VCCUVLO, REG50UVLO is
required.
The clock number of timer operation corresponds to the boost pulse clock.
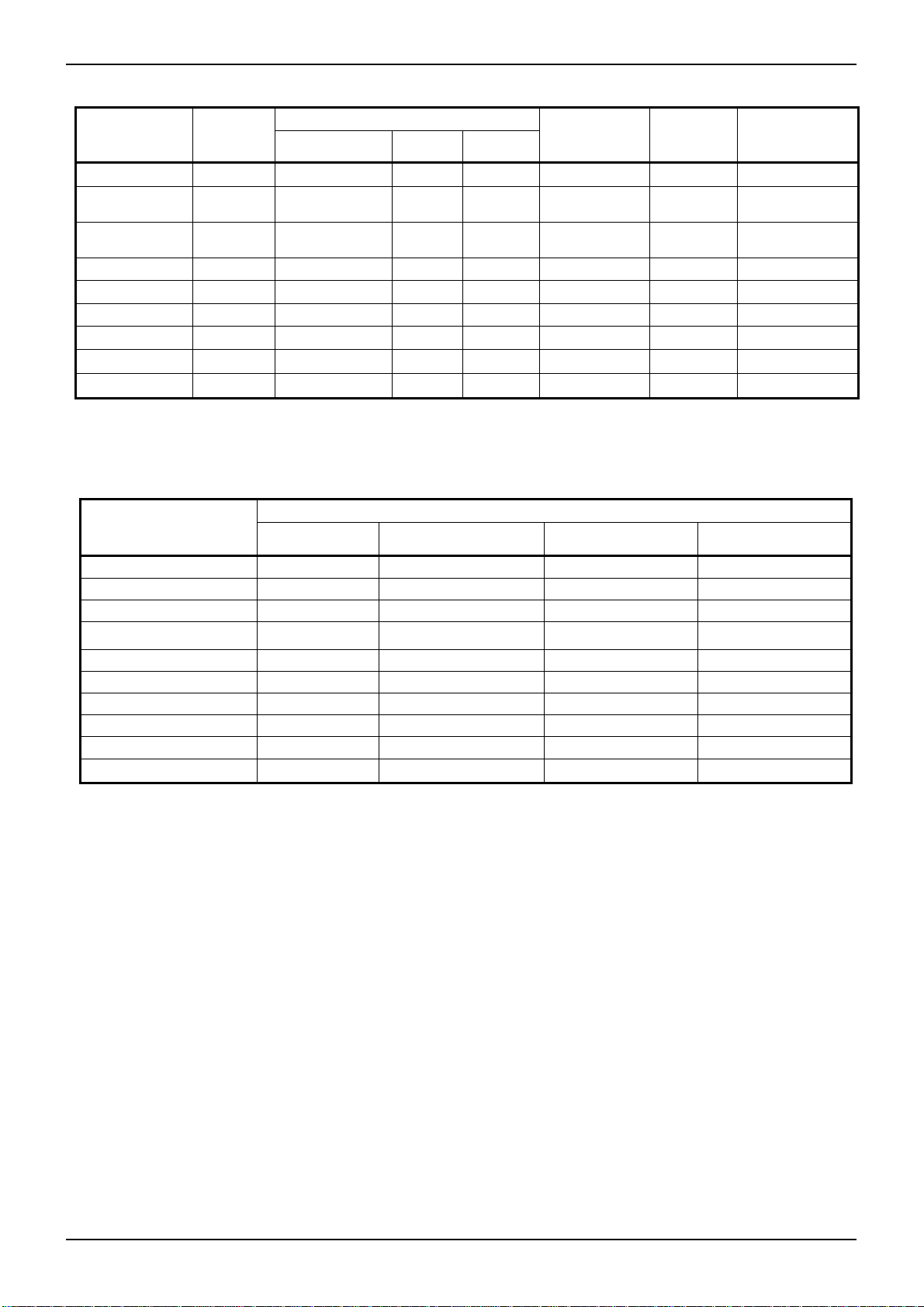
●2.7 Behavior List of the Protect Function
Operation of the Protect Function
Protect Function
FBMAX
LED OCP
RT GND SHORT
STB
UVLO
REG50UVLO
VCC UVLO
OVP
OCP
OCP LATCH
DC/DC Gate
Stops after latch L after latch discharge after latch L after latch
Stops immediately H immediately, L after latch discharge after latch L after latch
Stops immediately immediately L Not discharge -
Stops immediately
Stops immediately immediately L discharge immediately H (2.0V)
Stops immediately immediately L discharge immediately H (2.0V)
Stops immediately immediately L discharge immediately H (2.0V)
Stops immediately immediately L discharge after latch L after latch
Stops immediately Normal operation Not discharge H (2.0V)
Stops after latch L after latch discharge after latch L after latch
Output
Dimming Transistor
(DIMOUT) Logic
L after REG50UVLO
detects
SS Pin
discharge immediately
RT pin
(FAILB logic)
L after REG50UVLO
detects
Please refer to section “3.5 Timing Chart” for details.
www.rohm.com
© 2013 ROHM Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
TSZ22111・15・001
12/34
TSZ02201-0F1F0C100240-1-2
15.Feb.2016 Rev.006
Page 13

Datasheet
BD9486F
●3.1 Application Circuit Example
Introduce an example application using the BD9486F.
3.1.1 Basic Application Example
VCC
VIN
VCC
REG50
STB
RT
SS
CP
PWM
ADIM
GND
Figure 17. Basic application example
・3.1.2 Analog Dimming or PWM Dimming Examples
VCC
VIN
UVLO
Vout
OVP
GATE
CS
DIMOUT
ISENSE
FB
VCC
Datasheet
Vout
Rs
Vout
VIN
VCC
REG50
STB
RT
SS
CP
REG50
PWM
ADIM
UVLO
GND
OVP
GATE
CS
DIMOUT
ISENSE
FB
Figure 18. Example circuit for analog dimming Figure 19. Example circuit for PWM dimming
www.rohm.com
© 2013 ROHM Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
TSZ22111・15・001
OPEN
Rs
13/34
REG50
VCC
REG50
STB
RT
SS
CP
PWM
ADIM
UVLO
GND
OVP
GATE
CS
DIMOUT
ISENSE
FB
Rs
TSZ02201-0F1F0C100240-1-2
15.Feb.2016 Rev.006
Page 14

Datasheet
BD9486F
●3.2 External Components Selection
●3.2.1 Start Up Operation and Soft Start External Capacitance Setting
The below explanation is the start up sequence of this IC
1
Datasheet
STB
OSC
PWM
GATE
VOUT
ILED
LED_OK
SS
SLOPE
FB
SS
Css
2
FB
3
4
5
6
5V
SS=FB
Circuit
OSC
LED_OK
COMP
DRIVER
VOUT
GATE
CS
DIMOUT
ISENSE
PWM
Figure 20. Startup waveform Figure 21. Circuit behavior at startup
○Explanation of start up sequence
1. Reference voltage REF50 starts by STB=H.
2. SS starts to charge at the time of first PWM=H. At this moment, the SS voltage of slow-start starts to equal FB
voltage,and the circuit becomes FB=SS regardless of PWM logic.
3. When FB=SS reaches the lower point of internal sawtooth waveform, GATE terminal outputs pulse and starts to boost
VOUT.
4. It boosts VOUT and VOUT reaches the voltage to be able to flow LED current.
5. If LED current flows over decided level, FB=SS circuit disconnects and startup behavior completes.
6. Then it works normal operation by feedback of ISENSE terminal. If LED current doesn't flow when SS becomes over
3.7V, SS=FF circuit completes forcibly and FBMAX protection starts.
○Method of setting SS external capacitance
According to the sequence described above, start time Tss that startup completes with FB=SS condition is the time that
FB voltage reaches the feedback point.
The capacitance of SS terminal is defined as Css and the feedback voltage of FB terminal is defined as VFB. The
equality on T
is as follows.
FB
ss
T
ss
]V[VFB]Fμ[C
]Aμ[3
[sec]
If Css is set to a very small value, rush current flows into the inductor at startup.
On the contrary, if Css is enlarged too much, LED will light up gradually.
Since Css differs in the constant set up with the characteristic searched for and differs also by factors, such as a voltage
rise ratio, an output capacitance, DCDC frequency, and LED current, please confirm with the system.
【Setting example】
When Css=0.1μF,Iss=3μA,and startup completes at VFB=3.7V, SS setting time is as follows.
T
ss
6
6
]V[7.3]F[101.0
[sec]123.0
]A[103
www.rohm.com
© 2013 ROHM Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
TSZ22111・15・001
14/34
TSZ02201-0F1F0C100240-1-2
15.Feb.2016 Rev.006
Page 15

Datasheet
BD9486F
●3.2.2 Shutdown Method and REG50 Capacitance Setting
When this IC shuts down, VOUT discharge function works. Indicated below is the sequence.
Datasheet
Figure 22. The waveform and diagram at shutdown
○Sequence explanation of shutdo wn
1. When STB=L, GATE and REG50 stop.
2. While STB=L and REG50UVLO=H, DIMOUT asserts the same logic of PWM. And VOUT is discharged until
REG50=5.0V reaches 2.3V by -5μA(typ.).
3. When VOUT is discharged enough by ILED, ILED doesn’t get to flow.
4. When REG50 voltage reaches under 2.3V(typ), whole system is shutdown.
○Setting method of REG50 capacitance
When REG50 terminal capacitance is defined as C
When discharge function is used, PWM signal must be continuously inputted after STB=L.
VOUT discharge time is longest when PWM is set on mininum DUTY.
Please set C
Please refer “1.6External Components Recommended Range” when setting C
●3.2.3 VCC Series Resistance Setting
Here are the following effects of inserting series resistor Rvcc into VCC
line.
(i) In order to drop the voltage VCC, it is possible to suppress the heat
generation of the IC.
(ii) It can limit the inflow current to VCC line.
However, if resistance RVCC is set bigger, VCC voltage becomes under
minimum operation voltage (VCC<9V). RVCC must be set to an
appropriate series resistance.
Especially, after STB is set to High, IREG may become large and VCC
may fall greatly in the section charged to the capacitor of REG50
terminal depending on the external circuit of a VCC terminal.
Even in such a case, please set up to be set to VCC>9V in an operating
condition.
IC’s inflow current line I_IN has the following inflow lines.
・IC’s circuit current…ICC
・Current of RREG connected to REG50…IREG
・Current to drive FET’s Gate…I_GATE
These decide the voltage ΔV at RVCC.
VCC terminal voltage at that time can be expressed as follows.
Here, judgement is the 9V minimum operation voltage.
Please consider a sufficient margin when setting the series resistor of VCC.
capacitance value with margin so that the system is shutdown after VOUT is discharged enough.
REG
T
OFF
REG
, shutdown time T
REG
][5
A
][)3.20.5(][
VFC
[sec]
is decided by the following equation.
OFF
capacitance.
REG
]V[9]Ω[RVCC]A[IREG]A[IDCDC]A[ICC]V[VIN[V]VCC
Figure 23. VCC series resistance
circuit example
www.rohm.com
© 2013 ROHM Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
TSZ22111・15・001
15/34
TSZ02201-0F1F0C100240-1-2
15.Feb.2016 Rev.006
Page 16

Datasheet
BD9486F
【setting example】
Above equation is translated as follows.
When VIN=12V, ICC=2.0mA, IREG=50mA and IDCDC=2mA, RVCC’s value is calculated as follows.
(ICC is 2.6mA(typ.)) . Please set each values with tolerance and margin.
●3.2.4 LED current setting
LED current can be adjusted by setting the resistance R
Relationship between R
With DC dimming (ADIM<3.0V)
Without DC dimming (ADIM>3.0V)
【setting example】
If I
LED
●3.2.5 DCDC Oscillation Frequency Setting
which connects to RT pin sets the oscillation frequency fSW of DCDC.
R
RT
○Relationship between frequency f
【setting example】
When DCDC frequency fsw is set to 200kHz, R
]Ω[RVCC
][RVCC
and I
S
LED
R
current is 200mA and ADIM is 2.0V, we can calculate R
R
ISENSE
R
R
RT
RT
sw
1
3
LED
15000
SW
]V[ADIM
]A[I
]kHz[f
1500015000
200
]V[9]V[VIN
]A[IREG]A[IDCDC]A[ICC
]V[] V[
912
[.] A [.
]A
002 00020
current
ISENSE
R
ISENSE
and RT resistance (ideal)
SW
]k[
[A]
0.050
1
3
LED
LED
]V[0.231
]A[2.0
is as follows.
RT
75
]kHz[]kHz[f
][
56
[Ω] which connects to ISENSE pin and ADIM[V].
S
]V[ADIM
]Ω[
]A[I
]V[015.1
]Ω[
]A[I
as below.
ISENSE
]Ω[33.3
Figure 24. LED current setting example
]k[
Figure 25. RT terminal setting example
Datasheet
www.rohm.com
© 2013 ROHM Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
TSZ22111・15・001
16/34
TSZ02201-0F1F0C100240-1-2
15.Feb.2016 Rev.006
Page 17

Datasheet
BD9486F
●3.2.6 UVLO Setting
Under Voltage Lock Out pin is the input voltage of the power stage. IC starts boost operation if UVLO is more than
3.0V(typ.) and stops if lower than 2.7V(typ.).
The UVLO pin is high impedance, because the internal resistance is not connected to a certain bias.
So, the bias by the external components is required, because the open connection of this pin is not a fixed potential.
Detection voltage is set by dividing resistors R1 and R2. The resistor values can be calculated by the formula below.
○UVLO detection equation
As VIN decreases, R1 and R2 values are set in the following formula by the VIN
○UVLO release equation
R1 and R2 setting is decided by the equation above. The equation of UVLO
release voltage is as follows.
【setting example】
If the normal input voltage, VIN is 24V, the detect voltage of UVLO is 18V, R2 is
30kΩ, R1 is calculated as follows.
By using these R1 and R2, the release voltage of UVLO, VIN
CAN
CAN
]Ωk[2R1R
]k[RR
0170
21
03
DET
V0.3VIN
DET
]V[.VIN
])V[7.2]V[VIN(
]V[7.2
]Ωk[
])Ωk[2R]Ωk[1R(
]V[
]Ωk[2R
72
2
])V[.]V[VIN(
72
]V[.
])k[R]k[R(
21
]k[R
30
]k[
72
, can be calculated too as follows.
CAN
]V[.
03
30
])V[.]V[(
7218
]V[.
30170
]k[
that UVLO detects.
DET
]k[]k[
020
Figure 26. UVLO setting example
]k[.
]V[.]V[
Datasheet
www.rohm.com
© 2013 ROHM Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
TSZ22111・15・001
17/34
TSZ02201-0F1F0C100240-1-2
15.Feb.2016 Rev.006
Page 18

Datasheet
BD9486F
●3.2.7 OVP Setting
The OVP terminal is the input for over-voltage protection of output voltage.
The OVP pin is high impedance, because the internal resistance is not connected to a certain bias.
Detection voltage of VOUT is set by dividing resistors R1 and R2. The resistor values can be calculated by the formula
below.
○OVP detection equation
03
]V[.
2
]V[.
03
03
]A[.
03470
]A[.
DET, the detect
])V[.]V[VOVP(
03
21
])k[R]k[R(
]k[R
])V[.]V[VOVP(
03
2
]V[.]F[C
21
]k[R
[sec]
]V[.]F[.
])k[R]k[R(
470
10
]k[
]V[
Figure 27. OVP setting example
])V[]V[(
]k[
]V[.
82
348
]V[
3
CAN can be calculated as follows.
15010
]k[
10
]k[
]k[]k[
sec]m[
If VOUT is boosted abnormally, VOVP
voltage of OVP, R1, R2 can be expressed by the following formula.
○OVP release equation
By using R1 and R2 in the above equation, the release voltage of
OVP, VOVP
【setting example】
If the normal output voltage, VOUT is 40V, the detect voltage of OVP is 48V, R2 is 10k ohm, R1 is calculated as follows.
By using these R1 and R2, the release voltage of OVP, VOVP
●3.2.8 Interval Until Latch Off Setting
About over boost protection (FBMAX), the capacitance value of CP terminal can set the time of latch-off. About the
behavior from abnormal detection to latch-off, please refer to the section “3.5.6 Timing Chart”.
The condition FB>4.0V(typ.) and PWM=H continues more than four GATE clocks, the CP terminal charge is started by
3μA. After that, only the FB voltage is monitored. As the CP voltage reaches to 3.0V(typ.), IC will be latched off.
The time LATCH
LATCH
【setting example】
If the capacitor of CP pin is 0.47μF, the timer latch interval is as follows.
LATCH
]k[RR
21
CAN can be expressed as follows.
CAN
]k[RR
150
21
CAN
TIME
TIME
TIME
DET
82
V.VOVP
DET
]V[.VOVP
82
to reach to latch-off is set by CP terminal capacitance as follows.
CP
03
03
]V[.]V[
844
Datasheet
www.rohm.com
© 2013 ROHM Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
TSZ22111・15・001
18/34
TSZ02201-0F1F0C100240-1-2
15.Feb.2016 Rev.006
Page 19

Datasheet
BD9486F
●3.3 DCDC Parts Selection
3.3.1. OCP Setting / Calculation Method for the Current Rating of DCDC Parts
OCP detection stops the switching when the CS pin voltage is more than 0.4V. The resistor value of CS pin, RCS needs to
be considered by the coil L current. And the current rating of DCDC external parts is required more than the peak current
of the coil.
Shown below are the calculation method of the coil peak current, the selection method of Rcs (the resistor value of CS
pin) and the current rating of the external DCDC parts at Continuous Current Mode.
(the calculation method of the coil peak current, Ipeak at Continuous Current Mod e)
At first, since the ripple voltage at CS pin depends on the application
condition of DCDC, the following variables are used.
Vout voltage=VOUT[V]
LED total current=IOUT[A]
DCDC input voltage of the power stage =VIN[V]
Efficiency of DCDC =η[%]
And then, the average input current IIN is calculated by the following
equation.
And the ripple current of the inductor L (ΔIL[A]) can be calculated by using
DCDC the switching frequency, fsw, as follows.
On the other hand, the peak current of the inductor Ipeak can be expressed
as follows.
… (1)
Therefore, the bottom of the ripple current Imin is
or 0
If Imin>0, the operation mode is CCM (Continuous Current Mode),
otherwise the mode is DCM (Discontinuous Current Mode).
(the selection method of Rcs at Continuous Current Mode)
Ipeak flows into Rcs and that causes the voltage signal to CS pin. (Please
refer to the timing chart at the right)
Peak voltage VCSpeak is as follows.
As this VCSpeak reaches 0.4V, the DCDC output stops the switching.
Therefore, Rcs value is necessary to meet the condition below.
(the current rating of the external DCDC parts)
The peak current as the CS voltage reaches OCP level (0.4V) is defined as Ipeak_det.
… (2)
The relationship among Ipeak (equation (1)), Ipeak_det (equation (2)) and the current rating of parts is required to meet
the following
Please make the selection of the external parts such as FET, Inductor, diode meet the above condition.
I
IN
Δ
IL
peak
I
det_peak
IN
IN
]A[IinIm
IN
40
II
]A[I]V[V
OUTOUT
[%]]V[V
]A[IIpeak
2
]V[.
][Rcs
det_peakpeak
]A[
SWOUT
]A[IL
]V[V])V[V]V[V(
ININOUT
]A[
]Hz[f]V[V]H[L
]A[
2
]A[IL
]V[IpeakRcsVCS
]V[.]V[IpeakRcs 40
]A[
The current rating of parts
N[V]
IL[A]
VCS[V]
Figure 28. Coil current waveform
Datasheet
www.rohm.com
© 2013 ROHM Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
TSZ22111・15・001
19/34
TSZ02201-0F1F0C100240-1-2
15.Feb.2016 Rev.006
Page 20

Datasheet
BD9486F
[setting example]
Output voltage = VOUT [V] = 40V
LED total current = IOUT [A] = 0.48V
DCDC input voltage of the power stage = VIN [V] = 24V
Efficiency of DCDC =η[%] = 90%
Averaged input current IIN is calculated as follows.
If the switching frequency, f
calculated as follows.
Therefore the inductor peak current, Ipeak is
If Rcs is assumed to be 0.3Ω
The above condition is met.
And Ipeak_det, the current OCP works, is
If the current rating of the used parts is 2A,
This inequality meets the above relationship. The parts selection is proper.
And I
MIN
This inequality implies that the operation is continuous current mode.
]A[I
IN
IL
peak
I
det_peak
II
, the bottom of the IL ripple current, can be calculated as follows.
INMIN
IN
IN
40
30
det_peakpeak
]A[.]A[.]A[.]A[
]A[II
]A[IIpeak
]V[.
][.
The current rating …current rating confirmation
]A[I]V[V
OUTOUT
SW
[%]]V[V
= 200kHz, and the inductor, L=100μH, the ripple current of the inductor L (ΔIL[A]) can be
SWOUT
]A[IL
]V[V])V[V]V[V(
ININOUT
Δ
]Hz[f]V[V]H[L
2
331
]A[.
]A[IL
2
]A[.]V[
48040
[%]]V[
9024
480
]A[.]A[
890
Datasheet
890
2
]A[.
]V[])V[]V[(
242440
36
102004010100
]A[.
131
]A[.
…calculation result of the peak current
V.]V[.]A[.][.IpeakRcsVCS
40339013130
480
]Hz[]V[]H[
]A[.
…Rcs value confirmation
]A[.]A[.]A[. 02331131
of DCDC parts
0650480131
www.rohm.com
© 2013 ROHM Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
TSZ22111・15・001
20/34
TSZ02201-0F1F0C100240-1-2
15.Feb.2016 Rev.006
Page 21

Datasheet
BD9486F
3.3.2. Inductor Selection
The inductor value affects the input ripple current. As shown in section 3.3.1,
IL
Δ
ΔI
L
I
IN
IN
OUTOUT
[%]]V[V
]A[IIpeak
IN
Where
L: coil inductance [H] V
V
: input voltage [V]
IN
: output load current (the summation of LED current) [A]
I
OUT
I
: input current [A] fSW: oscillation frequency [Hz]
IN
: DCDC output voltage [V]
OUT
Figure 29. Inductor current waveform and diagram
In continuous current mode, ⊿IL is set to 30% to 50% of the output load current in many cases.
In using smaller inductor, the boost is operated by the discontinuous current mode in which the coil current returns to
zero at every period.
*The current exceeding the rated current value of inductor flown through the coil causes magnetic saturation, results in
decreasing in efficiency. Inductor needs to be selected to have such adequate margin that peak current does not
exceed the rated current value of the inductor.
*To reduce inductor loss and improve efficiency, inductor with low resistance components (DCR, ACR) needs to be
selected
3.3.3. Output Capacitance Cout Selection
V
IN
Output capacitor needs to be selected in consideration of equivalent series resistance
required to even the stable area of output voltage or ripple voltage. Be aware that set
I
L
L
V
OUT
LED current may not be flown due to decrease in LED terminal voltage if output ripple
component is high.
Output ripple voltage V
is determined by Equation (4):
OUT
R
ESR
R
CS
C
OUT
When the coil current is charged to the output capacitor as MOS turns off, much output
ESR
・・・・・ ΔΔ
ripple is caused. Much ripple voltage of the output capacitor may cause the LED current
Datasheet
]V[V])V[V]V[V(
ININOUT
]A[I]V[V
]Hz[f]V[V]H[L
SWOUT
]A[
]A[IL
]A[
]A[
2
(4)]V[RILVout
Figure 30. Output capacitor diagram
ripple.
* Rating of capacitor needs to be selected to have adequate margin against output voltage.
*To use an electrolytic capacitor, adequate margin against allowable current is also necessary. Be aware that the LED
current is larger than the set value transitionally in case that LED is provided with PWM dimming especially.
3.3.4. MOSFET Selection
There is no problem if the absolute maximum rating is larger than the rated current of the inductor L, or is larger than
the sum of the tolerance voltage of C
and the rectifying diode VF. The product with small gate capacitance (injected
OUT
charge) needs to be selected to achieve high-speed switching.
* One with over current protection setting or higher is recommended.
* The selection of one with small on resistance results in high efficiency.
3.3.5. Rectifying Diode Selection
A schottky barrier diode which has current ability higher than the rated current of L, reverse voltage larger than the
tolerance voltage of C
, and low forward voltage VF especially needs to be selected.
OUT
www.rohm.com
© 2013 ROHM Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
TSZ22111・15・001
21/34
TSZ02201-0F1F0C100240-1-2
15.Feb.2016 Rev.006
Page 22

Datasheet
BD9486F
●3.4.Loop Compensation
A current mode DCDC converter has each one pole (phase lag) fp due to CR filter composed of the output capacitor and
the output resistance (= LED current) and zero (phase lead) f
Moreover, a step-up DCDC converter has RHP zero (right-half plane zero point) f
converter. This zero may cause the unstable feedback. To avoid this by RHP zero, the loop compensation that the
cross-over frequency fc, set as follows, is suggested.
fc = f
Considering the response speed, the calculated constant below is not always optimized completely. It needs to be
adequately verified with an actual device.
Where I
Above equation is described for lighting LED without the oscillation. The value may cause much error if the quick
response for the abrupt change of dimming signal is required.
To improve the transient response, R
adequately verified with an actual device in consideration of variation from parts to parts since phase margin is
decreased.
/5 (f
ZRHP
i. Calculate the pole frequency fp and the RHP zero frequency f
ii. Calculate the phase compensation of the error amp output (fc = f
: RHP zero frequency)
ZRHP
f
p
R
1
FB
C
1FB
I
2
= the summation of LED current, (Continuous Current Mode)
LED
Figure 31. Output stage and error amplifier diagram
LED
CV
OUTOUT
OUTp
1
Rπ2
f
c
1FB
4
1004
needs to be increased, and C
FB1
]Hz[
IRf
LEDCSRHZP
15
)D(Vgmf
5
Rπ2
1FB
]S[.gm
by the output capacitor and the ESR of the capacitor.
Z
ZRHP
of DC/DC converter
ZRHP
2
)D(V
1
f
ZRHP
D
OUT
2
VV
V
OUT
IL
LED
INOUT
/5)
ZRHP
][
]F[
f
ZRHP
needs to be decreased. It needs to be
FB1
which is unique with the boost
]Hz[
Datasheet
www.rohm.com
© 2013 ROHM Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
TSZ22111・15・001
22/34
TSZ02201-0F1F0C100240-1-2
15.Feb.2016 Rev.006
Page 23

Datasheet
BD9486F
●3.5.Timing Chart
3.5.1 PWM Start up 1 (Input PWM Signal After Input STB Signal)
VCC
STB
PWM
7.5V
Datasheet
REG50
SS
GATE
RT
STATE
OFF
2.6V
3.7V
0.4V
2.0V
STANDBY
(*2) (*3) (*4) (*5)
(*1)
SS Normal
STANDBY
(*6)
0.4V
SS
Figure 32. PWM Start up 1 (Input PWM Signal After Input STB Signal)
(*1)…REG50 starts up when STB is changed from Low to High. In the state where the PWM signal is not inputted, SS terminal
is not charged and DCDC doesn’t start to boost, either.
(*2)…When REG50 is more than 2.6V, the reset signal is released.
(*3)…The charge of the pin SS starts at the positive edge of PWM=L to H, and the soft start starts. The GATE pulse outputs only
during the corresponding PWM=H. And while the SS is less than 0.4V, the pulse does not output. The pin SS continues
charging in spite of the assertion of PWM or OVP level.
(*4)…The soft start interval will end if the voltage of the pin SS, Vss reaches 3.7V. By this time, it boosts V
to the voltage
OUT
where the set LED current flows. The abnormal detection of FBMAX starts to be monitored.
(*5)…As STB=L, the boost operation is stopped instantaneously. (Discharge operation continues in the state of STB=L and
REGUVLO=L. Please refer to section 3.5.3)
(*6)…In this diagram, before the charge period is completed, STB is changed to High again. As STB=H again, the boost
operation restarts the next PWM=H. It is the same operation as the timing of (*2). (For capacitance setting of SS terminal,
please refer to section 3.2.1.
www.rohm.com
© 2013 ROHM Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
TSZ22111・15・001
23/34
TSZ02201-0F1F0C100240-1-2
15.Feb.2016 Rev.006
Page 24

Datasheet
BD9486F
3.5.2 PWM Start Up 2 (Input STB Signal after Inputted PWM Signal)
Datasheet
Figure 33. PWM Start Up 2 (Input STB Signal after Inputted PWM Signal)
(*1)…REG50 starts up when STB=H.
(*2)…When REG50UVLO releases or PWM is inputted to the edge of PWM=L→H, SS charge starts and soft start period is
started. The GATE pulse outputs only during the corresponding PWM=H. And while the SS is less than 0.4V, the pulse
does not output. The pin SS continues charging in spite of the assertion of PWM or OVP level.
(*3)…The soft start interval will end if the voltage of the pin SS, Vss reaches 3.7V. By this time, it boosts V
the set LED current flows. The abnormal detection of FBMAX starts to be monitored.
(*4)…As STB=L, the boost operation is stopped instantaneously (GATE=L, SS=L). (Discharge operation works in the state of
STB=L and REG50UVLO=H. Please refer to section 3.5.3)
(*5)…In this diagram, before the discharge period is completed, STB is changed to High again. As STB=H again, operation will
be the same as the timing of (*1).
to the point where
OUT
www.rohm.com
© 2013 ROHM Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
TSZ22111・15・001
24/34
TSZ02201-0F1F0C100240-1-2
15.Feb.2016 Rev.006
Page 25

Datasheet
BD9486F
3.5.3 Turn Off
Datasheet
STB
PWM
REG50 2.3V
REG50UVLO
DIMOUT
GATE
Vout
SS
RT 2.0V
STATE
ON
(*1)
Dischange
(*2)
OFF
Figure 34. Turn Off
(*1)…As STB=H→L、boost operation stops and REG50 starts to discharge.
(*2)…While STB=L, REG50UVLO=H, DIMOUT becomes same as PWM. REG50=5.0V is discharged by -5μA until
REG50=2.3V,and then IC becomes OFF state. REG50 is discharged rapidly and RT becomes 0V at the same time. V
OUT
is
discharged completely until this time. It should be set to avoid a sudden brightness.
About capacitance value setting of REG50, please refer to the section 3.2.2.
www.rohm.com
© 2013 ROHM Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
TSZ22111・15・001
25/34
TSZ02201-0F1F0C100240-1-2
15.Feb.2016 Rev.006
Page 26

Datasheet
BD9486F
3.5.4 Soft Start Function
STB
PWM
Datasheet
UVLO
VCCUVLO
REG50UVLO
OVP
RT
SS
2.0V
(*1) (*2)(*3) (*4) (*5) (*6) (*7)
2.7V 3.0V
7.2V
7.5V
2.3V 2.6V
3.0V 2.8V
4clk
Figure 35. Soft Start Function
(*1)…The SS pin charge does not start by just STB=H. PWM=H is required to start the soft start. In the low SS voltage, the
GATE pin duty depends on the SS voltage. And while the SS is less than 0.4V, the pulse does not output.
(*2)…By the time STB=L, the SS pin is discharged immediately. As REG50UVLO=H, RT is still High.
(*3)…As the STB recovered to STB=H, The SS charge starts immediately by the logic PWM=H in this chart.
(*4)…The SS pin is discharged immediately by the UVLO=L.
(*5)…The SS pin is discharged immediately by the VCCUVLO=L.
(*6)…The SS pin is discharged immediately by the REG50UVLO=L.
(*7)…The SS pin is not discharged by the abnormal detection of the latch off type such as OVP until the latch off.
www.rohm.com
© 2013 ROHM Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
TSZ22111・15・001
26/34
TSZ02201-0F1F0C100240-1-2
15.Feb.2016 Rev.006
Page 27

Datasheet
BD9486F
3.5.5 OVP Detection
Datasheet
Figure 36. OVP Detection
(*1)…As OVP is detected, the output GATE=L, DIMOUT=L, and the abnormal counter starts.
(*2)…If OVP is released within 4 clocks of abnormal counter of the GATE pin frequency, the boost operation restarts.
(*3)…As the OVP is detected again, the boost operation is stopped.
(*4)…As the OVP detection continues up to 4 count by the abnormal counter, IC will be latched off.
(*5)… Once IC is latched off, the boost operation doesn't restart even if OVP is released.
(*6)…The STB=L input can make IC reset.
(*7)…It normally starts as STB turns Low to High.
(*8)…The operation of the OVP detection is not related to the logic of PWM.
www.rohm.com
© 2013 ROHM Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
TSZ22111・15・001
27/34
TSZ02201-0F1F0C100240-1-2
15.Feb.2016 Rev.006
Page 28

Datasheet
BD9486F
3.5.6 FBMAX Detection
STB
PWM
REG50
Datasheet
2.0V
(*1)
4.0V
・・・・・ ・・・・・
SS
(*2)
FB
GATE
CP
SS
RT
STANDBY STANDBY
STATE
3.7V
NORMAL
4.0V
③
①
②
(*3) (*4)
④
CP COUNTOR
3.0V
latch
off
(*5) (*6) (*7)
SS
Figure 37. FBMAX Detection
(*2)…During the soft start, it is not judged to the abnormal state even if the FB=H(FB>4.0V).
(*3)…When the PWM=H and FB=H, the abnormal counter doesn’t start immediately.
(*4)…The CP charge will start if the PWM=H and the FB=H detection continues up to 4 clocks of the GATE frequency. Once the
count starts, only FB level is monitored.
(*5)…When the FBMAX detection continues till the CP charge reaches 3.0V, IC will be latched off. The latch off interval can be
calculated by the external capacitance of CP pin. (Please refer to section 3.2.8.)
(*6)…The latch off state can be reset by the STB=L.
(*7)…It is normally started by PWM=L to H, in this figure.
www.rohm.com
© 2013 ROHM Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
TSZ22111・15・001
28/34
TSZ02201-0F1F0C100240-1-2
15.Feb.2016 Rev.006
Page 29

Datasheet
BD9486F
3.5.7 LED OCP Detection
STB
PWM
REG50
Datasheet
ISENSE
Abnormal
COUNTOR
SS
GATE
DIMOUT
RT
STATE
2.0V
NORMAL
3.0V
Smaller than
START
4count
LEDOCP
(*1)
3.0V 3.0V 3.0V 3.0V 3.0V
START
(*8)
4count
abnormal
(*2)
RESET
NORMAL
4count
START
LEDOCP LEDOCP
abnormalabnormal
(*3) (*4) (*5)
END
Latch off
Reset
(OFF)
(*6) (*7)
0.4V
NORMAL
END
Latch off
Figure 38. LED OCP Detection
(*1)…If ISENSE>3.0V, LEDOCP is detected, and GATE becomes L. To detect LEDOCP continuously, The DIMOUT is
compulsorily high, regardless of the PWM dimming signal.
(*2)…When the LEDOCP releases within 4 counts of the GATE frequency, the boost operation restarts.
(*3) …As the LEDOCP is detected again, the boost operation is stopped.
(*4)…If the LEDOCP detection continues up to 4 counts of GATE frequency. IC will be latched off.
(*5)…Once IC is latched off, the boost operation doesn't restart even if the LEDOCP releases.
(*6)…The latch off state can be reset by the STB=L.
(*7)…It normally starts by STB=L to H.
(*8)…The operation of the LEDOCP detection is not related to the logic of the PWM.
www.rohm.com
© 2013 ROHM Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
TSZ22111・15・001
29/34
TSZ02201-0F1F0C100240-1-2
15.Feb.2016 Rev.006
Page 30

Datasheet
BD9486F
Operational Notes
1. Reverse Connection of Power Supply
Connecting the power supply in reverse polarity can damage the IC. Take precautions against reverse polarity when
connecting the power supply, such as mounting an external diode between the power supply and the IC’s power
supply terminals.
2. Power Supply Lines
Design the PCB layout pattern to provide low impedance supply lines. Separate the ground and supply lines of the
digital and analog blocks to prevent noise in the ground and supply lines of the digital block from affecting the analog
block. Furthermore, connect a capacitor to ground at all power supply pins. Consider the effect of temperature and
aging on the capacitance value when using electrolytic capacitors.
3. Ground Voltage
Ensure that no pins are at a voltage below that of the ground pin at any time, even during transient condition.
4. Ground Wiring Pattern
When using both small-signal and large-current ground traces, the two ground traces should be routed separately but
connected to a single ground at the reference point of the application board to avoid fluctuations in the small-signal
ground caused by large currents. Also ensure that the ground traces of external components do not cause variations
on the ground voltage. The ground lines must be as short and thick as possible to reduce line impedance.
5. Thermal Consideration
Should by any chance the power dissipation rating be exceeded the rise in temperature of the chip may result in
deterioration of the properties of the chip. The absolute maximum rating of the Pd stated in this specification is when
the IC is mounted on a 70mm x 70mm x 1.6mm glass epoxy board. In case of exceeding this absolute maximum
rating, increase the board size and copper area to prevent exceeding the Pd rating.
6. Recommended Operating Conditions
These conditions represent a range within which the expected characteristics of the IC can be approximately obtained.
The electrical characteristics are guaranteed under the conditions of each parameter.
7. Rush Current
When power is first supplied to the IC, it is possible that the internal logic may be unstable and inrush
current may flow instantaneously due to the internal powering sequence and delays, especially if the IC
has more than one power supply. Therefore, give special consideration to power coupling capacitance,
power wiring, width of ground wiring, and routing of connections.
8. Testing on Application Boards
When testing the IC on an application board, connecting a capacitor directly to a low-impedance output pin may
subject the IC to stress. Always discharge capacitors completely after each process or step. The IC’s power supply
should always be turned off completely before connecting or removing it from the test setup during the inspection
process. To prevent damage from static discharge, ground the IC during assembly and use similar precautions during
transport and storage.
9. Inter-pin Short and Mounting Errors
Ensure that the direction and position are correct when mounting the IC on the PCB. Incorrect mounting may result in
damaging the IC. Avoid nearby pins being shorted to each other especially to ground, power supply and output pin.
Inter-pin shorts could be due to many reasons such as metal particles, water droplets (in very humid environment) and
unintentional solder bridge deposited in between pins during assembly to name a few.
Datasheet
www.rohm.com
© 2013 ROHM Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
TSZ22111・15・001
30/34
TSZ02201-0F1F0C100240-1-2
15.Feb.2016 Rev.006
Page 31

Datasheet
BD9486F
Operational Notes – continued
10. Unused Input Terminals
Input terminals of an IC are often connected to the gate of a MOS transistor. The gate has extremely high impedance
and extremely low capacitance. If left unconnected, the electric field from the outside can easily charge it. The small
charge acquired in this way is enough to produce a significant effect on the conduction through the transistor and
cause unexpected operation of the IC. So unless otherwise specified, unused input terminals should be connected to
the power supply or ground line.
11. Regarding the Input Pin of the IC
This monolithic IC contains P+ isolation and P substrate layers between adjacent elements in order to keep them
isolated. P-N junctions are formed at the intersection of the P layers with the N layers of other elements, creating a
parasitic diode or transistor. For example (refer to figure below):
When GND > Pin A and GND > Pin B, the P-N junction operates as a parasitic diode.
When GND > Pin B, the P-N junction operates as a parasitic transistor.
Parasitic diodes inevitably occur in the structure of the IC. The operation of parasitic diodes can result in mutual
interference among circuits, operational faults, or physical damage. Therefore, conditions that cause these diodes to
operate, such as applying a voltage lower than the GND voltage to an input pin (and thus to the P substrate) should
be avoided.
Datasheet
12. Ceramic Capacitor
When using a ceramic capacitor, determine the dielectric constant considering the change of capacitance with
temperature and the decrease in nominal capacitance due to DC bias and others.
13. Area of Safe Operation (ASO)
Operate the IC such that the output voltage, output current, and power dissipation are all within the Area of Safe
Operation (ASO).
14. Thermal Shutdown Circuit(TSD)
This IC has a built-in thermal shutdown circuit that prevents heat damage to the IC. Normal operation should always
be within the IC’s power dissipation rating. If however the rating is exceeded for a continued period, the junction
temperature (Tj) will rise which will activate the TSD circuit that will turn OFF all output pins. When the Tj falls below
the TSD threshold, the circuits are automatically restored to normal operation.
Note that the TSD circuit operates in a situation that exceeds the absolute maximum ratings and therefore, under no
circumstances, should the TSD circuit be used in a set design or for any purpose other than protecting the IC from
heat damage.
15. Over Current Pro t ection Circuit (OCP)
This IC incorporates an integrated overcurrent protection circuit that is activated when the load is shorted. This
protection circuit is effective in preventing damage due to sudden and unexpected incidents. However, the IC should
not be used in applications characterized by continuous operation or transitioning of the protection circuit.
Figure 39. Example of monolithic IC structure
www.rohm.com
© 2013 ROHM Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
TSZ22111・15・001
31/34
TSZ02201-0F1F0C100240-1-2
15.Feb.2016 Rev.006
Page 32

Datasheet
BD9486F
Ordering Information
B D 9 4 8 6 F - E 2
Datasheet
Part Number
Marking Diagrams
SOP16 (TOP VIEW)
BD9486F
Package
F:SOP16
Part Number Marking
LOT Number
Packaging and forming specification
E2: Embossed tape and reel
1PIN MARK
www.rohm.com
© 2013 ROHM Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
TSZ22111・15・001
32/34
TSZ02201-0F1F0C100240-1-2
15.Feb.2016 Rev.006
Page 33

Datasheet
BD9486F
Physical Dimension, Tape and Reel Information
Package Name SOP16
(Max 10.35 (include.BURR))
Datasheet
<Tape and Reel information>
Embossed carrier tapeTape
Quantity
Direction
of feed
2500pcs
E2
The direction is the 1pin of product is at the upper left when you hold
()
reel on the left hand and you pull out the tape on the right hand
Reel
1pin
Order quantity needs to be multiple of the minimum quantity.
∗
Direction of feed
(UNIT : mm)
PKG : SOP16
Drawing No. : EX114-5001
www.rohm.com
© 2013 ROHM Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
TSZ22111・15・001
33/34
TSZ02201-0F1F0C100240-1-2
15.Feb.2016 Rev.006
Page 34

Datasheet
BD9486F
Revision History
Date Revision Changes
12.Jul.2013 001 New Release
p.4 delete REG50_UVLO_Hysteresis item
09.Sep.2013 002
19.Nev.2013 003
13.Feb.2014 004
01.Sep.2014 005
15.Feb.2016 006
p.4 modify REG50 Discharge Current limits
Min. 4.95uA -> 3.0uA Typ. 5.00uA -> 5.0uA Max. 5.05uA -> 7.0uA
p.3 Circuit Current (Icc) add condition GATE=L,IREG50=0mA
p.6 2.2 Pin ESD Type add REG50 schematic (PWM sch. Is moved to STB sch.)
p.10 Pin Description Pin11 ISENSE sentence ADIM analog dimming and 3.0V(typ)
→ADIM analog dimming and 1.0V(typ)
Figure.13 modify schematic (add ADIM=3.3V)
p.11 Modify DIMOUT explanation to ” the output H level is VCC”.
Modify GATE explanation to ” The high level is VCC”.
Modify the figure.15 of DIMOUT terminal circuit example.
p.15 3.2.3 VCC Series Resistance Setting add explanation
p.16 modify equation
p.2 add 1.6 External Components Recommended Range
Pin Configuration 1.6→1.7
Physical Dimension and Marking Diagram 1.7→1.8
p.3 Electrical Characteristics 1.8→1.9
p.4 Electrical Characteristics 1.8→1.9
p.15 add REG50 capacitance setting
Datasheet
www.rohm.com
© 2013 ROHM Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
TSZ22111・15・001
34/34
TSZ02201-0F1F0C100240-1-2
15.Feb.2016 Rev.006
Page 35

Notice-PGA-E Rev.003
© 2015 ROHM Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
JAPAN
USA
EU
CHINA
CLASSⅢ
CLASSⅢ
CLASSⅡb
CLASSⅢ
CLASSⅣ
CLASSⅢ
Notice
Precaution on using ROHM Products
1. Our Products are designed and manufactured for application in ordinary electronic equipments (such as AV equipment,
OA equipment, telecommunication equipment, home electronic appliances, amusement equipment, etc.). If you
intend to use our Products in devices requiring extremely high reliability (such as medical equipment
equipment, traffic equipment, aircraft/spacecraft, nuclear power controllers, fuel controllers, car equipment including car
accessories, safety devices, etc.) and whose malfunction or failure may cause loss of human life, bodily injury or
serious damage to property (“Specific Applications”), please consult with the ROHM sales representative in advance.
Unless otherwise agreed in writing by ROHM in advance, ROHM shall not be in any way responsible or liable for any
damages, expenses or losses incurred by you or third parties arising from the use of any ROHM’s Products for Specific
Applications.
(Note1) Medical Equipment Classification of the Specific Applications
2. ROHM designs and manufactures its Products subject to strict quality control system. However, semiconductor
products can fail or malfunction at a certain rate. Please be sure to implement, at your own responsibilities, adequate
safety measures including but not limited to fail-safe design against the physical injury, damage to any property, which
a failure or malfunction of our Products may cause. The following are examples of safety measures:
[a] Installation of protection circuits or other protective devices to improve system safety
[b] Installation of redundant circuits to reduce the impact of single or multiple circuit failure
3. Our Products are designed and manufactured for use under standard conditions and not under any special or
extraordinary environments or conditions, as exemplified below. Accordingly, ROHM shall not be in any way
responsible or liable for any damages, expenses or losses arising from the use of any ROHM’s Products under any
special or extraordinary environments or conditions. If you intend to use our Products under any special or
extraordinary environments or conditions (as exemplified below), your independent verification and confirmation of
product performance, reliability, etc, prior to use, must be necessary:
[a] Use of our Products in any types of liquid, including water, oils, chemicals, and organic solvents
[b] Use of our Products outdoors or in places where the Products are exposed to direct sunlight or dust
[c] Use of our Products in places where the Products are exposed to sea wind or corrosive gases, including Cl2,
H2S, NH3, SO2, and NO2
[d] Use of our Products in places where the Products are exposed to static electricity or electromagnetic waves
[e] Use of our Products in proximity to heat-producing components, plastic cords, or other flammable items
[f] Sealing or coating our Products with resin or other coating materials
[g] Use of our Products without cleaning residue of flux (even if you use no-clean type fluxes, cleaning residue of
flux is recommended); or Washing our Products by using water or water-soluble cleaning agents for cleaning
residue after soldering
[h] Use of the Products in places subject to dew condensation
4. The Products are not subject to radiation-proof design.
5. Please verify and confirm characteristics of the final or mounted products in using the Products.
6. In particular, if a transient load (a large amount of load applied in a short period of time, such as pulse. is applied,
confirmation of performance characteristics after on-board mounting is strongly recommended. Avoid applying power
exceeding normal rated power; exceeding the power rating under steady-state loading condition may negatively affect
product performance and reliability.
7. De-rate Power Dissipation depending on ambient temperature. When used in sealed area, confirm that it is the use in
the range that does not exceed the maximum junction temperature.
8. Confirm that operation temperature is within the specified range described in the product specification.
9. ROHM shall not be in any way responsible or liable for failure induced under deviant condition from what is defined in
this document.
Precaution for Mounting / Circuit board design
1. When a highly active halogenous (chlorine, bromine, etc.) flux is used, the residue of flux may negatively affect product
performance and reliability.
2. In principle, the reflow soldering method must be used on a surface-mount products, the flow soldering method must
be used on a through hole mount products. If the flow soldering method is preferred on a surface-mount products,
please consult with the ROHM representative in advance.
For details, please refer to ROHM Mounting specification
(Note 1)
, transport
Page 36

Notice-PGA-E Rev.003
© 2015 ROHM Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
Precautions Regarding Application Examples and External Circuits
1. If change is made to the constant of an external circuit, please allow a sufficient margin considering variations of the
characteristics of the Products and external components, including transient characteristics, as well as static
characteristics.
2. You agree that application notes, reference designs, and associated data and information contained in this document
are presented only as guidance for Products use. Therefore, in case you use such information, you are solely
responsible for it and you must exercise your own independent verification and judgment in the use of such information
contained in this document. ROHM shall not be in any way responsible or liable for any damages, expenses or losses
incurred by you or third parties arising from the use of such information.
Precaution for Electrostatic
This Product is electrostatic sensitive product, which may be damaged due to electrostatic discharge. Please take proper
caution in your manufacturing process and storage so that voltage exceeding the Products maximum rating will not be
applied to Products. Please take special care under dry condition (e.g. Grounding of human body / equipment / solder iron,
isolation from charged objects, setting of Ionizer, friction prevention and temperature / humidity control).
Precaution for Storage / Transportation
1. Product performance and soldered connections may deteriorate if the Products are stored in the places where:
[a] the Products are exposed to sea winds or corrosive gases, including Cl2, H2S, NH3, SO2, and NO2
[b] the temperature or humidity exceeds those recommended by ROHM
[c] the Products are exposed to direct sunshine or condensation
[d] the Products are exposed to high Electrostatic
2. Even under ROHM recommended storage condition, solderability of products out of recommended storage time period
may be degraded. It is strongly recommended to confirm solderability before using Products of which storage time is
exceeding the recommended storage time period.
3. Store / transport cartons in the correct direction, which is indicated on a carton with a symbol. Otherwise bent leads
may occur due to excessive stress applied when dropping of a carton.
4. Use Products within the specified time after opening a humidity barrier bag. Baking is required before using Products of
which storage time is exceeding the recommended storage time period.
Precaution for Product Label
A two-dimensional barcode printed on ROHM Products label is for ROHM’s internal use only.
Precaution for Disposition
When disposing Products please dispose them properly using an authorized industry waste company.
Precaution for Foreign Exchange and Foreign Trade act
Since concerned goods might be fallen under listed items of export control prescribed by Foreign exchange and Foreign
trade act, please consult with ROHM in case of export.
Precaution Regarding Intellectual Property Rights
1. All information and data including but not limited to application example contained in this document is for reference
only. ROHM does not warrant that foregoing information or data will not infringe any intellectual property rights or any
other rights of any third party regarding such information or data.
2. ROHM shall not have any obligations where the claims, actions or demands arising from the combination of the
Products with other articles such as components, circuits, systems or external equipment (including software).
3. No license, expressly or implied, is granted hereby under any intellectual property rights or other rights of ROHM or any
third parties with respect to the Products or the information contained in this document. Provided, however, that ROHM
will not assert its intellectual property rights or other rights against you or your customers to the extent necessary to
manufacture or sell products containing the Products, subject to the terms and conditions herein.
Other Precaution
1. This document may not be reprinted or reproduced, in whole or in part, without prior written consent of ROHM.
2. The Products may not be disassembled, converted, modified, reproduced or otherwise changed without prior written
consent of ROHM.
3. In no event shall you use in any way whatsoever the Products and the related technical information contained in the
Products or this document for any military purposes, including but not limited to, the development of mass-destruction
weapons.
4. The proper names of companies or products described in this document are trademarks or registered trademarks of
ROHM, its affiliated companies or third parties.
Page 37

DatasheetDatasheet
General Precaution
1. Before you use our Pro ducts, you are requested to care fully read this document and fully understand its contents.
ROHM shall not be in an y way responsible or liabl e for fa ilure, malfunction or acci dent arising from the use of a ny
ROHM’s Products against warning, caution or note contained in this document.
2. All information contained in this docume nt is current as of the issuing date and subj ect to change without any prior
notice. Before purchasing or using ROHM’s Products, please confirm the la test information with a ROHM sale s
representative.
3. The information contained in this doc ument is provi ded on an “as is” basis and ROHM does not warrant that all
information contained in this document is accurate an d/or error-free. ROHM shall not be in an y way responsible or
liable for any damages, expenses or losses incurred by you or third parties resulting from inaccuracy or errors of or
concerning such information.
Notice – WE Rev.001
© 2015 ROHM Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
 Loading...
Loading...